
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Vet. Sci., 04 February 2025
Sec. Parasitology
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2025.1539446
 Xialian Bu1,2
Xialian Bu1,2 Xianqi Peng1,2
Xianqi Peng1,2 Lei Huang1,2
Lei Huang1,2 Yu Zhao1
Yu Zhao1 Jinbiao Jiao1,2
Jinbiao Jiao1,2 Jian Zhu1
Jian Zhu1 Jing Chen1,2
Jing Chen1,2 Xiaohong Huang1,2
Xiaohong Huang1,2 Aqin Zheng1,2
Aqin Zheng1,2 Huantao Qu1
Huantao Qu1 Jiayun Yao1,2*
Jiayun Yao1,2*Introduction: The ectoparasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis, is the pathogen of white spot disease in freshwater fish, which parasitizes on gills, fins, and skins of fish, causing tissue damage and death of host. However, whether it influences gill and gut microbiota is still unknow.
Methods: In this study, H&E staining was used to show the gill and gut histopathological characteristics of I. multifiliis-infected and uninfected goldfish (Carassius auratus). Meanwhile, 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing was conducted to analyze the difference of gill and gut microbiota between I. multifiliis-infected and uninfected goldfish.
Results: Histopathological examination revealed that I. multifiliis has induced significant damage to the gills of goldfish, characterized by lamellae fusion, cell hyperplasia, cell hyperaemia, inflammatory infiltration, necrosis and desquamation. 16S rRNA gene sequencing result showed that alpha and beta diversity of gill microbiota was significantly reduced in the I. multifiliis-infected group, while no significant changes were observed in gut microbiota. Genus Candidatus Megaira exhibited the highest relative abundance in the I. multifiliis-infected group. Meanwhile, the abundance of opportunistic pathogens Aeromonas and Achromobacter were increased in the intestines of I. multifiliis-infected goldfish.
Discussion: The increased presence of Candidatus Megaira may originate from within the cells of I. multifiliis. The increase of opportunistic pathogens Aeromonas and Achromobacter may pose a threat to the health of goldfish. In summary, this study laid a foundation for further research on the interaction between I. multifiliis and host microbiota.
Ichthyophthiriasis is one of the most severe fish diseases of both wild and cultured freshwater fish, which results in significant economic losses in global aquaculture industry (1, 2). This disease also known as white spot disease and the pathogen of it is Ichthyophthirius multifiliis, a ciliated protozoan (3). Life cycle of I. multifiliis consists of four developmental stages including a parasitic trophont, a free-swimming protomont, a reproductive tomont, and an infective theront (4, 5). When it parasitizes fish’s gills or fins, it can easily invade fish epithelial cells and feed on the cells, mucus, and the tissue fragments, leading to severe tissue damage, increasing the opportunity of secondary infection, and causing a large number of host death in a short time (6, 7). However, there is still no safe and specific drugs for the prevention and control of Ichthyophthiriasis. It is urgent to find effective treatment methods to support the healthy culture of freshwater fish.
Microorganisms can be found on the fish’s skin surface, gills, fins, and in its gastrointestinal tract, which play important roles in host homeostasis and physiology (8). For instance, gut microbiota can produce short-chain fatty acids and contribute to hosts’ metabolism (9). It also shows fundamental roles in protection against pathogen invasion (10). However, apart from these beneficial commensal and symbiotic microorganisms, fish also face threats from pathogenic bacteria. Parasitic infection and exposure are likely to induce changes in fish’s microbiota. Research has shown that Dactylogyrus lamellatus infection can significantly reduce the diversity of the gut microbiota and increase the relative abundance of Cetobacterium in grass carp (11). An infection of endoparasite Khawia japonensis in common carp could lead to the increase of two pathogenic bacterial genera, Lawsonia and Plesiomonas (12). Protozoan I. multifiliis infection also led to a decreased abundance of skin commensals and increased colonization of opportunistic bacteria in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) (13). However, little is known about the interaction between gill and gut microbiota, and ectoparasite I. multifiliis.
Goldfish (Carassius auratus), is a popular ornamental species from all over the world. However, it is highly susceptible to I. multifiliis infection. This parasite can form visible white spots on fish gills, fins, and skins, affecting the ornamental value of goldfish and causing significant economic losses (14). Thus, goldfish is an ideal model organism for I. multifiliis infection.
In the present study, based on the goldfish infection model, the relationship between gill and gut microbiota, and I. multifiliis was characterized by 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing. The histopathological changes of gill and gut were observed and measured with the scoring system (15). These results demonstrated the relationship between gill and gut microbiota and I. multifiliis, which are beneficial for prevention and control of I. multifiliis infection in aquaculture.
Goldfish weighting 15–18 g, were purchased from a commercial supplier in Huzhou City, Zhejiang Province, China. The goldfish were kept in a large aquarium with a water temperature of 25 ± 2°C. To remove all ectoparasites and ensure no parasitic infections, fish were treated with three consecutive baths in 1:10000 formalin solution for 12 h at 48-h intervals. Then fish were cultured in 100 L aquariums with a water temperature of 25 ± 2°C. They were fed once a day with commercial fish pellet feed at 1% of their body weight.
Heavily infected goldfish from the laboratory were selected for trophonts collection. Then place the goldfish in a 1 L transparent box to allow trophonts to shed naturally. Subsequently, use a glass micropipette to collect the trophonts and place them into the tanks containing 90 healthy goldfish (30 goldfish per tank). Use a counter to tally the number of trophonts, with a final count of 500 for each tank. Another 30 healthy goldfish were set as control group. Both infection group and control group were kept under the same conditions as described above. The infection experiment lasted for 2 weeks. Monitor the behavior of the goldfish at 24 h intervals and randomly select 3 goldfish for microscopic examination to count the number of trophonts on their caudal fins.
Samples were collected on the fourteenth day of the experiment. All the experimental procedures and animal care were performed according to the protocols approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Zhejiang Institute of Freshwater Fisheries. First, fish were anaesthetized with 0.02% tricaine methane sulfonate (MS-222, Sigma) according to manufacturer’s instructions. Then gills and hindgut content were isolated and collected under sterile conditions, then were frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C for 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing.
Hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining was performed to assess the damage caused by I. multifiliis to the host gill tissues. First, gills were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin. After 48 h of fixation, gills were sectioned into cassettes, dehydrated through a series of graded ethanol solutions, cleared in xylene, embedded in paraffin wax and sliced into 5 μm thick sections and stained with HE. Then HE stained slides were examined using Axioplan 2 imaging and Axiophot 2 (Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). Histological changes like lamellae fusion, cell hyperplasia, necrosis, hyperemia, and desquamation were assessed according to the scoring system proposed by Baums et al. (15). Briefly, the score ranging from 1 to 7, represents the degree of change (1 - unchanged, 3 - mild, 5 - moderate, 7 - severe).
Extraction of microbial DNA from gills and hindgut content samples was performed using the QIAamp DNA Stool Mini Kit (Qiagen, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The DNA was detected by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and a NanoDrop® ND-2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific Inc., United States). Then hypervariable region V3-V4 of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene was amplified with primer pairs 338F and 806R (The forward primer 338F: 5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′, the reverse primer 806R: 5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′) using an ABI GeneAmp® 9700 PCR thermocycler (ABI, CA, United States). The PCR mixture was including 10 μL 2 × Pro Taq, 0.8 μL each primer (5 μM), 10 ng/μL of template DNA, and ddH2O to a final volume of 20 μL. The amplification conditions were as follows: initial denaturation at 95°C for 3 min; 25 cycles of denaturing at 95°C for 30 s, annealing at 53°C for 30 s and extension at 72°C for 45 s; and final extension at 72°C for 10 min. The PCR products were extracted from 2% agarose gel, purified using the AxyPrep DNA Gel Extraction Kit (Axygen Biosciences, Union City, CA, United States) and quantified using the QuantiFluorTM-ST Blue Fluorescence System (Promega, Beijing, China). Library was constructed by TruSeq™ DNA Sample Prep Kit (Illumina, California, United States) and subjected to sequence on an Illumina NextSeq 2000 platform to generate 300 paired-end reads.
The raw data were analyzed through the free online platform of majorbio cloud platform (cloud.majorbio.com). QIIME 2 V.2022.2 (16) was used to conduct Amplicon Sequence Variants (ASVs)-based analysis. First, reads were quality-filtered and denoised using qiime DADA2 denoising plugin to obtain the ASVs. Then ASVs were assigned taxonomic labels using qiime classify-sk-learn and SILVA database V.138 (17).
Alpha diversity was assessed using metrics including richness, shannon, phylogenetic diversity and pielou evenness indices. All the indices were calculated using Mothur V.1.30.2 (18). Beta-diversity was measured using Bray-Curtis distance. Principal Co-ordinates Analysis (PCoA) was carried out based on the beta-diversity index matrix to study the differences in sample community composition. Taxa were compared between I. multifiliis-infected group and control group by Linear discriminant analysis Effect Size (LEfSe). For the function prediction, KEGG annotation was conducted with the help of PICRUSt2 V.2.2.0 (19).
Kruskal-Wallis test was used to evaluate the intergroup difference of alpha diversity. Pairwised Wilcoxon Rank Sum test was used to determine microbiota that significantly differed between I. multifiliis-infected group and control group. All the statistical analysis were conducted in R language (version 3.3.1) (20).
