- School of Architecture, Nanjing Tech University, Nanjing, China
With the emergence of human-centered urban development goals and the increasing pursuit of a better quality of life, the architectural façades of cities are receiving growing attention. However, during the process of urban development, architectural façades often experience physical disorder. This phenomenon tends to be overlooked in targeted urban management practices or lacks cohesive urban renewal planning at a macro scale. This oversight can negatively impact the livability and attractiveness of a region. This study aims to quantify the architectural façades encountered daily by urban residents by measuring the physical disorder of architectural façades to inform better urban renewal using deep learning and space syntax. First, streetscape images of architectural façades were collected using the Baidu Maps Street View service. Subsequently, an evaluation system for architectural façades was developed, and machine learning was employed to conduct high-resolution measurements and assessments of these façades. Simultaneously, street network data is extracted and analyzed using space syntax to quantify the accessibility of architecture on each street. Finally, by integrating the analysis of architectural façades and accessibility, the study identifies priority areas for building renewal, thus providing a decision-support tool for sustainable urban renewal planning. Overall, the paper presents an innovative method that combines image data, deep learning, and space syntax-derived architectural accessibility for a quadrant analysis. It offers designers and decision makers new perspectives and enhances the livability of residents by focusing on the physical condition of architectural façades, thereby making urban renewal practices more human-centered and better aligned with the actual needs of city dwellers.
1 Introduction
Urban construction has slowed as cities enter a stage of high-quality development, and urban renewal has gradually shifted from incremental updates to stock updates (Dai et al., 2023). People have begun to pay more attention to the problems of extensive urban construction. Such as concerns over the quality and diversity of buildings and the loss of architectural diversity (Monastyrskaia, 2016), as well as how to adapt to current social development while preserving the historical façade of traditional buildings (Zhou et al., 2017), thereby creating a better urban appearance.
The decision-making process in Chinese urban renewal efforts is related to whether a specific area is within the urban renewal plans formulated by local governments (Cheshmehzangi et al., 2023). Most of these plans are macro-level controls from the top down (Wang et al., 2022), lacking public participation and failing to fully consider residents’ perceptions and needs for actual urban space. The development of urban renewal plans at this stage still relies on government officials’ assessments of social, economic, and environmental factors (Zheng et al., 2014). To address this, some scholars have proposed sustainable urban renewal decision theory models (Zheng et al., 2017) and comprehensive benefit evaluation indicators (Hao and Wang, 2023). Others suggest integrating urban planning principles with residents’ needs (Sheikh and van Ameijde, 2022) and studying livability indices about health and well-being data (Badland et al., 2014; Chi and Mak, 2021) to inform urban planning policies.
Architectural façades are one of the most crucial elements in urban spatial indicators. Current methods for assessing architectural façades include implicit association tests (IAT) (Mastandrea et al., 2011) and environmental perception and emotional evaluation of contemporary versus traditional styles through 360-degree videos of natural environments (Mouratidis and Hassan, 2020). However, there is still a lack of intuitive and quantitative measurement methods. Traditional aerial photography focuses more on building outline data. With the rapid development of artificial intelligence, street view images, and machine learning, they provide technical support for comprehensively and rapidly simulating perceptions of street views from pedestrain, offering new approaches to simulating people’s perceptions of buildings (Jiao and Zhao, 2019; Ma et al., 2021; Olaode and Naghdy, 2019).
Currently, many scholars are beginning to use space syntax to quantify some aspects of urban space. With the rise of artificial intelligence, digital technologies are being integrated into architectural design (Zhang Z. et al., 2023) and urban renewal processes and development (Shach-Pinsly, 2021). Through network topology measurement models, the order and disorder of street networks can be quantified (Mohajeri et al., 2013). Using OSM data and the OSMnx tool, combined with actual measurements, urban spatial order can be visualized (Boeing, 2019). Additionally, by defining physical disorder phenomena, visual characteristics, and auditing guidelines, physical disorders can be evaluated and monitored in community environments (Chen et al., 2023). Training diffusion models also explore the potential for preserving and renovating historical architecture (Zhang et al., 2024).
To objectively evaluate the physical disorder of architectural façades and street accessibility, thereby providing references for urban renewal, two key issues must be addressed: 1) How to quantitatively measure the degree of physical disorder in urban architectural façades; 2) The correlation between the degree of physical disorder in urban architectural façades and architectural accessibility, and its significance for urban renewal. To address these issues, this research combined machine learning, which simulates human perceptions of actual architectural façades, and space syntax, which can analyze architectural accessibility, revealing the relationship between spatial organization and human activity in a quantitative manner. By understanding spatial structures, we can infer how a city functions. Therefore, this study aims to use big data to collect information and machine learning to assess the condition of architectural façades. By integrating these assessments with architectural accessibility, the research forms a complete analytical loop—from human perceptions of urban spaces to inferring possible human activities based on urban spatial structure. This approach provides a solid foundation for more informed decisions in urban architectural renewal. To jointly analyze the accessibility and visibility of architectural façades from a human perspective, this paper: 1) Defines and quantitatively analyzes the physical disorder of architectural façades using street view images; 2) Analyzes architectural accessibility; 3) Integrates the physical disorder of architectural façades with architectural accessibility to determine building renovation priorities, proposing a more evidence-based workflow for urban renewal.
2 Literature review
2.1 Research on physical disorder in architectural façades
The architectural façade is an organic unity of a city’s external image and intrinsic spirit, intuitively displaying its heritage, uniqueness, and quality. It reflects the comprehensive and positive portrayal of the city’s physical characteristics, social culture, and economic features. The architectural façade of Chinese cities is influenced by natural geography, historical culture, lifestyle habits, and architectural technology (Zhao, 2020). With rapid urban development and a weakening of conservation awareness, some historic districts have suffered varying degrees of damage, with some even being demolished, leading to changes in local architectural façades. As urban construction enters a stage of stock development, finding a balance between preserving the historical character of traditional buildings and adapting to contemporary urban development is a crucial issue in urban renewal.
Physical disorder in architectural façades refers to irregularity, chaos, or disorder within a building and its environment. Since the 2010s, architects from China and abroad have increasingly focused on existing urban architectural façade issues. They initiated a series of studies on urban architectural façades and urban form, cultural identity, urban renewal and transformation, sustainable urban development, and social psychology. Research on the relationship between order and disorder in urban architecture has revealed a close connection between the spatial properties of urban environments produced by architectural façade physical disorder and antisocial behavior (Friedrich et al., 2009; González Martínez, 2020). Extensive related research indicates that disordered physical environments in districts can harm physical health (Chen et al., 2023), affect neighborhood relationships (Ross and Jang, 2000), and exacerbate racial issues (Franzini et al., 2008; Sampson and Raudenbush, 2004).
