- 1machineMD, Bern, Switzerland
- 2Department of Ophthalmology, University Hospital of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
In virtual reality (VR) systems that track eye movements using infra-red cameras, the precision of gaze measurement is crucial for reliable detection of eye movement disorders. To assess gaze measurement ability and gaze precision consistency of an HMD VR-based medical device system, neosTM, under optimal conditions, we used a robotized setup that provides the advantage of mimicking human eye movements with minimal movement variability. We assessed neos™’s gaze examination test twice for thirteen simulated conditions with different noise levels, and then assessed gaze precision and gaze consistency for each by computing the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC), standard error of measurements (SEM) and Bland-Altman analysis. We found excellent test-retest reliability (ICC > 0.99, SEM = 0.04) for neos™’s gaze precision, with good agreements between first and second gaze precision measurements observed via Bland-Altman analysis. The high ICC and low SEM of neos™ in all nine cardinal directions of gaze demonstrates its eye tracking reliability and measurement consistency. This is a crucial feature for eye-tracking applications for HMD-based VR devices when used in clinical settings. The use of a robotic eye to objectively validate a VR-based eye tracker can be applicable to other devices. Future research will investigate the longitudinal stability of the measurements in different human populations.
1 Introduction
Eye movements allow humans to foveate, follow and maintain their gaze on areas of interest. This is an important part of human vision. In addition to extraocular muscles, cranial nerves and an extensive neuronal network are responsible for oculomotor control. That is why examinations of eye movements are clinically used to identify diseases affecting oculomotor control. Such diseases may be in brain areas involved in planning and execution of gaze holding, saccades or pursuit eye movements. Oculomotor examination, in particular the alignment of eyes in different gaze directions, provides clinical information about cranial nerve function and function of extraocular muscles (Miller et al., 2004). Currently, manual clinical eye examinations are the gold standard for assessment of eye movements and ocular alignment (Rucker et al., 2011; Thurtell and Leigh, 2011). This is done by observation of eye movements while the examinee follows a moving target such as tip of a pen, or by observation of stability of gaze (Rucker et al., 2011). In another clinical examination the examinee moves his/her eyes between different targets. To test ocular alignment, the manual test consists of alternatingly covering eyes to force fixation of one eye (Rucker et al., 2011). Such manual eye movement examinations require extensive practice and yet they may sometimes fail to capture pathological features of eye movements (Stunkel et al., 2021). This is due to the fact that most of the eye movement features are qualitatively described, and the human eye of the observer may not be ideal to capture the velocity of fast eye movements or angles of gaze (Rucker et al., 2011; Rizzo et al., 2019). In people with nystagmus, for example, the fast changes of velocities may be impossible to be seen by an observer without technical support. Small deviations of ocular axis, i.e., strabismus, are also often missed (Rucker, 2019). Identification of all eye movement abnormalities is critical for establishing a diagnosis (Rizzo et al., 2019).
Eye-tracking technologies can provide a comprehensive and quantitative means for assessment of oculomotor function compared to manual examinations to help enhance the detection and confirmation of pathological eye movements during clinical examinations (Rizzo et al., 2019). Particularly, head-mounted display (HMD) virtual reality (VR) systems with inbuilt infra-red eye tracking offer closed-testing environments for more thorough evaluation of extra-ocular function with greater quantitative evidence of the user’s visual and attentional processes (González-Vides et al., 2023). Such systems can be useful in clinical assessments of oculomotor functions and can provide valuable insights when quantified and reported visually by capturing subtle clinical signs that may go undetected with manual assessments (González-Vides et al., 2023).
To ensure clinical utility of HMD VR based eye tracking systems various factors need to be taken into account. A central factor when evaluating the quality of eye tracking data is the precision of quantitative gaze measurement. Gaze precision indicates the reproducibility of a gaze point from one sample to the next and has a direct impact on a system’s ability to detect various ocular behaviors, such as saccadic intrusions or nystagmus (Adhanom et al., 2023). An intrinsic problem of precision testing of eye tracking in people, especially those with pathologies, is the lack of a ground truth and the biological variability. Thus, if eye tracking shows noise, drift, movements, some level of instability or loss of tracking, it either has a biological cause, such as instability of gaze and blinking or closure of the eye preventing eye tracking, or it may originate from insufficiencies of the eye tracking system.
To overcome these instabilities inherent to an human eye, we validated an eye-tracking system using a pair of robotic eyes. Robotic eyes allow the experimenter to know and control the gaze position of the eye at any moment. This can be used to simulate eye conditions, add noise and test the reliability of eye tracking in an experimentally fully controlled environment. Using this setup, in this study, we assessed gaze precision of a VR-based eye tracking system of a commercial medical device named neosTM via a test-retest reliability design.
