
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Vet. Sci., 06 December 2024
Sec. Animal Nutrition and Metabolism
Volume 11 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fvets.2024.1445216
 Xuelei Duan1
Xuelei Duan1 Xiao Wang1
Xiao Wang1 Zhaonian Li1
Zhaonian Li1 Chenggong Liu1
Chenggong Liu1 Lu Zhang1
Lu Zhang1 Yongzhan Bao1,2
Yongzhan Bao1,2 Wanyu Shi1,2,3*
Wanyu Shi1,2,3* Xinghua Zhao1*
Xinghua Zhao1*The aim of this study was to investigate the impact of supplementary feeding with Chinese herbal mixtures on perinatal sows, focusing on their reproductive performance, immunity and breast milk quality. Sixty healthy pregnant sows (Large white, 4 parities) were randomly allocated into five treatment groups (n = 12 per group): the control group received a basal diet, the TRT1 group received a basal diet supplemented with 2 kg/t Bazhen powder (BZP), while the TRT2, TRT3, and TRT4 groups received a basal diet supplemented with 1 kg/t, 2 kg/t, and 3 kg/t Qi-Zhu-Gui-Shao soothing liver and replenishing blood powder (QZGSP), respectively. The trial lasted for a duration of 5 weeks, commencing from day 100 of gestation and concluding on day 21 postpartum. The results showed that supplemental feeding of 2 kg/t and 3 kg/t QZGSP to periparturient sows significantly improved reproductive performance to different degrees, as evidenced by the shortened farrowing intervals and increased average daily feed intake and milk yield. Supplemental feeding of 2 kg/t and/or 3 kg/t QZGSP significantly elevated levels of IL-4, IL-10, IgG, and IgA in sow serum while reduced levels of TNF-α and IL-1β in sow serum. In addition, supplemental feeding of 2 kg/t and 3 kg/t QZGSP to perinatal sows significantly increased the protein and fat content in colostrum and milk. Analysis of 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing data in colostrum and milk microbiota revealed that supplemental feeding of QZGSP to perinatal sows is influenced the composition of colostrum and milk composition in sows. Specifically, at the genus level, a decrease in the relative abundance of Escherichia-Shigella, Staphylococcus and Streptococcus was observed in the TRT3 and/or TRT4 groups on day 0 of lactation. The findings from this study indicate that supplemental feeding of 2 kg/t and 3 kg/t QZGSP significantly improved the reproductive performance, immunity and milk quality in sows. Therefore, QZGSP is a beneficial feed additive for perinatal sows.
As we all know, sows play a pivotal role in modern intensive pig production conditions, and the health status and reproductive performance of sows are closely related to the production efficiency of pig enterprises. The health condition of sows before and after farrowing, as well as their lactation ability, directly affect the quantity and quality of colostrum and milk. This, in turn, affects the growth and development of piglets and their resistance to disease (1, 2). However, during late pregnancy and lactation periods, sows are frequently subjected to various stressors such as repeated services, environmental factors, and physiological changes etc. (3–5), which decrease their reproductive performance, lactation capacity, immunity while increasing susceptibility to diseases (6–8). Henceforth, appropriate nutritional strategies must be implemented to improve the reproductive potential and health of sows while maximizing breast milk quality.
Unfortunately, there is limited scientific research on the effects of Chinese herbal mixtures on perinatal sow reproductive performance, immunity, and breast milk quality. Bazhen powder (BZP), a traditional nourishing formula containing Codonopsis pilosula (Franch.) Nannf., Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz., Poria cocos (Schw.) Wolf, Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels, Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort, Paeonia lactiflora Pall., Rehmannia glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC., and Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch., is currently used to treat diseases with deficiency of qi and blood (9). Qi plays a crucial role in regulating vital physiological processes and immune defense in the human body (9). Previous studies have shown that BZP can enhance performance and/or health in chicken (10), sows (11, 12), and other animals (13, 14). Qi-Zhu-Gui-Shao soothing liver and replenishing blood powder (QZGSP) is a self-prepared formula based on the syndrome of “qi-blood deficiency and Gan-qi stagnancy.” Its main ingredients are Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge, A. macrocephala Koidz., A. sinensis (Oliv.) Diels, P. lactiflora Pall., Bupleurum chinense DC. P. cocos (Schw.) Wolf. A previous study found that A. membranaceus is commonly utilized in the enhancement and treatment of various aliments as a medical agent and dietary supplement to fortify the spleen and restore vital energy (15). The primary natural active ingredient in A. membranaceus is Astragalus polysaccharide (APS), which exhibits a wide range of pharmacological properties such as immunostimulant, antioxidant, antibacterial, antiviral, and so on (16). A. macrocephala is known for its medicinal and edible values that can enhance spleen function, boost energy, eliminate dampness, promote urination, and prevent miscarriage (17). It contains polysaccharide as one of its active ingredients offering various of pharmacological benefits like immunoregulation, growth promotion, antioxidant effects, liver protection, and anti-tumor properties (18). A. sinensis is a traditional medicine and edible plant known for its efficacy in tonifying, nourishing, and activating blood (19). A. sinensis polysaccharide (ASP), identified as a crucial bioactive component of A. sinensis has been extensively investigated and found to possess significant pharmacological activities including immunomodulation, hepatoprotection, and antioxidant properties, among others (20). Paeoniae Radix Alba (PRA), known as Baishao in China, refers to the dried root of P. lactiflora Pall (PLP, also known as shaoyao). It has traditional pharmacological functions such as nourishing blood, attenuating liver diseases, regulating menstruation, and relieving pain (21). Modern pharmacological studies have revealed that PRA exhibits various functions, including anti-inflammation properties, liver protection, immunoregulation, and regulation of gut microbiota (22, 23). According to the theory of traditional Chinese medicine, Chaihu has the functions of soothing the liver and regulating qi, reducing water and dampness, relieving heat and pain, and supplementing Yang qi (24). It is commonly used to treat depression by “soothing the liver and alleviating melancholia” (25). Modern pharmacological studies have shown that Saikosaponins (SSs), as the main bioactive compounds in RB (Radix Bupleuri), possess various effects such as anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor, antioxidant, anti-viral, and hepatoprotective effects, etc. (26). Poria cocos refers to a functional edible and medicinal fungus, with Poria cocos polysaccharide (PCP) being one of its main active components. PCP and its derivatives exhibit various biological functions such as immunoregulatory, antioxidant, and hepatoprotective, etc. (27). In general, Chinese herbal mixtures contain multiple bioactive ingredients that synergistically enhance efficacy compared to using a single herb alone (28). However, the factors influencing the health status of sows before and after farrowing are exceedingly intricate; therefore, the efficacy of a singular Chinese herbal medicine in addressing these complex issues arising from sows before and after postpartum is often limited (29). Based on the multiple efficacies of the drugs contained in QZGSP, we hypothesized that QZGSP may have positive effects on reproductive performance, immunity and breast milk quality in perinatal sows. In addition, considering the biology, genetics, and dietary similarities shared by pigs and humans, this research may provide valuable scientific insights into the nutritional management of perinatal mothers.
The experimental procedures of this study were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Hebei Agricultural University (grant No. 2022161). The animal experiments were conducted at Weijia great grandparent farm located in Pingu district, Beijing, China.
The formula of Bazhen powder (BZP) used in this study consisted of C. pilosula (Franch.) Nannf, A. macrocephala Koidz, P. cocos (Schw.) Wolf, A. sinensis (Oliv.) Diels, L. chuanxiong Hort, P. lactiflora Pall, R. glutinosa (Gaertn.) DC, and G. uralensis Fisch, in a ratio of 1:1:1: 1:1:1: 1:1. The formula of Qi-Zhu-Gui-Shao soothing liver and replenishing blood powder (QZGSP) used in this study consisted of A. membranaceus (Fisch.) Bunge, A. macrocephala Koidz, A. sinensis (Oliv.) Diels, P. lactiflora Pall, B. chinense DC, and P. cocos (Schw.) Wolf, in a ratio of 6:3:3: 4:2:2. The aforementioned Chinese herbal mixture was commissioned for processing and manufacturing by Wuhan HVSEN Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
Sixty healthy pregnant sows (Large white) with fourth parity, similar backfat thickness, and expected confinement period were selected. They were then randomly divided into five groups (n = 12 per group): the control group received a basal diet, the TRT1 group received a basal diet supplemented with 2 kg/t BZP, the TRT2 group, TRT3 group, and the TRT4 group were each given the basic diet supplemented with 1 kg/t, 2 kg/t, and 3 kg/t of QZGSP, respectively. The trial lasted for 5 weeks, starting from the 100th day of pregnancy and continuing until the 21st day after delivery. The basic diets were prepared to fulfill the nutrient needs of sows as outlined by the NRC (2012) guidelines. The composition and nutrition level of these diets were presented in Table 1.
During the period from day 100 to day 110 of gestation, pregnant sows were allocated to individual stalls and provided with a controlled diet of 3 kg per day. On day 111th day of gestation, sows were shifted to individual farrowing pens equipped with an enclosed heated creep area. Starting from this day until delivery, each sow was given a daily feed allowance of 2.5 kg. The sows were not fed on the day farrowing. On the first day after delivery, sows were fed a lactation meal twice a day (at 7:30 AM and 2:30 PM), starting with an intake of 2.5 kg/d and then gradually increasing by 0.5 kg/d until ad libitum feeding was reached, respectively. The amount of feed consumed by each sow on a daily basis was measured during lactation in order to determine the their average daily feed intake (ADFI). Throughout the experiment, water was available ad libitum for all sows and suckling piglets. All sows were exposed to the same controlled growing environment where relative humidity and temperature are automatically regulated.
The number of piglets per litter, including total piglets, live piglets, healthy piglets, weak piglets (birth weight: <800 g), and stillborn fetuses, was recorded at birth. The amount of feed consumed by sows was monitored daily from day 1 to day 21 of lactation. Farrowing duration and interval were also recorded for each sow. The backfat thickness of each sow was measured on day 100 of gestation and again on days 0 and 21 of lactation using a digital backfat meter (Renco Lean-Meatier®, Renco Corporation, Minneapolis, MN, USA). The measurement point was located at a distance of 6.5 cm from the dorsal midline along the external tangent line of the last rib.
On days 0 and 21 of lactation, six sows were randomly chosen from each group. A total of 10 mL blood samples were taken from the marginal veins in the ear of each sow. These samples were subsequently divided into two parts: 5 mL of blood samples were placed in EDTA-K2 evacuated tubes, thoroughly mixed, and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C for future analysis, while the remaining 5 mL was transferred into sterile vacuum tubes. After being kept at room temperature for a duration of 30 min, the tubes were subjected to centrifugation at 3,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C to obtain serum. The isolated serum was refrigerated at −20°C for subsequent examination.
On days 0, 11, and 21 of lactation, six sows were randomly selected from each group. Colostrum was obtained through manual expression from functional glands within 3 h after the start of farrowing. Milk collection followed an intramuscular injection of 20 IU oxytocin behind the ear. Approximately 20 mL of colostrum and milk samples were obtained per sow at each time point. Subsequently, the collected colostrum and milk samples were separated into two groups: 5 mL of milk samples were stored at −80°C for further analysis, while the remaining 15 mL of milk samples were centrifuged at 3,000 rpm for 20 min at a temperature of 4°C to obtain supernatant. The supernatant was refrigerated at −20°C for later analysis.
The levels of white blood cells (WBC), red blood cells (RBC), and hemoglobin (HGB) in whole blood samples from sows in each group were measured using a veterinary blood cell analyzer (BC-5000, Shenzhen Mindray Biomedical Electronics Co., LTD, Shenzhen, China).
