- Department of Civil Engineering, Jamia Millia Islamia, New Delhi, India
Rampant urbanization and undervaluing of the natural ecosystem have detrimental impacts on urban spaces – increased flooding risk, increased air and water pollution, water stress, resource inefficiency, loss of biodiversity, and increased risk of ill health. Climate change further exacerbates the adverse impacts of urbanization. Despite the importance of the natural ecosystem, the blue and green spaces of the cities in India have drastically decreased. The present study highlights the degrading natural ecosystem, the negative impacts, and the need for resilience in Indian cities. Eco-centric approaches like nature-based solutions (NBS) are closely related to sustainability and resilience, offering a more efficient and cost-effective approach to urban development than traditional approaches. The paper explores the concept of NBS, focusing on ecosystem services as a ‘living’ and ‘adaptable’ tool to make cities resilient and sustainable with many regional implementations. It also focuses on the role of NBS in achieving the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). The paper critically analyses the five notable NBS projects from different countries (USA, Canada, The Netherlands, China, and Australia) and further addresses the viabilities for NBS intervention in Indian cities. It is observed that the successful adaptation of NBS in urban development necessitates eco-centric policies, collaborative research, adaptive management practices, community engagement, and a strong emphasis on a multi-benefit approach. A proactive focus on ecosystem services is strongly recommended for Indian cities, which includes raising an understanding of the value of nature, introducing NBS at the planning stage, and encouraging investment in ecosystem-based approaches.
1 Introduction
Cities worldwide are grappling with resilience challenges arising from the complex interplay of climate risks, urbanization, biodiversity loss, diminishing ecosystem services, poverty, and increasing socioeconomic disparities (World Meteorological Organization (WMO), 2022; United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), 2023). The impact of climate change is projected to lead to more frequent and severe natural hazards and climate-related extremes like floods, droughts, and heat waves. Moreover, urbanization can increase the vulnerability of urban communities and infrastructure to these hazards due to rapidly declining natural land-use land-cover (LULC), i.e., blue (waterbodies) and green (vegetation) spaces (Ghofrani et al., 2017). The combined impacts of rampant urbanization and climate change have become evident at the global scale– nearly 2 billion people lacked access to safe drinking water till 2021, and over 90 billion USD of global economic losses from various natural disasters in the first half of 2021 alone (United Nations, 2022; United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), 2023). With the existing trends of rampant urbanization and climate change impacts, urban resilience challenges are anticipated to intensify (World Bank, 2021).
Disaster risk reduction and climate resilience used to focus mainly on grey infrastructure, which may not always be the most cost-effective, resilient, and sustainable option. Grey Infrastructure refers to the engineered assets and built structures like embankments, dams, stormwater drains, and wastewater treatment plants created to manage environmental and hydrological attributes. In recent decades, the significance of nature-based solutions (NBS) has been increasingly acknowledged for urban resilience. NBS is an umbrella concept covering a range of ecosystem-related approaches to address social, economic and environmental challenges while benefiting human well-being and biodiversity (Cohen-Shacham et al., 2016). In other words, the NBS interventions harness the natural elements and processes of healthy ecosystems to effectively address some of the most significant challenges of the present time, like climate change, water security, and natural disasters (Bozovic et al., 2017; Ghofrani et al., 2017; Dorst et al., 2019; Hamel and Tan, 2022). The benefits attained through NBS interventions are commonly referred to as ecosystem services. Numerous international agreements and initiatives, like the Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the Paris Climate Agreement, promote nature-based approaches and align with environmental and risk management goals to address climate risk and environmental degradation and promote investment in disaster risk reduction (Reguero et al., 2020; World Bank, 2021). In the present study, the concept of NBS, including its ecosystem services, has been discussed with various successful case studies across the globe, and the possibilities of adaptation for the development of resilient cities in India have been explored.
2 Declining natural LULC compromising resilience and sustainability of cities in India
2.1 A brief description of land use transition in a few major Indian cities
This section discusses the trend of urbanization and declining natural LULC of a few major Indian cities and their suburbs, emphasizing the need for resilient cities in India. The increase in built-up area in the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi was 162.7 sq. km to 531.2 sq. km from 1993 to 2018 (Bondwal and Bisht, 2019). The same study found that the forest cover in the NCT of Delhi decreased from 155.8 sq. km to 130 sq. km between 1993 and 2018. Land-use transitions are not only limited to the cities but also greatly affect suburban regions (Naikoo et al., 2020). Mumbai city experienced a significant decline in natural land use and land cover (LULC) from 1977 to 2017, with a 60 percent reduction in vegetation and a 65 percent reduction in waterbodies (Udas-Mankikar and Driver, 2021). Another study reported that the built-up area of Mumbai rose from 28 to 57% of the city’s total area from 1991 to 2018, and it is projected to reach 66% by 2030 (Naikoo et al., 2023). Similarly, the Chennai Metropolitan Area (CMA) witnessed an increase in built-up areas from 18 to 48% and a decrease in vegetation from 57 to 26% between 1988 and 2017 (Mathan and Krishnaveni, 2020). Developments have taken over 90 per cent of the wetlands of Chennai city (Ahmad and Hassan, 2024). Bengaluru city experienced a significant decrease in the green cover of the city, more than 50% from 2003 to 2021, while the built-up area almost doubled during the same period (Keerthi-Naidu and Chundeli, 2023).
2.2 Need for resilient and sustainable cities in India
The consequences of the rampant land use transition in urban and suburban landscapes in India can be seen as increased urban pressures, i.e., flood risk, water stress, water pollution, urban heat island (UHI) and air pollution. The natural drainage systems in most cities are facing threats from encroachment, inadequate maintenance, poor solid waste management, and lack of adequately designed stormwater drainage infrastructure. For example, Chennai city suffered the most disastrous flood of the century in 2015, causing more than 400 human casualties, nearly 2 million severely affected and about USD 80 billion of estimated loss (Vojinovic, 2015). On the contrary, four years later, in June 2019, the city was unexpectedly hit by ‘Day Zero,’ and all of its major reservoirs dried up. The city has a minimum of 108 Litre per capita per day (LPCD) of water supply, much less than the WHO minimum criteria of 150 LPCD (Rajaveni et al., 2016). The study confirms the presence of UHI in Chennai with an intensity of 4.5°C in winter and 2.5°C in summer (Rajan and Amirtham, 2021).
The annual economic impact of urban flooding in India is disastrous, ranging from USD 1.1 billion to USD 5 billion (Sharief and Vangipuram, 2022). The highest UHI intensity recorded internationally is as high as 12°C, while the observed maximum UHI intensity in India is 8–9°C. UHI can deteriorate the urban environment in multiple ways – increase in energy and water consumption, higher emissions of pollutants into the atmosphere resulting in the greenhouse effect, heat-related health discomfort, and degradation of water quality in streams, rivers, and other water bodies (Jain and Sarkar, 2017; Veena et al., 2020; Vujovic et al., 2021). Every city and its suburbs face the abovementioned urban pressures with varying intensities depending on the type of city (like coastal city, riverine city, or mountainous city). The lack of effective streamlining, regulation, and monitoring of urbanization processes is a key factor contributing to significant environmental degradation. Taking account of climate change, environmental risks, and socio-economic vulnerability, there is an urgent need for a paradigm shift in urban developments in India and the adaptation of nature-based solutions for the development of resilient cities. NBS strategies optimize the climate-related risks with other objectives to achieve multiple benefits regarding ecological, socio-economic and overall urban well-being (Roumeau et al., 2015; Vojinovic, 2015). The concept of nature-based solutions and the associated ecosystem services have been discussed in detail in the next section.
3 Nature-based solutions (NBS): an approach for resilient cities
3.1 Overview of the NBS concept
The World Bank introduced the NBS concept in the late 2000s to address increasing climate-related risks, promoting ecosystem-based approaches (World Bank, 2008). The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) has been taking the lead in conserving the ecosystem and promoting nature-based solutions (NBS) globally by formulating core principles and frameworks for mainstreaming NBS. Figure 1 highlights the timeline of major milestones in developing the NBS concept. In recent years, the definition and scope of nature-based solutions have become vast and diverse. The diversity of concepts and definitions has led to challenges in achieving conceptual clarity, making the term more subjective (European Commission, 2021; Cohen-Shacham et al., 2016; Albert et al., 2017; Dhyani et al., 2020). Table 1 enlists the two most widely accepted definitions of NBS. Fundamentally, NBS is a novel approach that primarily focuses on using ecosystems to address climatic, environmental, and socio-economic challenges (Balian et al., 2014; Cohen-Shacham et al., 2016; Depietri and McPhearson, 2017; Dorst et al., 2019). Figure 2 depicts a distinct range of ecosystem and natural capital-based approaches under the NBS concept (Dhyani et al., 2020). Ecosystems demonstrate a remarkable ability to mitigate the adverse effects of climate-related risks and safeguard communities (Diaz et al., 2015; Lo, 2016).
