- Department of Environment and Health, Tianjin Institute of Environmental & Operational Medicine, Key Laboratory of Risk Assessment and Control for Environment & Food Safety, Tianjin, China
Given its excellent performance against the pathogens, UV disinfection has been applied broadly in different fields. However, only limited studies have comprehensively investigated the response of bacteria surviving UV irradiation to the environmental antibiotic stress. Here, we investigated the antibiotic susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa suffering from the UV irradiation. Our results revealed that UV exposure may decrease the susceptibility to tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, and polymyxin B in the survival P. aeruginosa. Mechanistically, UV exposure causes oxidative stress in P. aeruginosa and consequently induces dysregulation of genes contributed to the related antibiotic resistance genes. These results revealed that the insufficient ultraviolet radiation dose may result in the decreased antibiotic susceptibility in the pathogens, thus posing potential threats to the environment and human health.
Introduction
In recent decades, antibiotic resistance has emerged as a growingly serious threat to global public health. According to estimates, antibiotic resistance will lead to as many as 10 million casualties annually by 2050 if we don’t take any action at present (O’Neill, 2015). In 2015, the World Health Organization (WHO) announced a global action plan that urges international participants to take immediate action to control and monitor the spread of antimicrobial resistance (WHO, 2015). Hence, antibiotic resistance is receiving increasing global attention (Pruden et al., 2006; Watkins and Bonomo, 2016; Zhu et al., 2017).
In order to control the spread of infectious diseases through the faecal–oral route, disinfection processes, such as chlorination and UV irradiation, are generally applied to kill pathogens during the water treatment (Berry et al., 2006; Gassie and Englehardt, 2017). Although disinfection processes substantially remove antibiotic resistant bacteria (ARB), the general observation is that they cannot completely eliminate antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs; Borjesson et al., 2009; Munir et al., 2011; Huang et al., 2013; Yuan et al., 2014). Accumulating evidence has revealed that chlorination increases the prevalence of ARGs both in and out of bacteria (Khan et al., 2016; Liu et al., 2018; Jin et al., 2020). The emergence of culturable chlorine-injured bacteria that are physiologically unhealthy and suffer from reversible damage due to partial or inappropriate chlorination (McFeters et al., 1986) may play important roles in ARB transmission. Such bacteria were found to be prone to absorbing extracellular ARGs (eARGs) by natural transformation (Jin et al., 2020). This also resulted in enhanced temporary physiological antibiotic resistance to ceftazidime and chloramphenicol in injured P. aeruginosa (Hou et al., 2019).
UV irradiation, which is considered a promising physical disinfectant in the water treatment without generating toxic by-products, can penetrate bacterial cell walls and is directly absorbed by nucleic acids, resulting in the inactivation of ARB and damage to ARGs via the formation of dimers of adjacent cytosines or thymine (Zhang et al., 2019). Considering its principal difference from the chlorination process, the UV-induced response in the bacteria may be quite different from the chlorine-induced response. A recent study revealed that UV exposure can lead to the enrichment of bacteria resistant to sulfadiazine, vancomycin, rifampicin, tetracycline and chloramphenicol due to the microbial selectivity of UV exposure to ARB (Guo et al., 2013). In addition, UV exposure strongly stimulates the ability of Legionella pneumophila to take up and integrate exogenous DNA (Charpentier et al., 2011). In contrast, a 1 mJ/cm2 UV dose can significantly decrease the conjugative transfer frequency of the surviving bacteria (Guo and Kong, 2019). However, few studies have comprehensively investigated the response of bacteria surviving UV irradiation to the environmental antibiotic stress.
In the present study, susceptibility to a panel of six antibiotics was explored in P. aeruginosa surviving UV irradiation. The mechanism of antibiotic susceptibility was further investigated by global transcriptional analyses, quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) validation and antioxidant measurement. The results serve to advance our understanding of the adaption of such pathogens, which can survive UV irradiation, to diverse environments.
Materials and Methods
Bacterial Strains and Antibiotics Used in the Study
The P. aeruginosa strain was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC 27853). Liquid cultures of P. aeruginosa were grown in LB medium [10 g/L tryptone (Difco, Detroit, MI, United States), 10 g/L NaCl and 5 g/L yeast extract (Difco)] at 37°C for 12 h. Cetrimide agar (BD Diagnostics, Franklin Lakes, NJ, United States) is a selective medium used for quantitative determination of P. aeruginosa. All viable bacteria in the samples were detected by TSYA, a repair medium for injured bacteria (Hou et al., 2019). In general, 1 L of TSYA contains 15 g agar (Oxoid, Basingstoke, United Kingdom), 3 g yeast extract (Oxoid) and 30 g trypticase soy broth (TSB, BD Diagnostics). All antibiotics, including tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, polymyxin B, ceftazidime, chloramphenicol and gentamicin, were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, United States). Fresh antibiotic solutions were prepared from powder stocks on a weekly basis, stored at -20°C and filter sterilized before use.
