- 1Department of Electrical Engineering, Amirkabir University of Technology, Tehran, Iran
- 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden
- 3Department of Information Science and Media Studies, University of Bergen, Bergen, Norway
Introduction: Application of Deep Learning (DL) methods is being increasingly appreciated by researchers from the biomedical engineering domain in which heart sound analysis is an important topic of study. Diversity in methodology, results, and complexity causes uncertainties in obtaining a realistic picture of the methodological performance from the reported methods.
Methods: This survey paper provides the results of a broad retrospective study on the recent advances in heart sound analysis using DL methods. Representation of the results is performed according to both methodological and applicative taxonomies. The study method covers a wide span of related keywords using well-known search engines. Implementation of the observed methods along with the related results is pervasively represented and compared.
Results and discussion: It is observed that convolutional neural networks and recurrent neural networks are the most commonly used ones for discriminating abnormal heart sounds and localization of heart sounds with 67.97% and 33.33% of the related papers, respectively. The convolutional neural network and the autoencoder network show a perfect accuracy of 100% in the case studies on the classification of abnormal from normal heart sounds. Nevertheless, this superiority against other methods with lower accuracy is not conclusive due to the inconsistency in evaluation.
1 Introduction
The context of biomedical engineering has been considerably enhanced after the development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Deep Learning (DL) methods. This enhancement can be profoundly seen in different applications of AI-based methods including automated cardiac disease diagnosis using a recording of heart sound signal, called Phonocardiograph (PCG), as the input to the DL method. This domain of computing methods has addressed various embodiment, from the traditional AI-based methods (Sepehri et al., 2008), to the hybrid models (Gharehbaghi et al., 2015a,b), and ultimately DL methods, over the previous decades (Gharehbaghi et al., 2019b, 2017b). The shift from the traditional to the hybrid methods was not indeed as effective as the leap from the hybrid to the DL method. Although Artificial Neural Networks (ANN) first emerged as an alternative to the statistical methods, i.e., Hidden Markov Model (HMM), the theoretical link between these two alternatives was later understood by the researchers (Bourlard and Wellekens, 1990). Regardless of using ANN or HMM, feature extraction is a step with fundamental importance, which has always tried to be elaborated to secure an acceptable performance of the learning method. On the contrary, a DL method can be designed in a manner to learn appropriate features for reliable performance. Such advancement was not seen in the former alternatives.
Application of DL methods has been expanded to PCG analysis mainly in two different ways: classification of abnormal heart conditions from the normal ones, and segmentation of PCG signal, where the latter implies the process by which onset and endpoint of the basic heart sounds are identified. It is worth noting that a heart creates two sounds, resulting from the valvular closure, named the first and second heart sound. These two sounds are known as the basic heart sounds and the time intervals between basic heart sounds carry important information about heart condition. The importance of an expert system for cardiac disease diagnosis is better understood if considering that cardiovascular disease is still the main cause of human mortality.
Several architectures of deep learning methods have been introduced for PCG analysis, either for classification or for segmentation purposes, however, result discrepancy along with the inconsistent training/validation circumstances make selection of a reliable DL method a complicated task.
To put this point into a better perspective a number of the challenges faced with the development of an expert system for cardiac disease diagnosis based on PCG analysis, are listed as follows:
• PCG signal by itself, is non-stationary, nonergodic, and cyclic signal (Gharehbaghi et al., 2019b).
• A recorded PCG may contain different contaminating sources such as noises and artifacts (Deperlioglu et al., 2020; Baghel et al., 2020).
• The frequency characteristics of the stethoscope can make models to be biased toward the majority sources of training data (Humayun et al., 2020).
It is, therefore, unrealistic to rely on the performance measures of the DL methods without considering the training/validation dataset. Such technical details can not be found in some of the review papers, in which the application of DL methods in cardiac disease diagnosis was highlighted (Fernando et al., 2021; Lakshmi et al., 2021; Abdullah Aloyuni, 2021). A number of review papers reported the power of deep learning methods for PCG classification (Bizopoulos and Koutsouris, 2018; Chen W. et al., 2021; Li S. et al., 2020). However, all the studies fail to provide sufficient details, in terms of the taxonomy as well as the computational methodology, for the researchers and engineers to select appropriate methods for their research objectives. For example, a great majority of the DL methods are applied to certain segments of PCG. This necessitates another computational step, named the segmentation process, since manual segmentation makes the method accurate, and user-dependent. Such computational details cannot be found in the review papers.
This paper represents the results of a comprehensive study on DL methods that were employed for PCG analysis. The main objective of the paper is to provide an overview of different DL methods along with their applicability, restrictions, and criteria, in light of PCG processing. The methodological taxonomy is based on the processing objectives, e.g. classification and segmentation. Results of each DL method in conjunction with the corresponding training/validation dataset are represented for each study objective separately. In addition to introducing technical contents of the common DL methods used for PCG processing, detailed results will be represented in tabular form to be used as a quick reference, categorized based on the DL focus. Moreover, the complexity of the DL methods as well as the corresponding performance will be described separately.
The main contributions of the paper are:
• Introducing a novel taxonomy for heart sound analysis based on the applicability of the published studies and performing a pervasive review of the studies according to the introduced taxonomy. The introduced taxonomy can help the researchers and developers to find the existing methodologies that suit their research questions.
• Presentation of the trend of the various DL methods for heart sound analysis using a new representation. This can help the researchers to understand the progress of various DL methods in the domain.
• Presentation of the technical details of DL methods used for PCG analysis, including the segmentation process.
• Pre metrics that exist within the related community. The existing studies have mostly overlooked the importance of the database in the learning process.
• Representing the survey results in terms of the applicative and the methodological taxonomy.
• Conclusive representation of the most popular and the most accurate DL methods based on the introduced taxonomy.
The paper provides a clear picture of the capabilities and restrictions of the DL methods to be used as a reliable computing method for PCG analysis. The DL methods are not studied based on the performance only, and the validation databases as well as the research questions are investigated. It is worth noting that DL methods are always accompanied by classification errors, and therefore, further medical measures might be eventually needed to admit the methods to the clinical settings. Nevertheless, representation of the method performance for a research question can provide a baseline for the researchers to further investigate. Moreover, the resulting computing method can be incorporated into an Internet of Things structure to serve as an easy-to-use decision support system for this demanding clinical application (Gharehbaghi and Lindén, 2015; Gharehbaghi et al., 2019c).
2 Medical background
A heart normally encompasses 4 chambers, two smaller on the top named atrium, and the larger ones named ventricle. A wall named septum separates the two ventricles from each other, and so do the atriums, however, the left/right atrium is separated from the left/right ventricle by mitral/tricuspid valves. There are two other valves between the left/right ventricle and the artery that carries blood to the body/lungs, named the aortic pulmonary valve. The heart walls are normally contracted and relaxed rhythmically, such that more than 55% of the incoming blood is typically ejected into the aortic root. A heart that is not capable of ejecting more than 40% of the blood is evidenced as the HEART FAILURE case. A normal heart has a cyclic mechanical activity that creates an acoustical signal. A recording of this acoustical, or PCG, contains two basic sounds, named the first heart sound (S1) and the second heart sound (S2), which result from the closure of the mitral/tricuspid and aortic/pulmonary valves, respectively. conditions such as an obstructed valve, a shunt on any of the septum, or valvular leakage results in blood turbulence, named murmur. Nevertheless, a normal heart might initiate a murmur, named innocent murmur, which is mostly heard in children. Discrimination between the murmurs is a complicated task, especially considering the non-stationary and ergodic properties of the PCG signal which makes a high between-class similarity. Figure 1 demonstrates two cycles of PCG for a case with a shunt in the ventricular septum (VSD), an aortic obstruction (AS), an aortic leakage (AR), a pulmonary obstruction (PS), an innocent murmur, and a normal (no murmur) condition. The signals were selected from our previous data acquisition in compliance with the codes of the World Medical Association, whose details can be found in Sepehri et al. (2008).
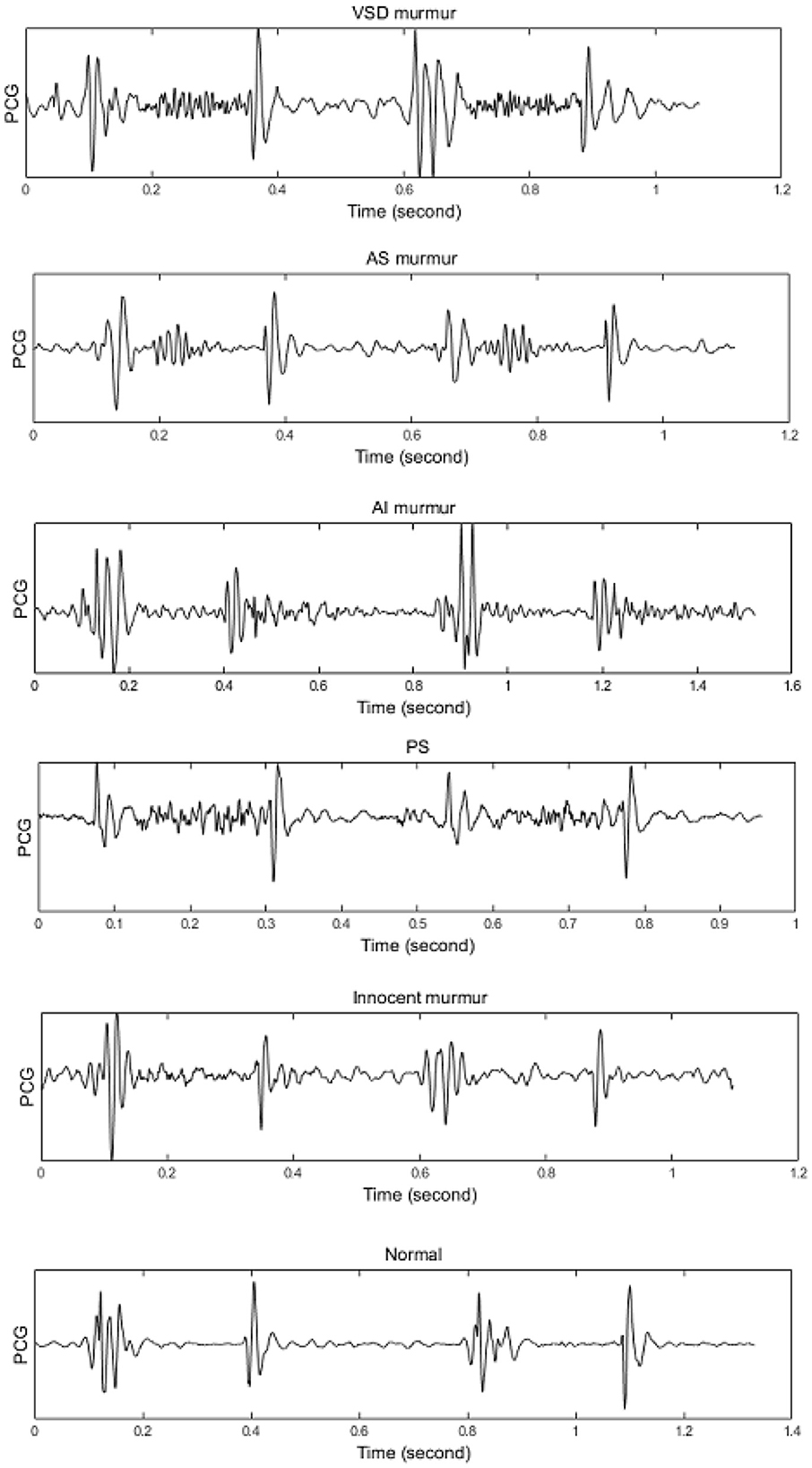
Figure 1. Illustrating different heart diseases including: VSD, AS, AR(AI), PS, Innocent Murmur, Normal. Source: Sepehri et al. (2008).