Serum concentrations of PROG (P), Estradiol (E2), and Prolactin (PRL) were determined through the double-antibody one-step sandwich assay utilizing porcine-specific ELISA kits (Shanghai Enzyme-linked Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Shanghai, China). The assays were performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) were quantified using commercial kits (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Research Institute, Nanjing, China). All operations were carried out according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
The levels of cytokines (IL-4, IL-10, IL-1β, and TNF-α) and immunoglobulins (IgA, IgG) in the serum, colostrum, and milk of sows were determined using porcine-specific ELISA kits (Shanghai Enzyme-linked Biotechnology Co., Ltd. Shanghai, China), employing a double-antibody one-step sandwich assay. All operations were carried out according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Colostrum and milk samples from sows in each group were analyzed for the content of fat, protein, lactose and non-fat solids using a multifunctional dairy analyzer (MILKOSCAN FT1, FOSS Group, Denmark).
Microbial genomic DNA was extracted from sow colostrum and milk using the Hipure Stool DNA Kit (Model D3141, Magen Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The DNA concentration was measured using a Nanodrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., DE, USA), and the integrity of the DNA was evaluated by agarose gel electrophoresis. Subsequently, PCR amplification of the V3-V4 variable region of the 16S rRNA gene was performed with primers (341F:5′-CCTACGGNGGCWGCAG-3′, 806R:5′-GGACTACHVGGTATCTAAT-3′) using isolated DNA as a template. Amplification products were visualized on 2% agarose gels and then purified using AMPure XP Beads (Beckman Coulter, Inc., USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Purified amplicons were mixed in equimolar amounts and subjected to paired-end sequencing on Novaseq 6000 platform following Gene Denovo Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Guangzhou, China). Bioinformatic analysis was performed using the Omicsmart online platform.1
Data from the experiments were organized and summarized using Excel software. Bar graphs were generated using GraphPad Prism 9.4.0 software (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA), and the results were displayed as “mean ± standard deviation.” IBM SPSS 26.0 Software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for one-way analysis of the data, and the experimental data were presented as “mean ± standard deviation,” with p < 0.05 indicating statistical significance.
As shown in Table 2, the number of piglets born alive and born healthy from sows in the TRT3 and TRT4 groups, as well as the litter weight at birth of piglets from the TRT3 group, exhibited significant increases compared to those in the CON group (p < 0.05). Sows in the TRT4, TRT3, and TRT1 groups demonstrated significantly lower farrowing duration and farrowing interval than those in the CON group (p < 0.05), while their average daily feed intake during lactation was significantly higher than that of the CON group (p < 0.05). Sows in the TRT4 and TRT3 groups also showed significantly lower farrowing duration and farrowing interval compared to those in the TRT1 group (p < 0.05), along with a significantly higher average daily intake during lactation than that of the TRT1 group (p < 0.05). Sows in the TRT1, TRT3, and TRT4 groups experienced a significant decrease in backfat thickness loss during lactation and a significant increase in average milk yield compared with sows in the CON group (p < 0.05). Sows in the TRT3 and TRT4 groups had a significant increase in average milk yield compared with sows in the TRT1 group (p < 0.05).
To assess the impacts of QZGSP on changes in complete blood or serum parameters of sows, levels of WBC, RBC, HGB, PRL, E2, AST, and ALT were measured. As shown in Figures 1A–C, the levels of WBC, RBC, and HGB in the complete blood of sows from the TRT4, TRT3, and TRT1 groups were significantly higher compared to the CON group on days of 0 and 21 lactation (p < 0.05). A significant increase was noted in total WBC count as well as RBC count and HGB level in the TRT4 and TRT3 groups compared to the TRT1 group (p < 0.05). The levels of E2 and PRL in the serum of sows from the TRT4, TRT3, and TRT1 groups were significantly higher than those in the CON group on days 0 and 21 of lactation (p < 0.05), as depicted in Figures 1D,E. On day 0 of lactation, the content of PRL in the serum of sows from the TRT4 and TRT3 groups were significantly greater than that in the TRT1 group (p < 0.05). On day 21 of lactation, as shown in Figure 1F, the level of PROG in the serum of sows from the TRT4 and TRT3 groups was significantly higher than that in the CON group (p < 0.05). The serum levels of AST and ALT activities in sows from the TRT4, TRT3 and TRT1 groups were significantly lower than those in the CON group on days 0 and 21 of lactation (p < 0.05), as shown in Figures 1G,H. In addition, AST and ALT activities were notably lower in the TRT3 group compared to the TRT1 group on days 0 and 21 of lactation (p < 0.05).
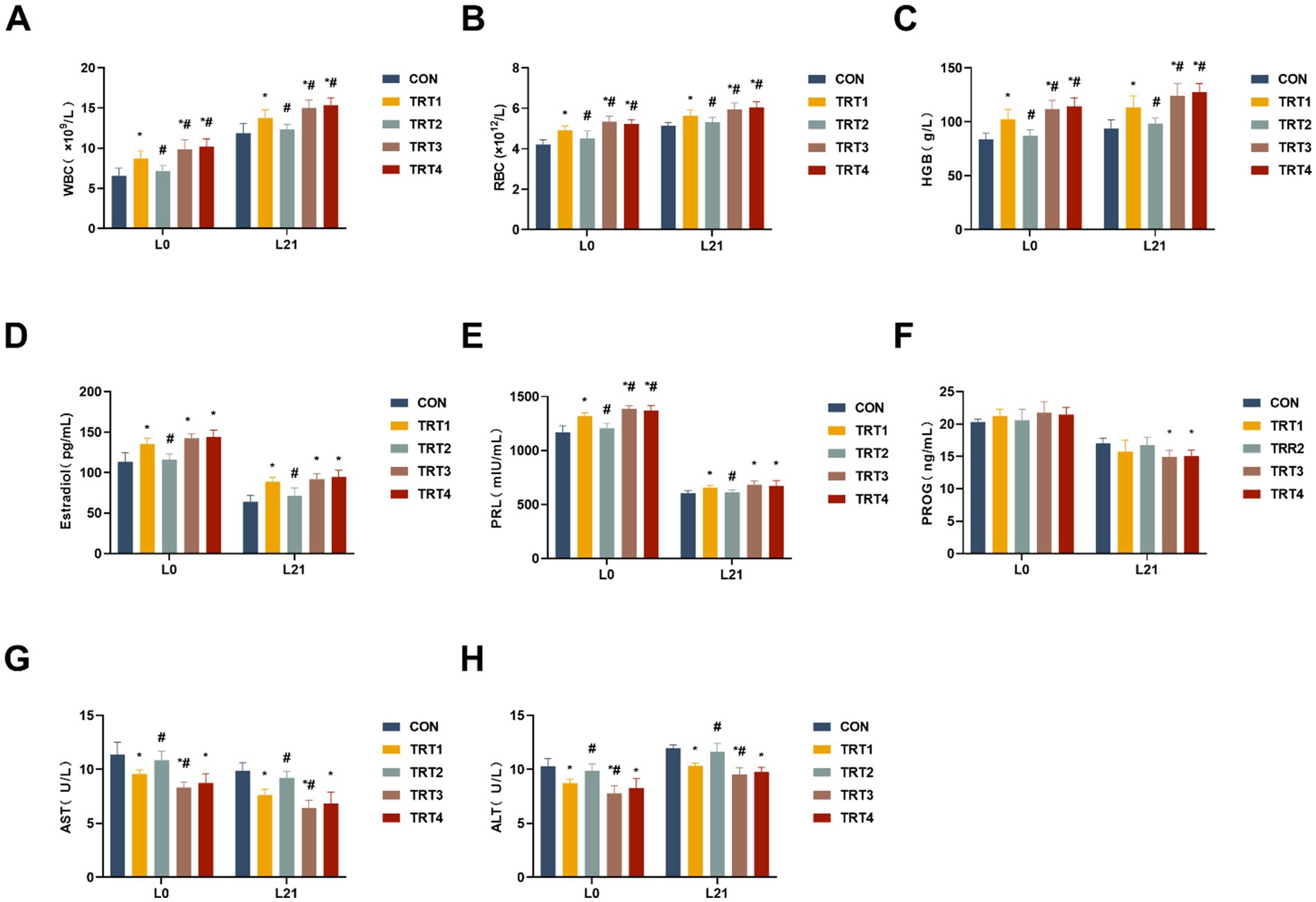
Figure 1. Effects of QZGSP on physiological and biochemical parameters in the blood or serum of sows during lactation. (A–C) Levels of WBC, RBC, and HGB in complete blood of sows on days 0 and 21 of lactation. (D–F) Levels of serum Estradiol, PRL, and PROG of sows on days 0 and 21 of lactation. (G,H) Levels of serum AST and ALT of sows on days 0 and 21 of lactation. CON, basic diet; TRT1 group, basic diet supplemented with 2 kg/t BZP; TRT2 group, basic diet supplemented with 1 kg/t QZGSP; TRT3 group, basic diet supplemented with 2 kg/t QZGSP; TRT4 group, basic diet supplemented with 3 kg/t QZGSP. “*”: indicates a significant difference compared with CON group (p < 0.05), “#”: indicates a significant difference compared with TRT1 group (p < 0.05). The same to below.
The impacts of QZGSP on the modulation of immunity were assessed by quantifying serum cytokines, including IL-4, IL-10, IL-1β, and TNF-α. As shown in Figures 2A,B, sows from the TRT4, TRT3, and TRT1 groups exhibited significantly higher serum concentrations of IL-4 and IL-10 compared to those in the CON group on days 0 and 21 of lactation (p < 0.05). Sows from the TRT4 group had significantly higher serum concentrations of IL-4 than those from the TRT1 group on days 0 and 21 of lactation (p < 0.05), while sows from the TRT4 and TRT3 groups had significantly higher serum concentrations of IL-10 than those from the TRT1 group on days 0 and 21 of lactation (p < 0.05).
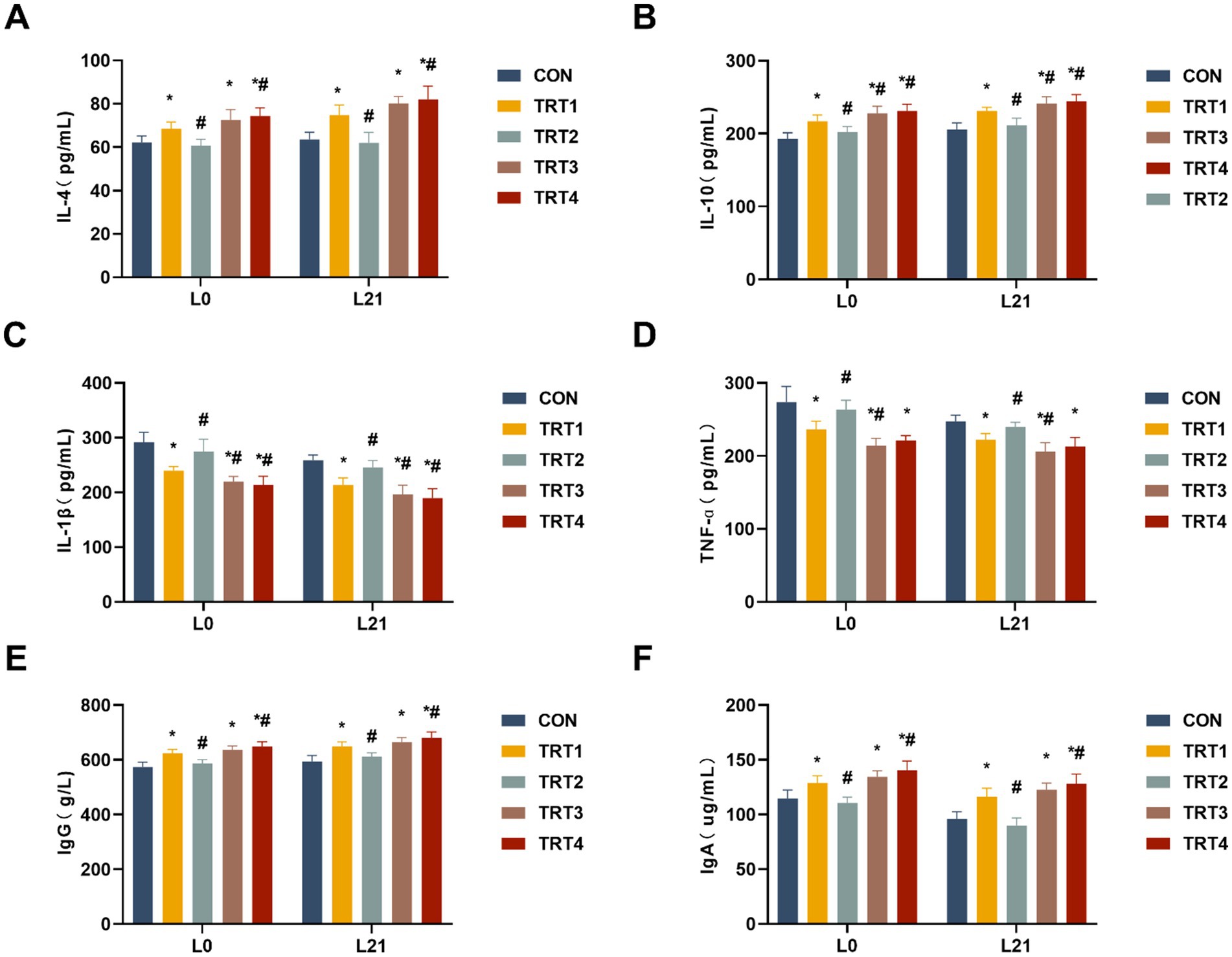
Figure 2. Effects of QZGSP on the immunity of sows. (A–D) Concentrations of IL-4, IL-10, IL-1β, and TNF-α in the serum of sows. (E,F) Concentrations of immunoglobulins IgG and IgA in serum of sows.
