- 1School of Humanities and Management, Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise, China
- 2School of Public Health and Management, Youjiang Medical University for Nationalities, Baise, China
This study proposes a more efficient discrete grey prediction model to describe the seasonalvariation trends of carbon dioxide emissions. The setting of the bernoulli parameter and the time powerterm parameter in the new model ensures that the model can capture the trend of nonlinear changesin the sequence. At the same time, the inclusion of dummy variables allows for the direct simulationof seasonal fluctuations in carbon dioxide emissions without the need for additional treatment of theseasonality in the sequence. The optimal search for the model’s hyperparameters is achieved using the MPA algorithm. The constructed model is applied to the monthly U.S. carbon dioxide emissions datafrom January 2003 to December 2022, a total of 240 months. The model is trained on 216 months of datafrom January 2003 to December 2020, and the monthly data from January 2021 to December 2022 is usedfor prediction, which is then compared with the actual values. The results show that the proposed modelexhibits higher forecasting performance compared to SARIMA and other models. Therefore, this methodcan effectively simulate the seasonal variation trends in carbon dioxide emissions, providing valuablereference information for relevant departments to formulate more effective policies.
1 Introduction
1.1 Research significance
The urgency of global climate change is intensifying, making it one of the most severe challenges facing the world today. In recent years, the persistent rise in global temperatures has led to widespread ecological imbalances, resulting in more frequent extreme weather events such as heatwaves, floods, hurricanes, and droughts, which pose serious threats to human habitats, agricultural production, and water security. Scientists warn that if global warming continues at its current pace, the Earth could reach an irreversible tipping point within the coming decades, causing irreparable ecological damage. Therefore, it is imperative that the world accelerates the implementation of emission reduction measures, promotes a shift to clean energy, and advances sustainable development. Carbon emission forecasting plays a critical role in the global fight against climate change. By predicting future emission trends, governments, businesses, and society can proactively develop strategies to reduce emissions, adjust energy systems, and promote the adoption of clean technologies. Forecasting data allows the quantification of different policies and technologies’ effectiveness, helping stakeholders make informed decisions to prevent irreversible environmental damage. Additionally, it provides scientific backing for countries’ carbon neutrality goals, fostering global collaboration in addressing the challenges posed by climate change. Accurate carbon emission forecasts are not only essential for environmental protection but also serve as a crucial tool for driving sustainable economic development. Carbon emission forecasting also serves as a crucial support tool in policy-making. By predicting future emission trends, policymakers can develop and assess environmental policies more scientifically, identify key areas for emission reduction, and allocate resources more effectively. Accurate carbon emission forecasts allow the quantification of the potential impact of different policies and technological measures on emission reduction, enabling governments, businesses, and society to make more effective plans backed by data. Monthly carbon emission forecasting, in particular, holds significant strategic importance. It provides more granular insights into emission trends, capturing seasonal variations, economic activity fluctuations, and the short-term impacts of policy measures. This high-frequency forecasting enables timely adjustments in response strategies, allowing key interventions at critical moments to better manage emission peaks and avoid the accumulation of harmful greenhouse gases. Monthly forecasts enhance the flexibility and precision of policy actions and provide vital support for accelerating progress toward global carbon neutrality.
1.2 Related research on carbon dioxide emissions prediction
The prediction of carbon dioxide emissions is a crucial step in addressing global climate change and formulating emission reduction policies. In recent years, researchers have employed various methods to forecast carbon dioxide emissions, which can generally be classified into several categories, including traditional statistical models, machine learning methods, and grey prediction models. Traditional statistical forecasting methods mainly include regression-based models and time series models represented by ARIMA. Kaur et al. (2023) develops a regression-based tool to estimate carbon dioxide emissions from cities, considering climatic and urban design factors. Applied to 3,646 cities, it examines the impact of electric vehicle adoption, urban density changes, and IPCC climate scenarios. Wang et al. (2019) employed input-output analysis and panel regression models to predict carbon emissions in China-Australia trade. They analyzed data from 2000 to 2014 and forecasted emissions for 2015 to 2022 under four development scenarios. The results showed a significant increase in net carbon outflow from China to Australia, with emissions varying greatly across different scenarios (Wang et al., 2024) constructed a carbon emission combination forecasting model based on the Generalized Induced Ordered Weighted Averaging (GIOWA) operator to address the limitations of using a single forecasting method and analyzed its carbon reduction performance. Empirical testing with China’s carbon emission data from 1980 to 2020 revealed that the GIOWA combination forecasting model significantly improved the accuracy of carbon emission predictions, achieving an average accuracy of over 99.5% during the sample period, surpassing various single forecasting methods. Malik et al. (2020) employed the ARIMA model to forecast carbon dioxide emissions in Pakistan up to 2030. The model demonstrated good accuracy, with a generally low Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) value consistently below 10%. Yang and O’Connell (2020) utilized the ARIMA model to forecast carbon emissions within the Shanghai aviation industry. Their findings revealed a projected continual increase in carbon emissions. Lin and Agyeman (2019) formulated an ARDL model to forecast carbon emissions in Ghana spanning from 2017 to 2030. In recent years, machine learning algorithms have played an important role in various fields, leading many scholars to attempt using different machine learning methods to predict carbon emissions. Li (2020) developed a new forecasting model called KLS, which integrates the Kalman filter (KF), long short-term memory (LSTM), and support vector machine (SVM) to enhance carbon emission (CE) predictions. LSTM is used for time series forecasting, while ridge regression selects relevant variables for SVM regression. Chai et al. (2023) used an improved particle swarm optimization (PSO) combined with deep neural networks (DNN) to predict building carbon emissions. The results showed that this method outperformed SVR, DNN, and other approaches in terms of prediction accuracy. Peng et al. (2024) proposed a method to predict carbon emissions in Sichuan Province’s construction industry for the period from 2021 to 2025 by optimizing a backpropagation (BP) neural network using a genetic algorithm (GA). The prediction results showed a MAPE value of 6.303% and a coefficient of determination of 0.853. Wu et al. (2024) developed a new deep learning model, the CNN-GRU-Attention model, which was used to predict carbon emissions in Jiangsu Province’s transportation sector in China.The results showed that this model achieved higher prediction accuracy compared to other models, with a mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.061582, root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.086, and an
