- Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, Faculty of Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada
Sunlight exposure is recognized as a risk factor for the development of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a common neurodegenerative retinal disease in the elderly. Specifically, the blue light wavelengths within sunlight can negatively impact the physiology of light-sensitive retinal cells, including retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) and photoreceptors. This review explores blue light-induced retinal degeneration, emphasizing the structural and functional impairments in RPE. The initial section provides a brief overview of blue light’s effects on photoreceptors, followed by a comprehensive analysis of its detrimental impact on RPE. In vitro studies reveal that blue light exposure induces morphological alterations and functional impairments in RPE, including reduced phagocytic activity, disrupted secretion of neurotrophic factors, and compromised barrier function. Mechanisms of retinal damage, including oxidative stress, inflammation, lipofuscin accumulation, mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress in RPE, are also explored. The strengths and limitations of in vitro, animal and ex vivo models for studying blue light exposure are discussed, with recommendations for improving reproducibility in future studies.
Introduction
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a degenerative retinal disease affecting the macula, leading to progressive central vision loss and is the leading cause of irreversible blindness in people aged 50 and older (Steinmetz et al., 2021). The pathogenesis of AMD is multifactorial, involving environmental and genetic factors. Several early changes are associated with aging, a major risk factor for AMD. Environmental risk factors include sunlight exposure, cigarette smoke and oxidative stress linked to age and diet (Evans, 2005; Jonasson et al., 2014; Lambert et al., 2016; Schick et al., 2016).
Sunlight, specifically the wavelengths associated with ultraviolet (UV) and blue light, impacts the physiology of retinal cells and is, to some extent, comparable to the photo-aging of the skin (Parkinson et al., 2015). An important distinction is that retinal cells may be affected by certain wavelengths of sunlight, such as blue light (400–500 nm), since most of the radiation in the UV range is absorbed by the cornea (100–315 nm) and lens (315–400 nm), thereby helping to protect the retina from UV-induced photo-oxidative damage (Behar-Cohen et al., 2011; Mallet and Rochette, 2011, 2013).
In recent years, there have been growing concerns about the long-term effects of artificial light exposure from light emitting diodes (LEDs) and modern electronic devices which emit a high proportion of their light in the blue wavelength (Behar-Cohen et al., 2011; Wong and Bahmani, 2022). Research in the field indicates that chronic exposure to blue light in the range of 400–490 nm may affect the function of photoreceptor and RPE due to its high energy, and contribute to the pathogenesis of AMD (Roehlecke et al., 2009; Lin et al., 2017; Gea et al., 2018; Baker et al., 2022; Françon et al., 2024). Nevertheless, evidence from clinical studies remains inconclusive and a definitive link between blue light and retinal damage has yet to be established.
Blue light: a risk factor for AMD?
Estimating the link between sunlight or blue light exposure and AMD risk is challenging due to inconsistent results from population-based studies and meta-analyses of the epidemiological literature (Cruickshanks et al., 2001; Tomany, 2004; Sui et al., 2013; Schick et al., 2016; Zhou et al., 2018; Achiron et al., 2021). The Beaver Dam Eye Study found a possible association between sunlight exposure and increased risk of retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE) abnormalities and early AMD (Cruickshanks et al., 2001; Tomany, 2004). The Chesapeake Bay study reported that AMD patients with extensive geographic atrophy had significantly higher exposure to blue light over the preceding 20 years, compared to age-matched controls (Taylor et al., 1990). The authors combined personal exposure histories with laboratory investigations and field measurements to determine ocular exposure to sunlight. Published ambient data on intensity and spectral distribution of visible light was used to calculate the yearly ocular exposure to blue light for each individual. In the European Eye Study (EUREYE), blue light exposure was estimated by combining meteorologic and questionnaire data regarding outdoor exposure. No link was found between blue light exposure and neovascular or early AMD. However, significant associations were found between blue light exposure and wet AMD in participants with low levels of antioxidants, specifically dietary zinc and zeaxanthin, vitamins C and E in blood. These nutrients are known to work synergistically to protect the retina from light-induced oxidative damage (Thomson et al., 2002; Wrona et al., 2003, 2004). This study emphasizes the complexity of these associations, and the need for further research in this direction (Fletcher, 2008).
Unlike sunlight, artificial lighting contains a fixed spectral distribution that peaks in the blue portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, and the long-term impact of chronic exposure to artificial light on retinal health is unclear (Contín et al., 2016; Wong and Bahmani, 2022). A recent case–control study conducted using nationwide population-based data in South Korea found that artificial light exposure at night significantly increased the risk of developing exudative AMD (Kim et al., 2024). Excessive blue light exposure consistently damages photoreceptors and RPE in culture and animal models, as detailed in the following two sections. However, this correlation has not yet been fully validated in human studies and remains an area of active research.
Effect of blue light on photoreceptors
Photoreceptors are specialized sensory cells in the retina and interact with the RPE to convert incoming light into neural signals, a process known as phototransduction (Molday and Moritz, 2015). Photoreceptor health is crucial for vision. Light-induced damage is classified into two types based on total dose, which includes irradiance (mW/cm2) and exposure duration: Class I, or Noell damage, predominantly studied in rats but also observed in primates and other species, occurs with longer exposures (>1.5 h) and lower irradiance (<1 mW/cm2), and primarily affects photoreceptors, although RPE damage can occur with extended exposure (>8 days) (Noell et al., 1966; Noell, 1980; Hunter et al., 2012). Class II, or Ham damage, predominantly studied in primates but also observed in rats and other species, results from shorter exposures (<5 h) at much higher irradiances (>10 mW/cm2), and mainly affects the RPE (Ham et al., 1979; Ham, 1983; Hunter et al., 2012; Cougnard-Gregoire et al., 2023; Youssef et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2024).
In rats, blue light damages photoreceptors through several cellular mechanisms, including reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, mitochondrial damage, and apoptosis (Busch et al., 1999; Theruveethi et al., 2022). In primates, blue light caused significantly more damage to the RPE and cone outer segments compared to longer wavelengths (Zhang et al., 2024). In rats,12 h/day of blue light for 28 days significantly disrupted the outer retinal structure, notably reducing photoreceptor nuclei, damaging their outer segments, and disrupting the outer plexiform layers (Theruveethi et al., 2022). Photoreceptor transcriptome profiling by RNA-seq after blue light exposure in Drosophila demonstrated an upregulation of a broad range of genes involved in oxidative stress response and neuroprotective pathways, with concomitant downregulation of genes required for light response including voltage-gated calcium, potassium and chloride ion channels. Interestingly, mature flies were more susceptible to these blue light-induced transcriptomic changes compared to very young flies (Hall et al., 2018).
In cultured murine photoreceptor-derived cells, blue light increased production of ROS, altered protein expression, and caused photoreceptor damage (Kuse et al., 2014). Photoreceptor cell death from blue light exposure was mainly caused by inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis through Bax and caspase-3 activation (Xu et al., 2023). Similarly, mouse retinal explant cultures showed increased ROS production, morphological changes including the disorganization of the outer segments, cell membrane disruption, and cell death with prolonged blue light exposure (Figure 1) (Roehlecke et al., 2011).
