
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Vet. Sci. , 26 March 2025
Sec. Animal Nutrition and Metabolism
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2025.1538623
 Can Yang1†
Can Yang1† XiaoWu Tang2*
XiaoWu Tang2* RunTao Wu1
RunTao Wu1 YunMiao Jiang1
YunMiao Jiang1 Qi Quan1
Qi Quan1 YuTian Xiao1
YuTian Xiao1 JiaXuan Kuang1
JiaXuan Kuang1 JiaYi Chen3
JiaYi Chen3 QingHai Tang1
QingHai Tang1 Zhi Jiang4
Zhi Jiang4This study investigated the effect of a traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) plant powder made from an equal proportion of Sarcococca ruscifolia Stapf, Hedera nepalensis var. sinensis (Tobl.) Rehd, and Clematis chinensis Osbeck on growth performance and intestinal health in Xianghuang chickens, focusing on intestinal histomorphology, antioxidant activity, and anti-inflammation function. A total of 100 10-day-old male Xianghuang chickens were randomly assigned to two groups, with five replicate cages per group containing 10 birds each. The birds in the control group received a corn-soybean–based diet, while the birds in the TCM group received the control diet supplemented with 2% of the TCM powder. The chickens were slaughtered for sample collection on D28. The results showed that the average daily feed intake (ADFI), average daily gain (ADG), and feed-to-gain (F:G) ratio were not affected by the TCM supplementation (p > 0.05). In the jejunum and ileum, the ratio of the villus height to the crypt depth was higher in the TCM group compared to the control group (p < 0.05). Supplementing the chickens with 2% TCM powder increased the total superoxide dismutase (T-SOD) and catalase (CAT) activities in the jejunal mucosa compared to the control group (p < 0.05). The gene expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) was downregulated in the jejunal mucosa and spleen in the TCM group compared to the control group (p < 0.05). In conclusion, TCM powder can be safely utilized to promote the development of the intestinal tract by enhancing antioxidant and anti-inflammatory functions without affecting the growth performance. Our findings suggest that TCM powder is an effective and low-toxicity natural additive for intestinal improvement in poultry.
Increasing consumer demand for antibiotic-free poultry products has driven the search for effective and safe additives in poultry production. Traditional Chinese medicinal plants are promising antibiotic substitutes and have been utilized in livestock for centuries. Sarcococca ruscifolia Stapf belongs to the Buxaceae family and is rich in pachysandra alkaloids, which have been shown to inhibit HepG2 cell migration and induce mitochondria-mediated intrinsic apoptosis (1). These pachysandra alkaloids contain cytotoxic pregnane derivatives that are effective against melanoma and lung cancer cells (2). Plants from Sarcococca Lindl. have anti-inflammatory (3) effects. The crude extract of Sarcococca saligna Muel showed dose-dependent antidiarrheal activities against castor oil-induced diarrhea in mice at doses of 500 and 1,000 mg/kg (4).
Hedera helix (ivy) belongs to the Araliaceae family, and its leaves contain saponins such as monodesmoside α-hederin and hederacoside (5), which have demonstrated antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects (6). Hedera species exhibited validated anti-inflammatory effects in ovalbumin-sensitized guinea pigs through the modulation of immune cell populations, such as a decrease in total white blood cell and eosinophil counts but an increase in neutrophils, lymphocytes, and monocytes (7).
Clematis chinensis Osbeck (C. chinensis) belongs to the Ranunculaceae family and has been extensively utilized for its root-derived preparations, which exhibit anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and analgesic properties (8). Novel phenolic glycosides and alkaloids have been isolated from the roots and rhizomes of C. chinensis; they displayed inhibitory effects on nitric oxide (NO) production and anti-inflammatory activity in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW 264.7 cells (9). Total saponins extracted from C. chinensis exhibited significant anti-inflammatory effects in both cellular and animal models. Oral administration of 100 mg/kg of saponin extract effectively attenuated inflammatory responses in LPS-challenged rabbits and primary human chondrocytes (10).
Previous studies have focused on in vitro or cellular experiments. To date, there have been few documented cases of the direct application of botanical additives in animal production practices. Our study revealed the presence of bioactive components, including polysaccharides, total flavonoids, polyphenols, and total protein, in an aqueous extract of a TCM plants mixture consisting of Sarcococca ruscifolia Stapf, Hedera nepalensis var. sinensis (Tobl.) Rehd, and C. chinensis. Notably, previous research has shown that flavonoid- and polysaccharide-enriched extracts from Astragalus spp. effectively mitigate E. coli infection in poultry (11). Extraction is a time-consuming process in itself, and the extractive organic solvents such as petroleum and ethanolic are also toxic. Historical documentation in the Compendium of Materia Medica (12) classifies plants such as Sarcococca ruscifolia Stapf, Hedera nepalensis var. sinensis (Tobl.) Rehd, and C. chinensis as non-toxic, despite their characteristic bitter taste. Safety assessments, corroborated by modern pharmacological evidence, show the therapeutic efficacy of Hedera helix (Ivy leaf) in managing respiratory symptoms (13). Xianghuang broilers have gained attention in poultry research due to their high-quality meat and adaptability. They are local, yellow-feathered, slow-growing breed found in southern China. Poultry, including Xianghuang broilers, generally have a low tolerance for bitter compounds and exhibit moderate tolerance to dietary fiber. It remains unclear whether chickens can tolerate the fiber and bitterness of these TCM plants without affecting their production performance. Based on these findings, we hypothesized that supplementation with these TCM plants may safely enhance gastrointestinal health in Xianghuang broilers through antioxidant-mediated epithelial barrier protection and immunomodulation of gut-associated lymphoid tissue responses, without affecting growth performance. This study may help identify highly effective and low-toxicity natural anti-inflammatory plant products from Chinese medicine.