2 Methods
2.1 Robotic eyes
We used a pair of robotic eyes to assess neos™ gaze direction capability in all nine cardinal positions of gaze, including primary gaze. This eye robot was custom developed to replicate human eye movements to specifically evaluate neos™’s eye tracking performance for its different examinations under various eye movement scenarios. The eye robot is designed to mimic human eye anatomy and eye movements accurately, with minimum effect of variability during gaze position changes of each eye. This custom device provides a simulation environment for testing eye movement responses and ensure measurement consistency and reliability. The eye robot prototype was developed in collaboration with the Bern University of Applied Sciences as part of a project focusing on objective validation of clinical eye tracking, and is comprehensively described in the corresponding project thesis (Portmann, 2023). Briefly, the eye robot consists of two independent artificial eyes that are mounted on a rotatable ring, and controlled by two servo motors, one controlling the horizontal movement of the eye, and the other the vertical movement. The VR headset was securely fixed in place using a specialized mounting mechanism. The eye robot setup and corresponding neos™ examination is shown in Figure 1. To ensure consistent lighting conditions during the measurements, minimize potential interference, and mimic the lighting conditions of a human use of the VR headset, the robotic setup was covered with a dark, opaque towel to shield the headset from ambient light.
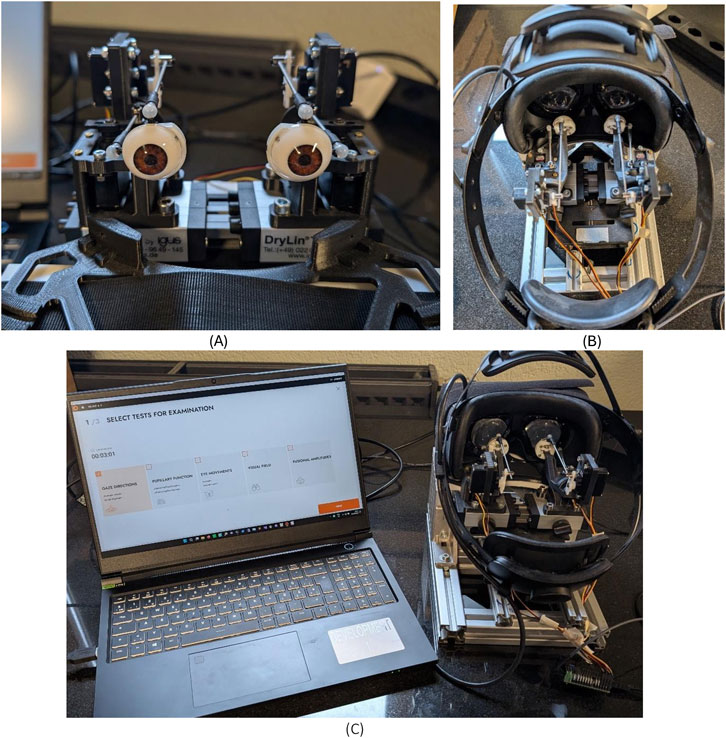

Figure 1. Robotic eye setup. (A) Robotic eyes. (B) Robotic eyes examination with neos headset. (C) Complete setup of robotic eyes examination with neos.
The interpupillary distance (IPD) of the robot eyes is configurable (range 50–100 mm) and was set to 61 mm for this study. We used a calibrated laser (MICRO-EPSILON ILD1220-50) to measure and quantify the eye robot’s displacement (Figure 1) and have thoroughly validated the eye robot by assessing its ability to accurately reproduce predefined eye movements within a range of ±10° and ±15° horizontally and vertically. The eye robot is capable of reliable repeated eye movements, with a high horizontal and vertical gaze accuracy and precision range (mean 0.15° ± 0.1° and range 0.01–0.36°, mean 0.12° ± 0.09° and range 0.04–0.37°, respectively).
2.2 Device
We used neos™ (machineMD AG, Bern, Switzerland), a VR headset-based eye tracker for medical use, consisting of both hardware and software components (Figure 2). neos™ is registered as a class I device in the USA (FDA registration number: 3029906225) and class IIa in Europe. With integrated measurement and proprietary analysis algorithms, neos™ can assess eight different aspects of eye function, including eye movements and pupillary responses, organized into five specific neos™ examination blocks to group examinations with similar visual stimuli requirements.

Figure 2. neos™, composed of a VR headset and a computer with customized proprietary software to allow for automated examination of eye movements and pupillary responses.
