- 1College of Animal Science and Technology, Yunnan Agricultural University, Kunming, Yunnan, China
- 2College of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, Yunnan Vocational and Technical College of Agriculture, Kunming, Yunnan, China
Melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine) is an essential small molecule with diverse biological functions. It plays several key roles, including regulating the secretion of reproductive hormones and the reproductive cycle, enhancing the functionality of reproductive organs, improving the quality of sperm and eggs, and mitigating oxidative stress in the reproductive system. Melatonin effectively inhibits and scavenges excess free radicals while activating the antioxidant enzyme system and reduces the production of inflammatory factors and alleviates tissue damage caused by inflammation by regulating inflammatory pathways. Additionally, melatonin contributes to repairing the intestinal barrier and regulating the gut microbiota, thereby reducing bacterial and toxin permeation. The use of melatonin as an endogenous hormone in animal husbandry has garnered considerable attention because of its positive effects on animal production performance, reproductive outcomes, stress adaptation, disease treatment, and environmental sustainability. This review explores the characteristics and biological functions of melatonin, along with its current applications in animal production. Our findings may serve as a reference for the use of melatonin in animal farming and future developmental directions.
1 Introduction
Antibiotics play a crucial role in animal husbandry by promoting growth and preventing diseases, but their misuse has led to a series of problems. Antibiotics overuse fosters bacterial resistance, reducing treatment efficacy in humans and animals (1). Furthermore, antibiotic residues in animal products entering the food chain pose health risks, disrupting environmental microbial balance and affecting ecosystem stability (2). Excessive antibiotic use also adversely impacts animal health, disrupts the gut microbiota balance, reduces digestive absorption, and prompts adverse drug reactions (3, 4). Subsequently, many nations have implemented stringent regulations governing antibiotic use in poultry and livestock production, prompting increased research focus on alternative and enhanced additives.
Melatonin is an amine hormone primarily secreted by the pineal gland in the brain, but it is also produced in other tissues such as the gastrointestinal tract, retina, skin, thymus, and immune cells (5). The melatonin secreted by the pineal gland plays a crucial role in regulating circadian rhythms, while extra-pineal melatonin possesses anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and mitochondrial protective properties (6–10). Melatonin receptors—MT1, MT2, and MT3—are widely distributed throughout the human body and perform various physiological functions (11, 12). MT1 regulates the biological clock, MT2 controls periodic melatonin activity, and MT3, part of the quinone reductase family, aids in detoxification. As members of the G protein-coupled receptor family on the cell surface, these receptors facilitate signal transduction, significantly influencing physiological and pathological cellular processes (13, 14).
Melatonin, through interactions with MT1 and MT2 receptors, modulates circadian rhythms, immune responses, antioxidation, neuroprotection, anti-aging, reproductive functions, and cell physiology (15–19). In humans, exogenous melatonin exhibits diverse effects, offering potential benefits in animal husbandry, including circadian regulation, health enhancement, stress reduction, and disease prevention (20). Despite the recognized roles of melatonin, current research has not fully explored its multifaceted effects across different animal species and production systems. The existing studies often focus on isolated functions of melatonin without considering its potential synergistic effects with other management practices. Furthermore, there is a lack of comprehensive reviews that integrate recent findings on melatonin’s impact on various aspects of animal production performance, reproductive outcomes, and stress adaptation. This review provides an overview of the physicochemical properties and biological functions of melatonin, highlighting the latest research findings on its potential to improve health and productivity in animal husbandry and laying the groundwork for prospective applications in animal production.
2 Structure and physicochemical properties of melatonin
Melatonin is an indoleamine compound with a molecular formula of C13H16N2O2, a relative molecular mass of 232.28, and a relative density of 1.175 g/cm3. It is sparingly soluble in water but readily soluble in propylene glycol and 2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (21–23). Melatonin exists as a white crystalline powder with a melting point of approximately 116–118°C and a boiling point of 374.44°C. It has a relatively short half-life (30–50 min) and low oral bioavailability (9–33%) (24). Following intravenous or oral administration, melatonin is rapidly metabolized primarily by the liver and kidneys (25). Originally extracted from bovine brain pineal glands in 1917, the name “melatonin” stems from its ability to lighten frogs’ dark skin.
Melatonin is synthesized predominantly in the pineal gland in response to light exposure. Intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells receive light during the day and initiate a neural signal cascade via the retinohypothalamic tract. This neural pathway involves the suprachiasmatic nucleus, paraventricular nucleus, brainstem, spinal cord (T1–T3 levels), and superior cervical ganglion, culminating in the pineal gland. Synthesis begins when tryptophan is converted to 5-hydroxytryptophan by tryptophan hydroxylases. Subsequently, 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase removes CO2 from 5-hydroxytryptophan to produce 5-hydroxytryptamine, also known as serotonin. Serotonin is transformed into N-acetylserotonin through serotonin N-acetyl transferase, aided by acetyl coenzyme A. Finally, N-acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase (ASMT) catalyzes the methylation of N-acetylserotonin to melatonin (Figure 1) (17, 18). Melatonin synthesis typically commences after sunset as the pineal gland converts serotonin to melatonin, releasing it into the bloodstream and impacting various organs (Figure 1). In addition, mitochondria from various organs can produce melatonin for localized use (26).
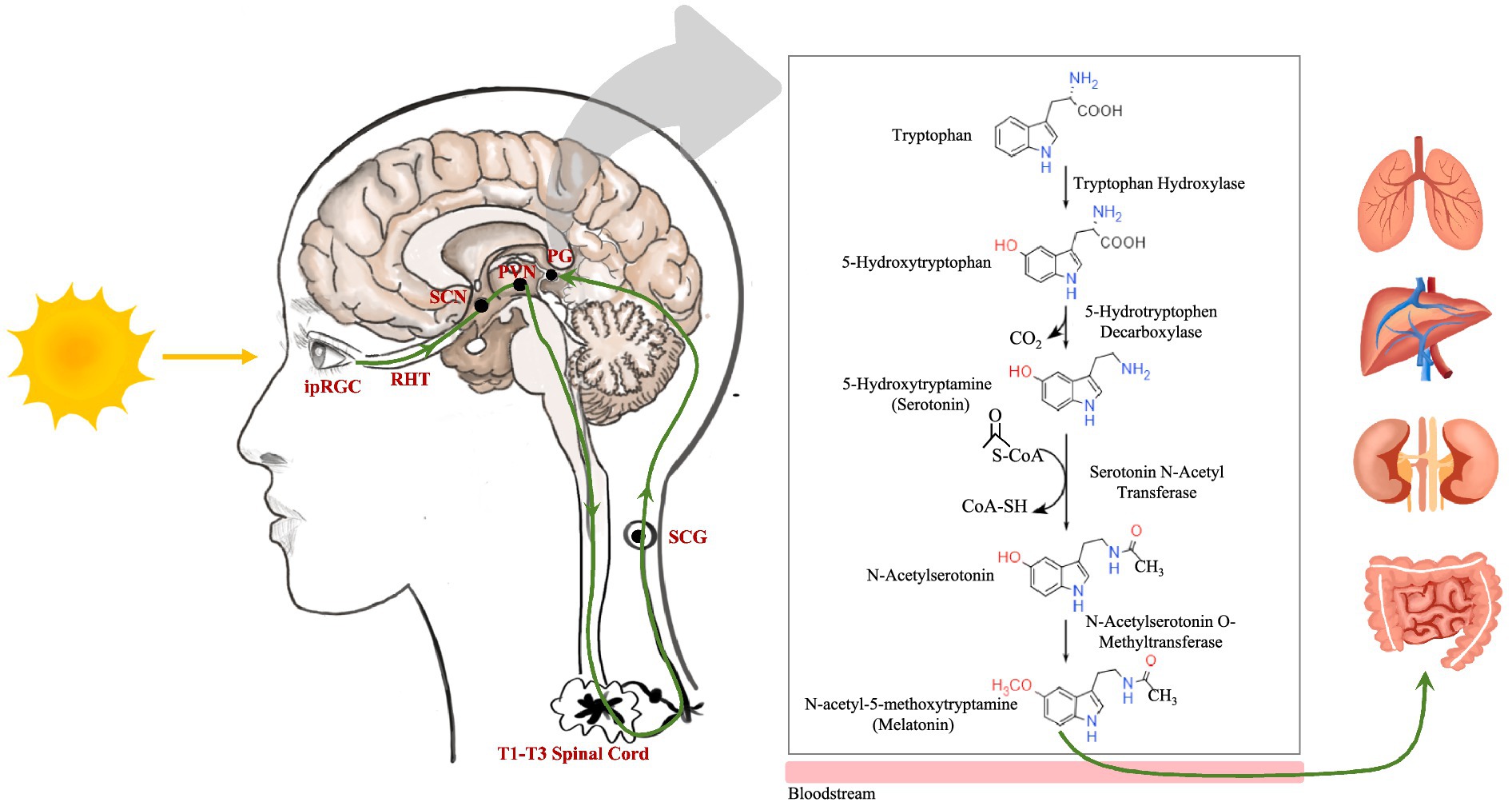
Figure 1. The neuroanatomical pathway of light stimulation on the pineal gland and the melatonin metabolic pathway. ipRGC, intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cell; RHT, retinohypothalamic tract; SCN, suprachiasmatic nucleus; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; SCG, superior cervical ganglion; PG, pineal gland.
3 Biological function of melatonin
3.1 Antioxidation
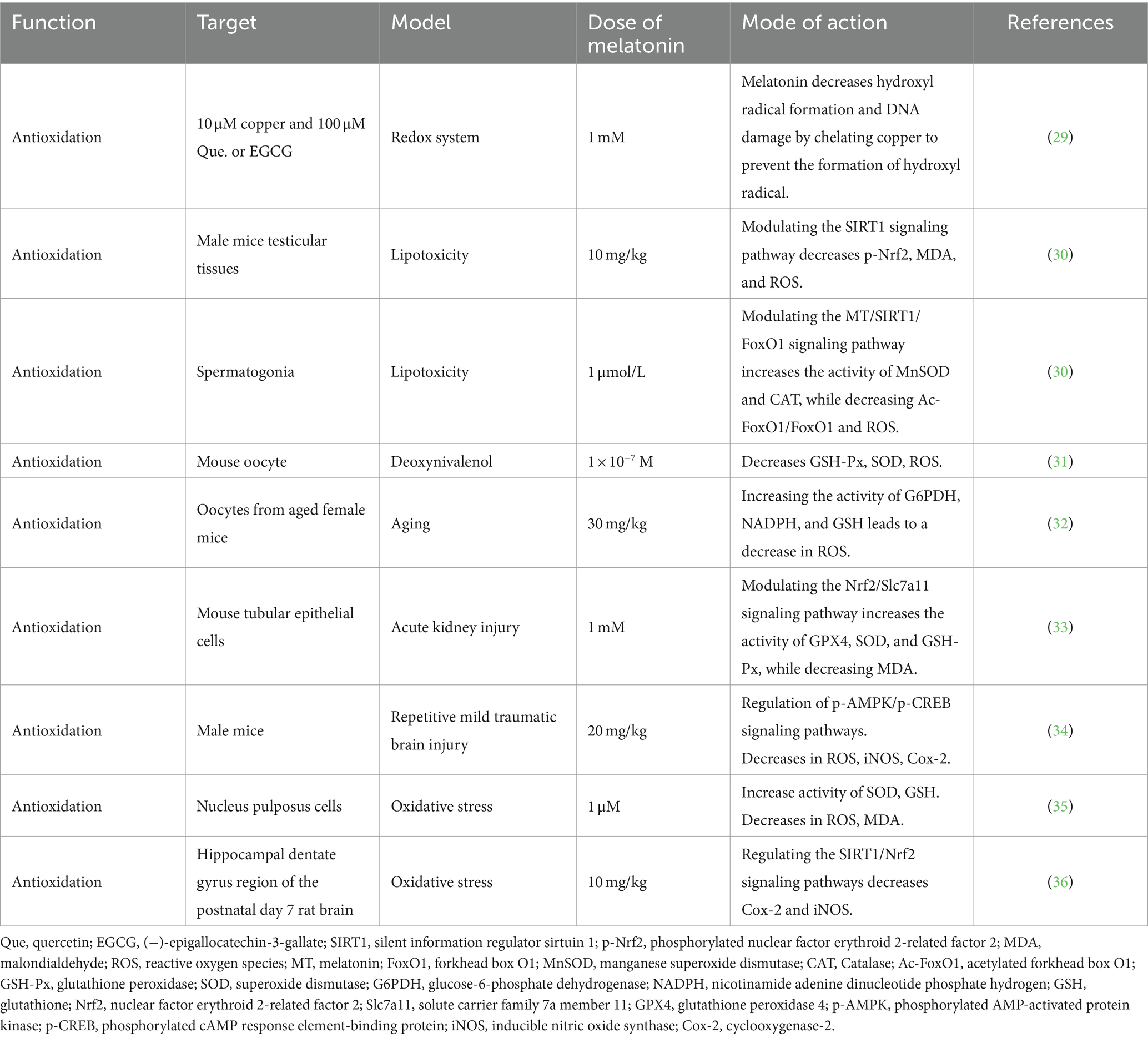
During metabolism, animals generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), including hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radicals, and superoxide anions. Elevated ROS levels under stress or disease conditions can inflict damage on proteins, lipids, and DNA, disrupt cell membranes, and compromise immune function (27). Melatonin, functioning as a robust antioxidant, effectively counters these detrimental effects by neutralizing free radicals and enhancing the production of antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), and catalase (CAT) (15, 28, 29). Numerous animal studies have demonstrated the ability of melatonin to mitigate oxidative damage through the activation of specific signaling pathways (Table 1). In a mouse model of testicular lipotoxicity, melatonin suppressed ROS production by activating the sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) signaling pathway. This action reduces the endoplasmic reticulum stress response (p-IRE1, p-PERK, and ATF4) and protein expression linked to apoptosis (B-cell lymphoma 2 [Bcl-2], Bcl-2-associated X [Bax], Caspase3, Caspase12, and CHOP), thereby alleviating oxidative damage in the testes (30). Similarly, melatonin exhibited protective effects against oxidative stress-induced damage in various animal models, including oocytes, renal tubular epithelial cells, brain cells, and myeloid cells (31–35). The protective mechanisms of melatonin involve the upregulation of key antioxidant response factors. For example, it activates the nuclear factor erythroid2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), reinforcing the cell’s antioxidant capability against oxidative stress (33, 36). Additionally, melatonin promotes reactions between glutathione (GSH), oxygen-free radicals, and other harmful oxidative substances, transforming them into harmless compounds (35). Moreover, it stabilizes mitochondrial membrane potential and enhances mitochondrial function, thereby mitigating mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis (37–39). In summary, melatonin counteracts oxidative stress-induced damage by scavenging reactive oxygen species, enhancing mitochondrial function, inhibiting lipid peroxidation, and preserving cell membrane fluidity, among other mechanisms.
3.2 Immune regulation
Immune stimulation is a critical defense strategy against infections, inflammation, and tumors. The removal of the pineal gland leads to immune suppression by impairing melatonin synthesis, while oral melatonin supplementation promptly restores immune system functionality (40, 41). Melatonin replacement therapy enhances immune memory and antibody responses, maximizing immune system efficacy (42). This suggests the potential of melatonin in immune enhancement by reshaping thymus function and promoting T-cell generation, which is pivotal for combating microbial invasion and sustaining immune system integrity (43).