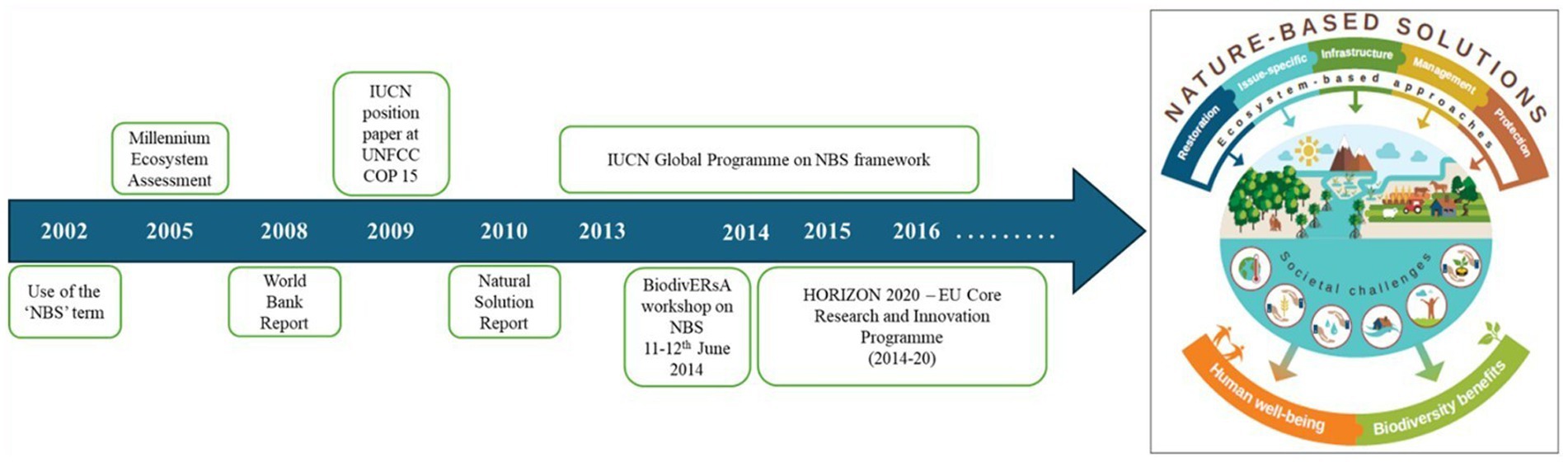
Figure 1. Milestones in the development of NBS concept [adapted from Cohen-Shacham et al. (2016)].
NBS encompass the use of natural processes and ecosystems to create infrastructure, provide services, and develop comprehensive strategies to enhance urban resilience. World Bank identifies some NBS typologies like urban forests, urban farming, green corridors, river and stream renaturation, river floodplains, bioretention areas, and wetlands (World Bank, 2021). These approaches typically transcend traditional boundaries and necessitate collaborative efforts across various sectors. Nature-based solutions offer diverse advantages for cities, such as mitigating disaster risks, strengthening climate resilience, ensuring food-water security, promoting biodiversity restoration, and overall community well-being. Numerous terminologies under nature-based concepts have been developed in different parts of the world, such as ‘green infrastructure’ (GI), ‘blue-green infrastructure’ (BGI), ‘natural infrastructure’ (NI), ‘low impact development’ (LID), and ‘ecosystem-based adaptation’ (EBA). The terms NBS, GI, BGI, LID, EBA and sustainable measures are interchangeably used in the present study.
3.2 Integration of NBS measures across a range of spatial scales
There is a hierarchy of approaches for implementing the NBS umbrella concept as strategic planning, i.e., ‘protection and sustainable management of existing natural infrastructure’, ‘restoration and rehabilitation of degraded one’ and then ‘creation of new NBS’ (Cohen-Shacham et al., 2019). It is essential to consider this hierarchy when identifying and prioritizing nature-based solutions opportunities at a strategic level, such as when evaluating investment options for a city. These three approaches must be applied to plan and prepare NBS projects across various spatial scales. Generally, NBS is implemented at three spatial scales – neighborhood scale, city scale and river basin scale. At each scale, various NBS families can be implemented. For instance, floodplain restoration projects that restore natural hydraulic and hydrological connectivity can effectively mitigate flood hazards at the river basin level, while green roofs and bioswales can be strategically designed for implementation at the neighborhood scale (Liberalesso et al., 2020; Puchol-Salort et al., 2021). Measures (like urban forests, constructed wetlands and rivers and streams renaturation) at the city scale aim to enhance urban land use planning and strengthen the city’s disaster risk management. Figure 3 depicts the schematic section of NBS at the neighborhood, city, and river basin scales.

Figure 3. Schematic section of NBS at different scales [adapted from World Bank (2021)].
3.3 Methodology
The study presents a constructive exploration of NBS and its associated ecosystem services, featuring a range of successful regional implementations, as shown in Table 2. The reviewed literature included technical reports, project summaries, academic publications, government publications, conference proceedings, and resources from web search engines and academic databases (‘Web of Sciences’ and ‘Scopus’) for regional and city-scale NBS interventions. Search keywords include various NBS measures – green corridors, green roofs, urban forests and parks, urban agriculture, bioswales, rain gardens, retention ponds, permeable pavements, natural wetlands, constructed wetlands, stream renaturation and floodplain restoration. Further, five long-term city-scale NBS projects were selected to gain a worldwide perspective and foster the development of resilient cities in India (as mentioned in section 3.5). The number of NBS measures adopted simultaneously and the wide range of ecosystem services were used as selection criteria for the city-scale NBS exemplars examined in the study. It is worth mentioning that while no formal surveys were conducted with city officials, the findings still offer valuable insights for future discussions and research in the context of the development of resilient cities in India.
3.4 Ecosystem services and SDGs linked to NBS
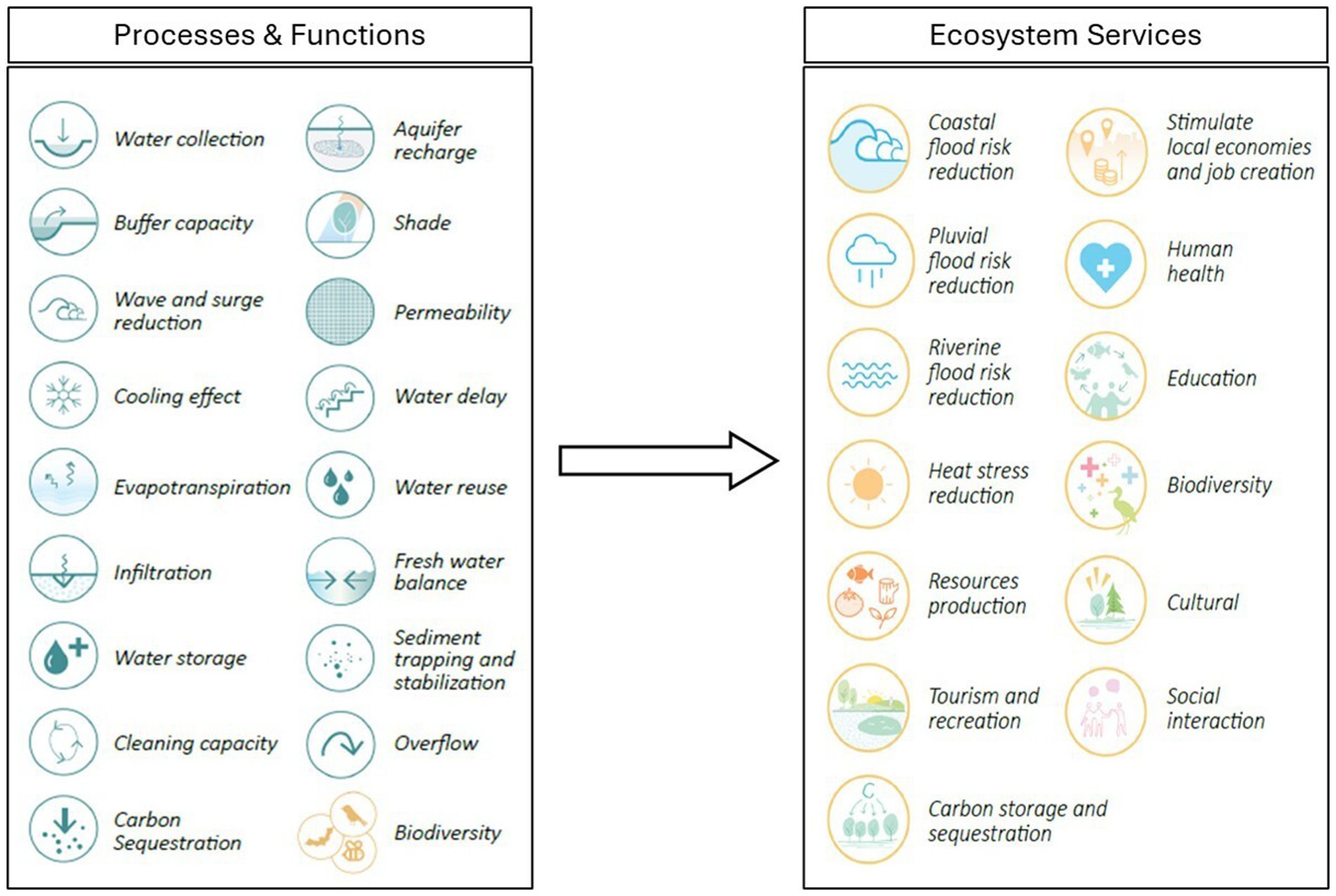
The natural ecosystem can deliver multiple environmental and socio-economic benefits, which are called ecosystem services. Figure 4 depicts the pertinent processes related to ecosystem services for urban resilience. A few major ecosystem services related to NBS are briefly discussed below, along with the role of NBS in achieving SDGs.
3.4.1 Stormwater management and flood risk mitigation
Cities worldwide face the challenges of stormwater management and flood risk management (pluvial, fluvial or coastal), depending on the rainfall patterns, urbanization-induced LULC transitions, location (riverine, coastal, mountainous), and population growth. Considering the rise in impervious surfaces and increased extreme weather events, NBS can be implemented in the cities to mitigate the risks due to floods and combined sewer overflow (CSO) events by promoting infiltration and evapotranspiration (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), 2010; Shakya and Ahiablame, 2021; Ahmad and Hassan, 2024). Reducing the volume of stormwater entering the sewer system during rain events can alleviate pressure on the sewer system. A study related to flood regulation in three Australian capital city regions, SEQ, Melbourne and Perth, emphasizes the importance of green open spaces (Victoria State Government (VSG), 2017; Schuch et al., 2017). Similarly, in a study from Taichung City in Taiwan, different NBS measures (infiltration ponds, infiltration swales, and rain barrels) were evaluated using the stormwater management model (SWMM), showing the reduced annual runoff by 43.5–54.5 percent (Lin et al., 2018).
