- 1College of Animal Science and Technology, Tarim University, Alar, China
- 2Engineering Laboratory of Tarim Animal Diseases Diagnosis and Control, Xinjiang Production and Construction Corps, Alar, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Livestock and Forage Resources Utilization around Tarim, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Alar, China
Introduction: Melophagus ovinus, a parasite on the body surface of sheep, directly attacks the host through biting and sucking blood and may also transmit pathogens in the process. There are currently only a few studies on the microbial composition of M. ovinus, while there are no such studies on pupae.
Methods: In this study, samples AT-1 to AT-4 each contained four M. ovinus individuals, while sample AT-5 comprised four M. ovinus pupae, all used for metagenomic sequencing and analysis. Melophagus ovinus adults and pupae were collected from four regions in Xinjiang, China. DNA was extracted from the samples, amplified, and sequenced using the Illumina Novaseq 6000 System; finally, the sequencing data were analyzed using molecular biology software.
Results and discussion: From all samples, a total of 32 phyla, comprising 372 genera and 1,037 species, were detected. The highest microbial diversity was observed in Kuqa City (AT-2) and Qira County (AT-4). Pupae exhibited 40 unique microbial genera (AT-5) but did not have the highest microbial diversity. Proteobacteria was the dominant phylum in all samples. The dominant genera included Bartonella, Wolbachia, Pseudomonas, and Arsenophonus. This is the first study to report most of the bacteria (e.g., Pseudomonas versuta and Arsenophonus nasoniae), fungi (e.g., Saitoella complicata), viruses (e.g., Orf virus and Wolbachia phage WO), and protozoa (e.g., Trypanosoma theileri and Babesia bigemina) in M. ovinus. This study has enriched the microbial diversity data of M. ovinus, and the pathogens it carries may pose a threat to public health safety and the economy of related industries, necessitating further research to develop effective biological control strategies.
1 Introduction
Melophagus ovinus is a blood-sucking parasite that parasitizes primarily on the body surface of sheep. This ectoparasite lacks wings and has a surface covered with bristles, robust mouthparts, and three pairs of sharp grappling hooks. Melophagus ovinus is a member of the Hippoboscidae (Diptera, Hippoboscoidea) (1); it also parasitizes the body surfaces of numerous animals, including sheep, Tibetan antelope (2), goats (3), rabbits (1), donkeys (4), and so on. The life cycle of this parasite consists of three distinct stages: larva, pupa, and wingless adult. Shortly after birth, female M. ovinus mates and produces offspring, giving birth to 12–15 offspring in her lifetime (1). The geographic distribution of M. ovinus is very wide and it has been reported in Europe [Slovakia (5), France (6), England (7), Hungary (8), Croatia (9), Czechia (10), Poland (11), and Russia (12)], Asia [Turkey (13) and China (14)], South America [Peru (4)], North America [USA (15)], Oceania [Australia (12) and New Zealand (16)] and Africa [Algeria (17) and Ethiopia (18)].
The parasitization of sheep with large amounts of M. ovinus results in two serious consequences. First, by biting and sucking blood, it makes the skin of sheep itchy and painful, leading to skin damage, wool loss, agitation, anemia, and weight loss. More severe cases can be secondary to pathogenic microbial infections and cutaneous myiasis (1). The infestation can lead to a loss in the quality and production from sheep products, such as skin, wool, meat, and milk, adversely affecting the economy of the fur and livestock industries. Massive infections of M. ovinus led to a loss of 1.6 million USD by two Ethiopian tanneries over 2 years (19).
More importantly, M. ovinus may carry a variety of pathogenic microorganisms that may infect the host in the process of sucking blood, such as viruses [e.g., Bluetongue virus (20), Border disease virus (21) and African swine fever virus (22)], Acinetobacter spp. (23) [e.g., Ac. lwoffii (24)], Anaplasma spp. [e.g., An. ovis, An. phagocytophilum, and An. bovis (25)], Arsenophonus spp. (26) [e.g., Ar. melophagi (27)], Bartonella spp. (11) [e.g., Ba. schoenbuchensis (6), Ba. chomelii (26), and Ba. melophagi (4)], Borrelia spp. [e.g., Bo. garinii, Bo. spirochetes belonging to the Bo. valaisiana-related group (28), and Bo. burgdorferi sensu lato (11)], Coxiella spp. [e.g., Co. burnetii (29)], Rickettsia spp. (8) [e.g., Ri. raoultii, Ri. slovaca (30), Ri. melophagi (10), Ri. massiliae, and Candidatus Rickettsia barbariae (14)], Theileria spp. [e.g., Th. ovis (2) and Th. luwenshuni (31)], Trypanosoma spp. (11) [e.g., Tr. theodori (1) and Tr. Melophagium (32)], Wolbachia sp. (23), etc.
Most studies on M. ovinus have focused specifically on one to three pathogens. Concurrently, few studies have also detected and identified the types of viruses they carry or analyzed their microbial communities. “Candidatus” is a term used to describe microorganisms that have been discovered solely through molecular biological techniques and have not yet been cultured. It is of significant importance for understanding the functions of ecosystems, advancing biotechnology, and promoting human health. Candidatus Rickettsia barbariae has also been detected in ticks and fleas (33–35).
Microorganisms colonize the body surfaces, intestines, hemocoels, and even cells of all insects, which can then serve as vectors for the microorganisms. Their microbial composition and abundance can be altered by a variety of conditions, including insect species, sex, developmental stage, blood-sucking behavior, survival strategies, and geographic location (36). Among these conditions, feeding on the blood reduces the bacterial diversity of the insect gut (37, 38). Insects and the microorganisms they carry may be in mutually beneficial symbiotic, parasitic, and competitive relationships. For example, microorganisms promote insect health, synthesize toxins or modify the insect immune system to protect it from pathogens, parasitize insects, and attack other hosts at opportune times (39). The most important function of microorganisms in symbiotic association with insects is the provision of nutrients, digestion and detoxification (40). For instance, the intestinal commensal bacteria of bees can encode a variety of enzymes, enabling bees to more effectively obtain and utilize carbohydrates from pollen. Experimental evidence also suggests that germ-free Drosophila larvae raised in the laboratory exhibit significant growth and developmental delays compared to larvae with a normal microbiota (41). Research by He et al. has confirmed that Citrobacter in the gut microbiome of Drosophila orientacea can produce 3-hexenyl acetate (3-HA), a compound that attracts female Drosophila to oviposit on the same fruit (42). Therefore, certain microbial communities of parasites hold great potential as biocontrol agents for pest management.
The study of the microbial community composition and abundance of M. ovinus contributes to scientific knowledge concerning its biology and epidemiology. Metagenomic sequencing involves the high-throughput sequencing of the genomes of microbial communities in a sample, and facilitates the study of microbial population structure. This technique is free from the limitations of microbial isolation and pure culture, and can detect microorganisms in trace numbers, providing an effective tool for studying microbial communities in samples. Currently, only four studies have reported using high-throughput sequencing to analyze the microbial composition and diversity in M. ovinus. In 2017, Duan et al. (23) researched the characterization of midgut microbial populations in male and female M. ovinus, and in 2020, their team (26) extracted DNA from fully satiated, newly hatched and unfed female M. ovinus the midgut and whole body for bacterial community studies. Later in 2021, Litov et al. (12) studied the virome of M. ovinus and annotated the full genomes of five novel viruses, and also proved that the Aksy-Durug Melophagus sigma virus can replicate in mammalian cells. In 2022, Liu et al. (22) studied adult M. ovinus from three regions of Tibet and discovered for the first time, 23 bacterial genera and multiple DNA viruses. In 2023, Zhang et al. (43) sequenced, assembled, and annotated the full genome of M. ovinus. They also discovered that contractions and losses of sensory receptors and vision-associated Rhodopsin genes were significant in M. ovinus, and could contribute to the removal of host-sequence contamination during the high-throughput sequencing data processing.
In this study, we employed the Illumina Novaseq 6000 System to metagenomic sequencing and analysis of the microbial composition and abundance in adult and pupae of M. ovinus from four regions in Xinjiang, China. This is the first report of the use of a technique has been used to study M. ovinus in the area surrounding the Taklamakan Desert, the second most mobile desert in the world, as well as the first study of microbial diversity in pupae.
