- 1State Key Laboratory of Phytochemistry and Plant Resources in West China, and Yunnan Key Laboratory of Natural Medicinal Chemistry, Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Kunming, China
- 2Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Drug Screening and Jiangsu Center for Pharmacodynamics Research and Evaluation, China Pharmaceutical University, Nanjing, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Pu-er Tea Science, College of Science, Ministry of Education, Yunnan Agricultural University, Kunming, China
- 4Key Laboratory of Medicinal Chemistry for Nature Resource, School of Chemical Science and Technology, Ministry of Education, Yunnan University, Kunming, China
- 5Department of Chemistry, Lakehead University, Thunder Bay, ON, Canada
Podophyllotoxin has long been used as an active substance for cytotoxic activity. Fourteen novel biotinylated podophyllotoxin derivatives were designed, synthesized, and evaluated for cytotoxic activity for this study. The synthesized compounds were evaluated for cytotoxic activity in the following human cancer cell lines, SW480, MCF-7, A-549, SMMC-7721, and HL-60 by MTT assay. Most of them exhibited potent cytotoxic effects and compound 15 showed the highest cytotoxic activity among the five cancer cell lines tested, having its IC50 values in the range of 0.13 to 0.84 μM. Apoptosis analysis revealed that compound 15 caused obvious induction of cell apoptosis. Compound 15 significantly down-regulated the expression level of the marker proteins (caspase-3 and PARP) in H1299 and H1975 cells, activated the transcription of IRE1α, increased the expression of GRP78 and XBP-1s, and finally induced apoptosis of H1299 cells. In vivo studies showed that 15 at a dose of 20 mg/kg suppressed tumor growth of S180 cell xenografts in icr mice significantly. Further molecular docking studies suggested that compound 15 could bind well with the ATPase domain of Topoisomerase-II. These data suggest that compound 15 is a promising agent for cancer therapy deserving further research.
Introduction
Cancer is a kind of frequently-occurring disease that seriously threatens human health. In recent years, more attention has been focused on targeting anti-cancer drugs. Development of targeted antitumor drugs, increase of bioavailability and decrease of toxicity are the key topics which are currently being studied. Research efforts in these topics have already led to the discovery of new drug leads and molecular scaffolds important for the development of novel antitumor agents (Fulda, 2010; Qiao et al., 2011; Wen et al., 2012). Currently, targeted cancer therapy has attracted a lot of interests in cancer research and has emerged as a new treatment option for various types of cancers.
Natural compounds are valuable sources with various structures, unique biological activities, and specific selectivity. Natural products have served as important sources of lead compounds for antitumor agents which have been developed for clinical use. However, many potential drugs lack tumor selectivity and often display significant toxic side effects, which hampers their development for clinical use (Holschneider et al., 1994; Bermejo et al., 2005). In order to enhance the therapeutic specificity of anticancer drugs, various targeting strategies have been explored, including antibodies (Wu and Ojima, 2004; Schrama et al., 2006; Lambert and Berkenblit, 2018), nanocarriers (Peer et al., 2007; Bonifácio et al., 2014; Hojjat-Farsangia et al., 2014; Senthilkumar et al., 2015), peptides (Mastrobattista et al., 1999; Dharap et al., 2005), and vitamins (Sawant et al., 2008; Chen et al., 2010; Guaragna et al., 2012). In each case, molecular features overexpressed on cancer cells are being targeted.
It has been widely recognized that all living cells depend on vitamins for survival and growth and obviously cancer cells must require higher amount of vitamins to meet the need of their rapid growth. Consequently, in order to sustain their rapid cell growth and enhanced proliferation, many cancer cells over-express receptors for certain vitamins. Therefore, vitamin receptors on the surface of these cells are important biomarkers for the delivery of tumor-targeted drugs (Russell-Jonesa et al., 2004; Leamon, 2008; Lu and Low, 2012). Biotin (vitamin H) is a nutrient required for cell growth, and tumor cells need substantially higher amounts of biotin than normal cells due to their rapid growth (Russell-Jonesa et al., 2004). Recent studies have shown that many cancer cell lines express higher levels of biotin receptors (BRs) than normal cells, e.g., L1210FR (leukemia), Ov2008 (ovarian), Colo-26 (colon), P815 (mastocytoma), M109 (lung), RENCA (renal), and 4T1 (breast) cancer cell lines (Russell-Jonesa et al., 2004; Chen et al., 2010). Thus, BR has emerged as a useful biomarker for targeted delivery of anti-tumor agent, and biotin as a tumor-targeting module has been successfully employed for the construction of small molecule antitumor drug conjugates (Chen et al., 2008; Ojima, 2008; Ojima et al., 2012).
The natural lignan podophyllotoxin (PPT, 1, Figure 1) is isolated from Dysosma versipellis and shows cytotoxic activity against a variety of cancer cell lines by inhibiting microtubule assembly. However, PPT lacks tumor specificity and its high toxicity toward normal cells prevents its use in clinic for cancer treatment (Jardine, 1980; Desbene and Giorgi-Renault, 2002; Liu et al., 2007). The biological activity of PPT has led to extensive structural modification, resulting in several clinically useful compounds including etoposide (2, Figure 1), a semisynthetic glucosidic cyclic acetal of PPT. Etoposide exerts cytotoxic activity by inhibiting DNA topoisomerase II and the discovery of its novel mechanism of action led to further studies on the structure-activity relationship of PPT derivatives resulted from the structural modification at the C-4-position (Reddy et al., 2008; Zhang et al., 2014). Studies have shown that improvement in topoisomerase II inhibitory activity, water solubility, cytotoxic activity, drug resistance profile, and antitumor spectra of this class of compounds might be achieved through rational modification at C-4 position (Bromberg et al., 2003).
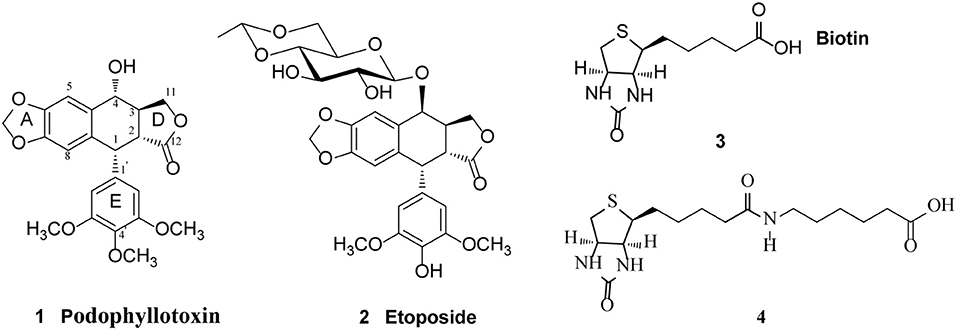
Figure 1. Structure of Podophyllotoxin (1), Etoposide (2), Biotin (3), and 6-biotinylaminocaproic acid (4).
With the aim to improve the therapeutic efficacy and reduce the toxic side effects of podophyllotoxin in the treatment of cancer, we have designed a group of biotin-podophyllotoxin (Bio-PT) conjugates by covalently linking a biotin residue to podophyllotoxin. Such Bio-PT conjugates are anticipated to be taken up by cells through receptor-mediated endocytosis and selective delivery of these conjugates to cancer cells may be achieved due to a higher level of biotion receptors expressed on cancer cells. Here we report the synthesis of 14 biotinylated podophyllotoxin derivatives and their anticancer activity against various cancer cell lines. The compound with the highest anticancer activity was further studied to reveal the anticancer mechanisms and its antitumor effect was evaluated through in vivo studies as well.
Materials and Methods
General Information
All cancer cells were obtained from a Shanghai cell bank in China. All reagents were commercially available and were used without further purification unless otherwise indicated. Podophyllotoxin was purchased from Shanghai Yuanye Bio-Technology Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). Anhydrous solvents were obtained by distillation from the indicated systems immediately prior to use: dichloromethane from calcium hydride and tetrahydrofuran from sodium. Uncorrected melting points were measured on a Beijing Taike XT-4. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) data were acquired on API Qstar Pulsar instrument; High resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HRESI-MS) data were obtained on LCMS-IT-TOF (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan); All NMR spectra were recorded with Bruker AV-400 or DRX-500 or Bruker AVANCE III-600 (Bruker BioSpin GmbH, Rheinstetten, Germany) instruments, with tetramethylsilane (TMS) as an internal standard: chemical shifts (δ) are given in ppm and coupling constants (J) in Hz. Column chromatography (CC) are carried out using silica gel (200–300 mesh; Qingdao Makall Group CO., LTD; Qingdao; China). All reactions were monitored by analytical thin-layer chromatography (TLC), which was visualized by ultraviolet light (254 nm) and/or 10% phosphomolybdic acid/EtOH.
Synthesis
General Procedure for the Preparation of Biotinylated Podophyllotoxin Derivatives 13–26
N,N′-diisopropylcarbodiimide (DIC, 0.6 mmol) and 4-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP, 0.2 mmol) were added to a solution of biotin or 6-biotinylaminocaproic acid (0.2 mmol), podophyllotoxin or its derivative (0.2 mmol) in N, N-dimethylformamide (DMF, 2.5 mL). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 24 h under N2. Solvents were removed under reduced pressure. The residue was purified by chromatography over silica gel (CHCl3/CH3OH = 9:1) to afford the desired product.
4α-(biotin)-4-deoxypodophyllotoxin 13
White amorphous powder, yield 64%; m.p. 210–215°C; : +34.6 (c 0.13, DMSO); 1H-NMR (C2D6SO, 500 MHz) δ 6.83 (s, 1H, C5-H), 6.60 (s, 1H, C8-H), 6.52 (s, 2H, C2′, C6′-H), 6.01–5.98 (m, 2H, OCH2O), 5.67 (d, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz, C4-H), 4.46–4.42 (m, 1H), 4.29 (d, 1H, J = 4.5 Hz, C1-H), 4.27–4.23 (m, 2H), 4.10–4.04 (m, 1H), 3.70 (s, 6H, C3′, C5′-OCH3), 3.62 (s, 3H, C4′-OCH3), 3.05–3.01 (m, 1H), 2.79 (dd, 1H, J = 4.5Hz, 11.5 Hz, C2-H), 2.57–2.54 (m, 2H), 2.43–2.40 (m, 1H, C3-H), 2.16 (t, 2H, J = 9.0 Hz, C8‴-CH2), 1.58–1.52 (m, 2H), 1.42–4.40 (m, 2H), 1.26–1.21 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (C2D6SO, 100 MHz) δ 177.5 (C-12), 172.6 (C-7‴), 162.8 (C-16‴), 152.7 (C-3′, C-5′), 147.5 (C-7), 146.3 (C-6), 138.4 (C-1′), 136.0 (C-4′), 132.4 (C-9), 126.8 (C-10), 109.2 (C-5), 108.2 (C-8), 105.6 (C-2′, C-6′), 101.3 (OCH2O), 72.1 (C-11), 70.5 (C-4), 61.0 (C-13‴), 60.0 (C-14‴), 59.2 (4′-OCH3), 55.9 (3′, 5′-OCH3), 55.3 (C-12‴), 43.6 (C-2), 43.5 (C-1), 40.1 (C-15‴), 38.9 (C-3), 33.4 (C-8‴), 28.0, 27.9, 24.4; ESIMS: m/z 641 [M + H] +, HRESIMS: calcd for C32H36N2O10SH [M + H]+ 641.2138, found 641.2163.
