
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Vet. Sci., 10 March 2025
Sec. Veterinary Infectious Diseases
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2025.1476232
This article is part of the Research TopicThe application of new technologies such as new vaccines, therapeutic cytokines and antibodies, and antiviral drugs in the prevention and treatment of animal infectious diseasesView all 15 articles
Mastitis is the most common and challenging disease that affects dairy animal welfare and causes huge economic loss in dairy industry globally. Conventional antibiotic treatment of mastitis raised the drug resistance and unsuccessful therapy. As an alternative approach, probiotic lactobacilli had shown multifunctional effects against diseases. Lactobacillus strains against mastitis are worth screening and evaluating. In this study, milk-derived Lactobacillus spp. from Ningxia, China were screened in vitro and the anti-mastitis effect of a candidate strain was evaluated through a Staphylococcus aureus-induced rat mastitis model. The results showed that Lactobacillus plantarum X86 exhibited a high adhesion rate of MAC-T cells, presented the best probiotic properties, and demonstrated anti-S. aureus effects in vitro through comprehensive assessment. Furthermore, L. plantarum X86 alleviated pathological damage to the mammary gland, liver, and colon, inhibited the mRNA expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines factors IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in mammary gland tissue; and increased the content of intestine SCFAs in a rat mastitis model induced by S. aureus. In conclusion, our results suggested that L. plantarum X86 could be a promising probiotic for the prevention and treatment of S. aureus-induced mastitis.
Cow mastitis is one of the major diseases in the dairy industry, causing substantial economic losses, reducing milk production and quality, as well as the life span of cows, and increasing the cost of subsequent treatment (1). Currently, a novel perspective suggests that there is a close relationship between the intestinal barrier and mastitis. For example, a study found that subacute ruminal acidosis (SARA) in dairy cows activate systemic inflammatory response and increase the permeability of blood-milk barrier, intestinal barrier and rumen barrier, which can cause mastitis (2). Mice with dysregulated intestinal flora exhibited an increase in the abundance of enterobacterium and a decrease in the number of SCFAs-producing bacteria, along with enhanced blood-milk barrier permeability and more severe Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis. This situation can be reversed through fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) in mice with impaired intestinal flora (3). Therefore, enhancing the integrity of the intestinal barrier, and preventing the passage of harmful substances and bacteria through the barrier can influence the health of the mammary gland.
Antibiotics are utilized in dairy cows for the treatment of clinical mastitis and during the dry period, which leads to issues such as bacterial resistance, antibiotic residues and transmission of resistance genes (4). Given the current emphasis within the global livestock and poultry industry on developing “non-resistance products,” there is an urgent need to develop anti-resistance products for the prevention and management of cow mastitis.
Lactic acid bacteria are a group of bacteria that produce a large amount of lactic acid by fermenting carbohydrates. Some lactic acid bacteria are recognized as food safety-grade strains (5). Lactic acid bacteria isolates had exhibited anti-mastitis effects both in vitro and in vivo, such as inhibiting the adhesion and internalization of mastitis pathogenic bacteria to BMECs (6), inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria (7), and reducing the pathological damage of cells (8–10) or animal models of mastitis through immunomodulatory effects (9) and enhancing the blood-milk barrier (11). Some potential Lactobacillus strains (L. salivarius CECT5713 & L. gasseri CECT5714) (12), L. fermentum CECT5716 (13) and L. salivarius PS2 (14) that replaced Staphylococcus spp. causing human mastitis were effective in clinical trials. Several studies have showed that Lactobacillus can reduce the abundance of enterococcus and streptococcus in the milk of dairy cows with mastitis and alleviate the inflammation of dairy cows suffering from mastitis (15, 16). Breast milk and cow milk are important sources of lactic acid bacteria (17, 18). Lactobacilli isolated from breast milk meet some of the main criteria for generally recommended human probiotics, including human origin, a safety history, long-term infant intake, and adaptation to a dairy matrix (19). Hence, it is promising to explore the probiotic lactic acid bacteria strains from milk for the prevention and treatment of mastitis in dairy cows.
Chandler was the first to establish a mouse model of bacterial mastitis (20), which is still utilized today (21, 22). Compared with mice, the milk duct opening of rats is more distinct and has higher operability during modeling, thus it is also widely employed (23, 24). Due to the high cost and non-standardized operation of direct experiments on cows, a rat model of S. aureus mastitis was established in this paper to assess the preventive effect and related mechanism of Lactobacillus plantarum X86 on mastitis.
Therefore, we hypothesized that the screened milk-derived Lactobacillus strains had an anti-mastitis effect in this paper, which was achieved by enhancing the mammary gland and intestinal barrier. This will provide a basis for alternatives for the prevention and control of bovine mastitis.
Animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the guidelines and regulations by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) to ensure the ethical treatment of animals. All procedures involving handing and restraint, gavage, blood collection, and anesthetized were carried out with rigorous ethical standards in place to minimize any potential harm or distress to the rats. The animal experiments had been approved by the Ethics Committee of the College of Life Sciences, Sichuan University (SCU2203016).
Twenty-four pregnant SD rats were individually housed in a barrier system at 22°C and 40–70% humidity (Chengdu Lilai biotechnology Co., Ltd.). After a 7-day adaptation period (14 ± 2 days after pregnancy), the rats were randomly assigned to three groups: Control (n = 8), X86 + S. aureus (n = 8) and S. aureus (n = 8). Rats in X86 + S. aureus group received daily gavage of 0.5 mL of L. plantarum X86 at a concentration of 1 × 109 CFU/mL, while rats in control and S. aureus groups received an equivalent volume of normal saline until the 14th day post-delivery. Subsequently, on the following day after completion of gavage, mastitis models were established in both the X86 + S. aureus and S. aureus groups.
Lactobacillus rhamnosus LGG was obtained from commercially available probiotic products. Lactobacilli spp. was isolated from raw milk collected from commercial farms in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region, China. The commercial dairy farms are located in the north (Farm A, N106.69, E39.12), mid (Farm B, N106.04, E38.42 and Farm C, N106.07, E38.67), and south (Farm D, N106.29, E37.75; Farm E, N106.30, E37.58; and Farm F, N106.24, E37.59) regions of Ningxia Province in China. The raw milk samples were collected from 2018 to 2019. The mammary tissue of the cows did not have visible signs of clinical mastitis, such as swelling or redness. Milk samples were collected from one teat for each cow. The sampling methods adhered to standard recommendations. In brief, the first streams of milk were discarded, and the teats were subsequently exposed to iodine tincture for 30 s and dried with individual towels by farm veterinarians. Subsequently, the first streams of milk were discarded and the milk samples were collected. Approximately 30 mL of milk was collected into a 50 mL sterile centrifuge tube and stored at −20°C. S. aureus strains SA2 and SA6 were isolated from the raw milk of cows with mastitis in the Ningxia region, while S. aureus ATCC29213 was preserved in the laboratory; MAC-T cells were gifted by Associate Professor Gao Jian, College of Veterinary Medicine, China Agricultural University.
Raw milk samples were collected from large-scale ranches in Ningxia and used as resources. The milk samples were then inoculated into MRS liquid medium (Qingdao Hope Bio-Technology Co., Ltd., China) at a 3% inoculum volume ratio in a sterile tube and cultured for 48 h at 37°C. Afterwards, the culture medium was diluted by 10-fold, and the bacterial solution was spread on MRS agar plates, which were then incubated at 37°C for 48 h. Subsequently, several colonies were randomly selected and subjected to two consecutive rounds of inoculation into MRS agar medium (Qingdao Hope Bio-Technology Co., Ltd., China) for purification.
The isolates were identified through 16S rRNA sequencing, following a process in which a single colony was selected and immersed in 100 μL of 20 mM NaOH solution, then boiled in hot water for 10 min. The solution was centrifuged at 12000 rpm for 2 min, and the supernatant used as template for PCR amplification. Universal bacterial 16S rRNA primers (27F: AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG, 1492R: CTACGGCTACCTTGTTACGA) were utilized for PCR amplification, consisting of 20 μL of 2 × Taq PCR PreMix (Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China) along with 1 μL each of forward and reverse primer (10 μM), 2 μL template, and finally adding ddH2O up to a total volume of 40 μL. The PCR protocol included an initial denaturation at 94°C for 5 min, followed by 35 cycling at 94°C for 30 s, 56°C for 30 s, and 72°C for 30 s, and with a final extension step at 72°C for 2 min. The PCR products were sent to Shanghai Sangon for sequencing. Sequence alignment was performed using the NCBI1, and those with homology of 97% or higher were considered to the same species.
The isolates were cultured in MRS liquid medium at pH 3.0 and incubated at 37°C and 180 rpm for 18–24 h for initial screening. Strains exhibiting obvious turbidity in the bacterial solution were chosen for subsequent experiments. Gram staining and microscopic morphological analysis of the bacteria were performed on these isolates. The phylogenetic tree of isolates and the control strain L. rhamnosus LGG was conducted using MEGA11 software (25) through the neighbor-joining method.
The bacterial growth curve was determined with appropriate modifications based on references (26, 27) as follows: isolates were inoculated in MRS broth at a ratio of 2% and cultured at 37°C, 180 rpm for 48 h. Subsequently, 200 μL of the bacterial solution was added to a 96-well plate every 3 h, with MRS broth used as a control, and the absorbance measured at OD600 nm using a microplate absorbance spectrophotometer (xMarkTM, Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, United States). Furthermore, the pH value of the bacterial solution was measured every 3 h using FE20-FiveEasy pH meter (Mettler Toledo Inc., United States) for drawing the pH curve.
