- Department of Civil, Environmental and Geomatic Engineering (D-BAUG), Institute for Spatial and Landscape Development (IRL), ETH Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland
Introduction: Virtual reality (VR) used for healthcare, particularly through exergames, is promising for improving therapeutic outcomes. However, effectively engaging patients and providing realistic environments for everyday situations remain major challenges. The technical aspects of developing engaging VR applications for rehabilitation are largely unexplored. This research presents the development of a head-mounted display VR (HMD-VR) exergame for gait therapy. The novelty lies in the use of high-fidelity immersive environments implementing 3D geospatial data and motion to create targeted therapeutic applications that closely mimic reality while harnessing the environment’s restorative functions.
Methods: We integrated 3D point clouds from laser scans and geolocated ambisonic sound recordings into a game engine. We combined different techniques for user motion tracking, while we used point cloud manipulation for integrating specific training elements. Feedback on the quality of the HMD-VR exergame was received from the first implementations.
Results: Our methodology demonstrates the successful, highly realistic VR replication of restorative real-world environments using 3D point clouds and environmental sounds. We illustrate the adaptability of the environment for therapeutic use through manipulation of the 3D point cloud, facilitating customizable training difficulty levels while promoting immersive experiences. Participant feedback (sample size: 49 sessions) confirms the HMD-VR exergame’s applicability as a restorative experience (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT06304077).
Discussion: Our research introduces a pioneering HMD-VR game for gait rehabilitation, leveraging immersive VR environments grounded in the real world. This innovative approach offers new possibilities for efficient and effective rehabilitation interventions. Future studies will analyze effects on gait patterns across different environments and their restorative functions and evaluate the HMD-VR xergame in clinical settings.
1 Introduction
Video games incorporating exercise (exergames) show potential for rehabilitation, pain management, and sensory disorder treatment (Lohse et al., 2014; Howard, 2017; Cano Porras et al., 2018; Massetti et al., 2018; Hamzeheinejad et al., 2019; Li et al., 2020). However, technological developments are slow due to challenges in creating environments with high realism (Huang et al., 2019) and intuitive controls, especially for older adults (Li et al., 2020). This lack of progress is further exacerbated by the absence of collaboration among developers, healthcare providers, and users (Li et al., 2020). This results in mostly non-immersive VR applications for patients (Montalbán and Arrogante, 2020), limiting their sense of presence and immersion. Immersion depends on the illusion of reality provided by VR interfaces (Wissen Hayek et al., 2016; Slater, 2018; Berkman and Akan, 2019). The feeling of presence is the user’s psychological perception of being in VR, influenced by the quality of sensing and the consistency of content (Slater and Wilbur, 1997; Gutiérrez et al., 2008; Wissen Hayek et al., 2016; Schulte-Fortkamp and Fiebig, 2023).
To address these issues, it is essential to foster collaboration, e.g., of therapists, patients and computer scientists as well as other disciplines, and focus on the development of HMD-VR exergames. These high-fidelity immersive HMD-VR exergames could not only provide immersive experiences for a variety of health conditions (McMahan et al., 2012; Tao et al., 2021), but also offer a secure and engaging way to enhance motor skills and improve overall wellbeing (Burdea, 2003; Keshner, 2004; Dockx et al., 2016; Calabrò et al., 2017; Kern et al., 2019; Winter et al., 2021).
In healthcare, patients often experience high stress levels (Cadore et al., 2013). The therapeutic value of natural environments, which can restore depleted cognitive resources, is increasingly recognized (Jamshidi et al., 2020; Ford et al., 2023). According to the Attention Restoration Theory (ART), exposure to low-demand environments can replenish these cognitive resources (Kaplan and Kaplan, 1989; Ulrich et al., 1991; Hartig et al., 1997b; White et al., 2018). ART identifies four recovery factors: being away, extent, fascination, and compatibility, which contribute to a sense of detachment, immersion, effortless attention, and comfort (Kaplan and Kaplan, 1989; Ulrich et al., 1991; Hartig et al., 1997b; White et al., 2018). Restorative environments, especially natural and certain urban ones, can restore concentration, reduce stress, and regulate mood (Kaplan, 1995; Howard, 2017). Consequently, the investigation of the integration of environments in HMD-VR exergames with restorative functions within rehabilitation holds both theoretical and practical significance in fostering mental wellbeing (Li H. et al., 2021).
Particularly inpatients often have limited access to restorative environments (Ulrich, 2001; Thake et al., 2017). Research shows that VR environments can match the restorative effects of real environments, reducing stress and improving mood (Anderson et al., 2017; Mattila et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2020; Li H. et al., 2021; Mollazadeh and Zhu, 2021). The use of high-fidelity immersive VR environments has been demonstrated to successfully promote the feeling of being away from the demands of daily life, which can foster attention restoration (de Kort et al., 2006). It can also significantly decrease negative affect, leading to restoration and recovery from mental fatigue (Frost et al., 2022). Recent advancements in 3D-VR technology offer superior restorative potential, providing a safe, engaging platform for skill improvement (Nukarinen et al., 2020; Yeo et al., 2020; Newman et al., 2022). Beyond that, VR facilitates the transfer of therapy-learned skills to real-world settings (Dockx et al., 2016; Tasseel-Ponche et al., 2023), creating meaningful tasks with reduced frustration (Montalbán and Arrogante, 2020).
While VR is increasingly applied in gait rehabilitation therapies, VR applications are only used to provide new motivating means for performing required exercises in controlled environments (Kizony et al., 2003; Brach and VanSwearingen, 2013; Howard, 2017; Paralkar et al., 2020; Horsak et al., 2021), but they do not yet harness the restorative functions of the visual stimuli. Despite the benefits of restorative environments (Lin et al., 2023), the ways in which these environments should be simulated have not been exploited in VR exergames. The research findings indicate that VR technology provides a viable alternative when it is not possible to visit a physical forest or other natural environment. Yet, current state-of-the-art primarily relies on non-immersive or semi-immersive VR systems (Montalbán and Arrogante, 2020; Nagashima et al., 2021; Winter et al., 2021), lacking free walking or high-fidelity simulation of real environments (Hamzeheinejad et al., 2018; Nagashima et al., 2021; Palacios-Navarro and Hogan, 2021; Winter et al., 2021). In the following, technical aspects are briefly presented that can help advance the development of HMD-VR applications for gait rehabilitation.
The emergence of 3D point clouds generated through laser scanning technologies has revolutionized environment modelling and analysis by offering unparalleled accuracy and realism (Girot, 2019; Urech et al., 2020; 2022; Zięba-Kulawik et al., 2021). Utilizing point clouds derived from Terrestrial Laser Scanners (TLS) offers a robust foundation conducive to crafting immersive environmental visualizations with game engines tailored for HMDs (Echevarria Sanchez et al., 2017; Wissen Hayek et al., 2023). Point clouds, defined as discrete spatial points collected by laser reflection from an object back to the scanner, provide an accurate representation of a three-dimensional environment (Heritage and Large, 2009). Concurrently captured photographic data can be utilized for the colorization of these point clouds. This data makes it possible to recreate real-world environments with exceptional detail and fidelity (Urech et al., 2020). Furthermore, terrestrial 3D point clouds, due to their manipulability (Urech et al., 2020), allow virtual environments to be altered to suit therapeutic needs and enhance resistance training (Cadore et al., 2013). Referred to as “point cloud modeling” (Urech et al., 2020), this approach facilitates the creation of varying levels of training difficulty, e.g., by adjusting environments to mimic real-life obstacles and simulating daily activities. Such high-fidelity VR environments can enhance the sense of presence and immersion for users exploring the simulated environment, making them feel as if they were there (Wissen Hayek et al., 2016; Nilsson et al., 2018).
Another factor enhancing perceived realism and immersion into the VR environment is the soundscape (Lindquist et al., 2020; Rajguru et al., 2022), i.e., the acoustic environment of a physical place as perceived by humans (Schulte-Fortkamp and Fiebig, 2023). Moreover, integrating natural sounds into VR environments enhances restorative potential and mental recovery (Ratcliffe et al., 2013; Benfield et al., 2014; Emfield and Neider, 2014; Lindquist, 2014; Sona et al., 2019; Smalley et al., 2023; Ruotolo et al., 2024). However, approaches to auralize the soundscape of specific real environments in HDM-VR are not yet standard (Stienen and Vorländer, 2015; Pieren, 2018; Rajguru et al., 2022; Ruotolo et al., 2024). Current approaches for auralizations include sound generations relying on recordings in situ, or parametric synthesis, each with their own strengths and limitations (Pieren, 2018). Interestingly, the impact of these sounds appears to be particularly significant among elderly, as it has been shown that the elderly prioritize acoustic over visual aspects in their evaluations (Ruotolo et al., 2024). The use of ambisonic environmental sounds in exergames, which represents full-sphere surround sound, as well as its effects, remains unexplored.
Especially for therapies involving physical movement, also the quality of the motion tracking influences engagement and realism in a virtual environment (Tao et al., 2021). Particularly, the accurate tracking ensures realistic movement within the VR environment (Nilsson et al., 2018; Li et al., 2020; Tao et al., 2021), directly affecting presence and immersion (Steinicke et al., 2013; Ennadifi et al., 2023). Such seamless walking, crucial for daily activities and societal participation, is a key focus of physical rehabilitation (Howard, 2017; Horsak et al., 2021). Prioritizing controller-free walking enhances engagement and aligns with therapeutic goals, creating an intuitive and immersive experience (Tao et al., 2021). This freedom of movement is vital for integrating the application into gait rehabilitation.
While research highlights the restorative functions of VR environments, connections between natural or urban settings and health opportunities remain sparse (de Kort et al., 2006; Valtchanov et al., 2010; Anderson et al., 2017; Ward Thompson, 2018; White et al., 2018; Appel et al., 2020a; Browning et al., 2020b; 2020a; Yu et al., 2020; Nukarinen et al., 2022). This paper introduces a novel HMD-VR exergame for gait rehabilitation, using immersive high-fidelity VR environments grounded in the real world. The novelty of our approach lies in three key aspects: (1) Using 3D laser scanning and ambisonics sound recordings to create high-fidelity audiovisual virtual environments simulating existing real environments. (2) Modifying the environment for various therapeutic exercises and training difficulty levels. (3) Facilitating physical motion in virtual environments to encourage natural gait patterns and functional rehabilitation. This approach addresses key challenges in current therapeutic practices. In the subsequent sections we present detailed insights into the developed approach for HMD-VR gait rehabilitation exergames. The suitability of the technical implementation, with respect to user experience in the VR environments and the exercise itself, as well as its restorative potential, is evaluated based on user feedback from an initial trial (ClinicalTrials.gov XXX).
2 Methods
2.1 Development of HMD-VR exergames with immersive restorative environments
We present a workflow for developing HMD-VR exergames with immersive restorative environments for gait rehabilitation (see Figure 1). We selected real-world environments that meet quality criteria for both restoration and gait and balance training. For these selected real-world environments, we acquired 3D point cloud data and audio recordings, which we integrated into a game engine to create a coherent audiovisual VR environment. By manipulating the point cloud, we displayed or concealed objects selectively, which allowed for difficulty level customization and adaptation to everyday settings for therapy. Implementing redirect walking (RDW) enabled us to track user motion, effectively translating real-world movements into the virtual environment.
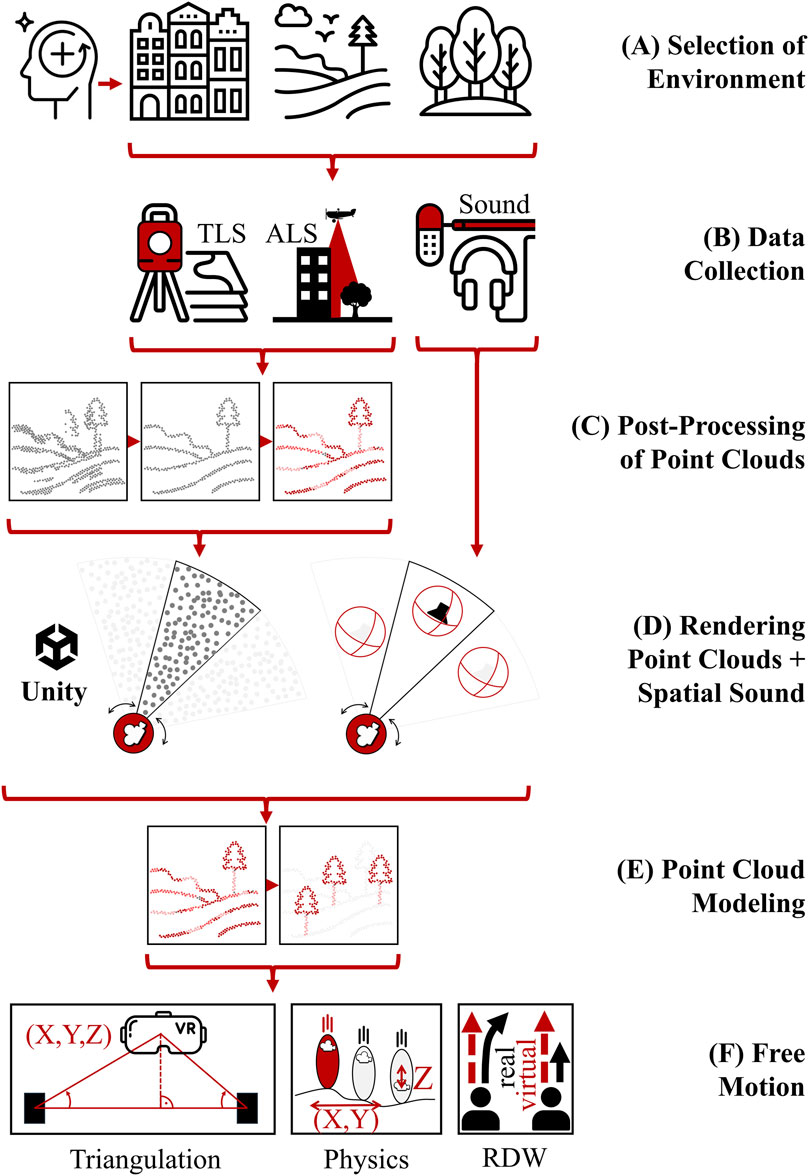
Figure 1. Methodological Workflow illustrating the process involved in creating immersive restorative exergames using head-mounted display virtual reality. (A) Selection of Restorative Environments: Environments were chosen based on Kaplan’s Attention Restoration Theory. (B) Data Collection: Terrestrial and Airborne Laser Scans and geolocated sound recordings were collected. (C) Post-Processing of Point Clouds: The collected data was processed to reduce noise points and add colorization. (D) Rendering Point Clouds and Immersive Soundscape: Using the Unity game engine, the processed point clouds were rendered employing Potree octree structure, and a head-tracked binaural audio reproduction of spatial sound was created. (E) Point Cloud Modeling: Targeted adjustment of the virtual environments by manipulating objects in the point cloud. (F) Free Motion: Integrating triangulation, a physics engine with terrain, and redirected walking (RDW) to enable seamless walking.