4α-(6-biotinylaminocaproic acid)-4-deoxypodophyllotoxin 14
White amorphous powder, yield 54%; m.p. 147–149°C; : −14.6 (c 0.10, Pyridine); 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz) δ 6.72 (s, 1H, C5-H), 6.50 (s, 1H, C8-H), 6.35 (s, 2H, C2′, C6′-H), 5.96 (d, 2H, J = 4.0 Hz, OCH2O), 5.85 (d, 1H, J = 9.2 Hz, C4-H), 4.57 (d, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz, C1-H), 4.50–4.48 (m, 1H), 4.34–4.27 (m, 2H), 4.17 (t, 1H, J = 9.6 Hz), 3.77 (s, 3H, C4′-OCH3), 3.73 (s, 6H, C3′, C5′-OCH3), 3.19–3.12 (m, 2H, C12‴-H, C3-H), 2.94–2.89 (m, 1H, C2-H), 2.88–2.84 (m, 2H), 2.79–2.69 (m, 2H), 2.40 (t, 2H, J = 7.2 Hz, C2‴-H), 2.18 (t, 2H, J = 6.8 Hz, C8‴-CH2), 1.68–1.64 (m, 4H), 1.51–1.49 (m, 2H), 1.40–1.35 (m, 2H), 1.31–1.29 (m, 2H), 1.18–1.17 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 100 MHz) δ 174.1 (C-12), 173.8 (C-1‴), 173.5 (C-7‴), 164.1 (C-16‴), 152.5 (C-3′, C-5′), 148.1 (C-7), 147.5 (C-6), 136.9 (C-1′), 134.9 (C-4′), 132.2 (C-9), 128.3 (C-10), 109.7 (C-5), 108.0 (C-2', C-6'), 106.9 (C-8), 101.6 (OCH2O), 73.4 (C-11), 71.3 (C-4), 61.8 (C-13‴), 60.7 (4′-OCH3), 60.3 (C-14‴), 56.1 (3′, 5′-OCH3), 55.7 (C-12‴), 45.4 (C-2), 43.6 (C-1), 40.5, 39.2, 38.7, 35.8, 34.1, 29.2, 28.2, 28.0, 26.4, 25.3, 24.5; ESIMS: m/z 789 [M + Cl]−, HRESIMS: calcd for C38H47N3O11SCl [M + Cl]− 789.2625, found 789.2625.
4β-(biotin)-4-deoxypodophyllotoxin 15
White amorphous powder, yield 65%; m.p. 110–112°C; : −51.6 (c 0.21, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz) δ 6.86 (s, 1H, C5-H), 6.54 (s, 1H, C8-H), 6.26 (s, 2H, C2′, C6′-H), 6.14 (d, 1H, J = 3.2 Hz, C4-H), 5.98–5.96 (m, 2H, OCH2O), 4.66 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, C1-H), 4.52–4.49 (m, 1H), 4.36–4.28 (m, 2H), 3.88 (t, 1H, J = 8.8 Hz), 3.79 (s, 6H, C3′, C5′-OCH3), 3.73 (s, 3H, C4′-OCH3), 3.24 (dd, 1H, J = 5.2 Hz, 14.4 Hz), 3.15–3.10 (m, 1H), 2.99–2.96 (m, 1H), 2.89 (dd, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, 12.8 Hz, C2-H), 2.75–2.71 (m, 2H), 2.38 (t, 2H, J = 7.2 Hz, C8‴-CH2), 1.71–1.66 (m, 4H), 1.45–1.43 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 100 MHz) δ 174.2 (C-12), 173.3 (C-7‴), 163.7 (C-16‴), 152.6 (C-3′, C-5′), 148.8 (C-7), 147.4 (C-6), 137.2 (C-1′), 134.6 (C-4′), 132.9 (C-9), 127.8 (C-10), 110.2 (C-5), 109.5 (C-8), 108.0 (C-2′, C-6′), 101.7 (OCH2O), 68.0 (C-11), 67.5 (C-4), 62.1 (C-13‴), 60.7 (4′-OCH3), 60.3 (C-14‴), 56.2 (3′, 5′-OCH3), 55.4 (C-12‴), 43.8 (C-2), 41.5 (C-1), 40.4, 36.7, 34.0, 28.4, 28.1, 24.7; ESIMS: m/z 663 [M + Na]+, HRESIMS: calcd for C32H36N2O10SNa [M + Na]+ 663.1983, found 663.1980.
4β-(biotin)-4-deoxy-4′-demethylpodophyllotoxin 16
White amorphous powder, yield 59%; m.p. 153–159°C; : −69.8 (c 0.17, Pyridine); 1H-NMR (C5D5N, 500 MHz) δ 7.64 (s, 1H, C5-H), 7.50 (s, 1H, C8-H), 7.24 (s, 2H, C2′, C6′-H), 6.82 (d, 1H, J = 3.2 Hz, C4-H), 6.02–6.00 (m, 2H, OCH2O), 4.89 (d, 1H, J = 5.3 Hz, C1-H), 4.69 (t, 1H, J = 2.3 Hz), 4.54 (t, 1H, J = 2.1 Hz), 4.40–4.37 (m, 1H), 3.85–3.84 (m, 1H), 3.71 (s, 6H, C3′, C5′-OCH3), 3.22–3.19 (m, 2H), 3.92 (dd, 1H, J = 5.0 Hz, 10.0 Hz, C2-H), 2.89–2.86 (m, 2H), 2.63 (t, 2H, J = 7.3 Hz, C8‴-CH2), 1.77–1.74 (m, 2H), 1.61–1.57 (m, 2H), 1.28–1.26 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (C5D5N, 125 MHz) δ 175.7 (C-12), 171.3 (C-7‴), 164.3 (C-16‴), 152.3 (C-3′, C-5′), 148.4 (C-7), 147.7 (C-6), 139.5 (C-1′), 136.1 (C-4′), 134.4 (C-9), 132.0 (C-10), 110.6 (C-5), 110.4 (C-8), 108.5 (C-2′, C-6′), 101.9 (OCH2O), 68.4 (C-11), 66.3 (C-4), 62.5 (C-13‴), 60.6 (C-14‴), 56.3 (3′, 5′-OCH3), 56.2 (C-12‴), 44.7 (C-2), 41.1 (C-1), 41.0, 39.7, 33.9, 29.1, 28.8, 25.4; ESIMS: m/z 661 [M + Cl]−, HRESIMS: calcd for C31H34N2O10SH [M + H]+ 627.2007, found 627.1978.
4β-(6-biotinylaminocaproic acid)-4-deoxypodophyllotoxin 17
White amorphous powder, yield 57%; m.p. 101–102°C; : −41.9 (c 0.13, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz) δ 6.84 (s, 1H, C5-H), 6.54 (s, 1H, C8-H), 6.26 (s, 2H, C2′, C6′-H), 6.14 (d, 2H, J = 3.2 Hz, C4-H), 5.99–5.98 (m, 2H, OCH2O), 4.66 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, C1-H), 4.52–4.50 (m, 1H), 4.36–4.32 (m, 2H), 3.87 (t, 1H, J = 8.8 Hz), 3.79 (s, 6H, C3′, C5′-OCH3), 3.73 (s, 3H, C4′-OCH3), 3.25–3.20 (m, 2H), 3.16–3.10 (m, 1H), 3.01–2.96 (m, 1H, C3-H), 2.89 (dd, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, 12.8 Hz, C2-H), 2.76–2.73 (m, 2H), 2.36 (t, 2H, J = 8.0 Hz, C2‴-CH2), 2.25 (t, 2H, J = 6.4 Hz, C8‴-CH2), 1.68–1.63 (m, 6H), 1.53–1.50 (m, 2H), 1.44–1.41 (m, 2H), 1.35–1.33 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 100 MHz) δ 174.3 (C-12), 173.7 (C-1‴), 173.3 (C-7‴), 163.9 (C-16‴), 152.6 (C-3′, C-5′), 148.9 (C-7), 147.4 (C-6), 137.2 (C-1′), 134.6 (C-4′), 132.8 (C-9), 127.8 (C-10), 110.2 (C-5), 109.5 (C-8), 108.0 (C-2′, C-6′), 101.7 (OCH2O), 67.9 (C-11), 67.5 (C-4), 61.9 (C-13‴), 60.7 (4′-OCH3), 60.4 (C-14‴), 56.2 (3′, 5′-OCH3), 55.6 (C-12‴), 43.7 (C-2), 41.5 (C-1), 40.5, 39.3, 36.7, 35.7, 34.1, 29.1, 28.0, 27.9, 26.4, 25.7, 24.5; ESIMS: m/z 788 [M + Cl]−, HRESIMS: calcd for C38H47N3O11SCl [M + Cl]− 788.2625, found 788.2627.
4β-(6-biotinylaminocaproic acid)-4-deoxy-4′-demethylpodophyllotoxin 18
White amorphous powder, yield 67%; m.p. 117°C; : −6.4 (c 0.11, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz) δ 6.88 (s, 1H, C5-H), 6.50 (s, 1H, C8-H), 6.29 (s, 2H, C2′, C6′-H), 5.96–5.94 (m, 2H, OCH2O), 4.79 (d, 1H, J = 3.2 Hz, C4-H), 4.60 (d, 1H, J = 5.2 Hz, C1-H), 4.49–4.46 (m, 1H), 4.36–4.32 (m, 2H), 4.30–4.27 (m, 1H), 3.65 (s, 6H, C3′, C5′-OCH3), 3.30–3.28 (m, 1H), 3.22–3.18 (m, 2H), 3.14–3.10 (m, 1H), 2.86 (dd, 1H, J = 5.2 Hz, 12.8 Hz, C2-H), 2.79–2.76 (m, 1H), 2.72–2.69 (m, 1H), 2.56 (t, 2H, J = 6.8 Hz, C2‴-CH2), 2.35–2.32 (m, 4H), 2.14 (t, 2H, J = 6.8 Hz, C8‴-CH2), 1.75–1.70 (m, 2H), 1.66–1.60 (m, 2H), 1.53–1.50 (m, 2H), 1.43–1.36 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 150 MHz) δ 175.8 (C-12), 173.8 (C-1‴), 171.9 (C-7‴), 163.9 (C-16‴), 151.5 (C-3′, C-5′), 148.4 (C-7), 147.5 (C-6), 138.2 (C-9), 132.3 (C-10), 131.5 (C-4′), 127.7 (C-1′), 110.4 (C-5), 109.6 (C-8), 107.7 (C-2′, C-6′), 101.7 (OCH2O), 68.1 (C-11), 66.3 (C-4), 62.1 (C-13‴), 60.5 (C-14‴), 56.3 (3′, 5′-OCH3), 55.6 (C-12‴), 44.1 (C-2), 40.7 (C-1), 40.5, 39.4, 38.6, 35.8, 33.7, 29.0, 28.3, 28.1, 26.2, 25.6, 24.6; ESIMS: m/z 738 [M – H]−, HRESIMS: calcd for C37H45N3O11SH [M + H]+ 740.2848, found 740.2809.