During the 14 days infection experiment, significant changes were observed in the behavior and body surface color of the goldfish. The body color of goldfish in the control group was very bright, and these goldfish swam in the same direction (Figure 1A). In the early stages of infection, the behavior of goldfish was normal, but some white spots on body surface were visible (Figure 1B). From the fifth day of infection, an outbreak of I. multifiliis occurred. The white spots were visible on the skin and fins of the goldfish (Figure 1C). The behavior of goldfish was becoming abnormal. Most fish often rubbed against the tank wall, swimming in different directions, and some showed unbalanced “backstroke.” Goldfish with severe infections developed white mucous membranes on their skin. Their respiratory rate was found to be significantly reduced by observing the movement of operculum. Then the goldfish was sinking to the bottom and floating with waves. The morphology of I. multifiliis was shown in Figure 1D.
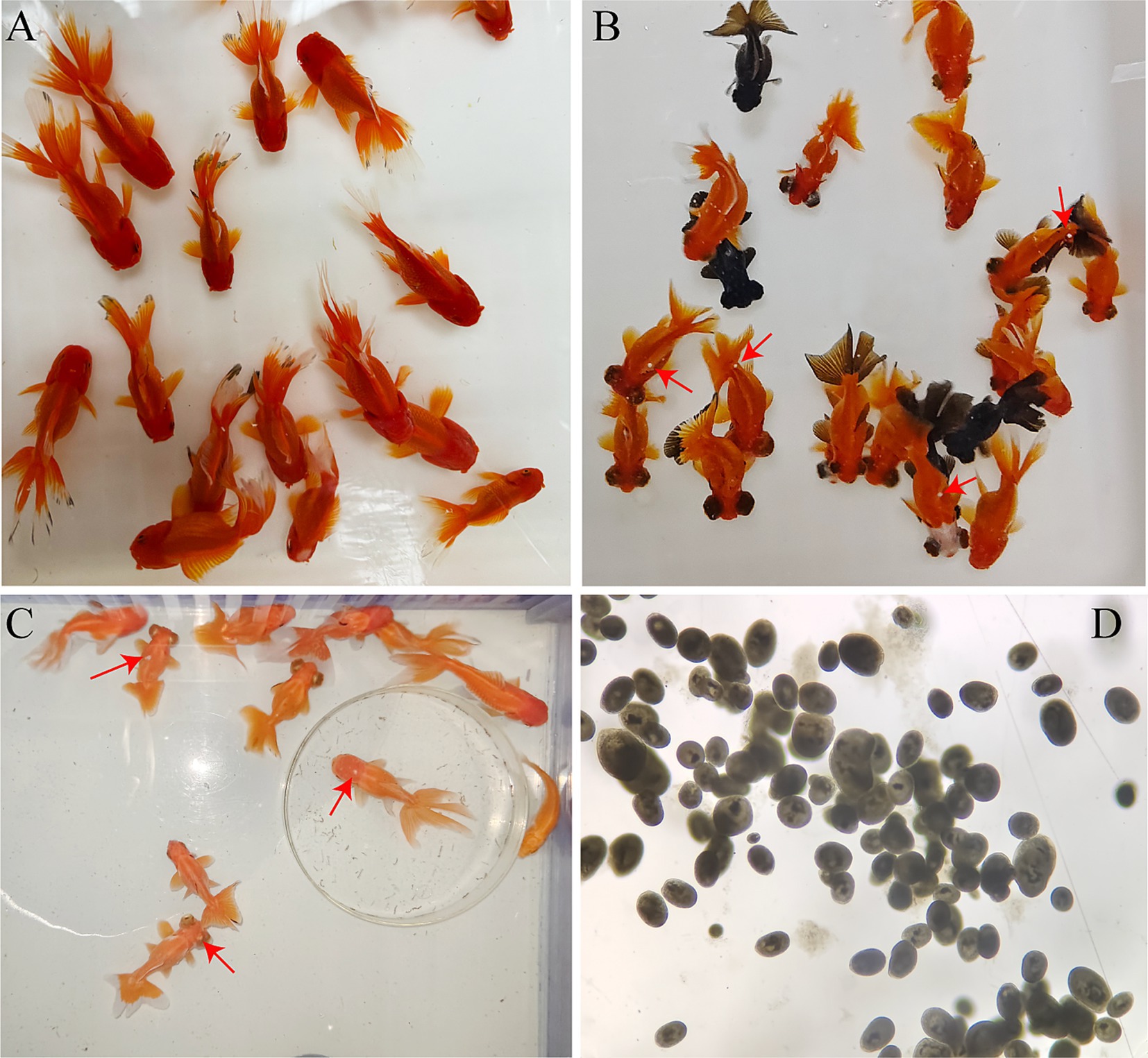

Figure 1. Infection status of the goldfish and morphology of I. multifiliis. (A) Goldfish in the control group. (B) Goldfish in the early stage of infection, red arrows to show white spots. (C) Behavior and body color of goldfish have changed after severe I. multifiliis infection, red arrows to show white spots. (D) Morphology of I. multifiliis during the peak infection period.
Meanwhile, the average number of I. multifiliis per goldfish and the number of dead goldfish each day was recorded (Table 1). The number of I. multifiliis on goldfish reached its peak on the 7th day of infection, which was 1,280, and then gradually decreased. However, there were still 660 trophonts on the last day (14th day) of the infection experiment. The total mortality rate of goldfish was 22.22%.
According to the H&E staining results, after 14 days I. multifiliis infection experiment, the gills of the control and infection group showed significant histological characteristics. The structures of gill filaments and gill lamellae of the control group were clear and regularly arranged (Figure 2A). The morphology and structure of respiratory epithelium and red blood cells were also very complete (Figures 2B,C). However, compared with the control group, the gills of I. multifiliis infected group showed gill filament swelling, eosinophilic granulocyte increases and cell hyperplasia (Figure 2D). Upon magnification, the epithelial cell detachment in Figure 2D can be clearly observed (Figure 2E). Meanwhile, the gills of infected group also showed inflammatory cell infiltration (Figure 2F). Vascular dilation and aneurysmal lesions, along with hyperaemia and swollen gill lamella also can be seen (Figures 2G,H). The gills of I. multifiliis infected group also showed the sign of cell necrosis, chromatin decrease and chromatin edge shift (Figure 2I).
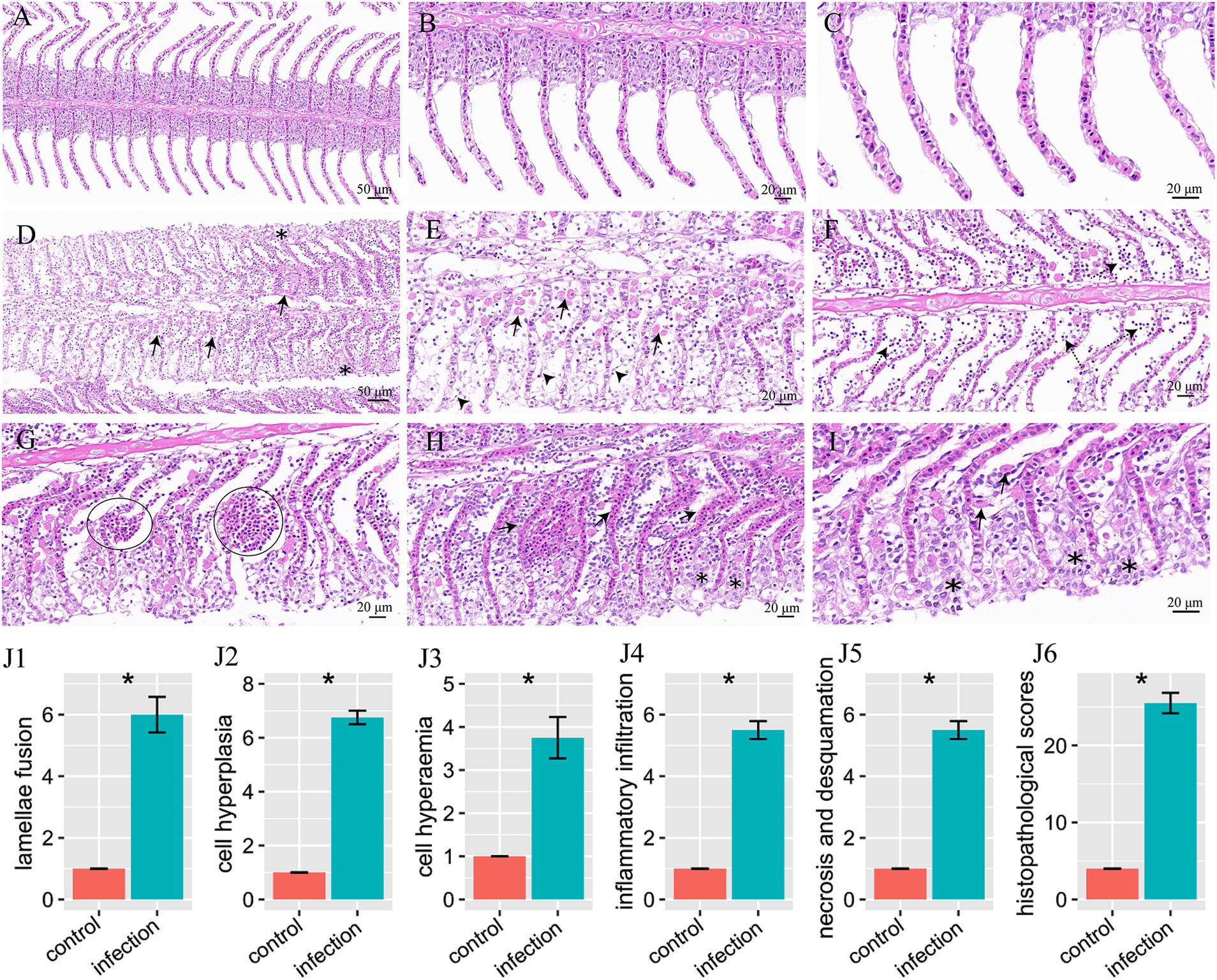
Figure 2. H&E staining results of goldfish gills and statistical results of gill histopathological score. (A–C) Gills of the control group, magnified 20×, 40×, 63×, respectively. (D–I) Gills of the infection group. (D) Eosinophilic granulocyte increases (arrows), cell hyperplasia and swollen gill filament (*). (E) Magnification of (D) to show eosinophilic granulocyte (arrows) and epithelial cell detachment (arrowheads). (F) To show inflammatory cell infiltration (dotted arrows). (G) Vascular dilation and aneurysmal lesions (circles). (H) Hyperemia (arrows) and swollen gill lamella (*). (I) To show cell necrosis, chromatin decrease, edge shift (*), and eosinophilic granulocyte (arrows). (J1–J6) Histopathological score of lamellae fusion, cell hyperplasia, cell hyperemia, inflammatory infiltration, necrosis and desquamation, and total histopathological scores, respectively.
