
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Vet. Sci. , 12 March 2025
Sec. Veterinary Epidemiology and Economics
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2025.1503904
This article is part of the Research Topic Biosecurity of Infectious Diseases in Veterinary Medicine View all 8 articles
 Melkie Dagnaw Fenta1*
Melkie Dagnaw Fenta1* Melaku Getahun Feleke2
Melaku Getahun Feleke2 Atsede Solomon Mebratu2
Atsede Solomon Mebratu2 Bemrew Admassu Mengistu3
Bemrew Admassu Mengistu3 Yitayew Demessie3
Yitayew Demessie3Background: In Ethiopia, bovine mastitis is a major problem affecting production, welfare, and public health. Streptococcus is a key pathogen that causes mastitis and is often treated with antimicrobials, which can lead to antimicrobial resistance. Nevertheless, the administration of antimicrobials can unintentionally facilitate the emergence of antimicrobial resistance. Thus, this study aimed to systematically review and estimate the pooled prevalence of streptococcal infection in bovine mastitis in Ethiopia, along with associated antimicrobial resistance profiles, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current situation and guide effective treatment this bacteria.
Methods: This systematic review was carried out according to the PRISMA guidelines. To estimate the pooled proportion and resistance, a random effects model was utilized with R software. The databases used included SCOPUS, PubMed, HINARI, Web of Science, Google, and Google Scholar.
Results: Twenty-five articles were included in this meta-analysis. The overall pooled proportion of mastitis associated with Streptococcus spp. was 20% (95% CI: 17–23%). Significant heterogeneity was observed in the studies included (I2 = 87%; p < 0.01). Among the regions, the highest proportion was reported for South Nation, Nationality of Peoples Region (SNNPR) at 26%, followed by Amhara (24%), Oromia and Addis Abeba (19%), and Tigray (15%). The highest proportion of Streptococcus isolates was found in patients with clinical mastitis (24%). Among the major Streptococcus spp., Str. agalactiae had the highest pooled prevalence at 13%. The greatest prevalence of resistant Streptococcus was observed against penicillin (52%), followed by streptomycin, tetracycline, and ampicillin (42, 38, and 35%, respectively). According to the information provided by this meta-analysis, evidence-based risk management measures should be established to prevent and control streptococcal infection in dairy cattle. Monitoring and reporting of streptococcal mastitis and antimicrobial resistance are needed in Ethiopia’s different regions. To minimize resistance, stricter guidelines should be implemented for antimicrobial use in dairy cattle, with a particular focus on reducing penicillin use.
Ethiopia has the largest livestock population in Africa, with an estimated total of approximately 70 million cattle. Cows constitute 55.9% of the country’s cattle population, with approximately 20.7% of the entire cattle population being composed of milking cows (1). The milk derived from dairy cows serves as an essential dietary resource for the majority of the urban and peri-urban population (2). A total of 85–89% of the overall national milk production is attributed to cattle (3). However, the quantity of milk falls significantly below the national demand owing to various factors that contribute to diminished milk production (4). Bovine mastitis is a major and serious disorder that has a significant effect on dairy production and is a high public health threat. It causes substantial economic losses due to reduced milk yield, treatment costs, the discarding of milk with antimicrobials, the lower price of poor-quality milk, and death from severe inflammation (5). The estimated economic losses associated with clinical mastitis are between $69 and $110 per cow on farms worldwide (6).
Mastitis can be classified by clinical signs, duration, and epidemiology. Clinical mastitis ranges from mild udder infection to severe systemic illness, with approximately 10% of cases resulting in mortality (7, 8). It presents with rapid onset, swelling, and redness of the affected quarter. In contrast, subclinical mastitis often remains undiagnosed because of the absence of visible changes in milk (9). In terms of duration, mastitis can be acute, sudden, or chronic and is characterized by a prolonged inflammatory process and the gradual development of fibrous tissue (10). Epidemiologically, mastitis can be classified into environmental and contagious forms, each caused by various agents (11). Globally, bovine mastitis affects 30 to 50% of cows annually (6).
Mastitis is caused by various pathogens, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, with approximately 150 agents identified, with bacteria being the most common (12). In bovine mastitis, Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and coliform bacteria are particularly harmful to the udder (13). Staphylococcus and Streptococcus are responsible for 85–95% of bovine mastitis cases (14, 15). Streptococcus accounts for 10–30% of cow mastitis cases (16). The pathogenicity of Streptococcus is reliant on its capacity to transfer (or acquire) a range of virulence factors through gene exchange (17). Streptococcus demonstrates proportions strong adsorption and ant phagocytic activity. Its virulence factors include neuraminidase, lipoteichoic acid, capsular polysaccharide antigen, pyrogenic exotoxin, M protein, CAMP factor, and hemolysin (18, 19). Different virulence factors are linked to specific genetic markers, such as the α-antigen and β-antigen, which are encoded by the bac and bca genes (20). Str. agalactiae is a leading cause of bovine mastitis and has significant economic impacts. It can persist in bovine mammary glands by forming biofilms and is strongly linked to subclinical mastitis (17). Typically, Str. agalactiae is beta-hemolytic and is responsible for most mastitis infections in Africa (49%) and Asia (40%).
Several epidemiological studies have examined streptococcal infections in dairy cattle in Ethiopia. Streptococcus occurrence in clinical and subclinical bovine mastitis ranges from 6% (21) to 37% (22). The prevalence of bovine mastitis associated with streptococcal infection varies between 1 and 26% at the species level (23, 24), with Str. uberis and Str. agalactiae being the most commonly identified isolates. Additionally, a study (25) reported the presence of Str. agalactiae in 10.3% of mastitis milk samples in the Haramaya district of eastern Ethiopia.
Antimicrobial agents are the primary treatment for bacterially induced bovine mastitis in most African countries, including Ethiopia, despite increasing antimicrobial resistance (AMR) globally (26, 27). If unchecked, AMR could cause more than 10 million deaths annually by 2050 and cost more than $100 billion (28). Common antimicrobials in Ethiopia include penicillin, sulphonamide, ampicillin, cloxacillin, oxy-tetracycline, penicillin-procaine, streptomycin, and intra-mammary ampicillin-cloxacillin combinations (22). The regulation of antimicrobial utilization and veterinary practices in livestock production plays a critical role in addressing mastitis, a prevalent and economically significant disease in dairy cattle. Examining the legal framework surrounding anti-mastitis therapy is particularly important in Ethiopia, where challenges such as limited access to veterinary care, inadequate enforcement of antimicrobial regulations, and unregulated drug distribution impact treatment choices (29, 30). Ethiopia has national guidelines on antimicrobial use in livestock, but enforcement remains inconsistent, leading to the misuse of antibiotics and the emergence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) (31, 32).
Streptococcus resistance can be phenotypic or genotypic, with genes such as tet(M) and tet(O) for tetracycline resistance and erm for macrolide resistance (33–35). The cure proportions for mastitis vary from 64 to 91% (36) and are influenced by pathogen resistance and virulence (37). In Ethiopia, resistance is high: 20% for Str. agalactiae, 40% for Str. dysgalactiae, and 33.3% for Str. uberis to penicillin; 40% for Str. agalactiae and 42.9% for Str. uberis to ampicillin (25, 38); 73.3% for Str. dysgalactiae to oxy-tetracycline; and 50% for Str. agalactiae to streptomycin (22, 39). The growing concern over Antimicrobial resistance further complicates this issue, as it limits the effectiveness of conventional treatments, leading to persistent infections and increased transmission risks. A survey in Ethiopia revealed that 31.8% of individuals consume raw milk (40), indicating health risks, as raw milk supports microorganism growth. Streptococcus spp. can cause severe human infections (41). The Ethiopian dairy sector is growing, with efforts to increase productivity and address animal diseases through epidemiological data. However, raw milk consumption and inadequate hygiene practices are concerns (42, 43). A One Health approach is essential for managing AMR and ensuring health outcomes. This review was prompted by repeated mastitis cases at the University of Gondar Veterinary Dairy Farm, in which Streptococcus spp. were isolated in 45% of 20 mastitis cases, 6 (30%) with Staphylococcus, 2 (20%) with E. coli, and 3 (10%) were unidentified. Therefore, this systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to estimate the pooled prevalence of streptococcal infections in bovine mastitis patients and their antimicrobial resistance profiles in Ethiopia. The findings will offer evidence-based recommendations for improved management practices, which are essential for enhancing dairy production, safeguarding animal health, and ensuring the sustainability of Ethiopia’s dairy industry. Additionally, this research will advance the understanding of the epidemiology of these infections, underscore the need for targeted interventions, and support the development of effective treatment protocols and monitoring systems for responsible antimicrobial use in veterinary medicine.
