- 1Joint School of Design and Innovation, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China
- 2XJTU-POLIMI Joint School of Design and Innovation, Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy
- 3School of Mechanical Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China
- 4School of Future Technology, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China
- 5Department of Orthopaedics, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China
- 6School of Automation Science and Engineering, Xi’an Jiaotong University, Xi’an, China
- 7Department of Electronics, Information and Bioengineering, Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy
- 8School of Basic Medicine, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
- 9Luhe Clinical Medical College, Capital Medical University, Beijing, China
- 10Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Independent University, Bangladesh, Dhaka, Bangladesh
- 11Department of Mechanical Engineering, Politecnico di Milano, Milan, Italy
- 12Department of Human-Centered Design, Faculty of Industrial Design Engineering, Delft Technology of University, Delft, Netherlands
Robotic surgery, also known as robotic-assisted surgery (RAS), has rapidly evolved during the last decade. RAS systems are developed to assist surgeons to perform complex minimally invasive surgeries, and necessitate augmented interfaces for precise execution of these image-guided procedures. Extended Reality (XR) technologies, augmenting the real-world perception via integrating digital contents, show promise in enhancing RAS efficacy in various studies. Despite multiple reviews on technological and medical aspects, the crucial elements of human-robot interaction (HRI) and user experience (UX) remain underexplored. This review fills this gap by elucidating HRI dynamics within XR-aided RAS systems, emphasizing their impact on UX and overall surgical outcomes. By synthesizing existing literature, this systematic review study identifies challenges and opportunities, paving the way for improved XR-enhanced robotic surgery, ultimately enhancing patient care and surgical performance.
1 Introduction
Robotic surgery, using “remote telepresence manipulators,” significantly enhances precision and control in surgical procedures (Herron and Marohn, 2008). Beginning as early concepts and now spanning over 3,000 sets globally, robotic-assisted surgery (RAS) systems have steadily garnered the acceptance in various clinical practices (Kalan et al., 2010; Marino et al., 2018; Ghezzi and Campos Corleta, 2016). RAS demonstrates transformative potential across oncology, orthopedics, cardiology, and neurosurgery by mitigating inherent limitations observed in conventional surgical approaches (Schweikard et al., 2015). FDA-approved robotic systems like the da Vinci Surgical System, Mazor X Stealth Edition, and Revo-i Robotic Surgical System have enhanced treatments across various medical fields including urology, gynecology, general surgery, thoracic surgery, spine surgery, orthopedics, and colorectal surgery. By reducing incisions and accelerating recovery, they play a crucial role in healthcare (Vijayakumar and Shetty, 2020). For instance, robotic surgery enhances precision, control, and access in complex areas, benefiting delicate surgeries like gynecology and urology (Buffi et al., 2015; Wimberger and Schindelhauer, 2013). It minimizes patients’ trauma, accelerates recovery (Weaver and Steele, 2016), offers superior 3D visualization for accurate interventions (Lanfranco et al., 2004), improves surgeon ergonomics (Camarillo et al., 2004), and enables complex procedures minimally invasive (Ibrahim et al., 2012).
Despite these advancements, the implementation of robotic surgery faces challenges, including instrument size limitations, difficulties in manipulating the instruments and the lack of tactile feedback, which can increase tissue damage risks (Corcione et al., 2004; Giugliano et al., 2022). Integrating these systems into operating environments demands new training protocols and adjustments to ergonomics and communication (Catchpole et al., 2024; Bolenz et al., 2010). Significant financial barriers, including high acquisition, operational costs, and the expenses for operating room adaptations, remain formidable obstacles to widespread RAS, highlighting the complexities of incorporating advanced surgical technologies in practice (Tandogdu et al., 2015; Souders et al., 2017).
Immersive technologies, bolstered by robust software-hardware integration, are revitalizing the medical field (Deng et al., 2023), particularly in RAS. The immersive feature of these technologies has shown efficacy in enhancing surgeons’ experiences. Tai et al. (2021) introduced an immersive augmented reality (AR) lobectomy training system, improving novice and surgical skills. Coelho and Defino (2018) devised an AR-based preoperative planning technique for metopic craniosynostosis treatment, enhancing surgical preparation. Additionally, Fukushima et al. (2007) developed a mixed reality (MR) surgical simulation, ManMoS, for orthognathic surgery, demonstrating its applicability in XR and RAS technologies. Moreover, advancements in head-mounted displays (HMDs) from MagicLeap, Microsoft, and Oculus, coupled with cost reductions, are facilitating further research and experimentation in XR and RAS applications in medical surgeries across various fields.
2 Related work
In the digital era, Extended Reality (XR) technologies redefine the boundaries between the real and virtual worlds. XR, comprising virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR), merges physical and digital realms, providing users with immersive and interactive experiences. VR offers a fully virtual environment, AR overlays virtual elements onto the real world, and MR integrates virtual elements interacting with reality. Originating from Milgram and Kishino’s reality-virtuality (RV) continuum in 1994, XR enables users to engage with digital environments replicating, superimposing, or blending with reality (Stanney et al., 2021).
Immersive experiences are central to XR, defining the degree of user absorption and engagement within digital environments. Both emerging from immersive experiences, immersion envelops users in digitally constructed worlds, while presence makes users feel physically present in virtual spaces rather than passively viewing computer-generated images (Witmer and Singer, 1998). The principle of immersion, which deeply engage users and evoke presence, enhances human-computer interaction, notably in the medical field. Studies demonstrated increased heterogeneity of performances in objective measures compared to 2D displays, particularly concerning anatomic complexity (Vardhan, 2022).
Robotic surgery demonstrates the opportunities of integrating advanced human-computer interaction (HCI) technologies to improve surgical precision and ergonomics (Yu et al., 2022; Staub et al., 2012). Such technologies like immersive interfaces offer precise control and enhanced spatial understanding (Yu et al., 2022). Immersive interfaces such ask HoloLens 2 could provide gaze-contingent controls and vocal protocals that integrate into surgical procedures smoothly, making interactions more intuitive (Staub et al., 2012). Force-feedback controllers replicate tactile sensations, increasing the realism of the surgical procedure (Greer et al., 2008). XR headsets like Vision Pro embedded environmental sensors and cameras that recognize gesture and movements, allowing surgeons to use natural movements for robot control, improving usability and efficiency (Li et al., 2020).
In recent years, XR technologies has been widely applied in RAS. In spinal medicine, Morimoto et al. (2022) summarized the significant contributions of XR combined with surgical robots. Elmi-Terander et al. (2019) found that the use of AR navigation significantly improved the accuracy of screw placement and reduced the risks associated with thoracic spine surgery. Regarding cardiovascular surgery, Andrews et al. (2019) examined the application of XR in combination with the da Vinci surgical robot. The 3D images provided by XR enabled surgeons to assess intraoperative conditions faster and thus significantly reduced the radiation exposure to surgeons during the operation. In the field of laparoscopy, Porpiglia et al. (2018) and Edgcumbe et al. (2016) attempted robotic-assisted laparoscopic partial Nephrectomy respectively. Ahmed stated that all surgical options for clamping were successful, avoiding ischemia of the healthy residual kidney. Edgcumbe et al. (2016) believed that the most useful function of the XR surgical robot was that the surgical system would alert the surgeon when the instruments had reached a certain distance from the tumor center. This warning helped surgeons to avoid the tumor and minimize the removal of healthy tissue. In summary, XR-enhanced robotic surgery indeed develops rapidly and contributes to the surgery and surgeons.
In XR-enhanced robotic surgery, the interaction between the surgeon and the system involves frequent communication through an advanced interface for precisely controlled surgical maneuvers. User experience plays a crucial role in this interaction, encompassing the feelings and perceptions of surgeons while using the system. According to Overbeeke (2002) and Russell (2003), user experience refers to the diverse experiences arising from the intricate interplay of perception, action, motivation, emotion, and cognition within an individual’s body, influencing his/her wellbeing. User experience closely aligns with general experience, combining various elements to encompass all affective episodes arising from human-computer interactions (Hassenzahl and Tractinsky, 2006; Desmet and Hekkert, 2007). Therefore, the main goal of user experience is to facilitate intuitive and seamless interactions between humans and other elements of a system. Research emphasizes the importance of user experience in human-computer interaction within surgical settings, such as evaluating UX in maxillofacial surgery planning (Filippi et al., 2021), exploring UX in immersive virtual environments for healthcare (Mäkinen et al., 2022), and assessing user acceptance of surgical technologies like intraoperative cameras (Song et al., 2024; Saun and Grantcharov, 2021). However, existing discussions on XR-enhanced robotic surgery primarily emphasize technology development, validity and its applications in surgical practices, yet they often overlook the critical analysis of interaction methods and user experience in this advanced surgical approach.
Therefore, this systematic review aims to answer the following review questions:
RQ1: What are the components of human-computer interaction in the XR-enhanced robotic surgery?
RQ2: What are the components and the corresponding measurements of user experience during XR-enhanced robotic surgery?
RQ3: What benefits can XR-enhanced robotic surgery contribute in improving the user experience of surgeons?
RQ4: What are the existing limitations of technology development in improving the user experience of surgeons in XR-enhanced robotic surgery?
3 Methodology
This systematic review followed the PRISMA extension for systematic reviews (PRISMA-S), and the authors demonstrated a broad overview of user experience during XR-enhanced human-computer interaction in robotic-assisted surgery through the literature review. In this section, the methods applied in this study are introduced as follows.
3.1 Paper search design
A comprehensive search on the PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, IEEE XPlore and ACM Digital Library was conducted from 14th January 2024 to 15th January 2024. The keywords searched in the title and abstract are adapted from a similar review study conducted by Qian et al. (2019): (“virtual reality” OR “augmented reality” OR “mixed reality” OR “extended reality”) AND (“surgical robot” OR “surgical robotics” OR “medical robot” OR “medical robotics” OR “da Vinci” OR “robot assisted” OR “robotic assisted” OR “robot aided” OR “robotic aided” OR “robotic surgery” OR “human-robot interaction in surgery” OR “human-robot collaboration in surgery”). In this study, various kinds of synonyms were applied to ensure enough relevant papers were included.
3.2 Inclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria of this study were: 1) studies written in English; 2) studies published in peer-reviewed journal or conference after 1995; 3) studies that have both XR facility and robotic-assisted surgery system; 4) studies that contain user study of the surgeons or medical trainees in XR-enhanced RAS. the authors also excluded the unqualified literature that were: 1) duplicated papers; 2) unable to get access to full text; 3) review papers; 4) in irrelevant topics.
