- 1College of Life Sciences, Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Biological Resources Protection and Utilization in Nanyue Mountain Area, Hengyang Normal University, Hengyang, Hunan, China
- 2College of Bioengineering, Hunan Vocational Technical College of Environment and Biology, Hengyang, Hunan, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Agro-ecological Processes in Subtropical Region, Institute of Subtropical Agriculture, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Changsha, China
- 4YiMin Ecological Agriculture Development Co., Ltd., Hengyang, China
This study investigated the fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS) on growth performance and meat quality in broilers. Total 160 Xianghuang broilers aged 2 months were randomly assigned into 2 groups, CON (control), FOS (supplemented 0.5% fructo-oligosaccharides in diet). After 38 days, the breast, thigh muscle and liver samples were collected for further analysis. Results showed that no significant effect of 0.5% FOS on growth performance such as average daily gain (ADG), average daily feed intake (ADFI) or feed-to-gain ratio (F:G) were observed (P > 0.05). Broilers in FOS group had a yellower breast than that in CON group (P < 0.05). Breast pH45min and thigh pH24h value of FOS group were greater than that in CON group (P < 0.05). Max shear force and work of shear of cooked breast (pectoralis major) muscle was lower in FOS group compared with CON group (P < 0.05). Hardness (P = 0.065), fracturability (P = 0.063), gumminess (P = 0.079), chewiness (P = 0.080) of cooked thigh meat tended to be higher in FOS group compared to the CON group. Addition of 0.5% FOS resulted in lower thigh total superoxide dismutase (T-SOD) activity compared to CON group (P < 0.05). The malonaldehyde (MDA) concentration (P = 0.066) of breast muscle tended to be lower in FOS group compared with CON group. There was an increasing trend for total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC) activity of thigh muscle in FOS group compared to CON group (P = 0.053). Relative mRNA expression of breast catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1), thioredoxin reductase 1 (TXNRD) were up-regulated by FOS supplementation compared with CON group (P < 0.05). In conclusion, FOS can be utilized at 0.5 % to improve meat quality such as elevating pH value, yellowness and decreasing max shear force of muscle through enhancing the antioxidant activity in broilers.
1 Introduction
Fructo-oligosaccharide is water-soluble dietary fiber which formed by D-fructose and sucrose binding by β-1,2 glycosidic bonds (1). It exists in wheat, potatoes, onion, garlic, bananas and other plants. FOS was reported as involved in the fat metabolism through mobilizing the intestinal bacteria and their metabolites. Supplementation of 1 g FOS per liter of water increased the mRNA expression of genes related to fat digestion and absorption, leucine and isoleucine biosynthesis in ileal mucosa of Taiping chickens (2). Supplemented with 5 g/kg FOS significantly inhibited cecal E.coli growth in 3-and 5-wk-old broilers (3), increased microbial diversity of ileal mucosa in 21-day-old broilers when compared with wheat-corn-soybean meal based diet (4). Cecal abundance of Escherichia coli decreased but Bifidobacterium spp. and Lactobacillus spp. increased after supplementation of FOS and beneficial microorganisms (Bifidobacterium animalis, Enterococcus faecium, Lactobacillus reuteri, Pediococcus acidilactici) in heat-stressed broilers (5). Increasing colonization of B. subtills in broilers’ gastrointestinal tract would be beneficial to their musculoskeletal health (6). Visual appearance of broilers’ thigh muscles was improved by Lactobacillus through increasing xanthophyll accumulation in soft tissues (7). B. subtilis-fed broilers had greater water holding capacity, better taste (flavor, texture, preference, and general aspect) in leg muscle, and these probiotic effects were greater in 0.5 g/kg group than in the 0.25 g/kg group (6). Further, broilers muscle is rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids (8), which makes it sensitive to oxidative deterioration. Due to the effect on bacterial fermentation in the intestine, mineral absorption increased when broilers supplemented with 0.4% (9) or 0.5% (10) FOS (11). Supplemented with coated trace minerals (Cu, Fe, Mn, Zn, Se) in broilers’ diet could decrease both serum and muscle MDA levels and then reduce drip loss of meat (12). Mineral element Zn and Cu is essential for SOD activity. Antioxidant enzymes such as SOD and glutathione peroxidase are able to protect polyunsaturated fatty acids in chicken muscle from free radicals and reactive oxygen species damage. Whether meat quality even meat texture could be improved by this 0.5% relatively high dosage FOS supplementation in broilers is still not well known.
There was positively correlation between the ratio of type I myofiber and antioxidized activities, pH value postmortem, intramuscular fat and saturated fatty acid (SFAs) content in Yak beef Semitendinosus muscles (13). Type IIB myofiber was fast glycolytic myofiber, it contained two-thirds of myoglobin as type I fibers (14), leading to a paler meta color. Compared to glycolytic-type fiber (Type IIX and IIB), oxidative-type muscle fibers (Type I and IIA) had smaller diameters and higher density (15), which contributes to decrease in shear force and increase in meta tenderness (16). Xianghuang broiler is a slower growing breed. Results showed that the breast (pectoralis major, PM) muscle only made up of type IIB fibers in slow-growing Xueshan chicken and fast-growing Ross 308 broiler (17) or Japanese quail (18) but little type I fibers could be found in thigh (gastrocnemius, GAS) muscle of Xueshan and Ross 308 broilers (17). If breast muscle and thigh muscle of Xianghuang broilers respond different to this relatively high dosage of FOS still need to further study. Therefore, we performed a comparative analysis of the effect of 0.5% of dietary FOS on breast and thigh muscle. The objectives of the current work were to evaluate the effect of dietary FOS on growth performance and meat quality in Xianghuang broilers. We hypothesized that high dosage FOS supplementation would improve meat quality through affecting muscle metabolic and antioxidant function in broilers.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Animal ethic statement
Animal work was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Hengyang Normal University, protocol HNUACUC-B202201005.
2.2 Animals and experimental treatments
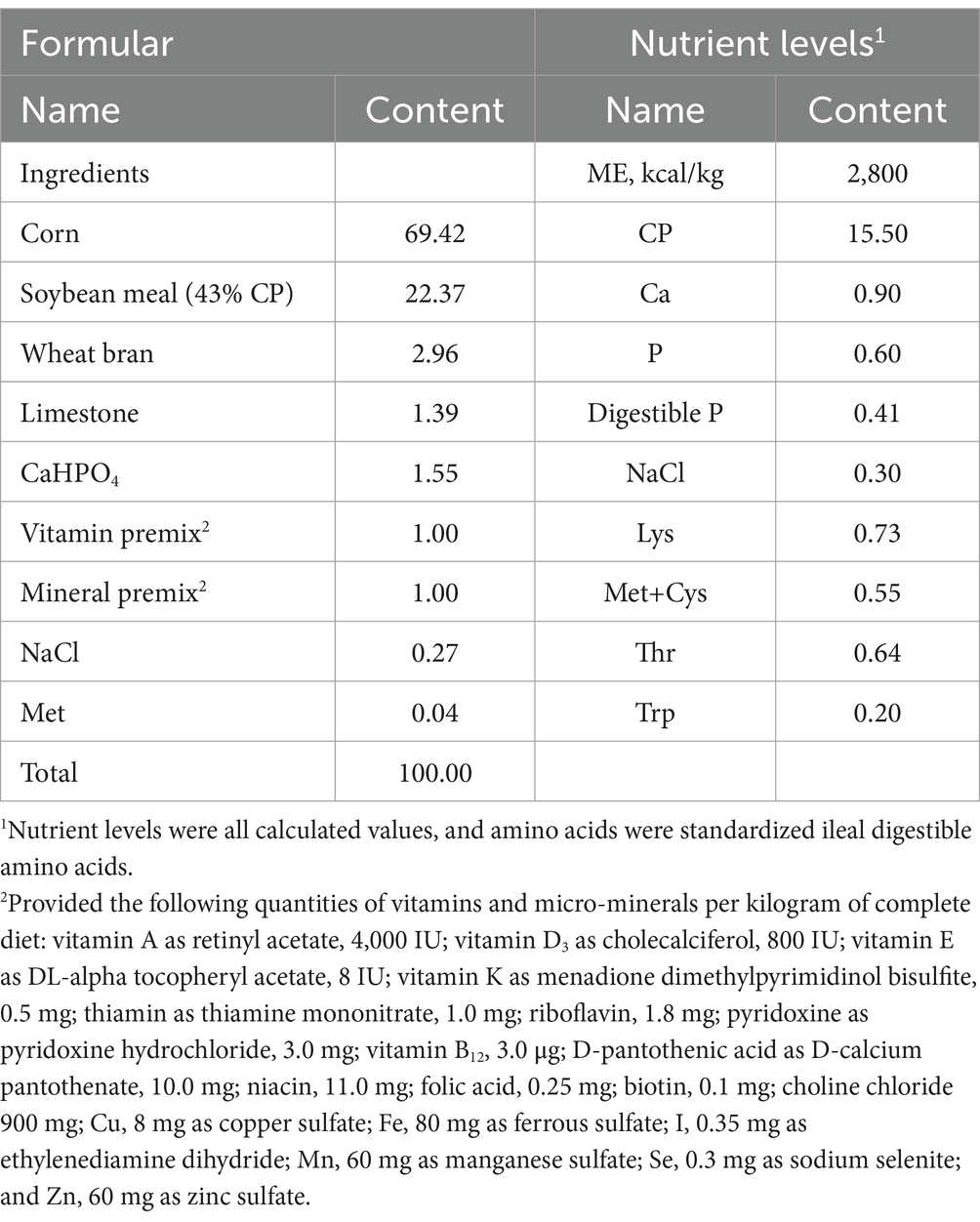
A total of 160 male Xianghuang broilers (0.876 ± 0.149 kg, 2 months old) were randomly assigned to 2 treatments. Each treatment had 8 replicates with 10 broilers per replicate cage. Broilers were fed a corn-soybean meal-based diet (Table 1) that met the nutritional recommendations for yellow-feathered broilers (19), but with or without 0.5% fructo-oligosaccharides, and named as FOS or CON, respectively. FOS was kindly provided by Shandong Longli Biological Technology Co., Ltd. (Shandong, China). Broilers were raised in floor commercial pens (about 0.1 m2/bird) with free access to semi-powder semi-pellet feed and water over the total period of 38 days. Room temperatures were maintained at 22°C by indoor air conditioning. Light was provided for 16 h at 10 lux throughout the experimental period.