The literature review was conducted from January 12–20, 2024, using the PRISMA checklist (44). This systematic evaluation of Streptococcus spp. in bovine mastitis and antimicrobial resistance involved seven key stages: suitability assessment, information sources, search strategy, outcome variables, data extraction, study quality evaluation, and data synthesis with statistical analysis. A comprehensive search was conducted using several databases, including PMC, SCOPUS, PubMed, HINARI, Web of Science, Google, and Google Scholar. Study selection was performed independently by two authors (M.D.F and A.S.M). The research question addressed the proportion, prevalence, and antimicrobial resistance of Streptococcus spp. causing bovine mastitis in Ethiopia. Meanwhile, the key words used were Streptococcus spp. OR Streptococcus infection, epidemiology OR prevalence OR infection proportion, cattle OR bovine OR animals, resistance proportion OR antimicrobial resistance AND (mastitis) AND Ethiopia. A restriction was placed on the language of publication as English. All identified studies were imported into EndNote 20 software to remove duplicates and citations of the references.
The meta-analysis was conducted in Ethiopia, which is located in the Horn of Africa between 3°00′–15°00′ N latitude and 32°30′–48°00′ E longitude. Covering 1.04 million square kilometers, Ethiopia is Africa’s second most populous country, with 123 million people. The country supports significant agricultural production, with approximately 70 million cattle, 52.5 million sheep, and 42.9 million goats (1). Its diverse topography includes highlands above 2,300 m, a. s.l. proportion transition zone between 1,500 and 2,300 m, and lowlands below 1,500 m.
To avoid reviewer bias, the search was carried out by three subject matter experts in veterinary clinical medicine, veterinary pharmacy, and veterinary public health and epidemiology. All of the primary descriptive studies that had been published in English and that showed the presence of Streptococcus spp. in dairy cattle were included in this meta-analysis. Articles that provided a precise estimate of the percentage of each bacterial isolate were required to meet the inclusion criteria. The research needed to come from observational studies, and the cause of bacterial mastitis in cows had to be determined from clinical or subclinical cases. The study animals were limited to domestic cattle, or cows, which are commonly raised for their milk. It was necessary to gather samples from animals that had not been exposed to an experimental infection. The geographical location of the bacterial isolates had to be Ethiopia, and the isolates were identified at least down to the genus level. The overall quantity of Streptococcus spp. investigated and the quantity of isolates that were resistant or sensitive may or may not have been disclosed. In cases where the scientific papers presented findings from identical sample times and methodologies but with varying Streptococcus spp., each occurrence was documented as an individual investigation within our database. Consequently, one scientific article could encompass multiple studies.
Studies focusing on milk from camels and other non-cattle species were excluded from the analysis. Additionally, studies that failed to provide clear and comprehensive estimates of the proportion of each bacterial species in relation to the affected host were not included. Review articles, duplicate studies, publications containing only abstracts, qualitative research, and studies based solely on KAP (knowledge, attitudes, and practices) questionnaires, book chapters, case reports, editorials, short communications, opinion pieces, and studies without original data were excluded. Furthermore, intervention studies that did not include baseline data on the association between animal exposure and disease were excluded from the meta-analysis.
In this review, we have two outcome variables: first, the pooled proportion/magnitude of Streptococcus spp. among the bacteria causing mastitis, and second, the antimicrobial resistance (AMR) profile of Streptococcus spp. In the first case, the proportion of mastitis-associated Streptococcus infection was estimated by considering the number of Streptococcus spp. isolates in the milk sample relative to the total number of bacterial isolates. In the second case, the resistance proportion of mastitis-associated Streptococcus isolates was calculated by determining the number of AMR isolates of Streptococcus spp. relative to the total number of isolates.
Two investigators (B.A.M and M.G.) extracted the data independently. Data extraction, both quantitative and qualitative, was performed via two tables and an Excel spread sheet from the included studies. The primary author’s name, the year the work was published, the region, the total number of bacterial isolates, the number of isolates of Streptococcus spp. (the main outcome of interest), diagnostic procedures, data collection, and ethical considerations were included in the extracted components. Information was extracted from each article and entered into a database, including the antimicrobial susceptibility testing methodology (disc diffusion or minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) estimation), MIC methodology (broth dilution method, agar dilution method, or other), number of Streptococcus isolates analyzed, number of resistant isolates, and type of mastitis (clinical or subclinical). Conflicts were settled through discussion and advice from a third author.
To confirm the review’s methodological quality, a quality assessment was carried out by two independent authors (Y.D and A.S.M). The AXIS quality tool (45) was used to evaluate the included studies’ quality. The study design, sample size justification, sample representativeness, target population, use of validated measures, diagnosis of statistical methods, sample selection, sample frame, and discussion of nonresponse bias, funding reporting, and conflicts of interest are just a few of the items included in this quality assessment tool.
R software was used to perform a meta-analysis via the “metaprop” function from the “meta” package version 4.1. 3–0 (46) and “metafor” in R Studio (47). The pooled proportion and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were estimated via a random effects model based on the restricted maximum likelihood (REML) method, which computes within-and between-study variability. It was applied to the resistance proportion, heterogeneity, overall effect size, and weight of each study in the meta-analysis. Furthermore, the pooled prevalence and resistance of bovine mastitis associated with streptococcal infection are illustrated via graphs and tables. The resulting variable is binary (i.e., the only parameter available to measure effect size for single groups (e.g., Streptococcus positive or negative); resistant/sensitive to the antimicrobial agent) was the raw proportion with 95% confidence intervals (48). In accordance with (49), a logistic-normal random-effect regression model was used to estimate pooled proportions via logit transformation, whereas a mixed effect logistic regression model was employed for subgroup analysis.
The sources of heterogeneity were evaluated via the Cochran’s Q test (reported as the p value), τ2 (variance between studies), and the inverse variance index (I2), which indicates the proportion of total variation observed between studies as opposed to heterogeneity as a result of chance. According to (50), the I2 index was calculated to correspond to values of 25, 50, and 75%, respectively, and was estimated to represent low, moderate and high heterogeneity. When the Q test produced a p value of less than 0.10 and the I2 value was greater than 50%, heterogeneity was deemed statistically significant. A forest plot was used to evaluate the level of heterogeneity among the studies. Each study’s weights, effect sizes, and 95% confidence intervals are displayed in a forest plot diagram.
A subgroup analysis of the proportion of Streptococcus spp. in bovine mastitis was carried out on the basis of the study year, study location or region, species of bacteria, and level of mastitis (clinical and subclinical) to ascertain specific between-study variability.
Publication bias is typically assessed via Egger’s test, Begg’s rank test, and a funnel plot, which allows for the visual assessment of asymmetry (48). Therefore, Egger’s regression test and funnel plot diagrams were used to evaluate publication bias.
A sensitivity analysis of the studies was performed to evaluate the effect of each individual study (51). The results revealed that the studies were the prime determinants of the pooled result.
A comprehensive search was performed in several databases, yielding 4,151 articles, along with 6 additional records identified from other sources (Figure 1). After removing duplicates, 3,901 records remained. Of these, 2,896 records were screened, and 1,891 were excluded based on their title and/or abstract. A total of 1,005 articles were assessed for full-text eligibility, with 984 excluded for various reasons. In the end, twenty five studies (n = 25) were included in the meta-analysis.
