
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Nutr., 23 September 2021
Sec. Nutritional Immunology
Volume 8 - 2021 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2021.727951
This article is part of the Research TopicNutrients, Gut Microbiome, and Intestinal InflammationView all 35 articles
 Guangying Weng1,2
Guangying Weng1,2 Yehui Duan2*
Yehui Duan2* Yinzhao Zhong2
Yinzhao Zhong2 Bo Song2,3
Bo Song2,3 Jie Zheng2,3
Jie Zheng2,3 Shiyu Zhang2,3
Shiyu Zhang2,3 Yulong Yin1,2
Yulong Yin1,2 Jinping Deng1*
Jinping Deng1*Obesity has become one of the most serious chronic diseases threatening human health. Its occurrence and development are closely associated with gut microbiota since the disorders of gut microbiota can promote endotoxin production and induce inflammatory response. Recently, numerous plant extracts have been proven to mitigate lipid dysmetabolism and obesity syndrome by regulating the abundance and composition of gut microbiota. In this review, we summarize the potential roles of different plant extracts including mulberry leaf extract, policosanol, cortex moutan, green tea, honokiol, and capsaicin in regulating obesity via gut microbiota. Based on the current findings, plant extracts may be promising agents for the prevention and treatment of obesity and its related metabolic diseases, and the mechanisms might be associated with gut microbiota.
In recent years, obesity has been increasing at an alarming rate worldwide and seriously affects not only developed countries but global people (1). Obesity is characterized by a series of metabolic disorders, especially lipid dysmetabolism and its complication (2). Lipid metabolism involves the biosynthesis and degradation of lipids such as triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids, and fatty acids (3). The disorder of lipid synthesis and decomposition processes can lead to lipid metabolism dysregulation (also known as lipid dysmetabolism), subsequently giving rise to the progression of obesity and its related metabolic diseases such as diabetes (4–7). Thus, maintaining the balance of lipid metabolism is of great importance to prevent and treat obesity.
Obesity is regulated by various factors such as genetic factors, dietary habits (e.g., high glycaemic diets), underlying diseases (e.g., insulinoma), and exercise (8). Recently, direct evidence pointed to a strong relationship between obesity and gut microbiota (9). The colonization of germ-free mice with a “normal microbiota” from conventionally raised mice resulted in an increase in body fat mass despite reduced food intake (10). Similarly, germ-free mice fed low-fat chow were colonized with obese co-twin's fecal microbiota presenting obese phenotype compare with those colonized with lean co-twins' fecal microbiota (11). Further evidence comes from the finding that total fecal microbiota transplantation from normal mice significantly attenuated high-fat diets-induced lipid dysmetabolism in mice (12). Moreover, obese individuals exhibited significant alteration in gut microbiota compared with lean controls, as manifested by increased ratio of Firmicutes toBacteroidetes (13, 14). In addition, increasing lines of evidence suggested that obesity and its related metabolic diseases exert seriously adverse effects on the structure of host gut microbiota, as indicated by a significant alteration in gut microbiota composition and diversity (11, 12, 15–17). In turn, gut microbiota dysregulation may not only increase the intestinal permeability to gut microbes but also elevate the production of harmful microbial metabolites, thus aggravating lipid dysmetabolism and resulting in obesity and its related diseases, such as diabetes and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) (18, 19). Accordingly, gut microbiota plays important role in the regulation of obesity and lipid metabolism, and it may be a potential therapeutic target for ameliorating obesity.
Over the past years, increasing evidence has demonstrated that diets and/or nutrients exert roles in the regulation of gut microbiota composition and obesity (3, 7, 20–22). In this review, we will discuss the anti-obesity activity of plant extracts, with highlighting of their potential mechanisms related to gut microbiota, in order to provide an updated understanding of the relationship among plants extracts, gut microbiota, and obesity (Figure 1). We hope that this review can provide some available information to develop dietary strategies for the treatment and prevention of obesity and its related diseases.
Flavonoids from mulberry leaves (FML) are one of the main functional components of mulberry leaf extracts, which are edible food and widely used as a kind of traditional Chinese medicine. It has been reported that mulberry leaf extracts such as FML possess multiple biological activities, such as antioxidant, improving skeletal muscle function, cardioprotective, and anti-cancer (23–26). In addition, there is evidence showing that mulberry leaf extracts confer anti-obesity effects (Figure 2).
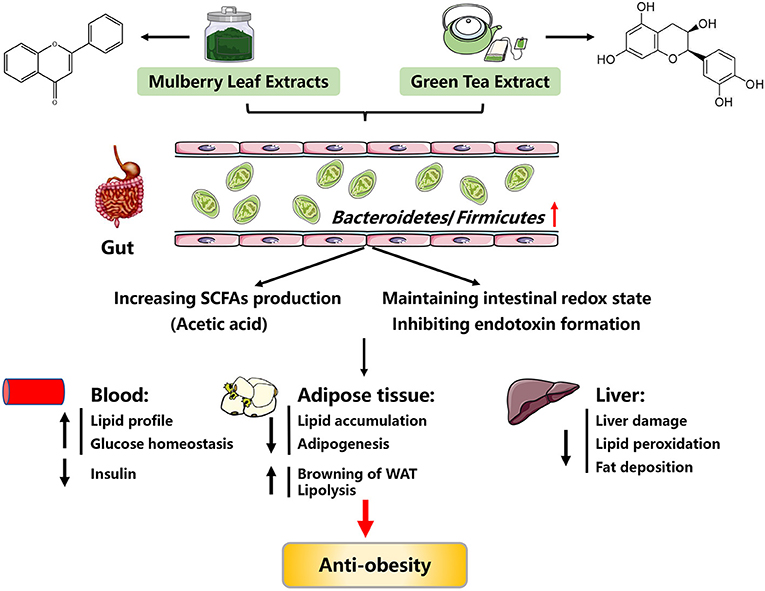
Figure 2. Possible mechanisms explaining the anti-obesity effects of mulberry leaf extracts and green tea extracts. SCFAs, short chain fatty acids; WAT, white adipose tissue.
Evidence from hyperlipidemic mice showed that FML treatment (30 mg kg−1 body weight) for 12 h improved blood lipid metabolism, as evidenced by reduced levels of serum total triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) by 152, 207, and 110 mg/100 mL, respectively (27). Similar improvements in blood lipid metabolism were also observed in high fat diets (HFD)-fed mice, in which FML administration (240 mg kg−1 body weight) for 6 weeks could also reduce body weight gain and adipose tissue mass, and alleviate the whitening of brown adipose tissue (BAT) (28). Moreover, mulberry water extracts could reduce lipid peroxidation and lipid accumulation in the liver of rats (29). Apart from using alone, mulberry leaf extracts combined with mulberry fruit extract also exhibited anti-obesity effects in HFD-induced obese mice, as evidenced by decreased body weight gain, improved fasting plasma glucose and insulin, and alleviated inflammation and oxidative stress (30). Consistent with in vivo studies, in vitro studies have also reported that treatment of mulberry leaf extracts to aortic vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) could inhibit its proliferation and migration, thus preventing atherosclerosis, a disease related to lipid dysmetabolism (31).
Although much of the work in this field has been done on rodent models, these models have yielded important insights into the anti-obesity mechanisms of mulberry leaf extracts. Since flavonoids are enzymatically hydrolyzed by gut microbiota and absorbed in the intestine (32), it is posited that the beneficial effects of FML might be via gut microbiota. In support, FML treated-obese mice exhibited increased Bacteroidetes abundance and decreased Firmicutes abundance (28, 33, 34). Increased Bacteroidetes abundance led to an elevation in the production of acetic acid, which further promotes lipolysis and inhibits lipid accumulation through activating G protein-coupled receptor 43 (GPR43), a short chain fatty acid receptor (28, 35). Taken together, the anti-obesity mechanisms of mulberry leaf extracts are summarized in Figure 2.
Policosanol is a natural mixture of long-chain aliphatic primary alcohols extracted from the wax constituent of plants and seeds, such as sugar cane, wheat, corn, sesame, soybean, perilla seed, grape seed and rice bran, whose main ingredient is octacosanol (36). Policosanol has multiple bioactivities, such as anti-nociceptive, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, and anti-parkinsonian properties (37–41). In addition, policosanol also exerts beneficial effects on lipid dysmetabolism and obesity, such as improving blood lipid profile, elevating BAT activity, improving glucose homeostasis, and regulating cholesterol synthesis (42–44).
First, evidence from human subjects has shown that the reduction of serum high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) levels and the elevation of serum TG, TC and glucose levels were reversed by policosanol treatment (10 mg day−1) for 8 weeks, indicative of an anti-obesity effect (42, 45). Similar reduction of serum TG levels was also obtained in HFD-fed rats, in which octacosanol treatment (10 g kg−1 diet) for 20 days also significantly reduced perirenal adipose tissue weight (46). Apart from the regulation of blood lipid profile and adipose tissue mass, policosanol treatment (60 mg kg−1 day−1, for 4 weeks) could attenuate insulin resistance and improve glucose homeostasis by elevating BAT activity and reducing hepatic lipid content in HFD-induced obese mice (43). In addition, policosanol also exerts roles in regulating cholesterol metabolism. For example, policosanol treatment (0.38–1.5 g kg−1 diets) in hamsters greatly decreased serum levels of total cholesterol by 15–25% and increased the excretion of acidic sterols (the cholesterol end-product) by 25–73%, indicating that policosanol lowered cholesterol via restraining the absorption of bile acids (44). One potential mechanism for the hypocholesterolemic effect of policosanol is its down-regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutary coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, the key rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis (47, 48). In support, an in vitro study found that policosanol suppressed HMG-CoA reductase activity by activating adenosine 5′-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) (48, 49).
Cholesterol degrading into bile acids functions as the main way to expel excess cholesterol from host, which can effectively reduce the risk of atherosclerosis (50). On the other hand, bile acids act as an important regulator of cholesterol metabolism. The biosynthesis and biotransformation of bile acids are closely associated with host gut microbiota. In detail, primary bile acids are synthesized and secreted by host hepatocytes, and then transformed into secondary bile acids with the chemical modification effect of gut microbiota (51). The disorder of gut microbiota results in bile acid dysmetabolism and in turn affects cholesterol metabolism, suggesting that the regulation effects of policosanol on cholesterol metabolism is partially mediated by gut microbiota (52–55). In summary, these findings show that policosanol seems to be a promising phytochemical alternative to classic cholesterol-lowing agents such as statins. However, the detailed mechanisms of the mode of policosanol's action remain unclear, but alterations in gut microbiota are probably involved.
Cortex Moutan (CM), the root bark of Paeonia suffruticosa Andrews, is widely used as a traditional Chinese herbal medicine that has multiple bioactive ingredients. Both CM and its bioactive ingredients possess many pharmacological properties on cardiovascular diseases, anti-tumor, and nervous system (56–58). The main pharmacological effects of CM are attributed to its bioactive component paeonol. Recently, more and more studies have found that CM and paeonol are also able to regulate preadipocyte differentiation, glucose homeostasis, lipid peroxidation, and inflammatory response, thus mitigating obesity (Figure 3).
