
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Immunol. , 23 October 2024
Sec. Immunological Tolerance and Regulation
Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1458209
In recent years, knowledge regarding immune regulation has expanded rapidly, and major advancements have been made in immunotherapy for immune-associated disorders, particularly cancer. The programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) pathway is a cornerstone in immune regulation. It comprises PD-1 and its ligands mediating immune tolerance mechanisms and immune homeostasis. Accumulating evidence demonstrates that the PD-1 axis has a crucial immunosuppressive role in the tumor microenvironment and autoimmune diseases. PD-1 receptors and ligands on immune cells and renal parenchymal cells aid in maintaining immunological homeostasis in the kidneys. Here, we present a comprehensive review of PD-1 immunology in various kidney disorders, including renal cell carcinoma, glomerulonephritis, kidney transplantation, renal aging, and renal immune-related adverse events secondary to PD-1 immunotherapy.
Immune checkpoint molecules are receptor-ligand pairs exerting stimulatory or inhibitory effects on immune responses. Programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) and programmed death ligands 1 and 2 (PD-L1 and PD-L2, respectively), as representative immunosuppressive checkpoints, are members of the cluster of differentiation 28 (CD28) and B7 families and constitute an inhibitory pathway, which maintains self-tolerance and affords immune homeostasis (1). PD-1 was first discovered in 1991 by Yasumasa Ishida using cDNA libraries from unstimulated and stimulated mouse T cells, and then was named programmed cell death 1 as a molecule associated with activation-induced cell death in T cells; next year, they published the first PD-1 paper in 1992 (2–4). The complete gene structure and chromosome location of human PD-1(hPD-1) was reported in 1997 (5). The identification of the interaction of PD-1 with PD-L1 in 2000 and PD-L2 in 2001 defined the PD-1 pathway (6–8). It is noteworthy that Galectin 9 (Gal-9) and galectin 3 (Gal-3) can interact with PD-1 and thus are emerging targets for cancer immunotherapy in different combinations (9–12) (Figure 1). The major immunosuppressive role of the PD-1 axis is responsible for the formation and maintenance of the tumor microenvironment (TME), autoimmunity, infectious immunity, transplantation immunity, allergy, and immune privilege (13, 14). Recent studies have demonstrated that PD-1 and PD-L1 overexpression on tumor cells and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is correlated with poor outcomes in some patients with cancer, and PD-1/PD-L1 blockade-based immunotherapy has been developed for cancers including solid tumors and hematologic malignancies (13). PD-1 was originally identified as an inducible surface receptor during programmed cell death and is mainly present on the surfaces of activated T, B, and natural killer (NK) cells, as well as dendritic cells (DCs), monocytes, macrophages, and myeloid cells (15, 16). PD-L2 expression is mainly confined to DCs, monocytes, and macrophages, whereas that of PD-L1 is more widely distributed on not only T, NK, and B cells and macrophages but also myeloid DCs, epithelial cells, vascular endothelial cells, various tumor cells, and various tumor-infiltrating cells (1). PD-L1 expression also occurs in immune-privileged sites such as the anterior chambers of the eyes, testes, and placenta (17).
In the kidneys, the PD-1 receptors and/or ligands have been confirmed to be present on resident innate immune cells in the renal interstitium and renal parenchymal cells, including proximal tubule epithelial cells and podocytes in vivo and in vitro (18, 19). Pippin et al. reported that in aged mouse and human kidneys, epithelial cells, including podocytes, proximal tubule epithelial cells, and tubular cells, but not glomerular mesangial and endothelial cells, demonstrated high PD-1 levels (19). Starke et al. reported that both PD-L1 and PD-L2 are expressed on human primary renal proximal tubular epithelial cells in vivo and in vitro, and PD-L1 upregulation on proximal tubular epithelial cells may attenuate acute T-cell-mediated rejection (20) (Figure 2). In addition, with the increasing therapeutic use of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint antibodies in clinical, immune-related adverse events (irAEs) involving the kidneys are being increasingly reported (21–23). As such, PD-1 and its ligands potentially play major roles in the kidneys. Here, we provide a comprehensive review of studies on the PD-1 pathway in the kidneys, with a focus on renal cell carcinoma, glomerulonephritis, kidney transplantation, renal aging, and renal complication secondary to PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor-related immunotherapy (Figure 3).
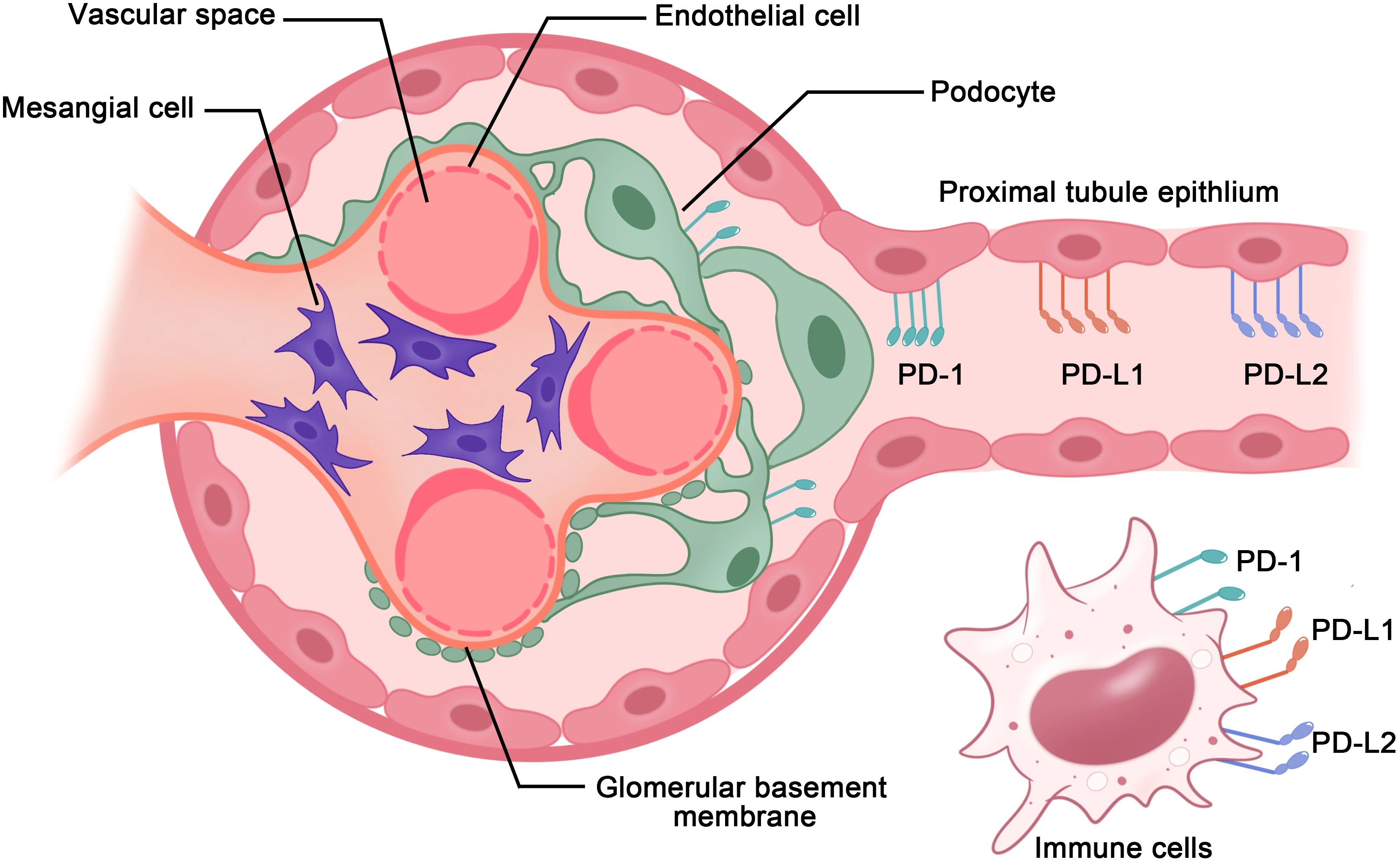
Figure 2. PD-1 axis in immune cells and renal parenchymal cells. PD-1 receptors and ligands on resident innate immune cells in the renal interstitium and renal parenchymal cells, including renal proximal tubule epithelial cells and podocytes, aid in maintaining immunological homeostasis within the kidneys.
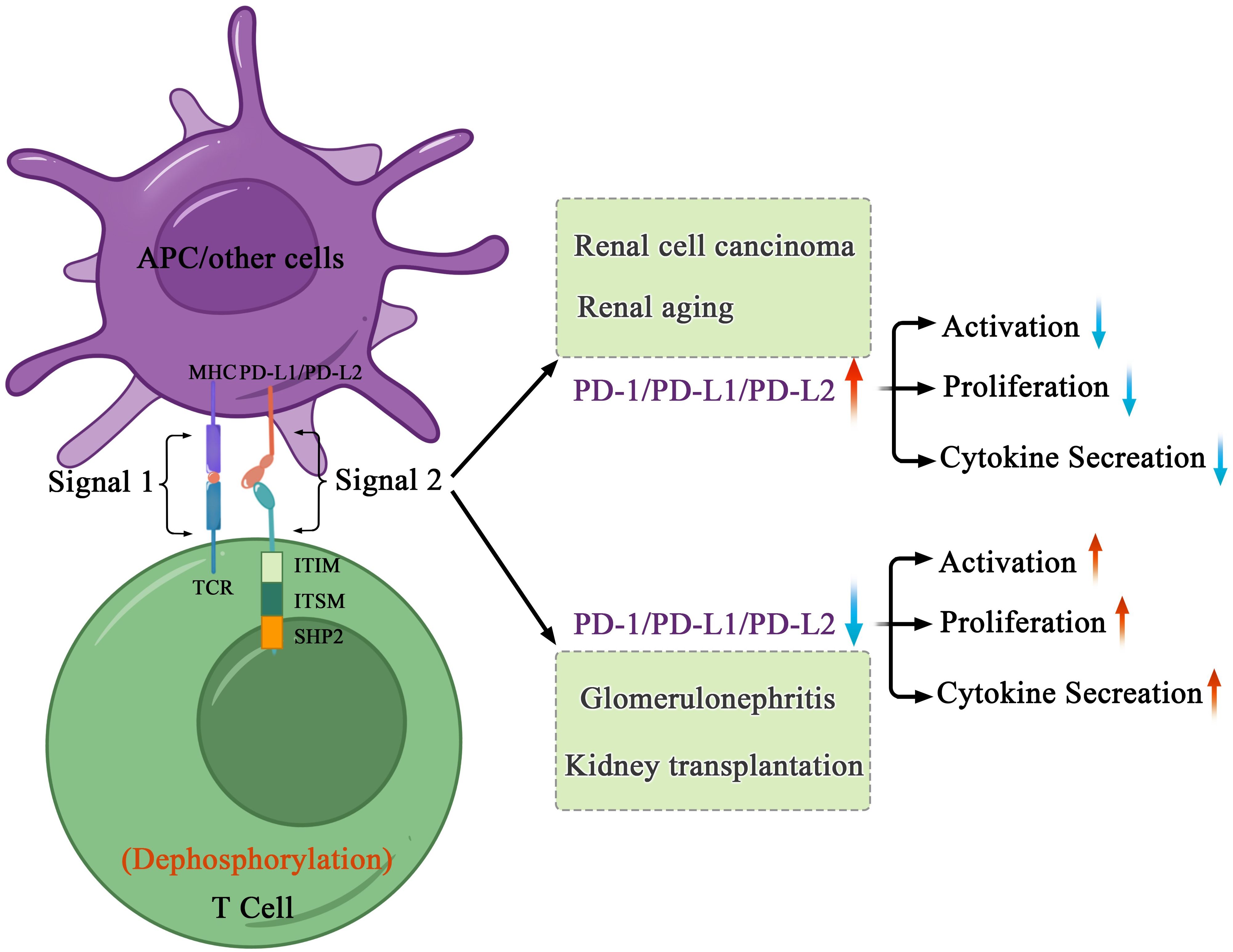
Figure 3. Mechanisms of PD-1-mediated inhibition in kidney health and disorders. After interacting with PD-L1 or PD-L2, PD-1 recruits the phosphatase SHP-2 in proximity to TCR, which attenuates key TCR proximal signaling. In cancers and age-related disorders, cancer or senescent cells escape the immune system because of the abnormal immune surveillance mediated by immune checkpoint molecules. In autoimmune disorders and allogenic transplantation, abnormal immune responses to self or foreign antigens expressed in transplant induce tissue damage and organ rejection.