2.3 Sample collection
All birds were weighed every week per replicate cage. Feed intake/leftover was recorded every day. Body weight gain and feed conversion ratio were calculated. On d 38, all birds were weighed individually and 2 medium-weight birds per cage were randomly taken and euthanized by carbon dioxide and then cervical dislocation. Liver, boned right breast and thigh muscle were weighed and their percentage were calculated as hot tissue weight/live body weight × 100%. After weighing the eviscerated carcasses, the giblets were removed and the head and toes of the chicken were preserved. Left breast and thigh muscles of 5 cm length were removed along the breastbone and placed in 4% paraformaldehyde for histological analysis. Residual muscle and liver were collected and stored frozen (−80°C) until gene analyses and enzymes analyses.
2.4 Meat quality and nutrient measurements
Meat color such as lightness (L*), redness (a*), yellowness (b*) were determined at 45 min and 24 h postmortem on left 3 cm thick deboned muscle sample using colorimeter (CR-410, Kinica Minolta Sensing Inc., Osaka, Japan). The evaluation was carried out three times on the posterior surface of the skinless breast and thigh muscle. The pH measurement was taken from three different regions of each muscle with portable pH probe (Matthaus pH Star, Germany). Drip loss of muscle was measured as follows, approximately 2 g of left fillet was weighed and suspended on a barbless hook in an inverted plastic cup, suspended for 24 h at 4°C before being removed from the hook, and reweighed. Approximately 5 g of right muscle was weighed, cooked on a steamer, boiling water (95°C) vapor in the bottom of the steamer rise and through the pore to boil the meat for 30 min until the inner temperature reached to 70°C, they were reweighed after these cooked samples cooled to room temperature, and cooking loss was expressed as percentage loss during cooking. Cooked samples were placed in silver paper and held at −20°C until texture profile analysis (TPA) and shear force analysis. Muscles and liver were freeze-dried for 72 h (YAMATO DC801, Japan). Crude fat content was extracted by petroleum ether under Soxhlet extraction method (20). Crude protein content were determined by Kjeldahl method (20).
2.5 Myofibrillar morphology
Muscle samples from the 4% polyformaldehyde were washed in running water overnight, treated with increasing concentrations of ethanol, transparence with xylene and embedded in solid paraffin. Slides of 5 μm thick were obtained on rotary microtome (Leica RM2135, Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany), and then hematoxylin and eosin staining. Images were recorded by Leica inverted microscope (Leica DM500) with camera (Leica MC170 HD). Fiber diameter, cross-sectional area and density were analyzed from 80 fibers per broiler using Image-Pro Plus software (Media Cybernetics Inc., Silver Spring, MD).
2.6 Shear force and texture parameters
Raw and cooked breast and thigh muscle were cut into 1.5 cm × 1.5 cm × 0.5 cm (height) parallel to the muscle fiber orientation 1 day postmortem. Shear force of muscle or meat were measured using Warner-Bratzler HDP/BSW under toughness program fitted with a 50-kg load cell on Texture Analyzer (TA. XT. Plus. Stable Micro systems, United Kingdom). Test settings included a button type trigger, 62 mm travel distance, 2 mm/s test speed, and 10 mm/s post-test speed (21). Max shear force (kg) and total shear energy (work of shear, kg.sec) were recorded.
Texture profile analysis (TPA) of muscle and meat was measured on Texture Analyzer (TA. XT. Plus. Stable Micro systems, United Kingdom) using probe P36R under TPA program. Testing conditions were as follows, holding time was 2 s, trigger force was 0.1 g, test speed was 5.0 mm/s (pre-test), 1 mm/s (test), and 5.0 mm/s (post-test) to reach a 50% compression (22). TPA parameters including hardness, fracturability, adhesiveness, springiness, cohesiveness, gumminess, chewiness, resilience were calculated from the Texture Expert version 1.0 software. Measurements were performed in triplicate for each meat sample and the average value was used for statistical analysis.
2.7 Antioxidant status measurement
Approximately 0.5 g fresh muscle or liver were homogenized in 4.5 mL of 0.9% NaCl solution using tissue grinder (SCIENTZ-12, Xinzhi Biotech logy, Ningbo, China), and then centrifuged (2,500 r/min (1845 g), 15 min, 4°C) to collect supernatant. Activities of total antioxidant capacity (T-AOC), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidase (GSHPX) and MDA concentration were tested according method mentioned in Tan et al. (23). Briefly, activity of T-AOC (mmol/L) was analyzed using its OD 593 nm value compared with standard curve of FeSO4. The Unit of CAT activity was defined as mg of hydrolyzed H2O2 in 1 min per mg protein of sample. One Unit of SOD enzyme was defined as the amount of enzyme that inhibits 50% of lighting reaction of nitroblue tetrazolium. Supernatant was extracted in 10% trichloroacetic acid and then was used to test MDA concentration. Protein concentrations were determined using Bradford method with bovine albumin as the standard.
2.8 Gene expression analysis
Total RNA from muscle and liver was extracted using Trizol reagent (Takara, Dalian, China). Sample concentration and quality were determined on BioSpec-nano (Shimadzu, Japan). 1.0 μg of total RNA was reverse-transcribed into cDNA using the Reverse Transcription Reagent Kit (Aikerui, Changsha, China). The mRNA expression levels of genes (Table 2) were determined using Real-time PCR performed on an QuantStudio 3 (Applied Biosystems, Branchburg, NJ) using SYBR Green quantitative PCR mix (Aikerui, Changsha, China). The 2−△△Ct method (24) was used to calculate the gene expression relative to β-actin which was used as housekeeping gene.
2.9 Statistical analysis
Pen was considered as the experimental unit. All experimental data were analyzed by One-way ANOVA procedure of SAS 8.2 software package (SAS Inst. Inc., Cary, NC). Differences between the means were determined with t tests. Data were presented as mean ± standard error. A value of P < 0.05 was considered significant and 0.05 < P < 0.10 was reported as a trend.
3 Results
3.1 Growth performance
Growth performance such as ADFI, ADG or F:G was not affected by dietary FOS treatment (P > 0.05) (Table 3).
