
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
EMPIRICAL STUDY article
Front. Psychol. , 10 November 2022
Sec. Educational Psychology
Volume 13 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1025754
This article is part of the Research Topic Metaverse and Education View all 4 articles
With the popularity of Internet technology, reading has developed in the direction of digitalization and mobileization. And entering the metaverse era, both the subject and object of reading may be redefined, presenting a new developmental pattern. This process brings a crisis to reading, such as the fragmentation of reading, the obstruction of reading needs, and the replacement of classical reading. However, reading is still an important way for college students to acquire new knowledge, broaden their horizons and improve their skills. The existence of reading crises inevitably affects the academic achievement of college students. Therefore, from the perspective of university management, this paper conducts regression analysis on 1,155 effective samples of colleges and universities in Anhui Province, extracts the factors that affect college students’ reading engagement, and further explores the relationship between college students’ reading engagement and academic achievement. The study concluded that: (1) in terms of family reading culture, students who grow up in families with good family reading culture perform better in reading engagement. The amount of family books, family reading education and family reading atmosphere all have significant positive effects on reading time and reflective reading strategies of college students. (2) In the cultivation of reading habits in colleges and universities, the course-driven mechanism and the atmosphere stimulating mechanism have a significant positive effect on students’ reading time. The course-driven mechanism, resource supporting mechanism and atmosphere stimulating mechanism have a significant positive effect on the critical reading strategy of college students. (3) In terms of reading time, it is only found that the reading time spent on paper books has a significant positive effect on college students’ academic achievement and professional quality. (4) In terms of reading strategies, the replicative reading strategy only has a significant positive effect on the improvement of college students’ academic achievement and professional quality. The critical reading strategy has a significant positive effect on the professional quality, general ability and career planning ability of college students.
The year 2021 is regarded as the “meta-universe year” (Zhao et al., 2021), and the phenomenon of “meta-universe” has received widespread attention, reflecting the new trend of digital technology development after new technologies such as big data, blockchain, 5G and cloud computing. The metaverse is linked and created by using technology, a virtual world mapped and interacted with the real world, and a digital living space with a new social system. Combing through the literature related to metaverse reveals that many scholars focus on the impact of metaverse on games, literary travel, education and other fields, but there are few studies on the connection between metaverse and reading and how metaverse will bring changes to reading. With the popularity of Internet technology, reading has developed in the direction of digitalization and mobilization. And entering the era of metaverse, both the subject and the object of reading may be redefined and take on a new developmental shape. This process brings a crisis to reading, such as reading fragmentation, hindered reading demand, and the replacement of classical reading (Cai and Zhao, 2022; Dwivedi et al., 2022; Zhu, 2022).
The acquisition of intellectual capabilities and development of high level manpower which is the goal of tertiary education implies a crop of students with good study habits because effective study habits and strategies have been attributed to the secret of success in school, graduation, entering the universities as well as the attainment of job advancement (Musingati and Zebron, 2014).
Reading is an important way for contemporary college students to acquire new knowledge, expand their horizons and improve their skills, which is not only beneficial to their academic progress and quality improvement, but also plays an important role in creating a good cultural atmosphere and playing the function of educating people in colleges and universities. As an important means of educating people in colleges and universities, reading is related to the mission of cultivating talents in colleges and universities and the effectiveness of cultivating talents in universities. Therefore, reading for college students is one of the very important research topics in college education management. (Leal-Rodriguez and Albort-Morant, 2019; Gao, 2021; Weli and Nwogu, 2022).
Based on the above, from the perspective of university management, this study explores: (1) What factors affect college students’ reading engagement? (2) What is the influence mechanism of college students’ reading engagement on their academic performance? Thus, the university reading management mechanism can be constructed to improve their academic achievement.
Different scholars hold different views on the connotation of reading engagement, and so far, there is no unified standard. Csikszentmihalyi (1990) believes that reading engagement is a state of concentration. Pearson et al. (2016) believed that reading engagement is the interaction between students’ motivation and strategies. Different scholars have different views on the dimensions of reading engagement. PISA2009 divides reading engagement into personal reading engagement and school reading engagement. Personal reading engagement includes four dimensions: love of reading, diversity of reading, online reading activities and reading time. The school reading engagement specifically includes four dimensions: text interpretation, use of non-consecutive texts, reading activities of traditional literary works, and instrumental text use. Zhang et al. (2014) drew on the PISA2009 definition of reading engagement, and divided reading engagement into reading time, reading quantity and reading interest. Wen et al. (2016) studied reading engagement from three dimensions: length of reading time, amount of reading, and diversity of reading content.
The reading engagement proposed in this study refers to the time and energy input of college students in the process of reading, which specifically includes college students’ reading time and reading strategies (Brookbank et al., 2018; McDaniel, 2018). See Table 1 for details.
Research on the academic achievement of college students can be traced back to the 1960s. In 1966, the American Educational Advisory Council created the “Cooperative Program on Institutional Research.” After the 1990s, countries all over the world began to pay attention to the investigation and research on the academic achievement of college students. This is not only an effective way to judge the value growth of college students, but also an important way to explore the learning and development of college students, and an effective method to measure the quality of college education (Douglass et al., 2012). Park et al. (2014) summarized the academic achievement of college students as knowledge, values and attitudes, skills or appropriate behaviors. American university scholars developed a standardized test tool CLA (Collegiate Learning Assessment), which reflects the academic achievement status of college students by measuring critical thinking ability, analytical reasoning ability, problem-solving ability and communication ability. Developmental psychology believes that there is an interaction mechanism between value orientation and behavioral choice, and there is a causal relationship between academic achievement orientation and behavior, that is, college students with higher academic achievement will have better future development (Morgan, 2004; Aharony and Bar-Ilan, 2018). Maniaci et al. (2021) evaluated the relationship between healthy lifestyle and academic performance of 373 Italian adolescents, and found that academic achievement was conducive to healthy lifestyle and good eating habits.
According to the input-environment-output model proposed by Astin (1984), output refers to students’ ability, that is, the target of education and teaching in colleges and universities, input refers to the personal characteristics of students before receiving higher education, including the student’s family background, academic qualifications before admission, etc., environment refers to all kinds of actual experiences that students experience in universities and colleges, including those from course teaching, campus activities, social practice, and others (Astin, 1984).
A study environment therefore refers to the physical, social and psychological situations that affect a student’s well being as well his studies. A study environment must be safe, healthy and promote the study life of a student (Dempsey, 2020). A satisfying learning environment is conducive to college students’ reading engagement (time and energy), which in turn enhances their academic achievement. Therefore, the more college students participate in various practical activities, the better their comprehensive ability and quality will be improved (Camelo and Elliott, 2019; Wu, 2019; Marley and Wilcox, 2022).