1.3 Related research on grey prediction model
In 1982, Deng (1982) proposed the grey system theory, tailored for modeling systems with partial unknowns, small samples, and limited information. The grey prediction model is a forecasting method that accumulates the original sequence and uses differential equations to simulate changes in the sequence. To address the limitations of traditional grey models, several significant innovative approaches have been proposed. To solve the issue of “inhomogeneity” between the time response function and parameter estimation, (Xie and Liu, 2009). Tntroduced the discrete grey prediction model. To capture the nonlinear characteristics of sequence changes, (Chen et al., 2008). Developed the classic nonlinear Bernoulli model and provided its solution process. The distinction of grey models from other forecasting models lies in performing modeling after accumulating the original sequence. Wu et al. (2013) proposed the classic fractional-order accumulation generation operator, which uses fractional-order accumulation to describe the nonlinear variation trends of sequences. While standard grey prediction models perform well for growth-type sequences, they are less effective for sequences with seasonal characteristics. Some scholars have attempted to construct grey prediction models capable of forecasting seasonal sequences. For example, Wang et al. (2012) built a seasonal fluctuation grey model [SFGM (1, 1)] to predict the monthly electricity demand in South Australia. Applying a seasonal accumulating generation operator, (Wang et al., 2018) proposed a seasonal GM (1, 1) model [SGM (1, 1)] to forecast the quarterly electricity consumption of the Chinese primary industries. The results showed that the SGM (1, 1) model possessed higher accuracy than its competitors. Li et al. (2023b) developed a multivariable seasonal grey model with time-power terms and applied it to solar power generation forecasting. Chen et al. (2023) proposed an optimized Hausdorff fractional grey seasonal model that integrates a seasonal index, Hausdorff fractional accumulation, and particle swarm optimization to address seasonal fluctuations and random oscillations. The model was applied to forecast quarterly natural gas production (Wang et al. 2019) combined seasonal fluctuation techniques with the optimization of background values, power indices, and fractional orders to develop a seasonally optimized fractional nonlinear grey Bernoulli model (SOFANGBM(1,1)), which was applied to the analysis and forecasting of quarterly CO2 emissions in the United States. In summary, the above methods emphasize preprocessing data to eliminate seasonal effects before applying grey modeling to the processed data. Wang et al. (2017) proposed a method of grouping time series from different seasons for grey prediction. Building on this, Zhou et al. (2021a) proposed a seasonal fractional-order grey forecasting model, which improves prediction accuracy by capturing seasonal and nonlinear fluctuations, demonstrating superior performance in electricity demand forecasting in Zhejiang Province.Although this approach performs well for some sequences, artificially separating the seasonal sequences leads to the loss of correlation information between different seasons. In order to accurately describe real systems that typically exhibit seasonal disturbances with monthly or quarterly cycles, (Zhou et al., 2021a) proposed a novel discrete grey seasonal model, namely DGSM(1,1), which simulates and forecasts seasonal fluctuation sequences by incorporating seasonal dummy variables into the traditional grey model. This model does not require data preprocessing but instead enhances the grey model’s ability to handle seasonal data through the design of dummy variables, making it a highly innovative and significant contribution.
1.4 Research on grey prediction models in carbon emission forecasting
Grey prediction models for carbon dioxide emission forecasting can be broadly categorized into univariate grey prediction models and multivariate grey prediction models. Univariate prediction models primarily utilize methods such as accumulation generation to uncover the inherent variation patterns of the sequence and achieve forecasting by simulating these characteristics with grey models. Zhou et al. (2021b) developed a grey forecasting model based on the new information priority principle and rolling mechanism, which was applied to predict China’s carbon dioxide emissions, demonstrating superior accuracy and stability compared to classical methods. Ding et al. (2023) proposes a new-information-based grey model combining damping accumulation, data smoothing, and particle swarm optimization to forecast carbon dioxide emissions across China’s 30 provinces. The model outperforms existing methods in accuracy and robustness, offering valuable insights for regional decarbonization policies. Jiang et al. (2024) developed a discrete fractional accumulation grey gompertz prediction model to forecast the annual carbon dioxide emissions of China and the United States. On the other hand, multivariate grey prediction models integrate multiple influencing factors and analyze and forecast the target variable by considering the relationships between the target variable and its related factors. However, the inclusion of additional variables also increases the complexity of the model. Yin et al. (2023) conducted a predictive study on China’s annual carbon dioxide emissions based on a new grey multivariate prediction model and related influencing factors. Xu et al. (2024).proposes a novel multivariate grey model, FBNGM(1, N, r), which incorporates a fractional-order operator and an intelligent optimization algorithm to enhance prediction accuracy by emphasizing new information and optimizing parameters. Through numerical experiments on CO2 emissions, the model demonstrates superior accuracy, effective data utilization, and robustness against overfitting compared to traditional models. It also highlights the importance of influencing factors in carbon dioxide emissions prediction and provides future forecasts to support policy-making. To address the time-lag effects in carbon emission forecasting, (Ye et al., 2022) developed a dynamic time-delay discrete grey forecasting model (DTDGM(1, N, t)). By introducing a time-lag driving term and linear correction, the model effectively captures the delayed relationships between carbon emissions and related factors and is applied to the prediction of China’s carbon emissions. In conclusion, grey prediction models are widely used for carbon dioxide emission forecasting. However, it is worth noting that most existing studies focus primarily on annual predictions. Therefore, developing grey prediction models capable of forecasting carbon dioxide emissions on a quarterly basis is highly necessary.