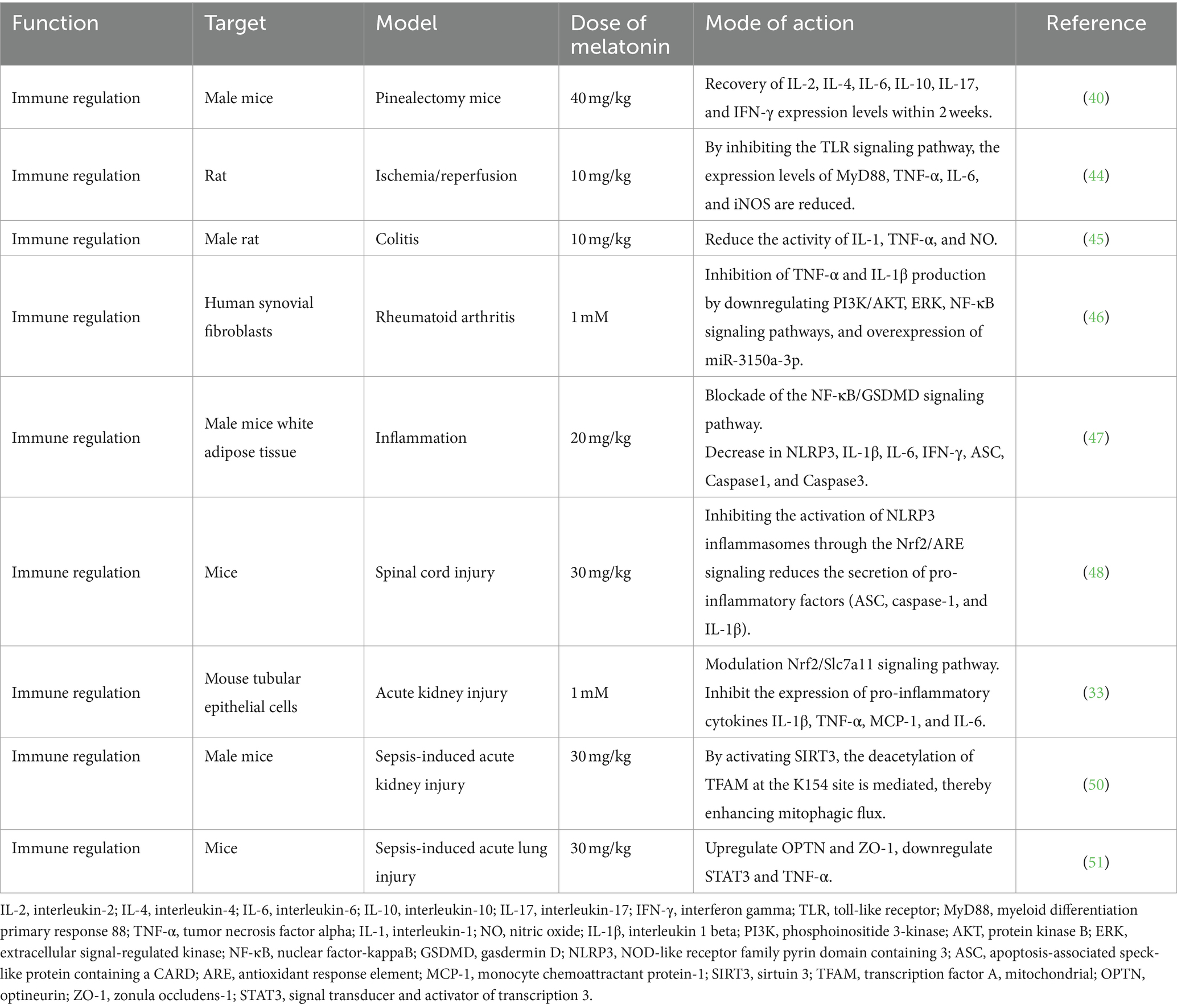
Melatonin exhibits anti-inflammatory effects through various mechanisms (44–46) (Table 2). It blocks the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)/gasdermin D signaling pathway, reducing the expression of inflammatory genes (IL-1β, IL-6, and IFN-γ), inhibiting inflammasome activation (NLR family pyrin domain-containing 3 [NLRP3] and ASC), and mitigating the release of inflammatory cytokines. These actions alleviate lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation in adipose tissue (47). In spinal cord injury models, melatonin suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome activation by activating the Nrf2 pathway and reducing pro-inflammatory factor secretion (48). In acute kidney injury models, melatonin reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine expression (IL-1β, TNF-α, MCP-1, and IL-6), enhances mitochondrial biogenesis protein expression (PGC1α and Tfam), and increases mitochondrial uncoupling proteins, alleviating kidney damage (33). Additionally, melatonin has significant potential as an adjunctive treatment for sepsis. It protects organ function by reducing inflammation, oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and apoptosis, while maintaining mitochondrial function and modulating various physiological pathways (49–51). Furthermore, melatonin produced by the lungs acts as a barrier against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, triggering immune responses, antibody production, and thwarting the virus from entering epithelial cells (52). In summary, melatonin offers promising benefits in bolstering the immune system, with its roles in immune enhancement, anti-inflammatory effects, and potential in combating specific diseases and infections.
3.3 Nerve protection
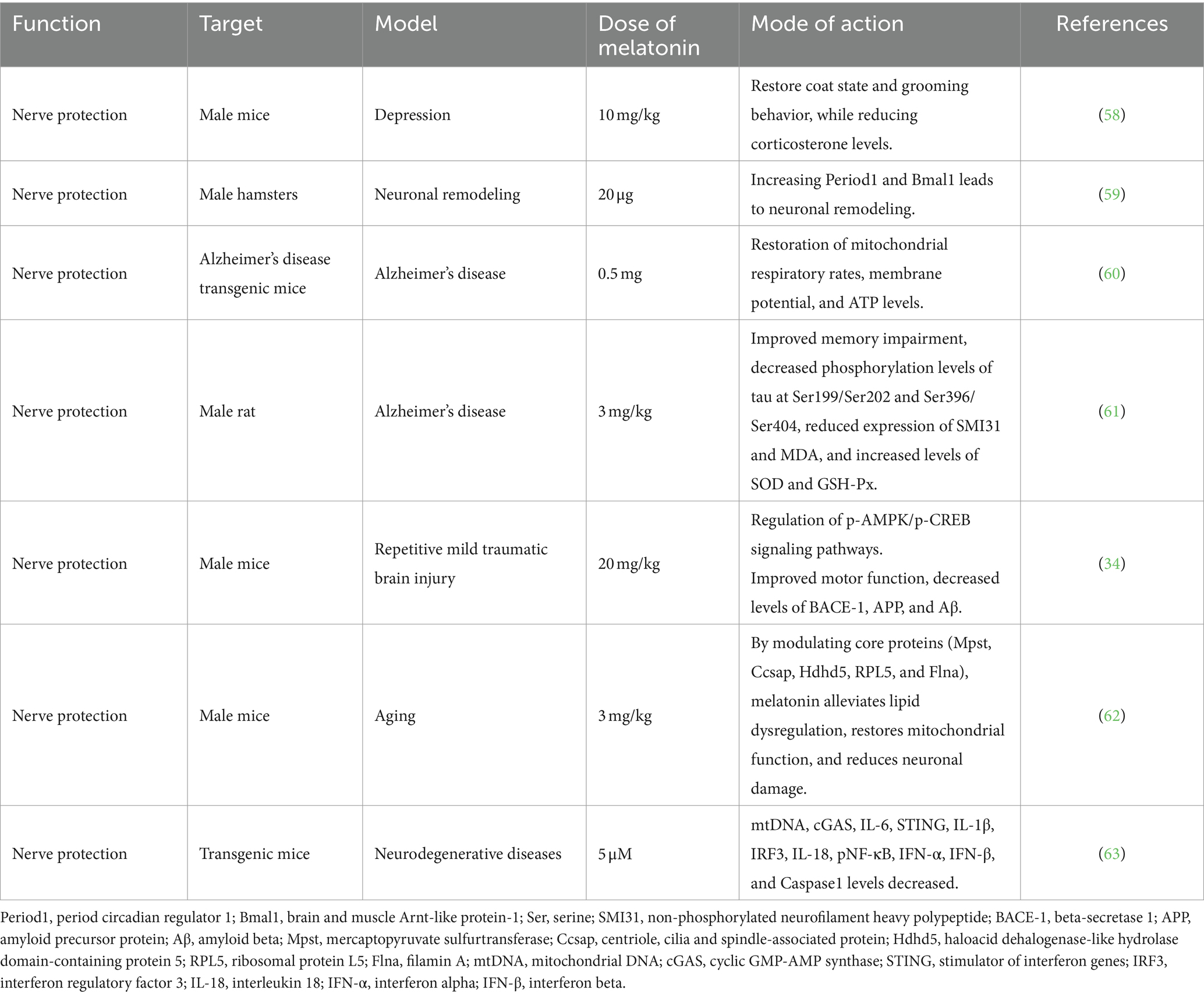
Melatonin plays a pivotal role in neuroprotection by maintaining neural function, preventing damage, fostering regeneration, and preventing neurodegenerative diseases (53). Moreover, melatonin regulates cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation in neural stem/progenitor cells, enhancing the maturity of neural precursor cells and the development of new neurons (54, 55). These neuroregulatory effects are particularly beneficial under conditions such as stress, anxiety, depression, and ischemic brain injury (56–61) (Table 3). In mouse brain injury models, melatonin regulates energy utilization through the phosphorylated 5’AMP-activated kinase/phospho-cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) response element-binding signaling pathway. It diminishes the expression of pro-apoptotic factors (Bax, PARP-1, and Caspase3) and increases the expression of anti-apoptotic factors (Bcl-2), thereby shielding the brain from damage (34). Additionally, melatonin may attenuates age-related decline in brain function by improving lipid metabolism disturbances, restoring mitochondrial function, reducing neuronal damage, and moderating mechanisms associated with brain aging, regulated by core proteins (Mpst, Ccsap, Hdhd5, Rpl5, and Flna) (62). Furthermore, melatonin deficiency in endogenous secretions may disrupt mitochondrial homeostasis, releasing mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and triggering neuroinflammatory responses in the cytoplasm. Chronic inflammation, a hallmark of aging and neurodegenerative diseases, is mitigated by melatonin supplementation. In neurodegenerative disease mouse models, melatonin supplementation inhibits mtDNA release, preventing ROS damage, curtails neuroinflammatory pathway activation (cGAS/STING/IRF3), and reduces inflammatory cytokine production (IL-6, IL-18, IL-1β, IFN-α, and IFN-β). These actions mitigate the effects of brain aging and neurodegenerative pathologies (63). In summary, melatonin protects neurons, enhances neural function, and mitigates neurodegenerative alterations through diverse mechanisms implicated in neurodegenerative diseases.
3.4 Anti-aging
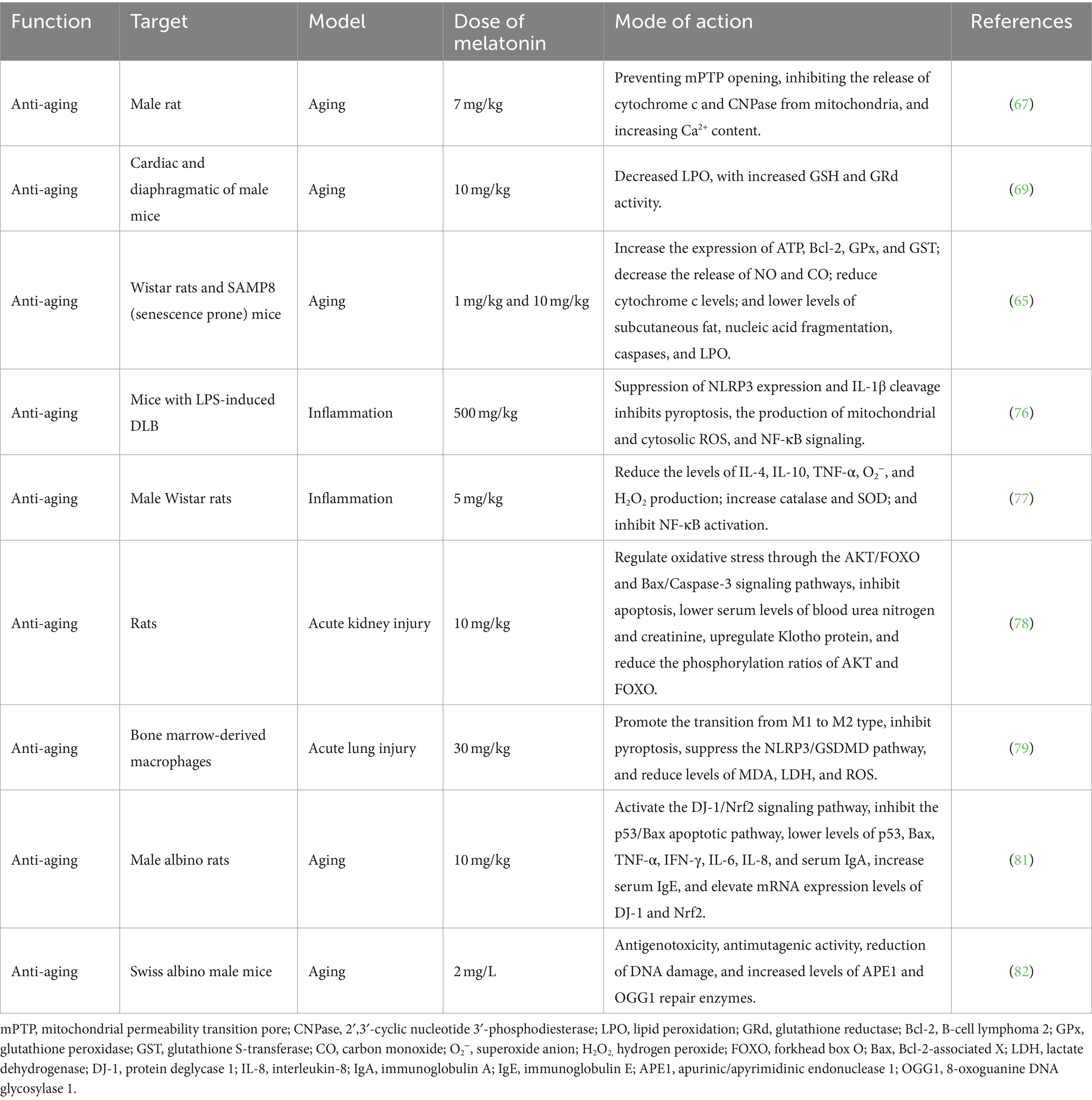
Aging is a progressive change within biological organisms, characterized by mitochondrial dysfunction, immune system damage, oxidative stress, and other related changes (64). The anti-aging effects of melatonin are primarily reflected in its protective role on mitochondrial function and its ability to alleviate mitochondrial dysfunction and cellular aging (38, 65, 66) (Table 4). Melatonin is found at higher concentrations in mitochondria within cells, where it effectively scavenges free radicals and reduces oxidative damage. According to the free radical theory of aging, high levels of melatonin help slow the onset and progression of aging and related diseases (38). Long-term administration of melatonin to aged rats can protect mitochondrial cytochrome c and 2′,3′-cyclic nucleotide 3′-phosphodiesterase levels by preventing the opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore, thereby enhancing mitochondrial function (67). Additionally, melatonin prevents mitochondrial dysfunction and cellular aging by limiting the oxidation of mitochondrial cardiolipin (68). Long-term intake of melatonin can also effectively prevent oxidative stress damage in the mitochondria of the heart and diaphragm in aging mice (69). Furthermore, exogenous melatonin administration has been shown to increase the expression of Bcl-2, glutathione peroxidase (GPx), and glutathione S-transferase (GST) in elderly rats, reduce the release of carbon monoxide (CO) and nitric oxide (NO), and lower the levels of cytochrome C, caspases, and lipid peroxidation (LPO), thereby contributing to melatonin’s anti-aging effects (65, 66).