The sows from the TRT4, TRT3, and TRT1 groups exhibited significantly lower serum levels of IL-1β and TNF-α compared to the CON group on days 0 and 21 of lactation (p < 0.05), as depicted in Figures 2C,D. The levels of IL-1β in the serum of sows from the TRT4 and TRT3 groups, as well as the levels of TNF-α in the serum of sows from the TRT3 group, were significantly lower than that in the TRT1 group on days 0 and 21of lactation (p < 0.05).
The concentrations of IgG and IgA in the serum of lactating sow were measured. As shown in Figures 2E,F, compared to sows in the CON group, sows in the TRT1, TRT3, and TRT4 groups exhibited significantly increased concentrations of IgG and IgA in their serum on days 0 and 21 of lactation (p < 0.05). Sows in the TRT4 group showed significantly higher concentrations of IgG and IgA in their serum on days 0 and 21 of lactation compared to those in the TRT1 group (p < 0.05).
The nutritional composition of colostrum and milk from sows was evaluated on days 0, 11, and 21 of lactation. As shown in Figures 3A,B, the concentration of fat and protein in sow colostrum and milk from TRT4, TRT3, and TRT1 groups was significantly higher than that in the CON group (p < 0.05). The concentration of fat and protein in sow colostrum and milk from TRT4 and TRT3 group was significantly higher than that in the TRT1 group (p < 0.05). Moreover, Figure 3C indicates that there were no significant differences in the concentrations of lactose in sow colostrum and milk among the different groups (p > 0.05). As shown in Figure 3D, the concentration of non-fat solid in sow colostrum and milk from TRT4 and TRT3 groups was significantly higher than that in the CON group on days 0 and 11 of lactation (p < 0.05).
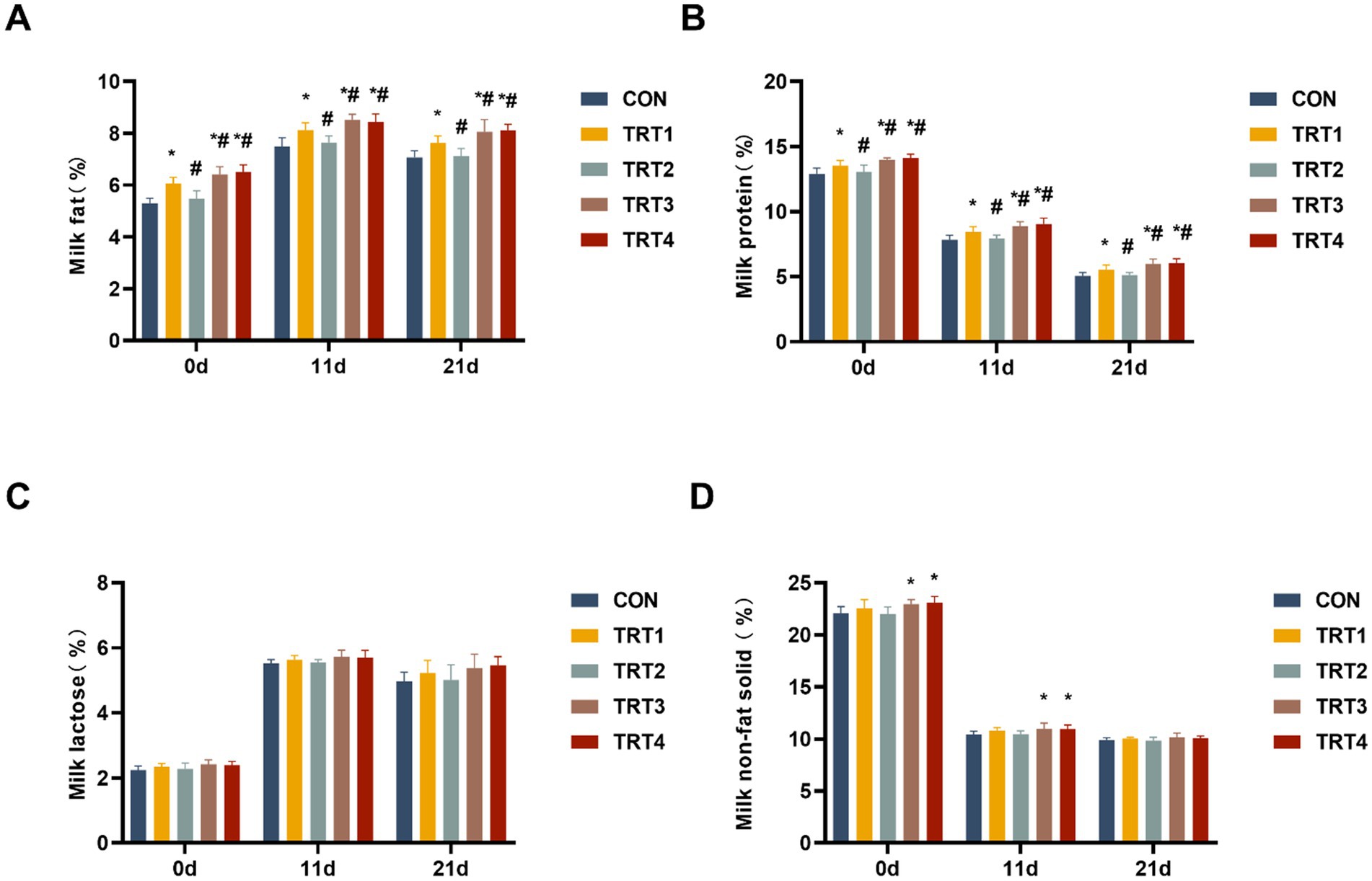
Figure 3. Effects of QZGSP on nutrient composition of colostrum and milk of sows. (A) Milk protein content. (B) Milk fat content. (C) Milk lactose content. (D) Milk non-fat-solid content.
Concentrations of cytokines (IL-4, IL-10, IL-1β, and TNF-α) in colostrum and milk were determined to investigate the impacts of QZGSP on changes in immune indexes. As shown in Figures 4A–D, sows from the TRT4, TRT3, and TRT1 groups exhibited significant increases in the levels of IL-4 and IL-10 in colostrum and milk, as well as significant decreases in the levels of IL-1β and TNF-α in colostrum and milk compared to the CON group on days 0, 11, and 21 of lactation (p < 0.05). Sows from the TRT4 and TRT3 groups showed significantly higher levels of IL-4 and IL-10 in colostrum and milk while also displaying significantly lower levels of IL-1β, and TNF-α in colostrum and milk, compared to the TRT1 group on days 0, 11, and 21 of lactation (p < 0.05).
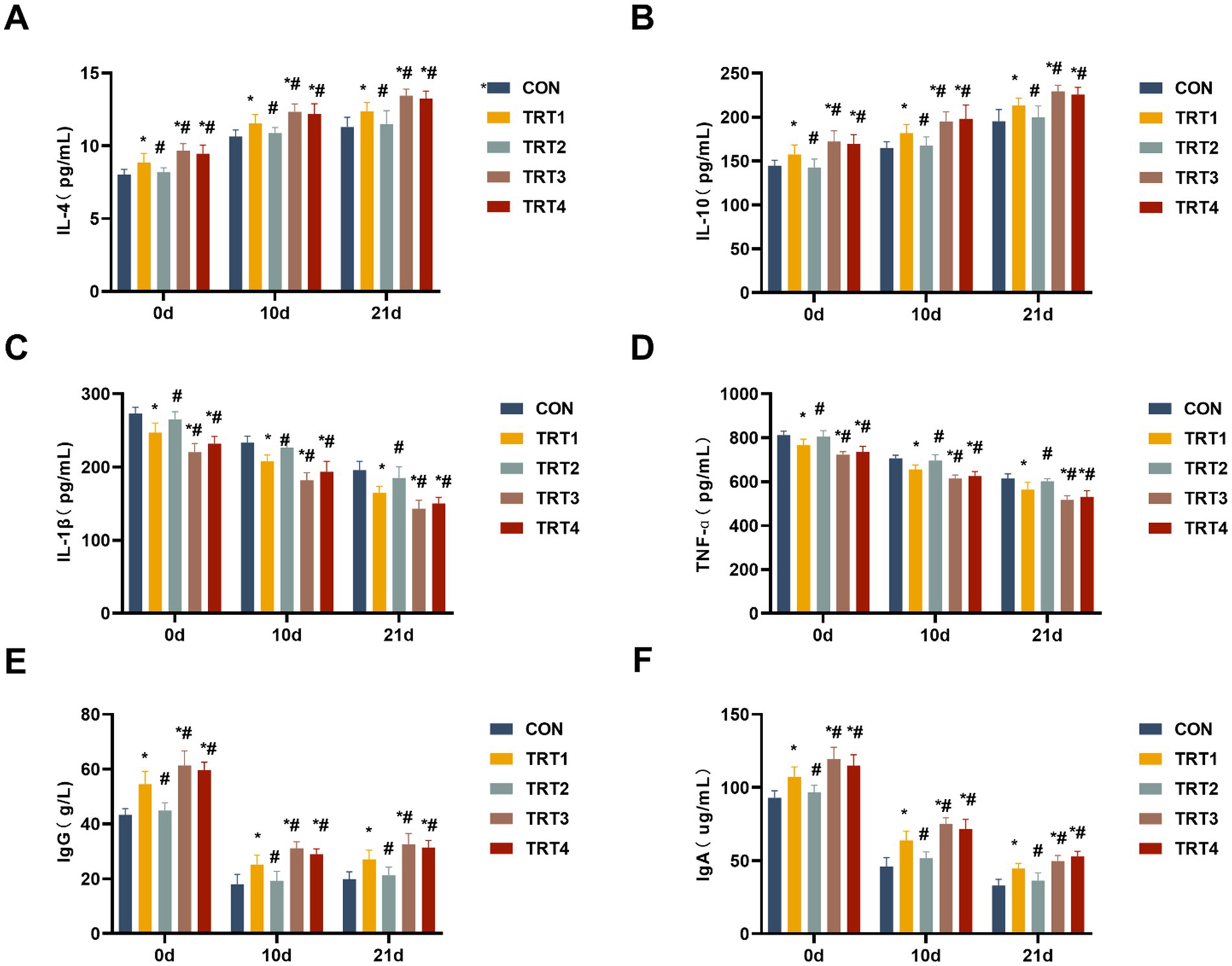
Figure 4. Effects of QZGSP on the colostrum and milk immune indexes of sows. (A–D) Concentrations of IL-4, IL-10, IL-1β, and TNF-α in the colostrum and milk of sows. (E,F) Concentrations of immunoglobulins IgG and IgA in the colostrum and milk of sows.
