
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Nutr. , 15 July 2020
Sec. Clinical Nutrition
Volume 7 - 2020 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2020.00086
This article is part of the Research Topic Ageing-Related Symptoms, Kampo Medicine and Treatment View all 16 articles
With the continued growth of the aging population in Japan, geriatric syndrome (GS), which is associated with aging-related symptoms, has become a social problem. GS is caused by physiological and pathological aging and may manifest various symptoms. Physicians use multidisciplinary approaches to provide treatment for individual GS symptoms. Kampo medicine, a Japanese traditional medicine that uses multiple pharmacologically active substances, is useful for many syndromes, conditions, disorders, and diseases associated with GS. Evidence of the effectiveness of Kampo medicine for GS has accumulated in recent years. The effects of Kampo treatment for symptoms related to functional decline of the cardiovascular, respiratory, and digestive systems, cognitive impairment and related disorders, pain and other sensory issues, among others, support the use of Kampo medicine for the management of GS. The role of Kampo medicine for GS is summarized in this review.
Geriatric syndrome (GS) is a well-known clinical entity characterized by symptoms highly prevalent in old age. It presents with multiple contributing factors, including physiological aging, and requires a multidisciplinary approach. When compared to the “disease” entity, the differences in features are unknown etiology and inclusion of physiological aging as a cause (1). There is no universal definition of GS; there are some variations in the features included in GS definitions. These variations in definition lead to ambiguity regarding the included symptoms. Originally, GS symptoms were expressed as the 3Ms (mentality, micturition, and mobility) or 4Is (immobility, instability, impaired cognition, and incontinence—also named the “geriatric giants”) (2). Today, 20 or more symptoms are listed (3). The majority of GS symptoms emerge slowly and are chronic, with a low risk of mortality by themselves. Consequently, they tend to be overlooked as physiological changes, resulting in increased dependency. GS is clinically significant as a warning sign for the risk of increased care dependency. When determining countermeasures for GS, we must exclude the possibility of a single cause before considering multifactorial etiology (3, 4) (e.g., endocrine disorders) (5). Then, we must exclude medication-related side effects (6).
Kampo medicine is effective in many cases of GS with multiple causes. Original GS symptoms (such as symptoms related to functional decline of the cardiovascular, respiratory, and digestive systems; cognitive impairment and related disorders; and pain and other sensory issues) are considered treatment targets. Because of the multifactorial nature of GS and specialization in medicine, care for those with GS tends to be fragmented. Kampo medicine could prevent fragmentation of patient care.
On the other hand, medical expenses amounted to more than one third of social security expenses in 2018 (7). With the growing “super-aging” society and the declining birth rate in Japan, medical expenses are only expected to increase. In light of these points, we have herein summarized the efficacy, safety, and social economic advantage associated with the use of Kampo medicine for GS.
In this review, we summarize randomized controlled trials (RCTs) for GS. When no RCT was available for specific conditions or disorders, some observational studies were described. Details of each Kampo medication are listed on the Standards of Reporting Kampo Products (STORK) website (http://mpdb.nibiohn.go.jp/stork/) (8). The names of Kampo medicines were abbreviated according to the Japan Society of Oriental Medicine (9).
Generally, cardiovascular disease and related disorders increase with age. The Japanese lifestyle has shifted toward a Western lifestyle; thus, cardiovascular disease has increased in the last half century. Western medications are commonly used to control hypertension and related diseases; furthermore, they have been shown to effectively suppress cardiovascular events. A few clinical trials have been conducted on Kampo medicine for the treatment of cardiovascular disease and related symptoms. Overall, these RCTs were conducted to manage symptoms difficult to control in Western medicine. Soft endpoints were the improvement of accessory symptoms of hypertension, orthopedic hypotension related to diabetes mellitus, and edema according to deep vein thrombosis of the lower limb (Table 1).
Arakawa et al. conducted a double-blinded (DB) RCT on orengedokuto (OGT) for the treatment of accessory symptoms of hypertension; the study included elderly subjects (10). Efficacy was significantly higher in the OGT group based on the total score for the accessory symptoms of hypertension; sub-analysis showed the efficacy to be higher for hot flashes and facial suffusion in the OGT group. However, there were no significant differences between the OGT and placebo groups regarding the decrease of blood pressure or the antihypertensive effect.
Nakamura et al. reported the efficacy of goreisan (GRS) for orthopedic hypotension related with diabetes mellitus in an RCT that included elderly subjects (11). The change in orthopedic systolic and diastolic pressure was significantly lower in the GRS group than in the placebo group. All patients complained of dizziness in the placebo group, but only 10% complained of the symptom in the GRS group.
Uchida reported the effect of keishibukuryogan (KBG) for edema according to deep vein thrombosis of the lower limb in an RCT of elderly subjects (12). The improvement rates of circumference difference between the affected and the normal limbs were significantly higher in the KBG group than in the conventional treatment group.
Respiratory disease is increasing with the aging of society. Kampo medicine has been effective at treating acute respiratory infection, and there are some reports that Kampo medicine has a prophylactic effect in aspiration pneumonia and acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (Table 2).
Pneumonia is one of the leading causes of death in the elderly. Therefore, preventing pneumonia, including aspiration pneumonia, is very important. Aspiration pneumonia occurs frequently in patients with cerebrovascular disease, patients with neurodegenerative disease, and bedridden patients with dysphagia and depression of swallowing and cough reflex. Patients with swallowing or coughing impairment have low levels of substance-P in their saliva (13, 14). Substance-P is a neuropeptide that plays an important role in swallowing and cough reflexes (13). Table 2A shows studies of Kampo medicine for aspiration pneumonia.
Iwasaki et al. reported that hangekobokuto (HKT) improves swallowing reflex and increases salivary levels of substance-P in patients who had a stroke (15). They also reported that HKT improves swallowing reflex in patients with Parkinson's disease despite no significant changes in their salivary levels of substance-P (16). Iwasaki et al. also showed that HKT improves cough reflex of patients with cerebral atrophy and lacunar infarction (17), reduces the risk of aspiration pneumonia in the elderly, and maintains self-feeding capacity better than the control (18). Additionally, Kawago et al. reported that HKT prevents aspiration pneumonia in patients after cardiovascular surgery (19). HKT is thought to act via regulation of the cerebral levels of 5-hydroxytryptamine, noradrenaline, and dopamine (20). Impairment of the swallowing reflex correlates strongly with decreased dopamine levels in the basal ganglia (21). Therefore, HKT-induced improvement of swallowing reflex may be associated with HKT-induced increase in brain dopamine levels. Hochuekkito (HET) is another Kampo formula for prevention of aspiration pneumonia. Tamano et al. reported that administration of HET, alone or in combination with rehabilitation, reduces the number of hospitalizations due to aspiration pneumonia (22, 23). HET also improves clinical symptoms such as appetite loss and general malaise, increases body weight and serum albumin, and increases temperature in patients with low body temperature. Mantani et al. reported that seihaito (SHT), added to conventional treatment, decreases the mean values of fever, C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, and antibiotics use compared with conventional therapy alone (24). However, SHT does not improve the latency of swallowing reflex. This study indicated that SHT has an anti-inflammatory effect in patients with recurrent aspiration pneumonia but does not improve swallowing reflex. Iwasaki et al. reported that xanthine oxidase activity in lung tissues is elevated in a mouse model of aspiration pneumonia and that SHT is able to reverse this elevation (25). The authors speculated that SHT pretreatment can reduce oxygen radical production in inflamed lungs. Dysphagia is also considered to relate to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
COPD does not affect solely the airways; it is considered a systemic inflammation. The treatment guidelines for COPD recommend the use of bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and rehabilitation. One of the main goals of COPD treatment is to prevent acute exacerbation, which is known to affect patient prognosis. Table 2B shows an RCT of Kampo medicine for COPD.
Among Kampo medications, bakumondoto (BAK) and SHT have been shown to improve the symptoms of COPD. Sasaki et al. reported that BAK significantly helps loosen phlegm of patients with chronic respiratory disease (26). Mukaida et al. showed that BAK significantly improves visual analog scale (VAS) scores for cough frequency, but not for cough intensity (27). Kato et al. reported that administration of SHT improves the clinical symptoms of COPD (28). BAK is thought to exert a peripheral antitussive effect by inhibiting the synthesis or release of nitric oxide (29). According to the traditional theory, BAK should be used for patients with dry cough and SHT for patients with productive cough.
Shinozuka et al. and Tatsumi et al. reported that HET reduces the number of common cold and acute exacerbation episodes in patients with COPD (30, 31). HET decreased serum CRP, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and interleukin-6 levels and increased serum prealbumin levels. Furthermore, HET resulted in a significant increase in body weight over 6 months and a decrease in St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire score, indicating an improvement in quality of life (QOL). HET has antiviral and anti-inflammatory effects, thus contributing to preventing exacerbation (32). Jo et al. reported that daikenchuto (DKT) reduces exacerbation in patients with COPD (33). Patients treated with DKT had a significantly lower risk of rehospitalization or death after discharge. By improving bowel movements and tolerance to muscarinic antagonists, DKT improves the respiratory status of patients with COPD. Recently, there have been a few DB-RCTs on traditional Chinese medicine for patients with COPD (34–36). In the majority of the studies, crude drugs added to the conventional therapy prevented recurrence of acute exacerbation.
Kampo medicine was developed to control and maintain the function of the digestive system. It is used to enhance motility in the gastrointestinal tract and promote digestion. Kampo medicine has recently been used for early recovery from surgical intervention, especially for elderly patients receiving cancer treatment. RCTs have explored the use of Kampo medicine for constipation, perioperative symptoms, and conditions in the gut, functional dyspepsia (FD), GERD, and nonerosive reflux disease (NERD) (Table 3). After development of a placebo of these Kampo medicines, DB-RCTs using DKT or rikkunshito (RKT) were conducted. RCTs showed that DKT can be used for preventing postoperative ileus, improving bowel movement in the early days, improving QOL, having anti-inflammatory effects, improving early oral intake, enhancing total oral/enteral caloric intake and portal venous flow volume, and minimizing weight loss after abdominal surgery in the perioperative stage. RCTs showed that RKT can be used for improving upper gastric symptoms (globus sensation, delayed gastric emptying, abdominal bloating, heavy feeling in the stomach, sick feeling after meals, heartburn after meals, and epigastric pain), psychological symptoms, appetite loss, acyl ghrelin levels, and a low body mass index in FD, GERD, and NERD. Table 3A shows an RCT of Kampo medicine for FD and GERD.