3.3 Study selection and data Collection
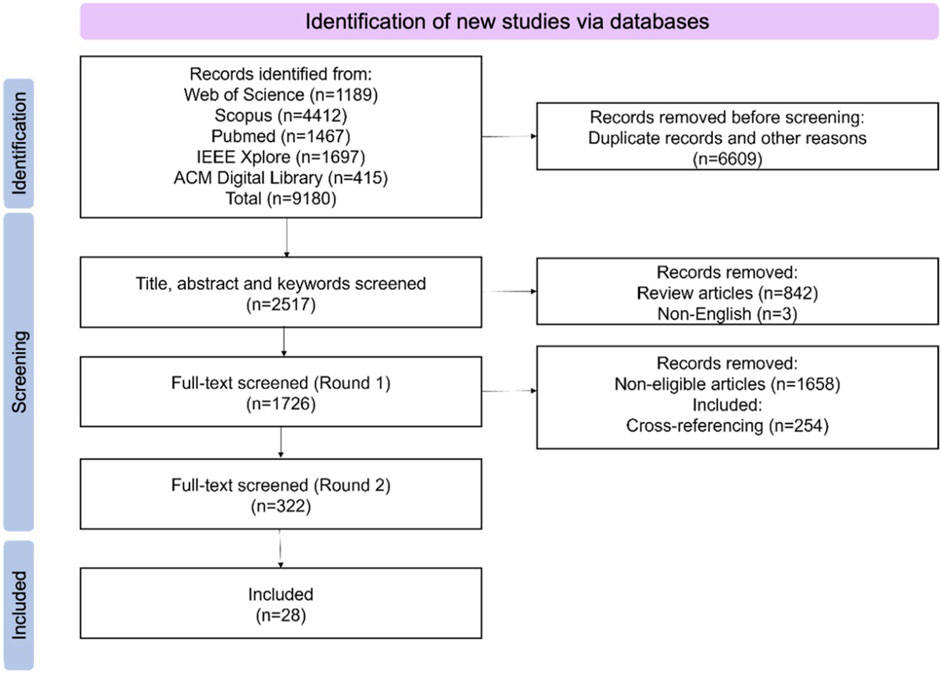
In total 9,180 articles were identified from the abovementioned databases after removing the duplications. The 28 articles were found by five authors collectively following PRISMA protocol and inclusion criteria. The screening process was performed using Zotero software in the following order: 1) eliminate the duplicated articles using an automatic plugin in Zotero and then check manually by two authors; 2) screen the title; 3) screen the abstract; 4) screen the full paper. The screening of articles from each database was conducted by two independent reviewers respectively, the final discussion ensured two reviewers achieved a consensus on the excluded articles. The number of articles included or excluded in each step was reported in PRISMA flowchart shown in Figure 1.
3.4 Quality assessment
To assess the quality of the selected studies, the authors considered the impact of the qualified studies using Google Scholar to obtain the total citations to date and then calculated the Average Citation Count (ACC), which is the “total citations to date” dived by “lifetime” (published year till now) as suggested by Dey et al. (2018):
The average of the ACC of the selected studies in this systematic review is 4.2, ranging from 0 to 19.3. The result indicates the overall selection had good impact in the related field despite several low-impact but highly relevant studies.
3.5 Data synthesis and analysis methods
In this systematic review, data were extracted and synthesized through Tencent Docs, a file-collaboration tool that allows users to create, share and edit documents online. The information extracted from the included papers were: 1) authors; 2) year of publication; 3) application scenarios; 4) demographics data of the subjects; 5) type of XR display; 6) surgical robotics; 7) experimental protocol; 8) data collected and corresponding measurement methods; 9) results; 10) conclusions; 11) limitations and future study. This process was carried out after the screening phase was completed and analysed deeply in order to answer the review questions of this systematic review.
3.6 Establishment of conceptual framework of components of user experience
The user experience contains different factors and needs a framework to measure its quality. Beauregard and Corriveau (2007) put forward a framework for conceptualizing the components of user experience, highlighting the roll of human perceptions, emotions, thoughts, attitudes and behaviours resulting from the interaction with all aspects of product over time. Hassenzahl et al. (2010) clarified what experience is and used action theories to define human-computer interaction (HCI) as goal-directed action mediated by an interactive product, presenting the concept of a hierarchical organization of goals which contains “be goals,” “do goals” and “motor goals.” Among the three levels, “be goals” refers to the basic demands and emotions, “do goals” focuses on the objectives of action and cognition, “motor goals” emphasizes perception and actions, designing and evaluating experience should take all three levels seriously. Robert and Lesage (2017) classified dimensions of user experience into functional, physical, psychological, perceptive, social and cognitive. Mustaffa et al. (2020) developed an experience measurement model containing cognitive-affective-behavioural responses in the healthcare industry, as the three responses represents the three phases of users’ journey in this field.
In line with the components of user experience highlighted in the abovementioned studies and the review objectives of this study, the authors have introduced a new comprehensive and systematic theoretical framework for classifying and measuring user experience. This framework divides user experience into 1) affective experience; 2) perceptual experience; 3) cognitive experience and 4) motor experience (see Figure 2).
4 Results
Forty eligible studies were included in this systematic review. The basic information of the included studies is summarized in Supplementary Table 1 of this paper regarding the reference, ACC, year of publication, country and type of publication. Through reviewing and analysing, the authors summarized the included papers according to the review questions thoroughly. The results of this systematic review are presented as follows.
4.1 Components of interaction in XR-enhanced robotic surgery
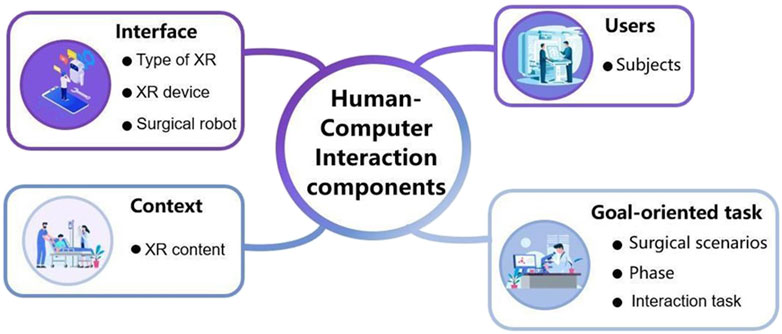
To answer RQ1, the components of human-computer interaction in XR-enhanced robotic surgery are summarized in Supplementary Table 2 of this paper. According to Kanade (2022)’s research, human-computer interaction (HCI) system is made up of four key components, 1) user, 2) goal-oriented task, 3) interface and 4) context. Based on this framework, the authors categorized extracted information as the components of human-computer interaction in XR-enhanced robotic surgery. In this classification, subjects refer to the user; surgical scenarios, phase and interactive tasks refer to the goal-oriented task; type of XR, XR device and surgical robot refer to the interface; and XR content refers to the contexts (see Figure 3).
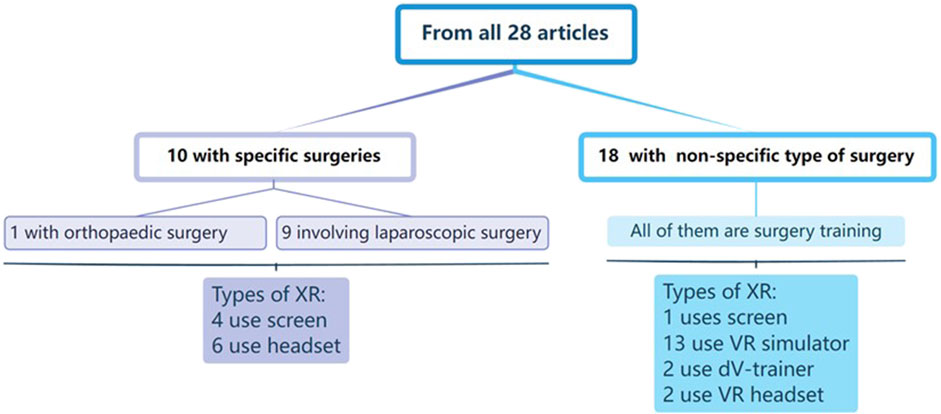
Considering goal-oriented task, there are 10 of the 28 articles involve specific surgical procedures (1 for orthopaedic surgery and 9 for laparoscopic surgery). These articles are divided into four categories based on their phases of surgery: four articles on surgical training, three about preoperative stage, and three about intraoperative stage. Regarding interfaces, two kinds of XR devices were utilized in these ten articles. Four cases used video see-though screen to show surgical environment and six used headset to create a realistic surgical setting (Figure 4). This review also included 18 studies on non-specific type of surgery, and they all focused on surgical training. Four main types of XR devices were used in these studies: VR simulator, dV-trainer, VR headset and video see though screen. The VR simulator is the most widely used platform with thirteen research to build an immersive surgical environment. Two studies used dV-trainer by Cho et al. (2013) and Schreuder et al. (2014) to train residents. Two studies used VR headset to render virtual content. Christensen et al. (2018) chose the HTC Vive headset while Qian et al. (2019) applied the Microsoft HoloLens. And one study used Tile-pro (video see-though screen) (see Table 1).
4.2 Classification of factors and measurements of user experience in XR-enhanced robotic surgery
To answer review RQ2, all the included works in this review containing user studies evaluated using some metrics were analysed. The authors summarize the considered measured factors and their measurement methods used in these studies. All the factors and the corresponding measurement methods are mapped into four dimensions of user experience mentioned in this section.