The preparation method for artificial gastric and intestine fluid was performed in accordance with the protocol outlined by Huang and Adams (28). The isolates were inoculated into MRS broth at a ratio of 2%, incubated at 37°C and 180 rpm, then centrifuged at 6000 rpm for 10 min. The pellet was washed twice with 5 mL of PBS buffer. Subsequently, the cells were adjusted to a concentration of 1 × 109 CFU/mL in artificial gastric fluid (pH 3.0) and cultured at 37°C and 180 rpm for 3 h. Following this, bacterial fluid was added to artificial intestinal fluid (pH 8.0) in a ratio of 1:9 and cultured at 37°C, 180 rpm for 8 h. Finally, a 10-fold dilution of the bacterial solution was prepared in artificial gastric and intestinal juice, and 1 mL of different concentrations of the bacterial solution was poured onto MRS agar at approximately 40°C. The cells were thoroughly mixed and cultured at 37°C for 48 h, followed by enumeration of colonies on plates. The survival rates of bacteria in artificial gastric fluid and intestinal fluid were calculated using the following formula (Equation 1) provided by Bao et al. (29):
where N1 = the viable count of lactic acid bacteria cultured in the artificial gastric/intestinal fluid, and N0 = the viable count of lactic acid bacteria prior to inoculation.
The viability of isolates in the culture medium containing bile salt was measured in vitro to evaluate their tolerance to bile salt. A volume of 1 mL of isolates (109 CFU/mL) was inoculated into 9 mL of MRS-THIO solution containing 0.3% bovine bile salt and incubated at 180 rpm for 24 h. Agar plate count and survival rate were determined following the method mentioned above.
The preparation of cell free supernatant (CFS) was conducted as follows: the MRS Broth medium was filled to 75% capacity (37.5 mL/50 mL), and the activated strain medium was inoculated at a ratio of 2% and incubated at 37°C for 48 h. The culture solution was then centrifuged at 6000 rpm for 10 min, and the supernatant was transferred into a sterile centrifuge tube and stored at 4°C until further use.
The experiment was conducted in accordance with the methods described by Bai et al. (30). CFS was diluted twofold with LB liquid medium (Qingdao Hope Bio-Technology Co., Ltd., China) to achieve concentrations of 1, 0.5, 0.25 and 0.125. 100 μL. Subsequently, 100 μL of S. aureus (2 × 105 CFU/mL) suspension and of 100 μL of CFS at different concentrations were added to a 96-well plate at 37°C for 24 h. The absorbance was measured at OD600 nm using a microplate absorbance spectrophotometer (xMark™, Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, United States). LB liquid medium served as the negative control while S. aureus suspension served as the positive control. The inhibition rate was calculated using the following formula (Equation 2):
where AOD600 = the mean value of positive control wells, BOD600 = the mean value of sample wells, and COD600 = the mean value of negative control wells.
The inhibition of S. aureus biofilm by the CFS of isolates was carried out in accordance with the protocol described by Bai et al. (30). The CFSs of isolates were twofold serially diluted with LB liquid medium containing 1% glucose to achieve concentrations of 1, 0.5, 0.25 and 0.125. Subsequently, 100 μL S. aureus (2 × 106 CFU/mL) was added to a 96-well plate, followed by the addition of 100 μL of each concentration of CFS and incubated at 37°C for 24 h to allow bacterial biofilms formation. After discarding the bacterial solution, the wells were washed twice with 200 μL PBS buffer to remove plankton cells. Then, a solution containing 200 μL of 0.4% crystal violet was added for 5 min and subsequently washed twice with distilled water (200 μL). Finally, a solution containing 200 μL of glacial acetic acid (20%) was added and incubated at 25°C for 30 min to dissolve the biofilm. LB liquid medium containing 1% glucose served as a negative control while S. aureus suspension (1 × 106 CFU/mL) served as a positive control for measuring absorbance at OD570 nm using a microplate absorbance spectrophotometer (xMark™, Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, United States). The inhibition rate was calculated using the following formula (Equation 3):
where AOD570 = the mean value of positive control wells, BOD570 = the mean value of sample wells, and COD570 = the mean value of negative control wells.
The broth microdilution method was employed to determine the drug resistance phenotype of lactic acid bacteria (26). The antibiotic stock solution was diluted using a twofold dilution method to obtain 12 concentrations commonly used in the determination antibiotic resistance phenotypes. Subsequently, 100 μL serial concentrations of the antibiotic solution were added to 96-well plates, followed by the addition of 100 μL suspension of lactic acid bacteria to be tested (2 × 105 CFU/mL). The cells were then cultured at 37°C for 24 h with shaking at medium speed for 1 min and measurement of OD600. A negative control using 200 μL MRS broth and a positive control using a lactic acid bacteria suspension (1 × 105 CFU/mL) were included. The cut-off value of antibiotic resistance of lactic acid bacteria as defined by the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) literature (31) was adopted, along with additional references (32–34). The cut-off values of antibiotic resistance by the broth microdilution method for various genera of lactobacilli were shown in Supplementary Table S1. Results were judged according to the following criteria: sensitivity (S): ≤ cut-off value; drug resistance (R): > cut-off value.
The ability of the adherence into host cells have a key role to provide the foundation for Lactobacillus to exert its benefits. The bovine mammary epithelial cell line (MAC-T) has been widely used for adhesion and invasion assays (6, 35). Therefore, the adhesion capability to MAC-T was assessed of L. plantarum X86 in this study. The adhesion of lactic acid bacteria to MAC-T cells was assessed following the protocol described in Bouchard et al. (6): MAC-T cells were seeded at a density of 2 × 105 cells/well in 12-well plates and incubated at 37°C in a 5% CO2 for 24 h. Subsequently, the cells were washed twice with PBS and exposed to lactic acid bacteria at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 2000:1, with a concentration of 5 × 108 CFU/mL, for adhesion. The co-culture was maintained at 37°C with 5% CO2 for 1 h. Following this incubation period, nonadherent lactic acid bacteria were removed by washing the MAC-T cells four times with PBS. Cell digestion was then carried out by adding 0.25 mL of trypsin (0.05%) to each well and incubating at 37°C for 10 min. Lysis of the cells was achieved by adding 100 μL of Triton (0.01%). Finally, all liquid from the wells was collected and cell counting performed using the plate counting method as previously described.
Based on the findings from the aforementioned experiments, the biological characteristics of lactic acid bacteria were categorized into five indicators: (1) growth (including growth curve and acid production curve); (2) fundamental probiotic benefits (encompassing artificial intestinal, gastric juice, and bile salt tolerance); (3) inhibitory effects on S. aureus (comprising growth and biofilm inhibition of S. aureus strains); (4) adhesion to MAC-T cells; and (5) resistance of isolates to antibiotics. Each of these five indicators is allocated 20 points, resulting in a total score of 100 points. Please refer to Supplementary Table S2 for detailed scoring criteria.
The rat mastitis model was established following the protocol outlined by Chandler (20). The specific procedures were as follows: (1) offspring rats were removed 2 h prior; (2) rats were anesthetized with isoflurane gas and maintained under anesthesia; (3) nipple and surrounding skin were disinfected with a 75% ethanol cotton ball, after identifying the opening of the breast duct under the operating microscope, the nipple was gently clamped by forceps, and a 30G syringe needle was inserted. Subsequently, the nipple was gently lifted by forceps and covered by the needle to inject liquid into the breast duct. After removing the needle, there should be no liquid exudation from the breast catheter and no obvious swelling upon touch; (4) The fourth and fifth pairs of mammary glands were perfused with 100 μL S. aureus (106 CFU/mL), while the Control group received an equivalent volume of normal saline; (5) Rats were returned to their cages for natural recovery and continued feeding; and (6) After 24 h, rats were anesthetized with intraperitoneal pentobarbital sodium for dissection and specimen collection.
The blood from the abdominal aorta was collected and the serum was separated, then stored at −20°C. The tissues were immediately preserved in liquid nitrogen and subsequently transferred to −86°C for future use. Breast tissues, jejunum and colon tissues were aseptically obtained for pathological examination. The specimens were promptly fixed in fixative solution with an exchange with 2 h. Tissue specimens were fixed in neutral formaldehyde, followed by routine paraffin sections stained with hematoxylin eosin staining.
Cytokines play a significant role in the process of breast inflammation, and exist in the form of a network, mutually influencing and inducing each other. Pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 play crucial roles in regulating infection and inflammation. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, a marker of neutrophils, serves as an indicator of inflammation in mammary tissue. To a certain degree, the content of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, as well as the activity of MPO are regarded as indicators of inflammation in mammary tissue (36, 37). The concentrations of pro-inflammatory factors (IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6 and TNF-α) and MPO in serum were determined using the ELISA method according to the instructions of ELISA kit (Chengdu Pengshida company) and MPO kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Co., Ltd., China).