2.2 Selection of environments
We applied our methodology to create three realistic immersive distinct HMD-VR exergame environments, each selected for their unique restorative qualities and alignment with our project’s objective of fostering restorative gait and balance training (Hartig et al., 2003; Hartig et al., 2014; Bowler et al., 2010; Ward Thompson, 2011; Bergeron et al., 2014; Hartig, 2021). There is strong evidence that the experience of the environment, especially the natural environment, can be beneficial to people’s health and wellbeing (Ward Thompson, 2011; Hartig et al., 2014; Hartig, 2021). Current evidence suggests that natural environments, i.e., those that are predominantly dominated by vegetation (e.g., gardens, parks, nature reserves or forests), are more valuable for restoring attention and reducing stress than non-vegetated urban environments (e.g., city streets or residential areas) (Hartig et al., 2003; Bowler et al., 2010). Other studies indicate that landscape preference is influenced more by structural parameters (e.g., complexity, openness, water sources) than by habitat type (Han, 2007; Ward Thompson, 2018). This can be connected to Ulrich’s qualities and components of a landscape, which promotes stress reduction as described in his theory of stress reduction (Ulrich et al., 1991). For example, landscapes should have moderate depth and complexity, as well as a focal point and natural content (vegetation or water) (Hartig et al., 2003).
Overall it has been shown, that there is a tendency to prefer forested landscapes over grassland (Han, 2007). However, it is noted that not only natural environments with lots of vegetation can have a positive effect on our health. Urban environments and familiar places evoke positive associations and memories, which in turn can impact wellbeing (Bergeron et al., 2014; Hartig et al., 2014; Hartig, 2021). This might not have a direct effect on recreation, but as meaningful content to remember the past, it can positively affect our wellbeing (Appel et al., 2020b). Moreover, it has been shown that emotional associations and attachments we form with a place, which are based on personal experiences such as the restorative effects of a favorite location, influence the value we attribute to a landscape and, consequently, our overall wellbeing (Eisenhauer et al., 2000). Expanding the restorative perspective in this way allows for a more comprehensive understanding of how different environments contribute to health and wellbeing, moving beyond traditional theories to encompass a wider range of phenomena, problems, and solutions (Hartig, 2021). To illustrate, one might consider the incremental impact of repeated restorative experiences on an individual’s connection to a specific place. Research demonstrates that people frequently form attachments to locations they regularly visit for restoration. These attachments can become a significant aspect of their identity. Over time, the emotional bonds with such a place might enhance its restorative qualities, creating a mutually reinforcing relationship between restorative experiences, place attachment, and personal identity (Korpela et al., 2001; Hartig, 2004).
Although landscapes are already utilized in healthcare, there remains limited research on patients’ preferences for different landscapes and their potential to enhance physical and mental recovery (Song et al., 2022). Therefore, we chose environments that encompass (1) an urban setting, replicating an attractive shopping area with outdoor cafés in an old Swiss town that is popular with national citizens and international tourists; (2) a rural nature reserve, offering psychological benefits like mental repose, revitalization, and the freedom of expansive surroundings (King et al., 2017); and (3) an open forest, a familiar and enriching gathering spot, as is often found in forests of the Swiss Plateau (see Figures 1A, 2). Each environment catered to the needs and preferences of our target audience, particularly the elderly, such as safety, aesthetics, naturalness, and opportunities for leisure and social engagement, offering unique opportunities for restorative experiences (Wen et al., 2018). Crucial for selecting environments for the prototype were practical considerations such as terrain complexity and spatial constraints. To ensure a seamless transition from physical to virtual space, environments with minimal slopes or steps were selected. Technical constraints, such as the need for an area with relatively low visual ranges of a few kilometres in all directions for smooth 3D point cloud-based visualization, were also considered to optimize the user experience and minimize potential discomfort. This limits the choice of suitable environments to smaller, contained areas.

Figure 2. Selected landscapes: (A) the old city center of St. Gallen (Switzerland), (B) the Hinter Guldenen nature conservation zone (Forch, Switzerland) representing the rural area, (C) and the open forest of Käferberg (Zürich, Switzerland).
The selection ensured comparability across environments based on restoration functions, following Kaplan’s ART criteria for the four components (see Table 1) (Kaplan, 1995). The component “Being Away” elucidates the sensation of emancipation and repose afforded by these environments. To illustrate, the rural setting provided tranquil soundscapes and interactions with distinctive flora, fostering a sense of tranquility. The concept of “Fascination” pertains to the manner in which the various elements within these settings—such as the vibrant café scenes in the urban environment, the prominent single tree surrounded by stones in the forest, or the platform with a small pond in the rural reserve—engage and captivate attention effortlessly. The term “Extent” is used to describe the perceived spaciousness of an environment. Even smaller areas, such as a cozy café terrace or the tree line on the horizon in the rural reserve, can evoke a sense of expansive, immersive space. The concept of “Compatibility” emphasizes how these environments align with human inclinations, making them more comfortable and enjoyable. This can be observed in the familiar layout of the urban area or the natural flow of the forest landscape (Kaplan, 1995).
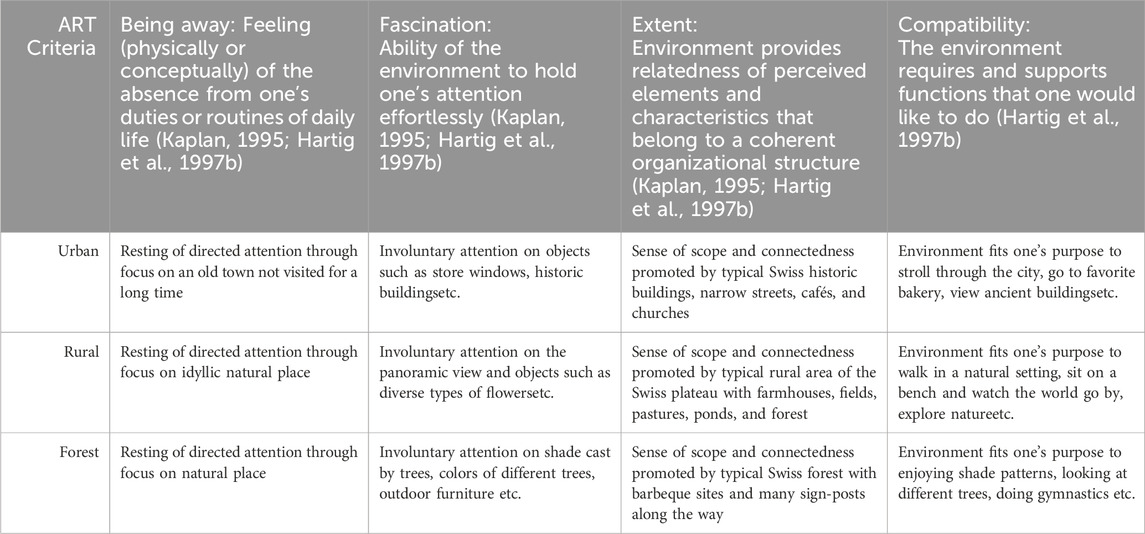
Table 1. Characterization of the three environments’ qualities considering the four components of Kaplan’s Attention Restoration Theory (ART) (Ward Thompson, 2018).
2.3 Collecting, processing and rendering point clouds
Terrestrial Laser Scanning (TLS) offers a reliable method to scan environments for 3D visualization of real-world settings (see Figure 1B, left). Scanner type choice is flexible, prioritizing high-density point cloud generation and accurate point colorization with scene photos. Our study used the TLS RIEGL VZ-1000 with a maximum measurement range of 1400 m and a calibrated Nikon D700 camera for 3D point cloud colorization (RIEGL Laser Measurement Systems, 2023). For each location, multiple scan positions were chosen in a strategic manner to ensure comprehensive coverage and capture the entire landscape in high detail (number of scan positions per environment: urban = 25, rural = 31, forest = 28). This approach was necessary to obtain overlapping regions and to gather all essential spatial data with the required precision and at the required level of detail (Tang and Alaswad, 2012; Zhang et al., 2016).
The choice of location determines whether a short-range scan with a range of 450 m or a long-range measurement with a range of typically 1,200 m is conducted. A short-range scan lasts approx. 5 min, whereas a long-range scan takes approx. 20 min. To extend the spatial coverage for allowing long-range views, we integrated Airborne Laser Scanning (ALS) point clouds (see Figure 1B, middle). We used for this purpose 1 km2 tiles of ALS data with an accuracy of 10 cm obtained from the Federal Office of Topograhy Swisstopo (Bundesamt für Landestopografie swisstopo, 2024).
The point cloud data underwent rigorous post-processing and refinement using a suite of specialized software tools, following methodologies outlined by Schalbetter et al. (2023) and Wissen Hayek et al. (2023) (see Figure 1C). The objective was to enhance data quality, eliminate noise, and prepare the point clouds for subsequent VR rendering. To ensure comprehensive coverage and minimize obstructions, at least two series of photos were taken for each scan location. This approach provided the images for colorizing the points and ensured that sections of the scanned environment were captured without cars or people obscuring the view.
The initial postprocessing step involved the use of Adobe Photoshop 25.6.0 (Adobe Systems Software Ireland Limited, 2024) to remove erroneous color information from the recorded images. The Layer Mask tool facilitated the seamless integration of portions of one image into the other when a moving object disrupted the initial shot. Furthermore, the Clone Stamp tool was employed to rectify color inconsistencies by duplicating colors from neighboring regions, particularly in areas that were covered several times (see Figure 3).
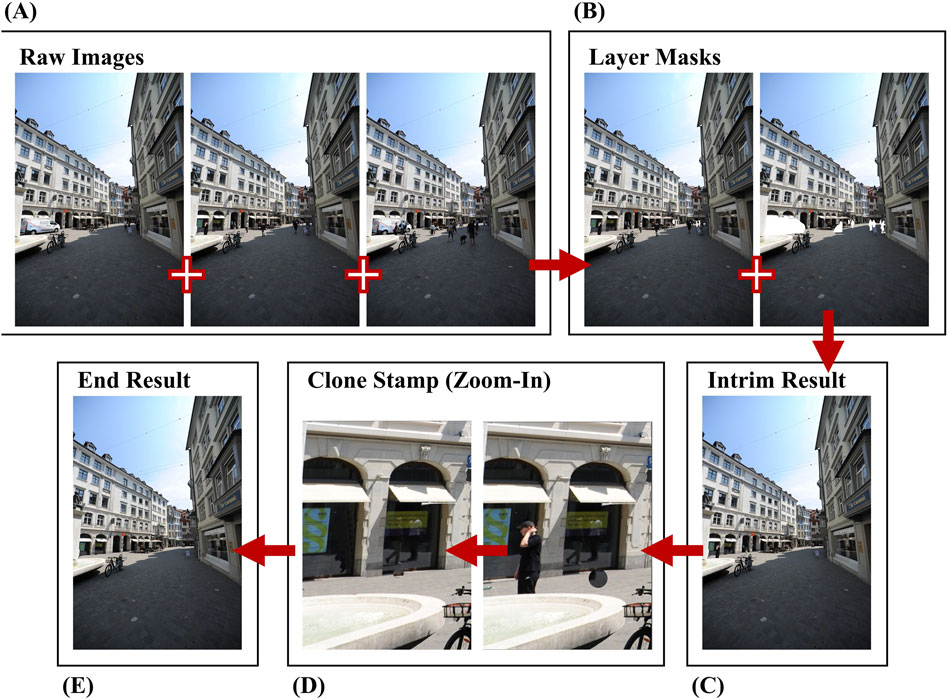
Figure 3. As many pedestrians passed by during the scanning process, three photographs were taken at this location (A). Layer masks were then applied to two of the photos to remove the majority of the human subjects (B). This resulted in the intermediate image (C), which was further refined using the clone stamp tool (D) to remove the remaining people in the image (E).