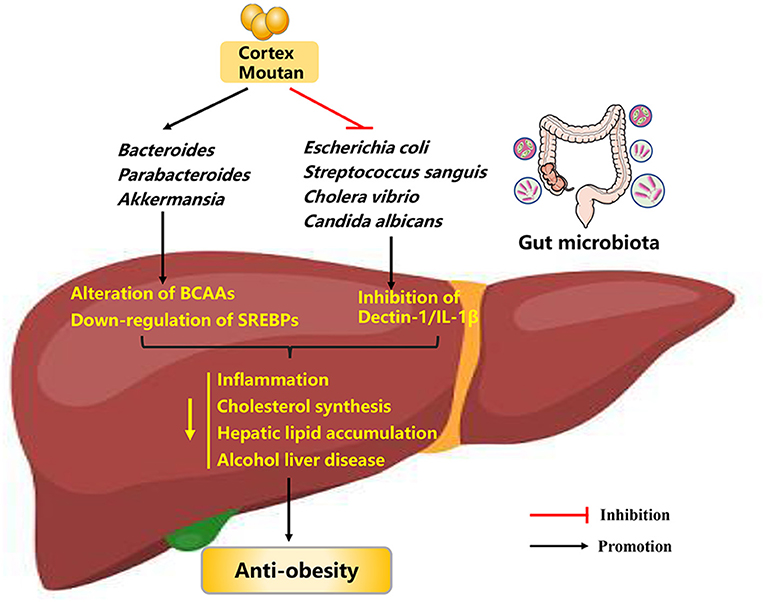
Figure 3. Possible mechanisms explaining the anti-obesity effects of cortex moutan. BCAAs, branched-chain amino acids; SREBPs, sterol-regulatory element binding proteins; IL-1β, interleukin-1β.
It has been reported that administration of paeonol (150 and 300 mg kg−1) to diabetic mice for 8 weeks resulted in a reduction in fasting blood glucose, serum TG and TC, hepatic TG and TC though activation of serine/threonine kinase B (Akt) (59). Similar improvements in lipid metabolism were obtained in myocardial ischemia rabbits (60). In addition, paeonol administration could ameliorate lipid peroxidation and inflammatory response (61, 62). In HFD-induced atherosclerotic rabbits, paeonol exerts anti-atherosclerosis effects by inhibition of lipid peroxidation and improvement of anti-inflammatory action (63). In accord with these findings in in vivo studies, several in vitro studies have reported that paeonol can markedly and dose-dependently reduce intracellular lipid accumulation in mouse preadipocytes and macrophages, and delay preadipocytes differentiation into mature adipocytes, thus protecting against metabolic diseases (64, 65). Overall, overwhelming evidence suggests that paeonol treatment can combat obesity and its related metabolic diseases such as atherosclerosis and steatohepatitis.
Since its low bioavailability and phenolic hydroxyl groups in its chemical structure, CM can interact with gut microbiota in the intestinal tract over extended periods of time (66, 67). These observations raise the possibility that gut microbiota may play a role in the mode of CM's action (Figure 3). Evidence to support this hypothesis is that CM possess antimicrobial activity against a broad range of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, Streptococcus sanguis, and Cholera vibrio (68, 69). Further evidence for a relationship between CM treatment and gut microbiota comes from the findings that CM administration (0.4 g crude drug kg−1, either along or as part of a therapeutic regimen) to HFD-induced obese mice for 6 weeks significantly reverse the composition and diversity of gut microbiota, as evidenced by restored abundances of Bacteroides, Parabacteroides, Akkermansia, and Mucispirillum. Subsequently, improved gut microbiota could affect the levels of blood metabolites such as branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), and down-regulate the expression of sterol-regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs, crucial regulators controlling cholesterol and fatty acid de novo synthesis) in the liver, thus alleviating obesity (70). In addition, paeonol can reduce intestinal fungal abundance (especially Candida albicans abundance) and inhibit the mycobiota-mediated dectin-1/interleukin-1β (IL-1β) signaling pathway, thus ameliorating alcohol liver disease in mice (71). In summary, CM and paeonol exert anti-obesity effects through the gut microbiota-blood metabolites-liver axis and microbiota-mediated signaling pathway, making them potential pharmaceutical agents against obesity.
Green tea, the unfermented dried leaves of Camellia sinensis, is one of the most popularly traditional beverages worldwide. The major bioactive ingredients of green tea are flavan-3-ols (also known as catechins), which are natural plant-derived and powerful antioxidant for alleviating oxidative stress. In particular, (–)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) is the most abundant and active catechin in green tea. Apart from antioxidant, green tea also possesses anti-obesity and anti-diabetic effects (72, 73).
In vitro studies presented evidence showing that catechin-rich green tea extract (GTE) could ameliorate lipid accumulation through inhibiting the differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes into adipocytes and stimulating the browning of white adipocytes (72, 74, 75). Similarly, in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, EGCG could improve glucose homeostasis through normalizing the redox imbalance and mitochondrial dysfunction (75). In line with these findings, in vivo studies also reported a beneficial role of GTE on obesity. For instance, evidence from human studies showed that daily ingestion of GTE (containing 583 mg of catechins) for 12 weeks resulted in decreases in body weight, adipose tissue mass, and serum LDL-C levels (76, 77). Similar observations were also obtained in diets-induced obese rodents, in which GTE was supplemented at a dose of 500 mg kg−1 body weight for 12 weeks, and the mechanisms might be related to AMPK activation and down-regulated microRNA 335 expression in the adipose tissue (78, 79). Apart from the above-mentioned roles, GTE supplementation could mitigate inflammation, enhance energy expenditure, and attenuate insulin resistance (80, 81). Altogether, GTE is a beneficial food constituent for preventing and treating obesity.
A potential mechanism for the anti-obesity of GTE was attributed to the alteration of gut microbiota, based on observations of increased Bacteroides abundance in response to GTE treatment (82–84). Two mechanisms may be responsible for the beneficial effects of GTE on obesity via improving gut microbiota. One hypothesized mechanism may be the increased production of short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and the inhibition of endotoxin formation and translocation, thus attenuating obesity-associated adipose inflammation and decreasing body weight (84, 85). Another hypothesized mechanism may be via gut microbiota-improved intestinal redox state (86). Despite these positive outcomes, there is evidence showing that treatment of obese mice with overdose tea polyphenols would present side effects on their intestinal health (86). Taken together, GTE can exert protective roles against obesity, and its underlying mechanisms might be associated with gut microbiota (Figure 2). In future, more efforts should be made to investigate how GTE targets the specific gut microbiota.
Resveratrol (3, 5, 4′-trihydroxystilbene, RES)is a plant-derived polyphenolic compound, which could be isolated and purified from a variety of plants, such as grape, peanut, mulberry and polygonum cuspidatum. Over the past decade, RES is also one of the most studied plant active ingredients, because of its presumed pharmacological effects on cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and alzheimer's diseases (87–90). Meanwhile, it has been reported that RES also plays a crucial role in mitigating obesity, as evidenced by increased energy expenditure, BAT activity, white adipose tissue (WAT) browning, and glucose homeostasis (Figure 4).
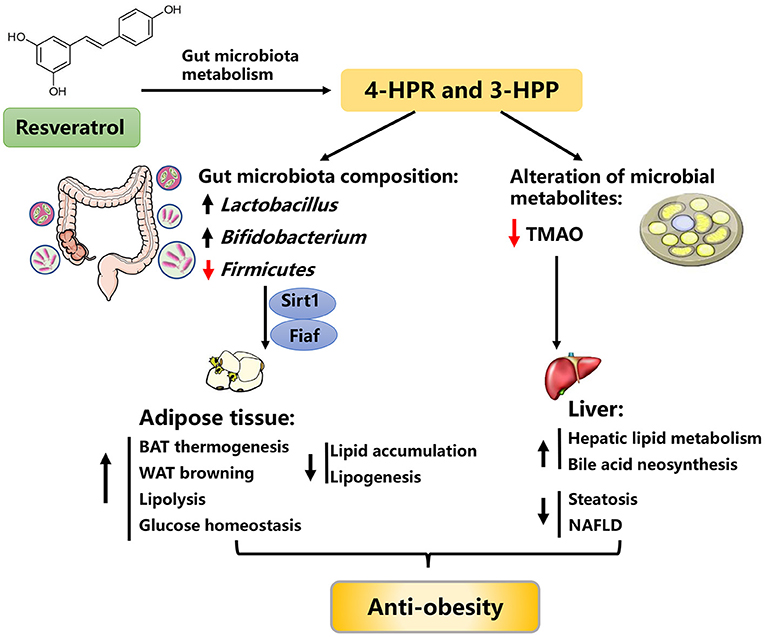
Figure 4. Possible mechanisms explaining the anti-obesity effects of resveratrol. 4-HPA, 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid; 3-HPP, 3-hydroxyphenylpropionic acid; Fiaf, fasting-induced adipose factor; Sirt1, sirtuin 1; TMAO, trimethylamine-N-oxide, BAT, brown adipose tissue, NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
In obesogenic diets-fed rats, RES supplementation (30 mg/kg/day, for 6 weeks) increased thermogenesis in skeletal muscle and BAT by upregulating uncoupling protein (UCP) expression, consequently improving whole-body energy dissipation and attenuating obesity (91). Likewise, supplementation of 4% RES to db/db mice for 10 weeks could enhance BAT activity and WAT browning and improve glucose homeostasis (92). Daily delivery of 300 mg kg−1 RES to HFD-fed mice for 16 weeks improved hepatic lipid metabolism and reduced liver steatosis, thus alleviating NAFLD (93). Administration of RES (10 mg/kg) to atherosclerotic mice for 24 weeks significantly reduced the intestinal fatty acid and monoglyceride accumulation, conferring beneficial effects on cardiovascular health (94). Consistent with these findings, several in vitro studies using stromal vascular cell model also demonstrated that RES could enhance brown adipocyte formation and thermogenic function and elevate oxygen consumption by activating AMPKα1 (95, 96). Besides, RES dose-dependently decreased triglyceride accumulation in mouse 3T3-L1 preadipocytes via up-regulation of Sirtuin1 (Sirtl) expression (97). Moreover, RES facilitated epinephrine-induced lipolysis, inhibited lipogenesis and glucose conversion to lipids, and counteracted insulin antilipolytic action in rat and human adipocytes (98, 99).
The colonization of HFD-fed obese mice with an “RES-microbiota” (RES-induced gut microbiota) is sufficient to improve lipid metabolism and to ameliorate obesity, suggesting the anti-obesity effects of RES may be partially mediated by the regulation of gut microbiota (100). Due to its poor bioavailability, RES mainly accumulates in the intestinal tract and rarely enters the circulatory system after intake. In the intestinal tract, RES can be metabolized into bioactive small molecules by gut microbiota, which greatly facilitates the regulation of RES on lipid metabolism (100–102). For instance, RES can be biotransformed into 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid (4-HPA) and 3-hydroxyphenylpropionic acid (3-HPP) by gut microbiota, which conversely improved the gut microbiota composition, as evidenced by the restored abundance of Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Firmicutes (103). Thereafter, the improved gut microbiota alleviated obesity through the fasting-induced adipose factor (Fiaf) and sirtuin-1 (Sirt1) signaling pathway (104, 105). On the other hand, RES can lower the level of gut microbial metabolite trimethylamine-N-oxide (a novel risk factor of metabolic syndrome) and enhance bile acid neosynthesis, possibly representing an additional mechanism for the beneficial effects of RES (106). Taken together, these observations raise the possibility that the beneficial effects of RES on obesity are associated with improved gut microbiota (93, 100, 104, 105, 107, 108).
Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract (a polymers of flavan-3-ols, GSPE) is the main polyphenolic compound of grape seed extracts, which can transform into anthocyanidin under acid and heating conditions. In addition to its antioxidant function, GSPE also possesses pharmacological effects on cardiovascular disease, inflammatory processes, muscle fatigue, and other metabolic complications (109–111). Recently, increasing evidence has found that GSPE is capable to normalize the disturbance of lipid metabolism and to mitigate obesity.
Works in rodent models found that daily administration of GSPE (250 mg kg−1 body weight) to hyperlipidemic rats for 7 days resulted in a 41% reduction in serum TG levels via increasing fecal bile acid and cholesterol excretion (112). In cafeteria diet-induced obese rats, daily delivery of GSPE (25 and 50 mg kg−1 body weight) for 21 days resulted in an improvement of mitochondrial function and thermogenic capacity of the BAT, thus increasing energy expenditure and ameliorating obesity (113). Further investigation found that long-term treatment of GSPE (12 weeks) could exert an anti-hyperlipidemia effect, as evidenced by decreased serum levels of TG, TC, and LDL-C and reduced visceral WAT mass (114, 115). Similar results were also obtained in the ovariectomized mice and weaned pigs (116, 117). Consistent with these findings, in vitro studies using murine and porcine cell models also elucidated that GSPE could suppress preadipocyte differentiation and proliferation, and promote lipolysis of adipocytes, thus inhibiting adipose cell formation and fat accumulation (118, 119). Besides, both in vivo and in vitro studies have found that GSPE could prevent low-grade inflammation through inhibiting the production of proinflammatory cytokines [cytokine C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α] and increasing the production of the anti-inflammatory adipokine adiponectin (120, 121).
Mechanically, GSPE can suppress the disorder of lipid metabolism through regulating gut microbiota. In support, GSPE can restore the obesogenic diet-induced gut microbiota dysbiosis, as manifested by the normalized ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes and the increased Bacteroides abundance (110, 116, 117). Further evidence comes from the finding that the beneficial effects of GSPE on obesity were abolished when gut microbiota was cleared by antibiotics treatment (110, 117). Interestingly, further investigation suggested that the bacterial metabolites SCFAs (especially propionate) could also communicate in the beneficial effects of GSPE. Alterations of gut microbiota in response to GSPE treatment (250 mg kg−1 body weight) in weaned pigs for 28 days led to a 30.2% elevation in the production of propionate compared with the control group (117). On one hand, propionate stimulated the secretion of glucagon like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and peptide YY (PYY, an important regulator of appetite and energy homeostasis) from colonic cells via activation of free fatty acid receptor 2 (FFAR 2), further inhibiting energy intake and fat accumulation (117, 122, 123). On the other hand, propionate could in turn restored the gut microbiota dysbiosis induced by HFD, thus reducing body weight and mitigating obesity (124). In conclusion, these findings suggest that the beneficial effects of GSPE on obesity are partially attributed to the gut microbiota-propionate axis.
Honokiol (HON) is a natural neolignan derived from the widely used Chinese medicinal herb, Magnolia officinalis. HON has been regarded as a promising therapeutic agent for various chronic diseases due to its bioactive effects, such as anti-parkinsonian, anti-inflammatory, anti-cancer, anti-fatigue, and antioxidant properties (125–129). Notably, recent evidence has indicated that HON exerts critical effects on obesity by regulating adipogenesis and lipolysis.
There is evidence showing that HON administration (at doses of 200, 400, and 800 mg kg−1 body weight) to diets-induced obese mice for 8 weeks dose-dependently reduced body weight and adipose tissue mass (130). Besides, upon HON treatment (200 mg kg−1, for 8 weeks), insulin sensitivity was improved in streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic mice by targeting protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) (131). Apart from using alone, HFD-fed mice fed HON plus magnolol for 16 weeks exhibited a drastically reduction in WAT weight and adipocyte size (132). Consistently, in vitro studies using 3T3-L1 adipocytes also demonstrated that HON could exert effects on lipid metabolism, including reducing viability, inducing apoptosis, promoting browning of white adipocytes, improving insulin resistance, and inhibiting apoptosis of brown adipocytes (133–135). Therefore, HON exerts regulatory effects on lipid metabolism and exhibits therapeutical potential against obesity.
Notably, due to its low bioavailability, <10% of HON is absorbed into circulatory system from intestine and the remainders are metabolized by gut microbiota in posterior intestine to generate bioactive molecules and to remodel gut microbiota structure (136). These findings indicate that gut microbiota exerts an irreplaceable role in the lipid metabolic benefits of HON. Using different sexes of HFD-induced obese mice, previous studies have reported that the male mice treated with HON exhibited a significant anti-obesity effect through regulating gut microbiota and metabolites, as manifested by increased Bacteroides abundance and reduced lipopolysaccharide (LPS) levels. Nevertheless, HON treatment in female mice did not exhibit the same impact as to male mice (130). In summary, HON plays a vital role in warding off obesity and the related mechanisms might be partially mediated by gut microbiota. However, the detailed mechanisms have not yet been fully identified.
Capsaicin (CAP) is the major pungent ingredient isolated from red chili peppers (genus Capsicum), which are widely consumed as foods and flavoring spices all over the world. CAP has been widely used to treat various diseases because of its bioactive effects, such as anti-cancer, analgesic, neuro-modulating, anti-fatigue, anti-inflammatory properties (137–141). Recently, accumulating evidence has suggested that CAP has beneficial effects on obesity, including reducing lipid accumulation, inducing the browning of WAT, and mitigating inflammation responses (Figure 5).
Using women with gestational diabetes mellitus model, previous studies shown that daily supplementation of 5 mg CAP for 4 weeks can improve serum lipid profiles, as evidenced by lowered levels of fasting serum lipids and postprandial plasma glucose (142). Similar improvements in serum lipid profile were observed in diets-induced obese mice, in which long-term supplementation (5 months) of dietary CAP at a low dose (0.01%) also resulted in a reduction in body weight and adipose tissues mass (143). Apart from the regulation of body weight and serum lipid profile, CAP treatment could improve glucose homeostasis. For instance, treatment of CAP (2 mg kg−1 body weight) to transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 (TRPV1)-knockout (KO) obese mice for 12 weeks significantly decreased serum glucose and insulin concentrations (144). Upon further investigation, CAP was found to promote WAT browning and increase thermogenesis (145, 146). Consistently, in 3T3-L1 white adipocytes, a combination treatment of CAP (25 μM) and capsiate (25 μM) could induce browning through activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ and β3-adrenergic receptor (PPARγ/β3-AR) signaling pathway (147). Moreover, CAP time- and dose-dependently inhibited lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via inducing apoptosis and suppressing adipogenesis (148). Likewise, an in vitro study also showed that palmitic acid-treated HepG2 cells exhibited an improvement in lipid metabolism upon CAP treatment (100 μM), as evidenced by decreased lipid accumulation and concentrations of TG and TC as well as increased HDL-C levels (149). In addition, CAP also attenuated obesity-induced inflammatory responses by regulating adipokine release from and macrophage behavior in adipose tissues of obese-mice (150).
Mechanically, CAP exerts anti-obesity effects via altering gut microbiota composition and elevating SCFAs production (Figure 5) (144). In particular, dietary CAP supplementation in diets-induced obese mice could increase the abundance of butyrate-producing bacteria (e.g., Roseburia spp.) and promote the generation of butyrate (a metabolic substrate for intestinal epithelial cells), thus improving gut barrier integrity. The improved gut barrier integrity prevented the bacterial endotoxins across the gut barrier and metabolic endotoxemia, thereby ameliorating chronic low-grade inflammation and obesity (151). In line with the alteration in the abundance of butyrate-producing bacteria, the abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila (a mucin-degrading bacterium proven to inversely correlate with adiposity) has also been shown to be increased in response to CAP supplementation. However, it remains unclear how dietary CAP supplementation elevated the relative abundance of Akkermansia muciniphila (152). Taken together, CAP can serve as a therapeutic agent in the prevention of obesity and the related mechanisms might be associated with gut microbiota-butyrate signaling.
Konjac flour (KF) is a powder processed from the konjac tuber (Amorphophallus konjac), which has traditionally been consumed as a food source and as a component for traditional Chinese medicine in Asian countries for centuries. Konjac glucomannan (KGM), a primary ingredient of KF, is a hydrophilic dietary fiber composed of D-glucose and D-mannose residues connected by β-1,4-glycosidic bonds. It has been widely used as a food additive and dietary supplements in medical practice, pharmaceutical engineering, nutraceutical and food industry (153). KGM has multiple pharmacological effects for the management of diseases such as constipation, wound healing, and colitis (154–156). Recently, growing evidence has suggested that KGM could ameliorate lipid dysmetabolism and exhibit hypoglycemic effects (Figure 6).
It has been shown that dietary KGM supplementation (3.6 g/day) in type 2 diabetic patients with hyperlipidemia for 4 weeks reduced the concentrations of plasma cholesterol, LDL-C, and fasting glucose by 11.1, 20.7, and 23.2%, respectively (157). When combined with exercise, treatment of overweight humans with KGM (3,000 mg/day) for 8 weeks significantly improved blood lipid levels and body composition (158). Similar results were also found in diabetic rodent models (159). In addition, long-term supplementation of dietary KGM (4%, for 16 weeks) to nutritional obese mice effectively decreased body weight, improved lipid metabolism, and inhibited insulin resistance (160, 161). Moreover, in type 2 diabetic rats induced by HFD and streptozotocin, KGM administration (80 mg kg−1 body weight, for 28 days) attenuated oxidative stress by regulation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) pathway and decreased inflammatory responses through regulating nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, thus ameliorating hyperglycemia (162). Taken together, KGM supplementation, alone or together with exercise, may be a good nutritional tool to prevent and to treat obesity.
KF is a native soluble dietary fiber with high molecular weight, viscosity, and swelling capacity in the intestine, which can remarkably speed up the peristalsis of bowel and slow down the movement of gut microbiota across the cecum (161, 163). Notably, low grain size of KF can swell in intestinal tract more easily and rapidly compared with the native KF (164). Evidence from rodents (161, 165, 166), sows (167), and humans (168) models suggests that alteration of gut microbiota is a contributing mechanism for the anti-obesity effects of KF or/and KGM supplementation. In detail, dietary KF supplementation could normalize the gut microbiota dysbiosis induced by HFD, such as improving the gut microbiota diversity and composition (161, 166). In turn, the amendatory gut microbiota could accelerate the fermentation of dietary KF to improve the SCFAs' concentration in the intestinal contents, thus ameliorating obesity and its-related complications (161, 163). On the other hand, it is well known that increased circulating BCAA concentrations can deteriorate host glucose and lipid metabolism, and subsequently prognosticate future risk of developing insulin resistance and diabetes (169). Interestingly, a recent study has demonstrated that KGM treatment (160 mg kg−1) of type 2 diabetic rats for 4 weeks reduced the abundance of BCAA-producing bacteria and improved BCAA metabolism, further ameliorating host lipid metabolism and diabetes (169). In summary, KF might be a promising agent to prevent and to treat obesity, and the potential mechanism was associated with reprogramming gut microbiota and metabolism, especially decreasing BCAA-producing bacteria abundance (Figure 6).