Tominaga et al. reported the effects of RKT administration on FD and its correlation with anxiety (37). RKT increased the overall treatment efficacy and improved upper gastrointestinal symptoms, especially postprandial fullness/early satiety and bloating. Improvement of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale was correlated with that of the Patient Assessment of Upper Gastrointestinal Disorders–Symptom Severity Index, the Global Overall Symptom scale, and the modified Frequency Scale for the Symptoms of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (postprandial fullness/early satiety, dyspepsia, and postprandial distress syndrome). This suggests that RKT may be beneficial for patients with FD to simultaneously treat gastrointestinal and psychological symptoms. Tominaga et al. also studied the use of RKT for patients with NERD refractory to proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) in a DB-RCT that included elderly subjects (38). The mental component summary scores improved more in the RKT group than in the control group, especially in patients with a low body mass index, and significantly improved the acid-related dysmotility symptoms in female and elderly patients. Sakata et al. reported additional analysis of this study (39). Especially in the elderly, the degrees of improvement in the total and acid-related dysmotility symptom scores were significantly greater in the RKT group. Combination therapy with RKT led to significant improvement in abdominal bloating, heavy feeling in the stomach, sick feeling after meals, and heartburn after meals. Kato et al. reported that HKT significantly improved respiratory symptoms associated with GERD (40). Suzuki et al. reported the efficacy and safety of RKT for FD in a DB-RCT that included elderly subjects (41). Administration of RKT reduced dyspepsia, particularly the symptoms of epigastric pain and postprandial fullness. Among the patients positive for Helicobacter pylori, RKT improved acyl ghrelin levels. In a DB-RCT, Hayakawa et al. reported the effects of RKT on enteral feeding and plasma ghrelin levels in critically ill elderly patients (42). The RKT group reached 50% of the target amount of enteral feeding significantly earlier than the metoclopramide group. RKT increased the plasma level of active ghrelin. Tokashiki et al. reported the effects of RKT on the globus sensation in patients with PPI-refractory laryngopharyngeal reflux in an RCT that included elderly subjects (43). RKT or RKT with PPI significantly decreased the globus sensation and improved delayed gastric emptying. A significant positive correlation was found between improvements in the globus sensation and gastric emptying. Tominaga et al. reported the efficacy of RKT for patients with GERD refractory to treatment with PPI in a DB-RCT that included patients from 20 to 90 years of age (44). RKT combined with PPI significantly decreased the frequency scale of the GERD symptoms' score, similar to the decrease seen after treatment with a double dose of PPI. Subgroup analysis showed that the improvement rate of male NERD patients in the RKT group was significantly greater. Subgroup analysis also showed that the patients of male sex or with a low body mass index showed more improvement than other subgroups. Furthermore, no adverse events were observed in this study. Additional RKT therapy for patients with GERD refractory to PPI treatment seemed to be more effective for NERD, male, or low-body mass index patients, and the therapy was shown to be safe. Arai et al. reported a significant improvement in dyspeptic symptoms in patients treated with either RKT or domperidone (45). The improvements of reflux and indigestion symptoms in patients treated with RKT showed good correlations with the increased levels of acylated ghrelin. Harasawa et al. conducted a DB-RCT on RKT for the treatment of dysmotility-like dyspepsia in elderly subjects (46). The regular dose of RKT improved dysmotility-like dyspepsia significantly more than the low dose of RKT. Tatsuta et al. reported the effects of RKT on gastric emptying and gastrointestinal symptoms in dyspeptic patients (47). Gastric emptying was significantly accelerated, and gastrointestinal symptoms were significantly reduced in patients treated with RKT. Miyoshi et al. examined the effects of RKT for complaints related to gastrointestinal function in an RCT that included elderly subjects (48). RKT significantly improved the symptoms of appetite loss, epigastric pain, abdominal discomfort, cold feelings of the limb, and dazzling when compared with cisapride. In a subanalysis, RKT was more effective in patients over 60 years of age, with a thin type body, and with water retention.
Table 3B shows an RCT of Kampo medicine for constipation. Numata et al. reported the efficacy of DKT for functional constipation in elderly patients after stroke (49). Constipation scoring system points, especially the frequency of bowel movements, feeling of incomplete evacuation, and need for an enema/disimpaction, improved significantly with the addition of DKT. The gas volume score also significantly reduced with the addition of DKT. Arita et al. performed a responder analysis of DKT treatment for constipation in poststroke patients (50). The total neurogenic bowel dysfunction score and Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS)-constipation subscale score were significantly reduced after DKT administration. The total neurogenic bowel dysfunction score, GSRS-constipation subscale score, and gas volume score at baseline were significantly correlated with the change in these scores, suggesting that higher scores in these categories and a higher gas volume in the gut may be predictors of response to DKT. Horiuchi et al. reported the effect of DKT in patients with chronic constipation in an RCT that included elderly subjects (51). The addition of DKT to sennoside resulted in a significant improvement in bloating and abdominal pain and a significant decrease in the gas volume score comparing a regular dose and a half dose of DKT. Miyoshi et al. reported the effect of daiokanzoto (DKZT) in patients with chronic constipation in an RCT that included elderly subjects (52). DKZT was significantly more effective for constipation than the placebo. A regular dose of DKZT has a strong effect on some patients; as such, the dose should be determined considering the patient's condition.
Table 3C shows an RCT of Kampo medicine for the perioperative period. Nishino et al. reported the effects of DKT after esophageal cancer resection in an RCT that included elderly subjects (53). The rate of weight loss at postoperative day 21 was significantly suppressed in the DKT group. Postoperative bowel symptoms tended to be rare, and the serum CRP level at postoperative day 3 tended to be lower in the DKT group. This suggests that DKT treatment after esophageal cancer resection may promote the recovery of gastrointestinal motility and minimize weight loss; it may also suppress the excess inflammatory reaction related to surgery. In a DB-RCT, Katsuno et al. reported the effect of DKT on elderly patients with colon cancer undergoing open surgery by transit analysis using radiopaque markers (54). The number of radiopaque markers in the anal side of the small intestine at 6 h was significantly greater in the DKT group. This suggests that DKT may contribute to early oral intake in the postoperative course. Okada et al. examined the efficacy of DKT for the prevention of paralytic ileus after pancreaticoduodenectomy in a DB-RCT of elderly patients (55). Perioperative treatment with DKT neither decreased the incidence of clinically relevant postoperative paralytic ileus nor shortened the time to the first postoperative flatus, suggesting that DKT may preclude the routine use of DKT in clinical practice after this operation. Akamatsu et al. reported the effects of DKT on intestinal motility after total gastrectomy in an RCT that included elderly subjects (56). DKT significantly improved the number of stools per day, stool consistency, and gas volume scores. This suggests that DKT promoted early postoperative bowel functions after total gastrectomy. In a DB-RCT, Katsuno et al. reported the clinical efficacy of DKT for gastrointestinal dysfunction following colon surgery in elderly patients (57). Bowel movement frequency in the DKT group at postoperative day 8 was significantly lower than that in the placebo group, suggesting that the moderate effects of DKT were observed in the early days after the operation. In a DB-RCT, Yoshikawa reported the effects of DKT after total gastrectomy for gastric cancer in elderly patients (58). DKT administration shortened the median time to the first bowel movement and resulted in fewer gastrointestinal dysfunctions on postoperative day 12. This suggests that DKT administration in the immediate postoperative period after total gastrectomy promotes early recovery of postoperative bowel function. Yaegashi et al. reported the effects of DKT on colonic motility after laparoscopic-assisted colectomy in elderly colon cancer patients (59). The DKT group had a significantly faster time until the first flatus and bowel movement and colonic transit time. This suggests DKT accelerates colonic motility in patients undergoing laparoscopic-assisted colectomy for colon cancer. Yoshikawa et al. reported the effects of DKT on the surgical inflammatory response following laparoscopic colorectal resection in an RCT that included elderly subjects (60). Postoperative DKT administration significantly suppressed the CRP level and shortened the time until first flatus. This suggests that DKT has anti-inflammatory effects and may help patients recover following surgery. Takahashi et al. reported the effects of RKT on the stasis of patients after pylorus-preserving gastrectomy in a crossover RCT that included elderly patients (61). RKT significantly reduced gastric stasis-related symptoms and improved emptying of solid meals from the remnant stomach. Endo et al. reported the effect of DKT on the stasis of patients with total gastrectomy and jejunal pouch interposition in a crossover RCT that included elderly subjects (62). DKT significantly reduced stasis-related symptoms. In the emptying test, DKT significantly accelerated emptying of both liquid and solid meals from the pouch. The pouch showed bursts of contractions, which were increased significantly by oral intake of DKT. This suggests that DKT increased intestinal motility and improved the QOL of patients with this condition. Itoh et al. reported the effects of DKT on postoperative ileus in an RCT that included elderly subjects (63). The need for further surgery was significantly reduced in patients receiving DKT. Patients receiving DKT also showed a lower tendency for recurrent ileus than those receiving the placebo. Takagi et al. reported the effects of DKT on paralytic ileus after repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm in elderly subjects (64). DKT administration significantly reduced intestinal gas. Kubo et al. reported the effects of DKT on ileus in an RCT that included elderly subjects (65). The duration to defecation, exhaust gas, and ileus tube removal did not differ significantly between the DKT and control groups. However, DKT administration reduced abdominal boating, nausea, and vomiting.
Kaido et al. reported the effect of DKT on oral and enteral caloric intake after liver transplantation in a DB-RCT that included elderly subjects (66). Postoperative total oral/enteral caloric intake was significantly accelerated in the DKT group. Portal venous flow volume and velocity were significantly higher in the DKT group. This suggests that postoperative administration of DKT may enhance total oral/enteral caloric intake and portal venous flow volume and velocity after liver transplantation and favorably contribute to the performance of the Enhanced Recovery After Surgery protocol. Shimada et al. reported the effect of DKT administered after hepatic resection in elderly patients with liver cancer (67). DKT improved gastrointestinal dysmotility and reduced serum CRP levels in patients with grade B liver damage after hepatectomy. This suggests that DKT is an effective and safe treatment option after hepatic resection in patients with liver cancer. Masaki et al. also reported the effect of DKT in patients who underwent hepatic resection. DKT significantly decreased the levels of CRP and beta-(1–3)-D-glucan on postoperative day 3. DKT significantly shortened postoperative periods for the first flatus, bowel movement, and full recovery of oral intake (68). Takahashi et al. reported the effect of DKT in patients with liver resection. DKT significantly lowered postoperative serum ammonia levels with low occurrence of diarrhea (69).
Table 3D shows an RCT of Kampo medicine for other conditions and symptoms related with the digestive system. Bessho et al. reported the effectiveness of saibokuto (SBT) for patients with glossodynia in an RCT that included elderly subjects (70). When compared with diazepam with vitamin B complex, SBT significantly reduced the symptoms of pain, burning sensation, and discomfort.
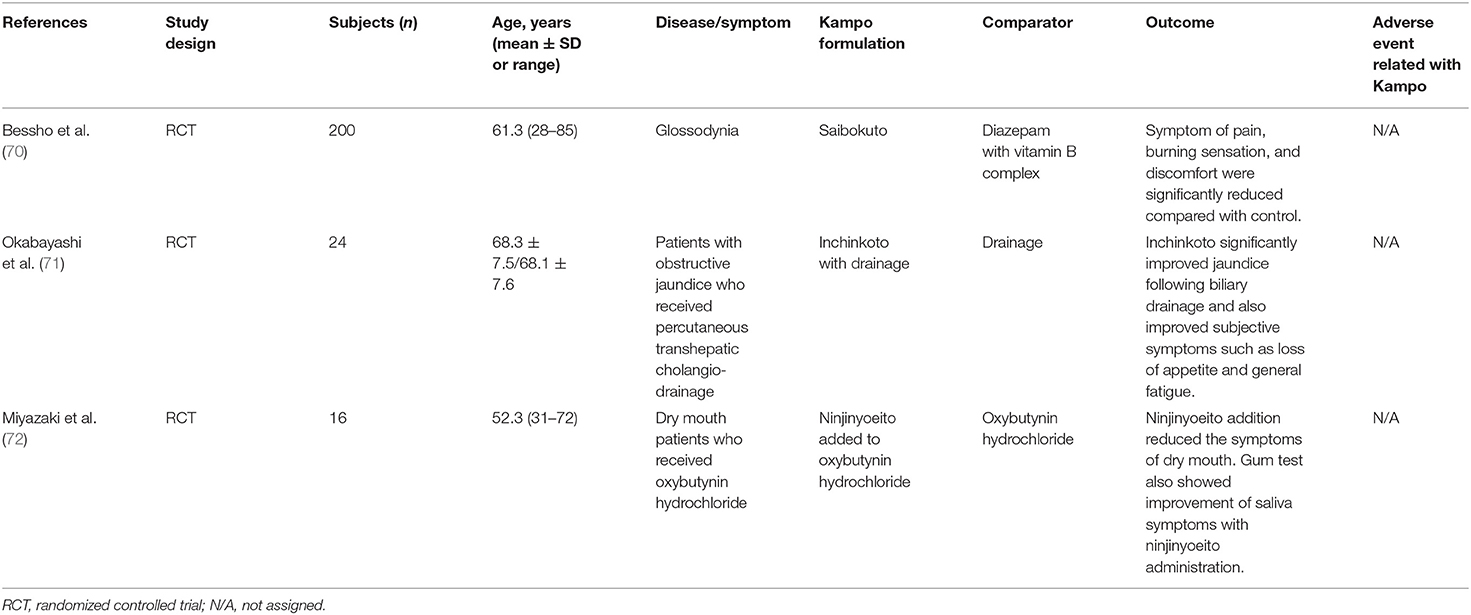
Table 3D. RCT of Kampo medicine for other conditions and symptoms related with the digestive system.
