- Department of Pathogenic Microorganisms and Biological Laboratory, Suzhou Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Suzhou, China
Background: Ten cases with Dabie bandavirus infection were identified in Suzhou City, China, from April 2023 to August 2024. All 10 cases were hospitalized patients, and three died. We detected and analyzed the cytokine concentrations and viral genomes in the serum samples of these patients to identify the possible causes of the patients’ deaths and to analyze the viral genetic characteristics.
Methods: Blood serum specimens were obtained from the 10 individuals with Dabie bandavirus infection in Suzhou City. The specific nucleic acid of Dabie bandavirus was detected using a real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assay (RT-qPCR). The cytokine concentrations in serum were detected by micro enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The genomes of Dabie bandavirus were amplified using a designated primer pool. The DNA sequencing libraries were prepared using a ligation method. The sequencing process was performed using a Nanopore GridION X5 instrument. Phylogenetic trees for the L, M, and S segments of Dabie bandavirus were constructed using the maximum likelihood (ML) method in MEGA 11 software, with the bootstrap value set at 1,000.
Results: All 10 patients with Dabie bandavirus infection exhibited a severe clinical course, resulting in three fatalities. The cytokine concentrations of CCL2, GM-CSF, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α were significantly elevated in the fatal patients compared with the recovered cases; all p-values for these cytokine analyses were under 0.05. The Dabie bandavirus strains identified in Suzhou belonged to three distinct genotypes: A, B, and F. The nucleotide identities for the L, M, and S segments were 95.65%–99.76%, 93.73%–99.81%, and 94.62%–99.88%, respectively. The average evolutionary rate of segment S was higher than that of segment M and segment L. The ratio of dN/dS in the membrane protein was the highest. SZ03-TXF was a recombinant strain with the location of possible breakpoints at nucleotides 795 and 1,432 in the CDS region of the L segment.
Conclusion: A recombination event was identified in SZ03-TXF strain. High viral load and cytokine storm may be associated with the case fatality of Dabie bandavirus infection. We should strengthen the monitoring of nucleotide substitutions and conduct health education for high-risk populations so as to effectively prevent and control an epidemic of the Dabie bandavirus infection in the future.
Introduction
Dabie bandavirus, formerly known as severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV), a major pathogen responsible for severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS), was first reported in 2011 (1, 2). According to the classification standards of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV, 2021) (https://ictv.global/taxonomy), Dabie bandavirus was classified within the genus Bandavirus of the family Phenuiviridae. The genome of Dabie bandavirus comprises three segments: large (L), medium (M), and small (S) (2). The L segment spans 6,368 nucleotides and encodes RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). The M segment is 3,378-nucleotides long and encodes the membrane protein precursor (GP) that gives rise to two membrane proteins, Gn and Gc, containing immunogenicity and neutralization sites. The S segment contains 1,744 nucleotides, which functions as an ambisense RNA and encodes two proteins, namely, nucleoprotein (NP) and nonstructural proteins (NSs) (3–5). Fu et al. (6, 7) classified the circulating strains of Dabie bandavirus into six genotypes (A–F) with high bootstrap supports of greater than 85 by phylogenetic analysis, and the genetic distances within these genotypes were ranging from 0.001 to 0.026, while the genetic distances between different genotypes varied from 0.035 to 0.062. The A–F genotyping method is presently widely adopted and has been reported in several publications (5, 6, 8–11). The Dabie bandavirus exhibits a wide prevalence primarily through tick bites, with reported cases in the provinces of Hubei, Henan, Anhui, Shandong, Zhejiang, Liaoning, and Jiangsu in China (12–17), as well as human infections were documented in Thailand, South Korea, and Japan (18–20). Although Dabie bandavirus is primarily transmitted to humans through tick bites, it can also be transmitted via direct contact with the blood of infected individuals or animals in the absence of tick bites (21–24). The majority of individuals infected with Dabie bandavirus exhibit severe clinical manifestations, and the mortality rates differ across various regions, often exceeding 10% (11, 16, 18, 25). Dabie bandavirus is a segmented RNA virus that facilitates the emergence of new recombinant strains (7). Therefore, it is crucial to conduct whole-genome sequencing analysis on newly discovered strains.
From April 2023 to August 2024, 10 cases were confirmed to be infection with Dabie bandavirus in Suzhou City. The 10 patients were all critically ill in the intensive care unit (ICU), and three of them died. Among these fatalities, SZ05 was the initial case recorded in Changshu, Suzhou City, a location previously free of reported infections involving Dabie bandavirus. The geographical distribution of Dabie bandavirus transmission may be expanding. High-throughput sequencing of the viral genome in serum samples from the 10 cases was conducted in Suzhou Center for Disease Control and Prevention (SZCDC). In this work, we describe the characteristics of the full-length genomes of the Dabie bandavirus strains identified from Suzhou City.
Materials and methods
Cytokine detection
The concentrations of cytokines, including IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, TNF-α, IFN-γ, CCL-2, and GM-CSF, were determined using an Ella automated microfluidic immunoassay system (ProteinSimple, USA). Serum separator tubes were left at room temperature for 30 min, followed by centrifugation at 1,500 rpm for 15 min to separate the serum. We pipetted 150 µL of serum sample into a 2-ml tube and added an equal volume of sample diluent. The mixture was vortexed for 10 s on medium intensity and then centrifuged at room temperature with 16,000g for 4 min to remove visible particulate/flocculent precipitate. We transferred 50 µL of the diluted samples into sample wells. The cytokine concentrations were measured using the default parameters of Ella-220401004 Analyzer version 4.1.0.22.
RNA extraction and RT-qPCR
We collected serum samples from suspected cases of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Suzhou City from April 2023 to August 2024. The 200-μL serum samples were added into the sample hole, and the total nucleic acid of the serum samples was extracted by using the EZ2 Connect automatic nucleic acid extraction instrument (Qiagen, Germany) according to the instructions of the Virus Mini Kit v2.0 kit (Qiagen, Germany). The nucleic acid of Dabie bandavirus was detected by one-step RT-qPCR assay using a commercial test kit (BioPerfectus, China). The primers (forward: GGGTCCCTGAAGGAGTTGTAAA, reverse: TGCCTTCACCAAGACTATCAATGT) and probe (FAM-TTCTGTCTTGCTGGCTCCGCGC-BHQ1) were employed to detect the conserved nucleic acid sequences in the S segment (26, 27). The reaction system of every sample was composed of 3.5 μL RNase free water, 7.5 μL RT-PCR reaction mix, 5 μL enzyme mixture, 4 μL specific primer and probe mixture, and 5 μL total nucleic acid and was prepared according to the kit instructions. The reaction procedure was 50°C for 30 min, 95°C for 5 min, 45 cycles of 95°C for 10 s, and 55°C for 40 s; fluorescence detection was performed at 55°C in the cyclic amplification step.
Genome sequencing
The complete viral genomes were amplified using the Dabie bandavirus whole-genome high-fidelity capture kit (Baiyi-tech, China). The amplified products were purified using 1.8-fold AMPure XP magnetic beads (Beckman, USA) and quantified using Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit (Thermofisher, USA). The sequencing library was prepared using Native Barcoding Kit 24 V14 (SQK-NBD114.24) (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, UK) according to the instructions provided in the sequencing library construction kit. The library preparation process required an input of 300 ng for each amplification product. Sequencing was performed on a GridION X5 instrument (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, UK) using FLO-MINI 114 chip.