By histopathological scoring, the pathological changes including lamellae fusion, cell hyperplasia, cell hyperaemia, inflammatory infiltration, necrosis and desquamation between the control group and I. multifiliis infected group showed significant difference (Figures 2J1–J6). However, the H&E staining results of intestine between the control group and I. multifiliis infected group had no difference (Figure 3).
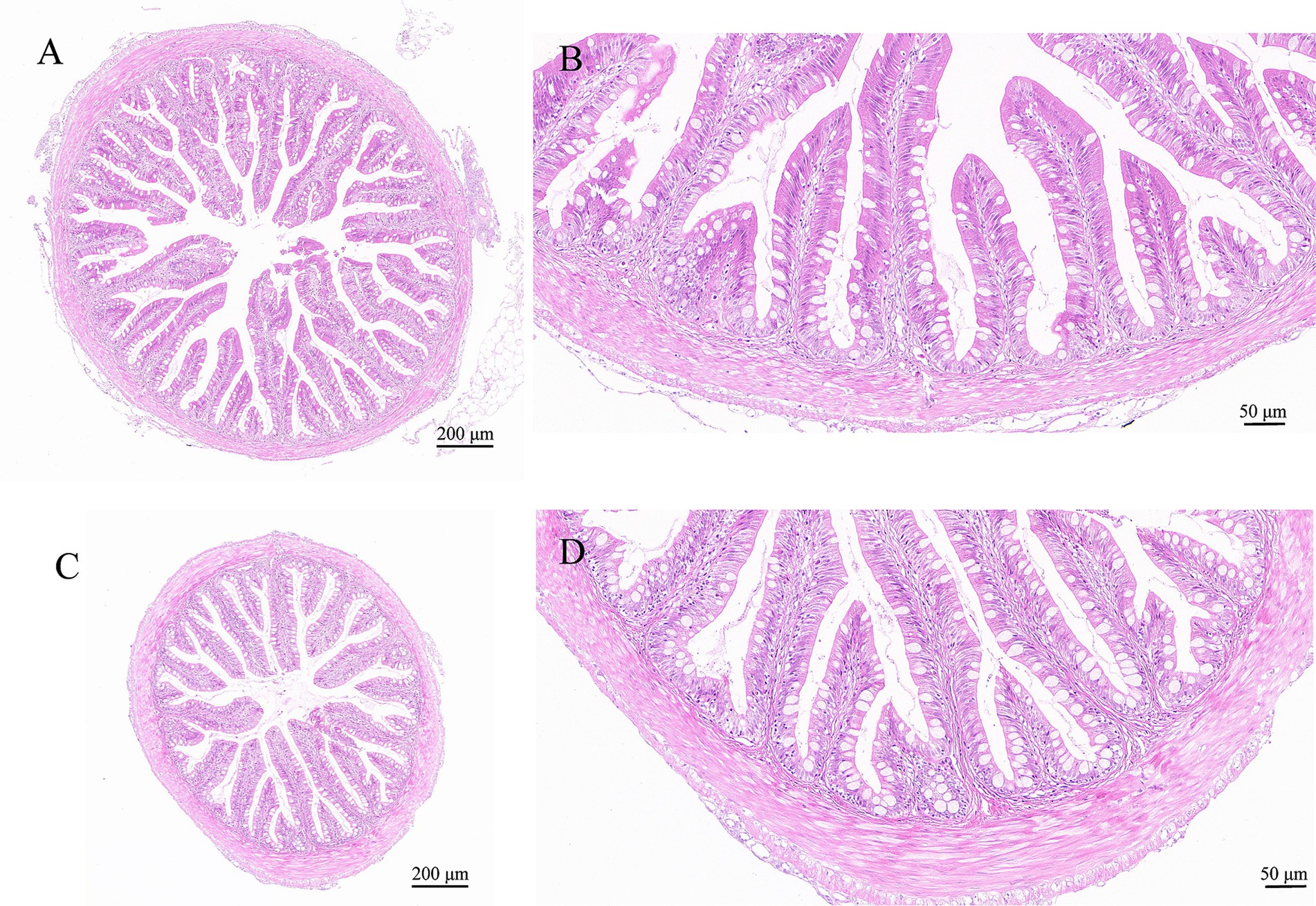
Figure 3. H&E staining results of goldfish intestines. (A,B) Intestine of the control group. (C,D) Intestine of the I. multifiliis infected group.
A total of 1,392,420 sequences were obtained after decontamination. Sequencing results showed that the average sequencing depth was 42,751. As seen in the Venn diagram (Figure 4), 3,636 ASVs were identified as either shared or unique among the four groups. The number of unique ASVs in the GH group (gills of the healthy/control group) was 983, while it was 305 in the GD group (gills of the diseased/infected group). The number of ASVs shared by GH group and GD group was 82. Additionally, the numbers of unique ASVs in the IH group (intestines of the healthy/control group) and in the ID group (intestines of the diseased/infected group) were 451 and 895, respectively. The number of ASVs shared by the two groups was 140. Moreover, there was 66 ASVs shared by the four groups. Overall, the numbers of ASVs in the GH, GD, IH, and ID groups were 1,398, 556, 853, and 1,318, respectively.
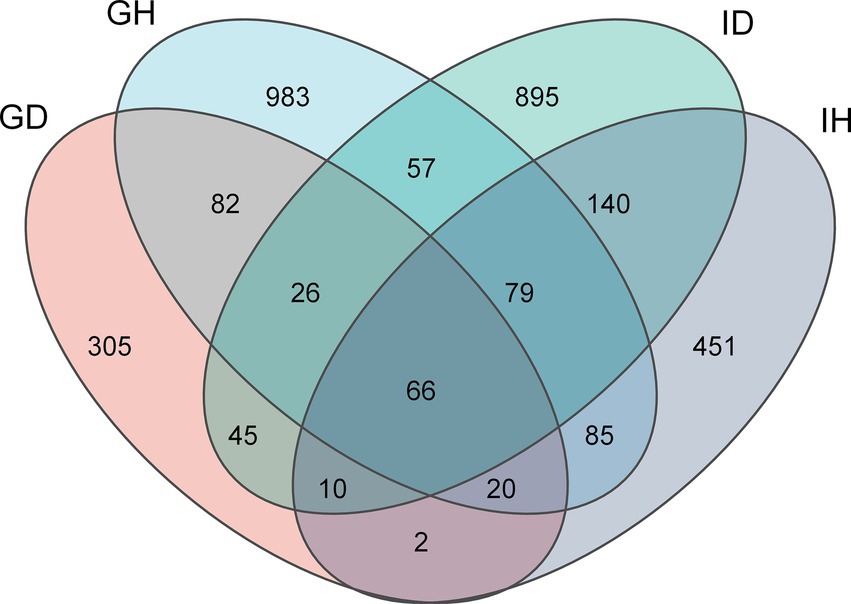
Figure 4. Venn diagram of gill and intestinal microbiota ASVs distribution in I. multifiliis-infected group and control group. GH: gills of the healthy/control group, GD: gills of the diseased/infected group; IH: intestines of the healthy/control group, ID: intestines of the diseased/infected group.
As for the alpha diversity, richness, phylogenetic diversity, shannon index, and pielou evenness indices were calculated and compared (Figure 5). The results showed that the alpha diversity in the GD group was significantly lower than that in the GH group (p < 0.05), whereas no significant differences were found between the IH and ID groups. Meanwhile, the richness, shannon, and pielou evenness indices in the GD group were significantly lower than that in the ID group. The four indices had no significant differences between the GH and IH groups.