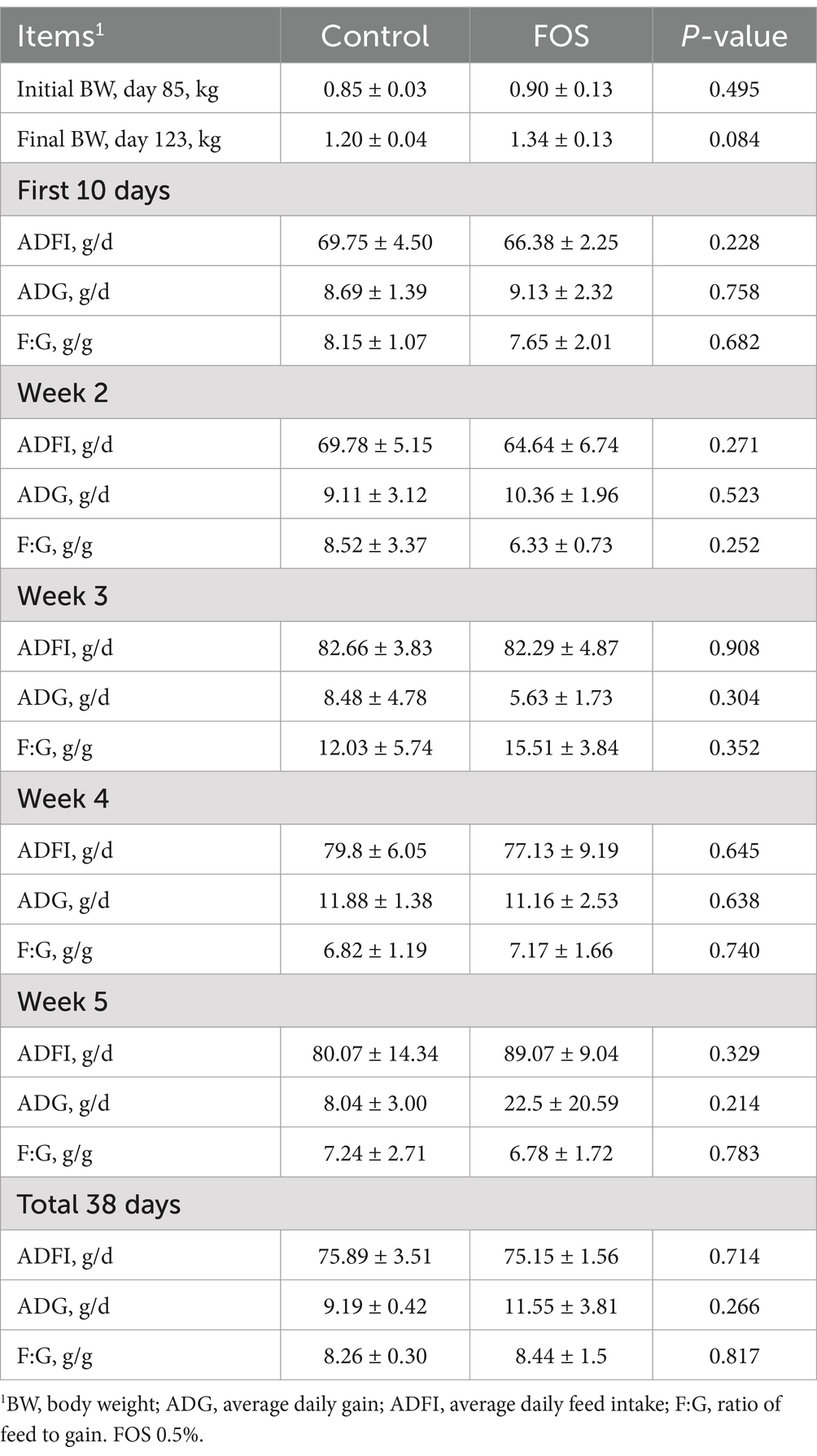
Table 3. Effect of fructo-oligosaccharides on growth performance of Xianghuang broilers1.
3.2 Carcass traits
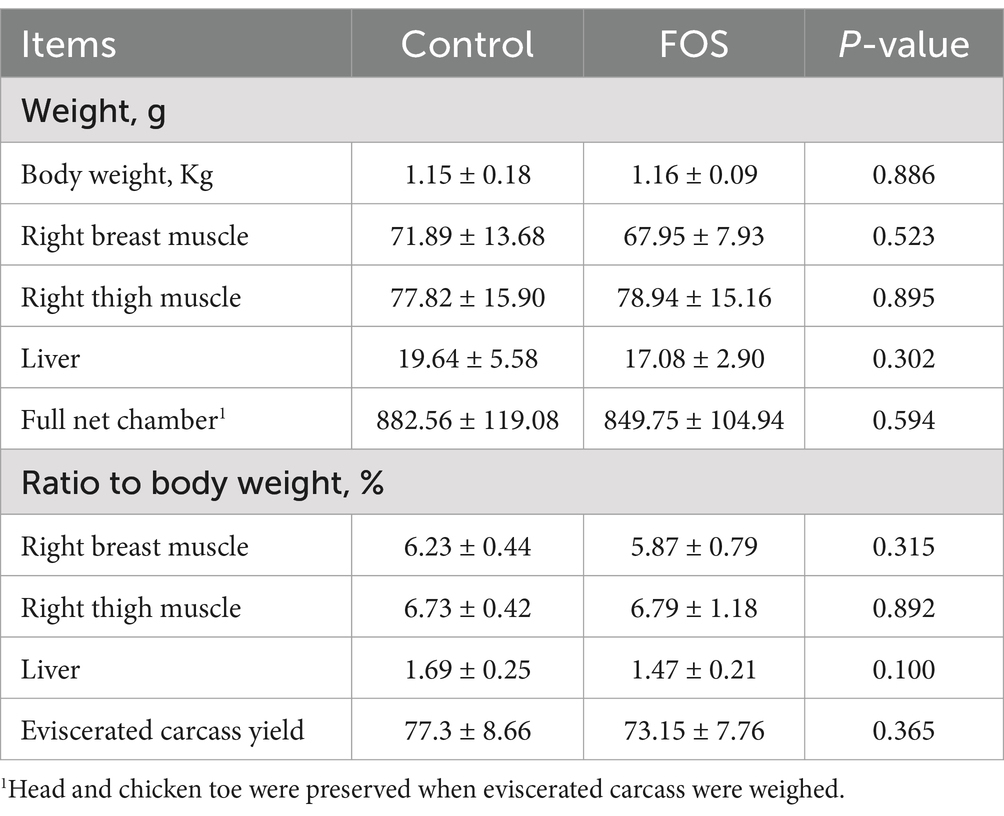
Dietary FOS supplementation did not affect breast or thigh muscle yield, liver weight and percentage, eviscerated carcass yield of Xianghuang broilers (P > 0.05) (Table 4).
3.3 Meat quality
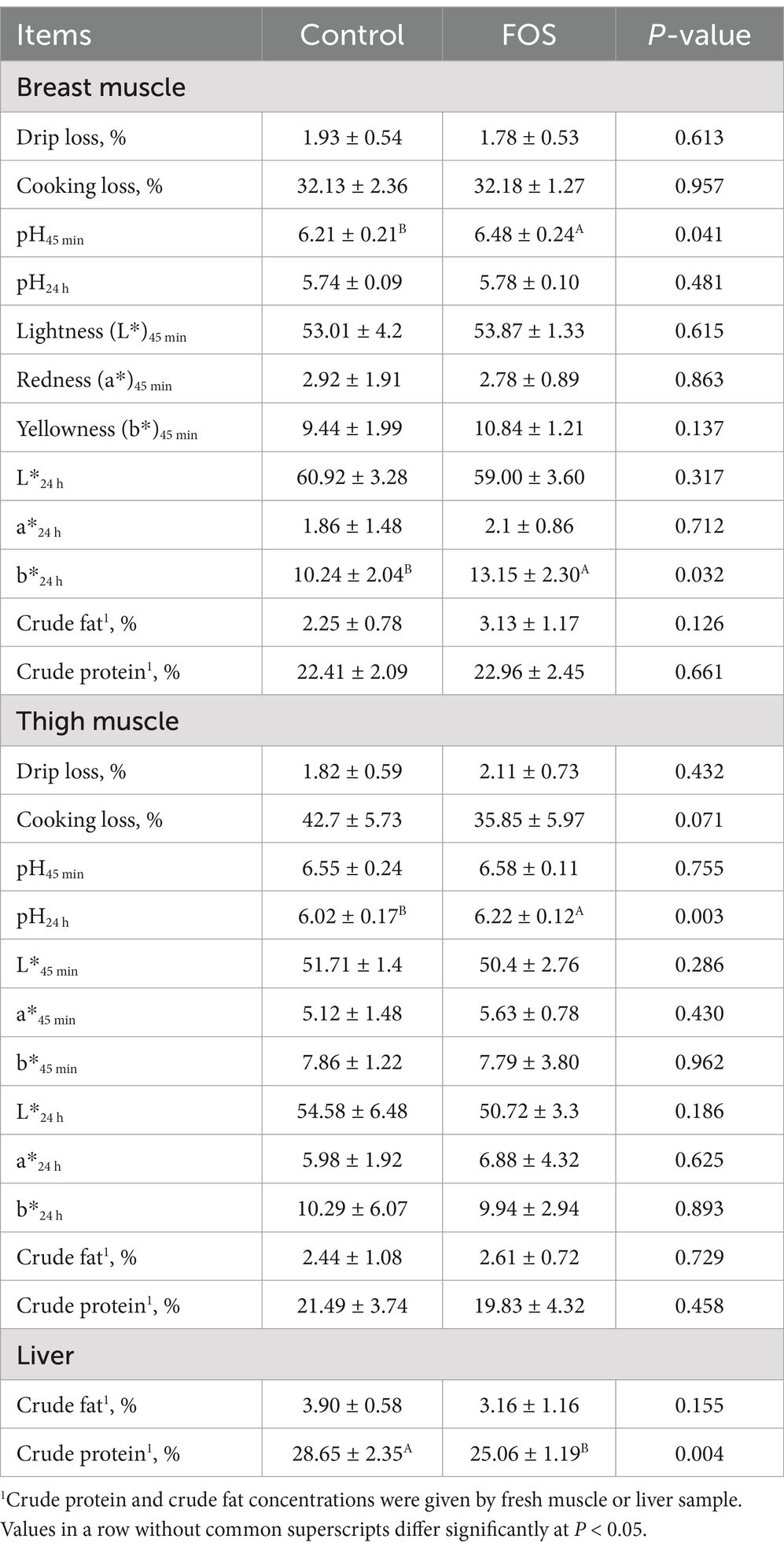
Breast filets from FOS birds had higher b*24h value than that in CON group (P < 0.05) (Table 5). The pH45min value of breast fillet and pH24h of thigh fillet were significantly higher for FOS broilers when compared to CON broilers (P < 0.05). For breast muscle, no significant difference was observed on drip loss, cooking loss, pH24h, meat color (L*, a*, b*) at 45 min, L* and a* index at 24 h between treatments (P > 0.05). There was no significant difference in drip loss, pH45min value, meat color at 45 min and 24 h of thigh muscle (P > 0.05). Cooking loss of thigh fillet tended to be affected by diet (P = 0.071), with decreased value occurring in FOS birds compared to CON group. Crude protein and fat content of breast and thigh muscle or liver were not affected by FOS supplementation (P > 0.05) expect that FOS group had lower crude protein content in liver compared to CON group (P < 0.05).