Chlorophyll is an abundant green pigment and non-nutrient compound ubiquitously found in higher plants and other photosynthetic organisms. Chlorophyll has been widely used to prevent various chronic diseases because of its numerous pharmacological effects, such as anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties (170–172). Recently, more and more studies have reported that chlorophyll also plays important roles in ameliorating obesity. A study found that daily consumption of 5 g green-plant membranes containing chlorophyll in overweight subjects for 3 months led to decreases in body weight and serum cholesterol levels (173). Similar results were obtained in HFD-induced obese mice, in which dietary supplementation of a chlorophyll-rich spinach extract (0.18 mg/10 g body weight, for 13 weeks) reduced body weight gain and inflammation as well as improved glucose tolerance (174, 175). Apart from in vivo studies, several in vitro studies using a 3T3-L1 cell model also discovered that chlorophyll could regulate lipid metabolism, including inhibition of adipocyte proliferation and differentiation, suppression of adipogenesis and lipid accumulation, and activation of browning (176–178).
Evidence from human and rodent models suggests that chlorophyll can modulate the composition and diversity of gut microbiota (179, 180). First, chlorophyll-rich thylakoid treatment of healthy human subjects for 12 weeks elevated the abundance of total bacteria, especially the Bacteriodes fragilis group (180). Studies performed in HFD-fed mice also found that chlorophyll increased the relative abundance of Blautia, Akkermansia, and norank_f_Bacteroidales_S24-7_group and decreased the relative abundance of Lactococcus and Lactobacillus (174, 175). Moreover, chlorophyllin, an extract isolated from chlorophyll, could alleviate hepatic fibrosis in mice through restoring the gut microbiota, as evidenced by reduced ratio of Firmicutes-to-Bacteroidetes populations (179). Therefore, chlorophyll, as the most plentiful green pigment in nature, confers beneficial effects on obesity and the mechanisms might be associated with gut microbiota. However, further research is required to examine the specific mechanisms of chlorophyll-gut microbiota-lipid metabolism axis.
Apart from the above-mentioned plant extracts, several others are also proved to exert roles in mitigating obesity via reprogramming gut microbiota. For instance, dietary supplementation of Luffa cylindrica (L.) Roem (2 g kg−1 body weight, for 14 weeks) in diets-induced obese mice could ameliorate adiposity and related metabolic complications via increasing the abundance of SCFAs-producing bacteria and the content of SCFAs (181). Coreopsis tinctoria, a multifunctional and widely cultivated plant, could improve blood lipid metabolism in hyperlipidemic models by normalizing the disorders of gut microbiota (182). Garcinol supplementation (0.1% or 0.5%) to HFD-fed mice for 13 weeks restored the gut dysbiosis, as evidenced by the augmented Bacteroidetes-to-Firmicutes ratio, which further dose-dependently improved plasma lipid profile and reduced adipose tissue weight and body weight gain (183). Similarly, diets-induced obese mice treated with a cranberry extract (200 mg kg−1, for 8 weeks) exhibited improved insulin resistance and ameliorated obesity through elevating the relative richness of Akkermansia, a mucin-degrading bacterium (184). Additionally, Nitzschia laevis extract supplementation (10 and 50 mg/kg/day, respectively) for 8 weeks to HFD-fed mice could inhibit lipid accumulation and body weight gain, and the effects were associated with the alteration of gut microbial richness and diversity (185).
Obesity is one of the most serious public health problems and has increased at an alarming rate worldwide. Currently, various plant extracts, such as mulberry leaf extracts, policosanol, CM, GTE, RES, GSPE, HON, CAP, KGM, and chlorophyll, are demonstrated to regulate serum lipid profile, inflammatory response, browning of WAT, insulin resistance, lipid and glucose metabolism, and other metabolic processes, thus improving obesity and related metabolic disorders (Table 1). A number of experimental studies have elucidated the potential regulatory mechanisms of beneficial effects of plant extracts on obesity and related diseases are closely associated with alterations in host gut microbiota. Hence, plant extracts seem to be promising agents to treat obesity and even other related metabolic syndrome. However, there are still many questions that need to be elucidated: the regulatory efficiency of plant extracts from different origins and conditions; the specific mechanisms of plant extracts targeting gut microbiota; and the anti-obesity effects of plant extracts in different animals and humans under different metabolic conditions. In the near future, more efforts should be made to fully understand the role of plant extracts in host lipid dysmetabolism, thus providing better nutritional strategies to control obesity and to maintain healthy life.
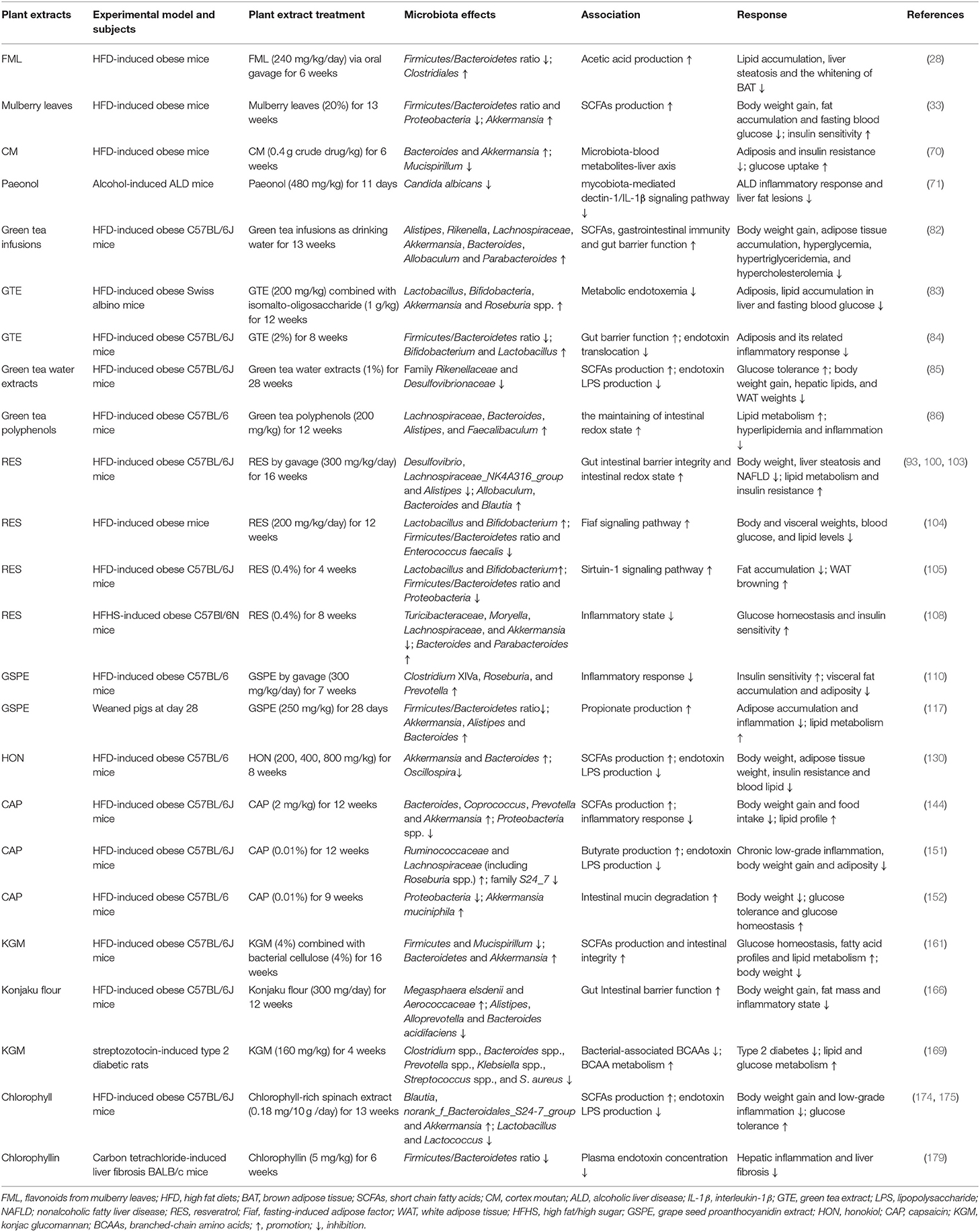
Table 1. Summary of the effects of plant extracts on gut microbiota, obesity and its related metabolic disorder.
YD, YY, and JD provided the topic of the review. GW, YZ, BS, JZ, and SZ prepared the manuscript and figures. YD revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript.