The characteristics of studies on Streptococcus spp. isolates are detailed as follows. The study subjects were lactating dairy cattle. A total of 25 articles were analyzed for the proportion of Streptococcus spp. associated with mastitis, and 54 articles were reviewed on the basis of species isolates. We identified the following isolates: Str. agalactiae (n = 18; 33%), Str. dysgalactiae (n = 13; 24%), Str. uberis (n = 11; 20%), Str. faecalis (n = 4; 7%), and unidentified Streptococcus spp. (n = 8; 14.8%). The studies included were conducted in various regions of Ethiopia between 2008 and 2024, predominantly in the southern (Oromia) and central regions. Diagnostic methods included CMT and bacterial culture, following procedures described by (52). The regional distributions of studies were as follows: Oromia (11 studies, 44%), Addis Ababa (7 studies, 27%), SNNPR (2 studies, 8%), Amhara (4 studies, 16%), and Tigray (2 studies, 8%). The minimum sample size was 79 cattle, and the maximum sample size was 1,019 (53). In this review, 7,073 dairy cows were evaluated. The prevalence of bovine mastitis associated with Streptococcus infection ranges from 1 to 26% (24, 54), with Str. uberis and Str. agalactiae being the most prevalent. Of the 25 studies, 18 focused on subclinical mastitis, and 15 focused on clinical mastitis. Three studies (55–57) addressed only subclinical mastitis. The detailed characteristics of the included studies are presented in Table 1.
In this review, a spectrum of studies was evaluated with respect to their quality, which ranged from low to medium proportion. None of the 25 quantitative studies met the criteria set by the AXIS tool, which encompasses details pertaining to risk factors and outcome variables. A majority of the articles, specifically 22 out of 25 (88%), utilized the simple random method procedure outlined by (58). Moreover, 20 studies (80%) successfully obtained a sample frame from a suitable population that closely resembled the target or reference population being investigated. Among the total number of studies, 17 (approximately 68%) fulfilled the requirements for six out of the 20 questions, namely, aims/objectives, definition of target/reference population, internal consistency of results, authors’ justification of the results, sample size justification, analysis of appropriate techniques in the methods and conflicts of interest, and description of the statistical methods used.
The meta-analysis included 25 articles investigating Streptococcus species associated with mastitis. Importantly, some articles were referenced multiple times because of their relevance in similar years but involved investigations of different bacterial strains. The studies included in this analysis showed a substantial level of heterogeneity (I2 = 87%, τ2 = 0.203; p < 0.01). The estimated pooled proportion of Streptococcus species associated with mastitis among all bacterial isolates was 20% (95% CI: 17–23%; Figure 2). The variability between studies was statistically significant (Q = 386.5, DF = 25, p < 0.001). The funnel plots (Figure 3) and Egger’s regression asymmetry did not suggest the presence of publication bias (p > 0.05).
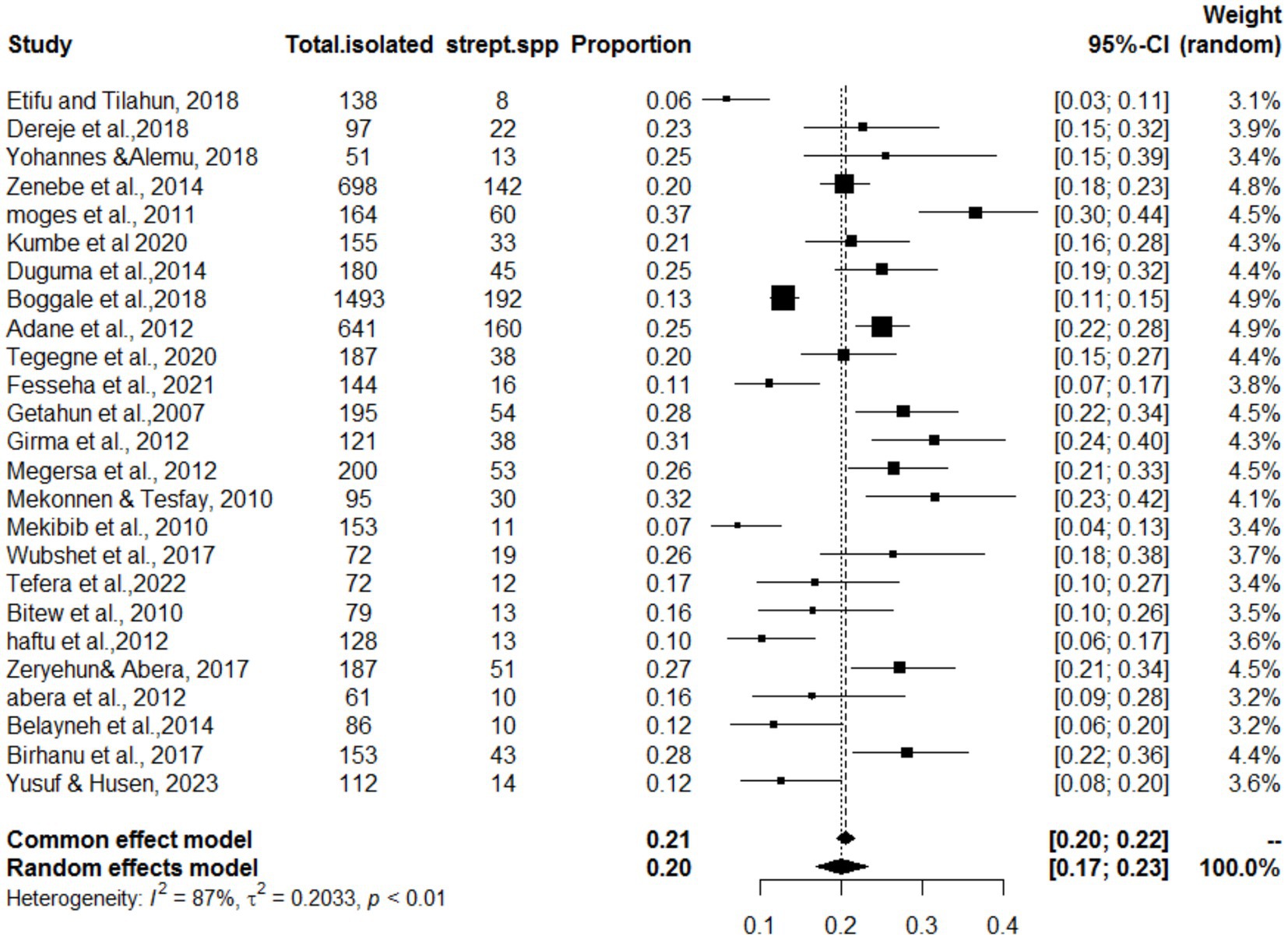
Figure 2. Forest plot for the proportion of Streptococcus spp. isolates in dairy cows in Ethiopia. As this figure showed Strep. spp. stands the isolation of Streptococcus species isolates.
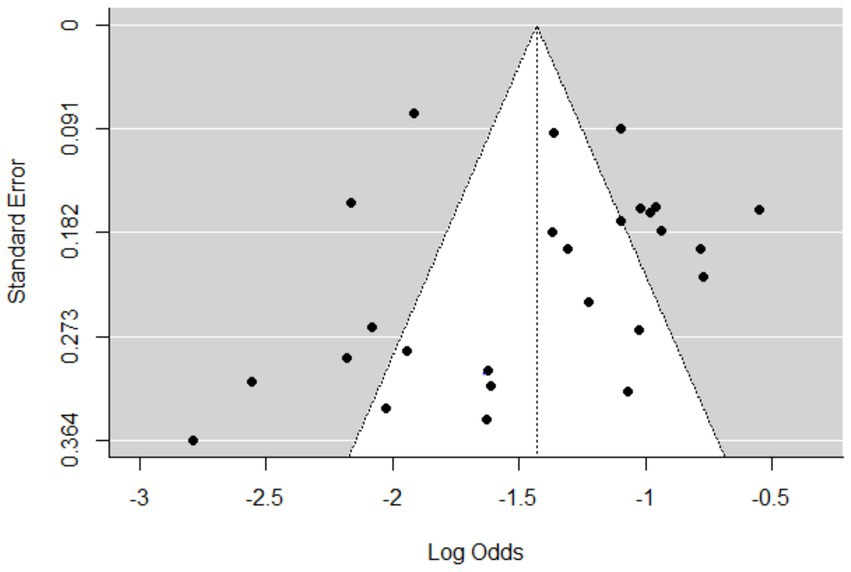
Figure 3. Funnel plots of standard error by log odds of the proportion of Streptococcus spp. isolates.