Subsequently, for further processing the point cloud scans we employed the RiSCAN Pro v2.14.1 (RIEGL Laser Measurement Systems, 2024) for Coarse Registration and Automatic Registration, aligning the overlapping scans to create a comprehensive representation of the entire scanned environment. With Automatic Registration the point clouds are shifted and rotated until the highest match between all scans is achieved. This automated workflow proved effective in the urban environment, as the building structure offers clear matching points. However, sufficiently flat surfaces and sharp edges are not given in landscapes with a high vegetation content. Therefore, Coarse Registration was used in the natural environments, where we searched individually in different scans for similar points and connected the clouds over them, with at least 4 connecting points per scan. This manual effort is relatively time-consuming, depending on the number of scan positions. Both registration methods resulted in an exact composition of all scans.
After registration of the individual scans, the Image Registration functionality enabled us to utilize the edited images for colorizing the point clouds for photorealistic representation of the environment. Then, with the Selection tool, we removed so-called noise points caused by reflective surfaces, such as windows, and other similar errors (see Figure 4). We additionally utilized CloudCompare v2.12.3 (CloudCompare, 2024) for tasks such as Scalar Field Filter by Value, Clone, Merge, and Segment. These functions were instrumental in eliminating superfluous points, such as those caused by moving vegetation. Further, gaps in the point clouds, e.g., due to objects blocking the laser beam, were filled by cloning and merging relevant sections of the point cloud. The Merge tool was further employed to combine the TLS and ALS point clouds. The rotation and transformation of the ALS data were adjusted based on the registration of the TLS data to align with the orientation of the TLS data. Subsequently, Lis Pro 3D v8.2.0 (Petrini-Monteferri, 2023) was utilized to Eliminate Isolated Points, thereby further reducing noise in the point cloud data.

Figure 4. Registered point cloud of the urban environment, with (A) showing the data before the deletion of reflection points in RiSCAN Pro, and (B) displaying the results after initial preprocessing steps conducted in RiSCAN Pro.
The sequence in which these software tools were applied was meticulously selected based on their specific functionalities and interdependencies. For example, for eliminating noise points in CloudCompare with the Scalar Field Filter, the point cloud needed to be colorized with the images beforehand to receive the noise points that are colored white.
A significant challenge in dynamic HMD-VR is smoothly displaying voluminous point clouds with millions of points (see Table 2 for point cloud sizes used in our project). When displaying such complex scenes, the frame rate can often drop when the computation time for each frame exceeds the refresh rate of the device. In turn, this is negatively impacting the user’s experience and comfort.
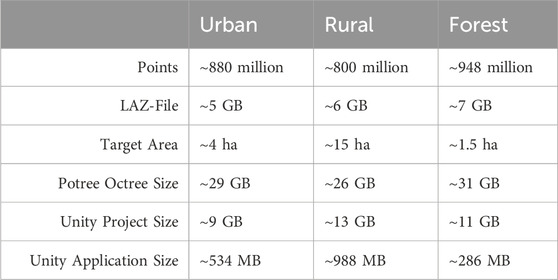
Table 2. Point cloud size in numbers of points, the size of the point cloud file (*.laz file format), and the size of the respective target area to be visualized and covered by the point cloud and the resulting size of the Unity project.
For real-time rendering, we stored point clouds using the potree octree structure (Schütz, 2024) and rendered them in a game engine. We employed Unity v2022.2.13f1 (Unity Technologies, 2024c) and imported the point clouds into a 3D Unity project using Fraiss’ Point Cloud Shader (Fraiss, 2017). This setup allowed for dynamic loading of point clouds with their full resolution from local storage into Unity, keeping the project size manageable (see Table 2). Potree adapts the modifiable nested octree structure, saving the original point cloud in node subsamples (Scheiblauer, 2014; Schütz, 2016). The rendering process is dynamic, tracking the camera’s orientation and streaming only the necessary point cloud data within the field of view (Fraiss, 2017) (see Figure 1D). The chosen rendering technique successfully maintains a stable frame rate of 90 Hz, which is optimal for the HTC Vive Pro Eye.
2.4 Integrating spatial sound
In general, the auralization of environments in VR can be done using recordings taken at specific locations, or acoustic environments can be designed from scratch by compiling different sounds from specific sources such as cars, church bells, birds, crickets etc. (Lindquist, 2014; Pieren, 2018; Ferreira, 2021). In our methodology, we prioritized fidelity, choosing to use auditory data recorded in-situ from the actual environment (Lindquist, 2014; Pieren, 2018), which was then edited for refinement.
Geolocated recordings were acquired by first dividing the environment into acoustically separate locations (forest, pasture, pond, church, café, etc.) (see Figure 1B, right). Second, we captured the sounds of these locations in the field utilizing an ambisonic sound-field microphone (Soundfield MKII Portable (SoundField, 2024)). We chose the ambisonic recording technique, which results in a four-channel signal that can be transcoded into various output formats for use in any playback setup, as it is well suited for interactive reproduction of spatial sound (Hong et al., 2017). Third, for postprocessing the ambisonic audio recordings, we used the digital audio workstation ProTools (Avid Technology, 2024), synthesizing the coherent sound sequences by cutting out unwanted sound (e.g., airplanes, humans passing, etc.) for each of the recording positions in their distinct location. In a fourth step, we integrated these sound sequences into Unity by positioning them in the VR environment at the respective position that corresponds to the recording position in the real world. Finally, we used Steam Audio (Valve Corporation, 2024) to decode the 4-channel audio of the ambisonic sequences to a binaural signal that is spatialized according to the head movement (Valve Corporation, 2017; Broderick et al., 2018). The head-tracked binaural audio reproduction technique allows the playback of spatial sounds with a pair of loudspeakers such as headphones on an HMD (Hong et al., 2017). This technique has been proven to enable soundscape representations with high ecological validity (Hong et al., 2019).
Some adjustments to the audio source settings in Steam Audio were necessary to ensure optimal integration within the VR environment. Specifically, the sound files were configured to play in a continuous loop and to activate automatically upon the application’s start, ensuring seamless and uninterrupted audio playback throughout the session. To enable the audio to adapt dynamically to user movements, the spatialize option was selected, and the audio was blended in 3D spatial mode. The audio spread was set to 360°, allowing the sound to be perceived from all directions. Additionally, the minimum and maximum audible distances were carefully adjusted to correspond to the characteristics of the sound recordings. These settings were customized for each project to ensure the most accurate and immersive auditory experience. By moving through the scene, the sound sequences fade in and out providing an immersive auditory environment.
2.5 Point cloud modeling
Point clouds provide a flexible means for manipulating virtual environments by adding or deleting points (Urech et al., 2020; 2022). This method enables the removal of elements that could detract from the restorative quality of the environment, such as parked cars in an urban setting. These removed point clouds of objects can be replaced, e.g., by segmented and cloned portions of the remaining point cloud using CloudCompare (see Figure 1E).
To enhance the training complexity in the HMD-VR exergame and support exercises such as dodging and leg lifts, we incorporated point clouds that could be toggled visible or invisible. This required scanning of common objects that fit naturally within the landscape, such as tree trunks for the forest and skateboards for the urban environment. Tree trunks, for example, were selected and exported from the processed point cloud of the forest landscape. To increase the quality and point density, we cloned and slightly transformed the selected point cloud subset multiple times.
When suitable objects were not found in the original point clouds, alternative methods were employed to acquire them. One approach involved using Polycam–LiDAR and 3D Scanner for iPhone and Android (Polycam, 2024), a cost-effective tool for scanning smaller 3D objects (Inal et al., 2023) (see Figure 5; left). The resulting scan was exported as *.laz file, imported into CloudCompare, where relevant parts of the scan were cut out, and then exported. Another approach was to download 3D objects (*.obj) from online sources and import them into CloudCompare. Using the “Sample Points” tool, a point cloud was automatically generated from these objects, with point density adjustments made based on the object’s size.
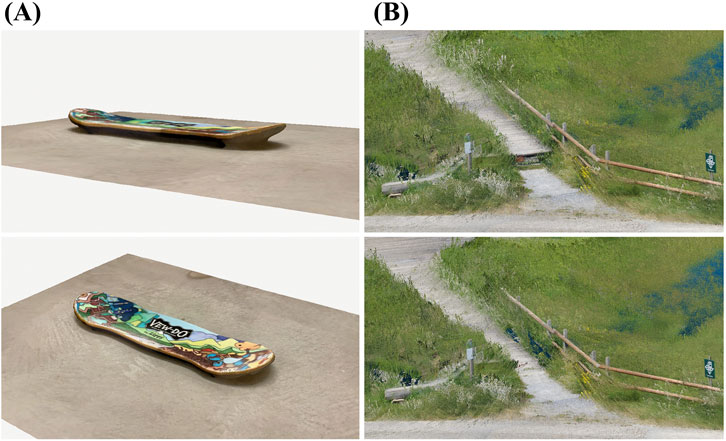

Figure 5. (A) Point cloud of a skateboard obtained using the Polycam–LiDAR and 3D Scanner for iPhone and Android (Polycam, 2024) application; (B) Platform in the rural area selected and adjusted in height to align with the surrounding ground.
The resulting point clouds, whether derived from the original point cloud, Polycam scans or transformed 3D objects, were exported from CloudCompare as *.ply files (binary) and then imported into Unity and converted into game objects using the Pcx plugin (Takahashi, 2019). We chose this plugin over the potree octree structure because it simplifies the process of placing and using point clouds as therapeutic objects in Unity.
In our work, we also utilized point cloud modification to spatially reposition entire sections of the environment. For instance, a slightly elevated platform could be adjusted to the same level as the surrounding ground, ensuring consistency between the virtual and physical gradients, e.g., a flat ground without steps in a training room. For this propose the virtual object (here: the elevated platform) had to be selected and then translated in the vertical direction to meet the ground level (see Figure 5; right).
2.6 Free motion
Utilizing point clouds for visualization in HMD-VR applications enables users to explore and interact with high-fidelity virtual environments in a natural and engaging manner, despite potential constraints in physical space (Nilsson et al., 2018). SteamVR™ Tracking (Valve Software, 2024a) provides an easy solution for free VR walking by tracking popular HMDs in 3D, easily integrated into Unity with the SteamVR Plugin (Unity Technologies, 2024b). We used the HTC VIVE Pro Eye headset (HTC Corporation, 2011b) with a wireless adapter (HTC Corporation, 2011c) and two VIVE SteamVR Base Stations 2.0 (HTC Corporation, 2011a), which track the HMD in the room (orientation, speed) using trigonometry (Valve Software, 2024b) (see Figure 1F left icon). Eliminating the need for tethered connections using the wireless adapter allows for greater freedom of movement, improving the overall user experience. Wireless VR headsets can minimize disruptions, and optimize user engagement and safety (Gonçalves et al., 2020).
The point cloud data imported into Unity are no game objects and, hence, no collider can be added to the points representing the ground surface. The collider is required to allow walking on the virtual ground. Therefore, we generated a digital surface model (DSM) to allow unimpeded traversal across the scanned point cloud terrain. This was achieved utilizing Esri’s ArcGIS v2.9.1 (ESRI, 2024) LAS Dataset To Raster, which is capable of directly interpolating the DSM from the point cloud files in the common LAS format. Depending on the environment and the point cloud itself, the interpolation type should be adjusted (e.g., binning, cell assignment: minimum/average, fill method: linear). The selection of the most appropriate interpolation type was an exploratory process, whereby several options were evaluated to identify the one that best matched the point cloud surface. In this regard, the specific landscape conditions to be accurately represented such as steps or slopes were of critical importance, which is why the interpolation type varied across different landscapes.
The resulting raster files (*.png) with an resolution of 25 cm were then imported into Unity through the Terrain Tools plugin (Makkonen, 2024). To guarantee that the raster is imported in the appropriate dimensions, it was essential to ascertain the maximum height discrepancy and the dimensions of the raster in ArcGIS. These values have to be entered as input in Unity for defining the extent and the extrusion of the raster cells. Subsequent minor adjustments were manually applied within the terrain tools as needed (e.g., set height, smooth height, raise or lower terrain).
The terrain model enabled the implementation of a game object equipped with a rigidbody component used to control the motion of an object by Unity’s physics engine. The rigidbody allows the virtual user’s game object (capsule) to react to movements in real-time, with the reactions being subject to gravity, preventing the virtual user from passing through or floating above the terrain. Working in tandem with the rigidbody, a capsule collider detects collisions between the virtual user and the terrain, facilitating realistic movement of the virtual user within the environment. A streaming camera, which is a child of the capsule, adapts its height based on the position data received from the VR headset in the real environment. This setup ensured that head movements, such as bending down, were accurately mimicked in the virtual world, thereby enhancing the realism of the VR experience (Wang et al., 2010) (see Figure 1F middle icon).