4β-amino-(biotin)-4-deoxypodophyllotoxin 19
White amorphous powder, yield 62%; m.p. 120°C; : +35.3(c 0.22, pyridine); 1H-NMR (C5D5N, 500 MHz) δ 6.90 (s, 1H, C5-H), 6.70 (s, 2H, C2′, C6′-H), 6.67 (s, 1H, C8-H), 5.96–5.93 (m, 2H, OCH2O), 4.84 (s, 1H, C4-H), 4.58 (d, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz, C1-H), 4.56–4.54 (m, 2H), 4.37–4.34 (m, 1H), 4.32–4.28 (m, 1H), 3.90 (s, 3H, C4′-OCH3), 3.69 (s, 6H, C3′, C5′-OCH3), 3.39 (t, 1H, J = 9.0 Hz), 3.17–3.12 (m, 1H, C3-H), 2.91 (dd, 1H, J = 6.0 Hz, 12.0 Hz, C2-H), 2.86–2.83 (m, 2H), 2.15 (t, 2H, J = 9.0 Hz, C8‴-CH2), 1.79–1.72 (m, 2H), 1.46–1.42 (m, 2H), 1.40–1.37 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (C5D5N, 125 MHz) δ 178.1 (C-12), 173.2 (C-7‴), 164.2 (C-16‴), 154.2 (C-3′, C-5′), 148.0 (C-7), 146.5 (C-6), 141.3 (C-1′), 136.4 (C-4′), 129.5 (C-9), 124.1 (C-10), 112.2 (C-5), 107.2 (C-8), 107.2 (C-2′, C-6′), 101.7 (OCH2O), 64.2 (C-11), 62.5 (C-4), 60.7 (C-13‴), 60.6 (4′-OCH3), 56.8 (C-14‴), 56.4 (3′, 5′-OCH3), 56.3 (C-12‴), 51.7 (C-2), 47.2 (C-1), 42.9, 41.1, 34.1, 29.0 (2), 25.3; ESIMS: m/z 662 [M + Na]+, HRESIMS: calcd for C32H37N3O9SNa [M + Na]+ 662.2143, found 662.2145.
4β-amino-(biotin)-4-deoxy-4′-demethylpodophyllotoxin 20
White amorphous powder, yield 41%; m.p. 153°C; : −22.6 (c 0.10, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 600 MHz) δ 6.82 (s, 1H, C5-H), 6.51 (s, 1H, C8-H), 6.44 (s, 2H, C2′, C6′-H), 5.98–5.94 (m, 2H, OCH2O), 5.62 (s, 1H, C4-H), 4.57 (d, 1H, J = 4.2 Hz, C1-H), 4.47–4.45 (m, 1H), 4.41 (t, 1H, J = 7.8 Hz), 4.28–4.26 (m, 1H), 4.16 (t, 1H, J = 9.6 Hz), 3.77 (s, 6H, C3′, C5′-OCH3), 3.14–3.10 (m, 1H), 2.90–2.86 (m, 2H), 2.75–2.70 (m, 1H, C3-H), 2.65–2.63 (m, 1H), 2.29–2.20 (m, 2H), 1.74–1.69 (m, 2H), 1.56–1.50 (m, 2H), 1.43–1.38 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 150 MHz) δ 175.0 (C-12), 174.2 (C-7‴), 164.5 (C-16‴), 147.7 (C-7), 147.7 (C-6), 146.6 (C-3′, C-5′), 134.7 (C-1′), 132.0 (C-4′), 131.6 (C-9), 130.7 (C-10), 110.4 (C-5), 109.2 (C-2′, C-6′), 106.6 (C-8), 101.7 (OCH2O), 71.8 (C-11), 69.7 (C-4), 61.9 (C-13‴), 60.4 (C-14‴), 57.1 (3′, 5′-OCH3), 56.1 (C-12‴), 46.3 (C-2), 43.9 (C-1), 40.8 39.5, 36.0, 28.5, 28.4, 25.9; ESIMS: m/z 660 [M + Cl]−, HRESIMS: calcd for C31H35N3O9SH [M + H]+ 626.2167, found 626.2145.
4β-amino-(6-biotinylaminocaproic acid)-4-deoxypodophyllotoxin 21
White amorphous powder, yield 46%; m.p. 100°C; : +58.3 (c 0.12, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz) δ 7.48 (s, 1H, NH), 6.66 (s, 1H, C5-H), 6.46 (s, 1H, C8-H), 6.29 (s, 2H, C2′, C6′-H), 5.94–5.90 (m, 2H, OCH2O), 4.50 (s, 1H, C4-H), 4.34–4.32 (m, 2H), 4.19–4.17 (m, 2H), 4.09–4.05 (m, 1H), 3.81 (s, 3H, C4′-OCH3), 3.76 (s, 6H, C3′, C5′-OCH3), 3.19–3.13 (m, 4H), 2.87–2.85 (m, 2H), 2.75–2.72 (m, 1H), 2.52–2.50 (m, 2H, C2‴-CH2), 2.24–2.23 (m, 6H), 1.69–1.64 (m, 2H), 1.51–1.48 (m, 2H), 1.45–1.42 (m, 2H), 1.29–1.24 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 100 MHz) δ 178.2 (C-12), 173.8 (C-1‴), 173.4 (C-7‴), 164.1 (C-16‴), 153.2 (C-3′, C-5′), 147.6 (C-7), 146.0 (C-6), 140.0 (C-1′), 136.7 (C-4′), 134.2 (C-9), 128.4 (C-10), 111.8 (C-5), 106.7 (C-8), 105.8 (C-2′, C-6′), 101.2 (OCH2O), 63.4 (C-11), 61.9 (C-4), 60.8 (4′-OCH3), 60.4 (C-13‴), 56.6 (C-14‴), 56.2 (3′, 5′-OCH3), 55.6 (C-12‴), 50.9 (C-2), 46.2 (C-1), 42.1, 40.5, 39.3, 35.6, 33.8, 28.9, 28.0, 27.9, 26.2, 25.7, 24.4; ESIMS: m/z 775 [M + Na]+, HRESIMS: calcd for C38H48N4O10SNa [M + Na]+ 753.3164, found 753.3154.
4β-amino-(6-biotinylaminocaproic acid)-4-deoxy-4′-demethylpodophyllotoxin 22
White amorphous powder, yield 64%; m.p. 100°C; : +15.1 (c 0.24, DMSO); 1H-NMR (C2D6SO, 500 MHz) δ 8.28 (s, 1H, NH), 7.78 (s, 1H, NH), 6.83 (s, 1H, C5-H), 6.45 (s, 1H, C8-H), 6.38 (s, 2H, C2′, C6′-H), 5.97–5.92 (m, 2H, OCH2O), 4.28 (d, 1H, J = 5.0 Hz, C4-H), 4.26 (d, 1H, J = 5.0 Hz, C1-H), 4.24 (s, 1H), 4.16 (s, 1H), 4.11–4.09 (m, 2H), 3.64 (s, 6H, C3′, C5′-OCH3), 3.30–3.27 (m, 2H), 3.09–3.05 (m, 1H, C3-H), 3.02–2.99 (m, 2H), 2.78 (dd, 1H, J = 5.0 Hz, 12.0 Hz, C2-H), 2.54–2.50 (m, 3H), 2.02 (t, 2H, J = 7.5 Hz, C8‴-CH2), 1.61–1.58 (m, 4H), 1.50–1.44 (m, 2H), 1.42–1.38 (m, 2H), 1.35–1.30 (m, 2H), 1.27–1.24 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (C2D6SO, 125 MHz) δ 177.2 (C-12), 171.9 (C-1‴), 170.8 (C-7‴), 162.7 (C-16‴), 151.4 (C-3′, C-5′), 146.6 (C-7), 145.2 (C-6), 143.4 (C-1′), 136.1 (C-4′), 128.4 (C-9), 126.7 (C-10), 111.1 (C-5), 106.9 (C-8), 105.4 (C-2′, C-6′), 100.9 (OCH2O), 61.1 (C-4), 60.6 (C-11), 59.2 (C-13‴), 55.9 (3′, 5′-OCH3), 55.4 (C-14‴), 54.9 (C-12‴), 50.1 (C-2), 45.6 (C-1), 44.8, 40.0, 38.2, 35.2, 33.0, 28.8, 28.2, 28.0, 25.6, 25.3, 24.3; ESIMS: m/z 761 [M + Na]+, HRESIMS: calcd for C37H46N4O10SH [M + Na]+ 761.2827, found 761.2829.
4β-{[4-hydroxymethyl-(biotin)-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl]}-4-deoxypodophyllotoxin 23
White amorphous powder, yield 39%; m.p. 110°C; : −21.6 (c 0.16, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz) δ 7.39 (s, 1H, C5″-H), 6.65 (s, 1H, C5-H), 6.62 (s, 1H, C8-H), 6.32 (s, 2H, C2', C6′-H), 6.10–6.00 (m, 3H, OCH2O, C4-H), 5.21–5.13 (m, 2H, C6″-CH2), 4.76 (d, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz, C1-H), 4.52–4.51 (m, 1H), 4.40–4.26 (m, 3H), 3.80 (s, 3H, C4′-OCH3), 3.76 (s, 6H, C3′, C5′-OCH3), 3.22–3.13 (m, 3H), 2.92–2.89 (m, 1H), 2.77–2.73 (m, 1H), 2.36 (t, 2H, J = 6.0 Hz, C8‴-CH2), 1.86–1.83 (m, 2H), 1.66–1.63 (m, 2H), 1.42–1.40 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 100 MHz) δ 173.6 (C-12), 173.6 (C-7‴), 152.7 (C-3′, C-5′), 149.4 (C-7), 148.0 (C-6), 142.9 (C-4″), 137.4 (C-1′), 134.3 (C-4′), 133.2 (C-9), 124.5 (C-10), 124.3 (C-5″), 110.5 (C-5), 108.8 (C-8), 108.1 (C-2′, C-6′), 102.0 (OCH2O), 67.4 (C-11), 62.0 (C-4), 60.7 (4′-OCH3), 60.3 (C-13‴), 58.7 (C-14‴), 57.3 (C6″-CH2), 56.3 (3′, 5′-OCH3), 55.4 (C-12‴), 43.6 (C-2), 41.5 (C-1), 40.4 37.1, 33.6, 28.1, 25.6, 24.6; ESIMS: m/z 744 [M + Na]+, HRESIMS: calcd for C35H39N5O10SNa [M + Na]+ 744.2310, found 744.2356.
