- 1Apex Veterinary Specialists, Denver, CO, United States
- 2Department of Surgical and Radiologic Sciences, School of Veterinary Medicine, University of California, Davis, Davis, CA, United States
- 3RedBank Veterinary Hospital, Tinton Falls, NJ, United States
Introduction: Oral malignant melanoma (OMM) is the most common malignant oral neoplasm in dogs. Tumor recurrence, progression, and regional and distant metastasis remain major obstacles despite advanced therapy. Tumor size has been a consistent, key independent prognostic factor; however, other clinical and histopathologic features impact prognosis and likely influence optimal treatment strategies. Adoption of a risk stratification scheme for canine OMM that stratifies groups of dogs on defined clinicopathologic features may improve reproducible and comparable studies by improving homogeneity within groups of dogs. Moreover, it would aid in the generation of multidisciplinary prospective studies that seek to define optimal treatment paradigms based on defined clinicopathologic features.
Methods: To build a platform upon which to develop a risk stratification scheme, we performed a systematic review of clinicopathologic features of OMM, with particular attention to levels of evidence of published research and the quantitative prognostic effect of clinicopathologic features.
Results: Tumor size and presence of bone lysis were repeatable features with the highest level of evidence for prognostic effects on survival. Overall, with strict inclusion criteria for paper review, the levels of evidence in support of other, previously proposed risk factors were low. Factors contributing to the challenge of defining clear prognostic features including inconsistencies in staging and reporting of prognostic variables, incomplete clinical outcome data, inhomogeneous treatment, and absence of randomized controlled studies.
Discussion: To overcome this in the future, we propose a risk stratification scheme that expands the TNM system to incorporate specific designations that highlight possible prognostic variables. The ability to capture key data simply from an expanded TNM description will aid in future efforts to form strong conclusions regarding prognostic variables and their influence (or lack thereof) on therapeutic decision-making and outcomes.
Introduction
Oral malignant melanoma (OMM) is the most common malignant oral neoplasm in dogs, comprising almost 40% of all oral tumors (1–9). The term OMM refers solely to melanocytic neoplasms originating from the oral cavity that carry aggressive biologic behavior and metastatic potential. This is biologically distinct from histologically well-differentiated melanocytic neoplasm (HWDMN), alternatively referred to as canine oral melanocytic neoplasms of low malignant potential. The distinguishing characteristic between classic OMM and HWDMN is a low mitotic count (< 4/10 mitoses per hpf) combined with a well-differentiated appearance, high pigmentation, and tumor cells with small nuclei that have mild atypia (3, 10). OMM is associated with a high mortality risk due to its propensity for locoregional and distant metastasis (11, 12). Yet, early diagnosis and definitive treatment can yield locoregional tumor control and good clinical outcomes (13).
Staging for dogs with OMM is based on the World Health Organization (WHO) staging scheme, with stage I tumors <2 cm diameter, stage II tumors 2 cm to <4 cm diameter, stage III tumors ≥4 cm diameter, and/or with locoregional lymph node (LN) metastasis, and stage IV tumors with distant metastasis (14). The treatment of choice for canine OMM is wide surgical excision with the intent for histopathologic margins free of neoplasia. Following curative-intent surgery alone, median survival times (MST) may be greater than two years for dogs with stage I and II OMM (13). However, wide ranges in MST have been reported across the literature, with historical literature reporting survival times of 12 months for stage I tumors and less than 12 months for stage II tumors (9, 15). Despite complete excision, the risk of recurrence is 8–17%, potentially due to pitfalls in pathologic processing of specimens, satellite metastasis or field cancerization, and distant metastasis remains a possibility for many dogs (4, 13, 16, 17).
Primary or adjuvant radiation therapy (RT) is integral to the locoregional management of canine OMM (18–32). Although an optimal fractionation scheme is unknown, OMM is radio-responsive, with reported response rates exceeding 80% (21, 24, 30, 32, 33). As with surgery, reported MST spans a wide range from 147–307 days, with reported prognostic factors including the presence or absence of gross disease, stage of disease, tumor location, and infiltration to bone (24, 27, 30–33). Like surgery, better outcomes following RT are reported for dogs with early-stage tumors, with MST up to 758 days for stage I OMM (32). However, the risk of recurrence or progression within the irradiated volume ranges from 15–45% (22, 24, 30). Recent literature supports that dogs with stage I or II OMM treated with surgery and adjuvant RT have improved progression-free survival and overall survival compared to dogs treated with RT alone (30). It is unclear if dogs with stage III or IV OMM have a similar benefit when RT is used postoperatively (30); however, further work is needed to evaluate the importance of combination therapy.
Adjuvant systemic treatment is often utilized, given the high likelihood for OMM to metastasize. Currently available systemic therapies, including chemotherapy and immunotherapy, have not consistently improved outcomes alone or when combined with local therapy (17, 18, 22, 24, 32, 34–39). Most studies have not shown a clear positive impact from the addition of chemotherapy or a commercially available DNA vaccine (ONCEPT®; Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health USA Inc., Athens, GA, USA) approved for use in stage II and III disease with adequate local control. However, the lack of uniform treatment in veterinary studies may conceal the benefit of systemic therapy for some dogs following adequate local control (18, 37, 39). Because melanoma is an immunogenic tumor (39, 40), much work is ongoing to develop novel immunotherapy agents, including hCSPG4 electrovaccination (16, 40) and canine immune checkpoint inhibitors. Specifically, anti-PD-1, anti-PD-L1, and anti-CTLA4 antibodies can potentially alter treatment paradigms for dogs with advanced OMM in the coming years (41–44). Additional strategies, such as electrochemotherapy, metronomic chemotherapy, tyrosine kinase inhibitors, intralesional chemotherapy or immunotherapy, cytokine treatment, hyperthermia, and others, have also been investigated and are reviewed elsewhere (45).
Regardless of therapy, tumor progression and metastasis pose a serious problem for most dogs with OMM. While the size of the primary tumor has historically been a key prognostic factor, other clinical and histopathologic features also impact prognosis and likely influence optimal treatment strategies (10, 13, 17, 27, 32, 34, 46, 47). One systematic review concluded that histological features, including nuclear atypia score, mitotic count, Ki67 index, and quantification of pigmentation, accurately predicted the likelihood of one-year survival in dogs with OMM (48). Unfortunately, clinical features such as stage, surgical intent, histopathological margin status, tumor location, and bone invasion were not incorporated with histologic features (48).
Prognostic risk stratification based on collective clinical and pathologic features may help guide evidence-based decision-making. For example, determining populations of dogs with OMM that have objective benefits from adjuvant or neoadjuvant therapies following surgery may help prevent suboptimal or unnecessary treatment for some dogs while selecting dogs most likely to benefit (33). Human head and neck mucosal melanoma (HNMM) shares a similar aggressive behavior to canine OMM (1, 11, 49–57). Two staging systems are currently available for HNMM, one specific to HNMM (mmTNM) and one broader system that encompasses primary nasal cavity, paranasal sinus, and oral cavity malignancies (sccTNM). It is currently recommended that both classifications be combined when staging human patients to improve risk stratification and appropriate treatment planning (51, 56). Adoption of a similar risk stratification scheme for canine OMM may allow for improved, reproducible, and comparable groups of dogs for which to build multidisciplinary prospective studies that seek to define optimal treatment paradigms. The aim of this study was to provide a platform upon which to develop a risk stratification scheme. To facilitate this objective, we performed a systematic review of clinicopathologic features of OMM, with particular attention to levels of evidence of published research and the quantitative prognostic effect of clinicopathologic features.
Materials and methods
A systematic literature search was performed, including articles available through April 31, 2023. The online databases Pubmed, Scopus, and Google Scholar were systematically searched using the terms: [(canine OR dog OR dogs) AND (oral OR mouth OR mucosal) AND (melanoma OR melanocytic) AND (prognosis OR survival OR disease-free interval OR DFI OR outcome)]. De-duplication of articles was performed with Sciwheel,1 and title/abstracts were screened for inclusion with Covidence.2 Screening was performed independently by a board-certified veterinary dentist and oral surgeon (SG) and a resident in dentistry and oral surgery (ES). Discrepancies on inclusion or exclusion criteria were reached by consensus.
Studies were excluded if they: (1) were not peer-reviewed (2) were not written in English, (3) represented a review or case report, (4) did not differentiate features and prognosis for oral lesions from other sites (e.g., cutaneous, ocular, digital) (5) did not detail clinical prognostic factors and outcomes (6) only included an abstract and not the entire manuscript for review, (7) did not statistically evaluate associations between the specified risk factor and outcome. Outcome data was defined as MST, progression-free interval (PFI), progression-free survival (PFS), disease-free interval (DFI), disease-free survival (DFS), survival probability at a defined time point (e.g., at one or two years), or hazards ratio (HR)/odds ratio (OR) for recurrence, progression, or death.
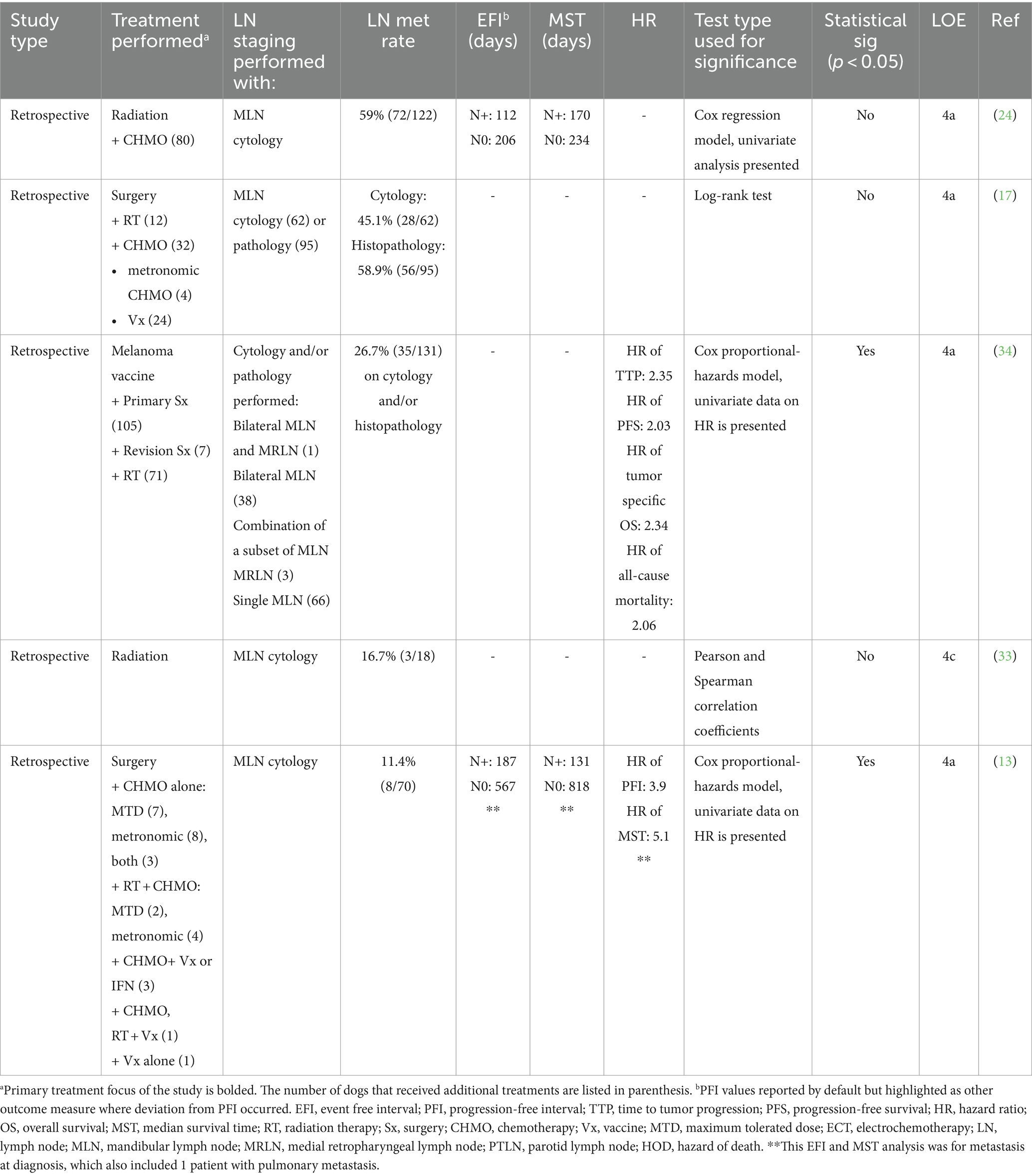
Data collection was performed by a dentistry and oral surgery resident (ES) and two veterinarians undergoing rotating internship training (EG, AC). Data extracted from the study included the following: number of dogs, study design, specific risk factor(s) evaluated, statistical analysis performed, treatment regimens, prognostic factors, and outcomes. Each study was classified by study design, with levels of evidence applied, as previously described (45) (Table 1). In line with a recent systematic review of veterinary use of mitotic activity, we reported mitotic count, even when prior literature used the term mitotic index (58). Data on each potential risk factor was collated separately for each paper. Data on a specific risk factor was excluded if a risk factor was defined but was not accompanied by numerical data or statistical analysis for prognostic significance. For studies in which both the size (T1-T3) and stage (1–4) were evaluated as risk factors, the size was collected. WHO staging was only applied for studies in which stage was reported without tumor size. Because stage III tumors include criteria for the primary tumor and LN metastatic status, data from studies that did not specify LN status were excluded from analysis because it could not be discerned that stage III tumors had confirmed LN metastasis.