This study aims to explore and analyze the composition of microbial communities within M. ovinus at different life cycle stages from various regions through metagenomic sequencing and analytical techniques. The hypothesis is that these microbial communities may impact the host’s adaptability and transmission capabilities. Additionally, the study will reveal the types of microorganisms that coexist with M. ovinus and analyze their roles in the life cycle of Melophagus ovinus. Through this research, we expect to provide a scientific basis for the discovery of new pathogens, assess their potential threats to public health safety and the economy of animal-related industries, develop effective strategies for preventing and controlling the spread of vector-borne pathogens, and innovate in pest biological control methods. This will provide valuable data support for scientific research and practical applications in related fields.
2 Methods
2.1 Sample collection and DNA extraction
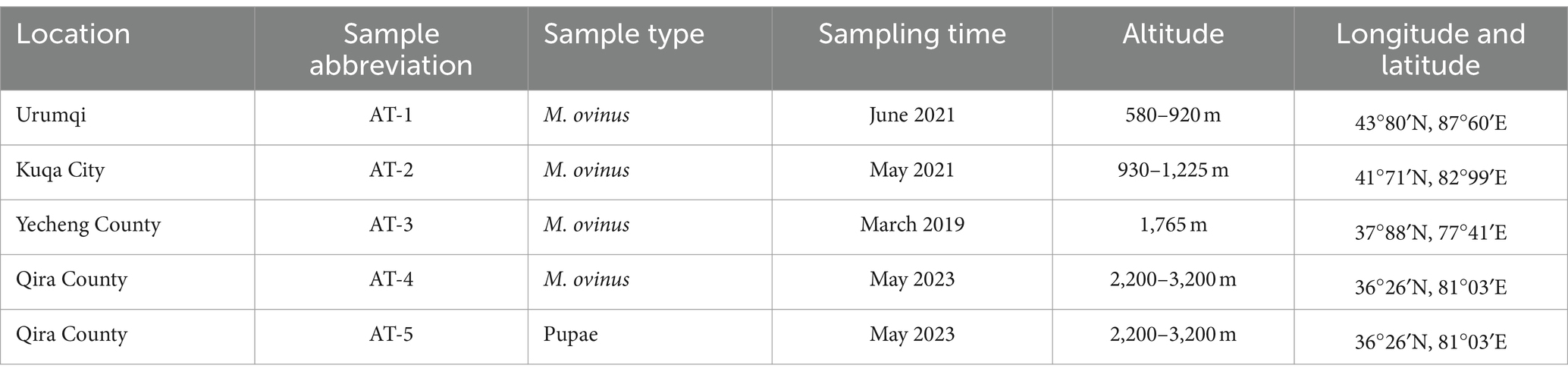
Melophagus ovinus adults and pupae (Figure 1) were collected from four locations in Xinjiang, China, in 2019 to 2023 (Table 1). All hosts were sheep. Melophagus ovinus was collected during the treatment of sheep for ectoparasites. The samples were stored in a −80°C refrigerator until use. Melophagus ovinus and its pupae were identified using morphological and molecular biology methods. For better description, the samples will be hence referred to by the abbreviations AT-1, AT-2, AT-3, AT-4, and AT-5 (Table 1).
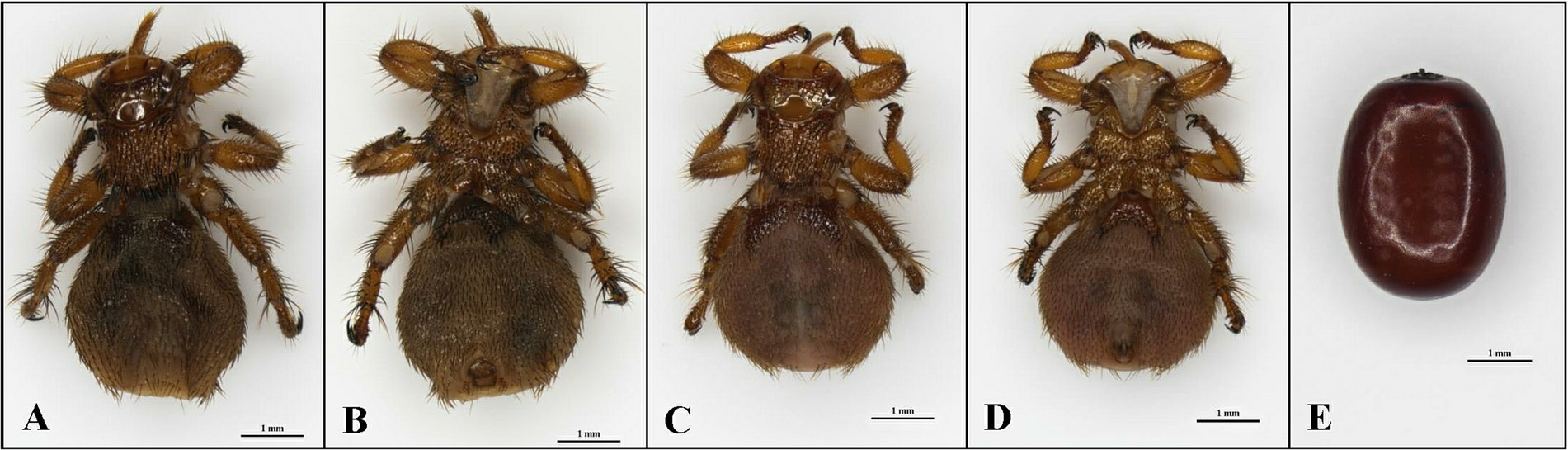

Figure 1. Photomicrographs of adult and pupae of Melophagus ovinus (scale bar: 1 mm). (A) Back view and (B) Ventral view of the female. (C) Back view and (D) Ventral view of the male. (E) Pupae of M. ovinus.
This study selected samples based on criteria such as geographical distribution, environmental conditions, developmental stages, and limb integrity. To ensure the comprehensiveness and representativeness of the research results, the samples from the same region consisted of two female and two male adult insects, while the pupal samples were limited in number, allowing for the selection of only four intact individuals for experimentation. The morphological features of M. ovinus and pupae are identified using a Leica stereomicroscope M165 C (Solms, Germany) and photomicrographs were taken. All samples were cleaned in ethanol gradient (70, 50, 30, and 10%) for 30 min at 37°C and 180 rpm in a culture oscillator at a constant temperature to remove any remaining debris. The samples were then cleaned three more times in sterile distilled water, and finally dried using a filter paper.
The steps for DNA extraction using the HiPure Soil DNA Kit B (Guangzhou Magen Biotechnology Co., Ltd., China) include: preparing homogenization tubes, bead-beating to lyse the tissue, optional further cell lysis, centrifugation to separate, transferring the supernatant, adding adsorbent and lysis solution, another centrifugation, transferring the supernatant to a new tube, adding buffer SBD, loading onto a DNA column, washing the DNA column, drying the DNA column, and finally eluting DNA with preheated elution buffer and storing it. The extracted DNA was stored at −20°C. Throughout this process, standard protocols are strictly followed to ensure the quality and yield of the DNA. In this study, all experimental operations were conducted within a biosafety cabinet, strictly adhering to aseptic technique protocols. To reduce the potential risk of contamination during the experimental process, both DNA extraction and sequencing steps employed commercial standardized reagents and procedures. Through these measures, we ensured the reliability and reproducibility of the experimental results, providing high-quality DNA templates for subsequent microbial community analysis.
2.2 Library preparation and sequencing
Next-generation sequencing libraries were prepared following the manufacturer’s instructions. Genomic DNA (200 μg) was randomly fragmented to an average size of 300–350 bp by Covaris. The fragments were treated using the end-prep enzyme mix for end repair, 5′ phosphorylation, and 3′ adenylated, to add adaptors to both ends. The adaptor-ligated DNA was size-selected by DNA Cleanup beads. Each sample was then amplified by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for eight cycles using P5 and P7 primers; both primers carry sequences which can anneal with flowcell to perform bridge PCR, while the P7 primer carried a six-base index for multiplexing. The PCR products were cleaned and validated using an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer. The qualified libraries were pair-end PE150 sequenced on the Illumina Novaseq 6000 System.
2.3 Data analysis
The raw image data of sequencing results were identified (base calling) using the software bcl2fastq (v2.17.1.14), and the quality was preliminarily analyzed to obtain the raw data of sequencing samples (Pass Filter Data), and the data were stored in FASTQ (fq) file format. The quality statistics software cutadapt (v1.9.1) was employed to remove junctions and low-quality sequences from the raw data (Pass Filter Data) (primers and junction sequences were removed; bases with quality values less than 20 at both ends were removed; sequences with N base content greater than 10% were removed; minimum reads length of 75 bp were retained). The samples had contamination from the host, the BWA software (v0.7.12) was used to compare with the host genome, and the reads that might be of host origin were filtered out.