1.5 Contributions and the organization of other parts
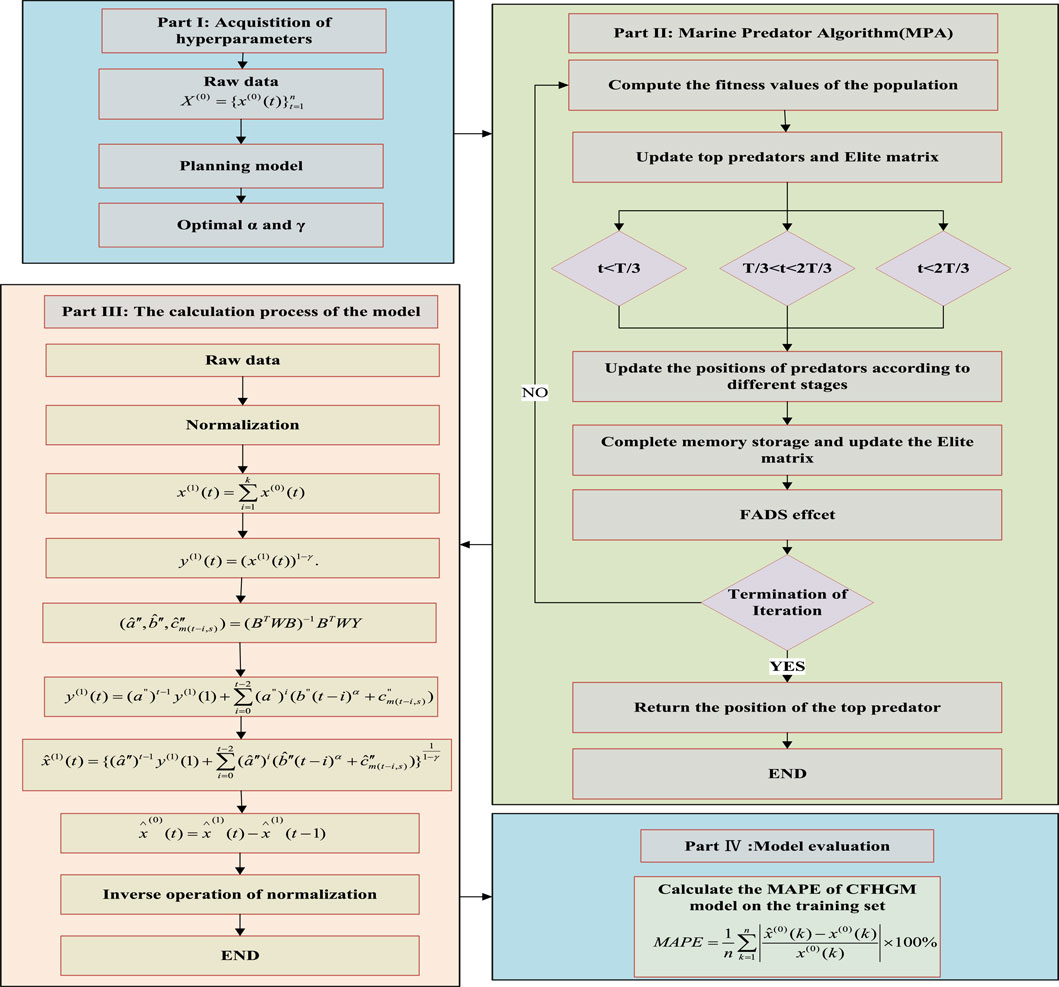
In order to more accurately predict seasonal carbon dioxide emissions, this paper constructs a seasonal grey prediction model based on discretization, dummy variables, Bernoulli parameters, and time power terms. Specifically, the model enhances its self-adaptive capability by using discretization operations, Bernoulli parameters, and time power terms, and it directly processes seasonal data by employing the dummy variables. For parameter optimization, the MPA algorithm is utilized to achieve optimal hyperparameter search, thereby improving computational efficiency. The advantages of the method proposed in this paper lie in its flexible modeling approach, simple modeling mechanism, and the ability to fit seasonal time series. Specifically, the introduction of dummy variables addresses the difficulties faced by traditional grey prediction models in dealing with seasonal time series, while Bernoulli parameters and time power terms enhance the model’s adaptability. The discretization operation not only solves the issue of lack of unbiasedness in traditional grey prediction models. The main contributions of this paper are as follows: 1) Compared to most carbon dioxide emission predictions that are only based on annual or quarterly data, this paper proposes a targeted seasonal grey prediction model based on the unique nonlinear characteristics of monthly carbon dioxide emissions. The construction of this model not only enriches the research on carbon dioxide emissions prediction at different time dimensions but also promotes the development of grey prediction theory. 2) This paper establishes a planning model for obtaining optimal hyperparameters and uses the MPA algorithm to solve the planning model instead of traditional mathematical methods, significantly improving the model’s computational efficiency. The rest of this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the process of building the model and its solution methods. Section 3 models the data from the United States from January 2003 to December 2022 using the constructed model and compares it with other comparative models to verify the effectiveness of the proposed model. The fourth part is the conclusion of this paper.
2 Methods
2.1 Basic concepts of the DGSM(1,1) model
The DSGM(1, 1) model, put forward by Li et al. (2023b), is a useful tool for confronting uncertain issues existing in insufficient information systems with sparse data. In comparison with the GM(1, 1) model, this model has significant advantages in reducing the inherent errors generated by the transformation from the discrete function to the continuous one. Thus, the detailed procedures of the DSGM(1, 1) model can be outlined below.