In an RCT, Okabayashi et al. reported the effects of inchinkoto (ICKT) on the bilirubin reduction rate after biliary drainage in elderly patients with obstructive jaundice (71). ICKT significantly improved jaundice following biliary drainage and also improved subjective symptoms such as loss of appetite and general fatigue. Miyazaki et al. reported the efficacy of ninjinyoeito (NYT) for dry mouth induced by oxybutynin hydrochloride to treat psychogenic frequency or unstable bladder in an RCT that included elderly subjects (72). The addition of NYT reduced the symptom of dry mouth in 75% of patients. Saliva secretion also improved after NYT addition.
Dementia has become a global health issue. The number of people living with dementia in the world was estimated to be 46.8 million in 2015 (73). Japan has one of the most rapidly aging societies; the prevalence of dementia was already beyond 3% (five million) in 2015, and it has been increasing, even though the Japanese population has begun to decline (74). This situation might drive doctors to conduct a number of clinical studies using Kampo medicine for the symptoms of dementia. Dementia is a syndrome associated with declines in memory, thinking, behavior, and the ability to perform daily activities. Cognitive disorders and noncognitive symptoms, that is, behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia (BPSD), are equally important clinical manifestations. Kampo medications are composed of multiple herbal ingredients and have different target symptoms. Therefore, based on the current clinical evidence, we herein introduce some Kampo medications and their target symptoms (Table 4).
Chotosan (CTS) was originally used for headache, tinnitus, and dizziness. In 1994, Shimada et al. conducted a multicenter placebo-controlled RCT using CTS (75). After 12 weeks of CTS treatment, patients with vascular dementia had a decrease in the score of cognitive dysfunctions (Hasegawa's Dementia Scale-Revised) when compared to baseline. CTS was superior to the placebo in the global improvement rating, utility rating, global rating for subjective symptoms, subjective symptoms (shoulder stiffness and palpations), global rating for psychiatric symptoms, psychiatric symptoms (decline in interest in television or books and lack of facial expression), and activities of daily living (ADLs). Terasawa et al. conducted another placebo-controlled RCT using CTS for vascular dementia (76). When compared with the placebo, the global improvement rating, global rating for subjective symptoms, psychiatric symptoms (decline in simple arithmetic ability, global intellectual ability, sleep disturbance, hallucination, and delusion), and ADLs significantly improved after a 12-week administration of CTS. In the study, cognitive dysfunctions did not improve. The overall safety rating did not differ significantly between the chitosan treatment group and the placebo group. Suzuki et al. reported that an 8-week treatment of CTS improved cognitive dysfunction [assessed by the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE)] and ADL when compared to the baseline in patients with Alzheimer's disease; goshajinkigan (GJG) treatment and the placebo did not improve these symptoms (77). In 2017, Imai et al. conducted a meta-analysis of the three above-mentioned RCTs to assess the effectiveness and acceptability of CTS (78). CTS was more effective than the placebo for short-term improvement of cognitive function. The acceptability, measured in terms of the number of dropouts due to adverse effects, did not differ between the CTS treatment group and the placebo group. However, the results are considered imprecise, partly because of the small number of participants. Iwasaki et al. conducted a placebo-controlled DB-RCT using hachimijiogan (HJG), a pill made with herbs and honey, for the treatment of dementia (79). Administration of HJG for 8 weeks significantly improved cognitive dysfunction (assessed by MMSE) and ADL (assessed by the Barthel index) when compared to baseline, while the placebo did not change those scores. No adverse events were observed. Maruyama et al. reported the effectiveness of a combination of donepezil and kamiuntanto on cognitive function and brain perfusion in patients with Alzheimer's disease (80). A 12-week observer-blinded RCT revealed that combination treatment with a donepezil and kamiuntanto decoction significantly improved cognitive function (MMSE and ADAS-cog) when compared with treatment with donepezil alone. Furthermore, cerebral blood flow in the frontal region (measured by single photon emission computed tomography) significantly increased in the combination treatment group. In 2007, Higashi et al. reported the effectiveness of kihito (KHT) extract granules on the cognitive function of patients with Alzheimer's disease (81). The MMSE showed significant improvement 3 months after treatment with KHT, but not in the nontreated or GJG-treated groups. The orientation and attention subscale scores of the MMSE improved significantly in the KHT treatment group when compared with those of the nontreatment group. No adverse events were observed in any of the groups.
Yokukansan (YKS) was originally used in children for the treatment of agitation and crying at night. Starting in the 1980s, when the Japanese society shifted to an aging society, YKS began to be used for the treatment of BPSD. Five RCTs and one meta-analysis have shown the efficacy of YKS for BPSD, especially for delusions, hallucinations, and agitation/aggression. In 2005, Iwasaki et al. firstly conducted a multicenter RCT using YKS for dementia patients (82). A 4-week administration of YKS significantly improved BPSD [assessed by the Neuropsychiatric Inventory (NPI)], especially hallucinations, agitation/aggression, irritability/lability, and aberrant motor activity. YKS also improved ADL (assessed by the Barthel index). In an RCT conducted by Mizukami et al., 88 dementia patients received 4 weeks of YKS treatment and spent another 4 weeks under observation (no treatment) in a crossover design (83). BPSD improved in the YKS treatment period, and no rebound phenomenon was observed in the following observation period. Monji et al. reported that 12 weeks of YKS treatment significantly improved BPSD in patients with Alzheimer's disease (84). The average dose of antipsychotics (sulpiride) tended to be less in the YKS treatment group than in the control group. The Barthel index did not change in the YKS treatment group or the control group. In 2010, Okahara et al. reported the efficacy of 4 weeks of treatment with YKS and donepezil for BPSD in patients with Alzheimer's disease (85). Among the NPI subscales, the agitation and irritability scores decreased significantly. Cognitive dysfunction, ADL, and caregiver burden scores did not change in the YKS treatment group or in the control group. Teranishi et al. reported the efficacy and safety of YKS compared with risperidone and fluvoxamine for BPSD in patients with dementia (86). All three drugs significantly alleviated BPSD, with no significant intergroup differences. The tolerability analysis revealed that adverse effects (constipation, muscle rigidity, and extrapyramidal symptoms) were more frequent in the risperidone treatment group. In 2016, Furukawa et al. conducted a placebo-controlled DB-RCT on patients with Alzheimer's disease (87). Both 4 weeks of YKS treatment and the placebo improved BPSD, with no significant intergroup differences. The subgroup scoring below 20 points on the MMSE at baseline showed a greater improvement in BPSD, especially in agitation/aggregation in the YKS treatment group, when compared to the placebo group. In the subgroup younger than 74 years of age, a significant decrease in the subcategory score for agitation/aggression was shown in the YKS treatment group when compared with the placebo group. In 2016, Matsunaga et al. conducted a meta-analysis of the above-mentioned RCTs using YKS for BPSD in dementia patients (88). YKS significantly decreased total BPSD scores when compared with the controls (placebo or usual care), especially the subscale scores for delusions, hallucinations, and agitation/aggression. However, only in the Alzheimer's disease patients, YKS was not superior to the controls for BPSD. YKS treatment significantly improved ADL when compared with the controls. MMSE scores did not improve in the YKS treatment group or in the control group. Incidence of adverse effects did not differ significantly between the YKS treatment and control groups. Various Kampo formulations are clinically effective for the treatment of dementia. A Kampo medicine may be selected according to the patients' symptoms. Adverse events due to Kampo medicine are not frequent. Therefore, Kampo medicine may be a treatment option for both cognitive dysfunction and BPSD.
In elderly individuals, physical, psychological, and social changes cause various types of chronic pain. Western analgesic medications are used as the basic approach for pain relief; however, modulation of organ systems and pharmacokinetics often induce adverse effects in aging patients. Furthermore, chronic pain often accompanies various symptoms such as coldness, fatigue, and depression. These conditions exacerbate pain and hinder the physical exercise needed to control pain.
Kampo medicine balances the equilibrium of mind and body disturbed due to external and internal factors. As a result, it is possible to relieve pain as well as multiple coexisting symptoms. In Japan, Kampo medicine is empirically assumed to be effective and widely applied for the treatment of pain. However, the suitable formula often differs depending on the patient's personality. This inhibits the performance of large clinical trials; most studies are case reports or case series (Table 5). However, animal studies have recently begun to elucidate the mechanisms of Kampo formulae.
Back pain has a prevalence of 24.4% in the Japanese population over 70 years of age (89). Degenerative spine conditions (spondylosis, spinal stenosis, interval disc disease, etc.) and osteoporosis (OP) induce skeletal deformities, joint imbalance, and tension in muscular structures (90), which lead to chronic musculoskeletal pain.
GJG is used to alleviate symptoms in the lower part of the body associated with aging. Hamaguchi et al. reported the efficacy of routine GJG administration for low back pain (LBP) (91). In a retrospective observational study, LBP improved within 6 months in 10 out of 28 patients. Patients with spinal stenosis were less likely to respond to GJG than those without spinal disease. GJG is expected to relieve LBP in patients without spinal disease. In a retrospective cohort study, Oohata et al. reported the efficacy of Kampo medicine in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis (92). Patients received routine medication with or without Kampo treatment. The frequently used Kampo medicines were GJG, HJG, and shakuyakukanzoto. The rate of reduced and discontinued use of pregabalin and opioid was significantly greater in the Kampo treatment group than in the non-Kampo treatment group. Side effects were observed in 6.3% of patients treated with Kampo medicine and in 62.5% of patients treated without Kampo medicine. Hamaguchi et al. reported the efficacy of Kampo medicine for symptoms in the lower extremities caused by various lumbar spinal diseases (93). In a retrospective observational study, the addition of Kampo medicine to Western medications relieved pain in 53% of patients and relieved coldness in 50% of patients. On the other hand, numbness was improved in only 21% of patients. The effective formulae included shimbuto, keishikajutsubuto (KSTJB), ryokeijutsukanto, and GJG. Coldness is an uncomfortable symptom that exaggerates chronic pain. Takahashi et al. reported the effectiveness and safety of tokishigyakukagoshuyushokyoto (TSGS) for improving coldness with LBP (94). This retrospective observation study showed that 74% of patients were satisfied with the relief from coldness. The VAS significantly decreased from 57.7 ± 11.4 to 43.7 ± 14.1. Routine treatment combined with Kampo medicine may be safer and more effective than treatment using only Western medicines. There are some case reports on back pain. In four case reports, Western treatment involving nerve block could not relieve the pain of geriatric patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. However, Kampo treatment was successful (95–98). In these case reports, some patients were able to avoid surgery. Patients often suffer from residual symptoms after operations for spinal diseases. Ogawa et al. reported a case of postoperative residual pain, coldness, and numbness treated with Kampo medicine (99).