Data regarding a specific risk factor was combined from all available studies when reported in multiple studies. A combined mean value for MST was manually calculated and presented with a range in parenthesis. Similarly, PFI, PFS, and DFI endpoint data were combined and considered an event-free interval (EFI) to include disease recurrence, progression, or death, and a mean combined EFI was manually calculated and presented with a range in parenthesis.
Results
Database searches provided 373 manuscripts. Twenty-one articles met the inclusion criteria after screening and review (Figure 1). Studies were excluded most commonly because they did not differentiate features and prognosis for oral lesions from other sites or did not sufficiently detail statistical data on associations between the specified risk factor and outcome. Although many manuscripts did not meet inclusion for systematic prognostic review, descriptive data from reviewed manuscripts are also briefly presented in justification of a proposed risk stratification scheme.
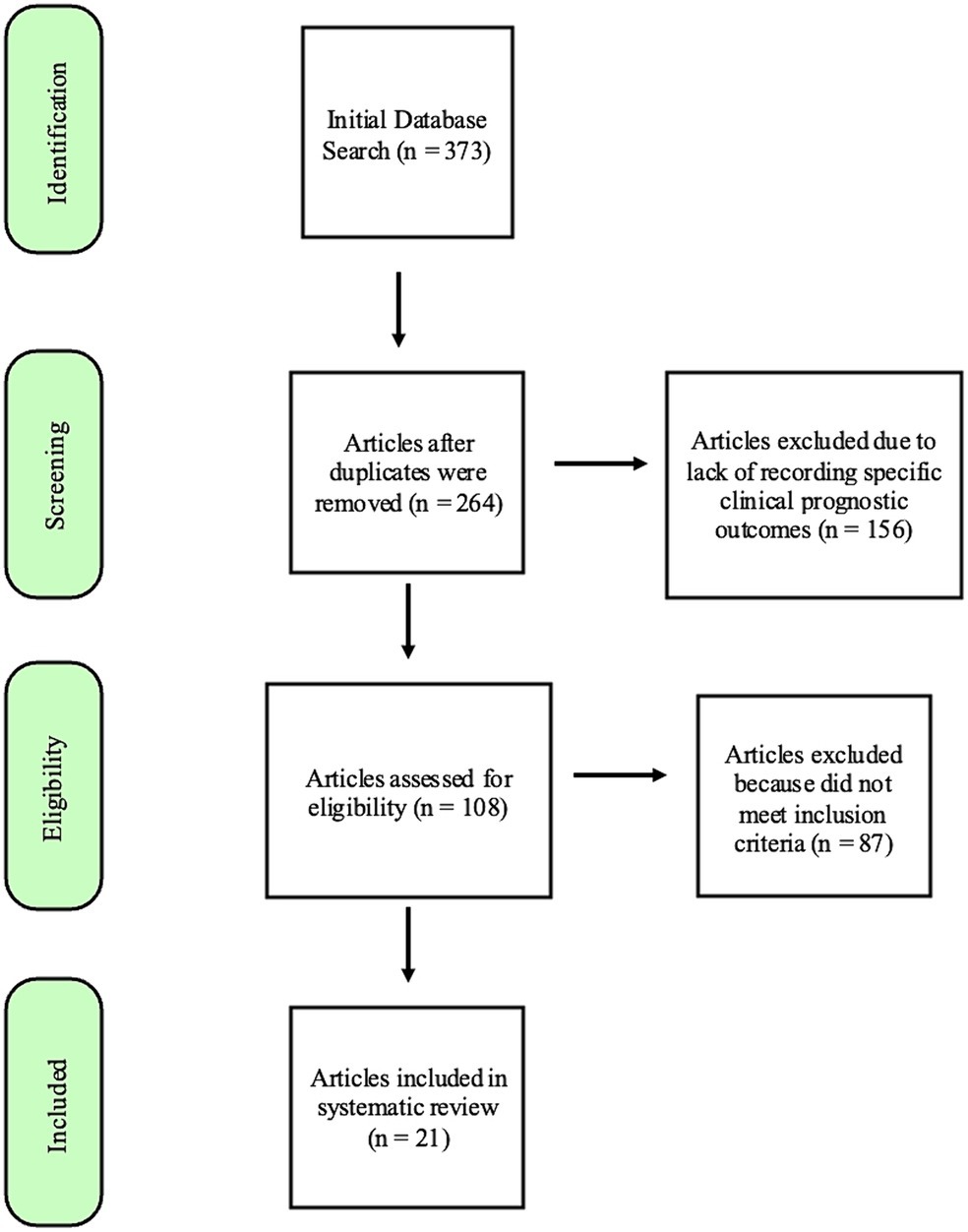
Figure 1. Flowchart modified from the “Preferred Reporting items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRiSMA) (REF) guidelines,” demonstrating the process by which the search results were narrowed to the 21 articles included in this systematic review.
Clinical and tumor-specific features
Patient signalment (N = 3)
OMM is more common in older dogs, with a mean age between 9 and 12 years (3, 17, 24, 34, 35, 47, 59–65). Poodles, Golden and Labrador Retrievers, Rottweilers, Yorkshire Terriers, Cocker Spaniels, Chow-chows, Scottish Terriers, Pekinese, Gordon Setters, and Dachshunds are overrepresented (2, 13, 59, 60, 63, 66). No studies compare breed prevalence to the hospital population or the relationship between breed and outcome measures.
Three articles provided prognostic information concerning clinical signalment (age and/or sex). Two studies documented age as a significant prognostic factor (17, 32). One retrospective study suggested that dogs <12 years old (n = 70) had significantly longer MST (433 days) compared to dogs ≥12 years of age (n = 77, MST of 224 days) when treated with surgery with or without adjuvant therapy (17). A second retrospective study (n = 111) suggested that increasing age was significantly associated with death within one year following RT (32). Both articles had level 4a evidence and an overall evidence grade of C. Inherited bias could not be controlled for, and it cannot be ignored that age may impact therapeutic decision-making.
Two reports evaluated sex as a prognostic factor (13, 32). One report found sex was not a prognostic factor following RT (32); the other study suggested that intact female dogs had poorer outcomes following surgery (13). This latter study had level 4a evidence; however, there were only two intact females in that study, and a type I error was possible (13). Overall, there is a lack of evidence to support that factors contributing to clinical signalment affect prognosis. Thus, the authors conclude these features should be excluded from risk stratification.
Tumor size (N = 8)
Evaluating tumor size is the first key clinicopathologic factor to evaluate in dogs with OMM (48). Eight studies evaluated the prognostic influence of tumor size (Table 2). All studies supported that smaller tumors are associated with improved outcomes compared to larger tumors (13, 17, 24, 27, 30, 32, 34, 67).

Table 2. Main findings and level of evidence for studies that evaluated tumor size as a prognostic factor for OMM.
Most studies (n = 6) categorized tumor size indirectly using the standard WHO staging scheme. Combined, there were 159 T1 (<2 cm), 181 T2 (2–4 cm), and 119 T3 (> 4 cm) tumors. The combined mean of the reported EFI for T1 tumors was 419 (158–622) days, T2 tumors was 140 (118–154) days, and T3 tumors was 214 (145–364) days. The combined mean of the reported MST for T1 tumors was 589 (312–758) days, for T2 tumors was 251 (234–278) days, and for T3 tumors was 173 (145–364) days. One study that evaluated outcome following surgery was excluded because it stratified tumors by <3 cm or > 3 cm, excluding it from combined analysis (13). Of note, this study reported longer MST (874 days) for tumors <3 cm (n = 23) compared to tumors >3 cm (n = 47, MST of 396 days). This study also suggested that for each increase in tumor size by 1 cm, there was an associated 32% increased hazard of recurrence or metastasis and a 29% increased hazard of death (13).
Most studies (7/8) (13, 17, 24, 27, 30, 32, 34) provided level 4a evidence to support that tumor size impacts prognosis. One study presented level 1b (67) evidence for this association. Despite an overall low level of evidence (grade C), tumor size is the most repeatable negative prognostic marker for outcome in dogs with OMM. Thus, we recommend incorporating tumor size, using the size guidelines within the WHO staging scheme, during risk stratification.
Tumor location within the oral cavity (N = 7)
The gingiva is the most common site for canine OMM, with 33–68% of tumors reported as gingival tumors (13, 63, 64, 68–71). There is no clear jaw predilection, with 34–38% reported in the mandible and 23–50% reported in the maxilla (17, 24, 32, 47, 61, 72). Other common locations include buccal mucosa (6–32% of lesions) (13, 32, 47, 63, 64, 69, 71, 72), lips (8.4–24.3% of lesions) (13, 17, 32, 47, 64, 69, 71, 72), tongue (1–14.3% of lesions) (13, 24, 32, 47, 63, 64, 69, 72), palate (1.4–14% of lesions) (13, 17, 24, 32, 47, 64, 69, 71, 72), and tonsil (1.4–2.9% of lesions) (13, 47). Notably, of malignant tonsillar tumors, OMM represents 12% of all neoplasms and is the most likely to metastasize to the tonsil (73).
Seven articles provided information on the prognostic impact of tumor location (13, 17, 24, 27, 32, 34, 70, 74) (Table 3). Three publications categorized tumors into rostral or caudal and defined caudal tumors as distal to the maxillary/mandibular fourth premolar (13, 24, 34, 70). The combined mean of the reported MST for rostral tumors (n = 92) was 354 (332–375) days, and for caudal tumors (n = 63) was 310 (204–416) days (13, 24, 70).
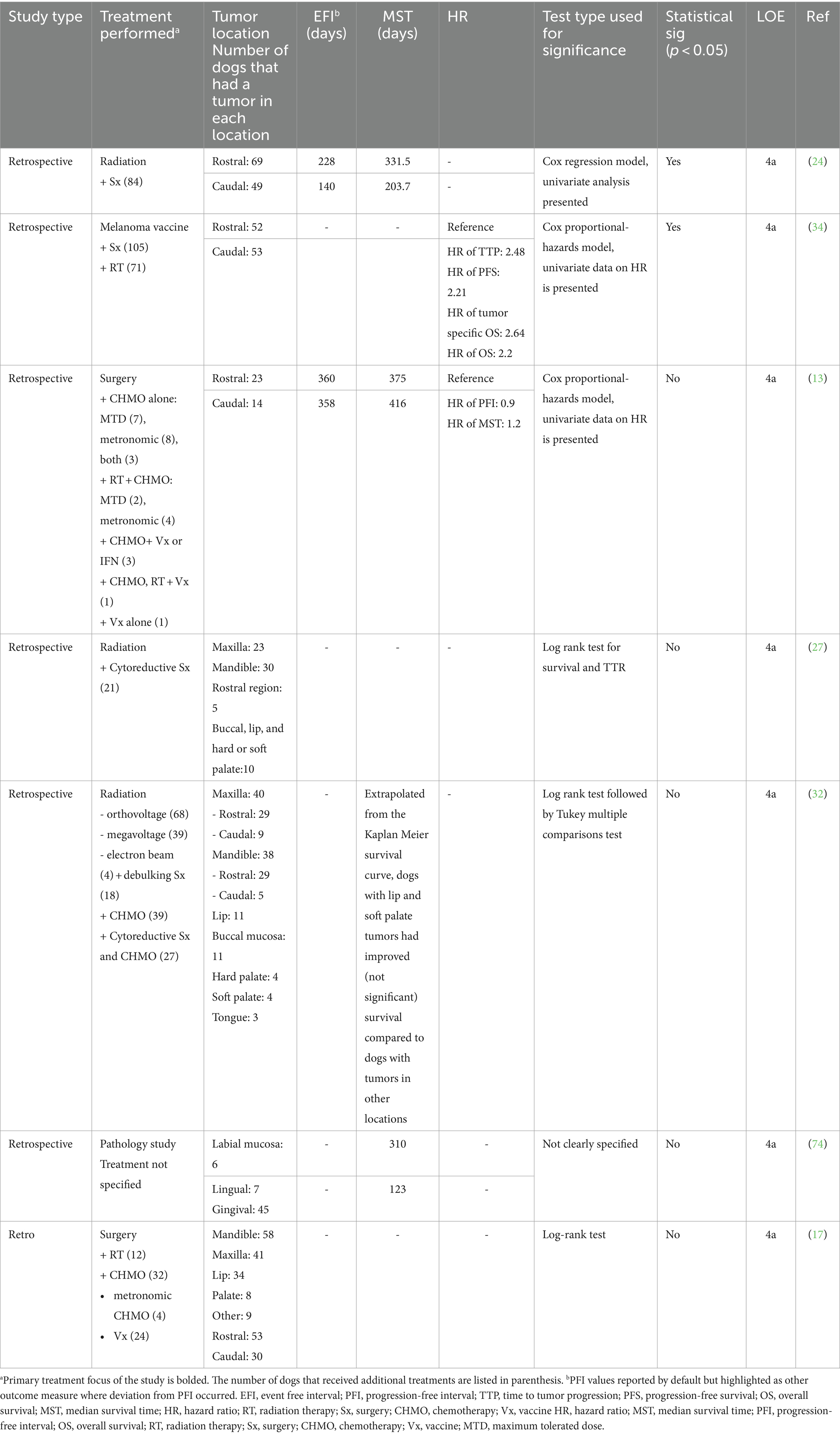
Table 3. Main prognostic findings and level of evidence of studies that evaluated the effect of tumor location on prognosis.
