
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Public Health , 04 November 2022
Sec. Infectious Diseases: Epidemiology and Prevention
Volume 10 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.1054878
This article is a correction to:
Epidemiological, clinical, and laboratory features of patients infected with Elizabethkingia meningoseptica at a tertiary hospital in Hefei City, China
A corrigendum on
Epidemiological, clinical, and laboratory features of patients infected with Elizabethkingia meningoseptica at a tertiary hospital in Hefei City, China
by Li, Y., Liu, T., Shi, C., Wang, B., Li, T., Huang, Y., Xu, Y., and Tang, L. (2022). Front. Public Health 10:964046. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.964046
In the published article, there was an error in Table 4 “In vitro of drug susceptibility results of patients infected with E. meningoseptica (N = 24)” as published. We are sorry for the percentage error, which is due to format conversion in the manuscript modification. This does not influence the P-value and the conclusion of the article. In the survival group, 85.7% of 14 strains was susceptible to piperacillin/tazobactam and 92.9% of 14 strains was susceptible to cotrimoxazole. In the death group, 70% of 10 strains was susceptible to levofloxacin and 60% of 10 strains was susceptible to piperacillin/tazobactam. The intermediate resistance of strains in the death group to levofloxacin was 10%. The resistance rates of all strains to levofloxacin and piperacillin/tazobactam were 20.8 and 8.3%, respectively. The resistance rate of strains in the survival group to amikacin, aztreonam, imipenem, and tobramycin was 92.9%. The resistance rate of strains in the death group to levofloxacin was 20%. The corrected Table 4 and its caption appear below.
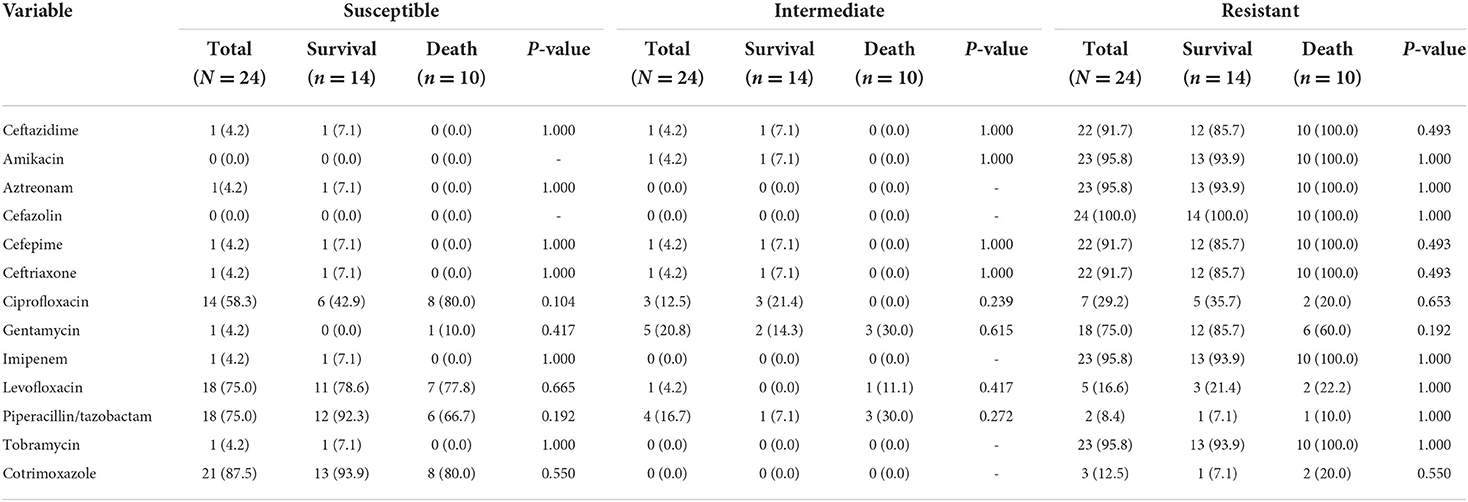
Table 4. The original “TABLE 4 In vitro of drug susceptibility results of patients infected with E. meningoseptica (N = 24).”
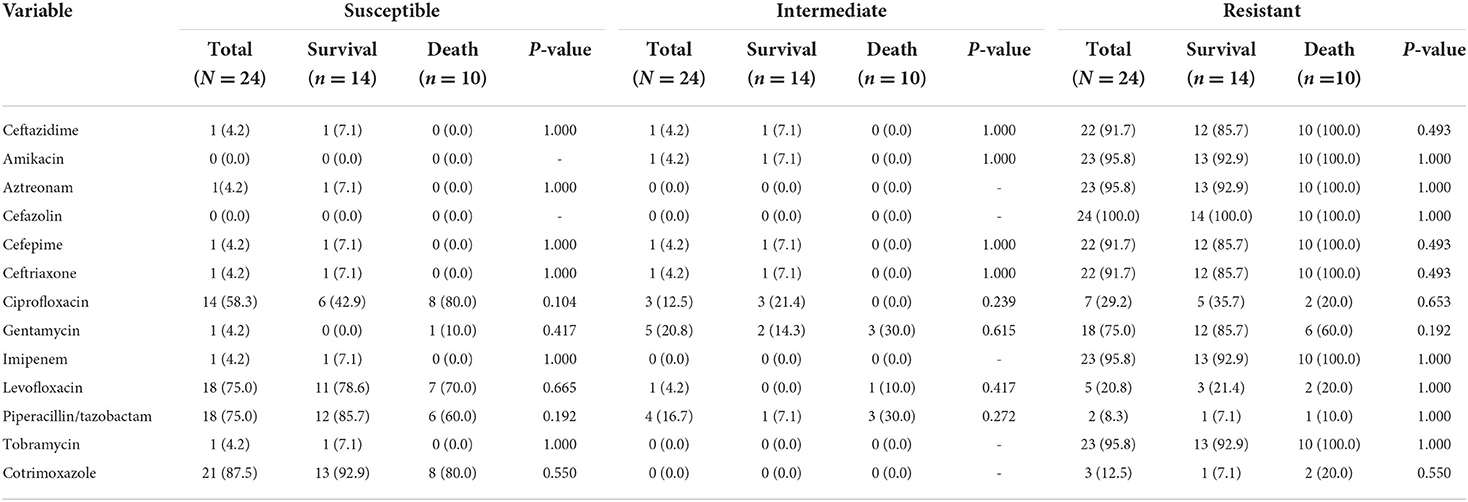
Table 4. The corrected “TABLE 4 In vitro of drug susceptibility results of patients infected with E. meningoseptica (N = 24).”
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: Elizabethkingia meningoseptica, infection, clinical and laboratory features, fever, hepatic disease
Citation: Li Y, Liu T, Shi C, Wang B, Li T, Huang Y, Xu Y and Tang L (2022) Corrigendum: Epidemiological, clinical, and laboratory features of patients infected with Elizabethkingia meningoseptica at a tertiary hospital in Hefei City, China. Front. Public Health 10:1054878. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1054878
Received: 27 September 2022; Accepted: 03 October 2022;
Published: 04 November 2022.
Edited and reviewed by: Jozsef Soki, University of Szeged, Hungary
Copyright © 2022 Li, Liu, Shi, Wang, Li, Huang, Xu and Tang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yuanhong Xu, eHlob25nMTk2NEAxNjMuY29t; Ling Tang, dGxpbmdAbWFpbC51c3RjLmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.