The hardware of neos™ consists of a VR HMD that utilizes infra-red eye tracking at 200 Hz frequency with sub-degree accuracy (Varjo Aero, https://varjo.com/products/aero/). This headset weighs around 700 g with active cooling to avoid fogging of optics. The headset’s VR display has 2880 × 2720 pixels per eye, a refresh rate of 90 Hz, and a field of view of 115° horizontally and 134° diagonally at 12 mm eye relief, respectively. Additionally, the headset design prevents ambient light from entering and interfering with the user’s field of vision, ensuring that external light is not interfering with the IR tracking. The VR headset is tethered via a cable to a high-performance laptop (Schenker Key15 E23) on which proprietary software platform to render visual stimuli using Unity (Unity Technologies, San Francisco, CA) and process and analyze with integrated measurement and analysis algorithms developed by machineMD to assess eye function.
The functional eye examination setup of neos™ provides a range of custom visual stimuli to the user, using the headset’s near eye displays, designed in Unity (Unity Technologies, San Francisco, CA) to trigger a specific eye movement or pupillary response for a corresponding neos™ examination block. Infra-red cameras within the headset track the user’s consequent eye movement and pupillary response, which is then sent to neos™’s cloud-based platform for further processing and quantitative analysis.
2.3 Power analysis
We conducted a power analysis to determine our sample size based on an expected reliable intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) of 0.9, precision of 0.1, and confidence level of 80% for two repetitions per test condition (k), referencing Bonett (2002). We determined that a minimum sample size of seven test conditions would be needed, given the robot’s ability to control and measure eye movements with high fidelity and anticipated minimal measurement error. This is also supported by the inherent precision and accuracy of the eye robot used for measuring eye movements (see Section 2.1). To be conservative, we decided to include in our experiment 10 robotic eye conditions without added noise and three conditions with additional noise, making a total of 13 robotic eye conditions.
2.4 Robotic eye conditions
To emulate human-gaze movement patterns in different directions of gaze, we introduced noise and offsets to the robotic eye for both horizontal and vertical eye movements. We added a random filter variation to the robot gaze measurement by sampling a Gaussian distribution with µ (mean) equal to 0 and σ (variance) being the respective value for “Gaze Noise Degrees [°].” Table 1 shows the variance (gaze noise degrees) added to each eye robot condition.
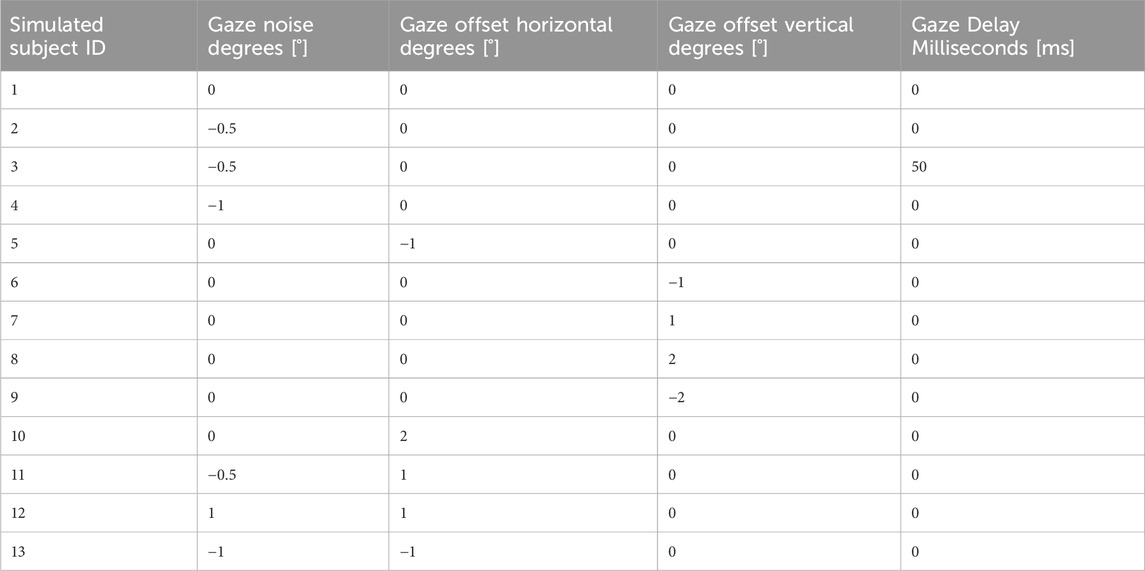
Table 1. Simulated robotic eye conditions: variance (gaze noise degrees) added to each eye robot condition.