UV Exposure Experiment
A 100 μL suspension of overnight cultured P. aeruginosa in LB medium was transferred into another 40 mL fresh LB medium and cultured overnight at 37°C, with shaking at 150 rpm. Bacteria were harvested by centrifugation at 8,000 rpm for 10 min and then washed thrice with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.2), and suspended in 40 mL PBS (the final concentration of P. aeruginosa was ∼109 CFU/mL). For UV irradiation, each 40 mL sample was placed onto a 90-mm-diameter petri dish. A low-pressure (LP) collimated beam apparatus containing an LP (120 W, 30% UVC, TL 120W/01, Philips, Holland) mercury UV lamp was used to perform the UV exposure process. The wavelength of the UVC lamp is 254 nm. The corresponding disinfection apparatus were described in more detail in a previous publication (Guo et al., 2013). The exposure time was changed for various plates to reach UV doses of 5.50, 8.25, 11.00, and 13.75 mJ/cm2, with irradiance values fixed at 0.275 mW/cm2. The exposed samples were preserved for microbial analysis. All the experiments were conducted in triplicate.
Numeration of the Injured and Total Viable P. aeruginosa
The number of viable injured bacteria in the UV-exposed samples was determined according to a previously reported method (Wang et al., 2017; Hou et al., 2019). TSYA medium was used for counting the total number of P. aeruginosa, while cetrimide agar plates used for the number of uninjured P. aeruginosa. After incubating at 37°C for 48 h, different counts between TSYA and cetrimide agar plates were taken as reference values for the detection of injured P. aeruginosa. The lethality rate of P. aeruginosa and the percentage of injured bacteria were calculated according to Eqs 1 and 2, respectively:
Here, A, detected on TSYA, is the initial concentration of viable P. aeruginosa before UV exposure; B, detected on TSYA, is the concentration of viable P. aeruginosa following various UV doses and C is the concentration of uninjured P. aeruginosa, as detected on cetrimide agar.
Minimum Inhibitory Concentration Assays
After the UV irradiation, we immediately tested the antibiotic susceptibility of the UV-exposed P. aeruginosa using a panel of six antibiotics. Antibiotic minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) assays were performed using the broth microdilution method according to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute guidelines (Cockerill, 2010). The treated bacteria in the UV exposure experiment were diluted 1:1,000 into fresh Mueller-Hinton (MH) broth (Solarbio, Beijing, China). The untreated P. aeruginosa were diluted 1, 000-, 10, 000-, 100,000-fold respectively, making it certain that control group was comparable to UV-treated group. To each cell, 135 μL of diluted bacterial suspension and 15 μL of serial twofold dilutions of antibiotics were added. For the positive control, wells were prepared by inoculating bacteria without antibiotics. A non-inoculated well was used as the negative control. The plates were sealed using an air-permeable membrane (Breathe-Easy, Diversified Biotech, Boston, MA, United States) and incubated at 37°C for 24 h. Then, the OD600 of each plate was measured using a microplate reader (BioTek, Shanghai, China), and MIC values were determined as previously described (Hou et al., 2019). All the tests were performed at least three times.
Measurement of the Activity of Antioxidant Enzymes
P. aeruginosa cell samples, at the indicated times following UV exposure, were prepared to assay the oxidative stress response. After sonication at 20 kHz (150 W) for 10 min to break down the bacteria using an ultrasonic cell cracker (VCX750, Sonics, Newtown, CT, United States), the collected samples were centrifuged at 5,000 × g at 4°C for 3 min. The levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) in the supernatant were assessed using kits obtained from the Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute (Nanjing, China), following the manufacturers’ instructions. The absorbance values of the indicators CAT, GSH-Px, and SOD were determined at 405, 412, and 550 nm, respectively, using a plate reader (BioTek). All the assays were performed in triplicate.
Total RNA Isolation and Whole Transcriptome Sequencing
P. aeruginosa cells exposed to a 11.00 mJ/cm2 UV dose were isolated using the Total RNA Isolation Kit (EZ-10 Spin Column, BBI Life Sciences, Shanghai, China), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Purity of total RNA was determined as 260 nm/280 nm absorbance ratio with expected value of 1.8–2.0 by the GeneQuant 1300 spectrophotometer (GE Healthcare, Milan, Italy). Total RNA was treated with DNase I (Ambion, Grand Island, NY, United States) to eliminate residual genomic DNA. Whole transcriptome sequencing was performed as described previously (Hou et al., 2019). The P. aeruginosa PAO1 genome (Genbank accession no. NC_002516.2) was used as a reference for annotation. Genes with fold change (FC) ≥ 2 were recruited as differentially expressed genes (You et al., 2018).
qRT-PCR Assays
cDNA was synthesized from 500 ng of total RNA using the PrimeScript RT Reagent Kit (Takara, Dalian, China), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The qRT-PCR assays were performed on the ViiATM 7 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, United States) using FastStart Universal SYBR® Green Master (Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany). The 16S rRNA was employed as a reference for normalization. The relative mRNA expression levels were calculated using the comparative ΔΔCt method (2–Δ Δ Ct). The primer sequences are described in Supplementary Table 1.