Reading is essentially the inheritance and innovation of knowledge (object) in the interactive relationship between subject (reader) and carrier (reading material). The differences of reading subjects (readers) mainly depend on individual preconditions and post-environments. In the preconditions, family reading characteristics (mainly the pros and cons of the students’ family cultural capital) play a leading role. In the post-endowment environment, the cultivation of reading habits in colleges and universities plays a leading role. Different kinds of colleges and universities play different roles in the cultivation of reading habits, which affects reading engagement. The object of reading is composed of explicit knowledge and tacit knowledge. Explicit knowledge is mainly composed of disciplinary professional knowledge, interdisciplinary integration knowledge and fragmented knowledge, while tacit knowledge is obtained through comprehension, and in university campus, it is mainly manifested as scholarly campus and cultural influence. Reading carriers are mainly composed of paper carriers and digital carriers. Under the background of technological change, intelligent knowledge production (IR, AI), interactive knowledge transmission and lively knowledge experience (AR, VR) are the inevitable trends of the development of reading carriers.
Therefore, this study explores the influence mechanism of college students’ reading engagement on the improvement of academic achievement from the perspective of students and universities. Based on this, this study puts forward the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 1: The characteristics of reading subjects (preconditions and college endowments) have a significant influence on the academic achievement of college students. The better the subject endowment, the better the academic achievement of college students.
Hypothesis 1a: Controlling other variables, the better the college students’ pre-existing conditions, the better their academic achievement;
Hypothesis 1b: Controlling other variables, the better the endowment of college students in colleges and universities, the better their academic achievement;
Hypothesis 2: College students’ reading engagement has a significant influence on academic achievement, that is, the more college students engage in reading, the better their academic achievement.
Hypothesis 2a: Controlling other variables, the more time college students devote to reading, the better their academic achievement;
Hypothesis 2b: Controlling other variables, the better the reading strategy of college students, the better their academic achievement;
Hypothesis 3: The cultivation of reading habits in colleges and universities has a significant impact on the academic achievement of college students by influencing their reading engagement, that is, the better the university’s curriculum driving mechanism, resource support mechanism, atmosphere stimulation mechanism and interaction promotion mechanism are played, the better the academic achievement of college students will be.
The logic of this research is to construct the relationship between reading engagement and academic achievement, and explore the influence mechanism of reading engagement on academic achievement by investigating the respective effects of reading engagement at the student level and the university level. The reading engagement (time and strategy) level of college students, from the individual level, is mainly affected by the individual’s preconditions. From the perspective of group characteristics, it is mainly affected by the endowment of colleges and the cultivation of college reading habits. The combined effect of the individual level and the university level constitutes a research system of college students’ reading engagement on academic achievement.
First of all, literature was sorted out to collect authoritative classical scales, and some mature scales were used for reference. In this study, the reading engagement questionnaire of college students draws on the questionnaire of “Research on Reading Motivation of College Students” by Chen Xiaoli of Jinan University and the questionnaire of “Chinese Reading Behavior in the Digital Age” by Li Xinxiang of Wuhan University. The college students’ academic achievement questionnaire was based on the “University Quality and Student Development Monitoring Project in Beijing” questionnaire and NSSE-China.
Secondly, through discussion among members of the research team and consultation with authoritative experts in this field, the contents of the questionnaire items and the wording of the questionnaire were modified, and the design content of the questionnaire was initially determined. In the first part, the purpose of the study was explained to the research subjects. The second part defines the background data of this study. The third part is mainly about the impact of college students’ reading engagement on academic achievement, including time reading motivation, family reading culture, college reading habit training, college organizational endowment and so on. The fourth part is the basic information of the research object, including age and other demographic variables.
Finally, a small number of qualified samples were screened, and the proposed questionnaire was used for pre-investigation, and the data of the recovered questionnaire was sorted out. At the same time, the reliability and validity of the questionnaire items were tested, and the inconsistent questions were deleted to form the final draft of the questionnaire.
After the preliminary questionnaire survey, the re-adjustment and modification of the questionnaire were completed to improve reliability and validity, and the final questionnaire of this study was formed.
In this study, cluster sampling method was mainly adopted. This method is to merge the units in the population into several non-intersecting and non-repeating sets, that is, cluster; and then use the cluster as a sampling unit to draw samples.
Considering the representativeness and comprehensiveness of the sample, three undergraduate universities in Anhui Province were selected, one is a university of Project 985, one is a government-run undergraduate university, and one is a private undergraduate university. The student sample covers freshmen to seniors, and the majors cover humanities and social sciences, science and engineering. In the questionnaire survey, we gathered the students together and conducted the survey in the form of answering online questionnaires through smartphones. Finally, a total of 1,155 valid questionnaires were obtained.
This study takes the academic achievement of college students as the dependent variable, which includes three dimensions, namely, professional ability, general competence, and career planning ability. The reading engagement of college students was taken as the explanatory variable, and the individual characteristics of college students, reading motivation, family reading culture, college reading habit training and college organizational endowment were used as control variables. The definitions of main explanatory variables, explained variables and control variables are shown in Table 2.
In order to verify the mechanism of college students’ reading engagement on college students’ academic achievement proposed in this paper, the following multiple regression models were used to analyze from the student level and the university level. The specific model is as follows:
Among them, Xij represents the reading engagement of college students, Aij represents the individual characteristics of college students; Bij represents the reading motivation of college students; Cij represents the reading culture of college students’ families; Dij represents the cultivation of reading habits in colleges and universities; Eij stands for organizational endowment of colleges and universities; Yij is for academic achievement of college students. βi is the regression coefficient.
In Model 1, the dependent variable is Xij, and other variables are independent variables, which are used to explore the factors affecting college students’ reading engagement. In Model 2, the dependent variable is Yij, and other variables are independent variables, which are used to explore the impact of college students’ reading engagement on their academic achievement.