2.5 Description of the gaze block examination with neos™
In this study, we evaluated gaze precision consistency of neos™’s first examination block, titled “Gaze directions” twice for each robotic eye condition. This exam block evaluates a user’s monocular and binocular gaze holding ability, i.e., fixation stability and ocular alignment within a total duration of 3 min. At the start of the test, users are presented with a virtual scenic background that gives the impression of depth, and they are then cued to following a virtual moving stimulus shaped like an unidentified flying object (UFO) moving in the field. The UFO stimulus is shown with a binocular disparity equalling to a simulated depth of 305 m and has a size of 1°. As the test proceeds, this VR stimulus is presented to both eyes in a sequence involving thirteen total fixations, displayed for 3 seconds each, in all nine directions of gaze (i.e., primary, left, right, up, down, up and left, up and right, down and left, down and right). The binocular fixation block is followed by a sequence of monocular fixations. The sequence involves five alternate eye-cover blocks lasting 1.5 s each. The user’s gaze positions are assessed in all nine cardinal directions of gaze, with fixation coordinates involving 0°, ±10°, and ±20° in the horizontal direction, and 0°, 10°, and 15° degrees in the vertical direction, respectively. We use a spherical coordinate system and then project the horizontal and vertical values to a Cartesian coordinate system, with the X-axis representing the horizontal direction (positive values indicate rightward direction, negative values indicate leftward direction), and the Y-axis representing the vertical direction (positive values indicate upward direction, negative values indicate downward direction).
In this study, the eye robot subscribes to the message queue, where a stimulus is published, and updates its gaze according to the message that has been shown.
2.6 Precision
We quantified the precision of gaze movements for the robotic eye conditions by calculating the standard deviation of the horizontal and vertical coordinates of each individual fixation points in all nine positions of gaze. We used standard deviation of this measurement to define the degree of precision, where a lower standard deviation indicates higher precision owing to the points clustering closer together and having a smaller error range.
2.7 Test-retest reliability
2.7.1 Interclass correlation coefficient
To assess test-retest reliability, we calculated ICC as it measures the consistency of measurements over time, with a higher ICC indicating better reliability of measurement.
We calculated the ICC as a 2-way, mixed effects, single measurement, absolute agreement model measure (Koo and Li, 2016), which is also referred to as ICC according to the Shrout and Fleiss Convention (Shrout and Fleiss, 1979):
Median Square Root (MSR) is defined as the mean square for rows, which is the between-measurement mean square value. The mean square for error or MSE is the within-measurement mean square value expressed with the mean square for columns (MSC) measurements, while k is the number of measurements conducted per subject, and n is the total number of subjects.
2.7.2 Standard error of measurements
While the ICC measures the consistency or agreement between repeated measurements, the standard error of measurements (SEM) estimates the random error associated with a single measurement. SEM is a good indicator of the reliability of the measurements: the smaller the SEM, the more precise the measurements are. We estimated the SEM as follows (Weir, 2005):
where: SD is the standard deviation.
3 Results
3.1 Gaze direction assessments
The eye movements for each robotic eye in all nine cardinal gaze directions are described in conditions without (Figure 3) and with the addition of noise to disrupt resultant measurements (Figure 4). Thus, gaze position is assessed in central (i.e., primary gaze) at zero degrees with binocular fixation of both eyes for 3 s in horizontal and vertical directions. Following which, the stimulus then moves to new gaze positions for left up, middle, and down gaze and right up, middle, and down gaze (±10° on y-axis) for 3 s each (x-axis). This allows for bilateral assessment of gaze holding (i.e., gaze stability) of each eye, with sufficient time to capture positional deviations that may appear at rest or triggered by movement from adjustment of the eyes to the new stimulus. For each new gaze-direction the stimulus position is represented by a black line while the resultant eye movement response for the left eye is represented as blue and for the right eye in red. With each change in main stimulus position, the robotic eyes have a slight lag (<0.5 s) to respond to the new position.