3 Deep learning methods
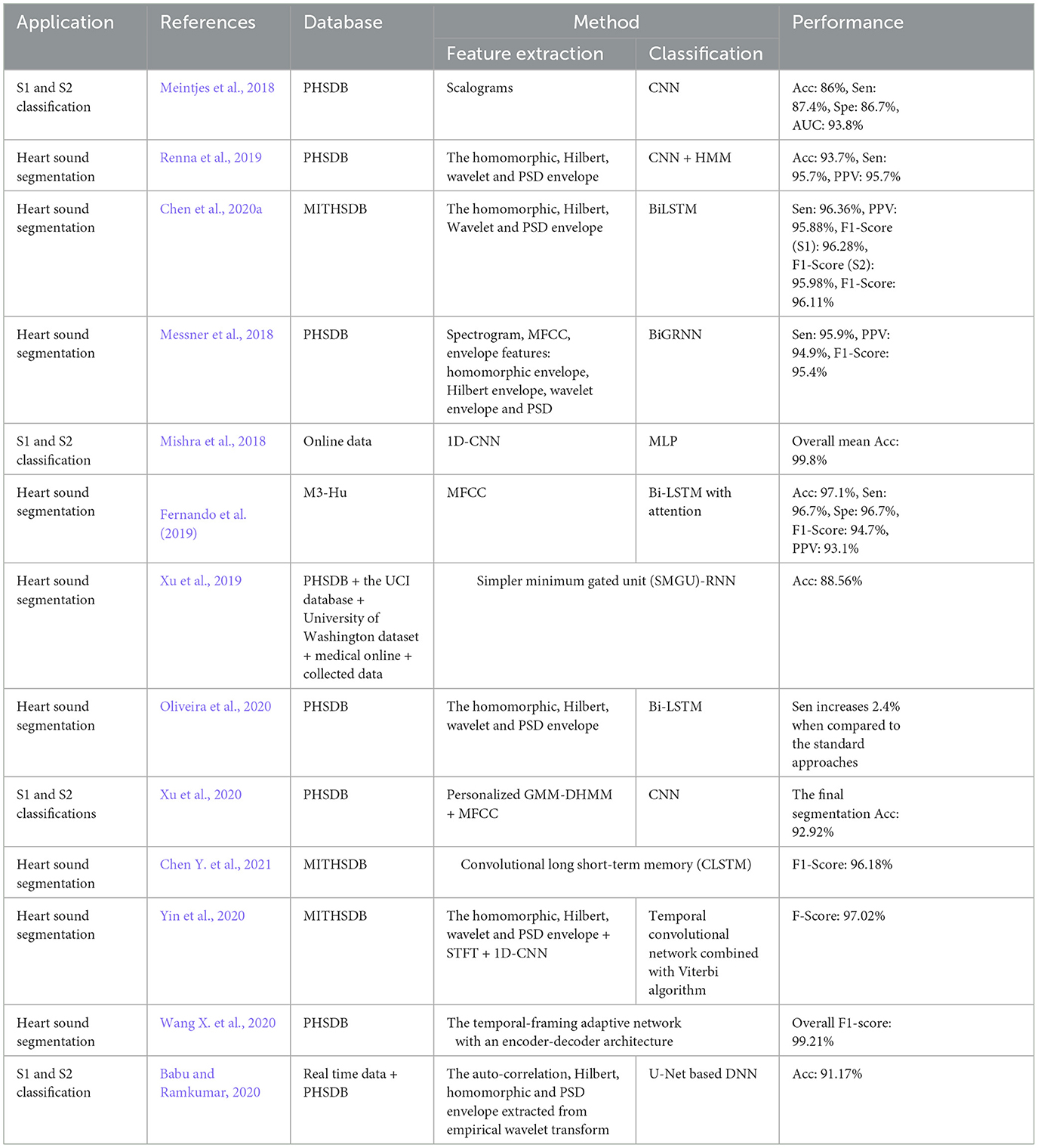
3.1 Convolutional neural networks
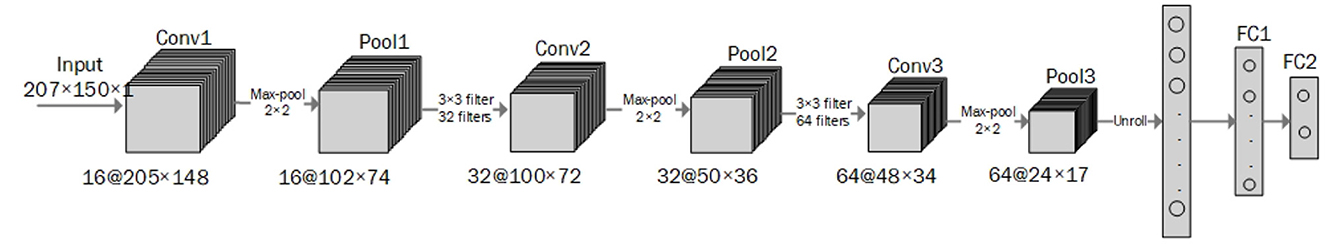
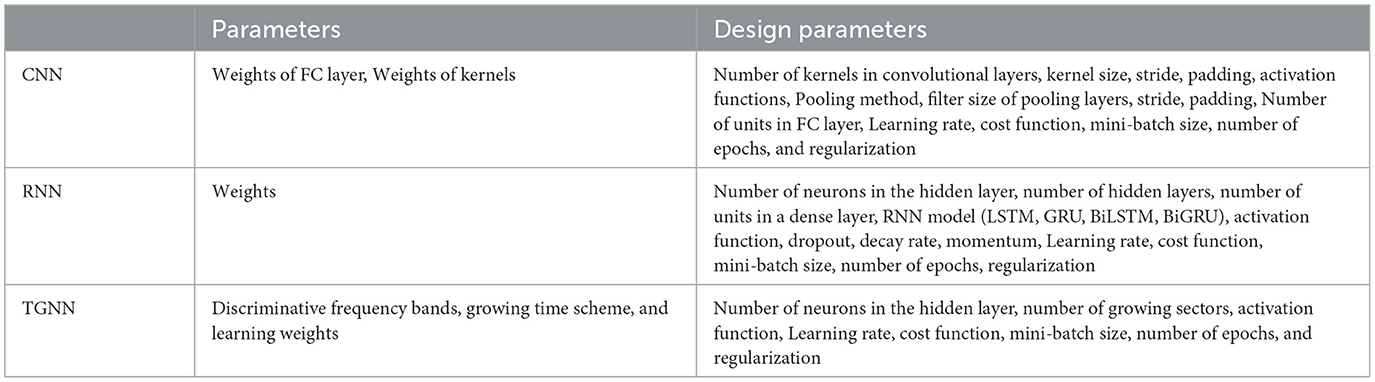
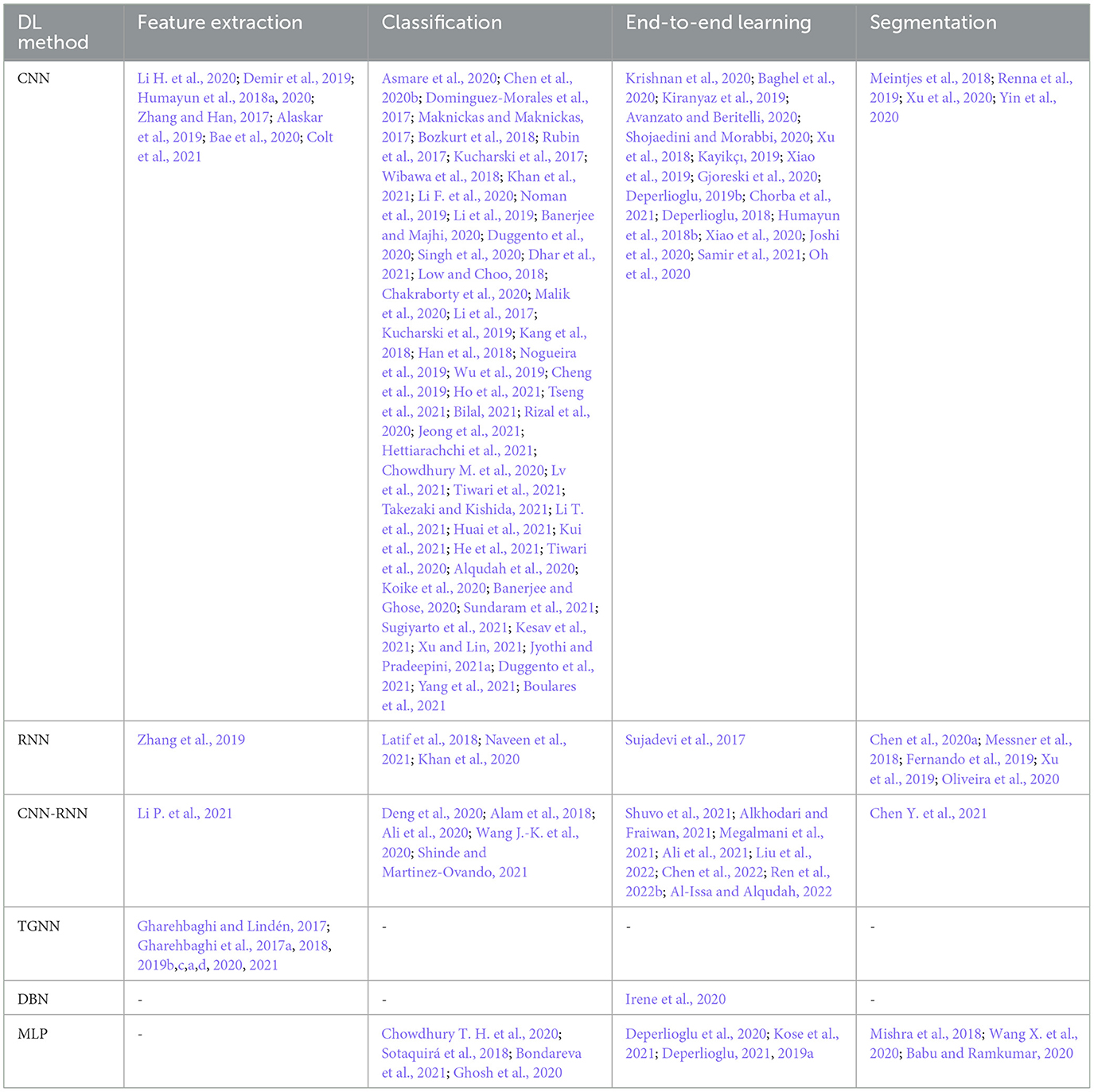
CNN is a deep learning method designed to process multiple arrays of data through back-propagation of the learning error using several layers such as convolution layers, batch normalization layers, pooling layers, and fully connected (FC) layers. The convolutional layers perform feature extraction by applying kernels (filters) to their inputs (LeCun et al., 2015; Meintjes et al., 2018; Yamashita et al., 2018). Two principal advantages of using a convolution layer instead of the fully connected layer are parameter sharing and sparsity of connections (Yamashita et al., 2018). The pooling layer down-samples the output of the middle layers to reduce overfitting. The max-pooling and global average pooling are considered two common operations of pooling (Meintjes et al., 2018; Renna et al., 2019; Yamashita et al., 2018). The batch normalization layer is responsible for developing a faster and more stable network through the normalization of the activation of each channel while, the fully connected layer is responsible for classification in which the output of the last convolution or pooling layer is unrolled into a vector and then connected to one or more fully connected layers (Meintjes et al., 2018; Yamashita et al., 2018). Rectified linear unit (ReLU) is an activation function used after each convolutional layer and has advantages over a sigmoid activation function in reducing the likelihood of vanishing gradient and sparsity (Maknickas and Maknickas, 2017). The activation function applied to the last fully connected layer is different for various classification problems (Yamashita et al., 2018). An architecture for the CNN used for the classification task is shown in Figure 2 (Meintjes et al., 2018). Table 1 shows a list of the learning and design parameters, commonly employed by CNNs.
3.2 Recurrent neural networks
RNN is designed to process sequential data and model temporal dependencies between sequential data (Messner et al., 2018). The network has an input layer with no size limit, a hidden layer (hidden state) that depends on all the previous hidden states, and an output layer. Vanishing and exploding gradients are the two major problems in RNN performance. Vanishing gradients occur when gradients become very small, leading to slow learning and poor performance on long-term dependencies. Conversely, exploding gradients happen when gradients become very large, causing to instability and failure to converge. Using gated architecture such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) or Gated Recurrent Units (GRUs) can help to overcome these problems (Mikolov et al., 2010; Latif et al., 2018). Figure 3A illustrates the RNN architecture.
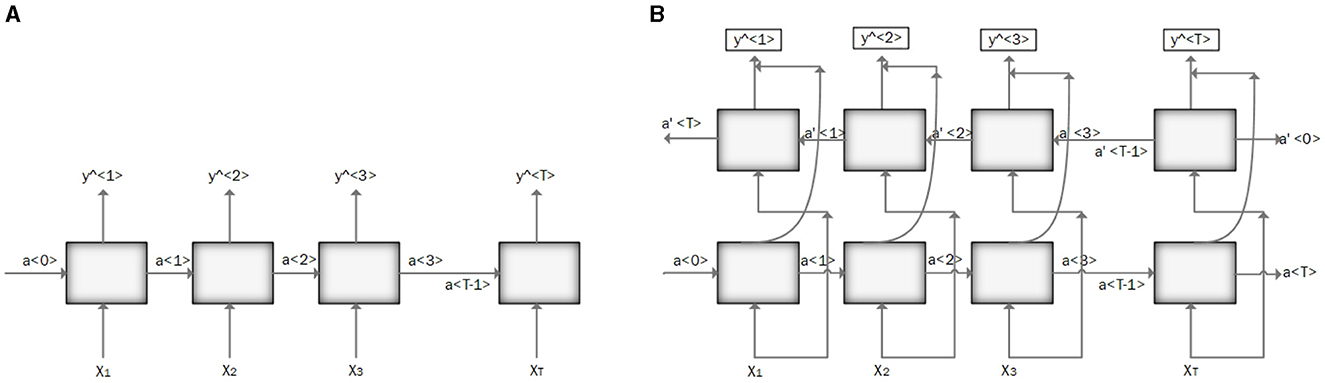
Figure 3. (A) Illustration of recurrent neural network (RNN) architecture. (B) Illustration of bidirectional recurrent neural network (BRNN) architecture.
Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Networks (BRNNs) have been proposed to incorporate future contents of a sequential into the learning process along with the past data points (Messner et al., 2018). This change can be applied to any model that uses RNN, GRU, or LSTM. It can make predictions anywhere in the sequence by considering information from the entire sequence. Figure 3B illustrates the BRNN architecture.
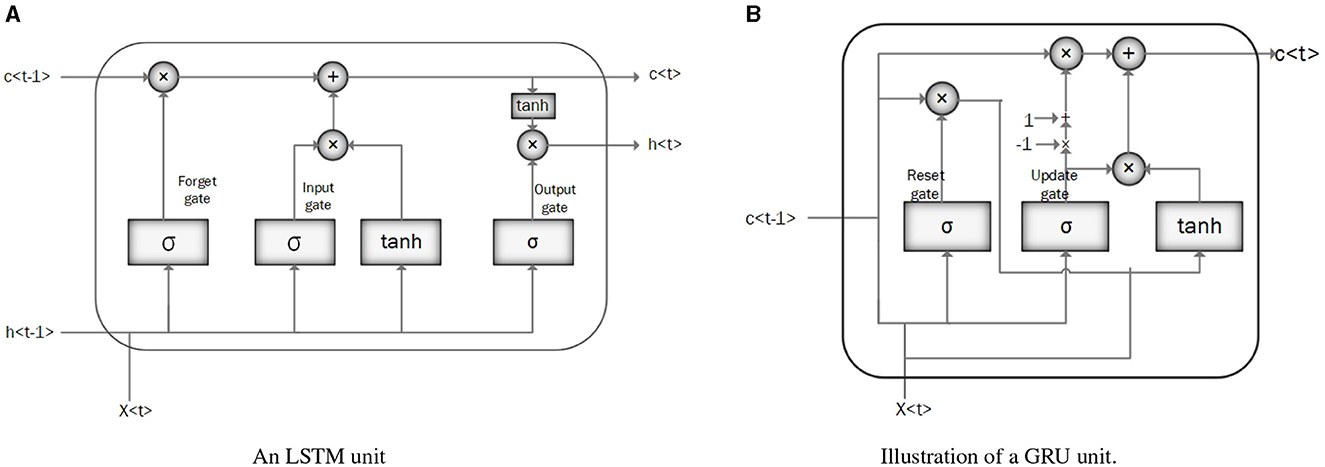
• Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM): LSTM is a modified version of RNN that resolves a common bottleneck of RNNs: vanishing and exploding gradients, by capturing long-term time dependencies (Chung et al., 2014; Latif et al., 2018). LSTM architecture consists of recurrent memory blocks. Each memory block consists of three gates, input, output, and forget gate to control its content (Messner et al., 2018). The general structure of the LSTM network is the same as in Figure 3A, except that instead of RNN units, the LSTM units. are employed. Figure 4A illustrates the LSTM unit.
• Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU): GRU is a simplified structure of LSTM with less computational cost. In GRU, the input gate and the forgetting gate, are combined to form a new gate, called the “update gate.” GRU also includes another gate called the reset gate in its structure to cope with the vanishing and exploding gradient efficiently. These gates adjust the information flow in the unit (Chung et al., 2014; Latif et al., 2018; Messner et al., 2018; Sujadevi et al., 2017). As mentioned in the previous section, the general structure of a GRU network is similar to the one in Figure 3A, except for the GRU units which are employed instead of RNN units. Figure 4B illustrates the GRU unit.
Table 1 shows a list of the learning and design parameters of an RNN.
3.3 Recurrent convolutional neural network
RCNN in the scope of our study refers to the combination of RNN and CNN, often a cascade of RNN and CNN, to capture long temporal context information and invariant spatial-temporal contents, respectively.
3.4 Time growing neural networks
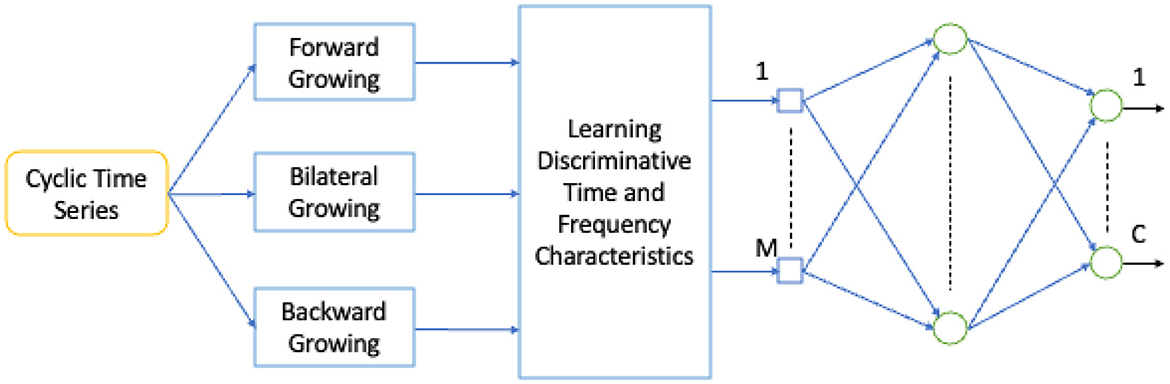
TGNN is a nonlinear deep learning method for learning the frequency contents of a set of temporal windows. There are three types of TGNN: forward, backward, and bilateral. In each type, a starting point is fixed and the window length grows in time until covering the entire learning segment of the signal. The use of the growing windows is specifically valuable for short-length signals, where the trade-off between temporal and spectral resolution is problematic (Gharehbaghi et al., 2014, 2015c). Deep Time Growing Neural Network (DTGNN) is an architecture of deep learning that uses TGNN units as the core of the learning process. DTGNN has three levels of learning that include between classes, over classes, and classification. A DTGNN at its deep level finds a set of discriminative frequency bands, defined as the frequency bands whose spectral contents provide an optimal separability between the classes. DTGNN introduced a way of finding the optimal discriminative frequency bands, by using the K-means method in conjunction with the Fisher criterion. Then, spectral contents of the discriminative frequency bands are considered as the input layer of the TGNN, and the training is performed using the backpropagation error method. An architecture for the TGNN used for the classification task is shown in Figure 5.
