- 1Institute of Geriatrics and Active Ageing, Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore, Singapore
- 2Joint NTU-UBC Research Centre of Excellence in Active Living for the Elderly, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore
- 3Department of Geriatric Medicine, Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore, Singapore
- 4Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore
- 5School of Computer Science and Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, Singapore
A corrigendum on
Effectiveness and usability of the system for assessment and intervention of frailty for community-dwelling pre-frail older adults: A pilot study
by Tan, R. S., Goh, E. F., Wang, D., Chan, R. C. L., Zeng, Z., Yeo, A., Pek, K., Kua, J., Wong, W. C., Shen, Z., and Lim, W. S. (2022). Front. Med. 9:955785. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.955785
In the published article, there were errors in the order of Figures 1–5 as published. The corrected Figures 1–5 and its captions appear below.
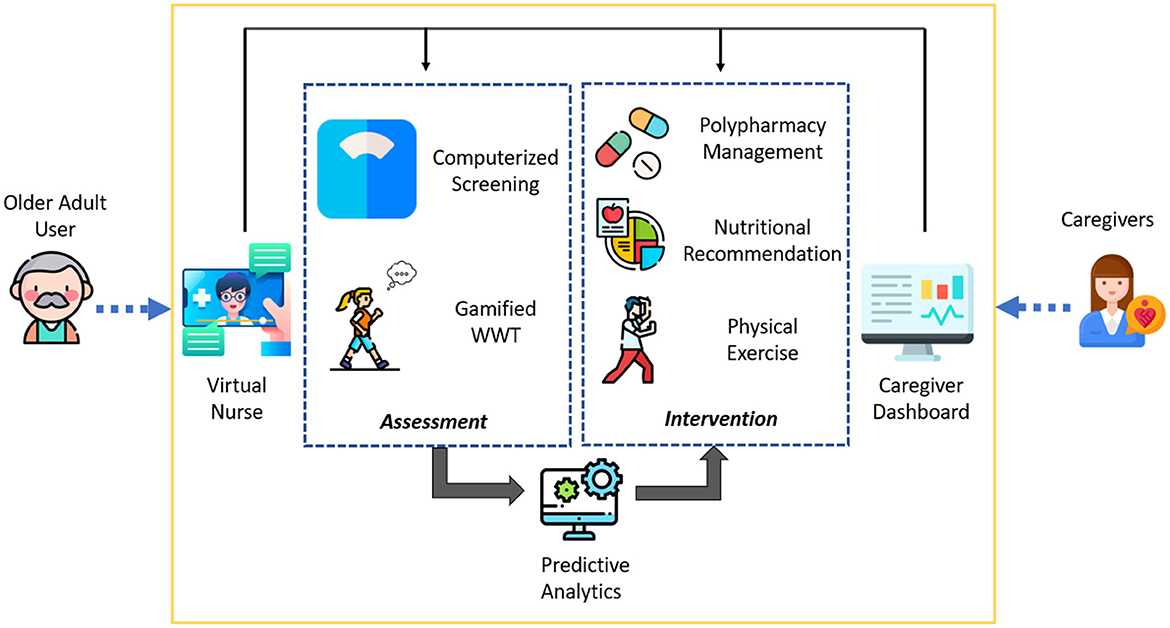
Figure 1. Conceptual diagram of system for assessment and intervention of frailty (SAIF) depicting the integrated elements of interface, assessment, and intervention components.
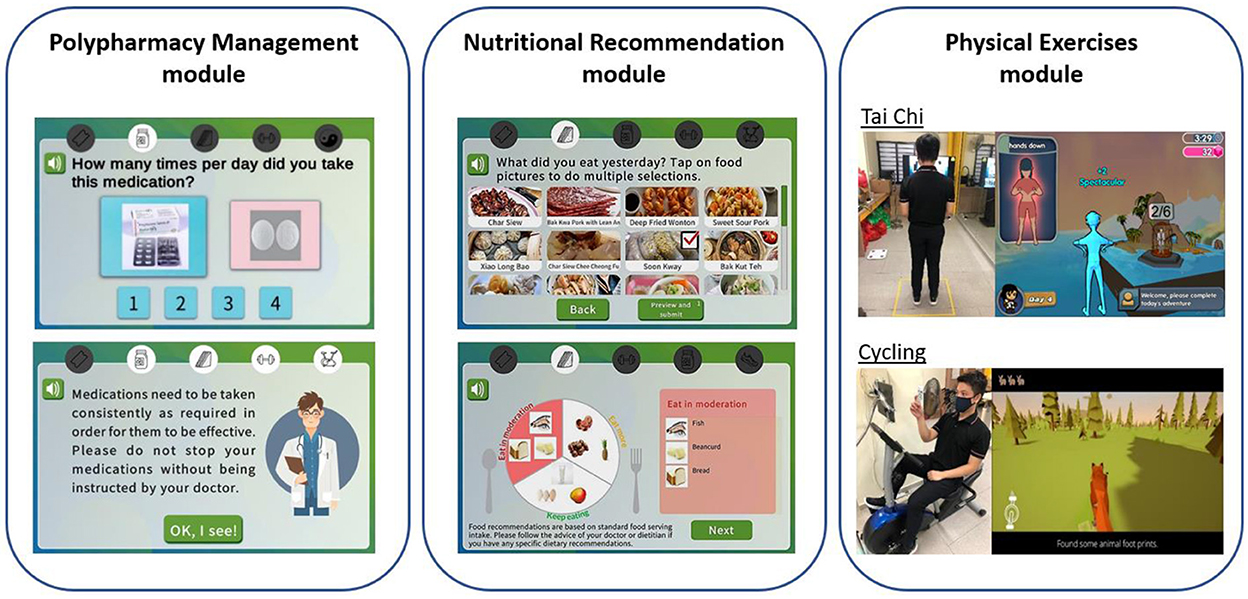
Figure 2. Illustration of system for assessment and intervention of frailty (SAIF) intervention modules which consist of polypharmacy management, nutritional recommendation, and physical exercises modules.