3.4 Myofibrillar morphology
Dietary FOS supplementation did not affect fiber diameter (Figure 1A), cross-sectional area (Figure 1B) of breast (Figures 2A,B) or thigh muscle (Figures 2C,D) (P > 0.05). Muscle breast fiber density in FOS group tended to be higher than that in CON group (Figure 1C) (P = 0.078), but the fiber density of thigh muscle was the same between FOS and CON group (P > 0.05).
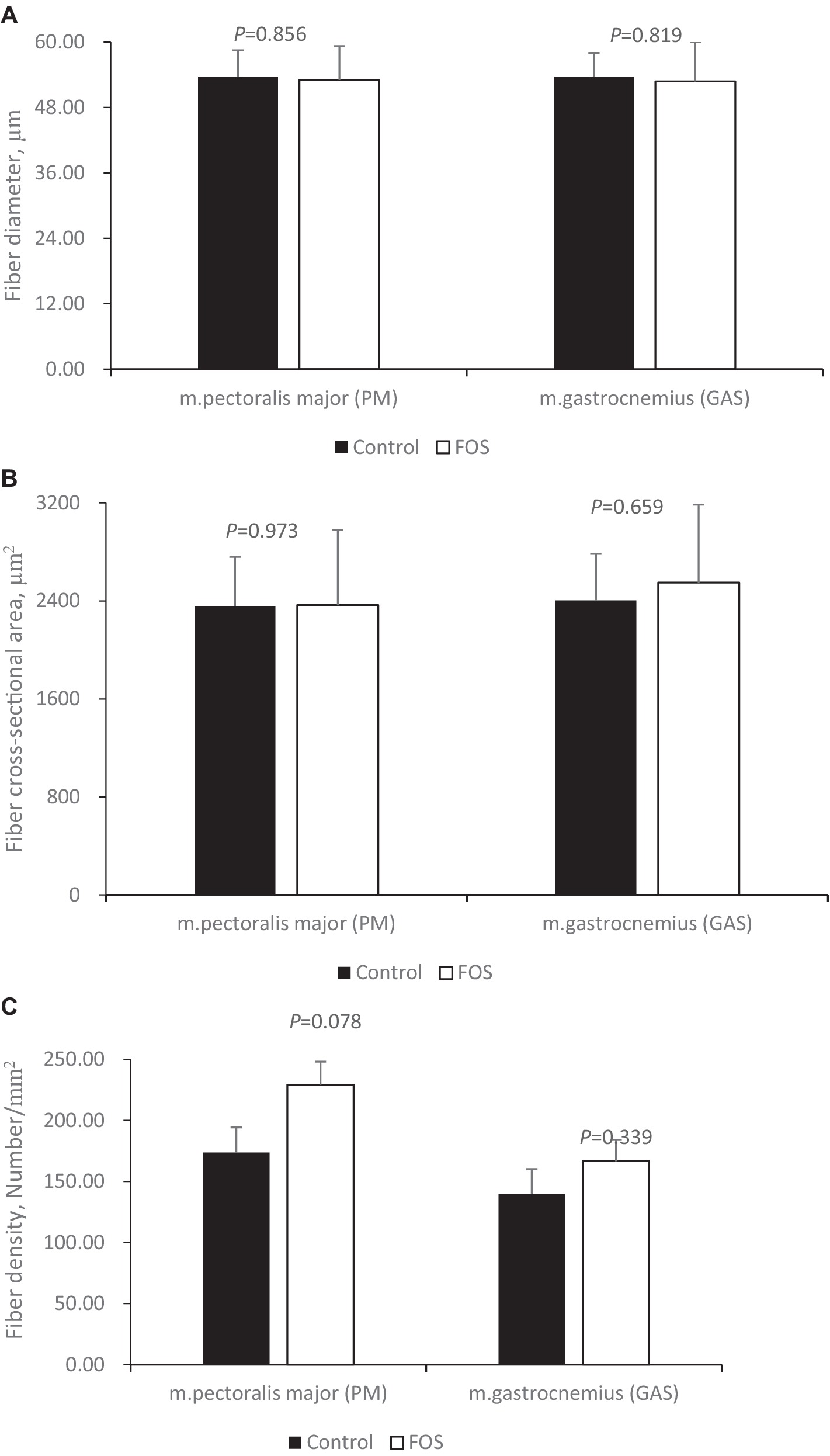
Figure 1. Muscle fiber morphology traits in breast (pectoralis major, PM) and thigh (gastrocnemius, GAS) muscle from control or 0.5% fructo-oligosaccharide (FOS) groups of Xianghuang broilers. Fiber diameter (A, μm), fiber cross-section area (B, μm2), fiber density (C, Number/mm2).
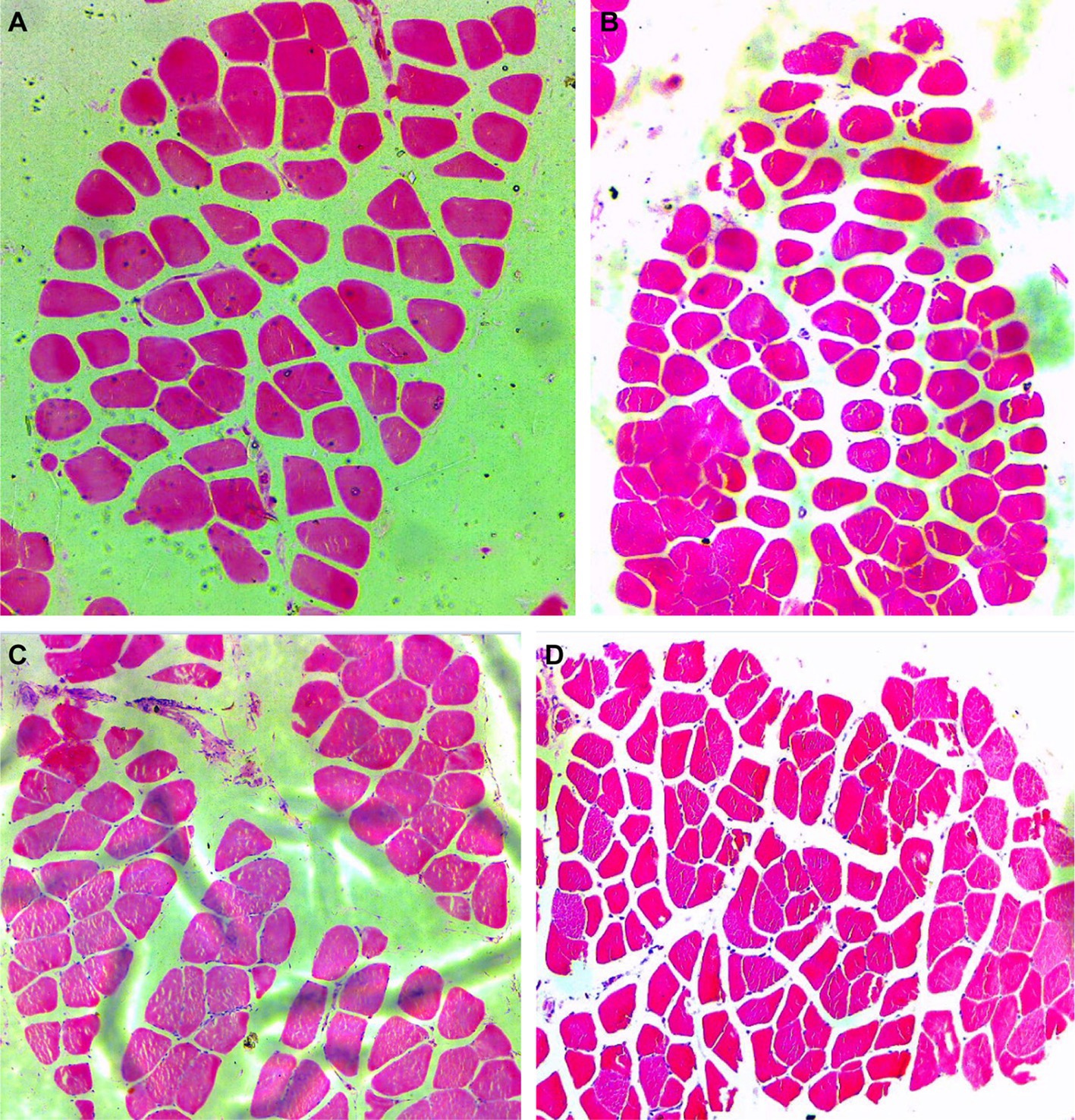
Figure 2. Hematoxylin and eosin staining in breast (pectoralis major, PM) and thigh (gastrocnemius, GAS) muscle from control or 0.5% fructo-oligosaccharide (FOS) groups of Xianghuang broilers. Magnification of 10*10 was used. PM in control group (A), PM in FOS group (B), GAS in control group (C), GAS in FOS group (D).
