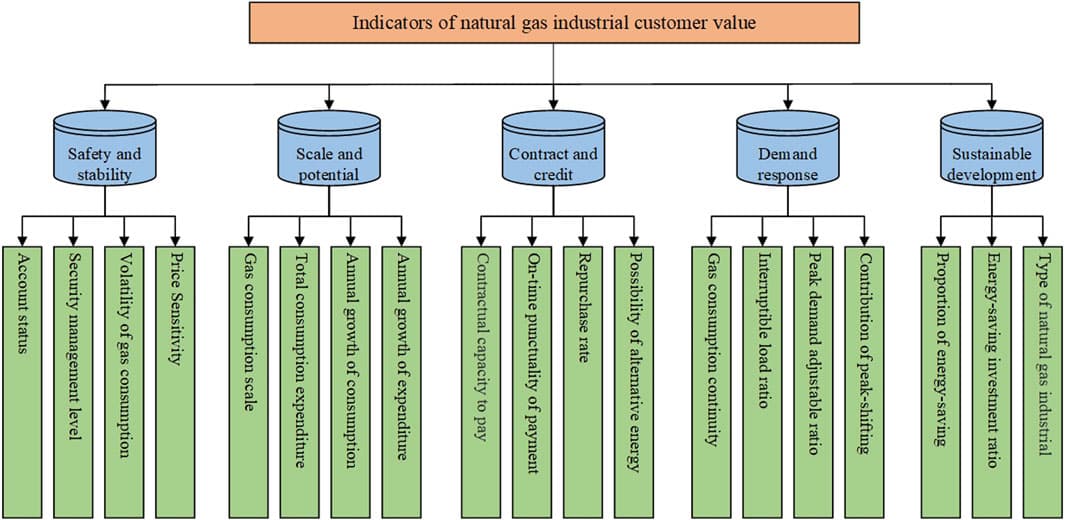
The smart grid, as a cyber-physical system, is vulnerable to attacks due to the diversified and open environment. The false data injection attack (FDIA) can threaten the grid security by constructing and injecting the falsified attack vector to bypass the system detection. Due to the diversity of attacks, it is impractical to detect FDIAs by fixed methods. This paper proposed a false data injection attack model and countering detection methods based on deep reinforcement learning (DRL). First, we studied an attack model under the assumption of unlimited attack resources and information of complete topology. Different types of FDIAs are also enumerated. Then, we formulated the attack detection problem as a Markov decision process (MDP). A deep reinforcement learning-based method is proposed to detect FDIAs with a combined dynamic-static detection mechanism. To address the sparse reward problem, experiences with discrepant rewards are stored in different replay buffers to achieve efficiency. Moreover, the state space is extended by considering the most recent states to improve the perception capability. Simulations were performed on IEEE 9,14,30, and 57-bus systems, proving the validation of attack model and efficiency of detection method. Results proved efficacy of the detection method in different scenarios.
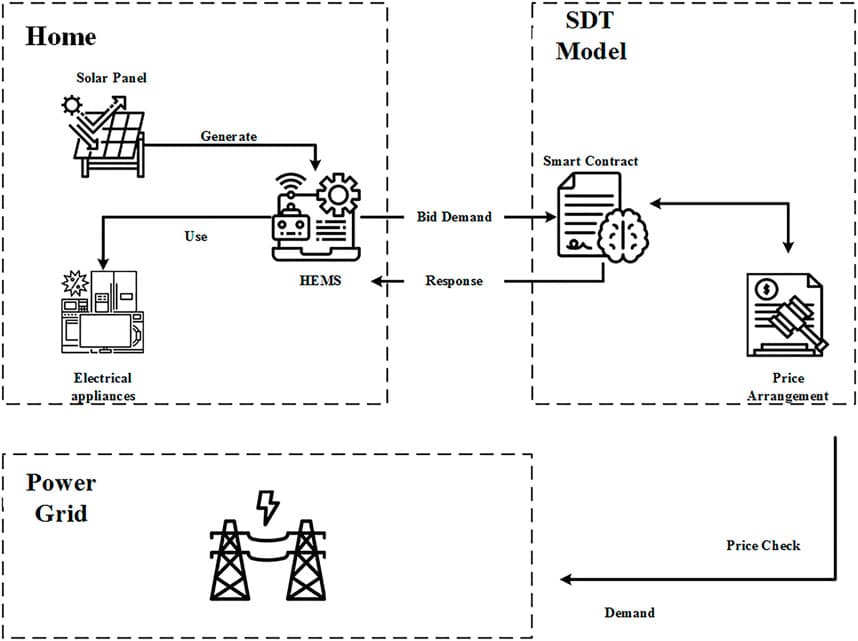
With the spread of distributed renewable energy, residents are shifting from being mere consumers to being energy producers and consumers. This role shift poses challenges to the electricity trading mechanism that connects distributed renewable energy sources to the grid. In this paper, a new efficient and secure blockchain-based distributed community energy trading mechanism is proposed, called CE-SDT. Our system is proved to be stable and scalable. It can also help shift loads and power peaks and reduce customer costs by 60%. As a result, our proposed blockchain-based trading mechanism, as compared to the centralized trading mechanism, is applied to microgrids formed by distributed renewable energy sources, not only obtaining greater economic benefits but also reducing the carbon footprint of residents, and furthermore, it promotes low or zero-carbon configurations of the power system, thereby achieving certain environmental benefits.