Because of high degree of heterogeneity, sub analyses were conducted on the basis of the study location or region, study year, degree of mastitis, and type of Streptococcus spp., as shown in Table 2 and Supplementary Figures 1–4. Significant heterogeneity between studies was found in the sub analysis by region-wise (p < 0.001). The subgroup analysis of Streptococcus bacteria associated to bovine mastitis by region revealed that SNNPR had the largest pooled proportion of mastitis-associated Streptococcus isolates (26%), followed by Amhara (24%), Oromia (19%), AA (18%), and Tigray (15%). However, Oromia region had the highest heterogeneity (I2 = 91%; p < 0.01) across studies. A sub analysis was conducted regarding the study year (studies grouped into before 2013 and studies after 2013). The magnitude of heterogeneity were I2 = 83% and I2 = 86%, respectively. The highest sub pooled proportion of Streptococcus isolates associated to mastitis (20%) occurred prior to 2013. The subgroup difference test results (Q = 0.18; DF = 1; p = 0.743) indicated the absence of a statistically significant group effect.
A sub-analysis on the basis of the degree of mastitis also revealed that, with study weights of 40 and 59.5%, the percentage of Streptococcus isolates at the species level was greater in clinical mastitis at 24% (95% CI; 16–34%) than in subclinical bovine mastitis at 18% (95% CI; 14–24%). Both the clinical and subclinical mastitis categories experienced significant study variability across studies (I2 = 89%; p < 0.01) and (I2 = 87%; p < 0.01), respectively. Five groups were formed from the sub-analysis of the included studies on the basis of the types of Streptococcus species: Str. agalactiae (n = 18), Str. dysgalactiae (n = 13), Str. uberis (n = 11), Str. Faecalis (n = 4) and unknown Streptococcus spp. (n = 8). Several publications did not identify the species level (21, 55, 59, 60). In the sub-analysis of the proportion of Streptococcus associated with mastitis by species type, there were notable differences. According to the subgroup analysis proportion shown in Supplementary Figure 4, the pooled proportion of unidentified spp. was the next highest at 15% (95% CI: 10–22%) and (I2 = 87%: τ2 = 0.370; p < 0.01) for Str. agalactie. 13% (95% CI: 11–16%) and (I2 = 79%) (τ2 = 0.146; p < 0.01). In the present meta-analysis, the proportion of Str. dysgalactiae was found to be 6% (95% CI: 5–8%) with low heterogeneity (I2 = 49%: τ2 = 0.126; p = 0.02).
In all included studies, the Kirby-Baur disc diffusion method was used as an antimicrobial sensitivity test. The present studies on antimicrobial resistance in Streptococcus for the treatment of mastitis in cattle are depicted in Table 3. Only studies accurately proportionally identifying Streptococcus species to the species level were included in the meta-analysis. This approach helped to exclude studies that may have misclassified or grouped different species, which could have had varying resistance profiles.
The highest prevalence of resistant Streptococcus was against penicillin (pool estimate = 52, 95% CI = 38–67%), followed by streptomycin, tetracycline, and ampicillin (pool estimates = 42, 38, and 35%, respectively). Gentamycin and erythromycin presented the lowest overall prevalence of resistance (pool estimates = 16 and 19%, respectively) (Table 3). In general, the I2 values were highest for the streptomycin antimicrobials tested (I2 = 80%). The I2 of amoxicillin, Co-trimazole and gentamycin were equal to zero since they were used in any of the included studies; therefore, there was no variability (Table 4).
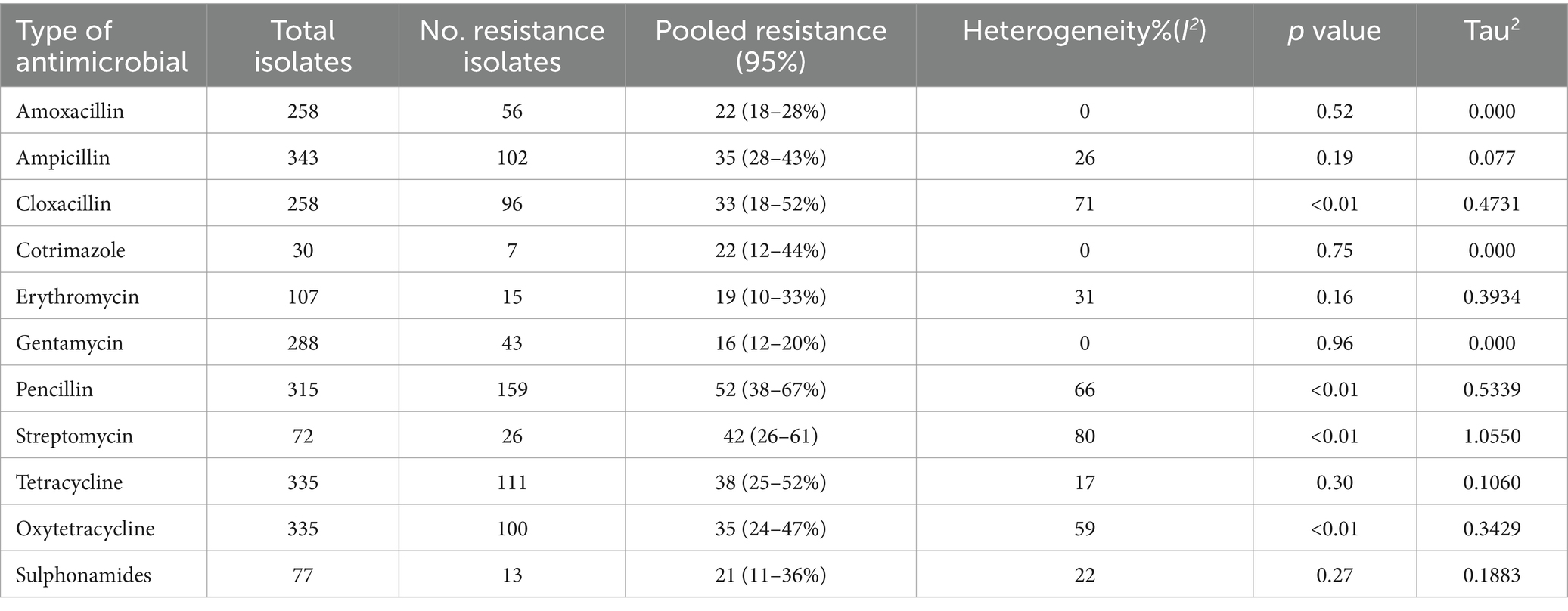
Table 4. Overall pooled estimate of the prevalence of Streptococcus AMR to specific antimicrobial agents.
This meta-analysis, comprising twenty-five observational studies, revealed that 20% of bovine mastitis cases in Ethiopia were associated with Streptococcus spp. Among the various species studied, the prevalence of Str. agalactiae was 13%, followed by Str. dysgalactiae at 6% and Str. uberis at 5%. Str. agalactiae had the highest prevalence, likely because it is a highly contagious obligate pathogen of the bovine mammary gland (61). The overall prevalence (20%) is similar to findings from the United States (20.8–23.3%), Bangladesh (28.75%) (62), and the Netherlands (25%) but lower than reports from China (36.23%) (63), Nigeria (56.7%), Egypt (38.3%), Tanzania (75.5%) (64), Europe (38%), Australia (50%), France (42.11%), and New Zealand (58.66%) (65, 66). This variability may be due to differences in climate, knowledge levels, management systems, cow breeds, laboratory facilities, and housing styles across countries (67). The pooled prevalence of Str. agalactiae (13%) and Str. dysgalactiae (6%) was lower than that in Bangladesh, where the prevalence of Str. agalactiae was 19.86% and that of Str. dysgalactiae was 17.81% (68), and in Egypt, where the prevalence of Str. dysgalactiae was 23% and that of Str. agalactiae was 20.1% (69). These disparities could be due to differences in geographic location, livestock rearing, husbandry, and hygiene practices (70–72). Subgroup analysis by region in Ethiopia revealed the highest prevalence of streptococcal infection in SNNPRS (26%) and the lowest in Tigray (15%). This variation could be due to differences in agroclimatic conditions, sampling methods, farm management practices, and cow-related factors. In terms of mastitis severity, this meta-analysis revealed a greater occurrence of streptococcal infection in clinical mastitis cases (24%) than in subclinical mastitis cases (18% in CMT-positive cows). Our findings show that clinical mastitis caused by Streptococcus is more prevalent than subclinical mastitis, contrary to some reports (59, 60, 73), but consistent with others (38, 39, 74).