Extensive data indicate a close relationship between oxidation and inflammation, as excessive oxidative stress can trigger inflammatory responses, with ROS being considered as effectors of inflammation (70, 71). Clinical data confirm that chronic inflammation promotes aging, with increased levels of chronic inflammation being referred to as inflammaging (72–75). Melatonin may also upregulate Nrf2 and downregulate NF-κB, thereby alleviating cellular-level inflammatory processes (76, 77). Similarly, melatonin upregulates the expression of the anti-aging protein Klotho, stimulates the release of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-4 and IL-10), and promotes the polarization of macrophages from a pro-inflammatory (M1) phenotype to an anti-inflammatory (M2) phenotype (78, 79). Additionally, melatonin inhibits various pro-inflammatory events, such as amyloid toxicity, NO release, cyclooxygenase-2 (Cox-2) and NLRP3 inflammasome activation, toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling, as well as the release of senescence-associated secretory phenotype cytokines. It also activates the protein deglycase 1 (DJ-1)/Nrf2 antioxidant signaling pathway and inhibits the p53/Bax apoptotic pathway (80, 81). Importantly, exogenous melatonin can increase levels of apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1) and 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 (OGG1) in mice, facilitating DNA damage repair (82). Thus, melatonin demonstrates pharmacological regulation of aging and has been proposed as a molecule with potential anti-aging effects, with the possibility of extending lifespan through promoting healthy aging.
3.5 Other biological functions
In addition to its multifaceted roles, melatonin has various beneficial effects, including the regulation of blood sugar, reduction of blood lipids, restoration of intestinal barrier function, and modulation of gut microbiota composition. Importantly, melatonin exerts an extensive effect on glucose homeostasis (83). In diabetic rodent models, melatonin and insulin co-administration enhance the sensitivity of white adipose tissue to insulin and improve blood glucose control (84). Melatonin plays a dual role by regulating glucose metabolism and safeguarding pancreatic β-cells. In addition, studies have indicated its potential in mitigating apoptosis in pancreatic β-cells exposed to high glucose conditions, reducing the expression of aging-related proteins (β-Galactosidase). Moreover, melatonin augments endogenous antioxidant defenses (CAT and Mn-SOD), enhances insulin secretion in response to glucose stimulation, and mitigates cell apoptosis and stress-induced premature aging in pancreatic β-cells caused by glucotoxicity and lipotoxicity (85). These orchestrated actions extend β-cell lifespan and fortify their function, underscoring melatonin’s significance in glucose regulation.
In diverse animal models, melatonin demonstrates an inhibitory effect on weight gain and phenotypes linked to visceral fat accumulation, particularly in models with high-fat and high-sugar diets (86). Melatonin significantly promotes fat cell lipolysis by increasing lipolysis-related gene and protein expressions, including hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL), adipocyte triglyceride lipase (ATGL), and perilipin 1, predominantly through the MT2 receptor (87).
Intestinal health is crucial for the overall well-being of animals. Melatonin exhibits a significant impact on intestinal damage by elevating the expression of intestinal tight junction proteins (ZO-1, Occludin, and Claudin-1), reducing intestinal permeability, and modulating gut microbiota composition by decreasing the abundance of Firmicutes and increasing the abundance of Bacteroidetes phyla (88). Overall, the broad application of melatonin across various domains signifies its pivotal role in regulating glucose and lipid metabolism, intestinal health, and the composition of the gut microbiota.
After exploring melatonin’s various biological functions such as antioxidation, immune modulation, and neuroprotection, it is evident that these functions could may enhance various aspects of animal husbandry. Melatonin’s abilities to mitigate oxidative stress, boost immune responses, protect neural tissues, and regulate metabolic processes provide a solid foundation for its application in animal production. Next, we will delve into how these biological functions can be translated into practical applications across different animal species, aimed at improving productivity, reproductive capabilities, and overall health and welfare of livestock.
4 Potentials of melatonin in animal production
4.1 Effect of melatonin on animal production performance
4.1.1 Poultry
Although the exact mechanisms underlying melatonin’s effects on poultry remain unclear, research suggests its potential impact on growth through various pathways, including the regulation of growth hormone (GH) secretion and metabolism. Melatonin influences the release and action of GH by promoting growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH) secretion and inhibiting somatostatin secretion (89, 90). Moreover, melatonin may modulate poultry growth by regulating the expression of growth-related genes and cell proliferation and differentiation. Studies have revealed that melatonin, which binds to the melatonin receptor subtypes Mel1b and Mel1c in the pituitary gland, triggers pituitary-specific transcription factor-1 expression in the anterior pituitary cells, thus boosting growth hormone secretion and fostering growth (91). Importantly, melatonin-mediated green light induction can engage diverse signaling pathways. The Mel1b receptor acts via the adenylate cyclase/protein kinase A (PKA)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) pathway, and the Mel1c receptor, regulated by ERK1/2, induces GH secretion in the chicken pituitary gland (92). Additionally, in vitro experiments demonstrated that exogenous melatonin augments chicken liver cell proliferation and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) secretion (93). However, the effects of melatonin on poultry body weight vary across studies and have not been consistently reported. Some studies have revealed that melatonin can reduce poultry feed intake, enhance feed efficiency, and elevate body weight under certain conditions, though results vary based on environmental factors.
For instance, oral administration of melatonin to broilers under continuous 24-h lighting and hot, dry conditions resulted in increased live weight and average weight gain but reduced feed consumption (94). Similar findings have demonstrated reduced feed consumption in broilers treated with melatonin under different lighting conditions (95). Additionally, melatonin supplementation in heat-stressed quails increased the final body weight and liver weight, highlighting the potential benefits of improving poultry growth performance under heat-stress conditions (96). However, in broilers raised under suitable temperature and lighting conditions, melatonin supplementation had a minimal effect on body weight and feed consumption, except for a reduction in the incidence of sudden death syndrome (97). Further investigations are warranted to elucidate the specific mechanisms underlying the effects of melatonin on poultry welfare and productivity. Nevertheless, its potential positive effects warrant continued attention and exploration.
4.1.2 Swine
Research on the impact of melatonin on pig production performance is limited, but evidence suggests that melatonin may have negligible effects in this context. However, melatonin is lipophilic and can traverse various subcellular compartments, promoting muscle development through multiple mechanisms (98). Exogenous melatonin supplementation stimulates fat breakdown and metabolism while promoting the differentiation of white adipocytes into brown adipocytes, thereby reducing fat content (99–101). In vitro experiments show that melatonin significantly promotes adipogenic differentiation of preadipocytes by increasing the expression of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α (C/EBPα) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) (102). Other studies reported that melatonin reduces fat content by promoting lipid metabolism in porcine oocytes (103). Importantly, melatonin promotes intramuscular fat breakdown by activating the PKA/ERK1/2 signaling pathway, enhancing mitochondrial biogenesis and mitochondrial respiration, and inhibiting preadipocyte proliferation in pig muscles (104). In weaned piglets, melatonin supplementation did not significantly affect growth performance but increased longissimus dorsi muscle weight and eye muscle area. Additionally, melatonin enhanced the expression of genes related to cell differentiation and muscle fiber development (PAX7, MYOG, MYHC IIA, MYHC IIB, IGF-1, and IGFBP5), modulated lipid metabolism (upregulating COX6A, COX5B, and CPT2, and downregulating PPARG, ACC, and FABP4), and activated mitochondrial function in muscle, thereby reducing fat deposition in muscle (105).
Melatonin also positively affects the intestinal health of pigs by regulating intestinal motility, expression of barrier integrity-related genes, and influencing absorption function and gut microbiota. Melatonin increased Actinobacteria abundance and decreased Selenomonadales abundance, enhancing piglet growth (106). Moreover, in in vitro embryo culture, exogenous melatonin enhances embryo development quality, reduces oxidative stress, enhances DNA integrity, and improves in vitro embryo development efficiency, especially during the maturation and fertilization stages (107). Although melatonin positively influences muscle development and fat metabolism in pigs, its impact on growth performance remains limited and requires further study for lean pig cultivation.
4.1.3 Ruminants
Supplementing pregnant ewes with melatonin significantly enhances twin lamb survival rates, particularly during prolonged labor, enhancing their hypoxia tolerance (108). Melatonin supplementation also positively affects the health and growth performance of ewes and lambs (109, 110). It improves fetal oxygen supply, increases birth weight, enhances twin lamb vitality, elevates immunoglobulin G concentrations in the colostrum, enhances colostrum quality, and increases milk production, subsequently benefiting lamb growth (111, 112).
Similarly, postpartum ewes treated with melatonin exhibited increased weaning weight, average daily gain, and higher milk fat content, whereas milk protein and lactose remained unaffected (113). However, direct melatonin implantation in lambs does not significantly affect the growth rate (114). Nonetheless, melatonin implantation in lambs enhances muscle fiber and adipocyte cross-sectional areas, along with related indicators such as red blood cell count, testosterone, growth hormone, and immunoglobulin A. Transcriptome and microbiome analyses suggest that melatonin promotes lamb growth and development by modulating cell apoptosis signaling pathways and the gut microbiota (115).
Conversely, melatonin supplementation in pregnant and postpartum cows does not significantly affect calf weight, morphometric measurements, growth, metabolic factors, or subsequent bull reproductive characteristics. Although melatonin may influence milk yield and fat percentage, these differences are not significant (116). Nonetheless, research indicates the potential of melatonin to improve dairy herd parameters, increase milk nutritional value, elevate lactose and protein contents, and reduce somatic cell counts in milk (117). In summary, melatonin generally does not affect the growth performance of adult ruminants but may positively influence newborn calves and lambs.
4.2 Effect of melatonin on reproductive performance of animals
4.2.1 Poultry
Melatonin influences poultry through various pathways, enhancing reproductive function and breeding performance. In male poultry, melatonin promotes the proliferation of chicken testicular supporting cells by activating the ERK/inhibin alpha subunit signaling pathway and increasing the expression of cell proliferation-associated genes and proteins (PCNA and CCND1) (118). Furthermore, melatonin mitigates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in rooster testicular interstitial cells by activating the protein kinase B (AKT)/Nrf2 signaling pathway, thereby reducing apoptosis (119). It also alleviates glyphosate (GLY)-induced damage to chicken testicular interstitial cells and seminiferous tubule structure, as well as declines in sperm quality, by mitigating mitochondrial dynamics imbalance and inhibiting mitochondrial autophagy. This improves GLY-suppressed testicular hormone synthesis (120). Additionally, melatonin supplementation to frozen–thawed rooster semen significantly enhances post-thaw sperm motility, plasma membrane integrity, and mitochondrial activity. It also maintains sperm integrity and function by reducing LPO and DNA fragmentation (121, 122).
In female poultry, in vitro experiments indicated that melatonin, through receptor activation, regulates the mTOR signaling pathway, upregulating cell cycle-related proteins (cyclin D1) and anti-apoptotic proteins (Bcl-2) and downregulating the pro-apoptotic protein Caspase3 and autophagy-related proteins (Beclin1 and LC3-II), which promotes the proliferation of chicken granulosa cells (123). In vivo experiments with laying hens demonstrated that exogenous melatonin increases melatonin receptor expression in the ovaries by activating the mTOR signaling pathway. This upregulates the expression of downstream components of mTOR, S6 kinase, and 4E-binding protein 1, leading to enhanced follicle growth, extended physiological peak of egg production, and increased egg-laying rate (124). Specifically, supplementation with 10 mg melatonin in chickens at 360 and 550 days of age resulted in an 8.38 and 7.93% increase in egg-laying rates, respectively. This improvement in egg production is associated with elevated serum oestradiol-17β and reduced gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone receptors in the ovaries (125). These findings underscore the critical role of melatonin in poultry reproductive performance, providing essential scientific evidence for enhancing egg production in poultry.
4.2.2 Swine
Melatonin plays crucial roles in oocyte maturation and embryonic development by enhancing these processes through multiple mechanisms. It upregulates the expression of genes related to lipid synthesis (ACACA, FASN, PPARγ, and SREBF1) and promotes the expression of lipolytic genes (ATGL, CGI-58, HSL, and PLIN2), thereby increasing fatty acid oxidation and improving mitochondrial biogenesis (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma co-activator 1 alpha [PGC-1α], TFAM, and PRDX2) to provide the energy required for oocyte development (103).
Additionally, melatonin improves the developmental rate and number of blastocyst cells in pig embryos, thereby promoting embryonic development (126, 127). Supplementing sows with melatonin in late pregnancy can yield multiple benefits, including increased litter size, enhanced birth survival rate, and higher weight, weaning weight, and survival rate of piglets. These effects may be achieved through the Nrf2 signaling pathway and upregulation of antioxidant genes [MGST1, GSTM3, and GSTA4 (128)].
Melatonin also improves oocyte maturation and embryonic development by activating the sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling pathway and upregulating the expression of related genes (SHH, PTHC1, SMO, and GLI1) (129). It promotes oocyte maturation by reducing granulosa cell apoptosis and stimulating estrogen synthesis (130, 131). In early pregnancy, melatonin improves the interaction between the uterus and conceptus by regulating SIRT1 and promoting the proliferation and migration of porcine trophoblast cells (132).
Moreover, melatonin regulates reproductive performance by modulating the release and synthesis of gonadotropin-releasing hormone and luteinizing hormone (LH) (133). It can counteract fungal toxins and toxic compounds, preventing oocyte maturation failure caused by ROS, improving the development of cloned embryos, and enhancing cloning efficiency (134–136). However, the effectiveness of melatonin in addressing seasonal breeding issues remains limited (137). In conclusion, melatonin promotes oocyte maturation and embryonic development, increases litter size and survival rates, and has antioxidant and protective characteristics, thereby playing a vital role in pig reproduction.
4.2.3 Ruminants
Studies have demonstrated the significant enhancement of developmental ability in in vitro matured (IVM) cattle oocytes and embryos with melatonin (138). Specifically, melatonin aids in the recovery of meiosis during IVM of cattle oocytes without stimulating nuclear maturation processes, resulting in a higher proportion of blastocyst formation, both in the oocytes of adult cows and prepubertal donors (139).
Furthermore, melatonin improves embryo quality by augmenting the number of inner cell mass (ICM) cells and the ratio of ICM cells to total cells, indicating its positive influence on embryo differentiation and quality (140). Research has also revealed the expression of ASMT and the melatonin receptor MTNR1A in cattle oocytes and cumulus cells, with MTNR1B expressed exclusively in oocytes. Additionally, 10 and 50 ng/mL of melatonin significantly enhanced nuclear maturation and cumulus cell expansion and induced alterations in mitochondrial distribution patterns and ROS levels (141).