Step 1. Assume that Equation 1.
is an original non-negative varying sequence, where n is the length of the sequence. Subsequently, by using the one-order accumulation generation (1-AGO), these above raw data can be transformed into Equation 2
for which the kth entry is denoted as
Step 2. Build the novel discrete seasonal grey model.
is called as a novel Discrete Grey Seasonal Model having one variable and one order, abbreviated as DGSM(1, 1), where s is the number of the seasonal cycle,
Step 3. Estimate the model parameters. Substitute the values of k into Equation 3, we can obtain Set that
Step 4. Calculate the time response function for generating predictions in the transformed domain. And the predicted sequence is given by Equations 5, 6.
where
2.2 Novel disctete grey Bernoulli seasonal model with a time powter term
In grey prediction models, the grey action quantity controls the trend of a sequence’s variation over time. Using time power terms as the grey action can better simulate the time-dependent trend of the sequence, while the introduction of Bernoulli parameters can more effectively capture the nonlinear characteristics of the sequence. Therefore, this paper combines these two improvements with the DGSM(1,1) model to propose a new grey model for modeling seasonal sequences. The principle of this model is illustrated below.
Definition 1. If
is called the new adaptive seasonal grey bernoulli forecasting model with a time powter term (DSNGBM(1,1,
Definition 2. If
Proof:
Let
where
Based on traditional grey modeling theory, equations similar to Equation 9 are typically integrated over the interval to obtain a discrete estimation formula for estimating parameters. However, this approach is not practical. For example, the integral of
Further simplifying Equation 10, we have Equation 11.
Where
Proof complete.
Theorem 1. If the hyperparameters are known, then the model parameters estimation is given by
Proof:
According to Equation 11, once the hyperparameters are obtained, an unconstrained optimization problem can be formulated
Equation 13 can be transformed into Equation 14.
According to the conditions for the existence of extreme, we can obtain Equation 15.
If
Proof complete.
Theorem 2. once the estimates of the parameters are obtained through Equation 13, then one can get the final prediction results shown in Equation 16.
Where the time response function is represented by Equation 17.
Proof: when t = 2, we can get
When t = 3, we can get
Combining Equation 18 with Equation 19, we get Equation 20, as shown below:
According to this law, we can obtain Equation 21.
Since
Finally, based on the first-order accumulated reduction calculation, the final prediction result can be obtained as
Proof complete.
2.3 The method for solving the model
Due to the presence of unknown hyperparameters in the DSNGBM (1.1,
For nonlinear normalization models, ordinary mathematical solving methods require a substantial amount of time. In prediction problem solving, quick execution of predictions is essential. Therefore, utilizing swarm intelligence algorithms is an effective method for addressing such issues. The Marine Predators Algorithm (MPA) is a bio-inspired optimization algorithm that simulates the behavior of marine predators while hunting for prey. It models different search phases and the interaction between predators and prey in the marine ecosystem to find optimal solutions for complex optimization problems (Faramarzi et al., 2020). The MPA algorithm simulates marine predation behavior by dividing the search process into three stages, progressively balancing global search, local search, and mixed search. This three-stage distributed search mechanism enables MPA to flexibly shift during optimization: it initially performs broad exploration to avoid local optima, then gradually converges near the optimal solution, enhancing both diversity and convergence. Additionally, strategies like “Levy flight” and “marine diffusion” allow MPA to achieve faster convergence and adaptability in high-dimensional, multimodal problems. The algorithm is structurally simple with convenient parameter settings, making it effective across various types of problems. Compared to other common optimization algorithms, MPA offers a stronger balance between global exploration and local exploitation. For example, genetic algorithms rely on genetic variation but often converge prematurely; particle swarm optimization (PSO), while effective in multidimensional searches, tends to be sensitive to initial solutions and risks getting trapped in local optima. Through its three-stage distributed search and marine-inspired strategies, MPA effectively balances global search and local refinement, excelling in convergence speed and locating global optima. Furthermore, MPA requires minimal parameter dependence, typically only needing settings for population size and maximum iterations, making it relatively easy to apply to complex or large-scale problems. The “Levy flight” mechanism in MPA also reduces the likelihood of local optima while maintaining global search capability, making MPA highly adaptable in dynamically changing or uncertain problem scenarios.
The specific solving process of the MPA algorithm is as follow: A population of candidate solutions is generated randomly. Each individual in the population represents a potential solution. Let the problem’s dimension bed, and the population size be n. The initial population matrix
(1) Parameter Setting
Set key algorithm parameters, including the maximum number of iterations
(2) Iterative Update Phase
MPA uses three distinct phases to simulate the hunting behavior: exploration, exploitation, and Levy flight. These phases mimic the process of predators gradually approaching and capturing prey.
(3) Exploration Phase (Linear Search)
This phase simulates the early stage where predators search broadly over large areas for prey. The predators move randomly, often based on Levy flight or other random search patterns:
Where.
(4) Exploitation Phase (Chase and Follow)
In this phase, the predator begins to focus on a smaller area, closely tracking the prey. The search becomes more focused as predators narrow in on the best solutions:
The population begins to converge toward the best current solution, refining the search in local regions to improve the quality of the solutions.
(5) Levy Flight Phase (Levy Walk)
This phase simulates random, long-distance movements that help the predator explore more widely and avoid local optima. Levy flight is used to enable long jumps and escape from local traps:
Where:
This phase ensures a balance between global exploration and local exploitation.
(6) Update and Correction Phase
Boundary Correction: Ensure that solutions remain within the defined search space. If any new solution exceeds the boundaries, it is corrected to fall within the allowable range:
Fitness Evaluation: Each individuals fitness is calculated based on the objective function of the problem. Solutions are evaluated to measure how well they solve the optimization problem:
Elite Preservation Strategy: Ensure that the current best solution is retained. If a newly generated solution is better than an existing one, it replaces the old solution in the population, preserving the quality of the search.