OP-induced fractures result in severe pain. Tetsumura et al. reported a case of multiple OP-induced fractures treated with Kampo medicine (100). KSTJB and other Kampo formulae diminished the suffering of a bedridden patient. The patient was able to stand 11 months after treatment. Nakae et al. performed an RCT to compare the efficacies of jidabokuippo (JDI) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in young and old patients with rib fracture (101). The treatment duration was significantly shorter in the JDI group than in the NSAID group. Furthermore, healthcare expenditure was significantly lower in the JDI group than in the NSAID group.
Osteoarthritis (OA) has a prevalence of 32.5% in the Japanese population over 60 years of age (102). The pain of OA is attributed to unstable joint structure, anatomical degeneration, and inflammation (103). Though standard pharmacotherapy is used for nociceptive pain, it is sometimes ineffective. Boiohito (BOT) is often used for arthritis of the knee. In an RCT, Majima et al. reported the clinical efficacy of BOT on OA of the knee (104). Patients were assigned to the concomitant-use group (both loxoprofen and BOT) and the loxoprofen group (loxoprofen alone). The knee score, based on the Knee Society Rating System and the 36-item short form from the Medical Outcome Study Questionnaire (SF-36), improved in both groups. However, the score for the ability to climb up and down a staircase, based on the Knee Society Rating System functional score and joint fluid, was significantly improved in the concomitant-use group compared to the loxoprofen group.
Bushi is a crude drug with an analgesic effect. In a nonrandomized prospective study, Nakae reported the efficacy and safety of bushimatu (powdered processed aconite root) for the treatment of pain associated with orthopedic disease (105). OA of the knee was the most common orthopedic disease. Patients were administered bushimatu (1.5–8 g/day) with other Kampo formulae without NSAIDs. Patients with ≥50% and ≥25% reductions in VAS accounted 102 and 84 out of 257 patients, respectively, 4 weeks after treatment. Three patients (1.2%) experienced side effects.
Neuropathic pain develops after difficult-to-treat injury of neurons along nociceptive pathways. YKS has a variety of neuropharmacological actions, such as neuroprotection, anti-stress effect, promotion of neuroplasticity, and anti-inflammatory effect (106). Therefore, YKS is sometimes used to treat neuropathic pain. Nakamura et al. reported 11 cases (36–85 years old) of successful treatment of neuropathic pain [postherpetic neuralgia (PHN), central pain, complex regional pain syndrome, and trigeminal neuralgia] using YKS (107). The patients had VAS scores of 17–81 despite Western conventional treatment. The VAS scores decreased to 0–22 after YKS administration for 2 days to 2 months.
PHN is a persisting neuropathic pain syndrome that occurs after resolution of a herpes zoster (HZ) rash. The frequency increases with age, occurring in 20% of people aged 60–65 years and in more than 30% of people aged >80 years who had acute HZ (108). Nakabayashi et al. published a case series on medication combined with KBG and bushimatsu for patients with PHN (2–92 months after HZ onset) (109). The VAS score improvement rate was 76.5 ± 27.7%. However, three of 15 patients could not continue the study due to hot flashes and gastric discomfort. There are some reports of successful PHN treatment with Kampo medicine (110–112). In these reports, patients had suffered from PHN from 2 months to 2 years. From 8 weeks to 4 months after treatment, their symptoms disappeared with Kampo medicine. However, in some cases, pain worsened again when the Kampo medication was discontinued. Radical treatment of PHN may be difficult, but it may be effective if Kampo medication is started during the acute stage of herpes infection.
In elderly people, the prevalence of diabetes increases due to glucose intolerance. Diabetic neuropathy is the most common chronic complication, with an estimated lifetime prevalence exceeding 50% (113). In an RCT, Watanabe et al. reported the efficacy of GJG on the progression of type 2 diabetes complications in middle-aged and older people (114). GJG significantly decreased glycated hemoglobin and progression of neuropathy (ankle reflex) when compared with the control. GJG is also used to prevent and relieve peripheral neuropathy due to chemotherapy (115).
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) represents atherosclerotic disease associated with aging. PAD has a prevalence of 15–20% in the Japanese population over 70 years of age (116). The clinical presentation of a reduction in limb blood flow includes peripheral coldness, atypical leg pain, or intermittent claudication; as it progresses, it may present with ischemic ulcer or critical limb ischemia.
In a prospective study, Kawago et al. reported the efficacy of HJG for improvement of the QOL in patients with PAD (117). The patients were administered HJG for 6 months without any new interventions. The pain score on the Japanese version of the Walking Impairment Questionnaire (WIQ) improved from 25.0 (0.0–50.0) at baseline to 75.0 (68.8–100.0). The absolute change was 37.5 (25.0–75.0). TSGS improved peripheral blood flow and perception of peripheral coldness (118). In a nonrandomized prospective study, Jojima reported the efficacy of TSGS for arteriosclerosis obliterans (ASO) (119). TSGS and cilostazol improved the absolute claudication distance 1 and 3 months after treatment. However, side effects were observed in 4% of patients treated with TSGS, while they were observed in 38% of patients treated without Kampo. One case report has been published regarding Kampo treatment for severe limb pain with ASO (120). A decoction of KBG and daisaikoto relieved pain, coldness, and ischemic ulcers and eliminated the need for limb amputation.
Physical exercise is necessary to improve pain and prevent secondary injuries. However, elderly individuals often cannot take exercise sufficiently due to frailty or sarcopenia.
Hozai is one group of Kampo formulations that restore vitality to patients who have lost psychological and physical energy due to various diseases or aging (121). These formulations improve pain in various conditions induced by sarcopenia and frailty, such as fatigue, anorexia, and mental problems. Sakamoto et al. reported their experience of using Kampo, mainly Hozai formulae (RKT, HET, NYT, etc.) for rehabilitation (122). In a prospective non-RCT, Sakisake et al. reported the efficacy of NYT against frailty (123). Administration of NYT for 24 weeks prevented deterioration of muscle mass and muscle quality score when compared to the control group. Furthermore, the NYT group significantly improved grip strength, whereas there was no change in the control group.
Here, we reviewed RCTs on the efficacy of Kampo medicine for GS. Figure 1 shows the relationship between Kampo medicines and organs and physiological systems. One of the characteristics of Kampo medicine is the use of multiple crude drugs (Table 6). Therefore, Kampo medicine can act upon multiple organs and physiological systems. HET is effective for COPD, nutrition, anti-inflammation, and QOL; RKT for GERD, NERD, FD, and appetite; and DKT for constipation and perioperative conditions. As GS symptoms are expressed by the 3Ms or 4Is, Kampo medicine can contribute to GS.
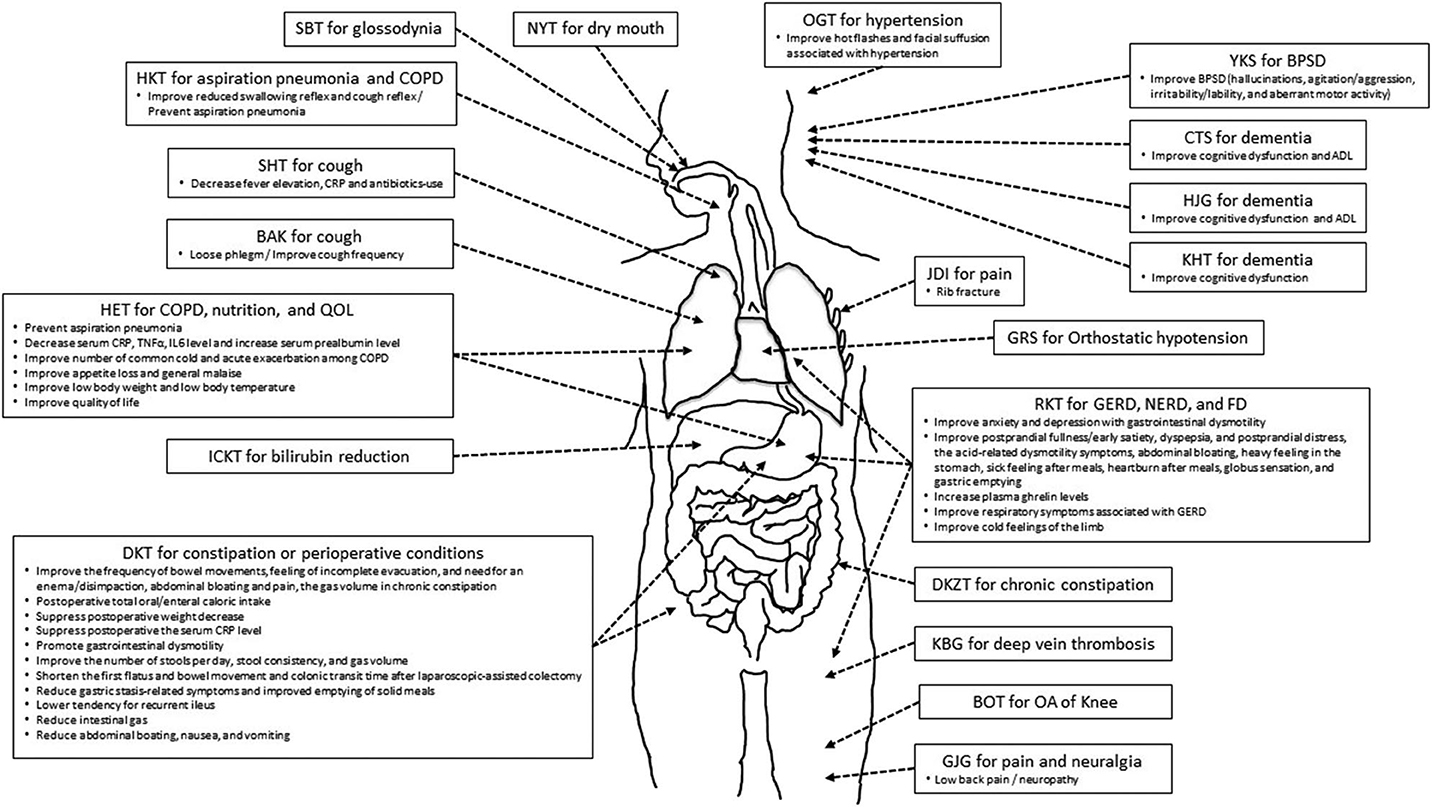
Figure 1. The relationship between Kampo medicines and symptome/condition/disorder in organs and viscera.