Importantly, melatonin also enhances the quality of thawed bull semen by increasing the average motion parameters, subpopulation structure, survival rate, and acrosomal integrity (142). In artificial insemination, melatonin improves the pregnancy rate and progesterone levels in female cattle, enhances uterine blood flow, and promotes placental development (143–145). For low-reproductive-season water buffaloes, melatonin injections significantly increase the ovulation rate, ovulation follicle diameter, and pregnancy rate (146).
Research involving melatonin implants in bulls revealed that the melatonin group exhibited higher hormone levels (FSH, LH, and testosterone) and melatonin concentrations than the control group. Simultaneously, bulls in the melatonin group showed improved sexual behavior scores, scrotal circumference, and testicular parameters (147). In summary, melatonin plays a crucial role in enhancing the reproductive protection and performance of ruminants, positively impacting the development and quality of oocytes and sperm, thereby facilitating the successful progression of the reproductive process.
4.3 Effects of melatonin on oxidative stress in animals
4.3.1 Poultry
Poultry faces various oxidative stressors, such as ROS, peroxides, heavy metal ions, environmental pollutants, and heat stress, during rearing, which can adversely impact their health and productivity (148, 149). Melatonin serves as a protective antioxidant by neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative damage. A study demonstrated that injecting melatonin (500 mg/kg) into chicks increased melatonin content in tissues, including the intestine, kidney, liver, and red blood cells, by 75–1,300% compared to the control group. Furthermore, melatonin increased GSH-Px activity in these tissues by 22–134% (150). In laying hens, melatonin mitigates ovarian oxidative stress by modulating the SIRT1-P53/forkhead box O1 (FoxO1) pathway (21).
Additionally, the study found that melatonin can alleviate oxidative damage in chicken Leydig cells by activating the AKT–Nrf2 signaling pathway, resulting in increased antioxidant enzyme activity (119). Furthermore, melatonin significantly mitigates mycotoxin-induced oxidative stress in broiler chickens, reducing tissue damage markers (AST, ALT, and LPO) while increasing concentrations of antioxidant enzymes (SOD and CAT) in the serum. A 30% increase in the bursa weight of the Fabricius was also observed (151). Therefore, melatonin, as an antioxidant, holds significant potential in poultry farming, offering effective protective measures to improve poultry health. Nevertheless, further research is imperative to elucidate the mechanisms of the antioxidant action of melatonin in poultry, optimize application methods and dosages, and fully harness its potential benefits.
4.3.2 Swine
The reproductive performance of boars closely correlates with their reproductive development and semen quality, which is frequently jeopardized by oxidative stress. Melatonin mitigates oxidative stress and cell apoptosis induced by tetrabromobisphenol A, reducing the disruption of the phosphatase and tensin homolog of chromosome 10/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT signaling pathway and suppressing excessive ROS generation. Under oxidative stress conditions, it enhances antioxidant capacity by activating kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1/Nrf2 signaling, cell cycle, and lysosomal pathways. Additionally, melatonin increases the expression of heat shock protein 90 and stabilizes hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, effectively alleviating oxidative stress and cell apoptosis in support cells of boars induced by heat stress and chloroquine (152–154).
Melatonin also protects porcine oocytes from oxidative stress by maintaining cell morphology, reducing apoptosis, and delaying mitochondrial dysfunction (155). Melatonin also alleviates oxidative stress in porcine oocytes exposed to ochratoxin A, aflatoxin B1, heat stress, and other damaging factors by increasing antioxidant (GSH) levels, reducing apoptosis (SIRT1 and AKT2), and promoting cellular autophagy (by upregulating Bcl-2 and downregulating Bax, Atg7, Lc3, LC3B, and Caspase3) (156–159).
Pig embryo development is susceptible to various oxidative stress factors in the environment, including maternal factors, diet, drugs, diseases, and infections. Melatonin alleviates oxidative stress during in vitro embryonic development by activating the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway and upregulating the expression of apoptosis-related genes (MT2, Nrf2, UCHL, HO-1, SOD1, and Bcl-2) (127). Additionally, melatonin reduces ROS production by promoting mitochondrial biogenesis (upregulating SIRT1 and PGC-1α), thereby rescuing early pig embryo development damage caused by pesticides such as rotenone (160).
In studies involving ischemia–reperfusion injury and allograft transplantation of porcine organs, melatonin significantly delayed the onset of rejection reactions, prolonged graft survival, and reduced oxidative stress (malondialdehyde [MDA] and 4-HDA) and inflammatory marker levels (pMAP and ITIH4) (161). Therefore, melatonin holds potential therapeutic value in transplantation. In conclusion, melatonin plays a crucial role in pig reproductive function, semen quality, embryo development, and the transplantation rejection response by inhibiting oxidative stress and promoting antioxidant capabilities.
4.3.3 Ruminants
Melatonin effectively mitigates mycotoxin-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in granulosa cells by inhibiting the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway. This is accompanied by a reduction in the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and increased levels of antioxidant enzymes (SOD and GSH-Px) (162). Similarly, melatonin protects bovine oocyte maturation and preimplantation embryo development from exposure to the herbicide paraquat by inhibiting the activation of the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Melatonin restores abnormal levels of chromatin protein trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 4 and histone H3 lysine 9, regulates the expression of redox-related genes (such as decreasing thioredoxin-interacting protein [Txnip] and increasing Trx expression), and inhibits the expression of proapoptotic proteins (Caspase3 and Bax) (163, 164).
Furthermore, melatonin acts by activating the SIRT1/FoxO1 signaling pathway, reducing ROS levels and Ca2+ concentration, releasing cytochrome C, and increasing mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm). It also promotes mitochondrial autophagy, alleviating oxidative stress-induced apoptosis and mitochondrial damage in bovine ovarian granulosa cells (165). Melatonin also protects cattle embryos from oxidative stress caused by hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) during in vitro culture, enhances the developmental quality of fertilized eggs, lowers intracellular ROS levels, and prevents mitochondrial dysfunction in zygotes (166, 167). Finally, melatonin alleviates heat stress in cattle exposed to high temperatures (168, 169). These findings underscore the critical role of melatonin in protecting ruminants from oxidative damage.
4.4 Effects of melatonin on animal immunity
4.4.1 Poultry
In poultry farming, various environmental stressors, such as toxins, drugs, viruses, and diseases, are encountered daily. These factors can compromise immunity and impede the development of immune organs, ultimately resulting in immune dysfunction in poultry (170). Melatonin exerts several immunomodulatory effects in poultry, enhancing immune system function and resilience. A study demonstrated that supplementing the diet of young chickens with melatonin effectively alleviated duodenal inflammation induced by LPS. This effect is primarily achieved by inhibiting the TLR4 signaling pathway, reducing epithelial cell apoptosis, decreasing the expression of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-ɑ, IL-6, IL-4, and Caspase3), and improving the intestinal immune barrier function (mucin 2 [MUC2] and immunoglobulin A) (171). During embryonic development in broiler chickens, melatonin supplementation enhances the intestinal immune barrier by increasing goblet cell numbers and upregulating MUC2 expression (172).
Moreover, in vitro experiments have demonstrated that melatonin promotes T lymphocytes in poultry peripheral blood, with minimal impact on B lymphocytes (173, 174). Green light with longer wavelengths stimulates photoreceptors in poultry retinas, influencing melatonin synthesis and release from the pineal gland. Compared to other light sources, green light stimulation increases the proliferation of B lymphocytes in the bursa of Fabricius by 16.49–30.83%. Green light also significantly upregulates the expression of the melatonin receptor subtypes Mel1a, Mel1b, and Mel1c (175, 176). Additionally, green light enhances the proliferation of T lymphocytes in the spleen by 2.46–6.83% by triggering the cAMP/PKA and phospholipase C/protein kinase C signaling pathways (177).
However, melatonin may produce varying effects on different types of immune cells and immune responses (174). Some studies have indicated that melatonin alone does not significantly affect lymphocyte proliferation in the chicken thymus, spleen, or bursa of Fabricius (178). Conversely, melatonin directly inhibits activated chicken lymphocytes in vitro through phytohemagglutinin stimulation, which may contribute to cell stimulation (179). In summary, the immunomodulatory effects of melatonin on poultry are multifaceted. It enhances poultry immune system function by inhibiting inflammatory responses, improving intestinal immune barrier function, and promoting lymphocyte proliferation. However, further research is required to better understand the specific mechanisms underlying the role of melatonin in immune modulation in poultry.
4.4.2 Swine
Melatonin holds promise for immune regulation in pigs, particularly in immune challenges such as infections and inflammation. The immature gastrointestinal immune system of weaned piglets is susceptible to pathogenic infections such as enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC). ETEC infection affects the serotonin pathway in piglet macrophages, leading to reduced melatonin production. However, melatonin treatment can modify macrophage function, enhancing antimicrobial and bactericidal activities while reducing cell death. Additionally, melatonin pretreatment improves the ability of porcine macrophages to clear ETEC bacteria (180).
In a pig model of acute pancreatitis, melatonin therapy showed potential benefits, including reduced pancreatic acinar cell necrosis, adipose tissue necrosis, and edema, thereby improving pig adaptability and health scores (181). Furthermore, during early pregnancy, melatonin promotes the proliferation and migration of porcine trophectoderm and endometrial luminal epithelial cells via the SIRT1/PI3K/MAPK signaling pathway. Further, it also prevents pregnancy-related complications by reducing the production of pro-inflammatory factors and endoplasmic reticulum stress-sensitive proteins induced by LPS and tunicamycin (132). In summary, melatonin plays a crucial role in the immune regulation and health maintenance of pigs through various mechanisms under different physiological and pathological conditions. These findings offer valuable insights into its potential applications in pig farming.
4.4.3 Ruminants
Melatonin exhibits promising potential in mitigating bovine mastitis, a prevalent inflammatory disease caused by bacterial infections that significantly impact dairy production and quality (182). Its multifaceted effects include the reduction of oxidative stress, inhibition of pro-inflammatory factors, and modulation of NF-κB signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs), positioning it as a valuable candidate for alleviating bovine mastitis (183). In bovine mammary epithelial cells challenged with LPS-induced inflammation, melatonin mitigates the inflammatory response by inhibiting the cluster of differentiation 14/TLR4 signaling pathway. Specifically, it decreases the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and GM-CSF), chemokines (CCL2 and CCL5), and positive acute-phase proteins, while augmenting the expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1Ra) and negative APP fibrinogen (184). Furthermore, melatonin inhibits Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis through the microRNA-16b/Yes-associated protein 1 pathway (185).
Melatonin enhances endometrial receptivity by reducing IL-6 levels and mitigating ammonia-induced inflammation and cell apoptosis by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway (186). In endometritis, melatonin effectively reduces the production of pro-inflammatory factors (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) in endometrial epithelial cells by inhibiting the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome (187). Additionally, by activating membrane receptors MT1 and MT2, melatonin exerts anti-inflammatory effects on ovine epididymal epithelial cells by reducing the expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and Cox-2 (188). Similar studies have found that melatonin, by activating membrane receptors MT1 and MT2 and activating the PI3K/AKT pathway, inhibits the LPS-induced inflammatory response in ovine endometrial epithelial cells (189). Furthermore, melatonin enhances sheep antibody titers against A1 and C strains of Dichelobacter nodosus and the efficacy of the bovine viral diarrhea virus vaccine (190, 191). In summary, melatonin exerts anti-inflammatory and antiviral potential in ruminants and may offer a novel strategy for preventing bovine mastitis, potentially serving as an alternative to antibiotics in the treatment of this disease. Further research is warranted to explore the full therapeutic potential of melatonin in ruminant health management.
4.5 Application of melatonin in aquatic animal production
The inclusion of melatonin in the diet of Cherax destructor significantly improved weight gain, specific growth rate, and digestive enzyme activity. It also enhanced the activity of antioxidant enzymes, reduced oxidative stress, and improved immune parameters. The optimal dosage for dietary melatonin supplementation falls within the range of 75–81 mg/kg (192). In Asian sea bass, melatonin treatment increased body weight and survival rates, lowered blood glucose levels, and enhanced testosterone levels, promoting overall growth and health (193). However, dietary melatonin supplementation significantly reduced the growth performance of juvenile golden pompanos (194).
Melatonin facilitated fish oocyte maturation, increased antioxidant enzyme activity, reduced oxidative stress markers, and inhibited apoptosis (195, 196). In the ovaries of common carp, melatonin accelerated oocyte growth, alleviated oxidative stress, and exhibited stage-dependent effects on the reproductive cycle. It stimulated gonadal activity during the reproductive preparation stage and exerted anti-gonadal effects before and during spawning (197). Moreover, the addition of melatonin to the cryoprotective medium improved the post-thaw sperm quality of fish (198).
In aquatic animals, melatonin plays a crucial role in regulating Na+/K+-ATPase function, particularly during recovery and stress responses under hypoxic conditions (199). Melatonin improves the oxidative status of fish liver cells by activating the ERK/Akt and NF-κB/Nrf2 signaling pathways, thereby regulating heat shock factor expression. This protection prevents damage, reduces oxidative markers such as MDA levels, and inhibits the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, and TNF-α), ultimately mitigating stress-induced damage and inflammation (200, 201).
Melatonin exerts multiple protective effects on fish health under various environmental conditions. It effectively mitigates the damage and toxic effects of harmful substances such as 2,2,4,4-tetra-brominated diphenyl ether, lead, imidacloprid (a pesticide), polystyrene microplastics, and radiation by modulating different pathways, including the miR-140-5p/TLR4/NF-κB pathway, AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α axis, miR-17-5p/TXNIP axis, and peptidoglycan/P38 MAPK pathway. These findings underscore the significant protective role of melatonin in the health of aquatic organisms by reducing inflammation, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and apoptosis, providing robust support for biological well-being under environmental toxin exposure (202–209). In summary, melatonin significantly enhances the growth, health, and reproductive success of various aquatic species. Its protective effects against oxidative stress, inflammation, and environmental toxins highlight its potential as a valuable supplement in aquaculture.
4.6 Potential effect of melatonin on meat quality
Several studies have demonstrated melatonin’s significant efficacy in mitigating muscle atrophy (210). In the eyelid skin of elderly individuals, melatonin downregulates the age-promoting mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) pathway and matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) expression, while promoting the expression of transmembrane collagen 17A1 (COL17A1) and mitochondrial markers (such as TFAM, MTCO-1, and VDAC/porin). This modulation leads to increased elastin content and enhanced structural organization of elastin (211). Additionally, melatonin maintains the normal structure, weight, muscle fiber count, and function of aging muscles. It also enhances lactate production, prevents mitochondrial damage and the formation of tubular aggregates, reduces the percentage of apoptotic cells in aging muscles, and restores the frailty index (212, 213).
In animal production, meat is a significant product and a primary source of income for farmers. However, consumer acceptance of meat products is largely influenced by their quality. Notably, melatonin has also shown positive effects on the quality of meat across various animal species. In broiler chicken incubation, monochromatic green light stimulation increases melatonin secretion, promoting GH activity and the IGF-1 axis. This activation is crucial for stimulating muscle satellite cell proliferation, muscle fiber formation, and overall muscle development, involving the gene expression of paired box 7 (PAX7) and myogenic regulatory factors. These factors contribute to the improvement of broiler growth and meat quality (214).
In pigs, melatonin supplementation enhances the cross-sectional area of weaned piglet muscle fibers and the weight of the longest back and eye muscle areas. Additionally, it reduces the triglyceride levels in the longest back and loin muscles. Melatonin further promotes muscle fiber development (upregulating PAX7, MTOG, and IGF-1) and reduces fat deposition in muscles (downregulating PPARγ, ACC, and FABP4) by modulating gene expression. Moreover, melatonin suppresses intramuscular fat cell proliferation by activating the MT2-mediated PKA/ERK1/2 signaling pathway (104, 105).