Most studies (5/7) have not demonstrated that location within the oral cavity carries a clear prognostic influence on outcome. However, with a broad categorization of rostral and caudal location, two studies have supported that caudal location was associated with poorer EFI and MST compared to tumors in the rostral oral cavity (n = 223 combined) (23, 33). Although subcategorization of tumor location has not clearly demonstrated prognostic significance, tumor location impacts therapeutic decision-making, as maxillary and mandibular tumors are more likely to be referred for wide surgical resection, and caudal-location impacts the ability to obtain neoplasia-free margins (75).
There is low level (4a-4b, grade C), contradictory evidence on the effect of oral location as a prognostic factor. Given that the literature to date supports that location is not a clear prognostic factor, the authors recommend that location be excluded from risk stratification at this time and that therapeutic decision-making not be influenced. However, tumor location should be documented separately, with anatomic descriptions to standardize location categorization, in future studies to determine its influence on therapeutic decision-making. Additionally, controlled studies may demonstrate that the location should be incorporated in the risk stratification schema revisions.
Bone invasion at presentation (N = 6)
Twelve of the screened studies reported the presence of bone invasion. Of OMM included, 28–92% of tumors presented with bone invasion at diagnosis (9, 16, 22, 24, 27, 33, 34, 47, 60, 65, 76, 77). Not all tumors were imaged before treatment, and imaging techniques varied from standard radiography to contrast-enhanced CT, limiting conclusions on the true prevalence of bone invasion.
Six studies provided prognostic significance of bone invasion secondary to the primary OMM (24, 27, 34, 47, 60) (Table 4). Combining data from these studies, 45% of OMM present with bone invasion (n = 159), and 55% do not (n = 194). All but one study supported that bone invasion at presentation is a significant negative prognostic indicator. The combined mean of the reported EFI for dogs with bone lysis was 240 (72–193) days compared to 271 (164–470) days for dogs without lysis. The combined mean of the reported MST following treatment for dogs with bone invasion was 217 (117–397) days compared to 522 (246–1,063) days for dogs without bony lysis.
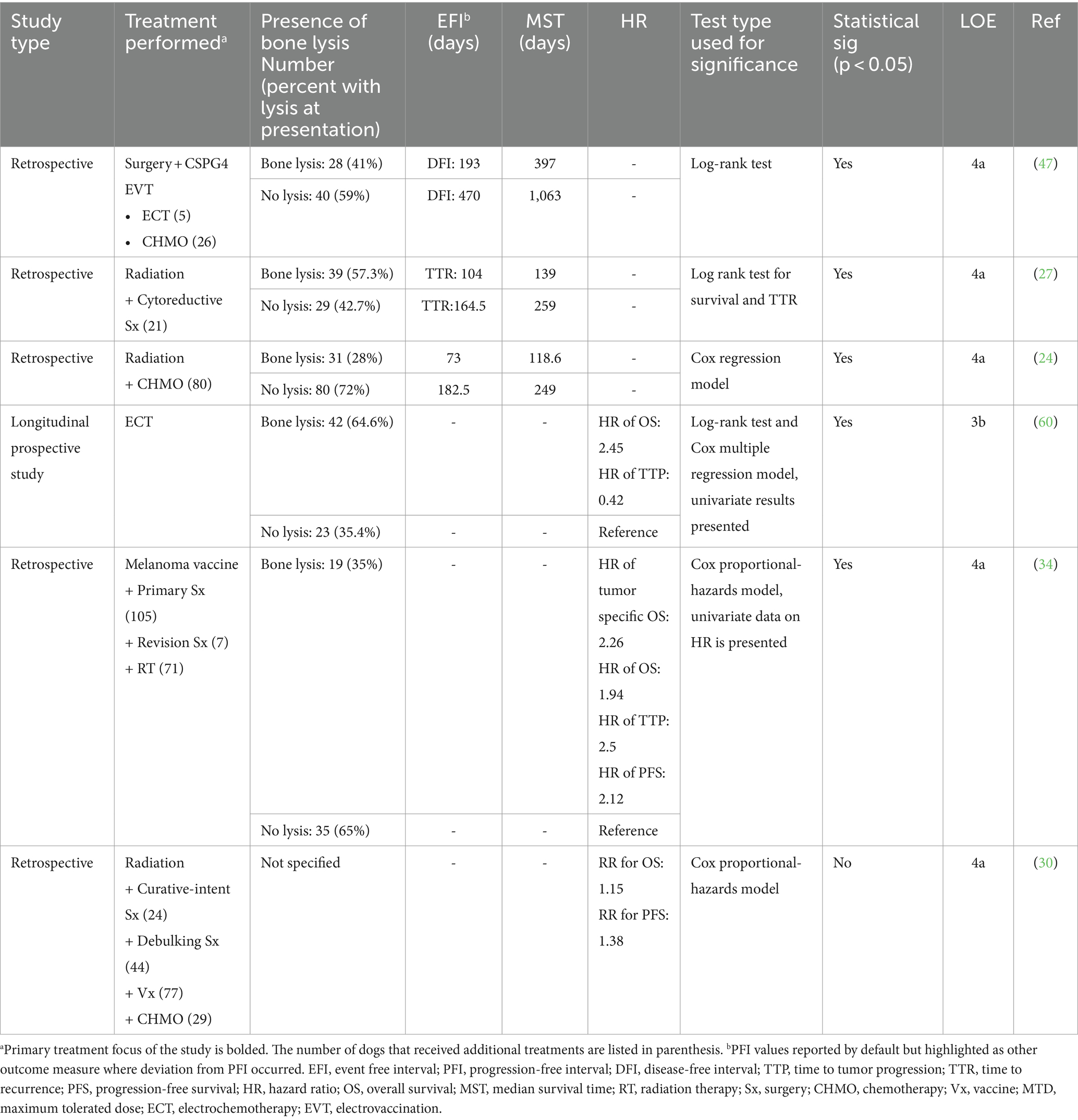
Table 4. Main prognostic findings and level of evidence of studies that evaluated the effect of bone lysis on prognosis.
There is a low level (3b-4a, grade C) of evidence for the role of bone invasion as a risk factor. Yet, all but one study (30) suggests bone invasion is a negative prognostic factor for outcome. Because bone invasion increases risks associated with local tumor control and has repeatedly negatively affected outcome measures, the presence or absence of bony lysis should be included in risk stratification.
Biologic behavior
Lymphatic metastasis at presentation (N = 5)
Seventeen of the screened studies reported LN metastatic rate. Collectively, 9–69% of local LN were metastatic at diagnosis (4, 9, 13, 17, 24, 30, 32–34, 47, 70, 77–82). Variable screening techniques (palpation, diagnostic imaging, cytology, pathology) and the number of LN tested (ranging from the ipsilateral mandibular node to complete bilateral neck dissection) were reported, limiting concrete conclusions regarding the metastatic risk of OMM to regional LN.
Five studies evaluated statistical prognostic information on the impact of lymphatic metastasis (Table 5). The combined mean of the reported EFI for dogs with LN metastasis was 150 (112–187) days compared to 386 (206–567) days for dogs without LN metastasis (13, 24). The combined mean of the reported MST for dogs with OMM and LN metastasis was 150 (131–170) days compared to 526 (234–818) days for dogs without confirmed LN metastasis (13, 24, 70). There was no consensus as to the impact of LN metastasis on outcome. Studies were divided on whether LN metastasis negatively impacted prognosis (N = 2) (13, 34, 70) or whether LN metastasis did not impact outcome measures (N = 3) (17, 24, 33).
LN screening and treatment were variable among the five studies. All reported mandibular lymph node cytology, with three studies relying solely on this approach (13, 24, 33). The combined mean of the reported metastatic rate determined by cytology was 30.9 (11.4–59) %, and by histopathology was 37.5 (16–58.9) % (13, 17, 24, 33, 34, 70). Two studies evaluated LN metastasis by both cytology and pathology (17, 34, 70); however, only one article (17) differentiated the metastatic rate based on cytology (45.1%) versus histopathology (58.9%).
Based on the studies included in this systematic review, there is a low level of evidence (4a-4c, grade C) supporting that LN metastasis influences prognosis, and there is conflicting evidence to this point. However, LN screening for many dogs may have been incomprehensive, thus missing metastatic LNs. Further confounding the literature is that stage III disease is associated with a poorer outcome than stages I and II. Because LN metastasis and dogs with large tumors and lack of LN metastasis are included within this staging group, further investigation is warranted to isolate the independent prognostic significance of LN status. The identification of LN metastasis needs to be consistent and sensitive, and treatment for dogs with LN metastasis needs to be standardized in future studies so reliable conclusions can be generated regarding their prognostic influence. This is especially true for cases of micro versus macro-metastasis and single versus multiple metastatic lymph nodes. In humans with malignant melanoma, LN metastasis is a negative prognostic factor and directly influences therapeutic decisions and prognosis (50–52, 54–57, 83–90). Taking into account the following factors: known uncertainties with imaging, confirmation of LN metastasis (or lack thereof) in most of the reported studies, the knowledge of locoregional metastatic prognostic implications in humans, and the recent expert-based canine consensus statement (75), LN status, including metastatic degree and number of LN affected, should be incorporated within the risk stratification scheme.
Distant metastasis at presentation (N = 4)
Excluding studies that purposely did not include dogs with stage IV OMM, eight reported the distant metastatic rate at presentation. Pulmonary metastasis was reported in 1.4–26% of patients, and abdominal metastasis in 0–5.3% (13, 17, 24, 30, 32, 60, 81, 91). Variable screening techniques were reported, limiting conclusions on OMM’s true distant metastatic risk. Further, because pulmonary metastasis may have been identified on thoracic imaging (e.g., radiographs), abdominal imaging may not have been performed to identify true abdominal metastasis. Indeed, thoracic radiographs were performed exclusively in three studies (13, 24, 81) and combined with thoracic computed tomography (CT) in three studies (17, 30, 91). Abdominal imaging was performed in two studies (30, 91). Both abdominal ultrasound and CT were used in one study (30), and only abdominal ultrasound was used in the other (91). When metastatic rate was specified by which imaging modality was used, pulmonary metastasis was diagnosed in a combined mean of 5.2% (n = 19/352; range 1.4–26%) (13, 17, 24, 81) and 6.5% (n = 16/246; range 5.7–16.7%) (16, 17, 91) by thoracic radiographs or CT, respectively.
Four studies reported the prognostic significance of distant metastasis at presentation (13, 24, 30, 32, 60) (Table 6). Most (3/4) studies concluded that distant metastasis was a negative prognostic factor (13, 30, 32, 60). Two studies reported the metastatic rate and MST time in their cohort; one had EFI data. The mean of the reported EFI for dogs with stage IV OMM (n = 11) was 120 days compared to 220 days for dogs without distant metastasis (n = 67) (13, 60). The combined mean of the reported MST for dogs with stage IV OMM (n = 42) was 115 (80–135) days compared to 562 (225–900) days for dogs with stage I-III OMM (n = 135) (13, 32, 60).