The gut tissues (colon and jejunum), mammary gland, and liver tissues were aseptically collected from rats for the assay of inflammatory cytokines mRNA expression. The tissues were homogenized and total RNA was extracted using the RNAprep pure Tissue Kit (JIANSHI Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China) according to the protocol. The quantification of RNA was measured using the Ultralow volume spectrometer BioDrop uLite+ (Biochrom Ltd., Cambridge, United Kingdom). Subsequently, cDNA was synthesized using PrimeScript™ RT reagent Kit (TaKaRa Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Dalian, China) with 0.5 μg of total RNA input normalized. qRT-PCR primers were designed using NCBI Primer Blast and an online primer design tool.2 The primer list was provided in Table 1. The qRT-PCR reaction system included Hieff UNICON® Universal Blue qPCR Green Master Mix (2×) (Yeasen Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) 10 μL, Primers (10 μM) 0.4 μL each, template (10-fold dilutions of cDNA) 3.0 μL, ddH2O was added to make up to 20 μL in total volume. The qRT-PCR procedure consisted of pre-denaturation at 95°C for 2 min for 1 cycle, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 10 s and annealing at 60°C for 30 s; the melting curve followed the instrument default settings. Data analysis was performed using QuantStudio™ Design & Analysis Software and changes in expression were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method with three repeated experiments conducted.
SCFAs, primarily composed of acetic acid, butyric acid and propionic acid, play a pivotal role in immune regulation and inflammatory states (38, 39). A negative correlation was identified between the level of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in the gut and the severity of mastitis (3). To evaluate the potential anti-mastitis mechanism of L. plantarum X86, the content of SCFAs during the S. aureus mastitis model was measured. The detection of gut SCFAs in rats was conducted using GC–MS. Fecal samples were aseptically collected and 25 mg fecal sample were added to 500 μL water (containing 0.5% phosphoric acid), followed by freezing and grinding twice for 3 min (50HZ), sonicated for 10 min, and centrifugation at 13000 g for 15 min at 4°C. Subsequently, the supernatant was mixed with 0.2 mL n-butyl alcohol solvent (containing internal standard 2-ethylbutyric acid at a concentration of 10 μg/mL) and vortexed for 10s, followed by sonication at 4°C for another 10 min and centrifugation at 13, 000 g at 4°C for 5 min. Finally, the supernatant transferred into the injection vial for analysis using the 8,890-7000D Triple Quad GC/MS (Agilent Technologies Inc., CA, United States). The Masshunter quantitative software was utilized for automatic identification and scoring with manual examination assistance. The concentration of each sample was calculated using a standard curve, and the actual content of SCFAS in the sample was determined accordingly.
GraphPad8.0 software was utilized for statistical analysis and graph drawing. The two-tailed t test was employed to calculate the p value for intergroup differences, while one-way ANOVA was used for multiple comparisons. All p values were calculated at the 95% confidence level; where p > 0.05 was considered no significant, p < 0.05 as significant, and p < 0.01 as extremely significant.
A total of 214 lactic acid bacteria strains were isolated and identified from 100 raw milk and cow colostrum samples (Supplementary Table S3). Among those, 12 strains successfully passed the initial screening in artificial gastrointestinal juice and bile salt, exhibiting vigorous grown in vitro. Subsequently, seven strains were selected (Table 2; Figure 1) based on their repeated occurrence. As shown in Figure 2, X86, X275 and X277 clustered into one branch with the closest evolutionary distance to L. plantarum BF1-13 on the phylogenetic tree, thus being identified as L. plantarum. Similarly, X130 was closely related to L. rhamnosus NIMBB006 and was therefore identified as L. rhamnosus; while X133, X135 and X145 clustered with L. paracasei strain Y526 were identified as L. paracasei. L. plantarum X86, L. plantarum X275 and L. plantarum X277 exhibited faster growth rates compared to other strains; additionally, the culture medium of L. plantarum X86 had the lowest pH value among all seven strains (Figures 3A,B).
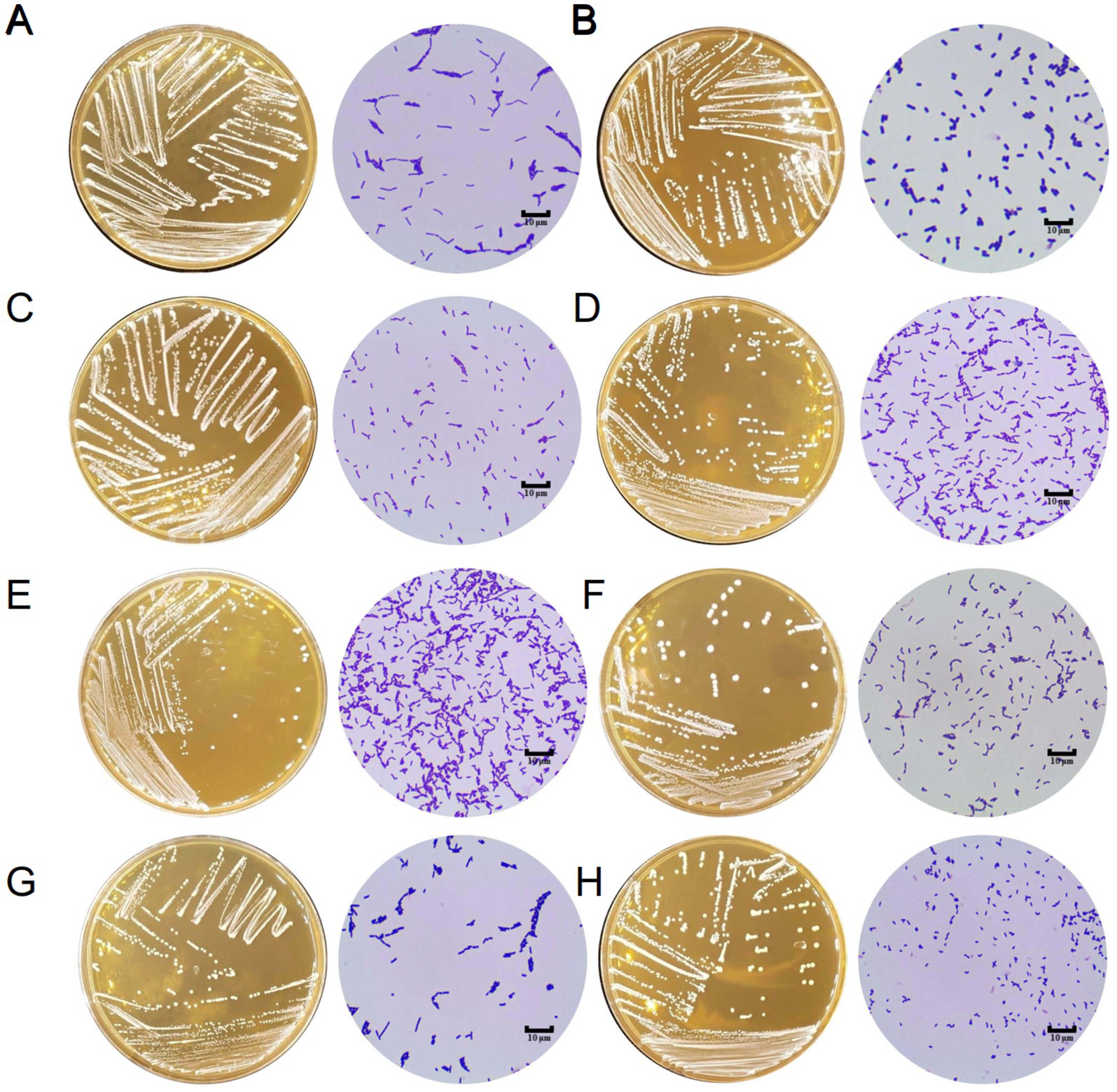
Figure 1. The morphology of Lactobacillus isolates on MRS agar and under microscope (1000×). (A) L. rhamnosus LGG. (B) L. plantarum X86. (C) L. rhamnosus X130. (D) L. paracasei X133. (E) L. paracasei X135. (F) L. paracasei X145. (G) L. plantarum X275. (H) L. plantarum X277.