Table 1 shows a list of parameters and design parameters in TGNNs.
3.5 Deep belief networks
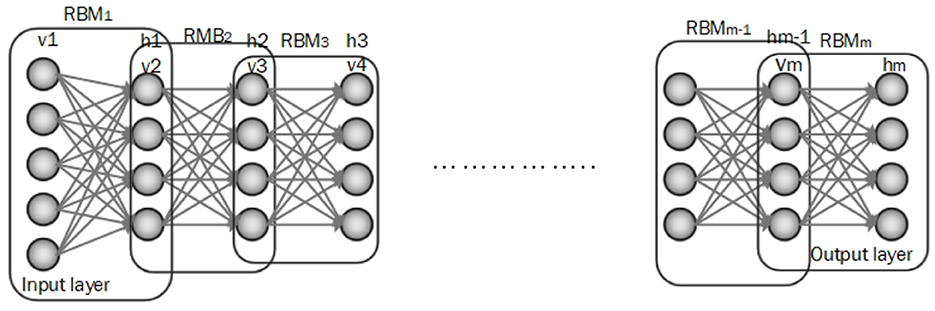
DBN is composed of multiple Boltzmann machines (RBMs) layers which are ordered subsequently. Each RBM includes a visible and hidden layer and is trained by the greedy learning algorithm to represent features. In DBN architecture input data is fed to the visible layer of the first RBM and then the hidden layer of the first RBM is an input of the next RBM and this process is continued until achieving a hidden layer of the final RBM. The top layer of DBN is the output layer (Irene et al., 2020; Hinton et al., 2006). An architecture for the DBN is shown in Figure 6.
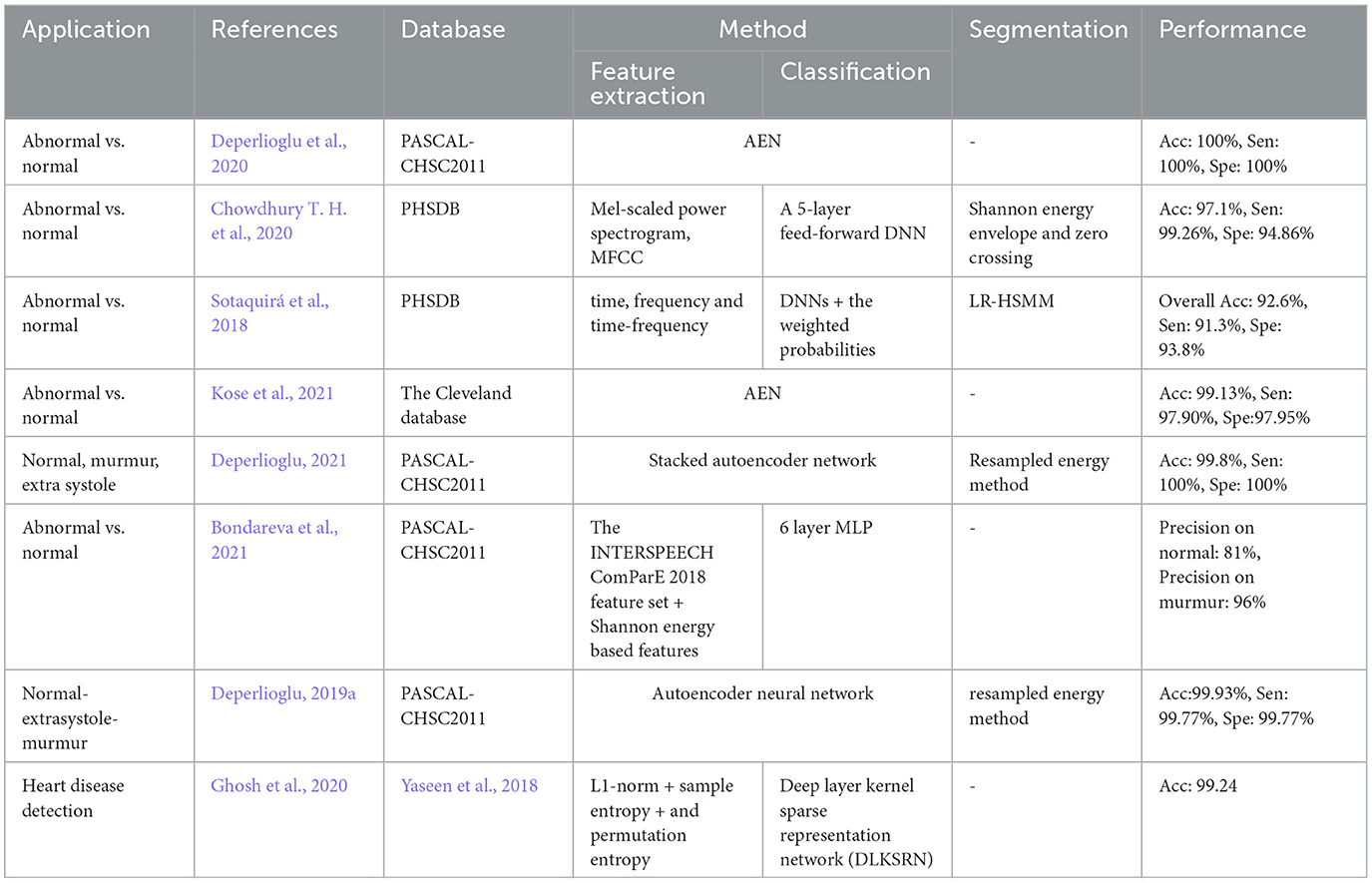
4 Database
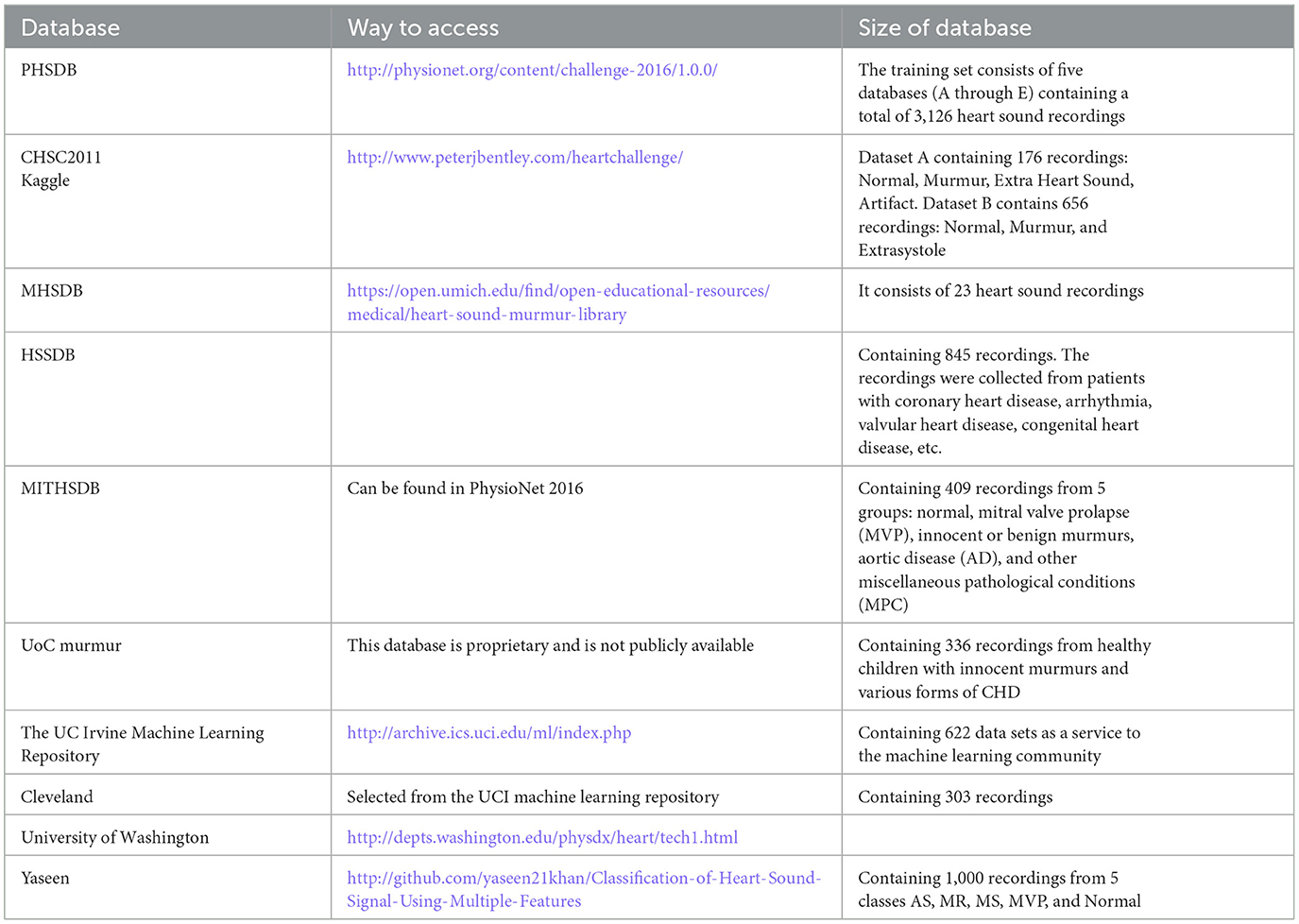
Most of the articles use existing online databases to train the proposed deep learning method and also test the performance of their PCG analysis system. The most common public databases used by the articles are:
Physionet PCG Dataset (PHSDB), The PASCAL Classifying Heart Sounds Challenge (CHSC2011), The Heart Sounds Shenzhen Database (HSSDB), The Michigan Heart Sound and Murmur database (MHSDB), The Massachusetts Institute of Technology heart sounds database (MITHSDB), Kaggle, UC Irvine Machine Learning Repository (UCI), UoC murmur, Cleveland, University of Washington, and Yaseen et al. (2018). These databases are listed in Table 2.
5 Performance measures
A formulation for quantitatively evaluating the performance of a classifier, based on the outcomes of the validation, is known as the performance measure. The performance measures which are commonly seen in the related publications reflect an aspect of the classification performance. In this study, we face binary classification, where the result of the classification can be either normal or abnormal. The classifier output can be either positive or negative, relying on abnormal or normal conditions, respectively. The prediction value of a classifier can be either true or false, for the correct and incorrect classification, respectively. We may, therefore, face one of the following situations:
True Positive (TP): The model predicts the positive class correctly
True Negative (TN): The model predicts the negative class correctly
False Positive (FP): The model predicts the positive class incorrectly
False Negative (FN): The model predicts the negative class incorrectly
Based on these definitions, the following performance measures named: Accuracy, Sensitivity, Specificity, Recall, Precision, Positive Predictive Value (PPV), Negative Predictive Value (NPV), G-mean, and F1-Score are calculated as follows:
Accuracy is a performance measure that reflects the ability of a classifier to segregate different classes. For example, in an abnormal-normal heart sound classification problem, the accuracy of a classifier shows how well the two classes are separated by the classifier. This performance measure considers the two classes equally.
The sensitivity of a classifier in the above example, is the performance measure that indicates the capability of the classifier in the correct classification of the abnormal class (low value of FN), while the sensitivity is the capability in the correct classification of the normal class (low FP).
The precision of a classifier indicates the capability of the classifier in the correct classification of the normal class concerning the normal labels assigned by the classifier.
The F1−Score, NPV, and PPV of a classifier, altogether indicate the capability of the classifier to provide a good balance between correct classification of the normal and abnormal classes. Unweighted Average Recall (UAR) and Geometric mean (G-mean) are used to evaluate model performance, especially when the learning dataset is imbalanced, such that a higher G-mean or UAR indicates that the model performs well on both classes of a binary case. These performance measures become important when a heavy class imbalance is seen in the learning database, as the class with the larger group size can overwhelm the minority class if accuracy is employed as the performance measure only.
6 Research methodology
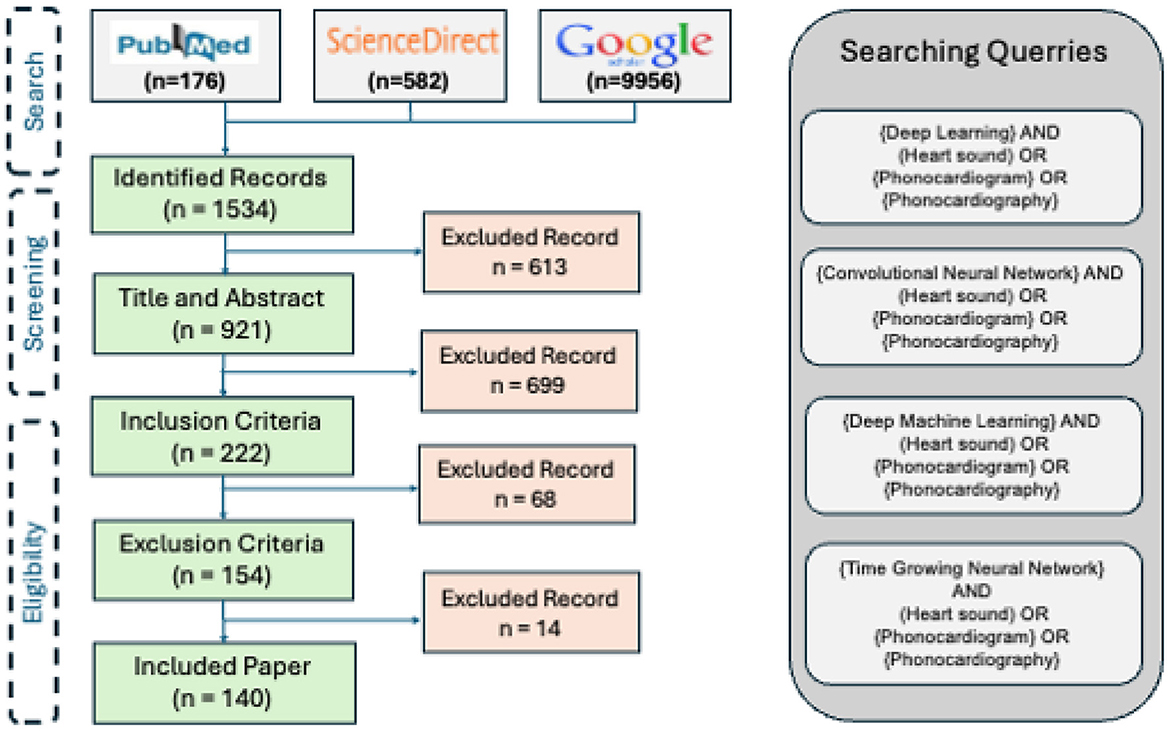
We performed a topical survey retrospectively using the reachable reports, published in the technical, interdisciplinary, and medical journals or conference proceedings between 2017 and 2023. The research method is composed of 3 steps: search, screening, and eligibility.
