
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
CORRECTION article
Front. Psychol., 20 February 2019
Sec. Developmental Psychology
Volume 10 - 2019 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00316
This article is part of the Research TopicSocial and Emotional Influences on Human Development: Perspectives from Developmental NeuroscienceView all 18 articles
This article is a correction to:
Reduced Mu Power in Response to Unusual Actions Is Context-Dependent in 1-Year-Olds
A Corrigendum on
Reduced Mu Power in Response to Unusual Actions Is Context-Dependent in 1-Year-Olds
by Langeloh, M., Buttelmann, D., Matthes, D., Grassmann, S., Pauen, S., and Hoehl, S. (2018). Front. Psychol. 9:36. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.00036
In the original article, there were mistakes in Figures 2–5 as published. We analyzed the artifact-free data segments in Fieldtrip (Oostenveld et al., 2011) using the “ft_freqanalysis” function. We configured this function to compute power, however, stated erroneously in the original text that we computed the “power spectral density (PSD).” Consequently, we labeled the y-axis units according to PSD but not power.
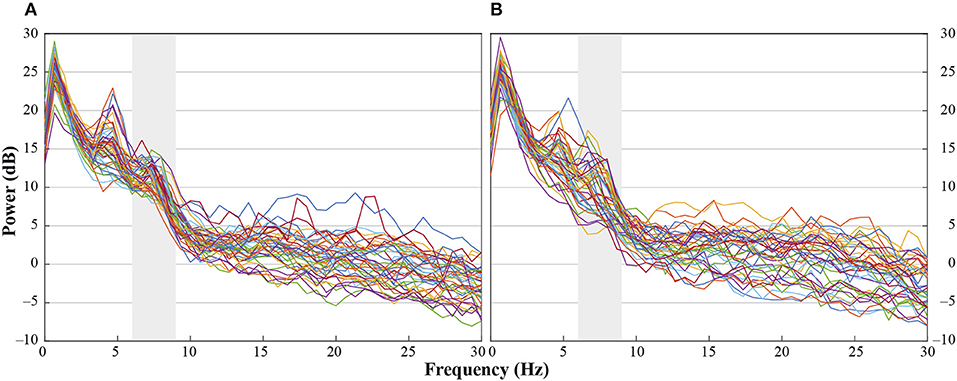
Figure 2. Individual power spectra across an average for hand- and head-touch actions across an average of frontal and central electrodes (F3, F4, C3, C4) for (A) hands-free and (B) hands-restrained condition.
The y-axis unit in Figure 3 was corrected to “μV2”, additionally, the scaling used in Figures 2, 4 and 5 was a natural logarithm instead of a common logarithm. The scaling has now been adjusted to the common logarithm and the y-axis unit has been adjusted to “dB” accordingly. The corrected Figures 2–5 appear below.
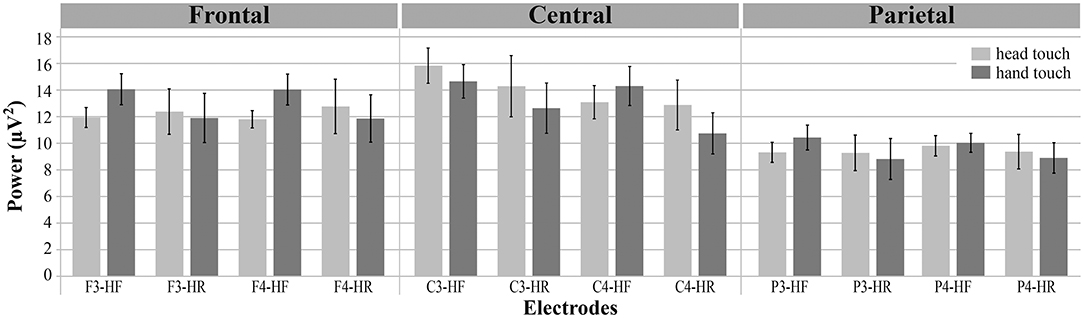
Figure 3. Grand average EEG power across mu frequency band (6–8Hz) for electrodes of interest (F3, F4, C3, C4, P3, P4) in response to hand touch (dark gray) and head touch (light gray) for both hands-free (HF) and hands-restrained (HF) condition. Error bars represent standard errors of the mean.