Additionally, a Redirect Walking (RDW) library, namely, OpenRDW (Li Y.-J. et al., 2021), was integrated into the Unity-based point cloud visualization framework. OpenRDW facilitates users to walk along virtual pathways, diverging slightly from their actual physical trajectories in the real environment (Razzaque, 2005; Li Y.-J. et al., 2021) (see Figure 1F right icon) while still providing high levels of immersion (Usoh et al., 1999; Lutfallah et al., 2024). Manipulation of the relationship between real and virtual motion is achieved by applying gains, including translation, rotation and curvature gains (Azmandian et al., 2016) which users do not notice since they primarily rely on their visual sense for orientation (Lutfallah et al., 2024). These gains create a subtle mismatch between the user’s perceived and actual movements, allowing for seamless redirection in the virtual environment. Each gain adjusts different aspects of motion, such as the user’s rotation, walking speed, or trajectory, while keeping changes within thresholds to ensure that the manipulations remain imperceptible (Steinicke et al., 2010; Williams and Peck, 2019; Lutfallah et al., 2024). This method is used to alter the user’s movements in the virtual environment, allowing redirection away from physical boundaries (Azmandian et al., 2016; Lutfallah et al., 2024). This feature lets users explore larger virtual environments beyond the 4 × 4 m2 confines of the physical tracked space in our setup.
2.7 Creation of a therapeutic game application
For the prototype of the HMD-VR exergame, we incorporated Unity’s default skybox with an unspectacular cloudless sky to establish a consistent natural ambiance across all environments. This choice represents a usual day conducive to outdoor recreation (Manyoky, 2015), providing a cost-effective way to achieve a convincing visual depiction of the sky (Raguman et al., 2019). Furthermore, we added a script to enable the navigation by jumping to predefined locations within the environment using get-key-down-commands (Unity Technologies, 2024a). The same commands were also used to manipulate the visibility of various training objects on the ground, such as skateboards or tree trunks (see Section 2.5). The final Unity scenes were compiled into a game application compatible with various platforms, including PC, Mac, and Linux, as well as VR headsets.
We configured our system with the following computational specifications: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090, Samsung SSD 980 PRO 2TB, 128 GB Memory, and 12th Gen Intel® Core™ i9-12900K CPU. Additionally, we utilized the Vive Pro Eye HMD, featuring a Dual OLED 2.5″ diagonal screen with a resolution of 1440 × 1600 pixels per eye and a refresh rate of 90 Hz, and including integrated Hi-Res stereo headphones (HTC Corporation, 2011b).
The VR exergame’s tasks were developed in close collaboration with physiotherapists to align with rehabilitation goals, particularly for gait security training. These tasks simulate real-world navigation and balance challenges that are common in Swiss hospital rehabilitation programs and are selected based on activities of daily living commonly performed by the elderly, as outlined in the Activities-Specific Balance Confidence (ABC) Scale (Powell and Myers, 1995). Examples include: “Walk to the restaurant (and read its name)”, “Walk to the large stone and take a seat” (with a real chair for sitting), “Bend down to have a closer look at something on the ground”, and “Walk beside the field (and count the purple flowers).” The exercises, including those in brackets, are dual-task exercises designed to increase difficulty by requiring users to divide their attention between walking and performing a secondary cognitive activity, thereby increasing both physical and cognitive engagement (Tasseel-Ponche et al., 2023). Additional tasks can be activated through modified point cloud elements, including: “Step over all the skateboards and scooters, starting with the left/right foot,” “Weave through obstacles in a slalom,” and “Side-step over tree trunks.” These exercises encourage participants to walk frequently, reinforcing gait security by improving coordination (Chiu and Chou, 2013), spatial awareness (Osoba et al., 2019), and step control (Okubo et al., 2017). Each task was selected to enhance users’ mobility and balance.
3 Gathering user feedback
Hospitalized participants aged 65 years or older with gait issues and requiring rehabilitation were recruited in three different hospitals between April and October 2024. Participants were eligible to complete multiple sessions within the same environment, with a maximum of one session per day. This study is part of a larger ongoing research project. The participants underwent 25-min VR sessions, starting with 5 min of sitting with the VR headset, followed by 20 min of gait and balance training with the HMD-VR exergame. Feedback was collected using the German translation of the Perceived Restoration Scale (PRS) (Cervinka et al., 2016) (see Table 3), semi-structured interviews, and observations during the session (see Supplementary Appendix SA). The PRS is a tool for assessing restorative qualities consisting of twenty-six items across seven dimensions, which can be aggregated into the four components of ART. Higher scores indicate greater restoration (Hartig et al., 1996; Hartig et al., 1997a; Ivarsson and Hagerhall, 2008; Berto, 2014; Pasini et al., 2014). The participants’ descriptions of why they rated specific scores on the PRS, in addition to the semi-structured interview guidelines and the observations done during the training sessions, provided further perspectives into how participants felt during the training session. It should be noted that some participants dropped out of the study due to a deterioration in their general health condition; however, none withdrew because of dissatisfaction with the VR experience or the study itself.
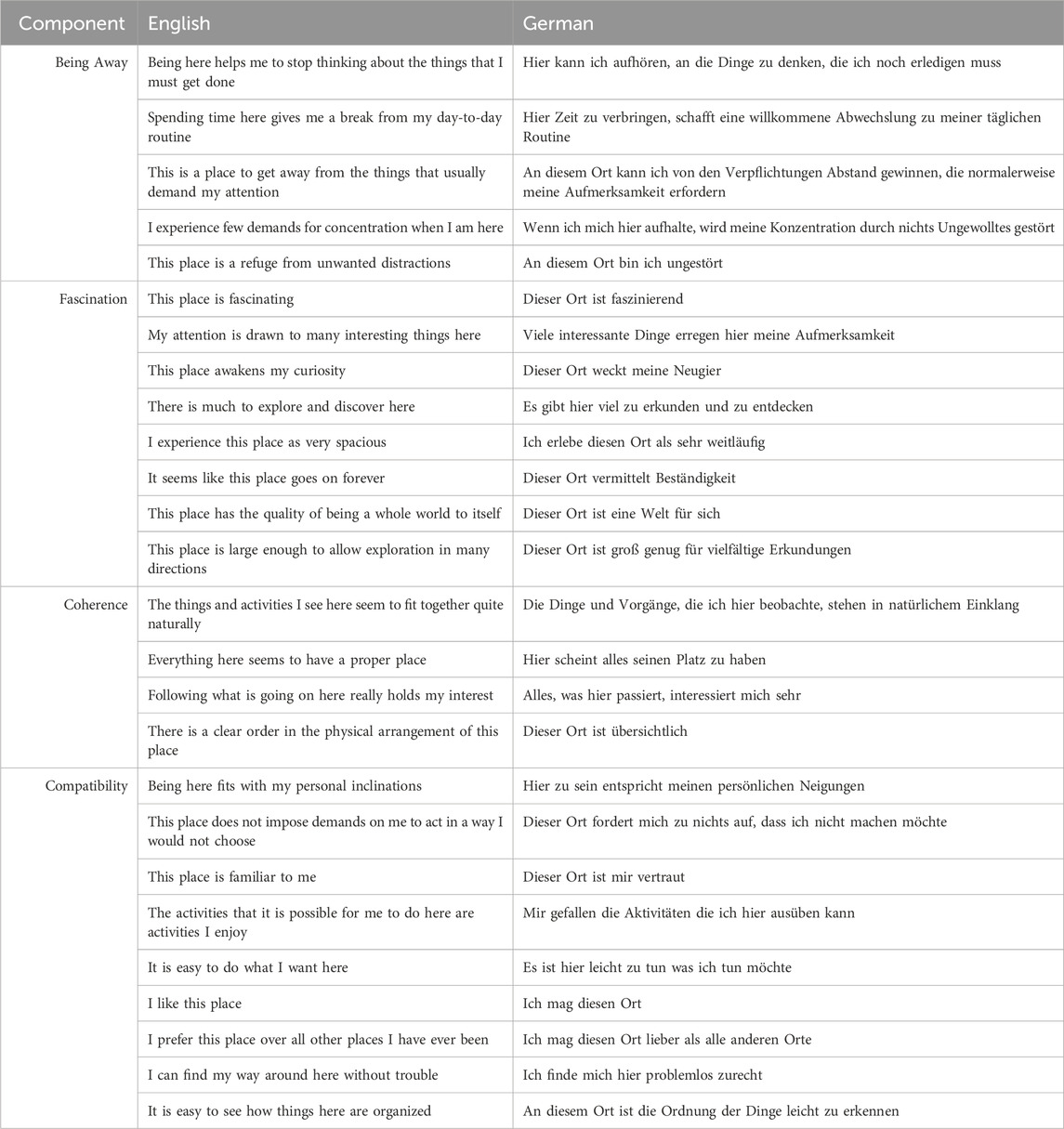
Table 3. Items from the Perceived Restoration Scales (PRS) in English, along with their corresponding German translations from Cervinka et al. (2016), and their related components of the Attention Restoration Theory (ART).
4 Results
The data was collected in 49 sessions with 19 participants (12 females, 7 males; mean age 85.08 ± 5.55 years), who engaged in 25 min of gait and balance training using the HMD-VR exergame across three virtual environments—urban (20 sessions), forest (20 sessions), and rural (9 sessions). Each participant was limited to one session per day, even if they participated in multiple sessions (ranging from 1 to 5). Furthermore, each participant experienced only one of the three environments. The analysis focused on: (1) the suitability of the technical methods, including 3D point cloud-based virtual environments, spatial sound, and motion tracking, assessed through technical evaluations and user feedback from observations; (2) the user experience regarding restoration, measured using the PRS scale and additional participant comments; and (3) the overall user experience of the VR exercise, gathered through semi-structured interviews and observational data.
4.1 Suitability of technical methods
Three distinct HMD-VR applications were successfully developed, each designed to replicate high-fidelity real-world environments using 3D point clouds from Terrestrial Laser Scanning (TLS) and Airborne Laser Scanning (ALS) data. These applications leveraged an advanced rendering method to ensure both high performance and visual fidelity. The applications utilized an advanced rendering method that ensured high performance and visual fidelity. The dynamic loading of point clouds facilitated smooth operation, even with large data sets, maintaining a stable frame rate of 90 Hz, which aligns with the graphics capabilities of the headset. No issues related to cyber sickness were reported by users, with none complaining of dizziness or other discomforts. Additionally, when asked about difficulties during the semi-structured interviews, several users reported no difficulties, noting that the movements within the virtual environment closely mirrored their real-world counterparts, contributing to a more natural and comfortable experience.
The auralization was effectively integrated, employing geolocated ambisonic sound recordings to create an immersive auditory environment. This environment was designed to dynamically adapt to users’ movements, aiming to enhance the sense of presence and engagement. Participant feedback gathered though the session observations indicated that this adaptive auditory environment contributed to a heightened sense of immersion. Several users specifically reported a noticeably calming effect of the natural sound, and appreciated the relaxing character of these auditory stimuli such as bird twittering or the rippling of water. Participants described specifically the rural environment’s sound atmosphere as calming. In contrast, the urban soundscape encouraged exploration and observation, with examples like searching for a church when hearing bells ring or being drawn to a bustling café after catching snippets of conversation. Overall, the participants in our study expressed appreciation for the soundscape with some variations in perception of its congruency depending on the environment. For instance, in the forest setting, participants often noted the sound of water sprinkling as a dominant feature, even when its source was not always visible. Additionally, some participants found the virtual environment visually quiet but perceived the ambient sound as noisy. In particular, participants in the urban setting criticized that the sounds of people engaged in conversation were particularly prominent, despite only a few individuals being visible within the VR scene.
The SteamVR™ Tracking system, combined with Unity’s rigidbody functionalities, enabled natural movement and terrain traversal within the VR environment (see Figure 6, or supplementary video). Redirect Walking (RDW), implemented via the OpenRDW library, allowed users to explore larger virtual spaces beyond the constraints of their physical area. Nevertheless, the activation of the redirected mechanism necessitates a certain degree of balance, as the resulting gains are still perceptible. In our clinical experience with patients exhibiting instability in their gait and preexisting balance issues, we found the RDW function unsuitable for this population. Due to their existing balance challenges, using RDW could have potentially introduced instability. Instead, we relied on get-key-down-inputs for changing location, which allowed participants to explore sufficient portions of the virtual landscape without the need for physical displacement. This method provided a safer and more controlled experience, eliminating the need for the RDW feature while maintaining an immersive and engaging environment. Additionally, the combination of simple, user-friendly tracking methods requires no technical expertise from either the patient or the physiotherapist, making it an ideal solution for gait rehabilitation in older adults.
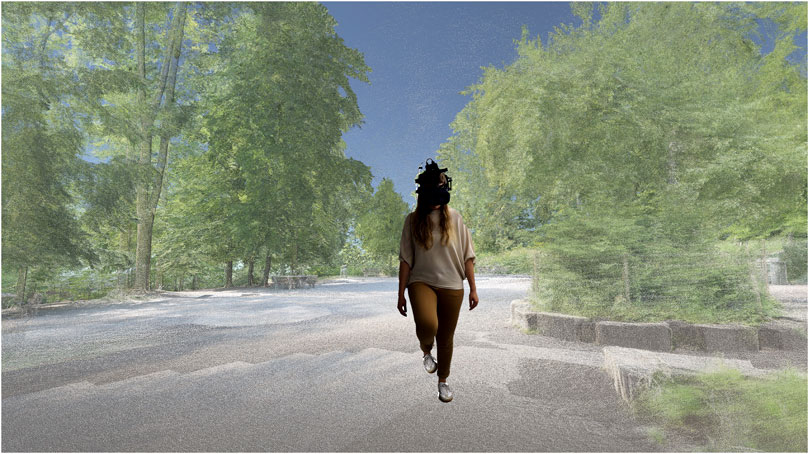

Figure 6. Illustration of free motion in the virtual reality environment that is enabled by tracking the real walking behavior and transforming it to the virtual reality. In this way, the user is exploring the virtual environment by physical walking in the real world.