3.5 Textural parameters
For toughness parameters, there were no significant differences between groups in regards to max shear force and work of shear of fresh breast (pectoralis major, PM) and thigh (gastrocnemius, GAS) muscle in broilers (P > 0.05) (Figure 3A). Max shear force and work of shear of cooked breast muscle was lower in FOS group compared with CON group (P < 0.05) (Figure 3B).
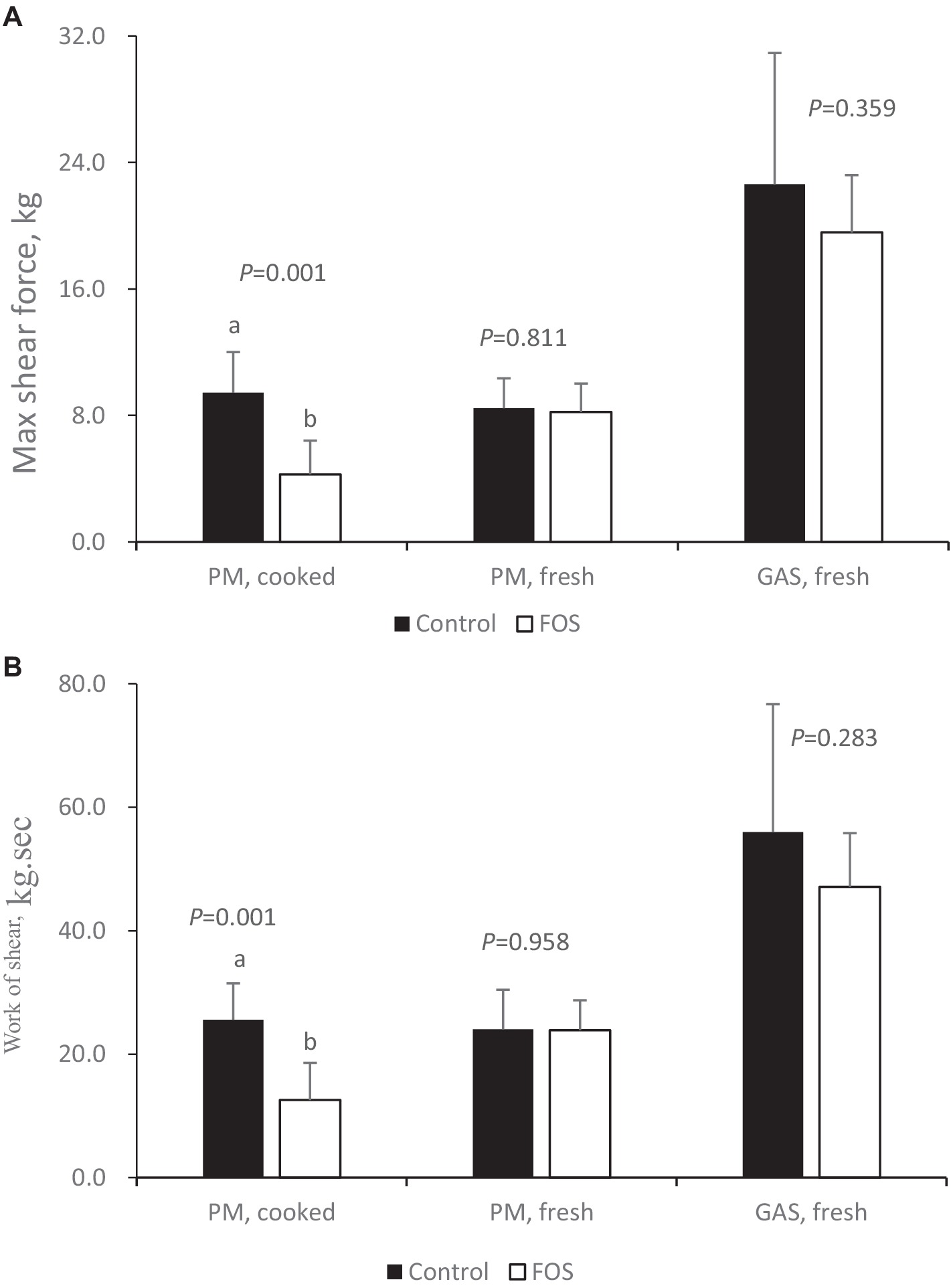
Figure 3. Toughness of cooked or fresh breast (pectoralis major, PM) and thigh (gastrocnemius, GAS) muscle from control or 0.5% fructo-oligosaccharide (FOS) groups of Xianghuang broilers. Probe: HDP/BSW. Max shear force (A), Work of shear (B). Data were presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. a, b Differs significantly at P < 0.05.
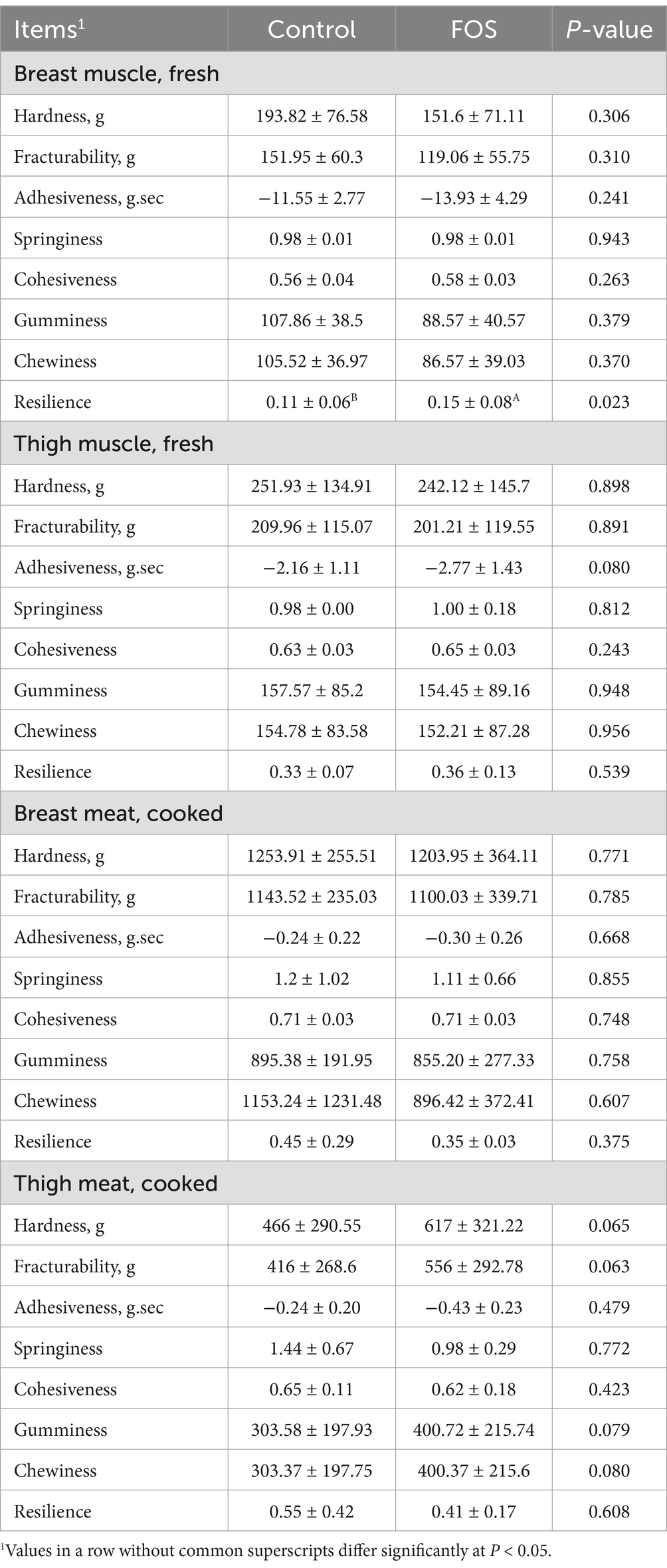
Fresh breast muscle in FOS group showed higher resilience compared to the CON group (Table 6). Adhesiveness of fresh thigh muscle tended to decrease (P = 0.080) in FOS group compared with CON group. Hardness (P = 0.065), fracturability (P = 0.063), gumminess (P = 0.079), chewiness (P = 0.080) of cooked thigh meat tended to be higher in FOS group compared to the CON group. Whereas, no significant differences were observed in the other TPA parameters such as adhesiveness, springiness, cohesiveness, resilience between the FOS and CON groups within fresh and cooked muscle (P > 0.05).