Assembly analysis was performed based on the optimized Clean Data, using MEGAHIT (v1.1.3) software, suitable for large or complex macro-genomic data assembly and was based on the construction of clean de Bruijn plots for low-memory assembly. Different de Bruijin graphs with different K-mer (59, 79, 99, 119, 141) for each sample, were constructed and pre-assembled. Then, the optimal result for that sample was combined with all assembly results as the final assembly result.
The coding gene was predicted using Prodigal (v3.02) software, followed by the integration of gene sequences of all samples and further de-redundant processed by the sequence clustering software MMseq2. The non-redundant gene set unigene sequences were obtained by clustering with 95% identity and 95% coverage by default. The number of reads of unigene in each sample on the alignment was obtained using the alignment software SoapAligner (version 2.21) to compare the clean reads obtained after pre-processing to the constructed non-redundant gene set unigene sequences. Then, based on the number of reads on each unigene pair and the length of the gene, the abundance information of unigene in each sample was estimated.
The microbial composition of the samples was explored by comparing the unigene sequences with the NR database using diamond. The results of species annotation for each sequence were obtained from the information on taxonomic annotation corresponding to each sequence in the NR database. Combining the results of species annotation of genes and the gene abundance tables, information on each species abundance at each taxonomic level (phylum, order, family, genus, species) could be counted for each sample; next, and for the abundance of a given species in a sample, the abundance was summed for genes annotated as that species.
The analysis of α-diversity was based on the species-level results, and the α-diversity indices such as Shannon and Chao1 were calculated to represent the species abundance and community diversity by using random sampling of sequences of samples for leveling, and the rank abundance curve were prepared to reflect the species richness as well as evenness.
3 Results
3.1 General statistics
3.1.1 Sequencing data statistics
After calibration, joints and low-quality sequences of the sequencing results were removed from five samples (AT-1, AT-2, AT-3, AT-4, and AT-5), a total of 86,427,864 optimized data sequences (AT-1, 21,989,176; AT-2, 14,431,232; AT-3, 27,058,326; AT-4, 21,176,652; AT-5, 1,772,478,) were obtained, and the respective length of this optimized data was 12,792,106,261 bp (respectively representing 3,272,729,898 bp, 2,132,276,512 bp, 3,997,349,546 bp, 3,130,724,974 bp, and 259,025,331 bp). The mean length of these optimized sequences was 147.66 bp (respectively representing 148.83 bp, 147.75 bp, 147.73 bp, 147.84 bp, and 146.14 bp).
3.1.2 Alpha-diversity analysis
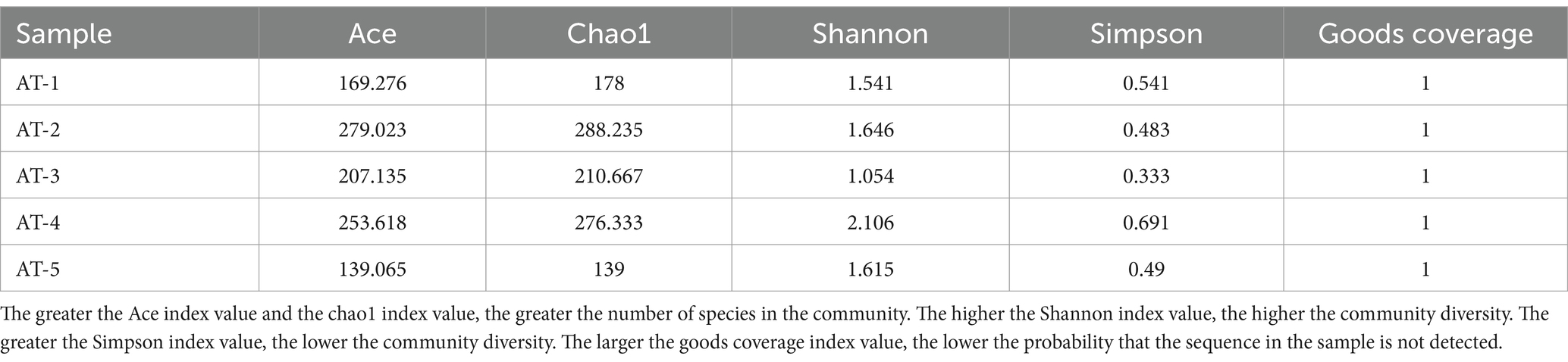
The AT-2 samples exhibited the highest Ace and Chao1 values, while the AT-4 samples had the highest Shannon and Simpson values. However, as per the guidelines, the Shannon and Simpson values of the AT-2 sample were the most reasonable. The goods coverage value of all the samples was 100%, indicating that the amount of data was sufficient (Table 2).
The rank abundance curve shows the diversity of each sample. A smoother decline and a longer curve indicate a high diversity of the sample, while a fast and steep decline indicates a high proportion of dominant flora and a low sample diversity. The order of the curve span for the five samples was AT-4 > AT-5 > AT-2 > AT-1 > AT-3, as shown in Figure 2. This result indicates that samples from the sites AT-4 and AT-5 had the highest microbial diversity.
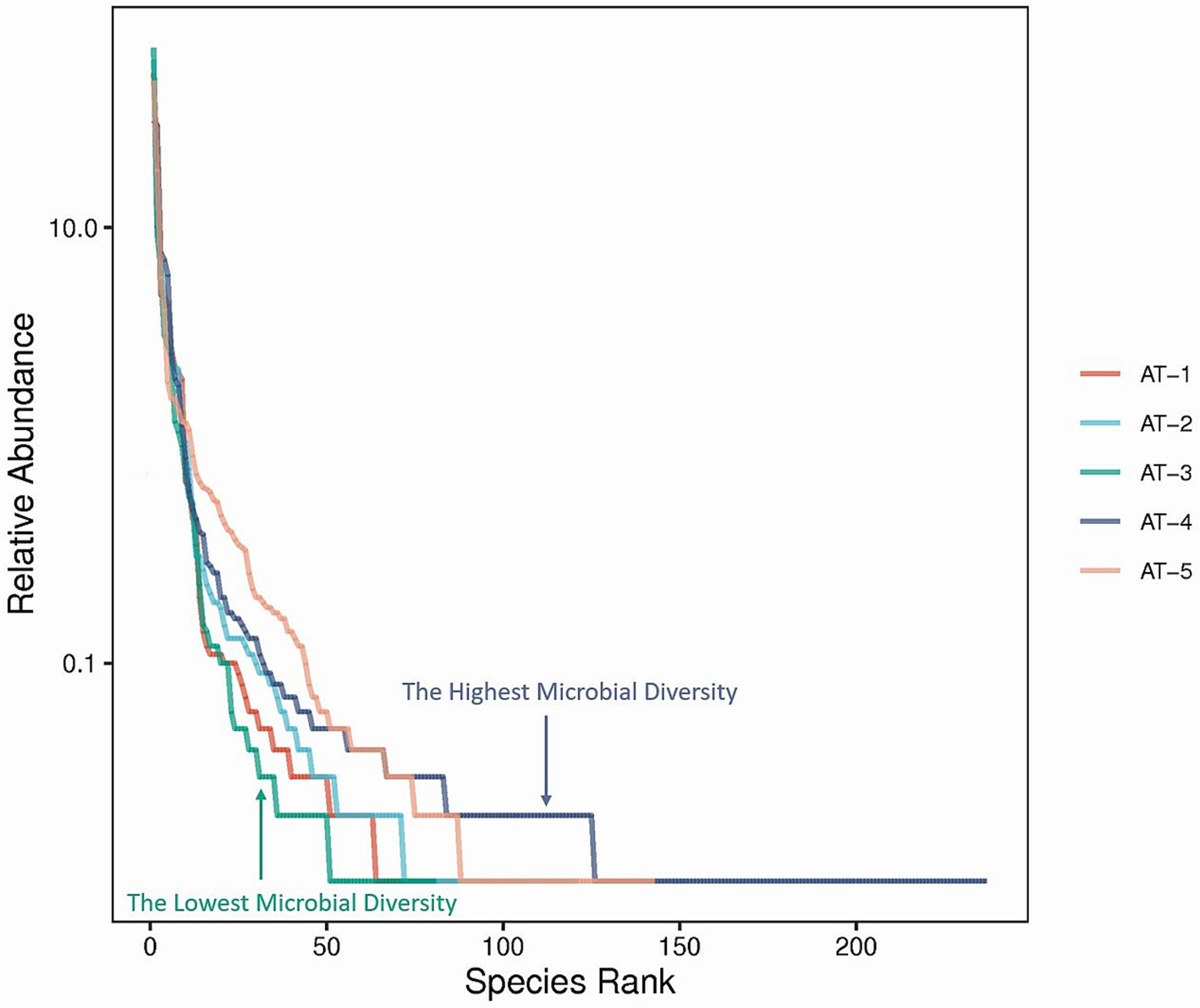
Figure 2. The rank abundance curve. The X-axis presents the rank of the microbial species, and the Y-axis presents the relative abundance of the microbial species. Curves of different colors represent different samples.