PD-1, also referred to as PDCD1 or CD279, is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein, weighing 50-55 kDa and comprising 288 amino acid residues (1). It includes an immunoglobulin superfamily domain, a 20-amino-acid stalk, a transmembrane domain, as well as an intracellular domain containing two tyrosine-based signaling motifs: immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM) and an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif (ITSM) (1, 24). According to a comparative analysis of PD-1 against other proteins demonstrated, PD-1 shares 15%, 20%, and 13% similarity to the amino acid sequences of CD28, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 (CTLA-4), and inducible costimulatory molecule (ICOS), respectively (13). PD-1 belongs to the CD28 superfamily and is encoded by PDCD1 on human chromosome 2 (1, 24). PDCD1 comprises five exons, each serving a distinct purpose. In particular, PDCD1 exons 1, 2, 3, and 4 encode a brief signal sequence, an immunoglobulin domain, stalk and transmembrane domains, and a truncated 12-amino-acid sequence marking cytoplasmic domain commencement, respectively; moreover, exon 5 encloses the C-terminal intracellular residues and a substantially lengthy 3′ untranslated region (UTR) (1, 25). Soluble PD-1 (sPD-1) is produced through alternative splicing of full-length PD-1 (flPD-1) transcript; only one splice variant lacking exon 3 but retaining other exons (PD-1Δx3) may encode sPD-1 (26, 27).
PDCD1 was initially identified as a gene induced only during programmed cell death (3). PD-1 is a key immunosuppressive checkpoint, predominantly present in activated T, B, and NK cells, as well as macrophages, DCs, monocytes, and myeloid cells (1). PD-1 expression is also strong in immune-privileged regions, such as the cornea, retina, and iris-ciliary body. Its distribution is wider than that of other CD28 family members, the expression of which is restricted on T cells, which results in PD-1 demonstrating broader spectra of immune responses (17).
PD-1 binds to two classical ligands: PD-L1 and PD-L2; this results in the inhibition of T-cell proliferation, activation, cytokine production, and altered metabolism, as well as cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) killer functions and eventual activated T-cell death (1). The inhibitory function of PD-1 depends on its relationship with SHP-2, a phosphatase (1). After interacting with its ligands PD-L1 or PD-L2, PD-1 becomes activated and recruits SHP-2 in proximity to T-cell antigen receptors (TCRs), which dephosphorylates protein molecules critical for TCR signaling and affects the downstream signaling pathways (28–31). The bonding of the SH2 domains of SHP-2 with ITSM in PD-1 triggers PD-1 dimerization and SHP-2 activation (1). sPD-1 functions as a PD-1 ligand blocker and suppresses the interactions of PD-1 with PD-L1 and PD-L2 and the those of PD-L1 with B7-1 (also called CD80) (27, 32). Gal-9 can interact with PD-1 on T-cell surfaces (12); this interaction plays a role in sustaining the presence of PD-1+TIM-3+ T cells and reducing Gal-9/TIM-3-induced cell death (12). Notably, studies have recently revealed the presence of direct PD-1-Gal-3 interactions, highlighting the significance of targeting Gal-3 in immunotherapy through various combination approaches (9–11) (Figure 4).
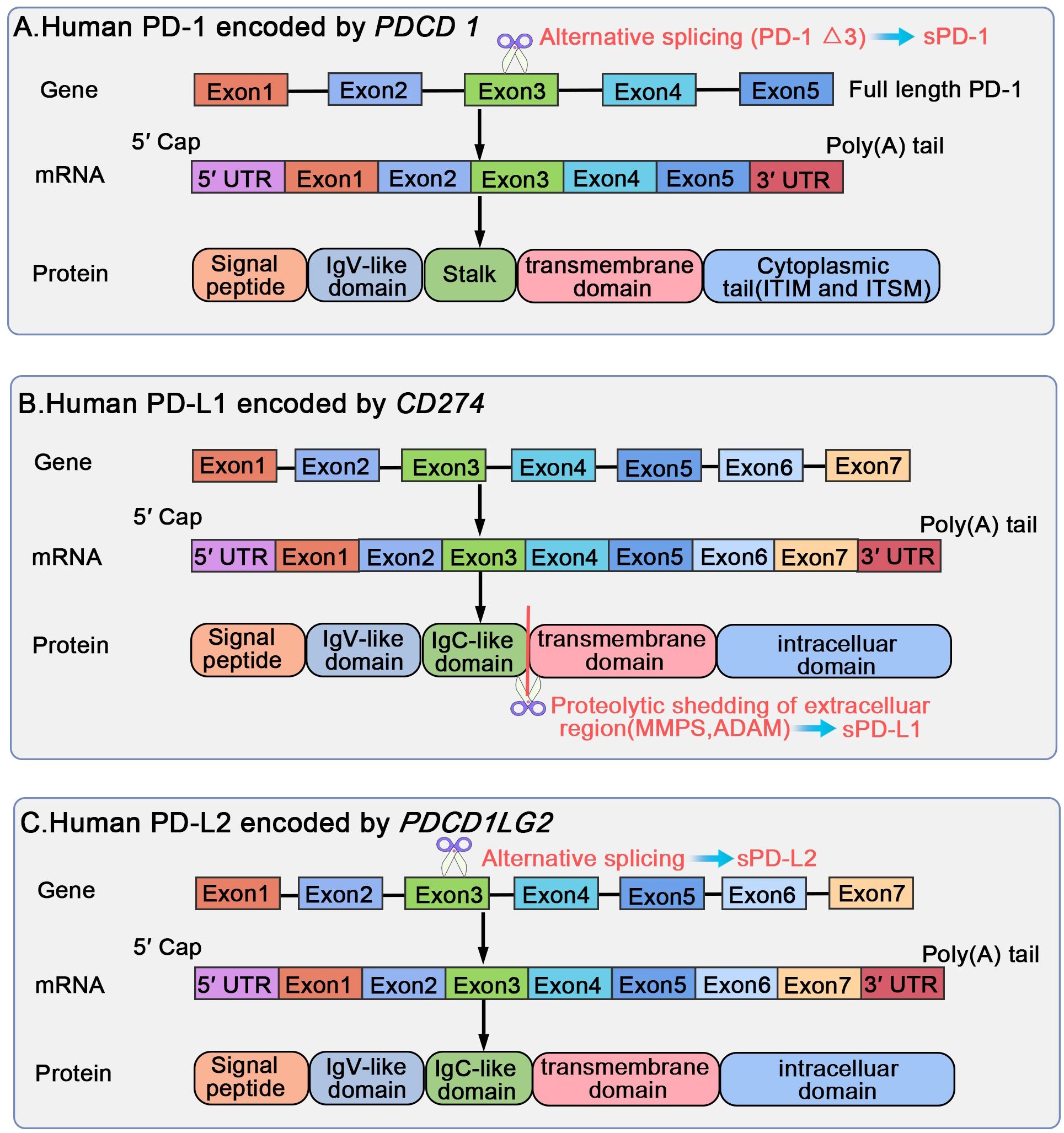
Figure 4. Biological regulation of human PD-1/PD-L1/PD-L2 gene, mRNA, and protein structural domains. PD-1 is encoded by PDCD1 on human chromosome 2, including five exons, each encoding a distinct protein. sPD-1 forms through alternative slicing of the full length PD-1 transcript, and only PD-1 Δx3 may encode for sPD-1. PD-L1 and PD-L2 are encoded by CD274 and PDCD1LG2 located on human chromosome 9, respectively. Both PDCD1LG2 and CD274 present an exon organization similar to 5′ UTR, followed by a signal sequence, an IgV domain, an IgC domain, transmembrane domains, and finally cytoplasmic exons 1 and exon 2 with 3′ UTR. sPD-L1 is generated through proteolytic cleavage of mPD-L1 by various proteases, such as endogenous MMPs and ADAM. The translated protein lacks the transmembrane domain, eliminated through splicing out of exon 3; the translated protein may exist as the soluble sPD-L2.
PD-L1, or B7 homolog 1 (B7-H1)/CD274, is a 33-kDa type I transmembrane protein, comprising 290 amino acid residues, encoded by CD274 on human chromosome 9, and belonging to the B7 family (1, 13). CD274 comprises seven exons (33), with exon 1 encoding a 5′-UTR, and exon 7 encoding a part of the intracellular domain and a 3′-UTR of mRNA. The first 18 amino acids form the signal peptide sequence, which is removed during protein processing (33). PD-L1 comprises a large extracellular region containing immunoglobulin (Ig) V-like and IgC-like domains, followed by a hydrophobic transmembrane domain and cytosolic tail (33). Extracellular PD-L1 can mainly be classified into free soluble (sPD-L1) and exosomal membrane-bound (mPD-L1) forms, distributed throughout the body via blood circulation (34). sPD-L1 forms through proteolytic cleavage of mPD-L1 (32). Various proteases, such as endogenous matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and a disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM), can cleave mPD-L1, thereby enabling sPD-L1 release (32).
PD-L1 is present in various immune cells including T, B, and NK cells, as well as epithelial cells, vascular endothelial cells, antigen-presenting cells (APCs), multiple tumor cells, and tumor-infiltrating cells (1). PD-L1 overexpression can be triggered on tumor cells either by genetic alterations (innate expression) or through stimulation with interferon (IFN) γ released from effector T cells, including CD8+ T cells (acquired expression) (13). PD-L1 expression is also observed in immune-privileged regions such as the eye and placenta, where its overexpression begins from the fourth gestation month (17). sPD-L1 can be detected in the plasma of healthy individuals, whereas sPD-L1 levels are elevated in individuals with an autoimmune disease or cancer (26, 35, 36). In general, cancer cells and mature DCs are considered the main sources of sPD-L1 (36–38).
PD-1-PD-L1 interactions hinder T-cell receptor-mediated cytotoxicity and CD8+ T-cell proliferation, impeding adaptive immune response against cancer cells; this allows cancer cells to escape destruction and evade immune monitoring (39). Notably, recent studies have revealed that the PD-L1-B7-1 ligand-ligand cis-interaction alters trans interactions with other immune checkpoints; this provides newer perspectives on mechanisms underlying the currently known immune pathways and immunotherapeutic modalities (6, 40). B7-1 is a type I transmembrane protein belonging to the B7 family and existing as a monomer or homodimer. B7-1 expressed on APCs binds to CD28 and CTLA-4 on T cells, eliciting costimulatory and coinhibitory signals, respectively (41). When PD-L1 binds to B7-1 in a cis configuration, PD-L1 cannot engage PD-1 (6, 40). The PD-L1-B7-1 cis-interaction disrupts the B7-1 homodimer and reduces its avidity to CTLA-4, thereby reducing B7-1 transendocytosis (6, 42). The binding of B7-1 to PD-L1 does not prevent the interaction of B7-1 with CD28, consequently leading to the formation of a trimeric complex (6). However, the effects of the PD-L1-B7-1 cis-heterodimer on the B7-1-CD28 interaction remain inconclusive due to conflicting reports (40). Sugiura et al. demonstrated that elimination of PD-1 restriction via targeting the cis-PD-L1-B7-1 duplex effectively alleviated autoimmune disease symptoms in murine models with arthritis, multiple sclerosis, or Sjögren’s syndrome (43). Moreover, the relative levels of PD-L1 and B7-1 affected the overall outcome (6). sPD-L1 retains binding ability and inhibitory properties identical to those of mPD-L1 and can bind with PD-1 or B7-1 (26, 32) (Figure 4).