The possible mechanisms of Kampo medicines have been reported in recent years. For example, YKS is composed of seven crude drugs (Table 6) and has been used to improve irritation, insomnia, muscle twitching, and pain. Several studies reported various neuropharmacological actions of YKS, namely, on serotonergic, glutamatergic, cholinergic, dopaminergic, adrenergic, and gamma-aminobutyric acidergic neural systems (124). These actions maintain neural signal conduction and neuronal function of neurons as well as glial cells (125). GJG is composed of 10 crude drugs and has been used to alleviate various types of age-related conditions, including muscle weakness of the lower limbs, dysuria, foot edema, and cold sensation of the lower limbs. Recently, GJG is used to prevent and relieve various types of peripheral neuropathy. GJG has antinociceptive effects via increasing produced nitric oxide (126), reduces hypersensitivity by suppressing the overexpression of TRPM8 and TRPA1 mRNA (127), and ameliorates allodynia via the suppression of TNF-α expression in the spinal cord (128). Furthermore, GJG has also been reported to suppress sarcopenia via the insulin growth factor-1/insulin pathway, maintains the expression of mitochondrial-related transcription factors, and suppresses the expression of TNF-α (129).
DKT is composed of four crude drugs and has been used to treat abdominal pain and abdominal bloating with abdominal coldness. DKT treats abdominal symptoms by enhancing the secretions of motilin (130), substance-P, calcitonin gene-related peptide, and adrenomedullin (131–133) and activating the transient receptor potential of the vanilloid receptor complex (134). RKT is composed of eight crude drugs and has been used to treat appetite loss, upper abdominal discomfort, and indigestion. A recent study reported that RKT increases plasma ghrelin levels in humans and mice (135) and restores decreased plasma ghrelin levels induced by serotonin release in rats. HKT is composed of five crude drugs and has been used for pharyngeal discomfort. It has been reported that HKT modulates cerebral levels of 5-hydroxytryptamine, noradrenaline, and dopamine in mice (20).
The efficacy and safety of Kampo medicine were investigated in several clinical studies. Based on these reports, clinical practice guidelines have recommended Kampo medicines for symptoms in geriatrics. Our previous study (136), conducted between January 1, 2012, and October 31, 2017, showed that the Clinical Practice Guideline for the Pruritus Cutaneous Universalis (137), Practical Guideline for the Management of Allergic Rhinitis in Japan (138), the Japanese Respiratory Society Guidelines for the Management of Cough (139), Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines for GERD (140), Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Functional Dyspepsia (141), Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Irritable Bowel Syndrome (142), Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Chronic Constipation (143), Clinical Guidelines for Overactive Bladder Syndrome (144), and Practice Guideline for Dementia (145) have recommended the use of Kampo medicines for skin symptoms, allergy, cough, gastrointestinal dysfunction, urinary dysfunction, and dementia.
In recent years, the usefulness of Kampo medicine in the clinical setting has been investigated using the diagnosis procedure combination (DPC) inpatient database in Japan (Table 7). A propensity score analysis using DPC is a retrospective investigation; however, the groups of patients with or without intervention can be matched, and the subject number is large. Thus, this method can show the intervention's effect and influence on the social economy. Jo et al. reported a reduction in the exacerbation of COPD in patients of advanced age using DKT (33). DKT users had a significantly lower risk of rehospitalization or death after discharge. Subgroup analysis of long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonist users showed a significant difference in rehospitalization or death, while subgroup analysis of long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonist nonusers showed no significant difference. Yasunaga reported the effects of GRS on reoperation rates after burr-hole surgery for chronic subdural hematoma (146). GRS use was significantly associated with a lower reoperation rate when compared with nonuse. These results suggest that GRS use reduced the need for reoperation after burr-hole surgery for chronic subdural hematoma. Yasunaga et al. also reported effects of DKT on postoperative adhesive small bowel obstruction requiring long-tube decompression (LTD) (147). DKT use was associated with a significantly shorter duration of LTD, a shorter duration between long-tube insertion and discharge, and lower hospital charges when compared with DKT nonuse. This suggests that DKT effectively reduces the duration of LTD and saves costs.
Not only the efficacy but also adverse drug reactions (ADRs) were reported in RCTs of Kampo medicine (148). The total incidence of ADRs was 2.47%, and those of pseudoaldosteronism and liver disorders caused by Kampo medicine were 0.02 and 0.16%, respectively. In our previous study, the incidence of ADRs was 0.09% for BAK, 0.44% for DKT, 2.04% for RKT, 1.7% for GJG, 3.45% for HET, 3.34% for CTS, 4.41% for NYT, and 5.17% for YKS. Many of the ADRs were gastrointestinal disorders.
Due to an increase in Japan's “super-aging population” and a decline in the country's birth rate, medical expenses are expected to increase and pose an important problem. Furthermore, medical expenses have grown every year. This review has shown the efficacy, safety, and the social and economic advantages associated with Kampo treatment.
ST designed this report. ST, NT, RO, RA, and AK collected and selected the articles and wrote the manuscript. TI revised the manuscript.
ST, AK, and TI belong to the Department of Kampo and Integrative Medicine at Tohoku University School of Medicine. The department received a grant from Tsumura, a Japanese manufacturer of Kampo medicine; however, the grant was used as per Tohoku University rules. Potential conflicts of interests were addressed by the Tohoku University Benefit Reciprocity Committee and were managed appropriately.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
BAK, Bakumondoto; BOT, Boiogito; CTS, Chotosan; DKT, Daikenchuto; DKZT, Daiokanzoto; GRS, Goreisan; GJG, Goshajinkigan; HJG, Hachimijiogan; HKT, Hangekobokuto; HET, Hochuekkito; ICKT, Inchinkoto; JDI, Jidabokuippo; KBG, Keishibukuryogan; KHT, Kihito; NYT, Ninjinyoeito; OGT, Orengedokuto; RKT, Rikkunshito; SBT, Saibokuto; SHT, Seihaito; YKS, Yokukansan.
1. Inouye SK, Studenski S, Tinetti ME, Kuchel GA. Geriatric syndromes: clinical, research, and policy implications of a core geriatric concept. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2007) 55:780–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2007.01156.x
2. Morley JE. A brief history of geriatrics. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2004) 59:1132–52. doi: 10.1093/gerona/59.11.1132
3. Walston JD. Geriatric syndromes in clinical practice. In: Michel JP, Beattie L, Martin FC, Walston JD, editors. Oxford Textbook of Geriatric Medicine, Third Edition. Oxford: Oxford University Press (2018).
4. Schwab WS. Geriatric syndromes. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2008) 56:363–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2007.01488.x
5. Nanao M, Kojima T, Yamaguchi Y, Ogawa S, Akishita M. An elderly man with rapidly progressive depression and activities of daily living decline: case report of late-onset hypogonadism syndrome. Geriatr Gerontol Int. (2015) 15:1098–9. doi: 10.1111/ggi.12502
6. Stevenson JM, Davies JG, Martin FC. Medication-related harm: a geriatric syndrome. Age Ageing. (2019) 49:7–11. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afz121
7. Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare in Japan. Trends in Medical Expenses. Tokyo: Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (2020). Available online at: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/topics/medias/year/18/index.html. Japanese.
8. STORK (2018). Available online at: http://mpdb.nibiohn.go.jp/stork/
9. Hagihara K, Abbreviation of Kampo Formulations Group, Yakubo S, Committee for Vocabulary in the Japan Society for Oriental Medicine, Namiki T, Makino T, et al. Abbreviation of kampo formulations and basic terminology in kampo medicine. Trad Kampo Med. (2017) 4:65–88. doi: 10.1002/tkm2.1078
10. Arakawa K, Saruta T, Abe K, Iimura O, Ishii M, Ogihara T, et al. Improvement of accessory symptoms of hypertension by TSUMURA Orengedokuto Extract, a four herbal drugs containing Kampo-Medicine Granules for ethical use: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Phytomedicine. (2006) 13:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2004.02.012
11. Nakamura H, Nakamura T, Nakagawa S, Aizawa Y. Efficacy of goreisan in treatment of orthostatic hypotension in patients with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Frontier. (2000) 11:561–3.
12. Uchida N. A randomized controlled trial of the Chinese herbal medicine keisi-bukuryo-gan (gui-zhi-fu-ling-wan) in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis. Jpn J Phlebol. (2009) 20:1–6.
13. Nakagawa T, Ohrui T, Sekizawa K, Sasaki H. Sputum substance P in aspiration pneumonia. Lancet. (1995) 345:1447. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(95)92638-0
14. Sasaki H, Sekizawa K, Yanai M, Arai H, Yamaya M, Ohrui T. New strategies for aspiration pneumonia. lntern Med. (1997) 36:851–5. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.36.851
15. Iwasaki K, Wang Q, Nakagawa T, Suzuki T, Sasaki H. The traditional Chinese medicine banxia houpo tang improves swallowing reflex. Phytomedicine. (1999) 6:103–6. doi: 10.1016/S0944-7113(99)80043-9
16. Iwasaki K, Wang Q, Seki H, Satoh K, Takeda A, Arai H, et al. The effects of the traditional Chinese medicine, “Banxia Houpo Tang (Hange-Koboku To)” on the swallowing reflex in Parkinson's disease. Phytomedicine. (2000) 7:259–63. doi: 10.1016/S0944-7113(00)80042-2
17. Iwasaki K, Cyong JC, Kitada S, Kitamura H, Ozeki J, Satoh Y, et al. A traditional Chinese herbal medicine, banxia houpo tang, improves cough reflex of patients with aspiration pneumonia. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2002) 50:1751–2. doi: 10.1046/j.1532-5415.2002.50479.x
18. Iwasaki K, Kato S, Monma Y, Niu K, Ohrui T, Okitsu R, et al. A pilot study of banxia houpu tang, a traditional Chinese medicine, for reducing pneumonia risk in older adults with dementia. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2007) 55:2035–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2007.01448.x
19. Kawago K, Nishibe T, Shindo S, Inoue H, Motohashi S, Akasaka J, et al. A double-blind randomized controlled trial to determine the preventive effect of hangekobokuto on aspiration pneumonia in patients undergoing cardiovascular surgery. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. (2019) 25:318–25. doi: 10.5761/atcs.oa.19-00128
20. Kaneko A, Cho S, Hirai K, Okabe T, Iwasaki K, Nanba Y, et al. Hange-koboku-to, a Kampo medicine, modulates cerebral levels of 5-HT (5-hydroxytryptamine), NA (noradrenaline) and DA (dopamine) in mice. Phytother Res. (2005) 19:491–5. doi: 10.1002/ptr.1669
21. Nakagawa T, Sekizawa K, Arai H, Kikuchi R, Manabe K, Sasaki H. High incidence of pneumonia in elderly patients with basal ganglia infarction. Arch Intern Med. (1997) 157:321–4. doi: 10.1001/archinte.157.3.321
22. Tamano M, Kato S, Okamura A, Ozone S, Hoshino T, Takahashi S. Clinical investigation of hochuekkito for prevention of aspiration pneumonia and improvement of QOL in the elderly. Sci Kampo Med. (2016) 40:238–41. Japanese.
23. Tamano M, Kato S, Okamura A, Hoshino T, Takahashi S. Clinical investigation on prevention of aspiration pneumonia and improvement of QOL in the elderly by combined use of hochuekkito and rehabilitation. Kampo and the Newest Study. (2017) 26:53–8. Japanese.
24. Mantani N, Kasahara Y, Kamata T, Sekiya N, Shimada Y, Usuda K, et al. Effect of Seihai-to, a Kampo medicine, in relapsing aspiration pneumonia–an open-label pilot study. Phytomedicine. (2002) 9:195–201. doi: 10.1078/0944-7113-00111
25. Iwasaki K, Wang Q, Satoh N, Yoshida S, Akaike T, Sekizawa K, et al. Effects of qing fei tang (TJ-90) on aspiration pneumonia in mice. Phytomedicine. (1999) 6:95–101. doi: 10.1016/S0944-7113(99)80042-7
26. Sasaki H, Satoh K, Sasaki M, Miyano M, Fujii M, Tezuka M, et al. Usefulness of bakumondoto in senile chronic respiratory disease patients having difficulty in expectoration: comparison with bromhexine hydrochloride preparations. Kampo and Immuno-allergy. (1993) 7:139–45. Japanese.