Statistical Analyses
Statistical analyses were performed using Microsoft Excel (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, United States), GraphPad Prism and SPSS 19.0. Spearman’s rank correlation test was used to analyze the potential correlations between bacterial composition and MICs of antibiotics. Student’s t-test was used to compare quantitative data between groups. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
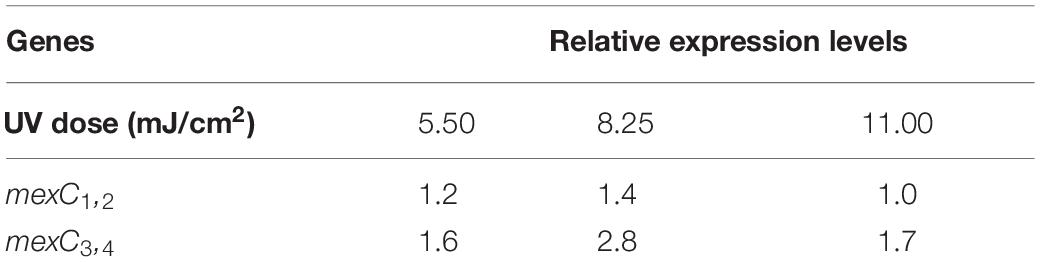
Inactivation Curves of P. aeruginosa During UV Exposure
To observe the dynamics of bacterial killing, the inactivation curves of P. aeruginosa following UV exposure were investigated during bench-scale inactivation experiments (Figure 1). The inactivation curves had two phases: an initial phase with faster kinetics and a subsequent phase with slower kinetics. The initial phase had a clear dose effect, with the inactivation rate increasing with the dose. More than 70% of cells were killed at a UV dose of 5.50 mJ/cm2. Subsequently, nearly 94% of cells were killed at a UV dose of 11.00 mJ/cm2. No significant increase was noted in bacterial inactivation, even when the UV dose was up to 13.75 mJ/cm2.
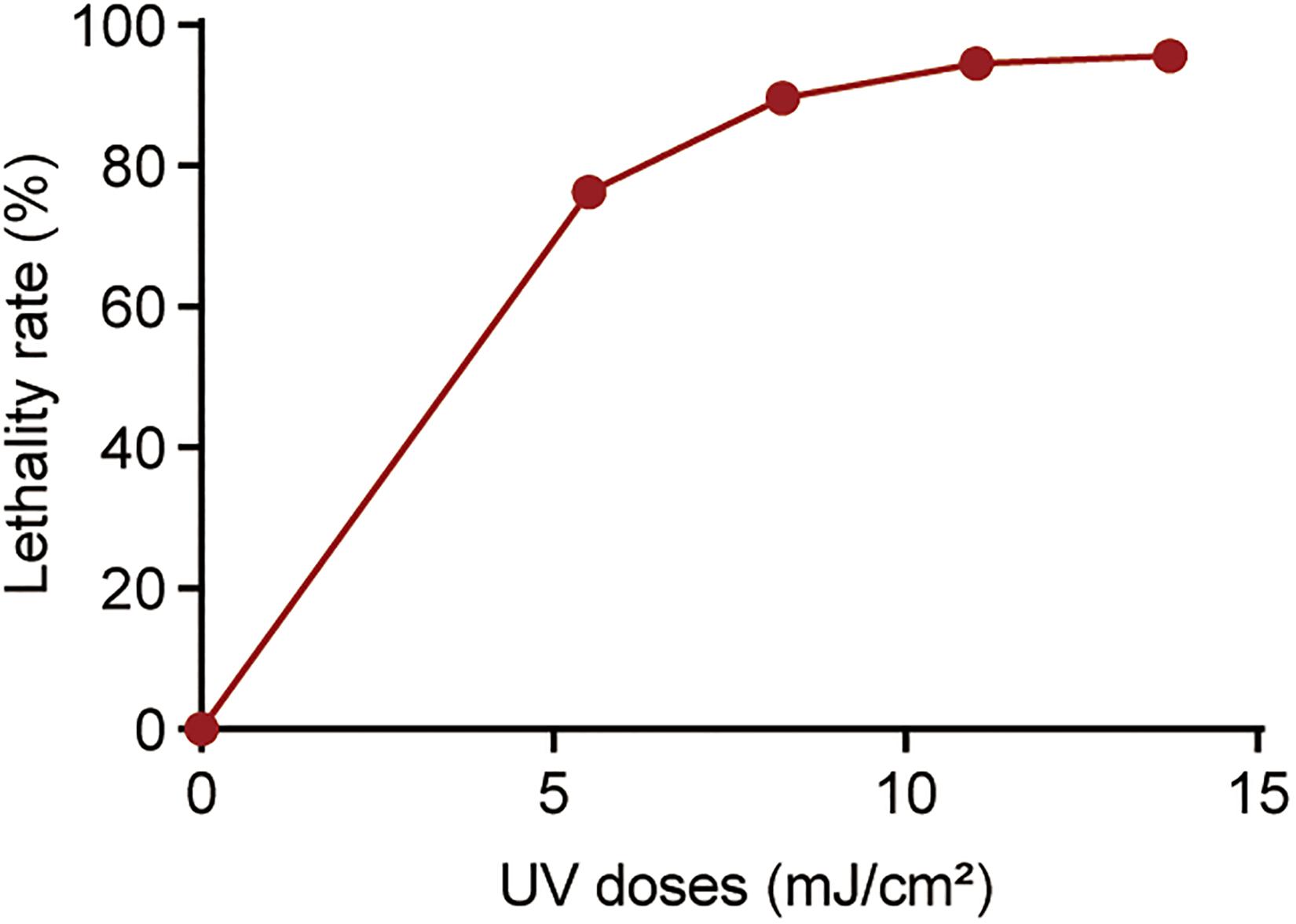
Figure 1. Percentage of killed bacteria following UV exposure. The baseline conditions were as follows: the initial concentration of P. aeruginosa was ∼109 CFU/mL (pH 7.2, 20°C). Data are shown as the mean ± standard deviation (s.d.). (n = 3).