Fresh plants were harvested from the mountainous area of ShaoYang, Hunan, China, based on advice from local older individuals. The plants, including the root, stem, and leaves, were sun-dried for five to seven days under strong sunlight on the ground. The plants were then cut into 5–10 cm-long segments using a chainsaw. The plant segments were sun-dried again, crushed using a traditional Chinese medicine grinder, and sieved through a 60-mesh (ø250 μm) screen. The powders of Sarcococca ruscifolia Stapf, Hedera nepalensis var. sinensis (Tobl.) Rehd, and Clematis chinensis Osbeck were mixed in a ratio of 1:1:1 to form the TCM mixture. The nutrient contents of the TCM plant powder, based on air-dried matter, were as follows: dry matter 90.98 ± 0.60%, total protein 13.81 ± 2.41%, crude fat 0.29 ± 0.05%, crude fiber 32.85 ± 0.50%, Ca 0.24 ± 0.04%, total phosphorus 0.14 ± 0.01%, and crude ash 3.95 ± 0.99%. Active ingredients, including polysaccharides (concentration 1.26 mg/mL, extraction rate 0.99%), total flavonoids (concentration 0.07 mg/mL extraction rate 0.57%), polyphenols (concentration 0.09 mg/mL, extraction rate 0.35%), and total protein (concentration 0.09 mg/mL, extraction rate 0.07%), were identified in the plant water extracts.
The research was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee at Hengyang Normal University under project number HNUACUC-B202111001.
A total of 100 10-day-old male native Xianghuang broilers, with an average initial body weight of 99.33 ± 4.41 g, were randomly assigned to two replicated experimental groups: control (C) and experimental (E), with five replicates per group and 10 birds per replicate. A corn-soybean-based diet was formulated to exceed the nutritional requirements of the yellow-feathered broilers (14) (Table 1) and was fed to the birds in the control group. The birds in the experimental group were supplemented with 2% of the TCM plant powder in the control diet. All birds were housed in pens (0.10 m2/bird) with padded rice hulls located at Yimin Farm and had ad libitum access to water and feed. The temperature of the room was maintained at around 29.0°C for the first week (when the broilers were 11 days old) and then gradually reduced by 3°C every week to 24°C until the end of the study using an air conditioner. The light was provided for 12 h at 20 lux using LED lights throughout the experimental period.
All broilers were individually weighed after 12 h of feed deprivation. The body weight (BW) and feed leftovers were recorded per replicate weekly through the experiment. The average daily feed intake (ADFI), average daily gain (ADG), and feed-to-gain (F:G) ratio (the ratio of ADFI to ADG) were calculated.
On day 28, 10 broilers were randomly selected from each of the control and experimental groups for sample collection. Blood was individually collected via the wing vein using a 22 g needle, a venous blood collection needle, and a red vacuum blood collection tube. After standing at room temperature for 3 h, 5 mL of blood was centrifuged at 3,000 rpm at 4°C for 15 min. The supernatants (serum) were collected and stored at −80°C until further analysis. After that, the broilers were euthanized by carbon dioxide followed by cervical dislocation. Organ samples, including the liver, spleen, intestine, kidney, bursa, and heart, were weighed, and the organ index was calculated as follows, Organ index = Organ weight*100%/live body weight. Approximately 5 cm segments of the proximal duodenum, mid jejunum, and distal ileum were washed with 0.9% saline to remove the intestinal contents and then carefully fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 48 h for histological examination. The remaining segments of the small intestine were washed with 0.9% sterile saline and scraped with a glass slide to collect the mucosa. The mucosa and spleen samples were frozen in liquid nitrogen and then stored at −80°C for further analysis.
The intestinal segments fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde were dehydrated with increasing concentrations of ethanol, vitrified with dimethylbenzene, embedded in paraffin, and then cut into 5-μm-thick slides. These were stained with hematoxylin and eosin according to the method mentioned in the report (15). An image of the villus was captured using a microscope (Leica RM2135, Wetzlar, Germany). The width of the baseline, villus height, villus width, and crypt depth of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum were measured from 50 villi per broiler using Image-Pro Plus (Media Cybernetics Inc., Silver Spring, MD, USA).
Antioxidant parameters, including the activities of T-SOD, CAT, total antioxidant activity (T-AOC), and malonaldehyde (MDA) concentration in the serum and the supernatants of the mucosal samples, were determined according to the method mentioned in the report (15, 16). Approximately 0.1 g of the mucosa was homogenized with 0.9 mL of 0.9% sterile saline using a tissue grinder (SCIENTZ-12, Xinzhi Biotech logy, Ningbo, China) and then centrifuged at 2,500 r/min for 15 min to collect the supernatant. The activity of T-AOC (mmol/L) was analyzed using the OD 593 nm value of the supernatant compared with a standard curve of FeSO4.7H2O. The unit of CAT was defined as the amount of hydrolyzed H2O2 in 1 min per mg of protein in the sample. One unit of T-SOD was defined as the amount that caused 50% inhibition of the nitroblue tetrazolium light reaction rate. The supernatant was extracted with 10% trichloroacetic acid and then used to test MDA concentration.
The mRNA expression levels of inflammation, intestinal barrier function, and apoptosis-related genes were examined using quantitative real-time PCR. Total RNA from the mucosa and spleen samples was isolated using TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The integrity of the RNA was determined by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. The concentration and purity of the RNA were measured using the NanoDrop ND-2000 spectrophotometer system (Thermo Fisher Scientific). One μg of the total RNA was reverse transcribed into DNA using an RT reagent kit (Aikerui, Changsha, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The RT-PCR was performed on a QuantStudio3 device (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) using a SYBR Green quantitative PCR mix (Aikerui, Changsha, China) following the manufacturer’s protocols. The primer sequences for the target and reference (β-actin) genes are listed in Table 2. The mRNA expression levels of the target genes were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCT method (17).
The data were analyzed using the one-way ANOVA procedure of SAS 8.0. The individual broiler was the experimental unit for all data, except for growth performance, where the replicate was the experimental unit. Differences between the treatments were evaluated using a t-test. The data were presented as means ± standard deviation. In this study, a p-value <0.05 was considered significant, and 0.05 ≤ p ≤ 0.10 was considered a tendency.
The effect of the TCM supplementation on the growth performance of the Xianghuang broilers is shown in Table 3. No significant differences in the ADFI, ADG, and F:G ratio between the control and experimental groups were observed (p > 0.05).
