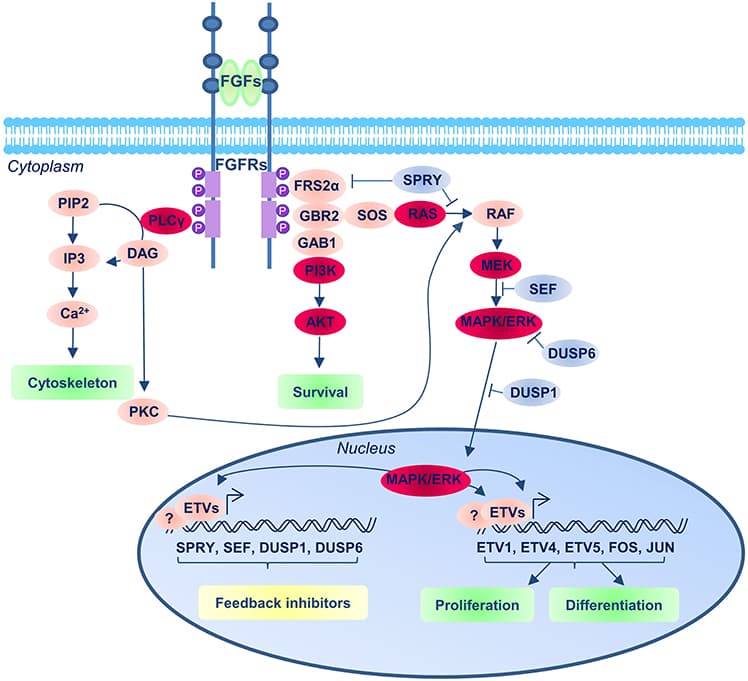
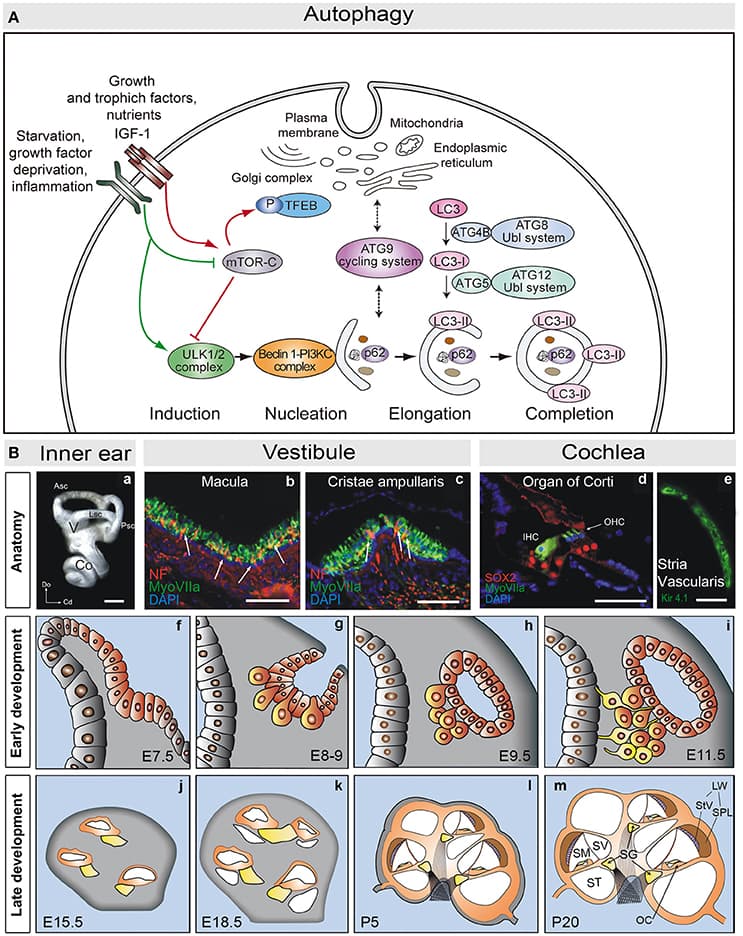
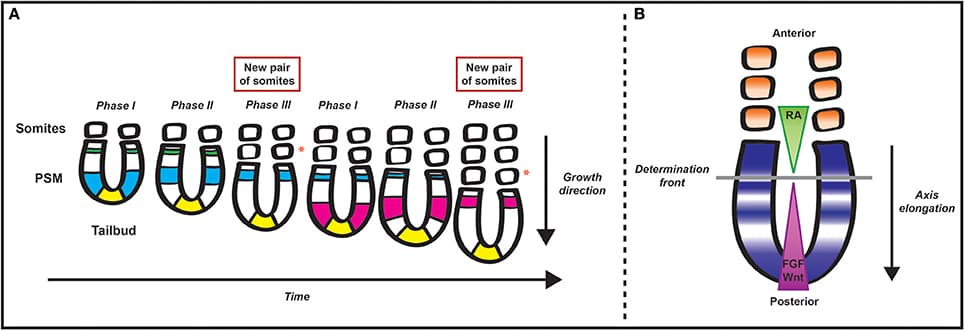
During vertebrate embryonic development, the spinal cord is formed by the neural derivatives of a neuromesodermal population that is specified at early stages of development and which develops in concert with the caudal regression of the primitive streak. Several processes related to spinal cord specification and maturation are coupled to this caudal extension including neurogenesis, ventral patterning and neural crest specification and all of them seem to be crucially regulated by Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) signaling, which is prominently active in the neuromesodermal region and transiently in its derivatives. Here we review the role of FGF signaling in those processes, trying to separate its different functions and highlighting the interactions with other signaling pathways. Finally, these early functions of FGF signaling in spinal cord development may underlay partly its ability to promote regeneration in the lesioned spinal cord as well as its action promoting specific fates in neural stem cell cultures that may be used for therapeutical purposes.
Skeletal muscles belong to the musculoskeletal system, which is composed of bone, tendon, ligament and irregular connective tissue, and closely associated with motor nerves and blood vessels. The intrinsic molecular signals regulating myogenesis have been extensively investigated. However, muscle development, homeostasis and regeneration require interactions with surrounding tissues and the cellular and molecular aspects of this dialogue have not been completely elucidated. During development and adult life, myogenic cells are closely associated with the different types of connective tissue. Connective tissues are defined as specialized (bone and cartilage), dense regular (tendon and ligament) and dense irregular connective tissue. The role of connective tissue in muscle morphogenesis has been investigated, thanks to the identification of transcription factors that characterize the different types of connective tissues. Here, we review the development of the various connective tissues in the context of the musculoskeletal system and highlight their important role in delivering information necessary for correct muscle morphogenesis, from the early step of myoblast differentiation to the late stage of muscle maturation. Interactions between muscle and connective tissue are also critical in the adult during muscle regeneration, as impairment of the regenerative potential after injury or in neuromuscular diseases results in the progressive replacement of the muscle mass by fibrotic tissue. We conclude that bi-directional communication between muscle and connective tissue is critical for a correct assembly of the musculoskeletal system during development as well as to maintain its homeostasis in the adult.