The concentrations of IgG and IgA in colostrum and milk from lactating sows were measured. As presented in the Figures 4E,F, the concentration of IgG and IgA in colostrum and milk from the TRT4, TRT3, and TRT1 groups was significantly higher than that in the CON group (p < 0.05). The concentrations of IgG and IgA in colostrum and milk from the TRT4 and TRT3 groups were significantly higher than those in the TRT1 group (p < 0.05).
The effects of dietary QZGSP supplementation with QZGSP on the diversity and richness of microorganisms in sow colostrum and milk were examined. We collected 298, 257, 334, 392 and 369 OUT samples from the CON, TRT1, TRT2, TRT3, and TRT4 groups, respectively. Among them, there were 93 OUT samples shared by all five groups (Figure 5A). We also collected 768, 1,052, 1,314, 740, and 1,418 OTU samples from the CON, TRT1, TRT2, TRT3, and TRT4 groups, with 297 OUT samples shared among the five groups (Figure 5B). We obtained 990, 1,031, 760, 871, and 981 OTU samples from the CON, TRT1, TRT2, TRT3, and TRT4 groups, respectively. Among them, there were 230 OUT samples shared by all five groups (Figure 5C).
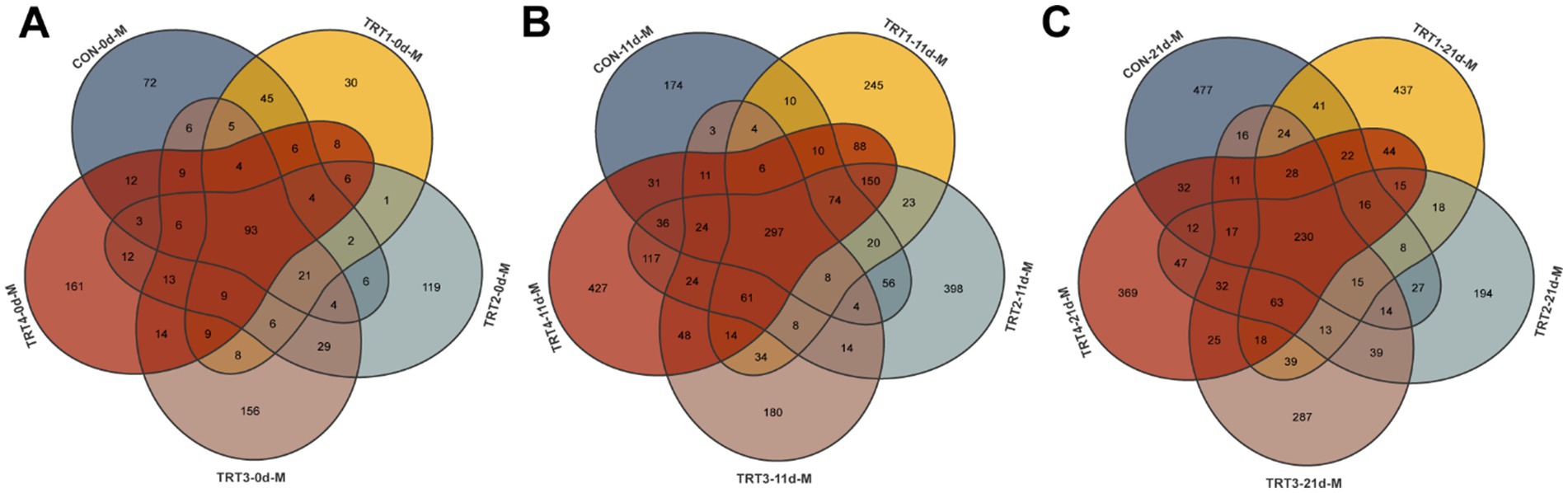
Figure 5. The Venn diagram for OTUs of the milk microbiota of sows among different groups. The Venn diagram for OTUs of milk microbiota of sows on days 0 (A), 11 (B) and 21 (C) of lactation.
The alpha diversity indices of colostrum and milk microbiota for sows are presented in Table 3. On day 11 of lactation, the Chao1 index and Ace index were significantly higher in the TRT3 and TRT4 groups compared to the CON group (p < 0.05), while the Simpson index was notably lower in the TRT3 group than in the CON group (p < 0.05). On day 21 of lactation, both Chao1 and Ace indices were significantly higher in the TRT2, TRT3, and TRT4 groups compared with those in the TRT1 group (p < 0.05). However, Shannon index was significantly lower in the TRT2 group than that of both CON and TRT1 groups (p < 0.05), whereas Simpson index was also significantly lower only in the TRT2 group than that of the TRT1 group (p < 0.05).
The effects of QZGSP on beta diversity of milk microbiota were explored using principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) to assess group differences. PCoA was performed based on the unweighted_unifrac distance of OUT relative abundance in sow milk microbiota. As depicted in Figure 6A, there was a distinct separation between the CON and TRT2 groups (Adonis: p = 0.002), as well as between the CON and TRT3 groups (Adonis: p = 0.017), and the CON and TRT4 groups (Adonis: p = 0.004). Similarly, in Figure 6B, a distinct separation was observed between the CON and TRT4 groups (Adonis, p = 0.009), along with the separation between the TRT1 and TRT4 groups (Adonis, p = 0.02). Furthermore, Figure 6C revealed separations between the CON and TRT2 groups (Adonis: p = 0.042), the CON and TRT3 groups (Adonis: p = 0.009), as well as the CON and TRT4 groups (Adonis: p = 0.011).
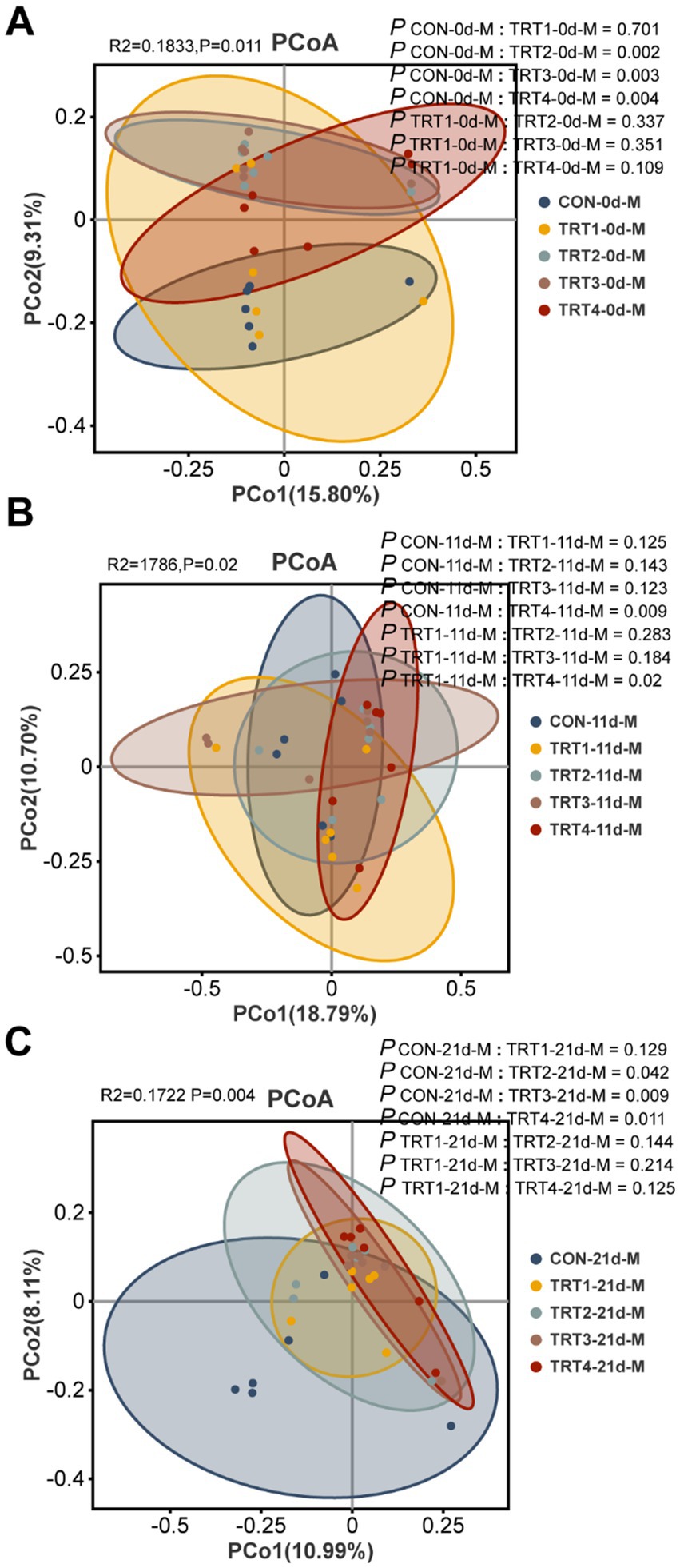
Figure 6. Effects of dietary QZGSP supplementation on beta-diversity of milk microbiota for sows. PCoA for sow among different groups based on unweighted_unifrac distance analysis on days 0 (A), 11 (B) and 21 (C) of lactation. Inter-group β-diversity comparisons using Adonis.
The composition of microflora species in sow milk from different groups at the phylum and genus levels were illustrated in Figure 7. As shown in Figures 7A,C,E, the dominant phylum observed throughout lactation were Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria. There was an increase in the abundance of Firmicutes in the TRT3 group on day 21 of lactation compared to days 0 and 11. As depicted in Figures 7B,D,F, Escherichia-Shigella, Streptococcus, and Staphylococcus emerged as the predominant genera within each group during lactation. On day 0 of lactation, the TRT4 group had lower levels of Escherichia-Shigella than the other groups. In addition, the TRT3 group had lower levels of Staphylococcus and Streptococcus on day 0 lactation compared to the other groups.
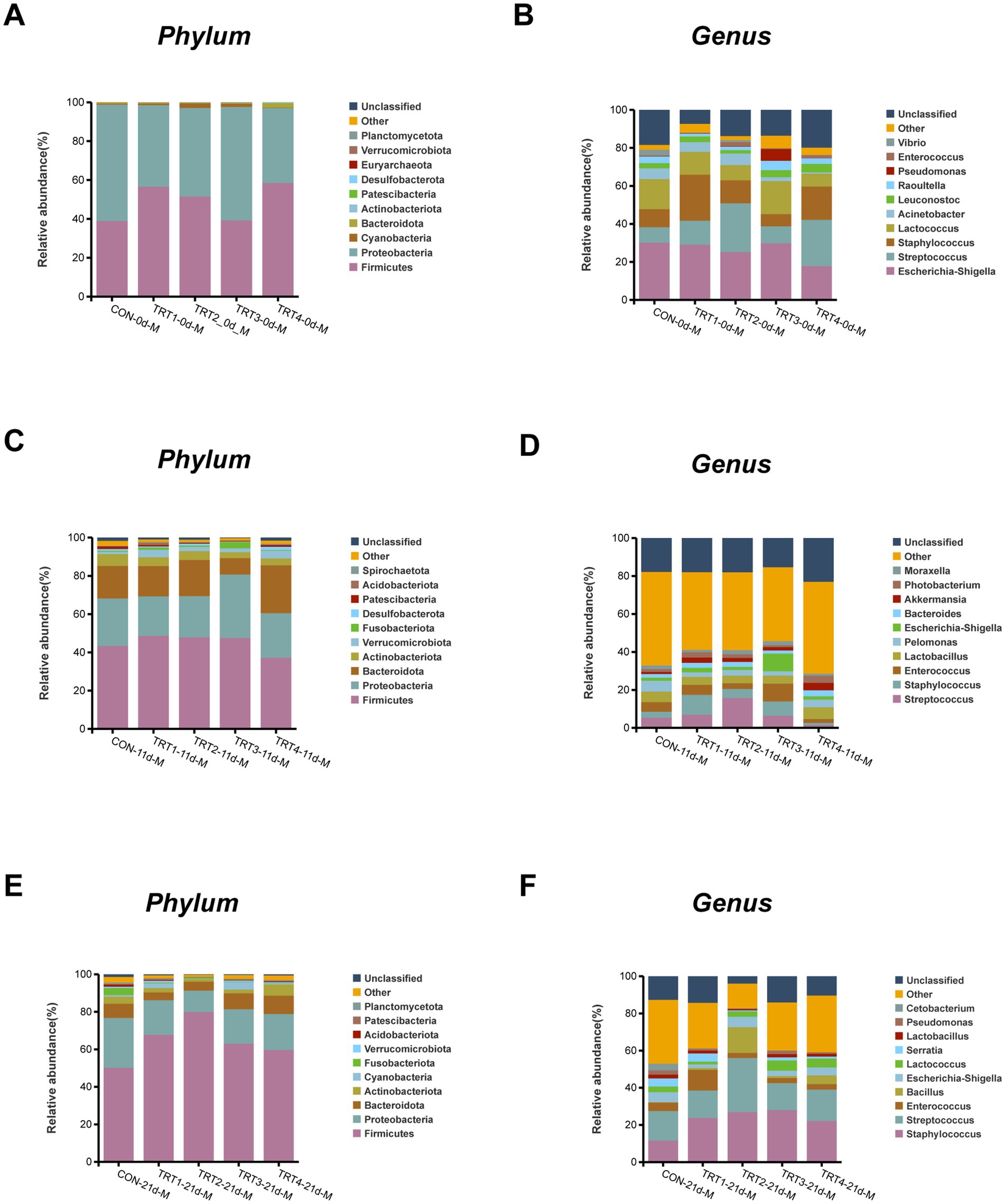
Figure 7. Effects of dietary QZGSP supplementation on the composition of milk microbiota in sows among different groups. The phylum-level composition of average relative abundance milk microbiota on day 0 (A), 11 (C) and 21 (E) of lactation. The genus-level composition of average relative abundance milk microbiota on days 0 (B), 11 (D) and 21 (F) of lactation. Values are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 6.
