- School of Veterinary and Life Sciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, Murdoch University, Perth, WA, Australia
A Corrigendum on
Hypocoagulability and Platelet Dysfunction Are Exacerbated by Synthetic Colloids in a Canine Hemorrhagic Shock Model
by Boyd, C. J., Claus, M. A., Raisis, A. L., Hosgood, G., Sharp, C. R., and Smart, L. (2018). Front. Vet. Sci. 5:279. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2018.00279
In the original article, there was a mistake in Table 2 as published. The EXTEM CFT baseline mean (95% confidence interval) for the HES group was slightly incorrect due to a data entry error. The corrected Table 2 appears below.
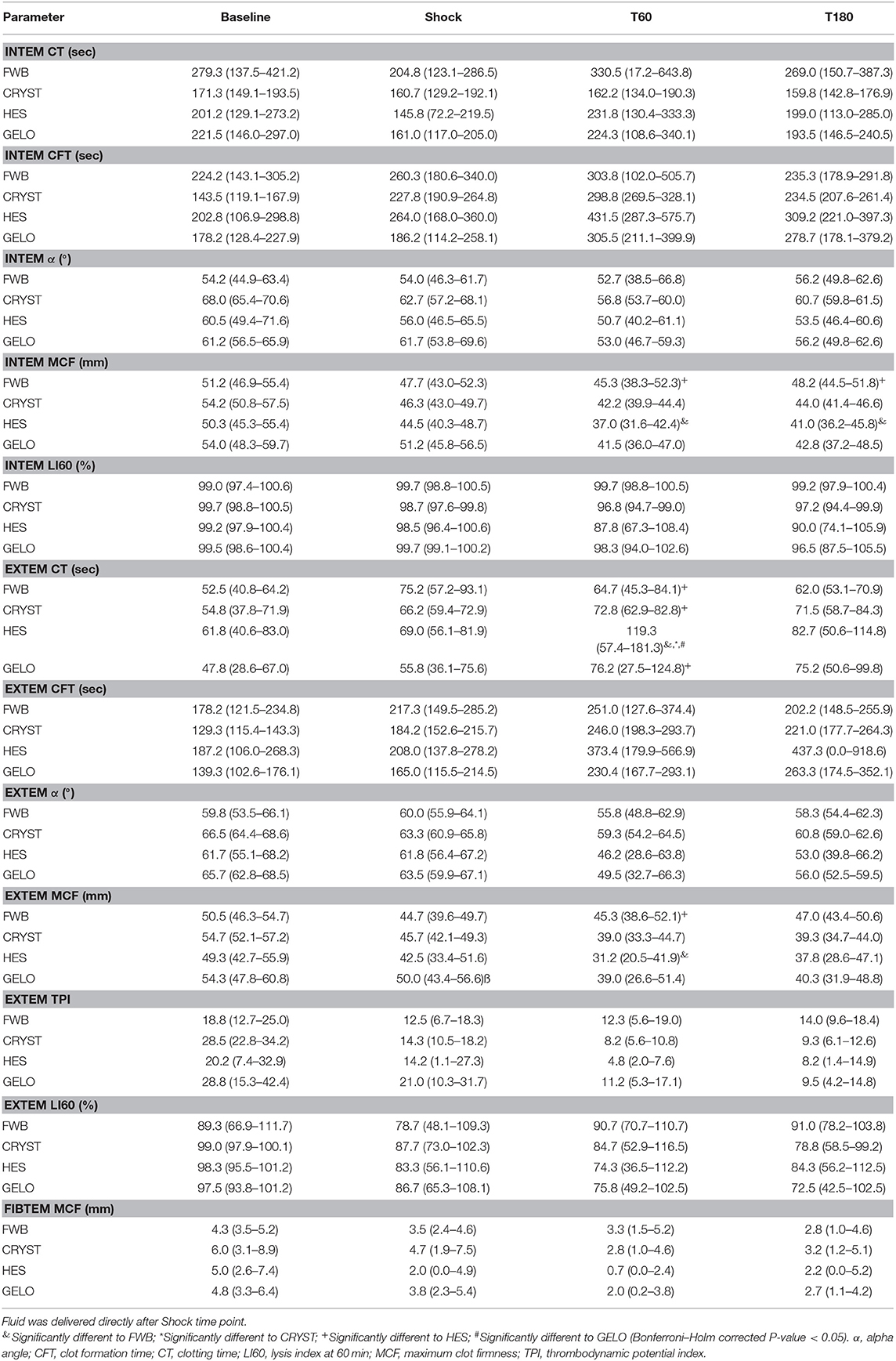
Table 2. Rotational thromboelastometry parameters (mean, 95% confidence interval) in dogs (n = 6 per group) with hemorrhagic shock given 20 mL kg−1 of either fresh whole blood (FWB), hydroxyethyl starch 130/0.4 (HES), 4% succinylated gelatin (GELO), or 80 mL kg−1 of balanced isotonic crystalloid (CRYST).