4.2.1 Factors and measurement methods related to affective experience
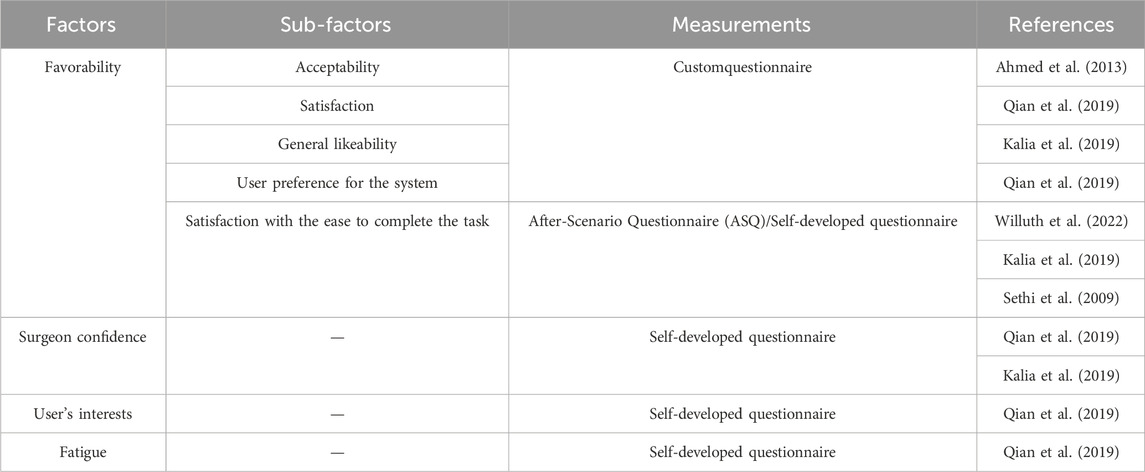
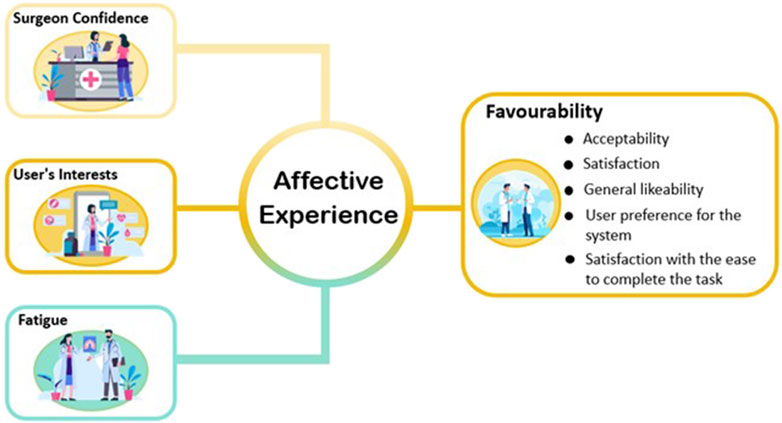
Affective experience refers to a person’s emotional reactions that he or she experiences during task performance. Seo et al. (2004) introduced that the core affect, meaning the core affective feelings and neurophysiological substrate, contains degree of pleasantness and activation as two independent dimensions. In this explanation, pleasantness encapsulates an individual’s performance in relation to a hedonic valence, such as pleasant-unpleasant, good-bad, positive-negative, or appetitive-aversive at the subjective experience level, while activation refers to a feeling of energy or mobilization and describes the degree of activation or deactivation of a person’s physiological condition. The authors grouped favourability, surgeon confidence, user’s interests and fatigue collected from the included papers into the dimension of affective experience (see Figure 5).
Table 1 shows different cases from the literature related to affective experience. Seven studies measured favourability by assessing acceptability, satisfaction, general likeability, user preference for the system and satisfaction with the ease to complete the task respectively through questionnaires. Krehbiel and Cropanzano (2000) states that favor and joy are two emotions associated with happiness, while disappointment is an emotion related to sadness. The studies conducted by Qian et al. (2019), and Kalia et al. (2019) all focused on the investigation of surgeons’ confidence in surgical planning or estimation of the distance between surgical tools and the tumour. Budin (2017) posited that the source of confidence stems from feelings of wellbeing, while wellbeing is a state of emotion. This indicates that confidence is related to its emotional or affective basis. The questionnaire applied in Qian et al. (2019) included questions about users’ interests. As mentioned in Silvia (2008)’s research, interest can be described as a peculiar emotion. Qian et al. (2019) survey also revealed that in terms of fatigue, the average rating for instrument insertion with AR assistance (IIAR) is not significantly higher than that for instrument insertion without AR assistance (IINA). Physiol (2012) states that fatigue is mostly an emotion that is a byproduct of intricate regulation designed to keep the body safe.
4.2.2 Factors and measurement methods related to perceptual experience
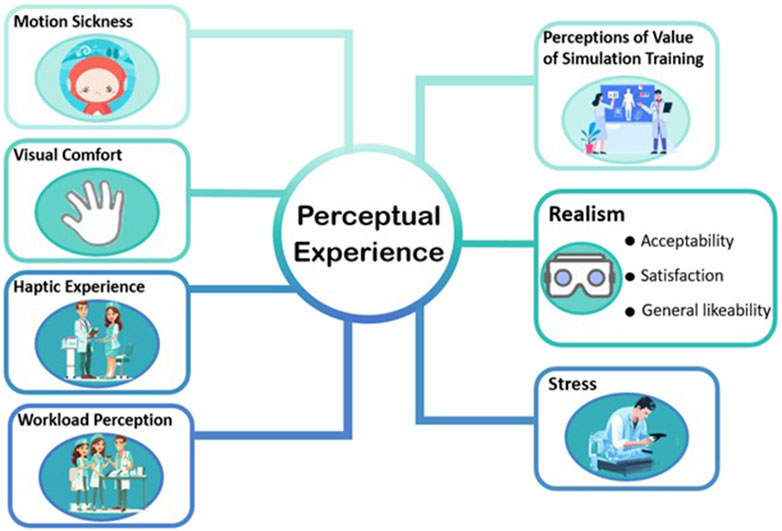
Perceptual experience is a process in which individuals receive external stimuli through sensory organs and process and understand them (Spielman et al., 2020). This process includes not only sensory experience, but also perceptual experience. It is subjective, active and constructive, involving the integration and reconstruction of external information. The essence of perceptual experience lies in its internal connection with the world we are in, which constitutes our direct way of understanding the world, and is an intuitive and non-conceptual cognitive process (Hill, 2022). Perceptual experience plays a crucial role in user experience by actively shaping and enhancing our understanding and interaction with the world around us, providing a subjective and intuitive framework for mental engagement. The authors included motion sickness, visual comfort, perceptions of value of simulation training, realism, haptic experience, workload, and stress into the dimension of perceptual experience (see Figure 6).
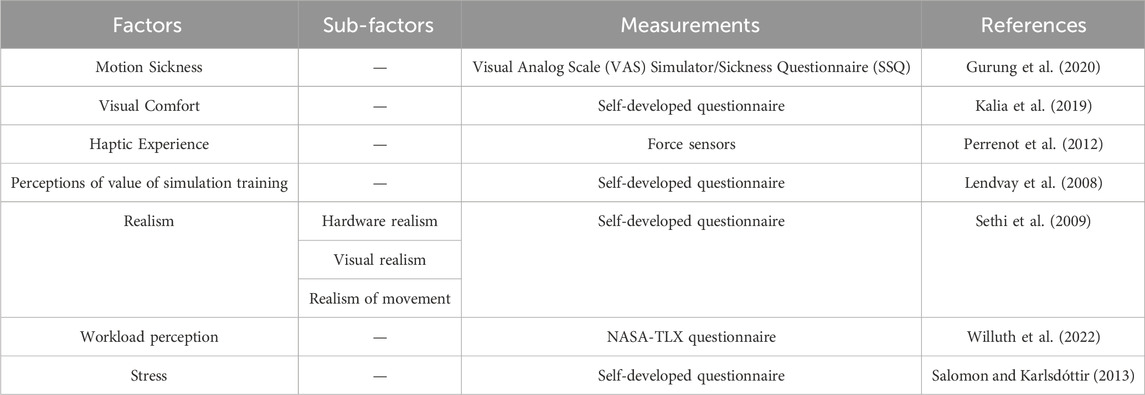
Table 2 demonstrates the factors and measurements of perceptual experience. Takata et al. (2021) measured proficiency thresholds for each task through the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) and Simulator Sickness Questionnaire (SSQ), and Keshavarz et al. (2015) proposed that the experience of visually induced motion sickness is often associated with the feeling of illusory self-motion, known as Vection. Kalia et al. (2019) required subjects to fill out a 5-point Likert scale to assess Visual Comfort. Khosravi et al. (2024) proposed that the visual comfort is related to the discomfort glare perceived by the human eye, which belongs to perceptual experience. Lendvay et al. (2008) conducted a survey to investigate perceptions of the value of simulation training. The study conducted by Sethi et al. (2009) utilized a 5-point Likert scale to evaluate the realism of the virtual reality simulator from four perspectives: realism of exercise, visual realism, hardware realism, and realism of movement. Wei et al. (2024) states that realism is a perceptual experience that arises from the stimulation of human senses, such as vision and hearing. Sethi et al. (2009) reported that all participants rated the Mimic dV-Trainer (MdVT) as “above average” to “high” on all parameters of realism. It was highlighted that all participants found the MdVT to perform exceptionally well in terms of realism, with the simulator receiving high praise for its realistic portrayal of exercises, visuals, hardware, and movement. Force feedback was evaluated using a force sensor by Perrenot et al. (2012). Based on study conducted by Lederman and Klatzky (2009), haptic experience is a subset of perceptual experience. Willuth et al. (2022), Sethi et al. (2009), Ferraguti et al. (2020), and Kunz et al. (2022) assessed workload of surgeons during the surgery through NASA Task Load Index (NASA-TLX) questionnaire. Salomon and Karlsdóttir (2013) stated that many well-known theoretical definitions of stress strongly emphasized perception as a crucial component of the experience of stress, while according to Alsuraykh et al., 2019 it had been found that there were significant correlation stress and mental workload (positive correlation) which meant when the subjects had higher mental workload and more negative emotion, they tended to experience more stress. Therefore, workload perception and stress are both aspects of perceptual experience.
4.2.3 Factors and measurement methods related to cognitive experience
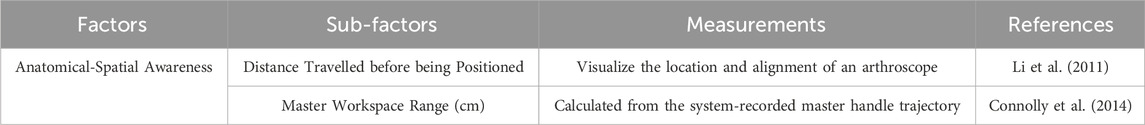
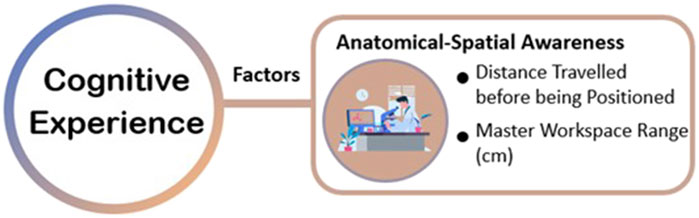
Cognitive experience refers to the experiences and feelings that a person acquires during the cognitive process. Bayne et al. (2019) explained the meaning of cognition like “knowing” or “having awareness to.” According to the Encyclopedia Britannica (2015 Ultimate Edition), cognition encompasses perception, recognition, conception, and reasoning, involving the states and processes associated with acquiring knowledge. Alternatively, cognition refers to a state or experience of awareness that can be distinguished from emotional or volitional experiences. Cognitive experience profoundly affects human thinking and action, particularly helping individuals to understand their surrounding environment and make corresponding responses and decisions. The authors grouped anatomical-spatial awareness and clinical decision making collected from the included papers into the dimension of cognitive experience (see Table 3; Figure 7).