PD-L2, also referred to as B7-DC or CD273, is a type I transmembrane protein, belonging to the B7 ligand family, comprising 270 amino acid residues, and encoded by PDCD1LG2 located on human chromosome 9. This gene is oriented in a direction identical to that of CD274, which encodes PD-L1, 42 kb apart (44–46). Both PDCD1LG2 and CD274 present similar exon organization with a 5′-UTR, followed by a signal sequence, an IgV domain, an IgC domain, transmembrane domains, and cytoplasmic exons 1 and 2 with 3′-UTR (46). Two novel variants of human PD-L2, other than the full-length isoform encoding the common PD-L2 mRNA (type I), have been discovered in activated leukocytes (1): A type II splice variant forms through the exclusion of exon 3 via splicing and retention of all other segments without frame alteration; the resulting protein lacks the IgC-like domain but retains the Ig constant-like domain, making it shorter in the extracellular area (2). A type III variant forms through the splicing of exon 3 into an alternative acceptor site located 5 bp downstream of the conventional site, which causes a frameshift; the translated protein, lacking a transmembrane domain, might exist in a soluble form as soluble PD-L2 (sPD-L2) (27, 47).
PD-L2 is mainly present on APCs, such as macrophages and DCs, and its expression can be induced in other immune and nonimmune cells by various microenvironmental stimuli, particularly T helper 2-related cytokines (48). In contrast, both immune and nonimmune cells express PD-L1 (45). PD-L2 expression has been detected in patients with various malignancies, and it is considered a predictor of a worse prognosis (45, 48, 49). In human tumor samples, PD-L2 and PD-L1 expression is typically correlated; however, in some subsets of patient samples, PD-L2 expression is also present in the absence of PD-L1 expression (50).
Compared with that on PD-1 and PD-L1, research on PD-L2 as a therapeutic target and predictive biomarker has been scant. Despite sharing the same receptor PD-1 and having 37% sequence homology with PD-L1, PD-L2 and PD-L1 exhibit variations in affinity and tissue expression (45). Studies have indicated that PD-L2 demonstrates a binding affinity to PD-1 that is twofold to sixfold higher than PD-L1 (44, 48, 49). Moreover, the role of PD-L2 has been highlighted in allergy and tolerance studies. Another crucial binding partner of PDL2 is the recently discovered repulsive guidance molecule b (RGMb) (6, 51, 52). RGMb, a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored protein, belongs to the repulsive guidance molecule family alongside repulsive guidance molecules a and c (6). Notably, RGMb acts as a coreceptor for bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP2) and bone morphogenetic protein 4 (BMP4), as well as neogenin, forming the supercomplex BMP-BMPR-RGMb-neogenin within the same cell membrane. PD-L2 can interact with this supercomplex in a trans configuration to regulate the downstream pathways (6, 51, 53). However, further relevant research on fully understanding the functional role of PD-L2 within this supercomplex is warranted (Figure 4).
Gal-9 is a β-galactoside-binding lectin encoded by LGALS9 located on human chromosome 17, long arm at locus 11.2 (17q11.2) in humans (54). It is a 34-39-kDa tandem repeat galectin, consisting of two carbohydrate-recognition domains (CRDs), N- and C-terminal CRDs, with similar but distinct specificities for glycans joined with a linker domain (54–56). Full-length Gal-9 is 355 amino acids long, and LGALS9, consists of 11 exons, and forms many splice variants undergoing posttranscriptional splicing, such as Gal-9Δ5, Gal-9Δ5/6, Gal-9Δ5/10, and Gal-9Δ5/6/10 (54). Gal-9 has been discovered in many tissues; it was first discovered and named in mouse embryonic kidneys (57). T cells can stimulate Gal-9 release in different human cancer cell lines originating from solid malignant tumors through two distinct pathways. The first pathway involves translocation of Gal-9 onto the cell surface, followed by its proteolytic shedding, whereas the second pathway depends on autophagy, followed by lysosomal secretion; because Gal-9 lacks a secretion sequence, both these pathways require a protein carrier or trafficker (58). Gal-9 belongs to the lectin family and thus functions via receptors such as T-cell immunoglobin and mucin domain-containing protein 3 (TIM-3), V-domain Ig suppressor of T-cell activation (VISTA), and PD-1 in CTLs (9, 12, 58, 59).
TIM-3 is a glycoprotein expressed on different immune cells such as T and B cells, macrophages, monocytes, DCs, NK cells, mast cells, and APCs (60–63). TIM-3 is involved in immune response and tolerance regulation. Interactions between Gal-9 and TIM-3 can lead to immunostimulatory or immunoinhibitory effects, depending on the type of immune cells involved (60). On T cells, a TIM-3-Gal-9 interaction leads to the weakening of the T helper 1-mediated immunity and T-cell apoptosis, resulting in an inhibition of the immune system. In contrast, on NK cells and DCs, this interaction leads to an immunostimulatory effect (60, 61). In addition, TIM-3 ligands also include Psdter, high mobility group box 1, and carcinoembryonic antigen-associated cell adhesion molecule 1, which have different effects after binding to different ligands on immune cells (64).
VISTA, also known as PD-1 homolog or B7-H5, belongs to the B7 family. Structural analysis has demonstrated that the IgV domain of VISTA has sequence homology with both CD28 and the B7 family proteins, whereas the full-length VISTA demonstrates the highest identity with PD-1 (20, 65). Yasinska et al. reported that VISTA interacts with Gal-9 with relatively strong affinity, without preventing interactions between Gal-9 and TIM-3 (59). Soluble VISTA released by acute myeloid leukemia cells enhances the effects of Gal-9, most likely by forming multiprotein complexes on the T-cell surfaces and possibly creating a molecular barrier Gal-9, which results in changes in the plasma membrane potential of T cells; this leads to activation of granzyme B inside CTLs, followed by their apoptosis (59). Furthermore, human VISTA has two confirmed binding partners with immunosuppressive functions, P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 and V-set and Ig domain-containing 3, and one less-confirmed partner, V-set and Ig domain-containing 8 (66). VISTA activity imposes quiescence in mammalian myeloid cells and naïve T cells and inhibits T-cell activation and cytokine production; this suggests that VISTA is a promising target for combination cancer immunotherapy (66).
Recent research has indicated that Gal-9 is a PD-1-binding protein (9, 12). The binding of Gal-9 to PD-1 is highly specific and is primarily mediated by the CRD of Gal-9 and the N116-linked glycan of PD-1. Nevertheless, this association does not affect the binding of PD-1 to PD-L1 (its natural ligand) or pembrolizumab and nivolumab (the therapeutic antibodies) (12). The interactions of PD-1 with Gal-9 and TIM-3 can attenuate Gal-9/TIM-3-induced apoptosis of PD-1+TIM-3+ T cells in cancers; this result provides a newer insight into the intricate conflict between cancer cells and the immune system (12). Moreover, similar to PD-1 and its ligands (PD-L1 and PD-L2), Gal-9 expression and secretion are upregulated by IFN signaling (67).
Gal-3, a lectin with a preference for β-galactoside-containing carbohydrates, is a structurally unique galectin family member (68). Full-length Gal-3, consisting of 250 amino acids, is encoded by LGALS3 on human chromosome 14 (68). Galectins can be classified into three types based on the number and arrangement of CRDs: prototype (a noncovalently bound isoform dimer), tandem repeat type (a covalently attached heterodimer), and chimeric type (consisting of a C-terminal CRD and an N-terminal peptide chain) (69, 70). Gal-3 is the only chimeric protein with a C-terminus CRD linked to an N-terminal domain rich in proline, glycine, and tyrosine, which can be oligomerized by the N-terminal CRD according to environmental conditions (69, 71). The N-terminal domain targets specific cellular targets, the repetitive collagen-like sequence serves as a substrate for MMP, and the C-terminal domain contains the carbohydrate-binding region (72, 73). The N-terminal peptide harbors two crucial phosphorylation sites: Ser6 (the major site with 90% phosphorylation) and Ser12 (the minor site with 10% phosphorylation) (68, 74). Both these sites are vital in facilitating nuclear export of Gal-3, and they are indispensable for the antiapoptotic functions of cytoplasmic Gal-3 (68, 75, 76). Thus far, the binding partners of Gal-3 have been reported to include lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (LAG-3), CD45, a galectin-3-binding-protein (Gal3BP), and PD-1 (9).
LAG-3 is an inhibitory receptor, highly expressed by exhausted T cells, as well as a promising immunotherapeutic target. Thus far, >20 LAG-3-targeting therapeutics are under clinical trials, and a fixed-dose combination of anti-LAG-3 and anti-PD-1 has been approved for unresectable or metastatic melanoma treatment (77). The canonical ligand of LAG-3 is a major histocompatibility complex class II protein (77, 78). Additional ligands for LAG-3 include Gal-3, liver and lymph node sinusoidal endothelial cell C-type lectin, fibrinogen-like protein 1, α-synuclein preformed fibrils, and the TCR-CD3 complex (77). In a pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma model, Gal-3 was noted to mediate suppression of effector CD8+ T-cell function by binding to LAG-3 (9, 79). Moreover, a blockade of the Gal-3/LAG-3 axis has been validated in T cells in patients with multiple myeloma (9, 80).
CD45 is a transmembrane protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type C, which is expressed exclusively in leukocytes; it has opposing effects on T-cell receptor activity (81, 82). Extracellular Gal-3 induces T-cell apoptosis by binding to CD45, whereas intracellular Gal-3 inhibits the apoptotic process by binding to BCL-2 (83, 84). Gal3BP, also known as tumor-associated antigen 90K or Mac-2-binding protein, is a multifunctional secreted glycoprotein encoded by LGAL3SBP involved in cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, upregulated in patients with cancer or a viral infection, including HIV-1, HCV, or SARS-CoV-2 infection, with a key role in regulating the antiviral immune response (85). Interactions between Gal3BP and Gal-3 can trigger IL-6 expression and release in various cells, such as bone marrow stromal cells, neuroblastoma cells, and macrophages; this is because Gal3BP downregulation leads to decreased IL-6 expression, and Gal3BP/Gal-3-mediated induction of IL-6 involves the Ras-Mek-Erk1/2 pathway (85–88). In a triple-negative breast cancer model, tumor-secreted Gal-3 and a Gal-3-binding protein have been noted to form a complex that interacts with the CD45 receptor on T cells and induce expansion of regulatory T cells (9, 83).
Notably, PD-1/PD-L1 have recently been demonstrated to directly interact with Gal-3, highlighting the importance of Gal-3 as an emerging immunotherapy target in different combination modalities (9–11). Pedersen et al. reported that PD-1 and Gal-3 can be present on mononuclear cells in blood and synovial fluid and that Gal-3 can inhibit PD-1 signaling when PD-L1 is present (11). Clinical trials on the use of Gal-3 inhibitors to improve the effectiveness of anti-PD-1 therapy for metastatic melanoma and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma are underway (11, 89). Much of knowledge of these immunosuppressive molecules has come from murine studies and lot needs to be worked out in human diseases.
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC), the most common form of kidney cancer, is associated with poor prognosis, with 25%-30% of the patients being diagnosed at the metastatic stage, and approximately 40% of the patients demonstrating recurrence after surgical excision (90, 91). Therefore, improved treatment modalities that may reduce the risk of recurrence in patients with advanced-stage disease, mainly including antiangiogenics and targeted immunotherapy, are under investigation. RCC presents as a heterogenous tumor, and it can be classified into several subtypes with unique characteristics. Clear-cell RCC (ccRCC) is the predominant subtype, accounting for approximately 75%-83% of all RCC cases (90, 92). Several other renal epithelial malignancies are collectively referred to as non-ccRCC; they include papillary RCC (pRCC), chromophobe RCC (chRCC), translocation RCC, collecting duct carcinoma, and unclassified RCC (93). RCC is considered immunogenic, characterized by the presence of abundant tumor-infiltrating immune cells, including CD8+ and CD4+ T cells, NK cells, and myeloid cells with the characteristics of macrophages and neutrophils (94). These tumor-infiltrating cells block the development of antitumor immune response in the TME, including inhibition of the activity of effector T cells and APCs via the upregulation of suppressive factors such as checkpoint molecules (93). Immune infiltration of tumors is closely associated with clinical outcomes in RCC. An increase in the proportion of regulatory T cells and the levels of the immunomodulator molecules CTLA-4 and LAG-3 worsens outcomes in ccRCC. Moreover, M2 macrophages and PD-L2 are associated with a poor prognosis in pRCC (94).