6.1 Search
The three major search engines of the field are invoked to find the publications: PubMed, ScienceDirect, and Google Schola. The following keywords are employed as the keywords for the query:
• “Deep Learning” and (“Heart sound” or “Phonocardiogram” or “Phonocardiography”)
• “Convolutional Neural Network” and (“Heart sound” or “Phonocardiogram” or “Phonocardiography”)
• “Deep Machine Learning” and (“Heart sound” or “Phonocardiogram” or “Phonocardiography”)
• “Time Growing Neural Network” and (“Heart sound” or “Phonocardiogram” or “Phonocardiography”)
In this step, the title of the papers is explored to exclude repetitive and irrelevant records. The identified papers are passed to the next step for the screening.
6.2 Screening
The abstracts of the papers found in the Search are studied in terms of both the technical contents and the application. Those papers addressing irrelevant topics and the ones that are not accessible by the mentioned search engines are excluded from the study.
6.3 Eligibility
In this step, the papers passing through the previous two steps are explored in terms of the availability of the full paper. Next, the inclusion criteria are investigated followed by exploring the exclusion criteria. The papers, passing through the whole filters will be selected to be thoroughly studied.
6.3.1 Inclusion criteria
• The central focus of the publications was the development or review of deep learning methods, applied to human heart sound signal.
• The publication dates lay between 2017 and 2023.
6.4 Exclusion criteria
Those publications which meet at least one of the exclusion criteria did not participate in the study:
• Incomplete reporting of the joint performance measures: either accuracy-sensitivity or accuracy-specificity (In biomedical studies, the balance between sensitivity and specificity is an important factor, reflecting the performance of the methods).
• Inaccessibility of the publication full-text.
• The paper is not a survey paper. The survey papers are studied for the discussiona.
7 Taxonomy of the survey
The articles found by the survey, tackle one of the following 6 research questions: feature extraction, classification, end-to-end learning (feature extraction + classification), and segmentation. Disease detection, disease classification, and severity assessment of cardiac disease are all considered as the applications of the study, fitting well into the classification category. Consequently, the survey taxonomy is based on the below-described research questions according to our findings. The results of the study will be presented in line with the taxonomy in the next section
7.1 Feature extraction problem
The extraction of concise and informative data content to improve segregation between different data groups is known as feature extraction. The effectiveness of the extracted should be validated considering dependencies over the feature space. This makes finding a feature set with an optimal discrimination power, problematic. Table 3 lists these papers. We observed that using deep learning techniques for feature extraction cannot noticeably improve the classification accuracy, unless dynamic contents of the features, or a fusion of the deep and the hand-crafted features are constructed.
7.2 Classification problem
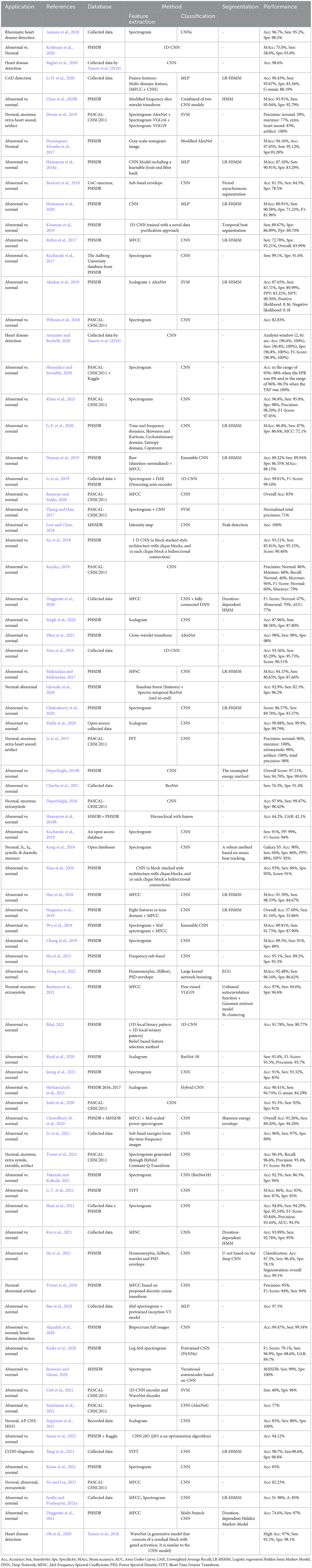
Likewise, DL methods have been dominantly used in many case studies to perform classification. In most of the cases of heart sound classification, discrimination between normal and abnormal heart is the study objective (Chen et al., 2020b; Dominguez-Morales et al., 2017; Bozkurt et al., 2018). However, the detection of a certain heart abnormality versus other heart abnormalities along and/or normal heart conditions is observed to be the main goal of some studies (Li H. et al., 2020; Wang J.-K. et al., 2020). Segregation between different classes of heart sound is also seen in a number of the studies on heart sound signal classification (Li et al., 2017; Kang et al., 2018; Boulares et al., 2021). Table 3 shows all these papers.
7.3 End-to-end learning
In the heart sound analysis domain, End-to-End learning implies studies in which feature extraction and classification are performed simultaneously. A considerable number of the reviewed papers used a DL method for end-to-end learning. Table 3 represents these papers.
7.4 Segmentation problem
In many studies, the heart sound signal is firstly pre-processed and the cardiac cycles as well as the first heart sound and the second heart sounds are fully localized on the heart sound recordings before the rest of the learning process. DL methods have been recently employed to perform this phase of the heart sound signal analysis by many researchers. Table 3 shows these papers.
8 Results
Figure 7 illustrates the results of the research methodology as was described in Section 6. The query performed in the mentioned search engines resulted in 10,716 records where most of the records were either repetitive or irrelevant (see Section 6). The number of records was 1,534 from which 222 recordings were observed to be relevant according to the Title and the Abstract, and the ultimate number of the papers to be studied was 140 papers. In total, 14 survey articles were found, whose results will be compared and described in the discussion, Section 9. Figure 7 illustrates the findings of the survey. In order to provide an understanding of the methodological superiority in terms of the experimental results, the outperforming methods will be represented together with the detailed results, according to the study taxonomy. Figure 8 demonstrates the accuracy of the outperforming methods according to the taxonomy.
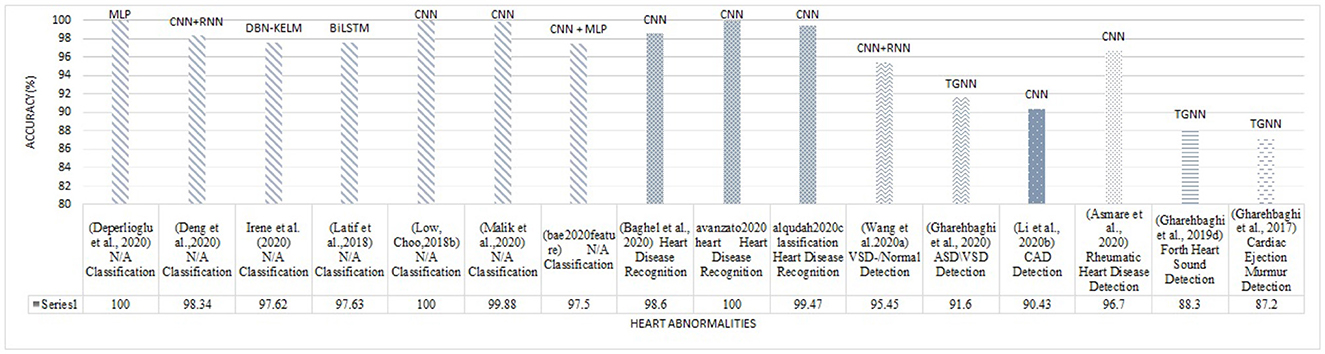
Figure 8. The best accuracy of each deep learning method for abnormalities classification (N/A: Normal/Abnormal).
The superior performance was found in the studies by Mishra et al. (2018) on the classification problem, and by Deperlioglu et al. (2020) on the segmentation problem, and by Avanzato and Beritelli (2020) on the End-to-End learning. It is important to note that providing a realistic comparison of the accuracy for different learning methods requires clear information about the validation method employed for accuracy estimation. This is tightly linked to the training, validation, and testing databases and also the classification question. Group size, class similarities, corresponding to the cardiac disease conditions, and the data percentage used for training/validation/testing as well as the data selection manner all affect the estimated accuracy. Classification question is, yet, another important point affecting the accuracy, as an abnormal/normal case exhibits a different learning than a classification question in which a single vs. all classes is the objective. Nevertheless, this figure demonstrates appropriate pointers to the references where the validation process is detailed. Tables 4–8, also represent more details of the results found by this survey, including the segmentation manner. Results of the outperforming methods along with the implementation and the validation details are described in the following sequels according to the study taxonomy.
8.1 Findings of the feature extraction problem
A number of the studies rely on using a DL method for feature extraction, in which the classification layer is independently trained for a certain study objective. The discrepancy in the methodologies and also in the study objectives, make the comparison problematic (see Table 3). Some papers use pre-trained networks to extract features, while others consider the classifier to be fixed and extract various features to evaluate its effect on classification problems. Thus the accuracy of feature extraction is reported as a measure. The DL methods, CNN, RNN, CNN-RNN, and TGNN, were differently employed by 19 studies, for feature extraction. Various types of CNN models are dominantly observed in these studies. As shown in Figure 8, a CNN model was reported to improve abnormal vs normal classification accuracy up to 97.5%, where the CNN was employed to extract discriminative features from mel-spectrum two-dimensional graphs (Bae et al., 2020). The ultimate classification was performed using an artificial neural network. In another study, a CNN model was employed for extracting powerful features from the colored images, resulting from applying the Mel-Frequency Cepstrum Coefficients (MFCC) to PCG signals.
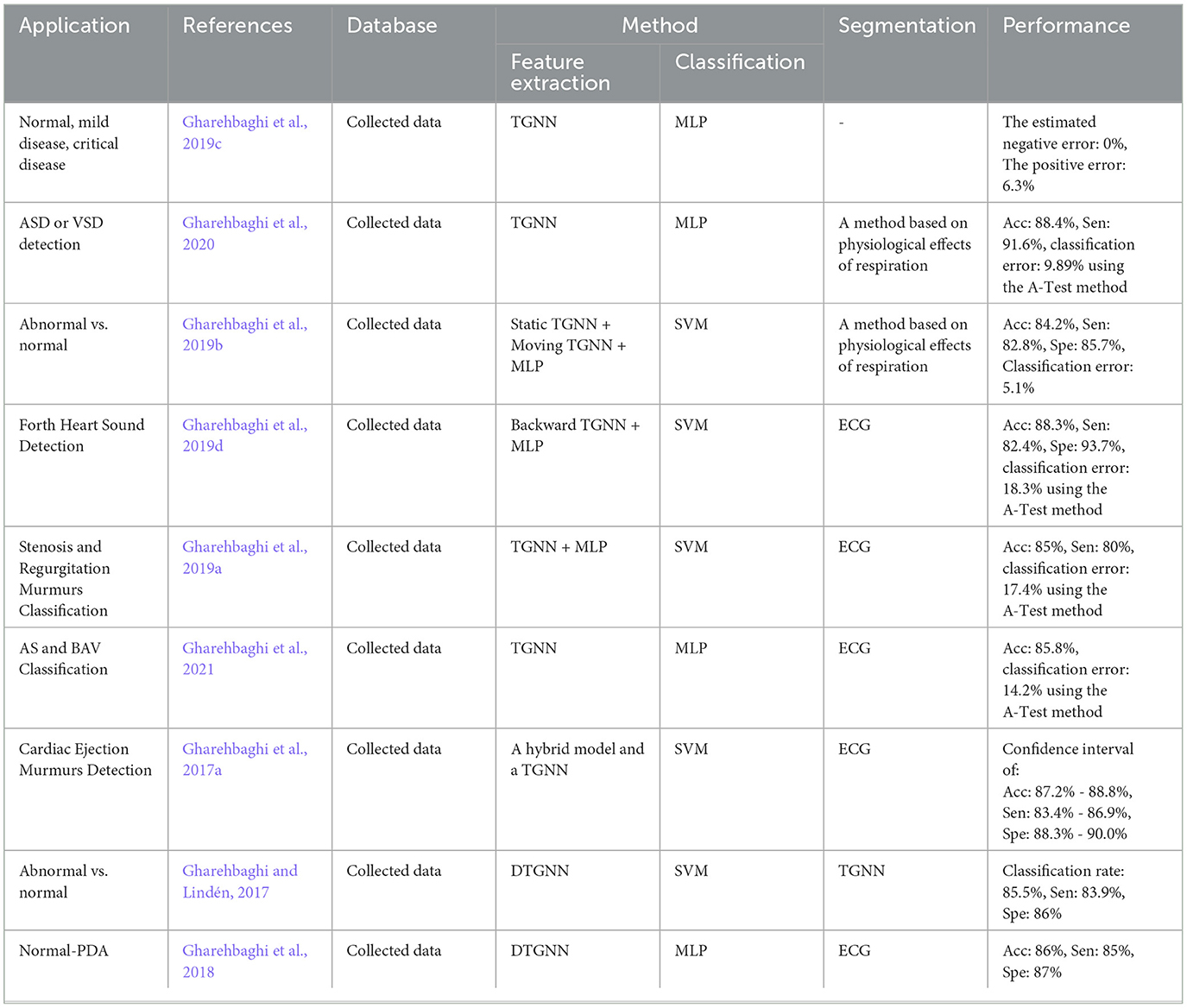
Detection of coronary artery diseases was the study objective, and the accuracy was estimated to be 90.43% when a Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) neural network was used for the classification. Performance of the method was evaluated 5-fold using a dataset of PCGs collected at the Shandong Provincial Qianfoshan Hospital (see Table 4) (Li H. et al., 2020). TGNN served as a powerful method for feature extraction in different studies of PCG signal analysis. In all the TGNN-based methods, the spectral features, obtained by periodogram, were learned using different schemes of the growing windows, i.e., forward, backward, and bilateral growing windows, along with the discriminant analysis methods such as Fisher criteria and k-means clustering. The main objective of the studies was anomaly detection using either a support vector machine (SVM) or MLP for binary classification. Several case studies including, ASD vs. VSD, AS vs. BAV, and fourth heart sound detection were performed based on this combination, and accuracy of 88.4%, 85.8%, and 88.3% was reported, respectively (Gharehbaghi et al., 2020, 2021, 2019d) (see Table 6 for more details). In another study, a hybrid model composed of TGNN and hidden Markov Model was proposed for extracting indicative features of PCG signal in light of detecting cardiac ejection murmur, and the accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity were estimated to be 88.1%, 85.1%, and 89.2%, respectively (Gharehbaghi et al., 2017a).
8.2 Findings of the classification problem
Classification of abnormal versus normal heart conditions is the major research question tackled by various DL methods (Table 3). A total of the 63 papers employed DL methods for the classification, in which different architectures of CNN, RNN, RCNN, and MLP are observed. CNN-based methods are dominantly seen in the majority of the papers, contributing in 67% of the studies (see Figure 9A), where a perfect 100% accuracy was reported in one of the studies (Low and Choo, 2018). Figure 9A demonstrates methodological frequencies for the classification question. Although validation inconsistencies are seen in the validation methods and database, which make a fair comparison questionable, the versatility of CNN in this research question is conclusive. Figure 8 shows the best performance of each method. The methods with the superior accuracy for the underlying case studies are described in this sequel, and a complete list of all the studies together with the technical details and the study objectives are separately tabulated for each method in Tables 4–8.