Genome assembly and phylogenetic analysis
The sequencing reads of the Dabie bandavirus were subjected to quality control and underwent whole-genome assembly using a microbial analysis platform (Baiyi-tech, China). Initially, we mapped the filtered sequencing reads to the reference genome (HB29) using the Minimap2 v2.24 software (28). Next, we eliminated duplicate reads from the BAM file with the aid of Picard v2.25.5 software. Subsequently, single-nucleotide variant (SNV) analysis was conducted using the Clair3 v1.0.4 software. Finally, we extracted the consensus sequences from the BAM file, which had already removed duplicate reads in the previous step, employing the bcftools software. Genome annotation was executed using the prokka v1.14.6 software (29), and the results were manually validated against the gbk file of the reference genome (HB29), which was sourced from the database of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). Multiple sequence alignment was conducted using MAFFT online version (30). MEGA 11 software (31) was utilized to find the best DNA model for the subsequent construction of maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic trees. The nucleotide substitution model with the lowest score of Bayesian information criterion (BIC) was selected for the following phylogenetic analysis. The model, general time reversible (GTR) with gamma-distributed substitution rate heterogeneity (G) and proportion of invariable sites (I), was selected for ML analysis for segment L. The model “GTR+G” was selected for ML analysis for both segment M and segment S. Maximum likelihood (ML) phylogenetic trees for L, M, and S segments of Dabie bandavirus were constructed using MEGA 11 software (31), with a bootstrap value of 1,000. ChiPlot online software (32) (https://www.chiplot.online/) was utilized for the visualization of phylogenetic trees. Jalview version 2.11.4.0 software (33) was used for amino acid substitutions visualization. The regression of root-to-tip distances (RTT) method with a strict molecular clock model in Treetime software (34) was utilized to estimate nucleotide substitution rates. The Nei–Gojobori method, as implemented in MEGA 11 software, was employed to compute the values of dN (non-synonymous substitution rate) and dS (synonymous substitution rate), thereby determining the dN/dS ratio. Reference sequences of A–F genotypes were downloaded from the GeneBank.
Recombination analysis
The recombination analysis of the L, M, and S segments was conducted by employing the bootscan method as implemented in the SimPlot v3.5.1 software. The parameters were set as follows: window size of 300 bp, step size of 20 bp, gap strip, 100 replicates, Kimura (two-parameter), and neighbor-joining method. Potential recombination events were validated using RDP, GENECONV, Bootscan, and 3Seq methods as provided by the recombination detection program version 4.10.1 (RDP4) (35).
Statistical analysis
The difference in the proportion of hypertensive individuals between the recovered and fatal groups was statistically analyzed using Fisher’s exact test. The concentration of cytokines in serum exhibits a normal distribution subsequent to logarithmic transformation. The differences between the two groups (fatal and recovered) were statistically analyzed using the t-test method. All statistical calculations were performed using GraphPad Prism version 9.0 software, and p <0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Case information
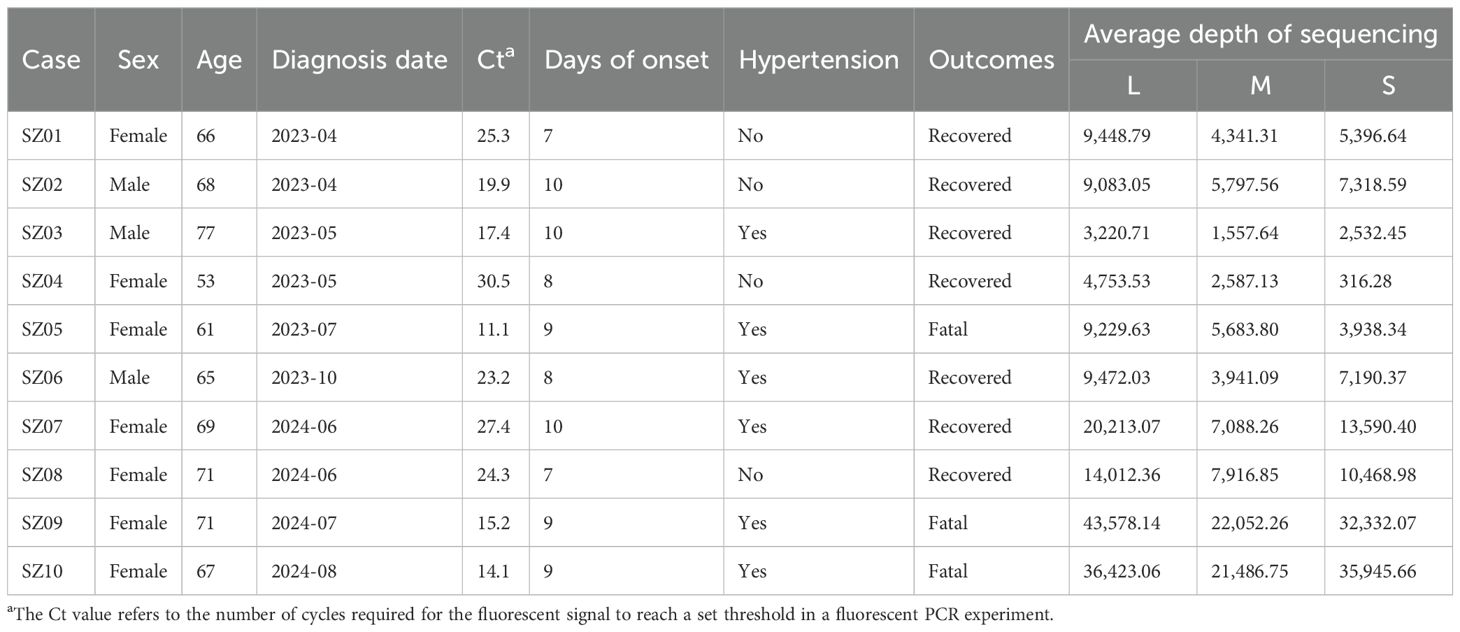
From April 2023 to August 2024, real-time RT-qPCR assay was conducted for nucleic acid detection of Dabie bandavirus in serum samples from 45 individuals suspected of having severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS) in Suzhou Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Ten patients, including three men and seven women, were confirmed to be infected with Dabie bandavirus. All of the 10 patients self-reported experiencing a tick bite within 2 weeks before symptom onset. Three fatalities were recorded, resulting in a case fatality rate of 30% (3/10). The basic data of the 10 cases are presented in Table 1. The mean Ct values of the fatal group and the recovered group were 13.5 and 24.0, respectively. It is significantly different between the fatal and the recovered groups (p = 0.0049). Nine of the 10 patients had visited places where SFTS cases had been previously reported prior to the onset of their illness. The remaining case SZ05 had not departed from Suzhou in the 2 weeks before the symptoms onset, and there was no epidemiological association with other patients. She was the first recorded case in Changshu, Suzhou City, an area where no cases had been documented. The ages of the 10 patients ranged from 53 to 77, with a mean age of 66.8 years old. Three individuals suffered from hypertension in the recovered group (3/7), and all of the fatal cases had hypertension (3/3). However, the difference between the two groups did not show statistical significance by Fisher’s exact test (p = 0.20). The samples of each patient used for RT-PCR and cytokine detection were in the range of 7–10 days since the disease onset.