For scientific method-based studies on the identification and analysis of architectural façades (Diego, n.d.), there are feature extraction modules based on Deformable Part Models (DPM) preprocessing of images (Zhao et al., 2018); architectural model selection based on style constraints (Chavez et al., 2009); computation of dark original color feature information of architectural images, improvement of architectural image clarity through adaptive wavelet denoising; feature detection for architectural images of different styles to achieve intelligent computation and classification recognition of architectural styles (Chen, 2018).
Dense convolutional networks (DenseNet) have found widespread application in image feature extraction. They alleviate the vanishing-gradient problem, strengthen feature propagation, encourage feature reuse, and substantially reduce the number of parameters (Huang et al., 2022). DenseNet performs exceptionally well in computer vision tasks, particularly image classification and object detection. The image classification performance under the DenseNet architecture is superior and can be applied to tasks such as detecting and classifying cracks in building concrete (Akgül, 2023; Zhang et al., 2019) and recognizing and classifying different types of waste (Oktaviana and Azhar, 2021). Additionally, when applied to pedestrian detection, the DenseNet model can accurately detect, track, and predict pedestrians’ expected behavior (Qi, 2024; Saleh et al., 2020).
2.2 Urban architectural accessibility: Space Syntax
Accessibility refers to the time, distance, and convenience required for people to reach their target buildings. It focuses on the travel distance needed to reach a target building, where shorter distances reduce travel time and costs, usually resulting in better accessibility. As a critical theory in urban planning, Space Syntax can quantitatively analyze the spatial relationship between buildings and street networks, assess their accessibility, and predict the flow of movement within the street network (Hillier and Iida, 2005). Space Syntax software such as Depthmap or sDNA can quantify traffic flow in street networks. Spatial Design Network Analysis (sDNA), developed by Cardiff University in 2011, is a widely used tool for sDNA (Malleson et al., 2015).
With the application of technologies like GIS, researchers have studied architectural accessibility at the human scale well. Scholars use Space Syntax to assist in quantifying the accessibility of urban parks and street vitality and to evaluate daily access to street greenery and housing prices (Huang et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2018; Ye et al., 2019b). From these, results evaluating the spatial quality of urban living streets can be concluded, and the findings provided the strategic basis for citywide planning (Duan et al., 2023; Xiao et al., 2017).
Some studies have linked space syntax with machine learning and deep learning. For example, systems have been developed that integrate space syntax and use street view images and deep learning to assess the quality of urban street greenery (Xia et al., 2021); measuring greenery in frequently visited streets (Ye et al., 2019a); evaluating the inequity of urban daily accessible green resources (Zhang J. et al., 2023). Additionally, some researchers have applied these methods to urban street space assessments, using machine learning and street view images of architectural façades to conduct large-scale evaluations of façade quality and building interface continuity (Liu et al., 2017).
In summary, with the support of image data and artificial intelligence, new research potential has emerged for in-depth evaluation of daily visible and accessible architectural façades. While some studies have applied AI to assess façade styles (Chen, 2018), the combination of everyday accessibility and visible architectural quality remains unexplored. Large-scale quantification of physical disorder in architectural façades is worth investigating. Additionally, integrating accessibility and visible architectural quality indices as critical indicators in urban renewal planning is a valuable direction for future research.
3 Research methods
3.1 Study area
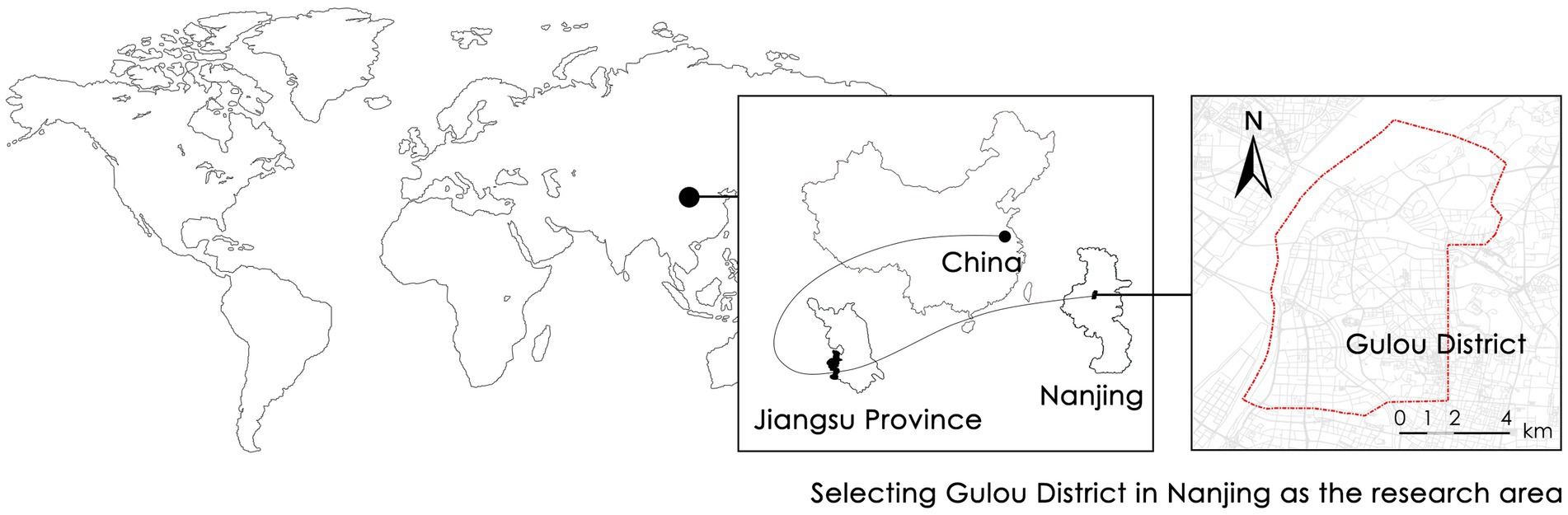
Nanjing, the capital of Jiangsu Province in eastern China, is a significant central city in the region. As a “National Historical and Cultural City,” the city greatly emphasizes its architectural façade. Gulou District, located in the central part of Nanjing and one of the eight main urban districts, serves as the center for economy, culture, and education in Nanjing, as well as the political, cultural, and administrative center of Jiangsu Province. The study area spans 54.18 square kilometers with a permanent population of 940,400, resulting in a high population density. With the city’s development, changes in the architectural façade have led to various degrees of disorder, thereby affecting architectural accessibility. Therefore, with its significant research value, the Gulou District of Nanjing has been selected as the study area (Figure 1).