3.1.3 Genus cluster analysis
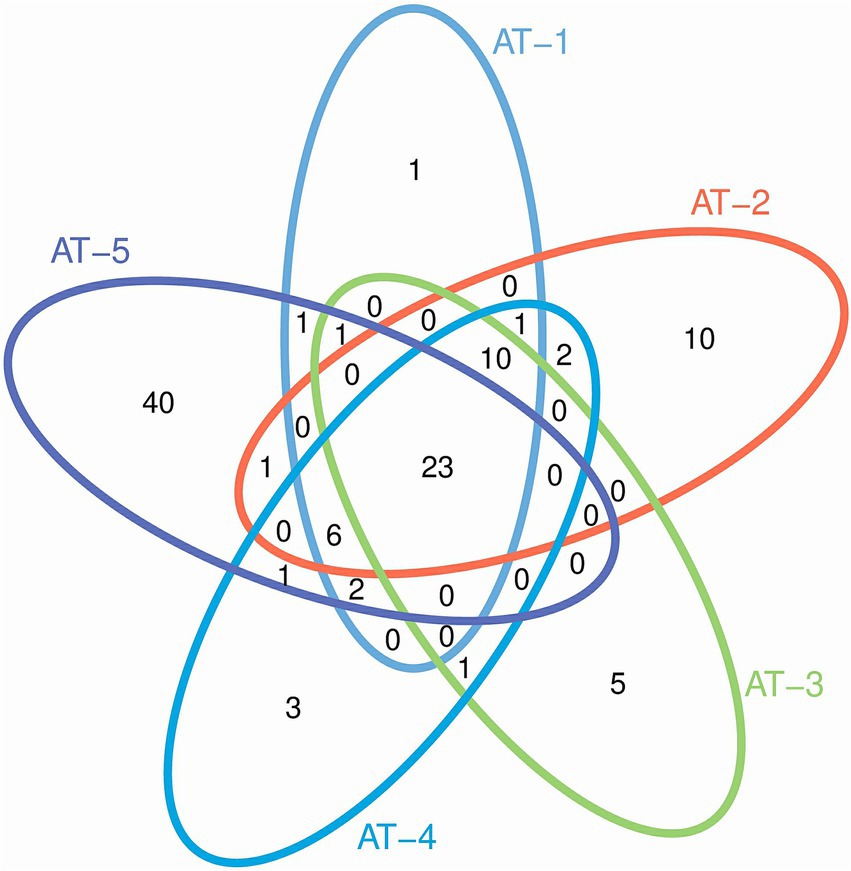
The Genus cluster analysis is shown as a Venn diagram (Figure 3). The respective numbers of Genus clusters obtained from five samples (AT-1, AT-2, AT-3, AT-4, and AT-5) were 45, 53, 40, 49, and 75. The five samples had 23 highly similar microbial genera, indicating the presence of more of the same microbial populations in the five samples. The AT-5 sample had 40 unique microbial genera, being the highest number of any sample.
3.2 Microbial population characteristics
3.2.1 Microbial characteristics at the phylum level
A total of 32 microbial phyla were detected in all samples. Among these, 26, 30, 23, 24, and 20 microbial phyla were detected, respectively, in AT-1, AT-2, AT-3, AT-4, and AT-5. The absolute abundance of these microbial phyla and the community bar plot are presented in Supplementary Table S1 and Supplementary Figure S1A. The dominant phyla were mainly Proteobacteria (respective relative abundance of 94.1, 91.4, 97.3, 92.8, and 93.9%) and Euglenozoa (respective relative abundance of 5.1, 7.3, 1.4, 6.5, and 0.0%). Proteobacteria exhibited a clear advantage across samples. Furthermore, Spirochaetes were present only in AT-1 samples, and Thaumarchaeota, Candidatus Moranbacteria, Verrucomicrobia, and Zoopagomycota were present only in AT-2 samples.
3.2.2 Characteristics of the microbial genera
In all samples, a total of 372 microbial genera were detected, of which 163, 266, 194, 243, and 125 microbial genera were, respectively, detected in AT-1, AT-2, AT-3, AT-4, and AT-5. The absolute abundance of these microbial genera and the community bar plot is presented in Supplementary Table S2 and Supplementary Figure S1B. The relative abundance of Bartonella in five samples (AT-1 to AT-5, respectively) was 60.9, 70.2, 80.3, 35.3, and 22.1%. Further, the relative abundance of AT-1, AT-2, and AT-3, was higher than that of AT-4 and AT-5. The relative abundance of Wolbachia in AT-5 was 67.8%, being much higher than that in the remaining four samples. A similar situation was noted for the AT-4 sample, with the relative abundance of Pseudomonas being 40.8%, also much higher than that in the other four samples. A comparison of relative abundance across samples for Arsenophonus (29.0, 13.2, 14.8, 11.1, and 2.8%) and Trypanosoma (5.1, 7.2, 1.4, 6.5, and 0.0%) revealed that AT-5 had the lowest relative abundance. The relative abundance of most of the microbial genera, except those mentioned above, was <1%.
3.2.3 Microbial characteristics at the species level
A total of 1,037 microbial species were detected in all samples, of which 302, 622, 464, 639, and 237 microbial species were, respectively, detected in AT-1, AT-2, AT-3, AT-4, and AT-5. The absolute abundance of these microbial species in terms of microbial community bar plot is shown in Supplementary Table S3 and Supplementary Figure S1C. All the samples had a high relative abundance of Bartonella melophagi (51.3, 59.1, 66.7, 29.6, and 18.5%), being significantly higher in AT-1, AT-2 and AT-3 than in AT-4 and AT-5. The AT-5 sample had a 47.3% relative abundance of the Wolbachia endosymbiont, which was significantly higher than that in the other samples. All the samples had Arsenophonus nasoniae (20.0, 9.1, 10.2, 7.7, and 2.0%) but AT-1 had the highest relative abundance. The AT-4 sample had a 31.0% relative abundance of Pseudomonas versuta and the rest of the samples was in the range of 0–0.1%. Besides the four bacteria mentioned above, a variety of other bacteria (e.g., Bartonella bovis and Enterobacter cloacae), archaea (e.g., Candidatus Nitrosotalea bavarica), fungi (e.g., Saitoella complicata), viruses (e.g., Orf virus and Wolbachia phage WO), and eukaryotes (e.g., Trypanosoma theileri and Babesia bigemina) were detected in this study, the details of which are presented in Supplementary Table S3.
4 Discussion
This study was based on the Illumina Novaseq 6,000 System for metagenomic sequencing. The research examined the microbial population diversity and disparity in four M. ovinus samples and one pupae sample obtained from Urumqi (AT-1), Kuqa City (AT-2), Yecheng County (AT-3), and Qira County (AT-4 and AT-5), Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China. Metagenomic sequencing can detect less abundant microorganisms that cannot be easily culturable, playing an important role in our research. Given the limitations of metagenomic sequencing, we will analyze the results from a more balanced perspective. The results of the study showed that a total of 1,037 species in 32 phyla and 372 genera were detected. After removing the sequences of non-microbial species, 873 microorganisms were detected. Among these, approximately 95 pathogens had varying pathogenicity, representing about 10% of the total. However, most of these pathogens were present in low abundance.