In recent years, the proportion of streptococcal infection in bovine mastitis has decreased, likely due to increased awareness through scientific training, research, technological advancements, and the implementation of biosecurity measures on farms. Furthermore, studies from China have demonstrated that subclinical mastitis is a significant issue in smallholder dairy farms, with a variety of bacterial pathogens, including Streptococcus spp., playing a major role in infections (75). The molecular characterization of antimicrobial-resistant pathogens such as Staphylococcus haemolyticus in dairy herds of Northwest China indicates that the dairy environment can act as a reservoir for resistant bacterial strains, further complicating treatment strategies (76).
The second aim of this review was to determine the antimicrobial resistance (AMR) profile of Streptococcus spp. in bovine mastitis. The pooled resistance proportion to penicillin was 52%, which was much higher than that reported in Uruguay (28.6%) (77), France (21%) (78), and Argentina (27.6%) (79). The antimicrobials that have been showing the greatest resistance were aminoglycosides, streptomycin, and penicillin, likely due to long-term and repeated use on dairy farms. The resistance proportions for erythromycin and tetracycline were 19 and 38%, respectively, similar to findings in France (20 and 38.5%) (80, 81) but lower than the resistance proportions reported in the USA and Europe, which ranged from 20 to 50% (82, 83). The resistance of Streptococcus spp. to gentamycin (16%) and tetracycline (38%) was greater than the proportions reported by (81) (2.4 and 18%, respectively). The 38% resistance proportion to tetracycline in this study is lower than the proportion reported in Denmark between 2002 and 2004 (84, 75.5, and 84.8%) (84, 85). Recent findings highlight that dairy farms are a potential reservoir for antibiotic-resistant bacteria and virulence genes, particularly among Escherichia coli strains that carry resistance to aminoglycosides and beta-lactam antibiotics (86). The One Health approach to AMR suggests that the transmission of resistant bacteria is not confined to animals but extends to the broader ecosystem, including farm workers and the surrounding environment. The rise of multidrug-resistant strains in dairy environments underscores the need for stringent antimicrobial stewardship (87).
The variation in antimicrobial resistance across regions may be attributed to differences in medication practices, with improper use of antimicrobial drugs being a significant contributor to the development of resistance (88). Our findings indicate a high prevalence of both contagious and environmental Streptococcus spp. in bovine mastitis in Ethiopia. Therefore, an extended ten-point mastitis control plan should be implemented, with components tailored specifically for Ethiopia, including increased awareness among farmers and milkers. Additionally, targeted interventions for regions with high infection proportions, research into alternative therapeutic approaches, and the development of new antimicrobials are critical measures that must be undertaken.
Most of the articles describe the frequency of the isolates and the percentage of the resistance isolates however no articles tried to identify the resistance genes. Most of the articles used the convenience method of the sample selection so it may lead to selection biased. This systematic review has several limitations, which must be taken into consideration. First, the review is focused exclusively on a single genus, namely, Streptococcus. Second, few studies were included in the analysis of antimicrobial resistance. Third, no studies were included in some regions. Finally, the protocol was not registered in the PROSPERO database.
The present meta-analysis showed the overall pooled proportion of mastitis associated with Streptococcus spp. at 20% (95% CI: 17–23%). The highest proportions were found in SNNPR (26%), followed in Amhara (24%), Oromia and Addis Ababa (19%), and Tigray (15%). Clinical mastitis had the highest proportion of streptococcal isolates (24%). Str. agalactiae had the highest pooled prevalence at 13%. Resistance was highest against penicillin (52%), followed by streptomycin (42%), tetracycline (38%), and ampicillin (35%). Specifically, Str. agalactiae accounted for the highest proportion of bovine mastitis-causing Streptococcus spp. infections. This particular species of Streptococcus falls under the category of a contagious group of bacterial pathogens, indicating that a notable proportion of contagious Streptococcus and the udder of infected cows serve as a significant reservoir. Among the commonly employed antimicrobials, the highest pooled resistance proportion of Streptococcus spp. was observed against penicillin. The data presented in this report will facilitate informed decision-making processes aimed at controlling and preventing bovine mastitis within the context of Ethiopia. The findings will benefit stakeholders and policymakers in enhancing the dairy industry. Increased monitoring and reporting of streptococcal mastitis and antimicrobial resistance across Ethiopia will improve the understanding of prevalence and resistance patterns. The implementation of stricter protocols for Antimicrobial use, especially those that reduce the reliance on highly resistant antimicrobials such as penicillin, is essential. Developing targeted interventions for regions with relatively high infection proportions, promoting research into alternative therapies, and innovating new antimicrobials are also critical steps.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
MF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MG: Data curation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. AM: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. BM: Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YD: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors thank the University of Gondar in Ethiopia for providing free statistical software and free internet access.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fvets.2025.1503904/full#supplementary-material
1. CSA. Central statistical authority of Ethiopia: report on livestock and livestock characteristics (private peasant holdings). Statistical Bulletin. (2020) 587. doi: 10.4236/oalib.1100572
2. Gizaw, S, Mulye, M, and Kefyalew, A. Milk production performances of local and crossbred dairy cows in west Gojam zone, Amhara region, Ethiopia. J Appl Anim Sci. (2017) 10:35–46.
3. WOAH. State of food insecurity in the world: 2014: Strengthening the enabling environment for food security and nutrition: Food & Agriculture Organization of the UN (FAO). Paris: WOAH (2014).
4. Ahmed, MA, Ehui, S, and Assefa, Y. Dairy development in Ethiopia. Intl Food Policy Res Inst. (2004)
5. Petrovski, K, Trajcev, M, and Buneski, G. A review of the factors affecting the costs of bovine mastitis. Jot SAVA. (2006) 77:52–60. doi: 10.4102/jsava.v77i2.344
6. Hogeveen, H, Huijps, K, and Lam, T. Economic aspects of mastitis: new developments. N Z Vet J. (2011) 59:16–23. doi: 10.1080/00480169.2011.547165
7. Ruegg, PL. New perspectives in udder health management. Vet Clin. (2012) 28:149–63. doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2012.03.001
8. Abebe, R, Hatiya, H, Abera, M, Megersa, B, and Asmare, K. Bovine mastitis: prevalence, risk factors and isolation of Staphylococcus aureus in dairy herds at Hawassa milk shed, South Ethiopia. BMC Vet Res. (2016) 12:1–11. doi: 10.1186/s12917-016-0905-3
9. Sharma, N, Singh, N, and Bhadwal, M. Relationship of somatic cell count and mastitis: an overview. Asian Australas J Anim Sci. (2011) 24:429–38. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2011.10233
10. IDF. International dairy federation: Bovine mastitis: Definition and guidelines for diagnosis. Bulletin of the international dairy federation, vol. 24. Schaerbeek: International Dairy Federation (1987). 211 p.