The utility of immune checkpoints as predictive biomarkers has been investigated extensively. PD-1 and PD-L1 are associated with worse clinical outcomes in RCC (92). An increase in PD-1 expression on CD14bright myelomonocytic cells, effector T cells, and NK cells is significantly correlated with the disease stage in patients with RCC (95). In addition, a rapid reduction in PD-1 expression on these cells can occur within weeks after surgical tumor resection (95). Measuring PD-1 levels in peripheral blood may be a useful indicator of disease progression and response to anti-PD-1. Among RCC tumor specimens, approximately 10%-57% have been observed to be positive for PD-L1 and associated with worse clinical outcomes (96–98). Abbas et al. retrospectively analyzed intratumoral expression of PD-L1 in patients with ccRCC and reported a significant association of PD-L1 positivity with poor clinical prognosis parameters and decreased overall survival (97). Moreover, PD-L1 expression does not differ between the various histologic subtypes of RCC (98). PD-L2 expression in RCC has also been found to be associated with adverse clinicopathological features. Shin et al. detected PD-L2 in 49.6% of the samples, with the highest frequency noted for pRCC; the positivity was significantly correlated with short progression-free and cancer-specific survivals in patients with ccRCC (98). Erlmeier et al. reported high PD-L2 expression in 28.4% of their chRCC cases and a significant difference in overall survival dependent on PD-L2 expression (99).
The targeted immunotherapeutic modalities have rapidly developed for RCC in recent years. The application of various immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), alone or in combination, has demonstrated strong responses in some patients with RCC. In the phase III CheckMate 025 trial, a 23% objective response rate was noted in advanced RCC patients treated with the anti-PD-1 nivolumab; in these patients, nivolumab demonstrated efficacy, safety, and tolerability superior to those of everolimus (100). In the phase II Keynote-427 study, single-agent pembrolizumab monotherapy (a humanized monoclonal anti-PD1 antibody) resulted in an overall objective response of 36% in patients with advanced ccRCC, and 68.2% of the patients demonstrated a decrease in the number of target lesions (101). Three recent phase III trials, namely Checkmate 214, Keynote-426, and Javelin Renal 101, have provided three novel, U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved regimens for treating ccRCC: nivolumab + ipilimumab, pembrolizumab + axitinib, and avelumab + axitinib, respectively (102). However, some patients with RCC may not benefit from checkpoint blockade. Trials assessing appropriate treatment regimens for enhancing antitumor immune responses are underway.
PD-1 and its ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, elicit inhibitory signals to terminate or attenuate the immune response and thus play a significant role in autoimmunity (17). Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a systemic autoimmune disorder, presenting as immune tolerance loss and immune cell hyperactivity. Lupus nephritis, a common, severe manifestation of SLE, is characterized by subendothelial immune complex depositions, subepithelial immune complex depositions, or both in the afflicted kidney, resulting in extensive injury and nephron loss (103). Dysregulated cell signals in SLE may identify pathways involved in controlling the PD-1 response (104). Expression of PD-1, PD-L1 and PD-L2 has been determined in tissue, cell and serum expression in SLE patients (105). George K. Bertsias et al. reported that PD-1 staining was detected in the glomeruli in 8 of 13 samples from patients with lupus nephritis compared with 0 of 9 control samples; similarly, PD-1 was detected in renal tubules in 6 of 13 samples from patients with lupus nephritis but in 0 of 9 control samples; all 8 PD-1+ lupus nephritis samples were also stained positive for CD3 expressed in the glomeruli and tubulointerstitial region, suggesting a correlation between PD-1 and CD3+ T cell infiltrates in lupus nephritis (106). Compared with healthy controls, patients with SLE demonstrate higher PD-1+ and lower PD-L1+ immune cell percentages among peripheral blood mononuclear cells (107). The inhibitory PD-1/PD-L1/2 pathway can also be restricted by the soluble form of PD-1 (sPD-1). SLE patients with high disease activity demonstrate significantly higher serum sPD-1 levels than those with low disease activity; this decrease occurs in accordance with disease amelioration after treatment (108). In a murine SLE model, the application of anti-PD-L1 could alleviate proteinuria and prolong survival via the suppression of CD4+ T-cell activation, T helper 17 differentiation, autoantibody-containing immune complex deposition in the kidneys, and cytokine production (including that of IFN-γ, IL-17, and IL-10) (109). In addition, blood sPD-L2 levels were lower in patients with SLE than in healthy individuals, and they are positively correlated with complements 3 and 4 (110). Guiteras et al. designed a human fusion recombinant protein (Hybri) with two domains: CTLA-4 (to block the CD28-CD80 costimulatory pathway) and PD-L2 (to exacerbate the PD-1-PD-L2 coinhibitory pathway); this protein prevented the progression of proteinuria and anti-dsDNA to levels similar to those of cyclophosphamide, as well as reduced the histological score, infiltration of B and T cells and macrophages, and immune deposition, in NZB/WF1 and MRL/lpr mouse models of lupus nephritis (Table 1) (111). Besides, the immune checkpoint blockade targeting PD-1 inhibitory pathways has been a successful treatment in several cancers; the blocking of these inhibitory immune checkpoint receptors is also associated with further irAEs that can resemble lupus-like autoimmune diseases (112, 113). Therefore, PD-1 and its ligands have been identified as immune regulatory molecules implicated in SLE pathogenesis and development (104).
Autoimmune glomerulonephritis occurs as a consequence of autoantibody and T-cell effector functions, which target either antigens intrinsic to the glomeruli or nonspecific antibodies that become trapped and accumulate in the glomeruli (15). Grywalska et al. reported that the frequencies of PD-1- and PD-L1-positive T and B cells were higher in patients with proliferative glomerulonephritis (PGN) (seven with IgA nephropathy, and three with membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis) than in patients with non-PGN or in control individuals (four with minimal change disease, and six with membranous glomerulonephritis) (114). Studies on experimental autoimmune glomerulonephritis have demonstrated that stimulation of PD-1 using PD-L1/Fc fusion protein leads to a significant reduction in albuminuria, serum urea, serum creatinine, crescent formation, and tubular damage, as well as the numbers of glomerular macrophages, CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and PD-1+ cells (115). However, studies on acute experimental foreign antigen-induced circulating immune complex glomerulonephritis have shown that the endogenous PD-1/PD-L pathway elicited by antimouse PD-1/PD-L1/PD-L2 antibody administration does not result in any significant pathological changes (116). IgA nephropathy (IgAN), the most common form of primary glomerulonephritis worldwide, is characterized by increased amounts of aberrantly glycosylated IgA1 (Gd-IgA1) present in patient serum and glomerular immune deposits (117). T cells promote IgA production and mediate the course of IgAN (118). In a study, the percentages of different subsets of circulating PD-1hiCXCR5− T and CD138+ B cells were significantly higher in patients with IgAN than in healthy individuals, and the percentage of these cells was correlated with disease severity (119). Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP), also an IgA-mediated systemic small-vessel vasculitis, was noted to result in renal manifestations in 40%-50% of the patients (120). Moreover, the number of circulating CD4+CXCR5+PD-1+ T follicular helper cells was significantly higher in patients with HSP nephritis than in healthy individuals, and it was negatively correlated with 24-hour urinary protein levels (121).
Allogenic transplantation is associated with allograft rejection risk due to exposure to foreign antigens, and a major factor triggering organ rejection is T-cell activation during immune allorecognition (122). PD-1 and its ligands are crucial regulators of T-cell activation and self-tolerance mechanisms. Both experimental and clinical evidence has indicated that PD-1 signaling can modulate transplant rejection. Murine models of kidney transplantation demonstrated that >90% of CD8+ T cells and approximately 75% of CD4+ T cells in early infiltrates of renal transplants express PD-1, and blocking PD-1-PD-L1 interactions using anti-PD-L1 early after transplantation can increase the amounts of T-cell infiltrates, resulting in terminal acute rejection (123). Besides, Zihuan Luo et al. developed a membrane-anchored-protein PD-L1 (map-PD-L1), which effectively anchored onto the surface of rat glomerular endothelial cells and could bind to PD-1 promoting T cell apoptosis and inhibiting T cell activation; ex vivo perfusion of donor kidneys with map-PD-L1 significantly protected grafts against acute injury without using any immunosuppressant in kidney transplantation models (124). Studies in humans have indicated that PD-L1, PD-L2, and PD-1 mRNA and protein expression is upregulated in biopsies of patients with renal allograft rejection compared with that in their pre-transplant biopsies, and a blockade of PD-L1 on tubular epithelial cells results in a significant increase in the proliferation of CD4+ T cells and cytokine production in CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in vitro (20). Melendreras et al. observed that high levels of soluble co-signaling molecules (sCD30, sCD40, sCD137, sCD40L, sPD-1, and sPD-L1) in the sera of kidney transplant recipients determined were strongly associated with a higher risk of graft failure at 3 months after transplantation than at 6 years after transplantation, suggesting that these soluble molecules may be useful biomarkers for predicting long-term graft function (125). Collectively, these findings underscore the importance of PD-1 co-inhibition in transplant immunology.
Organ transplant recipients have a higher cancer risk than the general population, and in these patients, cancer remains the second most common cause of death (126). Some organ transplant patients developing cancer are treated with ICIs. In contrast, ICIs can increase the risk of acute rejection related to T-type cellular immunity activation, and immunosuppressants can compromise the antitumor activity of immunotherapy (127). Therefore, the safety and efficacy of ICIs in organ transplant recipients should be discussed thoroughly. Data pooled from the literature demonstrated that the overall allograft rejection rate is 36%-41% in organ transplant recipients after ICI therapy; in particular, graft rejection rate is 40%-44% for kidney transplant recipients (126, 128). The highest risk is noted in patients treated with PD-1 inhibitors than in those treated with PD-L1 and CTLA-4 inhibitors, whereby nivolumab demonstrated the highest rejection rate, followed by pembrolizumab (126, 128). A multicenter retrospective study in kidney transplant recipients demonstrated that 42% of the patients receiving ICIs developed acute rejection within a median onset of <4 weeks, 65.5% required dialysis, and 27.5% lost their allograft; in contrast, the acute rejection rate was 5.4% in patients not treated with ICIs (129). Moreover, 50% of the rejections were T-cell-mediated rejection and the rest were mixed (T-cell and antibody mediated rejection) in their series of kidney transplant patients treated with ICIs. Suzuki et al. identified PD-1 agonists inhibiting T cells by triggering immunosuppressive signaling in murine disease models with acute graft versus host disease and colitis and indicated their clinical potential for treating issues related to allogeneic transplantation (130). Taken together, these results indicate the necessity of considering both rejection risks and objective response rates and maintaining two-agent immunosuppression regimens to achieve reasonable tumor response with a low rejection risk.
Senescent cell accumulation within tissues is a hallmark of the aging process. The immune system can clear senescent cells as part of normal tissue homeostasis. However, the excessive generation and insufficient elimination of senescent cells in various tissues promote inflammation and potentially contribute to pathological aging (131). Senescent cells expressing PD-L1 can escape immune surveillance, resulting in their accumulation and associated inflammation (132, 133). PD-L1 mRNA upregulation in bone, heart, liver, marrow, and lung has been observed in aged mice (132). Wang et al. recently reported an increase in PD-L1+ cell population among tdTomato− cells from the liver and kidneys of aged mice. The author also reported that anti-PD-1 administration reduced the total number of p16+ cells and the population of PD-L1+ cells in an activated CD8+ T-cell-dependent manner in naturally aging mice or a mouse model with normal livers or induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in vivo, ameliorating various aging-related phenotypes (134). Therefore, PD-1 and its ligands (PD-L1 and PD-L2) are overexpressed after podocyte injury and during cellular senescence. PD-1 upregulation activates caspase-3 and induces metabolic disruption, leading to podocyte injury and loss. Anti-PD-1 ameliorates these effects in vitro and in vivo (19, 134, 135). Preventing aging via PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade may be a promising therapeutic strategy.