Cytokine concentrations
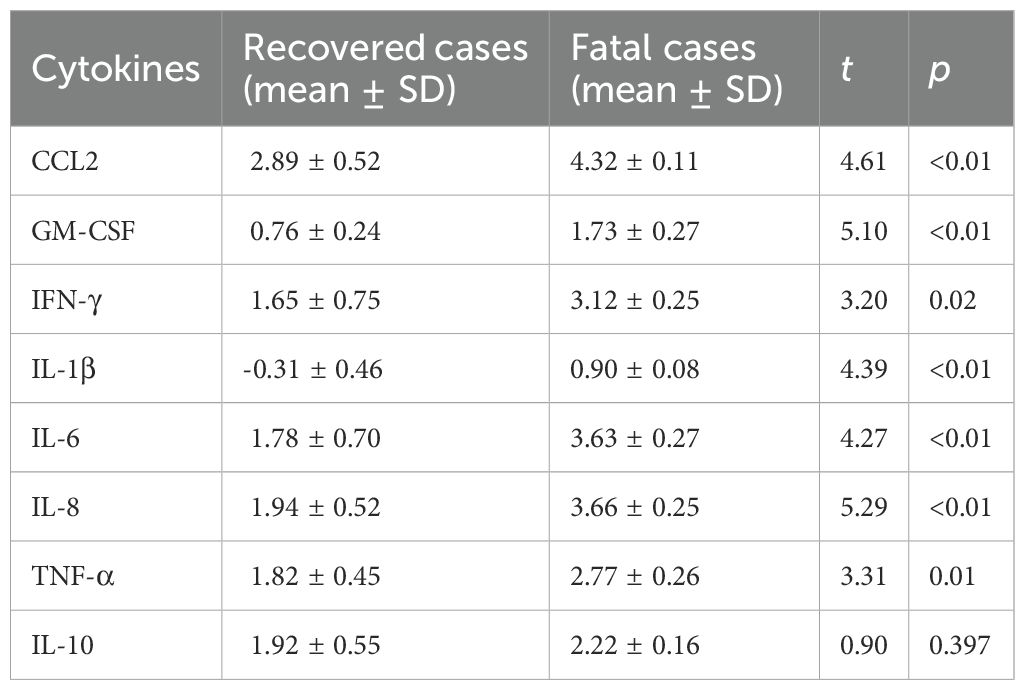
We categorized the Dabie bandavirus patients in this study into recovered and fatal groups. The cytokine concentrations were log-transformed, and the results are shown in Table 2. The concentrations of CCL2, GM-CSF, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α were significantly elevated in the fatal patients compared with the recovered cases, with all p-values for analyses being under 0.05. The concentration of IL-10 exhibited no statistically significant difference between the two groups (p > 0.05).
Genomic analysis
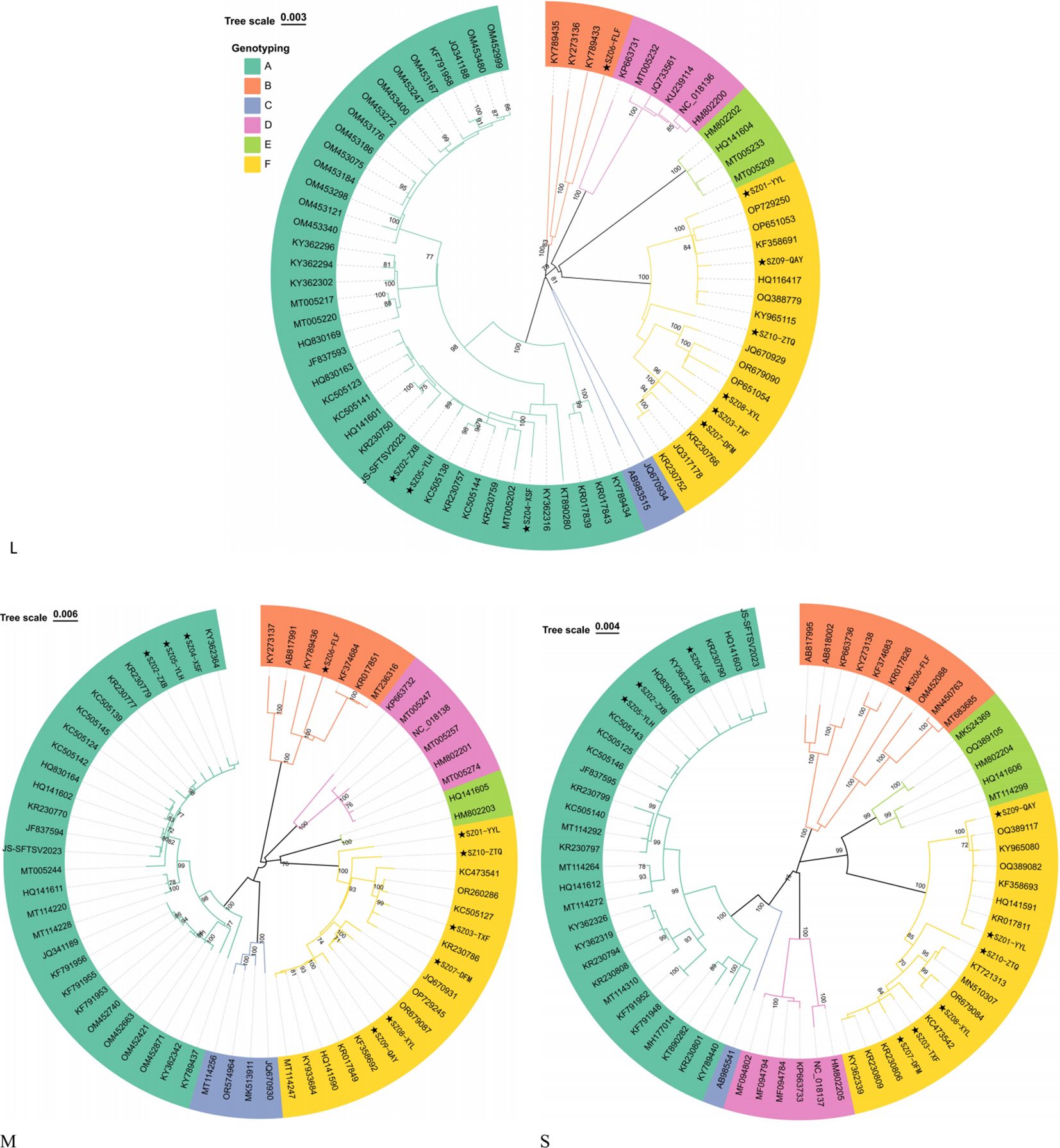
Using the HB29 Dabie bandavirus as a reference sequence, the raw data were filtered and the complete genomes were assembled. The minimum average sequencing depths for the L, M, and S segments of the 10 strains were 3,220.71, 1,557.64, and 316.28, respectively (Table 1), suggesting that the assembled sequences were credible. The nucleotide identities for the L, M, and S segments were in the ranges of 95.65%–99.76%, 93.73%–99.81%, and 94.62%–99.88%, respectively. Compared with the reference strain HB29, the nucleotide identities of the three segments were in the ranges of 95.56%–96.34%, 93.61%–95.65%, and 94.50%–95.46%, respectively. The source data for the accession numbers of the reference A–F genotypes are provided in Supplementary Table S1. The topological structures of the three phylogenetic trees were similar (Figure 1). Sequences of the same genotype clustered together in the phylogenetic trees. The phylogenetic trees of the L, M, and S segments all support that SZ02, SZ04, and SZ05 Suzhou strains belong to A genotype of Dabie bandavirus; SZ06 clustered with B genotype. The SZ01, SZ03, SZ07, SZ08, SZ09, and SZ10 strains were classified within F genotype. The L, M, and S segments of each virus were genotyped identically, suggesting the absence of reassortment in the 10 Dabie bandavirus strains.