3.6 Antioxidant function
The MDA concentration and T-SOD activity of breast muscle tended to be lower in FOS group compared with CON group (P = 0.066) (Table 7). Activities of T-AOC, CAT, GSHPX of breast muscle did not differ significantly from each other (P > 0.05). Broilers in FOS group showed lower T-SOD activity in thigh muscle compared with CON group (P < 0.05). There was an increasing trend for T-AOC activity of thigh muscle in FOS group compared to CON group (P = 0.053). There were no significant differences in concentration of MDA and activities of CAT, GSHPX of thigh muscle between FOS and CON groups (P > 0.05). Dietary FOS supplementation did not affect MDA concentration and activities of T-AOC, T-SOD, CAT in liver of broilers (P > 0.05).
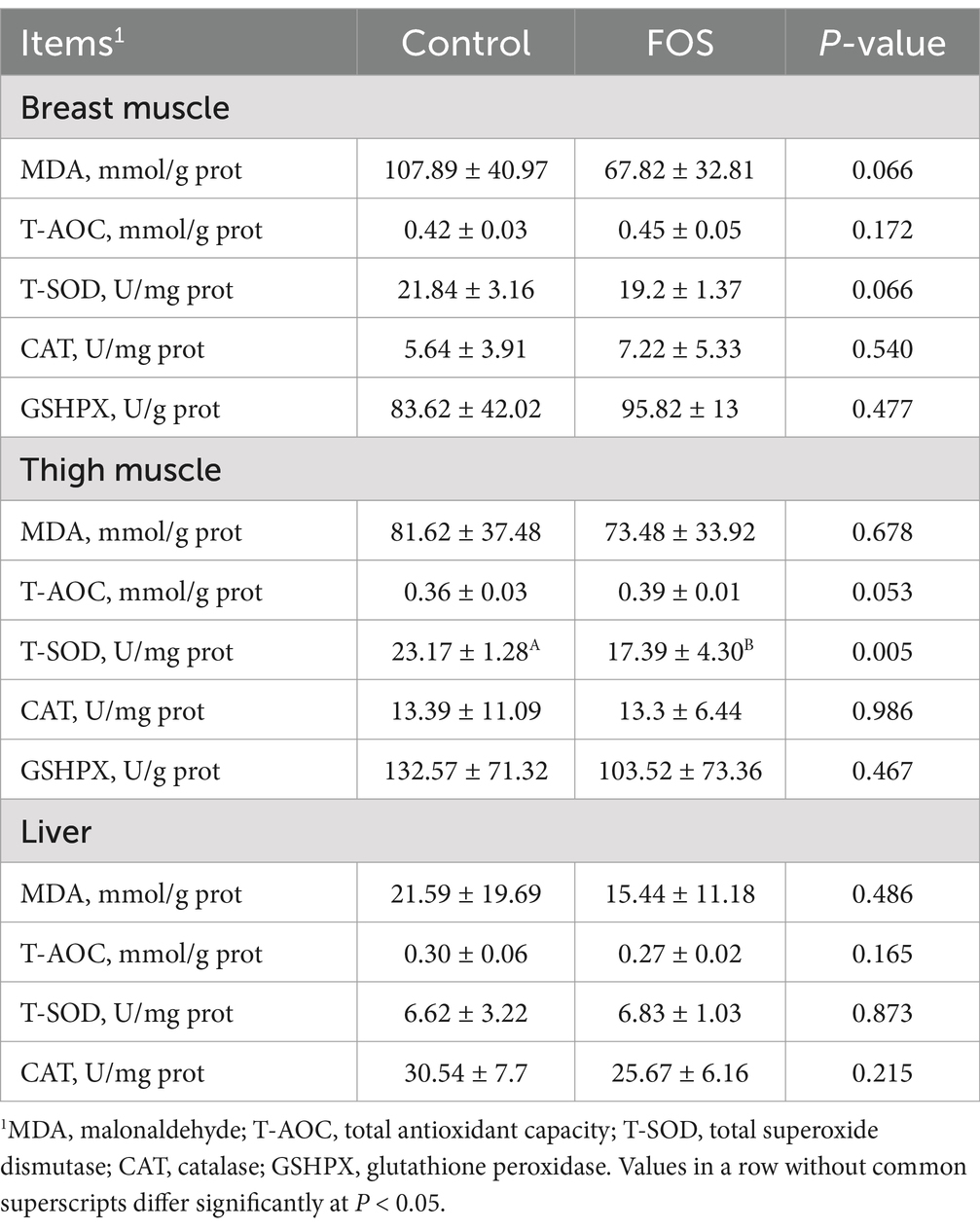
Table 7. Effect of fructo-oligosaccharides on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant activity in Xianghuang broilers.
3.7 Gene expression
Expression of genes related to inflammation and antioxidant function in muscle and liver were shown in Table 8. Hepatic genes’ mRNA expression such as heme oxygenase 1 (HMOX1), nuclear factor, erythroid 2 like 2 (NFE2L), CAT, SOD1, NAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1 (NQO1), thioredoxin reductase 1 (TXNRD), interleukin 1, beta (IL1β), interleukin 8-like 2 (IL8L2), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFa) were not affected by dietary FOS supplementation (P > 0.05). The mRNA expression of NFE2L, CAT, SOD1, NQO1,TXNRD were higher in FOS-fed broiler breast compared to the CON diet (P < 0.05). There was no significant difference in HMOX1, IL1β, IL8L2, TNFa mRNA expression in breast muscle between FOS and CON groups (P > 0.05). In thigh samples, expressions of HMOX1, TXNRD, SOD1 were down-regulated by FOS supplementation compared to the control group (P < 0.05). Birds from FOS group expressed higher IL1β in thigh muscle than that in CON group (P < 0.05). Gene expression of NFE2L, CAT, NQO1, and IL8L2 in thigh muscle were not affected by dietary FOS treatment (P > 0.05).
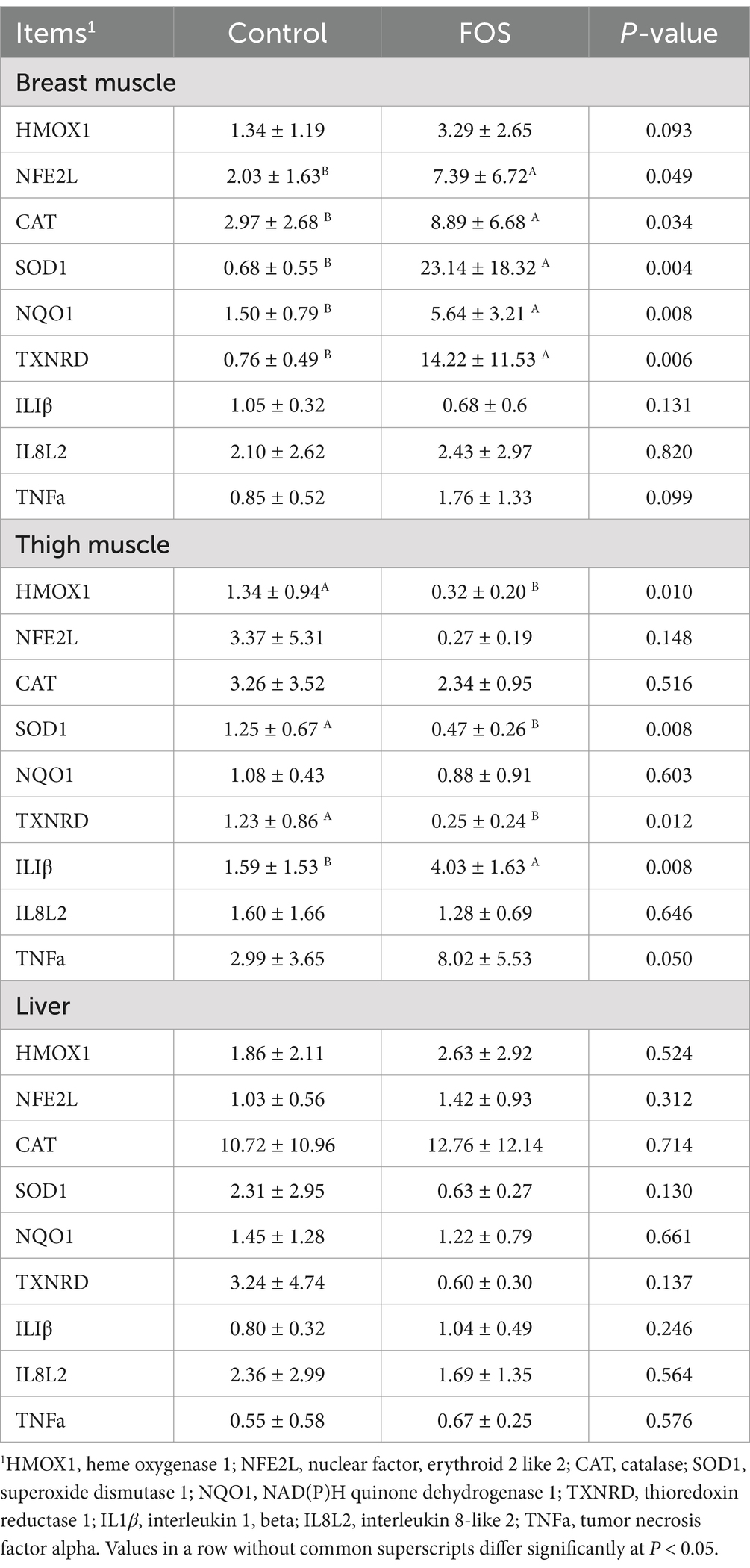
Table 8. Effect of fructo-oligosaccharides on gene relative mRNA expression in liver and muscle of Xianghuang broilers.