Connolly et al. (2014) and Schreuder et al. (2014) measured the master workspace range (i.e., the range of motion of the control handles) (cm) and found cognitive differences between experienced surgeons and novice surgeons. Additionally, Connolly et al. (2014) also assessed the distance travelled by the operator or robot before reaching the surgical area during operation.
4.2.4 Factors and measurement methods related to motor experience
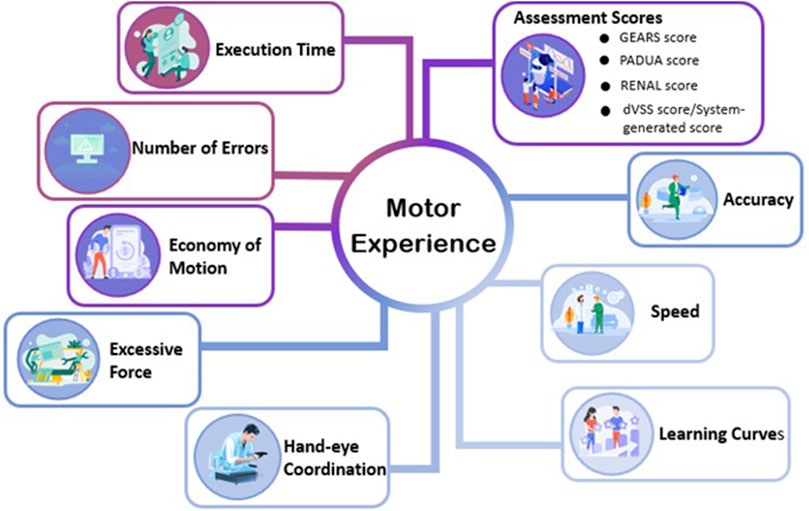
Motor experience is a kind of interact with objects in systematically different ways, it will determine and change some aspects of object knowledge (Chrysikou et al., 2017). The motor experiences are thought to facilitate predictions, whereas accumulated conceptual experience provides broader knowledge (Gerson et al., 2016). The authors grouped execution time, speed, number of errors, assessment scores, economy of motion, accuracy, learning curves, hand-eye coordination and excessive force collected from the included papers into the dimension of motor experience (see Figure 8).
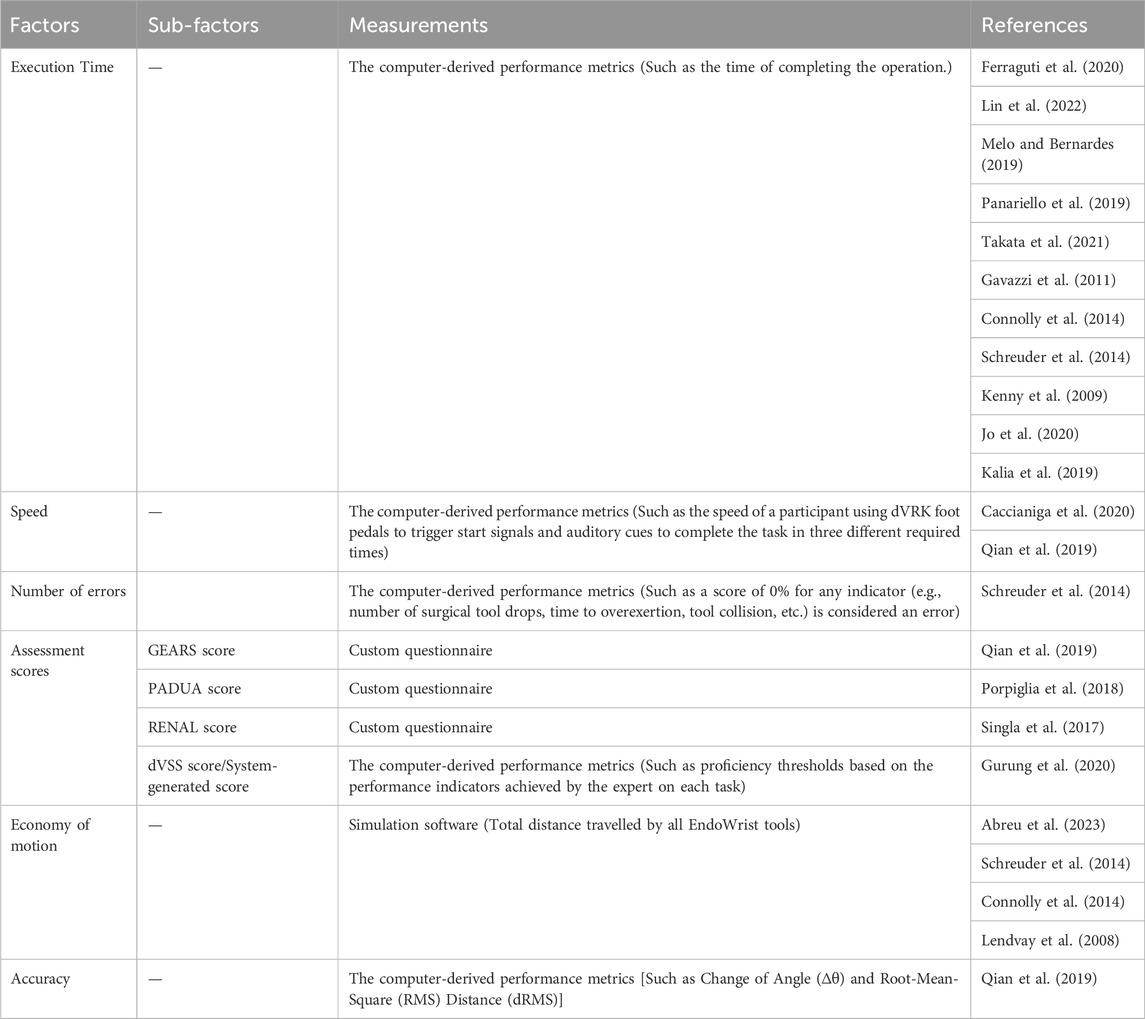
As shown in Table 4, Abreu et al. (2023), Connolly et al. (2014), Schreuder et al. (2014) and Lendvay et al. (2008) assessed the economy of motion (EOM) by using the simulation software. Wulf and Lewthwaite (2010) depicted effortlessness as a defining characteristic of motor skill, which means that effortlessness belongs to motor experience. Connolly et al. (2014) used a self-developed questionnaire to evaluate missed targets. Capio et al. (2012) conducted a study on the potential advantages of fewer errors in children’s motor skill acquisition; therefore, the quantity of errors is related to motor experience. Lin et al. (2022), Melo and Bernardes (2019), Jo et al. (2020), Gavazzi et al. (2011), Connolly et al. (2014), Schreuder et al. (2014), Kenny et al. (2009), Panariello et al. (2019) and Takata et al. (2021), Kalia et al. (2019) measured the execution time using the surgical robot surgery system. Melo and Bernardes (2019) and Balasundaram et al. (2008) had surgical novices repeatedly perform the same tasks on a DaVinci surgical simulator, and they studied their learning curves based on the scores. Reeves and Dasgupta (2021) proposed that surgical outcomes are influenced by the surgeon’s learning curve (LC) and assessing the LC of early results provides information on what is required to achieve proficiency in surgical manipulation. Wentink (2001) has emphasized the crucial impact of hand-eye coordination on the safety, accuracy, and efficiency of operations. Qian et al. (2019) collected subjective evaluations of operators’ hand-eye coordination through questionnaires. Connolly et al. (2014) and Perrenot et al. (2012) studied the excessive force indicator in the da Vinci system score. Qian et al. (2019) gave a post-experiment questionnaire included self-report ratings of speed Schreuder et al. (2014) measured face validity and used a questionnaire to confirm experts made less errors than novices. de Mongeot et al. (2023) performed a post hoc analysis using paired t-tests with Bonferroni correction Porpiglia et al. (2018) assessed PADUA Score of urologists during the surgery through self-developed questionnaire. Singla et al. (2017) measured RENAL Score of expert urologists during the surgery through self-developed questionnaire. Qian et al. (2019) assessed GEARS Global Rating Scale of inexperienced subjects during the surgery through self-developed questionnaire. Gurung et al. (2020) assessed dVSS Score or system-generated Score of medical students during surgical training through system automatic generation.
4.3 Benefits of XR-enhanced robotic surgery in improving UX
To answer RQ3, the results of the UX relevant factors included in the selected studies were reviewed, aiming to investigate what benefits can XR-enhanced robotic surgery bring to users to have a higher level of user experience (Figure 9). In this section, the benefits are analysed based on the results of the factors measured in included studies in the conceptual framework of user experience and measurement methods in XR-enhanced robotic surgery mentioned previously.
4.3.1 Benefits in improving affective experience
Firstly, as for the measurement of favourability, the results of the questionnaires used in the studies conducted by Ahmed et al. (2013), Qian et al. (2019), Kalia et al. (2019), Lendvay et al. (2008), Willuth et al. (2022) and Sethi et al. (2009) showed that the subjects in each experiment have a favorable attitude towards the technology applied in XR-enhanced robotic surgery. Secondly, the surgeons’ confidence in surgical procedures has notably increased according to the results of the questionnaires carried out by Qian et al. (2019) and Kalia et al. (2019). Thirdly, the subjective feedback from subjects in Qian et al. (2019) showed that the system increased users’ interests. However, the study conducted by Qian et al. (2019) revealed that the current use of AR did not alleviate surgeons’ fatigue. Therefore, based on the results from the included studies mentioned above, it can be concluded that XR-enhanced robotic surgery can enhance users’ affective experience in most cases.
