
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Vet. Sci. , 05 March 2025
Sec. Veterinary Infectious Diseases
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2025.1535719
This article is part of the Research Topic Reproductive biotechnologies and challenges in their application - volume II View all articles
Pig farming is essential to global agricultural economies and food security. However, reproductive disorders in sows significantly impact the economic viability and sustainability of the pig industry. These disorders often result from complex interactions between pathogenic and non-pathogenic factors. Preventing abortions is typically more cost-effective than managing and treating them, particularly in intensive pig farming system. This highlights the importance of comprehensively understanding the underlying causes of abortion in sows. This review explores the factors contributing to sow reproductive disorders, including both non-infectious factors (environmental conditions and management practices) and infectious factors (viruses, bacteria, and parasites). We also outline preventive and control strategies, alongside integrated management approaches, by analyzing the underlying causes and pathogenic mechanisms of pregnancy disorders. Overall, implementing the “One Health” concept in large-scale farming provides an effective strategy to reduce the incidence of sow abortion rate, ensure stable livestock production, and maintain a reliable global pork supply.
Pig production plays a significant role in global meat consumption, contributing 34% of the world’s meat supply (1). Over the last six decades, from 1962 to 2022, pork consumption has increased, leading to an impressive 130% increase in global pork production (2). By 2024, the global pig population reached 1.25 billion, with pork production reaching 114.20 million tons (3). China accounting for 54.0% of the world’s pig population (678.0 million heads), followed by the EU (232 million heads). Over the past decade, a key factor driving this growth has been significant improvements in reproductive performance, particularly advancements in the breeding and management of modern hybrid sows. These improvements have directly contributed to increase in the number of piglets weaned per sow per year (PWSY) (4, 5). However, reproductive disorders of sows seriously affect the economic and sustainable development of the pig farming industry.
Reproductive disorders in sows exhibit various clinical manifestations. Among these, the SMEDI (stillbirth, mummification, embryonic death, and infertility) syndrome (Figure 1) displays a disturbed gestation in sows (6). Abortions in sows can be caused by a range of factors, both non-infectious and infectious. The main non-infectious causes are linked to external environmental conditions (temperature, humidity, and air quality) and feeding management practices (feed quality and reproductive feeding techniques), which can stress the animals and affect their reproductive performance. Infectious factors are caused serious threat to reproductive health in pigs, The main infectious factors include viral infections (e.g., porcine parvovirus, porcine pseudorabies, porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus, Japanese encephalitis B virus, porcine circovirus, and classical swine fever virus), bacterial infections (e.g., brucellosis, listeriosis, chlamydiosis, leptospirosis, campylobacteriosis, and swine erysipelas), and parasitic infections (e.g., Toxoplasma gondii). The etiology of reproductive disorders in sows is not solely attributed to a single pathogen but often involves mixed infections of multiple pathogens. Non-infectious factors play a more significant role in sow reproductive disorders than that of infectious factors. However, reproductive disorders caused by non-infectious factors can be more effectively managed through changes in integrated management practices than infectious factors, which may pose a greater risk for epidemic outbreaks.
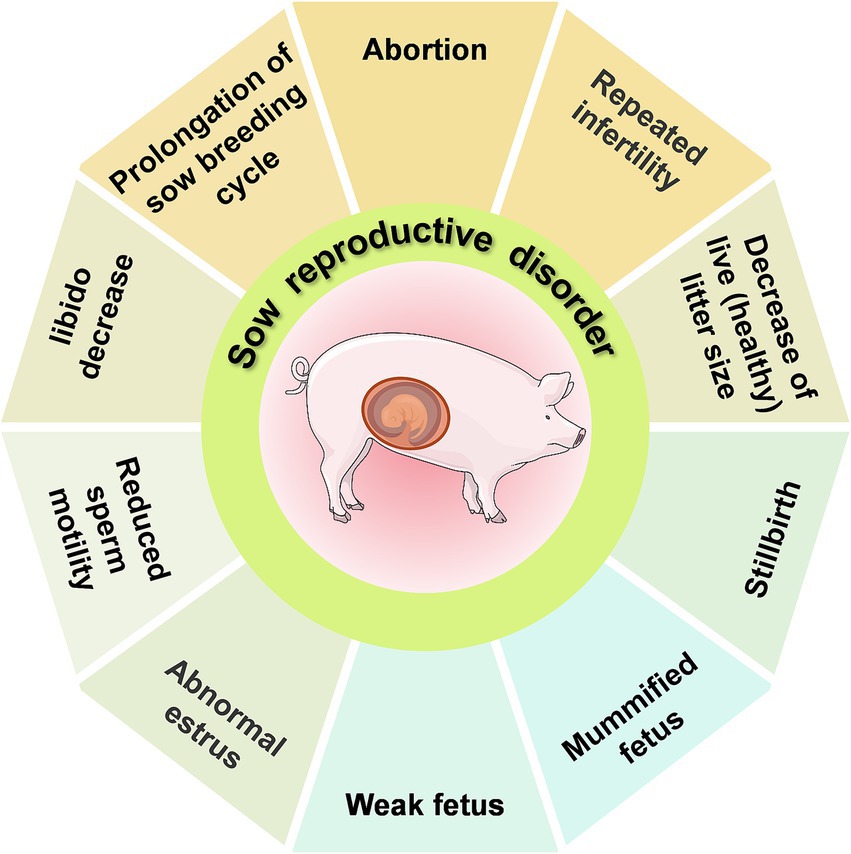
Figure 1. An overview of the SMEDI (stillbirth, mummification, embryonic death, and infertility) syndrome.
The One Health approach requires understanding the interactions between the pathogens that cause reproductive disorders in sows and other animal hosts, and considering the effects of external environmental conditions and management practices, to achieve One Health for all living organisms (including humans) on large farms. In this paper, we review the various non-infectious (seasonal, environmental, nutritional and mycotoxins) and infectious (viral, bacterial, and parasitic) factors associated with reproductive disorders in sows in terms of causes, pathogenesis and integrated management practices.
Non-infectious factors affecting the reproductive performance of sows account for more than 70.0% of abortions and fetal deaths in sows (7), with external environmental factors and management practices being the primary contributors. Temperature and humidity play a vital role in hormone secretion and overall reproductive health in sows. Specifically, high temperature and humidity can induce heat stress, which affects hormone secretion and can lead skin and limb diseases. Consequently, inappropriate rearing environments can disrupt the sow’s endocrine system, ultimately causing luteal regression and subsequent abortions (Table 1).
In addition to environmental factors, feeding practices are critical determinant of sow reproductive capacity. Feed quality directly impacts conception rates and fetal development. Overnutrition can lead to obesity, thereby reducing conception rates, while malnutrition decreases reproductive hormone synthesis, impeding reproductive system development and delaying estrus. Notably, sows consuming moldy feed accumulate toxins that induce reproductive disorders. Research indicates that mycotoxins, such as Zearalenone (ZEN), exhibit estrogen-like activity, compete for receptors, inhibit follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) secretion, and disrupt the endocrine system. T-2 toxin disrupts the reproductive endocrine axis and inhibits reproductive hormone synthesis. Deoxynivalenol (DON) inhibits oocyte maturation and embryonic development (8, 9). Ergot Alkaloids lead to agalactia in sows and to a high neonatal mortality rate (10). Aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) impairs oocyte maturation and damage early embryonic development through oxidative stress and mechanisms such as apoptosis and autophagy (11).
The impact of rearing and breeding techniques, such as stocking density and artificial insemination (AI), on sow reproductive performance should not be overlooked. In most major pork-producing countries, AI is highly efficient (12). However, Semen is an ideal medium for the establishment and growth of many microorganisms including bacteria and fungi (13). Consequently, during collection, semen is susceptible to contamination from sources such as boar feces, preputial secretions, and the environment in which it is collected and processed (14). Contamination of boar semen with bacteria (e.g., E. coli, Pseudomonas spp., Staphylococcus spp., Proteus spp.) and fungi (e.g., Candida spp., Aspergillus spp.) can reduce sperm viability and increase the risk of infection in inseminated sows, such as endometritis, ultimately reducing reproductive performance (15, 16).
Infectious factors have received more attention than non-infectious ones due to their association with epidemics of reproductive failure in sows (Table 2).
Porcine Parvovirus (PPV), an Ungulate parvovirus 1 in the Protoparvirus genus, was first recognized as a member of the Parvoviridae family and causative agent of SMEDI syndrome at the end of the 1960s (17). Seven distinct genotypes of PPV (PPV1-PPV7), which are prevalent worldwide, have been identified.
The Ministry of Agriculture in China has classified PPV as a Class II animal disease pathogen (18). In China, the positivity rate of PPV was significantly higher in pigs in the south-west, northern and southern parts of the country. For instance, in Haikou and Chongqing, China (2014), the serological positivity rate of PPV reached over 90% (19), while 85% of pig herds with reproductive dysfunction syndrome was positive for PPV in Yunnan Province (20). In Pakistan, Punjab (2016), the seroprevalence of PPV was 41.1% (21). In recent years, there has been an increase in the PPV variation and its co-infection with other pathogens. An epidemiological survey of the porcine reproductive syndrome in South-west China (2012) showed that the positive rate of PPV was 43.97%, while that of Pseudorabies virus (PRV) was 24.6%, and Chlamydia psittaci (Cps) was 36.98%. Of these, 39.6% were mono-infections, while 35.6% were mixed infections (22). It has been shown that PPV infection-induced cell apoptosis in pregnant sows is primarily caused by the non-structural protein NS1. This process is characterized by the induction of host cell DNA damage, reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and mitochondrial damage (23). A consequence of PPV infection is the nuclear fragmentation and subsequent nucleus consolidation of the luteal cells, which damages the luteal tissue of sows. Moreover, PPV impedes progesterone synthesis in luteal cells by inhibiting the expression of StAR, 3β-HSD and P450scc and induces apoptosis in luteal cells by activating the p38, p53 and mitochondrial pathways (Figure 2), culminating in abortion and infertility (24). Additionally, PPV induces apoptosis in embryonic trophoblasts by regulating the expression levels of Fas/Fas L, Bax/Bcl-2 and p53, ultimately resulting in embryonic death (25).

Figure 2. Mechanisms of reproductive dysfunction resulted from luteal cells and placental trophoblast cells apoptosis induced by porcine parvovirus (PPV) infection in sows.
PPV has a single serotype, and vaccine immunization has become the primary prevention and control strategy for the pathogen. The most commonly used vaccines in clinical settings are live and inactivated weakly-attenuated vaccines.