Antibiotic Susceptibility of P. aeruginosa Surviving UV Irradiation
To investigate the effect of UV exposure on antibiotic susceptibility in surviving P. aeruginosa, the antibiotic susceptibility of UV-exposed P. aeruginosa was tested using a panel of six antibiotics. The results revealed that the MICs of tetracycline, ciprofloxacin and polymyxin B increased quite significantly when the irradiation dose increased from 5.50 to 11.0 mJ/cm2; however, no significant increase in ceftazidime, chloramphenicol or gentamicin resistance was observed (Figure 2, Supplementary Table 2 and Supplementary Figure 1). Compared to untreated cells, the MIC of ciprofloxacin against surviving P. aeruginosa increased by an average of twofold following exposure to a 5.50 mJ/cm2 UV dose. The MIC values of tetracycline and ciprofloxacin increased by 1.8- and 3.5-fold when the UV dose was increased to 8.25 mJ/cm2 and by 2.5- and 4.5-fold when it was increased to 11.00 mJ/cm2. Moreover, at a UV dose of 11.00 mJ/cm2, the MIC of polymyxin B began to increase consistently, up to twofold, against surviving P. aeruginosa. Collectively, the results revealed that UV exposure results in a moderate decrease in antibiotic susceptibility in P. aeruginosa perhaps through so-called pleiotropic effects.
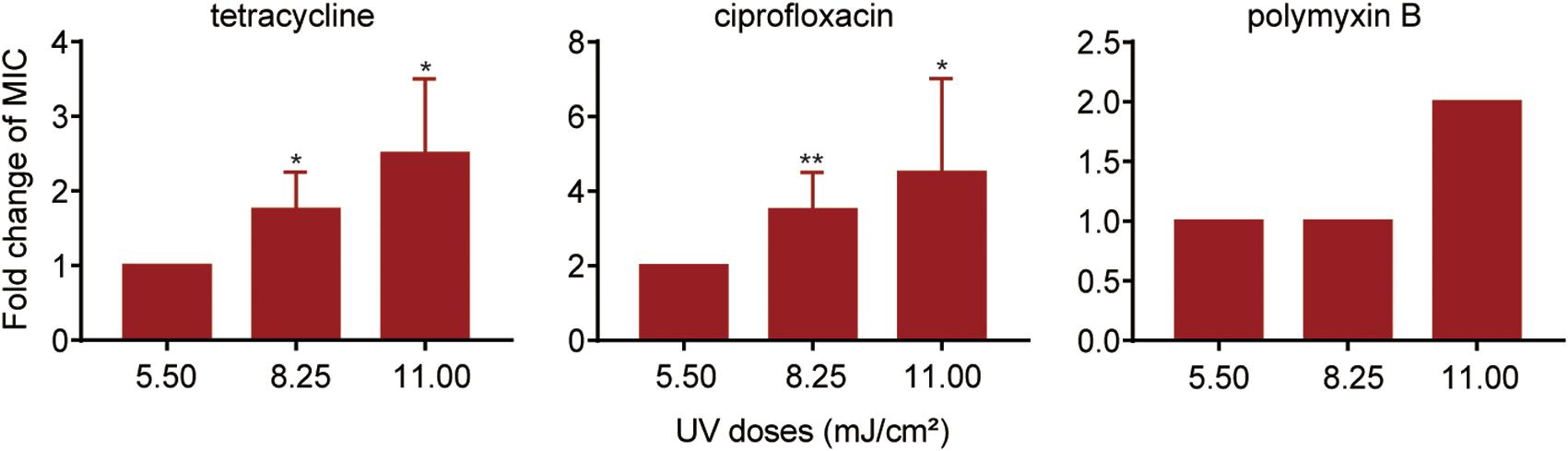
Figure 2. Fold changes in MICs of antibiotics against P. aeruginosa surviving UV irradiation, relative to the untreated controls. MIC assays of tetracycline, ciprofloxacin and polymyxin B were performed using the broth microdilution method in accordance with the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute guidelines. Data are shown as the mean ± standard deviation (s.d.). (n = 4). *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01; assessed by Student’s t-test.
Detection of UV-Injured P. aeruginosa and the Effect on UV Injury on Antibiotic Susceptibility
Previously, we found that chlorine-injured P. aeruginosa showed enhanced temporary physiological antibiotic resistance to ceftazidime and chloramphenicol (Hou et al., 2019). To investigate the contributors to increased MICs of antibiotics in P. aeruginosa surviving UV irradiation, the emergence of injured P. aeruginosa was investigated (Figure 3). Similar to chlorination, UV exposure led to the constant occurrence of injured P. aeruginosa. The percentage of injured P. aeruginosa in the viable bacteria increased gradually, and ultimately, almost 70% of the surviving populations with stronger UV tolerance were injured at a UV dose of 11.00 mJ/cm2. Their injury curves gradually flattened on increasing the UV dose. However, on analyzing the potential correlations between bacterial composition and MICs of antibiotics, we found no significant correlation between the injury of P. aeruginosa and reduced susceptibility to tetracycline, ciprofloxacin and polymyxin B (Table 1). Therefore, unlike P. aeruginosa injured during chlorination, the injury of P. aeruginosa on UV exposure may not contribute to decreased antibiotic susceptibility.
