- 1 The Alexander Silberman Institute of Life Sciences, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem, Israel
- 2 Edmond and Lily Safra Center of Brain Sciences, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Jerusalem, Israel
MicroRNAs (miRs) have emerged as important gene silencers affecting many target mRNAs. Here, we report the identification of 244 miRs that target the 3′-untranslated regions of different cholinesterase transcripts: 116 for butyrylcholinesterase (BChE), 47 for the synaptic acetylcholinesterase (AChE-S) splice variant, and 81 for the normally rare splice variant AChE-R. Of these, 11 and 6 miRs target both AChE-S and AChE-R, and AChE-R and BChE transcripts, respectively. BChE and AChE-S showed no overlapping miRs, attesting to their distinct modes of miR regulation. Generally, miRs can suppress a number of targets; thereby controlling an entire battery of functions. To evaluate the importance of the cholinesterase-targeted miRs in other specific biological processes we searched for their other experimentally validated target transcripts and analyzed the gene ontology enriched biological processes these transcripts are involved in. Interestingly, a number of the resulting categories are also related to cholinesterases. They include, for BChE, response to glucocorticoid stimulus, and for AChE, response to wounding and two child terms of neuron development: regulation of axonogenesis and regulation of dendrite morphogenesis. Importantly, all of the AChE-targeting miRs found to be related to these selected processes were directed against the normally rare AChE-R splice variant, with three of them, including the neurogenesis regulator miR-132, also directed against AChE-S. Our findings point at the AChE-R splice variant as particularly susceptible to miR regulation, highlight those biological functions of cholinesterases that are likely to be subject to miR post-transcriptional control, demonstrate the selectivity of miRs in regulating specific biological processes, and open new venues for targeted interference with these specific processes.
Introduction
MicroRNAs (miRs) are small RNA molecules which target many mRNA transcripts, leading to their post-transcriptional silencing (Bartel, 2009). Many mRNAs can be silenced by multiple miRs and miRs often target more than one mRNA participating in a particular biological function (Bartel, 2009). Together, this suggests that the miR networks affecting specific mRNA transcripts may provide useful information on the biological roles in which these transcripts are involved. Cholinesterases are involved in many biological functions (Massoulie, 2002). However, miR-132 is the only miR so far that has been experimentally validated as targeting AChE, with consequences on inflammatory responses (Shaked et al., 2009). To delineate additional miRs which might regulate cholinesterase functions, we explored the 3′-untranslated regions (3′-UTR) of human cholinesterase transcripts (acetyl- and butyrylcholinesterase, AChE, BChE; Soreq and Seidman, 2001).
Given that several of the proteins involved in a specific function are often repressed by the same miR (Girardot et al., 2010), changes in a particular miR might down-regulate the entire process. Hence, we surmised that those functions that are shared by cholinesterases and the other targets of the cholinesterase-complementary miRs would be more susceptible for being affected by miR control than other processes. That concept is schematically presented as a workflow in Figure 1.
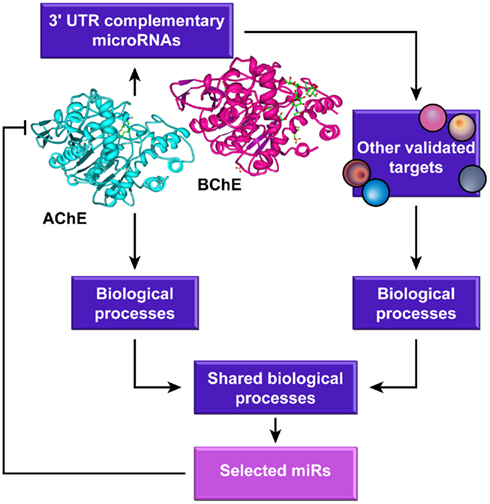
Figure 1. The study’s flow chart. MicroRNAs complementary to the 3′-UTR domains of AChE and BChE transcripts were identified using several algorithms and other validated targets for those miRs were searched for and analyzed for common biological processes in which both these miR targets and cholinesterases are involved.
Materials and Methods
MicroRNA candidates were identified on each of the 3′-UTR sequences of AChE and BChE, which are 235, 1030, and 478 nucleotides long for BChE, the major “synaptic” AChE-S variant and the stress-inducible AChE-R variant, respectively (Figure 2A). We used the PicTar1, miRanda2, miRbase3, and microCosm4 algorithms to identify these transcript-specific miRs. All predictions ensured a threshold P-value < 0.05, and analysis specifications allowed both evolutionarily conserved and non-conserved miRs, which enabled us to include primate-targeting miRs as well.
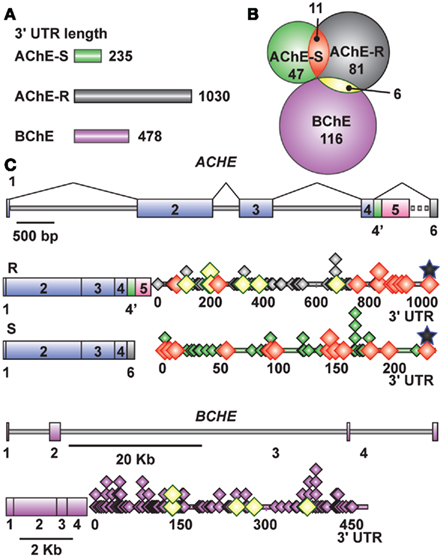