In ruminants, melatonin has limited effects on the carcass quality of cashmere goats and does not adversely impact meat production, composition, or quality (215). Studies have detected melatonin in meat, with chicken eggs showing the highest levels. Melatonin extends the shelf life of meat, preserving its quality and taste (216). Therefore, the consumption of these foods by humans and animals may offer potential health benefits. Although research on the role of melatonin in meat quality is not extensive, it shows promise in enhancing poultry and pork quality and extending shelf life.
5 General discussion
Following the prohibition on the use of antibiotics as feed additives, the search for alternative methods to sustain animal health and enhance production efficiency has become imperative. Although research on the impact of melatonin on animal production performance is limited, studies have revealed its moderately favorable effects on growth rate, weight gain, and feed conversion efficiency. The primary advantages of melatonin lie in its ability to enhance reproductive performance, exert antioxidative and immunoregulatory effects, improve disease resistance, and contribute to the overall health of animals.
In poultry, leveraging melatonin through green light exposure has shown promise in stimulating melatonin secretion and benefiting poultry health. In animal production, melatonin is typically considered a component of supplementary healthcare and health management rather than a primary means to boost production performance. However, a comprehensive understanding of the diverse biological activities of melatonin and its structural–functional relationship remains incomplete. Further exploration is required to determine the extent of the applicability of melatonin and the optimal conditions for its use, considering potential variations in responses across different animal species and growth stages.
Moreover, investigating the interactions between melatonin and other feed components is crucial to comprehending its synergistic effects with various ingredients and optimize feed formulations more efficiently. The primary limitation of this review lies in the existing heterogeneity across studies, encompassing variations in methodology, animal species, and environmental conditions. The scarcity of research specifically dedicated to melatonin’s impact on animal production further adds complexity, limiting the ability to draw universally applicable conclusions. Additionally, the concentration of current research in the medical domain, particularly in humans and mice, poses challenges in directly extrapolating findings to the diverse contexts of animal farming. However, with mounting interest in the potential use of melatonin in animal production, future research holds promise for providing more robust scientific evidence to support its widespread application and alignment with the needs of the animal farming industry.
6 Conclusions and perspectives
Overall, melatonin exhibits specific biological characteristics and physiological functions in animal farming, with the potential to serve as an alternative to antibiotics. The outcomes of our review underscore the need for targeted research efforts to unlock the full potential of melatonin in enhancing animal well-being and farm productivity. Looking ahead, researchers should focus on elucidating the mechanisms underlying melatonin’s effects, exploring optimal administration methods, and assessing its long-term impacts on different aspects of animal health and performance. By addressing these research gaps, we can harness the capabilities of melatonin to their fullest extent, paving the way for sustainable and effective practices in animal production.
Author contributions
RZ: Conceptualization, Project administration, Visualization, Writing – original draft. YB: Project administration, Visualization, Writing – original draft. FY: Conceptualization, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Editage (www.editage.cn) for English language editing.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Yang, Q, Gao, Y, Ke, J, Show, PL, Ge, Y, Liu, Y, et al. Antibiotics: An overview on the environmental occurrence, toxicity, degradation, and removal methods. Bioengineered. (2021) 12:7376–416. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1974657
2. Qiu, W, Chen, B, Tang, L, Zheng, C, Xu, B, Liu, Z, et al. Antibiotic Chlortetracycline Causes Transgenerational Immunosuppression via NF-κB. Environ Sci Technol. (2022) 56:4251–61. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.1c07343
3. Huang, C, Feng, S, Huo, F, and Liu, H. Effects of four antibiotics on the diversity of the intestinal microbiota. Microbiol Spectr. (2022) 10:e0190421. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01904-21
4. Wu, H, Ma, Y, Peng, X, Qiu, W, Kong, L, Ren, B, et al. Antibiotic-induced dysbiosis of the rat oral and gut microbiota and resistance to Salmonella. Arch Oral Biol. (2020) 114:104730. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2020.104730
5. Kvetnoy, I, Ivanov, D, Mironova, E, Evsyukova, I, Nasyrov, R, Kvetnaia, T, et al. Melatonin as the cornerstone of Neuroimmunoendocrinology. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:835. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031835
6. Reiter, RJ, Tan, DX, Mayo, JC, Sainz, RM, Leon, J, and Bandyopadhyay, D. Neurally-mediated and neurally-independent beneficial actions of melatonin in the gastrointestinal tract. J Physiol Pharmacol. (2003) 54:113–25. Available at: https://www.jpp.krakow.pl/journal/archive/12_03_s4/pdf/113_12_03_s4_article.pdf
7. Huang, H, Wang, Z, Weng, SJ, Sun, XH, and Yang, XL. Neuromodulatory role of melatonin in retinal information processing. Prog Retin Eye Res. (2013) 32:64–87. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2012.07.003
8. Tosini, G, Baba, K, Hwang, CK, and Iuvone, PM. Melatonin: an underappreciated player in retinal physiology and pathophysiology. Exp Eye Res. (2012) 103:82–9. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2012.08.009
9. Slominski, AT, Zmijewski, MA, Semak, I, Kim, TK, Janjetovic, Z, Slominski, RM, et al. Melatonin, mitochondria, and the skin. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2017) 74:3913–25. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2617-7
10. Rusanova, I, Martínez-Ruiz, L, Florido, J, Rodríguez-Santana, C, Guerra-Librero, A, Acuña-Castroviejo, D, et al. Protective effects of melatonin on the skin: future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:948. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194948
11. Liu, J, Clough, SJ, Hutchinson, AJ, Adamah-Biassi, EB, Popovska-Gorevski, M, and Dubocovich, ML. MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors: a therapeutic perspective. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. (2016) 56:361–83. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010814-124742
12. Zlotos, DP, Jockers, R, Cecon, E, Rivara, S, and Witt-Enderby, PA. MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors: ligands, models, oligomers, and therapeutic potential. J Med Chem. (2014) 57:3161–85. doi: 10.1021/jm401343c
13. Gunata, M, Parlakpinar, H, and Acet, HA. Melatonin: a review of its potential functions and effects on neurological diseases. Rev Neurol (Paris). (2020) 176:148–65. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2019.07.025
14. Boutin, JA, and Ferry, G. Is there sufficient evidence that the melatonin binding site MT(3) is Quinone reductase 2? J Pharmacol Exp Ther. (2019) 368:59–65. doi: 10.1124/jpet.118.253260
15. Reiter, RJ, Mayo, JC, Tan, DX, Sainz, RM, Alatorre-Jimenez, M, and Qin, L. Melatonin as an antioxidant: under promises but over delivers. J Pineal Res. (2016) 61:253–78. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12360
16. Kim, J, Li, W, Wang, J, Baranov, SV, Heath, BE, Jia, J, et al. Biosynthesis of neuroprotective melatonin is dysregulated in Huntington's disease. J Pineal Res. (2023) 75:e12909. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12909
17. Vasey, C, McBride, J, and Penta, K. Circadian rhythm dysregulation and restoration: the role of melatonin. Nutrients. (2021) 13:3480. doi: 10.3390/nu13103480
18. Bhattacharya, S, Patel, KK, Dehari, D, Agrawal, AK, and Singh, S. Melatonin and its ubiquitous anticancer effects. Mol Cell Biochem. (2019) 462:133–55. doi: 10.1007/s11010-019-03617-5
19. Hardeland, R . Melatonin and inflammation-story of a double-edged blade. J Pineal Res. (2018) 65:e12525. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12525
20. Paterson, AM, and Foldes, A. Melatonin and farm animals: endogenous rhythms and exogenous applications. J Pineal Res. (1994) 16:167–77. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.1994.tb00097.x
21. Wang, J, Jia, R, Gong, H, Celi, P, Zhuo, Y, Ding, X, et al. The effect of oxidative stress on the chicken ovary: involvement of microbiota and melatonin interventions. Antioxidants (Basel). (2021) 10:1422. doi: 10.3390/antiox10091422
22. Lee, BJ, Choi, HG, Kim, CK, Parrott, KA, Ayres, JW, and Sack, RL. Solubility and stability of melatonin in propylene glycol and 2-hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin vehicles. Arch Pharm Res. (1997) 20:560–5. doi: 10.1007/BF02975212
23. Ritwiset, A, Khajonrit, J, Krongsuk, S, and Maensiri, S. Molecular insight on the formation structure and dynamics of melatonin in an aqueous solution and at the water-air interface: a molecular dynamics study. J Mol Graph Model. (2021) 108:107983. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2021.107983
24. Boiko, DI, Shkodina, AD, Hasan, MM, Bardhan, M, Kazmi, SK, Chopra, H, et al. Melatonergic receptors (Mt1/Mt2) as a potential additional target of novel drugs for depression. Neurochem Res. (2022) 47:2909–24. doi: 10.1007/s11064-022-03646-5
25. Tordjman, S, Chokron, S, Delorme, R, Charrier, A, Bellissant, E, Jaafari, N, et al. Melatonin: pharmacology, functions and therapeutic benefits. Curr Neuropharmacol. (2017) 15:434–43. doi: 10.2174/1570159X14666161228122115
26. Tan, DX, Manchester, LC, Esteban-Zubero, E, Zhou, Z, and Reiter, RJ. Melatonin as a potent and inducible endogenous antioxidant: synthesis and metabolism. Molecules. (2015) 20:18886–906. doi: 10.3390/molecules201018886
27. Galano, A, and Reiter, RJ. Melatonin and its metabolites vs oxidative stress: from individual actions to collective protection. J Pineal Res. (2018) 65:e12514. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12514
28. Bocheva, G, Slominski, RM, Janjetovic, Z, Kim, TK, Böhm, M, Steinbrink, K, et al. Protective role of melatonin and its metabolites in skin aging. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:1238. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031238
29. Wang, J, Wang, X, He, Y, Jia, L, Yang, CS, Reiter, RJ, et al. Antioxidant and pro-oxidant activities of melatonin in the presence of copper and polyphenols in vitro and in vivo. Cells. (2019) 8:903. doi: 10.3390/cells8080903
30. Xu, D, Liu, L, Zhao, Y, Yang, L, Cheng, J, Hua, R, et al. Melatonin protects mouse testes from palmitic acid-induced lipotoxicity by attenuating oxidative stress and DNA damage in a SIRT1-dependent manner. J Pineal Res. (2020) 69:e12690. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12690
31. Lan, M, Han, J, Pan, MH, Wan, X, Pan, ZN, and Sun, SC. Melatonin protects against defects induced by deoxynivalenol during mouse oocyte maturation. J Pineal Res. (2018) 65:e12477. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12477
32. Zhang, H, Li, C, Wen, D, Li, R, Lu, S, Xu, R, et al. Melatonin improves the quality of maternally aged oocytes by maintaining intercellular communication and antioxidant metabolite supply. Redox Biol. (2022) 49:102215. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102215
33. Huang, YB, Jiang, L, Liu, XQ, Wang, X, Gao, L, Zeng, HX, et al. Melatonin alleviates acute kidney injury by inhibiting NRF2/Slc7a11 Axis-mediated Ferroptosis. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:4776243. doi: 10.1155/2022/4776243
34. Rehman, SU, Ikram, M, Ullah, N, Alam, SI, Park, HY, Badshah, H, et al. Neurological enhancement effects of melatonin against brain injury-induced oxidative stress, Neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration via AMPK/CREB signaling. Cells. (2019) 8:760. doi: 10.3390/cells8070760
35. He, R, Cui, M, Lin, H, Zhao, L, Wang, J, Chen, S, et al. Melatonin resists oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in nucleus pulposus cells. Life Sci. (2018) 199:122–30. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.03.020
36. Shah, SA, Khan, M, Jo, MH, Jo, MG, Amin, FU, and Kim, MO. Melatonin stimulates the SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway counteracting lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced oxidative stress to rescue postnatal rat brain. CNS Neurosci Ther. (2017) 23:33–44. doi: 10.1111/cns.12588
37. Murphy, MP . Mitochondrial dysfunction indirectly elevates ROS production by the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Metab. (2013) 18:145–6. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.07.006
38. Reiter, RJ, Tan, DX, Rosales-Corral, S, Galano, A, Zhou, XJ, and Xu, B. Mitochondria: central organelles for Melatonin's antioxidant and anti-aging actions. Molecules. (2018) 23:509. doi: 10.3390/molecules23020509
39. Tan, DX, Manchester, LC, Qin, L, and Reiter, RJ. Melatonin: a mitochondrial targeting molecule involving mitochondrial protection and dynamics. Int J Mol Sci. (2016) 17:2124. doi: 10.3390/ijms17122124
40. Luo, J, Zhang, Z, Sun, H, Song, J, Chen, X, Huang, J, et al. Effect of melatonin on T/B cell activation and immune regulation in pinealectomy mice. Life Sci. (2020) 242:117191. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117191
41. Carrillo-Vico, A, Lardone, PJ, Alvarez-Sánchez, N, Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A, and Guerrero, JM. Melatonin: buffering the immune system. Int J Mol Sci. (2013) 14:8638–83. doi: 10.3390/ijms14048638
42. Skwarlo-Sonta, K, Majewski, P, Markowska, M, Oblap, R, and Olszanska, B. Bidirectional communication between the pineal gland and the immune system. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. (2003) 81:342–9. doi: 10.1139/y03-026
43. Zhao, CN, Wang, P, Mao, YM, Dan, YL, Wu, Q, Li, XM, et al. Potential role of melatonin in autoimmune diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2019) 48:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2019.07.002
44. Kang, JW, Koh, EJ, and Lee, SM. Melatonin protects liver against ischemia and reperfusion injury through inhibition of toll-like receptor signaling pathway. J Pineal Res. (2011) 50:403–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00858.x
45. Mei, Q, Yu, JP, Xu, JM, Wei, W, Xiang, L, and Yue, L. Melatonin reduces colon immunological injury in rats by regulating activity of macrophages. Acta Pharmacol Sin. (2002) 23:882–6. Available at: https://www.chinaphar.com/article/view/7175/7834
46. Huang, CC, Chiou, CH, Liu, SC, Hu, SL, Su, CM, Tsai, CH, et al. Melatonin attenuates TNF-α and IL-1β expression in synovial fibroblasts and diminishes cartilage degradation: implications for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. J Pineal Res. (2019) 66:e12560. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12560