3.2 Research framework
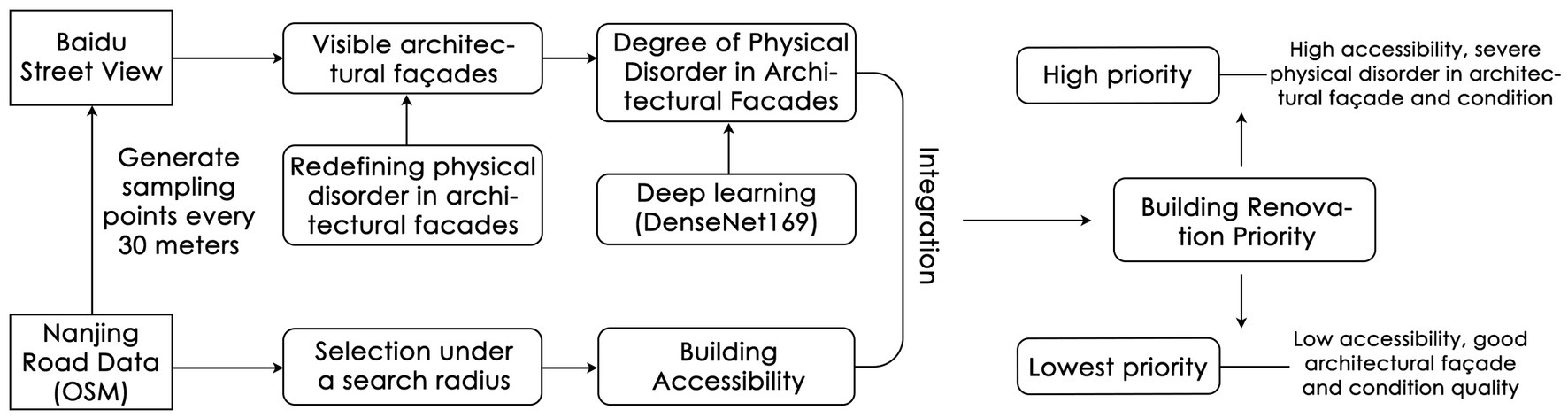
This study primarily encompasses four main stages. First, detailed road network data and Street View Images (SVI) of Gulou District are collected using Open Street Map (OSM) and the Baidu API. Then, through manual curation and preprocessing techniques, a machine learning model based on DenseNet169 is trained to discern whether architectural façades are disordered and identify physical disorders in the captured street view images. Subsequently, using the Space Syntax tool sDNA and considering a 15-min living circle with an 800 m travel distance as the standard, the accessibility of streets is quantified. Finally, by analyzing whether physical disorder exists in the architectural façade and the level of architectural accessibility, the study offers planning recommendations for urban architectural façade renewal from different dimensions (Figure 2).
3.3 Collection of street space street view images
This study’s road network data were sourced from the Open Street Map. To comprehensively display the extent of architectural façade disorder in the street views of Gulou District, we conducted a thorough analysis of 4 images in each site with 360°view using the Baidu open platform. Sampling points at equal intervals were generated based on a 30-meter sampling distance. For each sampling point, street view images from Baidu in four directions were collected, resulting in front, back, left, and right street view images for a total of 12,349 sampling points. Ultimately, two perspectives perpendicular to the street were selected to simulate the visual experience of a person observing the architectural façade while walking along the street, akin to a human viewpoint (Figure 3).
3.4 Developing an evaluation system for physical disorder in architectural façades and using deep learning for assessment
Redefining physical disorder in architectural façades on this basis allows for establishing more specific quantitative standards in the evaluation system for physical disorder in architectural façades. The evaluation criteria for architectural façade physical disorder are divided into four parts:
1) The comprehensive quality score of the façade; 2) the additional architectural decoration score; 3) the street-facing commercial storefront score; 4) the completeness score of the ancillary infrastructure of the building (Figure 4).
In terms of the overall quality of architectural façades, the study examines factors such as the building’s age, level of deterioration, harmony of different architectural styles, and unauthorized constructions. Except for buildings designated as cultural heritage, the longer a building has been in use, the more severe its damage, the less uniform its architectural style, and the greater the number of illegal constructions, the higher the degree of physical disorder in the architectural façades is likely to be.
Regarding additional architectural decorations, the chaotic sizes and colors of billboards, privately added long clotheslines and unauthorized network cables impact the overall architectural façade. The more types of additional decorations and the more disordered their scale and color, the higher the degree of physical disorder in the architectural façade.
For street-facing commercial storefronts, when renovating, businesses often focus solely on their own design rather than coordinating with neighboring shops. Therefore, it is essential to consider the overall harmony and tidiness of the storefront signage. The older the storefront and the more out of sync it is with surrounding shops, the higher the degree of physical disorder in the architectural façades will likely be.
Regarding the completeness of architectural ancillary infrastructure, factors such as temporary construction areas, differences in the styles of ancillary infrastructure from different eras, and disorderly vehicle parking can all impact the overall architectural façades (Figure 4).
This study employs deep learning to automatically extract pixel semantic information, simulate the human perception of architectural façades, and comprehensively analyze the degree of physical disorder in architectural façades using the Baidu API. The scoring standards for physical disorder in architectural façades were determined through manual scoring discussions, where examples corresponding to different scores for each sub-item were selected. Subsequently, machine deep learning was used to score each sample area individually.
After filtering out images without buildings, the remaining images were scored based on four aspects: comprehensive quality of the façade, quality of additional architectural decorations, condition of street-facing commercial storefronts, and completeness of the building’s ancillary infrastructure. According to the redefinition of physical disorder in architectural façades, a score of 3 is given for no disorder, 2 for one type of disorder or mild disorder, 1 for two types of disorder or severe disorder, and 0 for three types of disorder or extremely severe disorder.
The street view images obtained were then scored, forming a relatively complete evaluation system. A total score of 9–12 indicates good perception of architectural façade quality, 5–8 indicates some degree of physical disorder (medium quality of architectural façade), and 0–4 indicates severe physical disorder (low quality of architectural façade).
To enhance the accuracy of the evaluation, this study invited seven scholars with architectural education or experience in façade renovation design to score a sample of 2,786 sampling point images. Images without buildings were labeled as “none,” and the selected images with buildings were labeled as “high,” “medium,” or “low” according to the scoring standards. The other samples were also labeled as “high,” “medium,” or “low” based on the scoring criteria.
The scored samples are randomly fed into the deep learning training process. First, construct an image classification dataset and divide it into training and test sets. Next, a pre-trained image classification model from ImageNet will be used to make initial predictions. Then, train an image classification model using transfer learning in PyTorch, predicting images with the trained model and evaluating its classification accuracy on the test set. Finally, deploy the model.