4.3.2 Benefits in improving perceptual experience
Although the VAS and SSQ questionnaires of Gurung et al. (2020) show that training with VR simulators can cause motion sickness, this situation will be alleviated after multiple training. Meanwhile, Kalia et al. (2019) ‘s Likert scale, which asked subjects to fill out, confirmed that the use of Color Depth Encoding (CDE) technique can effectively improve visual comfort. On the other hand, NASA-TLX Questionaire conducted by Ahmed et al. (2013) and Sethi et al. (2009) showed that users’ Workload Perception and Stress Level had decreased, indicating that with the assistance of VR,both mental and physical fatigue were improved. In terms of effectiveness, the questionnaire results of Perrenot et al. (2012), Sethi et al. (2009), Kenney et al. (2009), Ahmed et al. (2013) show that simulators are an effective training form. In terms of Haptic Experience, the subjects of Perrenot et al. (2012) and Kenney et al. (2009) had more real tactile experience. In addition, the questionnaire results of Sethi et al. (2009) showed that users believed that multiple aspects of XR-assisted surgical robots were simulated very realistically. In addition, the subjects of Perrenot et al. (2012) all considered the dV-Trainer simulator to be a reliable tool. Finally, Lendvay et al. (2008) found that users generally considered simulation training to be a valuable surgical training method. Therefore, according to the above results, in many ways, XR-assisted robot-assisted surgery can enhance the emotional experience of users.
4.3.3 Benefits in improving cognitive experience
Firstly, according to the questionnaire, McDonald and Shirk (2021) found that utilizing XR surgical robot models significantly enhances decision-making in surgery, especially in adapting early pre-operative plans where changes are notably frequent. Secondly, Li et al. (2011) found XR Navigation in surgery improving the target localization ability of junior residents. Additionally, Singla et al. (2017) found that by using augmented reality technology, surgeons can significantly reduce the depth of resection when removing tumors. Moreover, According to Schreuder et al. (2014), the XR simulator was found to be realistic in terms of overall realism, visual graphics, instrument movement, interaction with objects, and depth perception. Also, Connolly et al. (2014) found that experienced surgeons significantly outperformed novice surgeons when completing tasks through XR devices. Therefore, based on these studies, we can conclude that XR-enhanced robotic surgery can enhance the cognitive experience of users.
4.3.4 Benefits in improving motor experience
Firstly, as for the measurement of the execution time, the results that the system automatically generated in the studies conducted by Lin et al. (2022), Gavazzi et al. (2011), Melo and Bernardes (2019), Panariello et al. (2019), Abreu et al. (2023), Jo et al. (2020), Takata et al. (2021), Connolly et al. (2014), Schreuder et al. (2014), Perrenot et al. (2012), Lendvay et al. (2008), Balasundaram et al. (2008) and Kalia et al. (2019) showed that XR surgical robots notably boost the efficiency of surgical procedures by significantly improving depth estimation, reducing task completion time, and accelerating suture placement. Secondly, the result that generated by the systems which were designed by Qian et al. (2019), Caccianiga et al. (2020) have revealed that using ARssist, an augmented reality application, can significantly boosts users’ surgical speed in performing surgeries by cutting navigation time, enhancing insertion path consistency, lowering root-mean-square path deviation, and reducing tool manipulation time. Furthermore, according to the data generated by the system, Rahman et al. (2022), Schreuder et al. (2014) and Connolly et al. (2014) found that VR-facilitated surgeries will lead to less missed targets. Additionally, Porpiglia et al. (2018), Qian et al. (2019), separately measured PADUA Score, GEARS Global Rating Scale through self-developed questionnaire, and Gurung et al. (2020) evaluated the da Vinci Skills Simulator (dVSS) Score or system-generated Score automatically generated by the system. These assessment scores confirmed the accuracy of the experiments. Moreover, Abreu et al. (2023), Connolly et al. (2014), Schreuder et al. (2014), Lendvay et al. (2008) have proven that the application of VR can help to optimize the economy of motion and make the system easy and effortless to handle. Equally important, using simulators can accelerate the learning process, complete the early part of the learning curve and help beginners reach a stable learning stage faster, it was founded by Melo and Bernardes (2019) and Indran (2008) through the system automatic generation. Also, through collecting subjective evaluations with questionnaire, Qian et al. (2019) measured operators’ hand-eye coordination, and the results showed that the ARssit system significantly improved hand-eye coordination abilities and efficiency. Finally, Connolly et al. (2014) and Perrenot et al. (2012) studied the excessive force indicator in the da Vinci system score, but obtained different results: Perrenot et al. (2012) believed that excessive force cannot be used as a key factor to distinguish different levels of operation, while Connolly et al. (2014) indeed found that experienced doctors were significantly better at controlling the force during operation. Anyway, their system scoring demonstrated the effectiveness of virtual fixtures in preventing excessive force and torque. Therefore, based on the results from the studies mentioned above, it can be concluded that XR-enhanced robotic surgery can enhance users’ motor experience.
4.4 Limitations and future work of XR-enhanced robotic surgery in improving user experience
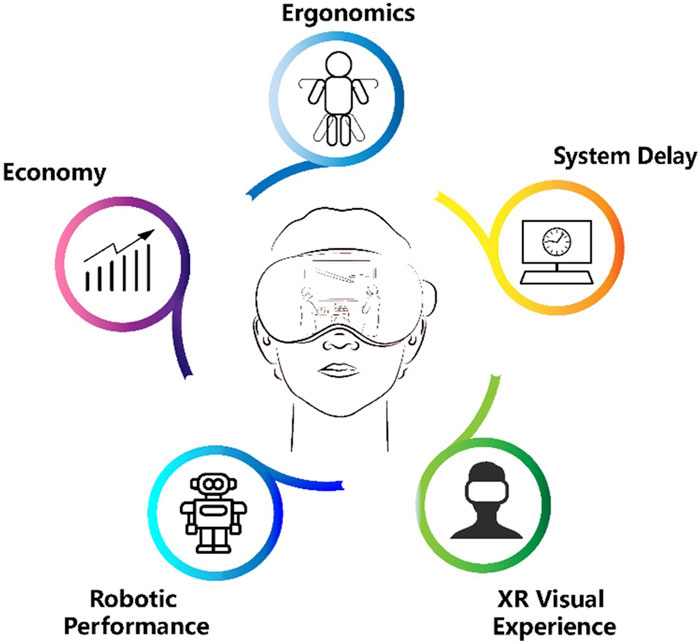
To answer RQ4, the authors summarized the existing limitations and potential future work of XR-enhanced robotic surgery in improving user experience during surgery collected from the included studies. In this section, the limitations and future work are divided into five aspects: ergonomics, system delay, XR visual experience, robotic performance and economy.
Firstly, the ergonomics play an important role in enhancing the user experience during the interaction between human and system. Rahman et al. (2022) intended to enhance the mechanical design of the robot in the future to design more realistic robot required for human body operations.
Secondly, system delay influences the surgeons’ prediction and performance during surgery. According to the study raised by Lin et al. (2022), the delay time produced by the motion mapping mainly results from the time of the kinematic and filter calculation, delay of the joint filter, data transmission from the clinician’s side to patient’s side, the motion of joints of the manipulator, and the manipulator state feedback. Rahman et al. (2022) believed that he video transmission component will be more tuned to reduce the latency. With more advanced or dedicated hardware entering the market, the problem can be gradually alleviated, as Qian et al. (2019) put forward.
Furthermore, the XR visual experience should be optimized to improve precision in operations. Rahman et al. (2022) will increase the simulator’s efficacy by producing a more accurate and superior virtual reality human body model. Kunz et al. (2022) found that because the anatomical features are tiny, the interaction appears challenging when the AR scene is exhibited in its original size. Qian et al. (2019) pointed out that the XR visual experience will be limited by the resolution of the endoscope and the accuracy of the virtual overlay.
Moreover, enhancing robotic performance in surgery is pivotal for operational precision. Porpiglia et al. (2018) emphasized adjusting in-console images to match in vivo anatomy for accurate navigation. Challenges include optomechanical sensors’ limited sensing range causing signal saturation, noted by Guidothe et al. (2020), and incorrect depth perception impacting procedure safety, highlighted by Kalia et al. (2019). Furthermore, Sethi et al. (2009) pointed out the da Vinci instruments’ limited lifespans, underscoring the need for ongoing innovation to improve robotic systems’ durability and reliability, essential for advancing surgical precision.
Additionally, the system cost will be a problem. Kunz et al. (2022) mentioned that interaction with the virtual holograms can be cumbersome without experience and requires training. One possibility to address this challenge in the future could be the additional visualization of the user’s hand in the virtually superimposed scene. Sethi et al. (2009) held the belief that Surgical system is associated not only with the costs of purchasing and maintaining the system, but also with the expenses related to hiring personnel needed to run the practice sessions, the training materials.
5 Discussions
In this systematic review, the authors searched for papers from 5 databases and finally selected 28 eligible papers in the review and analysis. To explore the human-computer interaction and user experience during XR-enhanced robotic surgery, a summary table of the components of human-computer interaction, a conceptual framework of components and corresponding measurement methods of user experience were established. Meanwhile, the authors also summarized the benefits and future work of XR-enhanced robotic surgery in improving the surgeons’ user experience during surgical practices. In this section, the discussions are put forward according to the sequence of the review questions.
Firstly, to establish a summary table of human-computer interaction during XR-enhanced robotic surgery, the authors chose XR display, XR content, type of XR, surgical robotics and interaction task as the components of human-computer interaction in the targeted scenarios, which is consistent with the previous review papers. In this study, the authors did not put forward a conceptual framework of the interaction paradigm. More work should be done to comprehensively summarized the human-computer interaction paradigm in the future. In the studies of involved articles, Edgcumbe et al. (2016), Porpiglia et al. (2018) and Kunz et al. (2022) conduct intraoperative studies. Mehralivand et al. (2019), Melo and Bernardes (2019) and McDonald and Shirk (2021) conduct the studies before the surgery. Other 22 scholars use XR-enhanced surgical robot for surgical training, which shows that predecessors have done sufficient research in the field of XR surgical robot training. However, it is worthing noting that none of the selected articles focused on post-operative XR-enhanced robotic technology so that more post-operative studies are worth exploring by scholars. Among the 22 scholars focused on surgical training, Ahmed et al. (2013) and Chowriappa et al. (2015) designed the same interactives task of performing the urethra-vesical anastomosis (UVA) task and Jo et al. (2020) designed the task of controlling the endoscope using the VR-based endoscope control system (ECS). These three studies focused on surgical training of laparoscopic surgery scenarios. Meanwhile, Panariello et al. (2019) designed the interactive task of reaming the cartilage from the acetabulum using a custom surgical instrument, which is a surgical training task for orthopedic surgical scenarios. Compared with the four surgical training studies mentioned above, other 18 studies focus on basic surgical skills rather than specific procedures. For instance, Gavazzi et al. (2011) designed the task of arrow manipulation and suturing. Liss et al. (2012) designed the task of pegboard transfer and tubes suturing. Rahman et al. (2022) designed the task of objects holding the moving. Furthermore, as for the presentation method of the contents in XR, Chowriappa et al. (2015), Jo et al. (2020) and Panariello et al. (2019) utilized 3D modelling, Chowriappa et al. (2015) showed an in-animate model of ureter and surrounding area, and stereo vision of abdominal cavity was shown by Jo et al. (2020).