Figure 2. Cholinesterase-targeted miRs show distinct 3′UTR distributions and partial overlaps. (A) The length of the studied 3′UTR domains. (B) Each 3′-UTR is targeted by many different miRs, part of which shared by BChE/AChE-R and AChE-R/AChE-S. (C) Gene and transcript compositions (exons shown as boxes, introns – as lines) and miR distribution patterns on the 3′-UTR domain (not to scale). Overlaps are color coded. MiR (diamonds) localizations are marked. Black stars show miR-132 position.
Validation of miR-target interactions generally involved a 3′UTR luciferase assay. In some cases, it was complemented by protein blots, real-time RT-qPCR, microarrays, transgenic technology, β-galactosidase, or GFP-tagged targets. See, for example the Shaked et al. (2009) report for several of the latter technologies used to explore the miR-132 target AChE, and (Hansen et al., 2010) for the “classical” 3′-UTR and transgenic approaches, in exploring p250GAP which is also a miR-132 target.
To search for gene ontology (GO) categories which are also relevant for the other mRNA targets of cholinesterase-related miRs, we used the DAVID functional annotation clustering tool5. For each of the miRs identified as targeting one of the cholinesterases we searched for other experimentally validated targets; and we then used the lists of the other validated targets as gene lists for the DAVID search. Each list was normalized to the entire human genome, which served as a background.
Results
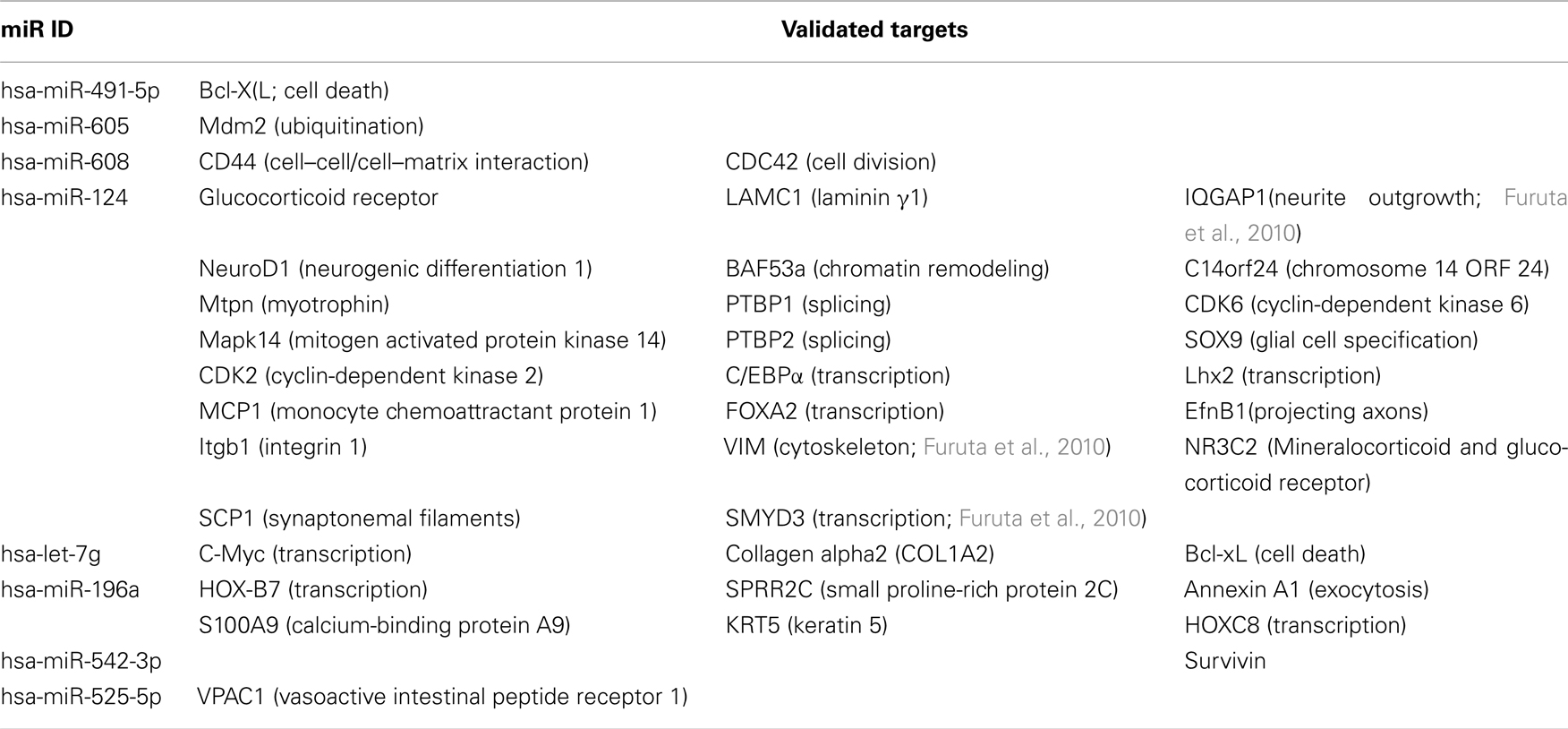
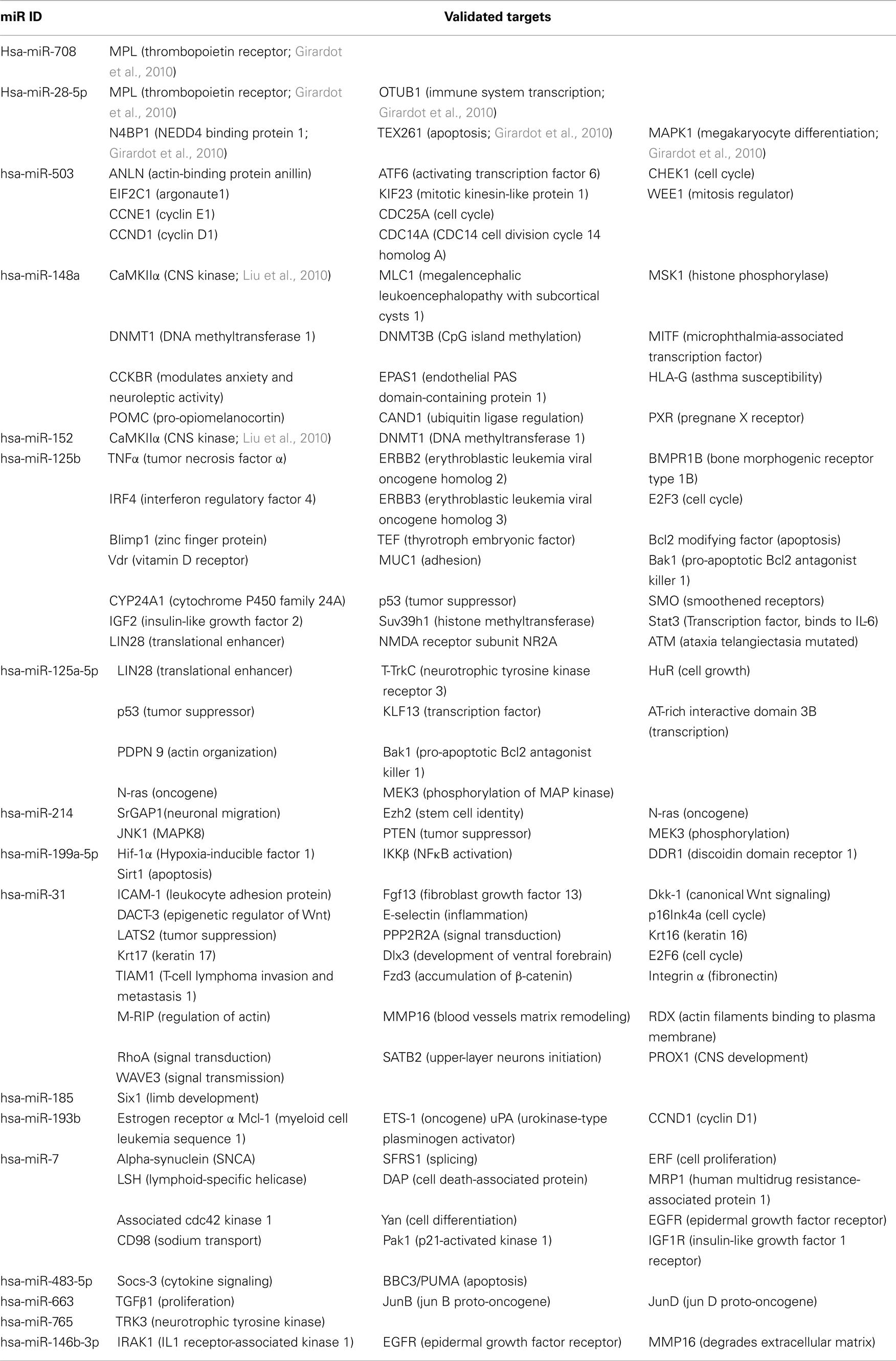
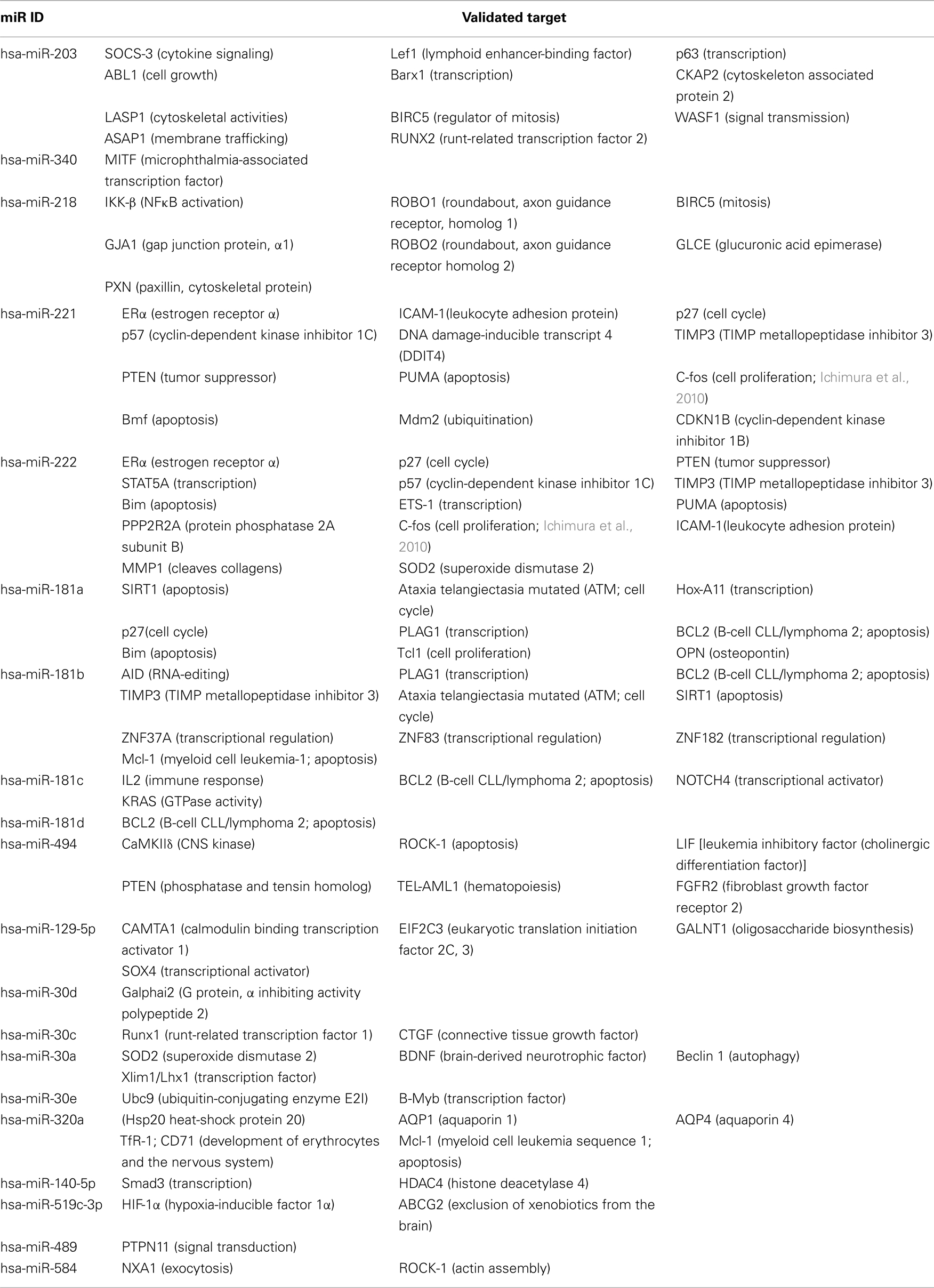
We identified 116, 81, and 47 miRs (24, 8, and 20 miRs/100 nucleotides) that are complementary to the 3′-UTR domains of the BChE, AChE-R, and AChE-S transcripts, respectively. Of these, 6 miRs target both BChE and AChE-R whereas 11 miRs are common to both AChE-R and AChE-S, but BChE and AChE-S do not share any miR (Figure 2B). Positions of the identified miRs are presented in Figure 2C, with miR-132 targeting a similar seed domain localized at the very 3′-end of the 3′-UTR in both the AChE-S and AChE-R transcripts. Of the cholinesterase-targeting miRs, seven had multiple binding sites to the target AChE-S, nine to AChE-R, and seven to the BChE transcript, suggesting that they have a higher prospect for being functional (John et al., 2004). Compatible with the different conceptual principles on which each of the algorithms employed is based, only 8.6, 17, and 13.7% (7/81), (8/47), (16/116) of the miRs identified as targeting AChE-R, AChE-S, and BChE, respectively, were predicted by more than one of the algorithms. For AChE-R, these are hsa-miR-28-5p, −423-3p, −484, −483-5p, −663, −582-3p, −380*. For AChE-S, hsa-miR-194, −939, −658, −608,-615-5p, −423-5p −920, and let-7f-2* and for BChE, hsa-miR-203, −218, −221, −222, −181a, −181b, −181c, −181d, −494, −200b, −200c, −576-3p, −16-2*, −625, −195*, −889.
These cholinesterase-targeting miRs and their other validated non-cholinesterase targets are listed in Tables 1– 3 with the corresponding functions attributed to these other targets. The relevant citations appear in Tables A1– A4 in Appendix. Of note, numerous cholinesterase-targeting miRs have no experimentally validated targets at this time, yet others have more than one validated target and associate with more than one biological function. Examples include miR-124 which targets both the AChE-S and IQGAP1-(Furuta et al., 2010), a GTPase activating protein which promotes neurite outgrowth (Table 1). Additionally miR-152 and miR-148a, which target AChE-R, also target the calmodulin regulating kinase CaMKIIα (Liu et al., 2010; Table 2). Lastly, the BChE-targeting cluster of miRs-222 and −221 also target the neuronal early immediate protein c-fos (Ichimura et al., 2010; Table 3).
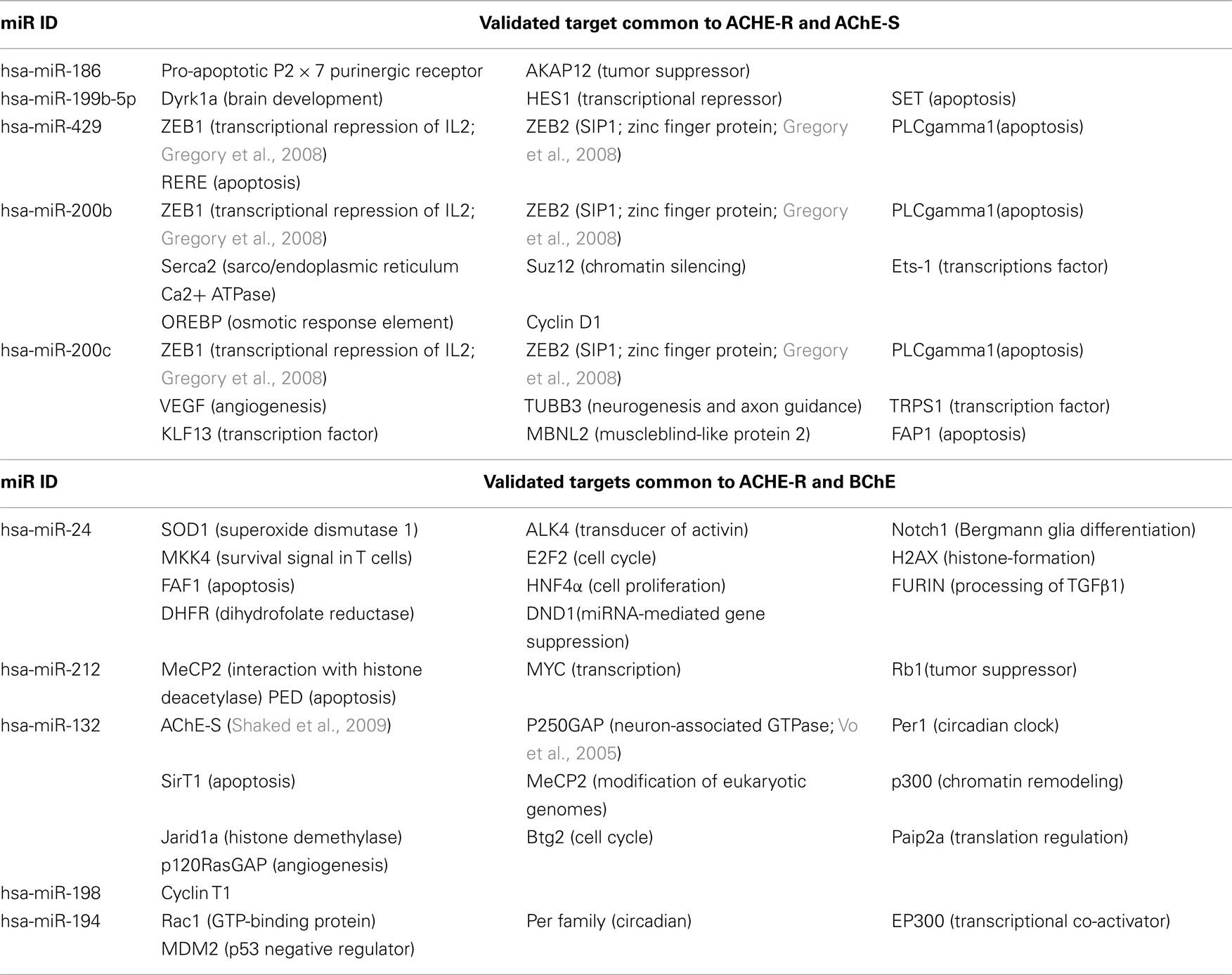
We focused our survey on those functions of those miRs for which experimental validation is available. Table 4 presents these miRs which are shared for AChE-R and AChE-S or AChE-R and BChE and some of their additional targets, highlighting the multitude of miR targets with predicted regulatory functions (e.g., the chromatin modulator zinc finger proteins ZEB1 and ZEB2 targeted by miR-200b, miR-200c, and miR-429 that are also directed to both AChE-R and AChE-S; Gregory et al., 2008). Likewise, the AChE-S-targeted miR-132 (Shaked et al., 2009; Soreq and Wolf, 2011) also targets the GTPase regulator p250GAP involved in neurite extension (Vo et al., 2005; Hansen et al., 2010; Table 4).