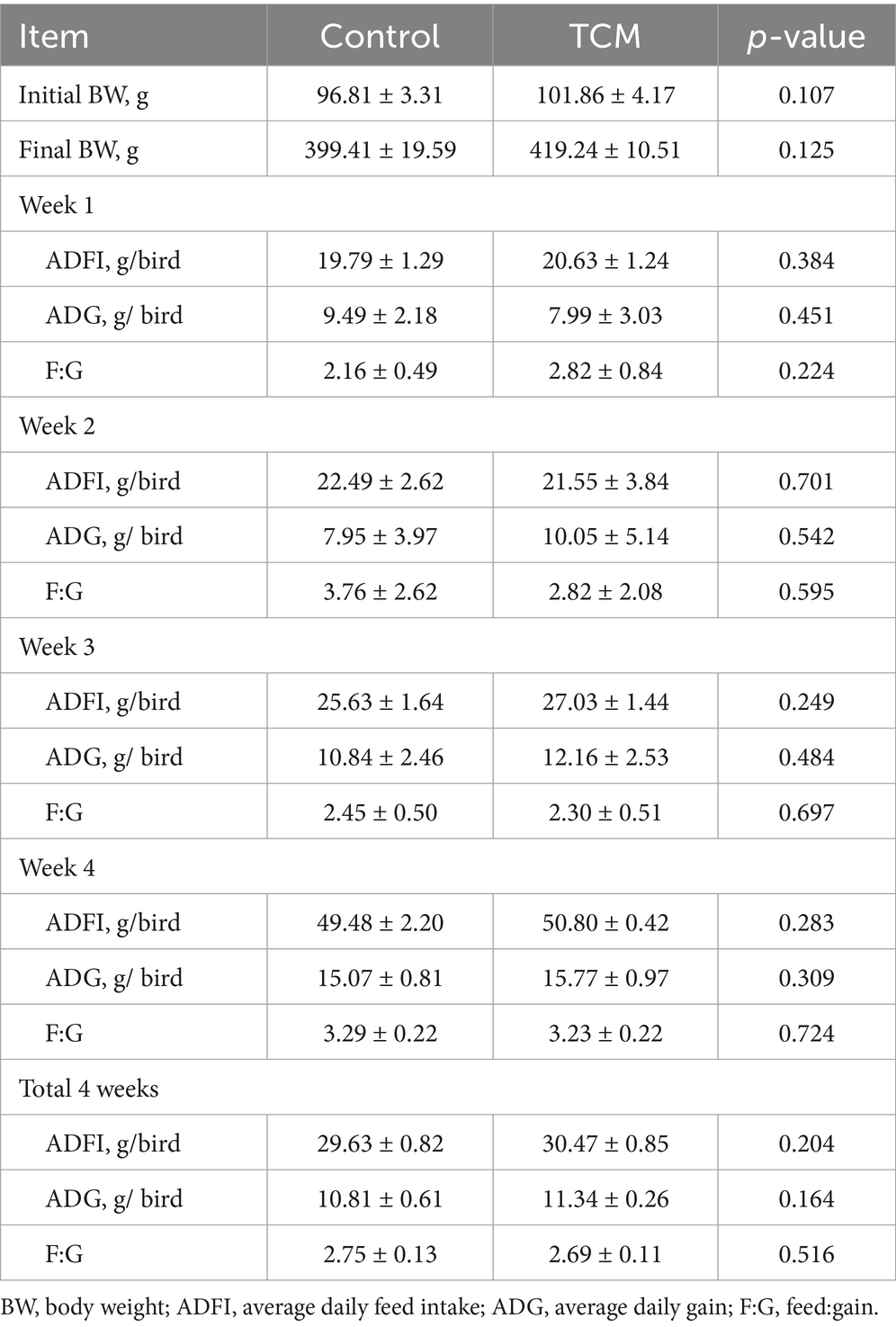
Table 3. Effect of the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) supplementation on the growth performance of the Xianghuang chickens.
The TCM plant powder supplementation had no significant effect on the weight and indices of the liver, intestine, kidney, bursa, spleen, and heart (p > 0.05) (Table 4).
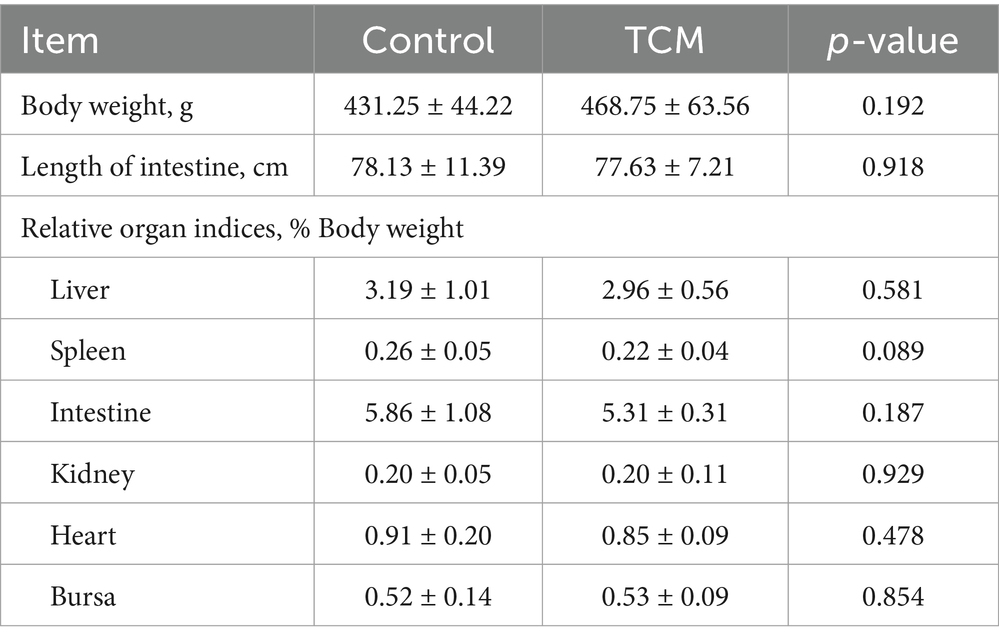
Table 4. Effect of the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) supplementation on the relative organ indices of the Xianghuang chickens.
The effects of the TCM supplementation on the small intestinal morphology of the broilers are presented in Table 5 and Figure 1. The duodenal villus height exhibited an increasing tendency in the TCM group compared to the control group (p = 0.092). However, the baseline width, villus width, and crypt depth of the duodenum remained unaffected by the treatment (p > 0.05) (Figures 1DA,DB). The supplementation with TCM notably augmented the baseline and villus widths in the jejunal segment compared to the control group (p < 0.05). Within the jejunal segment, there was an increasing trend toward the villus height (p = 0.068) and the ratio of the villus height to the crypt depth (p = 0.061) in the TCM group compared to the control group (Figures 1JA,JB). The birds in the TCM group had higher villus height and a higher ratio of the villus height to the crypt depth in the ileum compared to their control counterparts (p < 0.05). Nonetheless, the crypt depth in both the jejunum and ileum, along with the baseline and villus widths in the ileum, did not exhibit significant alterations due to the TCM treatment (p > 0.05) (Figures 1IA,IB).