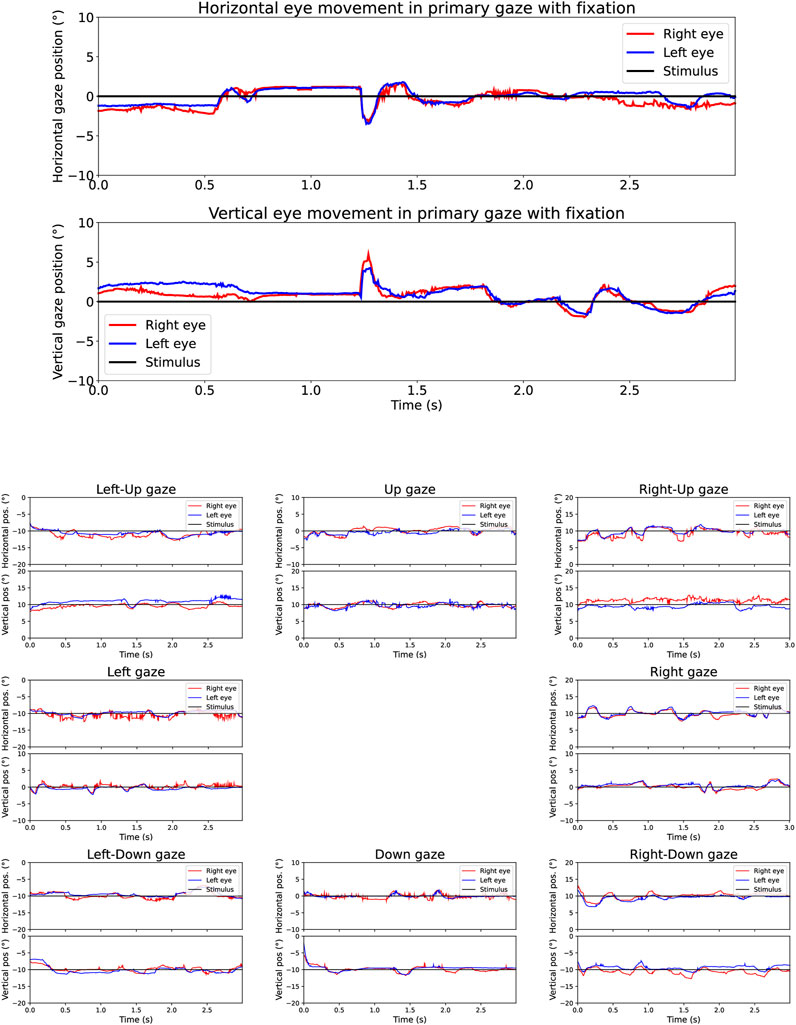
Figure 3. Gaze holding (fixation) across time for robotic eye condition 1 (without added noise) as presented in the neos™ report for a total duration of 3 seconds (X-axis). The Y-axis displays the degree of gaze deviation in each of the nine cardinal directions of gaze. The upper panel shows gaze holding in primary gaze (center). The lower panel shows gaze holding in the other eight gaze directions. In the upper plots, the eyes fixate the stimulus at central gaze position, i.e. 0°. In the left-up gaze plot, the eyes fixate the stimulus placed at 10° leftwards and 10° upwards. In the left gaze plot, the stimulus is placed at 10° leftwards. In the left-down gaze plot, the stimulus is placed at 10° leftwards and 10° downwards. In the up-gaze plot, the stimulus is placed at 10° upwards. In the down-gaze plot, the stimulus is placed at 10° downwards. In the right-up gaze plot, the stimulus is placed at 10° rightwards and 10° upwards. In the right gaze plot, the stimulus is placed at 10° rightwards. In the right-down gaze plot, the stimulus is placed at 10° rightwards and 10° downwards.
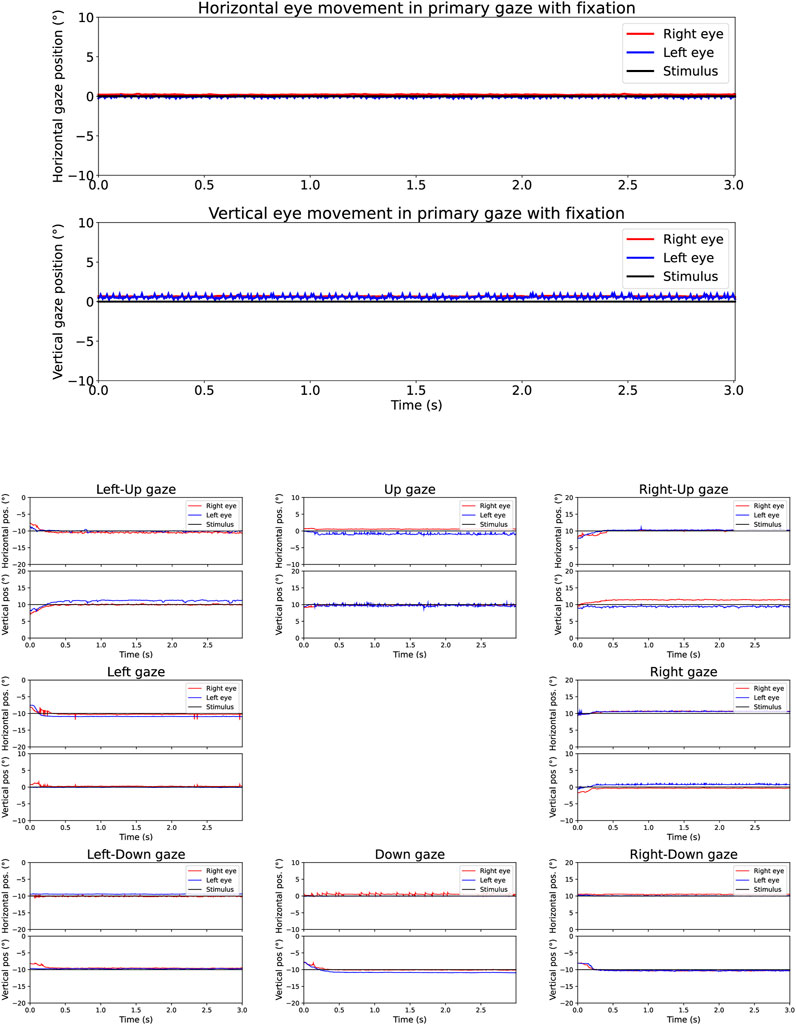
Figure 4. Gaze holding (fixation) across time for robotic eye condition 12 (with added noise) as presented in the neos™ report for a duration of 3 seconds (x-axis) with gaze deviations in degrees (y-axis). The upper panel shows gaze holding in primary fixation (center). The down panel shows gaze holding in the other eight gaze directions.