The process-regulation hypothesis of miR function predicts the existence of biological functions in which both cholinesterases, and those other targets which share miRs with cholinesterases, would be involved. To challenge this hypothesis, we first identified the GO categories in which AChE and BChE are involved, and found 24 and 11 biological processes for these two proteins, respectively. Twenty-three, 13, and 18 enriched biological processes emerged as shared processes for the other validated targets of AChE-R, AChE-S, and BChE-targeting miRs, respectively (P-value threshold < 0.05).
Out of over 20 ontology categories attributed to AChE, only two are shared with the categories attributed to the other validated targets of the cholinesterase-targeting miRs. These are: Response to wounding (GO: 0009611; 68 transcripts) and Neuron development (GO: 0048666), and specifically its AChE-relevant child terms Regulation of axonogenesis (GO: 0050770; 78 transcripts) and regulation of dendrite morphogenesis (GO: 0048814; 27 transcripts). Surprisingly, all 10 miRs that regulate Response to wounding and Neuron development selectively target the normally rare, stress-responsive AChE-R transcript, (miR-186, −125b, −200c, −199a-5p, −199b-5p, −125a, −214, −7, −663, −31, and −148a) whereas only three of these miRs also target the prevalent AChE-S mRNA (miR-194, −24, and −132). For BChE, we found only one shared category out of 11 relevant ontology groups: Response to glucocorticoid stimulus (GO: 0051384; 119 transcripts), and no overlap with the AChE-relevant categories (Figures 3A,B).
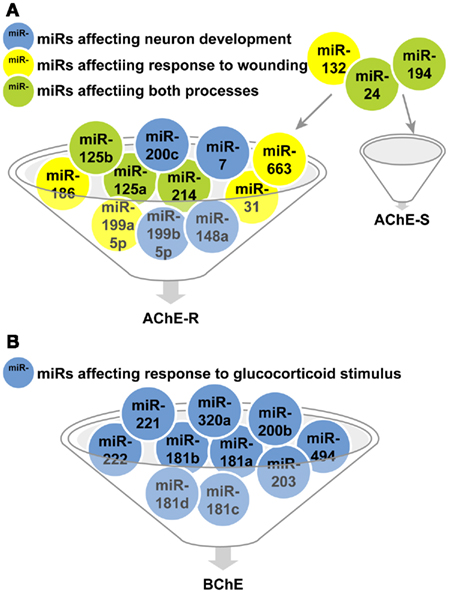
Figure 3. MiR regulators of biological processes shared by cholinesterases and validated targets of these miRs. (A) miRs targeting transcripts participating in the AChE-S and AChE-R relevant response to wounding (yellow)and neuron development processes(blue) or both categories(green). (B) miRs targeting transcripts participating in the BChE-relevant response to glucocorticoid stimulus category.
Discussion
Using a variety of available algorithms, we found a plethora of cholinesterase-targeted miRs. Some of these were already validated as functionally capable of silencing other mRNA transcripts. A study of the functionally relevant biological processes in which these other targets are involved revealed a highly focused overlap with only few of the biological processes in which cholinesterases participate. Given that miRs regulate targets which share biological processes, cholinesterases appear to be primarily subject to miR regulation when involved in neuronal development, response to wounding, and glucocorticoid stimulus; and specific cholinergic processes are regulated by miRs targeting both AChE and other targets participating in the same biological process.
Several limitations should be considered in the context of this study. First, the currently available search algorithms for miR candidates appear to differ substantially, which casts a shadow on the veracity of such identification. Second, research bias has focused much of the efforts in the miR field toward cancer research, whereas neuroscience-focused miRs were relatively neglected. Therefore, we might have overlooked important miRs simply because they have not yet been validated experimentally. This being said, that many of the biological functions in which cholinesterases are involved show no relevant cholinesterase-targeting miR sequences suggests other modes of regulation of cholinesterase levels for most of these functions [e.g., transcriptional (Hill and Treisman, 1995), epigenetic (Allshire and Karpen, 2008), or post-translational processes (Fukushima et al., 2009)]. Alternatively, or in addition, miRs might exist which control these functions, but have no role in cancer biology and are therefore not yet characterized. MiR regulation of cholinesterase functions will therefore need to be re-inspected in the near future.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to E. R. Bennett, Jerusalem, for critical evaluation of this manuscript. This work was supported by the Legacy Heritage Biomedical Science Partnership Program of the Israel Science Foundation (Grant No. 1876/08, to Hermona Soreq).
Footnotes
References
Allshire, R. C., and Karpen, G. H. (2008). Epigenetic regulation of centromeric chromatin: old dogs, new tricks? Nat. Rev. Genet. 9, 923–937.
Fukushima, N., Furuta, D., Hidaka, Y., Moriyama, R., and Tsujiuchi, T. (2009). Post-translational modifications of tubulin in the nervous system. J. Neurochem. 109, 683–693.
Furuta, M., Kozaki, K. I., Tanaka, S., Arii, S., Imoto, I., and Inazawa, J. (2010). miR-124 and miR-203 are epigenetically silenced tumor-suppressive microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 31, 766–776.
Girardot, M., Pecquet, C., Boukour, S., Knoops, L., Ferrant, A., Vainchenker, W., Giraudier, S., and Constantinescu, S. N. (2010). miR-28 is a thrombopoietin receptor targeting microRNA detected in a fraction of myeloproliferative neoplasm patient platelets. Blood 116, 437–445.
Gregory, P. A., Bert, A. G., Paterson, E. L., Barry, S. C., Tsykin, A., Farshid, G., Vadas, M. A., Khew-Goodall, Y., and Goodall, G. J. (2008). The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat. Cell Biol. 10, 593–601.
Hansen, K. F., Sakamoto, K., Wayman, G. A., Impey, S., and Obrietan, K. (2010). Transgenic miR132 alters neuronal spine density and impairs novel object recognition memory. PLoS ONE 5, e15497.
Hill, C. S., and Treisman, R. (1995). Transcriptional regulation by extracellular signals: mechanisms and specificity. Cell 80, 199–211.
Ichimura, A., Ruike, Y., Terasawa, K., Shimizu, K., and Tsujimoto, G. (2010). MicroRNA-34a inhibits cell proliferation by repressing mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 during megakaryocytic differentiation of K562 cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 77, 1016–1024.
John, B., Enright, A. J., Aravin, A., Tuschl, T., Sander, C., and Marks, D. S. (2004). Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol. 2, e363.
Liu, X., Zhan, Z., Xu, L., Ma, F., Li, D., Guo, Z., Li, N., and Cao, X. (2010). MicroRNA-148/152 impair innate response and antigen presentation of TLR-triggered dendritic cells by targeting CaMKII alpha. J. Immunol. 185, 7244–7251.
Massoulie, J. (2002). The origin of the molecular diversity and functional anchoring of cholinesterases. Neurosignals 11, 130–143.
Shaked, I., Meerson, A., Wolf, Y., Avni, R., Greenberg, D., Gilboa-Geffen, A., and Soreq, H. (2009). MicroRNA-132 potentiates cholinergic anti-inflammatory signaling by targeting acetylcholinesterase. Immunity 31, 965–973.
Soreq, H., and Seidman, S. (2001). Acetylcholinesterase – new roles for an old actor. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 294–302.
Soreq, H., and Wolf, Y. (2011). NeurimmiRs: micro-RNAs in the neuroimmune interface. Trends Mol. Med. [Epub ahead of print].
Vo, N., Klein, M. E., Varlamova, O., Keller, D. M., Yamamoto, T., Goodman, R. H., and Impey, S. (2005). A cAMP-response element binding protein-induced microRNA regulates neuronal morphogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 16426–16431.
Appendix
References
Agrawal, R., Tran, U., and Wessely, O. (2009). The miR-30 miRNA family regulates Xenopus pronephros development and targets the transcription factor Xlim1/Lhx1. Development 136, 3927–3936.
Alajez, N. M., Lenarduzzi, M., Ito, E., Hui, A. B., Shi, W., Bruce, J., Yue, S., Huang, S. H., Xu, W., Waldron, J., O’sullivan, B., and Liu, F. F. (2011). MiR-218 suppresses nasopharyngeal cancer progression through downregulation of survivin and the SLIT2-ROBO1 pathway. Cancer Res. 71, 2381–2391.
Alvarez-Saavedra, M., Antoun, G., Yanagiya, A., Oliva-Hernandez, R., Cornejo-Palma, D., Perez-Iratxeta, C., Sonenberg, N., and Cheng, H. Y. (2011). miRNA-132 orchestrates chromatin remodeling and translational control of the circadian clock. Hum. Mol. Genet. 20, 731–751.
Anand, S., Majeti, B. K., Acevedo, L. M., Murphy, E. A., Mukthavaram, R., Scheppke, L., Huang, M., Shields, D. J., Lindquist, J. N., Lapinski, P. E., King, P. D., Weis, S. M., and Cheresh, D. A. (2010). MicroRNA-132-mediated loss of p120RasGAP activates the endothelium to facilitate pathological angiogenesis. Nat. Med. 16, 909–914.
Aprelikova, O., Yu, X., Palla, J., Wei, B. R., John, S., Yi, M., Stephens, R., Simpson, R. M., Risinger, J. I., Jazaeri, A., and Niederhuber, J. (2010). The role of miR-31 and its target gene SATB2 in cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Cycle 9, 4387–4398.
Arvanitis, D. N., Jungas, T., Behar, A., and Davy, A. (2010). Ephrin-B1 reverse signaling controls a posttranscriptional feedback mechanism via miR-124. Mol. Cell. Biol. 30, 2508–2517.
Baroukh, N., Ravier, M. A., Loder, M. K., Hill, E. V., Bounacer, A., Scharfmann, R., Rutter, G. A., and Van Obberghen, E. (2007). MicroRNA-124a regulates Foxa2 expression and intracellular signaling in pancreatic beta-cell lines. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 19575–19588.
Ben-Ami, O., Pencovich, N., Lotem, J., Levanon, D., and Groner, Y. (2009). A regulatory interplay between miR-27a and Runx1 during megakaryopoiesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 238–243.
Bhatnagar, N., Li, X., Padi, S. K., Zhang, Q., Tang, M. S., and Guo, B. (2010). Downregulation of miR-205 and miR-31 confers resistance to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 1, e105.
Bhattacharya, S. D., Garrison, J., Guo, H., Mi, Z., Markovic, J., Kim, V. M., and Kuo, P. C. (2010). Micro-RNA-181a regulates osteopontin-dependent metastatic function in hepatocellular cancer cell lines. Surgery 148, 291–297.
Braconi, C., Huang, N., and Patel, T. (2010a). MicroRNA-dependent regulation of DNA methyltransferase-1 and tumor suppressor gene expression by interleukin-6 in human malignant cholangiocytes. Hepatology 51, 881–890.
Braconi, C., Valeri, N., Gasparini, P., Huang, N., Taccioli, C., Nuovo, G., Suzuki, T., Croce, C. M., and Patel, T. (2010b). Hepatitis C virus proteins modulate microRNA expression and chemosensitivity in malignant hepatocytes. Clin. Cancer Res. 16, 957–966.
Braig, S., Mueller, D. W., Rothhammer, T., and Bosserhoff, A. K. (2010). MicroRNA miR-196a is a central regulator of HOX-B7 and BMP4 expression in malignant melanoma. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 67, 3535–3548.
Bueno, M. J., Perez De Castro, I., Gomez De Cedron, M., Santos, J., Calin, G. A., Cigudosa, J. C., Croce, C. M., Fernandez-Piqueras, J., and Malumbres, M. (2008). Genetic and epigenetic silencing of microRNA-203 enhances ABL1 and BCR-ABL1 oncogene expression. Cancer Cell 13, 496–506.
Cao, X., Pfaff, S. L., and Gage, F. H. (2007). A functional study of miR-124 in the developing neural tube. Genes Dev. 21, 531–536.
Cha, S. T., Chen, P. S., Johansson, G., Chu, C. Y., Wang, M. Y., Jeng, Y. M., Yu, S. L., Chen, J. S., Chang, K. J., Jee, S. H., Tan, C. T., Lin, M. T., and Kuo, M. L. (2010). MicroRNA-519c suppresses hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression and tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 70, 2675–2685.
Chan, Y. C., Khanna, S., Roy, S., and Sen, C. K. (2011). miR-200b targets Ets-1 and is down-regulated by hypoxia to induce angiogenic response of endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 2047–2056.
Chao, A., Tsai, C. L., Wei, P. C., Hsueh, S., Chao, A. S., Wang, C. J., Tsai, C. N., Lee, Y. S., Wang, T. H., and Lai, C. H. (2010). Decreased expression of microRNA-199b increases protein levels of SET (protein phosphatase 2A inhibitor) in human choriocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 291, 99–107.