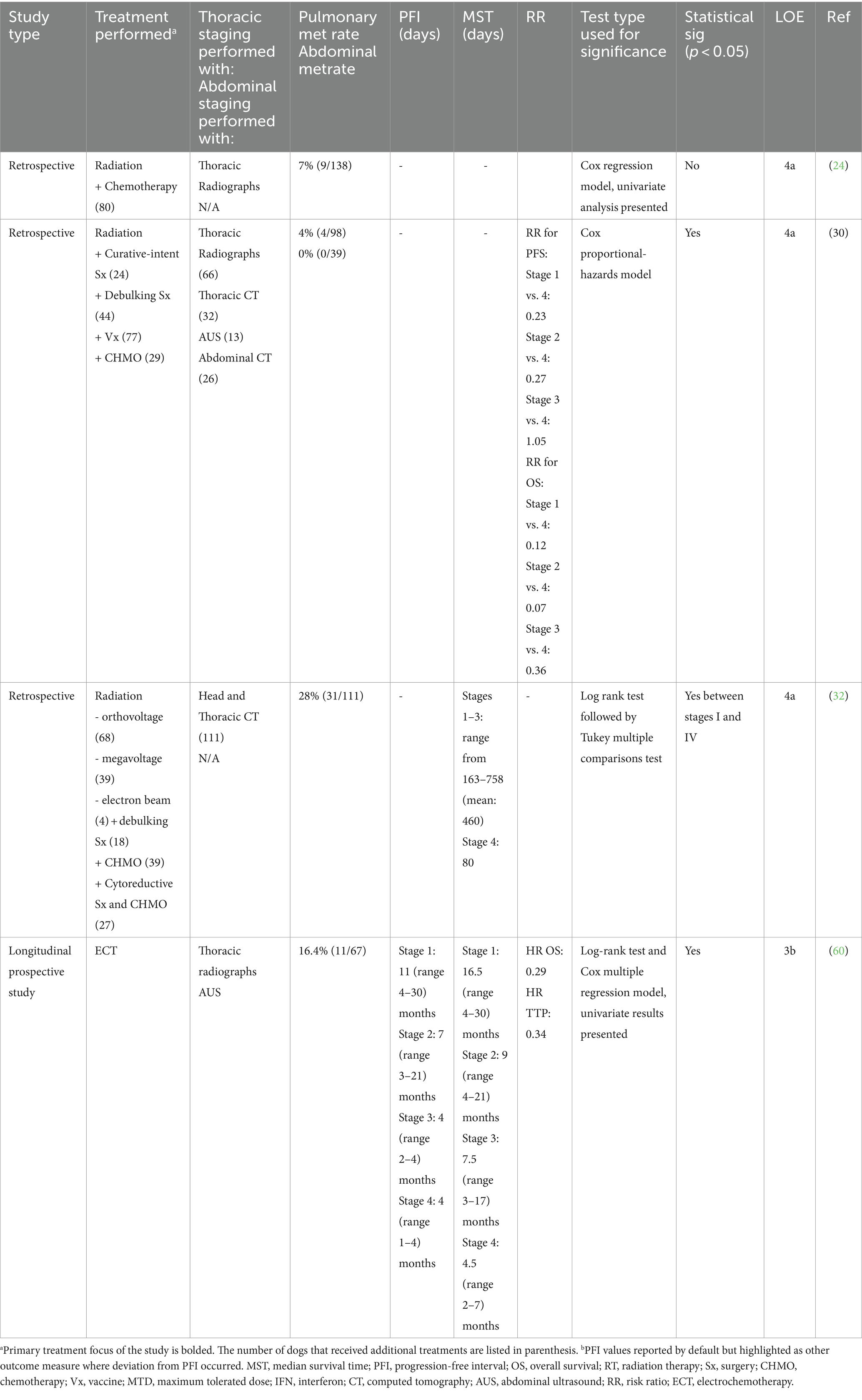
Table 6. Main findings and level of evidence of studies that evaluated the effect of distant metastasis on prognosis.
Overall, there is a low level (3b-4a, grade C) of evidence for the role of distant metastasis as a negative prognostic factor. Yet, there is a consistent negative prognostic implication in all studies (29, 31, 60) except for one (23), and survival ranges are generally narrow for dogs with stage IV OMM. Further, given the lack of a clear role for adjuvant chemotherapy and immunotherapy, the presence of distant metastasis negatively impacts prognosis. Thus, the presence or absence of metastasis should be included in risk stratification.
Pathologic features of the tumor
Ki67 (N = 4)
Four studies evaluated the prognostic significance of Ki67 (47, 62, 92, 93) (Table 7). The most common cutoff reported for Ki67 proliferation value was 19.5% (n = 2). Combined data cannot be presented, as outcomes were not standardized. One study demonstrated an overall survival of 484 days with Ki67 < 19.5% versus 224 days for those with Ki67 ≥ 19.5% (62).
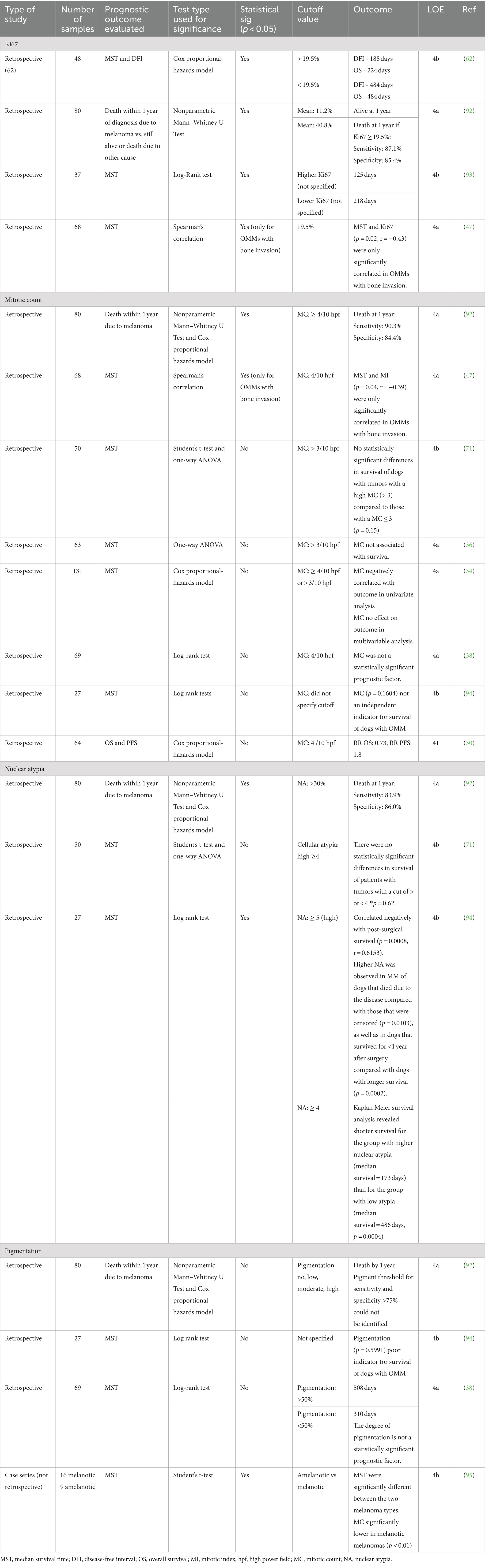
Table 7. Main findings and level of evidence of studies that evaluated the effect of pathologic features on prognosis.
There is an overall low level (4a-4b, grade C) of evidence that Ki67 is an independent negative prognostic factor for outcome. Given the small number of studies upon which to form a conclusion yet the lack of contradictory data, Ki67 may be valuable in risk stratification. Additional studies are needed to verify its independent pathologic prognostic significance.
Mitotic count (N = 8)
Eight studies evaluated the statistical prognostic implication of the mitotic count (34, 36, 38, 47, 70, 71, 92, 94) (Table 7). The most common cutoff for the mitotic count was <4/10 per high-power field [hpf] (5/8 publications). Most (6/8) studies concluded that the mitotic count was not independently associated with outcome measures when evaluated as a single variable (34, 36, 38, 70, 71, 94).
Overall, there is a low level (4a-4b, grade C) and contradictory evidence on the role of mitotic count. Despite this, mitotic activity should continue to be captured in risk stratification, and studies reporting both Ki-67 and MC are needed to better discern the value of each variable in the future.
Nuclear atypia (N = 3)
Three studies evaluated nuclear atypia score as a prognostic factor (71, 92, 94) (Table 7). The cutoff value was not standardized across the studies. Two studies concluded that the nuclear atypia score was statistically significant with clinical outcome (93, 95), while the remaining study found no association with outcome (71).
Overall, based on the studies included, there is a low level (4a-4b, grade C) of contradictory evidence on the role of nuclear atypia as a prognostic indicator. However, the majority support its inclusion into risk stratification, and the oncology-pathology working group have strongly endorsed its routine inclusion into pathologic prognostication for OMM (48). Thus, nuclear atypia should be considered in risk stratification.
Pigmentation (N = 4)
Four studies evaluated the degree of tumor pigmentation as a prognostic factor (38, 92, 94, 95) (Table 7). The degree of pigmentation used as a cutoff value was not standardized across the studies. One study demonstrated that pigmentation was associated with a survival advantage, as melanotic tumors had improved outcomes compared to amelanotic tumors (95). The remaining three studies did not demonstrate a clear survival advantage for dogs with pigmented tumors compared to dogs without (38, 92, 94).
Overall, there is a low level (4a-4b, grade C) of evidence supporting that the degree of tumor pigmentation significantly affects prognosis. Further, most studies do not support that it has significant prognostic value, and there is no clear cut-off for pigmentation. Therefore, we recommend that the degree of pigmentation be excluded from risk stratification at this time.
Other potential pathologic and clinical prognostic factors
Numerous other publications have recently emerged investigating pathologic and clinical features that may be associated with clinical outcomes. Of interest, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) were shown to affect prognosis, with a higher survival rate with higher TIL scores, a brisk or non-brisk TIL pattern, and an increased frequency of CD8+ T lymphocytes infiltrating the tumor (71). Similarly, one study highlighted that a higher frequency of regulatory T lymphocytes, both infiltrating and surrounding the tumor, was associated with poorer PFS and MST compared to dogs with lower frequency (71). Co-expression of α and β PDGFR and lower serum and plasma VEGF concentrations have been associated with a negative impact on prognosis (62, 96). Interestingly, serum and plasma VEGF concentrations were associated with survival in dogs that received curative-intent therapy but not in dogs that received palliative therapy (6). Dogs with a C-reactive-protein–albumin ratio (CRP/ALB) > 1.9 before tumor excision have been shown to be associated with shorter PFS and MST (97). Lastly, one study explored the prognostic value of somatic focal amplifications on chromosomes (Canis Familiaris [CFA]) 10 and 30 in canine OMM (98). This study concluded that CFA 30 amplification was significantly associated with a worse prognosis and correlated with amelanotic phenotype and high mitotic count. Many of these recently reported features may indeed contribute to risk stratification for therapeutic paradigms, such as tumor-infiltrating immune cells and immune checkpoint protein expression. Future work must evaluate inclusion into adapted versions of a risk stratification scheme.
Proposed risk stratification scheme
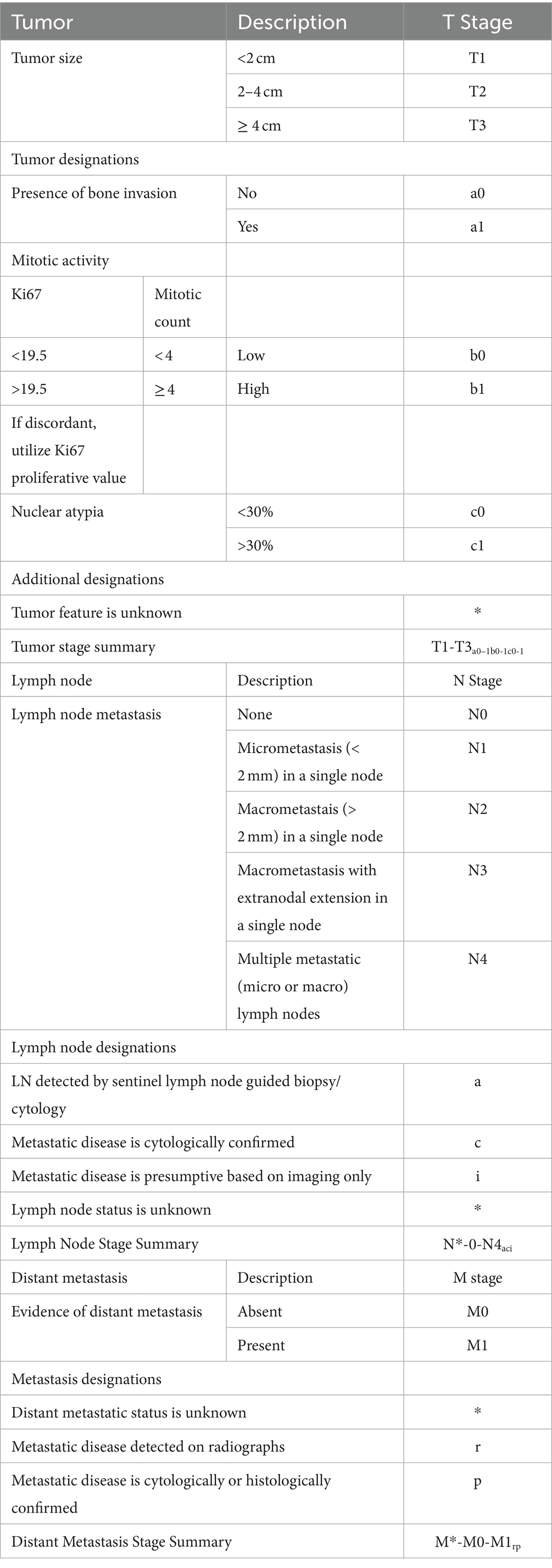
Based on the overall low level of evidence that supports that specific risk factors in canine OMM impart an objective negative impact on outcome, additional data is needed to solidify the impact of these risk factors. The WHO TNM system used for staging is routinely utilized in veterinary staging, and to capture data in future studies and systematic analyses, we propose an adaptation to the system (Table 8) that incorporates tumor-related features suggested to impact outcome, extent of lymph node involvement, and highlights what presumptions may be made during staging. Designations are also provided given that not all dogs may be fully staged or may not have confirmation of LN and distant metastasis. The key data collected with use of this scheme strengthens conclusions that can be made following interventional studies, and transparently acknowledges missing data. Examples for how use of the scheme may improve data used for studies is presented in Supplementary Table S1. Incorporation of this scheme into clinical practice, and adapted versions in the future, could be readily accomplished with use of a standardized worksheet (Supplementary Table S2), similar to the stomatitis disease activity index score (99).