In terms of the grade distribution of the sample, there are fewer seniors. The main reason is that the courses of seniors have finished, and many students have been practicing abroad, so the number of seniors in school is small. The sample number of freshmen, sophomores and juniors was relatively balanced, with 238 freshmen, accounting for 20.6%, 436 sophomore students, accounting for 37.7%, 359 juniors, accounting for 31.1 percent. In terms of the types of colleges and universities, 203 students are from 985 colleges and universities, accounting for 17.6%. The number of students from local public undergraduate universities is 283, accounting for 24.5%; the number of local private undergraduate students is 669, accounting for 57.9%. In terms of gender, there are 633 boys, accounting for 54.8%, and 522 girls, accounting for 45.2%. In terms of majors, 382 students are in humanities and social sciences, accounting for 28.5%, while 826 in science and engineering, accounting for 71.5%. In terms of the source of students, 606 students are from rural areas, accounting for 52.5%, and 549 from urban areas, accounting for 47.5%. In terms of the types of high schools, 788 students, accounting for 68.2%, are enrolled in key high schools, and 367 students, or 31.8 percent, are enrolled in regular high schools. From the perspective of annual family income, 58.4% (674 students) have an annual family income of 50,000 yuan or less, 25% (289 students) 60,000–100,000 yuan, and the remaining 17.6% (242 students) 100,000 yuan or more. See Table 3 for details.
The reliability test of the questionnaire is mainly to ensure the reliability of the questionnaire, so we conducted the reliability test of the questionnaire by using SPSS21.0. According to the structure of the questionnaire, we selected the following dimensions for reliability analysis, as shown in Table 4.
Cronbach’s α coefficient is used to measure the reliability of the internal consistency of the questionnaire. If the Cronbach’s α coefficient is larger, it indicates that the degree of internal consistency of the questionnaire is higher, and the reliability of the questionnaire results is stronger. It is generally believed that the reliability coefficient should be between 0 and 1. If the reliability coefficient of the questionnaire is above 0.9, it means that the reliability of the questionnaire is very good. If the reliability coefficient of the questionnaire is between 0.8 and 0.9, it indicates that the reliability of the questionnaire is acceptable. If the reliability coefficient of the questionnaire is between 0.7 and 0.8, it indicates that some items of the questionnaire need to be revised. If the reliability coefficient of the questionnaire is below 0.7, it indicates that some items in the questionnaire need to be deleted.
The reliability of this questionnaire can be found from the above table, the reliability of each dimension of the questionnaire is above 0.8, indicating that the reliability of the questionnaire in this paper is good.
The paper used structural equation modeling to test the construct validity of the main variables, including academic achievement and reading engagement. As can be seen from Figure 1, the path coefficients of the three abilities of academic achievement are all above 0.7, and other observation indicators meet the requirements, indicating that the validity of the academic achievement in the questionnaire is good. As can be seen from Figure 2, the path coefficients of the two aspects of reading engagement are both above 0.6, and the other observed indicators are consistent, indicating that the validity of reading engagement in the questionnaire is good.
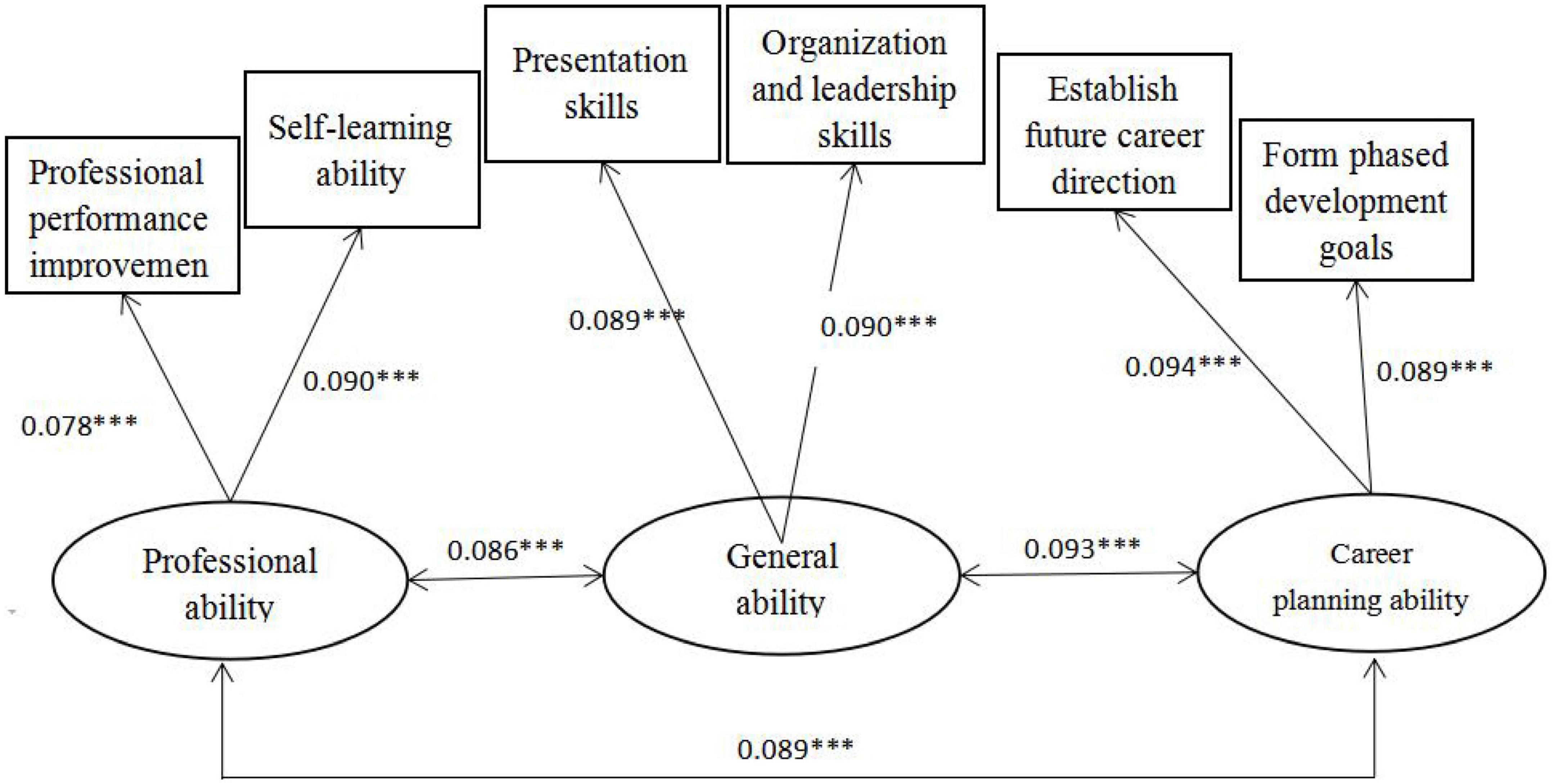
Figure 1. Construct validity analysis chart of academic achievement (after normalization). Significance level *P < 0.1, **P < 0.05, and ***P < 0.01.