The Alpha-diversity indices and the rank abundance curve showed the richest diversity of microbial populations M. ovinus samples from Kuqa City (AT-2) and Qira County (AT-4) contained. Similar to previous studies and as shown by the Venn diagrams, the AT-5 pupae sample, although not the most diverse, had 40 unique genera, consistent with previous results (26). Most of the bacteria, fungi, archaea, spirochetes, chlamydia, viruses, and protozoa in M. ovinus and pupae samples are reported for the first time in this study (see Supplementary Table S3 for details). Some microorganisms detected in this study have also been reported previously, such as Bartonella melophagi, Ba. schoenbuchensis, Arsenophonus endosymbiont, Wolbachia endosymbiont, Escherichia coli, Novosphingobium sp., and so on.
This study compared the findings of previous studies, including those of Duan et al. (23) in 2017, Duan et al. (26) in 2020, and Liu et al. (22) in 2022. For convenience in description, the abbreviations H1, H2, and H3 were used to represent these three studies, respectively. A total of 32 microbial phyla were detected in the present study, while H1, H2, and H3 detected 2, 7, and 5 bacterial phyla, respectively. The dominant bacterial phylum in all studies was Proteobacteria, while Euglenozoa was only found in the present study.
H1, H2, and H3 identified 9, 42, and 29 bacterial genera, respectively, while the present investigation detected 372 genera. These findings align with those of other studies, indicating that Bartonella, Arsenophonus, and Wolbachia were the predominant bacterial genera. Similar to H2, the present study observed that in M. ovinus and its pupae the abundance of Wolbachia in whole-body samples derived from newly hatched and unfed adult female M. ovinus (A.u) was higher than that in whole-body samples obtained from fully engorged adult female M. ovinus (A.f), with Bartonella showing the opposite trend in abundance. The abundance of Arsenophonus in both A.u and A.f found in H2 was around 38%; however, the current study found a lower abundance of Arsenophonus, particularly in the pupal samples.
In addition to the influence of geographical factors on the results, the composition of the samples may also be relevant. The samples in H2 were composed exclusively of female M. ovinus, whereas the samples in the present study included both male M. ovinus and pupal samples of undetermined sex. Individuals with low abundance in the samples can contribute to an overall reduction in abundance.
This study identified a total of 1,037 species, of which 873 were classified as microbes. In contrast, H1, H2, and H3 identified 3, 17, and 7 bacterial species, respectively. The present study observed the same species as H1, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus xylosus, as well as the same Escherichia coli as H2; however, the species did not match those detected by H3. The viral metagenomic sequencing used in H3 detected 22 different viruses, the majority of which were phages, a finding that is consistent with the results obtained in the present study.
In summary, the results of the present study have yielded a richer dataset compared with the other three studies, primarily due to the slightly different sequencing techniques employed. By conducting an analysis that spans different times and locations, it is possible to explore variations in the microbial composition of M. ovinus across different areas. This also aids in inferring the trends of microbial community evolution and provides a scientific basis for the monitoring and management of M. ovinus.
The symbiotic microbial communities of insects are crucial for the host’s adaptability. For instance, the gut microbiota of the Mormon cricket is primarily composed of Lactobacillaceae, Enterobacteriaceae, and Streptococcaceae, which influence the host’s adaptability and survival by improving nutrition, enhancing resistance, and regulating social behavior (44); Haloi et al. identified Bacillus thuringiensis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and found clear correlations between them and the flacherie disease in silkworms (45). The microbial composition of M. ovinus is unique compared to other insects, with Bartonella, Wolbachia, and Arsenophonus potentially affecting its health and sex. Future studies should conduct more in-depth research, such as using integrated omics analyses (e.g., proteomics and metabolomics) to systematically analyze the molecular mechanisms of microbe-host interactions.
Symbiotic microorganisms may grow in the gut, body cavity, or cells of insects, potentially causing either positive effects, negative effects, reciprocal effects, or no apparent effect on the host (46). The microbial population composition in insects can vary depending on diet, developmental stage, season, and geography (47). The most abundant microbial genera detected in the study were Bartonella, Arsenophonus, Wolbachia, Pseudomonas, and Trypanosoma. The microbial species referenced in the subsequent text are all derived from Supplementary Table S3.
Comparing the microbial composition between adult and pupal stages is a meaningful study. Researchers Xue et al. found that Adelphocoris suturalis exhibits dynamic changes in gut microbial diversity and composition across different developmental stages, which play a significant role in nutrient absorption and environmental adaptation, and are closely related to the insect’s growth, development, and reproduction (48). This study reveals significant differences in microbial composition between the adult and pupal stages of M. ovinus, primarily reflected in the distribution of dominant microbial groups. Bartonella dominates from the AT-1 to AT-3 adult stages but shows a marked decrease in relative abundance in the AT-4 and AT-5 pupal samples. This difference may be related to the inconsistency of environmental microbial community composition in high-altitude regions. Arsenophonus shows a lower relative abundance, which may suggest that Wolbachia influences the sex of M. ovinus during the pupal stage, and Arsenophonus may affect sex in the adult stage. The higher relative abundance of Pseudomonas in the AT-4 samples may be associated with the high abundance of Pseudomonas in the adult living environment.
As illustrated in the Venn diagrams (Figure 3), pupae possess a greater number of unique microbial genera compared to adult insects, potentially due to the heightened need for microbial support during their juvenile development for nutrient assimilation and defense against adverse environmental conditions. This analogous situation is also observed in mammals, as exemplified by the Tibetan Sheep (49). As shown in Figure 2, AT-4 and AT-5 have the highest microbial diversity, ranking first and second, respectively. This indicates that the environmental microbiota at the sampling site has a significant impact on the microbial composition of M. ovinus and should not be overlooked. Studies have demonstrated that the feeding of different feed components or the inclusion of certain proteases in the diet of ruminants can significantly impact the composition and abundance of rumen microbiota, as well as the metabolites and productive performance (50, 51). Melophagus ovinus, being hematophagous arthropods, occasionally bite and ingest blood from various hosts. Consequently, examining the microbial composition and diversity of M. ovinus that have fed on different hosts could potentially reveal insights into microbial functionality. Future studies should focus on collecting pupal samples and simultaneously obtaining blood samples from the animal hosts. This will facilitate a deeper investigation into the interactions between microbes, M. ovinus, and their animal hosts. Such research not only enhances our understanding of the relationships among these three entities but also provides foundational data for the development of innovative external parasites control strategies and models.
Bartonella is a gram-negative bacterium transmitted to humans through blood-sucking arthropod vectors, or contact with contaminated animal feces, or on being scratched by infected animals (52). Some studies have reported Bartonella sp. with a high rate of infection in M. ovinus samples (6, 11). The last common ancestor of Bartonella was a likely amino acid and cofactor self-reliant gut symbiont that recycles nitrogenous waste products from its insect host; these symbionts can adapt to blood-sucking insects, but may not necessarily adapt to mammalian hosts, causing only opportunistic infections (53). We detected Bartonella melophagi, Ba. schoenbuchensis, and Ba. bovis, among others, in our samples. Few studies have successfully isolated and cultured Bartonella directly from the bodies of arthropods. The investigation by Kosoy et al. appears to be the only study to have isolated and cultured Ba. melophagi from M. ovinus suspensions (15). Compared to many previous studies, the current findings on the identification of Ba. melophagi are of the highest credibility (22).
Wolbachia are considered insect symbionts that on the one hand, help their hosts to resist viruses and insecticides, and also aid in addressing some of the nutritional needs of their hosts (54, 55), on the other hand, enhance their transmission, induce feminization, male-specific killing, and parthenogenesis of insect hosts (56). The relative abundance of Wolbachia was as high as 67.8% in AT-5 pupae samples, much higher than that in adult M. ovinus. As reported by studied by Duan et al., the abundance of Wolbachia in newly hatched and unfed M. ovinus was about 29%, also higher than in the adult abundance (26). These values suggest that Wolbachia be supposed to have a greater effect on pupae or larvae than on adults.
The genus Arsenophonus is a group of symbiont widely present in a several kinds of insects (57). We detected Arsenophonus nasoniae, Ar. endosymbiont, Candidatus Arsenophonus lipoptenae, and Arsenophonus sp. ENCA in our study. Arsenophonus nasoniae infects people with symptoms of fever and pain (58). Most of these symbionts are vertically transmitted from mother to offspring, while a small percent can also be transmitted horizontally (59). They affect insects and may also make people or animals sick. Therefore, these symbionts need to be researched further.