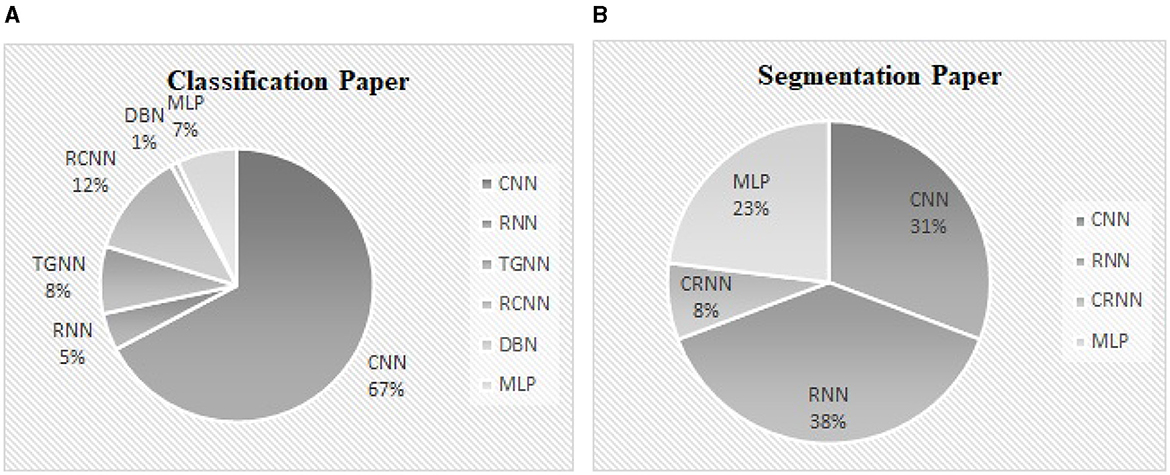
Figure 9. (A) The contribution percentage of different DL methods in the classification papers. (B) The contribution percentage of different DL methods in the segmentation papers.
A CNN with 2 convolutional layers, 2 max-pooling layers, and a kernel size of 11 × 11 was employed to classify abnormal PCGs from normal ones, using the intensity images obtained from the segmented PCG energies as the inputs. A perfect 100% accuracy was achieved by when the cross-validation with 80% 20% of training/test data was employed (Low and Choo, 2018). They used the MHSDB dataset for the validation and a dropout layer to avoid overfitting. As described in Table 4 and Figure 8, another study also reported a high accuracy of 98.7% for the CNN model when the bispectrum images of PCGs were employed as the input features (Alqudah et al., 2020). Classification of 5 heart diseases was the study objective. Their method was validated using a 10-fold method in conjunction with a dataset provided by Yaseen et al. (2018).
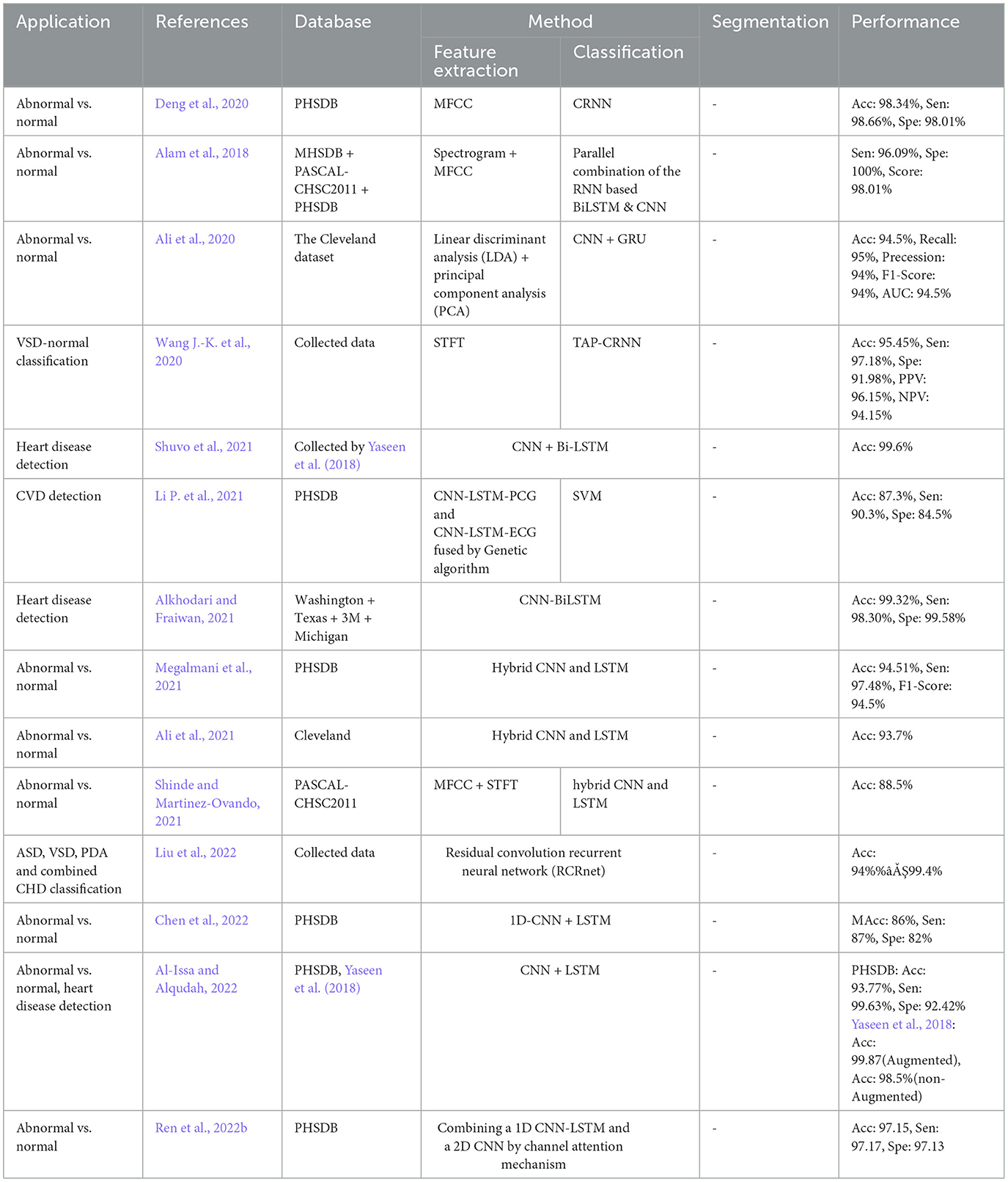
A combination of CNN and RNN was also proposed for the classification problem and results were compared to a parallel structure of RNN and CNN, named PRCNN, using MFCC as the input data (Deng et al., 2020). Proposed a method based on CRNNs for abnormalities classification. Accuracy, Recall, Precision, and F1-Score of the CRNN and PRCNN were calculated. As shown in Figure 8, the accuracy of the two methods was estimated to be 98.34% and 97.34%, respectively.
Temporal Attentive Pooling (TAP) was proposed for classifying the systolic murmur caused by VSD from the normal PCG (Wang J.-K. et al., 2020). Spectral features of PCGs were calculated using short-time Fourier transformation, and employed by the convolutional layers of a CNN-based architecture. The method architecture incorporated recurrent layers along with the TAP layers to learn the long-term dependencies of the convolutional layers. The classification was performed by the dense layers as the final layer. An accuracy of 95.45% was achieved when the 4-fold validation along with a dataset of PCGs prepared at the National Taiwan University Hospital was employed for the evaluation showing a performance improvement as compared to the CNN and the Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network (CRNN).
In another study, a CNN-based model was proposed using rheumatic heart disease as the case study for the classification (Asmare et al., 2020). Each PCG was divided into several temporal frames with a fixed length of 1.2 second. The mel-spectral contents were employed in their logarithmic form as the input features for a CNN with 5 convolutional layers and linear activation function. The method accuracy was estimated to be 96.7% using 80% 20% of training/test split of the dataset as shown in Table 4. The database for the evaluation was prepared at the Tikur Anbessa Referral Teaching Hospital College of Health Sciences, Addis Ababa University.
8.3 Findings of the end-to-end learning
End-to-End learning, implying learning heart sounds without performing the segmentation process, was found in 31 of the studies. Methods including, CNN, RNN, CNN-RNN, DBN, and MLP, were used to this end.
The best accuracy was obtained by an Auto Encoder Network (AEN) in two classification problems: a case with three classes, normal, murmur, and extra-systoles, and a case with two classes of normal and abnormal (Deperlioglu et al., 2020). An accuracy of 100% and 99.8% in the former and the later case, respectively when 80% 20% of training/test split was used for the validation, outperforming other methods such as ANNs, SVM, CNN, and DNN. Detail of the results can be found in Table 8.
An accuracy of 100% was also seen in another study for heart disease classification, in which CNN was employed for the learning process along with the recurrence filter with the temporal frames of 6 and 34 second (Avanzato and Beritelli, 2020). Cross-validation with 70%/30% of training/test data was employed in conjunction with the dataset in Yaseen et al. (2018).
Deep Belief Network was also employed through a hybrid method of fuzzy classifier, for the disease classification (Irene et al., 2020). Performance of the model was estimated using 10-fold validation, independently applied to three different datasets: Hungary dataset, Swiss dataset, and Cleveland dataset, and the accuracy was found to be 97.56%, 97.21%, and 97.62%, respectively.
8.4 Findings of the segmentation problem
Segmentation is by far less pronounced in the related studies on DL for PCG signals, observed in 15 of the studies. Different DL methods such as CNN, RNN, CNN-RNN and MLP were proposed for this research question, from which RNN and CNN are dominantly seen in the reports. As can be seen in Figure 9B, the DL methods which invoked RNN and CNN, contributed to 38%, 31% of the studies. The performance of the segmentation is evaluated by considering a window of 40 or 60 ms, where the predicted position of each heart sound must fall within this window to be correctly predicted. For example, a true positive is counted when the center of an S1 (S2) which occurs within the predicted label is closer than 40 ms to the center of the corresponding S1 (S2) in the ground truth label. Although metrics such as sensitivity and positive predictive have been used in some papers to evaluate segmentation performance, accuracy has been reported more often. Thus, we presented and compared the results based on their accuracy, even though it might sound inappropriate. However, there were 2 different DL methods that showed superiority over the rest of the methods found by the survey (Mishra et al., 2018). One of the methods was based on the one-dimensional CNN for the feature extraction, in conjunction with an MLP for S1-S2 classification. The other method employs a stacked auto-encoder for the classification which uses Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients as well as the related derivative as the input features. An accuracy of 100% and 99.8% was achieved by the two methods, respectively. Repeated random sub-sampling was used for the validation, and the three public datasets from the University of Washington, the University of Michigan, and Litman were invoked for the validation. Development and validation details of the DL methods for the segmentation found by the survey are included in Table 9.
9 Discussion
This paper considered all the scientific papers published in the well-used search engines within 2017–2023 and represented the results in the taxonomic order. Tables 4–8, listed all the methods along with the implementation details such as segmentation manner as well as validation database. The trend of the DL methodologies shows a shift toward further use of CNN for various applications of heart sound analysis (see Figure 10). It is seen that the total number of papers on heart sound analysis which were published within 2020–2021, is more than double the ones published within 2017–2020, showing a strictly positive trend of the research interest in this topic. This necessitates the need for a comprehensive survey study, to avail the researchers of the technical details along with the scope of the experimental results. A perfect 100% of the classification accuracy was observed in some of the DL-based studies (Deperlioglu et al., 2020; Low and Choo, 2018), showing a noticeable enhancement compared to the conventional methods (Rajamhoana et al., 2018). Nevertheless, strict conclusions about the performance of DL methods in this context demand further discussion, especially since the previous review papers fail to scrutinize the observed studies comprehensively.
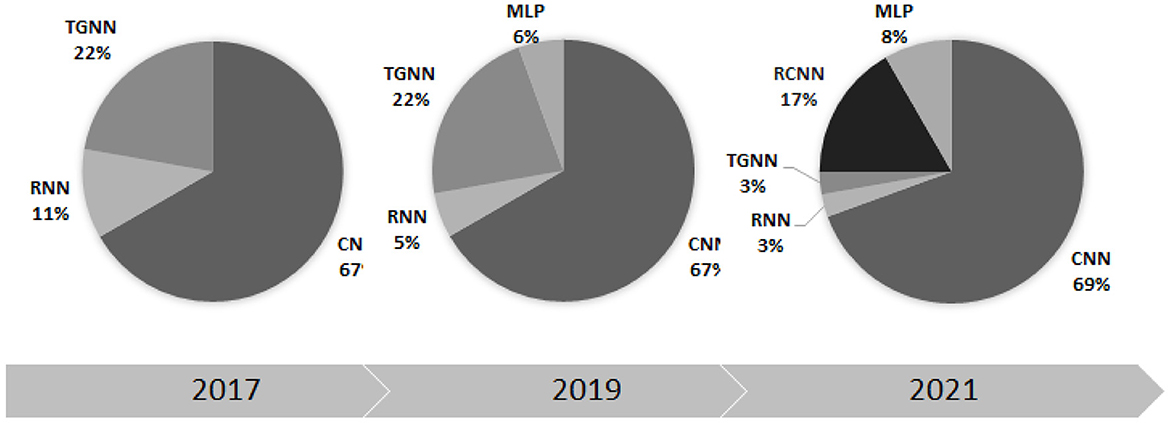
Figure 10. The percentage contribution of different deep learning methods in heart sound analysis for three recent years.
A fair conclusion about the appropriate DL method for a research question demands some considerations beyond the performance measures. The method complexity including the segmentation and feature extraction methods are two key points requiring further attention when it comes to DL comparison. For a research question, the validation database in conjunction with the validation method should be considered in addition to the performance measures while several DL methods are to be compared.
9.1 Comparison to the other surveys
In total, 14 review or survey papers have been found in this study. A review paper on DL methods for PCG classification was the objective of one of the papers (Chen W. et al., 2021), which failed to consider a pervasive taxonomic and methodological study. Moreover, a number of the important CNN-based studies with high accuracy, were not addressed, making the methodological comparison crippled. The lack of objectivity and comprehensiveness of the study are seen in the two other review papers (Li S. et al., 2020; Rath et al., 2021b). Other studies, either addressed the classification problems only (Rajamhoana et al., 2018; Brites et al., 2021; Rath et al., 2021a; Vasantrao and Rangasamy, 2021; Fernando et al., 2021), or dealt with a narrow scope of the field (El-Dahshan et al., 2021; Jyothi and Pradeepini, 2021b). Oppositely, other review studies put different applications of DL methods into a broad scope of health informatics and rendered the general results without providing sufficient details of the learning and the validation process for PCG analysis (Abdullah Aloyuni, 2021; Bizopoulos and Koutsouris, 2018; Amin et al., 2021). Although heart disease detection was regarded as a narrow application of the DL method in some of the review studies, technical details of the learning and validation along with the results of the important papers with superior performance were overlooked (Lakshmi et al., 2021; Vasantrao and Rangasamy, 2021).
To the best of our knowledge, this study uniquely provides a pervasive knowledge about the state-of-the-art of DL methods along with the corresponding results in PCG analysis, including heart abnormalities classification, PCG segmentation, and recovery. In addition to the methodological and taxonomic contents, technical details of the validation methods, such as the PCG databases, were consistently rendered for each method.
