Upregulation of Mir342 in Diet-Induced Obesity Mouse and the Hypothalamic Appetite Control
- 1Department of Nephrology, Rheumatology, Endocrinology and Metabolism, Okayama University Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Okayama, Japan
- 2Department of Cellular Physiology, Okayama University Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Okayama, Japan
A Corrigendum on
Upregulation of Mir342 in Diet-Induced Obesity Mouse and the Hypothalamic Appetite Control
By Zhang D, Yamaguchi S, Zhang X, Yang B, Kurooka N, Sugawara R, Albuayjan HHH, Nakatsuka A, Eguchi J, Hiyama TY, Kamiya A and Wada J (2021). Front. Endocrinol. 12:727915. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.727915
In the original article, the legends of Figure 6, (B) and (C) were interchanged. The correct legend appears below: “Figure 6. The expression and reporter assay of Snap25 (synaptosomal-associated protein, 25kDa). (A) Relative mRNA expression of Snap25 normalized by Rplp0 and Rn18s in brain and epididymal fat tissues detected by RT-qPCR. (B) Western blot analyses and quantification of SNAP25 protein levels in hypothalamus. (C) Dual-luciferase reporter assay. pmirGLO-Snap25 WT 3’-UTR, pmirGLO-Snap25 MT 3’-UTR, and pmirGLO no-insert control plasmids were co-transfected with Mir342 mimic, Mir342 inhibitor, negative control siRNA (mimic NC), inhibitor negative control (inhibitor NC) into HEK293T cells, respectively. (D) The expression of predicted target genes (Fat2, Msi1 and Nhlh2) in brain. Data are analyzed by independent t-test or one-way ANOVA with a Tukey test. All data are presented as mean ± SD (*p<0.05; **p<0.01).”
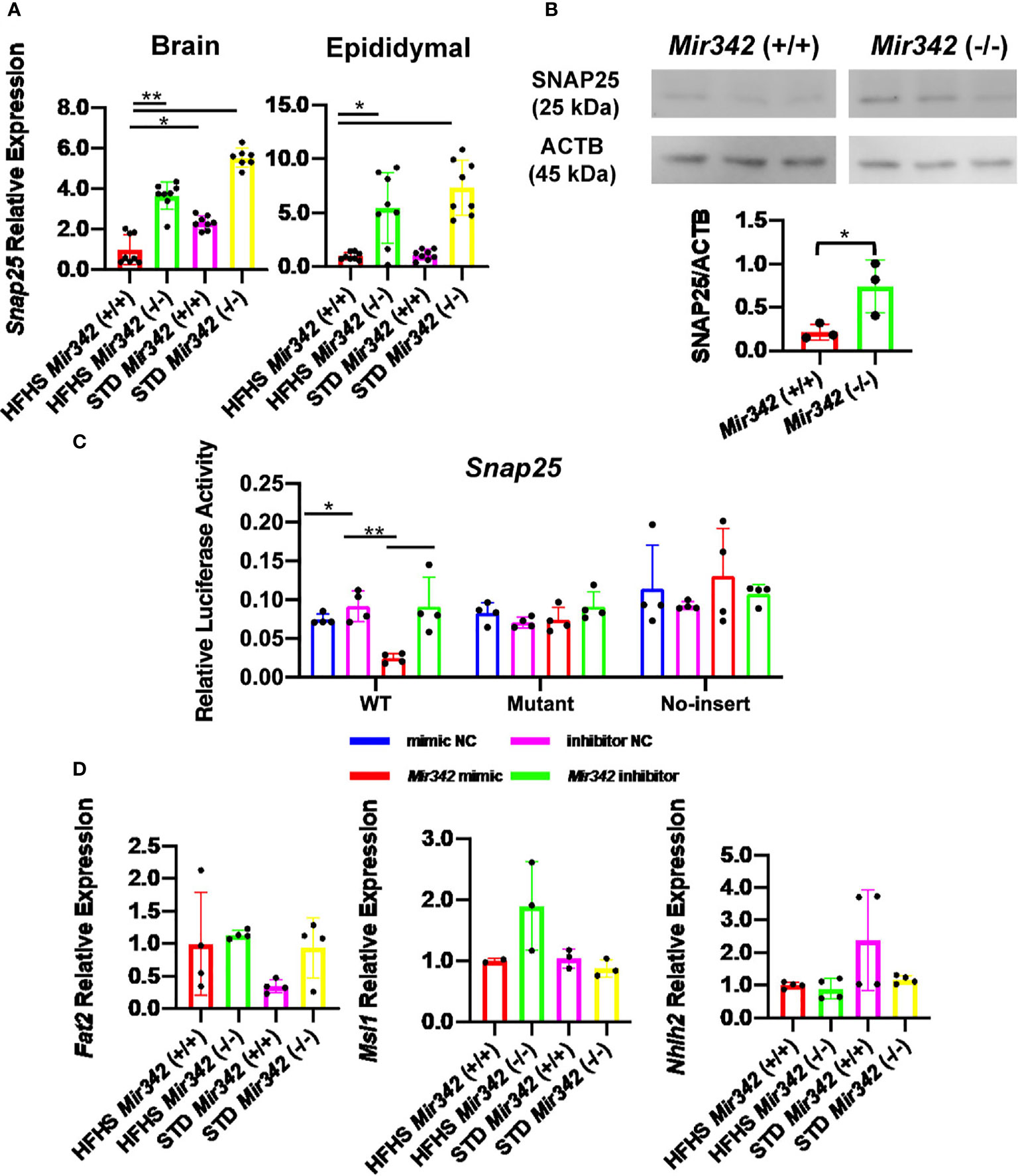