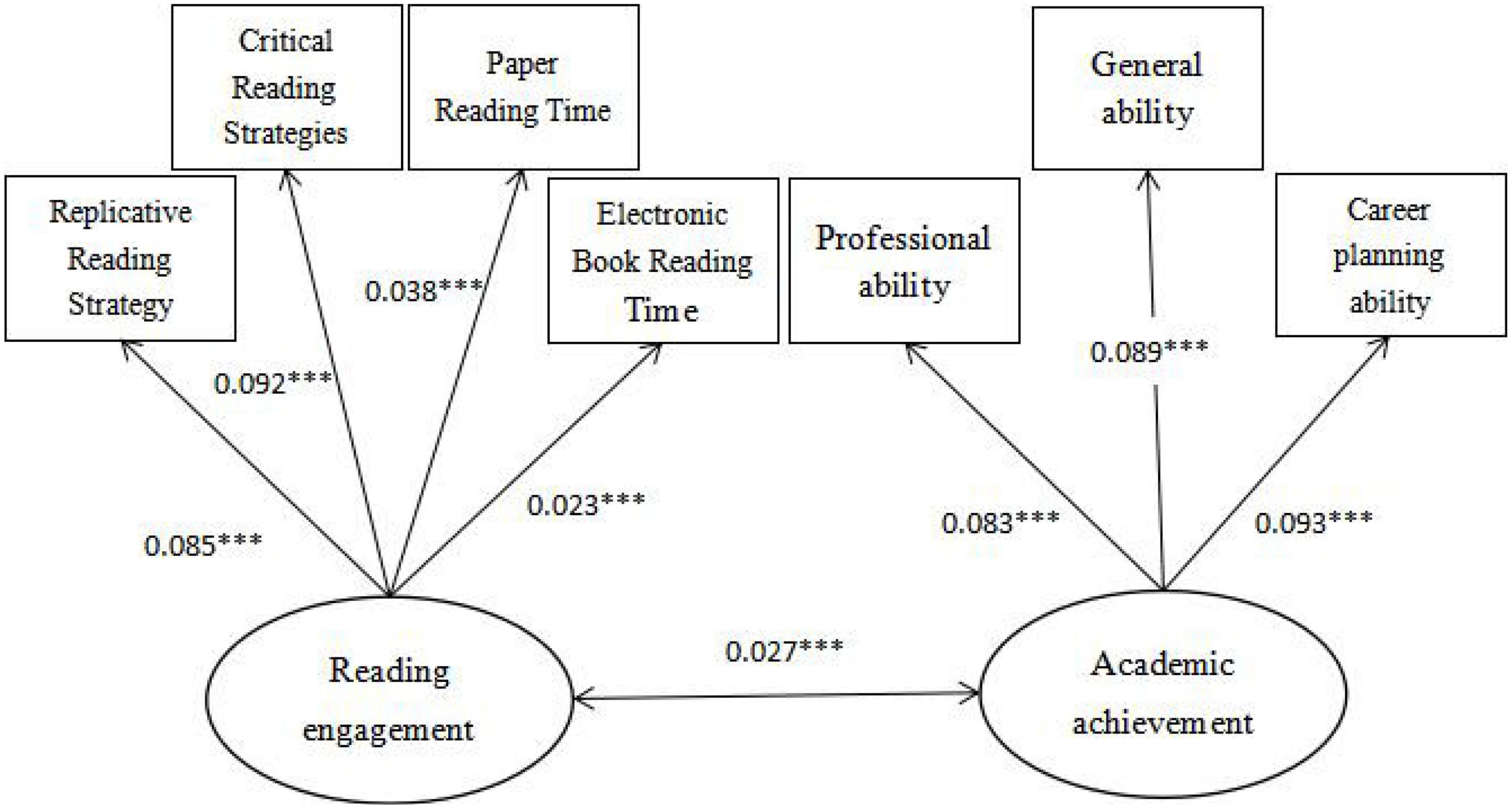
Figure 2. Construct validity analysis diagram of reading input (after standardization). Significance level *P < 0.1, **P < 0.05, and ***P < 0.01.
The above analysis shows that different individual characteristics, different reading motivation, different family reading culture, different reading habit cultivation and different organizational endowment of colleges and universities show different reading input. Therefore, the paper took college students’ reading engagement as the dependent variable and college students’ individual characteristics, reading motivation, family reading culture, college reading habit cultivation and college organizational endowment as independent variables to construct a multiple regression model and analyze the influencing mechanism of these factors on college students’ reading engagement. The regression results are shown in Table 5.
As can be seen from Table 5, in the prediction of paper reading time, the grade of college students has a positive and significant effect on reading time, that is, with the rise of grade, college students will spend more and more time on paper reading. In the prediction of reading strategies, the grade of college students plays a significant role in the replication reading strategy. With the rise of grade, college students are more and more inclined to choose the replication reading strategy. Gender of college students plays a significant role in critical reading strategies, and male students are more inclined to think and reflect when reading.
As can be seen from Table 5, in terms of reading motivation, both practical motivation and entertainment motivation have positive and significant effects on paper reading time, which also indicates that college students spend more time on practical and entertainment paper reading materials.
In terms of reading motivation, entertainment motivation has a positive and significant effect on e-reading time, while developmental motivation has a negative and significant effect on e-reading time. This also indicates that the main purpose of e-reading is entertainment, but college students choose to read from the perspective of their own development, so they spend less time on e-reading.
In terms of the impact of reading motivation on reading strategies, practical motivation, entertainment motivation and developmental motivation all play a positive and significant role in the replication and reflective reading strategies. In other words, on the whole, the stronger the reading motivation of college students, the better they will use the replication and reflective reading strategies.
As can be seen from Table 5, in the prediction of reading time, only the father’s education years play a negative and significant role in the paper reading time of college students. That is, the higher the father’s education level, the less reading time of college students, which is obviously not in line with our conventional cognition, and the specific reasons need to be further analyzed.
However, the amount of family books, family reading education and family reading atmosphere all have significant positive effects on the paper reading time and electronic reading time of college students, which indicates that the more books in the family, the better the family reading education, the better the family reading atmosphere, and the longer the reading time of college students.
In the prediction of reading strategies, family reading education and family reading atmosphere had positive and significant effects on college students’ duplicative reading strategies and reflective reading strategies. The amount of family books has a positive and significant effect on the reflective reading strategy, which also indicates that family reading education, family reading atmosphere and the amount of family books are an important factor affecting the reading strategy of college students.