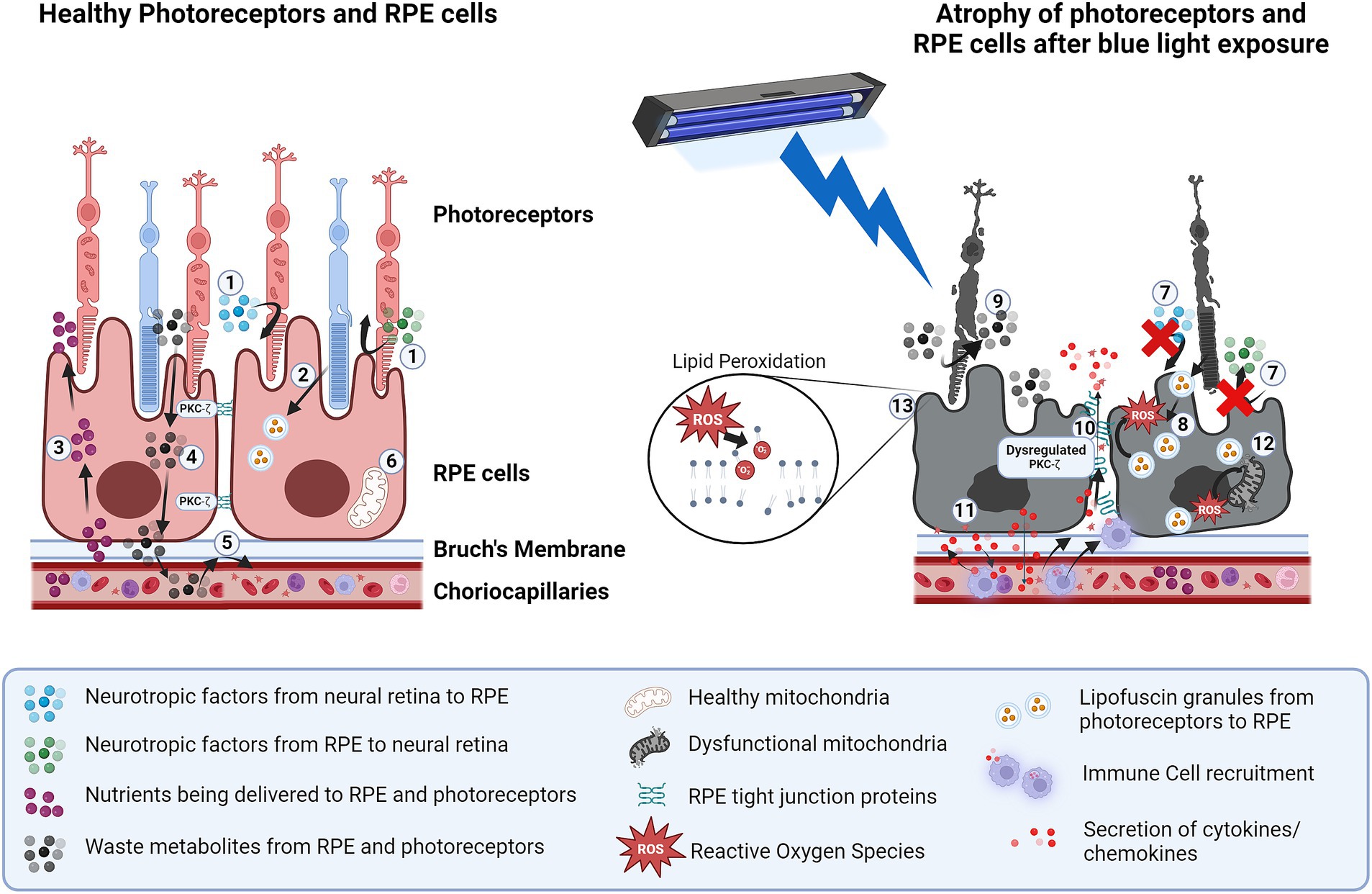
Figure 1. Structural and functional impairments in photoreceptors and RPE cells due to blue light exposure. In healthy photoreceptors and RPE cells: 1. secreted neurotropic factors such as HGF, VEGF and angiogenin help maintain homeostasis of the neural retina and RPE. 2. Phagocytosis of photoreceptor outer segments by RPE into lysosomes helps preserve photoreceptor function. 3. Nutrient uptake is controlled by RPE. 4. Metabolite exchange from retina to choroid is controlled by RPE. 5. Outer blood-retinal barrier is maintained due to RPE tight junctions. 6. Healthy mitochondria help manage oxidative stress in RPE. Blue light exposure of RPE causes: 7. Dysfunctional neurotrophic factors secretion between neural retina and RPE. 8. Dysfunction in phagocytosis of photoreceptor outer segments 9. Metabolite accumulation in the retina due to lack of uptake by RPE. 10. Breakdown of tight junctions due to blue light-induced dysfunction of PKC-ζ. 11. Secretion of cytokines/chemokines causes inflammation and exacerbates the recruitment of immune cells which further damage RPE. 12. Increase in oxidative stress from lipofuscin granules and ROS resulting in mitochondrial damage. 13. Lipid peroxidation from ROS resulting in cellular toxicity and reduced viability. Created in BioRender. BioRender.com/e21v624.
Effect of blue light exposure on retinal pigmented epithelium
The RPE forms a crucial interface between the neural retina and choroid, the vascular supply of the outer retina. The RPE controls the transportation of nutrients, ions, and water to photoreceptors, absorbs light and safeguards against photooxidation, converts all-trans-retinal to 11-cis-retinal to support the visual cycle, engulfs and discards photoreceptor membranes through phagocytosis, and secretes vital factors contributing to the structural integrity of the retina. The RPE is also important in combating lipid photooxidation and the generation of ROS, both of which are toxic to the retina, serving as the main defense system to counterbalance the high oxidative stress in the retina (Simó et al., 2010).
The outer blood-retinal barrier (oBRB), consisting of RPE monolayer and their tight junctions with Bruch’s membrane, controls nutrient and metabolite exchange vital for photoreceptor survival. Blue light exposure disrupts RPE tight junctions, resulting in loss of barrier function in rodents, rabbits and cultured human RPE cells. The decline in barrier function is associated with alterations in RPE tight junction proteins, specifically zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) (Putting et al., 1992; Ozkaya et al., 2019; Xie et al., 2021). Blue light (400–520 nm) at 50 J/cm2energy (0.014 W/cm2 for 1 h) causes oBRB dysfunction in rabbits, 30 times more effectively than yellow light (510–740 nm) at the same energy (Putting et al., 1992, 1994). In human RPE cells, this effect is attributed to the dysfunction of Protein Kinase C-ζ (PKC-ζ), a component of a protein scaffold complex that regulates the polarity of RPE tight junctions (Ozkaya et al., 2019).
Morphological changes observed in cultured human RPE cells exposed to blue light include the presence of cracked nuclei, swollen mitochondria, disappearance of the inner limiting membrane of the mitochondria, vacuole formation, and dilation of the rough endoplasmic reticulum (Busch et al., 1999; Zhang, 2005; Roehlecke et al., 2009; Song et al., 2022; Françon et al., 2024). Blue light also impairs the secretion of retinal neurotrophic factors important for the maintenance of retinal cells such as hepatocyte growth factor and angiogenin by human RPE cells and vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A) by porcine RPE cells (Chu et al., 2006; Vila et al., 2017; Marie et al., 2019). Transcriptome profiling by RNA-seq following blue light exposure of cultured human RPE cells demonstrated an upregulation of a broad range of genes involved not only in cell survival and cell cycle regulation, but also cell–cell interactions, cell morphology, inflammation and oxidative stress (Cheng et al., 2021).