Secondly, to establish a conceptual framework of components and corresponding measurements of user experience, the authors only selected the factors measured in the included papers. Therefore, this conceptual framework shows the limited types of factors regarding the user experience in XR-enhanced robotic surgery. In the studies of included papers, Qian et al. (2019), Kalia, M et al. (2019), Lendvay et al. (2008) and Salomon and Karlsdóttir (2013) used self-developed questionnaire to measure parts of affective experience and perceptual experience of the subjects. Meanwhile, in user experience research, quantitative and qualitative methods each have their strengths and weaknesses, often requiring a combined approach for comprehensive understanding. Quantitative methods, such as Perrenot et al. (2012)’s use of force sensors to measure haptic experience, and the objective measurements of anatomical-spatial awareness by Li et al. (2011) and Connolly et al. (2014), provide precise data. These methods are particularly suitable for evaluating factors of cognitive and motor experiences. In contrast, qualitative methods like questionnaires, while more subjective and potentially affecting the accuracy of conclusions, excel at exploring users’ personal feelings and perspectives. This approach offers unique advantages in capturing experience dimensions that are difficult to quantify. Future research should maintain objectivity while not overlooking the importance of subjective experiences. Therefore, future directions could include: 1) developing more standardized measurement methods for cognitive and motor experience factors; 2) exploring new ways to organically combine quantitative and qualitative methods to comprehensively assess all aspects of user experience. Through this integrated approach, we can obtain precise data without losing deep insights into the rich nuances of user experiences. Last but not least, compared with affective experience, perceptual experience and motor experience, single factor cognitive experience appears to be incomplete. A more comprehensive cognitive experience factor framework in XR-enhanced robotic surgery is worth studying.
Finally, to summarize the benefits and limitations of XR-enhanced robotic surgery, the authors collected related information from the results section and discussion section from the included papers. Through a comprehensive analysis of the involved articles, the authors mainly agree that the XR-enhanced robotic surgery can enhance users’ affective experience, perceptual experience, cognitive experience and motor experience. Meanwhile, the ergonomics, system delay, XR visual experience, robotic performance and economy are the mostly mentioned limitations of XR-enhanced robotic surgery.
The current systematic review also contains limitations that need future work to provide a more comprehensive review study in this interdisciplinary field. Firstly, in the paper searching phase, though the authors cross-referenced the eligible articles from 10 relevant review studies during the final selection and screened for their eligibility, some other useful studies from other databases or sources can also be included in the future. Secondly, the authors established a new conceptual framework to classify the components of user experience that divides user experience into affective-perceptual-cognitive-motor experience. However, the authors can extend this to consider more components in the future, increasing the descriptive capabilities of our proposed framework. Thirdly, as the authors only included the medical cases, other excluded studies may also have user experience factors that can also provide references for establishing the framework, which may lead to omissions in the summary of human-computer interaction methods and user experience. Finally, after we submitted the manuscript, there may be new articles published on related topics. However, due to the need to strictly adhere to the specifications of the systematic review framework, we are unable to include them in this article, which may also result in incomplete information in this article. In the future, we need to summarize these articles more comprehensively.
6 Conclusion
In conclusions, this systematic review mainly studies the human-computer interaction and user experience in XR-enhanced robotic surgery, and carried out the discussion on this basis. In this systematic review, the authors analyzed 28 eligible studies collected from 5 different databases, to (1) summarize the components of HCI, (2) propose a conceptual framework of components and corresponding measurements of user experience, (3) summarize the benefits and future work of XR-enhanced robotic surgery in improving the surgeons’ user experience during real surgical practices. This study contributes to the multi-disciplinary research in HCI, digital medicine and user experience, providing a new perspective for the academic community related to this topic and field.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
YL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. ML: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing–review and editing. SZ: Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing–original draft. LY: Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing–original draft. LP: Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing–original draft. CF: Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing–original draft. YC: Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft. CW: Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft. CC: Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing–original draft. BL: Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft. BX: Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft. SB: Writing–review and editing. YL: Formal Analysis, Writing–original draft. MS: Writing–review and editing. PP: Writing–review and editing. YZ: Supervision, Writing–review and editing. ED: Supervision, Writing–review and editing. DvE: Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research is supported by National Training Program of Innovation and Entrepreneurship for Undergraduates. Funding for publication of this article was contributed in part by the TU Delft Open Access Fund.
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank all the colleagues and reviewers supporting this systematic review study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frvir.2024.1461105/full#supplementary-material
References
Abreu, A. A., Rail, B., Farah, E., Alterio, R. E., Scott, D. J., Sankaranarayanan, G., et al. (2023). Baseline performance in a robotic virtual reality platform predicts rate of skill acquisition in a proficiency-based curriculum: a cohort study of surgical trainees. Surg. Endosc 37, 8804–8809. doi:10.1007/s00464-023-10372-8
Ahmed, K., Chowriappa, A., Din, R., Field, E., Shi, Y., Wilding, G., et al. (2013). A multi-institutional randomized controlled trial of an augmented-reality based technical skill acquisition module for robot-assisted urethro-vesical anastomosis. J. Urology 189 (6). doi:10.1016/j.juro.2013.02.3098
Alsuraykh, N. H., Wilson, M. L., Tennent, P., Sharples, S., and Zhang, H. (2019). “How stress and mental workload are connected,” in Proceedings of the 13th EAI International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare, 371–376.
Andrews, C., Southworth, M. K., Silva, J. N. A., et al. (2019). Extended reality in medical practice. Curr. Treat. Options Cardio Med. 21, 18. doi:10.1007/s11936-019-0722-7
Balasundaram, I., Aggarwal, R., and Darzi, A. (2008). Short-phase training on a virtual reality simulator improves technical performance in tele-robotic surgery. Int. J. Med. Robotics 4 (2), 139–145. doi:10.1002/rcs.181
Bayne, T., Brainard, D., Byrne, R. W., Chittka, L., Clayton, N., Heyes, C., et al. (2019). What is cognition? Curr. Biol. 29, R608–R615. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2019.05.044
Beauregard, R., and Corriveau, P. (2007). “User experience quality: a conceptual framework for goal setting and measurement,” in Digital human modeling. ICDHM 2007. Lecture notes in computer science. Editor V. G. Duffy (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer), 4561, 325–332. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-73321-8_38
Bolenz, C., Gupta, A., Hotze, T., Ho, R., Cadeddu, J. A., Roehrborn, C. G., et al. (2010). Cost comparison of robotic, laparoscopic, and open radical prostatectomy for prostate cancer. *European Urology* 57 (3), 453–458. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2009.11.008
Budin, W. C. (2017). Building confidence. *Journal of Perinatal Education* 26 (3), 107–109. doi:10.1891/1058-1243.26.3.107
Buffi, N., Lughezzani, G., Lazzeri, M., Casale, P., Fiorini, G., Hurle, R., et al. (2015). The added value of robotic surgery. Urologia Journal* 82, S11–S13. doi:10.5301/uro.5000149
Caccianiga, G., Mariani, A., De Momi, E., Cantarero, G., and Brown, J. D. (2020). An evaluation of inanimate and virtual reality training for psychomotor skill development in robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery. IEEE Transactions on Medical Robotics and Bionics 2 (2), 118–129. doi:10.1109/tmrb.2020.2990692
Camarillo, D. B., Krummel, T. M., and Salisbury, J. (2004). Robotic technology in surgery: past, present, and future. American Journal of Surgery 188 (4A Suppl. l), 2S–15S. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2004.08.025
Capio, C. M., Sit, C. H., Abernethy, B., and Masters, R. S. (2012). The possible benefits of reduced errors in the motor skills acquisition of children. Sports Medicine, Arthroscopy, Rehabilitation, Therapy, and Technology 4, 1. doi:10.1186/1758-2555-4-1
Catchpole, K., Cohen, T., Alfred, M., Lawton, S., Kanji, F., Shouhed, D., et al. (2024). Human factors integration in robotic surgery. Human Factors 66, 683–700. doi:10.1177/00187208211068946
Cho, J. S., Hahn, K. Y., Kwak, J. M., Kim, J., Baek, Se J., Shin, J. W., et al. (2013). Virtual Reality Training Improves da Vinci Performance: A Prospective Trial. Journal of Laparoendoscopic and Advanced Surgical Techniques 23 (12), 992–998. doi:10.1089/lap.2012.0396
Chowriappa, A., Raza, S. J., Fazili, A., Field, E., Malito, C., Samarasekera, D., et al. (2015). Augmented-reality-based skills training for robot-assisted urethrovesical anastomosis: a multi-institutional randomised controlled trial. BJU Int 115 (2), 336–345. doi:10.1111/bju.12704
Christensen, N. H., Hjermitslev, O. G., Stjernholm, N. H., Falk, F., Nikolov, A., Kraus, M., et al. (2018). “Feasibility of team training in virtual reality for robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery,” in Proceedings of the Virtual Reality International Conference - Laval Virtual, 1–4. doi:10.1145/3234253.3234295
Chrysikou, E. G., Casasanto, D., and Thompson-Schill, S. L. (2017). Motor experience influences object knowledge. Journal of experimental psychology general 146 (3), 395–408. doi:10.1037/xge0000269