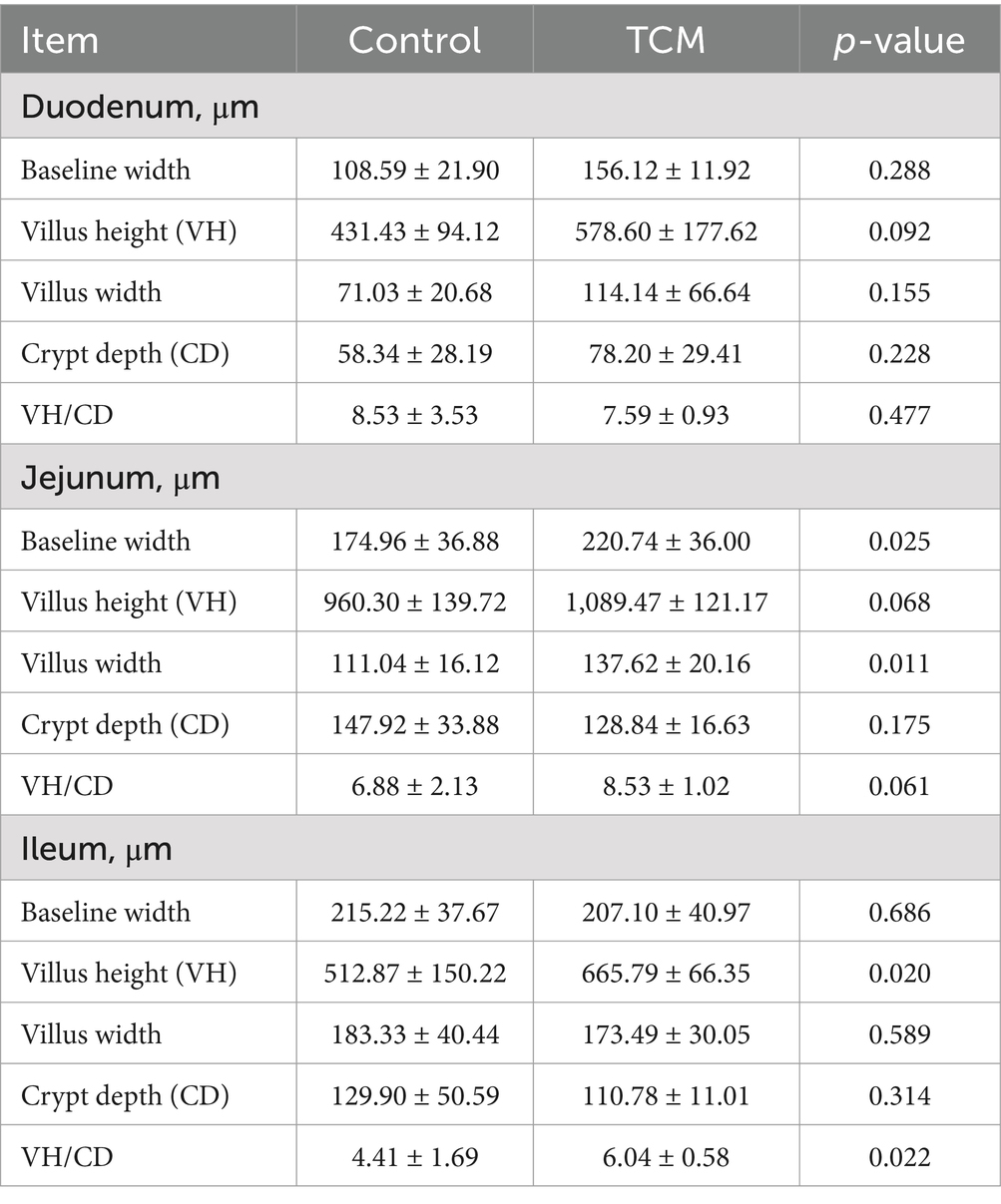
Table 5. Effect of the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) on the intestinal morphology of the Xianghuang chickens.
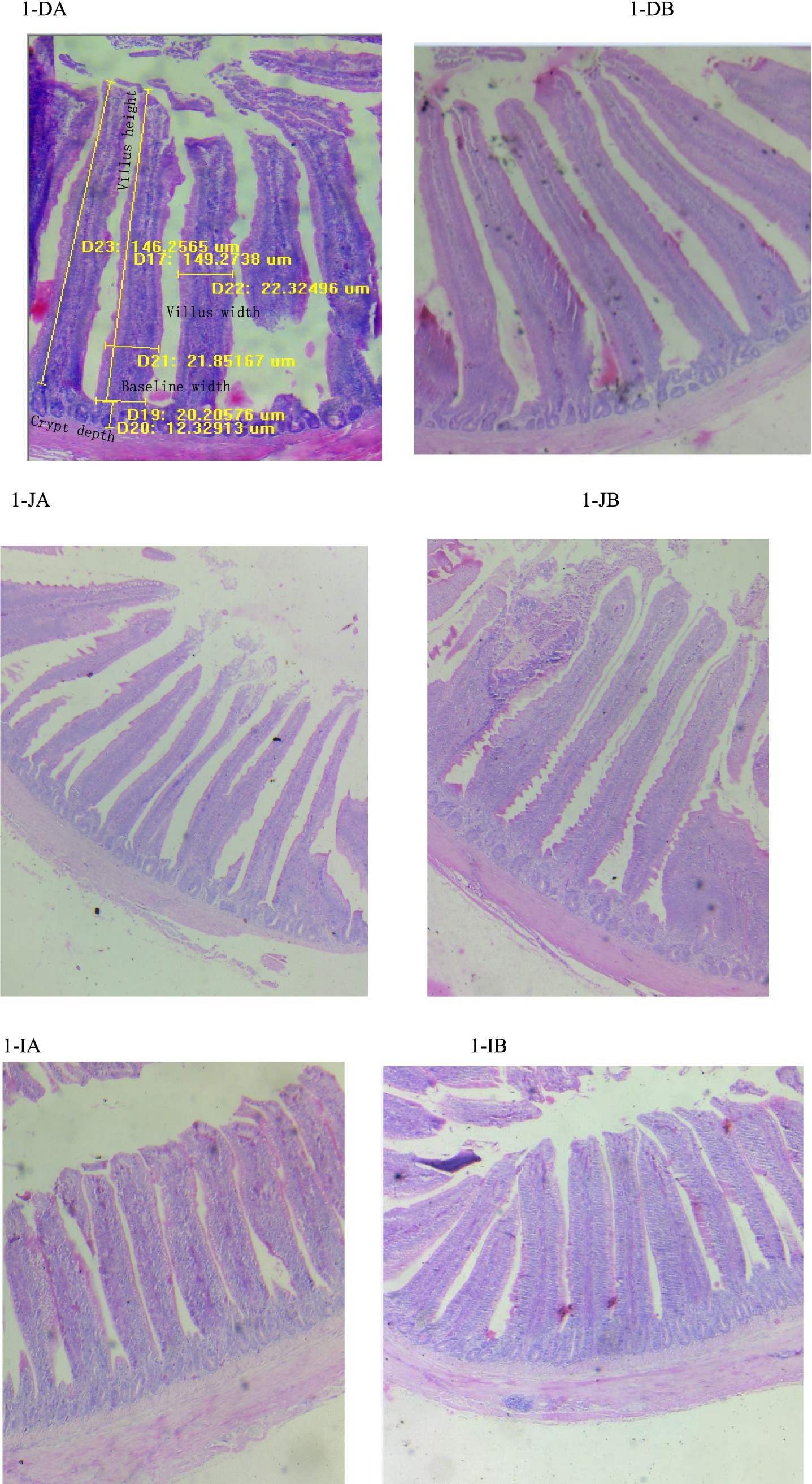
Figure 1. Influence of the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) supplementation on the intestinal histology of the Xianghuang chickens. A magnification of 10*4 was used. Duodenal villi in the control (DA) and TCM (DB) groups, jejunal villi in the control (JA) and TCM (JB) groups, and ileal villi in the control (IA) and TCM (IB) groups.