In terms of the prediction of reading time, the course-driven mechanism and the atmosphere stimulation mechanism have positive and significant effects on paper reading time and electronic reading time, which indicates that the opening of college guidance courses and the development of college reading activities will increase the reading time of college students.
In the prediction of reading strategies, the course-driven mechanism and the atmosphere stimulating mechanism play a positive and significant role in the replication reading strategy of college students, while the course-driven mechanism, the resource supporting mechanism and the atmosphere stimulating mechanism play a positive and significant role in the reflective reading strategy of college students. Generally speaking, the cultivation mechanism of college reading habits plays a very important role in the selection of reading strategies for college students. The more attention colleges pay to the cultivation of students’ reading habits, the better college students can use reading strategies.
In the prediction of organizational endowment of colleges and universities, the type of colleges and universities plays a positive and significant role in paper reading time, electronic reading time, replicative reading strategy and reflective reading strategy, that is, with the improvement of college selection, the longer the reading time of college students and the better the use of reading strategies.
Through the above analysis, we can find that college students with different levels of reading engagement show different levels of academic achievement. Therefore, taking college students’ reading engagement as the independent variable, college students’ academic achievement as the dependent variable, and college students’ individual characteristics, reading motivation, family reading culture and organizational endowment as control variables, we constructed a multiple regression model to test whether college students’ reading engagement has an impact on college students’ academic achievement. At the same time, it also examines whether the individual characteristics of college students, reading motivation, family reading culture and organizational endowment of colleges and universities affect the academic achievement of college students. The regression results are shown in Table 6.
(1) The influence of college students’ reading engagement on college students’ professional quality.
As can be seen from Table 6, paper reading time, replicative reading strategy and speculative reading strategy all play a significant positive role in the prediction of professional literacy of college students. However, e-reading time has no significant effect on college students’ professional quality. The explanatory power of the whole model is 58.3%. The data show that paper reading time and critical reading strategy can promote the improvement of college students’ professional ability, that is, the more paper reading time of college students, the more professional quality can be promoted. The use of critical reading strategy can also significantly improve the professional quality of college students. The measurement of professional literacy includes the improvement of professional performance and self-directed learning ability. It can be seen that if college students want to improve their professional knowledge and enhance their autonomous learning ability, they must first increase their reading time of paper books. Secondly, we should use the critical reading strategy, that is, we should keep thinking while reading, so as to improve our professional ability.
(2) The influence of college students’ reading engagement on college students’ general ability.
As can be seen from Table 6, only the critical reading strategy plays a significant positive role in predicting the general ability of college students. Paper reading time, electronic reading time and Replicative reading strategy have no significant effect on college students’ general ability. The explanatory power of the whole model is 48.3%. The data show that the critical reading strategy can promote the general ability of college students. The measurement of general ability includes two elements: expressive ability and organizational leadership ability. From the perspective of the function of reading, if college students want to improve their general ability, that is, their expressive ability and organizational leadership ability, they must strengthen the use of critical reading strategies in reading, think in reading, and constantly improve their general ability.
(3) The impact of reading engagement on college students’ career and career planning
As can be seen from Table 6, in terms of the prediction of career and career planning ability, the critical reading strategy has a significant positive effect on college students’ career and career planning ability. Paper reading time, electronic reading time and replicative reading strategy have no significant effect on college students’ general ability. The explanatory power of the whole model is 62.7%. The data show that the critical reading strategy can improve college students’ career and career planning ability. The measurement of career and career planning ability includes two elements: determining future career direction and forming stage development goals. The more college students use critical reading strategies in reading, the more they can improve their career and career planning ability.
The above multiple linear regression analysis shows the degree of influence of college students’ reading engagement on academic achievement. For how each dimension of college students’ reading engagement affects college students’ academic achievement, it is necessary to construct structural equation model to conduct path analysis and analyze the specific impact mechanism of college students’ reading engagement on academic achievement. AMOSS20.0 was used for path analysis in this paper. The chi-square of the model was 135.873, the degree of freedom was 13, and the overall significance probability of the model was P<. 0.001, the model fit is good, and the indicators are shown in Table 7.
According to the Maximum Likelihood method, the model is analyzed. Figure 3 summarizes the standardized influence mechanism between “reading engagement and academic achievement.” The effect of college students’ reading engagement on standardized academic achievement reached 0.57, and the probability of significance was P<. 0.001, which indicates that college students’ reading engagement can indeed have a positive role in promoting academic achievement. This also confirms the conclusion in the regression model that college students’ reading engagement has a significant promoting effect on academic achievement, and verifies the basic hypothesis of this paper.