Porcine pseudorabies (PR), also known as Aujeszky’s disease, is caused by the pseudorabies virus (PRV), which has a wide host range. The family Suidae (true pigs) are the natural hosts and reservoirs of PRV (26–28). There are two types of PRV infections: overt and latent. Adult pigs are mostly latently infected and can continuously excrete the virus (29). Following PRV infection in boars, the virus can be excreted in semen and transmitted to sows, leading to various reproductive disorders. Serological tests showed that the positivity rate of PRV gE antibody in the 3,449 serum samples collected from the Hebei Province, China (2022), was 46.27% (30). In Greece (2019), 28.6% of 42 selected pig farms were positive for antibodies against the wild-type strains of PRV (31).
PRV can enter the blood circulation via leukocyte uptake, allowing it to reach all body parts, including the placental tissues, where it can cause stillbirth or miscarriage following fetal invasion (32). PRV-infected mononuclear cells can cross the endothelial cell (EC) barrier of the maternal vasculature (33), and widespread EC infection can lead to detachment of membranes in early gestation, abortions of virus-negative fetuses, or fetal reabsorptions in the sow. Secondary replication in the EC of the uterus of pregnant sows can cause vasculitis and multifocal thrombosis, and microscopic uterine vasculopathy may lead to abortion or stillbirths of virus-positive fetuses in mid and late pregnancy. Additionally, the induction of cytokines and hormones in the local environment during pregnancy may accelerate the adhesion of PRV-infected monocytes to ECs, further contributing to miscarriage in sows (29).
The gE gene deletion-engineered vaccines are widely used to immunize commercial pig herds and wildlife against PRV. Since 2011, outbreaks of PR caused by emerging PRV variants have occurred in Chinese pig herds immunized with the Bartha-K61 strain. The classical PRV attenuated vaccines have been demonstrated to provide incomplete protection for pigs (34, 35). Scientists have conducted research and developed genetically engineered vaccines against the novel 2011 PR. Currently, only two vaccine types have been licensed: a genetically modified inactivated vaccine against the PRV HeN1201 strain (2019) and a natural four-gene deletion (gI/gE/Us9/Us2) vaccine against the PRV C strain (2017) (36, 37). The active ingredients of certain herbs have also been demonstrated to act as PRV inhibitors. For example, resveratrol (trans-3,4,5-trihydroxystilbene; Res) has been shown to possess immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral activities (38) and has been observed to protect rotavirus-infected piglets by reducing inflammatory responses and enhancing immune function (39).
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS), also referred to as porcine blue ear disease, is caused by the porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV). Infected sows exhibit reproductive disorders, which are primarily manifest in abortion, mummified fetus, weak fetuses and stillbirths. During the late gestation period, the abortion rate can exceed 30.0%, and the piglets exhibit severe respiratory disorders, with a mortality rate of 35.0% ~ 40.0%. Infected sows can be detoxified through excretion in feces, saliva, milk, and so forth, but the detoxification cycle is lengthy (40).
PRRSV primarily infects macrophages and cells of the monocyte lineage, including dendritic cells (DCs) (40). Infection in a breeding pig results in significantly reduced immunity, leading to the development of mixed and secondary infections, further exacerbating the disease severity. PRRSV can modulate various inflammatory cytokines (Figure 3), including interferon-α (IFN-α), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), as well as interleukins such as IL-1, IL-8 and IL-10, to regulate the host innate immune response (41). PRRSV infection also reduces the expression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules on the surface of antigen-presenting cells. Additionally, the virus has been shown to induce the death of host cells through both apoptotic and necrotic mechanisms, thus inhibiting the functions of DCs and evading the host’s adaptive immune response (42, 43). It is also possible that PRRSV may reach the endometrial connective tissue by infecting endometrial vascular migrating mononuclear cells. Viral replication leads to local cellular infection and peripheral cell death, which in turn causes fetal detachment from the placenta or cellular degeneration, ultimately causing fetal death (44). Furthermore, PRRSV infection may result in inflammatory damage to the endometrium, placenta, blood vessels, and myometrium of pregnant sows. This may reduce the intensity of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) immunostaining, which could affect cell proliferation at the maternal-fetal interface and submucosal angiogenesis and impact fetal viability (45, 46).
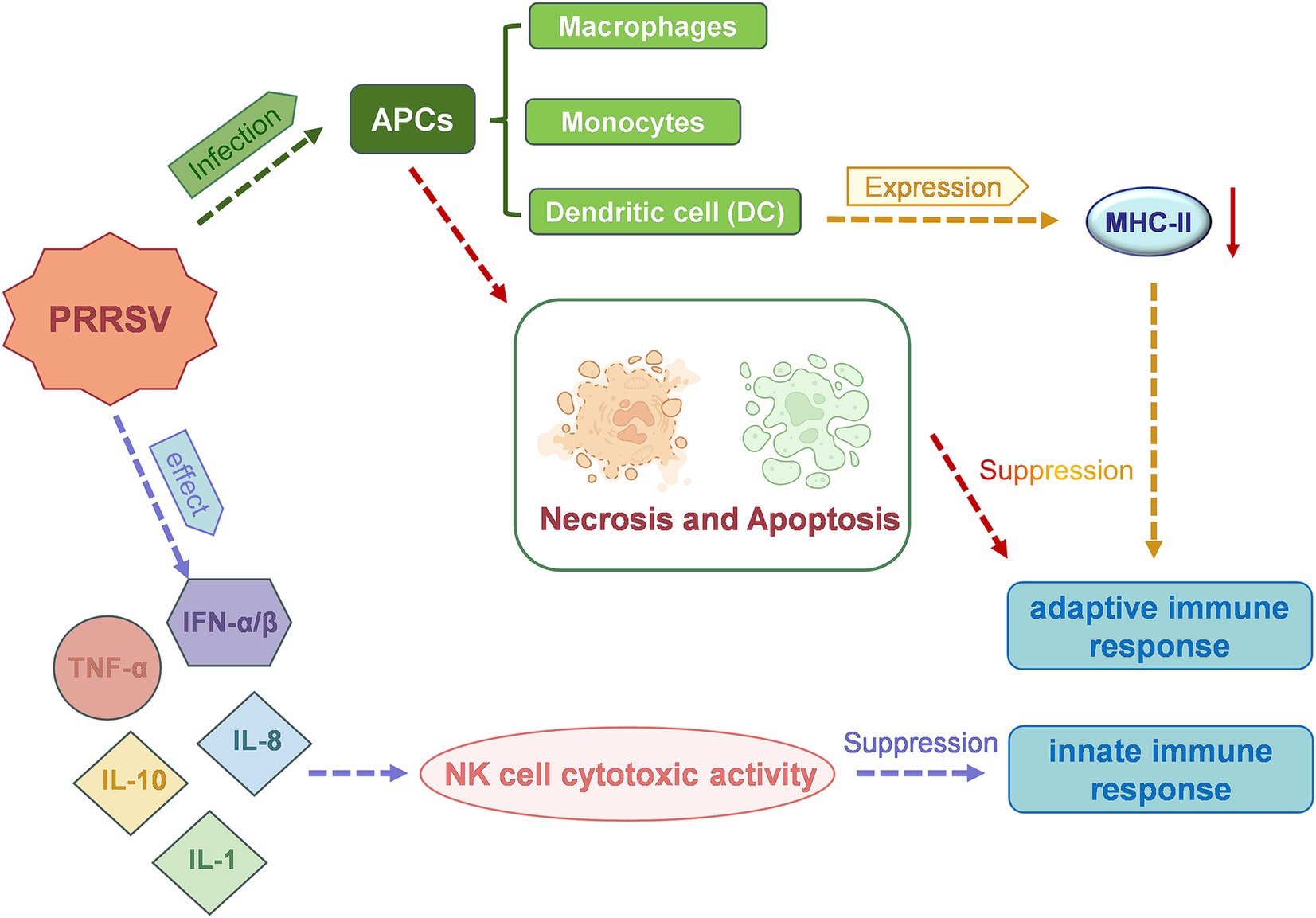
Figure 3. A schematic representation of the mechanism of action of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV), which leads to reproductive dysfunction in sows.
The primary objective of controlling PRRS is to prevent infection, establish optimal herd immunity, and minimize the risk of infection, which is a systematic process. PRRS vaccines can be broadly classified into live attenuated and inactivated vaccines. Two categories of live attenuated vaccines exist: those derived from classical strains and those derived from highly pathogenic strains (47). Given that PRRSV is an RNA virus, its high variability and rapid evolution pose significant challenges for the design and development of PRRS vaccines. Currently, attenuated applications are widely employed but face challenges such as revertant mutations, virulence enhancement, and strain recombination. Precise knowledge of the antibody titer of PRRS can ascertain the existence and severity of the disease, determine the immune status of the herd, and inform the improvement of the immunization strategy as needed, thereby reducing the clinical infection rate of PRRS and gradually achieving the goal of disease purification.
Epidemic encephalitis B is a zoonotic infection caused by the mosquito-borne Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV), which targets the central nervous system of both humans and animals. In its natural habitat, JEV primarily infects humans and animals via the “pig-mosquito-human” cycle. Pigs serve as “amplifying hosts” and represent the largest reservoir, multiplier and disperser of the virus. The virus can multiply in large quantities in pigs, resulting in overt viremia (48). JEV viral particles proliferate primarily in tissues, including connective tissue, skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, smooth muscle, lymphoreticular tissue, and endocrine and exocrine glands, among others. The virus can also cross the blood–brain barrier to access the central nervous system, infecting neuronal cells. The pro-inflammatory and chemotactic factors released from the infected neuronal cells can activate microglia to produce more inflammatory factors, leading to an “inflammatory storm” in the central nervous system, which ultimately causes viral encephalitis and massive neuronal death (49, 50). Infection with encephalitis B in pigs is largely asymptomatic, although it can cause several other clinical signs, including high fever in fattening pigs, abortion in pregnant sows, stillbirth, mummified fetuses, and premature or delayed delivery, among other symptoms. It can also cause acute inflammation of the testes in boars, resulting in enlarged testes on one or both sides, followed by atrophy, hardening, and, ultimately, the loss of breeding capacity (51).
Vaccination has been demonstrated to provide a beneficial protective effect on infectious diseases such as Japanese encephalitis (JE), which are zoonotic and transmitted by insect vectors. However, it is not feasible to eradicate these diseases through vaccination alone. The three major types of vaccine currently in use worldwide are the inactivated mouse brain vaccine, the inactivated cellular vaccine, and the live attenuated encephalitis vaccine. The inactivated mouse brain vaccine is the most widely produced and used vaccine and is the only inactivated Japanese encephalitis B vaccine approved by the World Health Organization (WHO) and commercialized for human use (52). Therefore, it is necessary to implement a comprehensive strategy that includes industrial structure adjustment, mosquito control, intermediate host prevention, and final host immunization to effectively control JE epidemics.