9.2 Methodological complexity
One of the negative aspects of DL methods in comparison to conventional machine learning methods, is their high methodological complexity. It mainly refers to the computational power as well as the memory, required for learning and testing. The reviewed studies failed to report the complexity of their methods in a consistent manner. Nevertheless, a comparative study was found in which the training time of a simpler minimum gated unit (SMGU), MGU, LSTM, CNN, autoencoder, and RNN was estimated to be 2,395, 2,436, 2,863, 10,583, 1,186, and 1,839 seconds, respectively (Xu et al., 2019). It was also observed that for the classification problem, a CNN can demand more than 6 h time for a 10-fold validation using an Intel Core-I7 PC with 16 GB of memory when the bispectrum images employed as the inputs (Alqudah et al., 2020). In another study, the average training and testing time of a CRNN model that employed the MFCC input features was reported to be 3 h and 2.5 seconds, respectively, on a PC with a 3.5 GHz Intel core i5 CPU and 8 GB memory (Deng et al., 2020).
9.3 Performance comparison
Providing a realistic comparison of the performance measures over the reviewed papers is a big challenge due to the inconsistent validation process in terms of the method and the database. For example, in the classification problem, different values for the accuracy were reported, even as high as 100%, were reported (Low and Choo, 2018; Malik et al., 2020; Latif et al., 2018) (see Figure 8). One of the studies which reported a perfect 100% of accuracy, performs the validation by using repeated random sub-sampling and a database of 23 subjects only (Low and Choo, 2018), while another study with 99.88% of accuracy did so, using 5-fold validation method and a database of 1, 000 subjects with 5 different classes of PCGs (Malik et al., 2020). In terms of reliability, the latter is obviously preferred even though the accuracy is slightly degraded. Such validation discrepancy was observed in two other studies with the same objective, VSD detection, but the methodological difference: one employed a TGNN (Gharehbaghi et al., 2020) and the other one used a CNN-based method (Wang J.-K. et al., 2020). The accuracy of the TGNN and the CNN was estimated to be 88.4% and 97.1%, respectively. However, the reliability of the former is privileged due to the realistic validation process which employed repeated random sub-sampling method using a dataset of 115 subjects with 6 classes of PCG, whereas the latter one which employed an overlapping 2-fold validation (unclear overlapping manner) using a dataset of 150 subjects with only 2 distinct classes. Another computational aspect, that can direct the performance accuracy, is the segmentation manner employed for the classification. Some of the studies, particularly one that yielded a very high accuracy of 97.63% (Latif et al., 2018), ignored to report of the segmentation method, making the method reproducibility questionable.
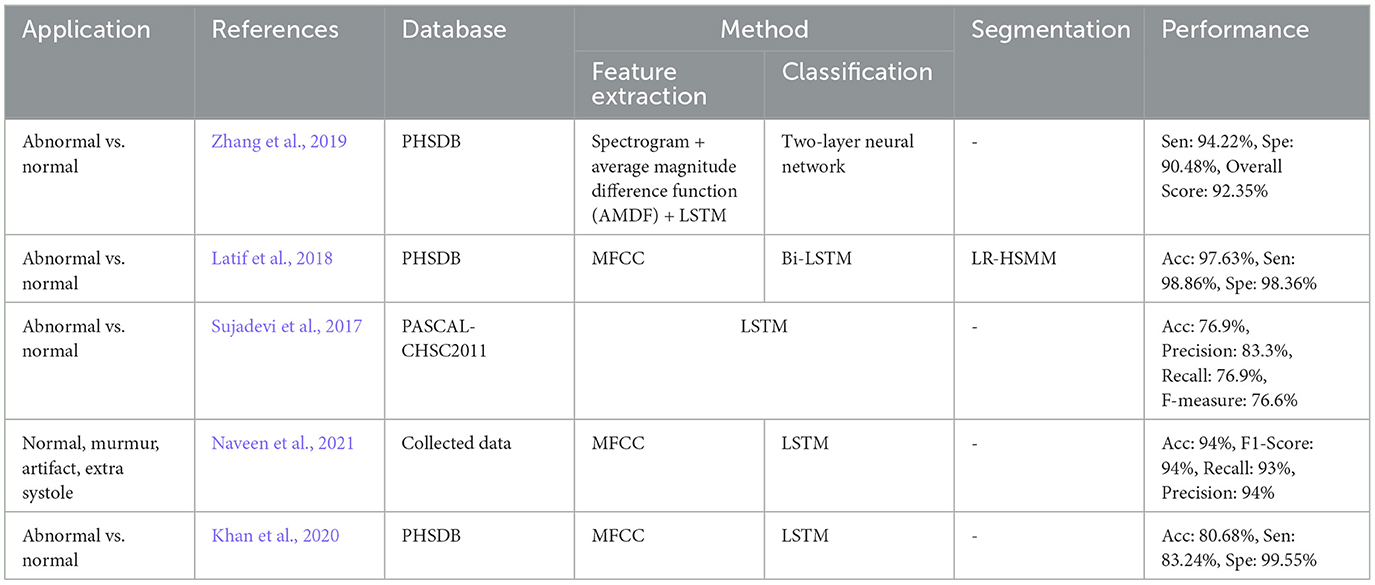
9.4 Other methods
In addition to the above-described methods, a minority of other DL methods were found for different applications of PCG analysis. Bidirectional RNN and LSTM have been reported in a study for the classification task using the Physionet dataset, however, a significant improvement couldn't be found compared to the CNN (Sujadevi et al., 2019). Sharma and Dhar (2019) examined various deep learning techniques to classify heart sounds into normal, abnormal, and artifact. A combination of LSTM and CNN showed an improvement in the classification problem compared to the CNN (Netto and Abraham, 2021). It is also found that a deep TGNN can outperform the conventional hidden Markov model (Gharehbaghi and Babic, 2018).
One of the reviewed papers proposed a CNN-based method using ECG and PCG signals, for a classification problem with 4 classes: normal, abnormal, others, and noisy (Balbin et al., 2021).
Recent studies employed the attention mechanism to improve the performance of a CNN and RNN, and an enhancement in the performance was observed (Ren et al., 2022a). In some other studies, various combinations of CNN and Bidirectional LSTM with an attention block, have been proposed for the classification problem (Tian et al., 2022; Frimpong et al., 2022), as well as for the segmentation problem (Monteiro et al., 2022; Guo et al., 2022). However, these studies failed to meet the criteria for participation in the study.
10 Conclusions
This paper presented the results of a pervasive survey on deep learning methods for heart sound analysis, the topic that has recently received special interest from researchers. The reviewed papers were mainly focused either on disease classification from the segmented heart sound signals or on the methodologies for heart sound segmentation. To a lesser extent, applications such as end-to-end learning, heart sound recovery, and denoising were also observed. Among the different deep learning methods, the CNN-based method was dominantly seen in the classification problems, where a very high accuracy was reported by several studies. For the segmentation problem, the majority of the studies employed either a CNN-based or an RNN-based method. Although the complexity of CNN-based methods was by far higher than the RNN-based ones, the privileges of CNN in this context are conclusive. Regardless of the methodological complexities, much attention should be paid both to the validation method and to the learning database.
Author contributions
EP: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. AB: Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing. AG: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the Department of Biomedical Engineering, Linköping University, Linköping, Sweden.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdullah Aloyuni, S. (2021). A systematic review on machine learning and deep learning based predictive models for health informatics. J. Pharmac. Res. Int. 33, 183–194. doi: 10.9734/jpri/2021/v33i47B33112
Alam, S., Banerjee, R., and Bandyopadhyay, S. (2018). Murmur detection using parallel recurrent &convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.04411.
Alaskar, H., Alzhrani, N., Hussain, A., and Almarshed, F. (2019). “The implementation of pretrained alexnet on pcg classification,” in International Conference on Intelligent Computing (Springer), 784–794. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-26766-7_71
Ali, A. A., Hassan, H. S., and Anwar, E. M. (2020). “Heart diseases diagnosis based on a novel convolution neural network and gate recurrent unit technique,” in 2020 12th International Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEENG) (IEEE), 145–150. doi: 10.1109/ICEENG45378.2020.9171739
Ali, A. A., Hassan, H. S., Anwar, E. M., and Khanna, A. (2021). “Hybrid technique for heart diseases diagnosis based on convolution neural network and long short-term memory,” in Applications of Big Data in Healthcare (Elsevier), 261–280. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-820203-6.00009-6
Al-Issa, Y., and Alqudah, A. M. (2022). A lightweight hybrid deep learning system for cardiac valvular disease classification. Sci. Rep. 12:14297. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18293-7
Alkhodari, M., and Fraiwan, L. (2021). Convolutional and recurrent neural networks for the detection of valvular heart diseases in phonocardiogram recordings. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 200:105940. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.105940
Alqudah, A. M., Alquran, H., and Qasmieh, I. A. (2020). Classification of heart sound short records using bispectrum analysis approach images and deep learning. Netw. Model. Anal. Health Inf. Bioinform. 9, 1–16. doi: 10.1007/s13721-020-00272-5
Amin, R., Al Ghamdi, M. A., Almotiri, S. H., Alruily, M., et al. (2021). Healthcare techniques through deep learning: Issues, challenges and opportunities. IEEE Access 9, 98523–98541. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3095312
Asmare, M. H., Woldehanna, F., Janssens, L., and Vanrumste, B. (2020). “Rheumatic heart disease detection using deep learning from spectro-temporal representation of un-segmented heart sounds,” in 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine &Biology Society (EMBC) (IEEE), 168–171. doi: 10.1109/EMBC44109.2020.9176544
Avanzato, R., and Beritelli, F. (2020). Heart sound multiclass analysis based on raw data and convolutional neural network. IEEE Sensors Lett. 4, 1–4. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2020.3039366
Babu, K. A., and Ramkumar, B. (2020). Automatic recognition of fundamental heart sound segments from PCG corrupted with lung sounds and speech. IEEE Access 8, 179983–179994. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3023044
Bae, J., Kim, M., and Lim, J. S. (2020). “Feature extraction model based on inception v3 to distinguish normal heart sound from systolic murmur,” in 2020 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC) (IEEE), 460–463. doi: 10.1109/ICTC49870.2020.9289317
Baghel, N., Dutta, M. K., and Burget, R. (2020). Automatic diagnosis of multiple cardiac diseases from PCG signals using convolutional neural network. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 197:105750. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105750
Balbin, J. R., Yap, A. I. T., Calicdan, B. D., and Bernabe, L. A. M. (2021). “Arrhythmia detection using electrocardiogram and phonocardiogram pattern using integrated signal processing algorithms with the aid of convolutional neural networks,” in 2021 IEEE International Conference on Automatic Control &Intelligent Systems (I2CACIS) (IEEE), 146–151. doi: 10.1109/I2CACIS52118.2021.9495913
Banerjee, M., and Majhi, S. (2020). “Multi-class heart sounds classification using 2D-convolutional neural network,” in 2020 5th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Security (ICCCS) (IEEE), 1–6. doi: 10.1109/ICCCS49678.2020.9277204
Banerjee, R., and Ghose, A. (2020). “A semi-supervised approach for identifying abnormal heart sounds using variational autoencoder,” in ICASSP 2020–2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (IEEE), 1249–1253. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP40776.2020.9054632
Bilal, E. M. (2021). Heart sounds classification using convolutional neural network with 1D-local binary pattern and 1D-local ternary pattern features. Appl. Acoust. 180:108152. doi: 10.1016/j.apacoust.2021.108152
Bizopoulos, P., and Koutsouris, D. (2018). Deep learning in cardiology. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 12, 168–193. doi: 10.1109/RBME.2018.2885714
Bondareva, E., Han, J., Bradlow, W., and Mascolo, C. (2021). “Segmentation-free heart pathology detection using deep learning,” in 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine &Biology Society (EMBC) (IEEE), 669–672. doi: 10.1109/EMBC46164.2021.9630203
Boulares, M., Alotaibi, R., AlMansour, A., and Barnawi, A. (2021). Cardiovascular disease recognition based on heartbeat segmentation and selection process. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18:10952. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182010952
Bourlard, H., and Wellekens, C. (1990). Links between markov models and multilayer perceptrons. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 12, 1167–1178. doi: 10.1109/34.62605
Bozkurt, B., Germanakis, I., and Stylianou, Y. (2018). A study of time-frequency features for cnn-based automatic heart sound classification for pathology detection. Comput. Biol. Med. 100, 132–143. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.06.026
Brites, I. S. G., da Silva, L. M., Barbosa, J. L. V., Rigo, S. J., Correia, S. D., and Leithardt, V. R. Q. (2021). “Machine learning and iot applied to cardiovascular diseases identification through heart sounds: a literature review,” in Informatics (Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute), 73. doi: 10.3390/informatics8040073
Chakraborty, D., Bhattacharya, S., Thakur, A., Gosthipaty, A. R., and Datta, C. (2020). “Feature extraction and classification of phonocardiograms using convolutional neural networks,” in 2020 IEEE 1st International Conference for Convergence in Engineering (ICCE) (IEEE), 275–279. doi: 10.1109/ICCE50343.2020.9290565
Chen, D., Xuan, W., Gu, Y., Liu, F., Chen, J., Xia, S., et al. (2022). Automatic classification of normal-abnormal heart sounds using convolution neural network and long-short term memory. Electronics 11:1246. doi: 10.3390/electronics11081246
Chen, W., Sun, Q., Chen, X., Xie, G., Wu, H., and Xu, C. (2021). Deep learning methods for heart sounds classification: a systematic review. Entropy 23:667. doi: 10.3390/e23060667
Chen, Y., Lv, J., Sun, Y., and Jia, B. (2020a). Heart sound segmentation via duration long-short term memory neural network. Appl. Soft Comput. 95:106540. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106540
Chen, Y., Sun, Y., Lv, J., Jia, B., and Huang, X. (2021). End-to-end heart sound segmentation using deep convolutional recurrent network. Complex Intell. Syst. 7, 2103–2117. doi: 10.1007/s40747-021-00325-w
Chen, Y., Wei, S., and Zhang, Y. (2020b). Classification of heart sounds based on the combination of the modified frequency wavelet transform and convolutional neural network. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 58, 2039–2047. doi: 10.1007/s11517-020-02218-5
Cheng, X., Huang, J., Li, Y., and Gui, G. (2019). Design and application of a laconic heart sound neural network. IEEE Access 7, 124417–124425. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2934827
Chorba, J. S., Shapiro, A. M., Le, L., Maidens, J., Prince, J., Pham, S., et al. (2021). Deep learning algorithm for automated cardiac murmur detection via a digital stethoscope platform. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 10:e019905. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.019905
Chowdhury, M., Poudel, K., and Hu, Y. (2020). “Detecting abnormal pcg signals and extracting cardiac information employing deep learning and the shannon energy envelope,” in 2020 IEEE Signal Processing in Medicine and Biology Symposium (SPMB) (IEEE), 1–4. doi: 10.1109/SPMB50085.2020.9353624
Chowdhury, T. H., Poudel, K. N., and Hu, Y. (2020). Time-frequency analysis, denoising, compression, segmentation, and classification of PCG signals. IEEE Access 8, 160882–160890. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3020806
Chung, J., Gulcehre, C., Cho, K., and Bengio, Y. (2014). Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv preprint arXiv:1412.3555.
Colt, R.-G., Várady, C.-H., Volpi, R., and Malagó, L. (2021). Automatic feature extraction for heartbeat anomaly detection. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.12289.
Demir, F., Şengür, A., Bajaj, V., and Polat, K. (2019). Towards the classification of heart sounds based on convolutional deep neural network. Health Inf. Sci. Syst. 7, 1–9. doi: 10.1007/s13755-019-0078-0
Deng, M., Meng, T., Cao, J., Wang, S., Zhang, J., and Fan, H. (2020). Heart sound classification based on improved mfcc features and convolutional recurrent neural networks. Neural Netw. 130, 22–32. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2020.06.015
Deperlioglu, O. (2018). Classification of phonocardiograms with convolutional neural networks. BRAIN 9, 22–33.