4β-{[4-hydroxymethyl-(6-biotinylaminocaproic acid)-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl]}-4-deoxy-4′-demethylpodophyllotoxin 24
White amorphous powder, yield 60%; m.p. 104°C; : −60.3 (c 0.19, Pyridine); 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz) δ 7.74 (s, 1H, C5″-H), 6.57 (s, 1H, C5-H), 6.45 (s, 2H, C2′, C6′-H), 6.20 (s, 1H, C8-H), 5.93–5.84 (m, 3H, OCH2O, C4-H), 5.23–5.15 (m, 2H, C6″-CH2), 4.65 (d, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz, C1-H), 4.46–4.44 (m, 1H), 4.22–4.16 (m, 2H), 4.11 (t, 1H, J = 9.2 Hz), 3.79 (s, 6H, C3′, C5′-OCH3), 3.30–3.25 (m, 1H), 3.03–2.99 (m, 3H), 2.79 (dd, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz, 10.0 Hz, C2-H), 2.32 (t, 2H, J = 6.8 Hz, C8‴-CH2), 1.65–1.55 (m, 4H), 1.35–1.33 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 100 MHz) δ 173.6 (C-12), 173.5 (C-7‴), 148.5 (C-7), 147.9 (C-6), 146.8 (C-3′, C-5′), 143.4 (C-4″), 134.1 (C-1′), 132.5 (C-4′), 129.9 (C-9), 126.6 (C-10), 123.1 (C-5″), 110.2 (C-5), 107.5 (C-2′, C-6′), 106.2 (C-8), 101.8 (OCH2O), 70.1 (C-11), 63.1 (C-4), 62.1 (C-13‴), 60.2 (C-14‴), 57.3 (C6″-CH2), 56.3 (3′, 5′-OCH3), 55.4 (C-12‴), 45.8 (C-2), 43.6 (C-1), 40.2 38.7, 33.5, 28.2, 28.1, 24.5; ESIMS: m/z 730 [M + Na]+, HRESIMS: calcd for C34H37N5O10SH [M + H]+ 708.2334, found 708.2302.
4β-{[4-hydroxymethyl-(6-biotinylaminocaproic acid)-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl]}-4-deoxypodophyllotoxin 25
White amorphous powder, yield 47%; m.p. 101°C; : −25.4 (c 0.24, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz) δ 7.41 (s, 1H, C5″-H), 6.62 (s, 1H, C5-H), 6.60 (s, 1H, C8-H), 6.30 (s, 2H, C2′, C6′-H), 6.11 (d, 1H, J = 3.2 Hz, C4-H), 6.00 (d, 2H, J = 4.8 Hz, OCH2O), 5.15 (s, 2H, C6″-CH2), 4.75 (d, 1H, J = 4.8 Hz, C1-H), 4.52–4.49 (m, 1H), 4.38–4.31 (m, 3H), 3.79 (s, 3H, C4′-OCH3), 3.75 (s, 6H, C3′, C5′-OCH3), 3.20–3.13 (m, 5H), 2.89–2.86 (m, 1H), 2.74–2.71 (m, 1H), 2.32 (t, 2H, J = 7.2 Hz, C2‴-CH2), 2.22 (t, 2H, J = 6.4 Hz, C8‴-CH2), 1.66–1.58 (m, 6H), 1.49–1.46 (m, 2H), 1.42–1.40 (m, 2H), 1.30–1.28 (m, 2H); 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 100 MHz) δ 173.7 (C-12), 173.5 (C-1‴), 173.3 (C-7‴), 164.0 (C-16‴), 152.7 (C-3′, C-5′), 149.4 (C-7), 148.0 (C-6), 142.9 (C-4″), 137.4 (C-1′), 134.3 (C-4′), 133.2 (C-9), 124.4 (C-10), 124.3 (C-5″), 110.5 (C-5), 108.8 (C-8), 108.1 (C-′, C-6′), 102.0 (OCH2O), 67.4 (C-11), 61.8 (C-4), 60.7 (4′-OCH3), 60.3 (C-13‴), 58.7 (C-14‴), 57.2 (C6″-CH2), 56.3 (3′, 5′-OCH3), 55.6 (C-12‴), 43.6 (C-2), 41.5 (C-1), 40.5 39.2, 37.1, 35.7, 33.8, 28.9, 28.1, 27.9, 26.1, 25.7, 24.3; ESIMS: m/z 857 [M + Na]+, HRESIMS: calcd for C41H50N6O11SH [M + H]+ 835.3331, found 835.3338.
4β-{[4-hydroxymethyl-(6-biotinylaminocaproic acid)-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl]}-4-deoxy-4′-demethylpodophyllotoxin 26
White amorphous powder, yield 58%; m.p. 119°C; : −9.6 (c 0.16, CHCl3); 1H-NMR (CDCl3, 400 MHz) δ 7.36 (s, 1H, C5″-H), 6.60 (s, 1H, C5-H), 6.59 (s, 1H, C8-H), 6.33 (s, 2H, C2', C6′-H), 6.10 (d, 1H, J = 4.0 Hz, C4-H), 5.99–5.96 (m, 2H, OCH2O), 4.75 (s, 1H, C1-H), 4.68 (s, 2H, C6″-CH2), 4.49–4.46 (m, 1H), 4.37–4.36 (m, 1H), 4.30–4.27 (m, 2H), 3.67 (s, 6H, C3′, C5′-OCH3), 3.20–3.10 (m, 6H), 2.85 (dd,1H, J = 4.8 Hz, 12.2 Hz, C2-H), 2.64 (m, 2H, J = 7.2 Hz, C2‴-CH2), 2.56 (t, 2H, J = 6.8 Hz, C8‴-CH2), 1.73–1.68 (m, 2H), 1.66–1.58 (m, 4H), 1.53–1.50 (m, 2H), 1.45–1.35 (m, 4H); 13C-NMR (CDCl3, 125 MHz) δ 174.0 (C-12), 173.6 (C-1‴), 171.7 (C-7‴), 164.0 (C-16‴), 151.6 (C-3′, C-5′), 149.4 (C-7), 148.1 (C-6), 148.0 (C-4″), 137.2 (C-1′), 132.8 (C-4'), 128.0 (C-9), 124.7 (C-10), 122.9 (C-5″), 110.5 (C-5), 108.9 (C-8), 107.6 (C-2′, C-6′), 102.0 (OCH2O), 67.5 (C-11), 62.1 (C-4), 60.4 (C-13‴), 58.7 (C-14‴), 56.1 (3′, 5′-OCH3), 55.6 (C6″-CH2), 55.4 (C-12‴), 43.6 (C-2), 41.4 (C-1), 40.1, 39.3, 37.0, 35.4, 33.5, 28.7, 28.1, 27.8, 26.0, 25.5, 24.4; ESIMS: m/z 843 [M + Na]+, HRESIMS: calcd for C40H48N6O11SH [M + H]+ 821.3175, found 821.3195.
Biology Assay
Cell Culture
All cell lines used in this study were cultured in DMEM or RMPI-1640 medium (Hyclone, Logan, UT, USA) which is supplemented with 50 mg/L of streptomycin, 50 IU/ml of penicillin (Solarbio, Beijing, China) and 10% fetal bovine serum (HyClone, CA, USA) in a humidified 5% CO2 incubator at 37°C. All cells were sub-cultured 3 times/week by trypsinisation.
Cell Viability Assay
Cell viability was evaluated by 3-(4,5-dimethyl-thiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. Briefly, in each well of a 96-well cell culture plate adherent cells (100 μL) with an initial density of 1 × 105 cells/mL were seeded and allowed to adhere for 12 h before a test drug was added. In contrast, suspended cells with the same initial density were seeded just before drug addition. Each tumor cell line was exposed to the test compound at various concentrations in triplicate for 48 h. After the incubation, MTT (100 μg) was added to each well, and the incubation continued at 37°C for 4 h. The cells were lysed with SDS (200 μL) after the removal of the medium. The absorbance of the lysate was measured at 595 nm by spectrophotometry (microtiter plate reader, Bio-Rad 680). Dose response curves of cell viability were plotted and the IC50 values of test compounds at which 50% reduction in cell growth were determined.
Cell Apoptosis Assay
The Annexin V/propidium iodide (PI) detection kit (BD Biosciences, PA, USA) was employed to quantify apoptosis using flow cytometry. H1299 and H1975 cells were seeded in each well of a 12-well plate at 2.5 × 105 cells/well. After incubation for 24 h, the cells were treated with compound 15 at 0.5, 1 and 2 μM or PPT (1 μM) for 24 h. Then, the cells were collected and binding buffer (100 μL), FITC annexinV (5 μL), and propidium iodide (PI, 10 μL) (eBioscience, San Diego, CA, USA) were added to the cell suspension. The cells were gently vortexed and incubated at room temperature in the dark for 15 min before measurement by flow cytometry (BD FACSCaliburTM) within 1 h.
Western Blotting Analysis
H1299 and H1975 cell lines were treated with compound 15 at different concentrations in 6-well plates, and then the cells were collected and lysed with lysis buffer. After sonication cells were centrifuged at 14,000 rpm at 4°C for 10 min, and total protein was extracted and detected using a bicinchoninc acid (BCA) assay kit. The samples were then separated by 10% SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and then the protein was transferred to nitrocellulose (NC) membranes. The membranes were probed for the following proteins with primary antibodies at 4°C overnight: caspase-3, cleaved caspase-3, PARP, cleaved PARP, GRP78, CHOP, XBP-1, XBP-1s, and Actin. After washing the membranes with PBST (× 1), the HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies were added and incubated for 1 h at room temperature. The membranes were then washed and the HRP was detected using Luminata™ Forte Western HRP Substrate reagent. The bands of interest were visualized and imaged under chemiluminescent detection using a FluorChem E System (ProteinSimple, San Jose, CA, USA).
Gene Expression Assay
H1299 cells were cultured in 12-well plated at 2.5 × 105 cell/well in the presence of compound 15 (0.5, 1, and 2 μM) for 24 h. Total RNAs present in the cultured cells were extracted using the TransZol™ Up Reagent (TransGen Biotech, Beijing, China). Gene expression was detected via quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) and SYBR® Premix EX Taq™ II (TaKaRa Bio, Otsu, Japan) was used to perform the analysis.
Animal Studies
All animal studies were conducted in accordance to procedures approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee at China Pharmaceutical University (Jiangsu, China). Forty icr male mice (10–20 g) were provided from the Comparative Medicine Centre of Yangzhou University (Jiangsu, China) and were housed in an SPE animal facility. S180 cancer cells were injected subcutaneously into the right axillaries of icr male mice (4.5–5.0 × 106 cells/spot). The mice were divided randomly into five groups: model; positive control; low-dose; medium-dose; high-dose. All mice of the therapeutic groups were injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) every day, and all mice in the positive control group were injected intravenously (i.v.) on the first day and the fourth day after inoculation. Tumor size was measured with caliper and the volume calculated using the previously reported method (Qin et al., 2015). The weight of the mice and the volume of the tumors were measured every day. At the end of the experiment, the mice were killed and the tumors were isolated and weighed.
Molecular Docking Studies
The crystal structure of Top-II (code ID: 3QX3) (Wu et al., 2011) was obtained in Protein Data Bank after eliminating the inhibitor and water molecules. The missing atoms were added by Sybyl-X 2.0 molecular modeling. The kinds of atomic charges were taken as Kollman-united-atom (Weiner et al., 1984) for the macromolecule and Gasteiger–Marsili (Gasteiger and Marsili, 1980) for the inhibitor. To find the binding mode of compound 15 to the active site of Top-II, the advanced docking program Autodock Tools v1.56 (Morris et al., 1998) was used for grid and docking. The enzyme structure was used as an input for the AutoGrid program. AutoGrid performed pre-calculated atomic affinity grid maps for each atom type in the ligand plus a separate desolvation map, and a separate desolvation map present in the substrate molecule. Docking parameters were set as the default values except docking runs was set to 100 on AutoGrid v4.01 and AutoDock v4.01.