Porcine circovirus (PCV) is a single-stranded circular DNA virus with four identified genotypes (PCV1 - PCV4) (53). PCV2 is the predominant genotype associated with postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome (PMWS) and reproductive disorders in sows (54). PCV2 infection in sows can result in increased rates of return to estrus, abortion, and stillbirths. Furthermore, PCV2 can be vertically transmitted from the mother to the fetus, causing myocarditis and interstitial pneumonia. In severe cases, fetal mummification and death may occur (55). Epidemiological surveys conducted in Italy (2013–2018) revealed a rising prevalence of PCV2d detection in domestic pigs, with a similar trend observed in wild boars (56).
PCV2 can bind to cellular receptors via its capsid protein. Given the diversity of viral attachment receptors, PCV2 has the ability to infect multiple tissues and organs in pigs. Studies have shown that the likelihood of PCV2 infection varies among different pig breeds, indicating that pig genetics can influence the infectivity of PCV2 in the host (57). PCV2 can penetrate mature oocytes through a compromised zona pellucida and has the capacity to reduce the developmental competence of oocytes (58). In embryos with compromised zona pellucida, PCV2 infection significantly reduces survival rates, with only 6.4% of infected embryos surviving compared to 65.4% of negative controls (59).
Panax notoginseng saponins and arctigenin (ACT) can alleviate oxidative stress in mice infected with PCV2, thereby partially suppressing viral replication (60, 61). These findings offer novel therapeutic perspectives for PCV diseases (PCVD). Commercial PCV2 vaccines currently available include inactivated vaccines (Fostera™ PCV, Circovac®) and subunit vaccines (Porcilis® PCV, Circumvent®, Ingelvac CircoFLEX®) (62).
Classical Swine Fever (CSF), an acute and highly contagious disease caused by Classical Swine Fever Virus (CSFV), poses a significant threat to pig health and the swine industry. CSFV, a single-stranded RNA virus, belongs to the genus Pestivirus within the family Flaviviridae (63).
CSF is endemic in regions of Central and South America, Eastern Europe, Asia, and Africa. While the prevalence of highly virulent CSFV strains has diminished in recent years, infections caused by moderately virulent strains persist. Morbidity can reach 100%, while mortality rates fluctuate according to viral strain virulence (64).
The effects of CSFV on sow reproduction are highly dependent on the gestational stage at which infection occurs. Early gestation infections may cause abortions, stillbirths, or fetal mummification. In contrast, infections during mid-to-late gestation that result in the live birth of persistently infected piglets can induce neurological disorders and growth retardation. CSFV exhibits immunosuppressive properties, causing a significant reduction in white blood cells in infected pigs, with apoptosis primarily occurring in the thymus, spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow (65). Moreover, CSFV can inhibit the host’s antiviral response through activation of the IL-10-STAT1 pathway (66).
Vaccination is a crucial strategy for CSF prevention. However, inactivated whole virus vaccines are neither effective nor available. Live attenuated vaccines (LAV) are extensively used in CSF-endemic regions but cannot distinguish between natural infection and vaccination. Conversely, the E2 subunit vaccine (Porcilis® Pesti) and the chimeric virus vaccine (Suvaxyn CSF Marker) have DIVA (differentiation of infected from vaccinated animals) capabilities, making them appropriate for settings where such differentiation is necessary (67).
Brucellosis is a zoonotic infection caused by the bacterium Brucella spp. (68), with approximately 500,000 new cases resulting from animal-to-human transmission occurring globally each year (69). The prevalence of Brucella in pig herds has been reported worldwide, with the infection rate in Europe being 17.4% (70). In the European Union, North America and Australia, the prevalence of Brucella suis (B. suis) in domestic pigs is lower due to the implementation of eradication programs. However, the risk of pathogen reintroduction in wild pigs persists (71), as shown by the higher prevalence in feral pigs (15.0%) than in domestic pigs (1.1%).
B. suis is currently subdivided into five biovars, with the primary biovars responsible for brucellosis in pigs being biovars 1, 2, and 3 (71). In regions outside of Europe, the main causative agents of swine brucellosis are biovars 1 and 3 (72), whereas in Europe, pigs are mainly infected with biovars 2 (73). Brucella is a facultative intracellular parasitic bacterium capable of evading the host’s innate and adaptive immune responses (74) and resistant to some antibiotics, thereby causing a characteristic pathological manifestation in the infected host. Cellular immunity plays a major role in eradication of the intercellular infection, while serum antibodies can only act against extracellular Brucella spp. Consequently, the immunity produced by immunization with inactivated vaccines is markedly weak. Currently, live attenuated vaccines are the most commonly used worldwide for preventing and controlling swine brucellosis. These include the live B. suis. Vaccine (S2 strain) developed in China, and the live B. abortus vaccine (SRB51 strain) developed in the United States (75, 76). These vaccines can be administered orally, subcutaneously, or intramuscularly to pigs. However, these live vaccines are inadequate for protecting swine against B. suis infection and pose a risk of infection to humans. Furthermore, it is difficult to differentiate between vaccine immunity and natural infection. At present, there are no commercially available vaccines for protecting domestic or feral swine against B. suis infection. Although not a feasible solution in all situations, whole-herd depopulation is the most effective regulatory mechanism for controlling swine brucellosis (71).
Listeriosis is a sporadic infectious disease of humans, livestock, and poultry caused by Listeria monocytogenes. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that there are approximately 1,600 infection cases and 260 deaths related to the disease annually (77). L. monocytogenes can invade various eukaryotic cells, including epithelial cells, fibroblasts and macrophages, among others (78) and disseminate to the placenta, fetus, and neonates, with approximately 14% of clinically confirmed cases occurring during pregnancy. In pigs, infection with L. monocytogenes is primarily associated with the development of meningitis, septicemia, and mononucleosis, as well as abortion in pregnant sows.
Once it has entered enterocytes, L. monocytogenes spreads throughout the body and subsequently crosses the placental and the blood–brain barriers, entering phagocytic and non-phagocytic epithelial cells and proliferating within these cells. Access to specialized phagocytic cells, such as macrophages, is a passive process, and active entry into non-phagocytic cells, such as intestinal cells, fibroblasts, endothelial cells, hepatocytes, and epithelial cells, necessitates the presence of two surface proteins, InlA and InlB (79). There is currently no effective vaccine available to prevent this disease. Treatment with antibiotics is usually needed for the control of the infection caused by Listeriosis (80). The administration of high doses of streptomycin, penicillin, gentamicin, and sulfonamides in pigs at the initial stages of the disease can result in favorable therapeutic outcomes. Nevertheless, treatment of suckling pigs with neurological symptoms often proves ineffective (81). In addition, certain Listeria strains have demonstrated resistance to commonly employed antibiotics (penicillin, gentamicin, and sulfonamides), complicating future control and treatment efforts (82).
Chlamydia is a febrile, chronic, and contact infectious disease caused by Chlamydia infection in pigs. Four species of Chlamydia can infect pigs: Chlamydia suis, C. psittaci (Cps), C. abortus, and C. pecorum (Cpe). The most prevalent form of cross-infection is between C. suis and C. abortus (83). Pregnant sows infected with Chlamydia tend to be asymptomatic, and the disease occurs most frequently in primiparous sows, with abortion rates ranging from 40.0 to 90.0%.
The pathogenic mechanisms of C. abortus and C. suis remain unknown. The infectious elementary body (EB) enters cells to form phagosomes, and Chlamydia’s major outer membrane protein family (MOMP) prevents phagosomes from fusing with lysosomes, thus facilitating the replication of Chlamydia within the phagosome and the destruction of host cells. Additionally, Chlamydia can produce endotoxin-like substances analogous to those produced by Gram-negative bacteria. These substances inhibit host cell metabolism and directly destroy host cells. The infected organism elicits a delayed hypersensitivity reaction, which results in immunopathological damage to tissue cells. Following infection, C. abortus induces the production of cytokines, including IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-4, and IL-10, which can alter the infected cells and result in miscarriage (84). A recent study has demonstrated that host animals infected with C. abortus exhibit gut microbial dysbiosis, which may also contribute to abortion in animals (85).
Chlamydia is a multisymptomatic contact zoonosis that represents a significant public health concern. The implementation of an efficacious vaccination program has the potential to mitigate the morbidity and post-illness severity observed in animal populations while also serving to impede the further regional dissemination of C. abortus and the emergence of antibiotic resistance. Currently, commercial vaccines for swine chlamydiosis are not widely used in the pig industry and are largely confined to laboratory development and preclinical trials. The CPAF protein of Chlamydia trachomatis has recently been shown to be highly immunogenic in pigs (86). An experimental subunit vaccine targeting C. abortus has demonstrated protective immunity in piglets (87). However, the commercial C. abortus 1B vaccine strain for ruminants (Cevac® Chlamydia, Ceva Animal Health Ltd.) may still induce abortions in vaccinated animals, potentially facilitating the spread of C. abortus (88).
Leptospira spp. are spiral-shaped bacteria capable of surviving in diverse environments, particularly in warm and humid conditions (89). These bacteria can infect a wide range of animals, including pigs, and cause various diseases. Transmission occurs through contact with contaminated urine, water, or soil (90). In pigs, the most important serovars associated with reproductive issues include Bratislava, Pomona, and Tarassovi (91). These serovars can induce lesions in the uterus and placenta, impairing fertilization and embryo implantation, ultimately resulting in infertility or reduced conception rates (92, 93).
Leptospira spp. can rapidly enter the bloodstream, causing leptospirosis bacteremia, which induces a robust inflammatory response, leading to tissue damage and organ dysfunction. Additionally, these bacteria can evade the host immune system, resulting in persistent damage. Regular vaccination can effectively reduce the incidence of leptospirosis (94). Furthermore, enhancing the hygiene management of pig pens and preventing contact with contaminated water and soil can significantly lower the risk of transmission (95).
Campylobacteriosis, caused by Campylobacter spp., can significantly affect the reproductive system of sows, with the specific manifestations and severity varying depending on the bacterial strain and the host’s immune status.
Campylobacter is a genus of Gram-negative, spiral-shaped bacteria that are highly motile and obligate microaerophilic (96). The most common species associated with swine are Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni (97, 98). Although, these bacteria primarily colonize the gastrointestinal tract of pigs, their potential to cause reproductive disorders remains less well-documented than their effects on the digestive system.
In sows, Campylobacter infection can cause reproductive tract inflammation, including endometritis and cervicitis (99). Such inflammation can disrupt normal reproductive processes, leading to early embryonic loss, reduced fertility, and prolonged inter-estrus intervals (100). However, the specific pathological changes in the reproductive system of sows due to Campylobacter infection are less well-documented compared to those in cattle.