Deperlioglu, O. (2019a). “Classification of segmented heart sounds with autoencoder neural networks,” in Proceeding &Abstract Book, 130.
Deperlioglu, O. (2019b). Classification of segmented phonocardiograms by convolutional neural networks. BRAIN 10, 5–13.
Deperlioglu, O. (2021). Heart sound classification with signal instant energy and stacked autoencoder network. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 64:102211. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102211
Deperlioglu, O., Kose, U., Gupta, D., Khanna, A., and Sangaiah, A. K. (2020). Diagnosis of heart diseases by a secure internet of health things system based on autoencoder deep neural network. Comput. Commun. 162, 31–50. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2020.08.011
Dhar, P., Dutta, S., and Mukherjee, V. (2021). Cross-wavelet assisted convolution neural network (alexnet) approach for phonocardiogram signals classification. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 63:102142. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2020.102142
Dominguez-Morales, J. P., Jimenez-Fernandez, A. F., Dominguez-Morales, M. J., and Jimenez-Moreno, G. (2017). Deep neural networks for the recognition and classification of heart murmurs using neuromorphic auditory sensors. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 12, 24–34. doi: 10.1109/TBCAS.2017.2751545
Duggento, A., Conti, A., Guerrisi, M., and Toschi, N. (2020). “Detection of abnormal phonocardiograms through the mel-frequency ceptrum and convolutional neural networks,” in 2020 11th Conference of the European Study Group on Cardiovascular Oscillations (ESGCO). (IEEE), 1–2. doi: 10.1109/ESGCO49734.2020.9158167
Duggento, A., Conti, A., Guerrisi, M., and Toschi, N. (2021). A novel multi-branch architecture for state of the art robust detection of pathological phonocardiograms. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 379:20200264. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2020.0264
El-Dahshan, E.-S. A., Bassiouni, M. M., Sharvia, S., and Salem, A.-B. M. (2021). PCG signals for biometric authentication systems: an in-depth review. Comput. Sci. Rev. 41:100420. doi: 10.1016/j.cosrev.2021.100420
Fernando, T., Gammulle, H., Denman, S., Sridharan, S., and Fookes, C. (2021). Deep learning for medical anomaly detection-a survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 54, 1–37. doi: 10.1145/3464423
Fernando, T., Ghaemmaghami, H., Denman, S., Sridharan, S., Hussain, N., and Fookes, C. (2019). Heart sound segmentation using bidirectional lstms with attention. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 24, 1601–1609. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2019.2949516
Frimpong, E. A., Zhiguang, Q., Kwadwo, T. E., Rutherford, P. A., Baagyere, E. Y., and Turkson, R. E. (2022). “Heart sound classification using residual neural network and convolution block attention module,” in 2022 19th International Computer Conference on Wavelet Active Media Technology and Information Processing (ICCWAMTIP) (IEEE), 1–7. doi: 10.1109/ICCWAMTIP56608.2022.10016549
Gharehbaghi, A., Ask, P., and Babic, A. (2015a). A pattern recognition framework for detecting dynamic changes on cyclic time series. Pattern Recognit. 48, 696–708. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2014.08.017
Gharehbaghi, A., Ask, P., Nylander, E., Janerot-Sjoberg, B., Ekman, I., Linden, M., et al. (2015b). “A hybrid model for diagnosing sever aortic stenosis in asymptomatic patients using phonocardiogram,” in World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering, June 7–12, 2015, Toronto, Canada (Cham: Springer), 1006–1009. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-19387-8_245
Gharehbaghi, A., and Babic, A. (2018). “Structural risk evaluation of a deep neural network and a markov model in extracting medical information from phonocardiography,” in Data, Informatics and Technology: An Inspiration for Improved Healthcare (IOS Press), 157–160.
Gharehbaghi, A., Babic, A., and Sepehri, A. A. (2018). “A machine learning method for screening children with patent ductus arteriosus using intelligent phonocardiography,” in EAI International Conference on IoT Technologies for HealthCare (Springer), 89–95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-30335-8_7
Gharehbaghi, A., Babic, A., and Sepehri, A. A. (2019a). “Extraction of diagnostic information from phonocardiographic signal using time-growing neural network,” in World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engineering 2018 (Springer), 849–853. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-9023-3_153
Gharehbaghi, A., Dutoit, T., Ask, P., and Sörnmo, L. (2014). Detection of systolic ejection click using time growing neural network. Med. Eng. Phys. 36, 477–483. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2014.02.011
Gharehbaghi, A., Dutoit, T., Sepehri, A., Kocharian, A., and Lindén, M. (2015c). A novel method for screening children with isolated bicuspid aortic valve. Cardiovasc. Eng. Technol. 6, 546–556. doi: 10.1007/s13239-015-0238-6
Gharehbaghi, A., and Lindén, M. (2015). “An internet-based tool for pediatric cardiac disease diagnosis using intelligent phonocardiography,” in Internet of Things. IoT Infrastructures. IoT360 2015. Lecture Notes of the Institute for Computer Sciences, Social Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering (Springer), 443–447. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-47063-4_46
Gharehbaghi, A., and Lindén, M. (2017). A deep machine learning method for classifying cyclic time series of biological signals using time-growing neural network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29, 4102–4115. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2754294
Gharehbaghi, A., Linden, M., and Babic, A. (2019b). An artificial intelligent-based model for detecting systolic pathological patterns of phonocardiogram based on time-growing neural network. Appl. Soft Comput. 83:105615. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105615
Gharehbaghi, A., Sepehri, A., and Babic, A. (2021). “Distinguishing aortic stenosis from bicuspid aortic valve in children using intelligent phonocardiography,” in 8th European Medical and Biological Engineering Conference, EMBEC 2020, 29 November 2020 through 3 December 2020 (Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH), 399–406. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-64610-3_46
Gharehbaghi, A., Sepehri, A. A., and Babic, A. (2019c). “An edge computing method for extracting pathological information from phonocardiogram,” in ICIMTH, 364–367.
Gharehbaghi, A., Sepehri, A. A., and Babic, A. (2019d). “Forth heart sound detection using backward time-growing neural network,” in International Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering (Springer), 341–345. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-17971-7_53
Gharehbaghi, A., Sepehri, A. A., and Babic, A. (2020). Distinguishing septal heart defects from the valvular regurgitation using intelligent phonocardiography. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 270, 178–182. doi: 10.3233/SHTI200146
Gharehbaghi, A., Sepehri, A. A., Linden, M., and Babic, A. (2017a). “A hybrid machine learning method for detecting cardiac ejection murmurs,” in EMBEC &NBC 2017 (Springer), 787–790. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-5122-7_197
Gharehbaghi, A., Sepehri, A. A., Linden, M., and Babic, A. (2017b). “Intelligent phonocardiography for screening ventricular septal defect using time growing neural network,” in Informatics Empowers Healthcare Transformation (IOS Press), 108–111.
Ghosh, S. K., Ponnalagu, R., Tripathy, R., and Acharya, U. R. (2020). Deep layer kernel sparse representation network for the detection of heart valve ailments from the time-frequency representation of PCG recordings. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020:8843963. doi: 10.1155/2020/8843963
Gjoreski, M., Gradišek, A., Budna, B., Gams, M., and Poglajen, G. (2020). Machine learning and end-to-end deep learning for the detection of chronic heart failure from heart sounds. IEEE Access 8, 20313–20324. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2968900
Guo, Y., Yang, H., Guo, T., Pan, J., and Wang, W. (2022). A novel heart sound segmentation algorithm via multi-feature input and neural network with attention mechanism. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Expr. 9:015012. doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/ac9da6
Han, W., Yang, Z., Lu, J., and Xie, S. (2018). Supervised threshold-based heart sound classification algorithm. Physiol. Meas. 39:115011. doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/aae7fa
He, Y., Li, W., Zhang, W., Zhang, S., Pi, X., and Liu, H. (2021). Research on segmentation and classification of heart sound signals based on deep learning. Appl. Sci. 11:651. doi: 10.3390/app11020651
Hettiarachchi, R., Haputhanthri, U., Herath, K., Kariyawasam, H., Munasinghe, S., Wickramasinghe, K., et al. (2021). “A novel transfer learning-based approach for screening pre-existing heart diseases using synchronized ecg signals and heart sounds,” in 2021 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS) (IEEE), 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ISCAS51556.2021.9401093
Hinton, G. E., Osindero, S., and Teh, Y.-W. (2006). A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Comput. 18, 1527–1554. doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527
Ho, W.-H., Huang, T.-H., Yang, P.-Y., Chou, J.-H., Qu, J.-Y., Chang, P.-C., et al. (2021). Robust optimization of convolutional neural networks with a uniform experiment design method: a case of phonocardiogram testing in patients with heart diseases. BMC Bioinform. 22, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04032-8
Huai, X., Kitada, S., Choi, D., Siriaraya, P., Kuwahara, N., and Ashihara, T. (2021). Heart sound recognition technology based on convolutional neural network. Inform. Health Soc. Care 46, 320–332. doi: 10.1080/17538157.2021.1893736
Humayun, A. I., Ghaffarzadegan, S., Ansari, M. I., Feng, Z., and Hasan, T. (2020). Towards domain invariant heart sound abnormality detection using learnable filterbanks. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 24, 2189–2198. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2020.2970252
Humayun, A. I., Ghaffarzadegan, S., Feng, Z., and Hasan, T. (2018a). “Learning front-end filter-bank parameters using convolutional neural networks for abnormal heart sound detection,” in 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC) (IEEE), 1408–1411. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2018.8512578
Humayun, A. I., Khan, M., Ghaffarzadegan, S., Feng, Z., Hasan, T., et al. (2018b). An ensemble of transfer, semi-supervised and supervised learning methods for pathological heart sound classification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1806.06506.
Irene, D. S., Sethukarasi, T., and Vadivelan, N. (2020). Heart disease prediction using hybrid fuzzy k-medoids attribute weighting method with dbn-kelm based regression model. Med. Hypotheses 143:110072. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110072
Jeong, Y., Kim, J., Kim, D., Kim, J., and Lee, K. (2021). Methods for improving deep learning-based cardiac auscultation accuracy: Data augmentation and data generalization. Appl. Sci. 11:4544. doi: 10.3390/app11104544
Joshi, H., Salunke, V., Dhabale, P., Yalawar, P., and Vidhate, K. (2020). Heart anomaly detection using deep learning approach based on pcg signal analysis. Heart 7, 1–4.
Jyothi, P., and Pradeepini, G. (2021a). “Classification of normal/abnormal heart sound recording through convolution neural network through the integration of baseline and adaboost classifier,” in Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computational and Bio Engineering (Springer), 441–447. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-1941-0_44
Jyothi, P., and Pradeepini, G. (2021b). “Review on cardiac arrhythmia through segmentation approaches in deep learning,” in International Conference on Intelligent and Smart Computing in Data Analytics: ISCDA 2020 (Springer Singapore), 139–147. doi: 10.1007/978-981-33-6176-8_15
Kang, S.-H., Joe, B., Yoon, Y., Cho, G.-Y., Shin, I., and Suh, J.-W. (2018). Cardiac auscultation using smartphones: pilot study. JMIR mHealth uHealth 6:e8946. doi: 10.2196/mhealth.8946
Kayikçı, Ş. (2019). “Cardiac sound analyzation using convolutional neural network,” in 2019 3rd International Symposium on Multidisciplinary Studies and Innovative Technologies (ISMSIT) (IEEE), 1–4. doi: 10.1109/ISMSIT.2019.8932952
Kesav, R. S., Bhanu Prakash, M., Kumar, K., Sowmya, V., and Soman, K. (2021). “Performance improvement in deep learning architecture for phonocardiogram signal classification using spectrogram,” in International Conference on Advances in Computing and Data Sciences (Springer), 538–549. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-81462-5_48
Khan, F. A., Abid, A., and Khan, M. S. (2020). Automatic heart sound classification from segmented/unsegmented phonocardiogram signals using time and frequency features. Physiol. Meas. 41:055006. doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/ab8770
Khan, K. N., Khan, F. A., Abid, A., Olmez, T., Dokur, Z., Khandakar, A., et al. (2021). Deep learning based classification of unsegmented phonocardiogram spectrograms leveraging transfer learning. Physiol. Measur. 42:095003. doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/ac1d59
Kiranyaz, S., Zabihi, M., Rad, A. B., Tahir, A., Ince, T., Hamila, R., et al. (2019). Real-time pcg anomaly detection by adaptive 1d convolutional neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.07238.
Koike, T., Qian, K., Kong, Q., Plumbley, M. D., Schuller, B. W., and Yamamoto, Y. (2020). “Audio for audio is better? An investigation on transfer learning models for heart sound classification,” in 2020 42nd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine &Biology Society (EMBC) (IEEE), 74–77. doi: 10.1109/EMBC44109.2020.9175450
Kose, U., Deperlioglu, O., Alzubi, J., and Patrut, B. (2021). “A practical method for early diagnosis of heart diseases via deep neural network,” in Deep Learning for Medical Decision Support Systems (Springer), 95–106. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-6325-6_6
Krishnan, P. T., Balasubramanian, P., and Umapathy, S. (2020). Automated heart sound classification system from unsegmented phonocardiogram (PCG) using deep neural network. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 43, 505–515. doi: 10.1007/s13246-020-00851-w
Kucharski, D., Grochala, D., Kajor, M., and Kańtoch, E. (2017). “A deep learning approach for valve defect recognition in heart acoustic signal,” in International Conference on Information Systems Architecture and Technology (Springer), 3–14. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-67220-5_1
Kucharski, D., Kajor, M., Grochala, D., Iwaniec, M., and Iwaniec, J. (2019). Combining spectral analysis with artificial intelligence in heart sound study. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 13, 112–118. doi: 10.12913/22998624/108447
Kui, H., Pan, J., Zong, R., Yang, H., and Wang, W. (2021). Heart sound classification based on log mel-frequency spectral coefficients features and convolutional neural networks. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 69:102893. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102893
Lakshmi, A. (2021). A review on deep learning algorithms in healthcare. Turkish J. Comput. Mathem. Educ. 12, 5682–5686. doi: 10.17762/turcomat.v12i10.5379
Latif, S., Usman, M., and Rana, J. Q. R. (2018). Abnormal heartbeat detection using recurrent neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1801.08322.