The bacterium Pseudomonas is one of the most ubiquitous and diverse genera across the world, especially in a wide range of environments, objects, and organisms (60). In this study, we detected a variety of Pseudomonas sp., with its abundance in the AT-4 adult M. ovinus samples being much higher than in other samples. This finding may be related to the suitable altitude and climate of the sample location for its growth. Test results included the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa, capable of causing serious infections in human respiratory and urinary tracts (61). We also detected a variety of bacterial pathogens, such as Brucella abortus, Acinetobacter baumannii, Enterobacter cloacae, Salmonella enterica, Staphylococcus aureus and so on, posing a potential threat to human or animal health.
Protozoa have a narrow host range and high specificity, and are thus also used as effective biocontrol agent of pest insects (62). In this study, a total of 45 parasitic protozoa were detected, except for Trypanosoma, with a relatively high abundance across samples, while all other protozoa had a relatively low abundance. Until now, no study has reported on the assessment of the interrelationships between M. ovinus and protozoa. The protozoa detected in this study are pathogenic, such as Trypanosoma theileri is an opportunistic pathogen that can cause mild to severe diseases either independently or in conjunction with other pathogens, sometimes leading to the death of fetuses or newborn calves (63). Following infection with Babesia bigemina, the host may exhibit symptoms including fever, anemia, jaundice, loss of appetite, muscle tremors, and death (64).
To date, only five studies have reported the detection of viruses from M. ovinus (12, 20–22, 65). In the current study, only the Orf virus and multiple phages were detected. The Orf virus is a DNA virus of genus Parapoxvirus, a highly contagious zoonotic disease causing a highly contagious vesiculo ulcerative pustular infection (66). Phages present in M. ovinus regulate the bacterial community. The absence of phages may cause an imbalance in the bacterial community in M. ovinus and adversely affect its health. In this study only 11 phage species, including Wolbachia phage WO, Escherichia phage L AB-2017, and Staphylococcus phage VB-SauS-SA2, with very low abundance, were detected.
In this study, due to the limited presence of M. ovinus, we were unable to collect additional samples from other regions of Xinjiang, including the inability to obtain concurrent pupal samples from the AT-1 to AT-3 sampling sites. Although this is the first study to investigate the symbiotic microbiota of M. ovinus in the Xinjiang region using metagenomic sequencing technology, the existing sample size is not sufficient to fully reflect the diversity of microbial species carried by M. ovinus across the entire Xinjiang territory. Therefore, future studies will need to collect M. ovinus samples from a broader range of areas in Xinjiang to gain a more comprehensive understanding of its microbial symbiosis.
This study identified a variety of congeneric microorganisms (e.g., Bartonella spp. and Trypanosoma spp.) together with identifying non- relevant species (e.g., Trichomonas vaginalis and Yersinia pestis). This inaccuracy is likely due to the lower resolution of the metagenomic analysis or DNA barcoding techniques. Therefore, the application of more specific markers is necessary for the identification of these species. For instance, the use of multi-locus sequence typing (MLST) based on the rpoB, gltA, ftsZ, groEL genes, and the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region for the identification of Bartonella sp. is warranted (67).
Microorganisms that parasitize insect hosts can positively affect the host, such as providing nutrients or enhancing the fitness of the host while obtaining nutrients for themselves. The microorganisms may also be pathogenic to the insect host, reducing the fitness or causing its death. Multiple studies have demonstrated that antimicrobial resistance is on the rise among various microorganisms, including bacteria and protozoa (68, 69). Consequently, there is an urgent need to develop a bio-inhibitor that is not only safe and economical but also highly effective. Therefore, studying microbial community diversity in M. ovinus and determining their roles and functions will make it possible to efficiently investigate a way to manage pests. In this study, multiple pathogens were found in only one or two locations, suggesting that some pathogens may be endemic. During blood-sucking, M. ovinus may lead to epidemics of these pathogens in sheep, which in turn may threaten public health safety or the stability of the sheep industry economy.
In this study, a variety of microorganisms were detected, and the data on the microbial diversity of M. ovinus in Xinjiang were enriched. However, the data on the microbial diversity of M. ovinus in various places is still insignificant to. In conclusion, our study has implications regarding veterinary and public health safety. Based on the pathogen diversity, we need to assess their potential risk of M. ovinus to animal husbandry and public health and control its infestations. The relationship, between microorganisms and M. ovinus and its transmission and function can be used to develop methods for biological prevention and control of the pests.
5 Conclusion
In this study, 32 microbial phyla were detected in M. ovinus in Xinjiang, China, with Proteobacteria being the dominant phylum. Bartonella, Wolbachia, Pseudomonas, and Arsenophonus were the dominant genera among the 372 genera detected. After eliminating non-microbial species, 873 microorganisms, containing nearly 100 pathogens were detected. This is the first study to report most of the bacteria (e.g., Pseudomonas versuta and Arsenophonus nasoniae), fungi (e.g., Saitoella complicata), viruses (e.g., Orf virus and Wolbachia phage WO), and protozoa (e.g., Trypanosoma theileri and Babesia bigemina) in M. ovinus. This study identified the dominant microbial communities in both adult and pupal whole-body samples of M. ovinus and revealed differences in microbial diversity and composition across different developmental stages. The findings lay a theoretical foundation for a deeper understanding of the symbiotic relationship between M. ovinus and its associated microbes, and provide new insights for the development and innovation of external parasites control strategies in the future.
Data availability statement
The raw tags have been deposited in the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) at the NCBI under the BioProject accession number PRJNA1074431. The individual run files have been assigned accession numbers SRR27908141, SRR27908142, SRR27908143, SRR27908144, and SRR27908145.
Ethics statement
The animal studies were approved by Ethics Committee of Tarim University, Xinjiang, China. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent was obtained from the owners for the participation of their animals in this study.
Author contributions
KH: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. XinZ: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. NX: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. LS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. XiaZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. KZ: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. JW: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by grants awarded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Granted Nos. 32160841 and 31960705), Key Laboratory of Tarim Animal Husbandry Science and Technology, Xinjiang Production & Construction Group (HS201802), and Tarim University Graduate Student Research Innovation Project (TDGRI202240).
Acknowledgments
We thank members of our laboratories for fruitful discussions.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fvets.2024.1462772/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
USD, United States dollar; PCR, Polymerase chain reaction; NR database, Non-redundant protein database; MLST, Multi-locus sequence typing; ITS, Internal transcribed spacer.
References
1. Small, RW. A review of Melophagus ovinus (L.), the sheep ked. Vet Parasitol. (2005) 130:141–55. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2005.03.005
2. Zhao, L, Wang, J, Ding, Y, Li, K, He, B, Li, F, et al. Theileria ovis (Piroplasmida: Theileriidae) detected in Melophagus ovinus (Diptera: Hippoboscoidea) and Ornithodoros lahorensis (Ixodida: Argasidae) removed from sheep in Xinjiang, China. J Med Entomol. (2020) 57:631–5. doi: 10.1093/jme/tjz193
3. Seyoum, Z, Tadesse, T, and Addisu, A. Ectoparasites prevalence in Small ruminants in and around Sekela, Amhara regional state, Northwest Ethiopia. J Vet Med. (2015) 2015:216085. doi: 10.1155/2015/216085
4. Flores-Mendoza, C, Loyola, S, Jiang, J, Farris, CM, Mullins, K, Estep, AS, et al. Molecular characterization ofBartonellaSpecies discovered in Ectoparasites collected from domestic animals, Cuzco, Peru. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. (2021) 21:330–41. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2020.2697
5. Hubálek, Z, Cerný, V, Mittermayer, T, Kilík, J, Halouzka, J, Juricová, Z, et al. Arbovirological survey in silica plateau area, Roznava District, Czechoslovakia. J Hyg Epidem (Praha). (1986) 30:87–98.