The pathogenicity of Campylobacter spp. is attributed to several virulence factors, including their ability to adhere to and invade host cells, produce toxins such as cytolethal distending toxin (CDT), and evade the host immune system (101, 102). Their spiral shape and motility facilitate penetration and colonization of mucosal surfaces, including those of the reproductive tract (103). In the context of reproductive disorders, these bacteria can trigger immune responses that cause inflammation and tissue damage, ultimately impairing reproductive function.
Preventing and controlling Campylobacter infections in swine requires a comprehensive approach. Regular monitoring of pig herds for Campylobacter presence facilitates early detection and management of infections. In cases of clinical infection, appropriate antibiotic treatment is essential; however, it should be used judiciously to prevent the development of antibiotic-resistant strains.
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, a Gram-positive bacterium, is the primary etiological agent of swine erysipelas (SE) and can adversely affect sow reproductive performance. The bacterium comprises multiple serotypes, among which types 1a, 1b, and 2 are predominant in causing disease in pigs (104).
Surface proteins of E. rhusiopathiae, including SpaA, promote bacterial adhesion to host cells and recruit host plasminogen, thereby enhancing pathogenicity (105). The pathogenesis of E. rhusiopathiae in sows involves its capacity to induce systemic infections or septicemia, causing inflammation and tissue damage in multiple organs, including the reproductive system (106). The bacterium disseminates through the bloodstream, inducing lesions in the placenta and fetal tissues, which can lead to fetal death and abortion (107). Chronic infections may also result in endocarditis and arthritis, further impairing the sow’s overall health and reproductive performance (108).
Vaccination is essential for controlling erysipelas, with live attenuated vaccines or bacterins being commonly used (109). Pre-farrowing vaccination of sows boosts maternal antibody levels in piglets, offering enhanced protection against the disease.
Toxoplasmosis is a common zoonotic protozoan disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, a parasite that infects animals, including pigs, which is prevalent in China and the United States (110). T. gondii is present in both domestic and wild pigs, with a global prevalence of T. gondii infection in domestic pigs being as high as 30.0% (111, 112). A national survey of boars in the United States (2022) revealed a seropositivity rate of T. gondii of approximately 27.0% (113). A study (2024) conducted in Italy investigating the prevalence of T. gondii IgG positivity in 174 wild boar meat juices collected from forest and peri-urban environments revealed a rate of 22.6% (114). Infection of pregnant sows with T. gondii may result in the transmission of the parasite to the fetus via the placenta, potentially leading to abortion, stillbirth, malformation of the fetus, or underdevelopment of the piglet (115). Toxoplasma cysts can form and persist in the body for a considerable period of time, rendering them difficult to eliminate. Combining sulfonamides with antimicrobial adjuncts has been demonstrated to be a more efficacious treatment. The definitive host of T. gondii, the cat, excretes feces containing infectious oocysts, which, when ingested by pigs, can lead to infection. Therefore, the most effective method of preventing toxoplasmosis in pigs is implementing efficient management strategies for cats.
Developing a toxoplasmosis vaccine is a challenging endeavor, primarily due to the intricate life history of T. gondii, the numerous infection routes, and the formation of cysts to evade the immune response of the host. No commercial vaccine for toxoplasmosis is currently available; however, two vaccine groups developed by the National Veterinary Quarantine Institute of Korea have been reported to be effective in preventing toxoplasmosis (116).
The occurrence of reproductive disorders in sows is attributable to a combination of single and superimposed factors (Figure 4). According to the biosecurity protocols for pig farms, introducing pigs from external sources should be kept to a minimum. It is recommended that non-potable water sources within the farm, including streams, ponds, and open drainage ditches, be treated and disinfected regularly to control the spread of diseases through water (116), as they may contain pathogenic organisms such as Leptospira. Additionally, the prompt removal of manure and feed residues, the maintenance of optimal ventilation within pig houses, and the implementation of appropriate nutritional balance can collectively enhance the pigs’ resistance to disease.
Vaccination represents one of the most efficient and cost-effective methods currently available to prevent reproductive disorders in pigs (Table 3). It is important to consider several factors when developing a comprehensive vaccination program, including the presence of maternal antibodies in sows, the onset age of the disease in pigs, and the season of occurrence. The use of antimicrobial medications for preventive purposes entails a shift in their application from treatment to prevention, thereby reducing the probability of bacterial disease occurrence. Regular blood tests and fecal examinations are recommended for parasitic eggs to ensure proper internal and external parasite control. Furthermore, pigs exhibiting low antibody levels should be promptly administered with booster vaccinations.
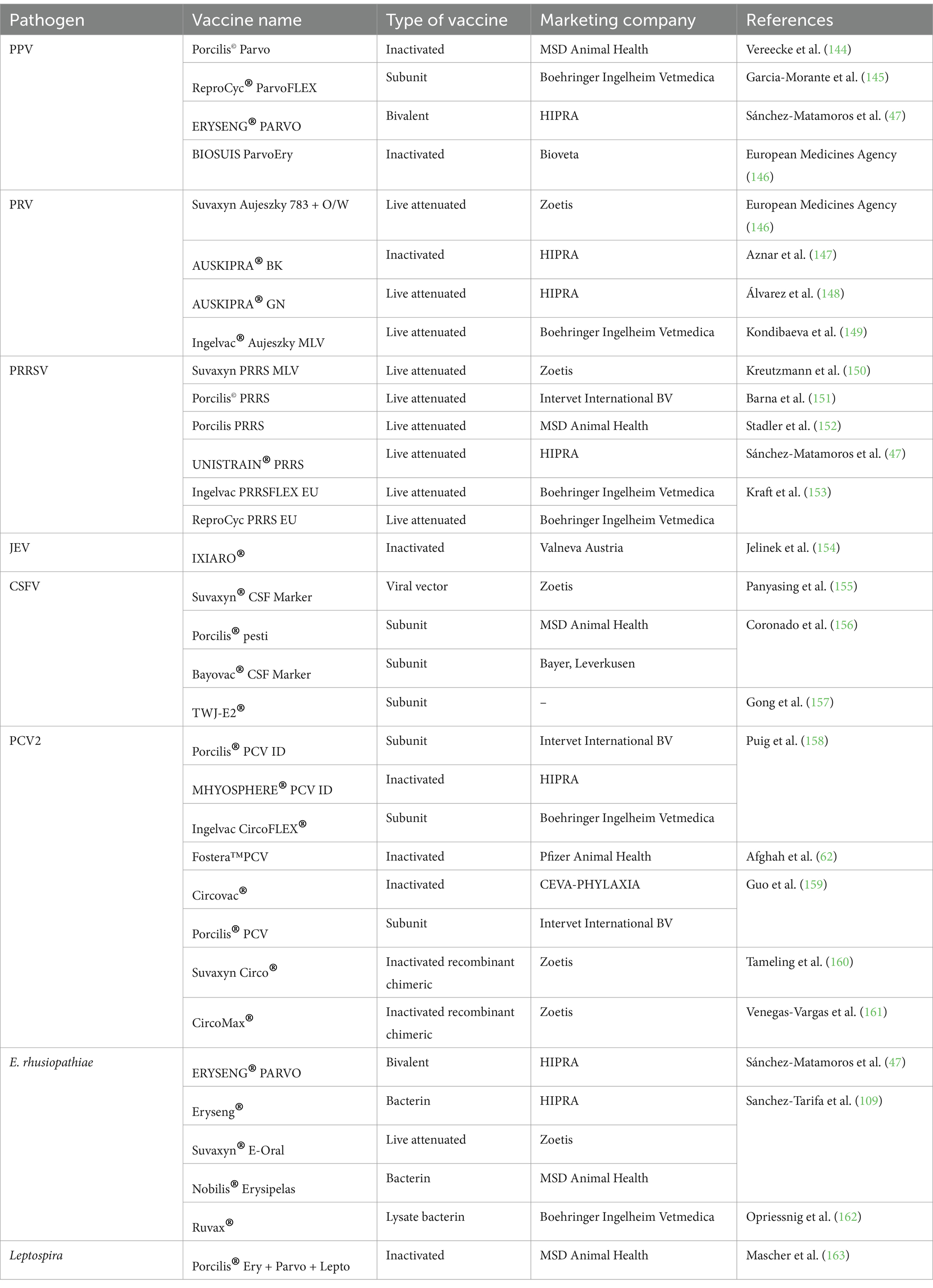
Table 3. Commercial vaccine developed against infectious pathogens involved in sow reproductive disorder.
Other disease vectors, such as rodents, reportedly transmit several bacterial diseases, including salmonellosis, swine erysipelas and leptospirosis (117), as well as several viral diseases, including parvovirus and Japanese encephalitis virus. In addition, insects such as mosquitoes and flies act as vectors for several diseases. It is, therefore, imperative to maintain high hygiene standards and implement effective pest control measures to eradicate insects and rodents within the farm.
Reproductive disorders in sows have always been a major risk factor for pig production, especially those caused by malignant, infectious and zoonotic diseases. It is necessary to monitor the zoonotic pathogens that cause reproductive disorders in sows and understand their interactions with both humans and animal hosts. It is also necessary to consider the effects of environmental perturbations, while implementing the One Health concept to achieve a holistic vision of the health of breeding sows. This concept encompasses not only the pigs, but also the interrelationships between humans, pigs, and other organisms within the agricultural ecosystem. This approach aims to comprehensively understand the health status of all biological organisms on large-scale farms. Therefore, the One Health concept is not only concerned with preventing health crises in pigs, but also closely related to maintaining health, environmental quality and nutritional standards in animal feed. It is reasonable to deduce that the health of both humans and pigs can be enhanced through the One Health approach.
The success of the One Health concept relies on collaborative efforts across multiple sectors, including human and veterinary medicine, as well as environmental and wildlife health. This collaborative approach will help to reduce and prevent future zoonotic disease outbreaks.
YiW: Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YJ: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. YaW: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. YL: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. XW: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This project was supported by the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Key R&D Program (2024BBF02017).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Meat Consumption. OECD. Available online at: https://www.oecd.org/en/data/indicators/meat-consumption.html (Accessed January 22, 2025).
2. FAOSTAT. Available online at: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (Accessed January 22, 2025).
3. Animals. USDA. Available online at https://www.usda.gov/topics/animals (Accessed October 11, 2024).
4. Koketsu, Y, Iida, R, and Piñeiro, C. A 10-year trend in piglet pre-weaning mortality in breeding herds associated with sow herd size and number of piglets born alive. Porcine Health Manag. (2021) 7:4. doi: 10.1186/s40813-020-00182-y
5. Pierozan, CR, Callegari, MA, Dias, CP, de Souza, KL, Gasa, J, and da Silva, CA. Herd-level factors associated with piglet weight at weaning, kilograms of piglets weaned per sow per year and sow feed conversion. Animal. (2020) 14:1283–92. doi: 10.1017/S175173111900346X
6. Eddicks, M, Gründl, J, Seifert, A, Eddicks, L, Reese, S, Tabeling, R, et al. Examination on the occurrence of coinfections in diagnostic transmittals in cases of stillbirth, mummification, embryonic death, and infertility (SMEDI) syndrome in Germany. Microorganisms. (2023) 11:1675. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11071675
7. Maes, D, Peltoniemi, O, and Malik, M. Abortion and fetal death in sows. Reprod Domest Anim. (2023) 58:125–36. doi: 10.1111/rda.14436
8. Oscar. Effects of mycotoxins on sow reproduction and health. MycotoxinSite (2024). Available online at: https://mycotoxinsite.com/effects-mycotoxins-sow-reproduction-health/?lang=en (Accessed February 10, 2025).