Blue light can also cause a reversible inhibition of phagocytic activity and reduce receptor proteins, likely arising from oxidative modifications of phagocytic machinery in human RPE (Olchawa et al., 2022). The build-up of lipofuscin (a fluorophore that increases with age in RPE and results in increased oxidative stress) contributes to this reduced ability of cultured rabbit RPE cells to phagocytose the photoreceptor outer segments (Brunk et al., 1995; Sundelin et al., 1998). Loss of this critical function of RPE leads to photoreceptor dysfunction (Olchawa et al., 2017) (Figure 1). A more recent study in Japanese quail demonstrates that blue light exposure-induced photo-oxidative stress contributes to lipofuscin accumulation in RPE cells in the form of melanolipofuscin-like granules, which is suggested to impair RPE function (Serejnikova et al., 2024).
Potential mechanisms of blue light-induced retinal damage
Activation of inflammatory pathways
It is well established that blue light induces RPE to secrete cytokines and chemokines and growth factors. Specifically, blue light exposure results in an increased release of IL-6, IL-8, IL-17a and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) in human RPE cells compared to other wavelengths (Sato et al., 2021). Additionally, chemokines involved in recruiting immune cells such as monocyte chemotactic protein-1(MCP-1) were also shown to be elevated in RPE-choroid complexes of mice exposed to blue light compared to other wavelengths (Narimatsu et al., 2015). This increase in cytokine secretion from blue light exposure has been shown to induce local proliferation and migration of activated immune cells such as microglia and macrophages in mice, which can contribute to further damage to the RPE (Figure 1) (Nakamura et al., 2018). Activation of these innate immune cells is not seen with white light (400–700 nm) exposure in mice, further highlighting the heightened effects of blue light on immune activation (Ebert et al., 2012).
Oxidative stress
A key mechanism of blue light-induced RPE injury is the generation of ROS, resulting in oxidative damage and reduced viability through increased lipid peroxidation in cultured human and bovine RPE cells (Nakanishi-Ueda et al., 2013; Abdouh et al., 2022). The major source of ROS in human RPE is the mitochondria, particularly the endogenous fluorophores in the inner mitochondrial membrane (King et al., 2004). By making RPE more vulnerable to oxidative stress, blue light exposure can thus promote necroptosis, a form of programmed cell death that has features of both necrosis and apoptosis, and is independent of caspase activity in human RPE cells (Song et al., 2022). Antioxidant compounds such as lipoxins reduce RPE oxidative stress injury in cultured human RPE and in mice exposed to blue light (Xie et al., 2021).
RPE photoreactivity increases with age due to lipofuscin accumulation, which arises from incomplete degradation of photoreceptor outer segments, as observed in primary porcine, bovine and human RPE cells (Rozanowska et al., 1996; Marie et al., 2018). Lipofuscin toxicity is driven by bisretinoid fluorophores, which oxidize in response to oxygen and blue light, forming toxic aldehydes and ketones (Feldman et al., 2022). The main fluorophore, N-retinylidene-N-retinylethanolamine (A2E), accumulates with age in humans and acts as a photosensitizer, increasing ROS levels and RPE damage (Sparrow et al., 2000). A2E can also disrupt lysosomal membrane permeability, leading to mitochondrial damage, DNA damage, and apoptotic signaling (Xu et al., 2022) It triggers apoptosis by increasing calcium leakage from mitochondria and lysosomes into the cytosol (Brini et al., 2013), ultimately activating the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway.
Mitochondrial dysfunction
Mitochondria play a crucial role in RPE damage from blue light exposure. At lower levels of blue light (1–3 mW/cm2), mitochondrial respiratory chain activity increases in RPE cells in Japanese quails (Serezhnikova et al., 2017). Human in vitro RPE models show a rise in mitochondria numbers and morphological changes, with larger, ring-shaped mitochondria forming, increasing membrane surface area. These adaptations likely enhance cellular resistance to ROS by boosting energy transfer efficiency and metabolic activity (Roehlecke et al., 2009).
At higher blue light intensities (>4 mW/cm2), the balance of mitochondrial fusion and fission is disrupted in mice and in cultured human RPE cells, leading to increased fragmentation (Anitua et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2023). This effect occurs in human RPE even without A2E loading (Alaimo et al., 2019). The fusion-fission balance is crucial for maintaining a healthy mitochondrial network, and its dysregulation marks an early step in apoptosis (McBride and Scorrano, 2013). Mitochondrial pathways, rather than purely ROS signaling, play a significant role in blue light-induced cell death in human RPE (Moon et al., 2017).
Overactivation of autophagy
Autophagy is a protective mechanism in RPE that maintains cellular homeostasis by the degradation of harmful material from the ER, mitochondria or lysosomes (Intartaglia et al., 2022). However, autophagy competes with LC3-associated phagocytosis (LAP), a form of non-canonical autophagy that combines components of autophagy with phagocytosis to facilitate clearance of cellular debris. LAP is the primary process utilized by RPE to degrade the shed photoreceptor outer segments (POS), produce 11-cis retinal for the visual cycle and recycle essential components for photoreceptor disc renewal (Kim et al., 2013). Therefore, autophagy must be tightly regulated to ensure LAP occurs efficiently, prevent accelerated lipofuscin buildup, maintain POS clearance, and support the visual cycle (Kim et al., 2013; Ferguson and Green, 2014). Excessive autophagy activation has been observed in human and rodent RPE exposed to blue light, potentially due to the increased ROS and lysosomes and mitochondria permeability, disrupting the balance of autophagy and LAP. This imbalance reduces RPE viability and promotes lipofuscin buildup (Figure 1) (Fujita et al., 2007; Shen et al., 2013; Lee et al., 2015; Galluzzi et al., 2018).
Experimental models of blue light stimulation
Experimental models are used to mimic environmental stressors associated with blue light stimulation through a variety of methods which are summarized below:
In vitro models
The ARPE-19 cell line is the most commonly used cell model, along with primary RPE cell cultures. Study parameters such as exposure duration and irradiance intensity vary extensively in the literature (Table 1). In vitro experiments range from low intensity (0.04–3.7 mW/cm2) and long duration (3–48 h) (Roehlecke et al., 2009; Moon et al., 2017; Marie et al., 2018; Cheng et al., 2021; Anitua et al., 2023; Françon et al., 2024) to high intensity (4.4–100 mW/cm2) and short duration (1–90 min) (Pautler and BIOPHYSICS, 1990; Rozanowska et al., 1996; Sparrow and Cai, 2001; King et al., 2004; Alaimo et al., 2019; Abdouh et al., 2022; Olchawa et al., 2022). Despite these variations, similar effects on RPE have been observed. For example, Jeong et al exposed A2E-laden ARPE-19 to 6,000 lux blue light for 5 min/day for 120 days, while Burght et al used a single 15 h exposure of 1 mW/cm2 of blue light, yet both found similar changes in apoptosis and inflammation and complement-related gene expression (Van Der Burght et al., 2013; Jin and Jeong, 2022).