Statistical Analysis
All data are presented as the means ± SD (n = 3). Significance was calculated using Student's t-test or one-way ANOVA. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed with the GraphPad Prism 5.0 (San Diego, CA, USA).
Results and Discussion
Chemical synthesis
Podophyllotoxin (PPT) served as the starting material for the preparation of all the derivatives. The incorporation of the azido, amino, and triazolyl groups at the 4-position of PPT followed standard procedures (Scheme 1). PPT was regioselectively demethylated with methanesulfonic acid and sodium iodide in dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) followed by weak basic hydrolysis (water-acetone, barium carbonate) to give 4′-O-demethylepipodophyllotoxin 6 by means of a previously described procedure (Kamal et al., 2000). When the reaction was carried out in acetonitrile (CH3CN) as a solvent, 4β-epipodophyllotoxin 5 was synthesized as product. Compound 5 and 6 were converted into the corresponding 4β-azides 7 and 8 by reaction with sodium azide and trifluoroacetic acid (NaN3-TFA) in chloroform (CHCl3) according to the known procedure (Hansen et al., 1993). The 4β-azides 7 and 8 were converted to 4β-amino substituted 9 and 10 by treatment with triphenylphosphine (Ph3P) and water overnight at 25°C as previously reported (Coleman and Kong, 1998). In addition, the 4β-triazole compounds of 11 and 12 were prepared in 85–89% yield by the reaction of 7 and 8, respectively, with 2-propyn-1-ol using copper (II) acetate and sodium ascorbate as promoters in tert-butanol and water (t-BuOH-H2O, 1:1) at room temperature (Tae et al., 2010). Finally, biotin (3)/6-biotinylaminocaproic acid (4) and those podophyllotoxin derivatives (1, 5, 6, and 9–12) were coupled via an ester or amide bond. As shown in Scheme 2, biotin (3)/6-biotinylaminocaproic acid (4) reacted with compounds 1, 5, 6, and 9–12 in the presence of diisopropylcarbodiimide (DIC) and 4-N,N-dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) at room temperature to afford the target compounds 13–26 in 39–65% yields.
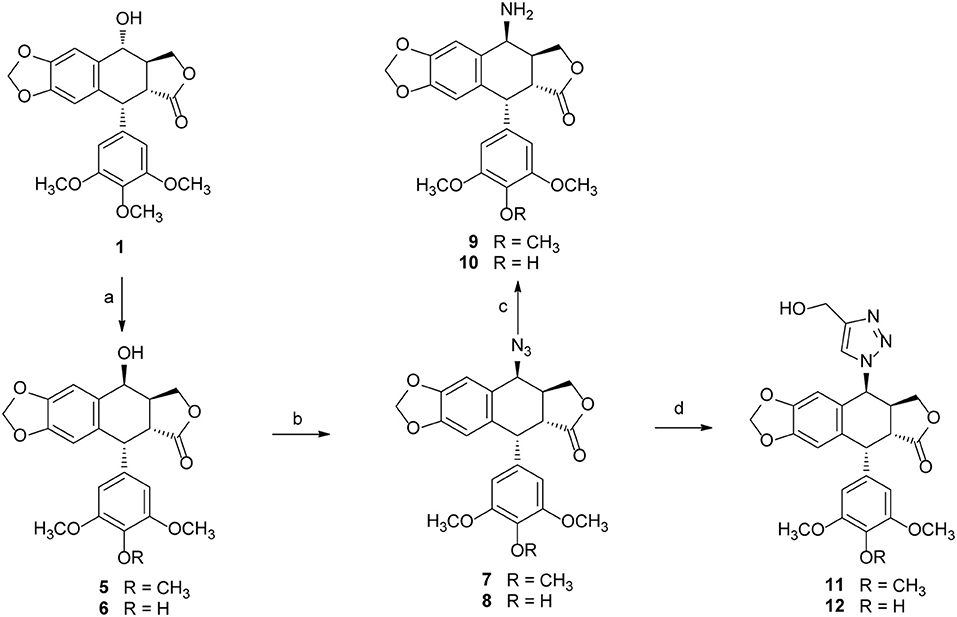
Scheme 1. The synthesis of podophyllotoxin derivatives (5–12). Reagents and reaction condition: (a) MeSO3H, NaI, CH3CN/CH2Cl2; then, H2O-Acetone, BaCO3, rt. 90–92%; (b) NaN3-TFA, CHCl3, 67–70%; (c) PPh3, THF, then H2O, 72–75%; (d) copper (II) acetate, propargyl alcohol, sodium ascorbate, t-BuOH-H2O, THF, rt. 85–89%.
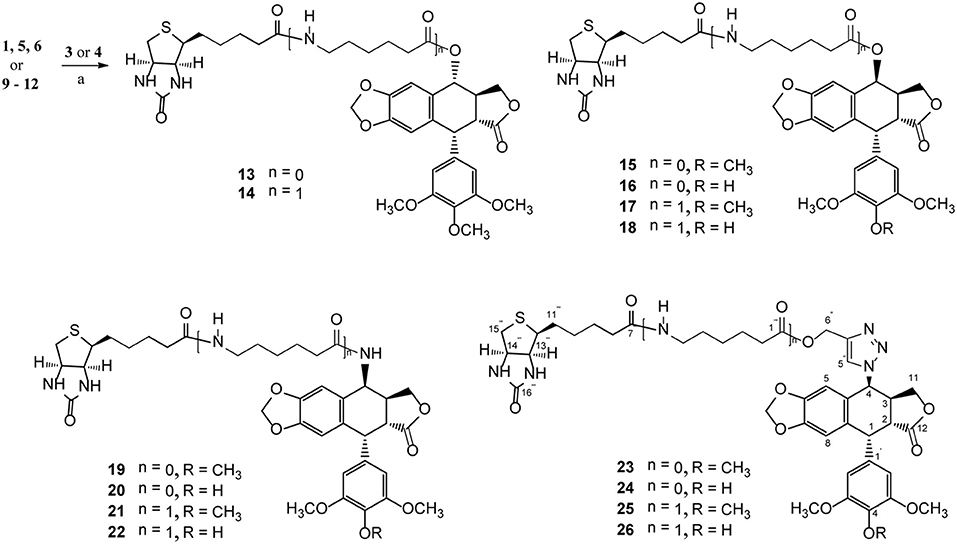
Scheme 2. The synthesis of biotinylated podophyllotoxin derivatives (13–26). Reagents and reaction condition: (a) DIC, DMAP, DMF, N2, rt. 39–65%.
All the products were structurally confirmed by 1H and 13C-NMR spectroscopies, as well as low resolution and high resolution mass spectrometry in electrospray ionization mode (ESI-MS and HRESI-MS). The proton and carbon-13 NMR data of these compounds were compared with those of podophyllotoxin. The configuration of C-4 in compounds 13–26 was assigned based on the coupling constant between H-3 and H-4 (J3, 4). Typically, compounds with C-4β-substitution have J3, 4 <5.0 Hz as a result of H-3 and H-4 in cis relationship. The protons at C-4 of compounds 19–21 appear as a singlet. On the other hand, compounds with C-4α-substitution have J3, 4 > 6.0 Hz because H-4 is trans to H-3 (Fred Brewer et al., 1979; Belen'kiib and Schinazi, 1994). In the 13C-NMR spectra, the C-4 of these derivatives produces a characteristic signal between 61.1 and 71.3 ppm. The triazole ting in 23–26 was readily confirmed by its C5“-H signal (δ 7.36–7.74 ppm) in the aromatic region in the 1H-NMR spectra, which was further supported by the characteristic carbon signals at around 123 ppm in the 13C-NMR spectra.
Biology
Cytotoxicity and Structure-Activity Relationship
The cytotoxicity of all biotinylated podophyllotoxin derivatives 13–26 was tested with the following cancer cell lines: SW480 (colon cancer), MCF-7 (breast cancer), A-549 (lung cancer), SMMC-7721 (hepatoma), and HL-60 (leukemia), Podophyllotoxin (PPT), etoposide, and cisplatin were included for study as control drugs. The IC50 values obtained from MTT assay are presented in Table 1. Most compounds possessed high level of cytotoxicity against all five cancer cell lines (Table 1) and were more active than etoposide which is an antitumor agent currently in clinical use.
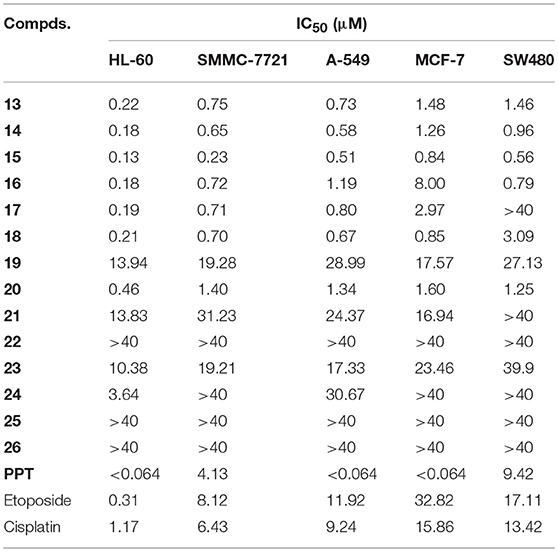
Table 1. The in vitro cytotoxic activity (IC50, μM) of biotinylated podophyllotoxin derivatives 13 – 26 and PPT.
Biotinylated podophyllotoxin derivatives are prepared by linking a biotinylating agent, biotin (3) or 6-biotinylaminocaproic acid (4), via an ester bond, an amide bond, or a trizolyl moiety. Those compounds with an ester linkage (13–18) display potent cytotoxicity with IC50 values in sub-μM to low μM (except compound 17 against SW480 cell line). Compounds 13 and 14 are esters of podophyllotoxin while 15–18 are esters of 4-epipodophyllotoxin, and their similar potency of activity indicates that the cytotoxic activity of these compounds is not much affected by the configuration of C-4. Among the synthesized compounds, compound 15 is the most active one with IC50 ranged from 0.13 to 0.84 μM. Compound 15 also exhibits higher activity than PPT in both SMMC-7721 and SW480 cell lines, with PPT having IC50 of 4.13 and 9.42 μM, respectively.
Compounds with an amide linkage (19–22) or a triazolyl moiety (23–26) show weaker cytotoxicity to all tested cell lines. Most of these compounds display moderate (IC50 > 10.36 μM) to very weak activity (IC50 > 40 μM; except compound 20, as well as compound 24 against HL-60 cell line). The 6-aminocaproic acid linking spacer present in C-4-substituent can affect the cytotoxic potency of these compounds but not in a uniform way. For example, compounds lacking the linking spacer (15, 20, and 23) show higher activity than their counterparts bearing the linking spacer (17, 22, and 25) in all cell lines tested. In contrast, compound 13 (lacking the linking spacer) is less active than 14 (bearing the linking spacer). In most cases, the effect of 6-aminocaproic acid linking spacer on the cytotoxic potency of these compounds are relatively small except for the pair of compounds 15 and 17 in SW480 cell line (IC50 0.56 and > 40 μM, respectively). However, it is very interesting to note that compound 20 (lacking the linking spacer, IC50 0.46–1.60 μM) is significantly more potent than 22 (bearing the linking spacer, IC50 > 40 μM) in all cell lines tested. Furthermore, compound 19, the 4'-O-methylated form of 20, shows much lower activity (IC50 13.94–28.99 μM) than 20, which is in good agreement with our earlier observation that the 4'-O-methylation can significantly affect the anticancer activity of podophyllotoxin derivatives (Zi et al., 2015, 2017).