9. Malekinejad, H, Schoevers, EJ, Daemen, IJJM, Zijlstra, C, Colenbrander, B, Fink-Gremmels, J, et al. Exposure of oocytes to the fusarium toxins zearalenone and deoxynivalenol causes aneuploidy and abnormal embryo development in pigs. Biol Reprod. (2007) 77:840–7. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.107.062711
10. Waret-Szkuta, A, Larraillet, L, Oswald, IP, Legrand, X, Guerre, P, and Martineau, G-P. Unusual acute neonatal mortality and sow agalactia linked with ergot alkaloid contamination of feed. Porcine Health Manag. (2019) 5:24. doi: 10.1186/s40813-019-0131-z
11. Shin, K-T, Guo, J, Niu, Y-J, and Cui, X-S. The toxic effect of aflatoxin B1 on early porcine embryonic development. Theriogenology. (2018) 118:157–63. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2018.06.002
12. Riesenbeck, A. Review on international trade with boar semen. Reprod Domest Anim. (2011) 46:1–3. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0531.2011.01869.x
13. Maroto Martín, LO, Muñoz, EC, De Cupere, F, Van Driessche, E, Echemendia-Blanco, D, Rodríguez, JMM, et al. Bacterial contamination of boar semen affects the litter size. Anim Reprod Sci. (2010) 120:95–104. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2010.03.008
14. Ciornei Ștefan, G, Drugociu, D, and Roşca, P. Candida genus maximum incidence in boar semen even after preservation, is it not a risk for AI though? Molecules. (2022) 27:7539. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217539
15. Nitsche-Melkus, E, Bortfeldt, R, Jung, M, and Schulze, M. Impact of hygiene on bacterial contamination in extended boar semen: an eight-year retrospective study of 28 European AI centers. Theriogenology. (2020) 146:133–9. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2019.11.031
16. Ciornei, Ş, Drugociu, D, Ciornei, LM, Mareş, M, and Roşca, P. Total Aseptization of boar semen, to increase the biosecurity of reproduction in swine. Molecules. (2021) 26:6183. doi: 10.3390/molecules26206183
17. Mészáros, I, Olasz, F, Cságola, A, Tijssen, P, and Zádori, Z. Biology of porcine parvovirus (ungulate parvovirus 1). Viruses. (2017) 9:393. doi: 10.3390/v9120393
18. Cadar, D, Dán, Á, Tombácz, K, Lőrincz, M, Kiss, T, Becskei, Z, et al. Phylogeny and evolutionary genetics of porcine parvovirus in wild boars. Infect Genet Evol. (2012) 12:1163–71. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2012.04.020
19. Wang, D, Feng, R, Ma, Z, Xie, J, et al. Epidemiological survey of porcine Encephalomyocarditis and porcine parvovirus in different regions of China. Chinese J Vet Med. (2014) 50:43–5. (in Chinese)
20. Tan, X, Luo, Y, Chen, H, Li, J, et al. Serological investigation of PPV in large-scale swine farms of Suining City. Sichuan Anim Vet Sci. (2016) 43:29–30+32. (in Chinese)
21. Kaur, A, Mahajan, V, Leishangthem, GD, Singh, ND, Bhat, P, Banga, HS, et al. Epidemiological and immunopathological studies on porcine parvovirus infection in Punjab. Vet World. (2016) 9:827–31. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2016.827-831
22. Wang, J, and Liu, B. Etiological studies on reproductive disorder syndrome of pigs in Honghe Prefectrue, Yunnan Province. China Anim Health Inspect. (2012) 29:42–5. (in Chinese)
23. Zhang, J, Fan, J, Li, Y, Liang, S, Huo, S, Wang, X, et al. Porcine parvovirus infection causes pig placenta tissue damage involving nonstructural protein 1 (NS1)-induced intrinsic ROS/mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. Viruses. (2019) 11:389. doi: 10.3390/v11040389
24. Zhang, L, Wang, Z, Zhang, J, Luo, X, Du, Q, Chang, L, et al. Porcine parvovirus infection impairs progesterone production in luteal cells through mitogen-activated protein kinases, p53, and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis†. Biol Reprod. (2018) 98:558–69. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioy014
25. Zhang, X, Ma, P, Shao, T, Xiong, Y, Du, Q, Chen, S, et al. Porcine parvovirus triggers autophagy through the AMPK/raptor/mTOR pathway to promote viral replication in porcine placental trophoblasts. Vet Res. (2022) 53:33. doi: 10.1186/s13567-022-01048-7
26. Laval, K, and Enquist, LW. The neuropathic itch caused by pseudorabies virus. Pathogens. (2020) 9:254. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9040254
27. Izzati, UZ, Kaneko, Y, Kaneko, C, Yoshida, A, Suwanruengsri, M, Okabayashi, T, et al. Distribution of pseudorabies virus antigen in hunting dogs with concurrent Paragonimus westermani infection. J Comp Pathol. (2021) 188:44–51. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2021.08.004
28. Zheng, H-H, Jin, Y, Hou, C-Y, Li, X-S, Zhao, L, Wang, Z-Y, et al. Seroprevalence investigation and genetic analysis of pseudorabies virus within pig populations in Henan province of China during 2018-2019. Infect Genet Evol. (2021) 92:104835. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104835
29. Zheng, H-H, Fu, P-F, Chen, H-Y, and Wang, Z-Y. Pseudorabies virus: from pathogenesis to prevention strategies. Viruses. (2022) 14:1638. doi: 10.3390/v14081638
30. Zhang, C, Cui, H, Zhang, W, Meng, L, Chen, L, Wang, Z, et al. Epidemiological investigation of porcine pseudorabies virus in Hebei Province, China, 2017-2018. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:930871. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.930871
31. Papageorgiou, K, Petridou, E, Filioussis, G, Theodoridis, A, Grivas, I, Moschidis, O, et al. Epidemiological investigation of pseudorabies in Greece In: A Theodoridis, A Ragkos, and M Salampasis, editors. Innovative approaches and applications for sustainable rural development. Cham: Springer International Publishing (2019). 103–17.
32. Verpoest, S, Cay, B, Favoreel, H, and De Regge, N. Age-dependent differences in pseudorabies virus Neuropathogenesis and associated cytokine expression. J Virol. (2017) 91:e02058–16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02058-16
33. Van de Walle, GR, Favoreel, HW, Nauwynck, HJ, Mettenleiter, TC, and Pensaert, MB. Transmission of pseudorabies virus from immune-masked blood monocytes to endothelial cells. J Gen Virol. (2003) 84:629–37. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.18796-0
34. Hu, D, Zhang, Z, Lv, L, Xiao, Y, Qu, Y, Ma, H, et al. Outbreak of variant pseudorabies virus in Bartha-K61–vaccinated piglets in Central Shandong Province, China. J Vet Diagn Invest. (2015) 27:600–5. doi: 10.1177/1040638715593599
35. Sun, Y, Luo, Y, Wang, C-H, Yuan, J, Li, N, Song, K, et al. Control of swine pseudorabies in China: opportunities and limitations. Vet Microbiol. (2016) 183:119–24. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.12.008
36. Cong, X, Lei, J-L, Xia, S-L, Wang, Y-M, Li, Y, Li, S, et al. Pathogenicity and immunogenicity of a gE/gI/TK gene-deleted pseudorabies virus variant in susceptible animals. Vet Microbiol. (2016) 182:170–7. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2015.11.022
37. Zhao, Y, Wang, L-Q, Zheng, H-H, Yang, Y-R, Liu, F, Zheng, L-L, et al. Construction and immunogenicity of a gE/gI/TK-deleted PRV based on porcine pseudorabies virus variant. Mol Cell Probes. (2020) 53:101605. doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2020.101605
38. Chen, X, Song, X, Li, L, Chen, Y, Jia, R, Zou, Y, et al. Resveratrol inhibits pseudorabies virus replication by targeting IE180 protein. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:891978. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.891978
39. Zhao, X, Cui, Q, Fu, Q, Song, X, Jia, R, Yang, Y, et al. Antiviral properties of resveratrol against pseudorabies virus are associated with the inhibition of IκB kinase activation. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:8782. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09365-0
40. Rahe, MC, and Murtaugh, MP. Mechanisms of adaptive immunity to porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Viruses. (2017) 9:148. doi: 10.3390/v9060148
41. Weesendorp, E, Morgan, S, Stockhofe-Zurwieden, N, Graaf, DJP-D, Graham, SP, and Rebel, JMJ. Comparative analysis of immune responses following experimental infection of pigs with European porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus strains of differing virulence. Vet Microbiol. (2013) 163:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.09.013
42. Wang, X, Eaton, M, Mayer, M, Li, H, He, D, Nelson, E, et al. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus productively infects monocyte-derived dendritic cells and compromises their antigen-presenting ability. Arch Virol. (2007) 152:289–303. doi: 10.1007/s00705-006-0857-1
43. Rodríguez-Gómez, IM, Gómez-Laguna, J, and Carrasco, L. Impact of PRRSV on activation and viability of antigen presenting cells. World J Virol. (2013) 2:146–51. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v2.i4.146
44. Lunney, JK, Fang, Y, Ladinig, A, Chen, N, Li, Y, Rowland, B, et al. Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV): pathogenesis and interaction with the immune system. Annu Rev Anim Biosci. (2016) 4:129–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev-animal-022114-111025
45. Novakovic, P, Detmer, SE, Suleman, M, Malgarin, CM, MacPhee, DJ, and Harding, JCS. Histologic changes associated with placental separation in gilts infected with porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Vet Pathol. (2018) 55:521–30. doi: 10.1177/0300985818765067
46. Barrera-Zarate, JA, Detmer, SE, Pasternak, JA, Hamonic, G, MacPhee, DJ, and Harding, JCS. Effect of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus 2 on angiogenesis and cell proliferation at the maternal-fetal interface. Vet Pathol. (2022) 59:940–9. doi: 10.1177/03009858221105053
47. Sánchez-Matamoros, A, Camprodon, A, Maldonado, J, Pedrazuela, R, and Miranda, J. Safety and long-lasting immunity of the combined administration of a modified-live virus vaccine against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus 1 and an inactivated vaccine against porcine parvovirus and Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae in breeding pigs. Porcine Health Manag. (2019) 5:11. doi: 10.1186/s40813-019-0118-9
48. Hazra, B, Chakraborty, S, and Basu, A. miR-301a mediated immune evasion by Japanese encephalitis virus. Oncotarget. (2017) 8:90620–1. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.21674