This study was jointly supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U19A2037, 31872985, 31802077), the services of alternative antibiotic feed and breeding technology (H20551), the Changsha Natural Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholar (kq2009020), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (2020JJA130102, 2018JJB130239), Special funds for the construction of innovative provinces in Hunan Project (2019RS3022), China Agriculture Research System of MOF and MARA (CARS-35), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDA24030204), and Open Fund of Key Laboratory of Agro-ecological Processes in Subtropical Region, Chinese Academy of Sciences (ISA2020203).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Dibaise JK, Zhang H, Crowell MD, Krajmalnik-Brown R, Decker GA, Rittmann BE. Gut microbiota and its possible relationship with obesity. Mayo Clin Proc. (2008) 83:460–9. doi: 10.4065/83.4.460
2. Wang HN, Xiang JZ, Qi Z, Du M. Plant extracts in prevention of obesity. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2020) 15:1–14. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1852171
3. Schoeler M, Caesar R. Dietary lipids, gut microbiota and lipid metabolism. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. (2019) 20:461–72. doi: 10.1007/s11154-019-09512-0
4. Duan J, Liang S, Feng L, Yu Y, Sun Z. Silica nanoparticles trigger hepatic lipid-metabolism disorder in vivo and in vitro. Int J Nanomedicine. (2018) 13:7303–18. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S185348
5. Ormazabal V, Nair S, Elfeky O, Aguayo C, Salomon C, Zuñiga FA. Association between insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2018) 17:122. doi: 10.1186/s12933-018-0762-4
6. Perry RJ, Samuel VT, Petersen KF, Shulman GI. The role of hepatic lipids in hepatic insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nature. (2014) 510:84–91. doi: 10.1038/nature13478
7. Yin J, Li Y, Han H, Chen S, Gao J, Liu G, et al. Melatonin reprogramming of gut microbiota improves lipid dysmetabolism in high-fat diet-fed mice. J Pineal Res. (2018) 65:e12524. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12524
8. Noland RC. Exercise and regulation of lipid metabolism. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. (2015) 135:39–74. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.06.017
9. Schwiertz A, Taras D, Schafer K, Beijer S, Bos NA, Donus C, et al. Microbiota and SCFA in lean and overweight healthy subjects. Obesity (Silver Spring). (2010) 18:190–5. doi: 10.1038/oby.2009.167
10. Bäckhed F, Ding H, Wang T, Hooper LV, Koh GY, Nagy A, et al. The gut microbiota as an environmental factor that regulates fat storage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2004) 101:15718–23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407076101
11. Ridaura VK, Faith JJ, Rey FE, Cheng J, Duncan AE, Kau AL, et al. Gut microbiota from twins discordant for obesity modulate metabolism in mice. Science. (2013) 341:1241214. doi: 10.1126/science.1241214
12. Zhou D, Pan Q, Shen F, Cao HX, Ding WJ, Chen YW, et al. Total fecal microbiota transplantation alleviates high-fat diet-induced steatohepatitis in mice via beneficial regulation of gut microbiota. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:1529. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01751-y
13. Ley RE, Bäckhed F, Turnbaugh P, Lozupone CA, Knight RD, Gordon JI. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2005) 102:11070–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504978102
14. Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature. (2006) 444:1022–3. doi: 10.1038/4441022a
15. Rabot S, Membrez M, Bruneau A, Gerard P, Harach T, Moser M, et al. Germ-free C57BL/6J mice are resistant to high-fat-diet-induced insulin resistance and have altered cholesterol metabolism. FASEB J. (2010) 24:4948–59. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-164921
16. Bäckhed F, Manchester JK, Semenkovich CF, Gordon JI. Mechanisms underlying the resistance to diet-induced obesity in germ-free mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2007) 104:979–84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605374104
17. Ellekilde M, Selfjord E, Larsen CS, Jakesevic M, Rune I, Tranberg B, et al. Transfer of gut microbiota from lean and obese mice to antibiotic-treated mice. Sci Rep. (2014) 4:5922. doi: 10.1038/srep05922
18. Chen J, Vitetta L. Gut microbiota metabolites in NAFLD pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:5214. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155214
19. Hu H, Lin A, Kong M, Yao X, Yin M, Xia H, et al. Intestinal microbiome and NAFLD: molecular insights and therapeutic perspectives. J Gastroenterol. (2020) 55:142–58. doi: 10.1007/s00535-019-01649-8
20. Duan Y, Zhong Y, Xiao H, Zheng C, Song B, Wang W, et al. Gut microbiota mediates the protective effects of dietary beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyrate (HMB) against obesity induced by high-fat diets. FASEB J. (2019) 33:10019–33. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900665RR
21. Shang A, Gan R-Y, Xu X-Y, Mao Q-Q, Zhang P-Z, Li H-B. Effects and mechanisms of edible and medicinal plants on obesity: an updated review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2021) 61:2061–77. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1769548
22. Cao S-Y, Zhao C-N, Xu X-Y, Tang G-Y, Corke H, Gan R-Y, et al. Dietary plants, gut microbiota, and obesity: effects and mechanisms. Trends Food Sci Technol. (2019) 92:194–204. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.08.004
23. Ma Q, Santhanam RK, Xue Z, Guo Q, Gao X, Chen H. Effect of different drying methods on the physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of mulberry leaves polysaccharides. Int J Biol Macromol. (2018) 119:1137–43. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.08.023
24. Meng Q, Qi X, Fu Y, Chen Q, Cheng P, Yu X, et al. Flavonoids extracted from mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaf improve skeletal muscle mitochondrial function by activating AMPK in type 2 diabetes. J Ethnopharmacol. (2020) 248:112326. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112326
25. Thaipitakwong T, Numhom S, Aramwit P. Mulberry leaves and their potential effects against cardiometabolic risks: a review of chemical compositions, biological properties and clinical efficacy. Pharm Biol. (2018) 56:109–8. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2018.1424210
26. Shu Y-H, Yuan H-H, Xu M-T, Hong Y-T, Gao C-C, Wu Z-P, et al. A novel Diels-Alder adduct of mulberry leaves exerts anticancer effect through autophagy-mediated cell death. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2020) 42:780–90 doi: 10.1038/s41401-020-0492-5
27. Chen J, Li X. Hypolipidemic effect of flavonoids from mulberry leaves in triton WR-1339 induced hyperlipidemic mice. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. (2007) 16(Suppl. 1):290–4. doi: 10.6133/apjcn.2007.16.s1.55
28. Zhong Y, Song B, Zheng C, Zhang S, Yan Z, Tang Z, et al. Flavonoids from mulberry leaves alleviate lipid dysmetabolism in high fat diet-fed mice: involvement of gut microbiota. Microorganisms. (2020) 8:860. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8060860
29. Hsu LS, Ho HH, Lin MC, Chyau CC, Peng JS, Wang CJ. Mulberry water extracts (MWEs) ameliorated carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damages in rat. Food Chem Toxicol. (2012) 50:3086–93. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2012.05.055
30. Lim HH, Lee SO, Kim SY, Yang SJ, Lim Y. Anti-inflammatory and antiobesity effects of mulberry leaf and fruit extract on high fat diet-induced obesity. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). (2013) 238:1160–9. doi: 10.1177/1535370213498982
31. Chan KC, Yang MY, Lin MC, Lee YJ, Chang WC, Wang CJ. Mulberry leaf extract inhibits the development of atherosclerosis in cholesterol-fed rabbits and in cultured aortic vascular smooth muscle cells. J Agric Food Chem. (2013) 61:2780–8. doi: 10.1021/jf305328d
32. Murota K, Nakamura Y, Uehara M. Flavonoid metabolism: the interaction of metabolites and gut microbiota. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. (2018) 82:600–10. doi: 10.1080/09168451.2018.1444467
33. Sheng Y, Liu J, Zheng S, Liang F, Luo Y, Huang K, et al. Mulberry leaves ameliorate obesity through enhancing brown adipose tissue activity and modulating gut microbiota. Food Funct. (2019) 10:4771–81. doi: 10.1039/c9fo00883g
34. Sheng Y, Zheng S, Ma T, Zhang C, Ou X, He X, et al. Mulberry leaf alleviates streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats by attenuating NEFA signaling and modulating intestinal microflora. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:12041. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12245-2
35. Kimura I, Ozawa K, Inoue D, Imamura T, Kimura K, Maeda T, et al. The gut microbiota suppresses insulin-mediated fat accumulation via the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR43. Nat Commun. (2013) 4:1829. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2852
36. Jung DM, Lee MJ, Yoon SH, Jung MY. A gas chromatography-tandem quadrupole mass spectrometric analysis of policosanols in commercial vegetable oils. J Food Sci. (2011) 76:C891–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02232.x
37. De Oliveira AM, Conserva LM, De Souza Ferro JN, De Almeida Brito F, Lyra Lemos RP, Barreto E. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of octacosanol from the leaves of Sabicea grisea var. grisea in mice. Int J Mol Sci. (2012) 13:1598–611. doi: 10.3390/ijms13021598
38. Guo T, Lin Q, Li X, Nie Y, Wang L, Shi L, et al. Octacosanol attenuates inflammation in both RAW264.7 macrophages and a mouse model of colitis. J Agric Food Chem. (2017) 65:3647–58. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b05465
39. Singh DK, Li L, Porter TD. Policosanol inhibits cholesterol synthesis in hepatoma cells by activation of AMP-kinase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2006) 318:1020–6. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.107144
40. Wang T, Liu Y, Yang N, Ji C, Chan P, Zuo P. Anti-parkinsonian effects of octacosanol in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6 tetrahydropyridine-treated mice. Neural Regen Res. (2012) 7:1080–7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5374.2012.14.006
41. Wang T, Liu Y-Y, Wang X, Yang N, Zhu H-B, Zuo P-P. Protective effects of octacosanol on 6-hydroxydopamine-induced Parkinsonism in rats via regulation of ProNGF and NGF signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2010) 31:765–74. doi: 10.1038/aps.2010.69
42. Cho KH, Kim SJ, Yadav D, Kim JY, Kim JR. Consumption of cuban policosanol improves blood pressure and lipid profile via enhancement of HDL functionality in healthy women subjects: randomized, double-blinded, and placebo-controlled study. Oxid Med Cell Longev. (2018) 2018:4809525. doi: 10.1155/2018/4809525
43. Sharma R, Matsuzaka T, Kaushik MK, Sugasawa T, Ohno H, Wang Y, et al. Octacosanol and policosanol prevent high-fat diet-induced obesity and metabolic disorders by activating brown adipose tissue and improving liver metabolism. Sci Rep. (2019) 9:5169. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41631-1
44. Ng CH, Leung KY, Huang Y, Chen ZY. Policosanol has no antioxidant activity in human low-density lipoprotein but increases excretion of bile acids in hamsters. J Agric Food Chem. (2005) 53:6289–93. doi: 10.1021/jf051269a
45. Kim JY, Kim SM, Kim SJ, Lee EY, Kim JR, Cho KH. Consumption of policosanol enhances HDL functionality via CETP inhibition and reduces blood pressure and visceral fat in young and middle-aged subjects. Int J Mol Med. (2017) 39:889–99. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.2907
46. Kato S, Karino K, Hasegawa S, Nagasawa J, Nagasaki A, Eguchi M, et al. Octacosanol affects lipid metabolism in rats fed on a high-fat diet. Br J Nutr. (1995) 73:433–41. doi: 10.1079/bjn19950045
47. Haim D, Valenzuela A, Brañes MC, Fuenzalida M, Videla LA. The oleic acid esterification of policosanol increases its bioavailability and hypocholesterolemic action in rats. Grasas y Aceites. (2012) 63:345–54. doi: 10.3989/gya.010612
48. Menéndez R, Amor AM, Rodeiro I, González RM, González PC, Alfonso JL, et al. Policosanol modulates HMG-CoA reductase activity in cultured fibroblasts. Arch Med Res. (2001) 32:8–12. doi: 10.1016/s0188-4409(00)00265-4