11. Blowey, RW, and Edmondson, P. Mastitis control in dairy herds. 2nd ed. Wallingford: CAB Internationational (2010).
12. Bradley, AJ. Bovine mastitis: an evolving disease. Vet J. (2002) 164:116–28. doi: 10.1053/tvjl.2002.0724
13. Keane, OM. Symposium review: Intramammary infections—major pathogens and strain-associated complexity. J Dairy Sci. (2019) 102:4713–26. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-15326
14. Dodd, P, and Warner, JB. On corpoproportion governance: a study of proxy contests. J Financ Econ. (1983) 11:401–38. doi: 10.1016/0304-405X(83)90018-1
15. Jarp, J, Bugge, HP, and Larsen, S. Clinical trial of three therapeutic regimens for bovine mastitis. The Veterinary Record. (1989) 124:630–4. doi: 10.1136/vr.124.24.630
16. Coffey, TJ, Pullinger, GD, Urwin, R, Jolley, KA, Wilson, SM, Maiden, MC, et al. First insights into the evolution of Streptococcus uberis: a multilocus sequence typing scheme that enables investigation of its population biology. Appl Environ Microbiol. (2006) 72:1420–8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.2.1420-1428.2006
17. Oliver, S. Frequency of isolation of environmental mastitis-causing pathogens and incidence of new intramammary infection during the nonlactating period. Am J Vet Res. (1988) 49:1789–93. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.1988.49.11.1789
18. González-Outeiriño, J, Kadirvelraj, R, and Woods, RJ. Structural elucidation of type III group B Streptococcus capsular polysaccharide using molecular dynamics simulations: the role of sialic acid. Carbohydr Res. (2005) 340:1007–18. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2004.12.034
19. Yeung, M, and Mattingly, SJ. Biosynthetic capacity for type-specific antigen synthesis determines the virulence of serotype III strains of group B streptococci. Infect Immun. (1984) 44:217–21. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.217-221.1984
20. Beigverdi, R, Jabalameli, F, Mirsalehian, A, Hantoushzadeh, S, Boroumandi, S, Taherikalani, M, et al. Virulence factors, antimicrobial susceptibility and molecular characterization of Str. Agalactiae isolated from pregnant women. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. (2014) 61:425–34. doi: 10.1556/amicr.61.2014.4.4
21. Etifu, M, and Tilahun, M. Prevalence of bovine mastitis, risk factors, isolation and anti-bio gram of major pathogens in mid rift valley, Ethiopia. Int J Livestock Product. (2019) 10:14–23. doi: 10.5897/IJLP2018.0517
22. Moges, N, Asfaw, Y, Belihu, K, and Tadesse, A. Aantimicrobial susceptibility of mastitis pathogens from smallholder dairy herds in and around Gondar, Ethiopia. J Anim Vet Adv. (2011) 10:1616–22. doi: 10.3923/javaa.2011.1616.1622
23. Megersa, B, Markemann, A, Angassa, A, Ogutu, JO, Piepho, H-P, and Zaráte, AV. Impacts of climate change and variability on cattle production in southern Ethiopia: perceptions and empirical evidence. Agric Syst. (2014) 130:23–34. doi: 10.1016/j.agsy.2014.06.002
24. Redeat, B, Kelay, B, and Asamenew, T. Microbiological study on bacterial causes of bovine mastitis and its antimicrobial suscebtibility patterns in east Showa zone, Akaki District, Ethiopia. J Vet Med Anim Health. (2014) 6:116–22. doi: 10.5897/JVMAH2013.0272
25. Lakew, BT, Fayera, T, and Ali, YM. Risk factors for bovine mastitis with the isolation and identification of Str. Agalactiae from farms in and around Haramaya district, eastern Ethiopia. Trop Anim Health Prod. (2019) 51:1507–13. doi: 10.1007/s11250-019-01838-w
26. Bassetti, M, Poulakou, G, Ruppe, E, Bouza, E, Van Hal, SJ, and Brink, A. Antimicrobial resistance in the next 30 years, humankind, bugs and drugs: a visionary approach. Intensive Care Med. (2017) 43:1464–75. doi: 10.1007/s00134-017-4878-x
27. Ferri, G, Lauteri, C, and Vergara, A. Antimicrobial resistance in the finfish aquaculture industry: a review. Antibiotics. (2022) 11:1574. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11111574
28. Cassini, A, Högberg, LD, Plachouras, D, Quattrocchi, A, Hoxha, A, Simonsen, GS, et al. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antimicrobial-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European economic area in 2015: a population-level modelling analysis. Articles. (2019) 19:56–66. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30605-4
29. Gebrewahid, TT, Abera, BH, and Menghistu, HT. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility profile of mastitis pathogens from dairy farms in northern Ethiopia. Trop Anim Health Prod. (2020) 52:2849–56. doi: 10.5455/vetworld.2012.103-109
30. Beyene, T, Tesega, B, and Disassa, H. Antibiotic residues in milk and its public health significance. World J Dairy Food Sci. (2016) 11:1–15. doi: 10.4172/2157-7579.1000285
31. Tadesse, BT, Ashley, EA, Ongarello, S, Havumaki, J, Wijegoonewardena, M, González, IJ, et al. Antimicrobial resistance in Africa: a systematic review. BMC Infect Dis. (2018) 17:616. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2713-1
32. WOAH (2022). WOAH strategy on antimicrobial resistance and the prudent use of antimicrobials. Available online at: www.woah.org (Accessed January 9, 2023).
33. Ding, Y, Zhao, J, He, X, Li, M, Guan, H, Zhang, Z, et al. Antimicrobial resistance and virulence-related genes of Streptococcus obtained from dairy cows with mastitis in Inner Mongolia, China. Pharm Biol. (2016) 54:162–7. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2015.1025290
34. Schmitt-Van de Leemput, E, and Zadoks, R. Genotypic and phenotypic detection of macrolide and lincosamide resistance in Streptococcus uberis. J Dairy Sci. (2007) 90:5089–96. doi: 10.3168/jds.2007-0101
35. Gao, J, Yu, F-Q, Luo, L-P, He, J-Z, Hou, R-G, Zhang, H-Q, et al. Antimicrobial resistance of Str. Agalactiae from cows with mastitis. Vet J. (2012) 194:423–4. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2012.04.020
36. Owens, W, Ray, C, Watts, J, and Yancey, R. Comparison of success of antimicrobial therapy during lactation and results of antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bovine mastitis. Basrah J Vet Res. (1997) 80:313–7. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(97)75940-X
37. McDougall, CW, Quilliam, RS, Hanley, N, and Oliver, DM. Freshwater blue space and population health: an emerging research agenda. Sci Total Environ. (2020) 737:140196. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.140196
38. Getahun, K, Kelay, B, Bekana, M, and Lobago, F. Bovine mastitis and antimicrobial resistance patterns in Selalle smallholder dairy farms, Central Ethiopia. Trop Anim Health Prod. (2008) 40:261–8. doi: 10.1007/s11250-007-9090-5
39. Girma, S, Mammo, A, Bogele, K, Sori, T, Tadesse, F, and Jibat, TJ. Study on prevalence of bovine mastitis and its major causative agents in west Harerghe zone, Doba district, Ethiopia. J Vet Med Anim Health. (2012) 4:116–23. doi: 10.5897/JVMAH12.016
40. Makita, K, Desissa, F, Teklu, A, Zewde, G, and Grace, D. Risk assessment of staphylococcal poisoning due to consumption of informally marketed milk and homemade yoghurt in Debre Zeit, Ethiopia. Int J Food Microbiol. (2012) 153:135–41. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2011.10.028
41. Holm, SE, Nordstrand, A, Stevens, DL, and Norgren, M, Microbiology molecular pathogenesis. Acute poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis. Oxford: Oxford University Press NY. (2000): 152–162.