49. Kumar, A, Sharma, P, Shukla, KK, Misra, S, and Nyati, KK. Japanese encephalitis virus: associated immune response and recent progress in vaccine development. Microb Pathog. (2019) 136:103678. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103678
50. Thongtan, T, Cheepsunthorn, P, Chaiworakul, V, Rattanarungsan, C, Wikan, N, and Smith, DR. Highly permissive infection of microglial cells by Japanese encephalitis virus: a possible role as a viral reservoir. Microbes Infect. (2010) 12:37–45. doi: 10.1016/j.micinf.2009.09.013
51. Tandan, JB, Ohrr, H, Sohn, YM, Yoksan, S, Ji, M, Nam, CM, et al. Single dose of SA 14-14-2 vaccine provides long-term protection against Japanese encephalitis: a case–control study in Nepalese children 5 years after immunization. Vaccine. (2007) 25:5041–5. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.04.052
52. Heffelfinger, JD, Li, X, Batmunkh, N, Grabovac, V, Diorditsa, S, Liyanage, JB, et al. Japanese encephalitis surveillance and immunization - Asia and Western Pacific regions, 2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. (2017) 66:579–83. doi: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6622a3
53. Yan, Y, and Sun, Y. Genotypic diversity and immunological implications of porcine circovirus: inspiration from PCV1 to PCV4. Microb Pathog. (2024) 196:106997. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2024.106997
54. Franzo, G, and Segalés, J. Porcine circovirus 2 genotypes, immunity and vaccines: multiple genotypes but one single serotype. Pathogens. (2020) 9:1049. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9121049
55. Segalés, J. Porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) infections: clinical signs, pathology and laboratory diagnosis. Virus Res. (2012) 164:10–9. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2011.10.007
56. Franzo, G, Tinello, S, Grassi, L, Tucciarone, CM, Legnardi, M, Cecchinato, M, et al. Free to circulate: an update on the epidemiological dynamics of porcine circovirus 2 (PCV-2) in Italy reveals the role of local spreading, wild populations, and foreign countries. Pathogens. (2020) 9:221. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9030221
57. Meng, X-J. Porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2): pathogenesis and interaction with the immune system. Ann Rev Anim Biosci. (2013) 1:43–64. doi: 10.1146/annurev-animal-031412-103720
58. Zhao, H, Ji, Q, Zhao, G, Song, Z, Du, B, Nie, Y, et al. Damage of zona pellucida reduces the developmental potential and quality of porcine circovirus type 2-infected oocytes after parthenogenetic activation. Theriogenology. (2014) 82:790–9. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2014.06.003
59. Mateusen, B, Maes, DGD, Van Soom, A, Lefebvre, D, and Nauwynck, HJ. Effect of a porcine circovirus type 2 infection on embryos during early pregnancy. Theriogenology. (2007) 68:896–901. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2007.07.014
60. Wu, L, Chen, J, Zhou, D, Chen, R, Chen, X, Shao, Z, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of arctigenin against PCV2 infection in a mouse model. Vet Med Sci. (2022) 8:700–9. doi: 10.1002/vms3.693
61. Cao, M-X, Wang, X-R, Hu, W-Y, Yin, D, Ren, C-Z, Chen, S-Y, et al. Regulatory effect of Panax notoginseng saponins on the oxidative stress and histone acetylation induced by porcine circovirus type 2. J Vet Med Sci. (2022) 84:600–9. doi: 10.1292/jvms.21-0126
62. Afghah, Z, Webb, B, Meng, X-J, and Ramamoorthy, S. Ten years of PCV2 vaccines and vaccination: is eradication a possibility? Vet Microbiol. (2017) 206:21–8. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.10.002
63. Ganges, L, Crooke, HR, Bohórquez, JA, Postel, A, Sakoda, Y, Becher, P, et al. Classical swine fever virus: the past, present and future. Virus Res. (2020) 289:198151. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198151
64. sop_csf_e-e.pdf. Available online at: https://www.aphis.usda.gov/sites/default/files/sop_csf_e-e.pdf (Accessed February 3, 2025).
65. Belák, K, Koenen, F, Vanderhallen, H, Mittelholzer, C, Feliziani, F, De Mia, GM, et al. Comparative studies on the pathogenicity and tissue distribution of three virulence variants of classical swine fever virus, two field isolates and one vaccine strain, with special regard to immunohistochemical investigations. Acta Vet Scand. (2008) 50:34. doi: 10.1186/1751-0147-50-34
66. Zhang, L, Liang, D, Tian, Y, Liang, J, Li, X, Liu, C, et al. Classical swine fever virus envelope glycoproteins erns, E1, and E2 activate IL-10-STAT1-MX1/OAS1 antiviral pathway via replacing classical IFNα/β. Biomol Ther. (2025) 15:200. doi: 10.3390/biom15020200
67. Fad-prep-nahems-appendix-b-classical-swine-fever.Pdf. Available online at: https://www.cfsph.iastate.edu/pdf/fad-prep-nahems-appendix-b-classical-swine-fever (Accessed February 3, 2025).
68. Yan, X, Hu, S, Yang, Y, Xu, D, Li, H, Liu, W, et al. The twin-arginine translocation system is important for stress resistance and virulence of Brucella melitensis. Infect Immun. (2020) 88:e00389–20. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00389-20
69. Bundle, DR, and McGiven, J. Brucellosis: improved diagnostics and vaccine insights from synthetic Glycans. Acc Chem Res. (2017) 50:2958–67. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00445
70. Gong, Q-L, Sun, Y-H, Yang, Y, Zhao, B, Wang, Q, Li, J-M, et al. Global comprehensive literature review and Meta-analysis of Brucella spp. in swine based on publications from 2000 to 2020. Front Vet Sci. (2021) 8:630960. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.630960
71. Olsen, SC, and Tatum, FM. Swine brucellosis: current perspectives. Vet Med (Auckland, NZ). (2017) 8:1–12. doi: 10.2147/VMRR.S91360
72. Lucero, NE, Ayala, SM, Escobar, GI, and Jacob, NR. Brucella isolated in humans and animals in Latin America from 1968 to 2006. Epidemiol Infect. (2008) 136:496–503. doi: 10.1017/S0950268807008795
73. Abril, C, Thomann, A, Brodard, I, Wu, N, Ryser-Degiorgis, M-P, Frey, J, et al. A novel isolation method of Brucella species and molecular tracking of Brucella suis biovar 2 in domestic and wild animals. Vet Microbiol. (2011) 150:405–10. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.02.056
74. Martirosyan, A, and Gorvel, J-P. Brucella evasion of adaptive immunity. Future Microbiol. (2013) 8:147–54. doi: 10.2217/fmb.12.140
75. Deqiu, S, Donglou, X, and Jiming, Y. Epidemiology and control of brucellosis in China. Vet Microbiol. (2002) 90:165–82. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(02)00252-3
76. Edmonds, MD, Samartino, LE, Hoyt, PG, Hagius, SD, Walker, JV, Enright, FM, et al. Oral vaccination of sexually mature pigs with Brucella abortus vaccine strain RB51. Am J Vet Res. (2001) 62:1328–11. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.2001.62.1328
77. Morrison, HA, Lowe, D, Robbins, JR, and Bakardjiev, AI. In vivo virulence characterization of pregnancy-associated Listeria monocytogenes infections. Infect Immun. (2018) 86:e00397–18. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00397-18
78. Freitag, NE, Rong, L, and Portnoy, DA. Regulation of the prfA transcriptional activator of Listeria monocytogenes: multiple promoter elements contribute to intracellular growth and cell-to-cell spread. Infect Immun. (1993) 61:2537–44. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.6.2537-2544.1993
79. Wadhwa Desai, R, and Smith, MA. Pregnancy-related listeriosis. Birth Defects Res. (2017) 109:324–35. doi: 10.1002/bdr2.1012
80. Rugna, G, Carra, E, Bergamini, F, Franzini, G, Faccini, S, Gattuso, A, et al. Distribution, virulence, genotypic characteristics and antibiotic resistance of Listeria monocytogenes isolated over one-year monitoring from two pig slaughterhouses and processing plants and their fresh hams. Int J Food Microbiol. (2021) 336:108912. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108912
81. Xu, X, Shan, Y, Cen, Y, Zhao, J, Yang, X, Liu, R, et al. Clinical characteristics and treatment of Listeria monocytogenes infections in the central nervous system. Infect Drug Resist. (2023) 16:5899–909. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S424012
82. Sosnowski, M, Lachtara, B, Wieczorek, K, and Osek, J. Antimicrobial resistance and genotypic characteristics of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from food in Poland. Int J Food Microbiol. (2019) 289:1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.08.029
83. Schautteet, K, and Vanrompay, D. Chlamydiaceae infections in pig. Vet Res. (2011) 42:29. doi: 10.1186/1297-9716-42-29
84. Häcker, G. Chlamydia in pigs: intriguing bacteria associated with sub-clinical carriage and clinical disease, and with zoonotic potential. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2024) 12:1301892. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1301892
85. Jin, Y, Li, W, Ba, X, Li, Y, Wang, Y, Zhang, H, et al. Gut microbiota changes in horses with Chlamydia. BMC Microbiol. (2023) 23:246. doi: 10.1186/s12866-023-02986-8
86. Proctor, J, Stadler, M, Cortes, LM, Brodsky, D, Poisson, L, Gerdts, V, et al. A TriAdj-Adjuvanted Chlamydia trachomatis CPAF protein vaccine is highly immunogenic in pigs. Vaccines (Basel). (2024) 12:423. doi: 10.3390/vaccines12040423
87. Ou, C, Tian, D, Ling, Y, Pan, Q, He, Q, Eko, FO, et al. Evaluation of an ompA-based phage-mediated DNA vaccine against Chlamydia abortus in piglets. Int Immunopharmacol. (2013) 16:505–10. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.04.027
88. Caspe, SG, Livingstone, M, Frew, D, Aitchison, K, Wattegedera, SR, Entrican, G, et al. The 1B vaccine strain of Chlamydia abortus produces placental pathology indistinguishable from a wild type infection. PLoS One. (2020) 15:e0242526. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242526
89. Bradley, EA, and Lockaby, G. Leptospirosis and the environment: a review and future directions. Pathogens. (2023) 12:1167. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12091167
90. Santos, GFD, Petri, FAM, Pires, GP, Panneitz, AK, Braga, ER, Malcher, CS, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of Leptospira spp. infection in backyard pigs in the state of Paraná, Brazil. Trop Med Infect Dis. (2023) 8:468. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed8100468
91. Leptospirosis. Global swine. Available online at: https://www.msd-animal-health-swine.com/diseases-solutions/sowcare/leptospirosis/ (Accessed February 7, 2025).