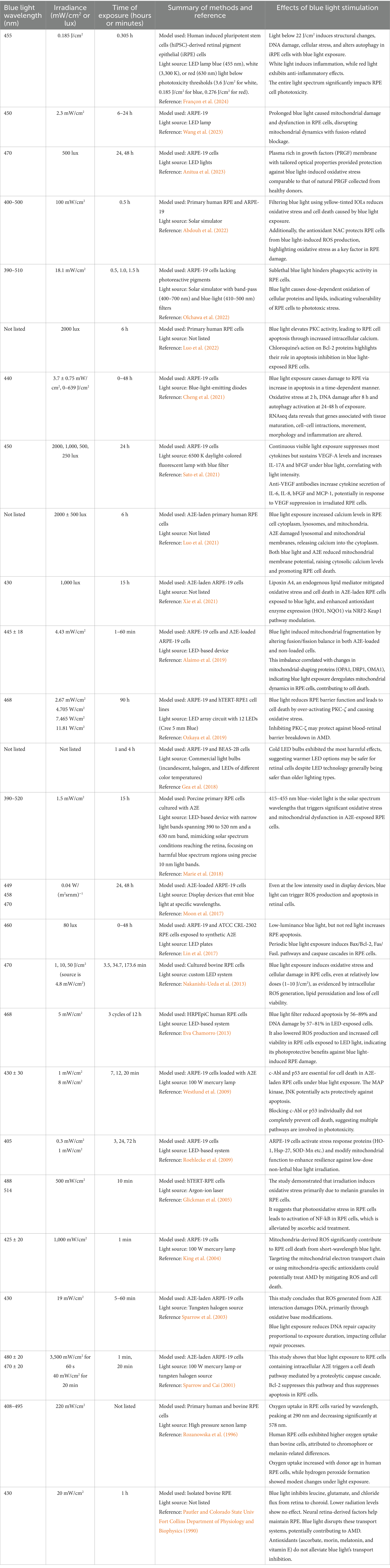
Table 1. Blue light wavelengths, irradiance and times of exposure from in vitro experimental studies reviewed here are compiled to compare and highlight the variability in the methodologies used.
The wavelength of blue light also varies between studies. Blue light typically refers to wavelengths around 445 nm, the “Blue Light Hazard” (BLH) wavelength which causes photochemical damage (Van Norren and Gorgels, 2011). BLH refers to the damage caused by light with a polychromatic profile containing peaks at 445 nm, often leading to visible morphological damage (Françon et al., 2024). Wavelength variations affect results, and using LED light sources with known peaks at 445 nm is recommended to prevent inconsistencies in experimental studies. Some studies use white fluorescent lamps or solar simulators, but their peak wavelengths are often unknown, complicating accurate irradiance calculations. Although less common in in vitro models compared to in vivo, white fluorescent lamps with a blue-light filter or solar light simulators may be used (Gea et al., 2018; Sato et al., 2021; Olchawa et al., 2022). Narrow-band interference filters or blue film filters allow for light exposure in the range of 400-490 nm, broad-band pass filters provide a range of 400-520 nm or 400-700 nm, and UV and infrared (IR) blocking filters remove wavelengths below 400 nm and above 740 nm, respectively (Putting et al., 1994; Olchawa et al., 2022). Neutral-density filters are used to standardize the intensity of light without altering its spectral composition (Ozkaya et al., 2019; Sato et al., 2021). However, the peak wavelength of these light sources is often unknown, leading to difficulties in accurate calculation of their irradiance intensities. Therefore, light sources with more uniform peak wavelengths such as LED devices should be utilized to prevent variance of wavelengths in blue light studies.
A common baseline for irradiance intensity is the phototoxic threshold, which is the threshold of irradiance intensity at which microscopic phototoxic damage occurs. The phototoxic threshold for blue light at 445 nm in humans was initially determined to be 22 J/cm2 (Van Norren and Gorgels, 2011). However, this threshold of the BLH may have been overestimated, as phototoxic damage has been observed in animal models at intensities lower than the estimated threshold by a factor of 20 (Hunter et al., 2012; Jaadane et al., 2020). Sub-threshold exposure in human in vitro RPE models also shows phototoxic changes in RPE morphology and immunological responses, suggesting that lower irradiance levels should be further explored (Françon et al., 2024).
A majority of studies measure blue light intensity in mW/cm2, which measures the intensity per unit area, but not the total amount of light energy received by the cells. This is problematic since exposure duration varies between studies, making it challenging to compare results. Measuring the total energy (J/cm2) would better reflect the cumulative light exposure, enabling easier comparisons across studies (Van Norren and Gorgels, 2011). Furthermore, the use of lux, a measure of illuminance, instead of mW/cm2, adds another layer of complexity, as lux measures light emitted rather than received. Therefore, providing mW/cm2, duration and total energy (J/cm2) in studies will allow for more consistent comparisons across studies.
In vivo and ex vivo models
While cell-based blue light experiments are easier to design and provide more reliable, reproducible results, in vivo models offer significant advantages over cultured RPE cells: (1) Animal studies offer more physiologically relevant insights into the complex structural and functional interactions between different cell types in retinal tissue which are often lacking in cultured systems, since these model systems preserve systemic responses such as neuronal activity, blood circulation and immune activation. (2) Cells in the neural retina such as photoreceptors lose their morphological integrity in vitro. This issue can be addressed by using in vivo or ex vivo models to study blue light-mediated effects on the retina and its interactions with the RPE/choroid in a more complex physiologic environment. (3) In vivo models also allow longitudinal studies for studying the effects of low intensity, long-term blue light exposure and tracking changes over time in the same animal.
Ex vivo models containing neural retina, RPE-Bruch’s membrane-choroid complexes or whole eyes can be used to assess chronic or intermittent blue light effects on ocular tissue under controlled conditions. One study utilized whole eyeball cultures to examine the impact of blue light exposure on mouse photoreceptors (Roehlecke et al., 2011). Eyeballs were punctured with a needle to enable fluid exchange and maintained in serum-containing medium at 37°C and 5%CO2. The eyes were positioned with corneas facing the blue light diodes and were irradiated from 0.5–24 h. In another study, whole porcine eyes were irradiated with blue light for 3 h and incubated for further 6 h in PBS. Isolated neural retina was also exposed to blue light for 1–2 h and maintained on cell culture inserts for 24–48 h (Fietz et al., 2023). Standardization of ex vivo models would greatly benefit the field of blue light study. Additionally, ex vivo models used for studying choroidal microvascular angiogenesis could be adapted for blue light research. Rodent or human RPE/choroid/scleral tissue can be readily isolated and cultured for up to 6 days, allowing for reproducible evaluation of specific pathways involved in blue light-induced responses (Shao et al., 2013; Tomita et al., 2020). Such explants can also be used to compare differences between genetically modified mouse tissue and wild type following blue light stimulation.
One limitation of rodent models for AMD and blue light research is the absence of a macula, an area critical to high-resolution vision in humans. Another challenge with using animal models is the inherent variability in irradiance intensities on the ocular tissue (Table 2) (Narimatsu et al., 2015; Lin et al., 2017; Xie et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023). Ex vivo models allow a more precise manipulation of illumination conditions, compared to animal models, thereby improving reproducibility and reducing complexity due to systemic influences. Despite some limitations, both in vivo and ex vivo model systems provide significant advantages.