(7) Termination
The algorithm terminates when either the maximum number of iterations
(8) Result Output
The algorithm outputs the optimal solution found
3 Experiment
3.1 Data sources
The United States is one of the largest carbon emitters in the world, with a profound impact on global climate change. By forecasting U.S. carbon emission trends, it becomes possible to assess the effectiveness of its energy policies and emission reduction measures, driving policy adjustments to achieve carbon neutrality. The U.S.’s large economy and complex energy consumption structure make predicting its emissions valuable as a reference for other nations, fostering international cooperation in addressing the climate crisis. Understanding U.S. carbon emission trends is crucial to the global reduction effort. Additionally, carbon emission forecasting helps assess future emission trends in advance, providing a scientific basis for developing effective reduction policies. It enables governments and businesses to optimize energy use, promote clean technologies, prevent irreversible impacts of climate change, and ensure the feasibility and effectiveness of achieving carbon neutrality goals. The raw data of U.S. Total Energy carbon dioxide Emissions [(Million Metric Tons of Carbon Dioxide)] are collected form the official website Energy Information Administration of USA (https://www.eia.gov/). The specific monthly carbon dioxide emission variation curve and statistical data indicators are shown in Figure 2 and Table 1.
3.2 Competing methods
Given the characteristics of the research subject, 3 seasonal statistical forecasting models [SARIMA, Holt-winter (Winters, , 1960), Prophet (Taylor et al., 2018)], 2 classical machine learning forecasting models [BPNN (Hecht-Nielsen, 1992) and ELM (Rahman et al., 2024)], and 5 classical seasonal grey forecasting models [GSLSSVR (Zhou et al., 2021c), SGM(1.1) (Wang et al., 2018), SIOGM(1.1) (Zhou et al., 2022),DDGM(1.1) (Wang et al., 2017), DSGM(1.1) (Zhou et al., 2021a)] are selected as competing methods. The calculation processes of (SARIMA, Holt-winter and Prophet are implemented using built-in functions in the R software, the other models were all implemented using MATLAB 2019a. It is worth mentioning that GSLSSVR are established based on a hybrid kernel function, which is a linear combination of Gaussian and polynomial kernel functions. By the way, all modeling parameters for models with unknown parameters are obtained through MPA. To evaluate the training and prediction performance of the model, this paper adopts four commonly used evaluation metrics, the definitions are shown in Equations 22–25. The mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), which is defined as follows
Mean Squared Error: MSE
Root Mean Squared Error: RMSE
Mean Absolute Error: MAE
3.3 Comparative analysis
In this paper, the training set consists of data from January 2003 to December 2020, and the test set comprises data from January 2021 to December 2022. Regarding the calculation of the DSNGBM(1,1,