3.2 Gaze precision
We measured gaze precision twice for neos™ “Gaze directions” examination and found a mean gaze precision for the first examination of 0.38 ± 0.32°, and for the second examination of 0.39 ± 0.35°, respectively.
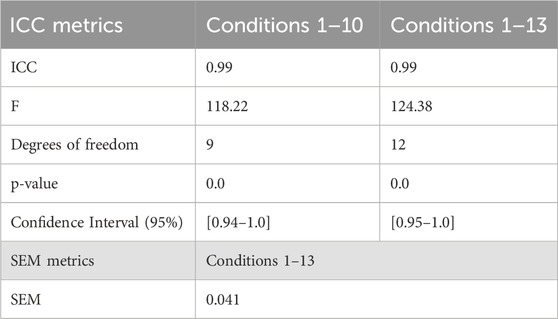
3.3 Test-retest reliability
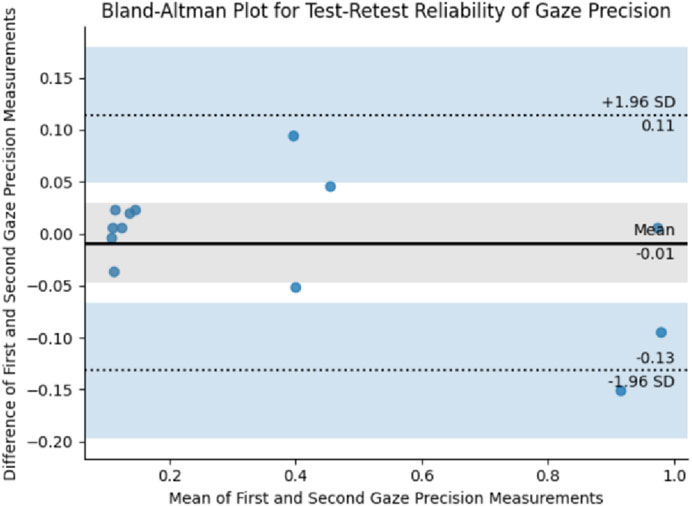
Table 2 contains the test-retest reliability metrics. ICC for conditions 1 to 10 (without added noise) was 0.99 and for conditions 11 to 13 (with added noise) was 0.99. SEM was 0.041. The Bland-Altman plot shows a mean difference of −0.01°, +1.96 SD 0.11° and −1.96 SD −0.13° (Figure 5).
4 Discussion
In this study, we described the technical aspects of neos™ and evaluated the test-retest reliability of gaze precision of neos™’s examination block “Gaze directions” in a pair of robotic eyes in all nine directions of gaze. The use of a pair of robotic eyes constitutes a novel method for determining the validity of VR-based eye trackers. By using a pair of robotic eyes designed to mimic human eye anatomy and movement, the biological variability caused by human participants is replaced by an eye robot that allows to control all aspects of eye movement. To our knowledge, the use of an objective robotic-based system to test the validity of a VR HMD-based eye tracker has not been published in a peer-reviwed journal before. In our search, we have only found one master thesis in which a robotic eye system was developed to test eye tracking devices (Tannfelt and Wu, 2018).
In this study, we assessed the gaze precision of neos™, however this objective methodology can be applied to assess other VR-based eye tracker systems, particularly those using an HMD headset.
By using the eye robot, we were able to systematically test the precision and reliability of the HMD system, including in conditions where external noise was introduced to simulate potential real-world conditions involving eye movement impairments. In Figure 3, the traces for both eyes generally follow the stimulus positions with high precision across all cardinal directions. Although the robotic eye system demonstrates a high degree of precision, minor deviations are observed between the expected stimulus position and the measured response of the robotic eyes. This is due to minor sensor noise, inherent to the robot’s measurement process that results in small fluctuations in the recorded eye-gaze data. This variability represents the system’s measurement precision, which is the key parameter that this study seeks to quantify. In Figure 4, where noise was deliberately introduced to disrupt measurements, the variability in both eyes’ responses is more pronounced, as expected. The combined observations from Figures 3, 4 highlight the neos system’s ability to maintain a high level of eye tracking precision and stability, even in the presence of noise. The eye robot’s gaze precision can therefore provide an objective lower bound for the neos™ device’s eye-tracking precision, offering valuable insights into the system’s baseline performance.