Discussion
The primary objective of this study was to systematically evaluate levels of evidence and quantitative effects of canine OMM clinicopathologic risk factors on outcome to develop a risk stratification scheme for therapeutic decision-making across specialties. Despite OMM being the most investigated oral tumor in veterinary literature, when strict inclusion criteria were selected, the levels of evidence in support of proposed risk factors were low. Factors including inconsistencies in staging and reporting of prognostic variables, incomplete clinical outcome data, inhomogeneous treatment, and absence of randomized controlled studies contributed to these low levels of evidence. In fact, only tumor size was associated with level 1b evidence to support a negative impact on outcome, whereas most studies included provided level 4a or 4b evidence.
Notably, our levels of evidence in support of risk factors for canine oral OMM were weaker than those reported in a recent report describing international consensus and guidelines for therapeutic decision-making (75). The narrow inclusion criteria in our study which required statistical evaluation of prognostic risk factors coupled with the inherent limitations of retrospective veterinary studies likely contributed to our low levels of evidence. However, it is clear from both studies that overall, the levels of evidence used to derive conclusions for canine OMM are low, rarely reaching level 1 or 2.
There are several gaps in reported literature pertaining to both tumor and staging features that can be captured in the future to strengthen associations between prognostic factors, and aid in stratifying dogs for treatment for optimal benefit. Therefore, we propose use of a risk stratification scheme based on the TNM staging system to ease collection of pertinent data. This scheme can be applied prospectively and retrospectively, and may lead to improved ability and quality of comparisons between publications and more uniform data collection. Like the goals associated with eight edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) human malignant melanoma staging system, the aim is to facilitate accurate risk stratification and guide therapeutic approaches (100). The proposed scheme incorporates several designations to aid in extraction of specific TNM data for analysis in future studies and acknowledges that not all dogs included in a future study will have complete data regarding disease status. The risk stratification scheme is not intended to discourage additional investigation of the presence or strength of risk factors not included, like histopathologic margin distance, peritumoral or intratumoral T lymphocyte subset infiltration, or tumor location. Rather, it is currently focused on risk factors with repeatable prognostic implications based on systematic review, with the aim to be adapted in the future as knowledge increases.
Currently, tumor size and bone invasion were the most repeatable tumor-related features associated with clinical outcomes. Tumor size has long been a key prognostic feature within the existing TNM staging system, with one study demonstrating a clear increased hazard of death with every 1 cm increase in tumor size (13). Unexpectedly, lymph node metastasis, which is an identified parameter of the TNM system, was not strongly supported as a negative risk factor in the studies included. While limitations including poor power and incomplete staging of LN metastasis in prior studies contributed to the inability to define a clear negative influence of LN metastasis on outcome measures, the presence or absence of LN metastasis clearly influences clinical therapeutic decision making (75, 101). The current TNM definition of stage 3, which includes dogs with tumors equal to or greater than 4 cm in diameter with dogs with lymph node metastasis regardless of tumor size or extent of metastasis (micro- or macro-metastasis) contributes to difficulties in interpreting associations between staging features and outcome. Specifically, the use of stage 3 to classify OMM dilutes the ability to determine the true prognostic effect of both large tumors and metastatic lymph nodes.
Establishing the true impact of LN metastasis is also difficult as prior studies may include dogs that are under-staged or those with presumptive metastasis based on palpation or imaging alone. Methods for LN screening and confirmation of LN metastasis have evolved in recent years to better capture known metastasis (61, 77, 78, 102–104). Lymphatic drainage within the canine head is complex, with multiple lymphocentrums including the parotid, mandibular, and medial retropharyngeal lymph centers. It has been shown that up to 62% of oral tumors have contralateral dissemination (79) and that 6–45.5% of neoplasms spread to lymphocentrums other than the mandibular LNs (80, 82, 105). Yet, only the lateral mandibular LNs are readily accessible without ultrasound guidance; indeed, three of the six critically reviewed studies included here with prognostic data pertaining to LN metastatic status relied only on mandibular LN cytology for staging, often only including the ipsilateral side (13, 24, 33). Cytology has moderate accuracy for canine cervical LNs but may not capture all metastatic LNs (105–107). Several studies have evaluated all six regional lymph nodes via histology in dogs with OMM to determine drainage and metastatic patterns (9, 108–110). However, the need for pathologic staging of all six LNs in dogs without presumptive overt metastasis (the N0 neck) remains controversial. Sentinel LN (SLN) mapping provides an alternative, lower-morbidity option (103, 104, 111, 112) in which to guide cytologic or histopathologic sampling.
Further, the current TNM staging system does not account for differences in the extent of cervical metastasis, which limits conclusions on how to stratify treatment in these patients. In humans, there is a distinct prognostic difference for melanoma between isolated tumor cells, micrometastasis (< 2 mm), macrometastasis, and extranodal extension (100). The number of positive LN is also directly related to tumor burden and clinical outcome (113–117), further solidifying the importance of comprehensive staging. Yet, treatment that results in complete nodal dissection or irradiation of the entire lymphatic basin should ultimately be influenced by the type and number of positive lymph nodes, reducing indiscriminate nodal extirpation or elective irradiation. Historically, human patients with melanoma at risk for nodal metastasis underwent SLN biopsy, with complete LN dissection in the event of a SLN positive for metastasis (118, 119). However, while local disease recurrence was reduced by this approach, there was no difference in survival compared to patients that did not undergo complete LN dissection (118, 119). Similarly, the addition of adjuvant hypofractionated RT to complete LN dissection following a positive SLN decreased nodal recurrence but did not improve survival (120, 121). Recent, dramatic shifts in the management of human melanoma have incorporated immunotherapy as a first line therapy for advanced melanoma (122). This reliance on immunotherapy as a cornerstone of treatment has forced a spotlight on the importance of preserving draining LNs and immune cells to promote a robust immune response (108, 109, 123, 124). Elective LN dissection or irradiation prior to checkpoint inhibitor therapy may indeed reduce the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors, supporting efforts to conserve functional anti-cancer immune cells (110, 123). As anti-canine checkpoint inhibitors become incorporated into therapeutic paradigms (125–128), it will be important to critically evaluate the prognostic role of LN metastasis in patient outcomes and rely on evidence based approaches to drive the need for LN extirpation or adjuvant nodal RT in the context of effective immune responses.
Because of the evolution of staging schemes, and lack of systematic approach to staging in veterinary oncology, the proposed risk stratification scheme incorporates specific designations within the N staging category to allow for prognostication of differences in type and number of nodal spread as well as allow for presumptive conclusions to be made and transparently shared. Of note, this stratification scheme has not addressed tonsillar invasion or metastasis. Although tonsillar involvement appears rare, one study that evaluated 53 dogs with tonsillar melanoma found that 47% represented metastatic lesions from a known primary lesion, yet only 17% had concurrent lymph node metastasis (73). Therefore, a thorough oral examination should include an assessment of the tonsillar crypts when dogs are evaluated for metastasis to further examine the incidence of tonsillar spread. Cytology/biopsy of the tonsil without gross enlargement does not appear necessary at this time for complete screening, especially as the tonsil was never found to be a primary source of draining during indirect CT lymphangiography (oral SLN mapping) (73).
Distant metastatic disease was clearly found to affect prognosis, despite low study numbers and low levels of evidence to support this conclusion. Thoracic radiographs alone were used in 60% of the studies evaluated here, highlighting bias from potential under-reporting of metastasis (91, 129). While it is recommended that thoracic CT scans be utilized for screening to help better stratify risk and understand the prognostic implications of small early nodules on OMM, the use of CT adds substantial cost for some pet owners. Further, the prognostic implications of small pulmonary nodules detected by CT, but absent on radiographs, is largely unknown. Acknowledging the potential lead-time bias posed by monitoring dogs with distant metastasis detected with advanced imaging as opposed to radiographs, the proposed stratification scheme adds a designation for detection method. Despite that distant metastasis is rarely confirmed, a designation to highlight confirmation of metastasis has been included. There are also several presumptions and assumptions within the distant metastatic category that could be clarified in future versions. Two primary presumptions include investigators interpret data similarly, such as the implications of a solitary pulmonary nodule or mass, and that thoracic imaging is the likely modality used for detection of distant metastasis. The other primary assumption is that distant metastatic disease in distinct anatomic organs confers the same prognostic effect.
Strong conclusions regarding signalment, tumor localization within the oral cavity, mitotic activity, and nuclear atypia were not consistently associated with impacts on outcome. A lack of association regarding oral localization may be due to the inconsistency in the reporting process of tumor location. For example, lip tumors may include several locations, including mucocutaneous junction, haired skin of the lip, or the buccal mucosa with lesions in haired skin having a markedly different biologic behavior (75). Further, the presence of bone invasion, a strong prognostic feature, is inherently associated with location, with only lesions located on the maxillary/mandibular gingiva and alveolar mucosa able to invade the underlying bone. Most articles were not specific enough with tumor localization to separate the prognostic implications of bone invasion from oral cavity location, which may have diluted the results. Conversely, rostral versus caudal tumors are unlikely to carry uniquely different biologic behavior, but rostral tumors are theoretically easier to completely excise compared to tumors in the caudal oral cavity (13, 24, 70). Modern surgical techniques and oral surgery training opportunities increase the potential for adequate margins regardless of intraoral location, and likely contribute to the lack of prognostic influence of the tumor location.
Histopathological criteria including nuclear atypia score, mitotic count, Ki67 proliferation value, and quantification of pigmentation can also act to improve predictive algorithms needed for therapeutic decision-making (92). Because of the low level of evidence in our analysis, consistent with that of the recent consensus (75) additional data is needed to firmly assess the prognostic impact of these variables both independently and when used in combination. The risk stratification scheme includes designations to highlight tumor-specific mitotic activity and nuclear atypia. Mitotic activity includes mitotic count and Ki67 values, which could be included independently or together. Because Ki67 immunohistochemistry is not standard on many histopathologic reports and may increase cost to clients without necessarily changing a therapeutic recommendation, it may not be consistently ordered. Additionally, as with pigmentation, there is subjectivity to its interpretation, and standardized protocols and assessments across laboratories pose additional challenges (75, 92, 130–132). However, critical evaluation of the literature suggests that Ki67 may be important for prediction of biologic behavior (62). Standardized reporting of Ki67 is strongly recommended to make future conclusions on utility and clinical use. This will be especially impactful in the rare clinical case of discordant MC and KI-67 proliferative value. In this case it is suggested that both values are reported for future analysis, but Ki-67 value is adopted for scoring.
Due to the limited literature on the degree of pigmentation on prognosis for canine OMM and the inherent subjectivity of its determination, we elected to exclude pigmentation from the proposed scheme. However, we acknowledge that the degree of pigmentation is currently essential in separating HDWMN (3, 10) from OMM, based on high pigment, low mitotic index, and lack of nuclear atypia. Yet, the methods to designate oral melanocytic tumors in dogs as HWDMN or OMM have been developed but have yet to be adequately validated and concern exists surrounding if these are truly two separate entities versus a spectrum of disease. Frankly, it is unknown if HWDMN has the potential to progress to OMM, which is a critical distinction. Ultimately, these questions need to be addressed by future prospective studies. Thus, rather than continuing to refer to these two tumors as separate entities based on pathologic features and excluding HDWMN from prospective analysis, we recommend that all oral melanocytic tumors be scored using the proposed risk stratification scheme. If clinically relevant, the degree of pigmentation and differentiation of the cells can be mentioned in “additional designations.” Inclusion of all melanocytic lesions in the stratification scheme will aid in defining less biologically aggressive subset(s) of OMM, answer relevant questions on the biologic behavior of the currently termed, HDWMN, and directly influence treatment recommendations, such as the need for wide surgical margins and staging frequency in these less aggressive lesions.