The comparative analysis was conducted among different groups to examine the top 10 dominant bacteria at the phylum level in sow colostrum and milk. On day 0 of lactation, the TRT4 group exhibited a significantly higher relative abundance of Bacteroidota compared to the TRT1 group (p < 0.05, Figure 8A). On day 0 of lactation, the TRT4 group showed a significantly higher relative abundance of Desulfobacterota compared to both CON and TRT1 groups (p < 0.05, Figure 8B), while the relative abundance of Euryarchaeota in TRT2, TRT3, and TRT4 groups was significantly lower than that in CON and TRT1 groups (p < 0.05, Figure 8C). On day 21 of lactation, the relative abundance of Actinobacteriota in the TRT4 group was significantly higher than that in the TRT1 group (p < 0.05, Figure 8D), whereas Fusobacteriota had a significantly higher relative abundance in the CON group on day 21 of lactation compared to other groups (p < 0.05, Figure 8E).
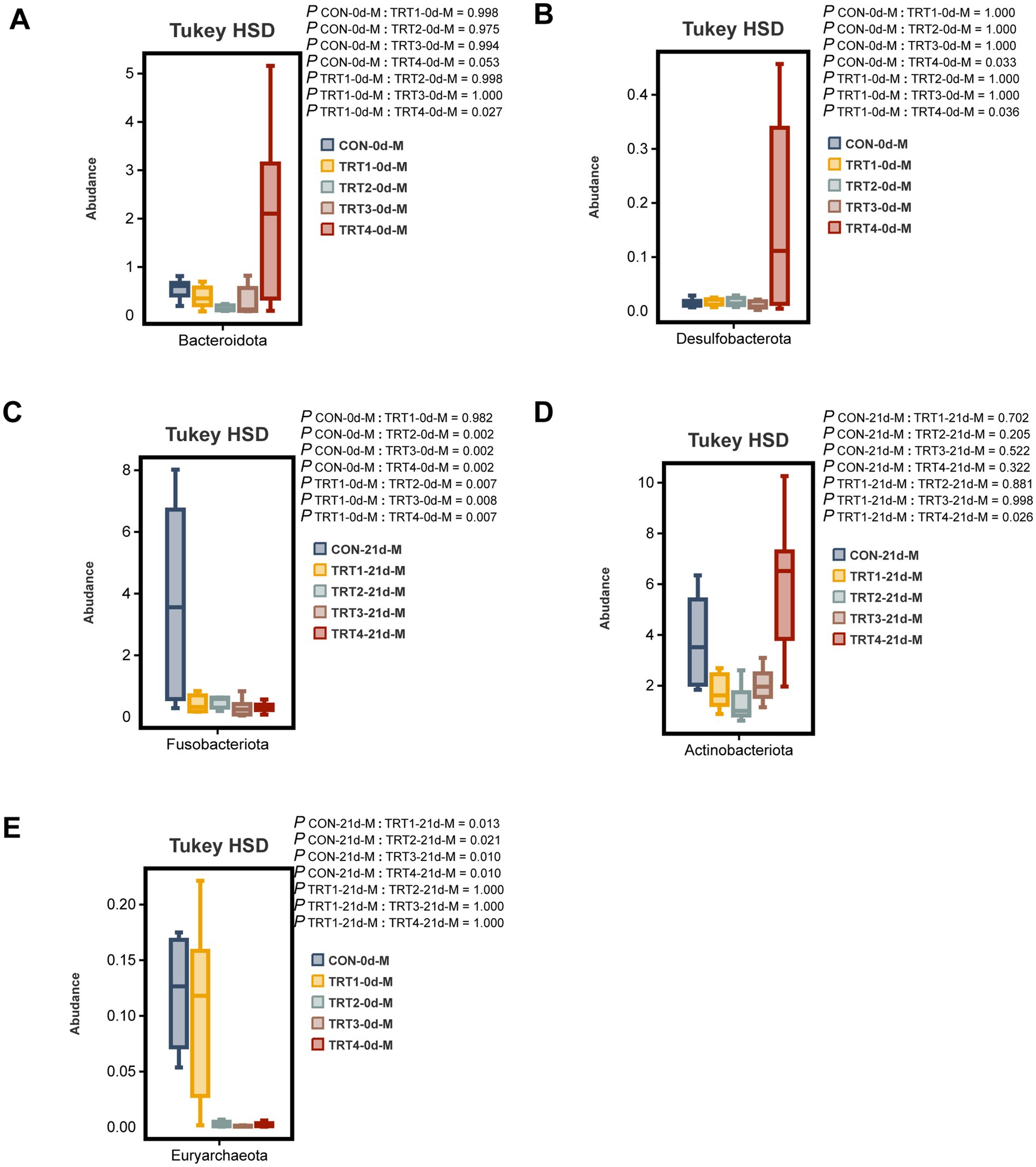
Figure 8. Effects of dietary supplementation with QZGSP on differences in milk microbiota of sows at the phylum level among different groups. The significant changes in the abundance of bacterial phyla found in milk (A–E). Values are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 6.
The comparative analysis was conducted among different groups to examine the top 10 dominant bacteria at the genus level in sow colostrum and milk. As depicted in Figure 9A, there was a significant decrease in the relative abundance of Pseudomonas in the TRT2 group compared to that in the CON group on day 21 of lactation (p < 0.05). Moreover, as shown in Figure 9B, the relative abundance of Rothia on day 21 of lactation was significantly higher in the TRT4 group than the CON and TRT1 groups (p < 0.05).
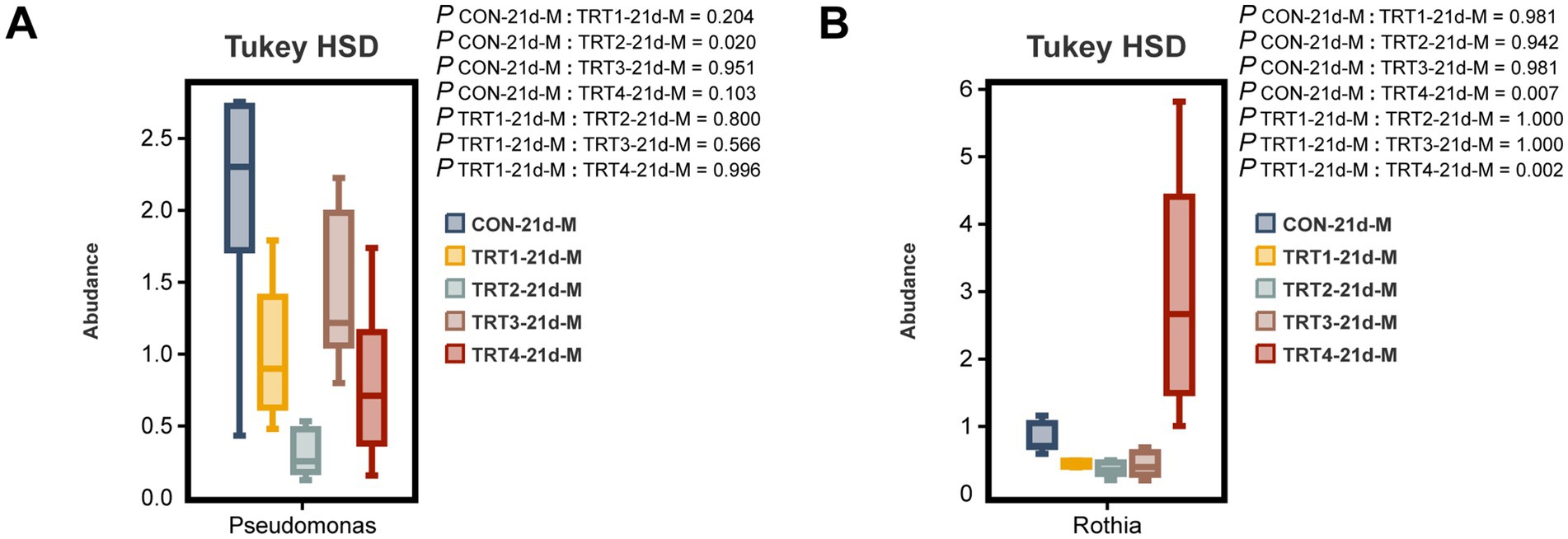
Figure 9. Effects of dietary supplementation with QZGSP on differences in milk microbiota of sows at the genus level among different groups. The significant changes in the abundance of bacterial genera found in milk (A,B). Values are expressed as mean ± SD, n = 6.
The health status of sows is crucial for modern intensive pig farming enterprises. The reproductive performance of sows serves as a vital indicator of the economic efficiency of pig enterprises. Chinese herbal medicines contain a wide range of bioactive compounds that offer various nutritional and health benefits to animals, making them commonly utilized as feed additives in livestock (30). Prior researches have shown that the utilization of CHMs as potential alternatives to antibiotic growth promoters (AGPs) for enhancing the reproductive performance of pigs has gained widespread recognition (31). In this study, we found that supplementing perinatal sows with 2 kg/t and 3 kg/t QZGSP significantly improved their reproductive performance, immunity, and breast milk quality. Overall, QZGSP is a beneficial feed additive for perinatal sows.