As shown in Table 6, the activities of T-AOC, SOD, and CAT and the concentration of MDA in the ileal mucosa and serum were not affected by the treatment (p > 0.05). T-AOC activity and MDA concentration were not affected by the treatment in the jejunal mucosa (p > 0.05); however, the jejunal mucosa from the TCM group had higher activities of SOD and CAT compared to the control group (p < 0.05).
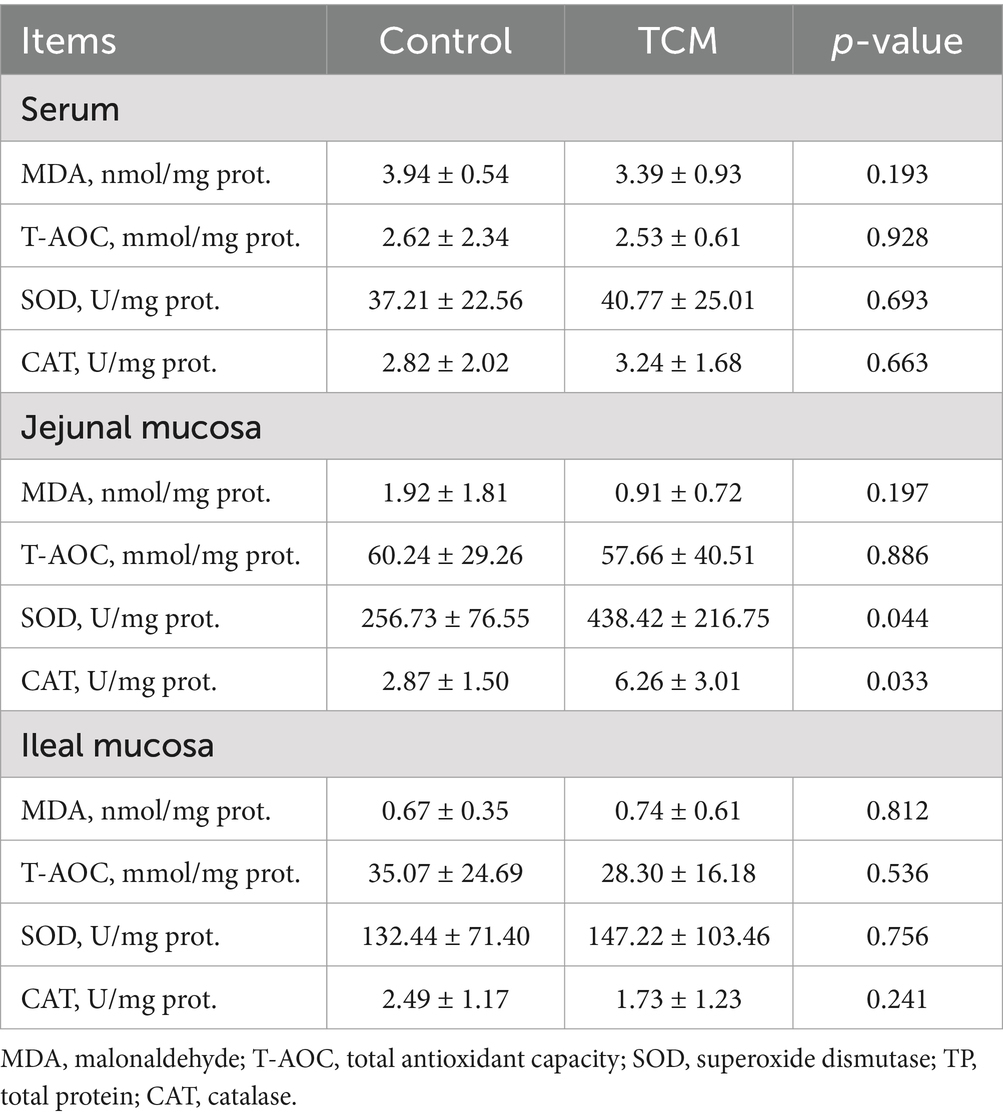
Table 6. Effect of the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) supplementation on the antioxidant indices of the Xianghuang chickens.
The mRNA expression levels of the genes associated with apoptosis, inflammation, and tight junctions in the jejunal mucosa, ileal mucosa, and spleen are shown in Figure 2. In the jejunal mucosa, the expression of the genes tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) was significantly downregulated in the birds supplemented with the TCM plant powder (p < 0.05). In addition, there was a tendency for lower expression of the claudin-1 (CLDN1) and B-cell lymphoma-2 (BCL2) genes (p = 0.081 and 0.091, respectively) in the TCM group compared to the control group. The expression of the IL-1β gene was not affected by the treatment (p > 0.05) (Figure 2A).