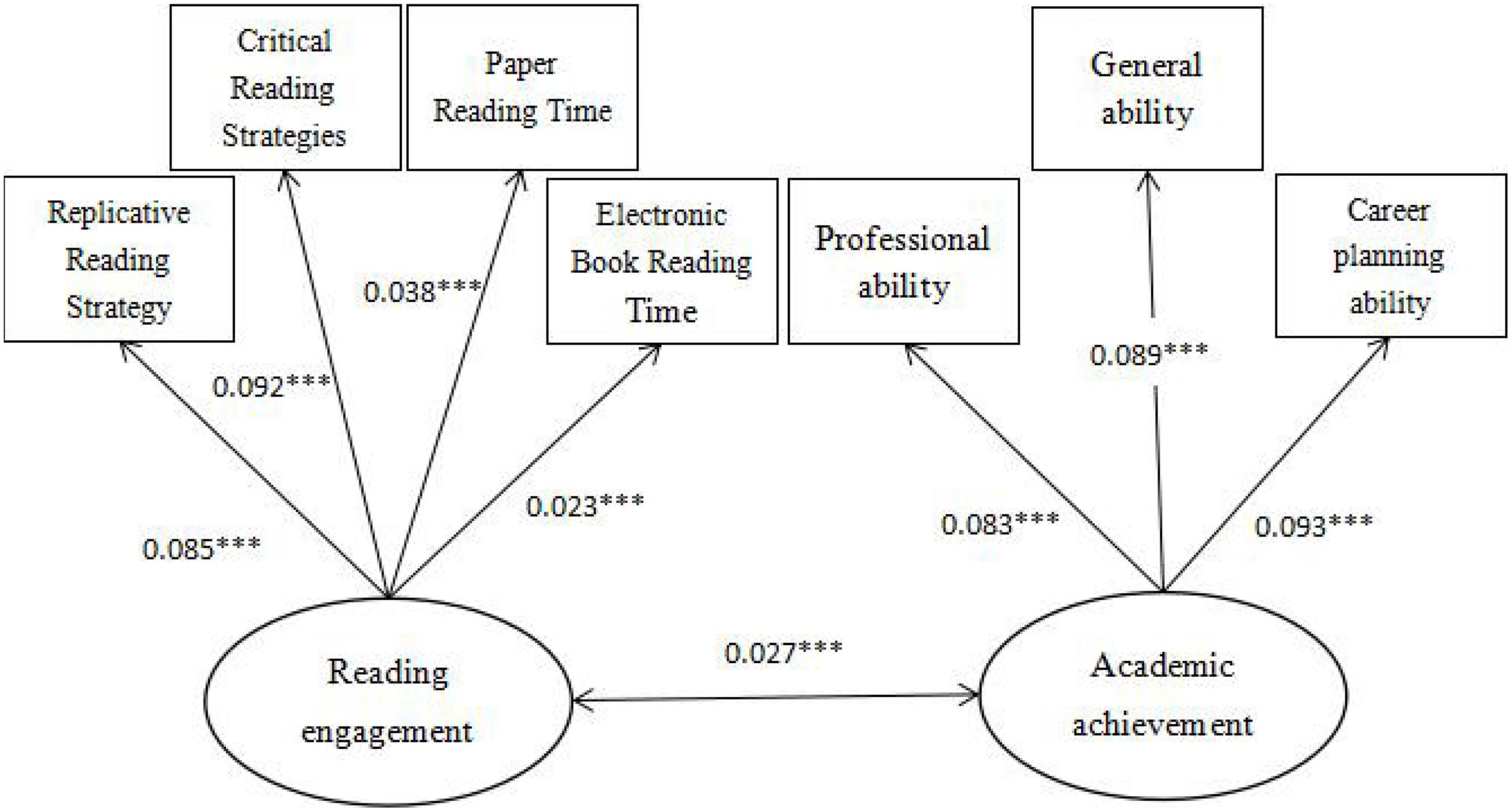
Figure 3. Structural equation model of college students’ reading engagement and academic achievement (after normalization). Significance level *P < 0.1, **P < 0.05, and ***P < 0.01.
In this study, the individual characteristics, reading motivation, family reading culture of college students and the organizational endowment of colleges and universities were added into the regression model as control variables. The regression model was used to test whether college students’ individual characteristics, reading motivation, family reading culture, reading habit training in colleges and universities, and organizational endowment in colleges and universities would have an impact on college students’ academic achievement. The regression results are shown in Table 6.
(1) The influence of college students’ individual characteristics on college students’ academic achievement.
In terms of professional literacy, it can be seen from Table 6 that both the place of origin and developmental motivation have significant positive effects on college students’ professional literacy, that is, the professional literacy of urban students is better than that of rural students, and the more college students read for their own development, the stronger their professional literacy will be.
In terms of general ability, it can be seen from Table 6 that grade, subject and place of origin all have negative and significant effects on college students’ general ability, that is, with the improvement of college students’ grade, their own general ability decreases. Compared with students majoring in science and engineering, students majoring in humanities and social sciences improve their general ability better. The origin of students has a positive and significant effect on the general ability of college students. Urban students improve their general ability more than rural students.
In terms of college students’ career planning ability, from Table 6, the grade of career and career planning ability of college students has negative significant effect, namely as college students’ grade rises, the cognitive ability of college students decreases in their career planning, and the reason may be that as their grade grows, especially when they need to find a job, their self-efficacy for their career planning ability becomes even lower. Discipline has a significant negative effect on career and lifetime planning ability, that is, the improvement of career planning ability of humanities and social science students is higher than that of science and engineering students.
(2) The impact of reading motivation on the academic achievement of college students.
In terms of professional quality, Table 6 shows that developmental motivation has a significant positive effect on the professional quality of college students, which indicates that the more they pay attention to long-term development in reading, the higher their career planning ability will be.
In terms of general ability, Table 6 shows that practical motivation, recreational motivation and developmental motivation all have a significant positive effect on general ability, which indicates that the stronger the reading motivation of college students, the better they can improve their general ability.
In terms of career planning ability, Table 6 shows that practical motivation and developmental motivation have a significant positive effect on career planning ability, which shows that the more college students pay attention to practicality and long-term development in reading, the better they can improve their career planning ability.
(3) The influence of family reading culture on the academic achievement of college students.
In terms of professional quality, Table 6 shows that the schooling years of fathers have a significant negative effect on the professional quality of college students, which is contradictory to conventional understanding. The possible reason is that most of the students come from private colleges and are not enthusiastic about their major. So the more educated their father, the more they will be motivated to learn knowledge. That being said, due to their psychological inversion, their professional quality is usually not very good.
In terms of general ability and career planning ability, Table 6 shows that the variables of family reading culture have no significant impact on the dimensions of college students’ academic achievement.
In terms of the organizational endowment of colleges, that is, the types of colleges, Table 6 shows that the types of colleges have a significant positive impact on students’ general ability, and as college selection improves, college students can better improve their general ability. This shows that the better the organizational endowment of colleges, the more prominent the general abilities of college students, including organizational and communication skills.
(1) From the perspective of college students, in terms of college students’ reading time, grades, practical motivation, recreational motivation, family collection of books, family reading education, and family reading atmosphere have a significant positive impact on paper reading time. The same is true of the education level of fathers. College students’ grade, recreational motivation, developmental motivation, family book collection, family reading education, and family reading atmosphere have a significant positive impact on e-reading time. In terms of reading strategies, grades, practical motivation, recreational motivation, developmental motivation, family reading education, and family reading atmosphere have significant positive effects on replicative reading strategies, while gender, practical motivation, recreational motivation, developmental motivation, family book collection, family reading education, and family reading atmosphere have significant positive effects on critical reading strategies.
(2) From the perspective of colleges, the curriculum-driven mechanism, atmosphere stimulation mechanism, and organizational endowment have a significant positive impact on paper reading time and e-reading time. In terms of reading strategies, curriculum-driven mechanism, atmosphere-based incentive mechanism, and college organizational endowment have a significant positive impact on replicative reading, while curriculum-driven mechanism, resource support mechanism, atmosphere incentive mechanism, and college organizational endowment have a significant positive impact on critical reading.