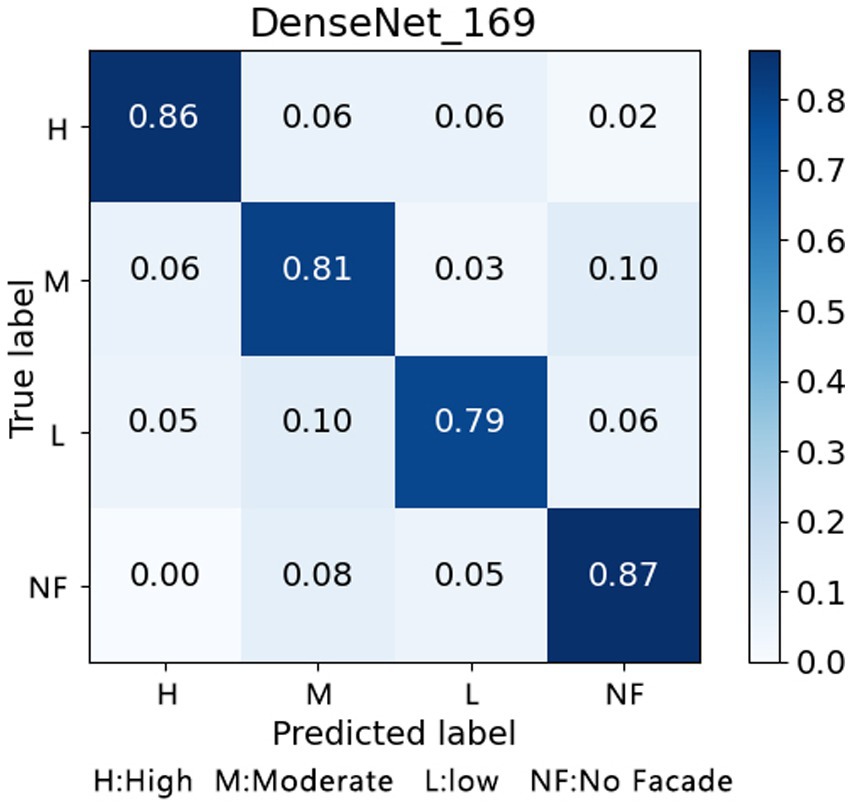
A CNN-based machine learning model under deep supervised learning is used to train an objective classification model. After multiple rounds of training with sample images of architectural façades and achieving an accuracy rate of 83% on comparison samples, the model is applied to sample images from the Gulou District of Nanjing for analysis. This results in 10,600 sampled street view images of buildings being labeled as “high,” “medium,” or “low” based on the scoring criteria (Figure 5).
3.5 Integration of architectural accessibility measurement and physical disorder of architectural façades
This study utilizes space syntax to analyze the street network, selecting an 800-meter radius as the daily activity radius to analyze the integration and choice of the street network (Kim and Penn, 2004). Based on this, a simulated analysis of architectural accessibility is conducted. Integration measures a space’s ability to attract traffic as a destination, reflecting its centrality within the system (Sharmin and Kamruzzaman, 2018). Choice examines the advantages a spatial unit has as the shortest path of travel, reflecting the possibility of the space being traversed. These two parameters complement each other and can reveal the street network’s impact on the city’s physical formation (Kim and Sohn, 2002), as well as pedestrian movement patterns under changes in spatial and temporal resolution (Ericson et al., 2021).
In Equation 1, represents the number of line segments experienced from the given line segment to all other line segments, and represents the sum of the shortest angles from the given line segment to all other line segments.
In Equation 2, refers to the shortest path from line segment j to line segment k, and refers to the shortest path from line segment j to line segment k that includes line segment i.
At the same time, Kernel Density Estimation (KDE) is used, which is a method for estimating the density of spatial point distributions (Cai et al., 2013; Okabe et al., 2009), based on the assumptions of smoothness, locality, and uniformity. By applying KDE to sample points with different qualities of architectural façades, it is possible to clearly observe the distribution of “low,” “medium,” and “high” categories of façades.
In Equation 3, () represents the position of each point, () is the distance from () to (), () determines the smoothness of the density estimation and the scope of influence of the kernel function, () is the kernel function, and the choice of this function affects the results of the density estimation.
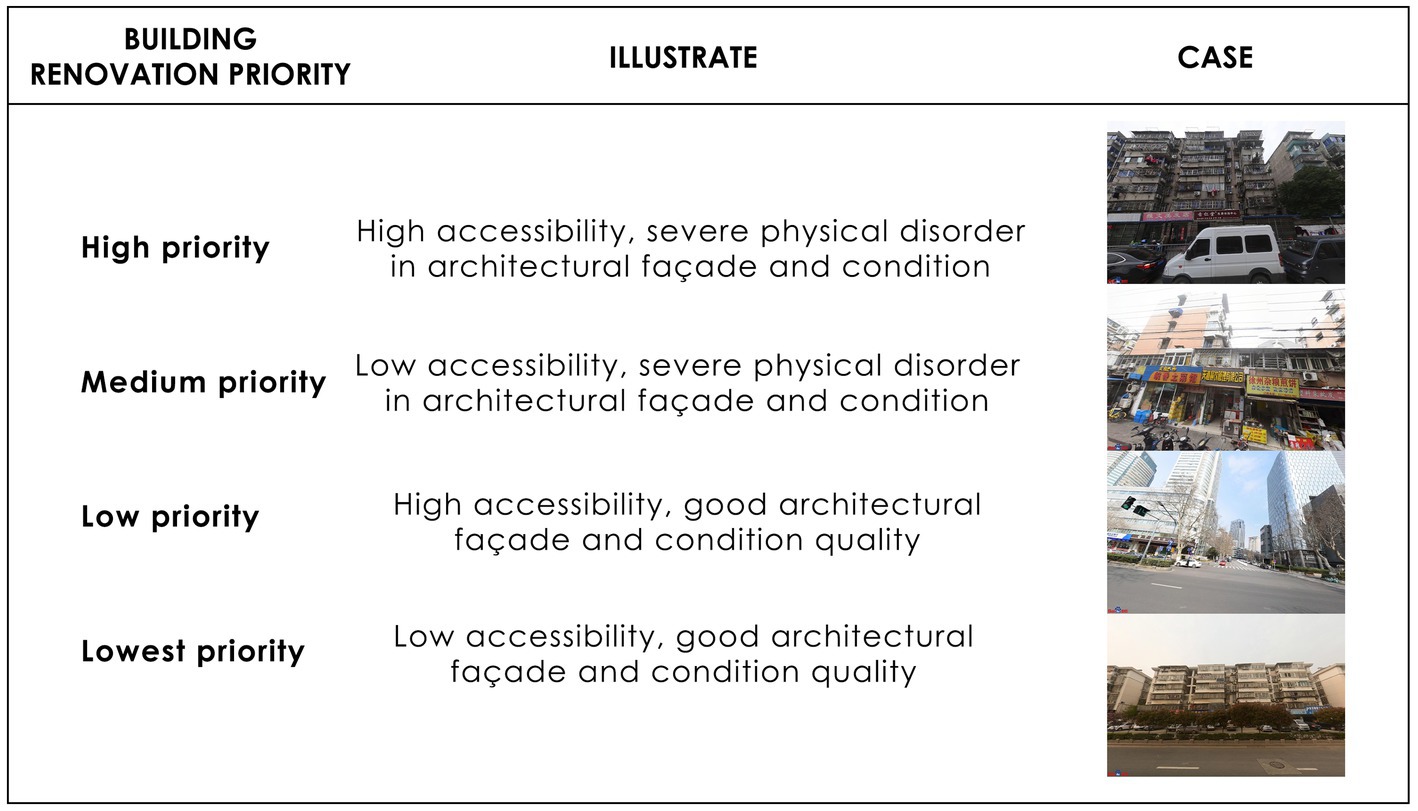
By integrating the analysis of the degree of physical disorder in architectural façades with architectural accessibility analysis, overlaying the accessibility analysis obtained from sDNA with the final score of each sampling point on a plane, a comprehensive judgment result of accessibility and façade quality scores is obtained. This result can identify areas with low degrees of physical disorder in architectural façades and high architectural accessibility. These areas, featuring pleasing architectural façades and convenient transportation, can be considered well-developed areas. Meanwhile, areas with severe physical disorder in architectural façades and high accessibility can be prioritized for architectural renovation.