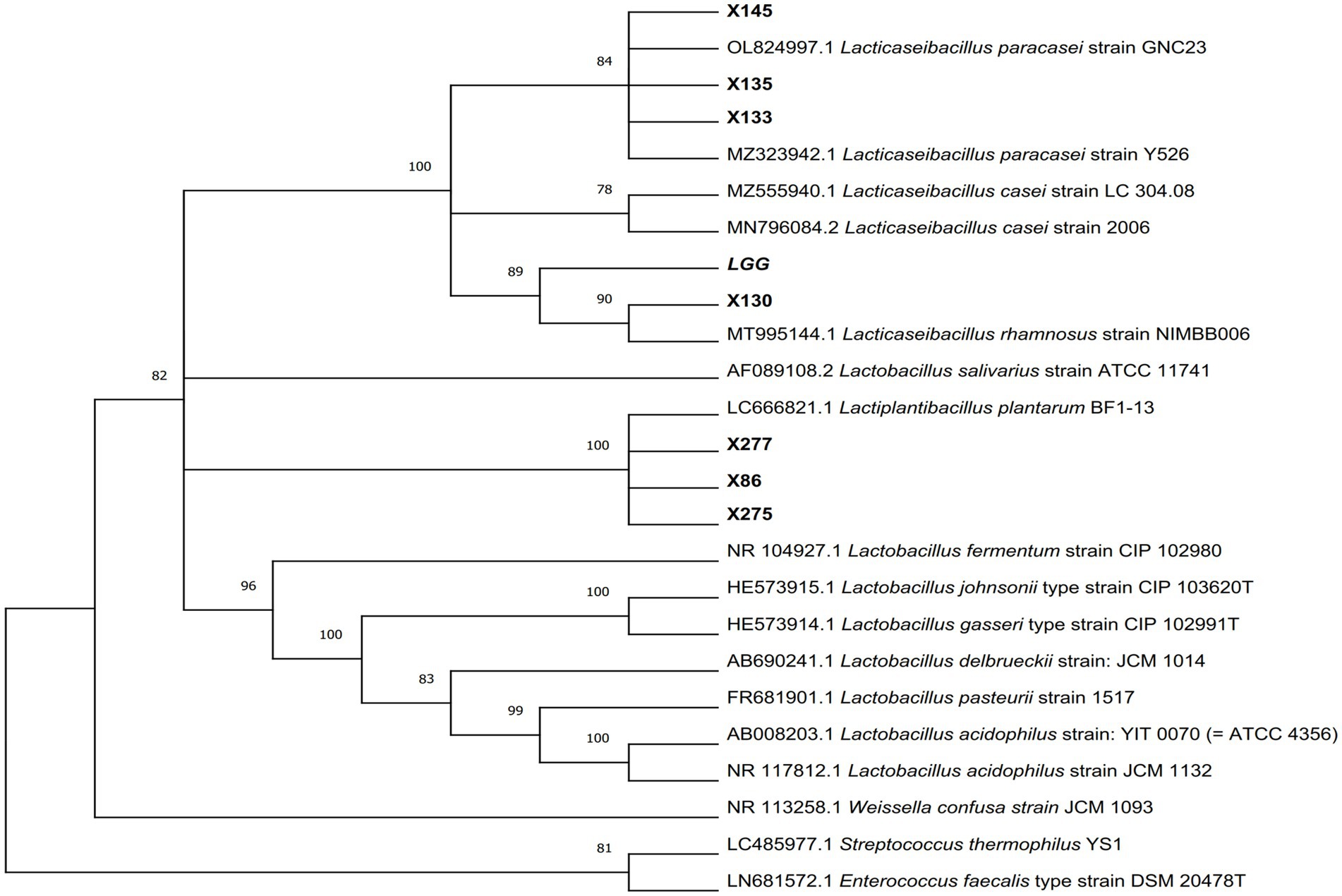
Figure 2. The phylogenetic tree of Lactobacillus isolates was constructed using Neighbor-Joining methods in MEGA11 software, with p-distance used for evolutionary distance based on 16S rRNA gene sequence. The number adjacent to each branch node represents the Bootstrap value, where a bootstrap value >70 indicates a reliable branch. A longer evolutionary branch length signifies more changes in the corresponding species or genes.
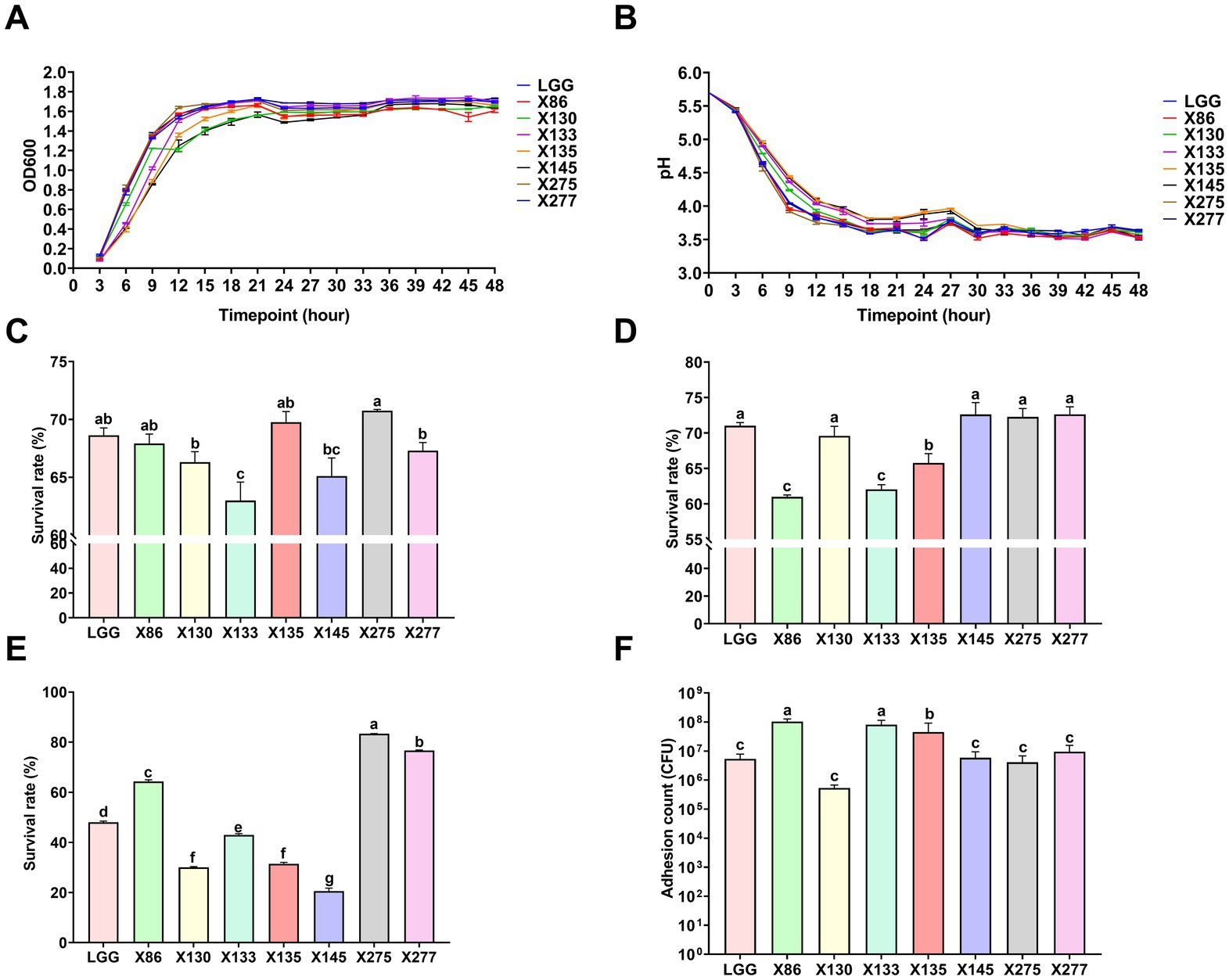
Figure 3. The basic characteristics of Lactobacillus ssp. (A) The growth curve of Lactobacillus ssp. in MRS Liquid medium. (B) The pH curve of Lactobacillus ssp. in MRS liquid medium. (C) The survival rate of Lactobacillus ssp. through the artificial gastric juice. (D) The survival rate of Lactobacillus ssp. through the artificial intestinal fluid. (E) The survival rate of Lactobacillus ssp. through the bovine bile salt. (F) Adhesion count of Lactobacillus spp. to MAC-T cells. The data were presented as Mean ± SD (n = 3), and Anova was employed to assess inter-group differences. Significant differences were indicated by distinct shoulder marks (p < 0.05), while the absence of significance difference was denoted by identical shoulder markers.
As shown in Figure 3C, the isolates showed varying tolerances to the artificial gastric and intestines juice. L. plantarum strains (X86, X145 and X275) demonstrated enhanced tolerance to artificial gastric juice at pH 3.0, with a survival rate of up to 70% after 3 h of treatment compared to other strains, while L. plantarum X86 and X133 exhibited the lowest survival rate (Figure 3D). The control strain LGG displayed the highest survival rate in both artificial gastric and intestinal fluid compared to the test strains. Among the L. plantarum strains (X275, X277 and X86), they showed superior bile salt tolerance with survival rates ranging from 63 and 80%, whereas L. paracasei X145 exhibited the poorest bile salt tolerance ability at only 20% (Figure 3E).
The growth of S. aureus strains SA2 and SA6 was significantly inhibited by the CFS, as demonstrated in Table 3. The inhibition rates for both strains ranged from 85.21–96.80% when the concentration of CFS was between 0.5–1.0. Furthermore, there was a noticeable decrease in antibacterial efficacy with lower concentrations of CFS. The CFS of lactic acid bacteria strains exhibited significant inhibitory effects on S. aureus biofilm, as indicated in Table 4. At concentrations ranging from 0.5 to 1.0, the inhibitory rates of two strains of S. aureus were between 88.39 and 101.23%. Additionally, at a concentration of 0.125, Lactobacillus paracasei X145 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus X130 still demonstrated inhibitory rates of 82.55 and 66.34%, respectively.
In addition, the adhesion of lactic acid bacteria to mammary epithelial cells was strain specific, and there was significant variation in adhesion ability even among different strains of the same species (Figure 3F). L. plantarum X86 and L. paracasei X133 exhibited the highest adhesion ability to MAC-T cells, with an adherent cell count of 108 CFU/mL.