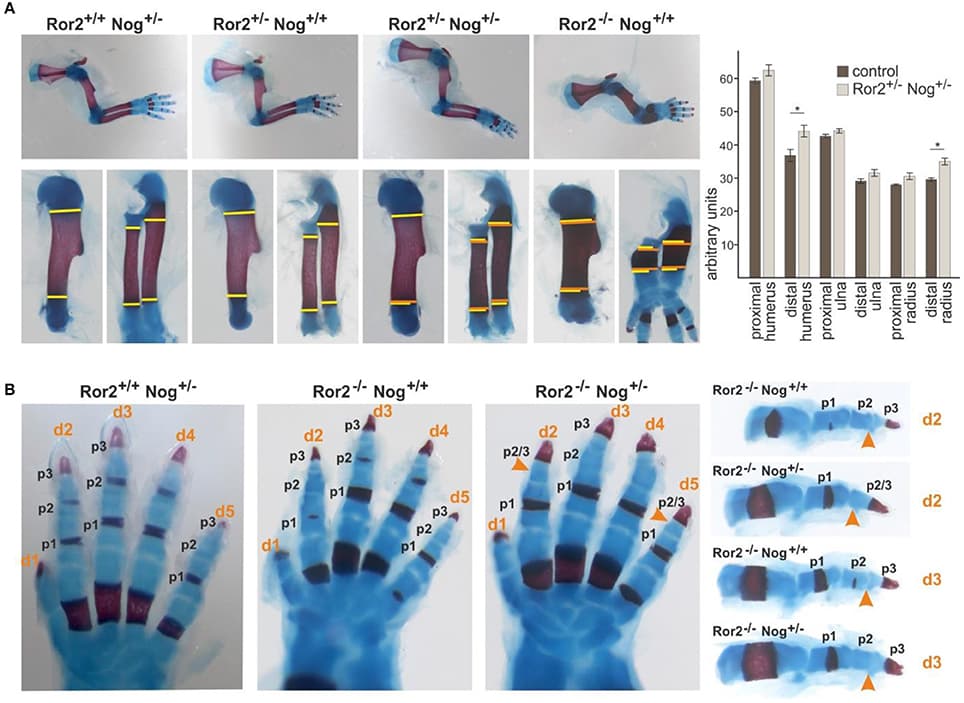
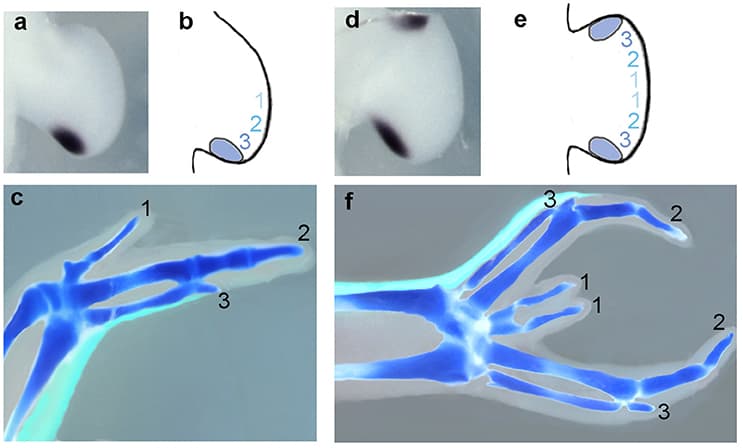
The gene encoding the secreted protein Sonic hedgehog (Shh) is expressed in the polarizing region (or zone of polarizing activity), a small group of mesenchyme cells at the posterior margin of the vertebrate limb bud. Detailed analyses have revealed that Shh has the properties of the long sought after polarizing region morphogen that specifies positional values across the antero-posterior axis (e.g., thumb to little finger axis) of the limb. Shh has also been shown to control the width of the limb bud by stimulating mesenchyme cell proliferation and by regulating the antero-posterior length of the apical ectodermal ridge, the signaling region required for limb bud outgrowth and the laying down of structures along the proximo-distal axis (e.g., shoulder to digits axis) of the limb. It has been shown that Shh signaling can specify antero-posterior positional values in limb buds in both a concentration- (paracrine) and time-dependent (autocrine) fashion. Currently there are several models for how Shh specifies positional values over time in the limb buds of chick and mouse embryos and how this is integrated with growth. Extensive work has elucidated downstream transcriptional targets of Shh signaling. Nevertheless, it remains unclear how antero-posterior positional values are encoded and then interpreted to give the particular structure appropriate to that position, for example, the type of digit. A distant cis-regulatory enhancer controls limb-bud-specific expression of Shh and the discovery of increasing numbers of interacting transcription factors indicate complex spatiotemporal regulation. Altered Shh signaling is implicated in clinical conditions with congenital limb defects and in the evolution of the morphological diversity of vertebrate limbs.