4.2 User experience regarding presence, immersion, and restoration
The user experience regarding restoration and its subscales, measured using the PRS, was assessed in 49 sessions across urban (20), forest (20) and rural (9) landscapes, where participants engaged in 25 min of gait and balance training using the HMD-VR exergame. The analysis revealed that all environments fostered restoration (see Figure 7).
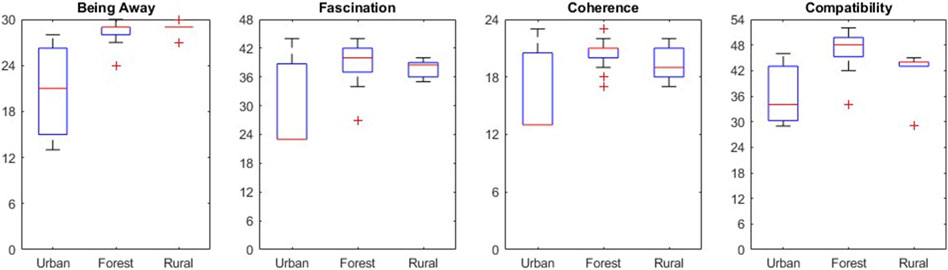
Figure 7. Perceived Restoration Scores (PRS) for each virtual environment (urban: n = 20, forest: n = 20, rural: n = 9), with the y-axis representing the range of min-max values for each sub-scale. The “Being Away” sub-scale reflects the participants’ sense of escape from daily routines, “Fascination” measures the degree to which the environment captivates attention, “Coherence” assesses the perceived organization and relatedness of environmental elements, and “Compatibility” evaluates how well the environment supports desired activities.
The ‘Being Away’ component, a measure of immersion, approached high value across all three virtual environments, indicating deep engagement [28.30 ± 2.91, (min 0 – max 30)]. The highest values were reached in the forest environment (28.80 ± 1.51), followed closely by the urban (27.78 ± 4.28) and rural (28.22 ± 1.79) environments. Participants frequently reported that they forgot they were in a hospital during the session, describing the experience as a welcome break from their daily routine and responsibilities.
The ‘Fascination’ component also recorded elevated scores in all environments, indicating that the environment effectively captured the participants’ attention [41.02 ± 5.61, (min 0 – max 48)]. The urban environment scored the highest with 42.39 ± 7.23, followed by the forest (40.35 ± 4.68) and rural (39.78 ± 3.31) environments. Distinctive landmarks such as fountains, ponds, and individual trees, helped participants orient themselves, as reported in the interviews and observed behaviors such as actively searching for these elements before performing the given task. Key features, like the church in the urban environment, the central tree in the stone circle in the forest, and in the rural environment the farm buildings (see Figure 2) served as reference points when participants navigated the virtual space or when the location in the virtual environment changed on get-key-down-inputs.
The “Coherence” and “Compatibility” components, which measure the comprehensibility of the environment and its support of participants’ needs, also demonstrated strong results [Coherence: 21.07 ± 2.58, (min 0 – max 24); Compatibility: 47.45 ± 6.09, (min 0 – max 54)]. In the Coherence scale, the urban and the forest environment almost scored the same (21.47 ± 3.41 vs. 21.25 ± 1.94). Also, in the Compatibility scale, the urban (48.89 ± 6.79) and forest (47.35 ± 4.78) environments both showed higher values than the rural environment (44.78 ± 6.96). None of the differences between the environment groups in the different components were significantly different from each other.
4.3 User experience of the exercise in the VR environment
The incorporation of dynamic point cloud manipulation features, such as the selective visibility of elements like skateboards and tree trunks, facilitated tailored simulations for various gait rehabilitation exercises like stepping over or around obstacles and navigating figure-eight patterns. For instance, when a patient felt secure in walking within the VR environment, stepping over obstacles could be introduced as a more challenging task. The ability to provide diverse exercise scenarios not only motivated participants but also facilitated repeated practice in varied contexts (see Figure 8). Users appreciated the varied training setups in the same VR environment made possible by these modifications, finding them engaging and beneficial. Patients mentioned, for example, that they would feel insecure stepping over obstacles in the real world and appreciated the opportunity to practice this skill in the VR environment. The integration of get-key-down-inputs for changing location allowed therapists to quickly change the user’s position within the virtual environment. Adding obstacles with this function enabled rapid adjustments to different training settings, providing a flexible and responsive training experience tailored to individual needs. For instance, some participants said that they did not feel able to step over obstacles in the first sessions so that they were switched off again, whereas in later sessions they had no problems with this task and the obstacles could be used as training elements.
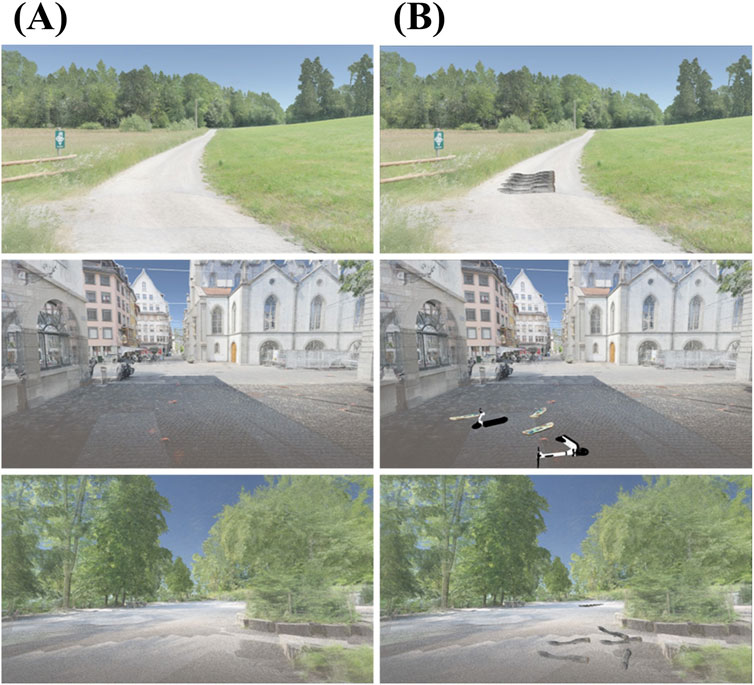

Figure 8. Examples of the three environments without (A) and with training objects (B), which can be manually turned visible or invisible depending on a user’s performance.
5 Discussion
5.1 Workflow for realistic VR environments
The aim was to establish a workflow for developing realistic environments that accurately mimic real-world settings using 3D geospatial data and motion tracking. Our prototypes allow users to navigate immersive environments and engage in tailored therapeutic activities. Dynamic point cloud manipulation in our prototypes presents users with challenges mirroring real-world obstacles in a safe environment (Dockx et al., 2016; Tasseel-Ponche et al., 2023). Our approach bridges the gap between traditional therapy and immersive virtual environments by accurately replicating real environments, facilitating easier skill transfer to everyday tasks (Montalbán and Arrogante, 2020). For instance, the elderly might navigate through a city, searching for restaurants and sitting down on a chair, or explore a forest, identifying the best path while avoiding tree roots. Future enhancements could be directed towards improving the adaptability and personalization of the exercises, such as enabling additional dual-task exercises or incorporating moving objects for dodging. However, the utilization of static 3D point clouds restricts the incorporation of moving objects, which could potentially enhance the realism of the environment and further facilitate the simulation of real-life tasks. Currently, approaches are being developed to coherently integrate animated point clouds for augmented reality, promising great opportunities for immersive experiences in virtual reality (Piazzolla et al., 2023).
Nevertheless, the generation of such realistic virtual reality environments is a time-consuming process. For instance, the capture of 20–30 point cloud scans for each environment requires approximately 10 h, exclusive of the planning phase. The subsequent postprocessing steps in RiSCAN Pro, CloudCompare, and Lis Pro 3D demand an additional 70 h per environment. These times were achieved by experienced users, although familiarity with the process does not significantly reduce the time and effort required due to the manual nature of these tasks. Additionally, the postprocessing time of images and the cleaning of point clouds are heavily influenced by moving objects; larger crowds and traffic can considerably extend the postprocessing duration. However, a well-planned process, where scanner locations are strategically chosen to minimize the number of scans (Jia and Lichti, 2022) while concurrently ensuring the inclusion of overlapping regions and the acquisition of all essential spatial data with the requisite levels of precision and granularity, can markedly diminish the workload (Tang and Alaswad, 2012; Zhang et al., 2016). In general, it takes about 40 h per landscape to integrate the processed data into Unity, depending on the amount of terrain modification required and the programmer’s familiarity with Unity’s features and dependencies.
5.2 Soundscape congruency and realism
Our system enhances realism and engagement by synchronizing sound with user interactions, which is known to contribute to the therapeutic effect by stress reduction (Lindquist et al., 2020). However, challenges remain in representing the sound of certain environments perceived as congruent in all aspects. Particularly, discrepancies between visual calm and auditory noise was identified as a potential disruptor to the immersive experience. Nevertheless, the user feedback underscores the potential of audiovisual HMD-VR exergames in providing immersive experiences during gait and balance training. This is highlighting the importance of further research and development in the field of the acoustic environment representation in VR to provide guidance for producing more realistic and congruent soundscapes.
5.3 Redirected walking versus get-key-down-inputs for navigation
Our exploration of RDW was motivated by the need to navigate longer distances in VR, despite limitations in real-world space (Schalbetter et al., 2022). Therefore, we adopted the RDW approach, which presents challenges associated with RDW-induced cybersickness (Rothacher, 2019). While RDW facilitates natural movement in confined spaces, it can also cause sensory conflicts and balance issues, especially in vulnerable populations, such as elderly participants in the exergame (Schmitz et al., 2018). Further advancements in RDW or better adjustments of its parameters are necessary to enable navigation through environments with reduced cybersickness risk, currently achievable only through SteamVR™ Tracking and additional manual keyboard inputs. However, this method does not allow for the expansion of environmental scope, calling for further research in motion translation. In the meantime, using get-key-down-inputs for changing locations is a viable solution, as it proved very suitable in the training sessions conducted.
5.4 Potential of restoration
Preliminary results from this ongoing study suggest that all three virtual environments (urban, forest, rural) promote restoration, as indicated by the PRS scale components. The ‘Being Away’ component, reflecting immersion, was high across all environments, with the forest environment showing the strongest engagement. This suggests that natural settings, which allow users to escape daily routines, provide greater immersion (Kaplan, 1995; Hartig et al., 1997b). Our results, consistent with previous studies (Han, 2007), show higher immersion in forested landscapes compared to rural settings, supporting the idea that forests are often favored for their restorative qualities.
However, in line with earlier research highlighting the positive effects of urban environments (Bergeron et al., 2014; Hartig et al., 2014; Hartig, 2021), the “Fascination” component—measuring the environment’s ability to capture attention—was highest in the urban environment. This is likely due to the variety of visual stimulus, such as historic buildings and store windows, that naturally draw attention. The “Coherence” component, which measures how well the environment’s elements are related and fit together, was similarly high in all three environments. These settings provided a strong sense of connectedness through their well-organized structures, whether it was the city’s historic buildings, the forest’s natural features, or the overview over the open rural landscape.
Finally, the “Compatibility” component, assessing how well the environment supports the participant’s intended activities, was also high in both the urban and forest environments. These settings aligned well with participants’ goals, whether it was strolling through the city or exploring nature, suggesting that both urban and natural environments can facilitate restorative activities in ways that enhance users’ experiences (Hartig et al., 1997b).
6 Conclusion
Our research, recognizing the need to connect restorative environments with health-promoting applications for gait rehabilitation, introduces a novel approach in developing an HMD-VR exergame. We developed a workflow for creating realistic environments using 3D geospatial data and motion tracking, enhancing realism through sound synchronization, and considering practical aspects of environment selection. Integrating spatial sounds and realistic environments in VR enables more immersive and engaging therapeutic experiences, potentially leading to better patients’ training outcomes. The exergame bridges the gap between traditional therapy and virtual environments, allowing participants to transfer therapeutic skills to real-world contexts.
Preliminary findings suggest that all three virtual environments—urban, forest, and rural—provide restorative effects, as indicated by the PRS scale components. These effects, driven by immersion, attention capture, coherence, and environmental compatibility, highlight the potential of immersive VR for promoting wellbeing during gait rehabilitation. However, further research is needed to explore the full range of benefits that restorative environments offer, including the incorporation of physiological assessments to measure attention restoration and stress reduction, e.g., employing electrodermal activity (van den Berg et al., 2003; Mavros et al., 2022; Rahma et al., 2022) or heart rate variability (Simons et al., 1999; Kim et al., 2018; Wilson et al., 2020).
Despite the promising results regarding the technical feasibility of developing such an exergame, our study faced limitations such as the static nature of 3D point clouds and the challenges associated with RDW-induced cybersickness. Further research is needed to address these issues and enhance the overall usability of the VR exergame. Future studies should focus on integrating moving objects into VR environments, developing advanced sound design techniques, and optimizing RDW parameters to minimize cybersickness. Additionally, future research should examine the effectiveness of these immersive VR interventions for rehabilitation, particularly for patients with gait impairments. Future studies analyzing gait patterns, stress reduction, and other therapeutic parameters across various environments will provide valuable insights into the clinical effectiveness of our HMD-VR exergame prototype.