47. Liu, Z, Gan, L, Xu, Y, Luo, D, Ren, Q, Wu, S, et al. Melatonin alleviates inflammasome-induced pyroptosis through inhibiting NF-κB/GSDMD signal in mice adipose tissue. J Pineal Res. (2017) 63:12414. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12414
48. Wang, H, Wang, H, Huang, H, Qu, Z, Ma, D, Dang, X, et al. Melatonin attenuates spinal cord injury in mice by activating the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway to inhibit the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Cells. (2022) 11:2809. doi: 10.3390/cells11182809
49. Liu, R, Luo, X, Li, J, Lei, Y, Zeng, F, Huang, X, et al. Melatonin: a window into the organ-protective effects of sepsis. Biomed Pharmacother. (2022) 154:113556. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113556
50. Deng, Z, He, M, Hu, H, Zhang, W, Zhang, Y, Ge, Y, et al. Melatonin attenuates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by promoting mitophagy through SIRT3-mediated TFAM deacetylation. Autophagy. (2024) 20:151–65. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2252265
51. Ling, J, Yu, S, Xiong, F, Xu, T, and Li, S. Melatonin attenuates Sepsis-induced acute lung injury via inhibiting excessive Mitophagy. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2023) 17:2775–86. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S423264
52. Fernandes, PA, Kinker, GS, Navarro, BV, Jardim, VC, and Markus, RP. Melatonin-index as a biomarker for predicting the distribution of presymptomatic and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 carriers. Melatonin Res. (2021) 4:189–205. doi: 10.32794/mr11250090
53. Luo, F, Sandhu, AF, Rungratanawanich, W, Williams, GE, Akbar, M, Zhou, S, et al. Melatonin and autophagy in aging-related neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:7174. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197174
54. Potes, Y, Cachán-Vega, C, Antuña, E, García-González, C, Menéndez-Coto, N, Boga, JA, et al. Benefits of the neurogenic potential of melatonin for treating neurological and neuropsychiatric disorders. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:4803. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054803
55. Leung, JW, Cheung, KK, Ngai, SP, Tsang, HW, and Lau, BW. Protective effects of melatonin on neurogenesis impairment in neurological disorders and its relevant molecular mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:5645. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165645
56. Valdés-Tovar, M, Estrada-Reyes, R, Solís-Chagoyán, H, Argueta, J, Dorantes-Barrón, AM, Quero-Chávez, D, et al. Circadian modulation of neuroplasticity by melatonin: a target in the treatment of depression. Br J Pharmacol. (2018) 175:3200–8. doi: 10.1111/bph.14197
57. Shen, S, Liao, Q, Wong, YK, Chen, X, Yang, C, Xu, C, et al. The role of melatonin in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer's disease. Int J Biol Sci. (2022) 18:983–94. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.66871
58. Detanico, BC, Piato, AL, Freitas, JJ, Lhullier, FL, Hidalgo, MP, Caumo, W, et al. Antidepressant-like effects of melatonin in the mouse chronic mild stress model. Eur J Pharmacol. (2009) 607:121–5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.02.037
59. Ikeno, T, and Nelson, RJ. Acute melatonin treatment alters dendritic morphology and circadian clock gene expression in the hippocampus of Siberian hamsters. Hippocampus. (2015) 25:142–8. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22358
60. Dragicevic, N, Copes, N, O'Neal-Moffitt, G, Jin, J, Buzzeo, R, Mamcarz, M, et al. Melatonin treatment restores mitochondrial function in Alzheimer's mice: a mitochondrial protective role of melatonin membrane receptor signaling. J Pineal Res. (2011) 51:75–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00864.x
61. Rong, K, Zheng, H, Yang, R, Liu, X, Li, L, Chen, N, et al. Melatonin and its metabolite N(1)-acetyl-N(1)-formyl-5-methoxykynuramine improve learning and memory impairment related to Alzheimer's disease in rats. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. (2020) 34:e22430. doi: 10.1002/jbt.22430
62. Jiang, X, Xu, Z, Yao, D, Liu, X, Liu, W, Wang, N, et al. An integrated multi-omics approach revealed the regulation of melatonin on age-dependent mitochondrial function impair and lipid dyshomeostasis in mice hippocampus. Pharmacol Res. (2022) 179:106210. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2022.106210
63. Jauhari, A, Baranov, SV, Suofu, Y, Kim, J, Singh, T, Yablonska, S, et al. Melatonin inhibits cytosolic mitochondrial DNA-induced neuroinflammatory signaling in accelerated aging and neurodegeneration. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130:3124–36. doi: 10.1172/JCI135026
64. Martín Giménez, VM, de Las Heras, N, Lahera, V, Tresguerres, JAF, Reiter, RJ, and Manucha, W. Melatonin as an anti-aging therapy for age-related cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. Front Aging Neurosci. (2022) 14:888292. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.888292
65. Tresguerres, JA, Kireev, R, Forman, K, Cuesta, S, Tresguerres, AF, and Vara, E. Effect of chronic melatonin administration on several physiological parameters from old Wistar rats and SAMP8 mice. Curr Aging Sci. (2012) 5:242–53. doi: 10.2174/1874609811205030012
66. Vinod, C, and Jagota, A. Daily Socs1 rhythms alter with aging differentially in peripheral clocks in male Wistar rats: therapeutic effects of melatonin. Biogerontology. (2017) 18:333–45. doi: 10.1007/s10522-017-9687-7
67. Baburina, Y, Odinokova, I, Azarashvili, T, Akatov, V, Lemasters, JJ, and Krestinina, O. 2′,3'-cyclic nucleotide 3′-phosphodiesterase as a messenger of protection of the mitochondrial function during melatonin treatment in aging. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. (1859) 2017:94–103.
68. Paradies, G, Paradies, V, Ruggiero, FM, and Petrosillo, G. Mitochondrial bioenergetics decay in aging: beneficial effect of melatonin. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2017) 74:3897–911. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2619-5
69. Rodriguez, MI, Escames, G, López, LC, García, JA, Ortiz, F, López, A, et al. Melatonin administration prevents cardiac and diaphragmatic mitochondrial oxidative damage in senescence-accelerated mice. J Endocrinol. (2007) 194:637–43. doi: 10.1677/JOE-07-0260
70. Hussain, T, Tan, B, Yin, Y, Blachier, F, Tossou, MC, and Rahu, N. Oxidative stress and inflammation: what polyphenols can do for us? Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2016) 2016:7432797. doi: 10.1155/2016/7432797
71. Mancini, A, Di Segni, C, Raimondo, S, Olivieri, G, Silvestrini, A, Meucci, E, et al. Thyroid hormones, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Mediat Inflamm. (2016) 2016:6757154. doi: 10.1155/2016/6757154
72. Laderoute, M . The paradigm of immunosenescence in atherosclerosis-cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). Discov Med. (2020) 29:41–51. Available at: https://www.discoverymedicine.com/Marian-P-Laderoute/2020/02/paradigm-of-immunosenescence-in-atherosclerosis-cardiovascular-disease-ascvd/
73. Klohs, J . An integrated view on vascular dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. Neurodegener Dis. (2019) 19:109–27. doi: 10.1159/000505625
74. Yin, F, Sancheti, H, Patil, I, and Cadenas, E. Energy metabolism and inflammation in brain aging and Alzheimer's disease. Free Radic Biol Med. (2016) 100:108–22. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.04.200
75. Franceschi, C, and Campisi, J. Chronic inflammation (inflammaging) and its potential contribution to age-associated diseases. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2014) 69:S4–9. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glu057
76. Arioz, BI, Tastan, B, Tarakcioglu, E, Tufekci, KU, Olcum, M, Ersoy, N, et al. Melatonin attenuates LPS-induced acute depressive-like behaviors and microglial NLRP3 Inflammasome activation through the SIRT1/Nrf2 pathway. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1511. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01511
77. Brazão, V, Colato, RP, Santello, FH, Duarte, A, Goulart, A, Sampaio, PA, et al. Melatonin regulates antioxidant defense and inflammatory response by activating Nrf2-dependent mechanisms and inhibiting NFkappaB expression in middle-aged T. cruzi infected rats. Exp Gerontol. (2022) 167:111895. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2022.111895
78. Ko, JW, Shin, NR, Jung, TY, Shin, IS, Moon, C, Kim, SH, et al. Melatonin attenuates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in rats via induction of anti-aging protein, klotho. Food Chem Toxicol. (2019) 129:201–10. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2019.04.049
79. Xu, MM, Kang, JY, Ji, S, Wei, YY, Wei, SL, Ye, JJ, et al. Melatonin suppresses macrophage M1 polarization and ROS-mediated Pyroptosis via activating ApoE/LDLR pathway in influenza A-induced acute lung injury. Oxidative Med Cell Longev. (2022) 2022:2520348. doi: 10.1155/2022/2520348
80. Hardeland, R . Aging, melatonin, and the pro- and anti-inflammatory networks. Int J Mol Sci. (2019) 20:1223. doi: 10.3390/ijms20051223
81. Ismail, IA, El-Bakry, HA, and Soliman, SS. Melatonin and tumeric ameliorate aging-induced changes: implication of immunoglobulins, cytokines, DJ-1/NRF2 and apoptosis regulation. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. (2018) 10:70–82. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5943606/
82. Damiani, AP, Strapazzon, G, de Oliveira Sardinha, TT, Rohr, P, Gajski, G, de Pinho, RA, et al. Melatonin supplementation over different time periods until ageing modulates genotoxic parameters in mice. Mutagenesis. (2020) 35:465–78. doi: 10.1093/mutage/geaa017
83. Karamitri, A, and Jockers, R. Melatonin in type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity. Nat Rev Endocrinol. (2019) 15:105–25. doi: 10.1038/s41574-018-0130-1
84. Oliveira, AC, Andreotti, S, Sertie, RAL, Campana, AB, de Proença, ARG, Vasconcelos, RP, et al. Combined treatment with melatonin and insulin improves glycemic control, white adipose tissue metabolism and reproductive axis of diabetic male rats. Life Sci. (2018) 199:158–66. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.02.040
85. Lee, YH, Jung, HS, Kwon, MJ, Jang, JE, Kim, TN, Lee, SH, et al. Melatonin protects INS-1 pancreatic β-cells from apoptosis and senescence induced by glucotoxicity and glucolipotoxicity. Islets. (2020) 12:87–98. doi: 10.1080/19382014.2020.1783162
86. Guan, Q, Wang, Z, Cao, J, Dong, Y, and Chen, Y. Mechanisms of melatonin in obesity: a review. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 23:218. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010218
87. Yang, W, Tang, K, Wang, Y, Zhang, Y, and Zan, L. Melatonin promotes triacylglycerol accumulation via MT2 receptor during differentiation in bovine intramuscular preadipocytes. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:15080. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12780-y
88. Liu, S, Kang, W, Mao, X, Ge, L, Du, H, Li, J, et al. Melatonin mitigates aflatoxin B1-induced liver injury via modulation of gut microbiota/intestinal FXR/liver TLR4 signaling axis in mice. J Pineal Res. (2022) 73:e12812. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12812
89. Zhang, L, Cao, J, Wang, Z, Dong, Y, and Chen, Y. Melatonin modulates monochromatic light-induced GHRH expression in the hypothalamus and GH secretion in chicks. Acta Histochem. (2016) 118:286–92. doi: 10.1016/j.acthis.2016.02.005
90. Qin, X, Liu, X, Yan, X, Long, M, Wang, Z, Dong, Y, et al. Melatonin mediates monochromatic light-induced expression of somatostatin in the hypothalamus and pituitary of chicks. Poult Sci. (2021) 100:101285. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2021.101285
91. Yue, L, Qin, X, Liu, X, Wang, Z, Dong, Y, Chen, Y, et al. Melatonin receptor Mel1b- and Mel1c-mediated green light induced the secretion of growth hormone in anterior pituitary of chicks. Photochem Photobiol. (2019) 95:1387–94. doi: 10.1111/php.13127
92. Liu, X, Wang, L, Wang, Z, Dong, Y, Chen, Y, and Cao, J. Mel1b and Mel1c melatonin receptors mediate green light-induced secretion of growth hormone in chick adenohypophysis cells via the AC/PKA and ERK1/2 signalling pathways. J Photochem Photobiol B. (2021) 225:112322. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2021.112322
93. Li, S, Cao, J, Wang, Z, Dong, Y, Wang, W, and Chen, Y. Melatonin mediates monochromatic light-induced insulin-like growth factor 1 secretion of Chick liver: involvement of membrane receptors. Photochem Photobiol. (2016) 92:595–603. doi: 10.1111/php.12594
94. Sinkalu, VO, Ayo, JO, Hambolu, JO, Adelaiye, AB, Zakari, FO, and Aluwong, T. Changes in feed consumption and water intake among broiler chickens subjected to melatonin treatment during the hot-dry season. Trop Anim Health Prod. (2020) 52:717–23. doi: 10.1007/s11250-019-02061-3
95. Apeldoorn, EJ, Schrama, JW, Mashaly, MM, and Parmentier, HK. Effect of melatonin and lighting schedule on energy metabolism in broiler chickens. Poult Sci. (1999) 78:223–9. doi: 10.1093/ps/78.2.223
96. Sahin, N, Onderci, M, Sahin, K, Gursu, MF, and Smith, MO. Ascorbic acid and melatonin reduce heat-induced performance inhibition and oxidative stress in Japanese quails. Br Poult Sci. (2004) 45:116–22. doi: 10.1080/00071660410001668941
97. Clark, WD, and Classen, HL. The effects of continuously or diurnally fed melatonin on broiler performance and health. Poult Sci. (1995) 74:1900–4. doi: 10.3382/ps.0741900
98. Chen, B, You, W, and Shan, T. The regulatory role of melatonin in skeletal muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. (2020) 41:191–8. doi: 10.1007/s10974-020-09578-3
99. Mohammadi, S, Rastmanesh, R, Jahangir, F, Amiri, Z, Djafarian, K, Mohsenpour, MA, et al. Melatonin supplementation and anthropometric indices: a randomized double-blind controlled clinical trial. Biomed Res Int. (2021) 2021:3502325. doi: 10.1155/2021/3502325
100. Zaminy, A, Kashani, IR, Barbarestani, M, Hedayatpour, A, Mahmoudi, R, Vardasbi, S, et al. Effects of melatonin on the proliferation and differentiation of rat adipose-derived stem cells. Indian J Plast Surg. (2008) 41:8–14. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1699220
101. Salagre, D, Chayah, M, Molina-Carballo, A, Oliveras-López, MJ, Munoz-Hoyos, A, Navarro-Alarcón, M, et al. Melatonin induces fat browning by transdifferentiation of white adipocytes and de novo differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Food Funct. (2022) 13:3760–75. doi: 10.1039/D1FO04360A
102. González, A, Alvarez-García, V, Martínez-Campa, C, Alonso-González, C, and Cos, S. Melatonin promotes differentiation of 3T3-L1 fibroblasts. J Pineal Res. (2012) 52:12–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00911.x
103. Jin, JX, Lee, S, Taweechaipaisankul, A, Kim, GA, and Lee, BC. Melatonin regulates lipid metabolism in porcine oocytes. J Pineal Res. (2017) 62:12388. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12388
104. Liu, K, Yu, W, Wei, W, Zhang, X, Tian, Y, Sherif, M, et al. Melatonin reduces intramuscular fat deposition by promoting lipolysis and increasing mitochondrial function. J Lipid Res. (2019) 60:767–82. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M087619
105. Chen, W, Tu, Y, Cai, P, Wang, L, Zhou, Y, Liu, S, et al. Melatonin supplementation promotes muscle fiber hypertrophy and regulates lipid metabolism of skeletal muscle in weaned piglets. J Anim Sci. (2023) 101:skad256. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad256