3.4.2 Urban heat island (UHI) mitigation
In urban areas, buildings and paved surfaces change thermal properties and radiative behavior compared to natural surroundings, creating distinct environmental impacts. These surfaces absorb solar radiation, contributing to elevated surface and ambient temperatures in urban areas as compared to rural areas, creating what is known as an “urban heat island” effect (Arrau and Peña, 2011; Killingsworth et al., 2011). The urban heat island phenomenon can lead to health issues such as heat stroke and even death during heat waves (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), 2003). Due to this effect, cities across the globe are becoming warmer than surrounding suburban areas in the summer. Implementing measures like green roofs and trees can lower temperatures through evapotranspiration, helping to mitigate urban heat island effects and improve public health (Killingsworth et al., 2011; Pitman et al., 2015). For instance, a study assessing the benefits and costs of green roofs in Toronto has shown that widespread adoption of green roofs could reduce local ambient air temperatures by 0.5°C to 2°C (Banting et al., 2005).
3.4.3 Improved water quality and groundwater recharge
NBS practices, such as green infrastructure (GI) measures, have proven effective in enhancing the quality of stormwater runoff. GI measures work by slowing down and filtering the polluted runoff before it enters adjacent water bodies such as lakes and rivers (Liu et al., 2015; Brumley et al., 2018; Yu and Li, 2023). Additionally, NBS include a range of measures (shown in Table 2) to improve water quality and promote groundwater replenishment (Brumley et al., 2018; Natural Resource Defence Council (NRDC), 2022). For instance, the restoration project of Genetta Park and Genetta Stream in Montgomery, in the United States, has been creating positive impacts on the Genetta Stream by mitigating downstream floods, improving water quality, enhancing stream biodiversity, and promoting groundwater recharge.
3.4.4 Improved air quality
Nature-based measures (such as green roofs, rain gardens, green facades, and green roads) are vital in mitigating air pollution, reducing emissions, and extending the distance between pollution sources and receptors (Hewitt et al., 2020). Vegetation enhances air quality by filtering out airborne pollutants and toxic gases, such as particulate matter (PM10) and ozone (O3). Additionally, the adoption of green infrastructure practices under NBS strategies in buildings leads to reduced energy consumption, which in turn helps improve air quality by lowering the emission of sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) (Yang et al., 2005; Wang et al., 2014). The Blue Green Wave is a one-hectare green roof, the largest in the entire Paris region in France, improving air quality with other ecosystem services like stormwater management and UHI mitigation (Brown and Mijic, 2019). Such initiatives have also been seen in Asian countries at different scales, like the Centenary Park in Bangkok, Thailand and ‘pocket parks’ in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia (Holmes, 2019; Hamel and Tan, 2022).
3.4.5 Recreation and community well-being
Recent studies highlight the significance of GI measures under NBS strategies in urban areas for providing essential ecosystem services. GI measures use natural processes for infrastructure development and land use planning to promote economic and social development (Osei et al., 2022). Incorporating GI practices like urban parks, forests, green roofs, streams, ponds, swales, wetlands and community gardens into new developments and urban renewal projects to create new green spaces has been proven to enhance community liveability and offer opportunities for recreational activities, thereby contributing to improved public health and well-being (Wolch et al., 2014; Pamukcu-Albers et al., 2021).
3.4.6 Achieving SDG targets through NBS
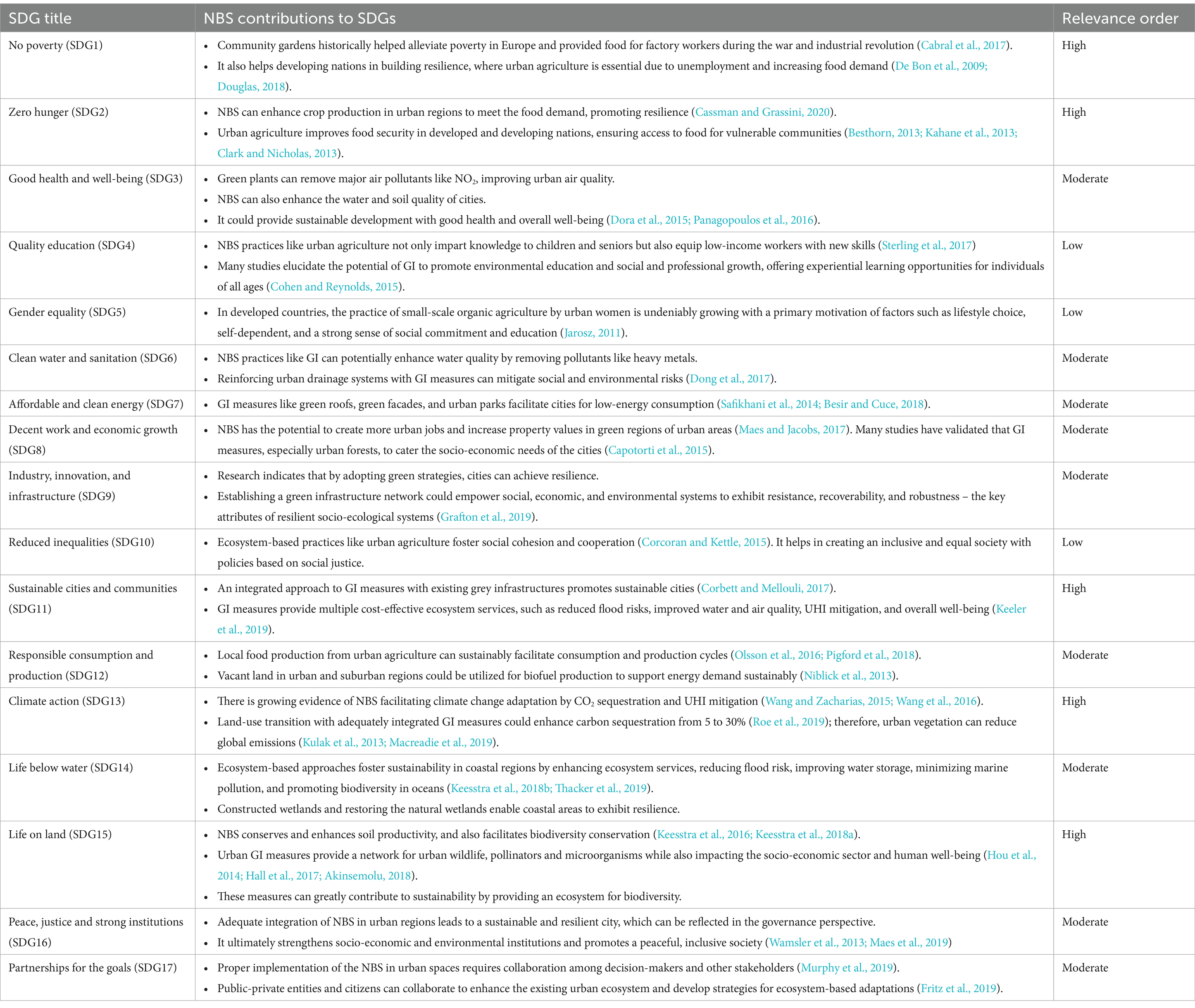
The effective adaptation of NBS diminishes urban susceptibility to climate-related risks and contributes to attaining the United Nations’ SDGs (Mahmoud et al., 2022; Kiribou et al., 2024). Acharya et al. (2020) investigated new methods to improve nature-based approaches to accomplish SDGs while focusing on transformative strategies and outlining responsibilities for communities, private sectors, and government organizations. Lombardía and Gómez-Villarino (2023) conducted a systematic review demonstrating how GI measures can facilitate SDGs in metropolitan regions and emphasized the need for increased support from policymakers and urban planners. Most SDGs are interconnected and mutually reinforce each other in various ways. An Australian study revealed that achieving 100% of the SDGs by 2030 is a significant challenge, but it is projected to achieve 70% (Allen et al., 2019). Table 3 summarizes the role of NBS in achieving all the SDGs and their varying relative importance (High >60%, moderate 30–60%, and low <30%), and each contribution is supported by a range of references. NBS directly contributes to SDG3, SDG6, SDG11, SDG13, and SDG15 by providing multiple cost-effective urban ecosystem services.