Ultimately, our work contributes to the development of VR technologies for rehabilitation, offering new opportunities for enhancing therapeutic outcomes. By providing a more immersive and realistic training environment, VR exergames could become a valuable tool for healthcare providers, improving the quality of care for patients with gait impairments.
Data availability statement
The data that support the findings of this study are not publicly available due to the ongoing nature of the research. However, individuals interested in accessing the data may contact the corresponding author with their request.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Kantonale Ethikkommission Zürich. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
LS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Writing–original draft. AG-R: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing–review and editing. FG: Data curation, Software, Writing–review and editing. UW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by an ETH Research Grant (Grant agreement no. ETH-01 22-1). Open access funding by ETH Zurich.
Acknowledgments
The clinical trial was approved by the Kantonale Ethikkommission Zürich (BASEC-Nr. 2023-01894) on December 22, 2023. We extend our gratitude to all the participants for their time, patience, and dedication during the training sessions. We would also like to thank N. Aeschlimann and L. Engler for their valuable assistance in conducting the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. We used ChatGPT 3.5 (https://chatgpt.com/), Copilot with GPT-4 architecture (https://copilot.microsoft.com/), and DeepL Write (Version 24.9.1.13742, https://deepl.com/) to edit and refine written content. All AI-generated content has been reviewed and adapted by the authors.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frvir.2024.1502802/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
ALS, Airbone Laser Scanning; ART, Attention Restoration Theory; DSM, Digital Surface Model; Exergames, Video games incorporating exercise; HMD-VR, Head-Mounted Display Virtual Reality; PRS, Perceived Restoration Scale; RDW, Redirect Walking; TLS, Terrestrial Laser Scanner; VR, Virtual Reality.
References
Adobe Systems Software Ireland Limited (2024). Start with Photoshop. Amazing will follow. Adobe. Available at: https://www.adobe.com/ch_de/homepage/fragments/loggedout/row-custom-pods/marquee/marquee-brick/wide-brick/row-mashup-marquee-ps-pod-121859 (Accessed September 7, 2024).
Anderson, A. P., Mayer, M. D., Fellows, A. M., Cowan, D. R., Hegel, M. T., and Buckey, J. C. (2017). Relaxation with immersive natural scenes presented using virtual reality. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 88, 520–526. doi:10.3357/AMHP.4747.2017
Appel, L., Appel, E., Bogler, O., Wiseman, M., Cohen, L., Ein, N., et al. (2020a). Older adults with cognitive and/or physical impairments can benefit from immersive virtual reality experiences: a feasibility study. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 6, 329. doi:10.3389/fmed.2019.00329
Appel, L., Appel, E., Bogler, O., Wiseman, M., Cohen, L., Ein, N., et al. (2020b). Older adults with cognitive and/or physical impairments can benefit from immersive virtual reality experiences: a feasibility study. Front. Med. 6, 329. doi:10.3389/fmed.2019.00329
Avid Technology (2024). Pro tools. AVID. Available at: https://www.avid.com/pro-tools (Accessed March 6, 2024).
Azmandian, M., Grechkin, T., Bolas, M., and Suma, E. (2016). “The redirected walking toolkit: a unified development platform for exploring large virtual environments,” in 2016 IEEE 2nd workshop on everyday virtual reality (WEVR) (Greenville, SC, USA: IEEE), 9–14. doi:10.1109/WEVR.2016.7859537
Benfield, J. A., Taff, B. D., Newman, P., and Smyth, J. (2014). Natural sound facilitates mood recovery. doi:10.1089/eco.2014.0028
Bergeron, J., Paquette, S., and Poullaouec-Gonidec, P. (2014). Uncovering landscape values and micro-geographies of meanings with the go-along method. Landsc. Urban Plan. 122, 108–121. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2013.11.009
Berkman, M. I., and Akan, E. (2019). “Presence and immersion in virtual reality,” in Encyclopedia of computer graphics and games. Editor N. Lee (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 1–10. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-08234-9_162-1
Berto, R. (2014). The role of nature in coping with psycho-physiological stress: a literature review on restorativeness. Behav. Sci. (Basel) 4, 394–409. doi:10.3390/bs4040394
Bowler, D. E., Buyung-Ali, L. M., Knight, T. M., and Pullin, A. S. (2010). A systematic review of evidence for the added benefits to health of exposure to natural environments. BMC Public Health 10, 456. doi:10.1186/1471-2458-10-456
Brach, J. S., and VanSwearingen, J. M. (2013). Interventions to improve walking in older adults. Curr Transl Geriatr Exp Gerontol Rep 2, 230–238. doi:10.1007/s13670-013-0059-0
Broderick, J., Duggan, J., and Redfern, S. (2018). “The importance of spatial audio in modern games and virtual environments,” in 2018 IEEE games, entertainment, media conference (GEM) (Galway: IEEE), 1–9. doi:10.1109/GEM.2018.8516445
Browning, M. H. E. M., Mimnaugh, K. J., van Riper, C. J., Laurent, H. K., and LaValle, S. M. (2020a). Can simulated nature support mental health? Comparing short, single-doses of 360-degree nature videos in virtual reality with the outdoors. Front. Psychol. 10, 2667. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02667
Browning, M. H. E. M., Shipley, N., McAnirlin, O., Becker, D., Yu, C.-P., Hartig, T., et al. (2020b). An actual natural setting improves mood better than its virtual counterpart: a meta-analysis of experimental data. Front. Psychol. 11, 2200. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2020.02200
Bundesamt für Landestopografie swisstopo (2024). “Beschaffung von LiDAR-Daten,” in Bundesamt für Landestopograpfie swisstopo. Available at: https://www.swisstopo.admin.ch/de/lidar-daten-swisstopo (Accessed November 4, 2024).
Burdea, G. C. (2003). Virtual rehabilitation – benefits and challenges. Methods Inf. Med. 42, 519–523. doi:10.1055/s-0038-1634378
Cadore, E. L., Rodríguez-Mañas, L., Sinclair, A., and Izquierdo, M. (2013). Effects of different exercise interventions on risk of falls, gait ability, and balance in physically frail older adults: a systematic review. Rejuvenation Res. 16, 105–114. doi:10.1089/rej.2012.1397
Calabrò, R. S., Russo, M., Naro, A., De Luca, R., Leo, A., Tomasello, P., et al. (2017). Robotic gait training in multiple sclerosis rehabilitation: can virtual reality make the difference? Findings from a randomized controlled trial. J. Neurological Sci. 377, 25–30. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2017.03.047
Cano Porras, D., Siemonsma, P., Inzelberg, R., Zeilig, G., and Plotnik, M. (2018). Advantages of virtual reality in the rehabilitation of balance and gait: systematic review. Neurology 90, 1017–1025. doi:10.1212/wnl.0000000000005603
Cervinka, R., Schwab, M., Schönbauer, R., Hämmerle, I., Pirgie, L., and Sudkamp, J. (2016). My garden – my mate? Perceived restorativeness of private gardens and its predictors. Urban For. and Urban Green. 16, 182–187. doi:10.1016/j.ufug.2016.01.013
Chiu, S.-L., and Chou, L. S. (2013). Variability in inter-joint coordination during walking of elderly adults and its association with clinical balance measures. Clin. Biomech. 28, 454–458. doi:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2013.03.001
CloudCompare (2024). CloudCompare 3D point cloud and mesh processing software OPen Source Project. Available at: https://www.danielgm.net/cc/(Accessed September 4, 2024).
de Kort, Y. A. W., Meijnders, A. L., Sponselee, A. A. G., and IJsselsteijn, W. A. (2006). What’s wrong with virtual trees? Restoring from stress in a mediated environment. J. Environ. Psychol. 26, 309–320. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2006.09.001
Dockx, K., Bekkers, E. M., Van den Bergh, V., Ginis, P., Rochester, L., Hausdorff, J. M., et al. (2016). Virtual reality for rehabilitation in Parkinson’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 12, CD010760. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD010760.pub2
Echevarria Sanchez, G. M., Van Renterghem, T., Sun, K., De Coensel, B., and Botteldooren, D. (2017). Using Virtual Reality for assessing the role of noise in the audio-visual design of an urban public space. Landsc. Urban Plan. 167, 98–107. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2017.05.018
Eisenhauer, B. W., Krannich, R. S., and Blahna, D. J. (2000). Attachments to special places on public lands: an analysis of activities, reason for attachments, and community connections. Soc. and Nat. Resour. 13, 421–441. doi:10.1080/089419200403848
Emfield, A. G., and Neider, M. B. (2014). Evaluating visual and auditory contributions to the cognitive restoration effect. Front. Psychol. 5, 548. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00548
Ennadifi, E., Ravet, T., Mancas, M., El Amine Mokhtari, M., and Gosselin, B. (2023). “Enhancing VR gaming experience using computational attention models and eye-tracking,” in Proceedings of the 2023 ACM international conference on interactive media experiences (New York, NY, USA: Association for Computing Machinery), 194–198. doi:10.1145/3573381.3597218
ESRI (2024). ArcGIS Pro. ESRI. Available at: https://www.esri.com/en-us/arcgis/products/arcgis-pro/overview (Accessed October 4, 2024).
Ferreira, C. R. D. (2021). Creating immersive audio in a historical soundscape context. Comput. Sci. Available at: https://run.unl.pt/bitstream/10362/138814/1/Ferreira_2022.pdf (Accessed September 7, 2024).
Ford, D. M., Budworth, L., Lawton, R., Teale, E. A., and O’Connor, D. B. (2023). In-hospital stress and patient outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 18, e0282789. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0282789
Fraiss, S. M. (2017). “Rendering large point clouds in unity,” in Bachelorarbeit institute of computer graphics and algorithms. Vienna: University of Technology. Available at: https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2017/FRAISS-2017-PCU/.
Frost, S., Kannis-Dymand, L., Schaffer, V., Millear, P., Allen, A., Stallman, H., et al. (2022). Virtual immersion in nature and psychological well-being: a systematic literature review. J. Environ. Psychol. 80, 101765. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2022.101765
Girot, C. (2019). “‘Cloudism’: towards a new culture of making landscapes,” in Routledge research companion to landscape architecture (London, United Kinfdom: Routledge). 113–123. Available at: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9781315613116-12/cloudism-christophe-girot (Accessed September 7, 2024).
Gonçalves, G., Monteiro, P., Melo, M., Vasconcelos-Raposo, J., and Bessa, M. (2020). A comparative study between wired and wireless virtual reality setups. IEEE Access 8, 29249–29258. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2970921
Gutiérrez, M. A. A., Vexo, F., and Thalmann, D. (2008). Stepping into virtual reality. London: Springer. doi:10.1007/978-1-84800-117-6
Hamzeheinejad, N., Roth, D., Götz, D., Weilbach, F., and Latoschik, M. E. (2019). “Physiological effectivity and user experience of immersive gait rehabilitation,” in 2019 IEEE conference on virtual reality and 3D user interfaces (VR), 1421–1429. doi:10.1109/VR.2019.8797763
Hamzeheinejad, N., Straka, S., Gall, D., Weilbach, F., and Erich Latoschik, M. (2018). “Immersive robot-assisted virtual reality therapy for neurologically-caused gait impairments,” in 2018 IEEE conference on virtual reality and 3D user interfaces (VR), 565–566. doi:10.1109/VR.2018.8446125
Han, K.-T. (2007). Responses to six major terrestrial biomes in terms of scenic beauty, preference, and restorativeness. Environ. Behav. 39, 529–556. doi:10.1177/0013916506292016
Hartig, T. (2004). “Restorative environments,” in Encyclopedia of applied psychology. Editor C. D. Spielberger (New York: Elsevier), 273–279. doi:10.1016/B0-12-657410-3/00821-7
Hartig, T. (2021). “Restoration in nature: beyond the conventional narrative,” in Nature and psychology: biological, cognitive, developmental, and social pathways to well-being. Editors A. R. Schutte, J. C. Torquati, and J. R. Stevens (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 89–151. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-69020-5_5
Hartig, T., Evans, G. W., Jamner, L. D., Davis, D. S., and Gärling, T. (2003). Tracking restoration in natural and urban field settings. J. Environ. Psychol. 23, 109–123. doi:10.1016/S0272-4944(02)00109-3
Hartig, T., Kaiser, F. G., and Bowler, P. A. (1997a). Further development of a measure of perceived environmental restorativeness. Institutet för bostads-och urbanforskning. Available at: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:141287842.
Hartig, T., Korpela, K., Evans, G. W., and Gärling, T. (1996). Validation of a measure of perceived environmental restorativeness. Göteborg, Sweden: Department of Psychology, Göteborg University. Göteborg Psychological Reports, 26: 7.