To assess consistency of gaze-precision measurements involving eye tracking with specific visual stimuli presented at fixed time-points, test-retest reliability metrics are commonly used. This is particularly relevant when using novel medical measuring tools to ensure consistency of response (Shrout and Fleiss, 1979; Weir, 2005; Tannfelt and Wu, 2018). The neos™ device, an HMD VR-based medical device, presents visual stimuli to both eyes individually and measures the resultant reactions of each eye. Our results demonstrate that this device offers excellent gaze precision consistency for tracking eye movements, with a gaze precision of 0.38° ± 0.34° and 0.39° ± 0.37° for repeated trials. The test-retest reliability, measured via ICC, was high (>0.9) for both standard and noisy conditions, highlighting neos™’s measurement consistency for gaze assessment, even in the presence of induced noise. These findings align with previous studies that emphasize the need for high-precision eye-tracking systems, particularly in clinical environments where subtle eye movement abnormalities are critical diagnostic markers (González-Vides et al., 2023; Adhanom et al., 2023).
In agreement with the high ICC, also the Bland-Altman plots reveal good agreement between the first and second gaze precision measurements. The points are clustered around the mean difference line close to zero, indicating no significant bias between the two measurements. The narrow spread of the points around the mean indicates small differences between the measurements with few data points falling outside the limits of agreement (represented by the dotted lines). These points are few and scattered around the zero line, suggesting their likelihood due to random error rather than a systematic bias. This further strengthens the confidence in the measurement consistency of neos™.
The introduction of noise in our robotic eye system, while simulating more challenging conditions for gaze tracking, did not significantly impact the reliability of the system. This resilience suggests that neos™ could perform well in real-world clinical scenarios where patient movement or environmental distractions may otherwise complicate assessments. This robustness in noisy conditions is particularly relevant for patients with conditions such as saccadic intrusions, nystagmus or strabismus.
Our study adds to the growing body of evidence supporting the utility of VR-based eye-tracking systems in clinical practice. One of the major advantages of using these systems over traditional manual eye examinations is their ability to objectively capture and quantify eye movement abnormalities that might go unnoticed during manual assessments. Traditional clinical methods, while effective for detecting gross abnormalities in eye movements, often fail to provide the quantitative precision necessary for detecting minute deviations that can be indicative of underlying neurological or ophthalmic issues (Rucker et al., 2011; Thurtell and Leigh, 2011; Rizzo et al., 2019). By automating the assessment and linking eye movement data directly to visual stimuli in a controlled VR environment, neos™ eliminates the variability and subjectivity inherent in manual evaluations.
Eye tracking implemented in HMD VR systems is being increasingly used worldwide in various applications, including in the medical field (Adhanom et al., 2023; Mistry et al., 2023). These systems can facilitate the acquisition of relevant quantitative information regarding human gaze behavior, and with that, increase the detection of eye movement impairments such as saccadic intrusions, nystagmus, or strabismus. These may be indicative of a neurologic or ophthalmic disorder, and thus can aid in establishing the proper diagnosis and effective treatment plan (Rizzo et al., 2019; González-Vides et al., 2023).
To ensure that an eye tracking system is measuring the correct gaze behaviours, it is crucial that it has a reliable precision (Adhanom et al., 2023). In this study, we chose to assess gaze precision only and not gaze accuracy. While gaze accuracy is an important parameter for ensuring data quality in eye tracking systems (Adhanom et al., 2023), it primarily affects the absolute position of gaze points. In our system, most eye movement analyses are based on relative changes in gaze position over time, making precision more critical. Furthermore, accuracy is affected by calibration while precision is not. Thus, even if the gaze points are slightly offset, if the precision of the system (i.e., consistency of this offset) is high, the relative changes can still be accurately captured and analyzed. Moreover, the ground truth for evaluating gaze accuracy in our system is the visual axis, defined as the line of sight from the eye to a known stimulus. However, involuntary or voluntary deviations from the fixation target can produce offsets in the measured gaze, making the reported accuracy appear lower than the system’s true performance. Because our primary goal is to identify specific ocular movement patterns (e.g., square-wave jerks, gaze stability), we emphasize the consistency of gaze precision over the consistency of offset from the target. Nonetheless, the eye robot’s measured gaze accuracy lies within a similar range as precision, with a mean of 0.15° ± 0.1° (range: 0.01°–0.36°), as reported in Section 2.1. The high precision and accuracy ensure the system’s reliability and clinical confidence for VR-based assessments.