42. Desissa, F, Makita, K, Teklu, A, and Grace, D. Contamination of informally marketed bovine milk with Staphylococcus aureus in urban and peri urban areas of Debre-Zeit, Ethiopia. African J Microbiol Res. (2012) 6:5852–6. doi: 10.5897/AJMR12.151
43. Wubete, A. Bacteriological quality of bovine milk in small holder dairy farms in Debre Zeit, Ethiopia. AAU FVM. (2004) 4:34–7. Available at: http://etd.aau.edu.et/handle/123456789/28416
44. Page, MJ, McKenzie, JE, Bossuyt, PM, Boutron, I, Hoffmann, TC, Mulrow, CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 88:105906. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2021.105906
45. Downes, MJ, Brennan, ML, Williams, HC, and Dean, RS. Development of a critical appraisal tool to assess the quality of cross-sectional studies (AXIS). BMJ Open. (2016) 6:e011458. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011458
46. Balduzzi, D, Garnelo, M, Bachrach, Y, Czarnecki, W, Perolat, J, Jaderberg, M, et al. Open-ended learning in symmetric zero-sum games. Int Conf Machine Learn. (2019) 2019:434–43. doi: 10.48550/arXiv.1901.08106
47. Viechtbauer, W. Conducting meta-analyses in R with the metafor package. J Stat Softw. (2010) 36:1–48. doi: 10.18637/jss.v036.i03
48. Borenstein, M, Hedges, LV, Higgins, JP, and Rothstein, H. A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Res Synth Methods. (2010) 1:97–111. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.12
49. Nyaga, VN, Arbyn, M, and Aerts, M. Metaprop: a Stata command to perform meta-analysis of binomial data. Arch Public Health. (2014) 72:1–10. doi: 10.1186/2049-3258-72-39
50. Higgins, JP, and Thompson, SG. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. (2002) 21:1539–58. doi: 10.1002/sim.1186
51. Viechtbauer, W, and Cheung, MWL. Outlier and influence diagnostics for meta-analysis. Res Synth Methods. (2010) 1:112–25. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.11
53. Boggale, K, Birru, B, Nigusu, K, and Asras, S. Prevalence of bovine mastitis, risk factors and major causative agents in west Hararghe zone, East Ethiopia. East African J Vet Anim Sci. (2018) 2:1–10.
54. Megersa, B, Manedo, A, Abera, M, Regassa, A, and Abunna, F. Mastitis in lactating cows at Hawassa town: prevalence, risk factors, major bacterial causes and treatment response to routinely used antimicrobial. American-Eurasian J Scientific Res. (2012) 7:86–91. doi: 10.5829/idosi.aejsr.2012.7.2.6391
55. Birhanu, M, Leta, S, Mamo, G, and Tesfaye, S. Prevalence of bovine subclinical mastitis and isolation of its major causes in Bishoftu town, Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes. (2017) 10:1–6. doi: 10.1186/s13104-017-3100-0
56. Yusuf, A, and Husen, M. Prevalence and incidence of bovine mastitis in dairy farm of Haramaya University, eastern Ethiopia. J Vet Sci Animal Husbandry. (2023) 10:2023.
57. Dereje, K, Kebede, A, Abebe, N, and Tamiru, Y. Isolation, identification and antimicrobial susceptibility test of mastitis causing bacteria at Holeta agricultural research Center dairy farms. Int J Animal Sci Technol. (2018) 2:6–13. doi: 10.11648/j.ijast.20180201.12
59. Kumbe, A, Bekele, B, Hussien, B, Onate, A, and Teshome, D. Study on bovine mastitis under different management in pastoral and agro-pastoral areas of Borana zone, southern Ethiopia. J Vet Sci Res. (2020) 5:000192:1–8. doi: 10.23880/OAJVSR-16000192
60. Abera, M, Habte, T, Aragaw, K, Asmare, K, and Sheferaw, D. Major causes of mastitis and associated risk factors in smallholder dairy farms in and around Hawassa, southern Ethiopia. Trop Anim Health Prod. (2012) 44:1175–9. doi: 10.1007/s11250-011-0055-3
61. Meiri-Bendek, I, Lipkin, E, Friedmann, A, Leitner, G, Saran, A, Friedman, S, et al. A PCR-based method for the detectionof Str. Agalactiae in milk. J Dairy Sci. (2002) 85:1717–23. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(02)74245-8
62. Bhuiyan, M, Shahadat, H, Chakma, S, Islam, F, Islam, R, Islam, T, et al. Prevalence of subclinical mastitis of dairy cows in Bijoynagar Upazila under Brahmanbaria District of Bangladesh. Adv Anim Vet Sci. (2020) 8:364–9. doi: 10.17582/journal.aavs/2020/8.4.364.369
63. Wang, N, Zhou, C, Basang, W, Zhu, Y, Wang, X, Li, C, et al. Mechanisms by which mastitis affects reproduction in dairy cow: a review. Reprod Domest Anim. (2021) 56:1165–75. doi: 10.1111/rda.13953
64. Karimuribo, E, Fitzpatrick, J, Swai, E, Bell, C, Bryant, M, Ogden, N, et al. Prevalence of subclinical mastitis and associated risk factors in smallholder dairy cows in Tanzania. Vet Rec. (2008) 163:16–21. doi: 10.1136/vr.163.1.16
65. McDougall, S. Prevalence of clinical mastitis in 38 Waikato dairy herds in early lactation. N Z Vet J. (1999) 47:143–9. doi: 10.1080/00480169.1999.36131
66. Ikawaty, R, Brouwer, E, Jansen, M, Van Duijkeren, E, Mevius, D, Verhoef, J, et al. Characterization of Dutch Staphylococcus aureus from bovine mastitis using a multiple locus variable number tandem repeat analysis. Vet Microbiol. (2009) 136:277–84. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.10.034
67. Hill, AE, Green, AL, Wagner, BA, and Dargatz, DA. Relationship between herd size and annual prevalence of and primary antimicrobial treatments for common diseases on dairy operations in the United States. Prev Vet Med. (2009) 88:264–77. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2008.12.001
68. Farzana, Z, Saha, A, and Siddiki, AZ. Molecular characterization of Str. Agalactiae and Streptococcus dysgalactiae causing bovine mastitis in the southern region of Bangladesh. J Adv Vet Animal Res. (2023) 10:178–84. doi: 10.5455/javar.2023.j667
69. Saed, HAE-MR, and Ibrahim, HMM. Antimicrobial profile of multidrug-resistant Streptococcus spp. isolated from dairy cows with clinical mastitis. J Adv Vet Animal Res. (2020) 7:186–97. doi: 10.5455/javar.2020.g409
70. Shiferaw, J, and Telila, I. Prevalence of bovine mastitis and assessment of risk factors in and around Wolayta Sodo, Ethiopia. Int J Homeopathy Natural Med. (2017) 2:1–6. doi: 10.23880/oajvsr-16000147
71. Zeryehun, T, Aya, T, and Bayecha, R. Study on prevalence, bacterial pathogens and associated risk factors for bovine mastitis in small holder dairy farms in and around Addis Ababa, Ethiopia. J Animal Plant Sci. (2013) 23:50–5.