In future variations of risk stratification scheme, several alterations can be made to reflect different therapeutic avenues. As immunotherapies emerge that have the potential to improve outcomes for dogs with OMM, the addition of categories such as intratumoral PD-L1, PD-1 and T lymphocyte infiltration will undoubtedly be needed (41–44, 133). Further, evaluation of the depth of invasion, also known as Breslow thickness, is a critical pathologic step in staging human melanoma (100) and may be of prognostic importance for canine OMM in the future. None of the reviewed articles described the pathologic depth of invasion limiting any conclusions on its current or future utility in dogs.
As previously stated, one limitation of the assessments made here includes the strict, pre-defined inclusion criteria, which were meant to minimize bias. Despite this, variables considered key to decision-making and development of future conclusions were similar to a recent consensus (75). A second potential limitation is that only peer-reviewed studies published in the English language were included. The authors are aware that the use of an expanded staging scheme to aid in risk stratification will increase effort. However, the ability to capture key data simply from an expanded TNM description will strengthen future efforts to form actionable conclusions regarding prognostic variables and their influence (or lack thereof) on therapeutic decision-making and outcomes.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ES: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JL: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Supervision. EG: Data curation, Writing – original draft. AC: Data curation, Writing – original draft. SG: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fvets.2024.1472748/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
1. Prouteau, A, and André, C. Canine melanomas as models for human melanomas: clinical, histological, and genetic comparison. Genes. (2019) 10:501. doi: 10.3390/genes10070501
2. Nishiya, A, Massoco, C, Felizzola, C, Perlmann, E, Batschinski, K, Tedardi, M, et al. Comparative aspects of canine melanoma. Vet Sci. (2016) 3:7. doi: 10.3390/vetsci3010007
3. Kim, WS, Vinayak, A, and Powers, B. Comparative review of malignant melanoma and histologically well-differentiated melanocytic neoplasm in the oral cavity of dogs. Vet Sci. (2021) 8:261. doi: 10.3390/vetsci8110261
4. Giacobino, D, Camerino, M, Riccardo, F, Cavallo, F, Tarone, L, Martano, M, et al. Difference in outcome between curative intent vs marginal excision as a first treatment in dogs with oral malignant melanoma and the impact of adjuvant CSPG4-DNA electrovaccination: a retrospective study on 155 cases. Vet Comp Oncol. (2021) 19:651–60. doi: 10.1111/vco.12690
5. Willcox, JL, Spriet, M, Zwingenberger, AL, Phillips, KL, Burton, JH, Skorupski, KA, et al. Evaluation of accuracy for 18 F-FDG positron emission tomography and computed tomography for detection of lymph node metastasis in canine oral malignant melanoma. Vet Comp Oncol. (2021) 19:463–72. doi: 10.1111/vco.12651
6. Taylor, KH, Smith, AN, Higginbotham, M, Schwartz, DD, Carpenter, DM, and Whitley, EM. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in canine oral malignant melanoma. Vet Comp Oncol. (2007) 5:208–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5829.2007.00130.x
7. Wingo, K. Histopathologic diagnoses from biopsies of the oral cavity in 403 dogs and 73 cats. J Vet Dent. (2018) 35:7–17. doi: 10.1177/0898756418759760
8. Brønden, LB, Eriksen, T, and Kristensen, AT. Oral malignant melanomas and other head and neck neoplasms in Danish dogs--data from the Danish veterinary Cancer registry. Acta Vet Scand. (2009) 51:54. doi: 10.1186/1751-0147-51-54
9. Sarowitz, BN, Davis, GJ, and Kim, S. Outcome and prognostic factors following curative-intent surgery for oral tumours in dogs: 234 cases (2004 to 2014). J Small Anim Pract. (2017) 58:146–53. doi: 10.1111/jsap.12624
10. Esplin, DG. Survival of dogs following surgical excision of histologically well-differentiated melanocytic neoplasms of the mucous membranes of the lips and oral cavity. Vet Pathol. (2008) 45:889–96. doi: 10.1354/vp.45-6-889
11. Palma, SD, McConnell, A, Verganti, S, and Starkey, M. Review on canine oral melanoma: an undervalued authentic genetic model of human oral melanoma? Vet Pathol. (2021) 58:881–9. doi: 10.1177/0300985821996658
12. Harvey, HJ, MacEwen, EG, Braun, D, Patnaik, AK, Withrow, SJ, and Jongeward, S. Prognostic criteria for dogs with oral melanoma. J Am Vet Med Assoc. (1981) 178:580–2.
13. Tuohy, JL, Selmic, LE, Worley, DR, Ehrhart, NP, and Withrow, SJ. Outcome following curative-intent surgery for oral melanoma in dogs: 70 cases (1998-2011). J Am Vet Med Assoc. (2014) 245:1266–73.
14. Owen, LN. Veterinary public health unit, WHO collaborating Center for Comparative Oncology. Geneva: World Health Organization (1980).
15. MacEwen, EG, Patnaik, AK, Harvey, HJ, Hayes, AA, and Matus, R. Canine oral melanoma: comparison of surgery versus surgery plus Corynebacterium parvum. Cancer Investig. (1986) 4:397–402. doi: 10.3109/07357908609017520
16. Piras, LA, Riccardo, F, Iussich, S, Maniscalco, L, Gattino, F, Martano, M, et al. Prolongation of survival of dogs with oral malignant melanoma treated by en bloc surgical resection and adjuvant CSPG4-antigen electrovaccination. Vet Comp Oncol. (2017) 15:996–1013. doi: 10.1111/vco.12239
17. Boston, SE, Lu, X, Culp, WTN, Montinaro, V, Romanelli, G, Dudley, RM, et al. Efficacy of systemic adjuvant therapies administered to dogs after excision of oral malignant melanomas: 151 cases (2001-2012). J Am Vet Med Assoc. (2014) 245:401–7. doi: 10.2460/javma.245.4.401
18. Cancedda, S, Rohrer Bley, C, Aresu, L, Dacasto, M, Leone, VF, Pizzoni, S, et al. Efficacy and side effects of radiation therapy in comparison with radiation therapy and temozolomide in the treatment of measurable canine malignant melanoma. Vet Comp Oncol. (2016) 14:e146–57. doi: 10.1111/vco.12122
19. Cunha, SCS, Holguin, PG, Corgozinho, KB, de Azevedo, SCS, de Carvalho, LAV, and Ferreira, AMR. Radiation therapy as an adjuvant therapy for the treatment of oral melanoma in a dog. Acta Sci Vet. (2013) 41
20. Hoopes, PJ, Moodie, KL, Petryk, AA, Petryk, JD, Sechrist, S, Gladstone, DJ, et al. Hypo-fractionated radiation, magnetic nanoparticle hyperthermia and a viral immunotherapy treatment of spontaneous canine Cancer. Proc SPIE. (2017):10066. doi: 10.1117/12.2256213
21. Hoopes, PJ, Wagner, RJ, Duval, K, Kang, K, Gladstone, DJ, Moodie, KL, et al. Treatment of canine Oral melanoma with nanotechnology-based immunotherapy and radiation. Mol Pharm. (2018) 15:3717–22. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.8b00126
22. Freeman, KP, Hahn, KA, Harris, FD, and King, GK. Treatment of dogs with oral melanoma by hypofractionated radiation therapy and platinum-based chemotherapy (1987-1997). J Vet Intern Med. (2003) 17:96–101.
23. Kinzel, S, Hein, S, Stopinski, T, Koch, J, Buecker, A, Treusacher, H-P, et al. Hypofractionated radiation therapy for the treatment of malignant melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma in dogs and cats. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr. (2003) 116:134–8.
24. Proulx, DR, Ruslander, DM, Dodge, RK, Hauck, ML, Williams, LE, Horn, B, et al. A retrospective analysis of 140 dogs with oral melanoma treated with external beam radiation. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. (2003) 44:352–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1740-8261.2003.tb00468.x
25. Kinzel, S, Hein, S, Stopinski, T, Koch, J, Buecker, A, Treusacher, HP, et al. The hypofractionated radiation therapy for the treatment of melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma in dogs and cats. Berliner Munchener Tierarztliche Wochenschrift. (2003) 116:134–8.
26. Cunha, S, Corgozinho, KB, Silva, FBF, Silva, K, and Ferreira, AM. Radiation therapy for oral melanoma in dogs: a retrospective study. Cienc Rural. (2018) 48:396. doi: 10.1590/0103-8478cr20160396
27. Noguchi, S, Yagi, K, Okamoto, N, Wada, Y, and Tanaka, T. Prognostic factors for the efficiency of radiation therapy in dogs with Oral melanoma: a pilot study of hypoxia in intraosseous lesions. Vet Sci. (2022) 10:10004. doi: 10.3390/vetsci10010004
28. Kaser-Hotz, B, Jacomet, R, Sumova, A, Fidel, J, Stankeova, S, Roos, M, et al. Radiation therapy of canine oral cavity tumours. Tierarztl Prax Ausg K Klientiere Heimtiere. (2002) 30:21–6.
29. Théon, AP, Rodriguez, C, and Madewell, BR. Analysis of prognostic factors and patterns of failure in dogs with malignant oral tumors treated with megavoltage irradiation. J Am Vet Med Assoc. (1997) 210:778–84. doi: 10.2460/javma.1997.210.06.778
30. Baja, AJ, Kelsey, KL, Ruslander, DM, Gieger, TL, and Nolan, MW. A retrospective study of 101 dogs with oral melanoma treated with a weekly or biweekly 6 Gy × 6 radiotherapy protocol. Vet Comp Oncol. (2022) 20:623–31.
31. Blackwood, L, and Dobson, JM. Radiotherapy of oral malignant melanomas in dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. (1996) 209:98–102.
32. Kawabe, M, Mori, T, Ito, Y, Murakami, M, Sakai, H, Yanai, T, et al. Outcomes of dogs undergoing radiotherapy for treatment of oral malignant melanoma: 111 cases (2006-2012). J Am Vet Med Assoc. (2015) 247:1146–53. doi: 10.2460/javma.247.10.1146
33. Bateman, KE, Catton, PA, Pennock, PW, and Kruth, SA. 0-7-21 radiation therapy for the treatment of canine oral melanoma. J Vet Intern Med. (1994) 8:267–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-1676.1994.tb03231.x
34. Turek, M, LaDue, T, Looper, J, Nagata, K, Shiomitsu, K, Keyerleber, M, et al. Multimodality treatment including ONCEPT for canine oral melanoma: a retrospective analysis of 131 dogs. Vet Radiol Ultrasound. (2020) 61:471–80. doi: 10.1111/vru.12860
35. Murphy, S, Hayes, AM, Blackwood, L, Maglennon, G, Pattinson, H, and Sparkes, AH. Oral malignant melanoma - the effect of coarse fractionation radiotherapy alone or with adjuvant carboplatin therapy. Vet Comp Oncol. (2005) 3:222–9.