3.5 NBS in practice on the ground: key lessons learnt from the exemplars across the globe
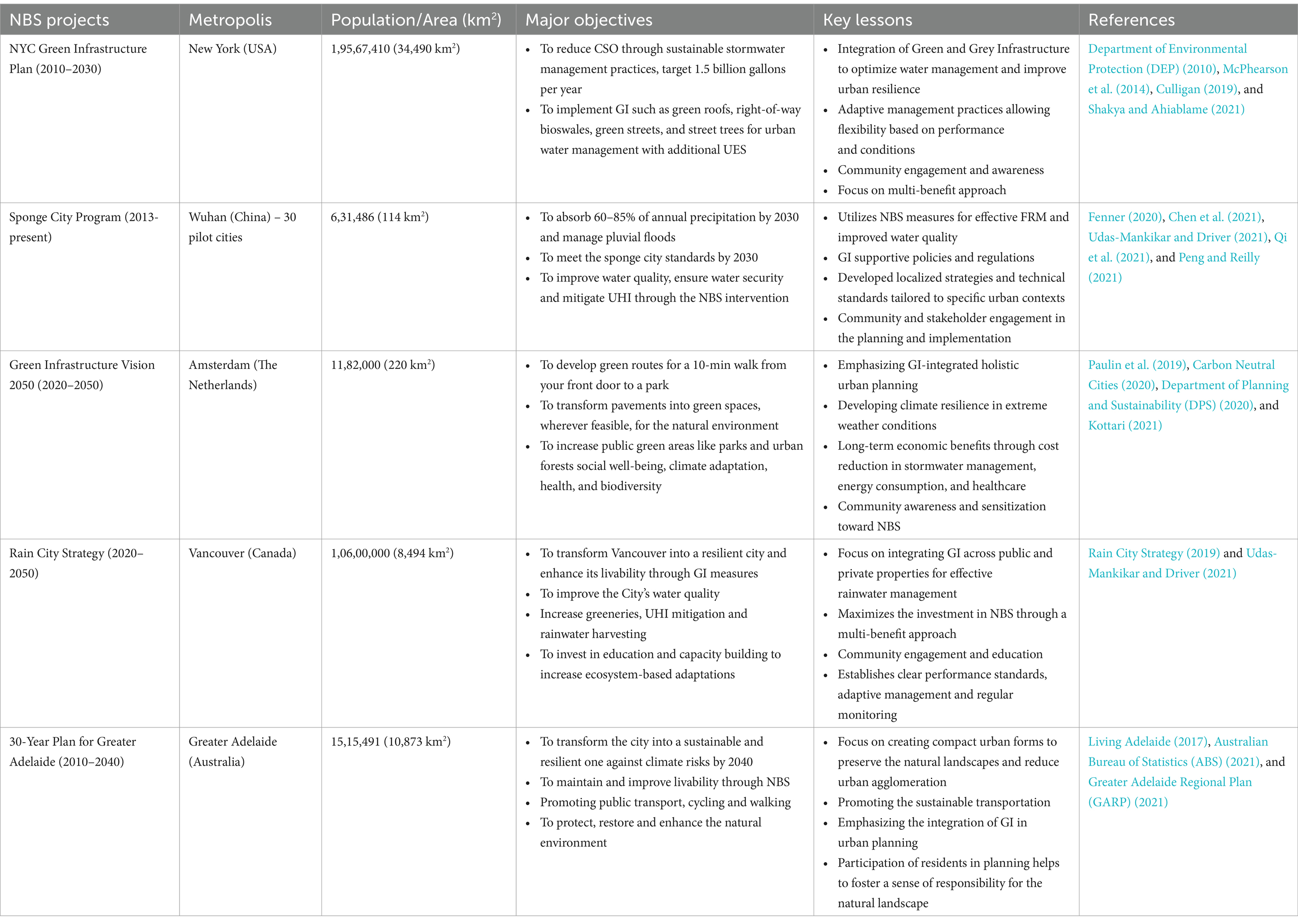
In recent decades, there has been a growing trend toward using nature-based solutions for sustainable and resilient cities. Countries like the United States, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Germany, and many more have seen notable success in managing urban pressures through nature-based practices. The European countries have tremendously succeeded in developing the NBS strategies for urban resilience. In Asia, countries like China, Malaysia, Singapore, Japan and Thailand have also been working on the NBS implementation for various urban ecosystem services for a long time. As research into nature-based intervention expands, many such projects have been launched and completed successfully in cities worldwide. Therefore, five NBS projects from different countries (USA, Canada, The Netherlands, China, and Australia) have been selected to understand a worldwide perspective. All the selected projects have been critically analyzed, and their major objectives and the key lessons learnt have been presented in Table 4. The key learnings from these city-scale NBS projects include the effective combination of green and grey infrastructure to optimize urban water management and enhance urban resilience, implementing adaptive management practices, community engagement and awareness, and a strong emphasis on a multi-benefit approach.
4 Addressing the viabilities for NBS implementation in Indian cities
4.1 Challenges in NBS intervention in the cities of India
As the demand for resilient cities grows and NBS intervention plans are being developed, several challenges have emerged in implementing NBS in urban areas. These challenges span technical, social, and institutional factors. Indian cities face unique urban pressures due to their diverse socio-economic culture, demography, and climate. Despite the vital role of blue and green spaces for the environment and community well-being, these natural spaces are decreasing, and impermeable surfaces are rising in the cities. Analyzing the factors responsible for increasing urban pressures in Indian cities, some of the major challenges in NBS intervention that need to be addressed are as follows.
4.1.1 Degrading natural landscapes in cities and limited space
Rapid and unplanned urbanization has reduced the blue and green spaces (waterbodies and vegetation) in many Indian cities over time. The older cities (like Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, and Bengaluru) have grappled with rampant urbanization and high population density. These factors create urban pressures like UHI and declined natural urban drainage, posing significant challenges for the existing combined sewer system. Designing and remodeling separate sewer systems with sustainable drainage measures or any NBS measures at the city scale in high-density areas will be intricate. This limitation of natural spaces hinders the integration of various nature and ecosystem-based measures such as urban parks, gardens, lakes, retention ponds, and wetlands within the city. Furthermore, implementing NBS at the building scales (like blue-green roofs, urban agriculture and rainwater harvesting measures) for other urban ecosystem services is also quite challenging due to unplanned settlements within and around the cities.
4.1.2 Climate and hydrology
Specific BGI measures can exhibit performance limitations due to varying climatic and hydrological behavior in different parts of the country. For instance, coastal cities with shallow groundwater levels will face challenges in implementing infiltration-based GI measures like bioswales and rain gardens. Cities with a minor rainy season and limited water resources may increase their water demand due to the water requirements of the crops, thereby limiting the use of green roofs, urban farming, and other vegetation-based infrastructures.
4.1.3 Limited NBS research and uncertainties
Due to the existing knowledge gaps and limited research on nature-based solutions in India, there are uncertainties regarding the hydrologic and ecologic performance of NBS. The lack of understanding and research regarding the adaptation of ecosystem-based approaches in India might result in initial resistance from urban planners and local authorities, who might overlook the potential ecosystem services linked to green infrastructure and other ecosystem-based strategies. Limited research with insufficient data also hinders NBS intervention on a city or river basin scale, creating uncertainty regarding the effectiveness of NBS, i.e., which approach would yield immediate versus sustained results.
4.1.4 Socio-economic constraints
Recent studies have provided more useful insights into the socio-economic constraints of non-traditional measures in urban development (Almaaitah et al., 2021; Mumtaz, 2021). Lack of community awareness and challenges in the economic valuation of the ecosystem services can create difficulties in justifying investments in nature-based approaches, especially compared to traditional methods. Apart from a social reluctance to support novel practices due to the lack of awareness, implementing NBS measures (like green roofs, urban agriculture, and rainwater harvesting) can be costly and challenging for retrofitting in dense urban agglomerations.
4.1.5 Lack of enforceable standards at the policymaking and planning level
The Government of India has taken significant steps to tackle urban transformation through the “Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation” (AMRUT) program. The program focuses on enhancing urban infrastructure in 500 cities, emphasizing areas such as stormwater drainage, water supply, sewerage, green spaces, and public transport (Gupta, 2020). ‘Smart City Mission’ is also an initiative emphasizing sustainable solutions for urban development. Nevertheless, there remains a need for enforceable standards for incorporating NBS with proper specifications at the planning and policy-making stage. The government needs to create a statutory body by institutionalizing the NBS framework, which will ensure the implementation of the projects at the local level with specific standards.
4.2 Overcoming the challenges in NBS intervention in India from a global perspective
Various studies have been conducted worldwide to develop strategies to address the challenges (social, institutional and technical) associated with NBS interventions. Financial constraints are recognized as an institutional challenge. Studies highlight that social and institutional barriers tend to outweigh technical barriers (O’Donnell et al., 2017; Thorne et al., 2018; O’Donnell et al., 2021). Case studies of numerous cities emphasize the importance of a comprehensive approach to overcome these challenges. It is crucial to raise awareness, secure diverse funding sources, integrate green infrastructures into new developments, and increase overall funding for nature-based projects within cities (Iojă et al., 2018; O’Donnell et al., 2021). Drawing insights from multiple studies and frameworks addressing the challenges in NBS intervention in urban areas worldwide (O’Donnell et al., 2017; Melville-Shreeve et al., 2018; Amaral et al., 2021; Toxopeus and Polzin, 2021; Suleiman, 2021; Castelo et al., 2023), six key steps have been identified for formulating strategies to tackle the implementation challenges in India. These steps include – (a) amending legislation and developing the policies to establish guidelines for nature-based measures with specific standards, (b) highlighting and promoting the numerous co-benefits of NBS-integrated multifunctional spaces, (c) encouraging collaborative efforts from research and planning to execution (d) increasing awareness through education, community events, and activities, (e) securing sustainable funding by involving the private sector (f) promoting the advanced scientific research on retrofitting NBS measures in existing urban settings and creating new ones.
Researchers also presented the strategies at various stakeholder levels to conceptualize and streamline the framework for NBS intervention (Qiao et al., 2018; Landscape Institute and the Construction Industry Council (LI and CIC), 2019; O’Donnell et al., 2020). Similarly, the stakeholders can be selected to institutionalize the NBS in the urban landscapes in India. It will define a framework at each stakeholder level to overcome these challenges. These stakeholders include the central government, state governments, academia, practitioners, and individuals. The central government should acknowledge the benefits of NBS and promote its nationwide adoption by revising legislation, establishing technical standards, empowering states to create regional policies, and facilitating collaborative research. State governments should promote the benefits of blue-green infrastructures at the local level, invest in outreach programs to educate communities, develop policies for adoption and maintenance, and secure funding through private-sector collaboration.
Taking on financial constraints and investing in blue-green infrastructure necessitates a proactive approach, including conducting a thorough cost–benefit analysis. For example, developing a robust framework to assess the socioeconomic impact of a flood event can provide valuable insights for comparing the economic benefits of blue-green infrastructure to the local community and the investors. The role of academia and practitioners in the development of strategies to overcome technical and financial issues is inevitable. The academia should enhance scientific understanding of the nature-based approaches through rigorous collaborative research with international organizations to fill the knowledge gaps and provide evidence regarding the hydrological and ecological performance of NBS. Researchers can also advocate for policy changes that support the implementation of NBS by publishing the research outcomes. With the collaboration of academia, practitioners need to develop low-maintenance blue-green infrastructure measures, assess their suitability for regional environments, create open-source toolkits to assess and monetize the ecosystem services and raise public awareness about the co-benefits. Assessing the ecosystem services and further monetizing them will also draw the attention of the private sector to invest in nature-based projects for urban sustainability and resilience.
Citizen engagement can facilitate cities through the problem-based model to identify the local challenges, connect people with nature and increase the sense of ownership of NBS-intervened places to overcome the challenges. Communities working with natural processes and systems can facilitate better adaptability of nature-based projects (Brown and Mijic, 2019). Individuals should take part in local stewardship efforts for nature conservation, actively engage in the ongoing NBS projects, provide valuable support, and strive for sustainable development. Encouraging behavior change among fellow citizens is also important, as it raises awareness about the multifaceted NBS-integrated urban spaces.