Substitutions of amino acids
The RdRP protein was encoded by the 17–6,271 bp in the coding sequences (CDS) of the L segment. The RdRP protein of the Suzhou strains consisted of a total of 2,084 amino acids, with sequence identities ranging from 99.33% to 100%. Compared to the reference strain HB29, the RdRP protein of the 10 Suzhou strains exhibited substitutions at 32 amino acid sites, seven of which were shared (F566Y, V651I, N719S, K835R, T1038S, V1447I, and K1648R) (Figure 2). All F genotype strains possessed substitution V479I in RdRP protein. The amino acid sequences of SZ02-ZXB and SZ05-YLH were identical and possessed substitution E161G. SZ04-XSF possessed an equal number of substitutions as SZ02-ZXB and SZ05-YLH, yet it exhibited differences at two distinct loci, namely, E161G was absent in SZ04-XSF but carried C1178S instead. The amino acid identity of the membrane protein encoded by the CDS region of 19–3,240 bp in the M segment ranged from 98.23% to 99.81%. R924W in the membrane protein was not observed in the 10 Suzhou strains; however, R962S substitution was identified in the 10 strains (Figure 2). All of the F genotypes of the Suzhou strains (SZ01-YYL, SZ03-TXF, SZ07-DFM, SZ08-XYL, SZ09-QAY, and SZ10-ZTQ) carried characteristic substitution sites L13F, V479I, and G562S. The S segment is a double-sense RNA segment. The amino acid identities of the nucleocapsid protein encoded by the CDS region of 43–780 bp ranges from 99.19% to 100%, and the amino acid identity of the nonstructural protein encoded by the complementary strand 835–1,716 bp was in the range of 97.62%–100%. Compared with the HB29 reference strain (Figure 2), a total of 12 substitutions were identified in the nonstructural proteins of the 10 Suzhou strains, of which five were common substitution sites (L197M, P207S, V223I, H245Q, and H249Y). SZ06-FLF carries two additional substitutions (M16V and N276S). The amino acid sequences of SZ04-XSF and SZ05-YLH were consistent, and no other substitutions were carried except for common substitutions. Compared with SZ04-XSF and SZ05-YLH, SZ02-ZXB carries an additional L147P mutation. The nonstructural protein of F genotype strains had identical amino acid sequences and carried additional substitutions of Q144R, K145R, E171D, and L289P.
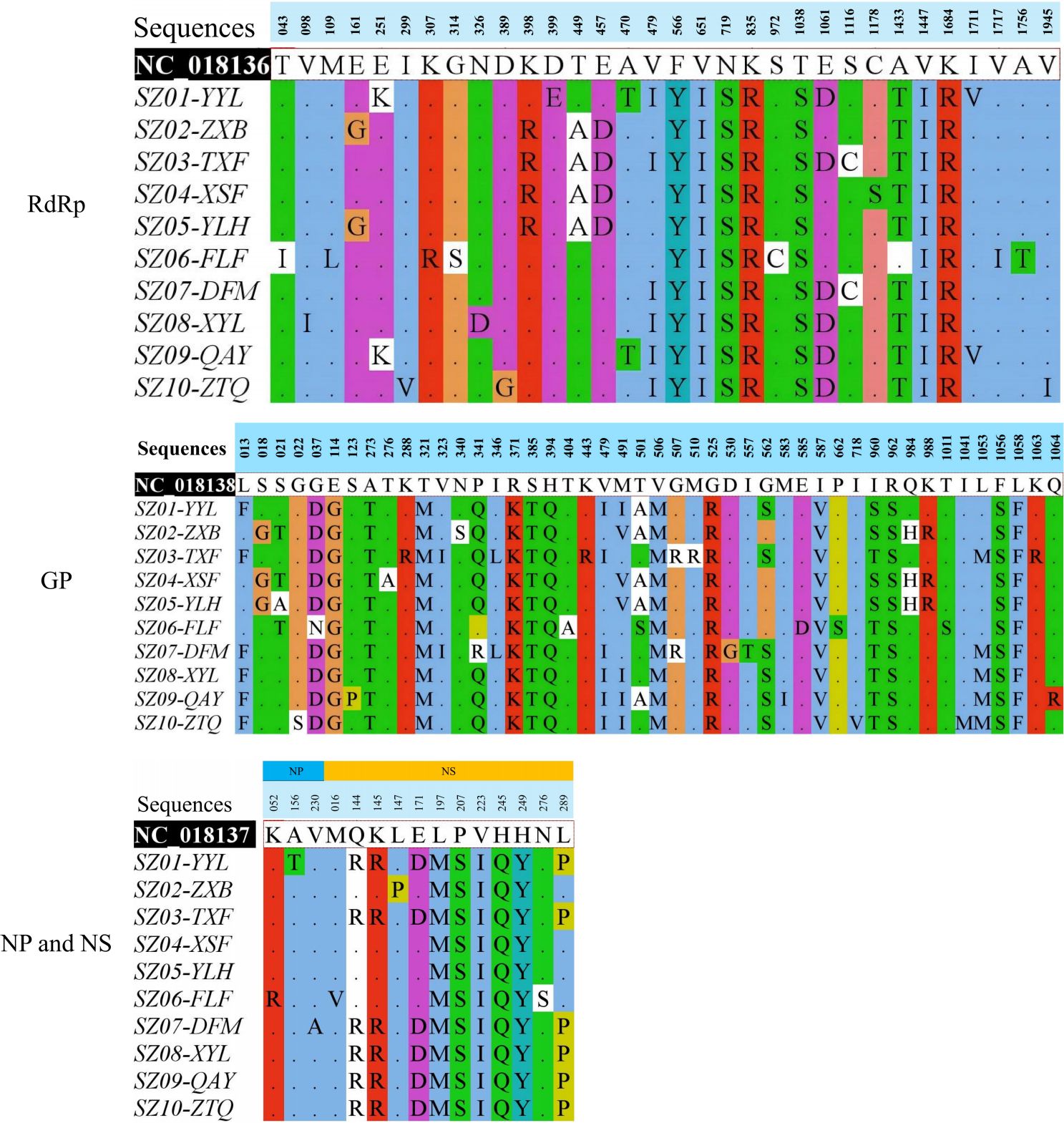
Figure 2. Identified amino acid substitutions in RdRP, GP, NP, and NS proteins of Suzhou Dabie bandavirus strains compared with HB29 (NC_018136-NC_018138).