As shown in Supplementary Table S4, all isolates and L. rhamnosus LGG exhibited resistance to gentamicin, kanamycin, streptomycin and neomycin while demonstrating sensitivity to ampicillin, tetracycline, rifampicin and chloramphenicol (with the exception of L. rhamnosus LGG which was resistant to chloramphenicol). The susceptibility of lactic acid bacteria to lincomycin and erythromycin showed variability. Based on the above findings, it can be concluded that the lactic acid bacteria isolates had developed varying degrees of antibiotic resistance. Overall, L. plantarum X86 displayed the highest susceptibility among all tested antibiotics.
The scores of isolates ranged from 63.57 to 76.20, with L. plantarum X86 achieving the highest score and L. paracasei X145 showing the lowest score (Supplementary Table S5).
The mammary gland appearance was shown in Figure 4. The mammary gland areas of the rats in the X86 + S. aureus group and S. aureus group exhibited varying degree of hyperemia, with a consistency resembling “tofu residue.” In contrast, the mammary glands of rats in the Control group appeared smooth without evident congestion and displayed normal histology without inflammatory cell infiltration upon examination by H-E staining under a microscope. Conversely, within the S. aureus group, significant dilation of the mammary acini and ducts was observed, along with severe necrotic of epithelial cells and presence of numerous neutrophils and necrotic 1exfoliated epithelial cells within the glandular cavity. Furthermore, noticeable pathological damage was also evident in the mammary gland tissue of rats in the X86 + S. aureus group; however, there was a marked reduction in lesion severity compared to that seen in the S. aureus group alone (Figure 5).

Figure 4. The morphological characteristics of mammary glands. (A) The Control group. (B) X86 + S. aureus group. (C) S. aureus group with hyperemia and presence of “particles” sensation (blank arrow).
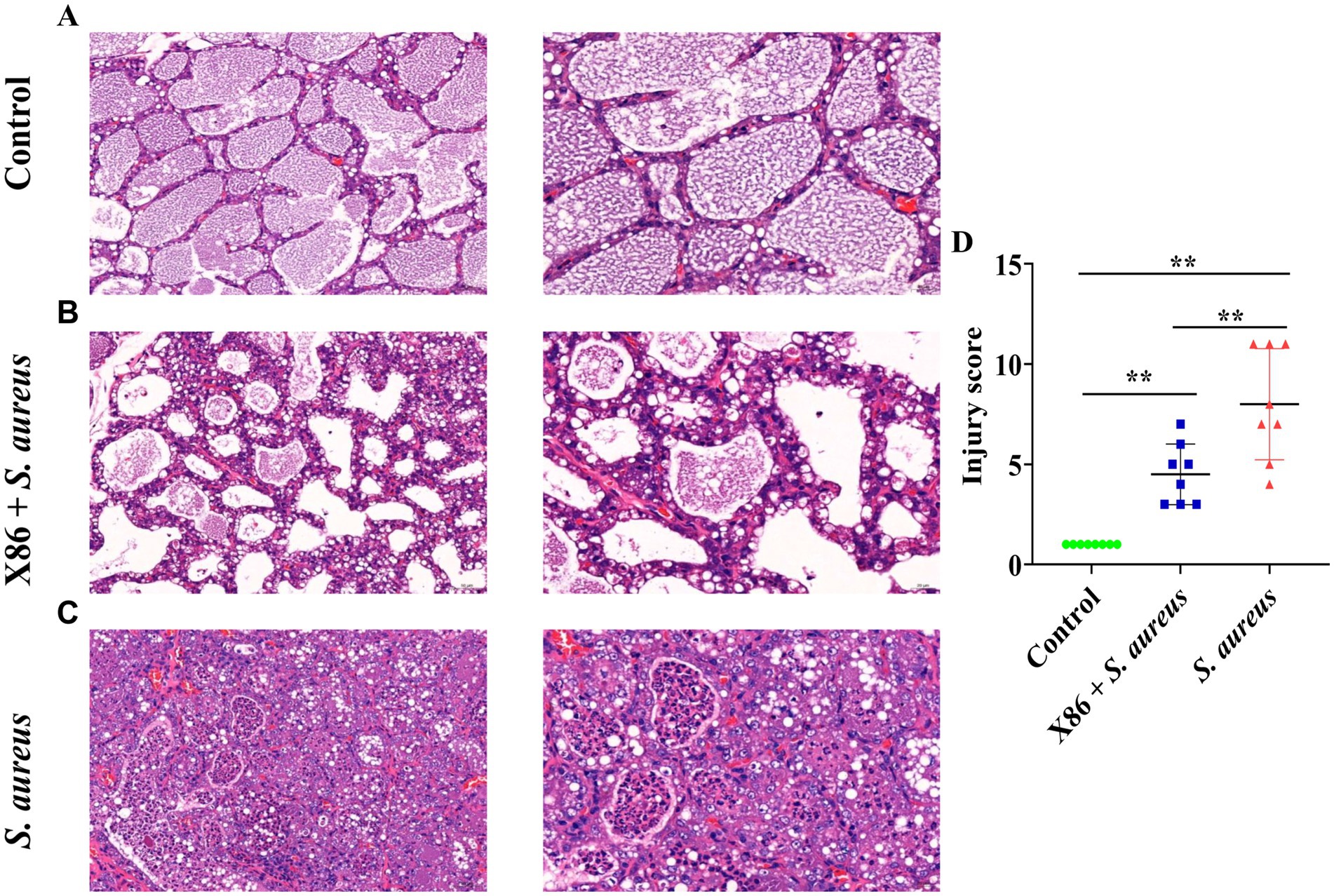
Figure 5. Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining of rat mammary gland. (A) Control group (left with 200×, right with 400×). (B) X86 + S. aureus group (left with 200×, right with 400×). (C) S. aureus group (left with 200×, right with 400×). (D) The comparison of the three groups. ** Indicates statistically significant difference (p < 0.01) (n = 8).
ELISA kits were utilized for the detection of two pro-inflammatory cytokines and MPO activity in the mammary glands of rats within each experimental group. In comparison to the Control group, a significant increase (p < 0.05) was observed in the levels of IL-1β and IL-6 as well as MPO activity in the mammary glands of rats within the S. aureus group, while no significant difference was noted in the X86 + S. aureus group (p > 0.05) (Figure 6). These findings indicated that L. plantarum X86 had the potential to mitigate pro-inflammatory factors and MPO levels within the mammary gland, thereby exerting a protective effect against mammary inflammation at a protein level.
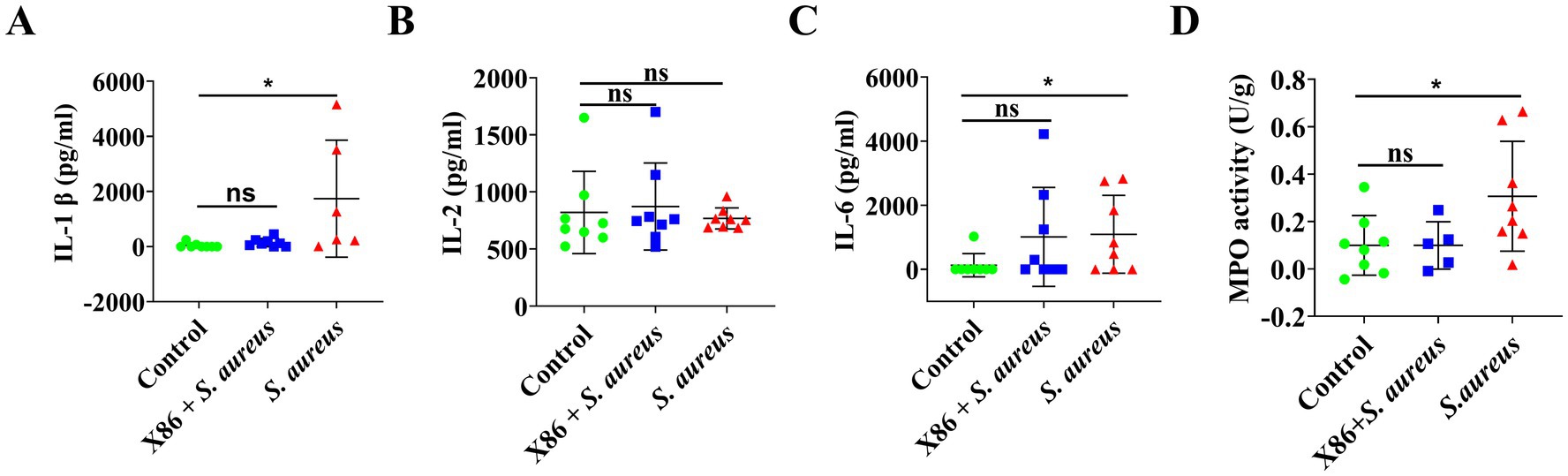
Figure 6. Elisa assay of proinflammatory cytokines and MPO activity test in rat mammary gland. (A) IL-1β. (B) IL-2. (C) IL-6. (D) MPO activity. The data were presented as Mean ± SD (n = 8), and inter-group differences were assessed using Anova. * Indicated a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05), while ns indicated no significant difference (p > 0.05).
The mRNA expression levels of tight junction proteins ZO-1, Occludin, and Claudin, as well as proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6 in mammary gland tissues of rats in each group were detected using qRT-PCR. Figures 7A–C illustrates that there was no statistically significant difference in ZO-1 expression among the three groups (p > 0.05). However, Occludin expression was significantly decreased in both X86 + S. aureus group and the S. aureus group (p < 0.05), while Claudin-1 was significantly decreased only in the S. aureus group (p < 0.05).