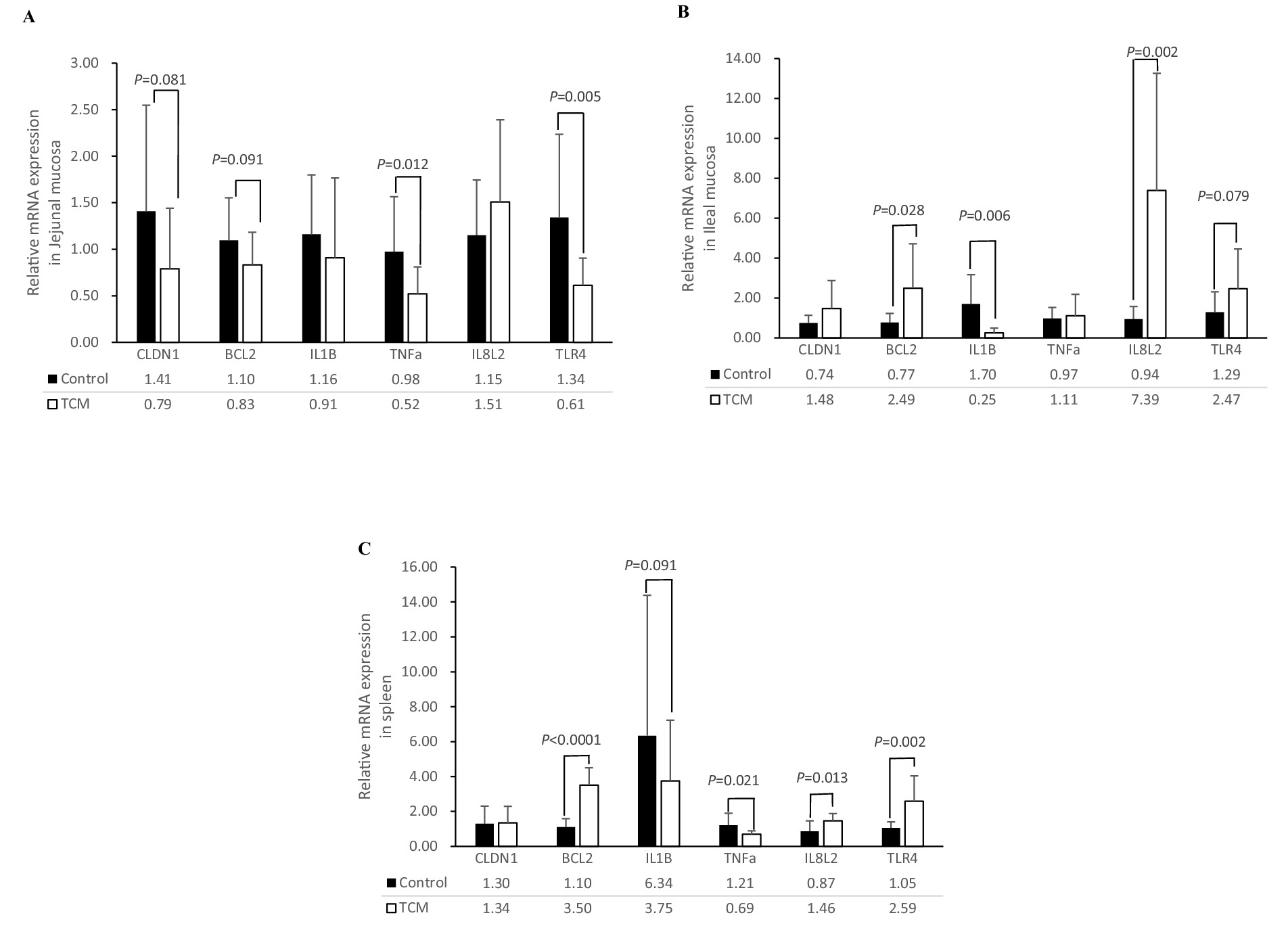
Figure 2. Influence of the traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) supplementation on the relative mRNA expression of the barrier function and inflammation-related genes in the jejunal mucosa (A), ileal mucosa (B), and spleen (C) of the Xianghuang chickens. The data are expressed as means ± standard error. The significant differences between the groups are indicated by p-values. TNF-a, tumor necrosis factor-a; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IL8L2, interleukin-8; TLR4, toll-like receptor 4; BCL2, B-cell lymphoma-2; CLDN1, claudin-1.
In the ileal mucosa, the expression of the BCL2 and IL-8 L2 genes was significantly upregulated (p < 0.05) in the TCM group compared to the control group. The Ileal TLR4 gene tended to be higher (p = 0.079) in the TCM group compared to the control group (p < 0.05). Interestingly, the mRNA expression of the IL-1β gene was lower in the TCM group compared to the control group (p < 0.05). No significant differences were observed in the expression of the CLDN1 and TNF-α genes in the ileal mucosa between the two groups (p > 0.05) (Figure 2B).
In the spleen, upregulation of BCL2 (p < 0.01), IL8L2 (p < 0.05), and TLR4 (p < 0.01) was observed in the TCM group compared to the control group. The mRNA expression of TNF-α (p < 0.05) was downregulated, and the expression of IL-1β (p = 0.091) tended to be lower in the TCM group compared to the control group. No effect was observed for the CLDN1 expression in the spleen (p > 0.05) (Figure 2C).
Growth performance was not affected by the TCM supplementation. A previous review pointed out that H. helix is effective in reducing cough and respiratory problems while being well-tolerated in patients (5). Several studies on Clematidis Radix et Rhizome (CRR), such as C. chinensis, have verified its effect in treating diseases, such as relieving rheumatism pain and treating hepatic carcinoma and gastrointestinal issues. However, long-term administration of excessive amounts of CRR was found to cause severe diarrhea and death in mice (18). The present study confirmed that the 2% TCM plant powder was very well tolerated as the birds in the TCM group had the same growth performance and organ index as those in the control group.