49. Ra JE, Woo SY, Lee KS, Lee MJ, Kim HY, Ham HM, et al. Policosanol profiles and adenosine 5'-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation potential of Korean wheat seedling extracts according to cultivar and growth time. Food Chem. (2020) 317:126388. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126388
50. Chambers KF, Day PE, Aboufarrag HT, Kroon PA. Polyphenol effects on cholesterol metabolism via bile acid biosynthesis, CYP7A1: a review. Nutrients. (2019) 11:2588. doi: 10.3390/nu11112588
51. Winston JA, Theriot CM. Diversification of host bile acids by members of the gut microbiota. Gut Microbes. (2020) 11:158–71. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2019.1674124
52. Zhang Y, Limaye PB, Renaud HJ, Klaassen CD. Effect of various antibiotics on modulation of intestinal microbiota and bile acid profile in mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. (2014) 277:138–45. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2014.03.009
53. Jones ML, Tomaro-Duchesneau C, Prakash S. The gut microbiome, probiotics, bile acids axis, and human health. Trends Microbiol. (2014) 22:306–8. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2014.04.010
54. Theriot CM, Koenigsknecht MJ, Carlson PE, Hatton GE, Nelson AM, Li B, et al. Antibiotic-induced shifts in the mouse gut microbiome and metabolome increase susceptibility to Clostridium difficile infection. Nat Commun. (2014) 5:3114. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4114
55. Duboc H, Rajca S, Rainteau D, Benarous D, Maubert M-A, Quervain E, et al. Connecting dysbiosis, bile-acid dysmetabolism and gut inflammation in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gut. (2013) 62:531–9. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302578
56. Wu H, Song A, Hu W, Dai M. The anti-atherosclerotic effect of paeonol against vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation by up-regulation of autophagy via the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. (2017) 8:948. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00948
57. Gao L, Wang Z, Lu D, Huang J, Liu J, Hong L. Paeonol induces cytoprotective autophagy via blocking the Akt/mTOR pathway in ovarian cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. (2019) 10:609. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-1849-x
58. Lin C, Lin H-Y, Chen J-H, Tseng W-P, Ko P-Y, Liu Y-S, et al. Effects of paeonol on anti-neuroinflammatory responses in microglial cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2015) 16:8844–60. doi: 10.3390/ijms16048844
59. Xu F, Xiao H, Liu R, Yang Y, Zhang M, Chen L, et al. Paeonol ameliorates glucose and lipid metabolism in experimental diabetes by activating akt. Front Pharmacol. (2019) 10:261. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00261
60. Yang Q, Wang S, Xie Y, Wang J, Li H, Zhou X, et al. Effect of salvianolic acid B and paeonol on blood lipid metabolism and hemorrheology in myocardial ischemia rabbits induced by pituitruin. Int J Mol Sci. (2010) 11:3696–704. doi: 10.3390/ijms11103696
61. Jing X, Sun C, Chen H, Sun J, Zhang Y, Wu J. Protection of paeonol against epirubicin-induced hepatotoxicity: a metabolomic study. BioScience Trends. (2019) 13:253–60. doi: 10.5582/bst.2019.01105
62. Hu S, Shen G, Zhao W, Wang F, Jiang X, Huang D. Paeonol, the main active principles of Paeonia moutan, ameliorates alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. (2010) 128:100–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2009.12.034
63. Li H, Dai M, Jia W. Paeonol attenuates high-fat-diet-induced atherosclerosis in rabbits by anti-inflammatory activity. Planta Med. (2009) 75:7–11. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1088332
64. Izumi M, Yoshida T, Nakamura T, Wakamori AM. Paeonol, an ingredient of kamishoyosan, reduces intracellular lipid accumulation by inhibiting glucocorticoid receptor activity in 3T3-L1 cells. Nutrients. (2020) 12:309. doi: 10.3390/nu12020309
65. Li X, Zhou Y, Yu C, Yang H, Zhang C, Ye Y, et al. Paeonol suppresses lipid accumulation in macrophages via upregulation of the ATPbinding cassette transporter A1 and downregulation of the cluster of differentiation 36. Int J Oncol. (2015) 46:764–74. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2757
66. Chen S, Zhang J, Wu L, Wu H, Dai M. Paeonol nanoemulsion for enhanced oral bioavailability: optimization and mechanism. Nanomedicine (Lond). (2018) 13:269–82. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2017-0277
67. Feng R, Chen J-H, Liu C-H, Xia F-B, Xiao Z, Zhang X, et al. A combination of Pueraria lobata and Silybum marianum protects against alcoholic liver disease in mice. Phytomedicine. (2019) 58:152824. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.152824
68. Chun SC, Jee SY, Lee SG, Park SJ, Lee JR, Kim SC. Anti-inflammatory activity of the methanol extract of moutan cortex in LPS-activated Raw264.7 cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2007) 4:327–33. doi: 10.1093/ecam/nel093
69. Lin SJ, Chen CS, Lin SS, Chou MY, Shih HC, Lee IP, et al. In vitro anti-microbial and in vivo cytokine modulating effects of different prepared Chinese herbal medicines. Food Chem Toxicol. (2006) 44:2078–85. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2006.07.010
70. Zhong L-J, Xie Z-S, Yang H, Li P, Xu X-J. Moutan Cortex and Paeoniae Radix Rubra reverse high-fat-diet-induced metabolic disorder and restore gut microbiota homeostasis. Chin J Natural Med. (2017) 15:210–9. doi: 10.1016/s1875-5364(17)30037-7
71. Wu J, Wu D, Ma K, Wang T, Shi G, Shao J, et al. Paeonol ameliorates murine alcohol liver disease via mycobiota-mediated Dectin-1/IL-1beta signaling pathway. J Leukoc Biol. (2020) 108:199–214. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3MA0120-325RR
72. Wolfram S, Wang Y, Thielecke F. Anti-obesity effects of green tea: from bedside to bench. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2006) 50:176–87. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200500102
73. Komorita Y, Iwase M, Fujii H, Ohkuma T, Ide H, Jodai-Kitamura T, et al. Additive effects of green tea and coffee on all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the fukuoka diabetes registry. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. (2020) 8:e001252. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001252
74. Furuyashiki T, Nagayasu H, Aoki Y, Bessho H, Hashimoto T, Kanazawa K, et al. Tea catechin suppresses adipocyte differentiation accompanied by down-regulation of PPARgamma2 and C/EBPalpha in 3T3-L1 cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. (2004) 68:2353–9. doi: 10.1271/bbb.68.2353
75. Mi Y, Liu X, Tian H, Liu H, Li J, Qi G, et al. EGCG stimulates the recruitment of brite adipocytes, suppresses adipogenesis and counteracts TNF-alpha-triggered insulin resistance in adipocytes. Food Funct. (2018) 9:3374–86. doi: 10.1039/c8fo00167g
76. Nagao T, Hase T, Tokimitsu I. A green tea extract high in catechins reduces body fat and cardiovascular risks in humans. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.). (2007) 15:1473–83. doi: 10.1038/oby.2007.176
77. Chen IJ, Liu CY, Chiu JP, Hsu CH. Therapeutic effect of high-dose green tea extract on weight reduction: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Clin Nutr. (2016) 35:592–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2015.05.003
78. Rocha A, Bolin AP, Cardoso CA, Otton R. Green tea extract activates AMPK and ameliorates white adipose tissue metabolic dysfunction induced by obesity. Eur J Nutr. (2016) 55:2231–44. doi: 10.1007/s00394-015-1033-8
79. Otton R, Bolin AP, Ferreira LT, Marinovic MP, Rocha ALS, Mori MA. Polyphenol-rich green tea extract improves adipose tissue metabolism by down-regulating miR-335 expression and mitigating insulin resistance and inflammation. J Nutr Biochem. (2018) 57:170–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2018.03.024
80. Zhou J, Mao L, Xu P, Wang Y. Effects of (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) on energy expenditure and microglia-mediated hypothalamic inflammation in mice fed a high-fat diet. Nutrients. (2018) 10:1681. doi: 10.3390/nu10111681
81. Jang HJ, Ridgeway SD, Kim JA. Effects of the green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate on high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2013) 305:E1444–51. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00434.2013
82. Liu Z, Chen Z, Guo H, He D, Zhao H, Wang Z, et al. The modulatory effect of infusions of green tea, oolong tea, and black tea on gut microbiota in high-fat-induced obese mice. Food Funct. (2016) 7:4869–79. doi: 10.1039/c6fo01439a
83. Singh DP, Singh J, Boparai RK, Zhu J, Mantri S, Khare P, et al. Isomalto-oligosaccharides, a prebiotic, functionally augment green tea effects against high fat diet-induced metabolic alterations via preventing gut dysbacteriosis in mice. Pharmacol Res. (2017) 123:103–13. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.06.015
84. Dey P, Sasaki GY, Wei P, Li J, Wang L, Zhu J, et al. Green tea extract prevents obesity in male mice by alleviating gut dysbiosis in association with improved intestinal barrier function that limits endotoxin translocation and adipose inflammation. J Nutr Biochem. (2019) 67:78–89. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.01.017
85. Liu J, Hao W, He Z, Kwek E, Zhao Y, Zhu H, et al. Beneficial effects of tea water extracts on the body weight and gut microbiota in C57BL/6J mice fed with a high-fat diet. Food Funct. (2019) 10:2847–60. doi: 10.1039/c8fo02051e
86. a H, Zhang B, Hu Y, Wang J, Liu J, Qin R, et al. Correlation analysis of intestinal redox state with the gut microbiota reveals the positive intervention of tea polyphenols on hyperlipidemia in high fat diet fed mice. J Agric Food Chem. (2019) 67:7325–35. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b02211
87. Rauf A, Imran M, Butt MS, Nadeem M, Peters DG, Mubarak MS. Resveratrol as an anti-cancer agent: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2018) 58:1428–47. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2016.1263597
88. Dyck GJB, Raj P, Zieroth S, Dyck JRB, Ezekowitz JA. The effects of resveratrol in patients with cardiovascular disease and heart failure: a narrative review. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:904. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040904
89. Yan Y, Yang H, Xie Y, Ding Y, Kong D, Yu H. Research progress on alzheimer's disease and resveratrol. Neurochem Res. (2020) 45: 989–1006. doi: 10.1007/s11064-020-03007-0
90. Meng X, Zhou J, Zhao C-N, Gan R-Y, Li H-B. Health benefits and molecular mechanisms of resveratrol: a narrative review. Foods. (2020) 9:340. doi: 10.3390/foods9030340
91. Alberdi G, Rodriguez VM, Miranda J, Macarulla MT, Churruca I, Portillo MP. Thermogenesis is involved in the body-fat lowering effects of resveratrol in rats. Food Chem. (2013) 141:1530–5. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.03.085
92. Hui S, Liu Y, Huang L, Zheng L, Zhou M, Lang H, et al. Resveratrol enhances brown adipose tissue activity and white adipose tissue browning in part by regulating bile acid metabolism via gut microbiota remodeling. Int J Obes (Lond). (2020) 44:1678–90. doi: 10.1038/s41366-020-0566-y
93. Wang P, Wang J, Li D, Ke W, Chen F, Hu X. Targeting the gut microbiota with resveratrol: a demonstration of novel evidence for the management of hepatic steatosis. J Nutr Biochem. (2020) 81:108363. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108363
94. Ye G, Chen G, Gao H, Lin Y, Liao X, Zhang H, et al. Resveratrol inhibits lipid accumulation in the intestine of atherosclerotic mice and macrophages. J Cell Mol Med. (2019) 23:4313–25. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14323
95. Wang S, Liang X, Yang Q, Fu X, Zhu M, Rodgers BD, et al. Resveratrol enhances brown adipocyte formation and function by activating AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) alpha1 in mice fed high-fat diet. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2017) 61:1600746. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201600746
96. Wang S, Liang X, Yang Q, Fu X, Rogers CJ, Zhu M, et al. Resveratrol induces brown-like adipocyte formation in white fat through activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) alpha1. Int J Obes (Lond). (2015) 39:967–76. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2015.23