6. Halos, L, Jamal, T, Maillard, R, Girard, B, Guillot, J, Chomel, B, et al. Role of Hippoboscidae flies as potential vectors of Bartonella spp. infecting wild and domestic ruminants. Appl Environ Microbiol. (2004) 70:6302–5. doi: 10.1128/aem.70.10.6302-6305.2004
7. Gibson, W, Pilkington, JG, and Pemberton, JM. Trypanosoma melophagium from the sheep ked Melophagus ovinus on the island of St Kilda. Parasitology. (2010) 137:1799–804. doi: 10.1017/s0031182010000752
8. Hornok, S, de la Fuente, J, Biró, N, Fernández de Mera, IG, Meli, ML, Elek, V, et al. First molecular evidence ofAnaplasma ovisandRickettsiaspp. In Keds (Diptera: Hippoboscidae) of sheep and wild ruminants. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. (2011) 11:1319–21. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2011.0649
9. Martinković, F, Matanović, K, Rodrigues, AC, Garcia, HA, and Teixeira, MM. Trypanosoma (Megatrypanum) melophagium in the sheep ked Melophagus ovinus from organic farms in Croatia: phylogenetic inferences support restriction to sheep and sheep keds and close relationship with trypanosomes from other ruminant species. J Eukaryot Microbiol. (2012) 59:134–44. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.2011.00599.x
10. Rudolf, I, Betášová, L, Bischof, V, Venclíková, K, Blažejová, H, Mendel, J, et al. Molecular survey of arthropod-borne pathogens in sheep keds (Melophagus ovinus) Central Europe. Parasitol Res. (2016) 115:3679–82. doi: 10.1007/s00436-016-5175-2
11. Werszko, J, Asman, M, Witecka, J, Steiner-Bogdaszewska, Ż, Szewczyk, T, Kuryło, G, et al. The role of sheep ked (Melophagus ovinus) as potential vector of protozoa and bacterial pathogens. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:15468. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-94895-x
12. Litov, AG, Belova, OA, Kholodilov, IS, Gadzhikurbanov, MN, Gmyl, LV, Oorzhak, ND, et al. Possible arbovirus found in virome of Melophagus ovinus. Viruses. (2021) 13:2375. doi: 10.3390/v13122375
13. Payzin, S. Epidemiological investigations on Q fever in Turkey. Bull World Health Organ. (1953) 9:553–8.
14. Li, SA, Zhang, L, Li, Z, Song, HN, Que, ZW, Zhao, SY, et al. Detection of Rickettsia spp. and Anaplasma ovis in Melophagus ovinus from southern Xinjiang, China. Med Vet Entomol. (2023) 37:865–70. doi: 10.1111/mve.12673
15. Kosoy, M, Bai, Y, Enscore, R, Rizzo, MR, Bender, S, Popov, V, et al. Bartonella melophagi in blood of domestic sheep (Ovis aries) and sheep keds (Melophagus ovinus) from the southwestern US: cultures, genetic characterization, and ecological connections. Vet Microbiol. (2016) 190:43–9. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.05.009
16. Heath, ACG, and Bishop, DM. Evaluation of two ‘pour-on’ insecticides against the sheep-biting louse, Bovicola ovis and the sheep ked, Melophagus ovinus. N Z J Agric Res. (1988) 31:9–12. doi: 10.1080/00288233.1988.10421357
17. Boucheikhchoukh, M, Mechouk, N, Benakhla, A, Raoult, D, and Parola, P. Molecular evidence of bacteria in Melophagus ovinus sheep keds and Hippobosca equina forest flies collected from sheep and horses in northeastern Algeria. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. (2019) 65:103–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cimid.2019.05.010
18. Hadgu, A, Lemma, A, Yilma, T, and Fesseha, H. Major causes of calf and lamb mortality and morbidity and associated risk factors in the mixed crop-livestock production system in Jamma District, south Wollo, Ethiopia. Vet Med Int. (2021) 2021:6689154. doi: 10.1155/2021/6689154
19. Sertse, T, and Wossene, A. Effect of ectoparasites on quality of pickled skins and their impact on the tanning industries in Amhara regional state, Ethiopia. Small Rumin Res. (2007) 69:55–61. doi: 10.1016/j.smallrumres.2005.12.011
20. Luedke, AJ, Jochim, MM, and Bowne, JG. Preliminary bluetongue transmission with the sheep ked Melophagus ovinus (L.). Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. (1965) 29:229–31.
21. Liu, YH, He, B, Li, KR, Li, F, Zhang, LY, Li, XQ, et al. First report of border disease virus in Melophagus ovinus (sheep ked) collected in Xinjiang, China. PLoS One. (2019) 14:e0221435. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0221435
22. Liu, YH, Ma, YM, Tian, HO, Yang, B, Han, WX, Zhao, WH, et al. First determination of DNA virus and some additional bacteria from Melophagus ovinus (sheep ked) in Tibet, China. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:988136. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.988136
23. Duan, DY, Liu, GH, Cheng, TY, and Wang, YQ. Microbial population analysis of the midgut of Melophagus ovinus via high-throughput sequencing. Parasit Vectors. (2017) 10:382. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2323-1
24. Kumsa, B, Socolovschi, C, Parola, P, Rolain, JM, and Raoult, D. Molecular detection of Acinetobacter species in lice and Keds of domestic animals in Oromia regional state, Ethiopia. PLoS One. (2012) 7:e52377. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052377
25. Zhang, QX, Wang, Y, Li, Y, Han, SY, Wang, B, Yuan, GH, et al. Vector-borne pathogens with veterinary and public health significance in Melophagus ovinus (sheep ked) from the Qinghai-Tibet plateau. Pathogens. (2021) 10:249. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10020249
26. Duan, DY, Zhou, HM, and Cheng, TY. Comparative analysis of microbial community in the whole body and midgut from fully engorged and unfed female adult Melophagus ovinus. Med Vet Entomol. (2020) 34:215–24. doi: 10.1111/mve.12424
27. Husnik, F, Hypsa, V, and Darby, A. Insect-symbiont gene expression in the midgut bacteriocytes of a blood-sucking parasite. Genome Biol Evol. (2020) 12:429–42. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evaa032
28. Chu, CY, Jiang, BG, Qiu, EC, Zhang, F, Zuo, SQ, Yang, H, et al. Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in sheep keds (Melophagus ovinus), Tibet, China. Vet Microbiol. (2011) 149:526–9. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2010.11.031
29. Pavilanis, V, Duval, L, Foley, AR, and L'Heureux, M. An epidemic of Q fever at Princeville, Quebec. Can J Public Health. (1958) 49:520–9.
30. Liu, D, Wang, YZ, Zhang, H, Liu, ZQ, Wureli, HZ, Wang, SW, et al. First report of Rickettsia raoultii and R. slovaca in Melophagus ovinus, the sheep ked. Parasite Vector. (2016) 9:600. doi: 10.1186/s13071-016-1885-7
31. Hao, L, Yuan, D, Li, S, Jia, T, Guo, L, Hou, W, et al. Detection of Theileria spp. in ticks, sheep keds (Melophagus ovinus), and livestock in the eastern Tibetan plateau, China. Parasitol Res. (2020) 119:2641–8. doi: 10.1007/s00436-020-06757-6
32. Huang, K, Xiong, N, Sun, L, Zhang, X, Zhao, X, Zhou, K, et al. Molecular investigation of Bartonella melophagi and the first report of Trypanosoma melophagium in Melophagus ovinus from southern Xinjiang, China. Pak Vet J. (2024) 44:384–90. doi: 10.29261/pakvetj/2024.149
33. Ravi, A, Ereqat, S, Al-Jawabreh, A, Abdeen, Z, Abu Shamma, O, Hall, H, et al. Metagenomic profiling of ticks: identification of novel rickettsial genomes and detection of tick-borne canine parvovirus. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. (2019) 13:e0006805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006805
34. Mura, A, Masala, G, Tola, S, Satta, G, Fois, F, Piras, P, et al. First direct detection of rickettsial pathogens and a new rickettsia, 'Candidatus Rickettsia barbariae', in ticks from Sardinia, Italy. Clin Microbiol Infect. (2008) 14:1028–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2008.02082.x
35. Zhao, SS, Li, HY, Yin, XP, Liu, ZQ, Chen, CF, and Wang, YZ. First detection of Candidatus Rickettsia barbariae in the flea Vermipsylla alakurt from North-Western China. Parasite Vector. (2016) 9:325. doi: 10.1186/s13071-016-1614-2
36. Yadav, KK, Datta, S, Naglot, A, Bora, A, Hmuaka, V, Bhagyawant, S, et al. Diversity of cultivable midgut microbiota at different stages of the Asian tiger mosquito, Aedes albopictus from Tezpur, India. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0167409. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167409