36. Brockley, LK, Cooper, MA, and Bennett, PF. Malignant melanoma in 63 dogs (2001-2011): the effect of carboplatin chemotherapy on survival. N Z Vet J. (2013) 61:25–31. doi: 10.1080/00480169.2012.699433
37. Dank, G, Rassnick, KM, Sokolovsky, Y, Garrett, LD, Post, GS, Kitchell, BE, et al. Use of adjuvant carboplatin for treatment of dogs with oral malignant melanoma following surgical excision. Vet Comp Oncol. (2014) 12:78–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5829.2012.00338.x
38. Verganti, S, Berlato, D, Blackwood, L, Amores-Fuster, I, Polton, GA, Elders, R, et al. Use of Oncept melanoma vaccine in 69 canine oral malignant melanomas in the UK. J Small Anim Pract. (2017) 58:10–6. doi: 10.1111/jsap.12613
39. Grosenbaugh, DA, Leard, AT, Bergman, PJ, Klein, MK, Meleo, K, Susaneck, S, et al. Safety and efficacy of a xenogeneic DNA vaccine encoding for human tyrosinase as adjunctive treatment for oral malignant melanoma in dogs following surgical excision of the primary tumor. Am J Vet Res. (2011) 72:1631–8. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.72.12.1631
40. Riccardo, F, Iussich, S, Maniscalco, L, Lorda Mayayo, S, La Rosa, G, Arigoni, M, et al. CSPG4-specific immunity and survival prolongation in dogs with oral malignant melanoma immunized with human CSPG4 DNA. Clin Cancer Res. (2014) 20:3753–62. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-3042
41. Mason, NJ, Chester, N, Xiong, A, Rotolo, A, Wu, Y, Yoshimoto, S, et al. Development of a fully canine anti-canine CTLA4 monoclonal antibody for comparative translational research in dogs with spontaneous tumors. MAbs. (2021) 13:2004638. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2021.2004638
42. Deguchi, T, Maekawa, N, Konnai, S, Owaki, R, Hosoya, K, Morishita, K, et al. Enhanced systemic antitumour immunity by Hypofractionated radiotherapy and anti-PD-L1 therapy in dogs with pulmonary metastatic Oral malignant melanoma. Cancers (Basel). (2023) 15:3013. doi: 10.3390/cancers15113013
43. Maekawa, N, Konnai, S, Hosoya, K, Kim, S, Kinoshita, R, Deguchi, T, et al. Safety and clinical efficacy of an anti-PD-L1 antibody (c4G12) in dogs with advanced malignant tumours. PLoS One. (2023) 18:e0291727. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291727
44. Igase, M, Inanaga, S, Tani, K, Nakaichi, M, Sakai, Y, Sakurai, M, et al. Long-term survival of dogs with stage 4 oral malignant melanoma treated with anti-canine PD-1 therapeutic antibody: a follow-up case report. Vet Comp Oncol. (2022) 20:901–5. doi: 10.1111/vco.12829
45. Pazzi, P, Steenkamp, G, and Rixon, AJ. Treatment of canine oral melanomas: a critical review of the literature. Vet Sci. (2022) 9:196. doi: 10.3390/vetsci9050196
46. Spangler, WL, and Kass, PH. The histologic and epidemiologic bases for prognostic considerations in canine melanocytic neoplasia. Vet Pathol. (2006) 43:136–49. doi: 10.1354/vp.43-2-136
47. Camerino, M, Giacobino, D, Manassero, L, Iussich, S, Riccardo, F, Cavallo, F, et al. Prognostic impact of bone invasion in canine oral malignant melanoma treated by surgery and anti-CSPG4 vaccination: a retrospective study on 68 cases (2010-2020). Vet Comp Oncol. (2022) 20:189–97. doi: 10.1111/vco.12761
48. Smedley, RC, Bongiovanni, L, Bacmeister, C, Clifford, CA, Christensen, N, Dreyfus, JM, et al. Diagnosis and histopathologic prognostication of canine melanocytic neoplasms: a consensus of the oncology-pathology working group. Vet Comp Oncol. (2022) 20:739–51. doi: 10.1111/vco.12827
49. Simpson, RM, Bastian, BC, Michael, HT, Webster, JD, Prasad, ML, Conway, CM, et al. Sporadic naturally occurring melanoma in dogs as a preclinical model for human melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. (2014) 27:37–47. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12185
50. Temam, S, Mamelle, G, Marandas, P, Wibault, P, Avril, M-F, Janot, F, et al. Postoperative radiotherapy for primary mucosal melanoma of the head and neck. Cancer. (2005) 103:313–9. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20775
51. Sun, S, Huang, X, Gao, L, Zhang, Y, Luo, J, Zhang, S, et al. Long-term treatment outcomes and prognosis of mucosal melanoma of the head and neck: 161 cases from a single institution. Oral Oncol. (2017) 74:115–22. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.09.020
52. Schmidt, MQ, David, J, Yoshida, EJ, Scher, K, Mita, A, Shiao, SL, et al. Predictors of survival in head and neck mucosal melanoma. Oral Oncol. (2017) 73:36–42. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.08.002
53. Jethanamest, D, Vila, PM, Sikora, AG, and Morris, LGT. Predictors of survival in mucosal melanoma of the head and neck. Ann Surg Oncol. (2011) 18:2748–56. doi: 10.1245/s10434-011-1685-4
54. Patel, SG, Prasad, ML, Escrig, M, Singh, B, Shaha, AR, Kraus, DH, et al. Primary mucosal malignant melanoma of the head and neck. Head Neck. (2002) 24:247–57. doi: 10.1002/hed.10019
55. Heppt, MV, Roesch, A, Weide, B, Gutzmer, R, Meier, F, Loquai, C, et al. Prognostic factors and treatment outcomes in 444 patients with mucosal melanoma. Eur J Cancer. (2017) 81:36–44. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2017.05.014
56. Moya-Plana, A, Mangin, D, Dercle, L, Taouachi, R, Casiraghi, O, Ammari, S, et al. Risk-based stratification in head and neck mucosal melanoma. Oral Oncol. (2019) 97:44–9. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2019.07.026
57. Sun, C-Z, Chen, Y-F, Jiang, Y-E, Hu, Z-D, Yang, A-K, and Song, M. Treatment and prognosis of oral mucosal melanoma. Oral Oncol. (2012) 48:647–52. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2012.01.019
58. Bertram, CA, Donovan, TA, and Bartel, A. Mitotic activity: a systematic literature review of the assessment methodology and prognostic value in feline tumors. Vet Pathol. (2024):3009858241239566. doi: 10.1177/03009858241239566
59. Hardwick, L. A comparative view on molecular alterations and potential therapeutic strategies for canine oral melanoma. Vet Sci. (2021) 8:286. doi: 10.3390/vetsci8110286
60. Tellado, MN, Maglietti, FH, Michinski, SD, Marshall, GR, and Signori, E. Electrochemotherapy in treatment of canine oral malignant melanoma and factors influencing treatment outcome. Radiol Oncol. (2020) 54:68–78. doi: 10.2478/raon-2020-0014
61. Przeździecki, R, Czopowicz, M, and Sapierzyński, R. Accuracy of routine cytology and immunocytochemistry in preoperative diagnosis of oral amelanotic melanomas in dogs. Vet Clin Pathol. (2015) 44:597–604. doi: 10.1111/vcp.12292
62. Iussich, S, Maniscalco, L, Di Sciuva, A, Iotti, B, Morello, E, Martano, M, et al. PDGFRs expression in dogs affected by malignant oral melanomas: correlation with prognosis. Vet Comp Oncol. (2017) 15:462–9. doi: 10.1111/vco.12190
63. Ramos-Vara, JA, Beissenherz, ME, Miller, MA, Johnson, GC, Pace, LW, Fard, A, et al. Retrospective study of 338 canine oral melanomas with clinical, histologic, and immunohistochemical review of 129 cases. Vet Pathol. (2000) 37:597–608. doi: 10.1354/vp.37-6-597
64. Carroll, KA, Kuntz, CA, Heller, J, Peters, A, Rotne, R, and Dunn, A. Tumor size as a predictor of lymphatic invasion in oral melanomas of dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. (2020) 256:1123–8. doi: 10.2460/javma.256.10.1123
65. Atherton, MJ, Morris, JS, McDermott, MR, and Lichty, BD. Cancer immunology and canine malignant melanoma: a comparative review. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. (2016) 169:15–26. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2015.11.003
66. Gillard, M, Cadieu, E, De Brito, C, Abadie, J, Vergier, B, Devauchelle, P, et al. Naturally occurring melanomas in dogs as models for non-UV pathways of human melanomas. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. (2014) 27:90–102. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12170
67. MacEwen, EG, Kurzman, ID, Vail, DM, Dubielzig, RR, Everlith, K, Madewell, BR, et al. Adjuvant therapy for melanoma in dogs: results of randomized clinical trials using surgery, liposome-encapsulated muramyl tripeptide, and granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Clin Cancer Res. (1999) 5:4249–58.
68. Smith, SH, Goldschmidt, MH, and McManus, PM. A comparative review of melanocytic neoplasms. Vet Pathol. (2002) 39:651–78. doi: 10.1354/vp.39-6-651
69. Silveira, TL, Pang, LY, Di Domenico, A, Veloso, ES, Silva, ILD, Puerto, HLD, et al. COX-2 silencing in canine malignant melanoma inhibits malignant behaviour. Front Vet Sci. (2021) 8:633170. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.633170
70. Raleigh, ML, Smith, MM, and Taney, K. Curative intent surgery of Oral malignant melanoma and regional lymph node biopsy assessment in 25 dogs: 2006-2017. J Vet Dent. (2021) 38:193–8. doi: 10.1177/08987564211072396
71. Yasumaru, CC, Xavier, JG, Strefezzi, RDF, and Salles-Gomes, COM. Intratumoral T-lymphocyte subsets in canine Oral melanoma and their association with clinical and histopathological parameters. Vet Pathol. (2021) 58:491–502. doi: 10.1177/0300985821999321
72. Almela, RM, and Ansón, A. A review of immunotherapeutic strategies in canine malignant melanoma. Vet Sci. (2019) 6:10015. doi: 10.3390/vetsci6010015
73. Mickelson, MA, Regan, D, Randall, EK, Worley, D, and Seguin, B. Canine tonsillar neoplasia and tonsillar metastasis from various primary neoplasms. Vet Comp Oncol. (2020) 18:770–7. doi: 10.1111/vco.12604
74. Newman, SJ, Jankovsky, JM, Rohrbach, BW, and LeBlanc, AK. C-kit expression in canine mucosal melanomas. Vet Pathol. (2012) 49:760–5. doi: 10.1177/0300985811414032
75. Polton, G, Borrego, JF, Clemente-Vicario, F, Clifford, CA, Jagielski, D, Kessler, M, et al. Melanoma of the dog and cat: consensus and guidelines. Front Vet Sci. (2024) 11:1359426. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1359426
76. Dewhirst, MW, Sim, DA, Forsyth, K, Grochowski, KJ, Wilson, S, and Bicknell, E. Local control and distant metastases in primary canine malignant melanomas treated with hyperthermia and/or radiotherapy. Int J Hyperth. (1985) 1:219–34.
77. Goldschmidt, S, Soltero-Rivera, M, Quiroz, A, Wong, K, Rebhun, R, Zwingenberger, A, et al. The diagnostic yield of preoperative screening for oral cancer in dogs over 15 years, part 1: locoregional screening. J Am Vet Med Assoc. (2023) 261:S14–23. doi: 10.2460/javma.23.05.0299
78. Williams, LE, and Packer, RA. Association between lymph node size and metastasis in dogs with oral malignant melanoma: 100 cases (1987-2001). J Am Vet Med Assoc. (2003) 222:1234–6. doi: 10.2460/javma.2003.222.1234
79. Skinner, OT, Boston, SE, and de Souza, CH. Patterns of lymph node metastasis identified following bilateral mandibular and medial retropharyngeal lymphadenectomy in 31 dogs with malignancies of the head. Vet comp. Oncologia. (2017) 15:881–9. doi: 10.1111/vco.12229
80. Grimes, JA, Mestrinho, LA, Berg, J, Cass, S, Oblak, ML, Murphy, S, et al. Histologic evaluation of mandibular and medial retropharyngeal lymph nodes during staging of oral malignant melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma in dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. (2019) 254:938–43. doi: 10.2460/javma.254.8.938
81. Rassnick, KM, Ruslander, DM, Cotter, SM, Al-Sarraf, R, Bruyette, DS, Gamblin, RM, et al. Use of carboplatin for treatment of dogs with malignant melanoma: 27 cases (1989–2000). J Am Vet Med Assoc. (2001) 218:1444–8. doi: 10.2460/javma.2001.218.1444
82. Odenweller, PH, Smith, MM, and Taney, KG. Validation of regional lymph node excisional biopsy for staging Oral and maxillofacial malignant neoplasms in 97 dogs and 10 cats (2006-2016). J Vet Dent. (2019) 36:97–103. doi: 10.1177/0898756419869841
83. Chatzistefanou, I, Kolokythas, A, Vahtsevanos, K, and Antoniades, K. Primary mucosal melanoma of the oral cavity: current therapy and future directions. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. (2016) 122:17–27.
84. Rapini, RP, Golitz, LE, Greer, RO, Krekorian, EA, and Poulson, T. Primary malignant melanoma of the oral cavity. A review of 177 cases. Cancer. (1985) 55:1543–51. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19850401)55:7<1543::AID-CNCR2820550722>3.0.CO;2-F
85. Owens, JM, Roberts, DB, and Myers, JN. The role of postoperative adjuvant radiation therapy in the treatment of mucosal melanomas of the head and neck region. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. (2003) 129:864–8. doi: 10.1001/archotol.129.8.864
86. Yii, NW, Eisen, T, Nicolson, M, A’Hern, R, Rhys-Evans, P, Archer, D, et al. Mucosal malignant melanoma of the head and neck: the Marsden experience over half a century. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). (2003) 15:199–204. doi: 10.1016/S0936-6555(03)00068-2
87. Tanaka, N, Mimura, M, Ogi, K, and Amagasa, T. Primary malignant melanoma of the oral cavity: assessment of outcome from the clinical records of 35 patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. (2004) 33:761–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2004.01.008
88. Liu, Y, Yang, C, Sun, Y, Geng, B, and Yuan, K. Multivariate analysis of the prognostic factors in 230 surgically treated oral mucosal malignant melanomas. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. (2005) 14:466–71.