Hartig, T., Korpela, K., Evans, G. W., and Gärling, T. (1997b). A measure of restorative quality in environments. Scandinavian Housing and Planning Research 14, 175–194. doi:10.1080/02815739708730435
Hartig, T., Mitchell, R., de Vries, S., and Frumkin, H. (2014). Nature and health. Annu. Rev. Public Health 35, 207–228. doi:10.1146/annurev-publhealth-032013-182443
Heritage, G., and Large, A. (2009). Laser scanning for the environmental sciences. John Wiley and Sons. doi:10.1002/9781444311952
Hong, J. Y., He, J., Lam, B., Gupta, R., and Gan, W.-S. (2017). Spatial audio for soundscape design: recording and reproduction. Appl. Sci. 7, 627. doi:10.3390/app7060627
Hong, J. Y., Lam, B., Ong, Z.-T., Ooi, K., Gan, W.-S., Kang, J., et al. (2019). Quality assessment of acoustic environment reproduction methods for cinematic virtual reality in soundscape applications. Build. Environ. 149, 1–14. doi:10.1016/j.buildenv.2018.12.004
Horsak, B., Simonlehner, M., Schöffer, L., Dumphart, B., Jalaeefar, A., and Husinsky, M. (2021). Overground walking in a fully immersive Virtual Reality: preliminary results of a comprehensive study on the effects on walking biomechanics. Gait and Posture 90, 100–101. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2021.09.051
Howard, M. C. (2017). A meta-analysis and systematic literature review of virtual reality rehabilitation programs. Comput. Hum. Behav. 70, 317–327. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2017.01.013
HTC Corporation (2011a). SteamVR Base station 2.0. VIVE European Union. Available at: https://www.vive.com/eu/accessory/base-station2/(Accessed June 24, 2024).
HTC Corporation (2011b). VIVE Pro eye specs and user guide - developer resources. Available at: https://developer.vive.com/resources/hardware-guides/vive-pro-eye-specs-user-guide/(Accessed April 12, 2024).
HTC Corporation (2011c). VIVE wireless adapter | VIVE United States. Available at: https://www.vive.com/us/accessory/wireless-adapter-full-pack/(Accessed November 14, 2024).
Huang, J., Lucash, M. S., Simpson, M. B., Helgeson, C., and Klippel, A. (2019). “Visualizing natural environments from data in virtual reality: combining realism and uncertainty,” in 2019 IEEE conference on virtual reality and 3D user interfaces (VR), 1485–1488. doi:10.1109/VR.2019.8797996
Inal, C. B., Bankoğlu Güngör, M., and Karakoca Nemli, S. (2023). Using a smartphone three dimensional scanning application (Polycam) to three dimensionally print an ear cast: a technique. J. Prosthet. Dent. doi:10.1016/j.prosdent.2023.04.026
Ivarsson, C. T., and Hagerhall, C. M. (2008). The perceived restorativeness of gardens – assessing the restorativeness of a mixed built and natural scene type. Urban For. and Urban Green. 7, 107–118. doi:10.1016/j.ufug.2008.01.001
Jamshidi, S., Parker, J. S., and Hashemi, S. (2020). The effects of environmental factors on the patient outcomes in hospital environments: a review of literature. Front. Archit. Res. 9, 249–263. doi:10.1016/j.foar.2019.10.001
Jia, F., and Lichti, D. D. (2022). A practical algorithm for the viewpoint planning of terrestrial laser scanners. Geomatics 2, 181–196. doi:10.3390/geomatics2020011
Kaplan, R., and Kaplan, S. (1989). The experience of nature: a psychological perspective. Cambridge: Press Syndicate of the University of Cambridge. Available at: https://books.google.com/books?hl=de&lr=&id=7l80AAAAIAAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PR7&dq=The+Experience+of+Nature:+A+Psychological+Perspective&ots=TrJWSFl73h&sig=BR8JzF1dchfa4c1tdGwOW1tnrC8.
Kaplan, S. (1995). The restorative benefits of nature: toward an integrative framework. J. Environ. Psychol. 15, 169–182. doi:10.1016/0272-4944(95)90001-2
Kern, F., Winter, C., Gall, D., Käthner, I., Pauli, P., and Latoschik, M. E. (2019). “Immersive virtual reality and gamification within procedurally generated environments to increase motivation during gait rehabilitation,” in 2019 IEEE conference on virtual reality and 3D user interfaces (VR), 500–509. doi:10.1109/VR.2019.8797828
Keshner, E. A. (2004). Virtual reality and physical rehabilitation: a new toy or a new research and rehabilitation tool? J. NeuroEngineering Rehabil. 1, 8. doi:10.1186/1743-0003-1-8
Kim, H.-G., Cheon, E.-J., Bai, D.-S., Lee, Y. H., and Koo, B.-H. (2018). Stress and heart rate variability: a meta-analysis and review of the literature. Psychiatry Investig. 15, 235–245. doi:10.30773/pi.2017.08.17
King, H. P., Morris, J., Graves, A., Bradbury, R. B., McGinlay, J., and Bullock, J. M. (2017). Biodiversity and cultural ecosystem benefits in lowland landscapes in southern England. J. Environ. Psychol. 53, 185–197. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2017.08.002
Kizony, R., Katz, N., and Weiss, P. L. (2003). Adapting an immersive virtual reality system for rehabilitation. J. Vis. Comput. Animat. 14, 261–268. doi:10.1002/vis.323
Korpela, K. M., Hartig, T., Kaiser, F. G., and Fuhrer, U. (2001). Restorative experience and self-regulation in favorite places. Environ. Behav. 33, 572–589. doi:10.1177/00139160121973133
Li, H., Dong, W., Wang, Z., Chen, N., Wu, J., Wang, G., et al. (2021). Effect of a virtual reality-based restorative environment on the emotional and cognitive recovery of individuals with mild-to-moderate anxiety and depression. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 18, 9053. doi:10.3390/ijerph18179053
Li, Y., Muñoz, J., Mehrabi, S., Middleton, L., Cao, S., and Boger, J. (2020). “Multidisciplinary iterative design of exergames (mide): a framework for supporting the design, development, and evaluation of exergames for health,” in HCI in games. Editor X. Fang (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 128–147. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-50164-8_9
Li, Y.-J., Wang, M., Steinicke, F., and Zhao, Q. (2021). “OpenRDW: a redirected walking library and benchmark with multi-user, learning-based functionalities and state-of-the-art algorithms,” in 2021 IEEE international symposium on mixed and augmented reality (ISMAR), 21–30. doi:10.1109/ISMAR52148.2021.00016
Lin, W., Zeng, C., Bao, Z., and Jin, H. (2023). The therapeutic look up: stress reduction and attention restoration vary according to the sky-leaf-trunk (SLT) ratio in canopy landscapes. Landsc. Urban Plan. 234, 104730. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2023.104730
Lindquist, M. (2014). The impact of sound on virtual landscape perception: an empirical evaluation of aural-visual interaction for 3D visualization. Sheffield, GB: University of Sheffield. Available at: https://etheses.whiterose.ac.uk/6675/(Accessed July 2, 2024).
Lindquist, M., Maxim, B., Proctor, J., and Dolins, F. (2020). The effect of audio fidelity and virtual reality on the perception of virtual greenspace. Landsc. Urban Plan. 202, 103884. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2020.103884
Lohse, K. R., Hilderman, C. G. E., Cheung, K. L., Tatla, S., and Loos, H. F. M. V. der (2014). Virtual reality therapy for adults post-stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis exploring virtual environments and commercial games in therapy. PLOS ONE 9, e93318. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0093318
Lutfallah, M., Ketzel, M., and Kunz, A. (2024). Redirected walking for exploration of unknown environments. Front. Virtual Real 4. doi:10.3389/frvir.2023.1259816
Makkonen, M. (2024). Terrain tools. Unity Doc. Available at: https://docs.unity3d.com/Manual/terrain-Tools.html (Accessed October 4, 2024).
Manyoky, M. (2015). Visual-acoustic simulation for landscape impact assessment of wind parks. Zurich: ETH Zurich. doi:10.3929/ethz-a-010497623
Massetti, T., da Silva, T. D., Crocetta, T. B., Guarnieri, R., de Freitas, B. L., Bianchi Lopes, P., et al. (2018). The clinical utility of virtual reality in neurorehabilitation: a systematic review. J. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Dis. 10, 1179573518813541. doi:10.1177/1179573518813541
Mattila, O., Korhonen, A., Pöyry, E., Hauru, K., Holopainen, J., and Parvinen, P. (2020). Restoration in a virtual reality forest environment. Comput. Hum. Behav. 107, 106295. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2020.106295
Mavros, P., J Wälti, M., Nazemi, M., Ong, C. H., and Hölscher, C. (2022). A mobile EEG study on the psychophysiological effects of walking and crowding in indoor and outdoor urban environments. Sci. Rep. 12, 18476. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-20649-y
McMahan, R. P., Bowman, D. A., Zielinski, D. J., and Brady, R. B. (2012). Evaluating display fidelity and interaction fidelity in a virtual reality game. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 18, 626–633. doi:10.1109/tvcg.2012.43
Mollazadeh, M., and Zhu, Y. (2021). Application of virtual environments for biophilic design: a critical review. Buildings 11, 148. doi:10.3390/buildings11040148
Montalbán, M. A., and Arrogante, O. (2020). Rehabilitation through virtual reality therapy after a stroke: a literature review. Rev. Científica la Soc. Enfermería Neurológica English52, 19–27. doi:10.1016/j.sedeng.2020.01.001
Nagashima, Y., Ito, D., Ogura, R., Tominaga, T., and Ono, Y. (2021). “Development of virtual reality-based gait training system simulating personal home environment,” in Annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society), 5764–5767. doi:10.1109/EMBC46164.2021.9631077
Newman, M., Gatersleben, B., Wyles, K. J., and Ratcliffe, E. (2022). The use of virtual reality in environment experiences and the importance of realism. J. Environ. Psychol. 79, 101733. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2021.101733
Nilsson, N. C., Serafin, S., Steinicke, F., and Nordahl, R. (2018). Natural walking in virtual reality: a review. Comput. Entertain. 16 (8), 1–22. doi:10.1145/3180658
Nukarinen, T., Istance, H. O., Rantala, J., Mäkelä, J., Korpela, K., Ronkainen, K., et al. (2020). “Physiological and psychological restoration in matched real and virtual natural environments,” in Extended abstracts of the 2020 CHI conference on human factors in computing systems (Honolulu, HI: ACM), 1–8. doi:10.1145/3334480.3382956
Nukarinen, T., Rantala, J., Korpela, K., Browning, M. H. E. M., Istance, H. O., Surakka, V., et al. (2022). Measures and modalities in restorative virtual natural environments: an integrative narrative review. Comput. Hum. Behav. 126, 107008. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2021.107008
Okubo, Y., Schoene, D., and Lord, S. R. (2017). Step training improves reaction time, gait and balance and reduces falls in older people: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 51, 586–593. doi:10.1136/bjsports-2015-095452
Osoba, M. Y., Rao, A. K., Agrawal, S. K., and Lalwani, A. K. (2019). Balance and gait in the elderly: a contemporary review. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 4, 143–153. doi:10.1002/lio2.252
Palacios-Navarro, G., and Hogan, N. (2021). Head-mounted display-based therapies for adults post-stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sensors 21, 1111. doi:10.3390/s21041111
Paralkar, S., Varas-Diaz, G., Wang, S., and Bhatt, T. (2020). Motor adaptation to real-life external environments using immersive virtual reality: a pilot study. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 24, 152–158. doi:10.1016/j.jbmt.2020.06.031
Pasini, M., Berto, R., Brondino, M., Hall, R., and Ortner, C. (2014). How to measure the restorative quality of environments: the PRS-11. Procedia - Soc. Behav. Sci. 159, 293–297. doi:10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.12.375
Petrini-Monteferri, F. (2023). LIS PRO 3D - point cloud processing. LASERDATA. Available at: https://www.laserdata.at/lis_pro_3d.html (Accessed September 4, 2024).
Piazzolla, P., Rossoni, M., Pozzi, M., Colombo, G., and Gribaudo, M. (2023). “Animated point clouds real-time rendering for extended reality,” in Volume 2: 43rd computers and information in engineering conference (CIE) (Boston, Massachusetts, USA: American Society of Mechanical Engineers). doi:10.1115/DETC2023-115124
Pieren, R. (2018). Auralization of environmental acoustical sceneries - Synthesis of Road Traffic. Railway and Wind Turbine Noise. doi:10.13140/RG.2.2.25324.00640
Polycam (2024). Polycam - LiDAR and 3D scanner for iPhone and android. Available at: https://poly.cam/(Accessed August 23, 2024).
Powell, L. E., and Myers, A. M. (1995). The activities-specific balance confidence (ABC) scale. Journals Gerontology Ser. A 50A, M28–M34. doi:10.1093/gerona/50A.1.M28
Raguman, R., Santhakumar, M., Thomas, X. P., and Revathi, M. (2019). 3D adventure game using unity. BIJSESC 9, 16–20. doi:10.9756/BIJSESC.9015
Rahma, O. N., Putra, A. P., Rahmatillah, A., Putri, Y. S. K. A., Fajriaty, N. D., Ain, K., et al. (2022). Electrodermal activity for measuring cognitive and emotional stress level. J. Med. Signals Sens. 12, 155–162. doi:10.4103/jmss.JMSS_78_20
Rajguru, C., Brianza, G., and Memoli, G. (2022). Sound localization in web-based 3D environments. Sci. Rep. 12, 12107. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-15931-y
Ratcliffe, E., Gatersleben, B., and Sowden, P. T. (2013). Bird sounds and their contributions to perceived attention restoration and stress recovery. J. Environ. Psychol. 36, 221–228. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2013.08.004
Razzaque, S. (2005). Redirected walking. NC, USA: CHapel Hill. Available at: https://www.proquest.com/docview/305393643?pq-origsite=gscholar&fromopenview=true&sourcetype=Dissertations%20&%20Theses.