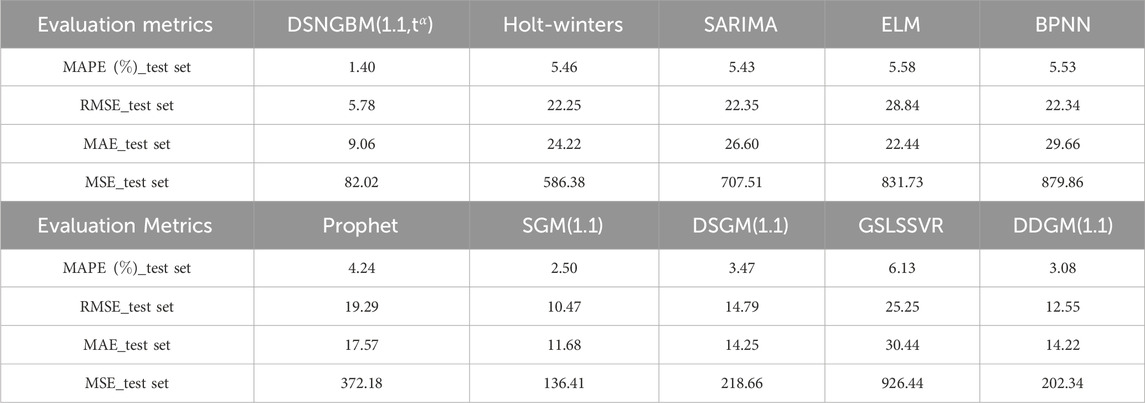
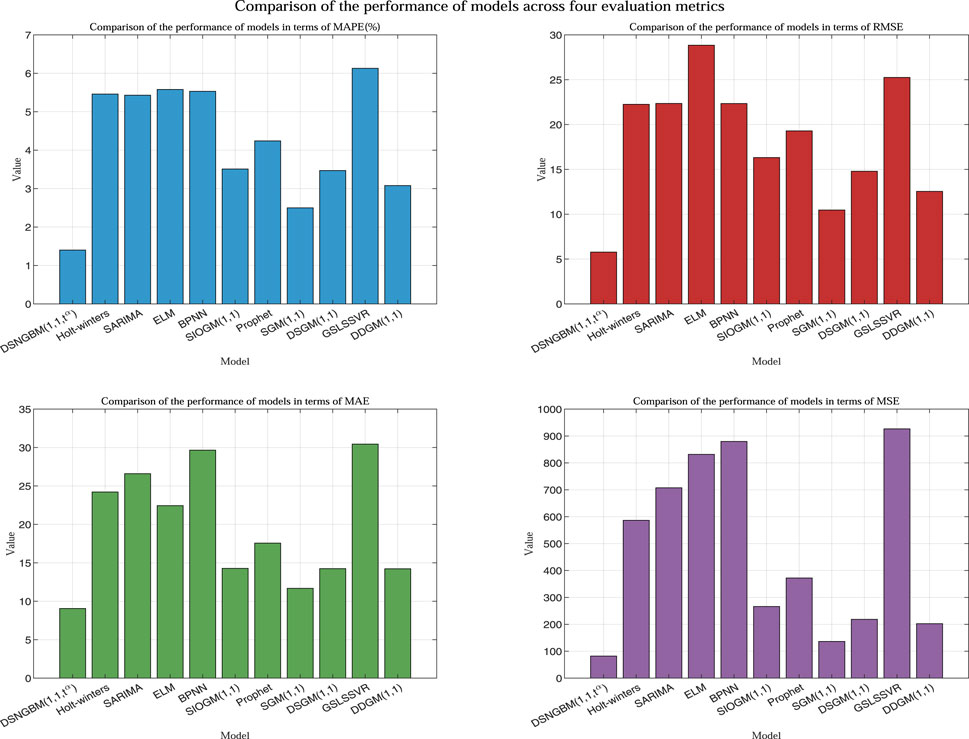
As shown in Table 3, the performance of each model across the four evaluation metrics (MAPE, RMSE, MAE, MSE) varies significantly. DSNGBM(1,1,t) stands out as the best-performing model, with a MAPE of only 1.40%, significantly lower than the other models, indicating its superior error control capability. Additionally, its RMSE (5.78) and MSE (82.02) are the lowest among all models, demonstrating its exceptional predictive accuracy and stability. The gray prediction models performed well overall, with SGM(1,1) achieving a MAPE of 2.50% and an RMSE of 10.47, closely following DSNGBM in error control and variability. Its MSE (136.41) is also relatively low, reflecting stable performance. Other gray prediction models, such as DDGM(1.1), DSGM(1,1), and SIOGM(1,1), also performed well, underscoring the unique advantages of gray prediction models in small-sample nonlinear prediction tasks. However, it is noteworthy that the GSLSSVR model performed the worst among all comparison models. This is likely due to the use of a hybrid kernel function to enhance nonlinear fitting capability during parameter optimization, which led to overfitting. Among traditional statistical models, Holt-winters and SARIMA demonstrated average performance with MAPE values of 5.46% and 5.43% and RMSE values of 22.25 and 22.35, respectively, falling short compared to gray prediction models. The poor performance of the Holt-Winters model may be attributed to overly optimized selection strategies, while the subpar performance of SARIMA might result from mismatches between the model assumptions and the data characteristics. In contrast, Prophet, as a time series forecasting tool bridging traditional statistical models and machine learning models, combines the ideas of statistical modeling with some automated features of machine learning. Consequently, it outperformed both statistical learning and machine learning models but fell short of gray prediction models. Prophet achieved a MAPE of 4.24%, better than other statistical models, but its MSE (372.18) indicates higher prediction volatility.The overall performance of machine learning models was poor. BPNN and ELM had high MAE values (29.66 and 22.44) and MSE values (879.86 and 831.73), reflecting limited error control capability. The suboptimal performance of machine learning models can be attributed to the limited training data, as each month only had 18 data points, leading to insufficient model training. The detailed performance of each model across the four evaluation metrics is shown in Figure 4, while the fitted curves of the models are illustrated in Figure 5.
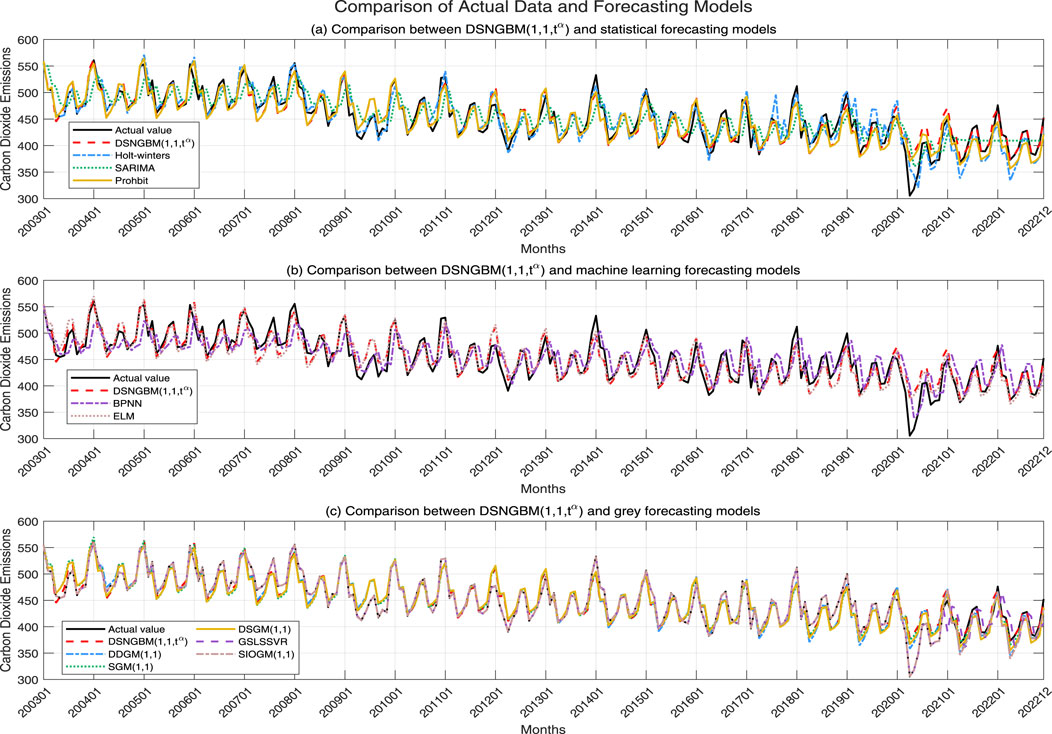
Figure 5. Comparison of the prediction performance of the DSNGBM (1,1,tα) model and three other models for monthly carbon dioxide emissions in the United States (A–C).