92. Gomes de Araújo, H, Limeira, CH, Ferreira, V, de Aquino, V, Longo Ribeiro Vilela, V, José Alves, C, et al. Global Seropositivity of swine leptospirosis: systematic review and Meta-analysis. Trop Med Infect Dis. (2023) 8:158. doi: 10.3390/tropicalmed8030158
93. Steinrigl, A, Willixhofer, D, Schindler, M, Richter, S, Unterweger, C, Ahmed, AA, et al. Isolation and characterization of Leptospira licerasiae in Austrian swine - a first-time case report in Europe. BMC Vet Res. (2024) 20:348. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04213-6
94. Regassa, AG, and Obsu, LL. The role of asymptomatic cattle for leptospirosis dynamics in a herd with imperfect vaccination. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:23775. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72613-7
95. Sun, A-H, Liu, X-X, and Yan, J. Leptospirosis is an invasive infectious and systemic inflammatory disease. Biom J. (2020) 43:24–31. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2019.12.002
96. Sm, M. The clinical importance of emerging Campylobacter species. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2011) 8:669–85. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2011.191
97. Bui, XT, Wolff, A, Madsen, M, and Bang, DD. Fate and survival of Campylobacter coli in swine manure at various temperatures. Front Microbiol. (2011) 2:262. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2011.00262
98. Sithole, V, Amoako, DG, Abia, ALK, Perrett, K, Bester, LA, and Essack, SY. Occurrence, antimicrobial resistance, and molecular characterization of Campylobacter spp. in intensive pig production in South Africa. Pathogens. (2021) 10:439. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10040439
99. Givens, MD, and Marley, MSD. Infectious causes of embryonic and fetal mortality. Theriogenology. (2008) 70:270–85. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2008.04.018
100. Muriel, A. Bovine genital Campylobacteriosis: understanding the impact, diagnosis, and control measures. J Vet Med Surg. (2023) 7:40–16. doi: 10.36648/2574-2868.7.4.33
101. Tion, MT, Ogbu, KI, Shima, FK, Tion, MT, Ogbu, KI, and Shima, FK. Campylobacter: virulence factors and pathogenesis In: Recent Advances in Bacterial Biofilm Studies - Formation, Regulation, and Eradication in Human Infections : IntechOpen (2024)
102. Lai, C-K, Chen, Y-A, Lin, C-J, Lin, H-J, Kao, M-C, Huang, M-Z, et al. Molecular mechanisms and potential clinical applications of Campylobacter jejuni Cytolethal distending toxin. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2016) 6:9. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2016.00009
103. Campylobacteriosis. CFSPH. Available online at: https://www.cfsph.iastate.edu/diseaseinfo/disease/ (Accessed February 5, 2025).
104. McNeil, M, Gerber, PF, Thomson, J, Williamson, S, and Opriessnig, T. Serotypes and Spa types of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae isolates from British pigs (1987 to 2015). Vet J. (2017) 225:13–5. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2017.04.012
105. Zhu, W, Wang, Y, Cai, C, Li, J, Wu, C, Kang, C, et al. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae recruits host plasminogen via the major protective antigen SpaA. FEMS Microbiol Lett. (2017) 364. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fnx036
106. Pozzi, P, and Loris, A. Reproductive diseases in sows (Sus scrofa domestica): a review. Israel J Vet Med. (2012) 67:24–33.
107. Wang, Q, Chang, BJ, and Riley, TV. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae. Vet Microbiol. (2010) 140:405–17. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2009.08.012
108. Gorby, GL, and Peacock, JE Jr. Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae endocarditis: microbiologic, epidemiologic, and clinical features of an occupational disease. Rev Infect Dis. (1988) 10:317–25. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.2.317
109. Sanchez-Tarifa, E, Alonso, C, Perez, I, García, LA, Fernández-Fontelo, A, Gómez-Duran, O, et al. A field comparison study of two vaccine protocols against Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae in two types of swine breeds in Spain. BMC Vet Res. (2024) 20:461. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-04065-0
110. Dubey, JP, Cerqueira-Cézar, CK, Murata, FHA, Kwok, OCH, Hill, D, Yang, Y, et al. All about toxoplasma gondii infections in pigs: 2009-2020. Vet Parasitol. (2020) 288:109185. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2020.109185
111. Limon, G, Beauvais, W, Dadios, N, Villena, I, Cockle, C, Blaga, R, et al. Cross-sectional study of toxoplasma gondii infection in pig farms in England. Foodborne Pathog Dis. (2017) 14:269–81. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2016.2197
112. Foroutan, M, Fakhri, Y, Riahi, SM, Ebrahimpour, S, Namroodi, S, Taghipour, A, et al. The global seroprevalence of toxoplasma gondii in pigs: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Vet Parasitol. (2019) 269:42–52. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2019.04.012
113. Dubey, JP, Cerqueira-Cézar, CK, Murata, FHA, Verma, SK, Kwok, OCH, Pedersen, K, et al. Genotyping of viable toxoplasma gondii from the first national survey of feral swine revealed evidence for sylvatic transmission cycle, and presence of highly virulent parasite genotypes. Parasitology. (2020) 147:295–302. doi: 10.1017/S0031182019001586
114. Dini, FM, Musto, C, De Nigris, VM, Bellinello, E, Sampieri, M, Merialdi, G, et al. Sero-epidemiological investigation on toxoplasma gondii infection in Apennine wolf (Canis lupus italicus) and wild boar (Sus scrofa) in Italy. BMC Vet Res. (2024) 20:62. doi: 10.1186/s12917-024-03922-2
115. McAllister, MM. A decade of discoveries in veterinary protozoology changes our concept of “subclinical” toxoplasmosis. Vet Parasitol. (2005) 132:241–7. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2005.07.003
116. Choi, WH, and Park, JS. Immunogenicity and protective effect of a virus-like particle containing the SAG1 antigen of toxoplasma gondii as a potential vaccine candidate for toxoplasmosis. Biomedicines. (2020) 8:91. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8040091
117. López-Osorio, S, Molano, DA, López-Arias, A, Rodríguez-Osorio, N, Zambrano, C, and Chaparro-Gutiérrez, JJ. Seroprevalence and molecular characterization of Leptospira spp. in rats captured near pig farms in Colombia. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19:11539. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191811539
118. Robbins, LA. Into the comfort zone: Understanding swine thermal preference. [thesis] Purdue University Graduate School (2021).
119. Muns, R, Malmkvist, J, Larsen, MLV, Sørensen, D, and Pedersen, LJ. High environmental temperature around farrowing induced heat stress in crated sows. J Anim Sci. (2016) 94:377–84. doi: 10.2527/jas.2015-9623
120. Zhang, W, Heng, J, Kim, SW, Chen, F, Deng, Z, Zhang, S, et al. Corrigendum to “dietary enzymatically-treated Artemisia annua L. supplementation could alleviate oxidative injury and improve reproductive performance of sows reared under high ambient temperature”. J Therm Biol. (2021) 100:103035. doi: 10.1016/j.jtherbio.2021.103035
121. Omtvedt, IT, Nelson, RE, Edwards, RL, Stephens, DF, and Turman, EJ. Influence of heat stress during early, mid and late pregnancy of gilts. J Anim Sci. (1971) 32:312–7. doi: 10.2527/jas1971.322312x
122. Ma, H, Xie, Y, Li, A, Zhang, T, Liu, Y, and Luo, X. A review on the effect of light-thermal-humidity environment in sow houses on sow reproduction and welfare. Reproduction in domestic animals =. Zuchthygiene. (2023) 58:1023–45. doi: 10.1111/rda.14400
123. Wenke, C, Pospiech, J, Reutter, T, Altmann, B, Truyen, U, and Speck, S. Impact of different supply air and recirculating air filtration systems on stable climate, animal health, and performance of fattening pigs in a commercial pig farm. PLoS One. (2018) 13:e0194641. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194641
124. Pejsak, Z, Zmudzki, J, and Wojnicki, P. Abortion in sows associated with carbon monoxide intoxication. Vet Rec. (2008) 162:417. doi: 10.1136/vr.162.13.417
125. Yang, X, Liu, P, Cui, Y, Xiao, B, Liu, M, Song, M, et al. Review of the reproductive toxicity of T-2 toxin. J Agric Food Chem. (2020) 68:727–34. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b07880
126. Meng, L, Coleman, V, Zhao, Y, Ost, M, Voigt, A, Bunschoten, A, et al. Pseudo-starvation driven energy expenditure negatively affects ovarian follicle development. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:3557. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073557
127. Fang, LH, Jin, YH, Jeong, JH, Hong, JS, Chung, WL, and Kim, YY. Effects of dietary energy and protein levels on reproductive performance in gestating sows and growth of their progeny. J Anim Sci Technol. (2019) 61:154–62. doi: 10.5187/jast.2019.61.3.154
128. Gu, F, Hou, L, Gao, K, Wen, X, Mi, S, Qin, G, et al. Effects of dietary net energy concentration on reproductive performance, immune function, Milk composition, and gut microbiota in Primiparous lactating sows. Animals. (2024) 14:3044. doi: 10.3390/ani14203044
129. Pinelli-Saavedra, A. Vitamin E in immunity and reproductive performance in pigs. Reprod Nutr Dev. (2003) 43:397–408. doi: 10.1051/rnd:2003034
130. Al Balawi, AN, Alblwi, NAN, Soliman, R, El-Far, AH, Hassan, MG, El-Sewedy, T, et al. Impact of vitamin D deficiency on immunological and metabolic responses in women with recurrent pregnancy loss: focus on VDBP/HLA-G1/CTLA-4/ENTPD1/adenosine-fetal-maternal conflict crosstalk. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. (2024) 24:709. doi: 10.1186/s12884-024-06914-0
131. McCauley, ME, van den Broek, N, Dou, L, and Othman, M. Vitamin a supplementation during pregnancy for maternal and newborn outcomes. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2015) 2016:CD008666. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008666.pub3
132. Surai, PF, and Fisinin, VI. Selenium in sow nutrition. Anim Feed Sci Technol. (2016) 211:18–30. doi: 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2015.11.006
133. Duffy, R, Yin, M, and Redding, LE. A review of the impact of dietary zinc on livestock health. J Trace Elements Miner. (2023) 5:100085. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemin.2023.100085
134. Liu, W-J, Li, L-S, Lan, M-F, Shang, J-Z, Zhang, J-X, Xiong, W-J, et al. Zinc deficiency deteriorates ovarian follicle development and function by inhibiting mitochondrial function. J Ovarian Res. (2024) 17:115. doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01442-z
135. Zang, J, Chen, J, Tian, J, Wang, A, Liu, H, Hu, S, et al. Effects of magnesium on the performance of sows and their piglets. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. (2014) 5:39. doi: 10.1186/2049-1891-5-39
136. Guo, Y, Zhang, G, Yuan, J, and Nie, W. Effects of source and level of magnesium and vitamin E on prevention of hepatic peroxidation and oxidative deterioration of broiler meat. Anim Feed Sci Technol. (2003) 107:143–50. doi: 10.1016/S0377-8401(03)00116-0
137. Halliwell, B. The wanderings of a free radical. Free Radic Biol Med. (2009) 46:531–42. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.11.008
138. Gao, D, Cao, X, Ren, H, Wu, L, Yan, Y, Hua, R, et al. Immunotoxicity and uterine transcriptome analysis of the effect of zearalenone (ZEA) in sows during the embryo attachment period. Toxicol Lett. (2022) 357:33–42. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2021.12.017
139. Zhou, J, Zhao, L, Huang, S, Liu, Q, Ao, X, Lei, Y, et al. Zearalenone toxicosis on reproduction as estrogen receptor selective modulator and alleviation of zearalenone biodegradative agent in pregnant sows. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. (2022) 13:36. doi: 10.1186/s40104-022-00686-3
140. Bertoldo, MJ, Holyoake, PK, Evans, G, and Grupen, CG. Seasonal variation in the ovarian function of sows. Reprod Fertil Dev. (2012) 24:822–34. doi: 10.1071/RD11249
141. Peltoniemi, O, Björkman, S, and Maes, D. Reproduction of group-housed sows. Porcine Health Manag. (2016) 2:15. doi: 10.1186/s40813-016-0033-2
142. Einarsson, S, Brandt, Y, Lundeheim, N, and Madej, A. Stress and its influence on reproduction in pigs: a review. Acta Vet Scand. (2008) 50:48. doi: 10.1186/1751-0147-50-48
143. Spoolder, HAM, Geudeke, MJ, Van der Peet-Schwering, CMC, and Soede, NM. Group housing of sows in early pregnancy: a review of success and risk factors. Livest Sci. (2009) 125:1–14. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2009.03.009
144. Vereecke, N, Kvisgaard, LK, Baele, G, Boone, C, Kunze, M, Larsen, LE, et al. Molecular epidemiology of porcine parvovirus type 1 (PPV1) and the reactivity of vaccine-induced antisera against historical and current PPV1 strains. Virus Evol. (2022) 8:veac053. doi: 10.1093/ve/veac053
145. Garcia-Morante, B, Noguera, M, Klocke, S, Sommer, K, and Bridger, P. Duration of immunity against heterologous porcine parvovirus 1 challenge in gilts immunized with a novel subunit vaccine based on the viral protein 2. BMC Vet Res. (2020) 16:184. doi: 10.1186/s12917-020-02394-4
146. European Medicines Agency. European public assessment reports: background and context. (2012). Available online at: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/what-we-publish-medicines-and-when/european-public-assessment-reports-background-and-context (Accessed September 17, 2024).