Regardless of the cause of podocyte disease, lost podocytes are irreplaceable because they are unique, highly specialized, terminally differentiated, and restricted in a postmitotic state with limited repair or regeneration ability (136, 137). Podocyte number and density decrease with advancing age (138, 139). Global transcriptomic changes that occur in aged mouse podocytes indicate that decreased expression of canonical podocyte marker genes, junctional and adhesion proteins, and prosurvival pathway proteins synergizes with an increase in the activities of inflammatory response pathways and a decrease in those of podocyte-specific signaling (139). Pippin et al. reported that the PD-1 pathway activity increases in aged mouse and human glomeruli and that it is correlated with glomerular scarring, vascular damage, and declined kidney function (19). Moreover, aged mouse and human kidneys displayed higher PD-1 levels in podocytes, parietal epithelial cells, and tubular cells but not in glomerular mesangial cells and endothelial cells (19). In an in vitro study, interfering with PD-1 signaling in mice by using neutralizing anti-PD-1 significantly improved the aging phenotype in the glomeruli, tubular epithelial cells, and the tubulointerstitium in the kidneys, as well as in the liver, and increased podocyte lifespan (19).
Age-related diseases are progressive conditions, typically involving inflammation and fibrotic degeneration. Emerging studies have indicated that the PD-1/PD-L1 axis plays a critical role in these diseases associated with the accumulation of senescent cells with inflammatory and degenerative alterations, such as those in atherosclerosis, chronic obstructive lung disease, coronary artery disease, and Alzheimer’s disease (133, 140–143). In fibrotic processes, fibroblasts are the primary source of myofibroblasts. PD-1/PD-L1 signaling mediates fibrotic pathological responses by modulating T-cell immunity, fibroblast activation, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (34, 144). In the fibrotic tissues of both mice and humans, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, and epithelial cells demonstrate high PD-L1 expression (34, 132, 145–147). Moreover, tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN) and renal fibrosis have been noted to occur after administration of PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitors for treating various cancers (34, 148).
The increase in clinical use of ICIs has led to an increase in the number of reported irAEs because ICIs exuberantly activate immune responses. The renal complications of ICI administration mainly include acute kidney injury (AKI), proteinuria, and electrolyte abnormalities, all attributable to renal or extrarenal irAEs. Compared with extrarenal irAEs, intrarenal irAEs are less common (149, 150). In a retrospective cohort study, 17% of patients who received PD-L1 inhibitors for 1 year developed AKI, and 6% developed sustained AKI; however, only <1% of the patients were suspected to have PD-L1-related AKI (151). In clinical trials on PD-1 inhibitors, the pooled incidence of all and grade 3-4 AKIs has been 2.2% and 19%, respectively (152). The mechanisms underlying ICI-associated AKIs include reactivation of effector T cells, loss of tolerance versus self-renal antigens, increase in PD-L1 expression by tubular cells, or establishment of a proinflammatory milieu with self-reactive antibody release (149). These AKIs are independent of the drug dose received, but they differ based on the drug type (152). The incidence of AKIs associated with anti-CTLA-4 + anti-PD-1 therapy (4.9%) is higher than that of AKIs associated with anti-PD-1 monotherapy, including nivolumab (2.3%) and pembrolizumab (2.0%) and that of AKIs associated with anti-PD-L1, including atezolizumab (1%), durvalumab (1%), or avelumab (0%) (151, 152). Available pharmacokinetic data have revealed that ICIs are cleared primarily by nonspecific proteolytic degradation in the plasma and peripheral tissues, not in the liver or kidneys (150). As such, ICI dose need not be adjusted for the prevention of kidney impairment; however, patients with high-grade nonselective proteinuria may develop impaired efficacy because of drug clearance through urinary loss (150).
Acute TIN (ATIN) is a predominant lesion observed in the kidney biopsies of 93% of ICI-related AKI cases (153). In their meta-analysis of clinical trials, Manohar et al. reported an estimated acute interstitial nephritis (AIN) rate of 16.6% among patients who developed AKI after treatment with PD-1 inhibitors; in particular, the AIN rates were 15% and 21.6% for nivolumab and pembrolizumab, respectively (152). Izzedine et al. observed that 33.3% of pembrolizumab-treated patients demonstrated AIN in renal biopsy and that pembrolizumab withdrawal coupled with corticosteroid therapy most effectively led to kidney function recovery, proteinuria improvement, or both (154). The lesions in renal tubules and interstitium present ATIN, alone or in combination with glomerulopathies (155). Hakroush et al. reported that all renal biopsies with AIN related to ICI therapy and 27.9% of ICI-naïve renal biopsies with underlying kidney diseases were positive for PD-L1, whereas all control kidneys with nephrectomy were PD-L1 negative (156). Both tubular and glomerular PD-L1 positivity occurs in patients with ICI-related AIN. However, Cassol et al. demonstrated that tubular epithelial cell membrane was positive for PD-L1 only in patients with PD-1 inhibitor-associated AIN but not in those with acute tubular necrosis or AIN secondary to other medications (157). Relatively few data, mainly in the form of case series, are available on glomerular diseases associated with ICIs (21, 22, 158–160). A systematic review indicated the most frequent biopsy-confirmed ICI-associated glomerular diseases were pauci-immune glomerulonephritis/renal vasculitis (27%), podocytopathies (24%), and complement 3 GN (11%) (161). Most patients demonstrated full or partial recovery after discontinuing ICIs or receiving corticosteroid treatment; however, 19% of the patients remained dialysis-dependent, and approximately one-third died. Other nephrotoxicities in the form of glomerular injury included IgA nephropathy, membranous nephropathy, antiglomerular basement membrane disease, lupus-like nephritis, thrombotic microangiopathy, and amyloid A amyloidosis (155, 161, 162). As such, distinguishing renal irAEs from other causes of AKI is critical, and kidney biopsy should be only considered when ICI-associated nephrotoxicity is suspected.
PD-1 and its ligands, representative immunosuppressive checkpoints, constitute an inhibitory pathway mediating immune tolerance and affording immune homeostasis. Recent years have enabled a rapid expansion of the current knowledge regarding PD-1 immunology, which involves cancer immunity, autoimmunity, infection immunity, transplantation immunity, allergy, immune privilege, and PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitor-related irAEs. Major advances have been made in immunotherapy for immune-associated disorders, particularly cancer therapy; moreover, therapies involving PD-1/PD-L1 blockade have been approved for the treatment of various cancers.
In this review, we highlighted the growing relationship between PD-1 immunology and the kidneys. PD-1 receptors, PD-1 ligands, or both on immune cells (kidney macrophages, DCs, and lymphocytes) and renal parenchymal cells (proximal tubule epithelial cells and podocytes) can aid in maintaining immunological homeostasis in the kidneys. Understanding these interconnected networks between PD-1 immunology and distinct cell populations related to renal cell carcinoma, glomerulonephritis, kidney transplantation, or renal aging will be critical to the development of novel drugs targeting PD-1 signaling. Despite the efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors in cancer therapy, several molecular targeted drugs have been implicated in the development of renal complications, which can range from distinct renal irAEs to extrarenal irAEs. Consequently, PD-1 and its ligands have significant roles in the kidneys, necessitating further mechanistic and clinical studies to delve deeper into their implications.
RC: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft. QL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HT: Writing – review & editing. XD: Writing – review & editing. LJ: Writing – review & editing. NC: Writing – review & editing. XL: Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the Suzhou Key Discipline Project of Pediatric Immunology (grant number SZXK202106) and the Suzhou Science and Technology Development Plan Project (grant number SS202067).
We thank the Departments of Nephrology and Immunology at Children’s Hospital of Soochow University for their support. We also thank the native English speaking scientists of Elixigen Company (Huntington Beach, California) for editing our manuscript.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
PD-1, programmed death 1; PD-L1, programmed death ligand 1; PD-L2, programmed death ligand 2; CD28, cluster of differentiation 28; Gal-9, galectin 9; Gal-3, galectin 3; TME, tumor microenvironment; NK, natural killer; DCs, dendritic cells; irAEs, immune-related adverse events; ITIM, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif; ITSM, immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif; CTLA-4, cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen-4; ICOS, inducible co-stimulatory molecule; UTR, untranslated region; sPD-1, soluble PD-1; flPD-1, full-length PD-1; CTLs, cytotoxic T lymphocytes; TCRs, T-cell antigen receptors; B7-H1, B7 homolog 1; sPD-L1, soluble PD-L1; mPD-L1, membrane-bound PD-L1; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases; ADAM, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase; APCs, antigen-presenting cells; IFN, interferon; sPD-L2, soluble PD-L2; RGMb, repulsive guidance molecule b; BMP2, bone morphogenetic proteins 2; BMP4, bone morphogenetic proteins 4; CRD, carbohydrate-recognition domain; TIM-3, T-cell immunoglobin and mucin domain-containing protein 3; VISTA, V-domain Ig suppressor of T-cell activation; LAG-3, lymphocyte-activation gene 3; Gal3BP, a galectin-3-binding-protein; RCC, renal cell carcinoma; ccRCC, clear-cell RCC; pRCC, papillary RCC; chRCC, chromophobe RCC; ICI, immune checkpoint inhibitor; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; PGN, proliferative glomerulonephritis; NPGN, non-proliferative glomerulonephritis; IgAN, IgA nephropathy; HSP, Henoch-Schönlein purpura; HSPN, HSP nephritis; TIN, tubulointerstitial nephritis; AKI, acute kidney injury; ATIN, acute TIN; AIN, acute interstitial nephritis.
1. Zhang Y, Zheng J. Functions of immune checkpoint molecules beyond immune evasion. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2020) 1248:201–26. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-3266-5_9
2. Chamoto K, Yaguchi T, Tajima M, Honjo T. Insights from a 30-year journey: function, regulation and therapeutic modulation of PD1. Nat Rev Immunol. (2023) 23:682–95. doi: 10.1038/s41577-023-00867-9
3. Ishida Y, Agata Y, Shibahara K, Honjo T. Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. (1992) 11:3887–95. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05481.x
4. Ishida Y. PD-1: its discovery, involvement in cancer immunotherapy, and beyond. Cells. (2020) 9:1–9. doi: 10.3390/cells9061376
5. Finger LR, Pu J, Wasserman R, Vibhakar R, Louie E, Hardy RR, et al. The human PD-1 gene: complete cDNA, genomic organization, and developmentally regulated expression in B cell progenitors. Gene. (1997) 197:177–87. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(97)00260-6
6. Pauken KE, Torchia JA, Chaudhri A, Sharpe AH, Freeman GJ. Emerging concepts in PD-1 checkpoint biology. Semin Immunol. (2021) 52:101480. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2021.101480
7. Latchman Y, Wood CR, Chernova T, Chaudhary D, Borde M, Chernova I, et al. PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation. Nat Immunol. (2001) 2:261–68. doi: 10.1038/85330
8. Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, Bourque K, Chernova T, Nishimura H, et al. Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7 family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte activation. J Exp Med. (2000) 192:1027–34. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.7.1027
9. Torres NI, Baudou FG, Scheidegger MA, Dalotto-Moreno T, Rabinovich GA. Do galectins serve as soluble ligands for immune checkpoint receptors? J Immunother Cancer. (2024) 12:1–4. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-008984
10. Sun L, Li CW, Chung EM, Yang R, Kim YS, Park AH, et al. Targeting glycosylated PD-1 induces potent antitumor immunity. Cancer Res. (2020) 80:2298–310. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-3133
11. Pedersen K, Nielsen MA, Juul-Madsen K, Hvid M, Deleuran B, Greisen SR. Galectin-3 interacts with PD-1 and counteracts the PD-1 pathway-driven regulation of T cell and osteoclast activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Scand J Immunol. (2023) 97:e13245. doi: 10.1111/sji.13245
12. Yang R, Sun L, Li CF, Wang YH, Yao J, Li H, et al. Galectin-9 interacts with PD-1 and TIM-3 to regulate T cell death and is a target for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:832. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21099-2
13. Han Y, Liu D, Li L. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: current researches in cancer. Am J Cancer Res. (2020) 10:727–42.