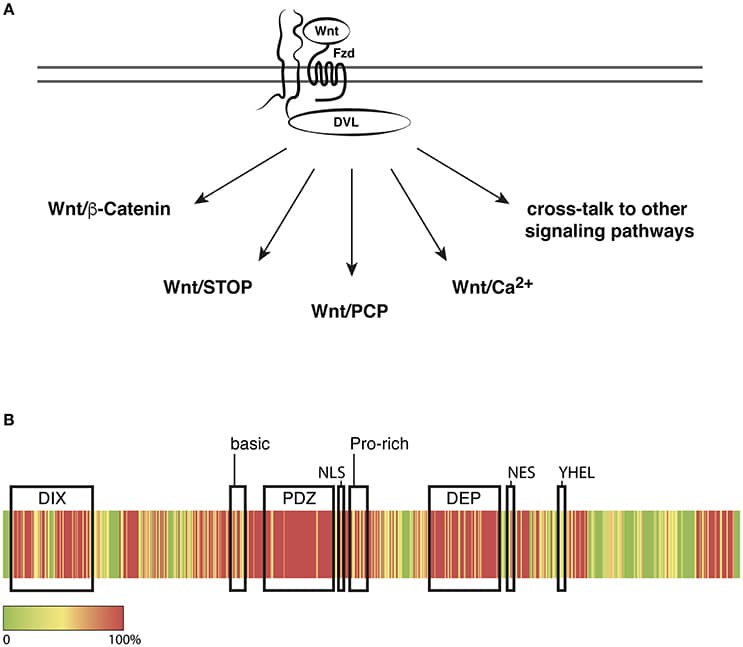
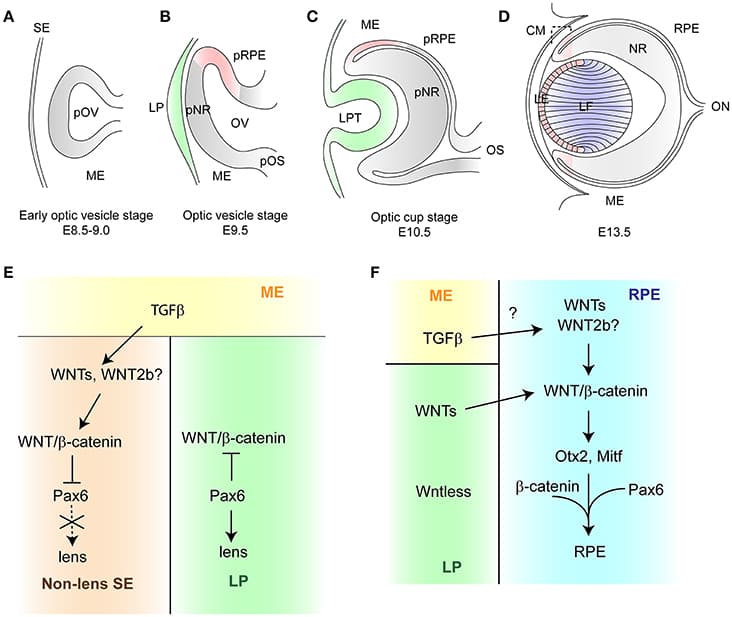
The vertebrate eye is a highly specialized sensory organ, which is derived from the anterior neural plate, head surface ectoderm, and neural crest-derived mesenchyme. The single central eye field, generated from the anterior neural plate, divides to give rise to the optic vesicle, which evaginates toward the head surface ectoderm. Subsequently, the surface ectoderm, in conjunction with the optic vesicle invaginates to form the lens vesicle and double-layered optic cup, respectively. This complex process is controlled by transcription factors and several intracellular and extracellular signaling pathways including WNT/β-catenin signaling. This signaling pathway plays an essential role in multiple developmental processes and has a profound effect on cell proliferation and cell fate determination. During eye development, the activity of WNT/β-catenin signaling is tightly controlled. Faulty regulation of WNT/β-catenin signaling results in multiple ocular malformations due to defects in the process of cell fate determination and differentiation. This mini-review summarizes recent findings on the role of WNT/β-catenin signaling in eye development. Whilst this mini-review focuses on loss-of-function and gain-of-function mutants of WNT/β-catenin signaling components, it also highlights some important aspects of β-catenin-independent WNT signaling in the eye development at later stages.