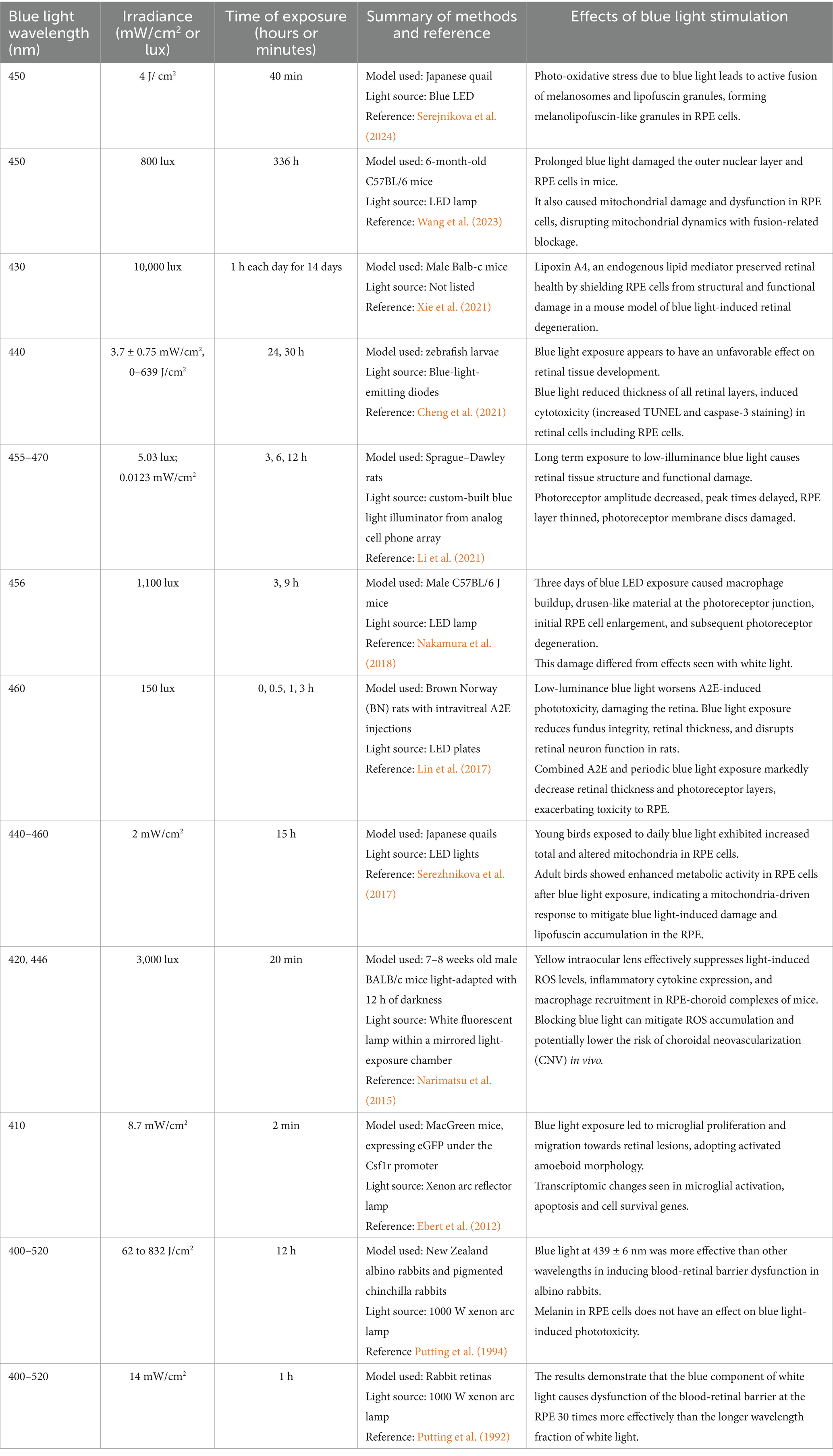
Table 2. Blue light wavelengths, irradiance and times of exposure from in vivo experimental studies reviewed here are compiled to compare and highlight the variability in the methodologies used.
Conclusion and future perspectives
In conclusion, while some evidence suggests a potential association between prolonged blue light exposure and increased AMD risk, more epidemiological studies are needed to establish a definitive link. Blue light induces oxidative stress, disrupts cell structures, and impairs essential RPE functions, leading to apoptosis and the AMD progression. Further research could also focus on protective strategies, including therapeutic interventions targeting pathways activated by blue light and improving blue-filtering technology to prevent retinal damage. Moreover, refining blue light exposure experiments—through standardized protocols, precise light irradiance measurements, and the development of novel in vivo and ex vivo models—will improve the consistency and relevance of findings across studies and enhance our understanding of blue light’s effects on the retina and ocular tissues.
Author contributions
HC: Conceptualization, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. VG: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CW: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. JM: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. We thank Fighting Blindness Canada, Vancouver Coastal Health Research Institute, Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council, Canadian Institutes of Health Research and Faculty of Medicine UBC for funding.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdouh, M., Lu, M., Chen, Y., Goyeneche, A., Burnier, J. V., and Burnier, M. N. (2022). Filtering blue light mitigates the deleterious effects induced by the oxidative stress in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 217:108978. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2022.108978
Achiron, A., Elbaz, U., Hecht, I., Spierer, O., Einan-Lifshitz, A., Karesvuo, P., et al. (2021). The effect of blue-light filtering intraocular lenses on the development and progression of Neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 128, 410–416. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2020.07.039
Alaimo, A., Liñares, G. G., Bujjamer, J. M., Gorojod, R. M., Alcon, S. P., Martínez, J. H., et al. (2019). Toxicity of blue led light and A2E is associated to mitochondrial dynamics impairment in ARPE-19 cells: implications for age-related macular degeneration. Arch. Toxicol. 93, 1401–1415. doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02409-6
Anitua, E., Muruzabal, F., De La Fuente, M., Del Olmo-Aguado, S., Alkhraisat, M. H., and Merayo-Lloves, J. (2023). PRGF membrane with tailored optical properties preserves the Cytoprotective effect of plasma rich in growth factors: in vitro model of retinal pigment epithelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:11195. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311195
Baker, J., Putnam, N., Kozlowski, R. E., Anderson, M., Bird, Z., Chmielewski, J., et al. (2022). Effects of chronic, daily exposures to low intensity blue light on human retinal pigment epithelial cells: implications for the use of personal electronic devices. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 10:100118. doi: 10.1016/j.jpap.2022.100118
Behar-Cohen, F., Martinsons, C., Viénot, F., Zissis, G., Barlier-Salsi, A., Cesarini, J. P., et al. (2011). Light-emitting diodes (LED) for domestic lighting: any risks for the eye? Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 30, 239–257. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2011.04.002
Brini, M., Calì, T., Ottolini, D., and Carafoli, E. (2013). The plasma membrane calcium pump in health and disease. FEBS J. 280, 5385–5397. doi: 10.1111/febs.12193
Brunk, U. T., Wihlmark, U., Wrigstad, A., Roberg, K., and Nilsson, S.-E. (1995). Accumulation of lipofuscin within retinal pigment epithelial cells results in enhanced sensitivity to photo-oxidation. Gerontology 41, 201–212. doi: 10.1159/000213743
Busch, E. M., Gorgels, T. G. M. F., and Van Norren, D. (1999). Temporal sequence of changes in rat retina after UV-A and blue light exposure. Vis. Res. 39, 1233–1247. doi: 10.1016/S0042-6989(98)00233-8
Cheng, K.-C., Hsu, Y.-T., Liu, W., Huang, H.-L., Chen, L.-Y., He, C.-X., et al. (2021). The role of oxidative stress and autophagy in blue-light-induced damage to the retinal pigment epithelium in zebrafish in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:1338. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031338
Chu, R., Zheng, X., Chen, D., and Hu, D. (2006). Blue light irradiation inhibits the production of HGF by human retinal pigment epithelium cells in vitro. Photochem. Photobiol. 82, 1247–1250. doi: 10.1562/2006-04-19-RA-880
Contín, M. A., Benedetto, M. M., Quinteros-Quintana, M. L., and Guido, M. E. (2016). Light pollution: the possible consequences of excessive illumination on retina. Eye 30, 255–263. doi: 10.1038/eye.2015.221
Cougnard-Gregoire, A., Merle, B. M. J., Aslam, T., Seddon, J. M., Aknin, I., Klaver, C. C. W., et al. (2023). Blue light exposure: ocular hazards and prevention—a narrative review. Ophthalmol. Ther. 12, 755–788. doi: 10.1007/s40123-023-00675-3
Cruickshanks, K. J., Klein, R., Klein, B. E., and Nondahl, D. M. (2001). Sunlight and the 5-year incidence of early age-related maculopathy: the beaver dam eye study. Arch. Ophthalmol. Chic. Ill 1960, 246–250.