In the original article, there was a mistake in Table 5 as published. The EXTEM CFT baseline mean (95% confidence interval) was slightly incorrect due to a data entry error. The corrected Table 5 appears below.
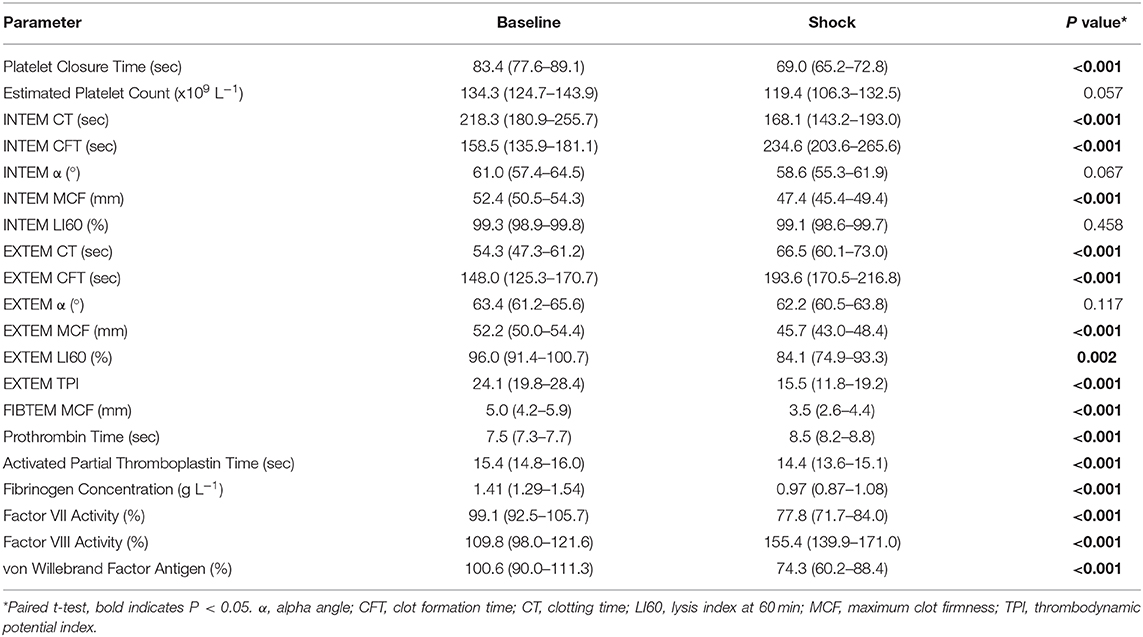
Table 5. Platelet closure time and count, rotational thromboelastometry, and plasma coagulation assay parameters (mean, 95% confidence interval) in dogs (n = 24) with hemorrhagic shock.
In the original article, there was an error. A conversion factor was inadvertently omitted from the equation for thrombodynamic potential index (TPI).
A correction has been made to Materials and Methods, Coagulation Parameters, Paragraph 3:
Rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM® delta, Tem International GmbH) was performed according to the manufacturer's instructions and PROVETS guidelines (28) using the INTEM (star-TEM and in-TEM reagents), EXTEM (star-TEM and r ex-TEM reagents), FIBTEM (r ex-TEM and fib-TEM reagents), and APTEM (r ex-TEM and ap-TEM reagents) profiles. Measurement was started 30 min after sample collection. Each profile was run for at least 1 h following initiation. Data recorded for the INTEM and EXTEM profiles included clotting time (CT), clot formation time (CFT), alpha angle (α), maximum clot firmness (MCF), and lysis index at 60 min (LI60). Thrombodynamic potential index (TPI) was recorded for the EXTEM profile as a measure of global coagulation (29), calculated using the equations:
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Keywords: hydroxyethyl starch, succinylated gelatin, crystalloid, fresh whole blood, platelet closure time, PFA-100, rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM), viscoelastic coagulation tests
Citation: Boyd CJ, Claus MA, Raisis AL, Hosgood G, Sharp CR and Smart L (2020) Corrigendum: Hypocoagulability and Platelet Dysfunction Are Exacerbated by Synthetic Colloids in a Canine Hemorrhagic Shock Model. Front. Vet. Sci. 7:641. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00641
Received: 29 June 2020; Accepted: 06 August 2020;
Published: 08 September 2020.
Edited and reviewed by: Katja-Nicole Adamik, University of Bern, Switzerland
Copyright © 2020 Boyd, Claus, Raisis, Hosgood, Sharp and Smart. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Corrin J. Boyd, Yy5ib3lkQG11cmRvY2guZWR1LmF1
 Corrin J. Boyd
Corrin J. Boyd Melissa A. Claus
Melissa A. Claus Anthea L. Raisis
Anthea L. Raisis Claire R. Sharp
Claire R. Sharp Lisa Smart
Lisa Smart