Figure 6 The expression and reporter assay of Snap25 (synaptosomal-associated protein, 25kDa). (A) Relative mRNA expression of Snap25 normalized by Rplp0 and Rn18s in brain and epididymal fat tissues detected by RT-qPCR. (B) Western blot analyses and quantification of SNAP25 protein levels in hypothalamus. (C) Dual-luciferase reporter assay. pmirGLO-Snap25 WT 3’-UTR, pmirGLO-Snap25 MT 3’-UTR, and pmirGLO no-insert control plasmids were cotransfected with Mir342 mimic, Mir342 inhibitor, negative control siRNA (mimic NC), inhibitor negative control (inhibitor NC) into HEK293T cells, respectively. (D) The expression of predicted target genes (Fat2, Msi1 and Nhlh2) in brain. Data are analyzed by independent t-test or one-way ANOVA with a Tukey test. All data are presented as mean ± SD (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: abdominal obesity, non-coding RNAs, adipose tissues, appetite regulation, hypothalamus
Citation: Zhang D, Yamaguchi S, Zhang X, Yang B, Kurooka N, Sugawara R, Albuayjan HHH, Nakatsuka A, Eguchi J, Hiyama TY, Kamiya A and Wada J (2021) Corrigendum: Upregulation of Mir342 in Diet-Induced Obesity Mouse and the Hypothalamic Appetite Control. Front. Endocrinol. 12:811189. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.811189
Received: 08 November 2021; Accepted: 08 November 2021;
Published: 26 November 2021.
Approved by:
Frontiers Editorial Office, Frontiers Media SA, SwitzerlandCopyright © 2021 Zhang, Yamaguchi, Zhang, Yang, Kurooka, Sugawara, Albuayjan, Nakatsuka, Eguchi, Hiyama, Kamiya and Wada. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jun Wada, anVud2FkYUBva2F5YW1hLXUuYWMuanA=
 Dongxiao Zhang
Dongxiao Zhang Satoshi Yamaguchi
Satoshi Yamaguchi Xinhao Zhang
Xinhao Zhang Boxuan Yang
Boxuan Yang Naoko Kurooka
Naoko Kurooka Ryosuke Sugawara1
Ryosuke Sugawara1 Atsuko Nakatsuka
Atsuko Nakatsuka Jun Eguchi
Jun Eguchi Takeshi Y. Hiyama
Takeshi Y. Hiyama Jun Wada
Jun Wada