Figure 3. Percentage of injured bacteria following UV exposure. The baseline conditions were as follows: the initial concentration of P. aeruginosa was ∼109 CFU/mL (pH 7.2, 20°C). Data are shown as the mean ± standard deviation (s.d.). (n = 3).
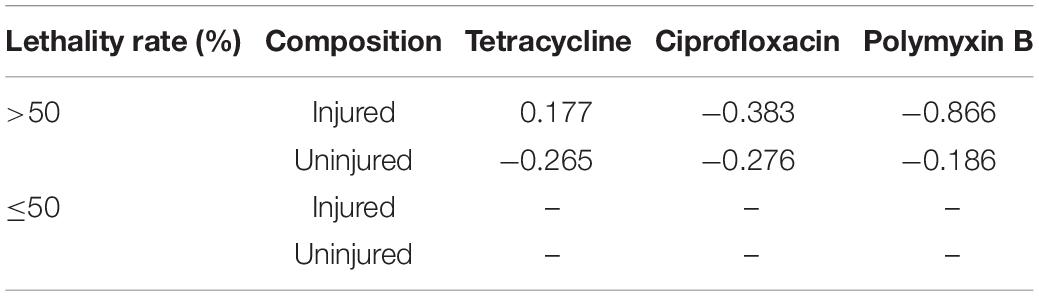
Table 1. Spearman’s correlations between bacterial composition during UV exposure and MICs of antibiotics against them.
Antibiotic Susceptibility and Differentially Expressed Genes Induced by UV Irradiation
To reveal the molecular mechanisms underlying the decreased antibiotic susceptibility in P. aeruginosa surviving UV irradiation, global transcriptional analyses were performed. In total, 686 genes, including 472 up-regulated genes and 214 down-regulated genes, were found to be dysregulated following exposure to a 11.00 mJ/cm2 UV dose (Supplementary Table 3). Eleven up-regulated genes may play a role in decreasing antibiotic susceptibility in P. aeruginosa (Supplementary Table 4). This involved the mexC gene encoding an accessary membrane protein of resistance-nodulation-division (RND) MexCD-OprJ multidrug efflux pump. The expression level was up-regulated by 2.03-fold (Supplementary Table 4).
To further validate whether mexC gene was overexpressed in P. aeruginosa, the expression level of mexC was monitored by qRT-PCR during exposure to several doses of UV (Table 2). We observed that the expression of mexC1,2 was increased by 1.4-fold at a UV dose of 8.25 mJ/cm2 but remained at the near-control level at UV doses of 5.50 and 11.00 mJ/cm2. Additionally, although mexC3,4 was up-regulated at all UV doses used in the present study, the maximum up-regulation, up to 2.83-fold, was observed with a UV dose of 8.25 mJ/cm2. MexC is a component of MexCD-OprJ, which is a multidrug efflux pump from the RND family (Poole et al., 1996). The MexCD-OprJ pump functions as a determinant of antimicrobial resistance to several clinical antimicrobials (Poole et al., 1996; Poole, 2005), disinfectants (Morita et al., 2003; Fraud et al., 2008), and other chemicals (Li et al., 1998; Srikumar et al., 1998) in P. aeruginosa. These observations indicate that the MexCD-OprJ pump may reduce antibiotic susceptibility in P. aeruginosa surviving UV irradiation. It is important to note that the reduced susceptibility is due to the combined action of differentially expressed genes induced by UV irradiation in P. aeruginosa. Many factors including MexCD-OprJ, contributed to the decreasing susceptibility in P. aeruginosa surviving UV irradiation.
Oxidative Stress in P. aeruginosa During UV Exposure
For protection against oxidative attack, bacteria can alleviate ROS levels by activating or increasing the expression of cellular antioxidant systems (Bae et al., 2011). We investigated the oxidative stress response in UV-exposed P. aeruginosa. A strong cellular antioxidant response was observed in UV-exposed P. aeruginosa, in addition to a significant increase in the expression of CAT, GSH-Px, and SOD (Figure 4). The CAT level was dramatically increased, by 98.35–105.42-fold, at UV doses of 5.50, 8.25, and 11.00 mJ/cm2. However, there was no apparent difference among these three dose groups. GSH-Px activity was up-regulated by 43. 95-, 76. 89-, and 64.95-fold on exposure to UV doses of 5.50, 8.25, and 11.25 mJ/cm2, respectively. Obviously, the 8.25 mJ/cm2 UV dose resulted in maximal GSH-Px activity. Moreover, the SOD level dramatically increased as the UV dose increased within the observed range. It increased by 1. 95-, 2. 59-, and 3.54-fold on exposure to UV doses of 5.50, 8.25, and 11.25 mJ/cm2, respectively. These results were further confirmed by the transcription of antioxidant enzymes. mRNA expression levels of the catalase genes katB and katE were up-regulated by 3.13- and 2.97-fold, respectively, after exposure to a UV dose of 11.00 mJ/cm2. Parallelly, the expression level of sodM was up-regulated by 3.29-fold (Supplementary Table 5).