Compound 15 Inhibits the Growth of Cancer Cell Lines
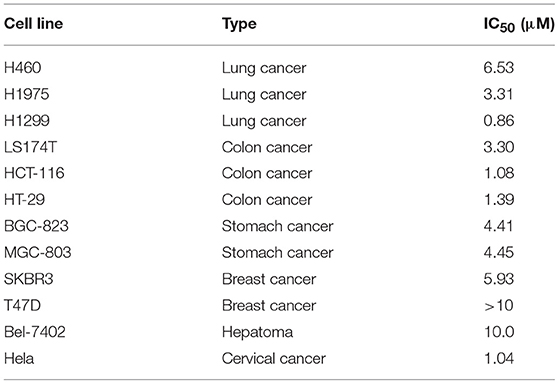
To further identify the anticancer effect and tumor selectivity of compound 15, we treated 12 more human cancer cell lines with compound 15, which included lung cancer (H460, H1975, H1299), colon cancer (LS174T, HCT-116, HT-29), stomach cancer (BGC-823, MGC-803), breast cancer (SKBR3, T47D), hepatoma (Bel-7402), and cervical cancer (Hela). MTT assay was employed to provide the IC50 values of compound 15 against all these tumor cell lines as shown in Table 2. H1299 cell line was most sensitive toward compound 15 (IC50 = 0.86 μM). For most other cancer cell lines, compound 15 showed potent anticancer activity with IC50 values in μM range. In order to test whether compound 15 can favorably target cancer cells over normal cells, the growth inhibitory effect of 15, in comparison with PPT, on a normal human bronchial epithelial cell line (BEAS-2B) was evaluated. The IC50 value was found to be 3.75 μM for 15 and 0.85 μM for PPT against BEAS-2B cells (see Table S1). Comparing with its IC50 values in Table 1 (0.13–0.84 μM) and Table 2 against various cancer cell lines, compound 15 does show some selectivity against certain tested cancer cell lines over the normal cells (BEAS-2B).
Compound 15 Induces Apoptosis in the H1299 and H1975 Cell Lines
Given that compound 15 exhibits broad spectrum inhibitory activity of cancer cell growth, we studied further the capacity of compound 15 in the induction of cell death through apoptosis. Lung cancer cells (H1299 and H1975) were treated with compound 15 and analyzed by flow cytometry after being stained with Annexin V/7AAD. Compound 15 at concentration of 2 μM increased significantly both H1299 and H1975 cells undergoing apoptosis when compared with the untreated control (Figure 2).
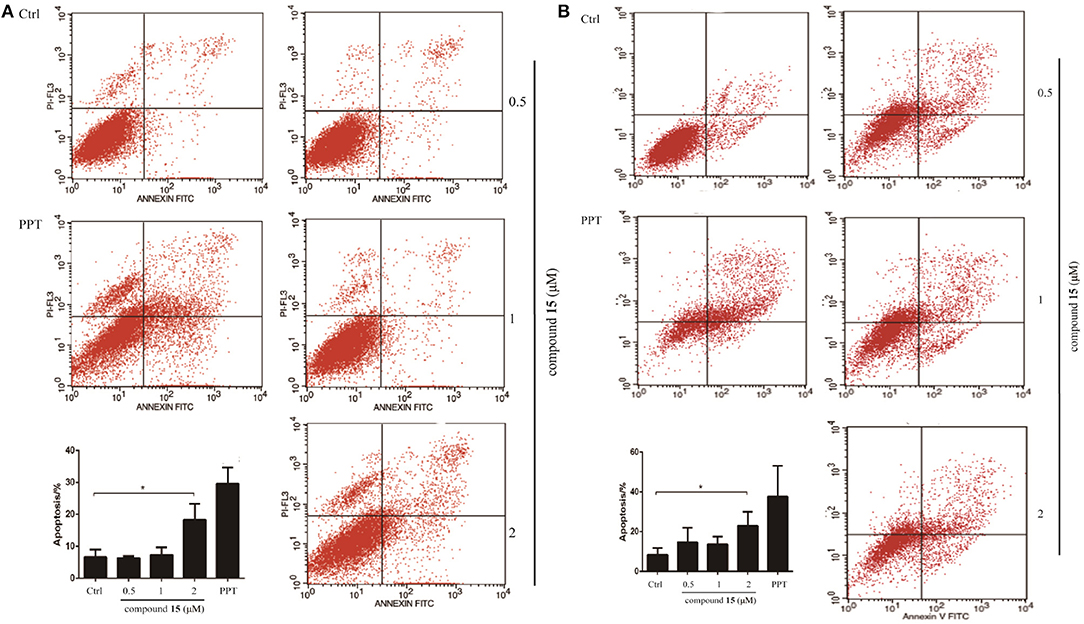
Figure 2. Flow cytometry analysis of lung cancer cell lines H1299 and H1975 after treatment with compound 15. Cells were treated with compound 15 (0.5, 1, and 2 μM) and PPT (1 μM) for 24 h, then stained with Annexin V/7AAD and analyzed by flow cytometry. The ratio of apoptotic cells in each group was expressed as percentage. (A) H1299 cell line; (B) H1975 cell line. The data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.01.
Compound 15 Regulates the Expression Levels of Apoptosis-Related Protein
It has been recognized that caspase-3 and PARP (poy ADP ribose polymerase) is a critical initiator and executioner of apoptosis (Hensley et al., 2013). H1299 and H1975 cells were treated with compound 15 at the concentration of 0.5, 1, 2 or μM for 24 h and the expression level of caspase-3, PARP, cleaved-caspase-3, and cleaved-PARP was monitored using western blot. The treatment of both H1299 and H1975 cell lines with compound 15 resulted in an increased expression level of cleaved-caspase-3 and cleaved-PARP in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 3). At the same time, the expression level of caspase-3 and PARP decreased, indicating that the treatment led to the activation of caspase-3 and the deactivation of PARP and ultimately apoptosis. These data confirmed that the compound 15 exhibits its anticancer activity through induction of apoptosis in both H1299 and H1975 cell lines.
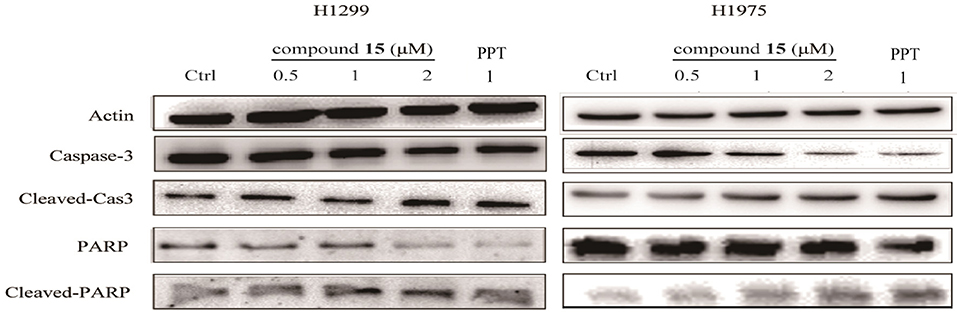
Figure 3. Compound 15 regulates the expression levels of apoptosis-related proteins: H1299 and H1975 cell lines were treated with compound 15 (0.5, 1, and 2 μM) and PPT (1 μM) for 24 h and the expression level of caspase-3, PARP, cleaved-caspase-3, and cleaved-PAPR was detected by western blot (WB). Actin was tested as a loading control.
Compound 15 Induces Apoptosis Through Activating IRE1α, a Key Mediator in the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) Stress Pathway
Many studies have indicated that endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress activates the unfolded protein response (UPR), through which tumor cells can become resistant to chemotherapeutic agents (Cheng et al., 2014). PKR-like ER kinase (PERK), inostitol-requiring transmembrane kinase and endonuclease 1α (IRE-1α), and activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6) are three primary UPR sensors that lead to distinct downstream signaling pathways (Ron and Walter, 2007). Therefore, we next studied the possible involvement of compound 15 in the activation of the ER stress pathway. H1299 cell line was treated with compound 15 at the concentration of 0.5, 1, or 2 μM for 24 h and the mRNA expression level of stress related proteins (GRP78, CHOP, XBP-1, XBP-1s, ATF4, IRE-1α, and ATF6) in ER was analyzed (Figure 4A). Interestingly, the mRNA level of all these proteins except IRE-1α was dramatically increased upon the treatment of compound 15 at 0.5 μM. The effect of 15 at other concentrations (1 or 2 μM) on the mRNA expression level of these proteins was less significant or negligible. In the case of IRE-1α, the expression level of mRNA increased by the treatment of 15 in a dose-dependent manner, suggesting that IRE-1α might play a crucial role in compound 15-induced apoptosis. We further examined the expression level of a number of these proteins (GRP78, CHOP, XBP-1, and XBP-1s) related to ER stress (Figure 4B). Compound 15 significantly up-regulated the expression of GRP78 and XBP-1s, and down-regulated the expression of CHOP and XBP-1.
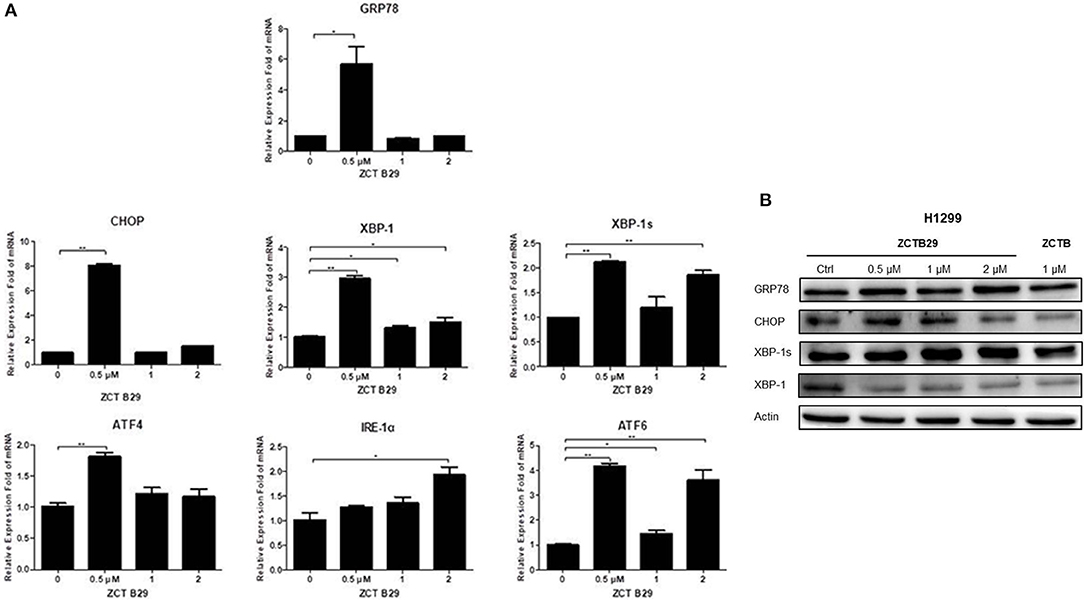
Figure 4. Compound 15 induces apoptosis through activating the ER stress pathway: (A) H1299 cell line was treated with compound 15 (0.5, 1, and 2 μM) for 24 h, GRP78, CHOP, XBP-1, XBP-1s, ATF4, IRE-1α, and ATF6 were measured by real-time RT-PCR. The data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3). *p < 0.01, **p < 0.001, ***p < 0.0001 and ****p < 0.00001. (B) H1299 cell line was treated with compound 15 (0.5, 1, and 2 μM) and PPT (1 μM) for 24 h, and WB was performed to detect the expression levels of protein in the ER stress pathway. Actin was tested as a loading control.