Integrating the analysis of the physical disorder of architectural façades and building accessibility, a quadrant analysis method can be used to determine renovation priorities. This method provides scientific evidence and decision support for urban renewal and development. It also identifies areas needing enhanced transportation infrastructure to improve accessibility and attractiveness. This method boasts high accuracy and applicability, holding broad prospects for application in actual urban renewal efforts (Figure 6).
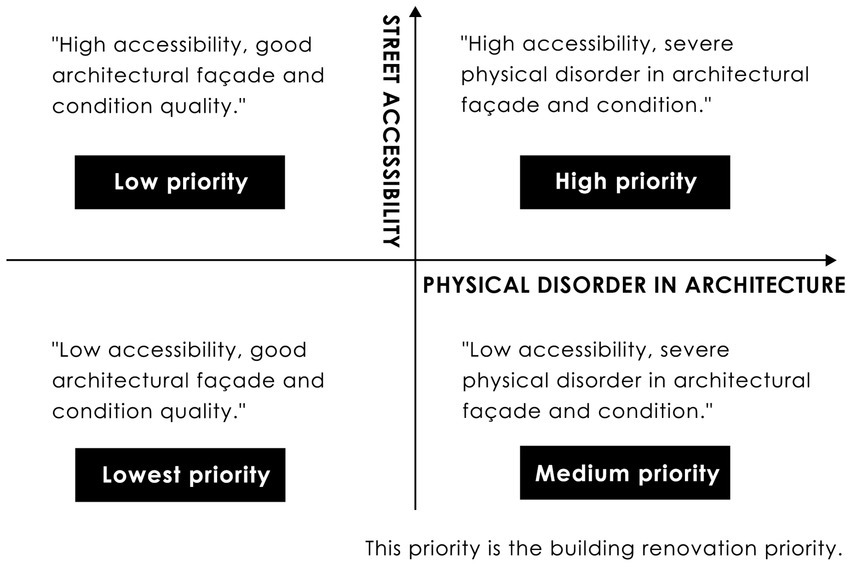
Figure 6. Architectural accessibility and its correlation with physical disorder in architectural façades.
4 Results
4.1 Analysis of architectural façade quality based on Baidu maps
Figure 7 shows the analysis integrating the evaluation of the physical quality of architectural façades at each sampling point. The evaluation of physical disorder in architectural façades for each street is expressed based on the average score of physical disorder in architectural façades from the Baidu API.
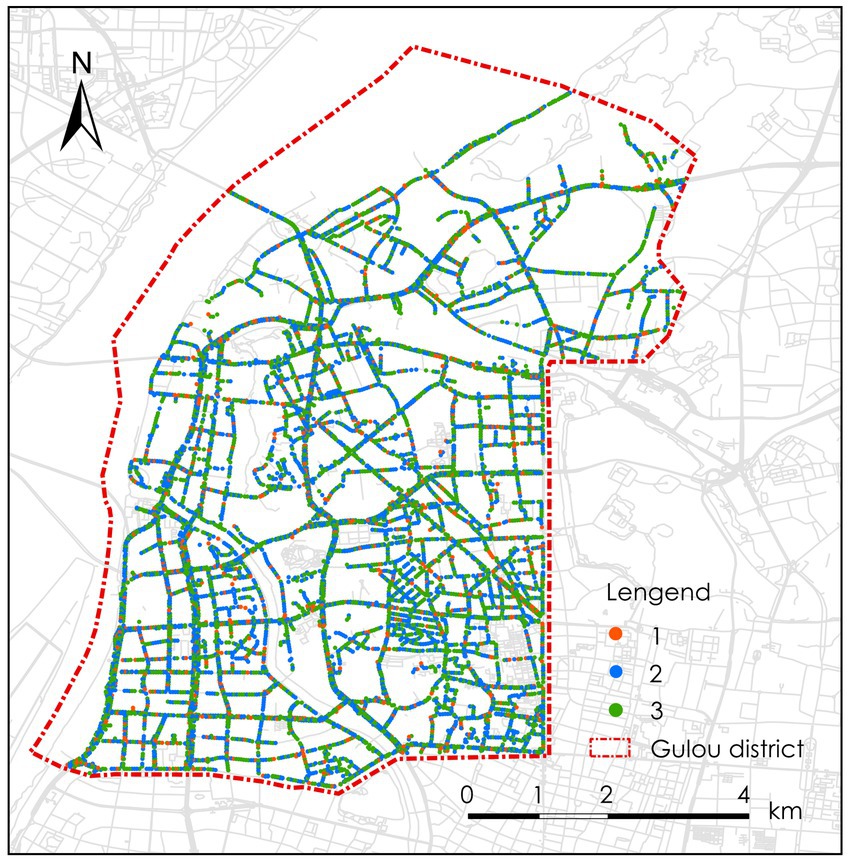
Figure 7. Schematic of the physical disorder of architectural façades in Gulou District, Nanjing City.
As shown in the chart below, the average score for physical disorder in architectural façades is 9.6. The highest score within the study area is 11, while the lowest score is 2. The majority of the area’s scores for physical disorder in architectural façades are concentrated between 8 and 10. Through classification based on DenseNet169, the quality of street architectural façades is divided into three categories: low, medium, and high.