5 Conclusion
The study emphasizes the declining natural LULC in Indian urban landscapes and the urgent need for sustainable and resilient cities. NBS has gained recognition for enhancing urban resilience, addressing environmental and climate challenges, and promoting community well-being and biodiversity. NBS offers various ecosystem services (such as flood risk mitigation, improved water and air quality, urban heat island mitigation, and resource efficiency). The present study provides a detailed analysis of the ecosystem services linked to NBS, focusing on how these ecosystem-based strategies can facilitate SDGs.
To explore the potential integration of NBS in India, five exemplary NBS projects from different countries have been analyzed – NYC Green Infrastructure Plan (USA), Sponge City Program (China), Green Infrastructure Vision (The Netherlands), Rain City Strategy (Canada), 30-Year Plan for Greater Adelaide (Australia). Learning from global initiatives can be a significant step toward developing ecosystem-based strategies to understand and address the resilience challenges against the increasing urban pressures in Indian cities. The valuable insights drawn from these city-scale projects highlight the integration of green and traditional infrastructure for improved urban water management and enhanced urban resilience. Additionally, these projects emphasize the significance of employing adaptive management techniques, fostering community involvement and awareness, and prioritizing a multi-faceted approach to achieve multiple benefits.
Various challenges (technical, social, and institutional) related to NBS intervention in Indian cities have also been discussed. Limited research exists to compare the effectiveness of NBS with traditional grey infrastructure alternatives. Comprehensive research on nature-based solutions, particularly implementation and suitability consideration frameworks, is very much needed in India. It will be instrumental in quantifying the environmental benefits, facilitating urban water management, and developing climate change adaptation and mitigation strategies. It will also support the formulation of ecosystem-based policies and encourage investment from the private sector. Moreover, introducing NBS during the planning and policymaking phase, setting clear standards for NBS deliverables, encouraging stakeholders’ participation and collaborative efforts, and ensuring practical implementation can maximize ecosystem services, enhancing sustainable development, economic growth, and urban resilience.
Author contributions
NA: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QH: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the reviewers for their constructive comments.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Acharya, P., Gupta, A. K., Dhyani, S., and Karki, M. (2020). “New pathways for NbS to realise and achieve SDGs and post 2015 targets: transformative approaches in resilience building” in Nature-based solutions for resilient ecosystems and societies. Disaster Resilience and Green Growth. eds. S. Dhyani, A. Gupta, and M. Karki (Singapore: Springer).
Agaton, C. B., and Guila, P. M. C. (2023). Ecosystem services valuation of constructed wetland as a nature-based solution to wastewater treatment. Earth 4, 78–92. doi: 10.3390/earth4010006
Ahmad, N., and Hassan, Q. (2021). An engineered and sustainable solution for flood and sediment Management in Kosi River, India. J Ecol Nat Resour 5:258. doi: 10.23880/jenr-16000258
Ahmad, N., and Hassan, Q. (2024). “Enhancing blue-green infrastructures for flood and water stress management: A case study of Chennai” in Recent developments in water resources and transportation engineering. TRACE 2022. Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering. eds. N. Nagabhatla, Y. Mehta, B. K. Yadav, A. Behl, and M. Kumari, vol. 353 (Singapore: Springer).
Akinsemolu, A. A. (2018). The role of microorganisms in achieving the sustainable development goals. J. Clean. Prod. 182, 139–155. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.02.081
Akter, S., and Gupta, B. (2022). Case studies in urban agriculture – A monograph by sustainable urban food systems class/group (2021–22). Available online at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/360354060
Albert, C., Spangenberg, J. H., and Schröter, B. (2017). Nature-based solutions: criteria. Nature 543:315. doi: 10.1038/543315b
Allen, C., Metternicht, G., Wiedmann, T., and Pedercini, M. (2019). Greater gains for Australia by tackling all SDGs but the last steps will be the most challenging. Nat Sustain 2, 1041–1050. doi: 10.1038/s41893-019-0409-9
Almaaitah, T., Appleby, M., Rosenblat, H., Drake, J., and Joksimovic, D. (2021). The potential of blue-green infrastructure as a climate change adaptation strategy: a systematic literature review. Blue-Green Syst. 3, 223–248. doi: 10.2166/bgs.2021.016
Amaral, M. H., Benites-Lazaro, L. L., de Almeida, A., Sinisgalli, P., da Fonseca, P., Alves, H., et al. (2021). Environmental injustices on green and blue infrastructure: urban nexus in a macrometropolitan territory. J. Clean. Prod. 289:125829. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.125829
Arrau, C. P., and Peña, M. A. (2011). The urban Heat Island (UHI) Effect. Available online at: http://www.urbanheatislands.com/
Artmann, M., and Sartison, K. (2018). The role of urban agriculture as a nature-based solution: A review for developing a systemic assessment framework. Sustain. For. 10:1937. doi: 10.3390/su10061937
Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS). (2021). Greater Adelaide Census Data, South Australia. Available online at: https://www.abs.gov.au/census/
Balian, E., Eggermont, H., and Le Roux, X. (2014). BiodivERsA: BiodivERsA workshop on nature-based solutions. Available online at: http://www.biodiversa.org/671
Banting, D., Doshi, H., Li, J., Missios, P., Au, A., Currie, B. A., et al. (2005). Report on the environmental benefits and costs of green roof Technology for the City of Toronto; City of Toronto and Ontario Centres of excellence—Earth and environmental technologies. Toronto, ON: Ryerson University.
Besir, A. B., and Cuce, E. (2018). Green roofs and facades: a comprehensive review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 82, 915–939. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.09.106
Besthorn, F. H. (2013). Vertical farming: social work and sustainable urban agriculture in an age of global food crises. Aust. Soc. Work. 66, 187–203. doi: 10.1080/0312407X.2012.716448
Bondwal, R. S., and Bisht, N. S. (2019). A temporal data analysis to identify land cover change trends in NCT Delhi. 2019. International conference on machine learning, big data, cloud and parallel computing (COMITCon).
Bozovic, R., Maksimovic, C., Mijic, A., Smith, K. M., Suter, I., and Van Reeuwijk, M. (2017) Blue green solutions. A systems approach to sustainable, resilient and cost-efficient urban development.
Brown, K., and Mijic, A. (2019). Integrating green and blue spaces into our cities: Making it happen. Grantham institute briefing paper, no 30. London: Imperial College London.
Brumley, J., Marks, C., Chau, A., Lowrance, R., Huang, J., Richardson, C., et al. (2018). The influence of green infrastructure practices on groundwater quality: the state of the science. Washington, DC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Cabral, I., Keim, J., Engelmann, R., Kraemer, R., Siebert, J., and Bonn, A. (2017). Ecosystem services of allotment and community gardens: a Leipzig, Germany case study. Urban For. Urban Green. 23, 44–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2017.02.008
Capotorti, G., Mollo, B., Zavattero, L., Anzellotti, I., and Celesti-Grapow, L. (2015). Setting priorities for urban forest planning. A comprehensive response to ecological and social needs for the metropolitan area of Rome (Italy). Sustainability 7, 3958–3976. doi: 10.3390/su7043958
Carbon Neutral Cities. (2020). https://carbonneutralcities.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/Amsterdam-Green-Infrastructure-Vision-2050toegankelijk02092020.pdf
Cassman, K. G., and Grassini, P. (2020). A global perspective on sustainable intensification research. Nat Sustain 3, 262–268. doi: 10.1038/s41893-020-0507-8
Castelo, S., Amado, M., and Ferreira, F. (2023). Challenges and opportunities in the use of nature-based solutions for urban adaptation. Sustain. For. 15:7243. doi: 10.3390/su15097243
Chen, S., van de Ven, F. H. M., Zevenbergen, C., Verbeeck, S., Ye, Q., Zhang, W., et al. (2021). Revisiting China’s Sponge City planning approach: lessons from a case study on Qinhuai District, Nanjing. Front. Environ. Sci. 9:748231. doi: 10.3389/fenvs.2021.748231
Clark, K. H., and Nicholas, K. A. (2013). Introducing urban food forestry: a multifunctional approach to increase food security and provide ecosystem services. Landsc. Ecol. 28, 1649–1669. doi: 10.1007/s10980-013-9903-z
Cohen, N., and Reynolds, K. (2015). Resource needs for a socially just and sustainable urban agriculture system: Lessons from new York City. Renew Agric Food Syst 30, 103–114. doi: 10.1017/S1742170514000210
Cohen-Shacham, E., Andrade, A., Dalton, J., Dudley, N., Jones, M., Kumar, C., et al. (2019). Core principles for successfully implementing and upscaling nature-based solutions. Environ. Sci. Pol. 98, 20–29. doi: 10.1016/j.envsci.2019.04.014
Cohen-Shacham, E., Walters, G., Janzen, C., and Maginnis, S. (Eds.) (2016). Nature-based solutions to address global societal challenges. Gland, Switzerland: IUCN, xiii.
Corbett, J., and Mellouli, S. (2017). Winning the SDG battle in cities: how an integrated information ecosystem can contribute to the achievement of the 2030 sustainable development goals. Inf. Syst. J. 27, 427–461. doi: 10.1111/isj.12138
Corcoran, M. P., and Kettle, P. C. (2015). Urban agriculture, civil interfaces and moving beyond difference: the experiences of plot holders in Dublin and Belfast. Local Environ. 20, 1215–1230. doi: 10.1080/13549839.2015.1038228
Culligan, P. J. (2019). Green infrastructure and urban sustainability: A discussion of recent advances and future challenges based on multiyear observations in New York City. Sci. Technol. Built Environ. 25, 1113–1120. doi: 10.1080/23744731.2019.1629243
De Bon, H., Parrot, L., and Moustier, P. (2009). Sustainable urban agriculture in developing countries: A review. Sustain Agric 30, 619–633. doi: 10.1007/978-90-481-2666-8_38
Department of Environmental Protection (DEP). (2010). NYC green infrastructure plan: A sustainable strategy for clean waterways. Available online at: https://www1.nyc.gov/assets/dep/downloads/pdf/water/stormwater/green-infrastructure/nyc-green-infrastructure-plan-2010.pdf
Department of Planning and Sustainability (DPS). (2020). Amsterdam green infrastructure vision 2050 – A liveable city for people, plants, and animals. City of Amsterdam, The Netherlands. Available online at: https://www.amsterdam.nl/en/policy/policy-green-space
Depietri, Y., and McPhearson, T. (2017). “Integrating the grey, green, and blue in cities: nature-based solutions for climate change adaptation and risk reduction” in Nature-based solutions to climate change adaptation in urban areas. eds. N. Kabisch, H. Korn, J. Stadler, and A. Bonn (New York: Springer), 91–109.