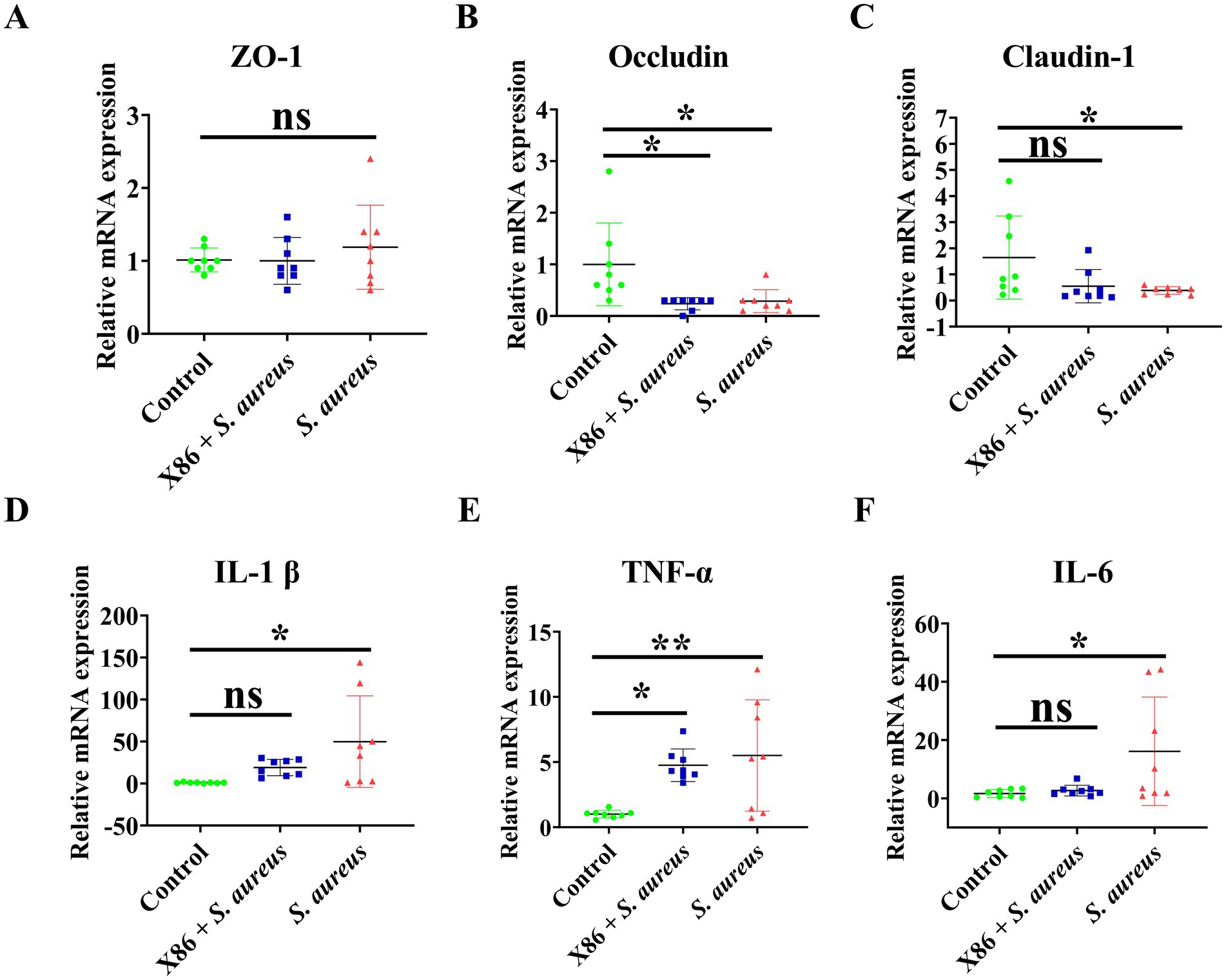
Figure 7. The mRNA expression of tight junction protein and proinflammatory cytokines in rat mammary gland. (A) ZO-1. (B) Occludin. (C) Claudin-1. (D) IL-1β. (E) TNF-α. (F) IL-6. The data were presented as Mean ± SD (n = 8), and inter-group differences were assessed using Anova. * Indicated a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05), ** indicated a statistically significant difference (p < 0.01), while ns indicated no significant difference (p > 0.05).
The results of proinflammatory factor assays were showed in Figures 7D–F. As illustrated in the figures, there was no significant difference in the gene expression of IL-1β and IL-6 between the Control group and X86 + S. aureus group (p > 0.05). However, it is noteworthy that the gene expression of Il-1β and IL-6 in the S. aureus group exhibited a substantial increase (p < 0.05), with the highest observed fold changes being 144.1 and 44 times, respectively. Compared to the Control group, the X86 + S. aureus group exhibited significant increase in TNF-α levels (p < 0.05), while the S. aureus group showed an even more pronounced increase (p < 0.01).
The fecal content of eight types of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in the rats from each experimental group was analyzed using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS). As shown in Table 5, the X86 + S. aureus group exhibited the highest SCFAs content, surpassing that of the Control group and six types of SCFAs in the S. aureus group; however, this difference did not reach statistical significance (p > 0.05).
S. aureus is the most important pathogen responsible for dairy cow mastitis and has the ability to invade mammary epithelial cells and form bacterial biofilms, thereby impacting the efficacy of antibiotic treatment (40). Certain strains of lactic acid bacteria had been shown to possess antagonistic properties against pathogenic bacterial biofilm (41). In this investigation, all lactic acid bacteria strains exhibited inhibitory effects on the bacterial biofilms produced by S. aureus SA2 and SA6, albeit with slight variations in their inhibitory capabilities. This finding suggested that lactic acid bacteria in this study had the ability to antagonize S. aureus biofilm. Lactic acid bacteria establish colonization within the host organism through adherence to host cells and exert antagonistic effects against pathogens. In a previous study, different strains of lactic acid bacteria significantly reduced the adhesion rate of S. aureus to MAC-T cells (6). Nevertheless, a comparable observation was not identified in present study. One possible explanation might be that lactic acid bacteria, such as L. plantarum X86, adhere to cell surfaces via nonspecific mechanisms like surface electrostatic interactions rather than specific binding to cell receptors, thereby lacking competitive repulsion effects on the adhesion sites of S. aureus on cells.
In our study, perfusion of S. aureus in the mammary gland of rats resulted in pathological damage to the liver and intestine (colon), indicating that mastitis is not confined to local inflammation. However, administration of L. plantarum X86 via gavage significantly alleviated the pathological changes in these tissues, suggesting a preventive effect on mastitis in rats. It is worth noting that the pathological changes observed in tissues other than the mammary gland are unlikely to be directly caused by S. aureus itself, as the pathogen was not detected in the blood or feces of the rats. Furthermore, while L. plantarum was detectable in rat feces, it was not found in their mammary glands (data not shown). These results may suggest that the protective effect of L. plantarum X86 on the mammary gland did not stem from direct action by bacteria themselves but rather through stimulation of the host immune system responses and secretion of anti-inflammatory metabolites to prevent mastitis (42, 43).
In the early stages of mammary gland infection, epithelial cells’ pattern recognition receptors (PRR), such as Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), interact with microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMP) to recognize pathogens, resulting in the secretion of cytokines like IL-1β and TNF-α and the recruitment of leukocytes (e.g., neutrophils) from the bloodstream to the mammary gland (10). Numerous studies had demonstrated that lactic acid bacteria can suppress NF-KB signaling activation (44, 45) and decrease proinflammatory factor expression in mouse mammary glands or BMECs (8, 10, 46). In the present study, S. aureus significantly elevated IL-1β expression (p < 0.05) and TNF-α expression of (p < 0.01) in the mammary gland, indicating the occurrence of mammary inflammation, while L. plantarum X86 inhibited the expression of these two cytokines to varying degrees. Furthermore, there were no changes observed in inflammatory factors with the gut (colon and jejunum). These results indicated that S. aureus mammary triggered inflammation in the mammary gland, but no significant change was observed in the intestinal tract. Analysis of serum inflammatory factors and MPO revealed no significant difference in the expression of pro-inflammatory factors IL-1β and TNF-α, as well as MPO levels in the bloodstream 24 h after infusion of S. aureus into mammary gland. The rapid onset of clinical symptoms following LPS infusion into cow’s mammary glands (47) was consistent with our results. The blood-milk barrier primarily consists of endothelial cells, connective tissue, basement membrane and epithelial cells. Occludin, ZO-1 and Claudin-1 are key tight junction proteins within the blood-milk barrier, with their expression levels serving as important indicators reflecting barrier integrity (11). In the current work, it was observed that the expression of Occludin gene in S. aureus group was significantly decreased compared to the control group (p < 0.05), while no change was noted in the expression of ZO-1 gene. Furthermore, S. aureus led to a reduction in the expression of Occludin, ZO-1 and Claudin-1 in the colon, with no significant changes observed in the jejunum. Interestingly, L. plantarum X86 demonstrated protective effects on breast epithelial cells against S. aureus-induced down-regulation of Claudin-1, as confirmed by immunohistochemistry (Supplementary Figure S1). These findings suggested that S. aureus had detrimental effect on both blood-milk barrier and intestinal barrier integrity. Previous studies had shown the ability of lactic acid bacteria to protect those barriers (48–50). It was worth noting that L. plantarum X86 exhibited strain-dependent weak protective effects on the blood-milk or intestinal barrier.