4.2 Architectural accessibility analysis based on space syntax
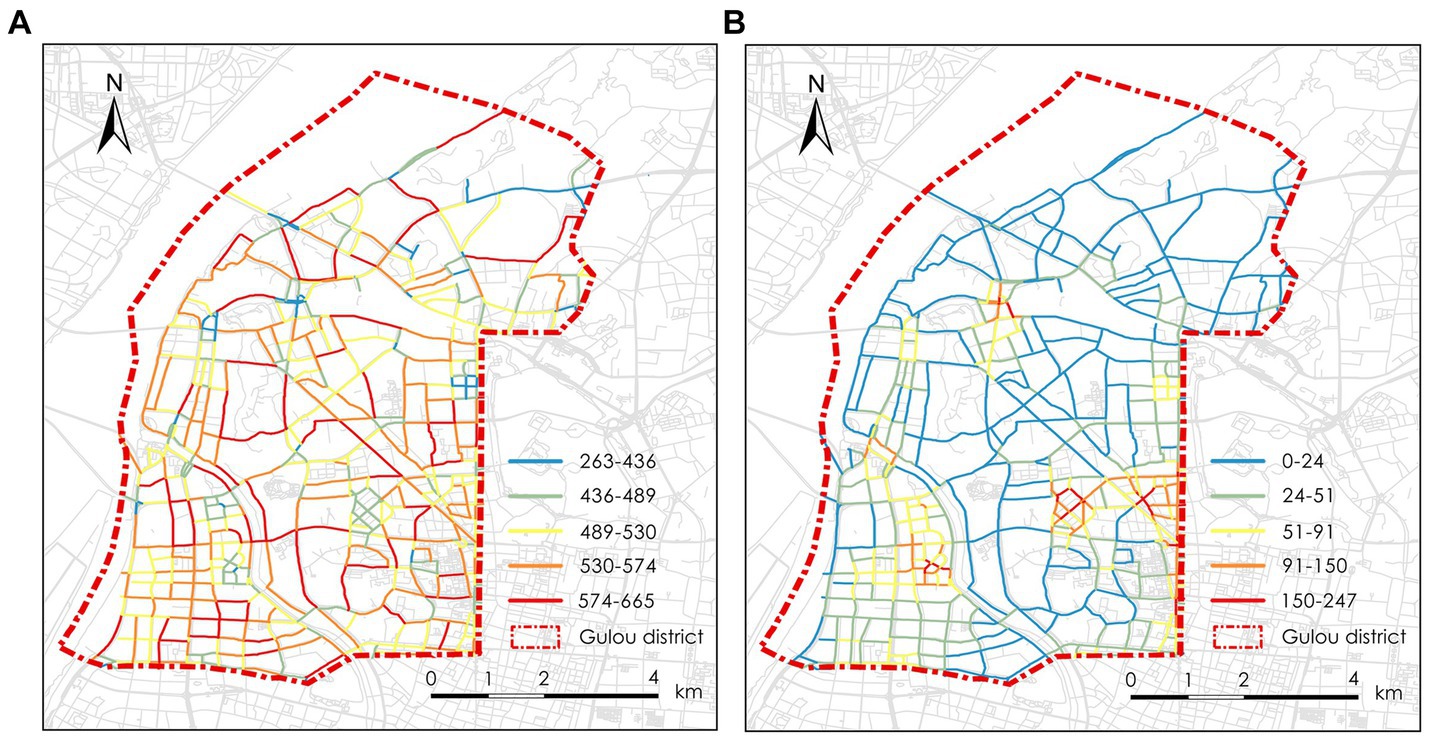
Figure 8 illustrates the architectural accessibility of the Gulou District in Nanjing, with varying shades representing different levels of street accessibility. In Figure 8A, accessibility is measured by the ability of a space to attract incoming traffic as a destination. The higher the integration of the space, the better its accessibility, making it more likely to attract foot traffic. Figure 8B reflects the likelihood of a space being traversed; spaces with higher choice values are more likely to be crossed by pedestrians.
Streets in red indicate higher accessibility, suggesting that these areas have well-developed transportation networks, allowing pedestrians or vehicles to reach these locations efficiently. Streets shown in blue indicate lower accessibility. The figure indicates that pedestrian accessibility in Gulou District is generally good, especially in historical, commercial, and residential areas with higher accessibility. However, Figure 8 also shows lower choice values in the northeastern part of the district, likely due to efforts to preserve the natural environment by limiting the density of transportation networks in that area.
4.3 Comprehensive analysis of physical disorder in architectural façades and architectural accessibility
Figure 9, through a kernel density map, shows the distribution of sampling points with “low-1, medium-2, and high-3” architectural façade quality across the city, along with accessibility results. The density distribution gradually increases from blue to red. This indicates a certain similarity between the distribution density of various sampling points and the distribution of accessibility results. Areas with higher accessibility tend to have more buildings, which are more likely to exhibit either pleasing architectural façades or cases of architectural façade disorder.
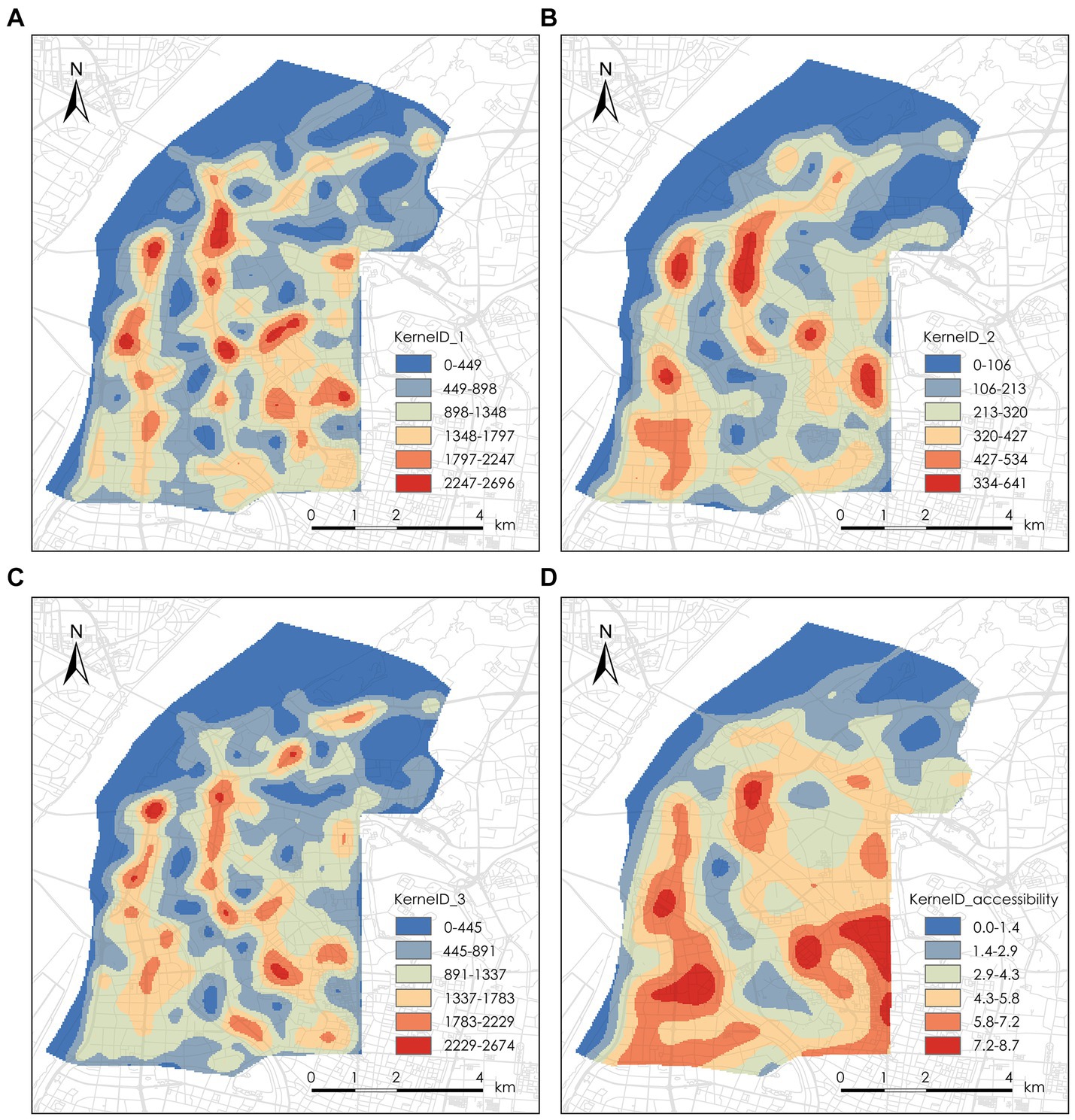
Figure 9. Kernel density map of sampling points by façade quality classification and accessibility kernel density map. (A) Low architectural façade quality kernel density map, (B) medium architectural façade quality kernel density map, (C) high architectural façade quality kernel density map, (D) accessibility kernel density map.