Chen, L., Yan, H. X., Yang, W., Hu, L., Yu, L. X., Liu, Q., Li, L., Huang, D. D., Ding, J., Shen, F., Zhou, W. P., Wu, M. C., and Wang, H. Y. (2009). The role of microRNA expression pattern in human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J. Hepatol. 50, 358–369.
Chen, R., Alvero, A. B., Silasi, D. A., Kelly, M. G., Fest, S., Visintin, I., Leiser, A., Schwartz, P. E., Rutherford, T., and Mor, G. (2008). Regulation of IKKbeta by miR-199a affects NF-kappaB activity in ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene 27, 4712–4723.
Cheng, H. Y., Papp, J. W., Varlamova, O., Dziema, H., Russell, B., Curfman, J. P., Nakazawa, T., Shimizu, K., Okamura, H., Impey, S., and Obrietan, K. (2007). microRNA modulation of circadian-clock period and entrainment. Neuron 54, 813–829.
Cheng, L. C., Pastrana, E., Tavazoie, M., and Doetsch, F. (2009). miR-124 regulates adult neurogenesis in the subventricular zone stem cell niche. Nat. Neurosci. 12, 399–408.
Chou, Y. T., Lin, H. H., Lien, Y. C., Wang, Y. H., Hong, C. F., Kao, Y. R., Lin, S. C., Chang, Y. C., Lin, S. Y., Chen, S. J., Chen, H. C., Yeh, S. D., and Wu, C. W. (2010). EGFR promotes lung tumorigenesis by activating miR-7 through a Ras/ERK/Myc pathway that targets the Ets2 transcriptional repressor ERF. Cancer Res. 70, 8822–8831.
Cocco, E., Paladini, F., Macino, G., Fulci, V., Fiorillo, M. T., and Sorrentino, R. (2010). The expression of vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor 1 is negatively modulated by microRNA 525-5p. PLoS ONE 5, e12067.
Cochrane, D. R., Spoelstra, N. S., Howe, E. N., Nordeen, S. K., and Richer, J. K. (2009). MicroRNA-200c mitigates invasiveness and restores sensitivity to microtubule-targeting chemotherapeutic agents. Mol. Cancer Ther. 8, 1055–1066.
Cortez, M. A., Nicoloso, M. S., Shimizu, M., Rossi, S., Gopisetty, G., Molina, J. R., Carlotti, C. Jr., Tirapelli, D., Neder, L., Brassesco, M. S., Scrideli, C. A., Tone, L. G., Georgescu, M. M., Zhang, W., Puduvalli, V., and Calin, G. A. (2010). miR-29b and miR-125a regulate podoplanin and suppress invasion in glioblastoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 49, 981–990.
Cottonham, C. L., Kaneko, S., and Xu, L. (2010). miR-21 and miR-31 converge on TIAM1 to regulate migration and invasion of colon carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 35293–35302.
Cowden Dahl, K. D., Dahl, R., Kruichak, J. N., and Hudson, L. G. (2009). The epidermal growth factor receptor responsive miR-125a represses mesenchymal morphology in ovarian cancer cells. Neoplasia 11, 1208–1215.
Cuesta, R., Martinez-Sanchez, A., and Gebauer, F. (2009). miR-181a regulates cap-dependent translation of p27(kip1) mRNA in myeloid cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 29, 2841–2851.
Da Costa Martins, P. A., Salic, K., Gladka, M. M., Armand, A. S., Leptidis, S., El Azzouzi, H., Hansen, A., Coenen-De Roo, C. J., Bierhuizen, M. F., Van Der Nagel, R., Van Kuik, J., De Weger, R., De Bruin, A., Condorelli, G., Arbones, M. L., Eschenhagen, T., and De Windt, L. J. (2010). MicroRNA-199b targets the nuclear kinase Dyrk1a in an auto-amplification loop promoting calcineurin/NFAT signalling. Nat. Cell Biol. 12, 1220–1227.
De Yebenes, V. G., Belver, L., Pisano, D. G., Gonzalez, S., Villasante, A., Croce, C., He, L., and Ramiro, A. R. (2008). miR-181b negatively regulates activation-induced cytidine deaminase in B cells. J. Exp. Med. 205, 2199–2206.
Dentelli, P., Rosso, A., Orso, F., Olgasi, C., Taverna, D., and Brizzi, M. F. (2010). microRNA-222 controls neovascularization by regulating signal transducer and activator of transcription 5A expression. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 30, 1562–1568.
Diakos, C., Zhong, S., Xiao, Y., Zhou, M., Vasconcelos, G. M., Krapf, G., Yeh, R. F., Zheng, S., Kang, M., Wiencke, J. K., Pombo-De-Oliveira, M. S., Panzer-Grumayer, R., and Wiemels, J. L. (2010). TEL-AML1 regulation of survivin and apoptosis via miRNA-494 and miRNA-320a. Blood 116, 4885–4893.
Duisters, R. F., Tijsen, A. J., Schroen, B., Leenders, J. J., Lentink, V., Van Der Made, I., Herias, V., Van Leeuwen, R. E., Schellings, M. W., Barenbrug, P., Maessen, J. G., Heymans, S., Pinto, Y. M., and Creemers, E. E. (2009). miR-133 and miR-30 regulate connective tissue growth factor: implications for a role of microRNAs in myocardial matrix remodeling. Circ. Res. 104, 170–178.
Duursma, A. M., Kedde, M., Schrier, M., Le Sage, C., and Agami, R. (2008). miR-148 targets human DNMT3b protein coding region. RNA 14, 872–877.
Dyrskjot, L., Ostenfeld, M. S., Bramsen, J. B., Silahtaroglu, A. N., Lamy, P., Ramanathan, R., Fristrup, N., Jensen, J. L., Andersen, C. L., Zieger, K., Kauppinen, S., Ulhoi, B. P., Kjems, J., Borre, M., and Orntoft, T. F. (2009). Genomic profiling of microRNAs in bladder cancer: miR-129 is associated with poor outcome and promotes cell death in vitro. Cancer Res. 69, 4851–4860.
Edbauer, D., Neilson, J. R., Foster, K. A., Wang, C. F., Seeburg, D. P., Batterton, M. N., Tada, T., Dolan, B. M., Sharp, P. A., and Sheng, M. (2010). Regulation of synaptic structure and function by FMRP-associated microRNAs miR-125b and miR-132. Neuron 65, 373–384.
Ferretti, E., De Smaele, E., Miele, E., Laneve, P., Po, A., Pelloni, M., Paganelli, A., Di Marcotullio, L., Caffarelli, E., Screpanti, I., Bozzoni, I., and Gulino, A. (2008). Concerted microRNA control of hedgehog signalling in cerebellar neuronal progenitor and tumour cells. EMBO J. 27, 2616–2627.
Ferretti, E., De Smaele, E., Po, A., Di Marcotullio, L., Tosi, E., Espinola, M. S., Di Rocco, C., Riccardi, R., Giangaspero, F., Farcomeni, A., Nofroni, I., Laneve, P., Gioia, U., Caffarelli, E., Bozzoni, I., Screpanti, I., and Gulino, A. (2009). MicroRNA profiling in human medulloblastoma. Int. J. Cancer 124, 568–577.
Forrest, A. R., Kanamori-Katayama, M., Tomaru, Y., Lassmann, T., Ninomiya, N., Takahashi, Y., De Hoon, M. J., Kubosaki, A., Kaiho, A., Suzuki, M., Yasuda, J., Kawai, J., Hayashizaki, Y., Hume, D. A., and Suzuki, H. (2010). Induction of microRNAs, mir-155, mir-222, mir-424 and mir-503, promotes monocytic differentiation through combinatorial regulation. Leukemia 24, 460–466.
Fujita, Y., Kojima, K., Ohhashi, R., Hamada, N., Nozawa, Y., Kitamoto, A., Sato, A., Kondo, S., Kojima, T., Deguchi, T., and Ito, M. (2010). MiR-148a attenuates paclitaxel resistance of hormone-refractory, drug-resistant prostate cancer PC3 cells by regulating MSK1 expression. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 19076–19084.
Fukuda, Y., Kawasaki, H., and Taira, K. (2005). Exploration of human miRNA target genes in neuronal differentiation. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser. (Oxf.) 49, 341–342.
Garofalo, M., Di Leva, G., Romano, G., Nuovo, G., Suh, S. S., Ngankeu, A., Taccioli, C., Pichiorri, F., Alder, H., Secchiero, P., Gasparini, P., Gonelli, A., Costinean, S., Acunzo, M., Condorelli, G., and Croce, C. M. (2009). miR-221&222 regulate TRAIL resistance and enhance tumorigenicity through PTEN and TIMP3 downregulation. Cancer Cell 16, 498–509.
Garofalo, M., Quintavalle, C., Di Leva, G., Zanca, C., Romano, G., Taccioli, C., Liu, C. G., Croce, C. M., and Condorelli, G. (2008). MicroRNA signatures of TRAIL resistance in human non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 27, 3845–3855.
Garzia, L., Andolfo, I., Cusanelli, E., Marino, N., Petrosino, G., De Martino, D., Esposito, V., Galeone, A., Navas, L., Esposito, S., Gargiulo, S., Fattet, S., Donofrio, V., Cinalli, G., Brunetti, A., Vecchio, L. D., Northcott, P. A., Delattre, O., Taylor, M. D., Iolascon, A., and Zollo, M. (2009). MicroRNA-199b-5p impairs cancer stem cells through negative regulation of HES1 in medulloblastoma. PLoS ONE 4, e4998.
Ge, Y., Sun, Y., and Chen, J. (2011). IGF-II is regulated by microRNA-125b in skeletal myogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 192, 69–81.
Geisler, A., Jungmann, A., Kurreck, J., Poller, W., Katus, H. A., Vetter, R., Fechner, H., and Muller, O. J. (2011). microRNA122-regulated transgene expression increases specificity of cardiac gene transfer upon intravenous delivery of AAV9 vectors. Gene Ther. 18, 199–209.
Giraud-Triboult, K., Rochon-Beaucourt, C., Nissan, X., Champon, B., Aubert, S., and Pietu, G. (2011). Combined mRNA and microRNA profiling reveals that miR-148a and miR-20b control human mesenchymal stem cell phenotype via EPAS1. Physiol. Genomics 43, 77–86.
Goeppert, B., Schmezer, P., Dutruel, C., Oakes, C., Renner, M., Breinig, M., Warth, A., Vogel, M. N., Mittelbronn, M., Mehrabi, A., Gdynia, G., Penzel, R., Longerich, T., Breuhahn, K., Popanda, O., Plass, C., Schirmacher, P., and Kern, M. A. (2010). Down-regulation of tumor suppressor A kinase anchor protein 12 in human hepatocarcinogenesis by epigenetic mechanisms. Hepatology 52, 2023–2033.
Goswami, S., Tarapore, R. S., Teslaa, J. J., Grinblat, Y., Setaluri, V., and Spiegelman, V. S. (2010). MicroRNA-340-mediated degradation of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor mRNA is inhibited by the coding region determinant-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 20532–20540.
Gramantieri, L., Fornari, F., Ferracin, M., Veronese, A., Sabbioni, S., Calin, G. A., Grazi, G. L., Croce, C. M., Bolondi, L., and Negrini, M. (2009). MicroRNA-221 targets Bmf in hepatocellular carcinoma and correlates with tumor multifocality. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 5073–5081.
Guidi, M., Muinos-Gimeno, M., Kagerbauer, B., Marti, E., Estivill, X., and Espinosa-Parrilla, Y. (2010). Overexpression of miR-128 specifically inhibits the truncated isoform of NTRK3 and upregulates BCL2 in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. BMC Mol. Biol. 11, 95.
Guo, S., Lu, J., Schlanger, R., Zhang, H., Wang, J. Y., Fox, M. C., Purton, L. E., Fleming, H. H., Cobb, B., Merkenschlager, M., Golub, T. R., and Scadden, D. T. (2010). MicroRNA miR-125a controls hematopoietic stem cell number. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 14229–14234.
Guo, X., Wu, Y., and Hartley, R. S. (2009). MicroRNA-125a represses cell growth by targeting HuR in breast cancer. RNA Biol. 6, 575–583.
Gutierrez, O., Berciano, M. T., Lafarga, M., and Fernandez-Luna, J. L. (2011). A novel pathway of TEF regulation mediated by microRNA-125b contributes to the control of actin distribution and cell shape in fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 6, e17169.