SCFAs, primarily composed of acetic acid, butyric acid and propionic acid, play a pivotal role in immune regulation and inflammatory states (38, 39). These SCFAs can enter host cells through transport or diffusion and interact with epithelial and immune cells by binding to G protein-coupled receptors such as GPR41, GPR43, and GPR109A (51). Furthermore, some SCFAs are capable of modulating the activation, recruitment, and differentiation of immune cells including neutrophils, DCs, macrophages and T lymphocytes leading to reduced expression of proinflammatory cytokines (9, 38). In a previous study, the authors observed a negative correlation between the levels of SCFAs in ileum mucosa and the proportion of associated opportunistic pathogens, suggesting their potential role in maintaining intestinal health in calves (52). Additionally, another study reported that the infusion of LPS into the mammary gland significantly decreased plasma level of SCFAs, especially propionate and butyrate (47). In the present investigation, it was observed that S. aureus perfusion led to a reduction in the levels of propionic acid, isobutyric acid and isovalaric acid in the rat intestine, indicating a close association between SCFAs content and mammary inflammation, which may impact the occurrence and outcome of mastitis. Previous study had demonstrated that SCFAs (butyric acid and propionic acid) possess inhibitory effects on pro-inflammatory cytokines production, activate the NF-κB signaling pathway, act as histone deacetylases in BMECs, and restore blood-milk barrier function. They played a protective role in LPS and S. aureus-induced mastitis models (53–56). In this study, it was found that L. plantarum X86 increased SCFA content in rats by approximately 1.8 times for butyrate, 1.4 times for valaric acid and 1.4 times for isovalaric acid. These findings suggested that L. plantarum X86 may modulate mammary gland inflammatory response of enhancing SCFAs, thereby potentially preventing S. aureus-induced mastitis in rats.
We characterized lactic acid bacteria strains derived from milk and identified a novel species of L. plantarum X86, which demonstrated resilience in gastrointestinal juice and bile salt, the ability to inhibit both planktonic and biofilm S. aureus, adherence rate to MAC-T cells, as well as the lowest antibiotic resistance. Additionally, L. plantarum X86 exhibited a preventive role in a rat mastitis model by reducing the inflammatory response and pathological damage while increasing the content of SCFAs.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
The animal study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the College of Life Sciences, Sichuan University. The study was conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements.
XX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MC: Formal analysis, Project administration, Writing – original draft. SY: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – original draft. HG: Project administration, Writing – original draft. YY: Project administration, Writing – original draft. JZ: Project administration, Writing – original draft. GZ: Project administration, Writing – original draft. JZ: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by grants from the Natural Science Foundation of Ningxia Hui Autonomous (grant number 2022AAC02051).
We thanked Associate Professor Gao Jian, College of Veterinary Medicine, China Agricultural University for giving the MAC-T cells.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fvets.2025.1476232/full#supplementary-material
CFS, Cell-free supernatant; BMEC, Bovine mammary epithelial cell; S. aureus, Staphylococcus aureus; L. plantarum, Lactobacillus plantarum.
1. Ruegg, PL. A 100-year review: mastitis detection, management, and prevention. J Dairy Sci. (2017) 100:10381–97. doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-13023
2. Hu, XY, Li, S, Mu, RY, Guo, J, Zhao, CJ, Gao, YG, et al. The rumen microbiota contributes to the development of mastitis in dairy cows. Microbiol Spectr. (2022) 10:e0251221. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02512-21
3. Hu, XY, Guo, J, Zhao, CJ, Jiang, P, Maimai, T, Yanyi, L, et al. The gut microbiota contributes to the development of Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis in mice. ISME J. (2020) 14:1897–910. doi: 10.1038/s41396-020-0651-1
4. El-Sayed, A, and Kamel, M. Bovine mastitis prevention and control in the post-antibiotic era. Trop Anim Health Prod. (2021) 53:236. doi: 10.1007/s11250-021-02680-9
5. Steinberg, RS, Silva, LCSE, de Souza, MR, Reis, RB, Bicalho, AF, Nunes, JPS, et al. Prospecting of potentially probiotic lactic acid bacteria from bovine mammary ecosystem: imminent partners from bacteriotherapy against bovine mastitis. Int Microbiol. (2022) 25:189–206. doi: 10.1007/s10123-021-00209-6
6. Bouchard, DS, Rault, L, Berkova, N, Le Loir, Y, and Even, S. Inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus invasion into bovine mammary epithelial cells by contact with live Lactobacillus casei. Appl Environ Microbiol. (2013) 79:877–85. doi: 10.1128/aem.03323-12
7. Bousmaha-Marroki, L, Boutillier, D, Marroki, A, and Grangette, C. In vitro anti-staphylococcal and anti-inflammatory abilities of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus from infant gut microbiota as potential probiotic against infectious women mastitis. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. (2021) 13:970–81. doi: 10.1007/s12602-021-09755-x
8. Wu, Q, Zhu, YH, Xu, J, Liu, X, Duan, C, Wang, MJ, et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 ameliorates Escherichia coli-induced activation of NLRP3 and NLRC4 inflammasomes with differential requirement for ASC. Front Microbiol. (2018) 9:1661. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01661
9. Chen, Q, Wang, S, Guo, J, Xie, Q, Evivie, SE, Song, Y, et al. The protective effects of Lactobacillus plantarum KLDS 1.0344 on LPS-induced mastitis in vitro and in vivo. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:770822. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.770822
10. Souza, RFS, Rault, L, Seyffert, N, Azevedo, V, Le Loir, Y, and Even, S. Lactobacillus casei BL23 modulates the innate immune response in Staphylococcus aureus-stimulated bovine mammary epithelial cells. Benef Microbes. (2018) 9:985–95. doi: 10.3920/BM2018.0010
11. Zheng, Y, Xue, S, Zhao, Y, and Li, S. Effects and prospect of Lactobacillus in preventing and treating dairy cow mastits. Chin J Vet Sci. (2021) 41:393–400. doi: 10.16303/j.cnki.1005-4545.2021.02.38
12. Jiménez, E, Fernández, L, Maldonado, A, Martín, R, Olivares, M, Xaus, J, et al. Oral administration of Lactobacillus strains isolated from breast milk as an alternative for the treatment of infectious mastitis during lactation. Appl Environ Microbiol. (2008) 74:4650–5. doi: 10.1128/aem.02599-07
13. Hurtado, JA, Maldonado-Lobón, JA, Díaz-Ropero, MP, Flores-Rojas, K, Uberos, J, Leante, JL, et al. Oral administration to nursing women of Lactobacillus fermentum CECT5716 prevents lactational mastitis development: a randomized controlled trial. Breastfeed Med. (2017) 12:202–9. doi: 10.1089/bfm.2016.0173
14. Fernandez, L, Cardenas, N, Arroyo, R, Manzano, S, Jimenez, E, Martin, V, et al. Prevention of infectious mastitis by oral administration of Lactobacillus salivarius PS2 during late pregnancy. Clin Infect Dis. (2016) 62:568–73. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ974
15. Gao, J, Liu, YC, Wang, Y, Li, H, Wang, XM, Wu, Y, et al. Impact of yeast and lactic acid bacteria on mastitis and milk microbiota composition of dairy cows. AMB Express. (2020) 10:22. doi: 10.1186/s13568-020-0953-8
16. Pellegrino, M, Berardo, N, Giraudo, J, Nader-Macías, MEF, and Bogni, C. Bovine mastitis prevention: humoral and cellular response of dairy cows inoculated with lactic acid bacteria at the dry-off period. Benef Microbes. (2017) 8:589–96. doi: 10.3920/BM2016.0194
17. Reuben, RC, Roy, PC, Sarkar, SL, Rubayet Ul Alam, ASM, and Jahid, IK. Characterization and evaluation of lactic acid bacteria from indigenous raw milk for potential probiotic properties. J Dairy Sci. (2020) 103:1223–37. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-17092
18. Martı́n, R, Langa, S, Reviriego, C, Jiménez, E, Marı́n, ML, Olivares, M, et al. The commensal microflora of human milk: new perspectives for food bacteriotherapy and probiotics. Trends Food Sci Technol. (2004) 15:121–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2003.09.010
19. Martin, R, Langa, S, Reviriego, C, Jiminez, E, Marin, ML, Xaus, J, et al. Human milk is a source of lactic acid bacteria for the infant gut. J Pediatr. (2003) 143:754–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2003.09.028
20. Chandler, RL. Experimental bacterial mastitis in the mouse. J Med Microbiol. (1970) 3:273–82. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-2-273
21. Camperio, C, Armas, F, Biasibetti, E, Frassanito, P, Giovannelli, C, Spuria, L, et al. A mouse mastitis model to study the effects of the intramammary infusion of a food-grade Lactococcus lactis strain. PLoS One. (2017) 12:e0184218. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184218
22. Wang, H, Chen, C, Chen, X, Zhang, J, Liu, Y, and Li, X. PK/PD modeling to assess rifaximin clinical dosage in a mouse model of Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis. Front Vet Sci. (2021) 8:651369. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.651369
23. Eslami, H, Batavani, RA, Asr I-Rezaei, S, and Hobbenaghi, R. Changes of stress oxidative enzymes in rat mammary tissue, blood and milk after experimental mastitis induced by E. coli lipopolysaccharide. Vet Res Forum. (2015) 6:131–6.