27. Mukaida K, Hattori N, Kondo K, Morita N, Murakami I, Haruta Y, et al. A pilot study of the multiherb Kampo medicine bakumondoto for cough in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Phytomedicine. (2011) 18:625–9. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2010.11.006
28. Kato S, Matsuda T, Nakajima T, Kaneko N, Iwasaki K. Clinical significance of combination therapy of smoking cessation and the traditional Kampo medicine, “qing fei tang (seihaito)” in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Kampo New Ther. (2005) 14:260–5.
29. Kamei J, Yoshikawa Y, Saito A. Antitussive effect of bakumondoto (mai-men-dong-tang) in guinea-pigs exposed to cigarette smoke. J Tradit Med. (2005) 22:44–8. doi: 10.11339/jtm.22.44
30. Shinozuka N, Tatsumi K, Nakamura A, Terada J, Kuriyama T. The traditional herbal medicine hochuekkito improves systemic inflammation in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2007) 55:313–4. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2007.01057.x
31. Tatsumi K, Shinozuka N, Nakayama K, Sekiya N, Kuriyama T, Fukuchi Y. Hochuekkito improves systemic inflammation and nutritional status in elderly patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2009) 57:169–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2009.02034.x
32. Yamaya M, Sasaki T, Yasuda H, Inoue D, Suzuki T, Asada M, et al. Hochu-ekki-to inhibits rhinovirus infection in human tracheal epithelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. (2007) 150:702–10. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707135
33. Jo T, Michihata N, Yamana H, Sasabuchi Y, Matsui H, Urushiyama H, et al. Reduction in exacerbation of COPD in patients of advanced age using the Japanese Kampo medicine Dai-kenchu-to: a retrospective cohort study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2019) 14:129–39. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S181916
34. Hong M, Hong C, Chen H, Ke G, Huang J, Huang X, et al. Effects of the Chinese herb formula Yufeining on stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Medicine (Baltimore). (2018) 97:e12461. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012461
35. Ma J, Zheng J, Zhong N, Bai C, Wang H, Du J, et al. Effects of YuPingFeng granules on acute exacerbations of COPD: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2018) 13:3107–14. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S170555
36. Guo S, Sun Z, Liu E, Feng J, Fu M, Li Y, et al. Effect of bufei granule on stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomized, double blinded, placebo-controlled, and multicenter clinical study. J Tradit Chin Med. (2014) 34:437–44. doi: 10.1016/S0254-6272(15)30043-1
37. Tominaga K, Sakata Y, Kusunoki H, Odaka T, Sakurai K, Kawamura O, et al. Rikkunshito simultaneously improves dyspepsia correlated with anxiety in patients with functional dyspepsia: a randomized clinical trial (the DREAM study). Neurogastroenterol Motil. (2018) 30:e13319. doi: 10.1111/nmo.13319
38. Tominaga K, Kato M, Takeda H, Shimoyama Y, Umegaki E, Iwakiri R, et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial of rikkunshito for patients with non-erosive reflux disease refractory to proton-pump inhibitor: the G-PRIDE study. J Gastroenterol. (2014) 49:1392–405. doi: 10.1007/s00535-013-0896-9
39. Sakata Y, Tominaga K, Kato M, Takeda H, Shimoyama Y, Takeuchi T, et al. Clinical characteristics of elderly patients with proton pump inhibitor-refractory non-erosive reflux disease from the G-PRIDE study who responded to rikkunshito. BMC Gastroenterology. (2014) 14:116. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-14-116
40. Kato S, Nakajima T, Matsuda T. Efficacy of hangekobokuto for respiratory symptom related with reflex esophagitis. Kampo and newest theray. (2005) 14:333–8. [in Japanese]
41. Suzuki H, Matsuzaki J, Fukushima Y, Suzaki F, Kasugai K, Nishizawa T, et al. Randomized clinical trial: rikkunshito in the treatment of functional dyspepsia–a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Neurogastroenterol Motil. (2014) 26:950–61. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12348
42. Hayakawa M, Ono Y, Wada T, Yanagida Y, Sawamura A, Takeda H, et al. Effects of Rikkunshito (traditional Japanese medicine) on enteral feeding and the plasma ghrelin level in critically ill patients: a pilot study. J Intensive Care. (2014) 2:53. doi: 10.1186/s40560-014-0053-4
43. Tokashiki R, Okamoto I, Funato N, Suzuki M. Rikkunshito improves globus sensation in patients with proton-pump inhibitor-refractory laryngopharyngeal reflux. World J Gastroenterol. (2013) 19:5118–24. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i31.5118
44. Tominaga K, Iwakiri R, Fujimoto K, Fujiwara Y, Tanaka M, Shimoyama Y, et al. Rikkunshito improves symptoms in PPI-refractory GERD patients: a prospective, randomized, multicenter trial in Japan. J Gastroenterol. (2012) 47:284–92. doi: 10.1007/s00535-011-0488-5
45. Arai M, Matsumura T, Tsuchiya N, Sadakane C, Inami R, Suzuki T, et al. Rikkunshito improves the symptoms in patients with functional dyspepsia, accompanied by an increase in the level of plasma ghrelin. Hepatogastroenterology. (2012) 59:62–6. doi: 10.5754/hge11246
46. Harasawa S, Miwa T, Miyoshi A, Masamune O, Matsuo Y, Mori H, et al. Double-blind multicenter post-marketing clinical trial of TJ-43 TSUMURA Rikkunshi-to for the treatment of dysmotility-like dyspepsia. Igaku Ayumi. (1998) 187:207–29. Japanese. Available online at: http://mol.medicalonline.jp/library/journal/download?GoodsID=aa7ayuma/1998/018703/013&name=0207-0229j&UserID=130.34.173.69
47. Tatsuta M, Iishi H. Effect of treatment with liu-jun-zi-tang (TJ-43) on gastric emptying and gastrointestinal symptoms in dyspeptic patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (1993) 7:459–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.1993.tb00120.x
48. Miyoshi A, Taniuchi A, Masamune K. Clinical evaluation of rikkunshito for complains related with gastrointestinal function, A randomized multi-center study using cisapride as control. Prog Med. (1991) 11:1605–31.
49. Numata T, Takayama S, Tobita M, Ishida S, Katayose D, Shinkawa M, et al. Traditional Japanese medicine daikenchuto improves functional constipation in poststroke patients. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2014) 2014:231258. doi: 10.1155/2014/231258
50. Arita R, Numata T, Takayama S, Obara T, Kikuchi A, Ohsawa M, et al. Responder analysis of daikenchuto treatment for constipation in poststroke patients: a subanalysis of a randomized control trial. J Evid Based Integr Med. (2019) 24:2515690X19889271. doi: 10.1177/2515690X19889271
51. Horiuchi A, Nakayama Y, Tanaka N. Effect of traditional Japanese medicine, daikenchuto (TJ-100) in patients with chronic constipation. Gastroenterology Res. (2010) 3:151–5. doi: 10.4021/gr219w
52. Miyoshi A, Masamune O, Fukutomi H, Mori H, Miwa T, Kojima K, et al. Clinical effect of Tsumura Daiokanzoto (TJ-84) for constipation, a Double-blinded study. Gastrienterology. (1994) 18:299-312. [in Japanese]. Available online at: https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/bpb/39/3/39_b15-00815/_article/-char/ja/
53. Nishino T, Yoshida T, Goto M, Inoue S, Minato T, Fujiwara S, et al. The effects of the herbal medicine Daikenchuto (TJ 100) after esophageal cancer resection, open label, randomized controlled trial. Esophagus. (2018) 15:75–82. doi: 10.1007/s10388-017-0601-9
54. Katsuno H, Maeda K, Ohya M, Yoshioka K, Tsunoda A, Koda K, et al. Clinical pharmacology of daikenchuto assessed by transit analysis using radiopaque markers in patients with colon cancer undergoing open surgery: a multicenter double-blind randomized placebo-controlled study (JFMC39-0902 additional study). J Gastroenterol. (2016) 51:222–229. doi: 10.1007/s00535-015-1100-1
55. Okada K, Kawai M, Hirono S, Yoshioka K, Tsunoda A, Koda K, et al. Evaluation of the efficacy of daikenchuto (TJ−100) for the prevention of paralytic ileus after pancreaticoduodenectomy: a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Surgery. (2016) 159:1333–41. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2015.11.019
56. Akamaru Y, Takahashi T, Nishida T, Omori T, Nishikawa K, Mikata S, et al. Effects of daikenchuto, a Japanese herb, on intestinal motility after total gastrectomy: a prospective randomized trial. J Gastrointest Surg. (2015) 19:467–72. doi: 10.1007/s11605-014-2730-y
57. Katsuno H, Maeda K, Kaiho T, Kunieda K, Funahashi K, Sakamoto J, et al. Clinical efficacy of Daikenchuto for gastrointestinal dysfunction following colon surgery: a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled study (JFMC39-0902). Jpn J Clin Oncol. (2015) 45:650–6. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyv056
58. Yoshikawa K, Shimada M, Wakabayashi G, Ishida K, Kaiho T, Kitagawa Y, et al. Effect of daikenchuto, a traditional Japanese herbal medicine, after total gastrectomy for gastric cancer: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II trial. J Am Coll Surg. (2015) 221:571–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2015.03.004
59. Yaegashi M, Otsuka K, Itabashi T, Kimura T, Kato K, Fujii H, et al. Daikenchuto stimulates colonic motility after laparoscopic-assisted colectomy. Hepatogastroenterology. (2014) 61:85–9. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24895799/
60. Yoshikawa K, Shimada M, Nishioka M, Kurita N, Iwata T, Morimoto S, et al. The effects of the Kampo medicine (Japanese herbal medicine) “Daikenchuto” on the surgical inflammatory response following laparoscopic colorectal resection. Surg Today. (2012) 42:646–51. doi: 10.1007/s00595-011-0094-4
61. Takahashi T, Endo S, Nakajima K, Souma Y, Nishida T. Effect of rikkunshito, a chinese herbal medicine, on stasis in patients after pylorus-preserving gastrectomy. World J Surg. (2009) 33:296–302. doi: 10.1007/s00268-008-9854-8
62. Endo S, Nishida T, Nishikawa K, Nakajima K, Hasegawa J, Kitagawa T, et al. Dai-kenchu-to, a Chinese herbal medicine, improves stasis of patients with total gastrectomy and jejunal pouch interposition. Am J Surg. (2006) 192:9–13. doi: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2006.01.022
63. Itoh T, Yamakawa J, Mai M, Yamaguchi N, Kanda T. The effect of the herbal medicine dai-kenchu-to on post-operative ileus. J Int Med Res. (2002) 30:428–32. doi: 10.1177/147323000203000410
64. Takagi Y, Kawasaki S, Komai H, Fujiwara K, Naito Y. The effect of Chinese herbal medicine (DAI-KENCHU-TO) on paralytic ileus after repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm. Nihon Rinsho Geka Gakkai Zasshi. (2000) 61:325–8. doi: 10.3919/jjsa.61.325
