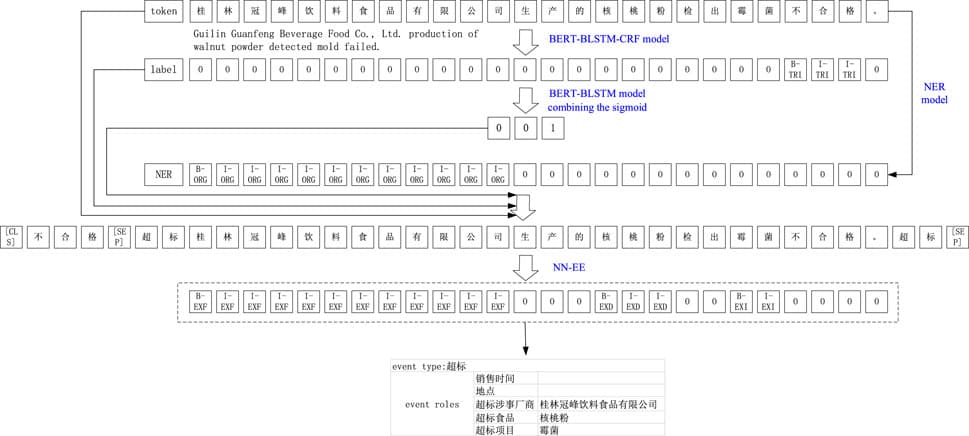
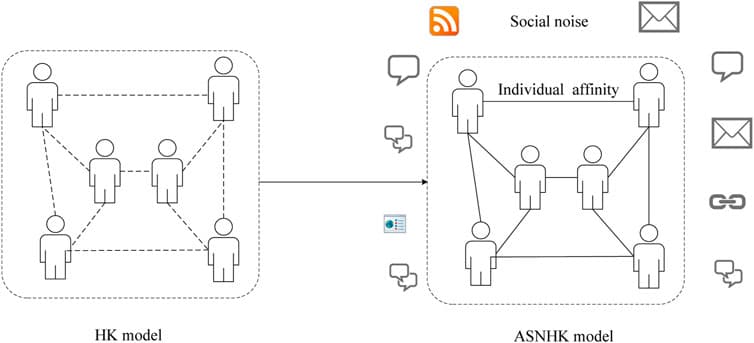
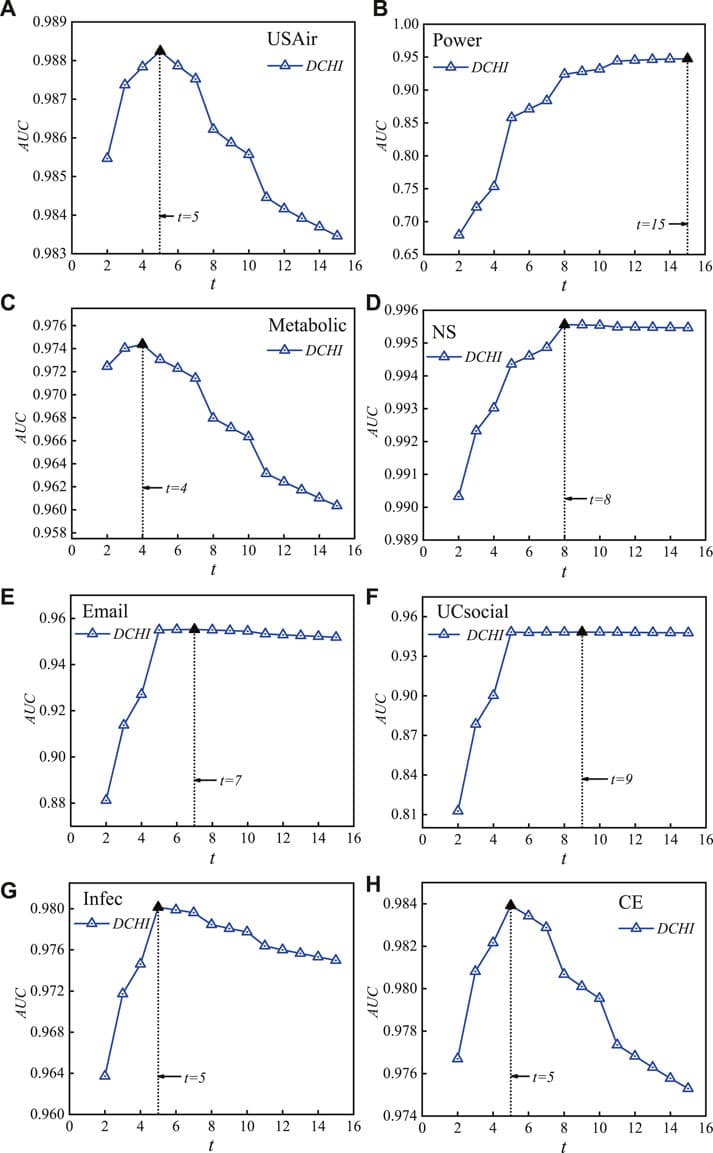
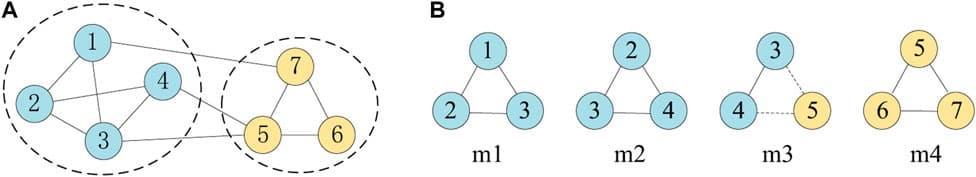
The Stock Market is a typical complex network composed of investors, stocks, and market information. The abnormal fluctuation of the Stock Market has a strong effect on the economy of a country and even that of the world. Fueled by the herd effect of the increasingly abundant social media, Internet rumors, as an important source of market information and an exogenous financial risk, can lead to the collapse of investor confidence and the further propagation of financial risks, which can damage the financial system and even lead to social unrest. With additional availability of computing techniques, we attempt to uncover the media information effects in the stock market and seek to provide researchers with 1) a theoretical reference for a comprehensive understanding of such a complex network, 2) accurate prediction of future data, and 3) design of efficient and reliable risk intervention models. Based on the data of China’s Stock Market, this study uses machine learning to investigate social media rumors to reveal the interplay of social media rumors and stock market volatility. In this work, we find patterns from social media rumors from financial forums using machine learning, quantify social media rumors based on statistics, and analyze the mechanism of propagation and influence of social media rumors on stock market volatility using econometric models. The empirical results show that rumors play an important information transmission effect on stock market volatility and the constructed Internet Financial Forum Rumor Index is helpful to sense the potential impact of rumors, i.e., a significant lagged negative effect. These findings are of guidance for the optimization of the information environment, and can serve to promote the healthy and stable development of the stock market.