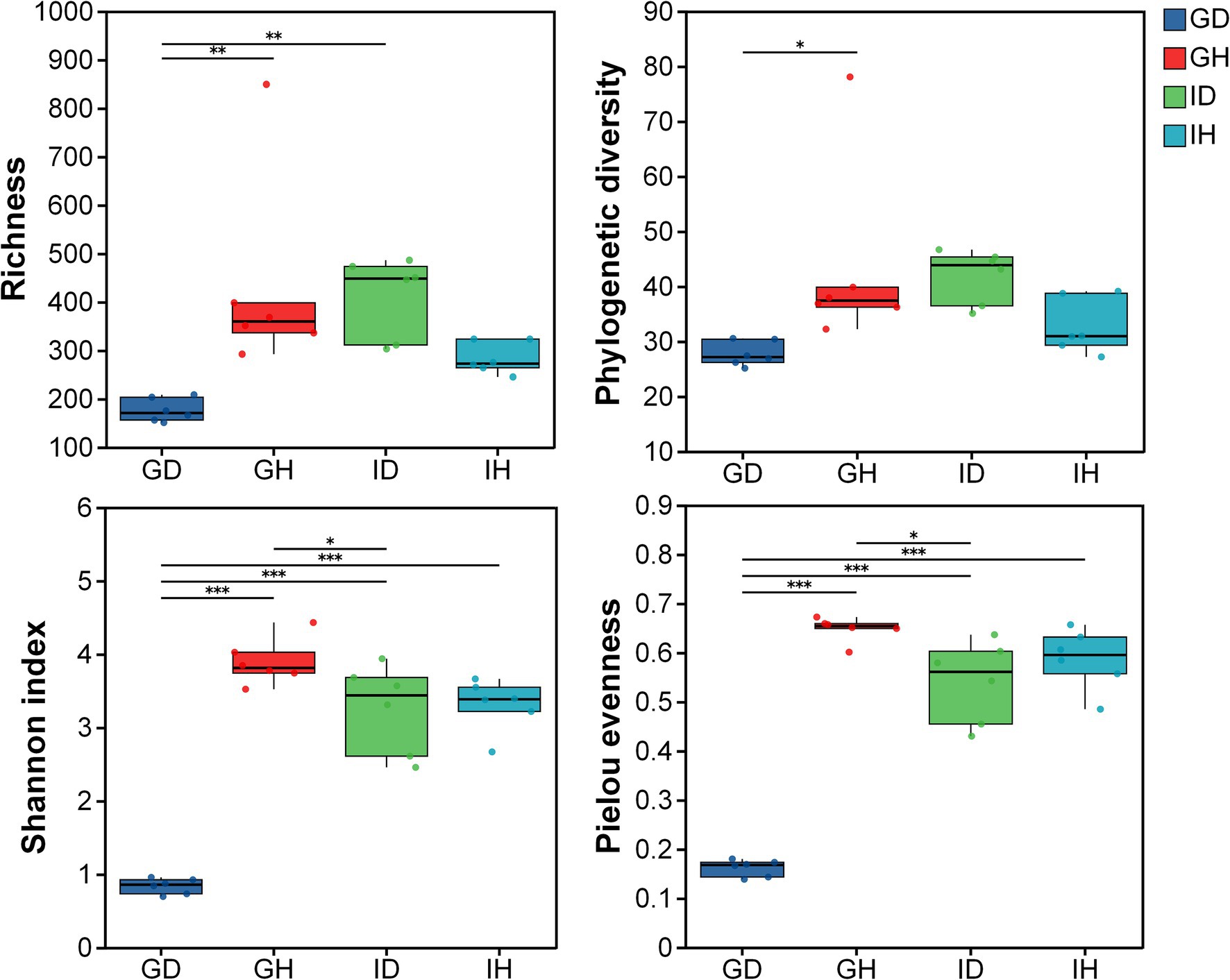
Figure 5. The alpha diversity of gill and intestinal microbiota in I. multifiliis-infected group and control group. * representing p < 0.05, ** representing p < 0.01, *** representing p < 0.001; GH: gills of the healthy/control group, GD: gills of the diseased/infected group; IH: intestine of the healthy/control group, ID: intestine of the diseased/infected group.
The Principal Co-ordinates Analysis (PCoA) results revealed that samples from different groups were distributed in different regions (Figure 6A) (PC1 = 49.61%, PC2 = 22.42%). It indicated that the bacterial community composition of the four groups were significantly different (p = 0.001). As shown in the Figure 6B, beta diversity in the GD group was significantly lower than that in the other three groups including GH, ID and IH groups.
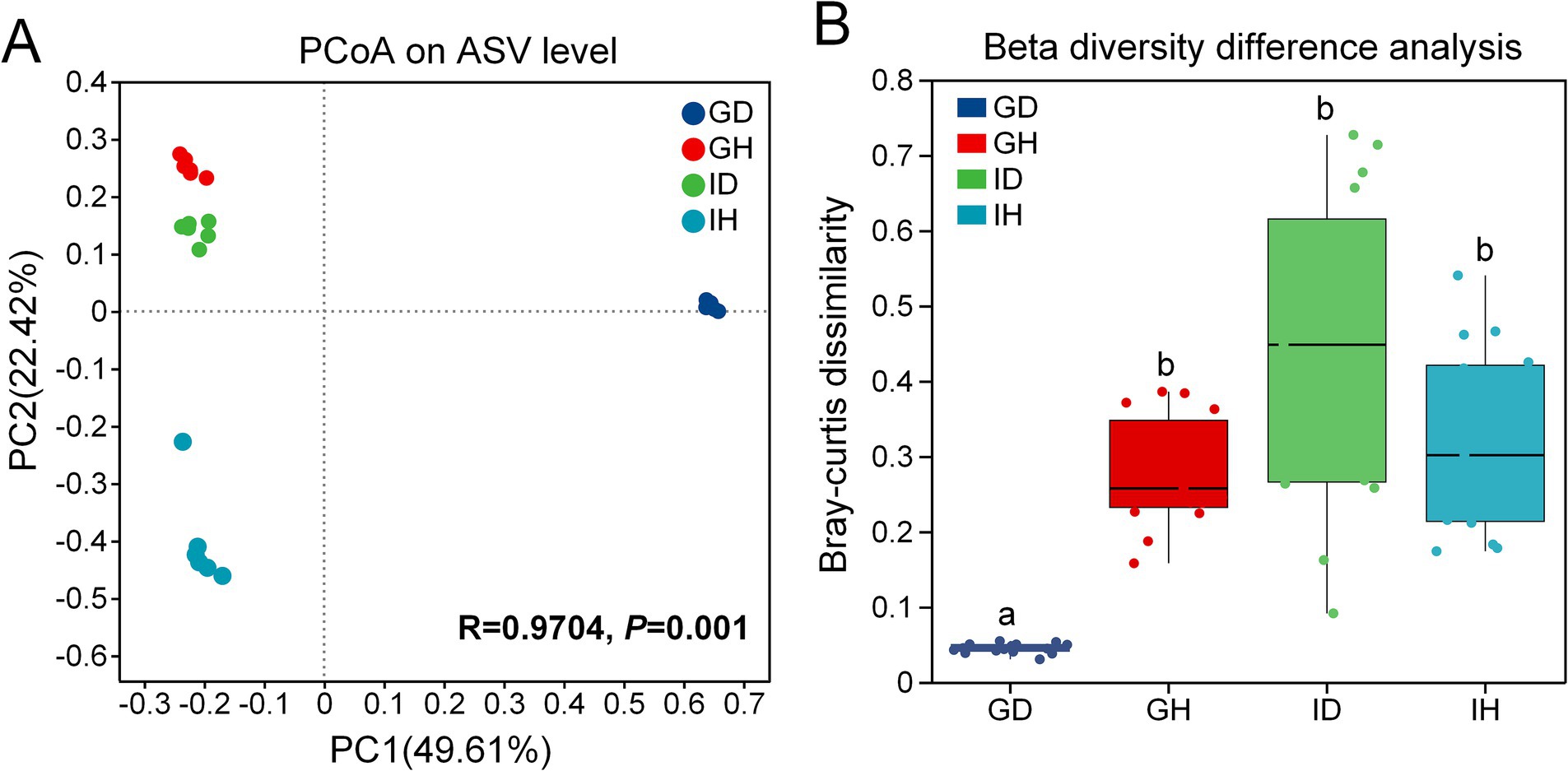
Figure 6. (A) the Principal Co-ordinates Analysis (PCoA) on ASV level. (B) Beta diversity difference analysis The beta diversity of gill and intestinal microbiota in I. multifiliis-infected group and control group. GH: gills of the healthy/control group, GD: gills of the diseased/infected group; IH: intestines of the healthy/control group, ID: intestines of the diseased/infected group.
At the class level, Alphaproteobacteria (over 90%) was the most abundant bacteria in the GD group (gills of the diseased/infected group), while Gammaproteobacteria (41.40%), Fusobacteriia (21.17%), and Alphaproteobacteria (11.18%) were the relatively abundant taxa in the GH group (gills of the healthy/control group) (Figure 7A; Table 2). In the ID group (intestines of the diseased/infected group), Fusobacteriia, Gammaproteobacteria, Alphaproteobacteria, and Bacilli were the top four relatively abundant taxa, which accounted for 39.88%, 23.11%, 13.40%, and 12.96%, respectively. Alphaproteobacteria, Gammaproteobacteria, and Actinobacteria were the top three abundant taxa in the IH group (intestines of the healthy/control group), accounting for 46.49%, 30.84%, and 11.87%, respectively (Table 2).