4 Discussion
Dietary FOS supplementation at 0.5% (5 g/kg) did not affect growth performance during late-growing period. This was the same that FOS did not affect ADG of broilers at 0.5% when compared with control group (25). Our earlier report showed that 200 mg/kg FOS had positive effect on ADG during first 5 weeks in chicken (26). No significant differences in breast, thigh yields were reported after dietary inclusion of 0.2 or 0.4% fructo-oligosaccharides (27). Earlier published studies also showed different results when considering of effects of FOS on growth performance of poultry. Birds given 0.6 g/kg fructo-oligosaccharides had lower ADFI and ADG compared with wheat based control group (28). Feeding 1.2 g/kg of inulin or 1.5 g/kg of FOS had a positive effect on ADFI and ADG of Archer Abro broilers aged 21 to 42 days (29). Study showed that trimmed asparagus by-products which contain 1.84% fructo-oligosaccharide led to higher ADFI, ADG at 30 and 50 g/kg but not 10 g/kg in Ross broiler chicks during first 0–25 days compared with control group (30). Synbiotic which containing probiotic and fructo-oligosaccharides showed an increasing effect on body weight of 42-day-old broilers subjected to daily cyclic heat stress episodes (31). Inulin which consists of fructose and glucose appeared to change the intestinal microbiota and showed a negative effect on growth performance before day 21 but positive effect subsequently up to day 42 (32). It seems that dosage of FOS and the age of broiler would affect the effect of FOS on growth performance.
In the present study, dietary inclusion of 0.5% FOS showed an increase in pH45min value of breast muscle. If inclusion proportion was as low as 0.1 or 0.2%, FOS supplementation will not influence pH and water holding capacity (WHC) of chicken meat (27). Higher muscle pH could reflect slower speed of muscle glycogen degradation after slaughter (33). High pH in FOS could be a result by enhancing Bifidobacterium growth in small intestinal and cecal digesta which confirmed by early report (4.0 g/kg FOS) (11). Oxidative stress after slaughter could speeds up pH drop (34). A higher ultimate pH value in the breast or thigh muscle may be related to less oxidative stress. The decrease tendency in MDA accumulation of breast muscle indicated that lipid peroxidation of meat decreased in FOS group. Lipid, protein carbonyls, and endogenous reducing sugars may promote the initiation of Maillard reactions, and lead to formation of compounds, this oxidation reaction might reduce protein solubility and enhance denaturation and aggregation (35). pH value exhibited significant negative correlation with yellowness and Warner Bratzler shear force (36). Our result confirmed that broilers from FOS treatment showed lower toughness in breast muscle compared with control group.
Supplementation 0.5% FOS resulted in lower T-SOD activity and lower SOD1 gene expression of thigh muscle compared with control group in present study. The effect of FOS on antioxidant function could be different when dosage was not the same. Report showed that inclusion of 0.1 or 0.2% FOS in broilers’ diet showed no significant difference in free radical inhibition percentage expressed by ABTS (2,2 azino-bis-3-ethyl benzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) values and DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) values in fresh meat (27). But serum T-AOC increased and hepatic MDA reduced when FOS was at 0.3, 0.5, or 0.7% in broilers’ diet (25). Inulin could protect breast muscle by elevating SOD activity when birds challenged with Clostridium perfringens (37). Preventing myoglobin from being oxidized could improve the meat color. The b* value of thigh muscle was the same in FOS and CON. Though interleukin 1 beta gene expression increased and heme oxygenase 1, thioredoxin reductase 1 mRNA expression decreased, the muscle percentage and MDA concertation of thigh muscle were not affected by 0.5% FOS supplementation in this study. FOS (3.5 g of fiber/100 g of the mixture) could decrease the firmness of low-fat meatballs when compared with the control (38). A higher level of pH value in thigh muscle may indicate better tenderness, meat color and water holding capacity (39). But hardness of cooked meat tended to be higher in broilers from FOS group compared with control group. Breast muscle had lower fiber cross-sectional area and higher fiber density than those of thigh muscle (17). Fiber type composition can influence postnatal meat quality. The freezing storage conditions of test cooked meat samples prior to texture analysis might also contribute textural differences between treatments. And it seems that breast and thigh muscle respond differently to dietary FOS especially on firmness.
5 Conclusion
In conclusion, 0.5% of FOS supplementation did not affect growth performance of slower-growing Xianghuang broilers. Furthermore, FOS at 0.5% in diet might help to mitigate oxidate stress and then improve meat quality traits through increasing pH value, yellowness and tenderness of muscle.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because no. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to Can Yang, eWFuZ2NhbnNreUAxNjMuY29t.
Ethics statement
Experimental procedure in this study was reviewed and approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Hengyang Normal University, protocol HNUACUC-B202201005. Animal production test were conducted in Yimin Ecological Agriculture Development Co., Ltd. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent was obtained from the owners for the participation of their animals in this study.
Author contributions
ZHY: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft. XWT: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. RTW: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. CY: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YMJ: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. XW: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – review & editing. QHT: Writing – review & editing. YLH: Writing – review & editing. LLW: Writing – review & editing. ZJ: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by Key Projects of the Education Department of Hunan Province (22A0504), Key Development Projects of the Hunan Science and Technology Department (2022WK2020), and Research Foundation of the Education Department of Hunan Province (21C1122).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Rahim, M, Saeed, F, Khalid, W, Hussain, M, and Anjum, F. Functional and nutraceutical properties of fructo-oligosaccharides derivatives: a review. Int J Food Prop. (2021) 24:1588–602. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2021.1986520
2. Ma, F, Luo, L, and Wang, Q. Response of the ileum transcriptome to fructo-oligosaccharides in Taiping chickens. Anim Biotechnol. (2022) 33:1217–28. doi: 10.1080/10495398.2021.1884565
3. Al-Khalaifa, H, Al-Nasser, A, Al-Surayee, T, Al-Kandari, S, Al-Enzi, N, Al-Sharrah, T, et al. Effect of dietary probiotics and prebiotics on the performance of broiler chickens. Poult Sci. (2019) 98:4465–79. doi: 10.3382/ps/pez282
4. Shang, Y, Kumar, S, Thippareddi, H, and Kim, WK. Effect of dietary fructooligosaccharide (FOS) supplementation on ileal microbiota in broiler chickens. Poult Sci. (2018) 97:3622–34. doi: 10.3382/ps/pey131
5. Mohammed, AA, Jiang, S, Jacobs, JA, and Cheng, HW. Effect of a synbiotic supplement on cecal microbial ecology, antioxidant status, and immune response of broiler chickens reared under heat stress. Poult Sci. (2019) 98:4408–15. doi: 10.3382/ps/pez246
6. Mohammed, AA, Zaki, RS, Negm, EA, Mahmoud, MA, and Cheng, HW. Effects of dietary supplementation of a probiotic (Bacillus subtilis) on bone mass and meat quality of broiler chickens. Poult Sci. (2021) 100:100906. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.11.073
7. Zhu, N, Zhang, R, Wu, H, and Zhang, B. Effects of Lactobacillus cultures on growth performance, xanthophyll deposition, and color of the meat and skin of broilers. J Appl Poult Res. (2009) 18:570–8. doi: 10.3382/japr.2009-00012
8. Zulkifli, I, Che Norma, MT, Israf, DA, and Omar, AR. The effect of early-age food restriction on heat shock protein 70 response in heat-stressed female broiler chickens. Br Poult Sci. (2002) 43:141–5. doi: 10.1080/00071660120109953
9. Ohta, A. Prevention of osteoporosis by foods and dietary supplements. The effect of fructooligosaccharides (FOS) on the calcium absorption and bone. Clin Calcium. (2006) 16:1639–45.