Dhyani, S., Karki, M., and Gupta, A. K. (2020). “Opportunities and advances to mainstream nature-based solutions in disaster risk management and climate strategy” in Nature-based solutions for resilient ecosystems and societies. eds. S. Dhyani, A. Gupta, and M. Karki (Singapore: Disaster Resilience and Green Growth, Springer).
Diaz, S., Demissew, S., Joly, C., Lonsdale, W. M., and Larigauderie, A. (2015). A Rosetta stone for nature’s benefits to people. PLoS Biol. 13:e1002040. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1002040
Dong, X., Guo, H., and Zeng, S. (2017). Enhancing future resilience in urban drainage system: green versus grey infrastructure. Water Res. 124, 280–289. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2017.07.038
Dora, C., Haines, A., Balbus, J., Fletcher, E., Adair-Rohani, H., Alabaster, G., et al. (2015). Indicators linking health and sustainability in the post-2015 development agenda. Lancet 385, 380–391. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60605-X
Dorst, H., van der Jagt, S., Raven, R., and Runhaar, H. (2019). Urban greening through nature-based solutions—key characteristics of an emerging concept. Sustain. Cities Soc. 49:101620. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2019.101620
Douglas, I. (2018). The challenge of urban poverty for the use of green infrastructure on floodplains and wetlands to reduce flood impacts in intertropical Africa. Landsc. Urban Plan. 180, 262–272. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2016.09.025
European Commission (2021). Evaluating the impact of nature-based solutions: a handbook for practitioners. Luxembourg: Publications office of the European Union.
European Environmental Agency (EEA). (2017). Green infrastructure and flood management: Promoting cost-efficient flood risk reduction via green infrastructure solutions. Copenhagen: European Environmental Agency. Available online at: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/green-infrastructure-and-flood-management
European Environmental Agency (EEA). (2018). The Dutch make Room for the river. Interview with Willem Jan Goossen. Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management. The Hague, Netherlands. Available online at: https://www.eea.europa.eu/signals/signals-2018-content-list/articles/interview-2014-the-dutch-make
Fenner, R. (2020). Urban flood resilience – philosophical transactions of the Royal Society A. London: The Royal Society Publishing.
Fritz, S., See, L., Carlson, T., Haklay, M., Oliver, J. L., Fraisl, D., et al. (2019). Citizen science and the United Nations sustainable development goals. Nat Sustain 2, 922–930. doi: 10.1038/s41893-019-0390-3
Ganapathi, H., Awasthi, S., and Vasudevan, P. (2024). “Wetlands as a nature-based solution for urban water management” in Nature-based solutions for circular Management of Urban Water. Circular Economy and Sustainability. eds. A. Stefanakis, H. V. Oral, C. Calheiros, and P. Carvalho (Cham: Springer).
Ghofrani, Z., Sposito, V., and Faggian, R. (2017). A comprehensive review of blue-green infrastructure concepts. Int J Environ Sustain 6, 15–36. doi: 10.24102/ijes.v6i1.728
Grafton, R. Q., Doyen, L., Béné, C., Borgomeo, E., Brooks, K., Chu, L., et al. (2019). Realising resilience for decision-making. NatSustain 2, 907–913. doi: 10.1038/s41893-019-0376-1
Greater Adelaide Regional Plan (GARP) (2021). Greater Adelaide Data, 2021, South Australia. Available online at: https://plan.sa.gov.au/regional-planning-program/
Gupta, K. (2020). Challenges in developing urban flood resilience in India. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. A 378:20190211. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2019.0211
Hall, D. M., Camilo, G. R., Tonietto, R. K., Ollerton, J., Ahrné, K., Arduser, M., et al. (2017). The city as a refuge for insect pollinators. Conserv. Biol. 31, 24–29. doi: 10.1111/cobi.12840
Hamel, P., and Tan, L. (2022). Blue-green infrastructure for flood and water quality management in Southeast Asia: evidence and knowledge gaps. Environ. Manag. 69, 699–718. doi: 10.1007/s00267-021-01467-w
Hermawan, A. A., Talei, A., Salamatinia, B., and Chua, L. H. C. (2020). Seasonal performance of stormwater biofiltration system under tropical conditions. Ecol. Eng. 143:105676. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoleng.2019.105676
Hewitt, C. N., Ashworth, K., and MacKenzie, A. R. (2020). Using green infrastructure to improve urban air quality (GI4AQ). Ambio 49, 62–73. doi: 10.1007/s13280-019-01164-3
Holmes, D. (2019). Chulalongkorn University Centenary Park—green infrastructure for the city of Bangkok. World Landscape Architecture. Available online at: https://worldlandscapearchitect.com/chulalongkorn-centenary-park-green-infrastructure-for-the-city-of-bangkok/#.Yg3IpThBzIU
Hou, Y., Zhou, S., Burkhard, B., and Müller, F. (2014). Socioeconomic influences on biodiversity, ecosystem services and human well-being: a quantitative application of the DPSIR model in Jiangsu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 490, 1012–1028. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.05.071
Iojă, I. C., Osaci-Costache, G., Breuste, J., Hossu, C. A., Grădinaru, S. R., Onose, D. A., et al. (2018). Integrating urban blue and green areas based on historical evidence. Urban Forestry Urban Green. 34, 217–225. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2018.07.001
Irvine, K., Sovann, C., Suthipong, S., Kok, S., and Chea, E. (2015). Application of PCSWMM to assess wastewater treatment and urban flooding scenarios in Phnom Penh, Cambodia: a tool to support eco-city planning. J. Water Manag Model. doi: 10.14796/jwmm.c389
Jain, G., and Sarkar, S. (2017). Urban Heat Island: causes effects and mitigating strategies. Imp. J. Interdiscip. Res. 3, 2098–2103.
Jarosz, L. (2011). Nourishing women: toward a feminist political ecology of community supported agriculture in the United States. Gend. Place Cult. 18, 307–326. doi: 10.1080/0966369X.2011.565871
Kahane, R., Hodgkin, T., Jaenicke, H., Hoogendoorn, C., Hermann, M., Dyno Keatinge, J. D. H., et al. (2013). Agrobiodiversity for food security, health and income. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 33, 671–693. doi: 10.1007/s13593-013-0147-8
Kato, S., Hishiyama, K., Darmadi, A. K., Ngurah, A., and Suprapta, D. (2017). Changing roles of traditional small urban green spaces (Telajakan) in Bali, Indonesia. Open J Ecol 7, 1–11. doi: 10.4236/oje.2017.71001
Keeler, B. L., Hamel, P., McPhearson, T., Hamann, M. H., Donahue, M. L., Meza Prado, K. A., et al. (2019). Social-ecological and technological factors moderate the value of urban nature. Nat Sustain 2, 29–38. doi: 10.1038/s41893-018-0202-1
Keerthi-Naidu, B., and Chundeli, F. A. (2023, 2023). Assessing LULC changes and LST through NDVI and NDBI spatial indicators: a case of Bengaluru, India. GeoJournal 88, 4335–4350. doi: 10.1007/s10708-023-10862-1
Keesstra, S. D., Bouma, J., Wallinga, J., Tittonell, P., Smith, P., Cerda, A., et al. (2016). The significance of soils and soil science towards realisation of the United Nations sustainable development goals. Soil 2, 111–128. doi: 10.5194/soil-2-111-2016
Keesstra, S., Mol, G., de Leeuw, J., Okx, J., Molenaar, C., de Cleen, M., et al. (2018a). Soil-related sustainable development goals: four concepts to make land degradation neutrality and restoration work. Land 7. doi: 10.3390/land7040133
Keesstra, S., Nunes, J., Novara, A., Finger, D., Avelar, D., Kalantari, Z., et al. (2018b). The superior effect of nature based solutions in land management for enhancing ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 610-611, 997–1009. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.077
Killingsworth, B., Lemay, L., and Peng, T. (2011). The urban Heat Island effect and Concrete’s role in mitigation. Available online at: http://www.nrmca.org/members/ConcreteInFocus/Enviro%20Library/NRC-S0511_urban.pdf
Kiribou, R., Djene, S., Bedadi, B., Ntirenganya, E., Ndemere, J., and Dimobe, K. (2024). Urban climate resilience in Africa: a review of nature-based solution in African cities' adaptation plans. Discov. Sustain. 5:94. doi: 10.1007/s43621-024-00275-6
Kondratenko, J., Boogaard, F. C., Rubulis, J., and Maļinovskis, K. (2024). Spatial and temporal variability in bioswale infiltration rate observed during full-scale infiltration tests: case study in Riga Latvia. Water 16:2219. doi: 10.3390/w16162219
Kottari, M. (2021). “Amsterdam’s pathway to climate neutrality: creating an enabling environment” in The Palgrave encyclopedia of urban and regional futures (Cham: Palgrave Macmillan).