97. Imamura H, Nagayama D, Ishihara N, Tanaka S, Watanabe R, Watanabe Y, et al. Resveratrol attenuates triglyceride accumulation associated with upregulation of Sirt1 and lipoprotein lipase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Genet Metab Rep. (2017) 12:44–50. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2017.05.003
98. Szkudelska K, Nogowski L, Szkudelski T. Resveratrol, a naturally occurring diphenolic compound, affects lipogenesis, lipolysis and the antilipolytic action of insulin in isolated rat adipocytes. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. (2009) 113:17–24. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2008.11.001
99. Gomez-Zorita S, Treguer K, Mercader J, Carpene C. Resveratrol directly affects in vitro lipolysis and glucose transport in human fat cells. J Physiol Biochem. (2013) 69:585–93. doi: 10.1007/s13105-012-0229-0
100. Wang P, Li D, Ke W, Liang D, Hu X, Chen F. Resveratrol-induced gut microbiota reduces obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice. Int J Obes (Lond). (2020) 44:213–25. doi: 10.1038/s41366-019-0332-1
101. Walle T. Bioavailability of resveratrol. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2011) 1215:9–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05842.x
102. Chimento A, De Amicis F, Sirianni R, Sinicropi MS, Puoci F, Casaburi I, et al. Progress to improve oral bioavailability and beneficial effects of resveratrol. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:1381. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061381
103. Wang P, Gao J, Ke W, Wang J, Li D, Liu R, et al. Resveratrol reduces obesity in high-fat diet-fed mice via modulating the composition and metabolic function of the gut microbiota. Free Radic Biol Med. (2020) 156:83–98. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.04.013
104. Qiao Y, Sun J, Xia S, Tang X, Shi Y, Le G. Effects of resveratrol on gut microbiota and fat storage in a mouse model with high-fat-induced obesity. Food Funct. (2014) 5:1241–9. doi: 10.1039/c3fo60630a
105. Liao W, Yin X, Li Q, Zhang H, Liu Z, Zheng X, et al. Resveratrol-induced white adipose tissue browning in obese mice by remodeling fecal microbiota. Molecules. (2018) 23:3356. doi: 10.3390/molecules23123356
106. Chen ML, Yi L, Zhang Y, Zhou X, Ran L, Yang J, et al. Resveratrol attenuates trimethylamine-N-Oxide (TMAO)-Induced atherosclerosis by regulating TMAO synthesis and bile acid metabolism via remodeling of the gut microbiota. mBio. (2016) 7:e02210–02215. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02210-15
107. Etxeberria U, Arias N, Boque N, Macarulla MT, Portillo MP, Martinez JA, et al. Reshaping faecal gut microbiota composition by the intake of trans-resveratrol and quercetin in high-fat sucrose diet-fed rats. J Nutr Biochem. (2015) 26:651–60. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.01.002
108. Sung MM, Kim TT, Denou E, Soltys C-LM, Hamza SM, Byrne NJ, et al. Improved glucose homeostasis in obese mice treated with resveratrol is associated with alterations in the gut microbiome. Diabetes. (2017) 66:418–25. doi: 10.2337/db16-0680
109. Chen F, Wang H, Zhao J, Yan J, Meng H, Zhan H, et al. Grape seed proanthocyanidin inhibits monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial hypertension via attenuating inflammation: in vivo and in vitro studies. J Nutr Biochem. (2019) 67:72–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.01.013
110. Liu W, Zhao S, Wang J, Shi J, Sun Y, Wang W, et al. Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract ameliorates inflammation and adiposity by modulating gut microbiota in high-fat diet mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2017) 61:1601082. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201601082
111. Xu M, Chen X, Huang Z, Chen D, Yu B, Chen H, et al. Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract promotes skeletal muscle fiber type transformation via AMPK signaling pathway. J Nutr Biochem. (2020) 84:108462. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108462
112. Downing LE, Heidker RM, Caiozzi GC, Wong BS, Rodriguez K, Del Rey F, et al. A grape seed procyanidin extract ameliorates fructose-induced hypertriglyceridemia in rats via enhanced fecal bile acid and cholesterol excretion and inhibition of hepatic lipogenesis. PLoS ONE. (2015) 10:e0140267. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140267
113. Pajuelo D, Quesada H, Diaz S, Fernandez-Iglesias A, Arola-Arnal A, Blade C, et al. Chronic dietary supplementation of proanthocyanidins corrects the mitochondrial dysfunction of brown adipose tissue caused by diet-induced obesity in Wistar rats. Br J Nutr. (2012) 107:170–8. doi: 10.1017/S0007114511002728
114. Pascual-Serrano A, Blade C, Suarez M, Arola-Arnal A. Grape seed proanthocyanidins improve white adipose tissue expansion during diet-induced obesity development in rats. Int J Mol Sci. (2018) 19:2632. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092632
115. Pons Z, Margalef M, Bravo FI, Arola-Arnal A, Muguerza B. Chronic administration of grape-seed polyphenols attenuates the development of hypertension and improves other cardiometabolic risk factors associated with the metabolic syndrome in cafeteria diet-fed rats. Br J Nutr. (2017) 117:200–8. doi: 10.1017/S0007114516004426
116. Jin G, Asou Y, Ishiyama K, Okawa A, Kanno T, Niwano Y. Proanthocyanidin-Rich grape seed extract modulates intestinal microbiota in ovariectomized mice. J Food Sci. (2018) 83:1149–52. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14098
117. Wu Y, Ma N, Song P, He T, Levesque C, Bai Y, et al. Grape seed proanthocyanidin affects lipid metabolism via changing gut microflora and enhancing propionate production in weaned pigs. J Nutr. (2019) 149:1523–32. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxz102
118. Pinent M, Blade MC, Salvado MJ, Arola L, Hackl H, Quackenbush J, et al. Grape-seed derived procyanidins interfere with adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells at the onset of differentiation. Int J Obes (Lond). (2005) 29:934–41. doi: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802988
119. Wei S, Zheng Y, Zhang M, Zheng H, Yan P. Grape seed procyanidin extract inhibits adipogenesis and stimulates lipolysis of porcine adipocytes in vitro. J Anim Sci. (2018) 96:2753–62. doi: 10.1093/jas/sky158
120. Terra X, Montagut G, Bustos M, Llopiz N, Ardevol A, Blade C, et al. Grape-seed procyanidins prevent low-grade inflammation by modulating cytokine expression in rats fed a high-fat diet. J Nutr Biochem. (2009) 20:210–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2008.02.005
121. Chacon MR, Ceperuelo-Mallafre V, Maymo-Masip E, Mateo-Sanz JM, Arola L, Guitierrez C, et al. Grape-seed procyanidins modulate inflammation on human differentiated adipocytes in vitro. Cytokine. (2009) 47:137–42. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2009.06.001
122. Chambers ES, Viardot A, Psichas A, Morrison DJ, Murphy KG, Zac-Varghese SE, et al. Effects of targeted delivery of propionate to the human colon on appetite regulation, body weight maintenance and adiposity in overweight adults. Gut. (2015) 64:1744–54. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307913
123. Psichas A, Sleeth ML, Murphy KG, Brooks L, Bewick GA, Hanyaloglu AC, et al. The short chain fatty acid propionate stimulates GLP-1 and PYY secretion via free fatty acid receptor 2 in rodents. Int J Obes (Lond). (2015) 39:424–9. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2014.153
124. Song B, Zhong YZ, Zheng CB, Li FN, Duan YH, Deng JP. Propionate alleviates high-fat diet-induced lipid dysmetabolism by modulating gut microbiota in mice. J Appl Microbiol. (2019) 127:1546–55. doi: 10.1111/jam.14389
125. Wang D, Dong X, Wang C. Honokiol ameliorates amyloidosis and neuroinflammation and improves cognitive impairment in alzheimer's disease transgenic mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2018) 366:470–8. doi: 10.1124/jpet.118.248674
126. Banik K, Ranaware AM, Deshpande V, Nalawade SP, Padmavathi G, Bordoloi D, et al. Honokiol for cancer therapeutics: a traditional medicine that can modulate multiple oncogenic targets. Pharmacol Res. (2019) 144:192–209. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.04.004
127. Lee IH, Im E, Lee H-J, Sim DY, Lee JH, Jung JH, et al. Apoptotic and antihepatofibrotic effect of honokiol via activation of GSK3β and suppression of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in hepatic stellate cells. Phytother Res. (2021) 35:452–62. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6824
128. Zhang B, Wang P-P, Hu K-L, Li L-N, Yu X, Lu Y, et al. Antidepressant-Like effect and mechanism of action of honokiol on the mouse lipopolysaccharide (LPS) depression model. Molecules. (2019) 24:2035. doi: 10.3390/molecules24112035
129. Caballero EP, Mariz-Ponte N, Rigazio CS, Santamaría MH, Corral RS. Honokiol attenuates oxidative stress-dependent heart dysfunction in chronic Chagas disease by targeting AMPK / NFE2L2 / SIRT3 signaling pathway. Free RadicBiol Med. (2020) 156:113–24. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.05.024
130. Ding Y, Song Z, Li H, Chang L, Pan T, Gu X, et al. Honokiol ameliorates high-fat-diet-induced obesity of different sexes of mice by modulating the composition of the gut microbiota. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:2800. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02800
131. Sun J, Fu X, Liu Y, Wang Y, Huo B, Guo Y, et al. Hypoglycemic effect and mechanism of honokiol on type 2 diabetic mice. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2015) 9:6327–42. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S92777
132. Kim Y-J, Choi M-S, Cha BY, Woo JT, Park YB, Kim SR, et al. Long-term supplementation of honokiol and magnolol ameliorates body fat accumulation, insulin resistance, and adipose inflammation in high-fat fed mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2013) 57:1988–98. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201300113
133. Yang JY, Della-Fera MA, Rayalam S, Baile CA. Enhanced effects of xanthohumol plus honokiol on apoptosis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Obesity (Silver Spring). (2008) 16:1232–8. doi: 10.1038/oby.2008.66
134. Lone J, Yun JW. Honokiol exerts dual effects on browning and apoptosis of adipocytes. Pharmacol Rep. (2017) 69:1357–65. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2017.06.004
135. Choi SS, Cha BY, Iida K, Sato M, Lee YS, Teruya T, et al. Honokiol enhances adipocyte differentiation by potentiating insulin signaling in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Nat Med. (2011) 65:424–30. doi: 10.1007/s11418-011-0512-3
136. Stevens JF, Maier CS. The chemistry of gut microbial metabolism of polyphenols. Phytochem Rev. (2016) 15:425–44. doi: 10.1007/s11101-016-9459-z
137. Aziz F, Xin M, Gao Y, Chakroborty A, Khan I, Monts J, et al. Induction and prevention of gastric cancer with combined and capsaicin administration and DFMO treatment, respectively. Cancers (Basel). (2020) 12:816. doi: 10.3390/cancers12040816
138. Botz B, Kriszta G, Bölcskei K, Horváth Á I, Mócsai A, Helyes Z. Capsaicin-Sensitive peptidergic sensory nerves are anti-inflammatory gatekeepers in the hyperacute phase of a mouse rheumatoid arthritis model. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:1682. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041682
139. Chiang C, Zhang M, Wang D, Xiao T, Zhu L, Chen K, et al. Therapeutic potential of targeting MKK3-p38 axis with Capsaicin for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Theranostics. (2020) 10:7906–20. doi: 10.7150/thno.45191
140. Hsu Y-J, Huang W-C, Chiu C-C, Liu Y-L, Chiu W-C, Chiu C-H, et al. Capsaicin supplementation reduces physical fatigue and improves exercise performance in mice. Nutrients. (2016) 8:648. doi: 10.3390/nu8100648
141. Arora V, Campbell JN, Chung M-K. Fight fire with fire: neurobiology of capsaicin-induced analgesia for chronic pain. Pharmacol Ther. (2021) 220:107743. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107743
142. Yuan LJ, Qin Y, Wang L, Zeng Y, Chang H, Wang J, et al. Capsaicin-containing chili improved postprandial hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, and fasting lipid disorders in women with gestational diabetes mellitus and lowered the incidence of large-for-gestational-age newborns. Clin Nutr. (2016) 35:388–93. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2015.02.011