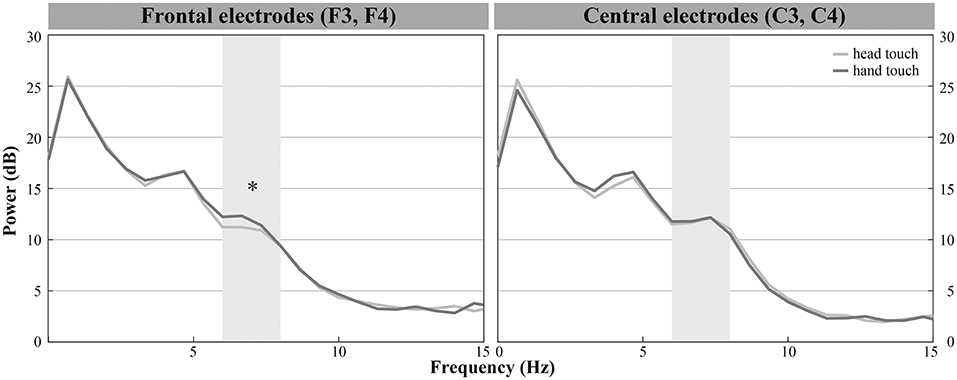
Figure 4. Grand average EEG mu power for hand touch (dark gray) and head touch (light gray) for an average of frontal electrodes (F3, F4) and for an average of central electrodes (C3, C4) in the hands-free condition. Asterisks depict significant differences with p < 0.05.
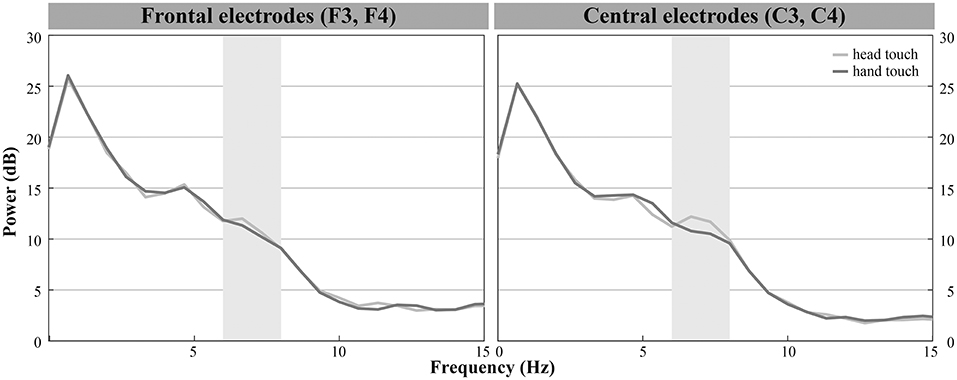
Figure 5. Grand average EEG mu power for hand touch (dark gray) and head touch (light gray) for an average of frontal electrodes (F3, F4) and for an average of central electrodes (C3, C4) in the hands-restrained condition.
A correction has also been made to the Materials and Methods, EEG Recording and Analyses, Frequency Domain Analysis, Paragraph one:
“Artifact-free data segments were submitted to fast Fourier transformations (FFTs). For each segmented test frame (hand or head touch), the power was computed from 0 to 1,500 ms relative to the onset of the related stimulus using a Hanning-tapered window of the same length (by applying the ‘ft freqanalysis’ function with ‘mtmfft’ method as implemented in Fieldtrip). Power estimates were calculated for frequencies (Hz bins) between 0 and 124.667 Hz. Grand averages of the FFTs were computed for both hand- and head-action outcomes in the hands-free and hand-restrained condition.”
Additionally, there was a mistake in the legend for Figure 2 as published. The legend has been rewritten to provide a better understanding of the figure content. The correct legend appears below.
“Figure 2. Individual power spectra across an average for hand- and head-touch actions across an average of frontal and central electrodes (F3, F4, C3, C4) for (A) hands-free and (B) hands-restrained condition.”
The authors apologize for these errors and state that they do not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: EEG, infants, action perception, action understanding, mu frequency, mirror neuron system
Citation: Langeloh M, Buttelmann D, Matthes D, Grassmann S, Pauen S and Hoehl S (2019) Corrigendum: Reduced Mu Power in Response to Unusual Actions Is Context-Dependent in 1-Year-Olds. Front. Psychol. 10:316. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00316
Received: 01 December 2018; Accepted: 01 February 2019;
Published: 20 February 2019.
Edited by:
Markus Paulus, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, GermanyReviewed by:
Janny Christina Stapel, Uppsala University, SwedenCopyright © 2019 Langeloh, Buttelmann, Matthes, Grassmann, Pauen and Hoehl. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Miriam Langeloh, bGFuZ2Vsb2hAY2JzLm1wZy5kZQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.