Ebert, S., Walczak, Y., Remé, C., and Langmann, T. (2012). Microglial activation and transcriptomic changes in the blue light-exposed mouse retina, 619–632. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-0631-0_79
Eva Chamorro, S. F. C. (2013). Photoprotective effects of blue light absorbing filter against LED light exposure on human retinal pigment epithelial cells in vitro. J. Carcinog. Mutagen. 1–7. doi: 10.4172/2157-2518.S6-008
Evans, J. R. (2005). 28 000 cases of age related macular degeneration causing visual loss in people aged 75 years and above in the United Kingdom may be attributable to smoking. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 89, 550–553. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2004.049726
Feldman, T., Ostrovskiy, D., Yakovleva, M., Dontsov, A., Borzenok, S., and Ostrovsky, M. (2022). Lipofuscin-mediated photic stress induces a dark toxic effect on ARPE-19 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:12234. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012234
Ferguson, T. A., and Green, D. R. (2014). Autophagy and phagocytosis converge for better vision. Autophagy 10, 165–167. doi: 10.4161/auto.26735
Fietz, A., Corsi, F., Hurst, J., and Schnichels, S. (2023). Blue light damage and p53: unravelling the role of p53 in oxidative-stress-induced retinal apoptosis. Antioxidants 12:2072. doi: 10.3390/antiox12122072
Fletcher, A. E. (2008). Sunlight exposure, antioxidants, and age-related macular degeneration. Arch. Ophthalmol. 126:1396. doi: 10.1001/archopht.126.10.1396
Françon, A., Delaunay, K., Jaworski, T., Lebon, C., Picard, E., Youale, J., et al. (2024). Phototoxicity of low doses of light and influence of the spectral composition on human RPE cells. Sci. Rep. 14:6839. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56980-9
Fujita, E., Kouroku, Y., Isoai, A., Kumagai, H., Misutani, A., Matsuda, C., et al. (2007). Two endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) systems for the novel variant of the mutant dysferlin: ubiquitin/proteasome ERAD(I) and autophagy/lysosome ERAD(II). Hum. Mol. Genet. 16, 618–629. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm002
Galluzzi, L., Vitale, I., Aaronson, S. A., Abrams, J. M., Adam, D., Agostinis, P., et al. (2018). Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 25, 486–541. doi: 10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4
Gea, M., Schilirò, T., Iacomussi, P., Degan, R., Bonetta, S., and Gilli, G. (2018). Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of light emitted by incandescent, halogen, and LED bulbs on ARPE-19 and BEAS-2B cell lines. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 81, 998–1014. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2018.1510350
Glickman, R. D., Natarajan, M., Rockwell, B. A., Denton, M., Maswadi, S., Kumar, N., et al. (2005) in Intracellular signaling mechanisms responsive to laser-induced photochemical and thermal stress. eds. S. L. Jacques and W. P. Roach.
Hall, H., Ma, J., Shekhar, S., Leon-Salas, W. D., and Weake, V. M. (2018). Blue light induces a neuroprotective gene expression program in Drosophila photoreceptors. BMC Neurosci. 19:43. doi: 10.1186/s12868-018-0443-y
Ham, W. T. (1983). Ocular hazards of light sources: review of current knowledge. J. Occup. Med. 25, 101–103
Ham, W. T., Mueller, H. A., Ruffolo, J. J., and Clarke, A. M. (1979). Sensitivity of the retina to radiation damage as a function of wavelength. Photochem. Photobiol. 29, 735–743. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1979.tb07759.x
Hunter, J. J., Morgan, J. I. W., Merigan, W. H., Sliney, D. H., Sparrow, J. R., and Williams, D. R. (2012). The susceptibility of the retina to photochemical damage from visible light. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 31, 28–42. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2011.11.001
Intartaglia, D., Giamundo, G., and Conte, I. (2022). Autophagy in the retinal pigment epithelium: a new vision and future challenges. FEBS J. 289, 7199–7212. doi: 10.1111/febs.16018
Jaadane, I., Villalpando Rodriguez, G., Boulenguez, P., Carré, S., Dassieni, I., Lebon, C., et al. (2020). Retinal phototoxicity and the evaluation of the blue light hazard of a new solid-state lighting technology. Sci. Rep. 10:6733. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63442-5
Jin, H. L., and Jeong, K. W. (2022). Transcriptome analysis of long-term exposure to blue light in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Biomol. Ther. 30, 291–297. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2021.155
Jonasson, F., Fisher, D. E., Eiriksdottir, G., Sigurdsson, S., Klein, R., Launer, L. J., et al. (2014). Five-year incidence, progression, and risk factors for age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 121, 1766–1772. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.03.013
Kim, S. H., Kim, Y. K., Shin, Y. I., Kang, G., Kim, S. P., Lee, H., et al. (2024). Nighttime outdoor artificial light and risk of age-related macular degeneration. JAMA Netw. Open 7:e2351650. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.51650
Kim, J.-Y., Zhao, H., Martinez, J., Doggett, T. A., Kolesnikov, A. V., Tang, P. H., et al. (2013). Noncanonical autophagy promotes the visual cycle. Cell 154, 365–376. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.012
King, A., Gottlieb, E., Brooks, D. G., Murphy, M. P., and Dunaief, J. L. (2004). Mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species mediate blue light-induced death of retinal pigment epithelial cells ¶. Photochem. Photobiol. 79, 470–475. doi: 10.1562/le-03-17.1
Kuse, Y., Ogawa, K., Tsuruma, K., Shimazawa, M., and Hara, H. (2014). Damage of photoreceptor-derived cells in culture induced by light emitting diode-derived blue light. Sci. Rep. 4:5223. doi: 10.1038/srep05223
Lambert, N. G., ElShelmani, H., Singh, M. K., Mansergh, F. C., Wride, M. A., Padilla, M., et al. (2016). Risk factors and biomarkers of age-related macular degeneration. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 54, 64–102. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2016.04.003
Lee, W.-S., Yoo, W.-H., and Chae, H.-J. (2015). ER stress and autophagy. Curr. Mol. Med. 15, 735–745. doi: 10.2174/1566524015666150921105453
Li, H., Zhang, M., Wang, D., Dong, G., Chen, Z., Li, S., et al. (2021). Blue light from cell phones can cause chronic retinal light injury: the evidence from a clinical observational study and a SD rat model. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 1–13. doi: 10.1155/2021/3236892
Lin, C.-H., Wu, M.-R., Li, C.-H., Cheng, H.-W., Huang, S.-H., Tsai, C.-H., et al. (2017). Editor’s highlight: periodic exposure to smartphone-mimic low-luminance blue light induces retina damage through Bcl-2/BAX-dependent apoptosis. Toxicol. Sci. 157, 196–210. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfx030
Luo, M.-M., Chen, L., Wang, S., Zeng, C., Li, D.-Z., Bi, Y., et al. (2021). The effect of A2E on the uptake and release of calcium in the lysosomes and mitochondria of human RPE cells exposed to blue light. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 1–10. doi: 10.1155/2021/5586659
Luo, M., Wang, S., Tang, Y., Zeng, C., and Cai, S. (2022). The effect of A2E on the Ca2+-PKC signaling pathway in human RPE cells exposed to blue light. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 1–7. doi: 10.1155/2022/2233223
Mallet, J. D., and Rochette, P. J. (2011). Ultraviolet light-induced Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers in rabbit eyes. Photochem. Photobiol. 87, 1363–1368. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.2011.00977.x
Mallet, J. D., and Rochette, P. J. (2013). Wavelength-dependent ultraviolet induction of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers in the human cornea. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 12, 1310–1318. doi: 10.1039/c3pp25408a
Marie, M., Bigot, K., Angebault, C., Barrau, C., Gondouin, P., Pagan, D., et al. (2018). Light action spectrum on oxidative stress and mitochondrial damage in A2E-loaded retinal pigment epithelium cells. Cell Death Dis. 9:287. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0331-5
Marie, M., Gondouin, P., Pagan, D., Barrau, C., Villette, T., Sahel, J., et al. (2019). Blue-violet light decreases VEGFa production in an in vitro model of AMD. PLoS One 14:e0223839. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223839