72. Addis, Z, Kebede, N, Sisay, Z, Alemayehu, H, Wubetie, A, and Kassa, T. Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of salmonella isolated from lactating cows and in contact humans in dairy farms of Addis Ababa: a cross sectional study. BMC Infect Dis. (2011) 11:1–7. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-11-222
73. Adane, B, Gizaw, Y, and Amde, B. Prevalence of bovine mastitis and isolation of causative major pathogens in and around Jigjiga, Somali region, Ethiopia. European J Appl Sci. (2017) 9:287–95. doi: 10.5829/idosi.ejas.2017.287.295
74. Ararsa, D, Tadele, T, and Aster, Y. Prevalence of clinical and subclinical mastitis on cross bred dairy cows at Holleta agricultural research Center, Central Ethiopia. J Vet Med Animal Health. (2014) 6:13–7. doi: 10.5897/JVMAH2013.0259
75. Zhang, T, Zhu, J, Xu, J, Shao, H, and Zhou, R. Regulation of (p) pp Gpp and its homologs on environmental adaptation, survival, and pathogenicity of streptococci. Front Microbiol. (2020) 11:1842. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01842
76. Wang, L, Haq, SU, Shoaib, M, He, J, Guo, W, Wei, X, et al. Subclinical mastitis in small-holder dairy herds of Gansu Province, Northwest China: prevalence, bacterial pathogens, antimicrobial susceptibility, and risk factor analysis. Microorganisms. (2024) 12:2643. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12122643
77. Nam, H-M, Lim, S-K, Kang, H-M, Kim, J-M, Moon, J-S, Jang, K-C, et al. Antimicrobial resistance of streptococci isolated from mastitic bovine milk samples in Korea. Zoonoses Public Health. (2009) 21:698–701. doi: 10.1177/104063870902100517
78. Guérin-Faublée, V, Tardy, F, Bouveron, C, and Carret, G. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Streptococcus species isolated from clinical mastitis in dairy cows. Int J Antimicrob Agents. (2002) 19:219–26. doi: 10.1016/S0924-8579(01)00485-X
79. Denamiel, G, Llorente, P, Carabella, M, Rebuelto, M, and Gentilini, E. Anti-microbial susceptibility of Streptococcus spp. isolated from bovine mastitis in Argentina. J Veterinary Med Ser B. (2005) 52:125–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0450.2005.00830.x
80. Botrel, M-A, Haenni, M, Morignat, E, Sulpice, P, Madec, J-Y, and Calavas, D. Distribution and antimicrobial resistance of clinical and subclinical mastitis pathogens in dairy cows in Rhône-Alpes, France. Foodborne Pathog Dis. (2010) 7:479–87. doi: 10.1089/fpd.2009.0425
81. Boireau, C, Cazeau, G, Jarrige, N, Calavas, D, Madec, J-Y, Leblond, A, et al. Antimicrobial resistance in bacteria isolated from mastitis in dairy cattle in France, 2006–2016. J Dairy Sci. (2018) 101:9451–62. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-14835
82. DiPersio, LP, and DiPersio, JR. High proportions of erythromycin and clindamycin resistance among OBGYN isolates of group B Streptococcus. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. (2006) 54:79–82. doi: 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2005.07.003
83. Sadowy, E, Matynia, B, and Hryniewicz, WJ. Population structure, virulence factors and resistance determinants of invasive, noninvasive and colonizing Str. Agalactiae in Poland. J Antimicrob Chemother. (2010) 65:1907–14. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkq230
84. Hendriksen, RS, Mevius, DJ, Schroeter, A, Teale, C, Meunier, D, Butaye, P, et al. Prevalence of antimicrobial resistance among bacterial pathogens isolated from cattle in different European countries: 2002–2004. Acta Vet Scand. (2008) 50:1–10. doi: 10.1186/1751-0147-50-28
85. Petrovski, K, Laven, R, and Lopez-Villalobos, N. A descriptive analysis of the antimicrobial susceptibility of mastitis-causing bacteria isolated from samples submitted to commercial diagnostic laboratories in New Zealand (2003–2006). N Z Vet J. (2011) 59:59–66. doi: 10.1080/00480169.2011.552853
86. Shoaib, M, Tang, M, Aqib, AI, Zhang, X, Wu, Z, Wen, Y, et al. Dairy farm waste: a potential reservoir of diverse antibiotic resistance and virulence genes in aminoglycoside-and beta-lactam-resistant Escherichia coli in Gansu Province, China. Environ Res. (2024) 263:120190. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2024.120190
87. Shoaib, M, He, Z, Geng, X, Tang, M, Hao, R, Wang, S, et al. The emergence of multi-drug resistant and virulence gene carrying Escherichia coli strains in the dairy environment: a rising threat to the environment, animal, and public health. Front Microbiol. (2023) 14:1197579. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1197579
88. Barkus, A, and Lisauskienė, I. Inappropriate habits of antimicrobial use among medical specialists and students in Vilnius. Acta Medica Lituanica. (2016) 23:135–41. doi: 10.6001/actamedica.v23i2.3330
89. Zenebe, N, Habtamu, T, and Endale, B. Study on bovine mastitis and associated risk factors in Adigrat, northern Ethiopia. Afr J Microbiol Res. (2014) 8:327–31. doi: 10.5897/AJMR2013.6483
90. Adane, B, Bayissa, B, Tuffa, S, Tola, T, and Mekonnen, S. Participatory impact assessment of ticks on cattle milk production in pastoral and agro-pastoral production systems of Borana zone, Oromia regional state, Southern Ethiopia. Ethiopian Vet J. (2012) 16:1–13. doi: 10.4314/evj.v16i1.1
91. Tegegne, DT, Yalew, ST, Emeru, BA, Equar, Y, Messele, GMW, Bora, SK, et al. Study of prevalence, associated risk factors and causative bacteria of bovine mastitis in Ethiopia. Int J Vet Sci Technol. (2020) 4:001–6.
92. Fesseha, H, Mathewos, M, Aliye, S, and Wolde, A. Study on prevalence of bovine mastitis and associated risk factors in dairy farms of Modjo town and suburbs, Central Oromia, Ethiopia. Vet Med. (2021) 12:271–83. doi: 10.2147/VMRR.S323460
93. Mekonnen, H, and Tesfaye, A. Prevalence and etiology of mastitis and related management factors in market oriented smallholder dairy farms in Adama, Ethiopia. cabidigitallibraryorg. (2010) 161:574–9. doi: 10.5555/20113044573
94. Mekibib, B, Furgasa, M, Abunna, F, Megersa, B, and Regassa, A. Bovine mastitis: prevalence, risk factors and major pathogens in dairy farms of Holeta town, Central Ethiopia. Vet World. (2010) 3:397–403. doi: 10.5455/vetworld.2010.397-403
95. Wubshet, A, Tesema, T, Sahile, M, Derib, B, and Haile, A. Incidence of heifer mastitis and identification of major associated pathogens in dairy farms at wolaita soddo town, southern Ethiopia. J Dairy Vet Anim Res. (2017) 5:169–76. doi: 10.15406/jdvar.2017.05.00156
96. Yohannes, K, and Alemu, B. Prevalence of bovine mastitis in lactating cows and associated risk factors in and around Wolayta Soddo, southern Ethiopia. Int J Adv Res Biol Sci. (2018) 5:60–9. doi: 10.22192/ijarbs.2018.05.12.008
97. Tefera, B, Tilki, T, Tefera, N, Bayene, Z, Belew, S, Haftu, R, et al. Antimicrobial resistance status of selected bacteria isolated from animal source foods and feed in Ethiopia. Ethiopian Vet J. (2022) 26:18–37. doi: 10.4314/evj.v26i2.2
98. Bitew, M, Tafere, A, and Tolosa, T. Study on bovine mastitis in dairy farms of Bahir Dar and its environs. J Anim Vet Adv. (2010) 9:2912–7. doi: 10.3923/javaa.2010.2912.2917
99. Haftu, R, Taddele, H, Gugsa, G, and Kalayou, S. Prevalence, bacterial causes, and antimicrobial susceptibility profile of mastitis isolates from cows in large-scale dairy farms of northern Ethiopia. Trop Anim Health Prod. (2012) 44:1765–71. doi: 10.1007/s11250-012-0135-z
100. Zeryehun, T, and Abera, G. Prevalence and bacterial isolates of mastitis in dairy farms in selected districts of eastern Harrarghe zone, eastern Ethiopia. J Vet Med. (2017) 2017:1–7. doi: 10.1155/2017/6498618
101. Mesele, A, Belay, E, Kassaye, A, Yifat, D, Kebede, A, and Desie, S. Major causes of mastitis and associated risk factors in smallholder dairy cows in Shashemene, southern Ethiopia. Afr J Agric Res. (2012) 7:3513–8. doi: 10.5897/AJAR11.1808
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance, bovine mastitis, meta-analysis, prevalence, Streptococcus
Citation: Fenta MD, Getahun Feleke M, Mebratu AS, Mengistu BA and Demessie Y (2025) Streptococcal infection and its antimicrobial resistance profile associated with bovine mastitis in Ethiopia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1503904. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1503904
Received: 18 October 2024; Accepted: 04 February 2025;
Published: 12 March 2025.
Edited by:
Joel Fernando Soares Filipe, University of Milan, ItalyReviewed by:
Piera Anna Martino, University of Milan, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Fenta, Getahun Feleke, Mebratu, Mengistu and Demessie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Melkie Dagnaw Fenta, bWlyZXR1ZGFnbmF3QGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.