24. Tong, J, Hou, X, Cui, D, Chen, W, Yao, H, Xiong, B, et al. A berberine hydrochloride-carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogel protects against Staphylococcus aureus infection in a rat mastitis model. Carbohydr Polym. (2022) 278:118910. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118910
25. Tamura, K, Stecher, G, and Kumar, S. MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol. (2021) 38:3022–7. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msab120
26. Kang, W, Pan, L, Peng, C, Dong, L, Cao, S, Cheng, H, et al. Isolation and characterization of lactic acid bacteria from human milk. J Dairy Sci. (2020) 103:9980–91. doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-18704
27. Pellegrino, MS, Frola, ID, Natanael, B, Gobelli, D, Nader-Macias, MEF, and Bogni, CI. In vitro characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from bovine milk as potential probiotic strains to prevent bovine mastitis. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. (2019) 11:74–84. doi: 10.1007/s12602-017-9383-6
28. Huang, Y, and Adams, MC. In vitro assessment of the upper gastrointestinal tolerance of potential probiotic dairy propionibacteria. Int J Food Microbiol. (2004) 91:253–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2003.07.001
29. Bao, Y, Zhang, Y, Zhang, Y, Liu, Y, Wang, S, Dong, X, et al. Screening of potential probiotic properties of Lactobacillus fermentum isolated from traditional dairy products. Food Control. (2010) 21:695–701. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2009.10.010
30. Bai, JR, Zhong, K, Wu, YP, Elena, G, and Gao, H. Antibiofilm activity of shikimic acid against Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control. (2019) 95:327–33. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.08.020
31. Efsa Panel on Additives and Products or Substances used in Animal Feed (FEEDAP)Rychen, G, Aquilina, G, Azimonti, G, Bampidis, V, Bastos, ML, et al. Guidance on the characterisation of microorganisms used as feed additives or as production organisms. EFSA J. (2018) 16:e05206. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2018.5206
32. Rozman, V, Mohar Lorbeg, P, Accetto, T, and Bogovic, MB. Characterization of antimicrobial resistance in lactobacilli and bifidobacteria used as probiotics or starter cultures based on integration of phenotypic and in silico data. Int J Food Microbiol. (2020) 314:108388. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2019.108388
33. Ammor, MS, Florez, AB, and Mayo, B. Antibiotic resistance in non-enterococcal lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria. Food Microbiol. (2007) 24:559–70. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2006.11.001
34. Danielsen, M, and Wind, A. Susceptibility of Lactobacillus spp. to antimicrobial agents. Int J Food Microbiol. (2003) 82:1–11. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1605(02)00254-4
35. Moliva, MV, Campra, N, Ibañez, M, Cristofolini, AL, Merkis, CI, and Reinoso, EB. Capacity of adherence, invasion and intracellular survival of Streptococcus uberis biofilm-forming strains. J Appl Microbiol. (2022) 132:1751–9. doi: 10.1111/jam.15362
36. Xie, Y, Li, X, Xu, D, He, D, Wang, J, Bi, J, et al. Hordenine alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis by suppressing inflammation and oxidative stress, modulating intestinal microbiota, and preserving the blood-milk barrier. J Agric Food Chem. (2024) 72:21503–19. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c02867
37. Yang, L, Zhou, G, Liu, J, Song, J, Zhang, Z, Huang, Q, et al. Tanshinone i and tanshinone iia/b attenuate lps-induced mastitis via regulating the NF-κB. Biomed Pharmacother. (2021) 137:111353. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111353
38. Li, M, van Esch, BCAM, Wagenaar, GTM, Garssen, J, Folkerts, G, and Henricks, PAJ. Pro- and anti-inflammatory effects of short chain fatty acids on immune and endothelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. (2018) 831:52–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.05.003
39. Ali, I, Raza, A, Ahmad, MA, and Li, L. Nutrient sensing mechanism of short-chain fatty acids in mastitis control. Microb Pathog. (2022) 170:105692. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105692
40. Bardiau, M, Detilleux, J, Farnir, F, Mainil, JG, and Ote, I. Associations between properties linked with persistence in a collection of Staphylococcus aureus isolates from bovine mastitis. Vet Microbiol. (2014) 169:74–9. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.12.010
41. Wallis, JK, Krömker, V, and Paduch, JH. Biofilm challenge: lactic acid bacteria isolated from bovine udders versus staphylococci. Food Secur. (2019) 8:79. doi: 10.3390/foods8020079
42. Ma, C, Sun, Z, Zeng, B, Huang, S, Zhao, J, Zhang, Y, et al. Cow-to-mouse fecal transplantations suggest intestinal microbiome as one cause of mastitis. Microbiome. (2018) 6:200. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0578-1
43. Pique, N, Berlanga, M, and Minana-Galbis, D. Health benefits of heat-killed (Tyndallized) probiotics: an overview. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:2534. doi: 10.3390/ijms20102534
44. Zhao, C, Hu, X, Bao, L, Wu, K, Feng, L, Qiu, M, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation by Lactobacillus reuteri tryptophan metabolism alleviates Escherichia coli-induced mastitis in mice. PLoS Pathog. (2021) 17:e1009774. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009774
45. Li, K, Yang, M, Tian, M, Jia, L, Liang, Y, and Ma, Y. The effect and mechanism of Lactobacillus casei against LPS-induced inflammatory injury in bovine mammary epithelial cells. Chin J Vet Sci. (2022) 42:1805–9. doi: 10.16303/j.cnki.1005-4545.2022.09.12
46. Fukuyama, K, Islam, MA, Takagi, M, Ikeda-Ohtsubo, W, Kurata, S, Aso, H, et al. Evaluation of the immunomodulatory ability of lactic acid bacteria isolated from feedlot cattle against mastitis using a bovine mammary epithelial cells in vitro assay. Pathogens. (2020) 9:410. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9050410
47. Johnzon, CF, Dahlberg, J, Gustafson, AM, Waern, I, Moazzami, AA, Ostensson, K, et al. The effect of lipopolysaccharide-induced experimental bovine mastitis on clinical parameters, inflammatory markers, and the metabolome: a kinetic approach. Front Immunol. (2018) 9:1487. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01487
48. Zheng, Y, Liu, G, Wang, W, Wang, Y, Cao, Z, Yang, H, et al. Lactobacillus casei Zhang counteracts blood-milk barrier disruption and moderates the inflammatory response in Escherichia coli-induced mastitis. Front Microbiol. (2021) 12:675492. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.675492
49. Barroso, FAL, de Jesus, LCL, de Castro, CP, Batista, VL, Ferreira, Ê, Fernandes, RS, et al. Intake of Lactobacillus delbrueckii (pExu:hsp65) prevents the inflammation and the disorganization of the intestinal mucosa in a mouse model of mucositis. Microorganisms. (2021) 9:107. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9010107
50. Mennigen, R, Nolte, K, Rijcken, E, Utech, M, Loeffler, B, Senninger, N, et al. Probiotic mixture VSL#3 protects the epithelial barrier by maintaining tight junction protein expression and preventing apoptosis in a murine model of colitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. (2009) 296:G1140–9. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.90534.2008
51. Rooks, MG, and Garrett, WS. Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. (2016) 16:341–52. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.42
52. Ma, T, O'Hara, E, Song, Y, Fischer, AJ, He, Z, Steele, MA, et al. Altered mucosa-associated microbiota in the ileum and colon of neonatal calves in response to delayed first colostrum feeding. J Dairy Sci. (2019) 102:7073–86. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-16130
53. Wang, J, Wei, Z, Zhang, X, Wang, Y, Yang, Z, and Fu, Y. Propionate protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced mastitis in mice by restoring blood-milk barrier disruption and suppressing inflammatory response. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:1108. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01108
54. Wei, Z, Xiao, C, Guo, C, Zhang, X, Wang, Y, Wang, J, et al. Sodium acetate inhibits Staphylococcus aureus internalization into bovine mammary epithelial cells by inhibiting NF-κB activation. Microb Pathog. (2017) 107:116–21. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2017.03.030
55. Silva, LG, Ferguson, BS, Avila, AS, and Faciola, AP. Sodium propionate and sodium butyrate effects on histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity, histone acetylation, and inflammatory gene expression in bovine mammary epithelial cells. J Anim Sci. (2018) 96:5244–52. doi: 10.1093/jas/sky373
Keywords: raw milk, Lactobacillus plantarum X86, Staphylococcus aureus , rat mastitis model, anti-inflammatory
Citation: Xie X, Cao M, Yan S, Gao H, Yang Y, Zeng J, Zhang G and Zhao J (2025) The preventive effect of probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum X86 isolated from raw milk on Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis in rats. Front. Vet. Sci. 12:1476232. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1476232
Received: 05 August 2024; Accepted: 07 February 2025;
Published: 10 March 2025.
Edited by:
Jin Cui, Northeast Agricultural University, ChinaReviewed by:
Maria Giovanna Ciliberti, University of Foggia, ItalyCopyright © 2025 Xie, Cao, Yan, Gao, Yang, Zeng, Zhang and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiulan Xie, eGlleGl1bGFuOTlAMTYzLmNvbQ==; Jian Zhao, emo4MDRAMTYzLmNvbQ==
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.