LeCun, Y., Bengio, Y., and Hinton, G. (2015). Deep learning. Nature 521, 436–444. doi: 10.1038/nature14539
Li, F., Liu, M., Zhao, Y., Kong, L., Dong, L., Liu, X., et al. (2019). Feature extraction and classification of heart sound using 1d convolutional neural networks. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2019, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s13634-019-0651-3
Li, F., Tang, H., Shang, S., Mathiak, K., and Cong, F. (2020). Classification of heart sounds using convolutional neural network. Appl. Sci. 10:3956. doi: 10.3390/app10113956
Li, H., Wang, X., Liu, C., Zeng, Q., Zheng, Y., Chu, X., et al. (2020). A fusion framework based on multi-domain features and deep learning features of phonocardiogram for coronary artery disease detection. Comput. Biol. Med. 120:103733. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2020.103733
Li, P., Hu, Y., and Liu, Z.-P. (2021). Prediction of cardiovascular diseases by integrating multi-modal features with machine learning methods. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 66:102474. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.102474
Li, S., Li, F., Tang, S., and Xiong, W. (2020). A review of computer-aided heart sound detection techniques. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020:5846191. doi: 10.1155/2020/5846191
Li, T., Qing, C., and Tian, X. (2017). “Classification of heart sounds based on convolutional neural network,” in International Conference on Internet Multimedia Computing and Service (Springer), 252–259. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-8530-7_24
Li, T., Yin, Y., Ma, K., Zhang, S., and Liu, M. (2021). Lightweight end-to-end neural network model for automatic heart sound classification. Information 12:54. doi: 10.3390/info12020054
Liu, J., Wang, H., Yang, Z., Quan, J., Liu, L., and Tian, J. (2022). Deep learning-based computer-aided heart sound analysis in children with left-to-right shunt congenital heart disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 348, 58–64. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2021.12.012
Low, J. X., and Choo, K. W. (2018). “Classification of heart sounds using softmax regression and convolutional neural network,” in Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Communication Engineering and Technology, 18–21. doi: 10.1145/3194244.3194255
Lv, J., Dong, B., Lei, H., Shi, G., Wang, H., Zhu, F., et al. (2021). Artificial intelligence-assisted auscultation in detecting congenital heart disease. Eur. Heart J.-Dig. Health 2, 119–124. doi: 10.1093/ehjdh/ztaa017
Maknickas, V., and Maknickas, A. (2017). Recognition of normal-abnormal phonocardiographic signals using deep convolutional neural networks and mel-frequency spectral coefficients. Physiol. Meas. 38:1671. doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/aa7841
Malik, A. E. F., Barin, S., and Yüksel, M. E. (2020). “Accurate classification of heart sound signals for cardiovascular disease diagnosis by wavelet analysis and convolutional neural network: preliminary results,” in 2020 28th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU) (IEEE), 1–4. doi: 10.1109/SIU49456.2020.9302491
Megalmani, D. R., Shailesh, B., Rao, A., Jeevannavar, S. S., and Ghosh, P. K. (2021). “Unsegmented heart sound classification using hybrid cnn-lstm neural networks,” in 2021 43rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine &Biology Society (EMBC) (IEEE), 713–717. doi: 10.1109/EMBC46164.2021.9629596
Meintjes, A., Lowe, A., and Legget, M. (2018). “Fundamental heart sound classification using the continuous wavelet transform and convolutional neural networks,” in 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC) (IEEE), 409–412. doi: 10.1109/EMBC.2018.8512284
Messner, E., Zöhrer, M., and Pernkopf, F. (2018). Heart sound segmentation event detection approach using deep recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 65, 1964–1974. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2018.2843258
Mikolov, T., Karafiát, M., Burget, L., Černocký, J., and Khudanpur, S. (2010). “Recurrent neural network based language model,” in Eleventh Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (ISCA). doi: 10.21437/Interspeech.2010-343
Mishra, M., Menon, H., and Mukherjee, A. (2018). Characterization of s_1 and s_2 heart sounds using stacked autoencoder and convolutional neural network. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 68, 3211–3220. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2018.2872387
Monteiro, S. M., Fred, A., and da Silva, H. P. (2022). Bidirectional long short-term memory networks for heart sound segmentation from the phonocardiogram. Available at SSRN 4113641. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.4113641
Naveen, A., Reddy, P. S. T., and Thenmozhi, T. (2021). Deep learning based classification of heart diseases from heart sounds. Int. J. Res. Eng. Sci. Manag. 4, 165–171.
Netto, A. N., and Abraham, L. (2021). “Detection and classification of cardiovascular disease from phonocardiogram using deep learning models,” in 2021 Second International Conference on Electronics and Sustainable Communication Systems (ICESC) (IEEE), 1646–1651. doi: 10.1109/ICESC51422.2021.9532766
Nogueira, D. M., Ferreira, C. A., Gomes, E. F., and Jorge, A. M. (2019). Classifying heart sounds using images of motifs, mfcc and temporal features. J. Med. Syst. 43, 1–13. doi: 10.1007/s10916-019-1286-5
Noman, F., Ting, C.-M., Salleh, S.-H., and Ombao, H. (2019). “Short-segment heart sound classification using an ensemble of deep convolutional neural networks,” in ICASSP 2019–2019 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (IEEE), 1318–1322. doi: 10.1109/ICASSP.2019.8682668
Oh, S. L., Jahmunah, V., Ooi, C. P., Tan, R.-S., Ciaccio, E. J., Yamakawa, T., et al. (2020). Classification of heart sound signals using a novel deep wavenet model. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 196:105604. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105604
Oliveira, J., Carvalho, M., Nogueira, D. M., and Coimbra, M. (2020). Segmentation and optimal region selection of physiological signals using deep neural networks and combinatorial optimization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2003.07981.
Rajamhoana, S., Devi, C. A., Umamaheswari, K., Kiruba, R., Karunya, K., and Deepika, R. (2018). “Analysis of neural networks based heart disease prediction system,” in 2018 11th International Conference on Human System Interaction (HSI) (IEEE), 233–239. doi: 10.1109/HSI.2018.8431153
Rath, A., Mishra, D., and Panda, G. (2021a). Deep learning neural network and cnn-based diagnosis of heart diseases. Techn. Adv. Mach. Learn. Healthcare 936:169. doi: 10.1007/978-981-33-4698-7_9
Rath, A., Mishra, D., Panda, G., and Satapathy, S. C. (2021b). An exhaustive review of machine and deep learning based diagnosis of heart diseases. Multim. Tools Applic. 81, 36069–36127. doi: 10.1007/s11042-021-11259-3
Ren, Z., Qian, K., Dong, F., Dai, Z., Nejdl, W., Yamamoto, Y., et al. (2022a). Deep attention-based neural networks for explainable heart sound classification. Mach. Learn. Applic. 9:100322. doi: 10.1016/j.mlwa.2022.100322
Ren, Z., Qiao, Y., Yuan, Y., Zhou, Y., Liang, Y., and Shi, X. (2022b). “Time and time-frequency features integrated cnn model for heart sound signals detection,” in 2022 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM) (IEEE), 1138–1143. doi: 10.1109/BIBM55620.2022.9995295
Renna, F., Oliveira, J., and Coimbra, M. T. (2019). Deep convolutional neural networks for heart sound segmentation. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 23, 2435–2445. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2019.2894222
Rizal, A., Adz-Dzikri, A. A., and Fauzi, M. A. G. (2020). Classification of normal and abnormal heart sound using continuous wavelet transform and resnet-50. Technol. Rep. Kansai Univ. 62, 2595–2601.
Rubin, J., Abreu, R., Ganguli, A., Nelaturi, S., Matei, I., and Sricharan, K. (2017). Recognizing abnormal heart sounds using deep learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1707.04642.
Samir, A. A., Rashwan, A. R., Sallam, K. M., Chakrabortty, R. K., Ryan, M. J., and Abohany, A. A. (2021). Evolutionary algorithm-based convolutional neural network for predicting heart diseases. Comput. Industr. Eng. 161:107651. doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2021.107651
Sepehri, A. A., Hancq, J., Dutoit, T., Gharehbaghi, A., Kocharian, A., and Kiani, A. (2008). Computerized screening of children congenital heart diseases. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 92, 186–192. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2008.06.015
Sharma, S., and Dhar, J. (2019). “Deep learning approach for analysis of artifacts in heart sound,” in Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Electronics, Electrical &Computational Intelligence (ICAEEC). doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3577626
Shinde, S., and Martinez-Ovando, J. C. (2021). “Heart disease detection with deep learning using a combination of multiple input sources,” in 2021 IEEE Fifth Ecuador Technical Chapters Meeting (ETCM) (IEEE), 1–3. doi: 10.1109/ETCM53643.2021.9590672
Shojaedini, S. V., and Morabbi, S. (2020). A new method to improve automated classification of heart sound signals: filter bank learning in convolutional neural networks. Iranian J. Med. Phys. 17, 331–339. doi: 10.22038/ijmp.2019.38169.1489
Shuvo, S. B., Ali, S. N., Swapnil, S. I., Al-Rakhami, M. S., and Gumaei, A. (2021). Cardioxnet: a novel lightweight deep learning framework for cardiovascular disease classification using heart sound recordings. IEEE Access 9, 36955–36967. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3063129
Singh, S. A., Meitei, T. G., and Majumder, S. (2020). “Short PCG classification based on deep learning,” in Deep Learning Techniques for Biomedical and Health Informatics (Elsevier), 141–164. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-819061-6.00006-9
Sotaquirá, M., Alvear, D., and Mondragón, M. (2018). Phonocardiogram classification using deep neural networks and weighted probability comparisons. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 42, 510–517. doi: 10.1080/03091902.2019.1576789
Sugiyarto, A. W., Abadi, A. M., and Sumarna, S. (2021). Classification of heart disease based on PCG signal using cnn. Telkomnika 19, 1697–1706. doi: 10.12928/telkomnika.v19i5.20486
Sujadevi, V., Soman, K., Vinayakumar, R., and Sankar, A. P. (2017). “Deep models for phonocardiography (PCG) classification,” in 2017 International Conference on Intelligent Communication and Computational Techniques (ICCT) (IEEE), 211–216. doi: 10.1109/INTELCCT.2017.8324047
Sujadevi, V., Soman, K., Vinayakumar, R., and Sankar, A. P. (2019). “Anomaly detection in phonocardiogram employing deep learning,” in Computational Intelligence in Data Mining (Springer), 525–534. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-8055-5_47
Sundaram, D. S. B., Damani, D. N., Kapoor, A., Shivaram, S., and Arunachalam, S. P. (2021). Deep learning based discrimination of phonocardiogram signal with normal heart sounds and murmur: feasiblity study. Biomed. Sci. Instrum. 57:2. doi: 10.34107/BiomedSciInstrum.57.0492
Takezaki, S., and Kishida, K. (2021). “Construction of cnns for abnormal heart sound detection using data augmentation,” in International MultiConference of Engineers and Computer Scientists 2021, IMECS 2021, 18–23.
Tian, G., Lian, C., Zeng, Z., Xu, B., Su, Y., Zang, J., et al. (2022). Imbalanced heart sound signal classification based on two-stage trained dsanet. Cognit. Comput. 14, 1378–1391. doi: 10.1007/s12559-022-10009-3
Tiwari, S., Jain, A., Sharma, A. K., and Almustafa, K. M. (2021). Phonocardiogram signal based multi-class cardiac diagnostic decision support system. IEEE Access 9, 110710–110722. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3103316
Tiwari, S., Sapra, V., and Jain, A. (2020). “Heartbeat sound classification using mel-frequency cepstral coefficients and deep convolutional neural network,” in Advances in Computational Techniques for Biomedical Image Analysis (Elsevier), 115–131. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-820024-7.00006-2
Tseng, K.-K., Wang, C., Huang, Y.-F., Chen, G.-R., Yung, K.-L., and Ip, W.-H. (2021). Cross-domain transfer learning for pcg diagnosis algorithm. Biosensors 11:127. doi: 10.3390/bios11040127
Vasantrao, B. T., and Rangasamy, S. (2021). Review on heart disease diagnosis using deep learning methods. Int. J. Next-Gener. Comput. 12, 91–102. doi: 10.14569/IJACSA.2021.0120944
Wang, J.-K., Chang, Y.-F., Tsai, K.-H., Wang, W.-C., Tsai, C.-Y., Cheng, C.-H., et al. (2020). Automatic recognition of murmurs of ventricular septal defect using convolutional recurrent neural networks with temporal attentive pooling. Sci. Rep. 10, 1–10. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-77994-z
Wang, X., Liu, C., Li, Y., Cheng, X., Li, J., and Clifford, G. D. (2020). Temporal-framing adaptive network for heart sound segmentation without prior knowledge of state duration. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 68, 650–663. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2020.3010241
Wibawa, M. S., Maysanjaya, I. M. D., Novianti, N. K. D. P., and Crisnapati, P. N. (2018). “Abnormal heart rhythm detection based on spectrogram of heart sound using convolutional neural network,” in 2018 6th International Conference on Cyber and IT Service Management (CITSM) (IEEE), 1–4. doi: 10.1109/CITSM.2018.8674341
Wu, J. M.-T., Tsai, M.-H., Huang, Y. Z., Islam, S. H., Hassan, M. M., Alelaiwi, A., et al. (2019). Applying an ensemble convolutional neural network with savitzky-golay filter to construct a phonocardiogram prediction model. Appl. Soft Comput. 78, 29–40. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2019.01.019
Xiao, B., Xu, Y., Bi, X., Li, W., Ma, Z., Zhang, J., et al. (2019). Follow the sound of children's heart: a deep-learning-based computer-aided pediatric chds diagnosis system. IEEE Internet Things J. 7, 1994–2004. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2961132
Xiao, B., Xu, Y., Bi, X., Zhang, J., and Ma, X. (2020). Heart sounds classification using a novel 1-D convolutional neural network with extremely low parameter consumption. Neurocomputing 392, 153–159. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.09.101
Xu, C., Zhou, J., Li, L., Wang, J., Ying, D., and Li, Q. (2019). “Heart sound segmentation based on smgu-rnn,” in BIBE 2019; The Third International Conference on Biological Information and Biomedical Engineering (VDE), 1–7.
Xu C.-D. and Lin, H.. (2021). “Convolutional neural network combined with wavelet denoising for multi-category analysis on heart sound,” in Thirteenth International Conference on Digital Image Processing (ICDIP 2021) (International Society for Optics and Photonics), 118780Z.
Xu, C. D., Zhou, J., Ying, D. W., Hou, L. J., and Long, Q. H. (2020). Heart sound segmentation based on personalized gaussian mixture model and convolutional neural network. doi: 10.21203/rs.2.20414/v2
Xu, Y., Xiao, B., Bi, X., Li, W., Zhang, J., and Ma, X. (2018). “Pay more attention with fewer parameters: a novel 1-D convolutional neural network for heart sounds classification,” in 2018 Computing in Cardiology Conference (CinC) (IEEE), 1–4.
Yamashita, R., Nishio, M., Do, R. K. G., and Togashi, K. (2018). Convolutional neural networks: an overview and application in radiology. Insights Imag. 9, 611–629. doi: 10.1007/s13244-018-0639-9
Yang, Y., Guo, X.-M., Wang, H., and Zheng, Y.-N. (2021). Deep learning-based heart sound analysis for left ventricular diastolic dysfunction diagnosis. Diagnostics 11:2349. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11122349
Yaseen, S.on, G.-Y., and Kwon, S. (2018). Classification of heart sound signal using multiple features. Appl. Sci. 8:2344. doi: 10.3390/app8122344
Yin, Y., Ma, K., and Liu, M. (2020). Temporal convolutional network connected with an anti-arrhythmia hidden semi-markov model for heart sound segmentation. Appl. Sci. 10:7049. doi: 10.3390/app10207049
Zhang, W., and Han, J. (2017). “Towards heart sound classification without segmentation using convolutional neural network,” in 2017 Computing in Cardiology (CinC) (IEEE), 1–4. doi: 10.22489/CinC.2017.254-164
Keywords: phonocardiogram, intelligent phonocardiography, deep learning, heart sound, heart sound segmentation, heart disease, end-to-end learning, heart sound classification
Citation: Partovi E, Babic A and Gharehbaghi A (2024) A review on deep learning methods for heart sound signal analysis. Front. Artif. Intell. 7:1434022. doi: 10.3389/frai.2024.1434022
Received: 16 May 2024; Accepted: 09 October 2024;
Published: 13 November 2024.
Edited by:
Cornelio Yáñez-Márquez, National Polytechnic Institute (IPN), MexicoReviewed by:
John Bush Idoko, Near East University, CyprusCharles Courchaine, National University, United States
Copyright © 2024 Partovi, Babic and Gharehbaghi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Arash Gharehbaghi, YXJhc2guZ2hhcmVoYmFnaGlAbGl1LnNl
 Elaheh Partovi
Elaheh Partovi Ankica Babic
Ankica Babic Arash Gharehbaghi
Arash Gharehbaghi