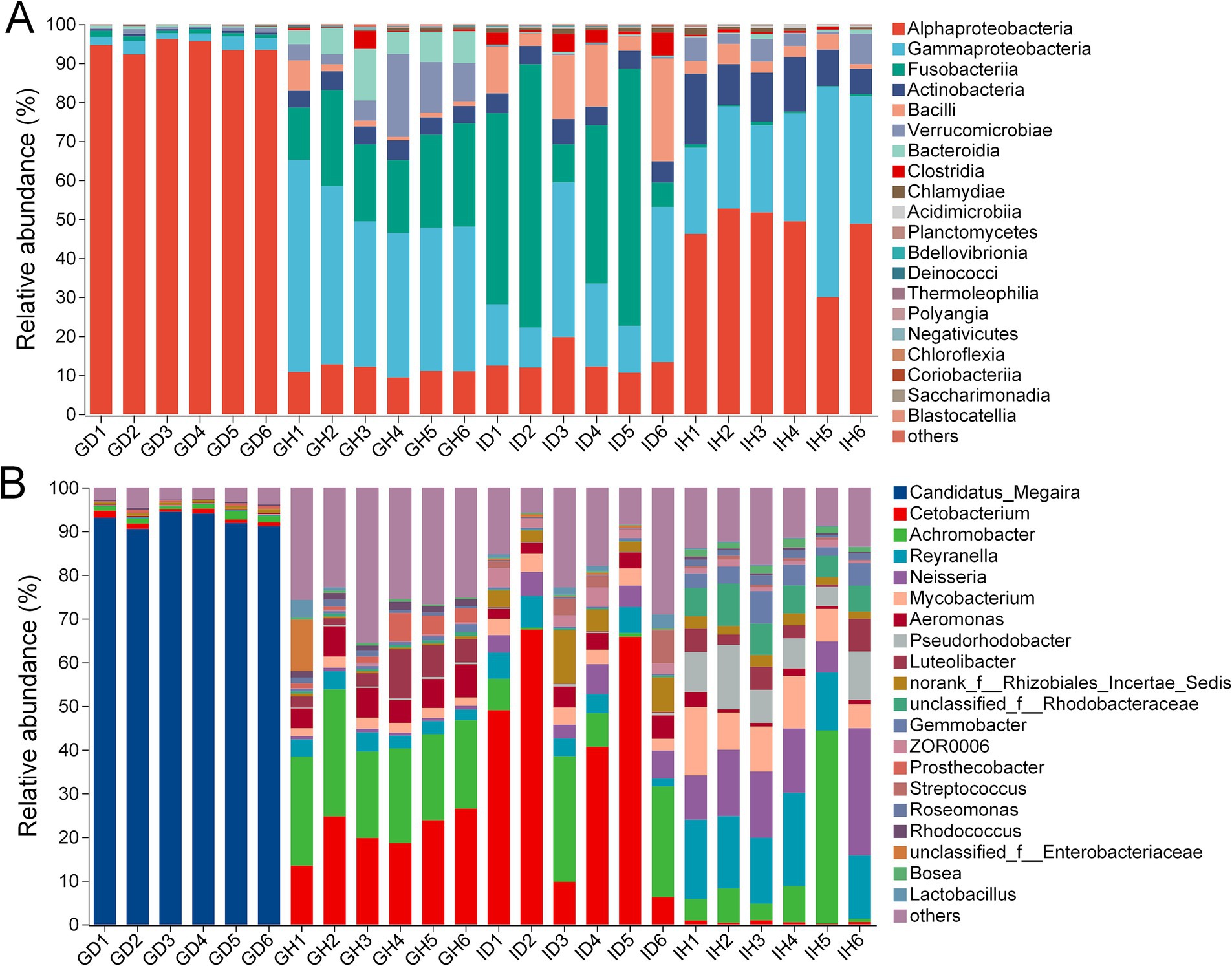
Figure 7. The relative abundance of gill and intestinal microbiota at class (A) and genus (B) levels of I. multifiliis-infected group and control group. GH: gills of the healthy/control group, GD: gills of the diseased/infected group; IH: intestine of the healthy/control group, ID: intestine of the diseased/infected group.
At the genus level, Candidatus Megaira was the most abundant bacteria in the GD group, while Cetobacterium and Achromobacter were the relatively abundant taxa in the GH group (Figure 7B). Cetobacterium and Achromobacter also were the relatively abundant taxa in the ID group. Reyranella, Neisseria, and Achromobacter accounted for 16.51%, 15.22%, and 11.64%, respectively, which were the three most relatively abundant taxa in the IH group.
Meanwhile, the distribution and difference of these top dominant species were shown in the Figure 8. It indicated that the difference of the four groups was significant. The content of ASV296_Rickettsiaceae in the GD group was significantly higher than that in the GH group. The relative amounts of ASV1_Achromobacter and ASV2_Cetobacterium in the GD group were lower than that in the GH group (Figure 8B). As for the intestinal microbiota, the relative abundance of ASV2_Cetobacterium and ASV4_ Aeromonas was significantly higher in the ID group than that in the IH group. Besides, the content of ASV33_Neisseria, ASV11_Mycobacterium, ASV13_Reyranella, ASV34_Pseudorhodobacter, ASV21_Reyranella, and ASV20_Rhodobacteraceae was significantly higher in the IH group, compared with the ID group (Figure 8C).
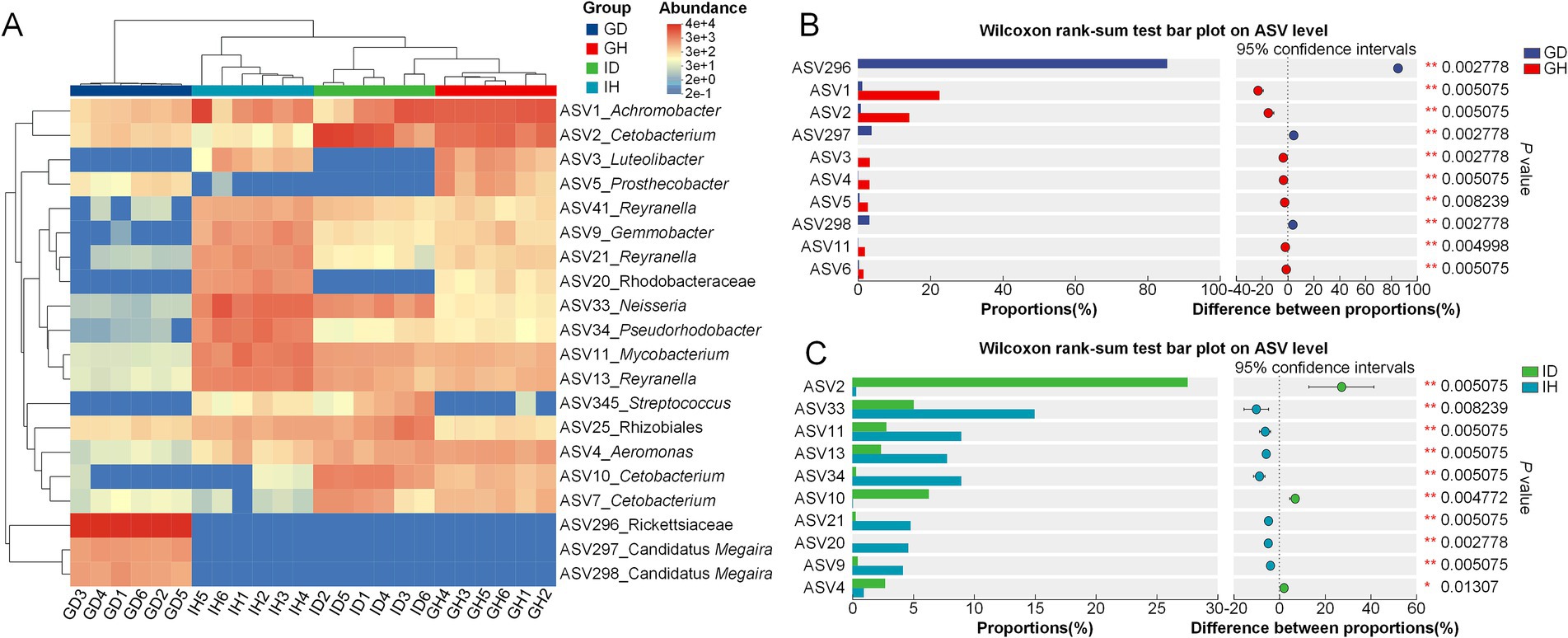
Figure 8. Community composition analysis of gill and intestinal microbiota in I. multifiliis-infected group and control group. (A) Heatmap showing the distribution of top dominant species in the four different groups. (B,C) Bar chart displaying the differences in average relative abundance of the same ASVs between groups.
Additionally, LEfSe was used to analyze the differences at multiple levels (Figure 9). It showed that microflora of the taxa including the phylum Proteobacteria, class Alphaproteobacteria, order Rickettsiales, family Rickettsiaceae, genus Candidatus Megaira, Clostridium sensu stricto 2, and Plesiomonas were significantly enriched in the GD group (Figure 9A). Compared with the IH group, the microorganisms in the class Bacilli, Clostridia, and Fusobacteria showed significant enrichment in the ID group, which also had a notable impact on the intergroup differences (Figure 9B).