Kulak, M., Graves, A., and Chatterton, J. (2013). Reducing greenhouse gas emissions with urban agriculture: a life cycle assessment perspective. Landsc. Urban Plan. 111, 68–78. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2012.11.007
Landscape Institute and the Construction Industry Council (LI and CIC) (2019). Achieving Sustainable drainage: A Review of delivery by Lead Local Flood Authorities, January 2019 London, UK. Available online at: https://landscapewpstorage01.blob.core.windows.net/wwwlandscapeinstitute-org/2019/01/11689_LI_SuDS-Report_v4a-Web.pdf (Accessed September 06, 2024)
Li, Y. H., Tung, C. P., and Chen, P. Y. (2017). Stormwater management toward water supply at the community scale – a case study in northern Taiwan. Sustain. For. 9:1206. doi: 10.3390/su9071206
Liberalesso, T., Cruz, C. O., Silva, C. M., and Manso, M. (2020). Green infrastructure and public policies: an international review of green roofs and green walls incentives. Land Use Policy 96:104693. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2020.104693
Lim, H. S., and Lu, X. X. (2016). Sustainable urban stormwater management in the tropics: an evaluation of Singapore’s ABC waters program. J. Hydrol. 538, 842–862. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.04.063
Lin, J.-Y., Chen, C.-F., and Ho, C.-C. (2018). Evaluating the effectiveness of green roads for runoff control. J. Sustain. Water Built. Environ. 4:4018001. doi: 10.1061/JSWBAY.0000847
Liu, A., Goonetilleke, A., and Egodawatta, P. (2015). Role of rainfall and catchment characteristics on urban Stormwater quality. Singapore: Springer.
Living Adelaide. (2017). The 30-year plan for greater Adelaide 2017 update. Department of Planning, Transport and Infrastructure (DPTI) Government of South Australia. Available online at: https://livingadelaide.sa.gov.au/
Lo, V. (2016). Synthesis report on experiences with ecosystem-based approaches to climate change adaptation and disaster risk reduction, technical series no.85. Secretariat of the convention on biological diversity, Montreal, 106.
Lombardía, A., and Gómez-Villarino, M. T. (2023). Green infrastructure in cities for the achievement of the un sustainable development goals: a systematic review. Urban Ecosyst. 26, 1693–1707. doi: 10.1007/s11252-023-01401-4
Macreadie, P. I., Anton, A., Raven, J. A., Beaumont, N., Connolly, R. M., Friess, D. A., et al. (2019). The future of blue carbon science. Nat. Commun. 10, 1–13. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11693-w
Maes, J., and Jacobs, S. (2017). Nature-based solutions for Europe’s sustainable development. Conserv. Lett. 10, 121–124. doi: 10.1111/conl.12216
Maes, M. J. A., Jones, K. E., Toledano, M. B., and Milligan, B. (2019). Mapping synergies and trade-offs between urban ecosystems and the sustainable development goals. Environ. Sci. Pol. 93, 181–188. doi: 10.1016/j.envsci.2018.12.010
Mahmoud, I. H., Morello, E., Rizzi, D., and Wilk, B. (2022). “Localizing sustainable development goals (SDGs) through co-creation of nature-based solutions (NBS)” in The Palgrave encyclopedia of urban and regional futures (Cham: Palgrave Macmillan).
Maryati, S., and Humaira, A. N. S. (2017). Implementation of green infrastructure concept in citarum watershed. In: Proceedings of the AIP conference proceedings. College Park, MD: American Institute of Physics Inc., 20031.
Mathan, M., and Krishnaveni, M. (2020). Monitoring spatio-temporal dynamics of urban and peri-urban land transitions using ensemble of remote sensing spectral indices—a case study of Chennai metropolitan area, India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 192:15. doi: 10.1007/s10661-019-7986-y
McPhearson, T., Hamstead, Z., and Kremer, P. (2014). Urban ecosystem Services for Resilience Planning and Management in new York City. Ambio ;43:502–515.
Melville-Shreeve, P., Cotterill, S., Grant, L., Arahuetes, A., Stovin, V., Farmani, R., et al. (2018). State of SuDS delivery in the United Kingdom. Water Environ. J. 32, 9–16. doi: 10.1111/wej.12283
Mentens, J., Raes, D., and Hermy, M. (2006). Green roofs as a tool for solving the rainwater runoff problem in the urbanized 21st century? Landsc. Urban Plan. 77, 217–226. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2005.02.010
Montgomery County Planning Commission (MCPC) (2011). Planning by design: green parking lots. Montgomery County, the state of Maryland, United States of America (USA). Available online at: https://www.montcopa.org/DocumentCenter/View/3017/GreenParking08292011
Mumtaz, M. (2021). Role of civil society organizations for promoting green and blue infrastructure to adapting climate change: evidence from Islamabad city, Pakistan. J. Clean. Product. 309:127296. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127296
Murphy, A., Enqvist, J. P., and Tengö, M. (2019). Place-making to transform urban social–ecological systems: insights from the stewardship of urban lakes in Bangalore India. Sustain. Sci. 14, 607–623. doi: 10.1007/s11625-019-00664-1
Naikoo, M. W., Rihan, M., Ishtiaque, M., and Shahfahad, M. (2020). Analyses of land use land cover (LULC) change and built-up expansion in the suburb of a metropolitan city: Spatio-temporal analysis of Delhi NCR using landsat datasets. J. Urban Manag. 9, 347–359. doi: 10.1016/j.jum.2020.05.004
Naikoo, M. W., Shahfahad,, Talukdar, S., das, T., Ahmad, M., Ishtiaque, M., et al. (2023). “Land use land cover change modeling and future simulation in Mumbai City by integrating cellular automata and artificial neural network” in Advancements in urban environmental studies. GIScience and geo-environmental modelling. eds. A. Rahman, S. Sen Roy, and S. Talukdar (Cham: Springer).
Natural Resource Defence Council (NRDC) (2022). Green infrastructure: how to manage water in a sustainable way. Available online at: https://www.nrdc.org/stories/green-infrastructure-how-manage-water-sustainable-way
Niblick, B., Monnell, J. D., Zhao, X., and Landis, A. E. (2013). Using geographic information systems to assess potential biofuel crop production on urban marginal lands. Appl. Energy 103, 234–242. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.09.036
Norton, B. A., Coutts, A. M., Livesley, S. J., Harris, R. J., Hunter, A. M., and Williams, N. S. G. (2015). Planning for cooler cities: a framework to prioritise green infrastructure to mitigate high temperatures in urban landscapes. Landsc. Urban Plan. 134, 127–138. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2014.10.018
O’Donnell, E. C., Lamond, J. E., and Thorne, C. R. (2017). Recognising barriers to implementation of blue-green infrastructure: a Newcastle case study. Urban Water J. 14, 964–971. doi: 10.1080/1573062X.2017.1279190
O’Donnell, E. C., Maskrey, S., Skenderian, M., O’Brien, H., and Vann, J. (2020). Overcoming barriers to innovation in urban flood risk management. Blue–Green Cities, 15–35. doi: 10.1680/bgc.64195.015
O’Donnell, E. C., Netusil, N. R., Chan, F. K. S., Dolman, N. J., and Gosling, S. N. (2021). International perceptions of urban blue-green infrastructure: a comparison across four cities. Water 13:544. doi: 10.3390/w13040544
O’Donnell, E. C., Thorne, C., and Yeakley, J. A. (2019). Managing urban flood risk in blue-green cities: the clean water for all initiative. J. Flood Risk Manag. 12. doi: 10.1111/jfr3.12513
Olsson, E. G. A., Kerselaers, E., Kristensen, L. S., Primdahl, J., Rogge, E., and Wästfelt, A. (2016). Peri-urban food production and its relation to urban resilience. Sustainability 8, 1–21. doi: 10.3390/su8121340
Osei, G., Pascale, F., Delle-Odeleye, N., and Pooley, A. (2022). “Green infrastructure” in The Palgrave encyclopedia of urban and regional futures. ed. R. C. Brears (Cham: Palgrave Macmillan).
Pamukcu-Albers, P., Ugolini, F., La Rosa, D., et al. (2021). Building green infrastructure to enhance urban resilience to climate change and pandemics. Landsc. Ecol. 36, 665–673. doi: 10.1007/s10980-021-01212-y
Panagopoulos, T., González Duque, J. A., and Bostenaru Dan, M. (2016). Urban planning with respect to environmental quality and human wellbeing. Environ. Pollut. 208, 137–144. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.07.038
Paulin, M., Remme, R., and De Nijs, T. (2019). Amsterdam’s green infrastructure valuing Nature’s contributions to people. 2019. RIVM letter report 2019-0021. National institute for public health and the environment – RIVM, The Netherlands. Available online at: http://hdl.handle.net/10029/623099
Peng, Y., and Reilly, K. (2021). Grow green-using nature to reshape cities and live with water: An overview of the Chinese sponge city programme and its implementation in Wuhan. Etterbeek: IUCN European Regional Office.
Pigford, A. A. E., Hickey, G. M., and Klerkx, L. (2018). Beyond agricultural innovation systems? Exploring an agricultural innovation ecosystems approach for niche design and development in sustainability transitions. Agric. Syst. 164, 116–121. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2018.04.007
Pitman, S. D., Daniels, C. B., and Ely, M. E. (2015). Green infrastructure as life support: urban nature and climate change. Trans. R. Soc. S. Aust. 139, 97–112. doi: 10.1080/03721426.2015.1035219
Puchol-Salort, P., O’Keeffe, J., Reeuwijk, M., and Mijic, A. (2021). An urban planning sustainability framework: systems approach to blue green urban design. Sustain. Cities Soc. 66:102677. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2020.102677
Qi, Y., Chan, F. K. S., O’Donnell, E. C., Feng, M., Sang, Y., Thorne, C. R., et al. (2021). Exploring the development of the sponge city programme (SCP): the case of Gui’an new district, Southwest China. Front. Water 3:676965. doi: 10.3389/frwa.2021.676965
Qiao, X. J., Kristoffersson, A., and Randrup, T. B. (2018). Challenges to implementing urban sustainable stormwater management from a governance perspective: a literature review. J. Clean. Prod. 196, 943–952. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.049
Rain City Strategy. (2019). A green rainwater infrastructure and rainwater management initiative. City of Vancouver, Canada. Available online at: https://vancouver.ca/files/cov/rain-city-strategy.pdf
Rajan, E. H. S., and Amirtham, L. R. (2021, 2021). Urban heat island intensity and evaluation of outdoor thermal comfort in Chennai, India. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 23, 16304–16324. doi: 10.1007/s10668-021-01344-w
Rajaveni, S. P., Nair, I. S., and Elango, L. (2016). Evaluation of impact of climate change on seawater intrusion in a coastal aquifer by finite element modelling. J. Clim Change 2, 111–118. doi: 10.3233/JCC-160022
Reguero, B. G., Beck, M. W., Schmid, D., Stadtmüller, D., Raepple, J., Schüssele, S., et al. (2020). Financing coastal resilience by combining nature-based risk reduction with insurance. Ecol. Econ. 169:106487. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2019.106487
Roe, S., Streck, C., Obersteiner, M., Frank, S., Griscom, B., Drouet, L., et al. (2019). Contribution of the land sector to a 1.5 °C world. Nat. Clim. Chang. 9, 817–828. doi: 10.1038/s41558-019-0591-9
Roumeau, S., Seifelislam, A., Jameson, S., and Kennedy, L. (2015). Water governance and climate change issues in Chennai, USR 3330 “Savoirs et Mondes Indiens” working papers series no. 8. 2015, 1–34.