From the analysis on how college students’ reading engagement affect their academic achievement, the following two points are drawn: (1) Among others, reading time is the most important factor affecting reading behavior and reading volume. It is found that the reading time of paper books has a significant positive effect on the professional quality of college students, but has no significant effect on the general ability, career and lifetime planning ability of college students. Many students prefer paper books while studying professional knowledge, because they can take notes on them and they are conducive to systemic learning. This may be an important reason why paper-book reading time has a significant positive effect on the professional quality of college students. In addition, e-book reading time has no significant effect on the three abilities concerning college students’ academic achievement, which to some extent reflects the drawbacks of e-book reading. E-book reading can easily lead to fragmented reading, and it is difficult to form a systematic knowledge system. Moreover, students also reported that e-books are basically recreational. Therefore, it is difficult for such reading to have a significant impact on the three abilities, but this does not mean that e-reading is useless. (2) In terms of reading strategies, critical reading strategies have a significant positive effect on college students’ professional quality, general ability, career and lifetime planning. While reading, college students should not only rely on passive memory, but also learn to think and make explorations actively, which is conducive to the improvement of academic achievement.
Based on the analysis on how the individual characteristics, reading motivation, family reading culture and institutional endowment of college students on the academic achievement of college students, the following four conclusions are drawn: (1) Grades have a significant negative effect on college students’ general ability and career and lifetime planning ability. With the increase of grades, the general ability and the ability of career and lifetime planning decrease. Disciplines have a significant negative effect on the general ability and ability of career and lifetime planning: feedback from students of humanities and social sciences shows that they can better improve their general ability through reading than those of science and engineering. The source of students has a positive effect on the professional quality, general ability, career and lifetime planning of college students, that is, the self-evaluation of urban students on their academic achievement is higher than that of rural students. (2) Practical motivation has a positive and significant effect on college students’ general ability and career planning ability. Students believe that practical reading can promote the two abilities; recreational motivation has a significant impact on general ability; motivation has a significant positive effect on academic achievement overall. (3) In terms of family reading culture, only the education level of fathers has a significant negative effect on college students’ professional quality, while that of others has no significant effect, which is contrary to our cognition and requires further verification and analysis. (4) The organizational endowment of colleges has a significant positive effect on general ability. With the improvement of college selectivity, college students have a higher evaluation of their general ability.
This research verifies the functional mechanism of reading subject, reading object and reading carrier, and concludes that the core of the operating mechanism of college reading management lies in the management of reading input (reading time and reading strategy), and the mechanism of college reading management makes sure that the reading subject, reading object and the reading carrier are effectively integrated. The joint effect of the operation mechanism and the action mechanism of reading management in colleges can promote the effective implementation of reading management, and then improve the academic achievement of college students.
First of all, find the individual, group and epochal characteristics of college students, and based on systematically grasping their individual characteristics, encourage them to read and improve their reading efficiency. Based on the cultivation of reading content tendencies and reading habits, actively promote the application and conversion of replicative reading and critical reading. Second, give play to the role of the reading object, well manage and serve knowledge content, promote the transformation between tacit knowledge and explicit knowledge, and play the role of tacit knowledge and tacit curriculum. In particular, promote reading atmosphere and provide a comfortable reading space for students to combine the role of the environment and culture in talent cultivation. Finally, in terms of reading carriers, combine technology and reading form. The construction of resources and platforms in colleges is the foundation of reading management. The construction and application of electronic resources and online platforms has become an inevitable trend under the background of technological change. The application of new technologies to improve and promote reading, especially the method of “intelligence plus reading” will be the main trend leading the development of reading carrier management.
A sound system can guarantee the effective operation of reading management. The study found that the intended purpose of reading management cannot be achieved only through encouragement and advocacy. It is also necessary to systematically build a flexible and rigid institutional system that combine universities, libraries, counselors, teachers and student.
(1) In the construction of flexible restraint system, requirements concerning the number of books that students should read (for example one hundreds Chinese and foreign classics) and thought sharing should be implemented in each term, and relevant achievements, such as the number of book sharing and essays on book reading, are directly linked to student awards, party membership, and student cadre elections.
(2) In terms of rigid system construction, the responsibility assessment system for university administrators such as librarians, counselors and teachers should consider whether they participate in and guide students’ reading activities. Libraries and curators promote reading services and counseling, extend the functions of libraries in a timely manner based on technological progress and actual needs. In particular, they are responsible for selecting and recommending classic books and offer monthly lectures on famous classics. The work assessment system for counselors should consider whether they organize and take part in reading group activities in class management activities. Teachers, especially those with senior professional titles, should regularly offer lectures on professional reading, which has become an important part of teacher assessment. At the same time, colleges have established a reading assistance system for students with financial difficulties through student scholarships and other means.
Reading resources and platforms are the material basis of reading management in colleges. Efforts should be made to strengthen the information construction of libraries, encourage teachers to develop relevant reading websites, share proper reading resources among students, and students with a “reading corner” for sharing and reading, thus building a bridge connecting teachers and students and promoting communication among students. In addition, new technologies should be used to improve college students’ reading strategies. In particular, the method of “artificial intelligence plus reading” such as virtual reality and augmented reality can effectively resolve shortcomings caused by “fragmented reading,” and find a reasonable and effective way for the promotion of classic reading.
(1) Establish a mechanism for reading promotion. The formation of a reading culture is a long-term and accumulative process, which cannot be achieved by just one or two reading activities. Through online and offline reading tutoring and various reading promotion activities (special lectures, reading salons, etc.), colleges can effectively improve students’ reading enthusiasm and participation, and form an institutionalized and systematic reading tradition. Libraries should improve their reading service, and introduce themselves to freshmen so that they know their services. Efforts should also be made to optimize the information building, and build a recommendation column for new and good books. At the same time, we should focus on guiding students to use electronic resources, and conduct regular activities to let them know how to use electronic resources better.
(2) Build a reading interaction system. The reading interaction between teachers and students and among students is an important part of campus interaction, and also a beautiful “learning landscape” on campus. On the one hand, it is necessary to construct a benign reading interaction mechanism between teachers and students, involving the reading interaction between professional teachers and students, and between counselors and students, and the informal reading organization of teachers and students. On the other hand, it is also necessary to build an active classmate reading interaction mechanism that include formal reading interaction and informal reading activities.
(3) Build a development mechanism for college students’ reading behavior. First, increase the reading time. Through opening characteristic reading courses, building a wealth of electronic reading resources, and providing an elegant and comfortable reading environment on campus, students are encouraged to read at any time. Second, use appropriate reading strategies. Encourage teachers to offer guidance on reading in their teaching process; organize clubs and library activities; invite famous teachers to give reading strategy lectures. Third, optimize the structure of reading contents, help students choose reading contents reasonably based on their needs and major, promote classic reading, and prevent recreational reading from becoming the main body of reading.
(1) Expand the distribution area and number of samples. The follow-up research will cover more samples, select some colleges and universities in the eastern, central and western regions as the survey objects, expand the sample size to about 4,000, and conduct interviews with graduates and teachers to further explore factors influencing college students’ reading and their relationship with academic achievement.