10. Shang, Y, Rogiewicz, A, Patterson, R, Slominski, BA, and Kim, WK. The effect of phytase and fructooligosaccharide supplementation on growth performance, bone quality, and phosphorus utilization in broiler chickens. Poult Sci. (2015) 94:955–64. doi: 10.3382/ps/pev044
11. Xu, ZR, Hu, CH, Xia, MS, Zhan, XA, and Wang, MQ. Effects of dietary fructooligosaccharide on digestive enzyme activities, intestinal microflora and morphology of male broilers. Poult Sci. (2003) 82:1030–6. doi: 10.1093/ps/82.6.1030
12. Yin, D, Tong, T, Moss, AF, Zhang, R, Kuang, Y, Zhang, Y, et al. Effects of coated trace minerals and the fat source on growth performance, antioxidant status, and meat quality in broiler chickens. J Poult Sci. (2022) 59:56–63. doi: 10.2141/jpsa.0200108
13. Bai, X, Yin, F, Ru, A, Tian, W, Li, J, Zhang, G, et al. Muscle fiber composition affects the postmortem redox characteristics of yak beef. Food Chem. (2022) 397:133797. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133797
14. Nemeth, PM, and Lowry, OH. Myoglobin levels in individual human skeletal muscle fibers of different types. J Histochem Cytochem. (1984) 32:1211–6. doi: 10.1177/32.11.6491255
15. Huo, W, Weng, K, Gu, T, Zhang, Y, Zhang, Y, Chen, G, et al. Effect of muscle fiber characteristics on meat quality in fast- and slow-growing ducks. Poult Sci. (2021) 100:101264. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101264
16. Ma, X, Guo, X, La, Y, Wu, X, Chu, M, Bao, P, et al. Integrative analysis of proteomics and transcriptomics of longissimus dorsi with different feeding systems in yaks. Foods. (2023) 12:257. doi: 10.3390/foods12020257
17. Huo, W, Weng, K, Li, Y, Zhang, Y, Zhang, Y, Xu, Q, et al. Comparison of muscle fiber characteristics and glycolytic potential between slow- and fast-growing broilers. Poult Sci. (2022) 101:101649. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101649
18. Choi, YM, Shin, S, Wick, MP, Choe, JH, and Lee, K. Muscle fiber characteristics of pectoralis major muscle as related to muscle mass in different Japanese quail lines. Animal. (2013) 7:1665–70. doi: 10.1017/s1751731113001298
19. NY/T33-2004. (2004). Feeding standard of chicken. Agricultural industry standards of the People's Republic of China. Beijing: Chinese Agricultural Press.
20. AOAC. (1990). Official Methods of Analysi.15th ed., Association of Official Analytical Chemists. Virginia, USA: Artington.
21. Zhuang, H, Nelson, SO, Trabelsi, S, and Savage, EM. Dielectric properties of uncooked chicken breast muscles from ten to one thousand eight hundred megahertz. Poult Sci. (2007) 86:2433–40. doi: 10.3382/ps.2006-00434
22. Aguirre, ME, Owens, CM, Miller, RK, and Alvarado, CZ. Descriptive sensory and instrumental texture profile analysis of woody breast in marinated chicken. Poult Sci. (2018) 97:1456–61. doi: 10.3382/ps/pex428
23. Tan, LP, Tao, YJ, Chen, L, Yang, C, Tang, XW, Ma, JJ, et al. Effects of fermented tofu processing wastewater on growth performance and meat quality of Xianghuang broilers. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). (2024) 108:1072–82. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13952
24. Livak, KJ, and Schmittgen, TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)). Method. (2001) 25:402–8. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262
25. Al-Surrayai, T, and Al-Khalaifah, H. Dietary supplementation of fructooligosaccharides enhanced antioxidant activity and cellular immune response in broiler chickens. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:857294. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.857294
26. Yang, C, Tang, XW, Liu, X, Yang, H, Bin, DM, Liu, HJ, et al. Effects of dietary oligosaccharides on serum biochemical index, intestinal morphology, and antioxidant status in broilers. Anim Sci J. (2022) 93:e13679. doi: 10.1111/asj.13679
27. Biswas, A, Mohan, N, Dev, K, Mir, NA, and Tiwari, AK. Effect of dietary mannan oligosaccharides and fructo-oligosaccharides on physico-chemical indices, antioxidant and oxidative stability of broiler chicken meat. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:20567. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99620-2
28. Williams, J, Mallet, S, Leconte, M, Lessire, M, and Gabriel, I. The effects of fructo-oligosaccharides or whole wheat on the performance and digestive tract of broiler chickens. Br Poult Sci. (2008) 49:329–39. doi: 10.1080/00071660802123351
29. Yang, GQ, Yin, Y, Liu, HY, and Liu, GH. Effects of dietary oligosaccharide supplementation on growth performance, concentrations of the major odor-causing compounds in excreta, and the cecal microflora of broilers. Poult Sci. (2016) 95:2342–51. doi: 10.3382/ps/pew124
30. Nopparatmaitree, M, Nava, M, Chumsangchotisakun, V, Saenphoom, P, Chotnipat, S, and Kitpipit, W. Effect of trimmed asparagus by-products supplementation in broiler diets on performance, nutrients digestibility, gut ecology, and functional meat production. Vet World. (2022) 15:147–61. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2022.147-161
31. Yan, FF, Mohammed, AA, Murugesan, GR, and Cheng, HW. Effects of a dietary synbiotic inclusion on bone health in broilers subjected to cyclic heat stress episodes. Poult Sci. (2019) 98:1083–9. doi: 10.3382/ps/pey508
32. Xia, Y, Kong, J, Zhang, G, Zhang, X, Seviour, R, and Kong, Y. Effects of dietary inulin supplementation on the composition and dynamics of cecal microbiota and growth-related parameters in broiler chickens. Poult Sci. (2019) 98:6942–53. doi: 10.3382/ps/pez483
33. Wang, T, Li, J, Shao, Y, Yao, W, Xia, J, He, Q, et al. The effect of dietary garcinol supplementation on oxidative stability, muscle postmortem glycolysis and meat quality in pigs. Meat Sci. (2020) 161:107998. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2019.107998
34. Chen, X, Zhang, L, Li, J, Gao, F, and Zhou, G. Hydrogen peroxide-induced change in meat quality of the breast muscle of broilers is mediated by ROS generation, apoptosis, and autophagy in the NF-κB signal pathway. J. Agric. Food Chem. (2017) 65:3986–94. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b01267
35. Soladoye, OP, Juárez, ML, Aalhus, JL, Shand, P, and Estévez, M. Protein oxidation in processed meat: mechanisms and potential implications on human health. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. (2015) 14:106–22. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12127
36. Le Bihan-Duval, E, Debut, M, Berri, CM, Sellier, N, Santé-Lhoutellier, V, Jégo, Y, et al. Chicken meat quality: genetic variability and relationship with growth and muscle characteristics. BMC Genet. (2008) 9:53. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-9-53
37. Guaragni, A, Boiago, MM, Bottari, NB, Morsch, VM, Lopes, TF, and Schafer da Silva, A. Feed supplementation with inulin on broiler performance and meat quality challenged with Clostridium perfringens: infection and prebiotic impacts. Microb Pathog. (2020) 139:103889. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2019.103889
38. Montoya, L, Quintero, N, Ortiz, S, Lopera, J, Millán, P, and Rodríguez-Stouvenel, A. Inulin as a fat-reduction ingredient in pork and chicken meatballs: its effects on physicochemical characteristics and consumer perceptions. Foods. (2022) 11:1066. doi: 10.3390/foods11081066
Keywords: fructo-oligosaccharides, growth performance, texture characteristics, myofibrillar morphology, muscle
Citation: Yan Z, Tang X, Wu R, Yang C, Jiang Y, Wang X, Tang Q, Hu Y, Wang L and Jiang Z (2025) Effect of fructo-oligosaccharides on growth performance and meat quality in broilers. Front. Vet. Sci. 11:1485077. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1485077
Edited by:
Juan D. Latorre, University of Arkansas, United StatesReviewed by:
Jesús Adonai Maguey-González, University of Arkansas, United StatesJ. P. Caldas-Cueva, University of Arkansas, United States
Copyright © 2025 Yan, Tang, Wu, Yang, Jiang, Wang, Tang, Hu, Wang and Jiang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Can Yang, eWFuZ2NhbnNreUAxNjMuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
‡ORCID: Can Yang, https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8973-6994
 ZhiHui Yan
ZhiHui Yan XiaoWu Tang2†
XiaoWu Tang2† Can Yang
Can Yang