According to the theory of traditional Chinese veterinary medicine, “qi and blood deficiency stagnation” is a major issue for sows before and after farrowing, which directly affects the health status and reproductive performance of sows. Therefore, the focus of sow healthcare before and after farrowing should be on addressing “qi and blood” through the use of Chinese herbs that replenish qi and blood, soothe the liver, strengthen the spleen, ultimately leading to improve production performance and overall health of sows. Some experiments have demonstrated that the including A. membranaceus in the basal diet leads to an augmentation in animal feed intake (32), enhances animal body condition, and promotes weight gain (33). Supplementing postpartum dairy cows with A. membranaceus significantly alleviated the extent of weight loss (34). Wu et al. (35) reported that a combination of soybean isoflavone (SI) and astragalus polysaccharide (APS) significantly improved average daily feed intake and lactation yield in lactating sows. A. macrocephala Koidz improved average daily feed intake in piglets (36). Dietary supplementation with 3% Aerial parts of A. sinensis significantly increased feed consumption in broiler (37). Dietary supplementation with peony pollen improved feed intake in common carp (38). Dietary supplementation of A. membranaceus or/and B. chinense significantly increased the specific growth rate and feed conversion ratio of shrimp (39). Dietary supplementation of Bupleurum falcatum L saikosaponins restored the growth performance of chickens exposed to NH3 through enhancing DWG and reducing FCR (40). The feed intake and body condition of periparturient sows are crucial for the lactation performance of sows and the growth and development of piglets (41). Sow farrowing duration is correlated with hemoglobin concentration (42), while highly productive sows may experience decrease hemoglobin levels after farrowing, resulting in weakness, fatigue, loss of appetite, prolonged farrowing time, and increased stillbirth rates (43). In our study, we found that supplemental feeding of QZGSP significantly increased hemoglobin concentration in whole blood of sows. In this study, we found that supplemental feeding of 2 kg/t and 3 kg/t QZGSP to perinatal sows significantly improved average daily feed intake and milk yield in sows while reduced farrowing duration in sows and backfat thickness loss. This phenomenon may be attributed to the synergistic effect of multiple bioactive ingredients in Chinese herbs of QZGSP, which increased feed intake, lactation performance and hemoglobin concentration of sows, thus shortening farrowing and reducing backfat thickness loss, and thus improving reproductive performance of sows to a certain extent.
Each component in the blood serves as the material basis for metabolism, and changes in its content can reflect alterations in metabolic function, nutrient metabolism, as well as the functioning of tissues and organs within the body. Ultimately, these changes can indicate the health or disease status of livestock and poultry (44). Aberrant levels of white blood cells (WBC) may suggest potential immune dysfunction within the body, thus signifying their significance as immunological markers (45). Red blood cells (RBC) play essential roles in transporting oxygen, carbon dioxide, and modulating the immune system. Hemoglobin (HGB) is crucial for their transport function. Lan et al. (46) reported that the use of an herbal mixture containing A. membranaceus, Codonopsis pilosula, and allicin as a dietary supplement significantly increased white blood cell concentrations in finishing pigs compared to the control group. Jiang et al. (47) reported that APS significantly enhances the immunological function of erythrocytes in chicken infected with infectious Bursa disease virus (BDV). Atractylodes lancea rhizome polysaccharide (ALP) effectively increased the blood cell count, including white blood cells, hemoglobin, and red blood cells, in immunosuppressed mice (48). Angelica sinensis at doses of 200 and 400 mg/kg/d significantly increased the levels of white blood cells (WBC) and red blood cells (RBC) in mice with aplastic anemia (49). In this study, supplemental feeding of 2 kg/t and 3 kg/t QZGSP to perinatal sows significantly elevate WBC, RBC, and HGB concentrations within the normal physiological range. These findings are consistent with prior research reports and suggest that supplemental feeding of QZGSP to perinatal sows enhances the body’s ability to transport oxygen, and a large number of red blood cells and hemoglobin combine to transport to various tissues and organs, thereby improving the body’s metabolic capacity as well as having a significant effect on the body’s immune performance.
The synthesis and secretion of milk are complex physiological processes regulated by the neuroendocrine system and involve a variety of endocrine hormones (50). After delivery, the concentration of estrogen and progesterone in the blood is greatly reduced in sows. This reduction lifts their inhibitory effect on prolactin, allowing prolactin to bing to mammary follicular epithelial receptors, thereby initiating and maintaining lactation. In addition, the sow serum prolactin concentrations increase due to the stimulation caused by piglets suckling on the sows. Previous studies have reported serum prolactin levels in primiparous sows are positively correlated with colostrum production, suggesting that higher concentrations of prolactin lead to an increase in colostrum production (51, 52). Other studies have shown that supplemental feeding of Astragalus to dairy cows after parturition can increase the level of prolactin secretion and milk production in dairy cows (34). Flavonoids found in Astragalus have estrogen-like effects (53, 54), which can stimulate prolactin synthesis and secretion in lactating sows by affecting the gonadal axis (55). In the study, supplemental feeding of 2 kg/t and 3 kg/t QZGSP to periparturient sows significantly increased estrogen and prolactin levels to some extent, which may be related to the regulation of hormone metabolism levels in sows after absorbing different levels of active components of the herbs in QZGSP. The levels of various hormones are different in different production stages of sows, and the specific mechanism of QZGSP needs to be further investigated.
AST and ALT are commonly chosen as key indicators for diagnosing liver diseases in clinical practice (56). Elevation of plasma AST and ALT generally reflects hepatocyte damage (57). Previous research has demonstrated that Angelica and A. Polysaccharide can dramatically lower serum AST and ALT levels in CCl4-treated mice, consequently reducing CCl4-induced liver injury (58). A. radix could decrease serum AST and ALT levels as well as ameliorate hepatic pathological damages caused by cisplatin (59). Adding 200 mg/kg or 400 mg/kg prepared A. macrocephala Koidz to a high-energy and low-protein laying hens diet reduces the levels of AST and ALT in plasma (60). R. Bupleuri exerts a significant hepatoprotective effect against acetaminophen (APAP)-induced acute liver injury by reducing the levels of AST and ALT in serum (61). Experiments on ethanol-induced acute liver injury showed that Angelica sinensis polysaccharide (ASP) reduced the expression of aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) (62). In this study, supplemental feeding of 2 kg/t and 3 kg/t QZGSP significantly decreased serum AST and ALT levels in sows, which was consistent with these reports, confirming supplemental feeding of QZGSP to perinatal sows could improve the liver health and alleviate oxidative damage to the livers.
Supplemental feeding of QZGSP to perinatal sows also resulted in improvements in the postpartum immunity of sows. We examined immunoglobulin and cytokine levels in sow serum, colostrum and milk to assess maternal antibody levels and transfer of passive immunity. As the main reactive substances of the humoral immune response, Ig levels can reflect the body’s immune function accurately (63). Previous research has shown that supplementing the diet with APS significantly increases levels of IgG and IgM in sow colostrum (64). Supplemental feeding of soybean isoflavone and astragalus polysaccharide mixture to lactating sows significantly increased the levels of IgA in colostrum (35). Hao et al. (32) demonstrated a significant enhancement in serum levels of IgA and IgG when 15 g/kg Astragalus powder was included in the diet of fattening lambs. Similarly, Xia et al.’s research revealed that Astragalus polysaccharide dietary supplementation effectively stimulated the secretion of IgA and IgG in the serum of weaned rabbits (65). The mice immunized with PCV2 antigen adsorbed A. sinensis polysaccharide (ASP)—Poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA)—polyethylenimine (PEI) nanoparticles significantly enhanced PCV2-specific IgG immune response (66). Our findings are consistent with previous studies, indicating that supplemental feeding of QZGSP to perinatal sows significantly enhances the synthesis of immunoglobulins. From the role of cytokines in inflammation, certain cytokines (e.g., TNF-α and IL-1β) are commonly referred to as pro-inflammatory cytokines due to their involvement in promoting inflammation. Conversely, other cytokines (such as IL-10 and IL-4) are known as anti-inflammatory cytokines due to their ability to inhibit inflammation (67). Flavonoids are the important active healthcare components in A. membranaceus (68). Dietary supplementation of a citrus total flavonoid extract in lactating dairy cows linearly decreased serum TNF-α and IL-1β levels (69). Feeding crude extracts of A. macrocephala and Glycyrrhiza Radix to a chicken model of oxidative stress significantly reduced the levels of TNF-α, while increasing the levels of IL-10 and IL-4 in serum (70). Danggui Buxue decoction (DBD) significantly reduced the levels of TNF-α, IL-1β in serum from GK rats with type 2 diabetes (71). Our results are consistent with previous reports, and the general trend of changes in sow cytokine levels aligns with the expectation that QZGSP can significantly enhance immunity in sows and outperform the other test groups. This suggests that supplementing periparturient sows with QZGSP can effectively regulate their cytokine secretion and enhance their cellular immunity level. In conclusion, supplementing periparturient sows with 2 kg/t or 3 kg/t of QZGSP significantly enhances their immunity after parturition. However, due to the influence of the African swine fever epidemic, there is a scarcity of literature related to the effect of Chinese herbs contained in QZGSP on sow health and production performance. Therefore, comprehensive comparisons cannot be made. Nevertheless, this remains the direction for future efforts by our group. Further in-depth research is still needed to investigate the specific mechanism by which periparturient sows’ immunity is enhanced through supplemental feeding of QZGSP.
Breast milk serve as the main nutritional source for newborn piglets, providing essential carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins (immunoglobulins) that are crucial for both nutrition and immune function (72). Therefore, the composition of breast milk can be used as an indicator of the nutritional levels of lactating sows. Previous research has shown that APS improves the components in sow colostrum and/or milk (64). Supplemental feeding of a mixture of soy isoflavones and A. polysaccharides increased lactation performance in sows, but did not significantly improve colostrum composition (35). Our findings revealed that supplementing perinatal sows with 2 kg/t and 3 kg/t of QZGSP significantly increases fat and protein contents in colostrum and milk compared to other experimental groups. This finding is consistent with previous reports, which suggests that supplemental feeding of QZGSP to periparturient sows significantly improves the conventional nutrient composition of sow milk. Breast milk not only plays a crucial role in nourishing and protecting newborn mammals but also shapes the development of their intestinal microbiota. α- and β-diversity are mainly used to assess the diversity of microflora. Our results shown that the diversity index (including Chao1 and Ace) of milk microbiota in sows from TRT3 and TRT4 groups was significantly higher than that in TRT2 group on day 21 of lactation, while there was no difference in the α-diversity of colostrum microbiota among different groups, which was inconsistent with Chen et al.’s research (73), and may be due to herd breed, rearing environment, and dietary addition of drugs. PCoA analysis based on unweighted_unifrac distance revealed significant differences was observed in colostrum and milk flora between the CON group and the TRT3 and TRT4 groups on days 0 and 21 of lactation, as well as a significant difference in milk flora between TRT1 and TRT4 groups on day 11 of lactation. These findings suggest that treatment with TRT3 and TRT4 can effectively modulate both the species composition and abundance of major colostrum and milk flora. Overall, supplemental feeding of QZGSP to perinatal sows could improve the diversity of microflora in sows’ colostrum and milk.
Supplemental feeding of QZGSP to perinatal sows resulted in changes in the microbiota structure in sow’s colostrum and milk. Specifically, the relative abundance of Escherichia-Shigella, Staphylococcus, and Streptococcus was decreased in the TRT3 and/or TRT4 groups on day 0 of lactation compared to other experimental groups. Species difference analysis showed that at the phylum level, the abundance of Bacteroidota, Desulfobacterota, and Actinobacteriota in the TRT4 group was significantly higher than that in the TRT1 group on days 0 and day 21 of lactation. At the genus level, the abundance of Rothia in the TRT4 group was significantly higher than that in the TRT1 group on day 21 of lactation. Previous reported that a combination herbal medicine with A. membranaceus and A. macrocephala Koidz. as the main components significantly reduced the relative abundance of Escherichia-Shigella in the intestinal tract of broiler chickens (74). Feeding fermented Chinese medicine to lambs can regulate the sensitivity of intestinal flora to pathogenic microorganisms such as Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus, reducing the relative abundance of harmful bacteria (75). Polysaccharides derived from A. membranaceus and Glycyrrhiza uralensis significantly decreased the abundance of Bacteroidetes and Desulfovibrio in broilers (76). Oral administration of A. sinensis polysaccharide (ASP) reduces mammary inflammation and damage to the blood-milk barrier (BMB) induced by Staphylococcus aureus in mice, primarily through the modulation of intestinal flora (77). The aqueous extract of P. lactiflora altered the abundance of intestinal microbiota in mice with dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis and reduced the levels of Bacteroides and Escherichia-Shigella (23). These results are consistent with our original study reporting (78), whereas maternal gut bacteria can enter breast milk via the entero-mammary pathway, this in turn affects neonatal intestinal colonization and immune system maturation (79). In the present experiment, supplemental feeding of 2 kg/t and/or 3 kg/t QZGSP to periparturient sows significantly decreased the relative abundance of harmful bacteria and increased the relative abundance of beneficial bacteria in sow colostrum and breast milk, suggesting that supplemental feeding of QZGSP to periparturient sows may affect the composition and structure of the microflora of sow colostrum and breast milk through modulation of the intestinal flora. In general, an increase in probiotic bacteria and a decrease in pathogenic bacteria in animal milk may contribute to improved milk quality in sows. It is reasonable to assume that the changes in the associated bacteria were caused by the herbal complexes. In conclusion, herbs play a very important role in regulating the microflora balance of breast milk during the perinatal period. Meanwhile, herbs, as alternatives to antibiotics and as feed additives, have great potential to improve the reproductive performance, immunity and breast milk quality of periparturient sows, but it is still important to note that the composition of herbs is very complex, and their mechanism of action needs to be investigated in detail in order to ensure their successful application in periparturient sows’ diets.