(2) Systematically carry out reading management in colleges and universities. Reading management needs to implement targeted reading intervention measures for 2–3 years and quantify specific indicators, which will inevitably produce good practical results. Reading management in colleges and universities should further expand its thinking and pay attention to the reading intervention of college students before they go to college. Especially for students who come from rural areas and have a relatively weak cultural background, it is necessary to transfer reading management to the stage of compulsory education.
(3) Promote classic reading. Classical reading has always been the most important part among college students, but there are various reading difficulties in practice. How to use the reform of reading carriers brought by technological reform, especially the method of “artificial intelligence plus classics” in practice, to improve the popularity and efficiency of classic reading is one of focuses for follow-up research.
(4) Research on the relationship between e-reading and academic achievement. With the increase of electronic resources and the popularization of media such as film, television media and e-readers, television, the Internet, and mobile phones have become the major reading methods used by the Chinese people. How to effectively use the “artificial intelligence plus reading” method, especially the application of VR and AR, to improve the academic achievement of college students, is worthy of further research in the context of technological innovation.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
X-WW proposed the research hypothesis and research design, analyzed the experimental data, and analyzed the experimental results. Y-JZ contributed to questionnaires and collected data. Y-CZ designed the framework of the manuscript and discussed the experimental results. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
This study was supported by the major teaching and research project of Anhui Province, Construction and Exploration of Quality Culture System of Private Universities (Project No. 2020jyxm0779) and the construction of school-level scientific research team of Anhui Xinhua College (Project No. kytd202206).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Aharony, N., and Bar-Ilan, J. (2018). Students’ academic reading preferences: an exploratory study. J. Libr. Inf. Sci. 50, 3–13. doi: 10.1177/0961000616656044
Astin, A. W. (1984). Student involvement: a developmental theory for higher education. J. Coll. Stud. Pers. 25, 297–308.
Brookbank, E., Davis, A. M., and Harlan, L. (2018). Don’t call it a comeback: popular reading collections in academic libraries. Ref. User Serv. Q. 58, 28–39. doi: 10.5860/rusq.58.1.6838
Cai, T., and Zhao, J. (2022). Perspectives on the reading landscape in an accelerating society. China Edit. 6, 26–32.
Camelo, K., and Elliott, M. (2019). Food insecurity and academic achievement among college students at a public university in the United States. J. Coll. Stud. Dev. 60, 307–318. doi: 10.1353/csd.2019.0028
Dempsey, A. (2020). How to Stay Focused While Studying Backed and Research. Suzhou: Duke Kunshan University.
Douglass, J. A., Thomson, G., and Zhao, C. (2012). The learning outcomes race: the value of self-reported gains in large research universities. High. Educ. 64, 317–335. doi: 10.1007/s10734-011-9496-x
Dwivedi, Y. K., Hughes, L., Baabdullah, A. M., Ribeiro-Navarrete, S., Giannakis, M., Al-Debei, M. M., et al. (2022). Metaverse beyond the hype: Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. Int. J. Inf. Manage. 66:102542. doi: 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2022.102542
Gao, Y. (2021). “Reading Promotion Activities in the Internet Environment Help to Shape the Personality of College Students in Application-Oriented Universities,” in Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Information Management and Technology, Jakarta. doi: 10.1145/3465631.3465813
Leal-Rodriguez, A. L., and Albort-Morant, G. (2019). Promoting innovative experiential learning practices to improve academic performance: empirical evidence from a Spanish Business School. J. Innov. Knowl. 4, 97–103. doi: 10.1016/j.jik.2017.12.001
Maniaci, G., Cascia, C. L., Giammanco, A., Ferraro, L., and Barbera, D. L. (2021). The impact of healthy lifestyles on academic achievement among Italian adolescents. Curr. Psychol. 3, 1–7. doi: 10.1007/s12144-021-01614-w
Marley, S. C., and Wilcox, M. J. (2022). Implicit theories of intelligence and achievement goal orientations: How are they associated with college student academic achievement? Soc. Educ. Res. 3, 279–298. doi: 10.37256/ser.3220221625
McDaniel, S. (2018). Library roles in advancing graduate peer-tutor agency and integrated academic literacies. Ref. Serv. Rev. 46, 23–49. doi: 10.1108/RSR-02-2018-0017
Morgan, S. L. (2004). Methodologist as arbitrator: five models for black-white differences in the causal effect of expectations on attainment. Sociol. Methods Res. 33, 43–53. doi: 10.1177/0049124104263657
Musingafi, M. C. C., and Zebron, S. (2014). The classroom situation: Improving study habits of secondary school students in zimbabwe. J. Educ. Literature 1, 133–138.
Park, S. Y., Cha, S. B., Lim, K., and Jung, S. H. (2014). The relationship between university student learning outcomes and participation in social network services, social acceptance and attitude towards school life. Br. J. Educ. Technol. 45, 97–111. doi: 10.1111/bjet.12013
Pearson, P. D., Kamil, M. L., Mosenthal, P. B., and Barr, R. (2016). Handbook of Reading Research. London: Routledge. doi: 10.4324/9781315200651
Weli, S., and Nwogu, C. M. (2022). Influence of a study environment and good note taking on educational management students’ academic performance in universities in Port Harcourt. Int. J. Soc. Sci. Manage. Stud. 1:78.
Wen, H., Liang, K., and Liu, X. (2016). Effect of family environment on reading ability: the mediating effects of reading engagement and reading interest among junior high school students. Acta Psychologica Sinica 48, 248–257. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1041.2016.00248
Wu, Z. (2019). Academic motivation, engagement, and achievement among college students. Coll. Stud. J. 53, 99–112.
Zhang, S., Su, M., Wang, L., and Wen, H. (2014). The effect of teachers on students’reading ability: the mediating effect of reading engagement. Chin. J. Spec. Educ. 9, 84–89.
Keywords: metaverse, reading engagement, academic achievement, college organizational endowment, college reading management
Citation: Wang X-W, Zhu Y-J and Zhang Y-C (2022) An empirical study of college students’ reading engagement on academic achievement. Front. Psychol. 13:1025754. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1025754
Received: 23 August 2022; Accepted: 21 September 2022;
Published: 10 November 2022.
Edited by:
Xuesong Zhai, Zhejiang University, ChinaReviewed by:
Hao Xu, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, ChinaCopyright © 2022 Wang, Zhu and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yi-Cheng Zhang, enljMjAxOUBtYWlsLnVzdGMuZWR1LmNu
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.