89. Meleti, M, Leemans, CR, de Bree, R, Vescovi, P, Sesenna, E, and van der Waal, I. Head and neck mucosal melanoma: experience with 42 patients, with emphasis on the role of postoperative radiotherapy. Head Neck. (2008) 30:1543–51. doi: 10.1002/hed.20901
90. Lourenço, SV, Fernandes, JD, Hsieh, R, Coutinho-Camillo, CM, Bologna, S, Sangueza, M, et al. Head and neck mucosal melanoma: a review. Am J Dermatopathol. (2014) 36:578–87. doi: 10.1097/DAD.0000000000000035
91. Goldschmidt, S, Soltero-Rivera, M, Quiroz, A, Wong, K, Rebhun, R, Zwingenberger, A, et al. The diagnostic yield of preoperative screening for oral cancer in dogs over 15 years, part 2: distant screening. J Am Vet Med Assoc. (2023) 261:S24–33. doi: 10.2460/javma.23.05.0300
92. Bergin, IL, Smedley, RC, Esplin, DG, Spangler, WL, and Kiupel, M. Prognostic evaluation of Ki67 threshold value in canine oral melanoma. Vet Pathol. (2011) 48:41–53. doi: 10.1177/0300985810388947
93. Choisunirachon, N, Tanaka, Y, Saeki, K, Sasaki, N, Nishimura, R, and Nakagawa, T. Proliferative index and microvessel density as potential prognostic markers of canine oral malignant melanomas. Thai J Vet Med. (2014) 44:435–43.
94. Vargas, THM, Pulz, LH, Ferro, DG, Sobral, RA, Venturini, MAFA, Corrêa, HL, et al. Galectin-3 expression correlates with Post-surgical survival in canine Oral melanomas. J Comp Pathol. (2019) 173:49–57. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2019.10.003
95. Teixeira, TF, Gentile, LB, da Silva, TC, Mennecier, G, Chaible, LM, Cogliati, B, et al. Cell proliferation and expression of connexins differ in melanotic and amelanotic canine oral melanomas. Vet Res Commun. (2014) 38:29–38. doi: 10.1007/s11259-013-9580-z
96. Grimes, JA, Matz, BM, Christopherson, PW, Koehler, JW, Cappelle, KK, Hlusko, KC, et al. Agreement between cytology and histopathology for regional lymph node metastasis in dogs with melanocytic neoplasms. Vet Pathol. (2017) 54:579–87. doi: 10.1177/0300985817698209
97. Garcia, JS, Nowosh, V, López, RVM, and de Massoco, CO. Association of systemic inflammatory and immune indices with survival in canine patients with oral melanoma, treated with experimental immunotherapy alone or experimental immunotherapy plus metronomic chemotherapy. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:888411. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.888411
98. Prouteau, A, Chocteau, F, de Brito, C, Cadieu, E, Primot, A, Botherel, N, et al. Prognostic value of somatic focal amplifications on chromosome 30 in canine oral melanoma. Vet Comp Oncol. (2020) 18:214–23. doi: 10.1111/vco.12536
99. Soltero-Rivera, M, Goldschmidt, S, and Arzi, B. Feline chronic gingivostomatitis current concepts in clinical management. J Feline Med Surg. (2023) 25:834. doi: 10.1177/1098612X231186834
100. Keung, EZ, and Gershenwald, JE. The eighth edition American joint committee on Cancer (AJCC) melanoma staging system: implications for melanoma treatment and care. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. (2018) 18:775–84. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2018.1489246
101. Congiusta, M, Lawrence, J, Rendahl, A, and Goldschmidt, S. Variability in recommendations for cervical lymph node pathology for staging of canine oral neoplasia: a survey study. Front Vet Sci. (2020) 7:506. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00506
102. Skinner, OT, Boston, SE, Giglio, RF, Whitley, EM, Colee, JC, and Porter, EG. Diagnostic accuracy of contrast-enhanced computed tomography for assessment of mandibular and medial retropharyngeal lymph node metastasis in dogs with oral and nasal cancer. Vet Comp Oncol. (2018) 16:562–70. doi: 10.1111/vco.12415
103. Goldschmidt, S, Stewart, N, Ober, C, Bell, C, Wolf-Ringwall, A, Kent, M, et al. Contrast-enhanced and indirect computed tomography lymphangiography accurately identifies the cervical lymphocenter at risk for metastasis in pet dogs with spontaneously occurring oral neoplasia. PLoS One. (2023) 18:e0282500. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282500
104. Wan, J, Oblak, ML, Ram, A, Singh, A, and Nykamp, S. Determining agreement between preoperative computed tomography lymphography and indocyanine green near infrared fluorescence intraoperative imaging for sentinel lymph node mapping in dogs with oral tumours. Vet Comp Oncol. (2021) 19:295–303. doi: 10.1111/vco.12675
105. Herring, ES, Smith, MM, and Robertson, JL. Lymph node staging of oral and maxillofacial neoplasms in 31 dogs and cats. J Vet Dent. (2002) 19:122–6. doi: 10.1177/089875640201900301
106. Ku, CK, Kass, PH, and Christopher, MM. Cytologic-histologic concordance in the diagnosis of neoplasia in canine and feline lymph nodes: a retrospective study of 367 cases. Vet Comp Oncol. (2016) 15:1206–17. doi: 10.1111/vco.12256
107. Fournier, Q, Cazzini, P, Bavcar, S, Pecceu, E, Ballber, C, and Elders, R. Investigation of the utility of lymph node fine-needle aspiration cytology for the staging of malignant solid tumors in dogs. Vet Clin Pathol. (2018) 47:489–500. doi: 10.1111/vcp.12636
108. Fransen, MF, van Hall, T, and Ossendorp, F. Immune checkpoint therapy: tumor draining lymph nodes in the spotlights. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:401. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179401
109. Mitra, D, Bishop, A, and Guadagnolo, BA. Adjuvant nodal radiation therapy for melanoma in the era of immunotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2020) 108:164–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.06.006
110. Kawaguchi, Y, Nishioka, N, Nakamura, T, Imai, K, Aoki, T, Kajiwara, N, et al. Impact of lymph node dissection on the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with postoperative recurrence of non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. (2024) 16:1960–70. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-1806
111. Ram, AS, Matuszewska, K, Petrik, J, Singh, A, and Oblak, ML. Quantitative and semi-quantitative methods for assessing the degree of methylene blue staining in sentinel lymph nodes in dogs. Front Vet Sci. (2021) 8:758295. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.758295
112. Liptak, JM, and Boston, SE. Nonselective lymph node dissection and sentinel lymph node mapping and biopsy. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. (2019) 49:793–807. doi: 10.1016/j.cvsm.2019.04.003
113. van Akkooi, ACJ, de Wilt, JHW, Verhoef, C, Schmitz, PIM, van Geel, AN, Eggermont, AMM, et al. Clinical relevance of melanoma micrometastases (<0.1 mm) in sentinel nodes: are these nodes to be considered negative? Ann Oncol. (2006) 17:1578–85. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdl176
114. Balch, CM, Soong, SJ, Gershenwald, JE, Thompson, JF, Reintgen, DS, Cascinelli, N, et al. Prognostic factors analysis of 17,600 melanoma patients: validation of the American joint committee on Cancer melanoma staging system. J Clin Oncol. (2001) 19:3622–34. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2001.19.16.3622
115. Scheri, RP, Essner, R, Turner, RR, Ye, X, and Morton, DL. Isolated tumor cells in the sentinel node affect long-term prognosis of patients with melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol. (2007) 14:2861–6. doi: 10.1245/s10434-007-9472-y
116. Francischetto, T, Spector, N, Neto Rezende, JF, de Azevedo, AM, de Oliveira, RS, Small, IA, et al. Influence of sentinel lymph node tumor burden on survival in melanoma. Ann Surg Oncol. (2010) 17:1152–8. doi: 10.1245/s10434-009-0884-8
117. Murali, R, DeSilva, C, McCarthy, SW, Thompson, JF, and Scolyer, RA. Sentinel lymph nodes containing very small (<0.1 mm) deposits of metastatic melanoma cannot be safely regarded as tumor-negative. Ann Surg Oncol. (2012) 19:1089–99. doi: 10.1245/s10434-011-2208-z
118. Faries, MB, Thompson, JF, Cochran, AJ, Andtbacka, RH, Mozzillo, N, Zager, JS, et al. Completion dissection or observation for sentinel-node metastasis in melanoma. N Engl J Med. (2017) 376:2211–22. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1613210
119. Leiter, U, Stadler, R, Mauch, C, Hohenberger, W, Brockmeyer, N, Berking, C, et al. Complete lymph node dissection versus no dissection in patients with sentinel lymph node biopsy positive melanoma (DeCOG-SLT): a multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2016) 17:757–67. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)00141-8
120. Henderson, MA, Burmeister, BH, Ainslie, J, Fisher, R, Di Iulio, J, Smithers, BM, et al. Adjuvant lymph-node field radiotherapy versus observation only in patients with melanoma at high risk of further lymph-node field relapse after lymphadenectomy (ANZMTG 01.02/TROG 02.01): 6-year follow-up of a phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. (2015) 16:1049–60. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)00187-4
121. Burmeister, BH, Henderson, MA, Ainslie, J, Fisher, R, Di Iulio, J, Smithers, BM, et al. Adjuvant radiotherapy versus observation alone for patients at risk of lymph-node field relapse after therapeutic lymphadenectomy for melanoma: a randomised trial. Lancet Oncol. (2012) 13:589–97. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70138-9
122. Boutros, A, Croce, E, Ferrari, M, Gili, R, Massaro, G, Marconcini, R, et al. The treatment of advanced melanoma: current approaches and new challenges. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. (2024) 196:104276. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2024.104276
123. Marciscano, AE, Ghasemzadeh, A, Nirschl, TR, Theodros, D, Kochel, CM, Francica, BJ, et al. Elective nodal irradiation attenuates the combinatorial efficacy of stereotactic radiation therapy and immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. (2018) 24:5058–71. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-3427
124. Darragh, LB, Gadwa, J, Pham, TT, Van Court, B, Neupert, B, Olimpo, NA, et al. Elective nodal irradiation mitigates local and systemic immunity generated by combination radiation and immunotherapy in head and neck tumors. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:7015. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-34676-w
125. Maekawa, N, Konnai, S, Okagawa, T, Nishimori, A, Ikebuchi, R, Izumi, Y, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of PD-L1 expression in canine malignant cancers and PD-1 expression on lymphocytes in canine Oral melanoma. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0157176. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157176
126. Maekawa, N, Konnai, S, Nishimura, M, Kagawa, Y, Takagi, S, Hosoya, K, et al. PD-L1 immunohistochemistry for canine cancers and clinical benefit of anti-PD-L1 antibody in dogs with pulmonary metastatic oral malignant melanoma. NPJ Precis Oncol. (2021) 5:10. doi: 10.1038/s41698-021-00147-6
127. Maekawa, N, Konnai, S, Takagi, S, Kagawa, Y, Okagawa, T, Nishimori, A, et al. A canine chimeric monoclonal antibody targeting PD-L1 and its clinical efficacy in canine oral malignant melanoma or undifferentiated sarcoma. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:8951. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09444-2
128. Stevenson, VB, Klahn, S, LeRoith, T, and Huckle, WR. Canine melanoma: a review of diagnostics and comparative mechanisms of disease and immunotolerance in the era of the immunotherapies. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:1046636. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.1046636
129. Nemanic, S, London, CA, and Wisner, ER. Comparison of thoracic radiographs and single breath-hold helical CT for detection of pulmonary nodules in dogs with metastatic neoplasia. J Vet Intern Med. (2006) 20:508–15. doi: 10.1892/0891-6640(2006)20[508:cotras]2.0.co;2
130. Smedley, RC, Spangler, WL, Esplin, DG, Kitchell, BE, Bergman, PJ, Ho, HY, et al. Prognostic markers for canine melanocytic neoplasms: a comparative review of the literature and goals for future investigation. Vet Pathol. (2011) 48:54–72. doi: 10.1177/0300985810390717
131. Robertson, S, Acs, B, Lippert, M, and Hartman, J. Prognostic potential of automated Ki67 evaluation in breast cancer: different hot spot definitions versus true global score. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2020) 183:161–75. doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05752-w
132. Varga, Z, Diebold, J, Dommann-Scherrer, C, Frick, H, Kaup, D, Noske, A, et al. How reliable is Ki-67 immunohistochemistry in grade 2 breast carcinomas? A QA study of the Swiss working Group of Breast- and Gynecopathologists. PLoS One. (2012) 7:e37379. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037379
Keywords: oral melanoma, canine, prognosis, oral cancer, malignant, oncology, dogs, OMM
Citation: Song E, Lawrence J, Greene E, Christie A and Goldschmidt S (2024) Risk stratification scheme based on the TNM staging system for dogs with oral malignant melanoma centered on clinicopathologic presentation. Front. Vet. Sci. 11:1472748. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1472748
Edited by:
Ana Nemec, University of Ljubljana, SloveniaReviewed by:
Philip J. Bergman, VCA Animal Hospitals, United StatesCynthia Bell, Specialty Oral Pathology for Animals, LLC, United States
Copyright © 2024 Song, Lawrence, Greene, Christie and Goldschmidt. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Stephanie Goldschmidt, U2dvbGRzY2htaWR0QHVjZGF2aXMuZWR1
†Present address: Anneka Christie, Town & Country Animal Hospital, Ocala, FL, United States
 Eric Song
Eric Song Jessica Lawrence
Jessica Lawrence Erica Greene
Erica Greene Anneka Christie
Anneka Christie Stephanie Goldschmidt
Stephanie Goldschmidt