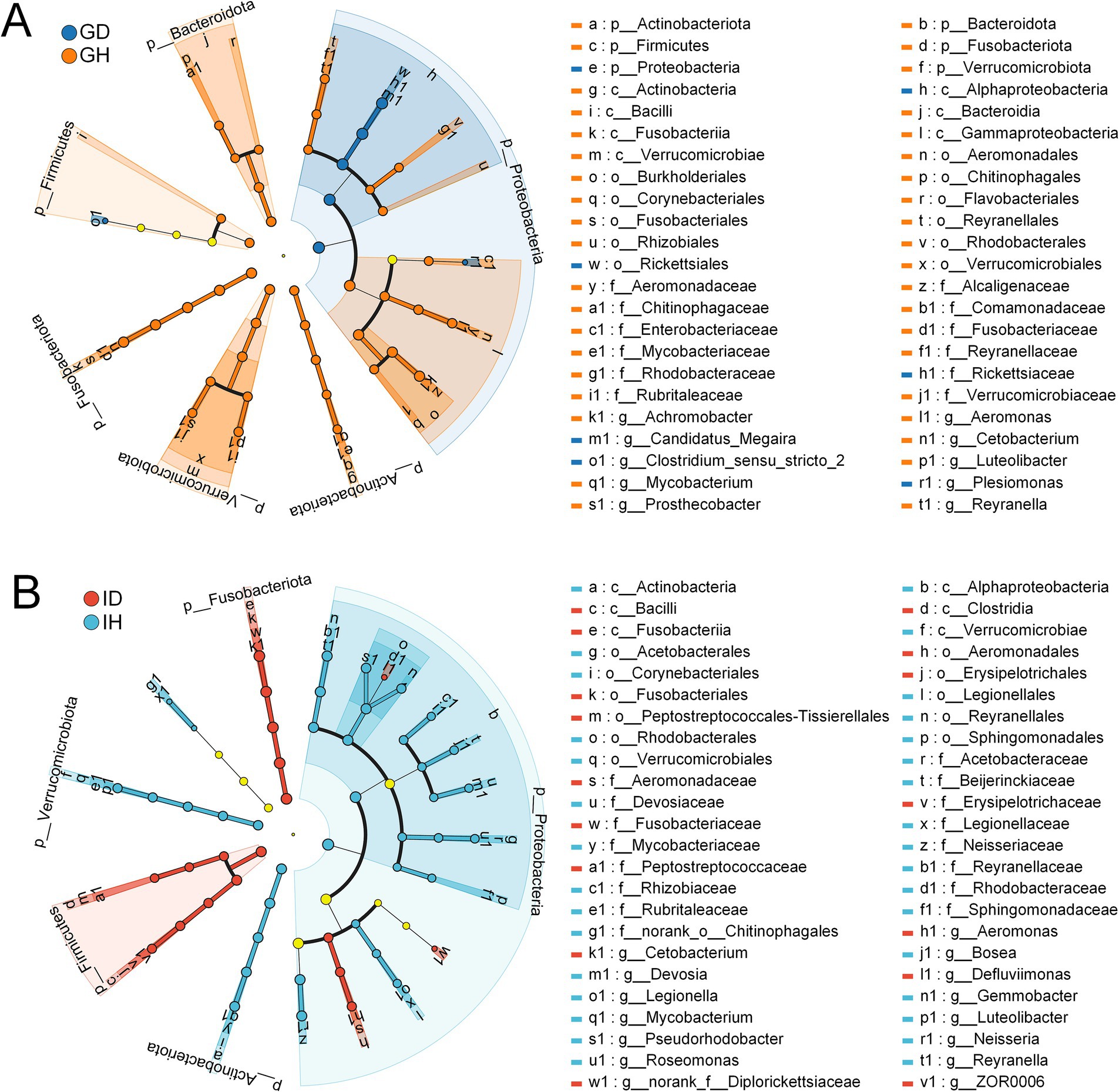
Figure 9. Linear discriminant analysis Effect Size (LEfSe) of gill and intestinal microbiota in I. multifiliis-infected group and control group. (A) Showing the difference between GD and GH group. (B) Showing the difference between ID and IH group. The light yellow nodes indicating no significant differences among different groups.
Based on the microbial community data, functional prediction was conducted to preliminarily explore the functions of microbial communities in the different groups (Figure 10). The KEGG result showed that there was a notable difference in the number of microorganisms related to main metabolism pathways including valine, leucine and isoleucine degradation, glycine, serine and threonine metabolism, citrate cycle (TCA cycle), fatty acid metabolism, pyruvate metabolism, oxidative phosphorylation, and carbon metabolism between the GD and GH groups (Figure 10A). These pathways have also been annotated in the ID and IH groups, however, the difference in these pathways between the ID and IH groups was not obvious (Figure 10B). Besides, both the ID and IH groups showed the function of methane metabolism.
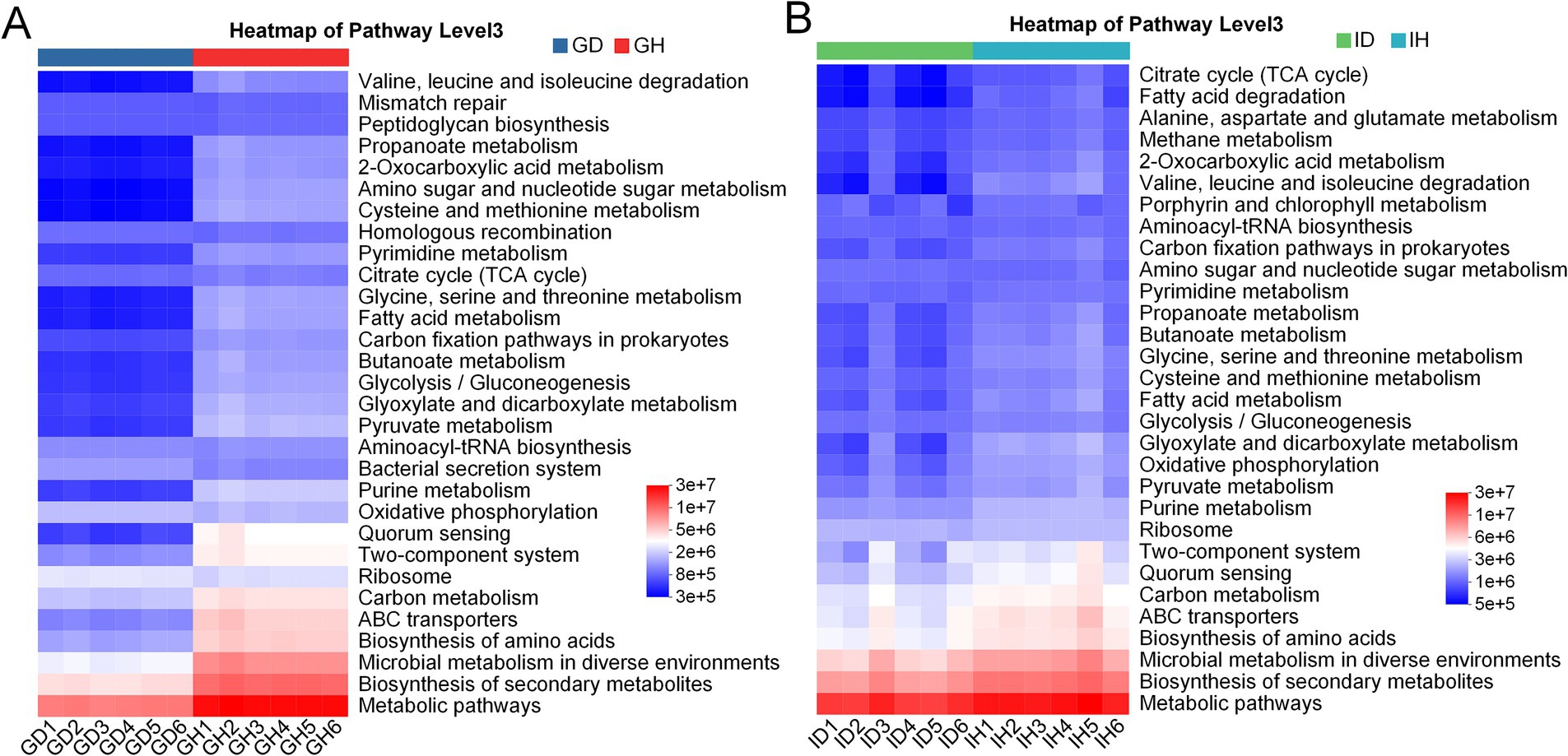
Figure 10. KEGG annotation of gill (A) and intestinal (B) microbiota in I. multifiliis-infected group and control group.
Ichthyophthirius multifiliis can infect a variety of common freshwater fish, and the “white spot disease” it causes, is considered as a fatal disease. In the present study, an artificial infection model using goldfish as the host of I. multifiliis was constructed, and the effects of I. multifiliis on host behavior, body color and histopathology, as well as the gill and gut microbiota, were further explored.
The histology characteristics of goldfish infected with and without I. multifiliis were analyzed. Compared with the uninfected goldfish, the gills of infected goldfish showed significantly lamellae fusion, cell hyperplasia, cell hyperaemia, inflammatory infiltration, necrosis and desquamation, which may directly induce the abnormal behavior of the I. multifiliis infected goldfish. Previous studies have reported the effects of histopathology of I. multifiliis on the wild snakehead murrel (Channa striata) (21), grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) (22), largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) (23), channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) (24), rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) (25), Schizothorax macropogon (26), white skirt tetra (Gymnocorymbus ternetzi) (27), as well as goldfish (C. auratus) (7). The damage to the primary lamellae and secondary lamellae caused by I. multifiliis is remarkably consistent across different species. Additionally, previous study also has indicated that goldfish infected by I. multifiliis exhibit an increase in the number of mucous cells in the gill tissue (7). Generally, fish gills play important roles in gaseous exchange, excretion, and circulation. The severe damage to the gills can directly lead to hypoxia in the host, eventually resulting in the death of the host.
In this study, Ichthyophthirius multifiliis infection led to an increase in eosinophilic granulocytes in the gills of goldfish. Eosinophilic granulocytes take important roles in host defense against parasitic protozoa and helminth (28, 29). Previous study on goldfish infected by another ectoparasite Chilodonella hexasticha showed that C. hexasticha infection also can increase the number of eosinophilic granulocytes, which may participate in resisting parasitic infections (30). Monogenean Dactylogyrus lamellatus not only affected the directly infected tissue gills, but also caused pathological changes in visceral tissues like liver, spleen, kidney, and intestines. It induced infiltration of a large number of immune cells into the mucosa and submucosa, leaded to a decrease in mucus-producing cells, and caused fracturing between the mucosa and the lamina propria (11). However, in this study, no pathological changes of the goldfish intestine were observed. The impact caused by I. multifiliis on intestine may manifest in other aspects.