Evolutionary rates of Dabie bandavirus
In this study, the evolutionary rates for the L, M, and S segments were determined to be 2.67 × 10-5 (substitutions/site/year), 1.35 × 10-4 (substitutions/site/year), and 2.60 × 10-4 (substitutions/site/year), respectively. At the amino acid level, the selective pressure can be described using the ratio of the rates of non-synonymous to synonymous substitutions (dN/dS). The ratio of dN/dS in the membrane protein was 0.12. The dN/dS ratio values for RNA polymerase, NP, and NS were 0.059, 0.030, and 0.10, respectively. The ratio value for the membrane protein was the highest, followed by the values of RdRP protein, NP, and NSs.
Recombination analysis
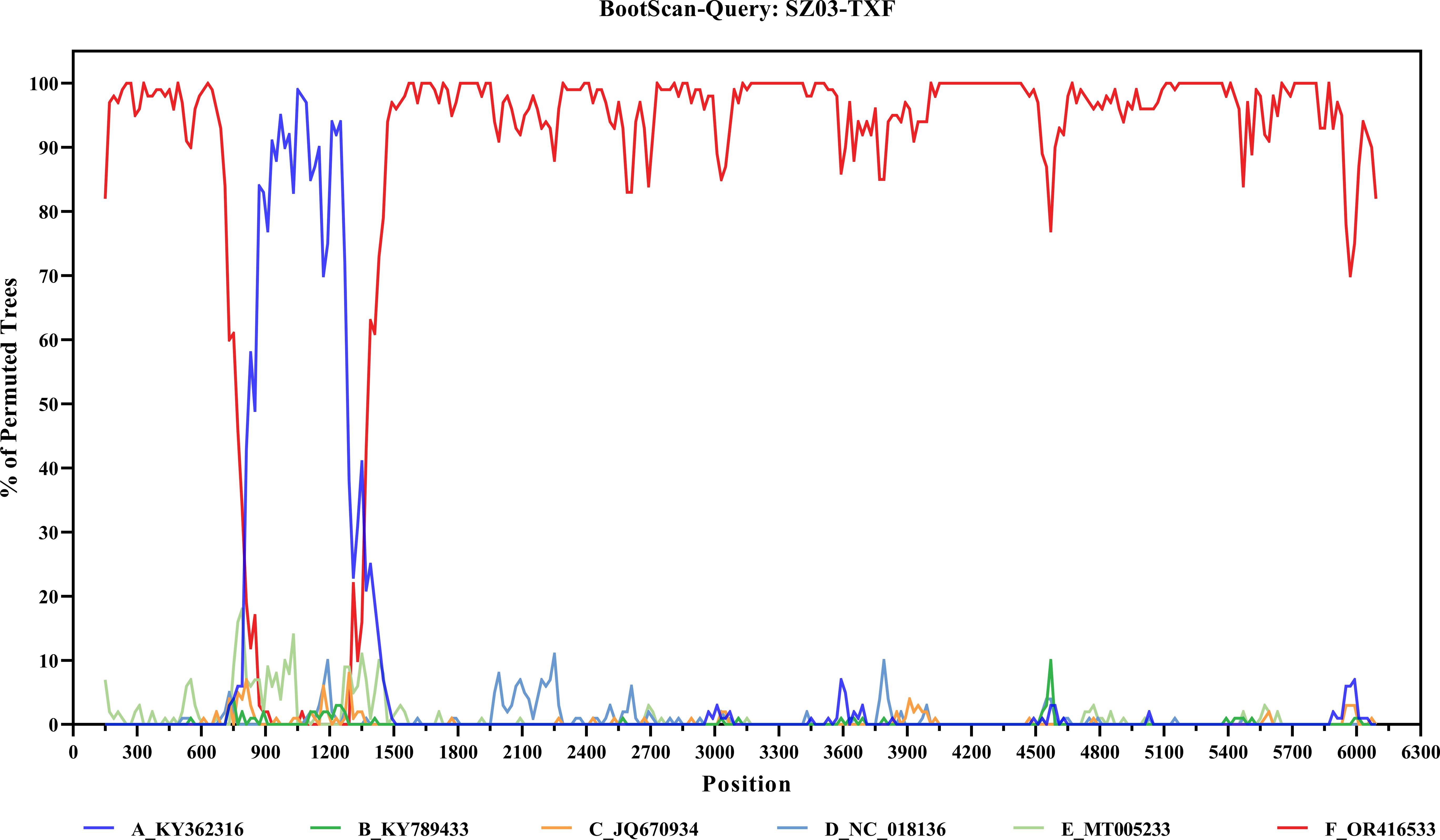
No potential recombination events were detected in segments M and S of the 10 viruses in this study. However, a potential recombination event was present in the L segment of the SZ03-TXF strain (Figure 3). The finding was confirmed by RDP, GENECONV, Bootscan, and 3Seq methods as implemented in RDP4 software and supported by significant p-values of 6.66 × 10-13, 2.87 × 10-9, 2.16 × 10-12, and 3.13 × 10-12, respectively. The location of possible breakpoints were at nucleotides 795 and 1,432 in the CDS region. We extracted three fragments of 1–795 bp (L1), 796–1,431 (L2), and 1,432–6,255 bp (L3) from the CDS region of the L segment of A and F genotypes. ML phylogenetic trees were constructed for L full-length, L1, L2, and L3 fragments, respectively. In the ML trees of L, L1, and L3, SZ03 clustered with F genotype viral strains. However, in the ML tree of L2, SZ03-TXF clustered with A genotype viral strains (Figure 4). The ML trees supported the results of the recombination analysis. It may be a recombinant virus with the L segment of the virus having a genotype F virus as the backbone and a genotype A fragment as the internal insertion.