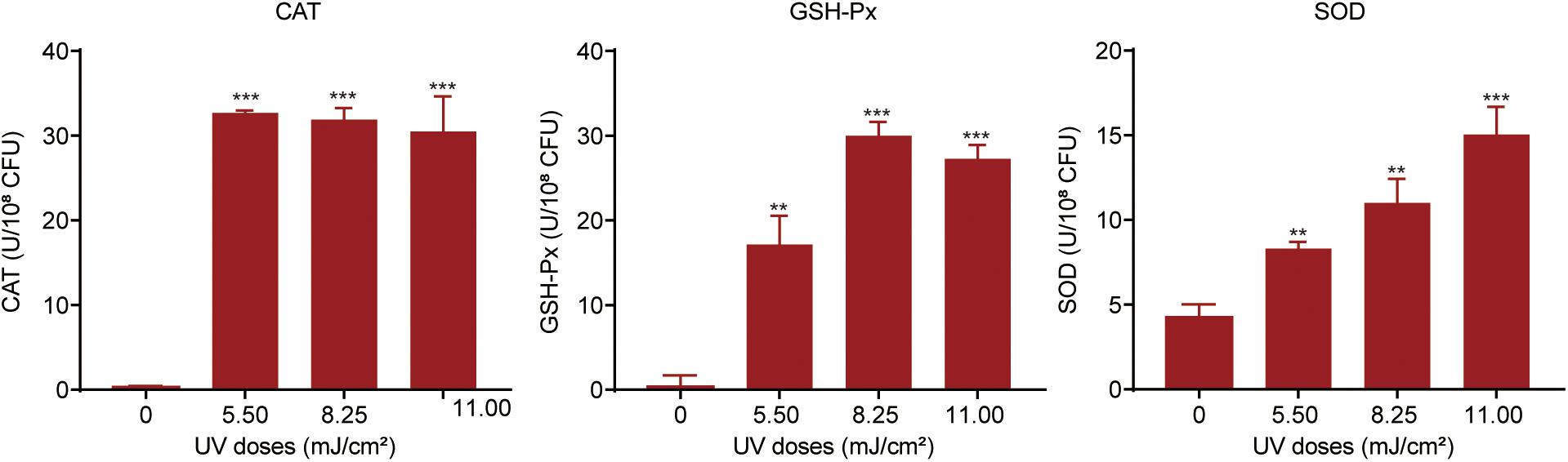
Figure 4. Oxidative stress response in P. aeruginosa during UV exposure. Bacterial suspensions were sonicated at 20 kHz for 10 min and then centrifuged at 5,000 × g at 4°C for 3 min. The levels of catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) in the supernatants were measured. Data are shown as the mean ± standard deviation (s.d.). (n = 3). **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001; assessed by Student’s t-test.
Discussion
Bacteria that can survive in adverse environments are receiving increasing global attention. In the present study, we found the reduced susceptibility to tetracycline, ciprofloxacin and polymyxin B in P. aeruginosa that survived UV irradiation. Mechanistically, we found that UV exposure causes oxidative stress in P. aeruginosa and thereby induces dysregulation of genes contributed to the related ARGs, which potentially decreases antibiotic susceptibility in this bacterium. These results reveal that the survival P. aeruginosa following UV exposure can survive in adverse environments, including antibiotic exposure, and thus pose lasting hazards to human health. This sheds light on the novel role of UV exposure in the reduction of antibiotic susceptibility in P. aeruginosa.
Our findings revealed that the elevated expression of MexCD-OprJ in UV-exposed P. aeruginosa may play a role in contributing to reduced susceptibility of antibiotics belonging to the substrates of the MexCD-OprJ pump such as ciprofloxacin and tetracycline (Masuda et al., 1995, 1996). It is of note that the susceptibility of UV-exposed cells to chloramphenicol, a known substrate of MexCD-OprJ, was not affected. Moreover, the reduced susceptibility to polymyxin B at the higher dose of UV irritation cannot be explained by MexCD-OprJ as polymyxins are not considered as the substrates of MexCD-OprJ and act as outer membrane permeabilizers. However, since the increased expression of mexC after UV exposure is quite limited, other mechanism(s) may also be possibly involved. A total of 686 genes were found to be dysregulated in UV-exposed P. aeruginosa. Among them, the related ARGs including mexC, potentially play a combined role in the reduced antibiotic susceptibility. Undeniably, the mechanism(s) affecting antibiotic susceptibility in P. aeruginosa remain elucidated, and need to be investigated in the future.
Recent studies indicate that the presence and level of ROS during antibiotic treatment can increase antibiotic lethality (Dwyer et al., 2007; Grant et al., 2012; Kottur and Nair, 2016; Liu et al., 2016), affect the survival of persisters (Grant et al., 2012; Wu et al., 2012) and contribute to the development of drug resistance (Kohanski et al., 2010). Furthermore, increasing evidence has shown that ROS induces the expression of multidrug efflux systems, thereby promoting antibiotic resistance in P. aeruginosa (Fraud and Poole, 2011). We have provided evidence that UV exposure increases the expression of cellular antioxidant systems, including CAT, GSH-Px, and SOD, thereby alleviating the ROS levels for protection against an oxidative attack. Collectively, these results indicate that UV-induced oxidative stress may contribute to decreased antibiotic susceptibility in the survival P. aeruginosa potentially through the induction of the MexCD-OprJ multidrug efflux pump and other unidentified mechanisms.