Hackanson, B., Bennett, K. L., Brena, R. M., Jiang, J., Claus, R., Chen, S. S., Blagitko-Dorfs, N., Maharry, K., Whitman, S. P., Schmittgen, T. D., Lubbert, M., Marcucci, G., Bloomfield, C. D., and Plass, C. (2008). Epigenetic modification of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha expression in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res. 68, 3142–3151.
Haflidadottir, B. S., Bergsteinsdottir, K., Praetorius, C., and Steingrimsson, E. (2010). miR-148 regulates Mitf in melanoma cells. PLoS ONE 5, e11574.
Hashimoto, Y., Akiyama, Y., Otsubo, T., Shimada, S., and Yuasa, Y. (2010). Involvement of epigenetically silenced microRNA-181c in gastric carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 31, 777–784.
Hu, G., Gong, A. Y., Liu, J., Zhou, R., Deng, C., and Chen, X. M. (2010). miR-221 suppresses ICAM-1 translation and regulates interferon-gamma-induced ICAM-1 expression in human cholangiocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 298, G542–G550.
Huang, L., Luo, J., Cai, Q., Pan, Q., Zeng, H., Guo, Z., Dong, W., Huang, J., and Lin, T. (2011a). MicroRNA-125b suppresses the development of bladder cancer by targeting E2F3. Int. J. Cancer 128, 1758–1769.
Huang, W., Liu, H., Wang, T., Zhang, T., Kuang, J., Luo, Y., Chung, S. S., Yuan, L., and Yang, J. Y. (2011b). Tonicity-responsive microRNAs contribute to the maximal induction of osmoregulatory transcription factor OREBP in response to high-NaCl hypertonicity. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, 475–485.
Huang, S., Wu, S., Ding, J., Lin, J., Wei, L., Gu, J., and He, X. (2010). MicroRNA-181a modulates gene expression of zinc finger family members by directly targeting their coding regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, 7211–7218.
Iliopoulos, D., Lindahl-Allen, M., Polytarchou, C., Hirsch, H. A., Tsichlis, P. N., and Struhl, K. (2010). Loss of miR-200 inhibition of Suz12 leads to polycomb-mediated repression required for the formation and maintenance of cancer stem cells. Mol. Cell 39, 761–772.
Ilnytskyy, Y., Zemp, F. J., Koturbash, I., and Kovalchuk, O. (2008). Altered microRNA expression patterns in irradiated hematopoietic tissues suggest a sex-specific protective mechanism. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 377, 41–45.
Im, H. I., Hollander, J. A., Bali, P., and Kenny, P. J. (2010). MeCP2 controls BDNF expression and cocaine intake through homeostatic interactions with microRNA-212. Nat. Neurosci. 13, 1120–1127.
Imam, J. S., Buddavarapu, K., Lee-Chang, J. S., Ganapathy, S., Camosy, C., Chen, Y., and Rao, M. K. (2010). MicroRNA-185 suppresses tumor growth and progression by targeting the Six1 oncogene in human cancers. Oncogene 29, 4971–4979.
Incoronato, M., Garofalo, M., Urso, L., Romano, G., Quintavalle, C., Zanca, C., Iaboni, M., Nuovo, G., Croce, C. M., and Condorelli, G. (2010). miR-212 increases tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting the antiapoptotic protein PED. Cancer Res. 70, 3638–3646.
Jeyapalan, Z., Deng, Z., Shatseva, T., Fang, L., He, C., and Yang, B. B. (2011). Expression of CD44 3′-untranslated region regulates endogenous microRNA functions in tumorigenesis and angiogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, 3026–3041.
Ji, J., Zhao, L., Budhu, A., Forgues, M., Jia, H. L., Qin, L. X., Ye, Q. H., Yu, J., Shi, X., Tang, Z. Y., and Wang, X. W. (2010). Let-7g targets collagen type I alpha2 and inhibits cell migration in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 52, 690–697.
Jiang, L., Liu, X., Chen, Z., Jin, Y., Heidbreder, C. E., Kolokythas, A., Wang, A., Dai, Y., and Zhou, X. (2010). MicroRNA-7 targets IGF1R (insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor) in tongue squamous cell carcinoma cells. Biochem. J. 432, 199–205.
Juan, A. H., Kumar, R. M., Marx, J. G., Young, R. A., and Sartorelli, V. (2009). Mir-214-dependent regulation of the polycomb protein Ezh2 in skeletal muscle and embryonic stem cells. Mol. Cell 36, 61–74.
Junn, E., Lee, K. W., Jeong, B. S., Chan, T. W., Im, J. Y., and Mouradian, M. M. (2009). Repression of alpha-synuclein expression and toxicity by microRNA-7. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 13052–13057.
Karres, J. S., Hilgers, V., Carrera, I., Treisman, J., and Cohen, S. M. (2007). The conserved microRNA miR-8 tunes atrophin levels to prevent neurodegeneration in Drosophila. Cell 131, 136–145.
Kefas, B., Godlewski, J., Comeau, L., Li, Y., Abounader, R., Hawkinson, M., Lee, J., Fine, H., Chiocca, E. A., Lawler, S., and Purow, B. (2008). microRNA-7 inhibits the epidermal growth factor receptor and the Akt pathway and is down-regulated in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 68, 3566–3572.
Kikkawa, N., Hanazawa, T., Fujimura, L., Nohata, N., Suzuki, H., Chazono, H., Sakurai, D., Horiguchi, S., Okamoto, Y., and Seki, N. (2010). miR-489 is a tumour-suppressive miRNA target PTPN11 in hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (HSCC). Br. J. Cancer 103, 877–884.
Kim, B. M., Woo, J., Kanellopoulou, C., and Shivdasani, R. A. (2011). Regulation of mouse stomach development and Barx1 expression by specific microRNAs. Development 138, 1081–1086.
Kim, D., Song, J., and Jin, E. J. (2010). MicroRNA-221 regulates chondrogenic differentiation through promoting proteosomal degradation of slug by targeting Mdm2. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 26900–26907.
Kim, Y. J., Bae, S. W., Yu, S. S., Bae, Y. C., and Jung, J. S. (2009a). miR-196a regulates proliferation and osteogenic differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells derived from human adipose tissue. J. Bone Miner. Res. 24, 816–825.
Kim, Y. K., Yu, J., Han, T. S., Park, S. Y., Namkoong, B., Kim, D. H., Hur, K., Yoo, M. W., Lee, H. J., Yang, H. K., and Kim, V. N. (2009b). Functional links between clustered microRNAs: suppression of cell-cycle inhibitors by microRNA clusters in gastric cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, 1672–1681.
Klein, M. E., Lioy, D. T., Ma, L., Impey, S., Mandel, G., and Goodman, R. H. (2007). Homeostatic regulation of MeCP2 expression by a CREB-induced microRNA. Nat. Neurosci. 10, 1513–1514.
Ko, H. Y., Lee, D. S., and Kim, S. (2009). Noninvasive imaging of microRNA124a-mediated repression of the chromosome 14 ORF 24 gene during neurogenesis. FEBS J. 276, 4854–4865.
Komagata, S., Nakajima, M., Takagi, S., Mohri, T., Taniya, T., and Yokoi, T. (2009). Human CYP24 catalyzing the inactivation of calcitriol is post-transcriptionally regulated by miR-125b. Mol. Pharmacol. 76, 702–709.
Kotani, A., Ha, D., Hsieh, J., Rao, P. K., Schotte, D., Den Boer, M. L., Armstrong, S. A., and Lodish, H. F. (2009). miR-128b is a potent glucocorticoid sensitizer in MLL-AF4 acute lymphocytic leukemia cells and exerts cooperative effects with miR-221. Blood 114, 4169–4178.
Krek, A., Grun, D., Poy, M. N., Wolf, R., Rosenberg, L., Epstein, E. J., Macmenamin, P., Da Piedade, I., Gunsalus, K. C., Stoffel, M., and Rajewsky, N. (2005). Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat. Genet. 37, 495–500.
Lagos, D., Pollara, G., Henderson, S., Gratrix, F., Fabani, M., Milne, R. S., Gotch, F., and Boshoff, C. (2010). miR-132 regulates antiviral innate immunity through suppression of the p300 transcriptional co-activator. Nat. Cell Biol. 12, 513–519.
Lal, A., Navarro, F., Maher, C. A., Maliszewski, L. E., Yan, N., O’day, E., Chowdhury, D., Dykxhoorn, D. M., Tsai, P., Hofmann, O., Becker, K. G., Gorospe, M., Hide, W., and Lieberman, J. (2009a). miR-24 inhibits cell proliferation by targeting E2F2, MYC, and other cell-cycle genes via binding to “seedless” 3′UTR microRNA recognition elements. Mol. Cell 35, 610–625.
Lal, A., Pan, Y., Navarro, F., Dykxhoorn, D. M., Moreau, L., Meire, E., Bentwich, Z., Lieberman, J., and Chowdhury, D. (2009b). miR-24-mediated downregulation of H2AX suppresses DNA repair in terminally differentiated blood cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 16, 492–498.
Lan, F. F., Wang, H., Chen, Y. C., Chan, C. Y., Ng, S. S., Li, K., Xie, D., He, M. L., Lin, M. C., and Kung, H. F. (2011). Hsa-let-7g inhibits proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by downregulation of c-Myc and upregulation of p16(INK4A). Int. J. Cancer 128, 319–331.
Le, M. T., Teh, C., Shyh-Chang, N., Xie, H., Zhou, B., Korzh, V., Lodish, H. F., and Lim, B. (2009). MicroRNA-125b is a novel negative regulator of p53. Genes Dev. 23, 862–876.
Leivonen, S. K., Makela, R., Ostling, P., Kohonen, P., Haapa-Paananen, S., Kleivi, K., Enerly, E., Aakula, A., Hellstrom, K., Sahlberg, N., Kristensen, V. N., Borresen-Dale, A. L., Saviranta, P., Perala, M., and Kallioniemi, O. (2009). Protein lysate microarray analysis to identify microRNAs regulating estrogen receptor signaling in breast cancer cell lines. Oncogene 28, 3926–3936.
Li, L. M., Hou, D. X., Guo, Y. L., Yang, J. W., Liu, Y., Zhang, C. Y., and Zen, K. (2011). Role of microRNA-214-targeting phosphatase and tensin homolog in advanced glycation end product-induced apoptosis delay in monocytes. J. Immunol. 186, 2552–2560.
Li, S. S., Yu, S. L., Kao, L. P., Tsai, Z. Y., Singh, S., Chen, B. Z., Ho, B. C., Liu, Y. H., and Yang, P. C. (2009a). Target identification of microRNAs expressed highly in human embryonic stem cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 106, 1020–1030.
Li, X. F., Yan, P. J., and Shao, Z. M. (2009b). Downregulation of miR-193b contributes to enhance urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) expression and tumor progression and invasion in human breast cancer. Oncogene 28, 3937–3948.
Li, X., and Carthew, R. W. (2005). A microRNA mediates EGF receptor signaling and promotes photoreceptor differentiation in the Drosophila eye. Cell 123, 1267–1277.
Liao, R., Sun, J., Zhang, L., Lou, G., Chen, M., Zhou, D., Chen, Z., and Zhang, S. (2008). MicroRNAs play a role in the development of human hematopoietic stem cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 104, 805–817.
Liu, H., Brannon, A. R., Reddy, A. R., Alexe, G., Seiler, M. W., Arreola, A., Oza, J. H., Yao, M., Juan, D., Liou, L. S., Ganesan, S., Levine, A. J., Rathmell, W. K., and Bhanot, G. V. (2010a). Identifying mRNA targets of microRNA dysregulated in cancer: with application to clear cell renal cell carcinoma. BMC Syst. Biol. 4, 51.
Liu, J., Luo, X. J., Xiong, A. W., Zhang, Z. D., Yue, S., Zhu, M. S., and Cheng, S. Y. (2010b). MicroRNA-214 promotes myogenic differentiation by facilitating exit from mitosis via down-regulation of proto-oncogene N-ras. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 26599–26607.
Liu, X., Sempere, L. F., Ouyang, H., Memoli, V. A., Andrew, A. S., Luo, Y., Demidenko, E., Korc, M., Shi, W., Preis, M., Dragnev, K. H., Li, H., Direnzo, J., Bak, M., Freemantle, S. J., Kauppinen, S., and Dmitrovsky, E. (2010c). MicroRNA-31 functions as an oncogenic microRNA in mouse and human lung cancer cells by repressing specific tumor suppressors. J. Clin. Invest. 120, 1298–1309.