In summary, supplemental feeding of QZGSP to perinatal sows significantly improved reproductive performance, immunity, and breast milk quality in sows. The optimum dosage of QZGSP in this study was 2 kg/t.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found at: NCBI, PRJNA1123000.
The animal studies were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Hebei Agricultural University (grant no. 2022161). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent was obtained from the owners for the participation of their animals in this study.
XD: Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XW: Data curation, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. CL: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. LZ: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YB: Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. WS: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XZ: Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFD1801104), Hebei Modern Agricultural Industry Technology System Innovation Team Construction Project (HBCT2024110202), and Research project of basic scientific research business expenses of Hebei provincial higher education institutions (KY20230003).
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
1. Devillers, N, Le Dividich, J, and Prunier, A. Influence of colostrum intake on piglet survival and immunity. Animal. (2011) 5:1605–12. doi: 10.1017/s175173111100067x
2. Ferrari, CV, Sbardella, PE, Bernardi, ML, Coutinho, ML, Vaz, IS Jr, Wentz, I, et al. Effect of birth weight and colostrum intake on mortality and performance of piglets after cross-fostering in sows of different parities. Prev Vet Med. (2014) 114:259–66. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2014.02.013
3. Berchieri-Ronchi, CB, Kim, SW, Zhao, Y, Correa, CR, Yeum, KJ, and Ferreira, ALA. Oxidative stress status of highly prolific sows during gestation and lactation. Animal. (2011) 5:1774–9. doi: 10.1017/s1751731111000772
4. Zhao, Y, and Kim, SW. Oxidative stress status and reproductive performance of sows during gestation and lactation under different thermal environments. Asian Australas J Anim Sci. (2020) 33:722–31. doi: 10.5713/ajas.19.0334
5. Zhao, Y, Flowers, WL, Saraiva, A, Yeum, KJ, and Kim, SW. Effect of social ranks and gestation housing systems on oxidative stress status, reproductive performance, and immune status of sows. J Anim Sci. (2013) 91:5848–58. doi: 10.2527/jas.2013-6388
6. Zhang, S, Wu, Z, Heng, J, Song, H, Tian, M, Chen, F, et al. Combined yeast culture and organic selenium supplementation during late gestation and lactation improve preweaning piglet performance by enhancing the antioxidant capacity and milk content in nutrient-restricted sows. Anim Nutr. (2020) 6:160–7. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2020.01.004
7. Sutherland, MA, Niekamp, SR, Rodriguez-Zas, SL, and Salak-Johnson, JL. Impacts of chronic stress and social status on various physiological and performance measures in pigs of different breeds. J Anim Sci. (2006) 84:588–96. doi: 10.2527/2006.843588x
8. Li, Q, Yang, S, Chen, F, Guan, W, and Zhang, S. Nutritional strategies to alleviate oxidative stress in sows. Anim Nutr. (2022) 9:60–73. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2021.10.006
9. Lu, S, Sun, X, Zhou, Z, Tang, H, Xiao, R, Lv, Q, et al. Mechanism of Bazhen decoction in the treatment of colorectal cancer based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental validation. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1235575. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1235575
10. Lien, TF, Lin, KJ, Yang, LL, and Chen, LG. Effects of supplemental levels of bazhen on growth performances, serum traits, immunity, meat quality and antioxidant activity of Taiwan country chickens. Asian Australas J Anim Sci. (2013) 26:675–82. doi: 10.5713/ajas.2012.12086
11. Geng, J, Jin, W, Hao, J, Huo, M, Zhang, Y, Xie, C, et al. Effects of dietary modified Bazhen on reproductive performance, immunity, breast milk microbes, and metabolome characterization of sows. Front Microbiol. (2021) 12:758224. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.758224
12. Lien, TF, Horng, YM, and Wu, CP. Feasibility of replacing antibiotic feed promoters with the Chinese traditional herbal medicine Bazhen in weaned piglets. Livest Sci. (2007) 107:97–102. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2006.09.008
13. Chun, Z, Luo, X, Chen, D, Yu, M, Cheng, Y, Yang, Z, et al. The influence of Bazhen decoction on hematopoietic modulator in anaemic mice. J Biomed Eng. (2004) 21:727–31.
14. Song, E, Fu, J, Xia, X, Su, C, and Song, Y. Bazhen decoction protects against acetaminophen induced acute liver injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in mice. PLoS One. (2014) 9:e107405. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107405
15. Zheng, Y, Ren, W, Zhang, L, Zhang, Y, Liu, D, and Liu, Y. A review of the pharmacological action of Astragalus polysaccharide. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:349. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00349
16. Du, Y, Wan, H, Huang, P, Yang, J, and He, Y. A critical review of Astragalus polysaccharides: from therapeutic mechanisms to pharmaceutics. Biomed Pharmacother. (2022) 147:112654. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112654
17. Yang, L, Yu, H, Hou, A, Man, W, Wang, S, Zhang, J, et al. A review of the ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, pharmacology, application, quality control, processing, toxicology, and pharmacokinetics of the dried rhizome of Atractylodes macrocephala. Front Pharmacol. (2021) 12:727154. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.727154
18. Li, X, Rao, Z, Xie, Z, Qi, H, and Zeng, N. Isolation, structure and bioactivity of polysaccharides from Atractylodes macrocephala: a review. J Ethnopharmacol. (2022) 296:115506. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115506
19. Wei, WL, Zeng, R, Gu, CM, Qu, Y, and Huang, LF. Angelica sinensis in China-a review of botanical profile, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and chemical analysis. J Ethnopharmacol. (2016) 190:116–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2016.05.023
20. Nai, J, Zhang, C, Shao, H, Li, B, Li, H, Gao, L, et al. Extraction, structure, pharmacological activities and drug carrier applications of Angelica sinensis polysaccharide. Int J Biol Macromol. (2021) 183:2337–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.05.213
21. Tan, YQ, Chen, HW, Li, J, and Wu, QJ. Efficacy, chemical constituents, and pharmacological actions of Radix Paeoniae Rubra and Radix Paeoniae Alba. Front Pharmacol. (2020) 11:1054. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01054
22. Xu, JX, Xu, J, Cao, Y, Zhu, YJ, Li, XY, Ge, DZ, et al. Modern research progress of traditional Chinese medicine Paeoniae Radix Alba and prediction of its Q-markers. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. (2021) 46:5486–95. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210818.201
23. Bao-Fei, Y, Xi, C, Ya-Fang, C, Sheng-Jin, L, Chen-Xin, X, Ling, C, et al. Aqueous extract of Paeoniae Radix Alba (Paeonia lactiflora pall.) ameliorates DSS-induced colitis in mice by tunning the intestinal physical barrier, immune responses, and microbiota. J Ethnopharmacol. (2022) 294:115365. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115365
24. Wang, Z, Tian, L, Xiao, Y, Zhao, M, Chang, Y, Zhou, Y, et al. Quantitative and differential analysis between Bupleurum chinense DC. And Bupleurum scorzonerifolium Willd. Using HPLC-MS and GC-MS coupled with multivariate statistical analysis. Molecules. (2023) 28:5630. doi: 10.3390/molecules28155630
25. Chen, C, Gong, W, Tian, J, Gao, X, Qin, X, du, G, et al. Radix Paeoniae Alba attenuates Radix Bupleuri-induced hepatotoxicity by modulating gut microbiota to alleviate the inhibition of saikosaponins on glutathione synthetase. J Pharm Anal. (2023) 13:640–59. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2023.04.016
26. Li, X, Li, X, Huang, N, Liu, R, and Sun, R. A comprehensive review and perspectives on pharmacology and toxicology of saikosaponins. Phytomedicine. (2018) 50:73–87. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.174
27. Xu, T, Zhang, H, Wang, S, Xiang, Z, Kong, H, Xue, Q, et al. A review on the advances in the extraction methods and structure elucidation of Poria cocos polysaccharide and its pharmacological activities and drug carrier applications. Int J Biol Macromol. (2022) 217:536–51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.07.070
28. Wang, L, Zhou, GB, Liu, P, Song, JH, Liang, Y, Yan, XJ, et al. Dissection of mechanisms of Chinese medicinal formula Realgar-indigo naturalis as an effective treatment for promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. (2008) 105:4826–31. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0712365105
29. Keith, CT, Borisy, AA, and Stockwell, BR. Multicomponent therapeutics for networked systems. Nat Rev Drug Discov. (2005) 4:71–8. doi: 10.1038/nrd1609
30. Abdallah, A, Zhang, P, Zhong, Q, and Sun, Z. Application of traditional Chinese herbal medicine by-products as dietary feed supplements and antibiotic replacements in animal production. Curr Drug Metab. (2019) 20:54–64. doi: 10.2174/1389200219666180523102920
31. Gong, J, Yin, F, Hou, Y, and Yin, Y. Review: Chinese herbs as alternatives to antibiotics in feed for swine and poultry production: potential and challenges in application. Can J Anim Sci. (2014) 94:223–41. doi: 10.4141/cjas2013-144
32. Hao, X, Wang, P, Ren, Y, Liu, G, Zhang, J, Leury, B, et al. Effects of Astragalus membranaceus roots supplementation on growth performance, serum antioxidant and immune response in finishing lambs. Asian Australas J Anim Sci. (2020) 33:965–72. doi: 10.5713/ajas.19.0295
33. Wu, S. Effect of dietary Astragalus membranaceus polysaccharide on the growth performance and immunity of juvenile broilers. Poult Sci. (2018) 97:3489–93. doi: 10.3382/ps/pey220
34. Huang, Y, Yan, Q, Jiang, M, Guo, S, Li, H, Lin, M, et al. Astragalus membranaceus additive improves serum biochemical parameters and reproductive performance in postpartum dairy cows. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:952137. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.952137
35. Wu, H, Yang, J, Wang, S, Zhang, X, Hou, J, Xu, F, et al. Effects of soybean Isoflavone and Astragalus polysaccharide mixture on colostrum components, serum antioxidant, immune and hormone levels of lactating sows. Animals. (2021) 11:132. doi: 10.3390/ani11010132
36. Xu, CL, Zhao, YF, Shang, XY, and Niu, WN. The effects of supplementing diets with Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz rhizomes on growth performance and immune function in piglets. J. Animal Feed Sci. (2012) 21:302–12. doi: 10.22358/jafs/66078/2012,
37. Xiangmin, Z, Shengyan, H, Jiawei, Z, Yali, Y, Lulu, L, Likun, S, et al. Aerial parts of Angelica sinensis supplementation for improved broiler growth and intestinal health. Poult Sci. (2024) 103:103473. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.103473
38. Ren, H, Huang, Y, and Lin, L. Effects of dietary supplementation with peony pollen on growth, intestinal function, fillet quality and fatty acids profiles of common carp. Aquac Nutr. (2021) 27:908–17. doi: 10.1111/anu.13235
39. Cornel, A, Weilong, W, Hongyu, L, Yue, Z, and Xuxiong, H. The effect of dietary supplementation of Astragalus membranaceus and Bupleurum chinense on the growth performance, immune-related enzyme activities and genes expression in white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2020) 107:379–84. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2020.10.014