Safikhani, T., Abdullah, A. M., Ossen, D. R., and Baharvand, M. (2014). A review of energy characteristic of vertical greenery systems. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 40, 450–462. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2014.07.166
Sanyé-Mengual, E., Specht, K., Vávra, J., Artmann, M., Orsini, F., and Gianquinto, G. (2020). Ecosystem Services of Urban Agriculture: perceptions of project leaders, Stakeholders and the General Public. Sustainability 12:10446. doi: 10.3390/su122410446
Schindler, S., Sebesvari, Z., Damm, C., Euller, K., Mauerhofer, V., Schneidergruber, A., et al. (2014). Multifunctionality of floodplain landscapes: relating management options to ecosystem services. Landsc. Ecol. 29, 229–244. doi: 10.1007/s10980-014-9989-y
Schuch, G., Serrao-Neumann, S., Morgan, E., and Choy, D. L. (2017). Water in the city: green open spaces, land use planning and flood management—an Australian case study. Land Use Policy 63, 539–550. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.01.042
Shafique, M., Reeho Kim, R., and Lee, D. (2016). The potential of green-blue roof to manage storm water in urban areas. Nat Environ Pollution Technol 15.
Shah, A. M., Liu, G., Chen, Y., Yang, Q., Yan, N., Agostinho, F., et al. (2023). Urban constructed wetlands: assessing ecosystem services and disservices for safe, resilient, and sustainable cities. Front. Eng. Manag. 10, 582–596. doi: 10.1007/s42524-023-0268-y
Shakya, R., and Ahiablame, L. (2021). A synthesis of social and economic benefits linked to green infrastructure. Water 13:3651. doi: 10.3390/w13243651
Sharief, M. A. J., and Vangipuram, B. (2022). “Assessment of socio-economic impact of urban flooding in Hyderabad due to climate change” in A system engineering approach to disaster resilience. Lecture notes in civil engineering. eds. C. Ghosh and S. Kolathayar, vol. 205 (Singapore: Springer).
Sidek, L. M., Muha, N. E., Noor, N. A. M., and Basri, H. (2013). Constructed rain garden systems for stormwater quality control under tropical climates. IOP Conf. Ser. 16:012020. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/16/1/012020
Steger, K., Fiener, P., Marvin-DiPasquale, M., Viers, J. H., and Smart, D. R. (2019). Human-induced and natural carbon storage in floodplains of the Central Valley of California. Sci. Total Environ. 651, 851–858. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.205
Sterling, E. J., Filardi, C., Toomey, A., Sigouin, A., Betley, E., Gazit, N., et al. (2017). Biocultural approaches to well-being and sustainability indicators across scales. Nat Ecol Evol 1, 1798–1806. doi: 10.1038/s41559-017-0349-6
Suleiman, L. (2021). Blue green infrastructure, from niche to mainstream: challenges and opportunities for planning in Stockholm. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 166:120528. doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120528
Surma, M. (2013). Green infrastructure planning as a part of sustainable urban development–case studies of Copenhagen and Wroclaw. Proc. Latv. Univ. Agric. 2013, 22–32.
Thacker, S., Adshead, D., Fay, M., Hallegatte, S., Harvey, M., Meller, H., et al. (2019). Infrastructure for sustainable development. Nat Sustain 2, 324–331. doi: 10.1038/s41893-019-0256-8
Thorne, C. R., Lawson, E. C., Ozawa, C., Hamlin, S. L., and Smith, L. A. (2018). Overcoming uncertainty and barriers to adoption of blue-green infrastructure for urban flood risk management. J. Flood Risk Manag. 11, S960–S972. doi: 10.1111/jfr3.12218
Toxopeus, H., and Polzin, F. (2021). Reviewing financing barriers and strategies for urban nature-based solutions. J. Environ. Manag. 289:112371. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112371
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (2003). Cooling summertime temperatures: Strategies to reduce urban Heat Islands; publication number: 430-F-03-014; United States Environmental Protection Agency. Washington, DC: U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 2003.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (2008). Green parking lot resource guide—February 2008. Cincinnati, OH: National Service Center for Environmental Publications (NSCEP), United States.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) (2010). Green infrastructure case studies: Municipal policies for managing Stormwater with green infrastructure; EPA-841-F-10-004. Washington, DC: Office of Wetlands, oceans and watersheds, 2010.
Udas-Mankikar, S., and Driver, B. (2021). Blue-green infrastructure: an opportunity for Indian cities. ORF occasional paper no. 317, May 2021, observer research foundation
United Nations (2022). The sustainable development goals report 2022. New York: USA, United Nations. Available online at: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2022/The-Sustainable-Development-Goals-Report-2022.pdf
United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) (2023). Nature-based infrastructure: how natural infrastructure solutions can address sustainable development challenges and the triple planetary crisis. Geneva: United Nations Environment Programme.
United States Army Corps of Engineers (USACE). (2012). ROOM FOR THE RIVER: Preparedness, response, recovery and mitigation – summary report of the 2011 Mississippi River flood and successful operation of the Mississippi River and tributaries system.
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Forest Service (2020). Urban forest systems and green stormwater infrastructure. FS 1146.
Veena, K., Parammasivam, K. M., and Venkatesh, T. N. (2020). Urban Heat Island studies: current status in India and a comparison with the international studies. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 129:85. doi: 10.1007/s12040-020-1351-y
Victoria State Government (VSG) (2017). Planning a green-blue city: A how-to guide for planning urban greening and enhanced stormwater management in Victoria, February 2017. Treasury Place: Department of Environment, Land, Water and Planning, Victoria, Australia.
Vojinovic, Z. (2015). Floor risk: The holistic perspective—From integrated to interactive planning for flood resilience, vol. 14. London: The International Water Association (IWA) Publishing.
Vujovic, S., Haddad, B., Karaky, H., Sebaibi, N., and Boutouil, M. S. (2021). Urban Heat Island: Causes, Consequences, and Mitigation Measures with Emphasis on Reflective and Permeable Pavements. CivilEng. 2, 459–484. doi: 10.3390/civileng2020026
Wamsler, C., Brink, E., and Rivera, C. (2013). Planning for climate change in urban areas: from theory to practice. J. Clean. Prod. 50, 68–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.12.008
Wang, Y., Bakker, F., De Groot, R., and Wörtche, H. (2014). Effect of ecosystem services provided by urban green infrastructure on indoor environment: A literature review. Build. Environ. 2014, 88–100.
Wang, Y., Berardi, U., and Akbari, H. (2016). Comparing the effects of urban heat island mitigation strategies for Toronto, Canada. Energ. Buildings 114, 2–19. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2015.06.046
Wang, J., Chua, L. H. C., and Shanahan, P. (2019). Hydrological modeling and field validation of a bioretention basin. J. Environ. Manag. 240, 149–159. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.03.090
Wang, Y., and Zacharias, J. (2015). Landscape modification for ambient environmental improvement in central business districts – A case from Beijing. Urban For. Urban Green. 14, 8–18. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2014.11.005
Wolch, J. R., Byrne, J., and Newell, J. P. (2014). Urban green space, public health, and environmental justice: the challenge of making cities ‘just green enough’. Landsc. Urban Plan. 125, 234–244. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2014.01.017
World Bank (2008). Biodiversity, climate change, and adaptation: Nature-based solutions from the World Bank portfolio. Washington, DC: World Bank.
World Bank (2013). “Urban agriculture: findings from four city case studies (English)” in Urban development series knowledge papers, vol. 18 (Washington D.C: World Bank Group).
World Bank (2021). A catalogue of nature-based solutions for urban resilience. Washington, DC: World Bank Group.
World Meteorological Organization (WMO) (2022). State of the global climate in 2021. Geneva: World Meteorological Organization.
Yang, J., McBride, J., Zhou, J., and Sun, Z. (2005). The urban forest in Beijing and its role in air pollution reduction. Urban For. Urban Green. 2005, 65–78.
Yu, Q., and Li, N. (2023). “Assessment of green infrastructures performance for water quality management” in Proceedings of the 5th international symposium on water resource and environmental management. WREM 2022. Environmental Science and Engineering. ed. H. Xu (Cham: Springer).
Zhu, Z., Wang, J., Chan, F. K. S., Xu, Y., Li, G., Xu, M., et al. (2023). Urban agriculture as nature-based solutions: three key strategies to tackle emerging issues on food security in Chinese cities under climatic and non-climatic challenges. Front. Eng. Manag. 10, 736–741. doi: 10.1007/s42524-023-0262-4
Keywords: urbanization, ecosystem services, nature-based solutions, climate change, sustainable development goals, resilient cities
Citation: Ahmad N and Hassan Q (2025) Ecosystem services linked to nature-based solutions for resilient and sustainable cities in India. Front. Water. 6:1504492. doi: 10.3389/frwa.2024.1504492
Edited by:
Vikram Kumar, Planning and Development, Govt. of Bihar, IndiaReviewed by:
Aviva Rahmani, University of Colorado Boulder, United StatesBrian Deal, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, United States
Copyright © 2025 Ahmad and Hassan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nadeem Ahmad, bmFkZWVtMjAwODY0M0BzdC5qbWkuYWMuaW4=Quamrul Hassan, cWhhc3NhbkBqbWkuYWMuaW4=
 Nadeem Ahmad
Nadeem Ahmad Quamrul Hassan*
Quamrul Hassan*