Intestinal health was significantly enhanced by the TCM supplementation, as evidenced by a notable increase in the villus height-to-crypt depth ratio in both the jejunum and ileum of the birds in the TCM group. The TCM supplementation demonstrated significant anti-inflammatory effects, which contributed to this improvement. Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), a critical mediator of inflammatory responses, is known to promote inflammation and exacerbate tissue damage (19). In chickens with diarrhea, the expression of TLR4 mRNA was elevated in intestinal tissues (11). However, in the present study, the TCM supplementation significantly reduced the TLR4 mRNA expression in the jejunum, highlighting its potential to mitigate inflammation. Similarly, Hederacoside C supplementation downregulated genes associated with pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, while upregulating the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 in S. aureus-induced RAW 264.7 cells and mice (20). In line with these findings, the present study confirmed that the TCM supplementation inhibited the gene expression of IL-1β while promoting the expression of IL8L2 in the ileal mucosa. Furthermore, TCM may confer significant benefits for villous growth through enhanced activities of SOD and CAT. As critical antioxidant enzymes, SOD facilitates the conversion of superoxide radicals (O2−) to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) (21), while CAT serves as a primary cellular defense mechanism by decomposing H2O2 into water and oxygen (22). The TCM used in this study contained bioactive constituents such as total flavonoids and polyphenols, which exhibit antioxidant properties. Black cumin (Nigella sativa L.), a plant from the Ranunculaceae family, has demonstrated potent antioxidant effects by upregulating key enzymes, including SOD, CAT, and glutathione (GSH) (23). It has also shown protective efficacy against aflatoxin-induced toxicity in ducks (24) and broilers (25). The present study demonstrated that the TCM supplementation significantly upregulated the expression of the anti-apoptosis gene Bcl2 in both the spleen and ileal mucosa. As Bcl2 protein is known to suppress apoptosis (26), this enhancement likely promotes villous cell survival as well. Similarly, steroidal alkaloids isolated from the root of Sarcococca hookeriana (Buxaceae) have demonstrated potent inhibitory effects on cancer cell proliferation (27). Chemically synthesized pachysandra alkaloids, following the molecular formula of Sarcococca ruscifolia alkaloids, have shown superior anticancer activity against HepG2 cells by regulating the JAK2/STAT3 pathway (1). Berberine, extracted from the roots of Ranunculaceae family plants such as Hydrastus carnadensis and Coptis rhizomes (28), has also exhibited notable anticancer properties, as evidenced by preclinical studies (29). The anti-apoptotic activity of this TCM may be attributed to the inclusion of Clematis chinensis Osbeck and Sarcococca ruscifolia Stapf, which are rich in berberine and steroidal alkaloids, respectively. Notably, gastrointestinal tract syndrome is characterized by primary lesions in gut microvascular endothelial apoptosis, and preserving endothelial integrity through apoptosis inhibition has been identified as a critical therapeutic target (30). The anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-apoptosis properties of the TCM appear to be key mechanisms through which it exerts its effects in stimulating intestinal villus proliferation and mucosal integrity. Furthermore, the observed optimization of intestinal morphology may confer adaptive advantages to poultry chicks under extreme environmental stressors. Its broader implications for juvenile livestock development—particularly in enhancing nutrient assimilation and metabolic resilience—represent a critical area for translational research.
In conclusion, the combination of Sarcococca ruscifolia Stapf, Hedera nepalensis var. sinensis (Tobl.) Rehd, and Clematis chinensis Osbeck is safe for broiler production. This TCM plant powder has also been demonstrated to effectively regulate intestinal histopathological changes through its anti-apoptosis, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties in chickens.
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the corresponding author.
The animal study was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Hengyang Normal University, protocol HNUACUC-B202111001. The authors confirm that the ethical policies of the journal, as noted on the journal’s author guidelines page, have been adhered to and the appropriate ethical review committee approval has been received. The authors confirm that they have followed EU standards for the protection of animals used for scientific purposes. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
CY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XT: Conceptualization, Resources,Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft. RW: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. YJ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. QQ: Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. YX: Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. JK: Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. JC: Validation, Writing – review & editing. QT: Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZJ: Investigation, Resources, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by key projects of the education department of Hunan province (22A0504); key development projects of the Hunan science and technology department (2022WK2020); Research foundation of the education department of Hunan province (21C1122).
ZJ was employed by Yimin Ecological Agriculture Development Co., LTD.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Zhao, J, Bai, J, Yu, X, Zhang, W, Zhao, C, Ye, J, et al. Synthesis, biological activities and mechanistic studies of C20-ketone pachysandra alkaloids as anti-hepatocellular carcinoma agents. Mol Divers. (2024). doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-10961-2
2. Yi, X, Dai, Z, Xie, TZ, Xiao, X, Liu, YP, Zhao, LX, et al. Cytotoxic androstane derivatives from Sarcococca ruscifolia. Fitoterapia. (2020) 144:104604. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2020.104604
3. Ullah Jan, N, Ali, A, Ahmad, B, Iqbal, N, Adhikari, A, Inayat-Ur-Rehman, AA, et al. Evaluation of antidiabetic potential of steroidal alkaloid of Sarcococca saligna. Biomed Pharmacother. (2018) 100:461–6. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.008
4. Giliani, AU, Ghayur, MN, Khalid, A, Zaheer-ul-Haq,, Choudhary, MI, and Atta-ur-Rahman,. Presence of antispasmodic, antidiarrheal, antisecretory, calcium antagonist and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory steroidal alkaloids in Sarcococca saligna. Planta Med. (2005) 71:120–5. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-837777
5. Baharara, H, Moghadam, AT, Sahebkar, A, Emami, SA, Tayebi, T, and Mohammadpour, AH. The effects of ivy (Hedera helix) on respiratory problems and cough in humans: a review. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2021) 1328:361–76. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-73234-9_23
6. Veldman, LBM, Belt-Van Zoen, E, and Baars, EW. Mechanistic evidence of andrographis paniculata (Burm. F.) wall. Ex Nees, pelargonium sidoides DC., echinacea species and a combination of Hedera helix L., Primula veris L./Primula elatior L. and Thymus vulgaris L./thymus zygis L. in the treatment of acute, uncomplicated respiratory tract infections: a systematic literature review and expert interviews. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). (2023) 16:1206. doi: 10.3390/ph16091206
7. Saadat, S, Mohammadi, M, Fallahi, M, Keyhanmanesh, R, and Aslani, MR. The protective effect of α-hederin, the active constituent of Nigella sativa, on tracheal responsiveness and lung inflammation in ovalbumin-sensitized Guinea pigs. J Physiol Sci. (2015) 65:285–92. doi: 10.1007/s12576-015-0367-6
8. Ye, S, Yan, L, Sun, YP, Li, XM, Si-Yi, W, Pan, J, et al. Two new terpenes from the aerial parts of Clematis chinensis Osbeck. Nat Prod Res. (2022) 36:3825–32. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2021.1889541
9. Jiang, HB, Shao, SY, Wei, YZ, Lin, MB, and Li, S. Phenolic glycosides and indole alkaloids isolated from the roots and rhizomes of Clematis chinensis and their anti-inflammatory activity. Phytochemistry. (2023) 215:113832. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2023.113832
10. Hsieh, MS, Wang, KT, Tseng, SH, Lee, CJ, Chen, CH, and Wang, CC. Using 18F-FDG microPET imaging to measure the inhibitory effects of Clematis chinensis Osbeck on the pro-inflammatory and degradative mediators associated with inflammatory arthritis. J Ethnopharmacol. (2011) 136:511–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.06.042
11. Liang, W, Li, H, Zhou, H, Wang, M, Zhao, X, Sun, X, et al. Effects of taraxacum and astragalus extracts combined with probiotic Bacillus subtilis and lactobacillus on Escherichia coli-infected broiler chickens. Poult Sci. (2021) 100:101007. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.01.030
12. Li, S. Compendium of Materia medica (Jinling edition printed version), vol. I, II, and III. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House (1999) Chinese.