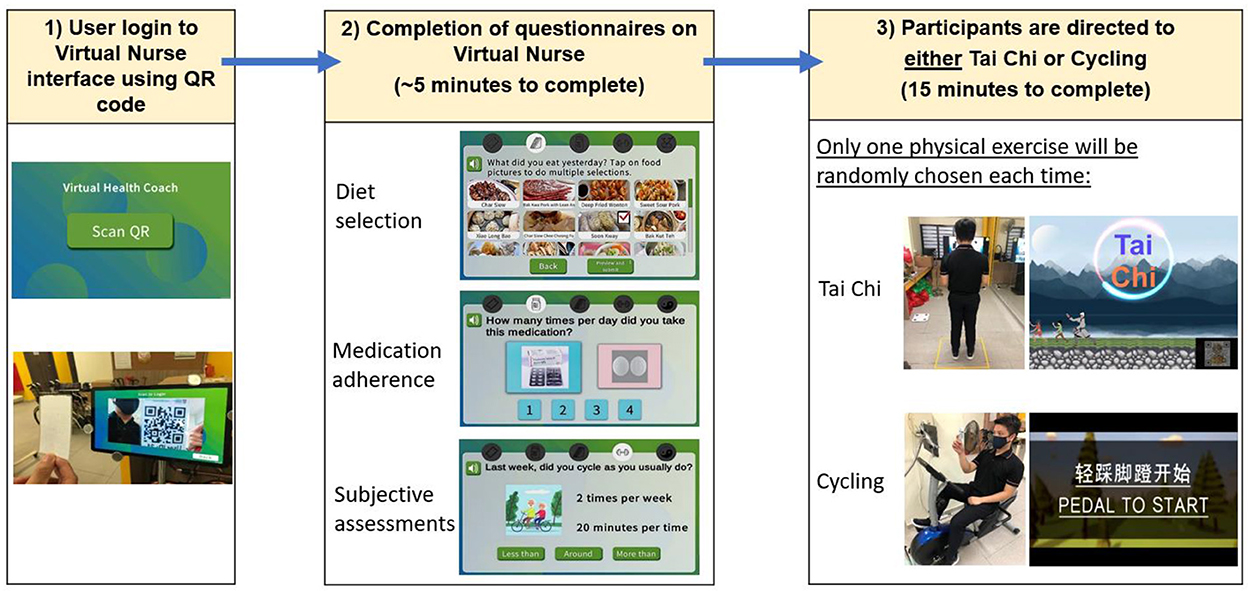
Figure 3. Overview of user interaction for system for assessment and intervention of frailty (SAIF) session: login to Virtual Nurse interface, followed by completion of diet, medication, and subjective assessment questionnaires, and then being directed to exercise module (either Tai Chi or cycling).
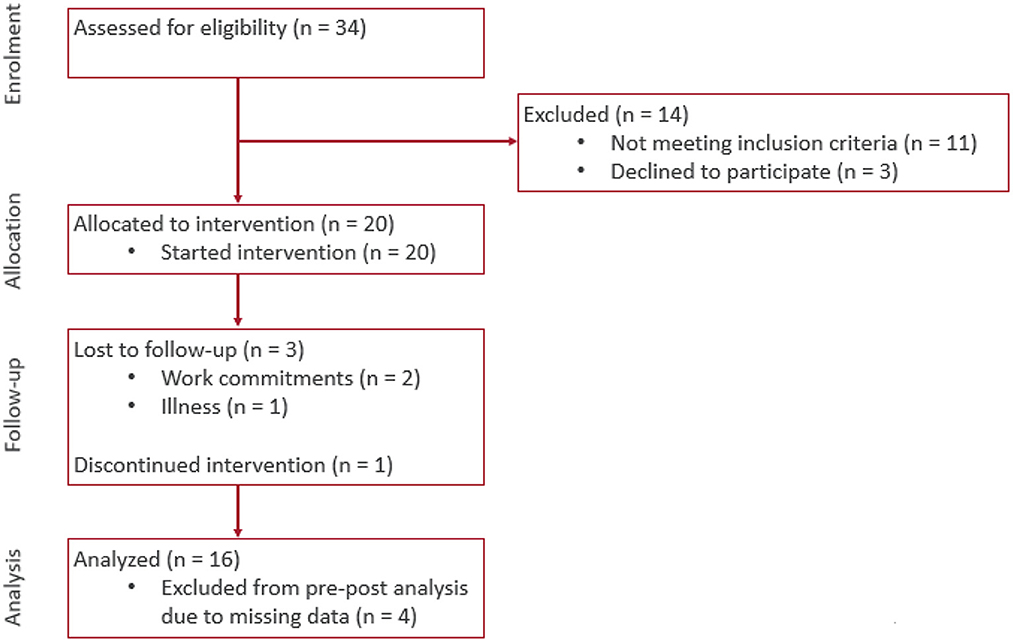
Figure 4. Consort flow diagram of progress through the phases of enrolment, allocation, follow-up, and data analysis.