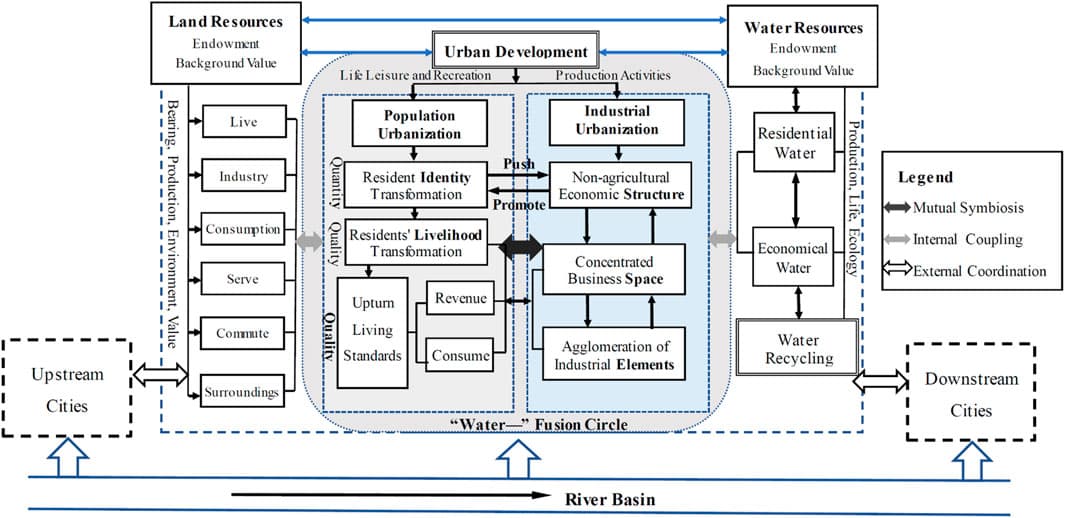
In the field of complex network research, complex network information transmission models based on infectious disease models are often used to study the mechanism of information transmission. This is helpful for the prediction of information transmission trends and the formulation of control strategies. However, the classification of node types in traditional information transmission models is too simple and cannot reflect the characteristics of each node. To solve the above problems, this study proposes a layered SITR complex network information transmission model. The model is layered according to the influence of nodes, and rational propagator nodes are added to optimize it. The propagation threshold of the model is deduced theoretically and the stability of the model is proved. To reduce the dissemination scale of the network’s public opinion information, an optimal control strategy is proposed based on the Pontryagin maximum principle to optimize the information dissemination process. Finally, combined with real events from social network platform, the simulation results show that the layered SITR model can describe the process of network information dissemination more accurately, and the optimal control strategy can effectively reduce the dissemination scale of the network’s public opinion information.
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology
Ecology and Biodiversity of Protozoa in the Environment and in the Clinic
Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology
Ecology and Biodiversity of Protozoa in the Environment and in the Clinic