Fish gills directly interact with aquatic environments, which contain a highly diverse group of microorganisms. When ectoparasites infect gills, the balance between fish and microbiota could be disrupted (31). The parasites and bacteria may have some interactions. In the previous studies, the relationship between I. multifiliis and Edwardsiella ictaluri was explored. It showed that E. ictaluri can survive and replicate inside the tomonts, resulting in high bacterial burdens in different organs and high mortality rates of channel catfish (32, 33). In this study, compared with the healthy/control group, the alpha and beta diversity of gill microbiota in I. multifiliis infected group was significantly lower. However, there was no significant difference observed in the alpha and beta diversity of the intestinal microbiota between the control group and I. multifiliis infected group. It could be due to the differences in parasitic sites. Previous studies found that internal parasites of fish or mammals that parasitize the gut can induce a decrease in gut microbiota diversity (12, 34–36). Ichthyophthirius multifiliis directly parasitize fish gills, thus having the opportunity to affect the diversity of gill microbiota. Meanwhile, from the venn diagram analyses, the ASVs results showed a decrease in gills of I. multifiliis infected goldfish (GH group), providing support for the significant decrease of alpha and beta diversity. These results suggest that I. multifiliis can directly affect the microbial diversity of the parasitic site gills.
As for the microbiota composition, in the gills of the healthy goldfish, the predominant bacteria at class level were Gammaproteobacteria, Fusobacteriia, and Alphaproteobacteria, respectively, which was consistent with previous reports (37, 38). However, in the gills of I. multifiliis infected goldfish, Alphaproteobacteria accounted for more than 90%, which showed an imbalance of the bacterial community. Candidatus Megaira was the most abundant genus within the class Alphaproteobacteria in the gills of I. multifiliis infected goldfish. Cetobacterium and Achromobacter were the predominant genera in the control goldfish, consistent with the previous study (39). Microbes from C. Megaira (Rickettsiales) are well-known as the endosymbionts of ciliates and other eukaryote, and the causative agents for some human diseases like typhus and Rocky Mountain spotted fever (40–42). It has been proved that C. Megaira is extensively distributed within I. multifiliis, being dispersed throughout the cytoplasm of trophonts and also present in majority theronts (43, 44). From these results above, it can be inferred that the significant increase of C. Megaira in goldfish gills may originate from I. multifiliis trophonts. Further research is needed to study the deep relationship between C. Megaira and I. multifiliis, providing new insights for the prevention and treatment of Ichthyophthiriasis.
Although no significant difference in intestinal microbiota diversity was detected between the I. multifiliis infected and control goldfish, it’s noteworthy that I. multifiliis infection corresponded to an increase in the abundance of several bacteria like Cetobacterium and Aeromonas. Meanwhile, we found that Cetobacterium and Achromobacter were the relatively abundant genera in the intestinal of I. multifiliis infected goldfish. Previous studies showed that Cetobacterium is the predominant genus within the gastrointestinal microbiota of goldfish and other freshwater fish, exhibiting a significant role in cellulose degradation, metabolic homeostasis, and is beneficial for the host (45–47). Aeromonas species primarily pose a threat to poikilothermic creatures, with mesophilic strains increasingly recognized as significant pathogens in humans, causing extraintestinal and systemic infections (48). Among the Aeromonas species, Aeromonas hydrophila, identified as an opportunistic pathogen, could induce intestinal inflammation in a variety of farmed fish including grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) and rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) (49, 50). Achromobacter is a type of opportunistic pathogen and potentially impacted fish health status (51, 52). Thus, it can be inferred that the increased relative abundance of Aeromonas and Achromobacter may threaten the health of host goldfish. In other words, I. multifiliis infection may increase the risk of dysbiosis of intestinal flora and enteritis.
In summary, we found that I. multifiliis infection could induce changes in the gill histopathological characteristics, gill and gut microbiota. The abnormal behavior of host may be attributed to the alteration of gill histopathology. Meanwhile the increase of genus Candidatus Megaira in gill microbiota was associated with the severe infection of I. multifiliis. The increased relative abundance of Aeromonas and Achromobacter in the intestine of I. multifiliis infected goldfish may be a threaten to goldfish health status. This study lay a foundation for further research on the interaction between I. multifiliis and host microbiota, which will promote the prevention and control of Ichthyophthiriasis.
The sequencing data of this study has been uploaded to NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) under the BioProject ID: PRJNA1193790.
The animal study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Zhejiang Institute of Freshwater Fisheries. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
XB: Writing – original draft. XP: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. LH: Data curation, Software, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JJ: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. JC: Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. XH: Funding acquisition, Validation, Writing – review & editing. AZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. HQ: Writing – review & editing. JY: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from Hubei Provincial Key Laboratory of Fish Resources Protection in the Three Gorges Project (2021045-ZHX), Huzhou Municipal Public Welfare Agricultural Applied Research Project (2022GZ31), and Zhejiang Technology Collaboration Project of “Jian Bing Ling Yan” (2024C02005).
XB, XP, LH, YZ, JJ, JZ, JC, XH, AZ, HQ, and JY were employed by China Three Gorges Corporation.
The authors declare that this study received funding from China Three Gorges Corporation. The funder had the following involvement in the study: preparation of the manuscript.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Buchmann, K, Sigh, J, Nielsen, C, and Dalgaard, M. Host responses against the fish parasitizing ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Vet Parasitol. (2001) 100:105–16. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4017(01)00487-3
2. Matthews, R. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Fouquet and ichthyophthiriosis in freshwater teleosts. Adv Parasitol. (2005) 59:159–241. doi: 10.1016/S0065-308X(05)59003-1
3. Dickerson, H, and Findly, R. Immunity to Ichthyophthirius infections in fish: a synopsis. Dev Comp Immunol. (2014) 43:290–9. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2013.06.004
4. LvG, J. The fish parasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis – host immunology, vaccines and novel treatments. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2017) 67:586–95. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2017.06.044
5. Huang, K, Hu, GR, Wang, RQ, Zeng, QW, Li, WX, Zou, H, et al. In vitro assessment of Berberine against Ichthyophthirius multifiliis in goldfish. Pathogens. (2022) 11:1207. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11101207
6. Zhang, QZ, Xu, DH, and Klesius, PH. Evaluation of an antiparasitic compound extracted from Galla chinensis against fish parasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Vet Parasitol. (2013) 198:45–53. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2013.08.019
7. Huang, X, Liu, S, Zuo, F, Luo, L, Chen, D, Ou, Y, et al. cMOS enhanced the mucosal immune function of skin and gill of goldfish (Carassius auratus Linnaeus) to improve the resistance to Ichthyophthirius multifiliis infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2022) 126:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2022.05.024
8. Yukgehnaish, K, Kumar, P, Sivachandran, P, Marimuthu, K, Arshad, A, Paray, BA, et al. Gut microbiota metagenomics in aquaculture: factors influencing gut microbiome and its physiological role in fish. Rev Aquac. (2020) 12:1903–27. doi: 10.1111/raq.12416
9. Nicholson, JK, Holmes, E, Kinross, J, Burcelin, R, Gibson, G, Jia, W, et al. Host-gut microbiota metabolic interactions. Science. (2012) 336:1262–7. doi: 10.1126/science.1223813
10. Nie, L, Zhou, Q-J, Qiao, Y, and Chen, J. Interplay between the gut microbiota and immune responses of ayu (Plecoglossus altivelis) during Vibrio anguillarum infection. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2017) 68:479–87. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2017.07.054
11. Wang, L, Zhang, DF, Xie, J, Chang, OQ, Wang, Q, Shi, CB, et al. Do ectoparasites on fish gills “talk” with gut microbiota far away? Aquaculture. (2023) 562:738880. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2022.738880
12. Gaulke, CA, Martins, ML, Watral, VG, Humphreys, IR, Spagnoli, ST, Kent, ML, et al. A longitudinal assessment of host-microbe-parasite interactions resolves the zebrafish gut microbiome’s link to Pseudocapillaria tomentosa infection and pathology. Microbiome. (2019) 7:1–16. doi: 10.1186/s40168-019-0622-9
13. Zhang, XT, Ding, LG, Yu, YY, Kong, WG, Yin, YX, Huang, ZY, et al. The change of teleost skin commensal microbiota is associated with skin mucosal transcriptomic responses during parasitic infection by Ichthyophthirius multifillis. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:2972. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02972
14. Mohammad, T, Moulick, S, and Mukherjee, CK. Economic feasibility of goldfish (Carassius auratus Linn.) recirculating aquaculture system. Aquac Res. (2018) 49:2945–53. doi: 10.1111/are.13750
15. Baums, C, Hermeyer, K, Leimbach, S, Adamek, M, Czerny, C-P, Hoerstgen-Schwark, G, et al. Establishment of a model of Streptococcus iniae meningoencephalitis in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). J Comp Pathol. (2013) 149:94–102. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2012.10.003
16. Bolyen, E, Rideout, JR, Dillon, MR, Bokulich, NA, Abnet, CC, Al-Ghalith, GA, et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol. (2019) 37:852–7. doi: 10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9
17. Quast, C, Pruesse, E, Yilmaz, P, Gerken, J, Schweer, T, Yarza, P, et al. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. (2013) 41:D590–6. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1219
18. Schloss, PD, Westcott, SL, Ryabin, T, Hall, JR, Hartmann, M, Hollister, EB, et al. Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol. (2009) 75:7537–41. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01541-09
19. Douglas, GM, Maffei, VJ, Zaneveld, JR, Yurgel, SN, Brown, JR, Taylor, CM, et al. PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat Biotechnol. (2020) 38:685–8. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0548-6
20. R Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna (2019) 14: 12–21.
21. Yunus, M, and Wijaya, A, editors. Histopathological changes in gills of wild snakehead murrel, Channa striata (Bloch, 1793) infected with Ichthyophthirius multifiliis Fouquet, 1876 from Surabaya river. 9th international seminar on tropical animal production (ISTAP 2021); (2022). Paris: Atlantis Press.