Liu, X., Wang, A., Heidbreder, C. E., Jiang, L., Yu, J., Kolokythas, A., Huang, L., Dai, Y., and Zhou, X. (2010d). MicroRNA-24 targeting RNA-binding protein DND1 in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. FEBS Lett. 584, 4115–4120.
Liu, X., Zhan, Z., Xu, L., Ma, F., Li, D., Guo, Z., Li, N., and Cao, X. (2010e). MicroRNA-148/152 impair innate response and antigen presentation of TLR-triggered dendritic cells by targeting CaMKIIalpha. J. Immunol. 185, 7244–7251.
Liu, K., Liu, Y., Mo, W., Qiu, R., Wang, X., Wu, J. Y., and He, R. (2011). MiR-124 regulates early neurogenesis in the optic vesicle and forebrain, targeting NeuroD1. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, 2869–2879.
Liu, X., Yu, J., Jiang, L., Wang, A., Shi, F., Ye, H., and Zhou, X. (2009). MicroRNA-222 regulates cell invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase 1 (MMP1) and manganese superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) in tongue squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 6, 131–139.
Luna, C., Li, G., Qiu, J., Epstein, D. L., and Gonzalez, P. (2011). MicroRNA-24 regulates the processing of latent TGFbeta1 during cyclic mechanical stress in human trabecular meshwork cells through direct targeting of FURIN. J. Cell. Physiol. 226, 1407–1414.
Luthra, R., Singh, R. R., Luthra, M. G., Li, Y. X., Hannah, C., Romans, A. M., Barkoh, B. A., Chen, S. S., Ensor, J., Maru, D. M., Broaddus, R. R., Rashid, A., and Albarracin, C. T. (2008). MicroRNA-196a targets annexin A1: a microRNA-mediated mechanism of annexin A1 downregulation in cancers. Oncogene 27, 6667–6678.
Lwin, T., Lin, J., Choi, Y. S., Zhang, X., Moscinski, L. C., Wright, K. L., Sotomayor, E. M., Dalton, W. S., and Tao, J. (2010). Follicular dendritic cell-dependent drug resistance of non-Hodgkin lymphoma involves cell adhesion-mediated Bim down-regulation through induction of microRNA-181a. Blood 116, 5228–5236.
Ma, N., Wang, X., Qiao, Y., Li, F., Hui, Y., Zou, C., Jin, J., Lv, G., Peng, Y., Wang, L., Huang, H., Zhou, L., Zheng, X., and Gao, X. (2011). Coexpression of an intronic microRNA and its host gene reveals a potential role for miR-483-5p as an IGF2 partner. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 333, 96–101.
Makeyev, E. V., Zhang, J., Carrasco, M. A., and Maniatis, T. (2007). The microRNA miR-124 promotes neuronal differentiation by triggering brain-specific alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 27, 435–448.
Malhas, A., Saunders, N. J., and Vaux, D. J. (2010). The nuclear envelope can control gene expression and cell cycle progression via miRNA regulation. Cell Cycle 9, 531–539.
Malumbres, R., Sarosiek, K. A., Cubedo, E., Ruiz, J. W., Jiang, X., Gascoyne, R. D., Tibshirani, R., and Lossos, I. S. (2009). Differentiation stage-specific expression of microRNAs in B lymphocytes and diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Blood 113, 3754–3764.
Marasa, B. S., Srikantan, S., Masuda, K., Abdelmohsen, K., Kuwano, Y., Yang, X., Martindale, J. L., Rinker-Schaeffer, C. W., and Gorospe, M. (2009). Increased MKK4 abundance with replicative senescence is linked to the joint reduction of multiple microRNAs. Sci. Signal. 2, ra69.
Mardaryev, A. N., Ahmed, M. I., Vlahov, N. V., Fessing, M. Y., Gill, J. H., Sharov, A. A., and Botchkareva, N. V. (2010). Micro-RNA-31 controls hair cycle-associated changes in gene expression programs of the skin and hair follicle. FASEB J. 24, 3869–3881.
Martinez, I., Cazalla, D., Almstead, L. L., Steitz, J. A., and Dimaio, D. (2011). miR-29 and miR-30 regulate B-Myb expression during cellular senescence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, 522–527.
Maru, D. M., Singh, R. R., Hannah, C., Albarracin, C. T., Li, Y. X., Abraham, R., Romans, A. M., Yao, H., Luthra, M. G., Anandasabapathy, S., Swisher, S. G., Hofstetter, W. L., Rashid, A., and Luthra, R. (2009). MicroRNA-196a is a potential marker of progression during Barrett’s metaplasia-dysplasia-invasive adenocarcinoma sequence in esophagus. Am. J. Pathol. 174, 1940–1948.
Mees, S. T., Mardin, W. A., Wendel, C., Baeumer, N., Willscher, E., Senninger, N., Schleicher, C., Colombo-Benkmann, M., and Haier, J. (2010). EP300 – a miRNA-regulated metastasis suppressor gene in ductal adenocarcinomas of the pancreas. Int. J. Cancer 126, 114–124.
Mellios, N., Huang, H. S., Grigorenko, A., Rogaev, E., and Akbarian, S. (2008). A set of differentially expressed miRNAs, including miR-30a-5p, act as post-transcriptional inhibitors of BDNF in prefrontal cortex. Hum. Mol. Genet. 17, 3030–3042.
Mishra, P. J., Song, B., Wang, Y., Humeniuk, R., Banerjee, D., Merlino, G., Ju, J., and Bertino, J. R. (2009). MiR-24 tumor suppressor activity is regulated independent of p53 and through a target site polymorphism. PLoS ONE 4, e8445.
Muinos-Gimeno, M., Espinosa-Parrilla, Y., Guidi, M., Kagerbauer, B., Sipila, T., Maron, E., Pettai, K., Kananen, L., Navines, R., Martin-Santos, R., Gratacos, M., Metspalu, A., Hovatta, I., and Estivill, X. (2011). Human microRNAs miR-22, miR-138-2, miR-148a, and miR-488 are associated with panic disorder and regulate several anxiety candidate genes and related pathways. Biol. Psychiatry 69, 526–533.
Murata, T., Takayama, K., Katayama, S., Urano, T., Horie-Inoue, K., Ikeda, K., Takahashi, S., Kawazu, C., Hasegawa, A., Ouchi, Y., Homma, Y., Hayashizaki, Y., and Inoue, S. (2010). miR-148a is an androgen-responsive microRNA that promotes LNCaP prostate cell growth by repressing its target CAND1 expression. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 13, 356–361.
Nagel, R., Clijsters, L., and Agami, R. (2009). The miRNA-192/194 cluster regulates the period gene family and the circadian clock. FEBS J. 276, 5447–5455.
Naguibneva, I., Ameyar-Zazoua, M., Polesskaya, A., Ait-Si-Ali, S., Groisman, R., Souidi, M., Cuvellier, S., and Harel-Bellan, A. (2006). The microRNA miR-181 targets the homeobox protein Hox-A11 during mammalian myoblast differentiation. Nat. Cell Biol. 8, 278–284.
Nakamachi, Y., Kawano, S., Takenokuchi, M., Nishimura, K., Sakai, Y., Chin, T., Saura, R., Kurosaka, M., and Kumagai, S. (2009). MicroRNA-124a is a key regulator of proliferation and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 secretion in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. (Munch.) 60, 1294–1304.
Nakano, H., Miyazawa, T., Kinoshita, K., Yamada, Y., and Yoshida, T. (2010). Functional screening identifies a microRNA, miR-491 that induces apoptosis by targeting Bcl-X(L) in colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 127, 1072–1080.
Nguyen, H. T., Dalmasso, G., Yan, Y., Laroui, H., Dahan, S., Mayer, L., Sitaraman, S. V., and Merlin, D. (2010). MicroRNA-7 modulates CD98 expression during intestinal epithelial cell differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 1479–1489.
Pais, H., Nicolas, F. E., Soond, S. M., Swingler, T. E., Clark, I. M., Chantry, A., Moulton, V., and Dalmay, T. (2010). Analyzing mRNA expression identifies Smad3 as a microRNA-140 target regulated only at protein level. RNA 16, 489–494.
Pallasch, C. P., Patz, M., Park, Y. J., Hagist, S., Eggle, D., Claus, R., Debey-Pascher, S., Schulz, A., Frenzel, L. P., Claasen, J., Kutsch, N., Krause, G., Mayr, C., Rosenwald, A., Plass, C., Schultze, J. L., Hallek, M., and Wendtner, C. M. (2009). miRNA deregulation by epigenetic silencing disrupts suppression of the oncogene PLAG1 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 114, 3255–3264.
Pan, W., Zhu, S., Yuan, M., Cui, H., Wang, L., Luo, X., Li, J., Zhou, H., Tang, Y., and Shen, N. (2010). MicroRNA-21 and microRNA-148a contribute to DNA hypomethylation in lupus CD4+ T cells by directly and indirectly targeting DNA methyltransferase 1. J. Immunol. 184, 6773–6781.
Papaioannou, M. D., Lagarrigue, M., Vejnar, C. E., Rolland, A. D., Kuhne, F., Aubry, F., Schaad, O., Fort, A., Descombes, P., Neerman-Arbez, M., Guillou, F., Zdobnov, E. M., Pineau, C., and Nef, S. (2011). Loss of Dicer in Sertoli cells has a major impact on the testicular proteome of mice. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 10, M900587MCP900200.
Park, J. K., Henry, J. C., Jiang, J., Esau, C., Gusev, Y., Lerner, M. R., Postier, R. G., Brackett, D. J., and Schmittgen, T. D. (2011). miR-132 and miR-212 are increased in pancreatic cancer and target the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 406, 518–523.
Pedrioli, D. M., Karpanen, T., Dabouras, V., Jurisic, G., Van De Hoek, G., Shin, J. W., Marino, D., Kalin, R. E., Leidel, S., Cinelli, P., Schulte-Merker, S., Brandli, A. W., and Detmar, M. (2010). miR-31 functions as a negative regulator of lymphatic vascular lineage-specific differentiation in vitro and vascular development in vivo. Mol. Cell. Biol. 30, 3620–3634.
Pekarsky, Y., Santanam, U., Cimmino, A., Palamarchuk, A., Efanov, A., Maximov, V., Volinia, S., Alder, H., Liu, C. G., Rassenti, L., Calin, G. A., Hagan, J. P., Kipps, T., and Croce, C. M. (2006). Tcl1 expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia is regulated by miR-29 and miR-181. Cancer Res. 66, 11590–11593.
Pichiorri, F., Suh, S. S., Rocci, A., De Luca, L., Taccioli, C., Santhanam, R., Zhou, W., Benson, D. M. Jr., Hofmainster, C., Alder, H., Garofalo, M., Di Leva, G., Volinia, S., Lin, H. J., Perrotti, D., Kuehl, M., Aqeilan, R. I., Palumbo, A., and Croce, C. M. (2010). Downregulation of p53-inducible microRNAs 192, 194, and 215 impairs the p53/MDM2 autoregulatory loop in multiple myeloma development. Cancer Cell 18, 367–381.
Pierson, J., Hostager, B., Fan, R., and Vibhakar, R. (2008). Regulation of cyclin dependent kinase 6 by microRNA 124 in medulloblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 90, 1–7.
Pineau, P., Volinia, S., Mcjunkin, K., Marchio, A., Battiston, C., Terris, B., Mazzaferro, V., Lowe, S. W., Croce, C. M., and Dejean, A. (2010). miR-221 overexpression contributes to liver tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 264–269.
Pogribny, I. P., Filkowski, J. N., Tryndyak, V. P., Golubov, A., Shpyleva, S. I., and Kovalchuk, O. (2010). Alterations of microRNAs and their targets are associated with acquired resistance of MCF-7 breast cancer cells to cisplatin. Int. J. Cancer 127, 1785–1794.
Qin, W., Shi, Y., Zhao, B., Yao, C., Jin, L., Ma, J., and Jin, Y. (2010). miR-24 regulates apoptosis by targeting the open reading frame (ORF) region of FAF1 in cancer cells. PLoS ONE 5, e9429.
Qiu, R., Liu, K., Liu, Y., Mo, W., Flynt, A. S., Patton, J. G., Kar, A., Wu, J. Y., and He, R. (2009). The role of miR-124a in early development of the Xenopus eye. Mech. Dev. 126, 804–816.