McBride, H., and Scorrano, L. (2013). Mitochondrial dynamics and physiology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Mol. Cell Res. 1833, 148–149. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.11.001
Molday, R. S., and Moritz, O. L. (2015). Photoreceptors at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 128, 4039–4045. doi: 10.1242/jcs.175687
Moon, J., Yun, J., Yoon, Y. D., Park, S.-I., Seo, Y.-J., Park, W.-S., et al. (2017). Blue light effect on retinal pigment epithelial cells by display devices. Integr. Biol. 9, 436–443. doi: 10.1039/c7ib00032d
Nakamura, M., Yako, T., Kuse, Y., Inoue, Y., Nishinaka, A., Nakamura, S., et al. (2018). Exposure to excessive blue LED light damages retinal pigment epithelium and photoreceptors of pigmented mice. Exp. Eye Res. 177, 1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2018.07.022
Nakanishi-Ueda, T., Majima, H. J., Watanabe, K., Ueda, T., Indo, H. P., Suenaga, S., et al. (2013). Blue LED light exposure develops intracellular reactive oxygen species, lipid peroxidation, and subsequent cellular injuries in cultured bovine retinal pigment epithelial cells. Free Radic. Res. 47, 774–780. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2013.829570
Narimatsu, T., Negishi, K., Miyake, S., Hirasawa, M., Osada, H., Kurihara, T., et al. (2015). Blue light-induced inflammatory marker expression in the retinal pigment epithelium-choroid of mice and the protective effect of a yellow intraocular lens material in vivo. Exp. Eye Res. 132, 48–51. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2015.01.003
Noell, W. K. (1980). Possible mechanisms of photoreceptor damage by light in mammalian eyes. Vis. Res. 20, 1163–1171. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(80)90055-3
Noell, W. K., Walker, V. S., Kang, B. S., and Berman, S. (1966). Retinal damage by light in rats. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 5, 450–473.
Olchawa, M. M., Furso, J. A., Szewczyk, G. M., and Sarna, T. J. (2017). Lipofuscin-mediated photic stress inhibits phagocytic activity of ARPE-19 cells; effect of donors’ age and antioxidants. Free Radic. Res. 51, 799–811. doi: 10.1080/10715762.2017.1380307
Olchawa, M. M., Herrnreiter, A. M., Skumatz, C. M. B., Krzysztynska-Kuleta, O. I., Mokrzynski, K. T., Burke, J. M., et al. (2022). The inhibitory effect of blue light on phagocytic activity by ARPE-19 cells. Photochem. Photobiol. 98, 1110–1121. doi: 10.1111/php.13596
Ozkaya, E. K., Anderson, G., Dhillon, B., and Bagnaninchi, P.-O. (2019). Blue-light induced breakdown of barrier function on human retinal epithelial cells is mediated by PKC-ζ over-activation and oxidative stress. Exp. Eye Res. 189:107817. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2019.107817
Parkinson, L. G., Toro, A., Zhao, H., Brown, K., Tebbutt, S. J., and Granville, D. J. (2015). Granzyme B mediates both direct and indirect cleavage of extracellular matrix in skin after chronic low-dose ultraviolet light irradiation. Aging Cell 14, 67–77. doi: 10.1111/acel.12298
Pautler, E. L.Colorado State Univ Fort Collins Department of Physiology and Biophysics. (1990). The Phototoxicity of’Blue Light’on the functional properties of the retinal pigment epithelium.
Putting, B. J., Van Best, J. A., Vrensen, G. F. J. M., and Oosterhuis, J. A. (1994). Blue-light-induced dysfunction of the blood-retinal barrier at the pigment epithelium in albino versus pigmented rabbits. Exp. Eye Res. 58, 31–40. doi: 10.1006/exer.1994.1192
Putting, B., Zweypfenning, R., Vrensen, G. F. J. M., Oosterhuis, J. A., and Best, J. A. V. (1992). Blood-retinal barrier dysfunction at the pigment epithelium induced by blue light. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. Available at: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Blood-retinal-barrier-dysfunction-at-the-pigment-by-Putting-Zweypfenning/0c16c6f69b1f85e7a4ae0d49a7939ce403de8fd7 33, 3385–3393
Roehlecke, C., Schaller, A., Knels, L., and Funk, R. H. W. (2009). The influence of sublethal blue light exposure on human RPE cells. Mol. Vis. 15, 1929–1938
Roehlecke, C., Schumann, U., Ader, M., Knels, L., and Funk, R. H. W. (2011). Influence of blue light on photoreceptors in a live retinal explant system. Mol. Vis. 17, 876–884
Rozanowska, M., Jarvis-Evans, J., Korytowski, W., Boulton, M. E., Burke, J. M., and Sarna, T. (1996). Blue light-induced reactivity of retinal age pigment. Retina 16:354. doi: 10.1097/00006982-199616040-00023
Sato, T., Takeuchi, M., Karasawa, Y., and Ito, M. (2021). Profiles of cytokines secreted by ARPE-19 cells exposed to light and incubated with anti-VEGF antibody. Biomedicines 9:1333. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101333
Schick, T., Ersoy, L., Lechanteur, Y. T. E., Saksens, N. T. M., Hoyng, C. B., Den Hollander, A. I., et al. (2016). History of sunlight exposure is a risk factor for age-related macular degeneration. Retina 36, 787–790. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000000756
Serejnikova, N. B., Trofimova, N. N., Yakovleva, M. A., Dontsov, A. E., Zak, P. P., and Ostrovsky, M. A. (2024). Blue light-induced accelerated formation of Melanolipofuscin-like organelles in Japanese quail RPE cells: an Electron microscopic study. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 65:31. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.11.31
Serezhnikova, N. B., Pogodina, L. S., Lipina, T. V., Trofimova, N. N., Gurieva, T. S., and Zak, P. P. (2017). Age-related adaptive responses of mitochondria of the retinal pigment epithelium to the everyday blue LED lighting. Dokl. Biol. Sci. 475, 141–143. doi: 10.1134/S0012496617040044
Shao, Z., Friedlander, M., Hurst, C. G., Cui, Z., Pei, D. T., Evans, L. P., et al. (2013). Choroid sprouting assay: an ex vivo model of microvascular angiogenesis. PLoS One 8:e69552. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0069552
Shen, K., Sun, L., Zhang, H., Xu, Y., Qian, X., Lu, Y., et al. (2013). A ROS-mediated lysosomal-mitochondrial pathway is induced by a novel Amonafide analogue, 7c, in human Hela cervix carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 333, 229–238. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.01.038
Simó, R., Villarroel, M., Corraliza, L., Hernández, C., and Garcia-Ramírez, M. (2010). The retinal pigment epithelium: something more than a constituent of the blood-retinal barrier—implications for the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 1–15. doi: 10.1155/2010/190724
Song, W., Zhu, R., Gao, W., Xing, C., and Yang, L. (2022). Blue light induces RPE cell necroptosis, which can be inhibited by minocycline. Front. Med. 9, 1–14. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.831463
Sparrow, J. R., and Cai, B. (2001). Blue light-induced apoptosis of A2E-containing RPE: involvement of caspase-3 and protection by Bcl-2. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 42, 1356–1362
Sparrow, J. R., Nakanishi, K., and Parish, C. A. (2000). The lipofuscin fluorophore A2E mediates blue light-induced damage to retinal pigmented epithelial cells. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 41, 1981–1989
Sparrow, J. R., Zhou, J., and Cai, B. (2003). DNA is a target of the photodynamic effects elicited in A2E-laden RPE by blue-light illumination. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 44, 2245–2251. doi: 10.1167/iovs.02-0746
Steinmetz, J. D., Bourne, R. R. A., Briant, P. S., Flaxman, S. R., Taylor, H. R. B., Jonas, J. B., et al. (2021). Causes of blindness and vision impairment in 2020 and trends over 30 years, and prevalence of avoidable blindness in relation to VISION 2020: the right to sight: an analysis for the global burden of disease study. Lancet Glob. Health 9, e144–e160. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30489-7
Sui, G.-Y., Liu, G.-C., Liu, G.-Y., Gao, Y.-Y., Deng, Y., Wang, W.-Y., et al. (2013). Is sunlight exposure a risk factor for age-related macular degeneration? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 97, 389–394. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2012-302281
Sundelin, S., Wihlmark, U., Nilsson, S. E. G., and Brunk, U. T. (1998). Lipofuscin accumulation in cultured retinal pigment epithelial cells reduces their phagocytic capacity. Curr. Eye Res. 17, 851–857. doi: 10.1080/02713689808951268
Taylor, H. R., Muñoz, B., West, S., Bressler, N. M., Bressler, S. B., and Rosenthal, F. S. (1990). Visible light and risk of age-related macular degeneration. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 88, 163–173.