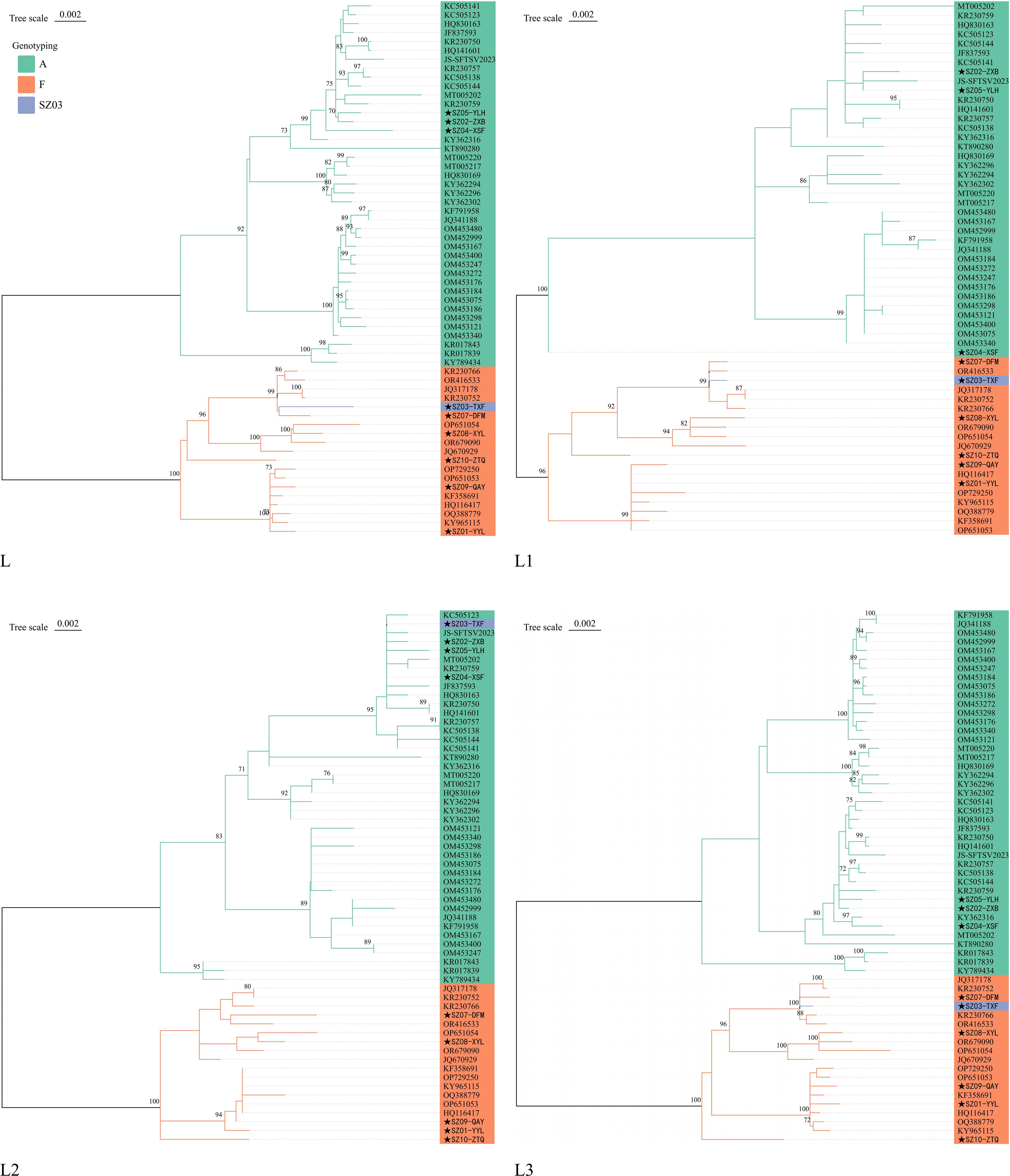
Figure 4. Phylogenetic trees of L, L1, L2, and L3 fragments of A and F genotypes. The stars (★) represent Suzhou strains.
Discussion
Dabie bandavirus belongs to the category of arboviruses, and the spatial distribution of SFTS patients exhibits a certain degree of clustering, which is concentrated in mountainous and hilly areas with rich vegetation and suitable for ticks and other vector organisms to reproduce (14, 36, 37). Human infections with Dabie bandavirus are usually identified from March to October, with the peak period occurring from May to August. In this study, the cases were all farmers, ranging in ages from a minimum of 53 years to a maximum of 77 years, with a mean age of 66.8 years old. The main epidemiological characteristics are consistent with existing literature reports (38, 39). Nine patients except SZ05 had visited places where SFTS cases had been previously reported prior to the onset of their illness. The possibility that they had been infected with Dabie bandavirus in other places before the onset of symptoms cannot be ruled out. In Changshu, Suzhou City, there were no documented instances of human infection with Dabie bandavirus prior to 2023, indicating that the geographical space of viral circulation may be expanding. We should take notice of this phenomenon.
The increased incidence of tick-borne diseases from March to October can be attributed to several factors, such as heightened tick activity, frequent outdoor activities, and, consequently, a greater likelihood of exposure to virus-carrying ticks (2, 8, 16, 25). Furthermore, the warmer temperatures lead to reduced clothing coverage and more exposed skin, increasing susceptibility to tick bites. All of the 10 cases in Suzhou had a history of tick bites within 14 days of symptom onset. Therefore, in order to significantly mitigate the disease burden of Dabie bandavirus infection, it is imperative to implement effective comprehensive prevention and control measures that encompass continuous monitoring of ticks’ density, activity intensity, and virus-carrying rates. Some studies noted that there was no statistical difference in the proportion of patients with hypertension between the fatal and recovered groups (13, 40). In this study, the difference between the two groups did not show statistical significance by Fisher’s exact test (p = 0.20). The result was consistent with the previously report (13). However, another study indicated that hypertension served as a risk factor to accelerate the death of SFTS patients (41). Multi-center studies with a larger sample size are required to explore whether hypertension is associated with death in SFTS patients.
Samples of the fatal cases had lower Ct values for viral detection, indicating that these samples contained a higher viral load. SZ03, which had the lowest Ct value in the recovered group, was 2.2 greater than that of SZ09, which had the highest Ct value in the fatal group, corresponding to a 4.6-fold lower in viral load. The mean Ct values of the fatal group and the recovered group were 13.5 and 24.0, respectively. Ct levels were significantly different between the fatal and recovered groups (p = 0.0049). Thus, the viral load of the fatal cases in this study was higher than those of the recovered cases. Higher viral loads of Dabie bandavirus result in cytokine storm, which leads to the emergence of hemophagocytic syndrome and disseminated intravascular coagulation (42, 43). Hemophagocytic syndrome, hemostatic dysfunction, and disseminated intravascular coagulation lead to severe hemorrhagic tendencies and multiple organ failure (38). In this study, the concentrations of CCL2, GM-CSF, IFN-γ, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 were significantly elevated in fatal patients compared with those of the recovered cases. The results were consistent with previous literature reports (42–44). The death of patients with Dabie bandavirus infection may be associated with hyperinduction of proinflammatory cytokine production. In contrast to previous documented literature (42–44), we did not observe statistically significant differences in IL-10 concentrations between the two groups, which may be attributed to the small sample size.
The genomes of Dabie bandavirus exhibit genetic diversity and recombination phenomena, with the predominant prevalence of type B in South Korea and Japan (11, 45, 46). Multiple genotypes including A, B, C, D, E, and F have been found to be co-circulated in China (19, 47). The genotypes A, B, and F of the 10 Dabie bandavirus strains have been detected in previous cases in China. The viruses in the fatal cases belonged to genotypes A and F. There may be differences in the severity of clinical symptoms caused by different viral genotypes. However, considering the small sample size of this study, these findings should not be overinterpreted.