Rajabi, H., Jin, C., Ahmad, R., Mcclary, C., Joshi, M. D., and Kufe, D. (2010). Mucin 1 oncoprotein expression is suppressed by the mir-125b oncomir. Genes Cancer 1, 62–68.
Rane, S., He, M., Sayed, D., Vashistha, H., Malhotra, A., Sadoshima, J., Vatner, D. E., Vatner, S. F., and Abdellatif, M. (2009). Downregulation of miR-199a derepresses hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and sirtuin 1 and recapitulates hypoxia preconditioning in cardiac myocytes. Circ. Res. 104, 879–886.
Reddy, S. D., Ohshiro, K., Rayala, S. K., and Kumar, R. (2008). MicroRNA-7, a homeobox D10 target, inhibits p21-activated kinase 1 and regulates its functions. Cancer Res. 68, 8195–8200.
Ren, X. P., Wu, J., Wang, X., Sartor, M. A., Qian, J., Jones, K., Nicolaou, P., Pritchard, T. J., and Fan, G. C. (2009). MicroRNA-320 is involved in the regulation of cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury by targeting heat-shock protein 20. Circulation 119, 2357–2366.
Saetrom, P., Biesinger, J., Li, S. M., Smith, D., Thomas, L. F., Majzoub, K., Rivas, G. E., Alluin, J., Rossi, J. J., Krontiris, T. G., Weitzel, J., Daly, M. B., Benson, A. B., Kirkwood, J. M., O’dwyer, P. J., Sutphen, R., Stewart, J. A., Johnson, D., and Larson, G. P. (2009). A risk variant in an miR-125b binding site in BMPR1B is associated with breast cancer pathogenesis. Cancer Res. 69, 7459–7465.
Salomonis, N., Schlieve, C. R., Pereira, L., Wahlquist, C., Colas, A., Zambon, A. C., Vranizan, K., Spindler, M. J., Pico, A. R., Cline, M. S., Clark, T. A., Williams, A., Blume, J. E., Samal, E., Mercola, M., Merrill, B. J., and Conklin, B. R. (2010). Alternative splicing regulates mouse embryonic stem cell pluripotency and differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 107, 10514–10519.
Saunders, L. R., Sharma, A. D., Tawney, J., Nakagawa, M., Okita, K., Yamanaka, S., Willenbring, H., and Verdin, E. (2010). miRNAs regulate SIRT1 expression during mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation and in adult mouse tissues. Aging (Albany NY) 2, 415–431.
Saydam, O., Senol, O., Wurdinger, T., Mizrak, A., Ozdener, G. B., Stemmer-Rachamimov, A. O., Yi, M., Stephens, R. M., Krichevsky, A. M., Saydam, N., Brenner, G. J., and Breakefield, X. O. (2011). miRNA-7 attenuation in schwannoma tumors stimulates growth by upregulating three oncogenic signaling pathways. Cancer Res. 71, 852–861.
Schaar, D. G., Medina, D. J., Moore, D. F., Strair, R. K., and Ting, Y. (2009). miR-320 targets transferrin receptor 1 (CD71) and inhibits cell proliferation. Exp. Hematol. 37, 245–255.
Schickel, R., Park, S. M., Murmann, A. E., and Peter, M. E. (2010). miR-200c regulates induction of apoptosis through CD95 by targeting FAP-1. Mol. Cell 38, 908–915.
Scott, G. K., Goga, A., Bhaumik, D., Berger, C. E., Sullivan, C. S., and Benz, C. C. (2007). Coordinate suppression of ERBB2 and ERBB3 by enforced expression of micro-RNA miR-125a or miR-125b. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 1479–1486.
Sepramaniam, S., Armugam, A., Lim, K. Y., Karolina, D. S., Swaminathan, P., Tan, J. R., and Jeyaseelan, K. (2010). MicroRNA 320a functions as a novel endogenous modulator of aquaporins 1 and 4 as well as a potential therapeutic target in cerebral ischemia. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 29223–29230.
Shao, M., Rossi, S., Chelladurai, B., Shimizu, M., Ntukogu, O., Ivan, M., Calin, G. A., and Matei, D. (2011). PDGF induced microRNA alterations in cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, 4035–4047.
Shen, Q., Cicinnati, V. R., Zhang, X., Iacob, S., Weber, F., Sotiropoulos, G. C., Radtke, A., Lu, M., Paul, A., Gerken, G., and Beckebaum, S. (2010). Role of microRNA-199a-5p and discoidin domain receptor 1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma invasion. Mol. Cancer 9, 227.
Shimizu, S., Takehara, T., Hikita, H., Kodama, T., Miyagi, T., Hosui, A., Tatsumi, T., Ishida, H., Noda, T., Nagano, H., Doki, Y., Mori, M., and Hayashi, N. (2010). The let-7 family of microRNAs inhibits Bcl-xL expression and potentiates sorafenib-induced apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 52, 698–704.
Small, E. M., Sutherland, L. B., Rajagopalan, K. N., Wang, S., and Olson, E. N. (2010). MicroRNA-218 regulates vascular patterning by modulation of Slit-Robo signaling. Circ. Res. 107, 1336–1344.
Smirnov, D. A., and Cheung, V. G. (2008). ATM gene mutations result in both recessive and dominant expression phenotypes of genes and microRNAs. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 83, 243–253.
Sober, S., Laan, M., and Annilo, T. (2010). MicroRNAs miR-124 and miR-135a are potential regulators of the mineralocorticoid receptor gene (NR3C2) expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 391, 727–732.
Song, L., Huang, Q., Chen, K., Liu, L., Lin, C., Dai, T., Yu, C., Wu, Z., and Li, J. (2010). miR-218 inhibits the invasive ability of glioma cells by direct downregulation of IKK-beta. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 402, 135–140.
Sossey-Alaoui, K., Downs-Kelly, E., Das, M., Izem, L., Tubbs, R., and Plow, E. F. (2010). WAVE3, an actin remodeling protein, is regulated by the metastasis suppressor microRNA, miR-31, during the invasion-metastasis cascade. Int. J. Cancer 129, 1331–1343.
Strum, J. C., Johnson, J. H., Ward, J., Xie, H., Feild, J., Hester, A., Alford, A., and Waters, K. M. (2009). MicroRNA 132 regulates nutritional stress-induced chemokine production through repression of SirT1. Mol. Endocrinol. 23, 1876–1884.
Suarez, Y., Wang, C., Manes, T. D., and Pober, J. S. (2010). Cutting edge: TNF-induced microRNAs regulate TNF-induced expression of E-selectin and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on human endothelial cells: feedback control of inflammation. J. Immunol. 184, 21–25.
Surdziel, E., Cabanski, M., Dallmann, I., Lyszkiewicz, M., Krueger, A., Ganser, A., Scherr, M., and Eder, M. (2011). Enforced expression of miR-125b affects myelopoiesis by targeting multiple signaling pathways. Blood 117, 4338–4348.
Taganov, K. D., Boldin, M. P., Chang, K. J., and Baltimore, D. (2006). NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 12481–12486.
Takagi, S., Nakajima, M., Kida, K., Yamaura, Y., Fukami, T., and Yokoi, T. (2010). MicroRNAs regulate human hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha, modulating the expression of metabolic enzymes and cell cycle. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 4415–4422.
Takagi, S., Nakajima, M., Mohri, T., and Yokoi, T. (2008). Post-transcriptional regulation of human pregnane X receptor by micro-RNA affects the expression of cytochrome P450 3A4. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 9674–9680.
Tan, Z., Randall, G., Fan, J., Camoretti-Mercado, B., Brockman-Schneider, R., Pan, L., Solway, J., Gern, J. E., Lemanske, R. F., Nicolae, D., and Ober, C. (2007). Allele-specific targeting of microRNAs to HLA-G and risk of asthma. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 81, 829–834.
Terasawa, K., Ichimura, A., Sato, F., Shimizu, K., and Tsujimoto, G. (2009). Sustained activation of ERK1/2 by NGF induces microRNA-221 and 222 in PC12 cells. FEBS J. 276, 3269–3276.
Thatcher, E. J., Paydar, I., Anderson, K. K., and Patton, J. G. (2008). Regulation of zebrafish fin regeneration by microRNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 18384–18389.
Tili, E., Michaille, J. J., Adair, B., Alder, H., Limagne, E., Taccioli, C., Ferracin, M., Delmas, D., Latruffe, N., and Croce, C. M. (2010a). Resveratrol decreases the levels of miR-155 by upregulating miR-663, a microRNA targeting JunB and JunD. Carcinogenesis 31, 1561–1566.
Tili, E., Michaille, J. J., Alder, H., Volinia, S., Delmas, D., Latruffe, N., and Croce, C. M. (2010b). Resveratrol modulates the levels of microRNAs targeting genes encoding tumor-suppressors and effectors of TGFbeta signaling pathway in SW480 cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 80, 2057–2065.
Tili, E., Michaille, J. J., Cimino, A., Costinean, S., Dumitru, C. D., Adair, B., Fabbri, M., Alder, H., Liu, C. G., Calin, G. A., and Croce, C. M. (2007). Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following lipopolysaccharide/TNF-alpha stimulation and their possible roles in regulating the response to endotoxin shock. J. Immunol. 179, 5082–5089.
To, K. K., Zhan, Z., Litman, T., and Bates, S. E. (2008). Regulation of ABCG2 expression at the 3′ untranslated region of its mRNA through modulation of transcript stability and protein translation by a putative microRNA in the S1 colon cancer cell line. Mol. Cell. Biol. 28, 5147–5161.
Tuddenham, L., Wheeler, G., Ntounia-Fousara, S., Waters, J., Hajihosseini, M. K., Clark, I., and Dalmay, T. (2006). The cartilage specific microRNA-140 targets histone deacetylase 4 in mouse cells. FEBS Lett. 580, 4214–4217.
Ueda, R., Kohanbash, G., Sasaki, K., Fujita, M., Zhu, X., Kastenhuber, E. R., Mcdonald, H. A., Potter, D. M., Hamilton, R. L., Lotze, M. T., Khan, S. A., Sobol, R. W., and Okada, H. (2009). Dicer-regulated microRNAs 222 and 339 promote resistance of cancer cells to cytotoxic T-lymphocytes by down-regulation of ICAM-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 10746–10751.
Ueno, K., Hirata, H., Shahryari, V., Chen, Y., Zaman, M. S., Singh, K., Tabatabai, Z. L., Hinoda, Y., and Dahiya, R. (2011). Tumour suppressor microRNA-584 directly targets oncogene Rock-1 and decreases invasion ability in human clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 104, 308–315.
Uhlmann, S., Zhang, J. D., Schwager, A., Mannsperger, H., Riazalhosseini, Y., Burmester, S., Ward, A., Korf, U., Wiemann, S., and Sahin, O. (2010). miR-200bc/429 cluster targets PLCgamma1 and differentially regulates proliferation and EGF-driven invasion than miR-200a/141 in breast cancer. Oncogene 29, 4297–4306.
Valastyan, S., Reinhardt, F., Benaich, N., Calogrias, D., Szasz, A. M., Wang, Z. C., Brock, J. E., Richardson, A. L., and Weinberg, R. A. (2009). A pleiotropically acting microRNA, miR-31, inhibits breast cancer metastasis. Cell 137, 1032–1046.
Venugopal, S. K., Jiang, J., Kim, T. H., Li, Y., Wang, S. S., Torok, N. J., Wu, J., and Zern, M. A. (2010). Liver fibrosis causes downregulation of miRNA-150 and miRNA-194 in hepatic stellate cells, and their overexpression causes decreased stellate cell activation. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 298, G101–G106.
Veronese, A., Lupini, L., Consiglio, J., Visone, R., Ferracin, M., Fornari, F., Zanesi, N., Alder, H., D’elia, G., Gramantieri, L., Bolondi, L., Lanza, G., Querzoli, P., Angioni, A., Croce, C. M., and Negrini, M. (2010). Oncogenic role of miR-483-3p at the IGF2/483 locus. Cancer Res. 70, 3140–3149.
Villeneuve, L. M., Kato, M., Reddy, M. A., Wang, M., Lanting, L., and Natarajan, R. (2010). Enhanced levels of microRNA-125b in vascular smooth muscle cells of diabetic db/db mice lead to increased inflammatory gene expression by targeting the histone methyltransferase Suv39h1. Diabetes 59, 2904–2915.
