- 1Department of Veterinary Diagnostic and Production Animal Medicine, Iowa State University College of Veterinary Medicine, Ames, IA, United States
- 2Analytical Chemistry Section, Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory, Iowa State University College of Veterinary Medicine, Ames, IA, United States
- 3Veterinary Pharmacotherapy and Pharmacy, Department of Population Health Sciences, Utrecht University, Utrecht, Netherlands
- 4Department of Anatomy and Physiology, Kansas State University College of Veterinary Medicine, Manhattan, KS, United States
- 5SMART Pharmacology, Department of Biomedical Sciences, Iowa State University College of Veterinary Medicine, Ames, IA, United States
A Corrigendum on
Comparative Pharmacokinetics of Meloxicam Between Healthy Post-partum vs. Mid-lactation Dairy Cattle
by Warner, R., Ydstie, J. A., Wulf, L. W., Gehring, R., Coetzee, J. F., Mochel, J. P., et al. (2020). Front. Vet. Sci. 7:548. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00548
In the original article, there was a mistake in the legend for Tables 2 and 4 as published. In these tables, the number of cows in each group were stated incorrectly. The correct legend appears below.
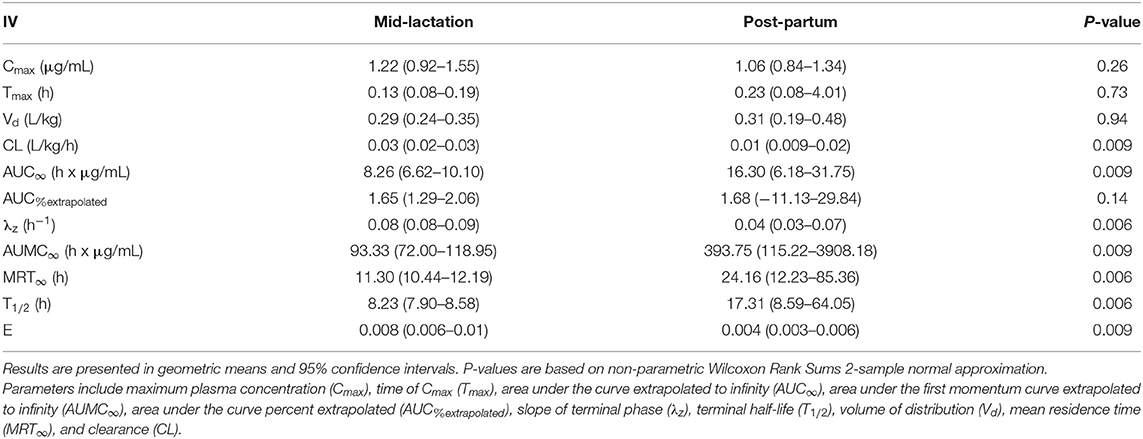
Table 4. Plasma pharmacokinetic parameters for meloxicam from seven post-partum cows compared to five mid-lactation cows intravenously administered a single dose of meloxicam at 0.2 mg/kg.
Table 2. Plasma concentrations (μg/mL) for meloxicam from seven post-partum cows compared to five mid-lactation cows that received intravenous administration of a single dose of meloxicam at 0.2 mg/kg. Results are presented as geometric means and 95% confidence interval.
Table 4. Plasma pharmacokinetic parameters for meloxicam from seven post-partum cows compared to five mid-lactation cows intravenously administered a single dose of meloxicam at 0.2 mg/kg. Results are presented in geometric means and 95% confidence intervals. P-values are based on non-parametric Wilcoxon Rank Sums 2-sample normal approximation.
In the original article, there was a mistake in Table 4 as published. In this table, the units for Vd should have been L/kg. The corrected Table 4 appears below.
In the original article, there was a mistake in Table 5 as published. In this table, the units for Vz/F should have been L/kg and the values for Vz/F were incorrectly reported as mL/kg. The corrected Table 5 appears below.
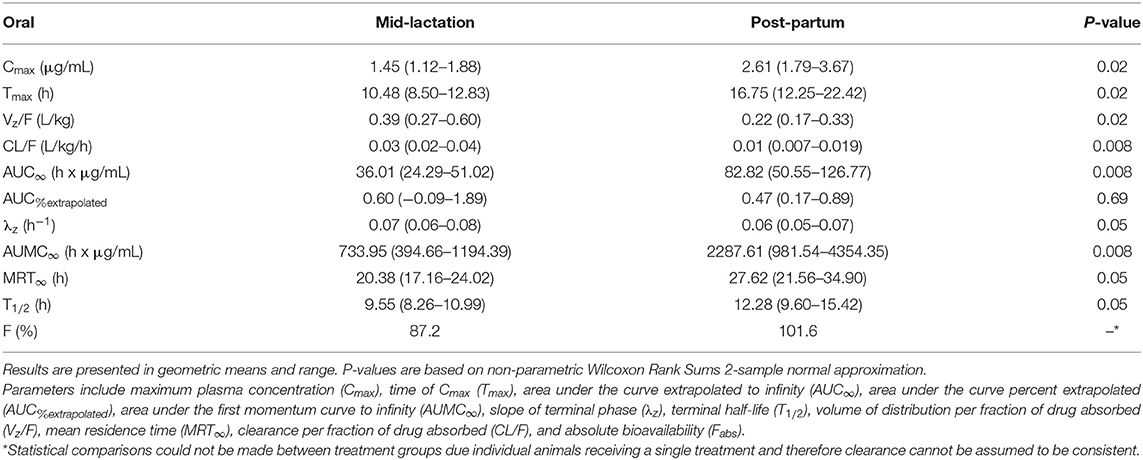
Table 5. Plasma pharmacokinetic parameters for meloxicam from six post-partum cows matched to mid-lactation cows orally administered a single dose of meloxicam at 1.0 mg/kg.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: meloxicam, pharmacokinetics, post-partum, NSAID, dairy
Citation: Warner R, Ydstie JA, Wulf LW, Gehring R, Coetzee JF, Mochel JP and Gorden PJ (2021) Corrigendum: Comparative Pharmacokinetics of Meloxicam Between Healthy Post-partum vs. Mid-lactation Dairy Cattle. Front. Vet. Sci. 8:665021. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.665021
Received: 06 February 2021; Accepted: 04 May 2021;
Published: 26 May 2021.
Edited and reviewed by: Arturo Anadón, Complutense University of Madrid, Spain
Copyright © 2021 Warner, Ydstie, Wulf, Gehring, Coetzee, Mochel and Gorden. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Patrick J. Gorden, cGdvcmRlbkBpYXN0YXRlLmVkdQ==
 Rochelle Warner1
Rochelle Warner1 Larry W. Wulf
Larry W. Wulf Ronette Gehring
Ronette Gehring Johann F. Coetzee
Johann F. Coetzee Jonathan P. Mochel
Jonathan P. Mochel Patrick J. Gorden
Patrick J. Gorden