106. Xia, S, Gao, W, Li, Y, Ma, J, Gong, S, Gao, Z, et al. Effects of melatonin on intestinal function and bacterial compositions in sucking piglets. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). (2022) 106:1139–48. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13675
107. Martinez, CA, Cuello, C, Parrilla, I, Maside, C, Ramis, G, Cambra, JM, et al. Exogenous melatonin in the culture medium does not affect the development of in vivo-derived pig embryos but substantially improves the quality of in vitro-produced embryos. Antioxidants (Basel). (2022) 11:1177. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061177
108. Flinn, T, McCarthy, NL, Swinbourne, AM, Gatford, KL, Weaver, AC, McGrice, HA, et al. Supplementing merino ewes with melatonin during the last half of pregnancy improves tolerance of prolonged parturition and survival of second-born twin lambs. J Anim Sci. (2020) 98:372. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa372
109. Flinn, T, Gunn, JR, Kind, KL, Swinbourne, AM, Weaver, AC, Kelly, JM, et al. Maternal melatonin implants improve twin merino lamb survival. J Anim Sci. (2020) 98:skaa344. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa344
110. Sales, F, Peralta, OA, Narbona, E, McCoard, S, González-Bulnes, A, and Parraguez, VH. Rapid communication: maternal melatonin implants improve fetal oxygen supply and body weight at term in sheep pregnancies. J Anim Sci. (2019) 97:839–45. doi: 10.1093/jas/sky443
111. Canto, F, González, E, and Abecia, JA. Effects of implanting exogenous melatonin 40 days before lambing on Milk and colostrum quality. Animals (Basel). (2022) 12:1257. doi: 10.3390/ani12101257
112. Abecia, JA, Garrido, C, Gave, M, García, AI, López, D, Luis, S, et al. Exogenous melatonin and male foetuses improve the quality of sheep colostrum. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl). (2020) 104:1305–9. doi: 10.1111/jpn.13362
113. Abecia, JA, Luis, S, and Canto, F. Implanting melatonin at lambing enhances lamb growth and maintains high fat content in milk. Vet Res Commun. (2021) 45:181–8. doi: 10.1007/s11259-021-09799-y
114. Bouroutzika, E, Ciliberti, MG, Caroprese, M, Theodosiadou, E, Papadopoulos, S, Makri, S, et al. Association of Melatonin Administration in pregnant ewes with growth, redox status and immunity of their offspring. Animals (Basel). (2021) 11:3161. doi: 10.3390/ani11113161
115. Ma, W, Wu, H, Li, G, Yan, L, Wang, L, Zhao, M, et al. Melatonin promotes the growth and development of lambs by increasing growth hormone and testosterone, targeting on apoptosis signaling pathway and intestinal microflora. Front Endocrinol. (2022) 13:966120. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.966120
116. Reid, DS, Geary, TW, Zezeski, AL, Waterman, RC, Van Emon, ML, Messman, RD, et al. Effects of prenatal and postnatal melatonin supplementation on overall performance, male reproductive performance, and testicular hemodynamics in beef cattle. J Anim Sci. (2023) 101:skad111. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad111
117. Wu, H, Yao, S, Wang, T, Wang, J, Ren, K, Yang, H, et al. Effects of melatonin on dairy herd improvement (DHI) of Holstein cow with high SCS. Molecules. (2021) 26:834. doi: 10.3390/molecules26040834
118. Xu, K, Wang, J, Liu, H, Zhao, J, and Lu, W. Melatonin promotes the proliferation of chicken Sertoli cells by activating the ERK/inhibin alpha subunit signaling pathway. Molecules. (2020) 25:1230. doi: 10.3390/molecules25051230
119. Dong, Y, Zhao, J, Zhu, Q, Liu, H, Wang, J, and Lu, W. Melatonin inhibits the apoptosis of rooster Leydig cells by suppressing oxidative stress via AKT-Nrf2 pathway activation. Free Radic Biol Med. (2020) 160:1–12. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.06.024
120. Ren, YL, Liang, Q, Lian, CY, Zhang, W, and Wang, L. Melatonin alleviates glyphosate-induced testosterone synthesis inhibition via targeting mitochondrial function in roosters. Environ Pollut. (2024) 348:123828. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2024.123828
121. Mehaisen, GMK, Partyka, A, Ligocka, Z, and Niżański, W. Cryoprotective effect of melatonin supplementation on post-thawed rooster sperm quality. Anim Reprod Sci. (2020) 212:106238. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2019.106238
122. Yan, L, Li, J, Li, G, Ma, W, Liu, Y, Liu, X, et al. Effect of melatonin on cryopreservation of Beijing you chicken (gallus gallus) spermatozoa. Cryobiology. (2024) 114:104794. doi: 10.1016/j.cryobiol.2023.104794
123. Hao, EY, Wang, DH, Chang, LY, Huang, CX, Chen, H, Yue, QX, et al. Melatonin regulates chicken granulosa cell proliferation and apoptosis by activating the mTOR signaling pathway via its receptors. Poult Sci. (2020) 99:6147–62. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.08.001
124. Hao, EY, Chen, H, Wang, DH, Huang, CX, Tong, YG, Chen, YF, et al. Melatonin regulates the ovarian function and enhances follicle growth in aging laying hens via activating the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. Poult Sci. (2020) 99:2185–95. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2019.11.040
125. Jia, Y, Yang, M, Zhu, K, Wang, L, Song, Y, Wang, J, et al. Melatonin implantation improved the egg-laying rate and quality in hens past their peak egg-laying age. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:39799. doi: 10.1038/srep39799
126. Rodriguez-Osorio, N, Kim, IJ, Wang, H, Kaya, A, and Memili, E. Melatonin increases cleavage rate of porcine preimplantation embryos in vitro. J Pineal Res. (2007) 43:283–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2007.00475.x
127. Kim, EH, Kim, GA, Taweechaipaisankul, A, Lee, SH, Qasim, M, Ahn, C, et al. Melatonin enhances porcine embryo development via the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. J Mol Endocrinol. (2019) 63:175–85. doi: 10.1530/JME-19-0093
128. Wang, L, Yan, L, Han, Q, Li, G, Wu, H, Ma, X, et al. Melatonin supplementation during the late gestational stage enhances reproductive performance of sows by regulating fluid shear stress and improving placental antioxidant capacity. Antioxidants (Basel). (2023) 12:688. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030688
129. Lee, S, Jin, JX, Taweechaipaisankul, A, Kim, GA, Ahn, C, and Lee, BC. Melatonin influences the sonic hedgehog signaling pathway in porcine cumulus oocyte complexes. J Pineal Res. (2017) 63:12424. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12424
130. Liu, Y, Yang, Y, Li, W, Ao, H, Zhang, Y, Zhou, R, et al. Effects of melatonin on the synthesis of estradiol and gene expression in pig granulosa cells. J Pineal Res. (2019) 66:e12546. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12546
131. He, YM, Deng, HH, Shi, MH, Bodinga, BM, Chen, HL, Han, ZS, et al. Melatonin modulates the functions of porcine granulosa cells via its membrane receptor MT2 in vitro. Anim Reprod Sci. (2016) 172:164–72. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2016.07.015
132. Bae, H, Yang, C, Lee, JY, Park, S, Bazer, FW, Song, G, et al. Melatonin improves uterine-conceptus interaction via regulation of SIRT1 during early pregnancy. J Pineal Res. (2020) 69:e12670. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12670
133. Zhang, W, Zhang, Z, Peng, J, Yang, S, and Tong, D. Effects of melatonin on the production of GnRH and LH in luteal cells of pregnant sows. J Mol Endocrinol. (2022) 68:111–23. doi: 10.1530/JME-21-0155
134. Yao, X, Jiang, H, Gao, Q, Li, YH, Xu, YN, and Kim, NH. Melatonin alleviates defects induced by zearalenone during porcine embryo development. Theriogenology. (2020) 151:66–73. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.04.005
135. Cao, Y, Li, R, Li, W, Liu, H, and Cai, Y. Melatonin attenuates Peroxynitrite-induced meiosis dysfunction in porcine oocytes. Reprod Sci. (2021) 28:1281–9. doi: 10.1007/s43032-020-00331-2
136. Qu, J, Sun, M, Wang, X, Song, X, He, H, and Huan, Y. Melatonin enhances the development of porcine cloned embryos by improving DNA methylation reprogramming. Cell Reprogram. (2020) 22:156–66. doi: 10.1089/cell.2019.0103
137. Arend, LS, Knox, RV, Greiner, LL, Graham, AB, and Connor, JF. Effects of feeding melatonin during proestrus and early gestation to gilts and parity 1 sows to minimize effects of seasonal infertility1. J Anim Sci. (2019) 97:4635–46. doi: 10.1093/jas/skz307
138. Li, Z, Zhang, K, Zhou, Y, Zhao, J, Wang, J, and Lu, W. Role of melatonin in bovine reproductive biotechnology. Molecules. (2023) 28:4940. doi: 10.3390/molecules28134940
139. Rodrigues-Cunha, MC, Mesquita, LG, Bressan, F, Collado, MD, Balieiro, JC, Schwarz, KR, et al. Effects of melatonin during IVM in defined medium on oocyte meiosis, oxidative stress, and subsequent embryo development. Theriogenology. (2016) 86:1685–94. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2016.05.026
140. Gutiérrez-Añez, JC, Lucas-Hahn, A, Hadeler, KG, Aldag, P, and Niemann, H. Melatonin enhances in vitro developmental competence of cumulus-oocyte complexes collected by ovum pick-up in prepubertal and adult dairy cattle. Theriogenology. (2021) 161:285–93. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.12.011
141. El-Raey, M, Geshi, M, Somfai, T, Kaneda, M, Hirako, M, Abdel-Ghaffar, AE, et al. Evidence of melatonin synthesis in the cumulus oocyte complexes and its role in enhancing oocyte maturation in vitro in cattle. Mol Reprod Dev. (2011) 78:250–62. doi: 10.1002/mrd.21295
142. Gutiérrez-Añez, JC, Henning, H, Lucas-Hahn, A, Baulain, U, Aldag, P, Sieg, B, et al. Melatonin improves rate of monospermic fertilization and early embryo development in a bovine IVF system. PLoS One. (2021) 16:e0256701. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0256701
143. Guo, L, Li, M, Gao, X, Yang, Y, Zhao, J, Wang, J, et al. Two melatonin treatments improve the conception rate after fixed-time artificial insemination in beef heifers following synchronisation of oestrous cycles using the CoSynch-56 protocol. Aust Vet J. (2021) 99:449–55. doi: 10.1111/avj.13100
144. Brockus, KE, Hart, CG, Gilfeather, CL, Fleming, BO, and Lemley, CO. Dietary melatonin alters uterine artery hemodynamics in pregnant Holstein heifers. Domest Anim Endocrinol. (2016) 55:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.domaniend.2015.10.006
145. Lemley, CO, and Vonnahme, KA. Physiology and endocrinology symposium: alterations in uteroplacental hemodynamics during melatonin supplementation in sheep and cattle. J Anim Sci. (2017) 95:2211–21. doi: 10.2527/jas.2016.1151
146. D'Occhio, MJ, Ghuman, SS, Neglia, G, Della Valle, G, Baruselli, PS, Zicarelli, L, et al. Exogenous and endogenous factors in seasonality of reproduction in buffalo: a review. Theriogenology. (2020) 150:186–92. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.01.044
147. Perumal, P, Chang, S, De, AK, Baruah, KK, Khate, K, Vupru, K, et al. Slow release exogenous melatonin modulates scrotal circumference and testicular parameters, libido, endocrinological profiles and antioxidant and oxidative stress profiles in mithun. Theriogenology. (2020) 154:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.05.017
148. Surai, PF, Kochish, II, Fisinin, VI, and Kidd, MT. Antioxidant Defence systems and oxidative stress in poultry biology: An update. Antioxidants (Basel). (2019) 8:235. doi: 10.3390/antiox8070235
149. Lauridsen, C . From oxidative stress to inflammation: redox balance and immune system. Poult Sci. (2019) 98:4240–6. doi: 10.3382/ps/pey407
150. Pablos, MI, Agapito, MT, Gutierrez, R, Recio, JM, Reiter, RJ, Barlow-Walden, L, et al. Melatonin stimulates the activity of the detoxifying enzyme glutathione peroxidase in several tissues of chicks. J Pineal Res. (1995) 19:111–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.1995.tb00178.x
151. Sirajudeen, M, Gopi, K, Tyagi, JS, Moudgal, RP, Mohan, J, and Singh, R. Protective effects of melatonin in reduction of oxidative damage and immunosuppression induced by aflatoxin B1-contaminated diets in young chicks. Environ Toxicol. (2011) 26:153–60. doi: 10.1002/tox.20539
152. Sun, K, Wang, X, Zhang, X, Shi, X, and Gong, D. The antagonistic effect of melatonin on TBBPA-induced apoptosis and necroptosis via PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in swine testis cells. Environ Toxicol. (2022) 37:2281–90. doi: 10.1002/tox.23595
153. Deng, CC, Zhang, JP, Huo, YN, Xue, HY, Wang, W, Zhang, JJ, et al. Melatonin alleviates the heat stress-induced impairment of Sertoli cells by reprogramming glucose metabolism. J Pineal Res. (2022) 73:e12819. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12819
154. Mou, Q, Yang, YW, Chen, L, Fang, T, Yao, YC, Du, ZQ, et al. Melatonin mitigates chloroquine-induced defects in porcine immature Sertoli cells. Theriogenology. (2022) 177:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2021.10.005
155. Wang, T, Gao, YY, Chen, L, Nie, ZW, Cheng, W, Liu, X, et al. Melatonin prevents postovulatory oocyte aging and promotes subsequent embryonic development in the pig. Aging (Albany NY). (2017) 9:1552–64. doi: 10.18632/aging.101252
156. Lan, M, Zhang, Y, Wan, X, Pan, MH, Xu, Y, and Sun, SC. Melatonin ameliorates ochratoxin A-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in porcine oocytes. Environ Pollut. (2020) 256:113374. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113374
157. Cheng, L, Qin, Y, Hu, X, Ren, L, Zhang, C, Wang, X, et al. Melatonin protects in vitro matured porcine oocytes from toxicity of aflatoxin B1. J Pineal Res. (2019) 66:e12543. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12543
158. Li, Y, Zhang, Z, He, C, Zhu, K, Xu, Z, Ma, T, et al. Melatonin protects porcine oocyte in vitro maturation from heat stress. J Pineal Res. (2015) 59:365–75. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12268
159. Zhan, C, Cao, X, Zhang, T, Guo, J, Xu, G, Wang, H, et al. Melatonin protects porcine oocyte from copper exposure potentially by reducing oxidative stress potentially through the Nrf2 pathway. Theriogenology. (2022) 193:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2022.09.004
160. Niu, YJ, Zhou, W, Nie, ZW, Shin, KT, and Cui, XS. Melatonin enhances mitochondrial biogenesis and protects against rotenone-induced mitochondrial deficiency in early porcine embryos. J Pineal Res. (2020) 68:e12627. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12627
161. García-Gil, FA, Albendea, CD, Escartín, J, Lampreave, F, Fuentes-Broto, L, Roselló-Catafau, J, et al. Melatonin prolongs graft survival of pancreas allotransplants in pigs. J Pineal Res. (2011) 51:445–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00908.x
162. Yang, F, Li, L, Chen, K, Li, C, Wang, Y, and Wang, G. Melatonin alleviates β-zearalenol and HT-2 toxin-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress in bovine ovarian granulosa cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. (2019) 68:52–60. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2019.03.005
163. Pang, YW, Jiang, XL, Wang, YC, Wang, YY, Hao, HS, Zhao, SJ, et al. Melatonin protects against paraquat-induced damage during in vitro maturation of bovine oocytes. J Pineal Res. (2019) 66:e12532. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12532
164. Pang, YW, Sun, YQ, Sun, WJ, Du, WH, Hao, HS, Zhao, SJ, et al. Melatonin inhibits paraquat-induced cell death in bovine preimplantation embryos. J Pineal Res. (2016) 60:155–66. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12297