Despite the promising results, this study has limitations. While the use of robotic eyes offers a highly controlled and ideal environment to assess the device performance in optimal conditions, it does not fully replicate the complexity of human eye movements. Future studies will evaluate the precision and reliability of neos™ in healthy examinees and in a broader clinical population, particularly in patients with known oculomotor dysfunctions.
In conclusion, neos™ demonstrates high precision and reliability for gaze assessment. Its potential clinical applications are vast, ranging from routine neuro-ophthalmic evaluations to more complex assessments of ocular motility in patients with neurological disorders. As VR and eye-tracking technologies continue to advance, devices like neos™ have the potential to become invaluable tools in enhancing both diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes in ophthalmology and neurology.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
AC: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. AN: Conceptualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. JL: Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing–review and editing. BH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing–review and editing. DB: Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing–review and editing. MA: Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by machineMD.
Conflict of interest
Authors AC, AN, JL, BH, DB and MA are employed by machineMD.
The authors declare that this study received funding from machineMD. The funder had the following involvement in the study: conducted the study.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adhanom, I. B., MacNeilage, P., and Folmer, E. (2023). Eye tracking in virtual reality: a Broad review of applications and challenges. Virtual Real 27 (2), 1481–1505. doi:10.1007/s10055-022-00738-z
Bonett, D. G. (2002). Sample size requirements for estimating intraclass correlations with desired precision. Stat. Med. 21 (9), 1331–1335. doi:10.1002/sim.1108
González-Vides, L., Hernández-Verdejo, J. L., and Cañadas-Suárez, P. (2023). Eye tracking in optometry: a systematic review. J. Eye Mov. Res. 16 (3). doi:10.16910/jemr.16.3.3
Koo, T. K., and Li, M. Y. (2016). A guideline of selecting and reporting intraclass correlation coefficients for reliability research. J. Chiropr. Med. 15 (2), 155–163. doi:10.1016/j.jcm.2016.02.012
Miller, N. R., Newman, N. J., Biousse, V., and Kerrison, J. B. (2004). Walsh and Hoyt’s clinical neuro-ophthalmology. 6th Edition. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins.
Mistry, D., Brock, C. A., and Lindsey, T. (2023). The present and future of virtual reality in medical education: a narrative review. Cureus 15 (12), e51124. doi:10.7759/cureus.51124
Portmann, M. D. (2023). Development of a mechatronic setup for validation of the eye recognition of VR goggles. Bern Univ. Appl. Sci.
Rizzo, J. R., Beheshti, M., Dai, W., and Rucker, J. C. (2019). Eye movement recordings: Practical applications in neurology. Semin. Neurol. 39 (6), 775–784. doi:10.1055/s-0039-1698742
Rucker, J. C. (2019). Nystagmus and saccadic intrusions. Contin. (Minneap Minn) 25 (5), 1376–1400. doi:10.1212/con.0000000000000772
Rucker, J. C., Kennard, C., and Leigh, R. J. (2011). The neuro-ophthalmological examination. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 102, 71–94. doi:10.1016/b978-0-444-52903-9.00009-1
Shrout, P. E., and Fleiss, J. L. (1979). Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol. Bull. 86 (2), 420–428. doi:10.1037//0033-2909.86.2.420
Stunkel, L., Newman-Toker, D. E., Newman, N. J., and Biousse, V. (2021). Diagnostic error of neuro-ophthalmologic conditions: State of the science. J. Neuroophthalmol. 41 (1), 98–113. doi:10.1097/wno.0000000000001031
Tannfelt Wu, J. (2018). Robot mimicking human eye movements to test eye tracking devices. KTH, Sch. Industrial Eng. Manag. (ITM), Mach. Des. (Dept.), Mechatronics.
Thurtell, M. J., and Leigh, R. J. (2011). “Nystagmus and saccadic intrusions,” in Handbook of Clinical Neurology (Elsevier), 333–378.
Keywords: eye movement, eye tracking, gaze, gaze precision, virtual reality, HMD, test-retest reliability
Citation: Coito A, Naidu A, Lehmann J, Hauser B, Brügger D and Abegg M (2025) Test-retest reliability of gaze precision of a novel virtual reality-based medical device. Front. Virtual Real. 6:1502679. doi: 10.3389/frvir.2025.1502679
Received: 27 September 2024; Accepted: 20 January 2025;
Published: 13 February 2025.
Edited by:
Omar Janeh, University of Technology, IraqReviewed by:
Manuela Chessa, University of Genoa, ItalyRijul Saurabh Soans, University of California, Berkeley, United States
Copyright © 2025 Coito, Naidu, Lehmann, Hauser, Brügger and Abegg. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ana Coito, YW5hLmNvaXRvQG1hY2hpbmVtZC5jb20=
 Ana Coito
Ana Coito Avantika Naidu
Avantika Naidu Julian Lehmann1
Julian Lehmann1 Dominik Brügger
Dominik Brügger