Coelho, G., and Defino, H. L. A. (2018). The role of mixed reality simulation for surgical training in spine: phase 1 validation. Spine 43 (22), 1609–1616. doi:10.1097/brs.0000000000002856
Connolly, M., Seligman, J., Kastenmeier, A., Goldblatt, M., and Gould, J. C. (2014). Validation of a virtual reality-based robotic surgical skills curriculum. Surg Endosc 28, 1691–1694. doi:10.1007/s00464-013-3373-x
Corcione, F., Esposito, C., Cuccurullo, D., Settembre, A., Miranda, N., Amato, F., et al. (2004). Advantages and limits of robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery: preliminary experience. Surgical Endoscopy and Other Interventional Techniques 19, 117–119. doi:10.1007/s00464-004-9004-9
de Mongeot, L. B., Galofaro, E., Ramadan, F., D’Antonio, E., Missiroli, F., Lotti, N., et al. (2023). Combining FES and exoskeletons in a hybrid haptic system for enhancing VR experience. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering 31, 4812–4820. doi:10.1109/TNSRE.2023.3334190
Deng, Z., Xiang, N., and Pan, J. (2023). State of the art in immersive interactive technologies for surgery simulation: a review and prospective. Bioengineering 10, 1346. doi:10.3390/bioengineering10121346
Desmet, P., and Hekkert, P. (2007). Framework of product experience. International Journal of Design. Available at: https://www.ijdesign.org/index.php/IJDesign/article/view/66/15
Dey, A., Billinghurst, M., Lindeman, R. W., and Swan, J. E. (2018). A systematic review of 10 years of augmented reality usability studies: 2005 to 2014. Frontiers in Robotics and AI 5 (2018), 37. doi:10.3389/frobt.2018.00037
Edgcumbe, P., Singla, R., Pratt, P., Schneider, C., Nguan, C., Rohling, R., et al. (2016). “Augmented reality imaging for robot-assisted partial nephrectomy surgery,” in Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Cham: Springer), 54–57. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-43775-0_13
Elmi-Terander, A., Burström, G., Rami, N., Skulason, H., Pedersen, K., Fagerlund, M., et al. (2019). Pedicle screw placement using augmented reality surgical navigation with intraoperative 3D imaging: a first in-human prospective cohort study. SPINE 44 (7), 517–525. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000002876
Ferraguti, F., Minelli, M., Farsoni, S., Bazzani, S., Bonfe, M., Vandanjon, A., et al. (2020). Augmented reality and robotic-assistance for percutaneous nephrolithotomy. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 5 (3), 4556–4563. doi:10.1109/lra.2020.3002216
Filippi, S., Robiony, M., Tel, A., and Paludet, G. (2021). “UX heuristic evaluation of maxillo-facial surgery,” in Advances in usability, user experience, wearable and assistive technology. Editors T. Z. Ahram, and C. S. Falcão (Cham: Springer), Vol. 275, 1120–1127. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-80091-8_133
Fukushima, K., Kobayashi, M., Konishi, H., Minaguchi, K., and Fukuchi, T. (2007). Real-time orthognathic surgical simulation using a mandibular motion tracking system. Computer Aided Surgery 12 (2), 91–104. doi:10.1080/10929080701253881
Gavazzi, A., Bahsoun, A. N., Van Haute, W., Ahmed, K., Elhage, O., Jaye, P., et al. (2011). Face, content, and construct validity of a virtual reality simulator for robotic surgery (SEP robot). Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England 93 (2), 152–156. doi:10.1308/003588411x12851639108358
Gerson, J., Plagnol, A. C., and Corr, P. J. (2016). Passive and active facebook use measure (PAUM): validation and relationship to the reinforcement sensitivity theory.” Computers in Human Behavior 63, 813–822. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2016.06.023
Ghezzi, , and Campos Corleta, O. (2016). 30 Years of robotic surgery. World Journal of Surgery 40, 2550–2557. doi:10.1007/s00268-016-3543-9
Giugliano, G., Capece, S., and Buono, M. (2022). “Multidimensional, intuitive and augmented interaction models for robotic surgery,” in Human factors in robots, drones and unmanned systems. Editors T. Ahram, and W. Karwowski (USA: AHFE International), 57. AHFE Open Access. doi:10.54941/ahfe1002320
Greer, A. D., Newhook, P. M., and Sutherland, G. R. (2008). Human–machine interface for robotic surgery and stereotaxy. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics 13, 355–361. doi:10.1109/tmech.2008.924118
Gurung, P. M. S., Campbell, T., Wang, B., Joseph, J. V., and Ghazi, A. E. (2020). Accelerated skills acquisition protocol (asap) in optimizing robotic surgical simulation training: a prospective randomized study. World Journal of Urology 38 (7), 1623–1630. doi:10.1007/s00345-019-02858-9
Hassenzahl, M., and Tractinsky, N. (2006). User experience - a research agenda. Behaviour and Information Technology 25 (2), 91–97. doi:10.1080/01449290500330331
Hassenzahl, M., Diefenbach, S., and Göritz, A. (2010). Needs, affect, and interactive products – facets of user experience. Inter. Computers. 22 (5), 353–362. doi:10.1016/j.intcom.2010.04.002
Herron, , and Marohn, M. (2008). A consensus document on robotic surgery. Surgical Endoscopy 22, 313–325. doi:10.1007/s00464-007-9727-5
Ibrahim, , Sarhane, K. A., Baroud, J. S., and Atiyeh, B. S. (2012). Robotics in plastic surgery, A review. European Journal of Plastic Surgery 35, 571–578. doi:10.1007/s00238-012-0737-8
Jo, Y., Kim, Y. J., Cho, M., Lee, C., Kim, M., Moon, H. M., et al. (2020). Virtual reality-based control of robotic endoscope in laparoscopic surgery. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems 18, 150–162. doi:10.1007/s12555-019-0244-9
Kalan, , Chauhan, S., Coelho, R. F., Orvieto, M. A., Camacho, I. R., Palmer, K. J., et al. (2010). History of robotic surgery. Journal of Robotic Surgery 4, 141–147. doi:10.1007/s11701-010-0202-2
Kalia, M., Navab, N., and Salcudean, T. (2019). “A real-time interactive augmented reality depth estimation technique for surgical robotics,” in 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Montreal, QC, Canada, 20-24 May 2019, 8291–8297. doi:10.1109/icra.2019.8793610
Kanade, V. (2022). What is HCl (Human-Computer interaction)? Meaning, Importance, Examples, and Goals.
Kenney, P. A., Wszolek, M. F., Gould, J. J., Libertino, J. A., and Moinzadeh, A. (2009). Face, content, and construct validity of dV-trainer, a novel virtual reality simulator for robotic surgery. Urology 73 (6), 1288–1292.
Keshavarz, B., Stelzmann, D., Paillard, A., and Hecht, H. (2015). Visually induced motion sickness can Be alleviated by pleasant odors. Experimental Brain Research 233, 1353–1364. Visually induced motion sickness can be alleviated by pleasant odors | Experimental Brain ReseaCrch (springer.com). doi:10.1007/s00221-015-4209-9
Khosravi, M., Huber, B., Decoussemaeker, A., Heer, P., and Smith, R. S. (2024). Model predictive control in buildings with thermal and visual comfort constraints. Energy and Buildings 306, 113831. doi:10.1016/j.enbuild.2023.113831
Krehbiel, P. J., and Cropanzano, R. (2000). Procedural justice, outcome favorability and emotion. Social Justice Research 13, 339–360. doi:10.1023/A:1007670909889
Kunz, C., Maierhofer, P., Gyenes, B., Franke, N., Younis, R., Müller-Stich, B. P., et al. (2022). Augmented reality-based robot control for laparoscopic surgery. Current Directions in Biomedical Engineering 8 (1), 54–57. doi:10.1515/cdbme-2022-0014
Lanfranco, , Castellanos, A. E., Desai, J. P., and Meyers, W. C. (2004). Robotic surgery: a current perspective. Annals of Surgery 239, 14–21. doi:10.1097/01.sla.0000103020.19595.7d
Lederman, S. J., and Klatzky, R. L. (2009). Haptic perception: a tutorial. Attention, Perception, and Psychophysics 71, 1439–1459. doi:10.3758/APP.71.7.1439
Lendvay, T. S., Casale, P., Sweet, R., and Peters, C. (2008). Initial validation of a virtual-reality robotic simulator. Journal of Robotic Surgery 2, 145–149. doi:10.1007/s11701-008-0099-1
Li, , et al. (2020). Human-robot interaction based on gesture and movement recognition. Signal Processing and Image Communication 81, 115686. doi:10.1016/j.image.2019.115686
Li, J. M., Bardana, D. D., and Stewart, A. J. (2011). “Augmented virtuality for arthroscopic knee surgery,” in Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention – miccai 2011. Miccai 2011. Editors G. Fichtinger, A. Martel, and T. Peters (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer), 6891, 186–193. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-23623-5_24
Lin, Z., Zhang, T., Sun, Z., Gao, H., Ai, X., Chen, W., et al. (2022). Robotic telepresence based on augmented reality and human motion mapping for interventional medicine. IEEE Transactions on Medical Robotics and Bionics 4 (4), 935–944. doi:10.1109/tmrb.2022.3201652
Liss, M. A., Abdelshehid, C., Quach, S., Lusch, A., Graversen, J., Landman, J., et al. (2012). Validation, Correlation, and Comparison of the da Vinci Trainer™ and the daVinci Surgical Skills Simulator™ Using the Mimic™ Software for Urologic Robotic Surgical Education. Journal of Endourology 26 (12), 1629–1634. doi:10.1089/end.2012.0328
Mäkinen, H., Haavisto, E., Havola, S., and Koivisto, J. M. (2022). User experiences of virtual reality technologies for healthcare in learning: an integrative review. Behaviour and Information Technology 41 (1), 1–17. doi:10.1080/0144929x.2020.1788162
Marino, , Shabat, G., Gulotta, G., and Komorowski, A. L. (2018). From illusion to reality: a brief history of robotic surgery. Surgical Innovation 25, 291–296. doi:10.1177/1553350618771417
McDonald, M., and Shirk, D. (2021). Application of three-dimensional virtual reality models to improve the pre-surgical plan for robotic partial nephrectomy. Journal of the Society of Laparoendoscopic Surgeons 25 (3), 00011. doi:10.4293/JSLS.2021.00011
Mehralivand, S., Kolagunda, A., Hammerich, K., Sabarwal, V., Harmon, S., Sanford, T., et al. (2019). A multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging-based virtual reality surgical navigation tool for robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy. Turkish Journal of Urology 45 (5), 357–365. doi:10.5152/tud.2019.19133
Melo, F. A., and Bernardes, M. C. (2019). “Virtual reality simulator for laparoscopic procedures performed with a robotic endoscope holder,” in XXVI Brazilian congress on biomedical engineering (Singapore: Springer), 152–156.
Morimoto, T., Kobayashi, T., Hirata, H., Otani, K., Sugimoto, M., Tsukamoto, M., et al. (2022). XR (extended reality: virtual reality, augmented reality, mixed reality) technology in spine medicine: status quo and quo vadis. Journal of Clinical Medicine 11 (2), 470. doi:10.3390/jcm11020470
Mustaffa, W. S. W., Rahman, R. A., Ab Wahid, H., and Ahmad, N. L. (2020). A cognitive-affective-behavioral responses of customer experience (CAB-CE) model for service delivery improvement in the healthcare industry. Int. J. Sup. Chain. Mgt. 9 (2), 252
Overbeeke, K. (2002). “Beauty in usability: forget ease of use,” in Pleasure with products: beyond usability. Editors W. Green, and P. Jordan (New York: Taylor and Francis Ltd).