22. Yu, H, Wang, Z-B, Lu, Y-J, Tan, S-W, Yan, Q-G, and Li, H. Histopathological study of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) experimentally infected with Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Afr J Microbiol Res. (2012) 6:3539–44. doi: 10.5897/AJMR12.369
23. Qu, SY, Tan, XP, Li, BK, Liu, JT, Wang, GX, and Ling, F. Malformed largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) are more susceptible and vulnerable to Ichthyophthirius multifiliis infections: immunological and histopathological study. Aquaculture. (2022) 548:737664. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737664
24. Maki, JL, Brown, CC, and Dickerson, HW. Occurrence of Ichthyophthirius multifiliis within the peritoneal cavities of infected channel catfish Ictalurus punctatus. Dis Aquat Org. (2001) 44:41–5. doi: 10.3354/dao044041
25. Heidarieh, M, Nowrozani, FR, Banaee, M, Gholamhosseini, A, Heidarieh, H, Shahbazfar, AA, et al. Histopathological changes in the skin and gut mucus layers of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) challenged with Ichthyophthirius multifiliis inactivated by gamma rays and formalin. Int J Aquat Biol. (2023) 11:431–8. doi: 10.22034/ijab.v11i5.1916
26. Li, WJ, Lyu, XM, Nie, P, and Liu, Y. Morphological, histopathological and molecular characterization of parasitic ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis infecting an indigenous and endangered fish, Schizothorax macropogon (Cyprinidae: Schizothoracinae) in high plateau, Tibet, China. Aquac Rep. (2022) 25:101192. doi: 10.1016/j.aqrep.2022.101192
27. Peyghan, R, Rezaie, A, Hassani, F, and Abyavi, T. Histopathological study of gill and fish treatment in Ichthyophthiriasis of white skirt tetra (Gymnocorymbus ternetzi). Iran Vet J. (2021) 17:106–10. doi: 10.22055/IVJ.2020.237783.2279
28. Klion, AD, and Nutman, TB. The role of eosinophils in host defense against helminth parasites. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2004) 113:30–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2003.10.050
29. Lechner, CJ, Komander, K, Hegewald, J, Huang, X, Gantin, RG, Soboslay, PT, et al. Cytokine and chemokine responses to helminth and protozoan parasites and to fungus and mite allergens in neonates, children, adults, and the elderly. Immun Ageing. (2013) 10:1–10. doi: 10.1186/1742-4933-10-29
30. Bu, XL, Zhao, WS, Zou, H, Li, WX, Li, M, and Wang, GT. Immune response and apoptosis of gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio) gills to Chilodonella hexasticha infection: insights from histopathological and multi-omics analyses. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2024) 147:109429. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109429
31. Kotob, MH, Menanteau-Ledouble, S, Kumar, G, Abdelzaher, M, and El-Matbouli, M. The impact of co-infections on fish: a review. Vet Res. (2017) 47:1–12. doi: 10.1186/s13567-016-0383-4
32. Xu, DH, Shoemaker, CA, Martins, ML, Pridgeon, JW, and Klesius, PH. Enhanced susceptibility of channel catfish to the bacterium Edwardsiella ictaluri after parasitism by Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Vet Microbiol. (2012) 158:216–9. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.02.007
33. Xu, DH, Shoemaker, CA, and Klesius, PH. Ichthyophthirius multifiliis as a potential vector of Edwardsiella ictaluri in channel catfish. FEMS Microbiol Lett. (2012) 329:160–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2012.02518.x
34. Holm, JB, Sorobetea, D, Kiilerich, P, Ramayo-Caldas, Y, Estellé, J, Ma, T, et al. Chronic Trichuris muris infection decreases diversity of the intestinal microbiota and concomitantly increases the abundance of lactobacilli. PLoS ONE. (2015) 10:e0125495. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125495
35. Ling, F, Steinel, N, Weber, J, Ma, L, Smith, C, Correa, D, et al. The gut microbiota response to helminth infection depends on host sex and genotype. ISME J. (2020) 14:1141–53. doi: 10.1038/s41396-020-0589-3
36. Cortes, A, Peachey, L, Scotti, R, Jenkins, TP, and Cantacessi, C. Helminth-microbiota cross-talk–a journey through the vertebrate digestive system. Mol Biochem Parasitol. (2019) 233:111222. doi: 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2019.111222
37. Ortiz, WE, Carlos-Shanley, C, and Huertas, M. Impact of sublethal concentrations of nitrite on goldfish (Carassius auratus) microbiomes. Microb Ecol. (2023) 86:1331–42. doi: 10.1007/s00248-022-02123-4
38. Ortiz, W, Carlos-Shanley, C, and Huertas, M. The impacts of sublethal nitrite exposure on goldfish (Carassius auratus) microbiomes. FASEB J. (2020) 34:1. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2020.34.s1.03702
39. Kuang, T, He, A, Lin, Y, Huang, X, Liu, L, and Zhou, L. Comparative analysis of microbial communities associated with the gill, gut, and habitat of two filter-feeding fish. Aquac Rep. (2020) 18:100501. doi: 10.1016/j.aqrep.2020.100501
40. Davison, H, Hurst, G, and Siozios, S. ‘Candidatus Megaira’ are diverse symbionts of algae and ciliates with the potential for defensive symbiosis. Microb Genom. (2023) 9:mgen000950. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000950
41. Walker, DH, and Ismail, N. Emerging and re-emerging rickettsioses: endothelial cell infection and early disease events. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2008) 6:375–86. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1866
42. Vannini, C, Petroni, G, Verni, F, and Rosati, G. A bacterium belonging to the Rickettsiaceae family inhabits the cytoplasm of the marine ciliate Diophrys appendiculata (Ciliophora, Hypotrichia). Microb Ecol. (2005) 49:434–42. doi: 10.1007/s00248-004-0055-1
43. Zaila, KE, Doak, TG, Ellerbrock, H, Tung, C-H, Martins, ML, Kolbin, D, et al. Diversity and universality of endosymbiotic Rickettsia in the fish parasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Front Microbiol. (2017) 8:189. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00189
44. Sun, HY, Noe, J, Barber, J, Coyne, RS, Cassidy-Hanley, D, Clark, TG, et al. Endosymbiotic bacteria in the parasitic ciliate Ichthyophthirius multifiliis. Appl Environ Microbiol. (2009) 75:7445–52. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00850-09
45. Liu, H, Guo, X, Gooneratne, R, Lai, R, Zeng, C, Zhan, F, et al. The gut microbiome and degradation enzyme activity of wild freshwater fishes influenced by their trophic levels. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:24340. doi: 10.1038/srep24340
46. Borsodi, AK, Szabó, A, Krett, G, Felföldi, T, Specziár, A, and Boros, G. Gut content microbiota of introduced bigheaded carps (Hypophthalmichthys spp.) inhabiting the largest shallow lake in Central Europe. Microbiol Res. (2017) 195:40–50. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2016.11.001
47. Wang, J, Kong, W, Sun, Q, Zheng, X, Wang, S, and Yan, Z. Toxic effects of naproxen on the intestine of the goldfish, Carassius auratus. Mol Cell Toxicol. (2023) 19:667–79. doi: 10.1007/s13273-022-00295-1
48. Tomás, JM. The main Aeromonas pathogenic factors. ISRN Microbiol. (2012) 2012:256261. doi: 10.5402/2012/256261
49. Song, X, Zhao, J, Bo, Y, Liu, Z, Wu, K, and Gong, C. Aeromonas hydrophila induces intestinal inflammation in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): an experimental model. Aquaculture. (2014) 434:171–8. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2014.08.015
50. Nya, EJ, and Austin, B. Use of garlic, Allium sativum, to control Aeromonas hydrophila infection in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Fish Dis. (2009) 32:963–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2761.2009.01100.x
51. Swenson, CE, and Sadikot, RT. Achromobacter respiratory infections. Ann Am Thorac Soc. (2015) 12:252–8. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201406-288FR
Keywords: Ichthyophthirius multifiliis, microbiota, histopathology, opportunistic pathogens, ectoparasite
Citation: Bu X, Peng X, Huang L, Zhao Y, Jiao J, Zhu J, Chen J, Huang X, Zheng A, Qu H and Yao J (2025) Effect of ectoparasite Ichthyophthirius multifiliis on the histopathology and gill and gut microbiota of goldfish (Carassius auratus). Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1539446. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1539446
Received: 04 December 2024; Accepted: 13 January 2025;
Published: 04 February 2025.
Edited by:
Calin Mircea Gherman, University of Agricultural Sciences and Veterinary Medicine of Cluj-Napoca, RomaniaReviewed by:
Bruno Araújo, Federal University of São Paulo, BrazilCopyright © 2025 Bu, Peng, Huang, Zhao, Jiao, Zhu, Chen, Huang, Zheng, Qu and Yao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiayun Yao, eWFvamlheXVuQDEyNi5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.