40. Gang, S, Dan, X, Chonglin, R, Lizi, Y, and Juchun, L. Protective effect of dietary supplementation of Bupleurum falcatum L saikosaponins on ammonia exposure–induced ileum injury in broilers. Poult Sci. (2021) 100:100803. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.10.057
41. Hansen, AV, Lauridsen, C, Sørensen, MT, Bach Knudsen, KE, and Theil, PK. Effects of nutrient supply, plasma metabolites, and nutritional status of sows during transition on performance in the next lactation. J Anim Sci. (2012) 90:466–80. doi: 10.2527/jas.2011-3984
42. Liu, Y, Zhou, Q, Theil, PK, Fang, Z, Lin, Y, Xu, S, et al. The differences in energy metabolism and redox status between sows with short and long farrowing duration. Animal. (2021) 15:100355. doi: 10.1016/j.animal.2021.100355
43. Rootwelt, V, Reksen, O, Farstad, W, and Framstad, T. Postpartum deaths: piglet, placental, and umbilical characteristics. J Anim Sci. (2013) 91:2647–56. doi: 10.2527/jas.2012-5531
44. Dondi, F, Vasylyeva, K, Serafini, F, Gruarin, M, Troìa, R, Giunti, M, et al. Heinz body-related interference with leukocyte and erythrocyte variables obtained by an automated hematology analyzer in cats. J Vet Diagn Invest. (2019) 31:704–13. doi: 10.1177/1040638719863088
45. Sealock, JM, Lee, YH, Moscati, A, Venkatesh, S, Voloudakis, G, Straub, P, et al. Use of the PsycheMERGE network to investigate the association between depression polygenic scores and white blood cell count. JAMA Psychiatry. (2021) 78:1365–74. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.2959
46. Lan, RX, Park, JW, Lee, DW, and Kim, IH. Effects of Astragalus membranaceus, Codonopsis pilosula and allicin mixture on growth performance, nutrient digestibility, faecal microbial shedding, immune response and meat quality in finishing pigs. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr. (2017) 101:1122–9. doi: 10.1111/jpn.12625
47. Junbing, J, Caihong, W, Hai, G, Jiande, S, and Hongquan, L. Effects of astragalus polysaccharides on immunologic function of erythrocyte in chickens infected with infectious bursa disease virus. Vaccine. (2010) 28:5614–6. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.06.025
48. Wang, D, Dong, Y, Xie, Y, Xiao, Y-L, Ke, C, Shi, K, et al. Atractylodes lancea rhizome polysaccharide alleviates immunosuppression and intestinal mucosal injury in mice treated with cyclophosphamide. J Agric Food Chem. (2023) 71:17112–17129. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c05173
49. Chen, Z, Cheng, L, Zhang, J, and Cui, X. Exploring the mechanism by which Angelica sinensis improves haematopoietic function in aplastic anaemia. Aging (Albany N Y). (2024) 16:11535–52. doi: 10.18632/aging.205971
50. Sandrine, T, and Edith, H-H. Physiology of milk secretion. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2017) 31:367–84. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2017.10.008
51. Loisel, F, Farmer, C, van Hees, H, and Quesnel, H. Relative prolactin-to-progesterone concentrations around farrowing influence colostrum yield in primiparous sows. Domest Anim Endocrinol. (2015) 53:35–41. doi: 10.1016/j.domaniend.2015.04.005
52. Foisnet, A, Farmer, C, David, C, and Quesnel, H. Relationships between colostrum production by primiparous sows and sow physiology around parturition. J Anim Sci. (2010) 88:1672–83. doi: 10.2527/jas.2009-2562
53. Park, JS, Sung, HK, Kim, SK, Lee, HS, and Shin, SM. Efficacy of Rubus coreanus Miq. and Astragalus membranaceus Bunge extract for postmenopausal syndrome: a randomised, double-blind, placebo comparative clinical trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2022) 2022:4066054–8. doi: 10.1155/2022/4066054
54. Li, X, Huang, C, Sui, CL, Liang, CM, Qi, GY, Ren, QY, et al. Formononetin, J1 and J2 have different effects on endothelial cells via EWSAT1-TRAF6 and its downstream pathway. J Cell Mol Med. (2020) 24:875–85. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14797
55. Suresh, L, and Radfar, L. Pregnancy and lactation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. (2004) 97:672–82. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2004.02.002
56. Chen, VL, Du, X, Chen, Y, Kuppa, A, Handelman, SK, Vohnoutka, RB, et al. Genome-wide association study of serum liver enzymes implicates diverse metabolic and liver pathology. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:816. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20870-1
57. Xuan, Y, Wu, D, Zhang, Q, Yu, Z, Yu, J, Zhou, D, et al. Elevated ALT/AST ratio as a marker for NAFLD risk and severity: insights from a cross-sectional analysis in the United States. Front Endocrinol. (2024) 15:1457598. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1457598
58. Pu, X, Fan, W, Yu, S, Li, Y, Ma, X, Liu, L, et al. Polysaccharides from Angelica and Astragalus exert hepatoprotective effects against carbon-tetrachloride-induced intoxication in mice. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. (2015) 93:39–43. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2014-0331
59. Ling, W, Xian-long, D, Xue-mei, Q, and Zhen-yu, L. Investigating the inter-individual variability of Astragali Radix against cisplatin-induced liver injury via 16S rRNA gene sequencing and LC/MS-based metabolomics. Phytomedicine. (2022) 101:154107. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154107
60. Miao, YF, Gao, XN, Xu, DN, Li, MC, Gao, ZS, Tang, ZH, et al. Protective effect of the new prepared Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz polysaccharide on fatty liver hemorrhagic syndrome in laying hens. Poult Sci. (2021) 100:938–48. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.11.036
61. Yu-Xin, W, Yi, DU, Xia-Fei, LIU, Fang-Xiu, Y, Xiao, WU, Li, T, et al. A hepatoprotection study of Radix Bupleuri on acetaminophen-induced liver injury based on CYP450 inhibition. Chin J Nat Med. (2019) 17:517–24. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(19)30073-1
62. Yu, Z, Haoyu, W, Yuheng, Z, Zhijing, W, Junxi, L, Fang, C, et al. Degradation of Angelica sinensis polysaccharide: structures and protective activities against ethanol-induced acute liver injury. Carbohydr Polym. (2024) 328:121745. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2023.121745
63. Prates, JAM, Freire, JPB, de Almeida, AM, Martins, C, Ribeiro, DM, Osório, H, et al. Influence of dietary supplementation with an amino acid mixture on inflammatory markers, immune status and serum proteome in LPS-challenged weaned piglets. Animals. (2021) 11:1143. doi: 10.3390/ani11041143
64. Tan, L, Wei, T, Yuan, A, He, J, Liu, J, Xu, D, et al. Dietary supplementation of Astragalus polysaccharides enhanced immune components and growth factors EGF and IGF-1 in sow colostrum. J Immunol Res. (2017) 2017:9253208–6. doi: 10.1155/2017/9253208
65. Mingming, X, Haihua, Z, Hongli, L, and Sufen, L. Effect of sietary Astragalus polysaccharide on growth performance, apparent digestibility of nutrients serum biochemical indices and immune organs index of weaned rabbit. Feed Res. (2023) 46:55–60. doi: 10.13557/j.cnki.issn1002-2813.2023.06.012
66. Pengfei, G, Adelijiang, W, Siyuan, W, Yue, Z, and Zhenguang, L. Polyethylenimine-coated PLGA nanoparticles-encapsulated Angelica sinensis polysaccharide as an adjuvant to enhance immune responses. Carbohydr Polym. (2019) 223:115128. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115128
67. Rossol, M, Heine, H, Meusch, U, Quandt, D, Klein, C, Sweet, MJ, et al. LPS-induced cytokine production in human monocytes and macrophages. Crit Rev Immunol. (2011) 31:379–446. doi: 10.1615/critrevimmunol.v31.i5.20
68. Lanting, Q, Yuxin, M, Lamei, Z, Zheng, Y, Huigai, S, and James, ER. Combined transcriptome and metabolome analysis highlights a central role of AmMYB30 in MeJA induced flavonoid accumulation in Astragalus membranaceus. Food Biosci. (2024) 61:104565. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2024.104565
69. Zhao, Y, Yu, S, Li, L, Zhao, H, Li, Y, Jiang, L, et al. Feeding citrus flavonoid extracts decreases bacterial endotoxin and systemic inflammation and improves immunometabolic status by modulating hindgut microbiome and metabolome in lactating dairy cows. Anim Nutr. (2023) 13:386–400. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2023.03.007
70. Zhang, C, Wang, S, Han, Y, Zheng, A, Liu, G, Meng, K, et al. Effects of crude extract of Glycyrrhiza Radix and Atractylodes macrocephala on immune and antioxidant capacity of SPF white Leghorn chickens in an oxidative stress model. Antioxidants. (2024) 13:578. doi: 10.3390/antiox13050578
71. Wang, WK, Fan, L, Ge, F, Li, Z, Zhu, J, Yin, K, et al. Effects of Danggui Buxue decoction on host gut microbiota and metabolism in GK rats with type 2 diabetes. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:1029409. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1029409
72. Zhang, S, Chen, F, Zhang, Y, Lv, Y, Heng, J, Min, T, et al. Recent progress of porcine milk components and mammary gland function. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. (2018) 9:77. doi: 10.1186/s40104-018-0291-8
73. Chen, W, Mi, J, Lv, N, Gao, J, Cheng, J, Wu, R, et al. Lactation stage-dependency of the sow milk microbiota. Front Microbiol. (2018) 9:945. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00945
74. Sun, Y, Zhang, M, Shi, D, Dai, X, and Li, X. Effects of designed herbal formula on growth performance, blood indices, organ traits, and cecum microbiology in broilers. Vet Sci. (2024) 11:107. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11030107
75. Fan, J, Cui, H, Mu, Z, Yao, C, Yang, M, Jin, Y, et al. Non-targeted metabolomics analysis of fermented traditional Chinese medicine and its impact on growth performance, serum biochemistry, and intestinal microbiome of weaned lambs. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:20385. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71516-x
76. Yingying, Q, Changzhong, L, Yongpeng, G, Wei, Z, Weibing, G, Kyselov, O, et al. Polysaccharides derived from Astragalus membranaceus and Glycyrrhiza uralensis improve growth performance of broilers by enhancing intestinal health and modulating gut microbiota. Poult Sci. (2022) 101:101905. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.101905
77. Ran, X, Li, Y, Guo, W, Li, K, Guo, W, Wang, X, et al. Angelica sinensis polysaccharide alleviates Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis by regulating the intestinal flora and gut metabolites. J Agric Food Chem. (2024) 72:24504–17. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c06094
78. Duan, X, Wang, X, Li, Z, Liu, C, Bao, Y, Shi, W, et al. Effects of supplemental feeding of Chinese herbal mixtures to perinatal sows on antioxidant capacity and gut microbiota of sows and their offspring piglets. Front Microbiol. (2024) 15:1459188. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1459188
Keywords: Chinese herbal mixtures, reproductive performance, immunity, breast milk, sows
Citation: Duan X, Wang X, Li Z, Liu C, Zhang L, Bao Y, Shi W and Zhao X (2024) Effects of supplemental feeding of Chinese herbal mixtures to perinatal sows on reproductive performance, immunity, and breast milk quality of sows. Front. Vet. Sci. 11:1445216. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1445216
Received: 07 June 2024; Accepted: 25 November 2024;
Published: 06 December 2024.
Edited by:
Teketay Anley, Oregon Health and Science University, United StatesReviewed by:
Aoyun Li, Huazhong Agricultural University, ChinaCopyright © 2024 Duan, Wang, Li, Liu, Zhang, Bao, Shi and Zhao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wanyu Shi, c2hpd2FueXUyMDEwQDEyNi5jb20=; Xinghua Zhao, eGlhbnpoYW94aW5naHVhQDE2My5jb20=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.