In summary, UV irradiation decreases physiological antibiotic susceptibility in the survival P. aeruginosa. It may help bacteria adapt to or survive in adverse environments. This also raises the concern that UV disinfection under insufficient dosage to kill all bacteria may pose a potential risk by reducing bacterial antibiotic susceptibility in the environment.
Data Availability Statement
RNA-seq data have been deposited in the ArrayExpress database at EMBL-EBI (www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress) under accession number E-MTAB-9613.
Author Contributions
MJ, JL, and HL conceived and designed the experiments and contributed reagents, materials, and analysis tools. AH performed the experiments. TC, DY, ZC, ZS, ZQ, JY, ZY, and HW participated in field research and initial treatment of the materials. MJ, HL, ZC, and SS contributed to the writing and editing of the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Key Program of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41831287).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2021.604245/full#supplementary-material
References
Bae, Y. S., Oh, H., Rhee, S. G., and Yoo, Y. D. (2011). Regulation of reactive oxygen species generation in cell signaling. Mol. Cells 32, 491–509. doi: 10.1007/s10059-011-0276-273
Berry, D., Xi, C., and Raskin, L. (2006). Microbial ecology of drinking water distribution systems. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 17, 297–302. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2006.05.007
Borjesson, S., Melin, S., Matussek, A., and Lindgren, P. E. (2009). A seasonal study of the mecA gene and Staphylococcus aureus including methicillin-resistant S. aureus in a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 43, 925–932. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2008.11.036
Charpentier, X., Kay, E., Schneider, D., and Shuman, H. A. (2011). Antibiotics and UV radiation induce competence for natural transformation in Legionella pneumophila. J. Bacteriol. 193, 1114–1121. doi: 10.1128/JB.01146-1110
Cockerill, F. R. (2010). Performance Standard for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing: Twentieth Informational Suppliment. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute.
Dwyer, D. J., Kohanski, M. A., Hayete, B., and Collins, J. J. (2007). Gyrase inhibitors induce an oxidative damage cellular death pathway in Escherichia coli. Mol. Syst. Biol. 3:91. doi: 10.1038/msb4100135
Fraud, S., Campigotto, A. J., Chen, Z., and Poole, K. (2008). MexCD-OprJ multidrug efflux system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: involvement in chlorhexidine resistance and induction by membrane-damaging agents dependent upon the AlgU stress response sigma factor. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 52, 4478–4482. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01072-1078
Fraud, S., and Poole, K. (2011). Oxidative stress induction of the MexXY multidrug efflux genes and promotion of aminoglycoside resistance development in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 55, 1068–1074. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01495-1410
Gassie, L. W., and Englehardt, J. D. (2017). Advanced oxidation and disinfection processes for onsite net-zero greywater reuse: a review. Water Res. 125, 384–399. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.08.062
Grant, S. S., Kaufmann, B. B., Chand, N. S., Haseley, N., and Hung, D. T. (2012). Eradication of bacterial persisters with antibiotic-generated hydroxyl radicals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 109, 12147–12152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203735109
Guo, M. T., and Kong, C. (2019). Antibiotic resistant bacteria survived from UV disinfection: safety concerns on genes dissemination. Chemosphere 224, 827–832. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.03.004
Guo, M. T., Yuan, Q. B., and Yang, J. (2013). Microbial selectivity of UV treatment on antibiotic-resistant heterotrophic bacteria in secondary effluents of a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 47, 6388–6394. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2013.08.012
Hou, A. M., Yang, D., Miao, J., Shi, D. Y., Yin, J., Yang, Z. W., et al. (2019). Chlorine injury enhances antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa through over expression of drug efflux pumps. Water Res. 156, 366–371. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.03.035
Huang, J. J., Hu, H. Y., Wu, Y. H., Wei, B., and Lu, Y. (2013). Effect of chlorination and ultraviolet disinfection on tetA-mediated tetracycline resistance of Escherichia coli. Chemosphere 90, 2247–2253. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2012.10.008
Jin, M., Liu, L., Wang, D. N., Yang, D., Liu, W. L., Yin, J., et al. (2020). Chlorine disinfection promotes the exchange of antibiotic resistance genes across bacterial genera by natural transformation. ISME J. 14, 1847–1856. doi: 10.1038/s41396-020-0656-659
Khan, S., Beattie, T. K., and Knapp, C. W. (2016). Relationship between antibiotic- and disinfectant-resistance profiles in bacteria harvested from tap water. Chemosphere 152, 132–141. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.02.086
Kohanski, M. A., DePristo, M. A., and Collins, J. J. (2010). Sublethal antibiotic treatment leads to multidrug resistance via radical-induced mutagenesis. Mol. Cell 37, 311–320. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2010.01.003
Kottur, J., and Nair, D. T. (2016). Reactive oxygen species play an important role in the bactericidal activity of quinolone antibiotics. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 55, 2397–2400. doi: 10.1002/anie.201509340
Li, X. Z., Zhang, L., and Poole, K. (1998). Role of the multidrug efflux systems of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in organic solvent tolerance. J. Bacteriol. 180, 2987–2991. doi: 10.1128/jb.180.11.2987-2991.1998
Liu, S. S., Qu, H. M., Yang, D., Hu, H., Liu, W. L., Qiu, Z. G., et al. (2018). Chlorine disinfection increases both intracellular and extracellular antibiotic resistance genes in a full-scale wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 136, 131–136. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2018.02.036
Liu, X., Marrakchi, M., Jahne, M., Rogers, S., and Andreescu, S. (2016). Real-time investigation of antibiotics-induced oxidative stress and superoxide release in bacteria using an electrochemical biosensor. Free Radic Biol. Med. 91, 25–33. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.12.001
Masuda, N., Gotoh, N., Ohya, S., and Nishino, T. (1996). Quantitative correlation between susceptibility and OprJ production in NfxB mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 40, 909–913. doi: 10.1128/AAC.40.4.909
Masuda, N., Sakagawa, E., and Ohya, S. (1995). Outer membrane proteins responsible for multiple drug resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 39, 645–649. doi: 10.1128/aac.39.3.645
McFeters, G. A., LeChevallier, M. W., Singh, A., and Kippin, J. S. (1986). Health significance and occurrence of injured bacteria in drinking water. Water Sci. Technol. 18, 227–231. doi: 10.2166/wst.1986.0133
Morita, Y., Murata, T., Mima, T., Shiota, S., Kuroda, T., Mizushima, T., et al. (2003). Induction of mexCD-oprJ operon for a multidrug efflux pump by disinfectants in wild-type Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J. Antimicrob Chemother 51, 991–994. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkg173
Munir, M., Wong, K., and Xagoraraki, I. (2011). Release of antibiotic resistant bacteria and genes in the effluent and biosolids of five wastewater utilities in Michigan. Water Res. 45, 681–693. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.08.033
O’Neill, J. (2015). Antimicrobial Resistance: Tackling a Crisis for the Health and Wealth of Nations. London: The Review on Antimicrobial Resistance.