143. Chen J, LiL LiY, Liang X, Sun Q, Yu H, et al. Activation of TRPV1 channel by dietary capsaicin improves visceral fat remodeling through connexin43-mediated Ca2+ influx. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2015) 14:22. doi: 10.1186/s12933-015-0183-6
144. Wang Y, Tang C, Tang Y, Yin H, Liu X. Capsaicin has an anti-obesity effect through alterations in gut microbiota populations and short-chain fatty acid concentrations. Food Nutr Res. (2020) 64:3525. doi: 10.29219/fnr.v64.3525
145. Baskaran P, Krishnan V, Ren J, Thyagarajan B. Capsaicin induces browning of white adipose tissue and counters obesity by activating TRPV1 channel-dependent mechanisms. Br J Pharmacol. (2016) 173:2369–89. doi: 10.1111/bph.13514
146. Kawabata F, Inoue N, Masamoto Y, Matsumura S, Kimura W, Kadowaki M, et al. Non-pungent capsaicin analogs (capsinoids) increase metabolic rate and enhance thermogenesis via gastrointestinal TRPV1 in mice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. (2009) 73:2690–7. doi: 10.1271/bbb.90555
147. Fan L, Xu H, Yang R, Zang Y, Chen J, Qin H. Combination of capsaicin and capsiate induces browning in 3T3-L1 white adipocytes via activation of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma/beta3-adrenergic receptor signaling pathways. J Agric Food Chem. (2019) 67:6232–40. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b02191
148. Hsu C-L, Yen G-C. Effects of capsaicin on induction of apoptosis and inhibition of adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 cells. J Agric Food Chem. (2007) 55:1730–6. doi: 10.1021/jf062912b
149. Zang Y, Fan L, Chen J, Huang R, Qin H. Improvement of lipid and glucose metabolism by capsiate in palmitic acid-treated HepG2 cells via activation of the AMPK/SIRT1 signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem. (2018) 66:6772–81. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b01831
150. Kang JH, Kim CS, Han IS, Kawada T, Yu R. Capsaicin, a spicy component of hot peppers, modulates adipokine gene expression and protein release from obese-mouse adipose tissues and isolated adipocytes, and suppresses the inflammatory responses of adipose tissue macrophages. FEBS Lett. (2007) 581:4389–96. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.07.082
151. Kang C, Wang B, Kaliannan K, Wang X, Lang H, Hui S, et al. Gut microbiota mediates the protective effects of dietary capsaicin against chronic low-grade inflammation and associated obesity induced by high-fat diet. mBio. (2017) 8:e00470-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00470-17
152. Shen W, Shen M, Zhao X, Zhu H, Yang Y, Lu S, et al. Anti-obesity effect of capsaicin in mice fed with high-fat diet is associated with an increase in population of the gut bacterium akkermansia muciniphila. Front Microbiol. (2017) 8:272. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00272
153. Chua M, Baldwin TC, Hocking TJ, Chan K. Traditional uses and potential health benefits of Amorphophallus konjac K. Koch ex N.E.Br. J Ethnopharmacol. (2010) 128:268–78. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.01.021
154. Lu Y, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Liang X, Liu T, Yi H, et al. Konjac glucomannan with probiotics acts as a combination laxative to relieve constipation in mice by increasing short-chain fatty acid metabolism and 5-hydroxytryptamine hormone release. Nutrition. (2021) 84:111112. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2020.111112
155. Gan J, Liu C, Li H, Wang S, Wang Z, Kang Z, et al. Accelerated wound healing in diabetes by reprogramming the macrophages with particle-induced clustering of the mannose receptors. Biomaterials. (2019) 219:119340. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2019.119340
156. Tian Y, Xu J, Li Y, Zhao R, Du S, Lv C, et al. MicroRNA-31 reduces inflammatory signaling and promotes regeneration in colon epithelium, and delivery of mimics in microspheres reduces colitis in mice. Gastroenterology. (2019) 156:2281-2296.e6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.02.023
157. Chen HL, Sheu WH, Tai TS, Liaw YP, Chen YC. Konjac supplement alleviated hypercholesterolemia and hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetic subjects–a randomized double-blind trial. J Am Coll Nutr. (2003) 22:36–42. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2003.10719273
158. Kraemer WJ, Vingren JL, Silvestre R, Spiering BA, Hatfield DL, Ho JY, et al. Effect of adding exercise to a diet containing glucomannan. Metabolism. (2007) 56:1149–58. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2007.04.010
159. Chen H, Nie Q, Hu J, Huang X, Zhang K, Pan S, et al. Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of glucomannan extracted from konjac on type 2 diabetic rats. J Agric Food Chem. (2019) 67:5278–88. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b01192
160. Zhai X, Lin D, Zhao Y, Li W, Yang X. Enhanced anti-obesity effects of bacterial cellulose combined with konjac glucomannan in high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice. Food Funct. (2018) 9:5260–72. doi: 10.1039/c8fo01211c
161. Zhai X, Lin D, Zhao Y, Li W, Yang X. Effects of dietary fiber supplementation on fatty acid metabolism and intestinal microbiota diversity in C57BL/6J mice fed with a high-fat diet. J Agric Food Chem. (2018) 66:12706–18. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b05036
162. Zhao Y, Jayachandran M, Xu B. In vivo antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of soluble dietary fiber Konjac glucomannan in type-2 diabetic rats. Int J Biol Macromol. (2020) 159:1186–96. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.105
163. Yin JY, Ma LY, Xie MY, Nie SP, Wu JY. Molecular properties and gut health benefits of enzyme-hydrolyzed konjac glucomannans. Carbohydr Polym. (2020) 237:116117. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116117
164. Li B, Xia J, Wang Y, Xie B. Grain-size effect on the structure and antiobesity activity of konjac flour. J Agric Food Chem. (2005) 53:7404–7. doi: 10.1021/jf050751q
165. Young W, Roy NC, Lee J, Lawley B, Otter D, Henderson G, et al. Bowel microbiota moderate host physiological responses to dietary konjac in weanling rats. J Nutr. (2013) 143:1052–60. doi: 10.3945/jn.113.174854
166. Kang Y, Li Y, Du Y, Guo L, Chen M, Huang X, et al. Konjaku flour reduces obesity in mice by modulating the composition of the gut microbiota. Int J Obes (Lond). (2019) 43:1631–43. doi: 10.1038/s41366-018-0187-x
167. Tan C, Wei H, Ao J, Long G, Peng J. Inclusion of konjac flour in the gestation diet changes the gut microbiota, alleviates oxidative stress, and improves insulin sensitivity in sows. Appl Environ Microbiol. (2016) 82:5899–909. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01374-16
168. Chen HL, Cheng HC, Liu YJ, Liu SY, Wu WT. Konjac acts as a natural laxative by increasing stool bulk and improving colonic ecology in healthy adults. Nutrition. (2006) 22:1112–9. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2006.08.009
169. Chen H, Nie Q, Hu J, Huang X, Yin J, Nie S. Multiomics approach to explore the amelioration mechanisms of glucomannans on the metabolic disorder of Type 2 diabetic rats. J Agric Food Chem. (2021) 69:2632–45. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c07871
170. Wang Y, Lü W-D, Lin B, Yang F, Feng M, Lv R. An optimized lanthanide-chlorophyll nanocomposite for dual-modal imaging-guided surgery navigation and anti-cancer theranostics. Biomater Sci. (2020) 8:1270–8. doi: 10.1039/c9bm02057h
171. Wunderlich ALM, Azevedo SCSF, Yamada LA, Bataglini C, Previate C, Campanholi KSS, et al. Chlorophyll treatment combined with photostimulation increases glycolysis and decreases oxidative stress in the liver of type 1 diabetic rats. Braz J Med Biol Res. (2020) 53:e8389. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20198389
172. Lauritano C, Helland K, Riccio G, Andersen JH, Ianora A, Hansen EH. Lysophosphatidylcholines and chlorophyll-derived molecules from the diatom with anti-inflammatory activity. Mar Drugs. (2020) 18:166. doi: 10.3390/md18030166
173. Montelius C, Erlandsson D, Vitija E, Stenblom EL, Egecioglu E, Erlanson-Albertsson C. Body weight loss, reduced urge for palatable food and increased release of GLP-1 through daily supplementation with green-plant membranes for three months in overweight women. Appetite. (2014) 81:295–304. doi: 10.1016/j.appet.2014.06.101
174. Li Y, Cui Y, Lu F, Wang X, Liao X, Hu X, et al. Beneficial effects of a chlorophyll-rich spinach extract supplementation on prevention of obesity and modulation of gut microbiota in high-fat diet-fed mice. J Funct Foods. (2019) 60:103436. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.103436
175. Li Y, Cui Y, Hu X, Liao X, Zhang Y. Chlorophyll supplementation in early life prevents diet-induced obesity and modulates gut microbiota in mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2019) 63:e1801219. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201801219
176. Wu SJ, Ng LT, Wang GH, Huang YJ, Chen JL, Sun FM. Chlorophyll a, an active anti-proliferative compound of Ludwigia octovalvis, activates the CD95 (APO-1/CD95) system and AMPK pathway in 3T3-L1 cells. Food Chem Toxicol. (2010) 48:716–21. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2009.12.001
177. Lee HG, Lu YA, Je JG, Jayawardena TU, Kang MC, Lee SH, et al. Effects of ethanol extracts from grateloupia elliptica, a red seaweed, and its chlorophyll derivative on 3T3-L1 adipocytes: suppression of lipid accumulation through downregulation of adipogenic protein expression. Mar Drugs. (2021) 19:91. doi: 10.3390/md19020091
178. Seo YJ, Kim KJ, Choi J, Koh EJ, Lee BY. Spirulina maxima extract reduces obesity through suppression of adipogenesis and activation of browning in 3T3-L1 cells and high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Nutrients. (2018) 10:712. doi: 10.3390/nu10060712
179. Zheng H, You Y, Hua M, Wu P, Liu Y, Chen Z, et al. Chlorophyllin modulates gut microbiota and inhibits intestinal inflammation to ameliorate hepatic fibrosis in mice. Front Physiol. (2018) 9:1671. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01671
180. Stenblom EL, Westrom B, Linninge C, Bonn P, Farrell M, Rehfeld JF, et al. Dietary green-plant thylakoids decrease gastric emptying and gut transit, promote changes in the gut microbial flora, but does not cause steatorrhea. Nutr Metab (Lond). (2016) 13:67. doi: 10.1186/s12986-016-0128-4
181. Zhang L, Shi M, Ji J, Hu X, Chen F. Gut microbiota determines the prevention effects of Luffa cylindrica (L.) Roem supplementation against obesity and associated metabolic disorders induced by high-fat diet. FASEB J. (2019) 33:10339–52. doi: 10.1096/fj.201900488R
182. Ren Z, Li Y, Liu J, Li H, Li A, Hong L, et al. Coreopsis tinctoria modulates lipid metabolism by decreasing low-density lipoprotein and improving gut microbiota. Cell Physiol Biochem. (2018) 48:1060–74. doi: 10.1159/000491973
183. Lee PS, Teng CY, Kalyanam N, Ho CT, Pan MH. Garcinol reduces obesity in high-fat-diet-fed mice by modulating gut microbiota composition. Mol Nutr Food Res. (2019) 63:e1800390. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201800390
184. Anhe FF, Roy D, Pilon G, Dudonne S, Matamoros S, Varin TV, et al. A polyphenol-rich cranberry extract protects from diet-induced obesity, insulin resistance and intestinal inflammation in association with increased Akkermansia spp. population in the gut microbiota of mice. Gut. (2015) 64:872–83. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307142
Keywords: plant extracts, obesity, gut microbiota, mechanisms, lipid metabolism
Citation: Weng G, Duan Y, Zhong Y, Song B, Zheng J, Zhang S, Yin Y and Deng J (2021) Plant Extracts in Obesity: A Role of Gut Microbiota. Front. Nutr. 8:727951. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.727951
Received: 20 June 2021; Accepted: 10 August 2021;
Published: 23 September 2021.
Edited by:
Yangchun Cao, Northwest A&F University, ChinaReviewed by:
Shanlin Ke, Harvard Medical School, United StatesCopyright © 2021 Weng, Duan, Zhong, Song, Zheng, Zhang, Yin and Deng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yehui Duan, ZHVhbnllaHVpQGlzYS5hYy5jbg==; Jinping Deng, ZGVuZ2ppbnBpbmdAc2NhdS5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.