In summary, when using the DSNGBM model to forecast the monthly carbon dioxide data in the United States, the model effectively captures the nonlinear variation characteristics of the series and extracts seasonal features through the setting of dummy variables. Based on various forecasting evaluation metrics, this method significantly outperforms most models, demonstrating its effectiveness. Additionally, the performance of other grey prediction models also confirms that grey prediction models have certain advantages in forecasting with small samples.
4 Conclusion
This paper proposes a novel seasonal grey prediction model that integrates discretization, dummy variables, Bernoulli parameters, and time power terms, with the Marine Predators Algorithm (MPA) used for optimal hyperparameter tuning. These innovations enhance the model’s adaptability and forecasting precision. Unlike traditional grey models, the proposed model leverages Bernoulli parameters and time power terms to capture the seasonal and nonlinear characteristics of time series data more effectively, representing a significant improvement in grey prediction methodologies. To validate the model’s effectiveness, an empirical analysis was conducted using monthly carbon dioxide emission data from the United States. The results demonstrate that the proposed model significantly outperforms existing statistical, machine learning, and grey models across multiple evaluation metrics, including MAPE, RMSE, MAE, and MSE. The model not only achieves superior forecasting accuracy but also provides a better simulation of the variation patterns of U.S. monthly carbon dioxide emissions, showcasing its robustness and adaptability in addressing seasonal and nonlinear time series prediction tasks. The model’s advantages highlight its potential for application in real-world forecasting scenarios, particularly in environmental and energy-related fields. However, this study has several limitations that warrant further exploration. Firstly, the model employs ordinary first-order accumulation, which, while effective, might constrain its adaptability to certain complex data structures. Secondly, the univariate nature of the model does not account for the influence of external factors, such as economic activity or energy consumption, which could improve forecasting accuracy. Lastly, the computational efficiency of the model could be further optimized to enhance its scalability for larger datasets. Future research could focus on extending the model to incorporate multivariate grey models, allowing external influencing factors to be included. This would enhance the model’s predictive adaptability and accuracy but would also increase its complexity. Challenges such as matrix non-invertibility in parameter estimation, rendering the least squares method unusable, and the risk of overfitting may arise. Additionally, improving the traditional first-order accumulation generation, such as adopting fractional-order accumulation, could further capture the nonlinear characteristics of the sequence. Exploring alternative optimization algorithms could also enhance the model’s adaptability and performance. These improvements would provide a broader foundation for the application of grey models in forecasting seasonal carbon dioxide emissions and other complex time series tasks.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://www.eia.gov/.
Author contributions
JJ: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing, Software. YB: Writing–review and editing, Resources. SN: Writing–review and editing, Writing–original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The research was supported by the Annual Project of Guangxi Philosophy and Social Science Research (Grant No. 24GLF015).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Chai, H.-D., Lin, B. J., Wang, Y., Li, Y. H., Xu, J. Y., Lin, Y. L., et al. (2023). Building carbon emissions prediction based on deep learning network with improved particle swarm optimization. Artif. Intell. Evol., 216–225. doi:10.37256/aie.4220233561
Chen, C.-I., Chen, H. L., and Chen, S.-P. (2008). Forecasting of foreign exchange rates of Taiwans major trading partners by novel nonlinear Grey Bernoulli model NGBM (1, 1). Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 13 (6), 1194–1204. doi:10.1016/j.cnsns.2006.08.008
Chen, Y., Wang, H., Li, S., and Dong, R. (2023). A novel grey seasonal model for natural gas production forecasting. Fractal Fract. 7 (6), 422. doi:10.3390/fractalfract7060422
Deng, J. L. (1982). Control-problems of grey systems. Syst. and Control Lett. 1 (5), 288C294. doi:10.1016/s0167-6911(82)80025-x
Ding, S., and Zhang, H. (2023). Forecasting Chinese provincial CO2 emissions: a universal and robust new-information-based grey model. Energy Econ. 121, 106685. doi:10.1016/j.eneco.2023.106685
Faramarzi, A., Heidarinejad, M., Mirjalili, S., and Gandomi, A. H. (2020). Marine predators algorithm: a nature-inspired metaheuristic. Expert Syst. Appl. 152, 113377. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2020.113377
Hecht-Nielsen, R. (1992). “Theory of the backpropagation neural network,” in Neural networks for perception (Academic Press), 65–93.
