
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Oncol. , 01 October 2021
Sec. Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy
Volume 11 - 2021 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.778039
This article is a correction to:
Short-Interval Sequential CAR-T Cell Infusion May Enhance Prior CAR-T Cell Expansion to Augment Anti-Lymphoma Response in B-NHL
 Yuan Meng1†
Yuan Meng1† Biping Deng2†
Biping Deng2† Luan Rong2
Luan Rong2 Chuo Li1
Chuo Li1 Weiliang Song3
Weiliang Song3 Zhuojun Ling3
Zhuojun Ling3 Jinlong Xu3
Jinlong Xu3 Jiajia Duan3
Jiajia Duan3 Zelin Wang3
Zelin Wang3 Alex H. Chang4
Alex H. Chang4 Xiaoming Feng1
Xiaoming Feng1 Xiujuan Xiong5
Xiujuan Xiong5 Xiaoli Chen6*
Xiaoli Chen6* Jing Pan1,7*
Jing Pan1,7*A Corrigendum on
Short-Interval Sequential CAR-T Cell Infusion May Enhance Prior CAR-T Cell Expansion to Augment Anti-Lymphoma Response in B-NHL
By Meng Y, Deng B, Rong L, Li C, Song W, Ling Z, Xu J, Duan J, Wang Z, Chang AH, Feng X, Xiong X, Chen X and Pan J (2021). 11:640166. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.640166
In the original article, there was a mistake in Figure 2A as published. In Figure 2A (in vivo treatment scheme), the subsequent injection time was on Day 10, not on Day 14. The corrected Figure 2 appears below.
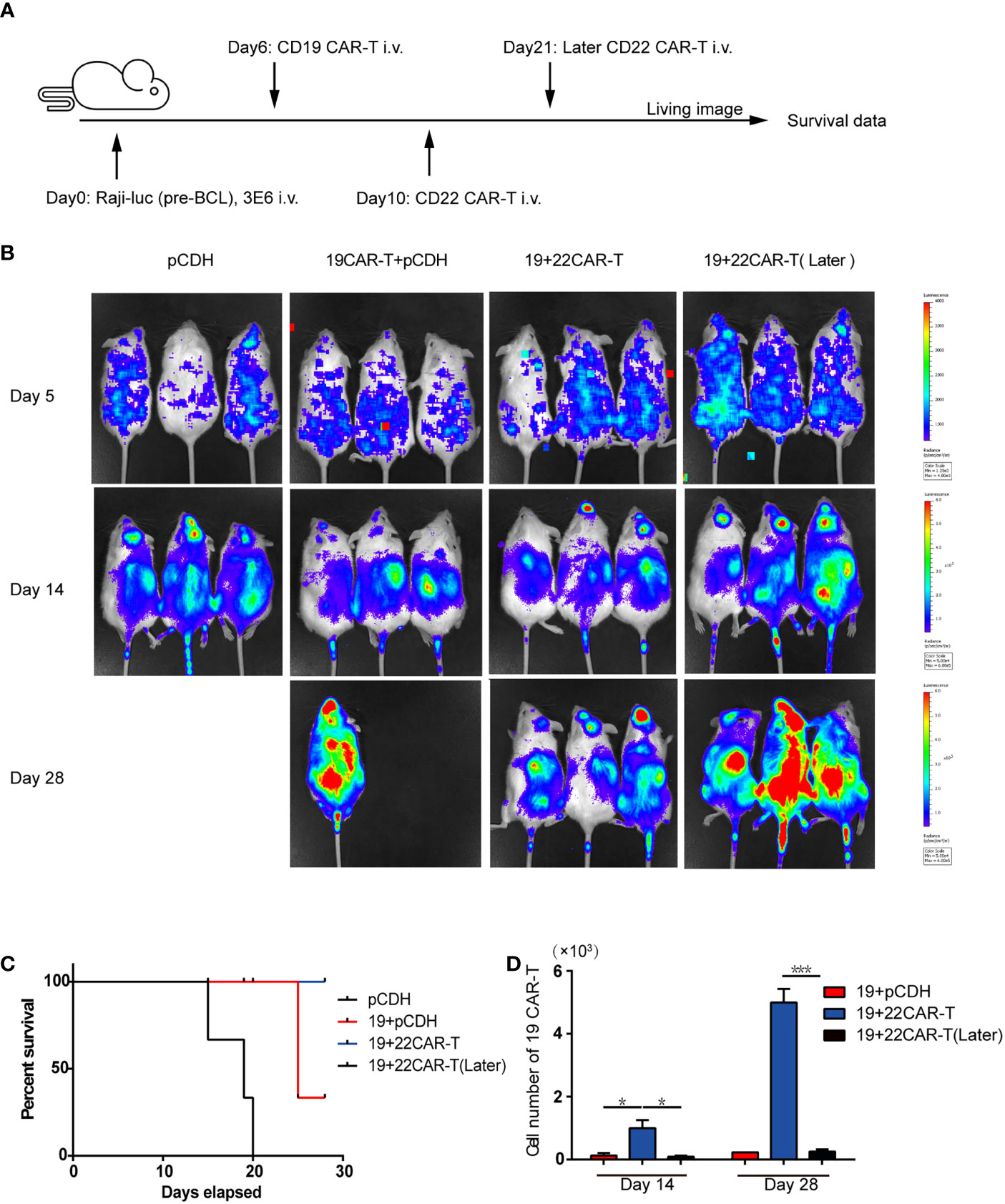
Figure 2 Enhanced antitumor effects after sequential administration of CAR-T cells in vivo. (A) In vivo treatment scheme. (B) Tumor burden measured by bioluminescence. (C) The overall survival. (D) The number of the prior CD19 CAR-T cells was counted before and after secondary CAR-T infusion on days 14 and 28, respectively. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001 compared with the control group. Standard error means (SEM) are indicated as error bars.
In the original article, there was an error. In the in vivo treatment scheme, after prior CD19 CAR-T infusion, the mice were subsequently injected with 1×106 sequential CD22 CAR-T cells or medium on Day 10 or Day 21, not on Day 14 or Day 21.
A correction has been made to Result, Enhanced Antitumor Effects After Sequential Administration of CAR-T Cells In Vivo, paragraph 1:
“The mice were subsequently injected with 1×106 sequential CD22 CAR-T cells or medium on Day 10 or Day 21 (Figure 2A).”
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: B-NHL, CAR-T, CD19, CD22, CD20
Citation: Meng Y, Deng B, Rong L, Li C, Song W, Ling Z, Xu J, Duan J, Wang Z, Chang AH, Feng X, Xiong X, Chen X and Pan J (2021) Corrigendum: Short-Interval Sequential CAR-T Cell Infusion May Enhance Prior CAR-T Cell Expansion to Augment Anti-Lymphoma Response in B-NHL. Front. Oncol. 11:778039. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.778039
Received: 16 September 2021; Accepted: 17 September 2021;
Published: 01 October 2021.
Edited and reviewed by:
Jonathan Bramson, McMaster University, CanadaCopyright © 2021 Meng, Deng, Rong, Li, Song, Ling, Xu, Duan, Wang, Chang, Feng, Xiong, Chen and Pan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jing Pan, cGFuakBib3Jlbmhvc3BpdGFsLmNvbQ==; Xiaoli Chen, Y3hscHVtY0AxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.