65. Kubo N, Uchida Y, Akiyoshi T. The effect of Daikenchuto on ileus, a multicenter trial. Prog Med. (1995) 15:1962–7.
66. Kaido T, Shinoda M, Inomata Y, Yagi T, Akamatsu N, Takada Y, et al. Effect of herbal medicine daikenchuto on oral and enteral caloric intake after liver transplantation: a multicenter, randomized controlled trial. Nutrition. (2018) 54:68–75. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2018.02.022
67. Shimada M, Morine Y, Nagano H, Hatano E, Kaiho T, Miyazaki M, et al. Effect of TU-100, a traditional Japanese medicine, administered after hepatic resection in patients with liver cancer: a multicenter, phase III trial (JFMC40-1001). Int J Clin Oncol. (2015) 20:95–104. doi: 10.1007/s10147-014-0678-2
68. Nishi M, Shimada M, Uchiyama H, Ikegami T, Arakawa Y, Hanaoka J, et al. The beneficial effects of Kampo medicine Dai-Ken-Chu-To after hepatic resection: a prospective randomized control study. Hepato-gastroenterology. (2012) 59:2290–4. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23435143/
69. Kaiho T, Tanaka T, Tsuchiya S, Yanagisawa S, Takeuchi O, Miura M, et al. Effect of the herbal medicine Dai-kenchu-to for serum ammonia in hepatectomized patients. Hepatogastroenterology. (2005) 52:161–5. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15783019/
70. Bessho K, Okubo Y, Hori S, Murakami KI, Iizuka T. Effectiveness of kampo medicine (sai-boku-to) in treatment of patients with glossodynia. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. (1998) 86:682–6. doi: 10.1016/S1079-2104(98)90204-9
71. Okabayashi T, Tanaka N, Orita K. The effect of a Kampo medicine, Inchinkoto for the bilirubin reduction rate after biliary drainage on the patients with obstructive jaundice. J Jpn Surg Assoc. (1998) 59:2495–500. doi: 10.3919/jjsa.59.2495
72. Miyazaki Y, Yamada A, Saitou M. Effect of Ninjin-Youei-tou on xerostomia induced by oxybutynin hydrochloride, Shinyaku to Rinsho. J N Rem Clin. (1994) 43:2613–7. Japanese.
73. Alzheimer's Disease International. World Alzheimer Report 2015. The Global Impact of dementia. An Analysis of Prevalence, Incidence, Cost & Trends. London: Alzheimer's Disease International (2015). Available online at: https://www.alz.co.uk/research/WorldAlzheimerReport2015.pdf
74. Cabinet Office. Annual Report in the Aging Society: 2016 (Summary). Available online at: https://www8.cao.go.jp/kourei/english/annualreport/2016/pdf/c1-2-1.pdf
75. Shimada Y, Terasawa K, Yamamoto T. A well-controlled study of Choto-san and placebo in the treatment of vascular dementia. J Tradit Med. (1995) 11:246-55.
76. Terasawa K, Shimada Y, Kita T, Yamamoto T, Tosa H, Tanaka N, et al. Choto-san in the treatment of vascular dementia: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Phytomedicine. (1997) 4:15–22. doi: 10.1016/S0944-7113(97)80022-0
77. Suzuki T, Futami S, Igari Y, Matsumura N, Watanabe K, Nakano H, et al. A Chinese herbal medicine, choto-san, improves cognitive function and activities of daily living of patients with dementia: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2005) 53:2238–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2005.00512_7.x
78. Imai H, Takeshima N, Oda H, Chen P, Sawada E, Furukawa TA. Choto-san versus placebo for patients with dementia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychogeriatrics. (2017) 17:466–78. doi: 10.1111/psyg.12275
79. Iwasaki K, Kobayashi S, Chimura Y, Taguchi M, Inoue K, Cho S, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of the Chinese herbal medicine “ba wei di huang wan” in the treatment of dementia. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2004) 52:1518–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2004.52415.x
80. Maruyama M, Tomita N, Iwasaki K, Ootsuki M, Matsui T, Nemoto M, et al. Benefits of combining donepezil plus traditional Japanese herbal medicine on cognition and brain perfusion in Alzheimer's disease: a 12-week observer-blind, donepezil monotherapy controlled trial. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2006) 54:869–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2006.00722.x
81. Higashi K, Rakugi H, Yu H, Moriguchi A, Shintani T, Ogihara T. Effect of kihito extract granules on cognitive function in patients with Alzheimer's-type dementia. Geriatr Gerontol Int. (2007) 7:245–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0594.2007.00407.x
82. Iwasaki K, Satoh-Nakagawa T, Maruyama M, Monma Y, Nemoto M, Tomita N, et al. A randomized, observer-blind, controlled trial of the traditional Chinese medicine Yi-Gan San for improvement of behavioral and psychological symptoms and activities of daily living in dementia patients. J Clin Psychiat. (2005) 66:248–52. doi: 10.4088/JCP.v66n0214
83. Mizukami K, Asada T, Kinoshita T, Tanaka K, Sonohara K, Nakai R, et al. A randomized cross-over study of a traditional Japanese medicine (kampo), yokukansan, in the treatment of the behavioural and psychological symptoms of dementia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. (2009) 12:191–9. doi: 10.1017/S146114570800970X
84. Monji A, Takita M, Samejima T, Takaishi T, Hashimoto K, Matsunaga H, et al. Effect of yokukansan on the behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia in elderly patients with Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. (2009) 33:308–11. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2008.12.008
85. Okahara K, Ishida Y, Hayashi Y, Inoue T, Tsuruta K, Takeuchi K et al. Effects of Yokukansan on behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia in regular treatment for Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. (2010) 34:532–6. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2010.02.013
86. Teranishi M, Kurita M, Nishino S, Takeyoshi K, Numata Y, Sato T, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of risperidone, yokukansan, and fluvoxamine for the treatment of behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia: a blinded, randomized trial. J Clin Psychopharmacol. (2013) 33:600–7. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0b013e31829798d5
87. Furukawa K, Tomita N, Uematsu D, Okahara K, Shimada H, Ikeda M, et al. Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled multicenter trial of Yokukansan for neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer's disease. Geriatr Gerontol Int. (2017) 17:211–8. doi: 10.1111/ggi.12696
88. Matsunaga S, Kishi T, Iwata N. Yokukansan in the treatment of behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia: an updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Alzheimers Dis. (2016) 54:635–43. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160418
89. Takahashi A, Kitamura K, Watanabe Y, Kobayashi R, Saito T, Takachi R, et al. Epidemiological profiles of chronic low back and knee pain in middle-aged and elderly Japanese from the Murakami cohort. J Pain Res. (2018) 11:3161–9. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S184746
90. Paolucci T, Saraceni VM, Piccinini G. Management of chronic pain in osteoporosis: challenges and solutions. J Pain Res. (2016) 9:177–86. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S83574
91. Hamaguchi T, Yoshino T, Horiba Y, Watanabe K. Goshajinkigan for low back pain: an observational study. J Alten Complement Med. (2017) 23:208–13. doi: 10.1089/acm.2016.0276
92. Oohata M, Aoki Y, Miyata M, Mizobe H, Suzuki KS. Japanese traditional herbal medicine reduces use of pregabalin and opioids for pain in patients with lumbar spinal canal stenosis: a retrospective cohort study. JA Clin Rep. (2017) 3:60. doi: 10.1186/s40981-017-0130-5
93. Hamaguchi S, Komatsuzaki M, Kitajima T, Egawa H. A retrospective study assessing kampo medicine for the treatment of lower extremity symptoms caused by lumbar spinal diseases. Kampo Med. (2017) 68:366–71. Japanese. doi: 10.3937/kampomed.68.366
94. Takahashi Y, Mitsuhata H, Kamiyama Y. The effectiveness of tokishigyakukagosyuyusyokyoto in lower back pain patients with coldness. Kampo Med. (2016) 67:390–3. Japanese. doi: 10.3937/kampomed.67.390
95. Takahashi H, Sakaki T, Koike Y, Ono M, Nanbu T, Koike Y, et al. Two cases of lumbar spinal cord stenosis successfully treated with Kampo medicine. J Japanese Society Study Chronic Pain. (2015) 34:170–4. Japanese.
96. Yoshinaga R, Goto Y, Inoue H, Yano H, Nabeshima S, Tahara E. A case of lower back with extremity pain successfully treated with kanzobushito. Kampo Med. (2019) 70:146–50. Japanese. doi: 10.3937/kampomed.70.146
97. Han C, Hirasaki Y, Okamoto H, Ueda K, Yagi A, Shimada H, et al. A case of prolonged lumbago with severe cold intolerance successfully treated with keppuchikuoto and uzushakusekishigan. Kampo Med. (2015) 66:112–8. Japanese. doi: 10.3937/kampomed.66.112
98. Nagasaka K, Hikiami H, Tatsumi T, Tosa H, Terasawa K. Effect of ryokyo-jutukanto ka bushi on low back pain. J Traditional Med. (1999) 16:83–9. Japanese.