To determine the priorities for building renovation, this study employs the quadrant analysis method, also known as the BCG Matrix. It analyzes two dimensions: the physical disorder of architectural façades and building accessibility. By integrating the degree of physical disorder in architectural façades with architectural accessibility, it is possible to help determine the priorities for architectural renovation, providing data support for urban renewal. Areas with severe physical disorder in architectural façades and high architectural accessibility indicate an urgent need for façade renovation. These areas have a higher priority for renovation because they are urban spaces that people use more conveniently and frequently, making architectural façade renovation significant. Conversely, areas with pleasing architectural façades and low architectural accessibility have a lower priority for renovation.
Additionally, areas with a medium level of architectural façade disorder and architectural accessibility should consider both factors’ results in a weighted manner when determining renovation priorities. In summary, in the process of urban renewal, areas with severe physical disorder in architectural façades and high architectural accessibility should be given priority. Following this principle, urban renewal efforts can be progressively implemented (Figure 10).
5 Discussion
5.1 Measuring architectural façade conditions: an exploration of urban renewal practice methods
By integrating the degree of physical disorder of architectural façades with the accessibility of architecture, the accuracy of assessing the practical benefits of renovation plans can be enhanced, providing a theoretical basis for urban renewal. This combined assessment offers a quantitative approach to identifying potential priority areas for architectural renovation by exploring the relationship between the physical disorder of architectural façades and their accessibility. It also helps prioritize renovation projects, improving decision-making accuracy for urban planners and, to some extent, reducing the costs associated with planning issues. In particular, the Gulou District of Nanjing, where urbanization occurred earlier, presents a strong demand for building renovations due to the presence of numerous aging neighborhoods and architectural sites from different periods. This district also has a high population density, leading to higher costs for building renovations.
In summary, this paper’s main contribution is introducing a quantitative and rapid method for measuring architectural façades, fully considering human perception of architecture. While a human-centered approach has always been emphasized in urban planning, it often remains superficial in practice due to the challenges of quickly and universally measuring human perception. Inspired by recent machine learning applications for Baidu API content processing, this study aims to explore further objective evaluations of human perception of architectural façades in practical renovation planning.
5.2 A framework for analyzing the condition of daily visible architectural façades
“Daily visible architectural façades” involves a comprehensive analysis of “Daily visibility,” or “Daily accessibility,” combined with “architectural façades.” This approach focuses on how people perceive actual architecture daily, resulting in theoretical data that better aligns with real-life scenarios. The visible architectural façades are analyzed from a human perspective, emphasizing what people actually see, allowing for a more accurate assessment of the potential impact of architectural façades on human perception. The analytical framework used in this study can be replicated in other areas of architectural perception research.
For the façades themselves, a bottom-up approach can more intuitively and efficiently reflect the architectural façades perceived by everyday city users. Conversely, a top-down evaluation effectively quantifies the state of architectural façades in real-life contexts, focusing on the broader social, cultural, and psychological effects of architectural perception. Therefore, combining these two methods is applicable in this study. By profoundly exploring people’s everyday experiences of architectural perception and quantifying the impact of façades, this research enhances the understanding of the interaction between architecture and human behavior, providing both theoretical and practical foundations for creating more attractive and human-centered urban environments.
5.3 Future applicability and limitations
This study proposes a method for accurately and quickly assessing visible architectural façades over a large area, providing urban planners with crucial data for evaluating urban renewal potential. Traditional urban planning often employs a top-down approach, which frequently lacks insight into the actual perceptions of urban users. By measuring people’s perceptions of physical disorder in architectural façades, this method can effectively reflect public evaluations of façade quality and renewal needs, making it a critical factor in urban renewal decision-making.
However, the architectural renovation potential assessment method proposed in this paper still has room for improvement. Additional important livability indicators, such as street greenery rates and traffic density, must be considered in urban renewal planning. Research should focus on how these indicators affect people’s perception of architectural façades and their needs regarding the urban environment to better highlight the city’s livability. Although street view images supplement perceptions of architectural façades from a human perspective, limitations in image update frequency might lead to cognitive biases regarding newly constructed or renovated buildings. Furthermore, since street view images only capture façades on either side of the street, they do not provide a comprehensive understanding of the internal building conditions within urban blocks, potentially missing some renewal potential.
Future research should explore integrating multidimensional data and advanced algorithms to assess urban architectural façades and renewal potential comprehensively and precisely. Building on this study, the criteria for evaluating physical disorder in façades could be refined, such as identifying the proportion of disorder in specific areas, measuring the severity of the disorder, and examining the weights of different types of disorder in the scoring formula. Additionally, since urban renewal is an ongoing process, future studies should investigate how to align this assessment method with practical urban renewal practices to ensure that renewal activities genuinely enhance the urban environment.
6 Conclusion
This study integrates street view image data and machine learning techniques to construct a measure of the physical disorder of architectural façades. This approach allows for the quantification of architectural conditions over large areas. Additionally, it innovatively combines machine perception of architectural façades with sDNA of building accessibility, using a quadrant analysis method to determine renovation priorities and critical points. This method not only helps identify areas in need of building renovation but also provides theoretical support for urban planners.