14. Chen RY, Zhu Y, Shen YY, Xu QY, Tang HY, Cui NX, et al. The role of PD-1 signaling in health and immune-related diseases. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1163633. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1163633
15. Nagai K. Co-inhibitory receptor signaling in T-cell-mediated autoimmune glomerulonephritis. Front Med (Lausanne). (2020) 7:584382. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.584382
16. Tang Q, Chen Y, Li X, Long S, Shi Y, Yu Y, et al. The role of PD-1/PD-L1 and application of immune-checkpoint inhibitors in human cancers. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:964442. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.964442
17. Zamani MR, Aslani S, Salmaninejad A, Javan MR, Rezaei N. PD-1/PD-L and autoimmunity: A growing relationship. Cell Immunol. (2016) 310:27–41. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2016.09.009
18. Curran CS, Kopp JB. PD-1 immunobiology in glomerulonephritis and renal cell carcinoma. BMC Nephrol. (2021) 22:80. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02257-6
19. Pippin JW, Kaverina N, Wang Y, Eng DG, Zeng Y, Tran U, et al. Upregulated PD-1 signaling antagonizes glomerular health in aged kidneys and disease. J Clin Invest. (2022) 132:1–20. doi: 10.1172/JCI156250
20. Starke A, Lindenmeyer MT, Segerer S, Neusser MA, Rusi B, Schmid DM, et al. Renal tubular PD-L1 (CD274) suppresses alloreactive human T-cell responses. Kidney Int. (2010) 78:38–47. doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.97
21. Daanen RA, Maas R, Koornstra R, Steenbergen EJ, van Herpen C, Willemsen A. Nivolumab-associated nephrotic syndrome in a patient with renal cell carcinoma: A case report. J Immunother. (2017) 40:345–48. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000189
22. Kitchlu A, Fingrut W, Avila-Casado C, Chan CT, Crump M, Hogg D, et al. Nephrotic syndrome with cancer immunotherapies: A report of 2 cases. Am J Kidney Dis. (2017) 70:581–85. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.04.026
23. Di Giacomo AM, Guarnieri A, Tripodi SA, Maccari M, Mancianti N, Guido G, et al. Brief communication PD1-related nephrotoxicity: optimizing its clinical management through histopathologic features. J Immunother. (2022) 45:217–21. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000412
24. Chen W, Huang Y, Pan W, Xu M, Chen L. Strategies for developing PD-1 inhibitors and future directions. Biochem Pharmacol. (2022) 202:115113. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2022.115113
25. Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. (2008) 26:677–704. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.26.021607.090331
26. Khan M, Arooj S, Wang H. Soluble B7-CD28 family inhibitory immune checkpoint proteins and anti-cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:651634. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.651634
27. Brosseau JP. Regulations on messenger RNA: wires and nodes. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2020) 1248:251–63. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-3266-5_11
28. Niogret C, Birchmeier W, Guarda G. SHP-2 in lymphocytes' Cytokine and inhibitory receptor signaling. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:2468. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02468
29. Baldanzi G. Immune checkpoint receptors signaling in T cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:1–19. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073529
30. Ai L, Xu A, Xu J. Roles of PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: signaling, cancer, and beyond. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2020) 1248:33–59. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-3266-5_3
31. Christofides A, Katopodi XL, Cao C, Karagkouni D, Aliazis K, Yenyuwadee S, et al. SHP-2 and PD-1-SHP-2 signaling regulate myeloid cell differentiation and antitumor responses. Nat Immunol. (2023) 24:55–68. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01385-x
32. Niu M, Liu Y, Yi M, Jiao D, Wu K. Biological characteristics and clinical significance of soluble PD-1/PD-L1 and exosomal PD-L1 in cancer. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:827921. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.827921
33. Fabrizio FP, Trombetta D, Rossi A, Sparaneo A, Castellana S, Muscarella LA. Gene code CD274/PD-L1: from molecular basis toward cancer immunotherapy. Ther Adv Med Oncol. (2018) 10:433536658. doi: 10.1177/1758835918815598
34. Zhao Y, Qu Y, Hao C, Yao W. PD-1/PD-L1 axis in organ fibrosis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1145682. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1145682
35. Du Y, Nie L, Xu L, Wu X, Zhang S, Xue J. Serum levels of soluble programmed death-1 (sPD-1) and soluble programmed death ligand 1(sPD-L1) in systemic lupus erythematosus: Association with activity and severity. Scand J Immunol. (2020) 92:e12884. doi: 10.1111/sji.12884
36. Takahashi N, Iwasa S, Sasaki Y, Shoji H, Honma Y, Takashima A, et al. Serum levels of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 as a prognostic factor on the first-line treatment of metastatic or recurrent gastric cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. (2016) 142:1727–38. doi: 10.1007/s00432-016-2184-6
37. Frigola X, Inman BA, Krco CJ, Liu X, Harrington SM, Bulur PA, et al. Soluble B7-H1: differences in production between dendritic cells and T cells. Immunol Lett. (2012) 142:78–82. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2011.11.001
38. Frigola X, Inman BA, Lohse CM, Krco CJ, Cheville JC, Thompson RH, et al. Identification of a soluble form of B7-H1 that retains immunosuppressive activity and is associated with aggressive renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. (2011) 17:1915–23. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0250
39. Ghosh C, Luong G, Sun Y. A snapshot of the PD-1/PD-L1 pathway. J Cancer. (2021) 12:2735–46. doi: 10.7150/jca.57334
40. Nishimura CD, Pulanco MC, Cui W, Lu L, Zang X. PD-L1 and B7-1 cis-interaction: new mechanisms in immune checkpoints and immunotherapies. Trends Mol Med. (2021) 27:207–19. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2020.10.004
41. Chen R, Ganesan A, Okoye I, Arutyunova E, Elahi S, Lemieux MJ, et al. Targeting B7-1 in immunotherapy. Med Res Rev. (2020) 40:654–82. doi: 10.1002/med.21632
42. Zhao Y, Lee CK, Lin CH, Gassen RB, Xu X, Huang Z, et al. PD-L1:CD80 cis-heterodimer triggers the co-stimulatory receptor CD28 while repressing the inhibitory PD-1 and CTLA-4 pathways. Immunity. (2019) 51:1059–73. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.11.003
43. Sugiura D, Okazaki IM, Maeda TK, Maruhashi T, Shimizu K, Arakaki R, et al. PD-1 agonism by anti-CD80 inhibits T cell activation and alleviates autoimmunity. Nat Immunol. (2022) 23:399–410. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-01125-7
44. Lazar-Molnar E, Scandiuzzi L, Basu I, Quinn T, Sylvestre E, Palmieri E, et al. Structure-guided development of a high-affinity human Programmed Cell Death-1: Implications for tumor immunotherapy. EBioMedicine. (2017) 17:30–44. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.02.004
45. Yang Y, Wang X, Bai Y, Feng D, Li A, Tang Y, et al. Programmed death-ligand 2 (PD-L2) expression in bladder cancer. Urol Oncol. (2020) 38:603–09. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2020.01.001
46. Muraro E, Romano R, Fanetti G, Vaccher E, Turturici I, Lupato V, et al. Tissue and circulating PD-L2: moving from health and immune-mediated diseases to head and neck oncology. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2022) 175:103707. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2022.103707
47. Dai S, Jia R, Zhang X, Fang Q, Huang L. The PD-1/PD-Ls pathway and autoimmune diseases. Cell Immunol. (2014) 290:72–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2014.05.006
48. Ahmad SM, Martinenaite E, Holmstrom M, Jorgensen MA, Met O, Nastasi C, et al. The inhibitory checkpoint, PD-L2, is a target for effector T cells: Novel possibilities for immune therapy. Oncoimmunology. (2018) 7:e1390641. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1390641
49. Dowell AC, Munford H, Goel A, Gordon NS, James ND, Cheng KK, et al. PD-L2 is constitutively expressed in normal and Malignant urothelium. Front Oncol. (2021) 11:626748. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.626748
50. Yearley JH, Gibson C, Yu N, Moon C, Murphy E, Juco J, et al. PD-L2 expression in human tumors: relevance to anti-PD-1 therapy in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. (2017) 23:3158–67. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-1761
51. Perez-Cruz M, Iliopoulou BP, Hsu K, Wu HH, Erkers T, Swaminathan K, et al. Immunoregulatory effects of RGMb in gut inflammation. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:960329. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.960329
52. Nie X, Chen W, Zhu Y, Huang B, Yu W, Wu Z, et al. B7-DC (PD-L2) costimulation of CD4(+) T-helper 1 response via RGMb. Cell Mol Immunol. (2018) 15:888–97. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2017.17
53. Xiao Y, Yu S, Zhu B, Bedoret D, Bu X, Francisco LM, et al. RGMb is a novel binding partner for PD-L2 and its engagement with PD-L2 promotes respiratory tolerance. J Exp Med. (2014) 211:943–59. doi: 10.1084/jem.20130790
54. Moar P, Tandon R. Galectin-9 as a biomarker of disease severity. Cell Immunol. (2021) 361:104287. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2021.104287
55. Yang RY, Rabinovich GA, Liu FT. Galectins: structure, function and therapeutic potential. Expert Rev Mol Med. (2008) 10:e17. doi: 10.1017/S1462399408000719
56. Hirabayashi J, Hashidate T, Arata Y, Nishi N, Nakamura T, Hirashima M, et al. Oligosaccharide specificity of galectins: a search by frontal affinity chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. (2002) 1572:232–54. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(02)00311-2
57. Wada J, Kanwar YS. Identification and characterization of galectin-9, a novel beta-galactoside-binding mammalian lectin. J Biol Chem. (1997) 272:6078–86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.9.6078
58. Schlichtner S, Yasinska IM, Lall GS, Berger SM, Ruggiero S, Cholewa D, et al. T lymphocytes induce human cancer cells derived from solid Malignant tumors to secrete galectin-9 which facilitates immunosuppression in cooperation with other immune checkpoint proteins. J Immunother Cancer. (2023) 11:1–13. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-005714
59. Yasinska IM, Meyer NH, Schlichtner S, Hussain R, Siligardi G, Casely-Hayford M, et al. Ligand-receptor interactions of galectin-9 and VISTA suppress human T lymphocyte cytotoxic activity. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:580557. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.580557
60. Mittelberger J, Seefried M, Franitza M, Garrido F, Ditsch N, Jeschke U, et al. The role of the immune checkpoint molecules PD-1/PD-L1 and TIM-3/gal-9 in the pathogenesis of preeclampsia-A narrative review. Medicina (Kaunas). (2022) 58:1–12. doi: 10.3390/medicina58020157
61. Kandel S, Adhikary P, Li G, Cheng K. The TIM3/Gal9 signaling pathway: An emerging target for cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. (2021) 510:67–78. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2021.04.011
62. Sauer N, Janicka N, Szlasa W, Skinderowicz B, Kolodzinska K, Dwernicka W, et al. TIM-3 as a promising target for cancer immunotherapy in a wide range of tumors. Cancer Immunol Immunother. (2023) 72:3405–25. doi: 10.1007/s00262-023-03516-1
63. Ding QQ, Chauvin JM, Zarour HM. Targeting novel inhibitory receptors in cancer immunotherapy. Semin Immunol. (2020) 49:101436. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2020.101436
64. Zhao L, Cheng S, Fan L, Zhang B, Xu S. TIM-3: An update on immunotherapy. Int Immunopharmacol. (2021) 99:107933. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107933
65. Qin S, Xu L, Yi M, Yu S, Wu K, Luo S. Novel immune checkpoint targets: moving beyond PD-1 and CTLA-4. Mol Cancer. (2019) 18:155. doi: 10.1186/s12943-019-1091-2
66. Yuan L, Tatineni J, Mahoney KM, Freeman GJ. VISTA: A mediator of quiescence and a promising target in cancer immunotherapy. Trends Immunol. (2021) 42:209–27. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2020.12.008
67. Garcia-Diaz A, Shin DS, Moreno BH, Saco J, Escuin-Ordinas H, Rodriguez GA, et al. Interferon receptor signaling pathways regulating PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression. Cell Rep. (2017) 19:1189–201. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.04.031
68. Blanchard H, Yu X, Collins PM, Bum-Erdene K. Galectin-3 inhibitors: a patent review (2008-present). Expert Opin Ther Pat. (2014) 24:1053–65. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2014.947961
69. Zheng L, Xia J, Ge P, Meng Y, Li W, Li M, et al. The interrelation of galectins and autophagy. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 120:110336. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110336