13. Sierocinski, E, Holzinger, F, and Chenot, JF. Ivy leaf (Hedera helix) for acute upper respiratory tract infections: an updated systematic review. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. (2021) 77:1113–22. doi: 10.1007/s00228-021-03090-4
14. NY/T33-2004. Feeding standard of chicken Agricultural Industry Standards of the People's Republic of China (2004). Beijing.
15. Tan, L, Tao, Y, Chen, L, Yang, C, Tang, X, Ma, J, et al. Effects of fermented tofu processing wastewater on growth performance and meat quality of Xianghuang broilers. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). (2024) 108:1072–82. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13952
16. Habibi, R, Sadeghi, G, and Karimi, A. Effect of different concentrations of ginger root powder and its essential oil on growth performance, serum metabolites and antioxidant status in broiler chicks under heat stress. Br Poult Sci. (2014) 55:228–37. doi: 10.1080/00071668.2014.887830
17. Livak, KJ, and Schmittgen, TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods (San Diego, Calif). (2001) 25:402–8. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262
18. Lin, TF, Wang, L, Zhang, Y, Zhang, JH, Zhou, DY, Fang, F, et al. Uses, chemical compositions, pharmacological activities and toxicology of Clematidis radix et rhizome- a review. J Ethnopharmacol. (2021) 270:113831. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113831
19. Peng, KY, Gu, JF, Su, SL, Zhu, Y, Guo, JM, Qian, DW, et al. Salvia miltiorrhiza stems and leaves total phenolic acids combination with tanshinone protect against DSS-induced ulcerative colitis through inhibiting TLR4/PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in mice. J Ethnopharmacol. (2021) 264:113052. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113052
20. Akhtar, M, Shaukat, A, Zahoor, A, Chen, Y, Wang, Y, Yang, M, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of Hederacoside-C on Staphylococcus aureus induced inflammation via TLRs and their downstream signal pathway in vivo and in vitro. Microb Pathog. (2019) 137:103767. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103767
21. Miao, L, and St Clair, DK. Regulation of superoxide dismutase genes: implications in disease. Free Radic Biol Med. (2009) 47:344–56. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.05.018
22. Ayala, A, Muñoz, MF, and Argüelles, S. Lipid peroxidation: production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2014) 2014:360438. doi: 10.1155/2014/360438
23. Hannan, MA, Rahman, MA, Sohag, AAM, Uddin, MJ, Dash, R, Sikder, MH, et al. Black cumin (Nigella sativa L.): a comprehensive review on phytochemistry, health benefits, molecular pharmacology, and safety. Nutrients. (2021) 13:1784. doi: 10.3390/nu13061784
24. Ayoub, MM, Elfar, AH, Taha, NM, Korshom, MA, Mandour, AA, Abdelhamid, HS, et al. The biochemical protective role of some herbs against aflatoxicosis in duckingls: II. Nigella sativa. Thin Solid Films. (2011) 55:68–77. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2007.01.027
25. Ates, MB, and Ortatatli, M. The effects of Nigella sativa seeds and thymoquinone on aflatoxin phase-2 detoxification through glutathione and glutathione-S-transferase alpha-3, and the relationship between aflatoxin B(1)-DNA adducts in broilers. Toxicon. (2021) 193:86–92. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2021.01.020
26. Maji, S, Panda, S, Samal, SK, Shriwas, O, Rath, R, Pellecchia, M, et al. Bcl-2 antiapoptotic family proteins and chemoresistance in cancer. Adv Cancer Res. (2018) 137:37–75. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2017.11.001
27. He, K, Wang, J, Zou, J, Wu, J, Huo, S, and Du, J. Three new cytotoxic steroidal alkaloids from Sarcococca hookeriana. Molecules. (2018) 23:1181. doi: 10.3390/molecules23051181
28. Wang, J, Wang, L, Lou, GH, Zeng, HR, Hu, J, Huang, QW, et al. Coptidis Rhizoma: a comprehensive review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology. Pharm Biol. (2019) 57:193–225. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2019.1577466
29. Lenka, G, Jií, D, and Marek, R. Quaternary protoberberine alkaloids. Phytochemistry. (2007) 68:150–75. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2006.10.004
Keywords: Chinese medicinal plant, antioxidant function, intestinal health, chickens, anti-inflammation
Citation: Yang C, Tang X, Wu R, Jiang Y, Quan Q, Xiao Y, Kuang J, Chen J, Tang Q and Jiang Z (2025) Effects of a powder made from three medicinal plants on growth performance, intestinal health, antioxidant activity, and anti-inflammatory ability in Xianghuang chickens. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1538623. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1538623
Received: 03 December 2024; Accepted: 25 February 2025;
Published: 26 March 2025.
Edited by:
Giovanni Buonaiuto, University of Bologna, ItalyReviewed by:
Bochen Song, Shandong Agricultural University, ChinaCopyright © 2025 Yang, Tang, Wu, Jiang, Quan, Xiao, Kuang, Chen, Tang and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: XiaoWu Tang, dGFuZ3hpYW93dXM3MDRAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†ORCID: Can Yang, orcid.org/0000-0001-8973-6994
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.