37. Wang, Y, Gilbreath, TM 3rd, Kukutla, P, Yan, G, and Xu, J. Dynamic gut microbiome across life history of the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae in Kenya. PLoS One. (2011) 6:e24767. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024767
38. Telleria, EL, Martins-da-Silva, A, Tempone, AJ, and Traub-Csekö, YM. Leishmania, microbiota and sand fly immunity. Parasitology. (2018) 145:1336–53. doi: 10.1017/s0031182018001014
39. Douglas, AE. Multiorganismal insects: diversity and function of resident microorganisms. Annu Rev Entomol. (2015) 60:17–34. doi: 10.1146/annurev-ento-010814-020822
40. Jing, TZ, Qi, FH, and Wang, ZY. Most dominant roles of insect gut bacteria: digestion, detoxification, or essential nutrient provision? Microbiome. (2020) 8:38. doi: 10.1186/s40168-020-00823-y
41. Wang, Y, Wang, L, Li, D, Chen, Z, Luo, Y, Zhou, J, et al. Advancements in the impact of insect gut microbiota on host feeding behaviors. Genes. (2024) 15:1320. doi: 10.3390/genes15101320
42. He, M, Chen, H, Yang, X, Gao, Y, Lu, Y, and Cheng, D. Gut bacteria induce oviposition preference through ovipositor recognition in fruit fly. Commun Biol. (2022) 5:973. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03947-z
43. Zhang, Q, Zhou, Q, Han, S, Li, Y, Wang, Y, and He, H. The genome of sheep ked (Melophagus ovinus) reveals potential mechanisms underlying reproduction and narrower ecological niches. BMC Genomics. (2023) 24:54. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09155-1
44. Smith, CC, Srygley, RB, Healy, F, Swaminath, K, and Mueller, UG. Spatial structure of the Mormon cricket gut microbiome and its predicted contribution to nutrition and immune function. Front Microbiol. (2017) 8:801. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00801
45. Haloi, K, Kalita, MK, Nath, R, and Devi, D. Characterization and pathogenicity assessment of gut-associated microbes of muga silkworm Antheraea assamensis Helfer (Lepidoptera: Saturniidae). J Invertebr Pathol. (2016) 138:73–85. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2016.06.006
46. Hosokawa, T, and Fukatsu, T. Relevance of microbial symbiosis to insect behavior. Curr Opin Insect Sci. (2020) 39:91–100. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2020.03.004
47. Bascuñán, P, Niño-Garcia, JP, Galeano-Castañeda, Y, Serre, D, and Correa, MM. Factors shaping the gut bacterial community assembly in two main Colombian malaria vectors. Microbiome. (2018) 6:148. doi: 10.1186/s40168-018-0528-y
48. Xue, H, Zhu, X, Wang, L, Zhang, K, Li, D, Ji, J, et al. Gut bacterial diversity in different life cycle stages of Adelphocoris suturalis (Hemiptera: Miridae). Front Microbiol. (2021) 12:670383. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.670383
49. Ding, X, Jiang, H, Zhang, R, Chen, X, Yu, H, Zu, Y, et al. Comparative analysis of nasal microbial community between Tibetan sheep with different ages. Pak Vet J. (2023) 43:723–31. doi: 10.29261/pakvetj/2023.075
50. Yue, S, Li, X, Qian, J, Du, J, Liu, X, Xu, H, et al. Impact of enzymatic hydrolyzed protein feeding on rumen microbial population, blood metabolites and performance parameters of lactating dairy cows. Pak Vet J. (2023) 43:804–8. doi: 10.29261/pakvetj/2023.081
51. Ren, Y, Zhaxi, Y, Liu, M, Idrees, A, and Li, K. Revealing the Fungi microbiome difference of Suffolk cross with Tibetan sheep on plateau. Pak Vet J. (2023) 43:748–56. doi: 10.29261/pakvetj/2023.112
52. Zhang, L, Peng, Q, Gu, XL, Su, WQ, Cao, XQ, Zhou, CM, et al. Host specificity and genetic diversity of Bartonella in rodents and shrews from eastern China. Transbound Emerg Dis. (2022) 69:3906–16. doi: 10.1111/tbed.14761
53. Segers, FH, Kešnerová, L, Kosoy, M, and Engel, P. Genomic changes associated with the evolutionary transition of an insect gut symbiont into a blood-borne pathogen. ISME J. (2017) 11:1232–44. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2016.201
54. Hedges, LM, Brownlie, JC, O'Neill, SL, and Johnson, KN. Wolbachia and virus protection in insects. Science. (2008) 322:702. doi: 10.1126/science.1162418
55. Miller, WJ. Bugs in transition: the dynamic world of Wolbachia in insects. PLoS Genet. (2013) 9:e1004069. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004069
56. Werren, JH, Baldo, L, and Clark, ME. Wolbachia: master manipulators of invertebrate biology. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2008) 6:741–51. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1969
57. Nováková, E, Hypsa, V, and Moran, NA. Arsenophonus, an emerging clade of intracellular symbionts with a broad host distribution. BMC Microbiol. (2009) 9:143. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-143
58. Liew, KC, Graves, S, Croft, L, Brettell, LE, Cook, J, Botes, J, et al. First human case of infection with Arsenophonus nasoniae, the male killer insect pathogen. Pathology. (2022) 54:664–6. doi: 10.1016/j.pathol.2021.08.011
59. Parratt, SR, Frost, CL, Schenkel, MA, Rice, A, Hurst, GD, and King, KC. Superparasitism drives heritable symbiont epidemiology and host sex ratio in a wasp. PLoS Pathog. (2016) 12:e1005629. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005629
60. Peix, A, Ramírez-Bahena, MH, and Velázquez, E. The current status on the taxonomy of Pseudomonas revisited: an update. Infect Genet Evol. (2018) 57:106–16. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2017.10.026
61. Silby, MW, Winstanley, C, Godfrey, SA, Levy, SB, and Jackson, RW. Pseudomonas genomes: diverse and adaptable. FEMS Microbiol Rev. (2011) 35:652–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2011.00269.x
62. Gurung, K, Wertheim, B, and Falcao Salles, J. The microbiome of pest insects: it is not just bacteria. Entomol Exp Appl. (2019) 167:156–70. doi: 10.1111/eea.12768
63. Kostygov, AY, Frolov, AO, Malysheva, MN, Ganyukova, AI, Drachko, D, Yurchenko, V, et al. Development of two species of the Trypanosoma theileri complex in tabanids. Parasit Vectors. (2022) 15:95. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05212-y
64. Jaimes-Dueñez, J, Triana-Chávez, O, Holguín-Rocha, A, Tobon-Castaño, A, and Mejía-Jaramillo, AM. Molecular surveillance and phylogenetic traits of Babesia bigemina and Babesia bovis in cattle (Bos taurus) and water buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) from Colombia. Parasit Vectors. (2018) 11:510. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-3091-2
65. Setién, Á, Baltazar, AG, Leyva, IO, Rojas, MS, Koldenkova, VP, García, MP, et al. Ectoparasitic hematophagous dipters: potential reservoirs of dengue virus? Gac Med Mex. (2017) 153:S82–90. doi: 10.24875/gmm.M17000009
66. Bergqvist, C, Kurban, M, and Abbas, O. Orf virus infection. Rev Med Virol. (2017) 27:e1932. doi: 10.1002/rmv.1932
67. Kosoy, M, McKee, C, Albayrak, L, and Fofanov, Y. Genotyping of Bartonella bacteria and their animal hosts: current status and perspectives. Parasitology. (2018) 145:543–62. doi: 10.1017/s0031182017001263
68. Van Nguyen, P, Le, CT, Ho, XTT, Truong, PH, Van Loi, B, and Nguyen, KCT. First report of antimicrobial resistance of Mannheimia haemolytica from phan rang sheep in Vietnam. Pak Vet J. (2023) 43:41–8. doi: 10.29261/pakvetj/2023.007
Keywords: Melophagus ovinus , pupae, metagenomics sequencing, microbial population, Xinjiang
Citation: Huang K, Zhang X, Xiong N, Sun L, Zhao X, Zhou K and Wu J (2024) First metagenomic sequencing for the analysis of microbial community populations of adults and pupae of Melophagus ovinus in Xinjiang, China. Front. Vet. Sci. 11:1462772. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1462772
Edited by:
Giulio Grandi, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, SwedenReviewed by:
Houshuang Zhang, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, ChinaHafiz Ishfaq Ahmad, University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Pakistan
Copyright © 2024 Huang, Zhang, Xiong, Sun, Zhao, Zhou and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Junyuan Wu, dGFydV93anlAMTI2LmNvbQ==
 Kaijun Huang
Kaijun Huang Xing Zhang1,2,3
Xing Zhang1,2,3 Kun Zhou
Kun Zhou Junyuan Wu
Junyuan Wu