Viticchie, G., Lena, A. M., Latina, A., Formosa, A., Gregersen, L. H., Lund, A. H., Bernardini, S., Mauriello, A., Miano, R., Spagnoli, L. G., Knight, R. A., Candi, E., and Melino, G. (2011). MiR-203 controls proliferation, migration and invasive potential of prostate cancer cell lines. Cell Cycle 10, 1121–1131.
Vreugdenhil, E., Verissimo, C. S., Mariman, R., Kamphorst, J. T., Barbosa, J. S., Zweers, T., Champagne, D. L., Schouten, T., Meijer, O. C., De Kloet, E. R., and Fitzsimons, C. P. (2009). MicroRNA 18 and 124a down-regulate the glucocorticoid receptor: implications for glucocorticoid responsiveness in the brain. Endocrinology 150, 2220–2228.
Wang, B., Hsu, S. H., Majumder, S., Kutay, H., Huang, W., Jacob, S. T., and Ghoshal, K. (2010a). TGFbeta-mediated upregulation of hepatic miR-181b promotes hepatocarcinogenesis by targeting TIMP3. Oncogene 29, 1787–1797.
Wang, X., Zhang, X., Ren, X. P., Chen, J., Liu, H., Yang, J., Medvedovic, M., Hu, Z., and Fan, G. C. (2010b). MicroRNA-494 targeting both proapoptotic and antiapoptotic proteins protects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac injury. Circulation 122, 1308–1318.
Wang, Q., Huang, Z., Xue, H., Jin, C., Ju, X. L., Han, J. D., and Chen, Y. G. (2008). MicroRNA miR-24 inhibits erythropoiesis by targeting activin type I receptor ALK4. Blood 111, 588–595.
Wang, Y., Yu, Y., Tsuyada, A., Ren, X., Wu, X., Stubblefield, K., Rankin-Gee, E. K., and Wang, S. E. (2011). Transforming growth factor-beta regulates the sphere-initiating stem cell-like feature in breast cancer through miRNA-181 and ATM. Oncogene 30, 1470–1480.
Wei, T., Orfanidis, K., Xu, N., Janson, P., Stahle, M., Pivarcsi, A., and Sonkoly, E. (2010). The expression of microRNA-203 during human skin morphogenesis. Exp. Dermatol. 19, 854–856.
Wong, Q. W., Ching, A. K., Chan, A. W., Choy, K. W., To, K. F., Lai, P. B., and Wong, N. (2010). MiR-222 overexpression confers cell migratory advantages in hepatocellular carcinoma through enhancing AKT signaling. Clin. Cancer Res. 16, 867–875.
Wu, D. W., Cheng, Y. W., Wang, J., Chen, C. Y., and Lee, H. (2010a). Paxillin predicts survival and relapse in non-small cell lung cancer by microRNA-218 targeting. Cancer Res. 70, 10392–10401.
Wu, H., Sun, S., Tu, K., Gao, Y., Xie, B., Krainer, A. R., and Zhu, J. (2010b). A splicing-independent function of SF2/ASF in microRNA processing. Mol. Cell 38, 67–77.
Wu, F., Zhu, S., Ding, Y., Beck, W. T., and Mo, Y. Y. (2009). MicroRNA-mediated regulation of Ubc9 expression in cancer cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 1550–1557.
Wu, L., and Belasco, J. G. (2005). Micro-RNA regulation of the mammalian lin-28 gene during neuronal differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 9198–9208.
Xi, S., Yang, M., Tao, Y., Xu, H., Shan, J., Inchauste, S., Zhang, M., Mercedes, L., Hong, J. A., Rao, M., and Schrump, D. S. (2010). Cigarette smoke induces C/EBP-beta-mediated activation of miR-31 in normal human respiratory epithelia and lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 5, e13764.
Xia, H., Qi, Y., Ng, S. S., Chen, X., Li, D., Chen, S., Ge, R., Jiang, S., Li, G., Chen, Y., He, M. L., Kung, H. F., Lai, L., and Lin, M. C. (2009a). microRNA-146b inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion by targeting MMPs. Brain Res. 1269, 158–165.
Xia, H. F., He, T. Z., Liu, C. M., Cui, Y., Song, P. P., Jin, X. H., and Ma, X. (2009b). MiR-125b expression affects the proliferation and apoptosis of human glioma cells by targeting Bmf. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 23, 347–358.
Xia, W., Li, J., Chen, L., Huang, B., Li, S., Yang, G., Ding, H., Wang, F., Liu, N., Zhao, Q., Fang, T., Song, T., Wang, T., and Shao, N. (2010). MicroRNA-200b regulates cyclin D1 expression and promotes S-phase entry by targeting RND3 in HeLa cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 344, 261–266.
Xia, X. G., Zhou, H., Samper, E., Melov, S., and Xu, Z. (2006). Pol II-expressed shRNA knocks down Sod2 gene expression and causes phenotypes of the gene knockout in mice. PLoS Genet. 2, e10.
Xiao, J., Lin, H., Luo, X., and Wang, Z. (2011). miR-605 joins p53 network to form a p53:miR-605:Mdm2 positive feedback loop in response to stress. EMBO J. 30, 524–532.
Xu, C., Liu, S., Fu, H., Li, S., Tie, Y., Zhu, J., Xing, R., Jin, Y., Sun, Z., and Zheng, X. (2010a). MicroRNA-193b regulates proliferation, migration and invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Eur. J. Cancer 46, 2828–2836.
Xu, L., Wang, F., Xu, X. F., Mo, W. H., Xia, Y. J., Wan, R., Wang, X. P., and Guo, C. Y. (2010b). Down-regulation of miR-212 expression by DNA hypermethylation in human gastric cancer cells. Med. Oncol.
Xue, Q., Guo, Z. Y., Li, W., Wen, W. H., Meng, Y. L., Jia, L. T., Wang, J., Yao, L. B., Jin, B. Q., Wang, T., and Yang, A. G. (2011). Human activated CD4(+) T lymphocytes increase IL-2 expression by downregulating microRNA-181c. Mol. Immunol. 48, 592–599.
Yang, Z., Chen, S., Luan, X., Li, Y., Liu, M., Li, X., Liu, T., and Tang, H. (2009). MicroRNA-214 is aberrantly expressed in cervical cancers and inhibits the growth of HeLa cells. IUBMB Life 61, 1075–1082.
Yao, J., Liang, L., Huang, S., Ding, J., Tan, N., Zhao, Y., Yan, M., Ge, C., Zhang, Z., Chen, T., Wan, D., Yao, M., Li, J., Gu, J., and He, X. (2010). MicroRNA-30d promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by targeting Galphai2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 51, 846–856.
Yi, R., Poy, M. N., Stoffel, M., and Fuchs, E. (2008). A skin microRNA promotes differentiation by repressing “stemness.” Nature 452, 225–229.
Yoo, A. S., Staahl, B. T., Chen, L., and Crabtree, G. R. (2009). MicroRNA-mediated switching of chromatin-remodelling complexes in neural development. Nature 460, 642–646.
Yoon, S., Choi, Y. C., Lee, S., Jeong, Y., Yoon, J., and Baek, K. (2010). Induction of growth arrest by miR-542-3p that targets survivin. FEBS Lett. 584, 4048–4052.
Yu, J. Y., Reynolds, S. H., Hatfield, S. D., Shcherbata, H. R., Fischer, K. A., Ward, E. J., Long, D., Ding, Y., and Ruohola-Baker, H. (2009). Dicer-1-dependent Dacapo suppression acts downstream of insulin receptor in regulating cell division of Drosophila germline stem cells. Development 136, 1497–1507.
Zhang, C. Z., Zhang, J. X., Zhang, A. L., Shi, Z. D., Han, L., Jia, Z. F., Yang, W. D., Wang, G. X., Jiang, T., You, Y. P., Pu, P. Y., Cheng, J. Q., and Kang, C. S. (2010). MiR-221 and miR-222 target PUMA to induce cell survival in glioblastoma. Mol. Cancer 9, 229.
Zhang, H. Y., Zheng, S. J., Zhao, J. H., Zhao, W., Zheng, L. F., Zhao, D., Li, J. M., Zhang, X. F., Chen, Z. B., and Yi, X. N. (2011a). MicroRNAs 144, 145, and 214 are down-regulated in primary neurons responding to sciatic nerve transection. Brain Res. 1383, 62–70.
Zhang, L., Stokes, N., Polak, L., and Fuchs, E. (2011b). Specific MicroRNAs are preferentially expressed by skin stem cells to balance self-renewal and early lineage commitment. Cell Stem Cell 8, 294–308.
Zhang, Y., Gao, J. S., Tang, X., Tucker, L. D., Quesenberry, P., Rigoutsos, I., and Ramratnam, B. (2009). MicroRNA 125a and its regulation of the p53 tumor suppressor gene. FEBS Lett. 583, 3725–3730.
Zhao, J. J., Lin, J., Yang, H., Kong, W., He, L., Ma, X., Coppola, D., and Cheng, J. Q. (2008). MicroRNA-221/222 negatively regulates estrogen receptor alpha and is associated with tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 31079–31086.
Zhao, X., Tang, Y., Qu, B., Cui, H., Wang, S., Wang, L., Luo, X., Huang, X., Li, J., Chen, S., and Shen, N. (2010). MicroRNA-125a contributes to elevated inflammatory chemokine RANTES levels via targeting KLF13 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. (Munch.) 62, 3425–3435.
Zhong, X., Li, N., Liang, S., Huang, Q., Coukos, G., and Zhang, L. (2010). Identification of microRNAs regulating reprogramming factor LIN28 in embryonic stem cells and cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 41961–41971.
Zhou, L., Qi, X., Potashkin, J. A., Abdul-Karim, F. W., and Gorodeski, G. I. (2008). MicroRNAs miR-186 and miR-150 down-regulate expression of the pro-apoptotic purinergic P2X7 receptor by activation of instability sites at the 3′-untranslated region of the gene that decrease steady-state levels of the transcript. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 28274–28286.
Zhou, M., Liu, Z., Zhao, Y., Ding, Y., Liu, H., Xi, Y., Xiong, W., Li, G., Lu, J., Fodstad, O., Riker, A. I., and Tan, M. (2010). MicroRNA-125b confers the resistance of breast cancer cells to paclitaxel through suppression of pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 antagonist killer 1 (Bak1) expression. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 21496–21507.
Zhu, H., Wu, H., Liu, X., Li, B., Chen, Y., Ren, X., Liu, C. G., and Yang, J. M. (2009). Regulation of autophagy by a beclin 1-targeted microRNA, miR-30a, in cancer cells. Autophagy 5, 816–823.
Zhu, N., Zhang, D., Chen, S., Liu, X., Lin, L., Huang, X., Guo, Z., Liu, J., Wang, Y., Yuan, W., and Qin, Y. (2011). Endothelial enriched microRNAs regulate angiotensin II-induced endothelial inflammation and migration. Atherosclerosis 215, 286–293.
Zhu, W., Shan, X., Wang, T., Shu, Y., and Liu, P. (2010). miR-181b modulates multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human cancer cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 127, 2520–2529.
Zimmerman, E. I., Dollins, C. M., Crawford, M., Grant, S., Nana-Sinkam, S. P., Richards, K. L., Hammond, S. M., and Graves, L. M. (2010). Lyn kinase-dependent regulation of miR181 and myeloid cell leukemia-1 expression: implications for drug resistance in myelogenous leukemia. Mol. Pharmacol. 78, 811–817.
Keywords: AChE, BChE, microRNA
Citation: Hanin G and Soreq H (2011) Cholinesterase-targeting microRNAs identified in silico affect specific biological processes. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 4:28. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2011.00028
Received: 25 July 2011; Paper pending published: 23 August 2011;
Accepted: 14 September 2011; Published online: 05 October 2011.
Edited by:
Karl Tsim, The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, ChinaReviewed by:
Sheriar Hormuzdi, University of Dundee, UKJavier Saez-Valero, Universidad Miguel Hernandez, Spain
Copyright: © 2011 Hanin and Soreq. This is an open-access article subject to a non-exclusive license between the authors and Frontiers Media SA, which permits use, distribution and reproduction in other forums, provided the original authors and source are credited and other Frontiers conditions are complied with.
*Correspondence: Hermona Soreq, The Silberman Institute of Life Sciences, The Hebrew University of Jerusalem, The Edmond Safra Campus, Givat Ram, Jerusalem 91904, Israel. e-mail: soreq@cc.huji.ac.il
 Geula Hanin1,2
Geula Hanin1,2