Theruveethi, N., Bui, B. V., Joshi, M. B., Valiathan, M., Ganeshrao, S. B., Gopalakrishnan, S., et al. (2022). Blue light-induced retinal neuronal injury and amelioration by commercially available blue light-blocking lenses. Life 12:243. doi: 10.3390/life12020243
Thomson, L. R., Toyoda, Y., Langner, A., Delori, F. C., Garnett, K. M., Craft, N., et al. (2002). Elevated retinal zeaxanthin and prevention of light-induced photoreceptor cell death in quail. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 43, 3538–3549
Tomany, S. C. (2004). Sunlight and the 10-year incidence of age-related maculopathy: the beaver dam eye study. Arch. Ophthalmol. 122, 750–757. doi: 10.1001/archopht.122.5.750
Tomita, Y., Shao, Z., Cakir, B., Kotoda, Y., Fu, Z., and Smith, L. E. H. (2020). An ex vivo choroid sprouting assay of ocular microvascular angiogenesis. J. Vis. Exp. 162:61677. doi: 10.3791/61677
Van Der Burght, B. W., Hansen, M., Olsen, J., Zhou, J., Wu, Y., Nissen, M. H., et al. (2013). Early changes in gene expression induced by blue light irradiation of A2E-laden retinal pigment epithelial cells. Acta Ophthalmol. 91, e537–e545. doi: 10.1111/aos.12146
Van Norren, D., and Gorgels, T. G. M. F. (2011). The action Spectrum of photochemical damage to the retina: a review of monochromatic threshold data. Photochem. Photobiol. 87, 747–753. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.2011.00921.x
Vila, N., Siblini, A., Esposito, E., Bravo-Filho, V., Zoroquiain, P., Aldrees, S., et al. (2017). Blue-light filtering alters angiogenic signaling in human retinal pigmented epithelial cells culture model. BMC Ophthalmol. 17:198. doi: 10.1186/s12886-017-0592-2
Wang, L., Yu, X., Zhang, D., Wen, Y., Zhang, L., Xia, Y., et al. (2023). Long-term blue light exposure impairs mitochondrial dynamics in the retina in light-induced retinal degeneration in vivo and in vitro. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 240:112654. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2023.112654
Westlund, B. S., Cai, B., Zhou, J., and Sparrow, J. R. (2009). Involvement of c-Abl, p53 and the MAP kinase JNK in the cell death program initiated in A2E-laden ARPE-19 cells by exposure to blue light. Apoptosis 14, 31–41. doi: 10.1007/s10495-008-0285-7
Wong, N. A., and Bahmani, H. (2022). A review of the current state of research on artificial blue light safety as it applies to digital devices. Heliyon 8:e10282. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10282
Wrona, M., Korytowski, W., Różanowska, M., Sarna, T., and Truscott, T. G. (2003). Cooperation of antioxidants in protection against photosensitized oxidation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 35, 1319–1329. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2003.07.005
Wrona, M., Różanowska, M., and Sarna, T. (2004). Zeaxanthin in combination with ascorbic acid or α-tocopherol protects ARPE-19 cells against photosensitized peroxidation of lipids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 36, 1094–1101. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.02.005
Xie, T., Cai, J., Yao, Y., Sun, C., Yang, Q., Wu, M., et al. (2021). LXA4 protects against blue-light induced retinal degeneration in human A2E-laden RPE cells and Balb-c mice. Ann. Transl. Med. 9:1249. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-3390
Xu, Y., Li, D., Su, G., and Cai, S. (2022). The effect of A2E on lysosome membrane permeability during blue light-induced human RPEs apoptosis. BMC Ophthalmol. 22:241. doi: 10.1186/s12886-022-02464-1
Xu, Z., Zhang, H., Zhang, C., Yu, S., Yuan, J., Jin, K., et al. (2023). REG1A protects retinal photoreceptors from blue light damage. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1527, 60–74. doi: 10.1111/nyas.15045
Youssef, M. A., Shehata, A. R., Adly, A. M., Ahmed, M. R., Abo-Bakr, H. F., Fawzy, R. M., et al. (2024). Efficacy of repeated low-level red light (RLRL) therapy on myopia outcomes in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Ophthalmol. 24:78. doi: 10.1186/s12886-024-03337-5
Zhang, J. (2005). Blue-light-induced apoptosis of cultured human retinal pigment epithelial cells in vitro. Chin. J. Ocul. Fundus Dis. SPIE (The International Society for Optics and Photonics) Publisher for Pautler 1990: U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) through the Defense Technical Information Center (DTIC). Available at: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:87873832
Zhang, J., Sabarinathan, R., Bubel, T., Jia, W., Williams, D. R., and Hunter, J. J. (2024). Spectral dependence of light exposure on retinal pigment epithelium disruption in living primate retina. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 65:43. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.2.43
Keywords: phototoxicity, retinal inflammation, photoreceptors, retinal pigmented epithelial (RPE) cells, age-related macular degeneration (AMD), blue light exposure, LED, blue light
Citation: Chakravarthy H, Georgyev V, Wagen C, Hosseini A and Matsubara J (2024) Blue light-induced phototoxicity in retinal cells: implications in age-related macular degeneration. Front. Aging Neurosci. 16:1509434. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2024.1509434
Edited by:
Simona Eleuteri, Harvard Medical School, United StatesReviewed by:
Ajeet Kumar, Washington University in St. Louis, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Chakravarthy, Georgyev, Wagen, Hosseini and Matsubara. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Joanne Matsubara, am9hbm5lLm1hdHN1YmFyYUB1YmMuY2E=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Harshini Chakravarthy
Harshini Chakravarthy Vasil Georgyev†
Vasil Georgyev† Cole Wagen
Cole Wagen Amir Hosseini
Amir Hosseini