70. von Hundelshausen P, Wichapong K, Gabius HJ, Mayo KH. The marriage of chemokines and galectins as functional heterodimers. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2021) 78:8073–95. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-04010-6
71. Slack RJ, Mills R, Mackinnon AC. The therapeutic potential of galectin-3 inhibition in fibrotic disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. (2021) 130:105881. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2020.105881
72. Henderson NC, Mackinnon AC, Farnworth SL, Poirier F, Russo FP, Iredale JP, et al. Galectin-3 regulates myofibroblast activation and hepatic fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2006) 103:5060–65. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0511167103
73. Li LC, Li J, Gao J. Functions of galectin-3 and its role in fibrotic diseases. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2014) 351:336–43. doi: 10.1124/jpet.114.218370
74. Huflejt ME, Turck CW, Lindstedt R, Barondes SH, Leffler H. L-29, a soluble lactose-binding lectin, is phosphorylated on serine 6 and serine 12 in vivo and by casein kinase I. J Biol Chem. (1993) 268:26712–18. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)74371-3
75. Yoshii T, Fukumori T, Honjo Y, Inohara H, Kim HR, Raz A. Galectin-3 phosphorylation is required for its anti-apoptotic function and cell cycle arrest. J Biol Chem. (2002) 277:6852–57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M107668200
76. Takenaka Y, Fukumori T, Yoshii T, Oka N, Inohara H, Kim HR, et al. Nuclear export of phosphorylated galectin-3 regulates its antiapoptotic activity in response to chemotherapeutic drugs. Mol Cell Biol. (2004) 24:4395–406. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.10.4395-4406.2004
77. Aggarwal V, Workman CJ, Vignali D. LAG-3 as the third checkpoint inhibitor. Nat Immunol. (2023) 24:1415–22. doi: 10.1038/s41590-023-01569-z
78. Maruhashi T, Sugiura D, Okazaki IM, Shimizu K, Maeda TK, Ikubo J, et al. Binding of LAG-3 to stable peptide-MHC class II limits T cell function and suppresses autoimmunity and anti-cancer immunity. Immunity. (2022) 55:912–24. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2022.03.013
79. Kouo T, Huang L, Pucsek AB, Cao M, Solt S, Armstrong T, et al. Galectin-3 shapes antitumor immune responses by suppressing CD8+ T cells via LAG-3 and inhibiting expansion of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Cancer Immunol Res. (2015) 3:412–23. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-14-0150
80. Bae J, Accardi F, Hideshima T, Tai YT, Prabhala R, Shambley A, et al. Targeting LAG3/GAL-3 to overcome immunosuppression and enhance anti-tumor immune responses in multiple myeloma. Leukemia. (2022) 36:138–54. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01301-6
81. Al BM, Ali A, McMullin MF, Mills K. Protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type C (PTPRC or CD45). J Clin Pathol. (2021) 74:548–52. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2020-206927
82. Courtney AH, Shvets AA, Lu W, Griffante G, Mollenauer M, Horkova V, et al. CD45 functions as a signaling gatekeeper in T cells. Sci Signal. (2019) 12:1–15. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaw8151
83. Raiter A, Lipovetsky J, Stenbac A, Lubin I, Yerushalmi R. TNBC-derived Gal3BP/Gal3 complex induces immunosuppression through CD45 receptor. Oncoimmunology. (2023) 12:2246322. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2023.2246322
84. Chen HY, Fermin A, Vardhana S, Weng IC, Lo KF, Chang EY, et al. Galectin-3 negatively regulates TCR-mediated CD4+ T-cell activation at the immunological synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2009) 106:14496–501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0903497106
85. Gallo V, Arienzo A, Iacobelli S, Iacobelli V, Antonini G. Gal-3BP in viral infections: an emerging role in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:1–13. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137314
86. Fukaya Y, Shimada H, Wang LC, Zandi E, DeClerck YA. Identification of galectin-3-binding protein as a factor secreted by tumor cells that stimulates interleukin-6 expression in the bone marrow stroma. J Biol Chem. (2008) 283:18573–81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M803115200
87. Song L, Asgharzadeh S, Salo J, Engell K, Wu HW, Sposto R, et al. Valpha24-invariant NKT cells mediate antitumor activity via killing of tumor-associated macrophages. J Clin Invest. (2009) 119:1524–36. doi: 10.1172/JCI37869
88. Silverman AM, Nakata R, Shimada H, Sposto R, DeClerck YA. A galectin-3-dependent pathway upregulates interleukin-6 in the microenvironment of human neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. (2012) 72:2228–38. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2165
89. Marino KV, Cagnoni AJ, Croci DO, Rabinovich GA. Targeting galectin-driven regulatory circuits in cancer and fibrosis. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. (2023) 22:295–316. doi: 10.1038/s41573-023-00636-2
90. Deleuze A, Saout J, Dugay F, Peyronnet B, Mathieu R, Verhoest G, et al. Immunotherapy in renal cell carcinoma: the future is now. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:1–22. doi: 10.3390/ijms21072532
91. Chowdhury N, Drake CG. Kidney cancer: an overview of current therapeutic approaches. Urol Clin North Am. (2020) 47:419–31. doi: 10.1016/j.ucl.2020.07.009
92. Erlmeier F, Weichert W, Schrader AJ, Autenrieth M, Hartmann A, Steffens S, et al. Prognostic impact of PD-1 and its ligands in renal cell carcinoma. Med Oncol. (2017) 34:99. doi: 10.1007/s12032-017-0961-y
93. Diaz-Montero CM, Rini BI, Finke JH. The immunology of renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2020) 16:721–35. doi: 10.1038/s41581-020-0316-3
94. Zhang S, Zhang E, Long J, Hu Z, Peng J, Liu L, et al. Immune infiltration in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci. (2019) 110:1564–72. doi: 10.1111/cas.13996
95. MacFarlane AT, Jillab M, Plimack ER, Hudes GR, Uzzo RG, Litwin S, et al. PD-1 expression on peripheral blood cells increases with stage in renal cell carcinoma patients and is rapidly reduced after surgical tumor resection. Cancer Immunol Res. (2014) 2:320–31. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-13-0133
96. Leite KR, Reis ST, Junior JP, Zerati M, Gomes DO, Camara-Lopes LH, et al. PD-L1 expression in renal cell carcinoma clear cell type is related to unfavorable prognosis. Diagn Pathol. (2015) 10:189. doi: 10.1186/s13000-015-0414-x
97. Abbas M, Steffens S, Bellut M, Eggers H, Grosshennig A, Becker JU, et al. Intratumoral expression of programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). Med Oncol. (2016) 33:80. doi: 10.1007/s12032-016-0794-0
98. Shin SJ, Jeon YK, Kim PJ, Cho YM, Koh J, Chung DH, et al. Clinicopathologic analysis of PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression in renal cell carcinoma: association with oncogenic proteins status. Ann Surg Oncol. (2016) 23:694–702. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4903-7
99. Erlmeier F, Weichert W, Autenrieth M, Wiedemann M, Schrader AJ, Hartmann A, et al. PD-L2: A prognostic marker in chromophobe renal cell carcinoma? Med Oncol. (2017) 34:71. doi: 10.1007/s12032-017-0926-1
100. Motzer RJ, Escudier B, George S, Hammers HJ, Srinivas S, Tykodi SS, et al. Nivolumab versus everolimus in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: Updated results with long-term follow-up of the randomized, open-label, phase 3 CheckMate 025 trial. Cancer. (2020) 126:4156–67. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33033
101. McDermott DF, Lee JL, Bjarnason GA, Larkin J, Gafanov RA, Kochenderfer MD, et al. Open-label, single-arm phase II study of pembrolizumab monotherapy as first-line therapy in patients with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:1020–28. doi: 10.1200/JCO.20.02363
102. Gurram S, Al HM, Ball MW. The changing landscape of systemic therapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma: an update. Discovery Med. (2020) 29:191–99.
103. Parodis I, Tamirou F, Houssiau FA. Prediction of prognosis and renal outcome in lupus nephritis. Lupus Sci Med. (2020) 7:e000389. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2020-000389
104. Curran CS, Gupta S, Sanz I, Sharon E. PD-1 immunobiology in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Autoimmun. (2019) 97:1–09. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2018.10.025
105. Sagrero-Fabela N, Chavez-Mireles R, Salazar-Camarena DC, Palafox-Sanchez CA. Exploring the role of PD-1 in the autoimmune response: insights into its implication in systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:1–22. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147726
106. Bertsias GK, Nakou M, Choulaki C, Raptopoulou A, Papadimitraki E, Goulielmos G, et al. Genetic, immunologic, and immunohistochemical analysis of the programmed death 1/programmed death ligand 1 pathway in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. (2009) 60:207–18. doi: 10.1002/art.24227
107. Lee JM, Chen MH, Chou KY, Chao Y, Chen MH, Tsai CY. Novel immunoprofiling method for diagnosing SLE and evaluating therapeutic response. Lupus Sci Med. (2022) 9:1–9. doi: 10.1136/lupus-2022-000693
108. Hirahara S, Katsumata Y, Kawasumi H, Kawaguchi Y, Harigai M. Serum levels of soluble programmed cell death protein 1 and soluble programmed cell death protein ligand 2 are increased in systemic lupus erythematosus and associated with the disease activity. Lupus. (2020) 29:686–96. doi: 10.1177/0961203320916517
109. Liao W, Zheng H, Wu S, Zhang Y, Wang W, Zhang Z, et al. The systemic activation of programmed death 1-PD-L1 axis protects systemic lupus erythematosus model from nephritis. Am J Nephrol. (2017) 46:371–79. doi: 10.1159/000480641
110. Tong M, Fang X, Yang J, Wu P, Guo Y, Sun J. Abnormal membrane-bound and soluble programmed death ligand 2 (PD-L2) expression in systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with disease activity. Immunol Lett. (2020) 227:96–101. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2020.09.001
111. Guiteras J, Crespo E, Fontova P, Bolanos N, Goma M, Castano E, et al. Dual costimulatory and coinhibitory targeting with a hybrid fusion protein as an immunomodulatory therapy in lupus nephritis mice models. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:1–24. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158411
112. Lu KL, Wu MY, Wang CH, Wang CW, Hung SI, Chung WH, et al. The role of immune checkpoint receptors in regulating immune reactivity in lupus. Cells. (2019) 8:1–28. doi: 10.3390/cells8101213
113. van der Vlist M, Kuball J, Radstake TR, Meyaard L. Immune checkpoints and rheumatic diseases: what can cancer immunotherapy teach us? Nat Rev Rheumatol. (2016) 12:593–604. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2016.131
114. Grywalska E, Smarz-Widelska I, Krasowska-Zajac E, Korona-Glowniak I, Zaluska-Patel K, Mielnik M, et al. The PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitory pathway is altered in primary glomerulonephritides. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). (2018) 66:133–43. doi: 10.1007/s00005-017-0485-3
115. Reynolds J, Sando GS, Marsh OB, Salama AD, Evans DJ, Cook HT, et al. Stimulation of the PD-1/PDL-1 T-cell co-inhibitory pathway is effective in treatment of experimental autoimmune glomerulonephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2012) 27:1343–50. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr529
116. Ooi JD, Li M, Kourkoutzelos K, Yagita H, Azuma M, Holdsworth SR, et al. Programmed death 1 and its ligands do not limit experimental foreign antigen-induced immune complex glomerulonephritis. Nephrol (Carlton). (2015) 20:892–98. doi: 10.1111/nep.12532
117. Stamellou E, Seikrit C, Tang S, Boor P, Tesar V, Floege J, et al. IgA nephropathy. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2023) 9:67. doi: 10.1038/s41572-023-00476-9
118. Taliercio JJ, Mehdi A. IgA nephropathy. Cleve Clin J Med. (2023) 90:e5–08. doi: 10.3949/ccjm.90.e-s1.02
119. Wang X, Li T, Si R, Chen J, Qu Z, Jiang Y. Increased frequency of PD-1(hi)CXCR5(-) T cells and B cells in patients with newly diagnosed IgA nephropathy. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:492. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-57324-8
120. Leung A, Barankin B, Leong KF. Henoch-schonlein purpura in children: an updated review. Curr Pediatr Rev. (2020) 16:265–76. doi: 10.2174/1573396316666200508104708
121. Zhang Z, Zhao S, Zhang L, Crew R, Zhang N, Sun X, et al. A higher frequency of CD4(+)CXCR5(+) T follicular helper cells in patients with newly diagnosed Henoch-Schonlein purpura nephritis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2016) 32:8–15. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.12.037
122. Xu Z, Tsai HI, Xiao Y, Wu Y, Su D, Yang M, et al. Engineering programmed death ligand-1/cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen-4 dual-targeting nanovesicles for immunosuppressive therapy in transplantation. ACS Nano. (2020) 14:7959–69. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b09065