Compared with HB29, the nucleotide identities of the L, M, and S three segments of the 10 Dabie bandavirus strains identified in Suzhou were in the range of 95.56%–96.34%, 93.61%–95.65%, and 94.50%–95.46%, respectively. There were significant nucleotide differences between the Suzhou strains and the early HB29 virus, indicating that the viruses are constantly evolving. Although there were differences in the calculation methods used in literature to estimate the average evolutionary rate, the conclusions were similar. The average evolutionary rate of segment S was higher than that of segment M and segment L. The ratio of dN/dS in the membrane protein was the highest (6, 10, 48). The R624W substitution in segment M induced more efficient cell fusion, whereas the R962S substitution induced membrane fusion (7). Fortunately, R624W in the membrane protein was not observed in the 10 Suzhou strains. However, R962S substitution was identified in the 10 strains. Segment L of Dabie bandavirus exhibits critical functions in transcription and genome RNA replication. Single amino acid substitution of N1891K in segment L can enhance polymerase activity. In this study, the N1891K substitution was not detected in the 10 sequences from Suzhou, but additional 32 amino acid substitutions were identified (Figure 2). The biological significance of these substitutions remains unclear and requires further study. The Dabie bandavirus identified from the fatal case SZ05-YLH shared the identical amino acid sequences of RdRP protein with SZ02-ZXB and possessed the same amino acid sequences of nucleocapsid protein and nonstructural protein with SZ04-XSF. The sequences of Suzhou strains exhibited the highest nucleotide identities with other sequences uploaded from neighboring areas within Jiangsu Province in the NCBI database, suggesting that the prevalence of Dabie bandavirus has spatial clustering.
Yao Wang et al. (45) identified 54, 36, and 11 potential recombination events in the L, M, and S segments of Dabie bandavirus, respectively. Additionally, Yu-ting Ren et al. (13) also reported eight recombination events in Dabie bandavirus, with four occurring in the M segment, three in the S segment, and one in the L segment, respectively. The recombination event (SZ03) identified in this study involved the L segment. Recombination events have been observed in L, M, and S segments of the Dabie bandavirus. However, it remains unclear whether the recombination events will affect viral biological properties such as antigenicity, transmissibility, and virulence. The biological significance of recombination events deserves further in-depth investigation.
The present investigation sought to characterize the cytokines and viral genomes in the serum of patients infected with Dabie bandavirus in Suzhou City. However, it is essential to acknowledge the inherent limitations associated with the research framework and methodologies utilized. Initially, the sample size of patients examined in this study was relatively small, potentially restricting the representativeness of the findings. Secondly, the potential effects of multiple substitutions within the same protein and the effects of substitutions across different proteins in Dabie bandavirus were unclear. The interactions could either enhance or mitigate the effects of individual substitutions, and their omission limits the depth of our understanding of the biological significance of amino acid substitutions. Consequently, further research are required, incorporating a larger sample size and experiments that are more biologically pertinent, to fully understand the complexity and influence of these substitutions in Dabie bandavirus.
In summary, human infection with Dabie bandavirus usually leads to severe clinical symptoms and even death. We should pay close attention to the biological significance of nucleotide substitutions, increase the investment in scientific research related to Dabie bandavirus, and develop effective vaccines and drugs as soon as possible.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/Supplementary Material.
Ethics statement
The blood samples in this manuscript were collected for infectious disease pathogen testing with the patients’ consent. Genomic sequencing was also for the purpose of obtaining the viral molecular characterization and protecting public health. The interests of the participants involved in this study have been adequately protected, and they were beneficial for the disease diagnosis and treatment. This study was approved by Suzhou Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Ethics Committee. All of the experiments were in line with relevant rules and regulations.
Author contributions
ZD: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. MY: Writing – review & editing. YX: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. HZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. QS: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by Suzhou Key Technologies for the Prevention and Control of Major Infectious Diseases (GWZX202202, GWZX202302), Suzhou Key Medical Discipline (SZXK202117), “National Tutorial System” Training Project for Young Health Backbone Talents in Suzhou (QNGG2022030), and the Project of Science and Education for Promoting Health Development (QNXM2024058, QNXM2024061).
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude to the authors and submitting laboratories for sharing their Dabie bandavirus sequences in the public databases.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fviro.2024.1529730/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Yu X, Liang M, Zhang S, Liu Y, Li J, Sun Y, et al. Fever with thrombocytopenia associated with a novel bunyavirus in China. New Engl J Med. (2011) 364:1523–32. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1010095
2. Kim E, Park S. Emerging tick-borne dabie bandavirus: virology, epidemiology, and prevention. Microorg (Basel). (2023) 11:2309. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11092309
3. Casel MA, Park SJ, Choi YK. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus: emerging novel phlebovirus and their control strategy. Exp Mol Med. (2021) 53:713–22. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00610-1
4. Seo J, Kim D, Yun N, Kim D. Clinical update of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Viruses. (2021) 13:1213. doi: 10.3390/v13071213
5. Zhan J, Wang Q, Cheng J, Hu B, Li J, Zhan F, et al. Current status of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China. Virol Sin. (2017) 32:51–62. doi: 10.1007/s12250-016-3931-1
6. Fu Y, Li S, Zhang Z, Man S, Li X, Zhang W, et al. Phylogeographic analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus from Zhoushan Islands, China: implication for transmission across the ocean. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:19563. doi: 10.1038/srep19563
7. Liu B, Zhu J, He T, Zhang Z. Genetic variants of Dabie bandavirus: classification and biological/clinical implications. Virol J. (2023) 20:68. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02033-y
8. Seo M, Noh B, Lee HS, Kim T, Song B, Lee HI. Nationwide temporal and geographical distribution of tick populations and phylogenetic analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus in ticks in Korea, 2020. Microorg (Basel). (2021) 9:1630. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9081630
9. Lee J, Moon K, Kim M, Lee W, Lee H, Park JK, et al. Seasonal distribution of Haemaphysalis longicornis (Acari: Ixodidae) and detection of SFTS virus in Gyeongbuk Province, Republic of Korea, 2018. Acta Tropica. (2021) 221:106012. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2021.106012
10. Yun M, Ryou J, Choi W, Lee J, Park S, Kim D. Genetic diversity and evolutionary history of Korean isolates of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus from 2013-2016. Arch Virol. (2020) 165:2599–603. doi: 10.1007/s00705-020-04733-0
11. Yun S, Park S, Kim Y, Park S, Yu M, Kwon H, et al. Genetic and pathogenic diversity of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) in South Korea. JCI Insight. (2020) 5:e129531. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.129531
12. Wang Y, Pang B, Ma W, Kou Z, Wen H. Spatiotemporal analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Shandong Province, China, 2014-2018. BMC Public Health. (2022) 22:1998. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-14373-5
13. Ren Y, Tian H, Xu J, Liu M, Cai K, Chen S, et al. Extensive genetic diversity of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus circulating in Hubei Province, China, 2018-2022. PloS Negl Trop Dis. (2023) 17:e11654. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011654
14. Wang W, Zhang A, Wu Q, Wu Q, Zhu L, Yang J, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in southern Anhui Province, China, 2011-2020. Japanese J Infect Dis. (2022) 75:133–9. doi: 10.7883/yoken.JJID.2021.391