RIEGL Laser Measurement Systems (2023). RIEGL - RiSCAN PRO. Available at: http://www.riegl.com/products/software-packages/riscan-pro/(Accessed August 14, 2023).
RIEGL Laser Measurement Systems (2024). Data sheet RIEGL VZ-1000. Available at: http://www.riegl.com/uploads/tx_pxpriegldownloads/DataSheet_VZ-1000_2017-06-14.pdf (Accessed May 13, 2024).
Ruotolo, F., Rapuano, M., Masullo, M., Maffei, L., Ruggiero, G., and Iachini, T. (2024). Well-being and multisensory urban parks at different ages: the role of interoception and audiovisual perception. J. Environ. Psychol. 93, 102219. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2023.102219
Schalbetter, L., Salliou, N., Sonderegger, R., and Grêt-Regamey, A. (2023). From board games to immersive urban imaginaries: visualization fidelity’s impact on stimulating discussions on urban transformation. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 104, 102003. doi:10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2023.102003
Schalbetter, L., Wissen Hayek, U., and Gutscher, F. (2022). “VR landscapes for therapy of gait insecurity,”. Berlin, Germany: DE: Wichmann Verlag. doi:10.14627/537724034
Scheiblauer, C. (2014). Interactions with gigantic point clouds. Wien: TU Wien Fakultät für Informatik. Available at: https://www.cg.tuwien.ac.at/research/publications/2014/scheiblauer-thesis/scheiblauer-thesis-thesis.pdf (Accessed May 13, 2024).
Schmitz, P., Hildebrandt, J., Valdez, A. C., Kobbelt, L., and Ziefle, M. (2018). You spin my head right round: threshold of limited immersion for rotation gains in redirected walking. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 24, 1623–1632. doi:10.1109/TVCG.2018.2793671
Schulte-Fortkamp, B., and Fiebig, A. (2023). “Soundscape: the development of a new discipline,” in Soundscapes: humans and their acoustic environment. Editors B. Schulte-Fortkamp, A. Fiebig, J. A. Sisneros, A. N. Popper, and R. R. Fay (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 1–21. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-22779-0_1
Schütz, M. (2016). Potree: renderin large point clouds in web browsers. Vienna: TU Wien Fakultät für Informatik. doi:10.34726/hss.2015.27710
Schütz, M. (2024). PotreeConverter GitHub. Available at: https://github.com/potree/PotreeConverter (Accessed September 4, 2024).
Simons, R. F., Detenber, B. H., Roedema, T. M., and Reiss, J. E. (1999). Emotion processing in three systems: the medium and the message. Psychophysiology 36, 619–627. doi:10.1111/1469-8986.3650619
Slater, M. (2018). Immersion and the illusion of presence in virtual reality. Br. J. Psychol. 109, 431–433. doi:10.1111/bjop.12305
Slater, M., and Wilbur, S. (1997). A framework for immersive virtual environments (FIVE): speculations on the role of presence in virtual environments. Presence Teleoperators and Virtual Environ. 6, 603–616. doi:10.1162/pres.1997.6.6.603
Smalley, A. J., White, M. P., Sandiford, R., Desai, N., Watson, C., Smalley, N., et al. (2023). Soundscapes, music, and memories: exploring the factors that influence emotional responses to virtual nature content. J. Environ. Psychol. 89, 102060. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2023.102060
Sona, B., Dietl, E., and Steidle, A. (2019). Recovery in sensory-enriched break environments: integrating vision, sound and scent into simulated indoor and outdoor environments. Ergonomics 62, 521–536. doi:10.1080/00140139.2018.1491643
Song, R., Chen, Q., Zhang, Y., Jia, Q., He, H., Gao, T., et al. (2022). Psychophysiological restorative potential in cancer patients by virtual reality (VR)-based perception of natural environment. Front. Psychol. 13, 1003497. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1003497
SoundField (2024). ST450 MKII soundfield portable. Soundfiled. Available at: https://www.soundfield.com/#/products/st450mk2 (Accessed March 6, 2024).
Steinicke, F., Bruder, G., Jerald, J., Frenz, H., and Lappe, M. (2010). Estimation of detection thresholds for redirected walking techniques. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 16, 17–27. doi:10.1109/TVCG.2009.62
Steinicke, F., Visell, Y., Campos, J., and Lécuyer, A. (2013). Hum. Walk. Virtual Environ. Percept. Technol. Appl. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-8432-6
Stienen, J., and Vorländer, M. (2015). Auralization of urban environments – concepts towards new applications.
Takahashi, K. (2019). Pcx - point cloud importer/renderer for unity GitHub. Available at: https://github.com/keijiro/Pcx (Accessed October 4, 2024).
Tang, P., and Alaswad, F. S. (2012). Sensor modeling of laser scanners for automated scan planning on construction jobsites. Construction Research Congress 2012Construction 1021–1031. doi:10.1061/9780784412329.103
Tao, G., Garrett, B., Taverner, T., Cordingley, E., and Sun, C. (2021). Immersive virtual reality health games: a narrative review of game design. J. NeuroEngineering Rehabil. 18, 31–21. doi:10.1186/s12984-020-00801-3
Tasseel-Ponche, S., Roussel, M., Toba, M. N., Sader, T., Barbier, V., Delafontaine, A., et al. (2023). Dual-task versus single-task gait rehabilitation after stroke: the protocol of the cognitive-motor synergy multicenter, randomized, controlled superiority trial (SYNCOMOT). Trials 24, 172. doi:10.1186/s13063-023-07138-x
Thake, C. L., Bambling, M., Edirippulige, S., and Marx, E. (2017). A psychoevolutionary approach to identifying preferred nature scenes with potential to provide restoration from stress. HERD 10, 111–124. doi:10.1177/1937586717705085
Ulrich, R. (2001). “Effects of healthcare environmental design on medical outcomes,” in Design and health: proceedings of the second international conference on health and design (Stockholm, Sweden: Svensk Byggtjanst), 49, 59.
Ulrich, R. S., Simons, R. F., Losito, B. D., Fiorito, E., Miles, M. A., and Zelson, M. (1991). Stress recovery during exposure to natural and urban environments. J. Environ. Psychol. 11, 201–230. doi:10.1016/S0272-4944(05)80184-7
Unity Technologies (2024a). Input.GetKeyDown. Unity Doc. Available at: https://docs.unity3d.com/ScriptReference/Input.GetKeyDown.html (Accessed December 4, 2024).
Unity Technologies (2024b). “SteamVR plugin,” in Unity asset store. Available at: https://assetstore.unity.com/packages/tools/integration/steamvr-plugin-32647 (Accessed July 5, 2024).
Unity Technologies (2024c). Unity - go create. Unity - Go Create. Available at: https://unity.com/(Accessed September 4, 2024).
Urech, P. R. W., Dissegna, M. A., Girot, C., and Grêt-Regamey, A. (2020). Point cloud modeling as a bridge between landscape design and planning. Landsc. Urban Plan. 203, 103903. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2020.103903
Urech, P. R. W., Mughal, M. O., and Bartesaghi-Koc, C. (2022). A simulation-based design framework to iteratively analyze and shape urban landscapes using point cloud modeling. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 91, 101731. doi:10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2021.101731
Usoh, M., Arthur, K., Whitton, M. C., Bastos, R., Steed, A., Slater, M., et al. (1999). “Walking > walking-in-place > flying, in virtual environments,” in Proceedings of the 26th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques - siggraph ’99 (Los Angeles, CA: Not Known: ACM Press), 359–364. doi:10.1145/311535.311589
Valtchanov, D., Barton, K. R., and Ellard, C. (2010). Restorative effects of virtual nature settings. Cyberpsychology, Behav. Soc. Netw. 13, 503–512. doi:10.1089/cyber.2009.0308
Valve Corporation (2017). Steam audio - introducing Steam audio - Steam news. Available at: https://store.steampowered.com/news/app/596420/view/1589135317218111209 (Accessed April 10, 2024).
Valve Corporation (2024). A benchmark in immersive audio solutions for games and VR. Steam. Audio. Available at: https://valvesoftware.github.io/steam-audio/(Accessed October 4, 2024).
Valve Software (2024a). SteamVR tracking. Available at: https://partner.steamgames.com/vrlicensing (Accessed July 5, 2024).
Valve Software (2024b). Welcome to steamworks. Available at: https://partner.steamgames.com/vrlicensing (Accessed May 7, 2024).
van den Berg, A. E., Koole, S. L., and van der Wulp, N. Y. (2003). Environmental preference and restoration: (How) are they related? J. Environ. Psychol. 23, 135–146. doi:10.1016/S0272-4944(02)00111-1
Wang, S., Mao, Z., Zeng, C., Gong, H., Li, S., and Chen, B. (2010). “A new method of virtual reality based on Unity3D,” in 2010 18th international conference on geoinformatics (Beijing, China: IEEE), 1–5.
Ward Thompson, C. (2011). Linking landscape and health: the recurring theme. Landsc. Urban Plan. 99, 187–195. doi:10.1016/j.landurbplan.2010.10.006
Ward Thompson, C. (2018). “Landscape perception and environmental psychology,” in The routledge companion to landscape studies (London, United Kingdom: Routledge). Available at: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9781315195063-2/landscape-perception-environmental-psychology-catharine-ward-thompson (Accessed September 7, 2024).
Wen, C., Albert, C., and Von Haaren, C. (2018). The elderly in green spaces: exploring requirements and preferences concerning nature-based recreation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 38, 582–593. doi:10.1016/j.scs.2018.01.023
White, M. P., Yeo, N. L., Vassiljev, P., Lundstedt, R., Wallergård, M., Albin, M., et al. (2018). A prescription for “nature”—the potential of using virtual nature in therapeutics. Neuropsychiatric Dis. Treat. 14. doi:10.2147/NDT.S179038
Williams, N. L., and Peck, T. C. (2019). Estimation of rotation gain thresholds considering FOV, gender, and distractors. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 25, 3158–3168. doi:10.1109/TVCG.2019.2932213
Wilson, K. A., James, G. A., Kilts, C. D., and Bush, K. A. (2020). Combining physiological and neuroimaging measures to predict affect processing induced by affectively valent image stimuli. Sci. Rep. 10, 9298. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-66109-3
Winter, C., Kern, F., Gall, D., Latoschik, M. E., Pauli, P., and Käthner, I. (2021). Immersive virtual reality during gait rehabilitation increases walking speed and motivation: a usability evaluation with healthy participants and patients with multiple sclerosis and stroke. J. Neuroeng Rehabil. 18, 68. doi:10.1186/s12984-021-00848-w
Wissen Hayek, U., Gutscher, F., Braune, P., Dantas, N., Roost, D., Schürch, J., et al. (2023). Sensing River and floodplain biodiversity – developing a prototype. J. Digital Landsc. Archit. 8, 523–532. doi:10.14627/53774005
Wissen Hayek, U., Waltisberg, D., Philipp, N., and Grêt-Regamey, A. (2016). Exploring issues of immersive virtual landscapes for the support of participatory spatial planning support. Research Collection 1, 100–108. doi:10.14627/537612012
Yeo, N. L., White, M. P., Alcock, I., Garside, R., Dean, S. G., Smalley, A. J., et al. (2020). What is the best way of delivering virtual nature for improving mood? An experimental comparison of high definition TV, 360° video, and computer generated virtual reality. J. Environ. Psychol. 72, 101500. doi:10.1016/j.jenvp.2020.101500
Yu, C.-P., Lee, H.-Y., Lu, W.-H., Huang, Y.-C., and Browning, M. H. E. M. (2020). Restorative effects of virtual natural settings on middle-aged and elderly adults. Urban For. and Urban Green. 56, 126863. doi:10.1016/j.ufug.2020.126863
Zhang, C., Kalasapudi, V. S., and Tang, P. (2016). Rapid data quality oriented laser scan planning for dynamic construction environments. Adv. Eng. Inf. 30, 218–232. doi:10.1016/j.aei.2016.03.004
Keywords: head-mounted display virtual reality (HMD-VR) exergame, gait and balance training, audiovisual simulation, motion tracking, 3D point cloud modeling, restorative environments
Citation: Schalbetter L, Grêt-Regamey A, Gutscher F and Wissen Hayek U (2025) High-fidelity immersive virtual reality environments for gait rehabilitation exergames. Front. Virtual Real. 5:1502802. doi: 10.3389/frvir.2024.1502802
Received: 27 September 2024; Accepted: 29 November 2024;
Published: 06 January 2025.
Edited by:
Gerrit Meixner, Heilbronn University, GermanyReviewed by:
Stefan Marks, Auckland University of Technology, New ZealandStavroula Ntoa, Foundation for Research and Technology Hellas (FORTH), Greece
Copyright © 2025 Schalbetter, Grêt-Regamey, Gutscher and Wissen Hayek. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Laura Schalbetter, c2NoYWxhdXJAZXRoei5jaA==
 Laura Schalbetter
Laura Schalbetter Adrienne Grêt-Regamey
Adrienne Grêt-Regamey Fabian Gutscher
Fabian Gutscher Ulrike Wissen Hayek
Ulrike Wissen Hayek