123. Shim YJ, Khedraki R, Dhar J, Fan R, Dvorina N, Valujskikh A, et al. Early T cell infiltration is modulated by programed cell death-1 protein and its ligand (PD-1/PD-L1) interactions in murine kidney transplants. Kidney Int. (2020) 98:897–905. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.03.037
124. Luo Z, Liao T, Zhang Y, Zheng H, Sun Q, Han F, et al. Ex vivo anchored PD-L1 functionally prevent in vivo renal allograft rejection. Bioeng Transl Med. (2022) 7:e10316. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10316
125. Melendreras SG, Martinez-Camblor P, Menendez A, Bravo-Mendoza C, Gonzalez-Vidal A, Coto E, et al. Soluble co-signaling molecules predict long-term graft outcome in kidney-transplanted patients. PloS One. (2014) 9:e113396. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113396
126. Kumar V, Shinagare AB, Rennke HG, Ghai S, Lorch JH, Ott PA, et al. The safety and efficacy of checkpoint inhibitors in transplant recipients: A case series and systematic review of literature. Oncologist. (2020) 25:505–14. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0659
127. Bermejo S, Bolufer M, Riveiro-Barciela M, Soler MJ. Immunotherapy and the spectrum of kidney disease: should we individualize the treatment? Front Med (Lausanne). (2022) 9:906565. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.906565
128. Fisher J, Zeitouni N, Fan W, Samie FH. Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in solid organ transplant recipients: A patient-centered systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol. (2020) 82:1490–500. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2019.07.005
129. Murakami N, Mulvaney P, Danesh M, Abudayyeh A, Diab A, Abdel-Wahab N, et al. A multi-center study on safety and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in cancer patients with kidney transplant. Kidney Int. (2021) 100:196–205. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.12.015
130. Suzuki K, Tajima M, Tokumaru Y, Oshiro Y, Nagata S, Kamada H, et al. Anti-PD-1 antibodies recognizing the membrane-proximal region are PD-1 agonists that can down-regulate inflammatory diseases. Sci Immunol. (2023) 8:eadd4947. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.add4947
131. Giannoula Y, Kroemer G, Pietrocola F. Cellular senescence and the host immune system in aging and age-related disorders. BioMed J. (2023) 46:100581. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2023.02.001
132. Onorati A, Havas AP, Lin B, Rajagopal J, Sen P, Adams PD, et al. Upregulation of PD-L1 in senescence and aging. Mol Cell Biol. (2022) 42:e0017122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.00171-22
133. Salminen A. The role of the immunosuppressive PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint pathway in the aging process and age-related diseases. J Mol Med (Berl). (2024) 102:733–50. doi: 10.1007/s00109-024-02444-6
134. Wang TW, Johmura Y, Suzuki N, Omori S, Migita T, Yamaguchi K, et al. Blocking PD-L1-PD-1 improves senescence surveillance and ageing phenotypes. Nature. (2022) 611:358–64. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05388-4
135. De Cos M, Campbell KN. PD-1 inhibition in aged podocytes and glomerular disease. Kidney Int. (2023) 103:18–20. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2022.11.005
136. Sobh MM, El KG, Moustafa F, Eid R, Hamdy N, Tharwat S. Role of detached podocytes in differentiating between minimal change disease and early focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, can we rely on routine light microscopy? J Nephrol. (2022) 35:2313–24. doi: 10.1007/s40620-022-01456-0
137. Nagata M. Podocyte injury and its consequences. Kidney Int. (2016) 89:1221–30. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.01.012
138. Puelles VG, Cullen-McEwen LA, Taylor GE, Li J, Hughson MD, Kerr PG, et al. Human podocyte depletion in association with older age and hypertension. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2016) 310:F656–68. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00497.2015
139. Wang Y, Eng DG, Kaverina NV, Loretz CJ, Koirala A, Akilesh S, et al. Global transcriptomic changes occur in aged mouse podocytes. Kidney Int. (2020) 98:1160–73. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.05.052
140. Saresella M, Calabrese E, Marventano I, Piancone F, Gatti A, Farina E, et al. A potential role for the PD1/PD-L1 pathway in the neuroinflammation of Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. (2012) 33:611–24. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.03.004
141. Weyand CM, Berry GJ, Goronzy JJ. The immunoinhibitory PD-1/PD-L1 pathway in inflammatory blood vessel disease. J Leukoc Biol. (2018) 103:565–75. doi: 10.1189/jlb.3MA0717-283
142. Polverino F, Mirra D, Yang CX, Esposito R, Spaziano G, Rojas-Quintero J, et al. Similar programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression profile in patients with mild COPD and lung cancer. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:22402. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26650-9
143. Kummer MP, Ising C, Kummer C, Sarlus H, Griep A, Vieira-Saecker A, et al. Microglial PD-1 stimulation by astrocytic PD-L1 suppresses neuroinflammation and Alzheimer's disease pathology. EMBO J. (2021) 40:e108662. doi: 10.15252/embj.2021108662
144. Lu Y, Zhong W, Liu Y, Chen W, Zhang J, Zeng Z, et al. Anti-PD-L1 antibody alleviates pulmonary fibrosis by inducing autophagy via inhibition of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2022) 104:108504. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108504
145. Guo X, Sunil C, Adeyanju O, Parker A, Huang S, Ikebe M, et al. PD-L1 mediates lung fibroblast to myofibroblast transition through Smad3 and beta-catenin signaling pathways. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:3053. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-07044-3
146. Jiang A, Liu N, Wang J, Zheng X, Ren M, Zhang W, et al. The role of PD-1/PD-L1 axis in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Friend or foe? Front Immunol. (2022) 13:1022228. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1022228
147. Ahmadvand N, Carraro G, Jones MR, Shalashova I, Noori A, Wilhelm J, et al. Cell-surface programmed death ligand-1 expression identifies a sub-population of distal epithelial cells enriched in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Cells. (2022) 11:1–16. doi: 10.3390/cells11101593
148. Palamaris K, Alexandris D, Stylianou K, Giatras I, Stofas A, Kaitatzoglou C, et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors' Associated renal toxicity: A series of 12 cases. J Clin Med. (2022) 11:1–15. doi: 10.3390/jcm11164786
149. Franzin R, Netti GS, Spadaccino F, Porta C, Gesualdo L, Stallone G, et al. The use of immune checkpoint inhibitors in oncology and the occurrence of AKI: where do we stand? Front Immunol. (2020) 11:574271. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.574271
150. Perazella MA, Shirali AC. Immune checkpoint inhibitor nephrotoxicity: what do we know and what should we do? Kidney Int. (2020) 97:62–74. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2019.07.022
151. Seethapathy H, Zhao S, Strohbehn IA, Lee M, Chute DF, Bates H, et al. Incidence and clinical features of immune-related acute kidney injury in patients receiving programmed cell death ligand-1 inhibitors. Kidney Int Rep. (2020) 5:1700–05. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2020.07.011
152. Manohar S, Kompotiatis P, Thongprayoon C, Cheungpasitporn W, Herrmann J, Herrmann SM. Programmed cell death protein 1 inhibitor treatment is associated with acute kidney injury and hypocalcemia: meta-analysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2019) 34:108–17. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfy105
153. Cortazar FB, Kibbelaar ZA, Glezerman IG, Abudayyeh A, Mamlouk O, Motwani SS, et al. Clinical features and outcomes of immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated AKI: A multicenter study. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2020) 31:435–46. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019070676
154. Izzedine H, Mathian A, Champiat S, Picard C, Mateus C, Routier E, et al. Renal toxicities associated with pembrolizumab. Clin Kidney J. (2019) 12:81–8. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfy100
155. Mamlouk O, Selamet U, MaChado S, Abdelrahim M, Glass WF, Tchakarov A, et al. Nephrotoxicity of immune checkpoint inhibitors beyond tubulointerstitial nephritis: single-center experience. J Immunother Cancer. (2019) 7:2. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0478-8
156. Hakroush S, Kopp SB, Tampe D, Gersmann AK, Korsten P, Zeisberg M, et al. Variable expression of programmed cell death protein 1-ligand 1 in kidneys independent of immune checkpoint inhibition. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:624547. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.624547
157. Cassol C, Satoskar A, Lozanski G, Rovin B, Hebert L, Nadasdy T, et al. Anti-PD-1 immunotherapy may induce interstitial nephritis with increased tubular epithelial expression of PD-L1. Kidney Int Rep. (2019) 4:1152–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2019.06.001
158. Gao B, Lin N, Wang S, Wang Y. Minimal change disease associated with anti-PD1 immunotherapy: a case report. BMC Nephrol. (2018) 19:156. doi: 10.1186/s12882-018-0958-6
159. Bickel A, Koneth I, Enzler-Tschudy A, Neuweiler J, Flatz L, Fruh M. Pembrolizumab-associated minimal change disease in a patient with Malignant pleural mesothelioma. BMC Cancer. (2016) 16:656. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2718-y
160. Saito S, Kadota T, Gochi M, Takagi M, Kuwano K. Re-administration of pembrolizumab with prednisolone after pembrolizumab-induced nephrotic syndrome. Eur J Cancer. (2020) 126:74–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.12.015
161. Kitchlu A, Jhaveri KD, Wadhwani S, Deshpande P, Harel Z, Kishibe T, et al. A systematic review of immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated glomerular disease. Kidney Int Rep. (2021) 6:66–77. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2020.10.002
162. Meraz-Munoz A, Amir E, Ng P, Avila-Casado C, Ragobar C, Chan C, et al. Acute kidney injury associated with immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: incidence, risk factors and outcomes. J Immunother Cancer. (2020) 8:1–9. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2019-000467
163. You Y, Wang J, Wang Z. Programmed death 1 monoclonal antibody helped to treat mixed chimeric and reactivation of Epstein-Barr virus in a patient with adult-onset chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A case report. Med (Baltimore). (2022) 101:e28542. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028542
164. Ma Y, Zhang P, Bao Y, Luo H, Wang J, Huang L, et al. Outcomes of programmed death protein-1 inhibitors treatment of chronic active Epstein Barr virus infection: A single center retrospective analysis. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1093719. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1093719
165. Song Y, Wang J, Wang Y, Wu L, You Y, Song D, et al. PD-1 blockade and lenalidomide combination therapy for chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. (2023) 29:796–97. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2023.01.017
166. Chen R, Lin Q, Zhu Y, Shen Y, Xu Q, Tang H, et al. Sintilimab treatment for chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection and Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in children. Orphanet J Rare Dis. (2023) 18:297. doi: 10.1186/s13023-023-02861-9
167. Liu P, Pan X, Chen C, Niu T, Shuai X, Wang J, et al. Nivolumab treatment of relapsed/refractory Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adults. Blood. (2020) 135:826–33. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019003886
168. Brahmer JR, Drake CG, Wollner I, Powderly JD, Picus J, Sharfman WH, et al. Phase I study of single-agent anti-programmed death-1 (MDX-1106) in refractory solid tumors: safety, clinical activity, pharmacodynamics, and immunologic correlates. J Clin Oncol. (2010) 28:3167–75. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.26.7609
Keywords: programmed death 1, programmed death ligand 1, renal cell carcinoma, glomerulonephritis, kidney transplantation, renal aging, immune-related adverse events
Citation: Chen R, Lin Q, Tang H, Dai X, Jiang L, Cui N and Li X (2024) PD-1 immunology in the kidneys: a growing relationship. Front. Immunol. 15:1458209. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1458209
Received: 02 July 2024; Accepted: 07 October 2024;
Published: 23 October 2024.
Edited by:
Yasuhiro Shimojima, Shinshu University, JapanReviewed by:
Ranjana Walker Minz, Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research (PGIMER), IndiaCopyright © 2024 Chen, Lin, Tang, Dai, Jiang, Cui and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ningxun Cui, Y3VpbmluZ3h1bkAxMjYuY29t; Xiaozhong Li, eGlhb3pob25nbGljbkB5ZWFoLm5ldA==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.