99. Ogawa K, Namiki T, Sekiya N, Kasahara Y, Chino A, Raimura M, et al. A case with lumbar spinal canal stenosis successfully treated with kigikenchutokauzu. Kampo Med. (2009) 60:167–70. Japanese. doi: 10.3937/kampomed.60.167
100. Tetsumura S, Kimira H, Sato M, Kota K, Mitsuma T. A case of painful bedridden patient with multiple fractures due to osteoporosis successfully treated with keishi-bushi-to. Kampo Med. (2005) 56:103–8. Japanese. doi: 10.3937/kampomed.56.103
101. Nakae H, Yokoi A, Kodama H, Horikawa A. Comparison of the effects on rib fracture between the traditional Japanese medicine jidabokuippo and nonsteroal anti-inflammatory drugs: a randomized controlled trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2012) 2012:837958. doi: 10.1155/2012/837958
102. Yoshimura N, Muraki S, Oka H, Mabuchi A, En-Yo Y, Yoshida M, et al. Prevalence of knee osteoarthritis, lumbar spondylosis, and osteoporosis in Japanese men and women: the research on osteoarthritis/osteoporosis against disability study. J Bone Miner Metab. (2009) 27:620–8. doi: 10.1007/s00774-009-0080-8
103. Skou ST, Roos E. Physical therapy for patients with knee and hip osteoarthritis: supervised, active treatment is current best practice. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2019) 120:112–7. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31621559/
104. Majima T, Inoue M, Kasahara Y, Onodera T, Takahashi D, Minami A. Effect of the Japanese herbal medicine, boiogito, on the osteoarthritis of the knee with joint effusion. Sports Med Arthrosc Rehabil Ther Technol. (2012) 4:1–6. doi: 10.1186/1758-2555-4-3
105. Nakae H. Efficacy of aconite tuber powder in patients with arthralgia and somatic pain. Kampo Med. (2009) 60:81–5. Japanese. doi: 10.3937/kampomed.60.81
106. Mizoguchi K, Ikarashi Y. Multiple psychopharmacological effects of the traditional Japanese Kampo medicine yokukansan, and the brain regions it affects. Front Pharmacol. (2017) 8:149 doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00149
107. Nakamura Y, Tajima K, Kawagoe I, Kanai M, Mitsuhata H. Efficacy of traditional herbal medicine yokukansan on patients with neuropathic pain. Masui. (2009) 58:1248–55. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19860227/
108. Mallick-Searle T, Snodgrass B, Brant JM. Postherpetic neuralgia: epidemiology pathophysiology, and pain management pharmacology. Multidiscip Healthc. (2016) 9:447–54. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S106340
109. Nakanishi M, Arimitsu J, Kageyama M, Otsuka S, Inoue T, Nishida S, et al. Efficacy of traditional Japanese herbal medicines - Keishikajutsubuto (TJ-18) and Bushi-matsu (TJ-3022) - against postherpetic neuralgia aggravated by self-reported cold stimulation: a case series. J Altern Complement Med. (2012) 18:686–92. doi: 10.1089/acm.2010.0745
110. Kogure T, Harada N, Yamamoto K, Tatsumi T. Positive effects of Uyakujunkisan therapy (Kampo medicine) for postherpetic neuralgia with concomitant pregabalin: two case reports with a literature review. Altern Ther Health Med. (2016) 22:40–4. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27866180/
111. Fukuda S, Nambu T, Takahashi H, Kuroki K, Nishiyama H, Mitsuma T. Two patients with ophthalmic symptoms due to post herpetic infection dramatically improve with chitosan. Kampo Med. (2010) 61:912–6. Japanese. doi: 10.3937/kampomed.61.912
112. Nogami T, Oka H, Fujimoto M, Hikiami H, Goto H, Shibahara N, et al. Two cases of postherpetic neuralgia recurring after withdrawal of Kampo medicine including Uzu. Kampo Med. (2011) 62:369–73. Japanese. doi: 10.3937/kampomed.62.369
113. Albers JW, Pop-Busui R. Diabetic neuropathy: mechanisms, emerging treatments, and subtypes. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. (2014) 14:473. doi: 10.1007/s11910-014-0473-5
114. Watanabe K, Shimada A, Miyaki K, Hirakata A, Matsuoka K, Omae K, et al. Long-term effects of goshajinkigan in prevention of diabetic complications: a randomized open-labeled clinical trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2014) 2014:128726. doi: 10.1155/2014/128726
115. Hoshino N, Ganeko, Hida K, Sakai Y. Goshajinkigan for reducing chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Clin Oncol. (2018) 23:434–42. doi: 10.1007/s10147-017-1229-4
116. Dua A, Lee CJ. Epidemiology of peripheral arterial disease and critical limb ischemia. Tech Vasc Interv Radiol. (2016) 19:91–5. doi: 10.1053/j.tvir.2016.04.001
117. Kawago K, Shindo S, Inoue H, Akasaka J, Motohashi S, Urabe G, et al. The effect of hachimi-jio-gan (Ba-Wei-Di-Huang-Wan) on the quality of life in patients with peripheral arterial disease - a prospective study using Kampo Medicine. Ann Vasc. (2016) 9:289–94. doi: 10.3400/avd.oa.15-00133
118. Nishida S, Eguchi E, Ohira T, Kitamura A, Kato YH, Hagihara K, et al. Effects of a traditional herbal medicine on peripheral blood flow in women experiencing peripheral coldness: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Complement Altern Med. (2015) 15:105. doi: 10.1186/s12906-015-0617-4
119. Jojima K. The clinical effectiveness of traditional Japanese herbal-medicine, tokishigyakukagosyuyusyokyoto for vascular intermittent claudication. Kampo Med. (2011) 62:529–36. Japanese. doi: 10.3937/kampomed.62.529
120. Raimura M, Terasawa K, Sekiya N, Chino A, Hashimoto S, Namiki T, et al. A case of intermittent claudication and skin ulcers of lower limb due to arteriosclerosis obliterans successfully treated with prepared in the hospital keisibukuryogan and daisaikoto. Kampo Med. (2009) 60:365–9. Japanese. doi: 10.3937/kampomed.60.365
121. Uto NS, Amitani H, Atobe Y, Sameshima Y, Sakaki M, Rokot N, et al. Herbal medicine ninjin'yoeito in the treatment of sarcopenia and frailty. Front Nutr. (2018) 5:126. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2018.00126
122. Sakamoto R, Asari H. Benefit of Kampo medicine for stroke rehabilitation. Jpn Rehabi Med. (2018) 55:968–77. Japanese. doi: 10.2490/jjrmc.55.968
123. Sakisaka N, Mitani K, Sempuku S, Imai T, Takemoto Y, Shimomura H, et al. A clinical study of ninjin'yoeito with regard to frailty. Front Nutr. (2018) 5:73. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2018.00073
124. Ikarashi Y, Mizoguchi. Neuropharmacological efficacy of the traditional Japanese Kampo medicine yokukansan and its active ingredients. Phamacol Ther. (2016) 166:84–95. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2016.06.018
125. Mizoguchi K, Ikarashi Y. Cillular pharmacological effects of the traditional Japanese Kampo medicine yokukansan on brain cells. Front Pharmacol. (2017) 20:655. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00655
126. Suzuki Y, Goto K, Ishida A, Komura Y, Kamei J. Antinociceptive mechanism of Gosha-jinki-gan in streptozotocin-induced diabetic animals: role of nitric oxide in theperiphery. Jpn J Phamacol. (1999) 79:387–91. doi: 10.1254/jjp.79.387
127. Kato Y, Tateai Y, Ohkubo M, Saito Y, Amagai SY, Kimura YS, et al. Gosha-jinki-gan reduced oxaliplatin-induced hypersensitivity to cold sensation and its effect would be related to suppression of the expression of TRPM8 and TRPA1 in rats. Anticancer Drugs. (2014) 25:39–43. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000000022
128. Matsumura Y, Yokoyama Y, Hirakawa H, Shigeto T, Futagami M, Mizumura H. The proohylactic effects of a traditional Japanese medicine, goshoajinkigan, on paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy and its mechanism of action. Mol Pain. (2014) 10:61. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-10-61
129. Kishida Y, Kagawa S, Arimitsu J, Nakanishi M, Sakashita N, Otsuka S, et al. Go-sha-jinki-Gan (GJG), a traditional Japanese herbal medicine, protects against sarcopenia in senescence-accelerated mice. Phytomedicine. (2015) 22:16–22. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2014.11.005
130. Nagano T, Itoh H, Takeyama M. Effect of Dai-kenchu-to on levels of 3 brain-gut peptides (motilin, gastrin and somatostatin) in human plasma. Biol Pharm Bull. (1999) 22:1131–3. doi: 10.1248/bpb.22.1131
131. Kono T, Koseki T. Chiba S, Ebisawa Y, Chisato N, Iwamoto J, et al. Colonic vascular conductance increased by Daikenchuto via calcitonin gene-related peptide receptoractivity modifying protein 1. J Surg Res. (2008) 150:78–84. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2008.02.057
132. Kono T, Kaneko A, Hira Y, Suzuki T, Chisato N, Ohtake N, et al. Anticolitis -adhesion effects of Daikenchuto via endogenous adrenomedullin enhancement in Crohn's disease mouse model. J Crohns Colitis. (2010) 4:161–70. doi: 10.1016/j.crohns.2009.09.006
133. Kono T, Omiya Y, Hira Y, Kaneko A, Chiba S, Suzuki T, et al. Daikenchuto (TU-100) ameliorates colon microvascular dysfunction via endogenous adrenomedullin in Crohn's disease rat model. J Gastroenterol. (2011) 46:1187–96. doi: 10.1007/s00535-011-0438-2
134. Kikuchi D, Shibata C, Imoto H, Naitoh T, Miura K, Unno M. Intragastric Dai-Kenchu-To, a Japanese herbal medicine, stimulates colonic motility via transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 in dogs. Tohoku J Exp Med. (2013) 230:197–204. doi: 10.1620/tjem.230.197
135. Matsumura T, Arai M, Yonemitsu Y, Maruoka D, Tanaka T, Suzuki T, et al. The traditional Japanese medicine Rikkunshito increases the plasma level of ghrelin in humans and mice. J Gastroenterol. (2010) 45:300–7. doi: 10.1007/s00535-009-0166-z
136. Takayama S, Arita R, Kikuchi A, Ohsawa M, Kaneko S, Ishii T. Clinical practice guidelines and evidence for the efficacy of traditional japanese herbal medicine (kampo) in treating geriatric patients. Front Nutr. (2018) 5:66. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2018.00066
137. Satoh T, Yokozeki H, Katayama I, Murota H, Tokura Y, Boku N, et al. Clinical practice guideline for the Pruritus cutaneus universalis [in Japanese]. Jpn J Dermatol. (2012) 122:267–80. Available online at: https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/dermatol/122/2/122_267/_article/-char/ja
138. Okubo K, Kurono Y, Ichimura K, Enomoto T, Okamoto Y, Kawauchi H, et al. Practical Guideline for the Management of Allergic Rhinitis in Japan. Tokyo: Life Science Press [in Japanese]. (2015).
139. Kohno S, Okada K, Kadota J, Shioya T, Tanaka H, Tokuyama K, et al. The Japanese Respiratory Society Guidelines for Management of Cough. Tokyo: Medical Revew Co., Ltd. [in Japanese]. (2012).
140. Kinoshita Y, Iwakiri K, Ashida K, Iwakiri R, Oshima T, Ohara S, et al. Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines for GERD 2015. 2nd ed. Tokyo: Nankodo Press [in Japanese] (2015).
141. Miwa H, Kusano M, Arisawa T, Oshima T, Kato T, Joh T, et al. Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Functional Dyspepsia. Tokyo: Nankodo Press [in Japanese]. (2014).
142. Fukudo S, Kaneko H, Akiho H, Inamori M, Endo Y, Okumura T, et al. Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Tokyo: Nankodo Press [in Japanese]. (2014). doi: 10.1007/s00535-014-1017-0
143. Miwa H, Torii A, Maeda K, Akiho H, Araki Y, Iijima H, et al. Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Chronic Constipation 2017. Tokyo: Nankodo Press [in Japanese]. (2017).
144. Takeda M, Yokoyama O, Goto M, Homma Y, Asakura H, Yamanishi T, et al. Clinical Guidelines for Overactive Bladder Syndrome. 2nd ed. Tokyo: RichHill Medical Inc. [in Japanese] (2015).
145. Nakashima K, Tomimoto H, Aiba I, Akishita M, Kurita S, Iijima S, et al. Practice Guideline for Dementia 2017. Tokyo: Igaku-Shoin Ltd. [in Japanese]. (2017).
146. Yasunaga H. Effect of japanese herbal kampo medicine goreisan on reoperation rates after burr-hole surgery for chronic subdural hematoma: analysis of a national inpatient database. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2015) 2015:817616. doi: 10.1155/2015/817616
147. Yasunaga H, Miyata H, Horiguchi H, Kuwabara K, Hashimoto H, Matsuda S. Effect of the Japanese herbal kampo medicine dai-kenchu-to on postoperative adhesive small bowel obstruction requiring long-tube decompression: a propensity score analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2011) 2011:264289. doi: 10.1155/2011/264289
Keywords: aging, Kampo medicine, geriatric syndrome, elderly, evidence
Citation: Takayama S, Tomita N, Arita R, Ono R, Kikuchi A and Ishii T (2020) Kampo Medicine for Various Aging-Related Symptoms: A Review of Geriatric Syndrome. Front. Nutr. 7:86. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2020.00086
Received: 22 March 2020; Accepted: 12 May 2020;
Published: 15 July 2020.
Edited by:
Akio Inui, Kagoshima University, JapanReviewed by:
Dario Coletti, Sapienza University of Rome, ItalyCopyright © 2020 Takayama, Tomita, Arita, Ono, Kikuchi and Ishii. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shin Takayama, dGFrYXlhbWFAbWVkLnRvaG9rdS5hYy5qcA==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.