15. Liang S, Xie W, Li Z, Zhang N, Wang X, Qin Y, et al. Analysis of fatal cases of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Jiangsu province, China, between 2011 and 2022: A retrospective study. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1076226. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1076226
16. Tao M, Liu Y, Ling F, Chen Y, Zhang R, Ren J, et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in southeastern China, 2011-2019. Front Public Health. (2022) 9:803660. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.803660
17. Han X, Ma Y, Liu H, Li D, Wang Y, Jiang F, et al. Identification of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus genotypes in patients and ticks in Liaoning Province, China. Parasites Vectors. (2022) 15:120. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05237-3
18. Kobayashi Y, Kato H, Yamagishi T, Shimada T, Matsui T, Yoshikawa T, et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome, Japan, 2013-2017. Emerging Infect Dis. (2020) 26:692–9. doi: 10.3201/eid2604.191011
19. Yun S, Park S, Park S, Choi W, Jeong HW, Choi Y, et al. Molecular genomic characterization of tick- and human-derived severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus isolates from South Korea. PloS Negl Trop Dis. (2017) 11:e5893. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005893
20. Rattanakomol P, Khongwichit S, Linsuwanon P, Lee KH, Vongpunsawad S, Poovorawan Y. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus infection, Thailand, 2019-2020. Emerging Infect Dis. (2022) 28:2572–4. doi: 10.3201/eid2812.221183
21. Mekata H, Kawaguchi T, Iwao K, Umeki K, Yamada K, Umekita K, et al. Possible transmission of severe fever with the thrombocytopenia syndrome virus to an individual who buried an infected cat. Japanese J Infect Dis. (2023) 76:211–4. doi: 10.7883/yoken.JJID.2022.425
22. Tao M, Liu Y, Ling F, Zhang R, Shi X, Ren J, et al. Characteristics of three person-to-person transmission clusters of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in southeastern China. Am J Trop Med Hygiene. (2021) 105:794–800. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.21-0366
23. Liu T, Zhang N, Li H, Li H, Hou S, Liu X. Analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome cluster in east China. Virol J. (2023) 20:199. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-02155-3
24. Mao L, Deng B, Liang Y, Liu Y, Wang Z, Zhang J, et al. Epidemiological and genetic investigation of a cluster of cases of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome bunyavirus. BMC Infect Dis. (2020) 20:346. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05072-w
25. Miao D, Liu M, Wang Y, Ren X, Lu Q, Zhao G, et al. Epidemiology and ecology of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China, 2010-2018. Clin Infect Dis. (2021) 73:e3851–8. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1561
26. Song P, Zheng N, Zhang L, Liu Y, Chen T, Bao C, et al. Downregulation of interferon-β and inhibition of TLR3 expression are associated with fatal outcome of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:6511–32. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06921-6
27. Baba M, Okamoto M, Toyama M, Sakakibara N, Shimojima M, Saijo M, et al. Amodiaquine derivatives as inhibitors of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) replication. Antiviral Res. (2023) 210:105479. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2022.105479
28. Heng L. Minimap2: pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics. (2018) 34:3094–100. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty191
29. Seemann T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics. (2014) 30:2068–9. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153
30. Katoh K, Rozewicki J, Yamada KD. MAFFT online service: multiple sequence alignment, interactive sequence choice and visualization. Briefings Bioinf. (2019) 20:1160–6. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx108
31. Koichiro T, Glen S, Sudhir K. MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol. (2021) 38:3022–7. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab120
32. Xie J, Chen Y, Cai G, Cai R, Hu Z, Wang H. Tree Visualization By One Table (tvBOT): a web application for visualizing, modifying and annotating phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. (2023) 51:W587–92. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad359
33. Waterhouse AM, Procter JB, Martin DMA, Clamp M, Barton GJ. Jalview Version 2 — a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. BIOINFORMATICS. (2009) 25:1189–91. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp033
34. Sagulenko P, Puller V, Neher RA. TreeTime: Maximum-likelihood phylodynamic analysis. Virus Evol. (2018) 4:x42. doi: 10.1093/ve/vex042
35. Martin DP, Murrell B, Golden M, Khoosal A, Muhire B. RDP4: Detection and analysis of recombination patterns in virus genomes. Virus Evol. (2015) 1:v3. doi: 10.1093/ve/vev003
36. Liu W, Dai K, Wang T, Zhang H, Wu J, Liu W, et al. Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome incidence could be associated with ecotone between forest and cultivated land in rural settings of central China. Ticks Tick-borne Dis. (2023) 14:102085. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2022.102085
37. Liang S, Li Z, Zhang N, Wang X, Qin Y, Xie W, et al. Epidemiological and spatiotemporal analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in Eastern China, 2011-2021. BMC Public Health. (2023) 23:508. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-15379-3
38. Gong L, Zhang L, Wu J, Lu S, Lyu Y, Zhu M, et al. Clinical progress and risk factors for death from severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome: A multihospital retrospective investigation in Anhui, China. Am J Trop Med Hygiene. (2021) 104:1425–31. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.20-0270
39. He F, Zheng X, Zhang Z. Clinical features of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome and analysis of risk factors for mortality. BMC Infect Dis. (2021) 21:1253. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06946-3
40. Zhang Y, Huang L, Shu Z, Wu W, Cai H, Shi Y. Prediction of prognosis in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Japanese J Infect Dis. (2024). doi: 10.7883/yoken.JJID.2024.015
41. Zhao J, Ge H, Wang G, Lin L, Yuan Y, Xu Y, et al. Fatal patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in China. Int J Infect Dis. (2022) 125:10–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2022.10.008
42. He Z, Wang B, Li Y, Hu K, Yi Z, Ma H, et al. Changes in peripheral blood cytokines in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. J Med Virol. (2021) 93:4704–13. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26877
43. Xu D, Zhang X, Tian X, Wang X, Zhao L, Gao M, et al. Changes in cytokine levels in patients with severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. J Inflammation Res. (2024) 17:211–22. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S444398
44. Liu M, Lei X, Yu H, Zhang J, Yu X. Correlation of cytokine level with the severity of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome. Virol J. (2017) 14:6. doi: 10.1186/s12985-016-0677-1
45. Wang Y, Pang B, Wang Z, Tian X, Xu X, Chong X, et al. Genomic diversity and evolution analysis of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome in East Asia from 2010 to 2022. Front Microbiol. (2023) 14:1233693. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1233693
46. Lee K, Seok JH, Kim H, Park S, Lee S, Bae J, et al. Genome-informed investigation of the molecular evolution and genetic reassortment of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. PloS Negl Trop Dis. (2023) 17:e11630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011630
47. Zu Z, Lin H, Hu Y, Zheng X, Chen C, Zhao Y, et al. The genetic evolution and codon usage pattern of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus. Infect Genet Evol. (2022) 99:105238. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2022.105238
Keywords: Dabie bandavirus, cytokine, RT-qPCR, substitution, sequencing
Citation: Dong Z, Yuan M, Xing Y, Zhang H and Shen Q (2025) Characterizations of cytokines and viral genomes in serum of patients with Dabie bandavirus infection. Front. Virol. 4:1529730. doi: 10.3389/fviro.2024.1529730
Received: 17 November 2024; Accepted: 27 December 2024;
Published: 28 January 2025.
Edited by:
Haider Al-Hello, Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare, FinlandReviewed by:
Paul W. Denton, University of Nebraska Omaha, United StatesYang Li, Peking University Chongqing Research Institute of Big Data, China
Carmen Baur Vieira, Fluminense Federal University, Brazil
Hussein Alburkat, University of Helsinki, Finland
Copyright © 2025 Dong, Yuan, Xing, Zhang and Shen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qiang Shen, c3F0b21AMTI2LmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Zefeng Dong
Zefeng Dong Man Yuan†
Man Yuan† Hongkai Zhang
Hongkai Zhang