Jiang, J., Ban, Y., Zhang, M., and Huang, Z. (2024). New discrete fractional accumulation Grey Gompertz model for predicting carbon dioxide emissions. Front. Environ. Sci. 12, 1450354. doi:10.3389/fenvs.2024.1450354
Kaur, J., Singh Parmar, K., and Singh, S. (2023). Autoregressive models in environmental forecasting time series: a theoretical and application review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (8), 19617–19641. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-25148-9
Li, H., Wu, Z., Qian, S., and Duan, H. (2023a). A novel fractional-order grey prediction model: a case study of Chinese carbon emissions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30 (51), 110377–110394. doi:10.1007/s11356-023-29919-2
Li, X., Ding, S., Cao, Y., and Li, Y. (2023b). A novel data-driven seasonal multivariable grey model for seasonal time series forecasting. Inf. Sci. 642, 119165. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2023.119165
Li, Y. (2020). Forecasting Chinese carbon emissions based on a novel time series prediction method. Energy Sci. and Eng. 8 (7), 2274–2285. doi:10.1002/ese3.662
Lin, B., and Agyeman, S. D. (2019). Assessing Ghana’s carbon dioxide emissions through energy consumption structure towards a sustainable development path. J. Clean. Prod. 238, 117941. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.117941
Malik, A., Hussain, E., Baig, S., and Khokhar, M. F. (2020). Forecasting CO2 emissions from energy consumption in Pakistan under different scenarios: the China–Pakistan economic corridor. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 10 (2), 380–389. doi:10.1002/ghg.1968
Peng, S., Tan, J., and Ma, H. (2024). Carbon emission prediction of construction industry in Sichuan Province based on the GA-BP model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 31 (16), 24567–24583. doi:10.1007/s11356-024-32585-7
Rahman, M., Rashid, F., Roy, S. K., and Habib, M. A. (2024). Application of extreme learning machine (ELM) forecasting model on CO2 emission dataset of a natural gas-fired power plant in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Data Brief 54, 110491. doi:10.1016/j.dib.2024.110491
Taylor, S. J., and Benjamin, L. (2018). Forecasting at scale. Am. Statistician 72 (1), 37–45. doi:10.1080/00031305.2017.1380080
Wang, H., Wei, Z., Fang, T., Xie, Q., Li, R., and Fang, D. (2024). Carbon emissions prediction based on the GIOWA combination forecasting model: a case study of China. J. Clean. Prod. 445, 141340. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2024.141340
Wang, J., Ma, X., Wu, J., and Dong, Y. (2012). Optimization models based on GM (1, 1) and seasonal fluctuation for electricity demand forecasting. Int. J. Electr. Power and Energy Syst. 43 (1), 109–117. doi:10.1016/j.ijepes.2012.04.027
Wang, S., Zhao, Y., and Wiedmann, T. (2019). Carbon emissions embodied in China–Australia trade: a scenario analysis based on input–output analysis and panel regression models. J. Clean. Prod. 220, 721–731. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.071
Wang, Z., Li, Q., and Pei, L.-L. (2018). A seasonal GM (1, 1) model for forecasting the electricity consumption of the primary economic sectors. Energy 154, 522–534. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2018.04.155
Wang, Z. X., Li, Q., and Pei, L. L. (2017). Grey forecasting method of quarterly hydropower production in China based on a data grouping approach. Appl. Math. Model. 51, 302–316. doi:10.1016/j.apm.2017.07.003
Winters, P. R. (1960). Forecasting sales by exponentially weighted moving averages. Manag. Sci. 6 (3), 324–342. doi:10.1287/mnsc.6.3.324
Wu, L., Liu, S., Yao, L., Yan, S., and Liu, D. (2013). Grey system model with the fractional order accumulation. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 18 (7), 1775–1785. doi:10.1016/j.cnsns.2012.11.017
Wu, X., Chen, L., Zhao, J., He, M., and Han, X. (2024). CNN-GRU-Attention neural networks for carbon emission prediction of transportation in Jiangsu Province. Sustainability 16 (19), 8553. doi:10.3390/su16198553
Xie, N.-ming, and Liu, S.-feng (2009). Discrete grey forecasting model and its optimization. Appl. Math. Model. 33 (2), 1173–1186. doi:10.1016/j.apm.2008.01.011
Xu, Y., Lin, T., Du, P., and Wang, J. (2024). The research on a novel multivariate grey model and its application in carbon dioxide emissions prediction. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 31 (14), 21986–22011. doi:10.1007/s11356-024-32262-9
Yang, H., and O’Connell, J. F. (2020). Short-term carbon emissions forecast for aviation industry in Shanghai. J. Clean. Prod. 275, 122734. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122734
Ye, L., Yang, D., Dang, Y., and Wang, J. (2022). An enhanced multivariable dynamic time-delay discrete grey forecasting model for predicting China’s carbon emissions. Energy 249, 123681. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2022.123681
Yin, F., Bo, Z., Yu, L., and Wang, J. (2023). Prediction of carbon dioxide emissions in China using a novel grey model with multi-parameter combination optimization. J. Clean. Prod. 404, 136889. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136889
Zhou, W., Cheng, Y., Ding, S., Chen, L., and Li, R. (2021c). A grey seasonal least square support vector regression model for time series forecasting. ISA Trans. 114, 82–98. doi:10.1016/j.isatra.2020.12.024
Zhou, W., and Ding, S. (2021a). A novel discrete grey seasonal model and its applications. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 93, 105493. doi:10.1016/j.cnsns.2020.105493
Zhou, W., Li, H., and Zhang, Z. (2022). A novel seasonal fractional grey model for predicting electricity demand: a case study of Zhejiang in China. Math. Comput. Simul. 200, 128–147. doi:10.1016/j.matcom.2022.04.004
Zhou, W., Zeng, B., Wang, J., Luo, X., and Liu, X. (2021b). Forecasting Chinese carbon emissions using a novel grey rolling prediction model. Chaos, Solit. and Fractals 147, 110968. doi:10.1016/j.chaos.2021.110968
Keywords: carbon dioxide emissions forecasting, grey system theory, grey seasonal model, DSNGBM (1,1,tα) model, marine predators algorithm
Citation: Jiang J, Ban Y and Nong S (2025) Novel disctete grey Bernoulli seasonal model with a time powter term for predicting monthly carbon dioxide emissions in the United States. Front. Environ. Sci. 12:1513387. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2024.1513387
Received: 21 October 2024; Accepted: 06 December 2024;
Published: 03 January 2025.
Edited by:
Deepak Kumar, Texas Tech University, United StatesReviewed by:
Kai Zhang, Shandong University of Finance and Economics, ChinaWenhao Zhou, Huaqiao University, China
Lianyi Liu, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, China
Copyright © 2025 Jiang, Ban and Nong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sheng Nong, eXluczIwMjRAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Jianming Jiang1
Jianming Jiang1 Sheng Nong
Sheng Nong