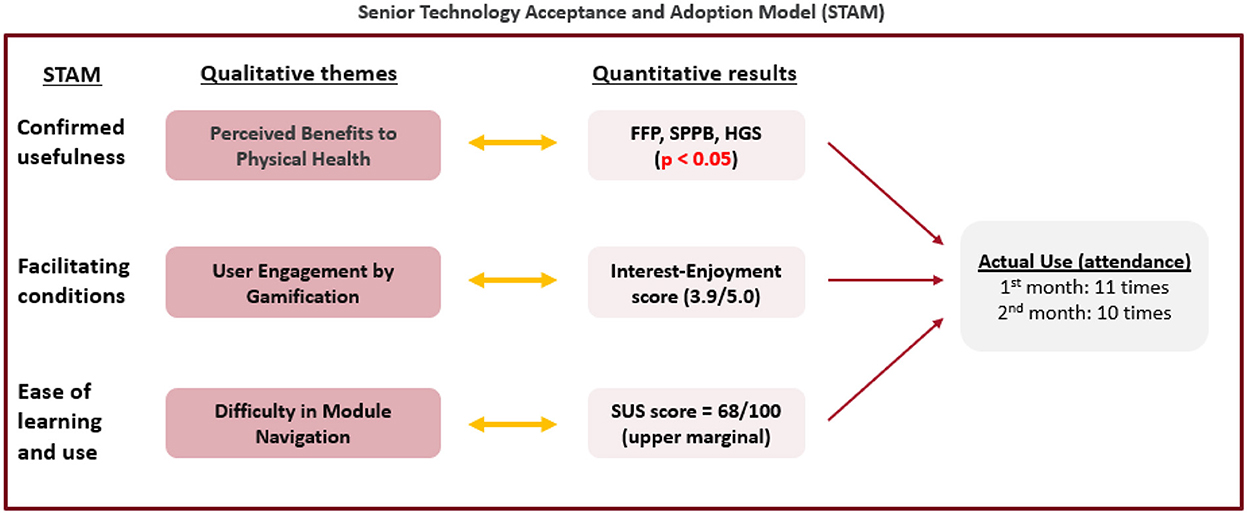
Figure 5. Joint-display of qualitative themes and quantitative results using the senior technology acceptance and adoption model (STAM).
In the published article, Figures 2, 3 contain identifiable images and the written informed consent obtained was not clearly stated in the Ethics statement.
A correction has been made to the Ethics statement section, paragraph 1. This sentence previously stated:
“The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by National Healthcare Group IRB. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by National Healthcare Group IRB. Written informed consent to participate in this study was obtained from study participants. In addition, written informed consent was obtained from the individual for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.”
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: frailty, pre-frail, older adults, community research, health technology, intervention, usability
Citation: Tan RS, Goh EF, Wang D, Chan RCL, Zeng Z, Yeo A, Pek K, Kua J, Wong WC, Shen Z and Lim WS (2022) Corrigendum: Effectiveness and usability of the system for assessment and intervention of frailty for community-dwelling pre-frail older adults: A pilot study. Front. Med. 9:1105448. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1105448
Received: 22 November 2022; Accepted: 12 December 2022;
Published: 22 December 2022.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2022 Tan, Goh, Wang, Chan, Zeng, Yeo, Pek, Kua, Wong, Shen and Lim. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wee Shiong Lim,  d2VlX3NoaW9uZ19saW1AdHRzaC5jb20uc2c=
d2VlX3NoaW9uZ19saW1AdHRzaC5jb20uc2c=
 Ren Siang Tan
Ren Siang Tan Eileen Fabia Goh
Eileen Fabia Goh Di Wang
Di Wang Robin Chung Leung Chan
Robin Chung Leung Chan Zhiwei Zeng
Zhiwei Zeng Audrey Yeo1
Audrey Yeo1 Zhiqi Shen
Zhiqi Shen Wee Shiong Lim
Wee Shiong Lim