147. Aznar, MN, Bessone, FA, Segurado, R, and Duffy, SJ. Assessment of an Aujeszky’s disease control strategy in a highly prevalent pig farm based on systematic vaccination with an inactivated gE-negative marker vaccine. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:852650. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.852650
148. Álvarez, E, Prieto, C, Martínez-Lobo, FJ, and Castro, JM. Biological characterization of a recombinant pseudorabies virus. Span J Agric Res. (2008) 6:521–30. doi: 10.5424/sjar/2008064-346
149. Kondibaeva, ZB, Yespembetov, BA, Abeuov, KB, Mussayeva, AK, Siyabekov, ST, Nussupova, ST, et al. Inactivated vaccine against Aujeszky’s disease. Vet World. (2021) 14:2957–63. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2021.2957-2963
150. Kreutzmann, H, Dürlinger, S, Knecht, C, Koch, M, Cabana, M, Torrent, G, et al. Efficacy of a modified live virus vaccine against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus 1 (PRRSV-1) administered to 1-day-old piglets in front of heterologous PRRSV-1 challenge. Pathogens (Basel, Switzerland). (2021) 10:1342. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10101342
151. Barna, T, Milovanović, A, Apić, J, and Gvozdić, D. Uticaj vakcine Porcilis PRRS na kvalitet sperme nerastova – Prikaz slučaja. Zbornik predavanja - 10 Naučni simpozijum “Reprodukcija domaćih životinja i bolesti mlečne žlezde”, 10-1310 2019, Divčibare (2019). Available online at: https://repo.niv.ns.ac.rs/xmlui/handle/123456789/169 (Accessed September 12, 2024).
152. Stadler, J, Naderer, L, Beffort, L, Ritzmann, M, Emrich, D, Hermanns, W, et al. Safety and immune responses after intradermal application of Porcilis PRRS in either the neck or the perianal region. PLoS One. (2018) 13:e0203560. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203560
153. Kraft, C, Hennies, R, Dreckmann, K, Noguera, M, Rathkjen, PH, Gassel, M, et al. Evaluation of PRRSv specific, maternally derived and induced immune response in Ingelvac PRRSFLEX EU vaccinated piglets in the presence of maternally transferred immunity. PLoS One. (2019) 14:e0223060. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0223060
154. Jelinek, T, Cromer, MA, Cramer, JP, Mills, DJ, Lessans, K, Gherardin, AW, et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an inactivated Vero cell_derived Japanese encephalitis vaccine (IXIARO®, JESPECT®) in a pediatric population in JE non-endemic countries: an uncontrolled, open-label phase 3 study. Travel Med Infect Dis. (2018) 22:18–24. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2018.03.003
155. Panyasing, Y, Gimenez-Lirola, L, Thanawongnuwech, R, Prakobsuk, P, Kawilaphan, Y, Kittawornrat, A, et al. Performance of a differentiation of infected from vaccinated animals (DIVA) classical swine fever virus (CSFV) serum and Oral fluid erns antibody AlphaLISA assay. Animals. (2023) 13:3802. doi: 10.3390/ani13243802
156. Coronado, L, Perera, CL, Rios, L, Frías, MT, and Pérez, LJ. A critical review about different vaccines against classical swine fever virus and their repercussions in endemic regions. Vaccines (Basel). (2021) 9:154. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9020154
157. Gong, W, Li, J, Wang, Z, Sun, J, Mi, S, Xu, J, et al. Commercial E2 subunit vaccine provides full protection to pigs against lethal challenge with 4 strains of classical swine fever virus genotype 2. Vet Microbiol. (2019) 237:108403. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2019.108403
158. Puig, A, Bernal, I, Sabaté, D, Ballarà, I, Montané, J, Nodar, L, et al. Comparison of effects of a single dose of MHYOSPHERE® PCV ID with three commercial porcine vaccine associations against Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae (Mhyo) and porcine circovirus type 2 (PCV2) on piglet growth during the nursery period under field conditions. Vet Res Commun. (2022) 46:1167–73. doi: 10.1007/s11259-022-09971-y
159. Guo, J, Hou, L, Zhou, J, Wang, D, Cui, Y, Feng, X, et al. Porcine circovirus type 2 vaccines: commercial application and research advances. Viruses. (2022) 14:2005. doi: 10.3390/v14092005
160. Tameling, A, Könighoff, P, Beilage, EG, Menrath, A, Heimann, M, Köhrmann, A, et al. Performance parameters and pathogen detection in pig groups differently vaccinated with respect to porcine circovirus type 2 and Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae. Tierarztl Prax Ausg G Grosstiere Nutztiere. (2022) 50:21–9. doi: 10.1055/a-1696-1578
161. Venegas-Vargas, C, Taylor, LP, Foss, DL, Godbee, TK, Philip, R, and Bandrick, M. Cellular and humoral immunity following vaccination with two different PCV2 vaccines (containing PCV2a or PCV2a/PCV2b) and challenge with virulent PCV2d. Vaccine. (2021) 39:5615–25. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2021.08.013
162. Opriessnig, T, Forde, T, and Shimoji, Y. Erysipelothrix Spp.: past, present, and future directions in vaccine research. Front Vet Sci. (2020) 7:174. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00174
163. Mascher, S, Mück, S, Pausenberger, A, Ullerich, A, and Strutzberg-Minder, K. MAT seroconversion in sows after leptospirosis basic vaccination. Prakt Tierarzt. (2023) 104:1100–15. doi: 10.2376/0032-681X-2333
CPI– Consumer price index
SMEDI– Stillbirths, mummification, embryonic death, and infertility
PPV– Porcine parvovirus
PRV– Pseudorabies virus
Cps– Chlamydophila psittaci
ROS– Reactive oxygen species
StAR– Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein
3β-HSD– 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
P450scc– P450 cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme
PR– Porcine pseudorabies
EC– Endothelial cell
PRRS– Porcine respiratory and reproductive syndrome
PRRSV– Porcine respiratory and reproductive syndrome virus
DCs– Dendritic cells
IFN-α– interferon-α
TNF-α– Tumor necrosis factor-α
MHC– Major histocompatibility complex
VEGF– Vascular endothelial growth factor
APCs– Antigen presenting cells
JEV– Japanese encephalitis virus
JE– Japanese encephalitis
WHO– World Health Organization
PCV– Porcine circovirus
ACT– Arctigenin
CSF– Classical swine fever
CSFV– Classical swine fever virus
LAV– Live attenuated vaccines
CDT– Cytolethal distending toxin
SE– Swine erysipelas
B. suis– Brucella suis
CDC– Centers for disease control and prevention
Cpe– Chlamydia pecorum
C. suis– Chlamydia suis
C. abortus– Chlamydia abortus
EB– Elementary body
MOMP– Major outer membrane protein family
T. gondii– Toxoplasma gondii
PCR– Polymerase chain reaction
ELISA– Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
LAT– Latex agglutination test
IHC– Immunohistonchemistry
FAVN– Fluorescent antibody virus neutralization
MAT– Microscopic agglutination test
Keywords: sows, reproductive disorders, abortion, vaccine, integrated management measures
Citation: Wang Y, Jin Y, Wang Y, Li Y, Wang X, Li Z and Zhou J (2025) Sow reproductive disorders: a key issue affecting the pig industry. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1535719. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1535719
Received: 27 November 2024; Accepted: 20 February 2025;
Published: 05 March 2025.
Edited by:
Stefan Gregore Ciornei, Iasi University of Life Science (IULS), RomaniaReviewed by:
Georgios Papadopoulos, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, GreeceCopyright © 2025 Wang, Jin, Wang, Li, Wang, Li and Zhou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jizhang Zhou, emhvdWp6QGx6dS5lZHUuY24=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.