Compound 15 Significantly Inhibits the Growth of S180 Tumor Xenografts in Icr Mice
Since compound 15 suppressed lung cancer cell proliferation in vitro, we further investigated its ability to suppress the growth of S180 tumor xenografts in icr mice (Figure 5). As shown in Figure 5, compound 15 (5, 15, or 20 mg/kg) suppressed the growth of S180 xenografts over the course of 7 days (Figure 5A) comparing to the Taxol® control (10 mg/kg) and the inhibition rates of compound 15 were 8.8, 15.7, and 37.7% (Figure 5D), respectively. Tumors were collected at the end of the experiment (Figure 5B) and the tumor weights were measured. The data showed that compound 15 significantly decreased tumor weight when compared to the untreated control, indicating that 15 effectively inhibited the growth S180 tumor xenograft. In addition, compound 15 did not cause mice to die and did not affect mouse body weight significantly at a dose of up to 20 mg/kg (Figure 5C).
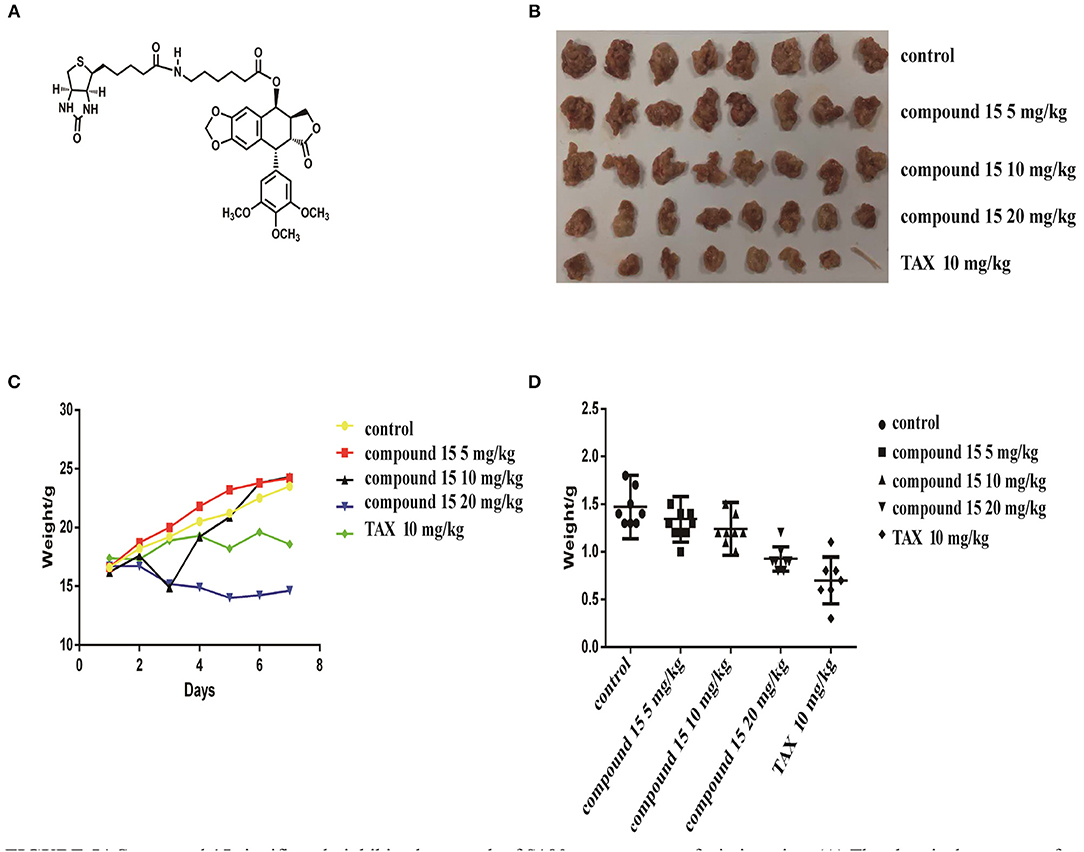
Figure 5. Compound 15 significantly inhibits the growth of S180 tumor xenografts in icr mice: (A) The chemical structure of compound 15. (B) Tumors collected at the end of the treatment (day 7). (C) Mouse's body weights were weighed for those treated with compound 15 (5, 15, 20 mg/kg) compared to TAX control (10 mg/kg) TAX: Taxol. (D) Tumor weights were presented for the groups treated with compound 15 (5, 15, 20 mg/kg).
Docking Studies
Based on the X-ray crystal structure of Topoisomerase-II inhibitors bound to the ATPase domain of Topo-II (PDB: 3QX3) (Wu et al., 2011), the binding mode between Topoisomerase-II and 15 or PPT was established by autodocking (Figure 6). Compound 15 binds Topo-II between the base pairs immediately flanking the two cleaved scissile phosphates (Figure 6A). Its polycyclic podophyllotoxin core (rings A to D) sits between base pairs, while the biotin side chain and the E ring protrude toward the DNA major and minor grooves, respectively. All parts of the podophyllotoxin core contribute to drug-DNA interaction by being located between base pairs. The E ring is anchored by both interacting with GLY-478, ASP-479, and ARG-503 residues of the enzyme and being sandwiched between R503 and the deoxyribose ring of the +1 nucleotide. Compared to PPT (Figure 6B), compound 15 shows additional hydrophobic interaction with GLN-778 and ARG-820 residues through the biotin moiety. The biotin moiety in 15 provides an additional hydrophobic moiety and multiple H-bond donors/acceptor, which allows the molecule to interact more favorably with Topo-II and might lead to improved selectivity.
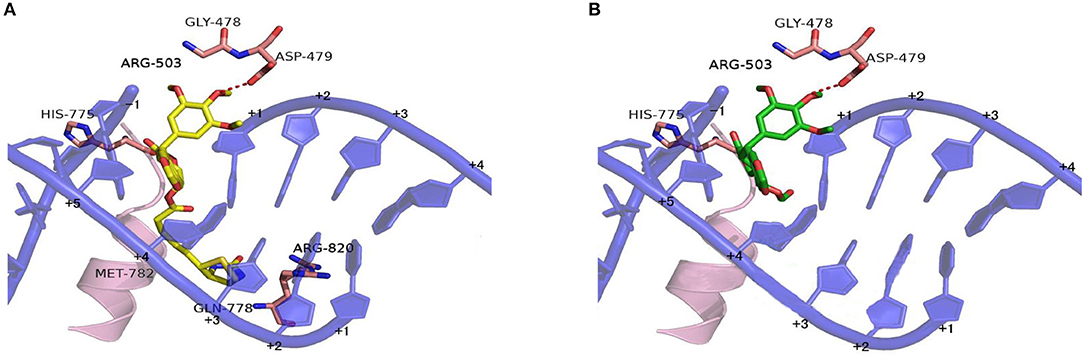
Figure 6. Proposed binding models of compounds 15 and PPT to the ATPase domain of Topoisomerase-II. Based on the X-ray co-crystal structure of Top-II in complex with Etoposide. (A) Binding mode of compound 15 with Topoisomerase-II. (B) Binding mode of PPT with Topoisomerase-II.
Chemical Stability Investigation
The chemical stability of compound 15 in aqueous phase was investigated together with podophyllotoxin (PPT, 1) for comparison. The results indicate that compound 15 degrades slowly under the physiological condition (37 ± 1°C, pH 7.0) with 70% material remaining after 12 h (see Figures S1–S3). A similar stability profile was observed for PPT with 75% material remaining after 12 h.
Conclusion
In summary, a series of biotinylated podophyllotoxin derivatives (13–26) were designed, synthesized, and evaluated for cytotoxicity against five tumor cell lines (HL-60, SMMC-7721, A-549, MCF-7, and SW480) by using MTT assay. Among them, compound 15 showed the highest anticancer activity with its IC50 values at 0.13–0.84 μM. Preliminary structure-activity relationship (SAR) analysis indicated that derivatives bearing an amide or triazolyl linking moiety showed weaker activity than those with an ester linkage. The 6-aminocaproic acid linking spacer affected the cytotoxic potency of these compounds in an ununiform manner. Compound 15 also reduced the expression levels of caspase-3 and PARP. Importantly, the pro-apoptotic activity of compound 15 in H1299 cell line was mediated by the transcription of IRE-1α, which plays an important role in the endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway. Finally, compound 15 at a dose of 20 mg/kg suppressed the growth of S180 tumor xenografts in icr mice significantly. Molecular docking studies suggested that compound 15 could bind well with the ATPase domain of Topoisomerase-II. Continuing studies to substantiate the further development of compound 15 as an anticancer agent are underway in our laboratory and will be reported in due course.
Data Availability
This manuscript contains previously unpublished data. The name of the repository and accession number are not available.
Author Contributions
JZ, J-MH, and Z-HJ designed and guided this study. C-TZ and F-WD conducted the chemical synthesis. LY and YL performed the cell assay. YH and F-QX participated in the cell assay. S-TY, Y-SG, and S-YF performed animal experiments. YJ performed molecular docking. LS and Z-TD performed the SPR binding assay. LS, Z-TD, and J-MH contributed reagents, materials, and analysis tools. C-TZ and Y-SG analyzed the data. C-TZ, LY, Y-SG, Z-HJ, and J-MH wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by grants from Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department (Nos. 2017ZF003, 2015FB168, 2015HB093, and 2018HA001), and the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 21602196).