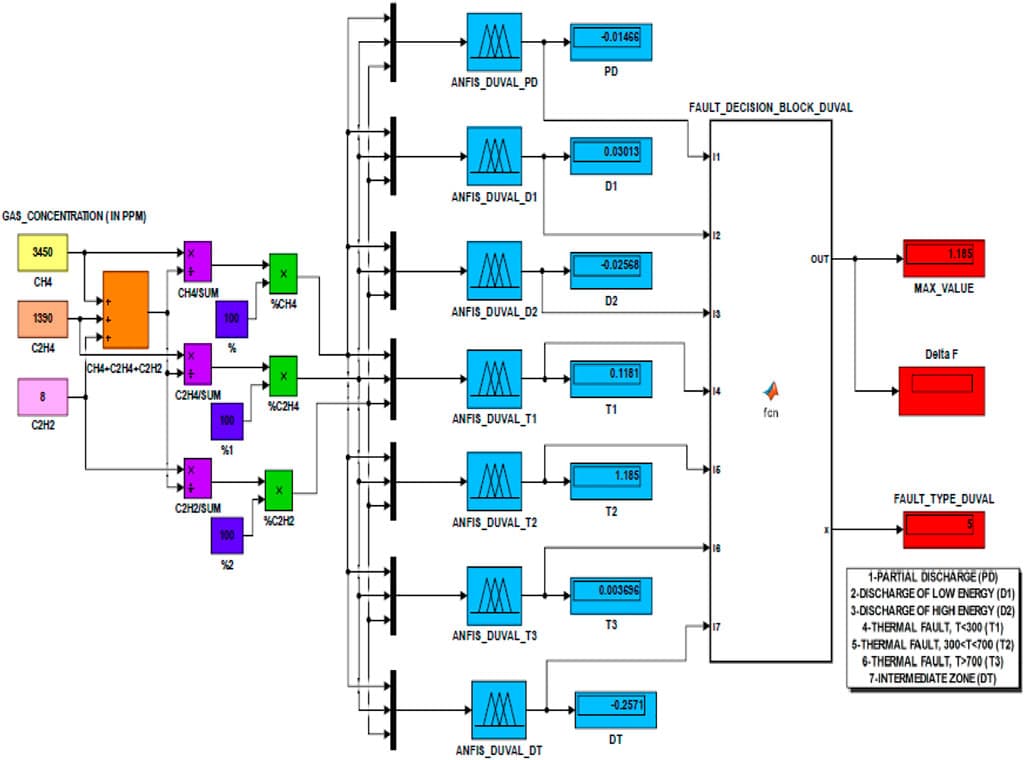
E-Nose finds its use in a wide range of applications such as quality assessment in food processing to toxic gas identification in chemical industry either in the offline or online mode. Their usage can be extended to transformer condition monitoring in the online mode. Considering the importance of transformers in power system and the impact it could create if faults in them are unidentified or left unattended, their functioning should be monitored on a real time basis. This work, describes the realization of a prospective E-Nose for online transformer incipient fault identification. The resistive gas sensor array has been simulated in real time using variable resistances forming one arm of a Wheatstone bridges. Separate variable resistances have been calibrated using characteristics of different fault gas sensors. The sensor array of the E-Nose helps to identify the transformer fault gases resulting from an incipient fault condition at the nascent stage itself and prompts for the necessary corrective action well before a catastrophic situation arises. Furthermore, ANFIS model of the Duval’s Triangle (DT) method have been developed to facilitate the online classification of incipient faults. The ANFIS models of other popularly used incipient fault interpretation methods, reported in earlier works, have also been used for a comparative analysis on their diagnostic capabilities. The developed model has been tested using the fault cases of IEC-TC10 fault database and the results thus obtained have been found to be very promising.
The use of corrosion inhibitors can effectively avoid the corrosion of metals and alloys, but the conventional organic/inorganic corrosion inhibitors have certain toxic and side effects and environmental pollution problems (including some expensive toxic reagents and catalysts), prompting researchers to turn their attention to the research of water-soluble polymer corrosion inhibitors with green environment friendly and low pollution. This paper reviews the action mechanism of polymer inhibitors, the research status of natural polymer inhibitors (chitosan-based inhibitors, cellulose and its derivatives inhibitors, other carbohydrate inhibitors, protein inhibitors) and synthetic polymer inhibitors (epoxy resin inhibitors, polyethylene glycol inhibitors, conductive polymer inhibitors), The purpose is to provide some reference for the development of eco-friendly metal coatings.
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology
Extracellular Vesicles Signaling in Embryogenesis and Morphogenesis
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology
Extracellular Vesicles Signaling in Embryogenesis and Morphogenesis