Panariello, D., Caporaso, T., Grazioso, S., Di Gironimo, G., Lanzotti, A., Knopp, S., et al. (2019). “Using the KUKA LBR iiwa robot as haptic device for virtual reality training of hip replacement surgery,” in 2019 Third IEEE International Conference on Robotic Computing (IRC), 449–450. doi:10.1109/irc.2019.00094
Perrenot, C., Perez, M., Tran, N., Jehl, J. P., Felblinger, J., Bresler, L., et al. (2012). The virtual reality simulator dV-Trainer® is a valid assessment tool for robotic surgical skills. Surgical Endoscopy 26, 2587–2593. doi:10.1007/s00464-012-2237-0
Physiol (2012): Wrong citation, please delete the whole sentence: physiol (2012) states that fatigue is mostly an emotion that is a byproduct of intricate regulation designed to keep the body safe.
Porpiglia, F., Fiori, C., Checcucci, E., Amparore, D., and Bertolo, R. (2018). Hyperaccuracy three-dimensional reconstruction is able to maximize the efficacy of selective clamping during robot-assisted partial nephrectomy for complex renal masses. European Urology 74 (5), 651–660. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2017.12.027
Qian, L., Deguet, A., Wang, Z., Liu, Y. H., and Kazanzides, P. (2019). “Augmented reality assisted instrument insertion and tool manipulation for the first assistant in robotic surgery,” in 2019 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 5173–5179. doi:10.1109/icra.2019.8794263
Rahman, M. M., Ishmam, M. F., Hossain, M. T., and Haque, M. E. (2022). “Virtual reality based medical training simulator and robotic operation system,” in 2022 International Conference on Recent Progresses in Science, Engineering and Technology (ICRPSET), 1–4. doi:10.1109/icrpset57982.2022.10188546
Reeves, F., and Dasgupta, P. (2021). Assessing the learning curve of single-port robot-assisted prostatectomy. BJU Int 128, 657–658. doi:10.1111/bju.15624
Robert, J. M., and Lesage, A. (2017). “Designing and evaluating user experience,” in The handbook of human-machine interaction (CRC Press), 321–338Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CRC_Press
Russell, J. A. (2003). Core affect and the psychological construction of emotion. Psychological Review 110 (1), 145–172. doi:10.1037//0033-295x.110.1.145
Salomon, K., and Karlsdóttir, M. (2013). Perceptions of stress. Psychology Faculty Publications, 1837. Available at: https://digitalcommons.usf.edu/psy_facpub/1837
Saun, T. J., and Grantcharov, T. P. (2021). Development of the user experience (UX) and video quality evaluation (VQE) instruments for assessment of intraoperative video capture technology. Journal of Surgical Education 78 (1), 201–206. doi:10.1016/j.jsurg.2020.06.011
Schreuder, H. W., Persson, J. E. U., Wolswijk, R. G. H., Ihse, I., Schijven, M. P., and Verheijen, R. H. M. (2014) “Validation of a novel virtual reality simulator for robotic surgery,”, 2014. Scientific World Journal, 1–10. doi:10.1155/2014/507076
Schweikard, A., et al. (2015). Applications of surgical robotics. Medical Robotics. Available at: https://support.Springer.com/en/support/solutions/articles/6000245683-group-offices-and-postal-addresses
Seo, M.-Gu, Barrett, L., and Bartunek, J. (2004). The role of affective experience in work motivation. Academy of management review 29, 423–439. doi:10.2307/20159052
Sethi, A. S., Peine, W. J., Mohammadi, Y., and Sundaram, C. P. (2009). Validation of a novel virtual reality robotic simulator. Journal of Endourology 23 (3), 503–508. doi:10.1089/end.2008.0250
Silvia, P. J. (2008). Interest: the curious emotion. Current Directions in Psychological Science 17 (1), 57–60. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8721.2008.00548.x
Singla, R., Edgcumbe, P., Pratt, P., Nguan, C., and Rohling, R. (2017). Intra-operative ultrasound-based augmented reality guidance for laparoscopic surgery. Healthc Technol Lett 4 (5), 204–209. doi:10.1049/htl.2017.0063
Skarbez, R., Smith, M., and Whitton, M. C. (2021). Revisiting Milgram and Kishino's reality-virtuality continuum. Frontiers in Virtual Reality 2, 647997. doi:10.3389/frvir.2021.647997
Song, Y., Xia, L., Ju, X., Wang, W., Ge, X., and Hong, J. (2024). Development of a supportive care needs eHealth application for patients with cervical cancer undergoing surgery: a feasibility study. *BMC Health Services Research* 24 (3), 3. doi:10.1186/s12913-023-10437-3
Souders, C. P., Catchpole, K. R., Wood, L. N., Solnik, J. M., Avenido, R. M., Strauss, P. L., et al. (2017). Reducing operating room turnover time for robotic surgery using a motor racing pit stop model. World Journal of Surgery 41 (8), 1943–1949. doi:10.1007/s00268-017-3936-4
Spielman, R. M., Jenkins, W., and Lovett, M. (2020). Psychology 2e. Available at: https://openstax.org/details/books/psychology-2e/
Stanney, K. M., Nye, H., Haddad, S., Hale, K. S., Padron, C. K., and Cohn, J. V. (2021). “Extended reality (XR) environments,” in Handbook of human factors and ergonomics, 782–815.
Staub, , Can, S., Jensen, B., Knoll, A., and Kohlbecher, S. (2012). “Human-computer interfaces for interaction with surgical tools in robotic surgery,” in Proceedings of the 4th IEEE RAS and EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics (BioRob), 81–86. doi:10.1109/biorob.2012.6290850
Suh, I. H., Siu, K. C., Mukherjee, M., Monk, E., Oleynikov, D., and Stergiou, N. (2009). Consistency of performance of robot-assisted surgical tasks in virtual reality. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics 142, 369–373. Available at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19377186/.
Tai, Y., Shi, J., Pan, J., Hao, A., and Chang, V. (2021). Augmented reality-based visual-haptic modeling for thoracoscopic surgery training systems. Virtual Reality and Intelligent Hardware 3, 274–286. doi:10.1016/j.vrih.2021.08.002
Takata, R., Kanehira, M., Kato, Y., Matsuura, T., Kato, R., Maekawa, S., et al. (2021). Improvement of three-dimensional motion sickness using a virtual reality simulator for robot-assisted surgery in undergraduate medical students: a prospective observational study. BMC Medical Education 21 (1), 498. doi:10.1186/s12909-021-02872-9
Tandogdu, Z., Vale, L., Fraser, C., and Ramsay, C. (2015). A systematic review of economic evaluations of the use of robotic assisted laparoscopy in surgery compared with open or laparoscopic surgery. Applied Health Economics and Health Policy 13 (5), 457–467. doi:10.1007/s40258-015-0185-2
Vardhan, M. (2022). “The role of extended reality for planning coronary artery bypass graft surgery,” in 2022 IEEE visualization and visual analytics (VIS) (Oklahoma City, OK, USA), 115–119.
Vijayakumar, , and Shetty, R. (2020). Robotic surgery in oncology. Indian Journal of Surgical Oncology 11, 549–551. doi:10.1007/s13193-020-01251-y
Weaver, , and Steele, S. (2016). Robotics in colorectal surgery. F1000Research 5 5, 2373. doi:10.12688/f1000research.9389.1
Wei, R., Zhou, S., He, R., and Huang, K. (2024). Communicating environment protection from plastic waste via VR: effects of realism and spatial presence on risk perception. Telematics and Informatics Reports 13, 100121. doi:10.1016/j.teler.2024.100121
Wentink, B. (2001). Eye-hand coordination in laparoscopy - an overview of experiments and supporting aids. Minimally Invasive Therapy and Allied Technologies 10, 155–162. doi:10.1080/136457001753192277
Willuth, E., Hardon, S. F., Lang, F., Haney, C. M., Felinska, E. A., Kowalewski, K. F., et al. (2022). Robotic-assisted cholecystectomy is superior to laparoscopic cholecystectomy in the initial training for surgical novices in an ex vivo porcine model: a randomized crossover study. Surgical Endoscopy 36 (2), 1064–1079. doi:10.1007/s00464-021-08373-6
Wimberger, P., and Schindelhauer, A. (2013). Robotic surgery in gynecology. Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics 289, 5–6. doi:10.1007/s00404-013-3066-7
Witmer, B. G., and Singer, M. J. (1998). Measuring presence in virtual environments: a presence questionnaire. Presence 7, 225–240. doi:10.1162/105474698565686
Wulf, G., and Lewthwaite, R. (2010). Effortless motor learning? an external focus of attention enhances movement effectiveness and efficiency, 75, 102. doi:10.7551/mitpress/8602.003.0004
Keywords: extended reality, robotic-assisted surgery, human-computer interaction, user experience, surgical robots
Citation: Li Y, Li M, Zheng S, Yang L, Peng L, Fu C, Chen Y, Wang C, Chen C, Li B, Xiong B, Breschi S, Liu Y, Shidujaman M, Piazzolla P, Zhang Y, De Momi E and van Eijk D (2024) Exploring the dynamics of user experience and interaction in XR-enhanced robotic surgery: a systematic review. Front. Virtual Real. 5:1461105. doi: 10.3389/frvir.2024.1461105
Received: 07 July 2024; Accepted: 31 October 2024;
Published: 21 November 2024.
Edited by:
Xueni Pan, Goldsmiths University of London, United KingdomReviewed by:
Ozan Tokatli, United Kingdom Atomic Energy Authority, United KingdomDaniele Meli, University of Verona, Italy
Copyright © 2024 Li, Li, Zheng, Yang, Peng, Fu, Chen, Wang, Chen, Li, Xiong, Breschi, Liu, Shidujaman, Piazzolla, Zhang, De Momi and van Eijk. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Meng Li, bGltZW5nLjgxQG1haWwueGp0dS5lZHUuY24=; Daan van Eijk, ZC5qLnZhbmVpamtAdHVkZWxmdC5ubA==
 Yaning Li
Yaning Li Meng Li3*
Meng Li3* Mohammad Shidujaman
Mohammad Shidujaman Elena De Momi
Elena De Momi