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fchem.2019.00434/full#supplementary-material
References
Belen'kiib, M. S., and Schinazi, R. F. (1994). Multiple drug effect analysis with confidence interval. Antiviral Res. 25, 1–11. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(94)90089-2
Bermejo, A., Figadere, B., Zafra-Polo, M. C., Barrachina, I., Estornell, E., and Cortes, D. (2005). Acetogenins from Annonaceae: recent progress in isolation, synthesis and mechanisms of action. Nat. Prod. Rep. 22, 269–303. doi: 10.1039/b500186m
Bonifácio, B. V., da Silva, P. B., dos Santos Ramos, M. A., Silveira Negri, K. M., Bauab, T. M., and Chorilli, M. (2014). Nanotechnology-based drug delivery systems and herbal medicines: a review. Int. J. Nanomed. 9, 1–15. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S52634
Bromberg, K. D., Burgin, A. B., and Osheroff, N. (2003). A two-drug model for etoposide action against human topoisomerase Iiα. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 7406–7412. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M212056200
Chen, J. Y., Chen, S. Y., Zhao, X. R., Kuznetsova, L. V., Wong, S. S., and Ojima, I. (2008). Functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes as rationally designed vehicles for tumor-targeted drug delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 16778–16785. doi: 10.1021/ja805570f
Chen, S. Y., Zhao, X. R., Chen, J. Y., Chen, J., Kuznetsova, L., Wong, S. S., et al. (2010). Mechanism-based tumor-targeting drug delivery system. Validation of efficient vitamin receptor-mediated endocytosis and drug release. Bioconjugate Chem. 21, 979–987. doi: 10.1021/bc9005656
Cheng, X., Liu, H., Jiang, C. C., Fang, L., Chen, C., Zhang, X. D., et al. (2014). Connecting endoplasmic reticulum stress to autophagy through IRE1/JNK/beclin-1 in breast cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 34, 772–781. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.1822
Coleman, R. S., and Kong, J. S. (1998). Stereocontrolled synthesis of the fully elaborated aziridine core of the azinomycins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 120, 3538–3539. doi: 10.1021/ja9801386
Desbene, S., and Giorgi-Renault, S. (2002). Drugs that inhibit tubulin polymerization: the particular case of podophyllotoxin and analogues. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti-Cancer Agents 2, 71–90. doi: 10.2174/1568011023354353
Dharap, S. S., Wang, Y., Chandna, P., Khandare, J. J., Qiu, B., Gunaseelan, S., et al. (2005). Tumor-specific targeting of an anticancer drug delivery system by LHRH peptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 12962–12967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504274102
Fred Brewer, C., Loike, J. D., Horwitz, S. B., Sternlicht, H., and Gensler, W. J. (1979). Conformational analysis of podophyllotoxin and its congeners. Structure-activity relationship in microtubule assembly. J. Med. Chem. 22, 215–221. doi: 10.1021/jm00189a001
Fulda, S. (2010). Modulation of apoptosis by natural products for cancer therapy. Planta Med. 76, 1075–1079. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1249961
Gasteiger, J., and Marsili, M. (1980). Iterative partial equalization of orbital electronegativity-a rapid access to atomic charges. Tetrahedron 36, 3219–3228. doi: 10.1016/0040-4020(80)80168-2
Guaragna, A., Chiaviello, A., Paolella, C., D'Alonzo, D., and Palumbo, G. (2012). Synthesis and evaluation of folate-based chlorambucil delivery systems for tumor-targeted chemotherapy. Bioconjug Chem. 23, 84–96. doi: 10.1021/bc200410d
Hansen, H. F., Jesen, R. B., Willumsen, A. M., Norsko-Lauritsen, N., Ebbesen, P., Nielen, P. E., et al. (1993). New compounds related to podophyllotoxin and congeners: Synthesis, structure elucidation and biological testing. Acta Chem. Scand. 47, 1190–1200. doi: 10.1002/chin.199416284
Hensley, P., Mishra, M., and Kyprianou, N. (2013). Targeting caspases in cancer therapeutics. Bio. Chem. 394, 831–843. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2013-0128
Hojjat-Farsangia, M., Moshfegha, A., Daneshmanesha, A. H., Khana, A. S., Mikaelssona, E., Österborga, A., et al. (2014). The receptor tyrosine kinase ROR1–An oncofetal antigen for targeted cancer therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 29, 21–31. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2014.07.005
Holschneider, C. H., Johnson, M. T., Knox, R. M., Rezai, A., Ryan, W. J., and Montz, F. J. (1994). Bullatacin-in vivo and in vitro experience in an ovarian Cancer model. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 34, 166–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00685935
Jardine, I. (1980). “Podophyllotoxins,” in Anticancer Agents Based on Natural Product Models, eds J. M. Cassady and J. D. Douros (New York, NY: Academic Press, 319–351.
Kamal, A., Laxman, N., and Ramesh, G. (2000). Facile and efficient one-pot synthesis of 4β-arylaminopodophyllotoxins: synthesis of DNA topoisomerase II inhibitors (NPF and W-68). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 10, 2059–2062. doi: 10.1016/S0960-894X(00)00407-8
Lambert, J. M., and Berkenblit, A. (2018). Antibody-drug conjugates for cancer treatment. Annu. Rev. Med. 69, 191–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-061516-121357
Leamon, C. P. (2008). Folate-targeted drug strategies for the treatment of cancer. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 9, 1277–1286. doi: 10.2174/092986708786848505
Liu, Y. Q., Yang, L., and Tian, X. (2007). Podophyllotoxin: Current Perspectives. Curr. Bioact. Compd. 3, 37–66. doi: 10.2174/157340707780126499
Lu, Y. J., and Low, P. S. (2012). Folate-mediated delivery of macromolecular anticancer therapeutic agents. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 64, 342–352. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2012.09.020
Mastrobattista, E., Koning, G. A., and Storm, G. (1999). Immunoliposomes for the targeted delivery of antitumor drugs. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 40, 103–127. doi: 10.1016/S0169-409X(99)00043-5
Morris, G. M., Goodsell, D. S., Halliday, R. S., Huey, R., Hart, W. E., Belew, R. K., et al. (1998). Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J. Comput. Chem. 19, 1639–1662.
Ojima, I. (2008). Guided molecular missiles for tumor-targeting chemotherapy-case studies using the second-generation taxoids as warheads. Acc. Chem. Res. 41, 108–119. doi: 10.1021/ar700093f
Ojima, I., Zuniga, E. S., Berger, W. T., and Seitz, J. D. (2012). Tumor-targeting drug delivery of new-generation toxoids. Future Med. Chem. 4, 33–50. doi: 10.4155/fmc.11.167
Peer, D., Karp, J. M., Hong, S., Farokhzad, O. C., Margalit, R., and Langer, R. (2007). Nanocarriers as an emerging platform for cancer therapy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2, 751–760. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2007.387
Qiao, W. J., Cheng, H. Y., Li, C. Q., Jin, H., Yang, S. S., Li, X., et al. (2011). Identification of pathways involved in paclitaxel activity in cervical cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 12, 99–102. doi: 10.1097/01.cad.0000390767.85658.83
Qin, J. Y., Zhou, Z. M., Chen, W. L., Wang, W. L., Zhang, H. L., Ge, G. Z., et al. (2015). BAP1 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by deubiquitinating KLF5. Nat. Commun. 6:8471. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9471
Reddy, P. B., Paul,1, D. V., Agrawal, S. K., Saxena, A. K., Kumar, H. M. S., and Qazi, G.N. (2008). Design, synthesis, and biological testing of 4β-[(4-Substituted)-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl]podophyllotoxin Analogues as Antitumor Agents. Archiv. Pharm. 341, 126–131. doi: 10.1002/ardp.200700116
Ron, D., and Walter, P. (2007). Signal integration in the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio. 8, 519–529. doi: 10.1038/nrm2199
Russell-Jonesa, G., McTavisha, K., McEwana, J., Riceb, J., and Nowotnikb, D. (2004). Vitamin-mediated targeting as a potential mechanism to increase drug uptake by tumours. J. Inorg. Biochem. 98, 1625–1633. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2004.07.009
Sawant, R. R., Sawant, R. M., and Torchilin, V. P. (2008). Mixed PEG–PE/vitamin E tumor-targeted immunomicelles as carriers for poorly soluble anti-cancer drugs: improved drug solubilization and enhanced in vitro cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 70, 51–57. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2008.04.016
Schrama, D., Reisfeld, R. A., and Becker, J. C. (2006). Antibody targeted drugs as cancer therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 5, 147–159. doi: 10.1038/nrd1957
Senthilkumar, R., Karaman, D. S., Paul, P., Björk, E. M., Odén, M., Eriksson, J. E., et al. (2015). Targeted delivery of a novel anticancer compound anisomelic acid using chitosan-coated porous silica nanorods for enhancing the apoptotic effect. Biomater. Sci. 3, 103–111. doi: 10.1039/c4bm00278d
Tae, H. S., Hines, J., Schneekloth, A. R., and Crews, C. M. (2010). Total synthesis and biological evaluation of tyroscherin. Org. Lett. 12, 4308–4311. doi: 10.1021/ol101801u
Weiner, S. J., Kollamn, P. A., Case, D. A., Singh, U. C., Ghio, C., Alagona, G., et al. (1984). A new force field for molecular mechanical simulation of nucleic acids and proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 106, 765–784. doi: 10.1021/ja00315a051
Wen, X. S., Li, D., Zhang, Y. Y., Liu, S. P., Ghali, L., and Iles, R. K. (2012). Arsenic trioxide induces cervical cancer apoptosis, but specifically targets human papillomavirus-infected cell populations. Anticancer Drugs 23, 280–287. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0b013e32834f1fd3
Wu, C. C., Li, T. K., Farh, L., Lin, L. Y., Lin, T. S., Yu, Y. J., et al. (2011). Structural basis of type II topoisomerase inhibition by the anticancer drug etoposide. Science 333, 459–462. doi: 10.1126/science.1204117
Wu, X., and Ojima, I. (2004). Tumor specific novel taxoid-monoclonal antibody conjugates. Curr. Med. Chem. 11, 429–438. doi: 10.2174/0929867043455963
Zhang, Z. J., Tian, J., Wang, L. T., Wang, M. J., Nan, X., Yang, L., et al. (2014). Design, synthesis and cytotoxic activity of novel sulfonylurea derivatives of podophyllotoxin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 22, 204–210. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.11.035
Zi, C. T., Yang, D., Dong, F. W., Li, G. T., Li, Y., Ding, Z. D., et al. (2015). Synthesis and antitumour activity of novel per-butyrylated glycosides of podophyllotoxin and its derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 23, 1437–1446. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.02.021
Keywords: podophyllotoxin derivatives, biotin, anticancer activity, synthesis, apoptosis
Citation: Zi C-T, Gao Y-S, Yang L, Feng S-Y, Huang Y, Sun L, Jin Y, Xu F-Q, Dong F-W, Li Y, Ding Z-T, Zhou J, Jiang Z-H, Yuan S-T and Hu J-M (2019) Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of Novel Biotinylated Podophyllotoxin Derivatives as Potential Antitumor Agents. Front. Chem. 7:434. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00434
Received: 13 March 2019; Accepted: 28 May 2019;
Published: 18 June 2019.
Edited by:
Simone Brogi, University of Pisa, ItalyReviewed by:
Angel Diaz-Ortiz, University of Castilla La Mancha, SpainCarlos Alberto Manssour Fraga, Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Jean Jacques Vanden Eynde, University of Mons, Belgium
Copyright © 2019 Zi, Gao, Yang, Feng, Huang, Sun, Jin, Xu, Dong, Li, Ding, Zhou, Jiang, Yuan and Hu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zi-Hua Jiang, emppYW5nQGxha2VoZWFkdS5jYQ==; Sheng-Tao Yuan, Y3B1WXVhbnN0QDE2My5jb20=; Jiang-Miao Hu, aHVqaWFuZ21pYW9AbWFpbC5raWIuYWMuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Cheng-Ting Zi
Cheng-Ting Zi Ying-Sheng Gao2†
Ying-Sheng Gao2† Liu Yang
Liu Yang Yue Huang
Yue Huang Yi Jin
Yi Jin Fa-Wu Dong
Fa-Wu Dong Jun Zhou
Jun Zhou Zi-Hua Jiang
Zi-Hua Jiang Jiang-Miao Hu
Jiang-Miao Hu