165. Xu, G, Dong, Y, Wang, Z, Ding, H, Wang, J, Zhao, J, et al. Melatonin attenuates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis of bovine ovarian granulosa cells by promoting Mitophagy via SIRT1/FoxO1 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:12854. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612854
166. An, Q, Peng, W, Cheng, Y, Lu, Z, Zhou, C, Zhang, Y, et al. Melatonin supplementation during in vitro maturation of oocyte enhances subsequent development of bovine cloned embryos. J Cell Physiol. (2019) 234:17370–81. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28357
167. El-Sheikh, M, Mesalam, AA, Kang, SM, Joo, MD, Soliman, SS, Khalil, AAK, et al. Modulation of apoptosis and autophagy by melatonin in Juglone-exposed bovine oocytes. Animals (Basel). (2023) 13:1475. doi: 10.3390/ani13091475
168. Yaacobi-Artzi, S, Shimoni, C, Kalo, D, Hansen, PJ, and Roth, Z. Melatonin slightly alleviates the effect of heat shock on bovine oocytes and resulting blastocysts. Theriogenology. (2020) 158:477–89. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2020.09.039
169. Cavallari, FC, Leal, CLV, Zvi, R, and Hansen, PJ. Effects of melatonin on production of reactive oxygen species and developmental competence of bovine oocytes exposed to heat shock and oxidative stress during in vitro maturation. Zygote. (2019) 27:180–6. doi: 10.1017/S0967199419000236
170. Zhao, RH, Yang, FX, Bai, YC, Zhao, JY, Hu, M, Zhang, XY, et al. Research progress on the mechanisms underlying poultry immune regulation by plant polysaccharides. Front Vet Sci. (2023) 10:1175848. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1175848
171. Li, RX, Li, J, Zhang, SY, Mi, YL, and Zhang, CQ. Attenuating effect of melatonin on lipopolysaccharide-induced chicken small intestine inflammation. Poult Sci. (2018) 97:2295–302. doi: 10.3382/ps/pey084
172. Li, J, Li, RX, Liu, G, Lv, CF, Mi, YL, and Zhang, CQ. Effect of melatonin on renewal of chicken small intestinal mucosa. Poult Sci. (2017) 96:2942–9. doi: 10.3382/ps/pex085
173. Kliger, CA, Gehad, AE, Hulet, RM, Roush, WB, Lillehoj, HS, and Mashaly, MM. Effects of photoperiod and melatonin on lymphocyte activities in male broiler chickens. Poult Sci. (2000) 79:18–25. doi: 10.1093/ps/79.1.18
174. Chen, F, Reheman, A, Cao, J, Wang, Z, Dong, Y, Zhang, Y, et al. Effect of melatonin on monochromatic light-induced T-lymphocyte proliferation in the thymus of chickens. J Photochem Photobiol B. (2016) 161:9–16. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2016.05.001
175. Li, J, Wang, Z, Cao, J, Dong, Y, and Chen, Y. Melatonin receptor subtypes Mel1a and Mel1c but not Mel1b are associated with monochromatic light-induced B-lymphocyte proliferation in broilers. Domest Anim Endocrinol. (2013) 45:206–15. doi: 10.1016/j.domaniend.2013.09.003
176. Xiong, J, Wang, Z, Cao, J, Dong, Y, and Chen, Y. Melatonin mediates monochromatic light-induced proliferation of T/B lymphocytes in the spleen via the membrane receptor or nuclear receptor. Poult Sci. (2020) 99:4294–302. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.06.008
177. Guo, Q, Wang, Z, Dong, Y, Cao, J, and Chen, Y. Physiological crosstalk between the AC/PKA and PLC/PKC pathways modulates melatonin-mediated, monochromatic-light-induced proliferation of T-lymphocytes in chickens. Cell Tissue Res. (2017) 369:555–65. doi: 10.1007/s00441-017-2644-6
178. Markowska, M, Mrozkowiak, A, and Skwarlo-Sonta, K. Influence of melatonin on chicken lymphocytes in vitro: involvement of membrane receptors. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. (2002) 23:67–72. Available at: https://www.nel.edu/userfiles/articlesnew/NEL230702A05.pdf
179. Markowska, M, Waloch, M, and Skwarło-Sońta, K. Melatonin inhibits PHA-stimulated chicken lymphocyte proliferation in vitro. J Pineal Res. (2001) 30:220–6. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-079X.2001.300405.x
180. Du, L, Liu, B, Han, Z, Xia, Y, Wu, M, and Liu, S. Melatonin shapes bacterial clearance function of porcine macrophages during enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection. Anim Nutr. (2022) 11:242–51. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2022.06.018
181. Grupp, K, Erbes, J, Poppe, A, Wodack, K, Gocht, A, Trepte, C, et al. Melatonin treatment of pigs with acute pancreatitis reduces inflammatory reaction of pancreatic tissue and enhances fitness score of pigs: experimental research. World J Emerg Surg. (2019) 14:18. doi: 10.1186/s13017-019-0237-2
182. Sharun, K, Dhama, K, Tiwari, R, Gugjoo, MB, Iqbal Yatoo, M, Patel, SK, et al. Advances in therapeutic and managemental approaches of bovine mastitis: a comprehensive review. Vet Q. (2021) 41:107–36. doi: 10.1080/01652176.2021.1882713
183. Li, H, and Sun, P. Insight of melatonin: the potential of melatonin to treat Bacteria-induced mastitis. Antioxidants (Basel). (2022) 11:1107. doi: 10.3390/antiox11061107
184. Yu, GM, Kubota, H, Okita, M, and Maeda, T. The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of melatonin on LPS-stimulated bovine mammary epithelial cells. PLoS One. (2017) 12:e0178525. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178525
185. Chen, Z, Wang, K, Guo, J, Zhou, J, Loor, JJ, Yang, Z, et al. Melatonin maintains homeostasis and potentiates the anti-inflammatory response in Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis through microRNA-16b/YAP1. J Agric Food Chem. (2022) 70:15255–70. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.2c05904
186. Zheng, P, Qin, X, Feng, R, Li, Q, Huang, F, Li, Y, et al. Alleviative effect of melatonin on the decrease of uterine receptivity caused by blood ammonia through ROS/NF-κB pathway in dairy cow. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2022) 231:113166. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113166
187. Gao, Y, Li, Y, Wang, J, Zhang, X, Yao, D, Ding, X, et al. Melatonin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced Endometritis by inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome through autophagy. Animals (Basel). (2023) 13:2449. doi: 10.3390/ani13152449
188. Ge, WB, Xiao, LF, Duan, HW, Li, ZS, Jiang, YT, Yang, SS, et al. Melatonin protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced epididymitis in sheep epididymal epithelial cells in vitro. Immunol Lett. (2019) 214:45–51. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2019.09.001
189. Ge, W, Duan, H, Zeng, J, Zhao, X, Li, J, and Hu, J. Melatonin protects sheep endometrial epithelial cells against lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in vitro. Reprod Domest Anim. (2022) 57:1602–14. doi: 10.1111/rda.14237
190. Regodón, S, Ramos, A, Morgado, S, Tarazona, R, Martín-Palomino, P, Rosado, JA, et al. Melatonin enhances the immune response to vaccination against A1 and C strains of Dichelobacter nodosus. Vaccine. (2009) 27:1566–70. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.01.001
191. Wang, YX, Yang, GH, Zhang, LL, Wang, J, and Wang, JF. Melatonin as immune Potentiator for enhancing subunit vaccine efficacy against bovine viral diarrhea virus. Vaccines (Basel). (2021) 9:1039. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9091039
192. Yang, Y, Xu, W, Du, X, Ye, Y, Tian, J, Li, Y, et al. Effects of dietary melatonin on growth performance, antioxidant capacity, and nonspecific immunity in crayfish, Cherax destructor. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2023) 138:108846. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2023.108846
193. Rani, NF, Abduh, MY, Norazmi-Lokman, NH, and Aripin, SA. Data on growth performance, glucose concentration and testosterone level of Asian seabass, Lates calcarifer juveniles fed with exogenous melatonin at different concentration. Data Brief. (2022) 44:108495. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2022.108495
194. Amri, A, Kessabi, K, Bouraoui, Z, Sakli, S, Gharred, T, Guerbej, H, et al. Effect of melatonin and folic acid supplementation on the growth performance, antioxidant status, and liver histology of the farmed gilthead sea bream (Sparus aurata L.) under standard rearing conditions. Fish Physiol Biochem. (2020) 46:2265–80. doi: 10.1007/s10695-020-00879-5
195. Chattoraj, A, Bhattacharyya, S, Basu, D, Bhattacharya, S, Bhattacharya, S, and Maitra, SK. Melatonin accelerates maturation inducing hormone (MIH): induced oocyte maturation in carps. Gen Comp Endocrinol. (2005) 140:145–55. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2004.10.013
196. Zhang, J, Li, F, Zhang, X, Xie, T, Qin, H, Lv, J, et al. Melatonin improves turbot oocyte meiotic maturation and antioxidant capacity, inhibits apoptosis-related genes mRNAs in vitro. Antioxidants (Basel). (2023) 12:1389. doi: 10.3390/antiox12071389
197. Mondal, P, Hasan, KN, Pal, PK, and Maitra, SK. Influences of exogenous melatonin on the oocyte growth and oxidative status of ovary during different reproductive phases of an annual cycle in carp Catla catla. Theriogenology. (2017) 87:349–59. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2016.09.021
198. Motta, NC, Egger, RC, Monteiro, KS, Vogel de Oliveira, A, and Solis Murgas, LD. Effects of melatonin supplementation on the quality of cryopreserved sperm in the neotropical fish Prochilodus lineatus. Theriogenology. (2022) 179:14–21. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2021.11.012
199. Peter, MCS, Gayathry, R, Simi, S, and Peter, VS. Melatonin integrates multidimensional regulation of Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase in ionocytes and promotes stress and ease response in hypoxia-induced air-breathing fish: lessons from integrative approach. Front Physiol. (2022) 13:1012729. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1012729
200. Moniruzzaman, M, Ghosal, I, Das, D, and Chakraborty, SB. Melatonin ameliorates H(2)O(2)-induced oxidative stress through modulation of Erk/Akt/NFkB pathway. Biol Res. (2018) 51:17. doi: 10.1186/s40659-018-0168-5
201. Moniruzzaman, M, Maiti, AK, Chakraborty, SB, Saha, I, and Saha, NC. Melatonin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide induced brain inflammation through modulation of oxidative status and diminution of cytokine rush in Danio rerio. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. (2022) 96:103983. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2022.103983
202. Li, X, Zhang, H, Qiao, S, Ma, W, Cai, J, Zhang, X, et al. Melatonin administration alleviates 2,2,4,4-tetra-brominated diphenyl ether (PBDE-47)-induced necroptosis and secretion of inflammatory factors via miR-140-5p/TLR4/NF-κB axis in fish kidney cells. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2022) 128:228–37. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2022.08.004
203. Miao, Z, Miao, Z, Liu, M, and Xu, S. Melatonin ameliorates imidacloprid-induced intestinal injury by negatively regulating the PGN/P38MAPK pathway in the common carp (Cyprinuscarpio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2022) 131:1063–74. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2022.11.018
204. Zhang, Y, Zhang, X, Yan, Q, Xu, C, Liu, Q, Shen, Y, et al. Melatonin attenuates polystyrene microplastics induced motor neurodevelopmental defect in zebrafish (Danio rerio) by activating nrf2 – isl2a Axis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2022) 241:113754. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2022.113754
205. Moniruzzaman, M, Mukherjee, M, Das, D, and Chakraborty, SB. Effectiveness of melatonin to restore fish brain activity in face of permethrin induced toxicity. Environ Pollut. (2020) 266:115230. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.115230
206. Oh, KH, Rah, YC, Hwang, KH, Lee, SH, Kwon, SY, Cha, JH, et al. Melatonin mitigates neomycin-induced hair cell injury in zebrafish. Drug Chem Toxicol. (2017) 40:390–6. doi: 10.1080/01480545.2016.1244679
207. Miao, Z, Miao, Z, Teng, X, and Xu, S. Melatonin alleviates lead-induced fatty liver in the common carps (Cyprinus carpio) via gut-liver axis. Environ Pollut. (2023) 317:120730. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2022.120730
208. Furusawa, Y, Yamamoto, T, Hattori, A, Suzuki, N, Hirayama, J, Sekiguchi, T, et al. De novo transcriptome analysis and gene expression profiling of fish scales isolated from Carassius auratus during space flight: impact of melatonin on gene expression in response to space radiation. Mol Med Rep. (2020) 22:2627–36. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11363
209. Miao, Z, Miao, Z, Teng, X, and Xu, S. Melatonin alleviates lead-induced intestinal epithelial cell pyroptosis in the common carps (Cyprinus carpio) via miR-17-5p/TXNIP axis. Fish Shellfish Immunol. (2022) 131:127–36. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2022.09.071
210. Stacchiotti, A, Favero, G, and Rodella, LF. Impact of melatonin on skeletal muscle and exercise. Cells. (2020) 9:288. doi: 10.3390/cells9020288
211. Samra, T, Gomez-Gomez, T, Linowiecka, K, Akhundlu, A, Lopez de Mendoza, G, Gompels, M, et al. Melatonin exerts prominent, differential epidermal and dermal anti-aging properties in aged human eyelid skin ex vivo. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:15963. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115963
212. Sayed, RKA, Fernández-Ortiz, M, Diaz-Casado, ME, Rusanova, I, Rahim, I, Escames, G, et al. The protective effect of melatonin against age-associated, sarcopenia-dependent tubular aggregate formation, lactate depletion, and mitochondrial changes. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2018) 73:1330–8. doi: 10.1093/gerona/gly059
213. Sayed, RKA, Fernández-Ortiz, M, Diaz-Casado, ME, Aranda-Martínez, P, Fernández-Martínez, J, Guerra-Librero, A, et al. Lack of NLRP3 Inflammasome activation reduces age-dependent sarcopenia and mitochondrial dysfunction, favoring the prophylactic effect of melatonin. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. (2019) 74:1699–708. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glz079
214. Bai, X, Cao, J, Dong, Y, Wang, Z, and Chen, Y. Melatonin mediates monochromatic green light-induced satellite cell proliferation and muscle growth in chick embryo. PLoS One. (2019) 14:e0216392. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0216392
215. Duan, T, Wu, Z, Zhang, H, Liu, Y, Li, Y, and Zhang, W. Effects of melatonin implantation on carcass characteristics, meat quality and tissue levels of melatonin and prolactin in inner Mongolian cashmere goats. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. (2019) 10:70. doi: 10.1186/s40104-019-0377-y
Keywords: melatonin, reproductive performance, antioxidation, immune regulation, animal application
Citation: Zhao R, Bai Y and Yang F (2024) Melatonin in animal husbandry: functions and applications. Front. Vet. Sci. 11:1444578. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1444578
Edited by:
Ramy K. A. Sayed, Sohag University, EgyptReviewed by:
Duan Xing, Zhejiang Agriculture and Forestry University, ChinaKun-Lin Chen, Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences (JAAS), China
Marisol Fernandez Ortiz, The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, United States
Copyright © 2024 Zhao, Bai and Yang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fangxiao Yang, MTM3MjMxMDQ0QHFxLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Ruohan Zhao
Ruohan Zhao Yicheng Bai
Yicheng Bai Fangxiao Yang
Fangxiao Yang