Poole, K. (2005). Efflux-mediated antimicrobial resistance. J. Antimicrob Chemother 56, 20–51. doi: 10.1093/jac/dki171
Poole, K., Gotoh, N., Tsujimoto, H., Zhao, Q., Wada, A., Yamasaki, T., et al. (1996). Overexpression of the mexC-mexD-oprJ efflux operon in nfxB-type multidrug-resistant strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol. 21, 713–724. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1996.281397.x
Pruden, A., Pei, R., Storteboom, H., and Carlson, K. H. (2006). Antibiotic resistance genes as emerging contaminants: studies in northern Colorado. Environ. Sci. Technol. 40, 7445–7450. doi: 10.1021/es060413l
Srikumar, R., Kon, T., Gotoh, N., and Poole, K. (1998). Expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa multidrug efflux pumps MexA-MexB-OprM and MexC-MexD-OprJ in a multidrug-sensitive Escherichia coli strain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 42, 65–71. doi: 10.1128/aac.42.1.65
Wang, X., Devlieghere, F., Geeraerd, A., and Uyttendaele, M. (2017). Thermal inactivation and sublethal injury kinetics of Salmonella enterica and Listeria monocytogenes in broth versus agar surface. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 243, 70–77. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2016.12.008
Watkins, R. R., and Bonomo, R. A. (2016). Overview: global and local impact of antibiotic resistance. Infect. Dis. Clin. North Am. 30, 313–322. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2016.02.001
Wu, Y., Vulic, M., Keren, I., and Lewis, K. (2012). Role of oxidative stress in persister tolerance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56, 4922–4926. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00921-912
You, J., Sun, L., Yang, X., Pan, X., Huang, Z., Zhang, X., et al. (2018). Regulatory protein SrpA controls phage infection and core cellular processes in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nat. Commun. 9:1846. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04232-4236
Yuan, Q. B., Guo, M. T., and Yang, J. (2014). Monitoring and assessing the impact of wastewater treatment on release of both antibiotic-resistant bacteria and their typical genes in a Chinese municipal wastewater treatment plant. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 16, 1930–1937. doi: 10.1039/c4em00208c
Zhang, Z., Li, B., Li, N., Sardar, M. F., Song, T., Zhu, C., et al. (2019). Effects of UV disinfection on phenotypes and genotypes of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in secondary effluent from a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Water Res. 157, 546–554. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2019.03.079
Keywords: UV irradiation, P. aeruginosa, antibiotic susceptibility, oxidative stress, antibiotic resistance genes
Citation: Li H-b, Hou A-m, Chen T-j, Yang D, Chen Z-s, Shen Z-q, Qiu Z-g, Yin J, Yang Z-w, Shi D-y, Wang H-r, Li J-w and Jin M (2021) Decreased Antibiotic Susceptibility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Surviving UV Irradition. Front. Microbiol. 12:604245. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.604245
Received: 11 September 2020; Accepted: 11 January 2021;
Published: 03 February 2021.
Edited by:
Yuji Morita, Meiji Pharmaceutical University, JapanReviewed by:
Xian-Zhi Li, Health Canada, CanadaPaul Michael Petersen, Technical University of Denmark, Denmark
Copyright © 2021 Li, Hou, Chen, Yang, Chen, Shen, Qiu, Yin, Yang, Shi, Wang, Li and Jin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Min Jin, amlubWluemhAMTI2LmNvbQ==; Jun-wen Li, anVud2VuOTk5OUBob3RtYWlsLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Hai-bei Li
Hai-bei Li Ai-ming Hou†
Ai-ming Hou† Zhi-qiang Shen
Zhi-qiang Shen Zhi-gang Qiu
Zhi-gang Qiu Jun-wen Li
Jun-wen Li Min Jin
Min Jin