Unlike single-dimension studies that rely solely on CNN for semantic recognition and classification of architectural styles, this research analyzes the physical disorder of architectural façades and building accessibility as two dimensions. Quadrant analysis determines renovation priorities based on a feedback loop between people’s perception of urban architectural façades and the feasibility of activities in urban space. Areas with severe physical disorder and high accessibility are prioritized for renovation, while areas with good architectural conditions and low accessibility are given lower priority. Thus, urban renewal should focus on areas with severe physical disorders and high accessibility. This method highlights specific regions that may require attention for building improvements, offering a new perspective and data support for urban planning and renewal.
In summary, this study establishes a rapid and scalable architectural façade scoring system. It analyzes renovation priorities based on the perception of architectural façades and the inherent patterns of human activity in urban space, providing valuable insights for urban renewal.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
HX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HS: Data curation, Investigation, Resources, Writing – original draft. YS: Data curation, Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors is grateful to Prof. Dr. Jiaxin Zhang and Prof. Dr. Feng Liu for their invaluable intellectual support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frsc.2024.1430071/full#supplementary-material
References
Akgül, İ. (2023). Mobile-DenseNet: detection of building concrete surface cracks using a new fusion technique based on deep learning. Heliyon 9:e21097. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21097
Badland, H., Whitzman, C., Lowe, M., Davern, M., Aye, L., Butterworth, I., et al. (2014). Urban liveability: emerging lessons from Australia for exploring the potential for indicators to measure the social determinants of health. Soc. Sci. Med. 111, 64–73. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2014.04.003
Boeing, G. (2019). Urban spatial order: street network orientation, configuration, and entropy. Appl. Netw. Sci. 4:67. doi: 10.1007/s41109-019-0189-1
Cai, X., Wu, Z., and Cheng, J. (2013). Using kernel density estimation to assess the spatial pattern of road density and its impact on landscape fragmentation. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 27, 222–230. doi: 10.1080/13658816.2012.663918
Chavez, C., Garcia, A., Batista, T., Oliveira, M., Sant’Anna, C., and Rashid, A. (2009). Composing architectural aspects based on style semantics. Proceedings of the 8th ACM international conference on aspect-oriented software development.
Chen, W. (2018). Architectural style analysis method based on intelligent computing technology. 2018 10th international conference on measuring technology and mechatronics automation (ICMTMA).
Chen, J., Chen, L., Li, Y., Zhang, W., and Long, Y. (2023). Measuring physical disorder in urban street spaces: a large-scale analysis using street view images and deep learning. Ann. Am. Assoc. Geogr. 113, 469–487. doi: 10.1080/24694452.2022.2114417
Cheshmehzangi, A., Chen, W., Mangi, E., and Heath, T. (2023). Practical challenges of urban regeneration in China. Front. Sustain. Cities 5:913500. doi: 10.3389/frsc.2023.913500
Chi, Y. L., and Mak, H. W. L. (2021). From comparative and statistical assessments of Liveability and health conditions of districts in Hong Kong towards Future City development. Sustain. For. 13:8781. doi: 10.3390/su13168781
Dai, P., Fu, H., Yang, X., Han, S., Fu, G., and Wang, Y. (2023). Exploring the urban renewal strategy based on transit-oriented development concept—a case study of Japan and Hong Kong. Front. Mater. 10:1098027. doi: 10.3389/fmats.2023.1098027
Diego, M. (n.d.). Applying the scientific method in the definition and analysis of a new architectural style.
Duan, J., Liao, J., Liu, J., Gao, X., Shang, A., and Huang, Z. (2023). Evaluating the spatial quality of urban living streets: a case study of Hengyang City in central South China. Sustain. For. 15:10623. doi: 10.3390/su151310623
Ericson, J. D., Chrastil, E. R., and Warren, W. H. (2021). Space syntax visibility graph analysis is not robust to changes in spatial and temporal resolution. Environ. Plan. B: Urban Anal. City Sci. 48, 1478–1494. doi: 10.1177/2399808319897624
Franzini, L., Caughy, M. O., Nettles, S. M., and O’Campo, P. (2008). Perceptions of disorder: contributions of neighborhood characteristics to subjective perceptions of disorder. J. Environ. Psychol. 28, 83–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvp.2007.08.003
Friedrich, E., Hillier, B., and Chiaradia, A. (2009). Using space syntax to understand spatial patterns of socio-environmental disorder. In Proceedings of the 7th International Space Syntax Symposium, Stockholm.
González Martínez, P. (2020). Designing disorder. Experiments and disruptions in the city. J. Urban Des. 25, 665–667. doi: 10.1080/13574809.2020.1794803
Hao, Z., and Wang, Y. (2023). Evaluation of socio-economic-ecological environmental benefits of urban renewal projects based on the coupling coordination degree. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30, 56946–56968. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-26284-y
Hillier, B., and Iida, S. (2005). “Network and psychological effects in urban movement” in Spatial information theory. eds. A. G. Cohn and D. M. Mark (Berlin Heidelberg: Springer), 475–490.
Huang, B.-X., Chiou, S.-C., and Li, W.-Y. (2020). Accessibility and street network characteristics of urban public facility spaces: equity research on parks in Fuzhou City based on GIS and space syntax model. Sustain. For. 12:3618. doi: 10.3390/su12093618
Huang, G., Liu, Z., Pleiss, G., Maaten, L. V. D., and Weinberger, K. Q. (2022). Convolutional networks with dense connectivity. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 44, 8704–8716. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2918284
Jiao, L., and Zhao, J. (2019). A survey on the new generation of deep learning in image processing. IEEE Access 7, 172231–172263. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2956508
Kim, Y. O., and Penn, A. (2004). Linking the spatial syntax of cognitive maps to the spatial syntax of the environment. Environ. Behav. 36, 483–504. doi: 10.1177/0013916503261384
Kim, H.-K., and Sohn, D. W. (2002). An analysis of the relationship between land use density of office buildings and urban street configuration. Cities 19, 409–418. doi: 10.1016/S0264-2751(02)00071-9
Liu, L., Silva, E. A., Wu, C., and Wang, H. (2017). A machine learning-based method for the large-scale evaluation of the qualities of the urban environment. Comput. Environ. Urban. Syst. 65, 113–125. doi: 10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2017.06.003
Ma, X., Ma, C., Wu, C., Xi, Y., Yang, R., Peng, N., et al. (2021). Measuring human perceptions of streetscapes to better inform urban renewal: a perspective of scene semantic parsing. Cities 110:103086. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2020.103086
Malleson, N., Addis, N., Durham, H., Heppenstall, A., Lovelace, R., Norman, P., et al. (2015). GIS research UK (GISRUK) 2015 proceedings. London: figshare.
Mastandrea, S., Bartoli, G., and Carrus, G. (2011). The automatic aesthetic evaluation of different art and architectural styles. Psychol. Aesthet. Creat. Arts 5, 126–134. doi: 10.1037/a0021126
Mohajeri, N., French, J., and Gudmundsson, A. (2013). Entropy measures of street-network dispersion: analysis of coastal cities in Brazil and Britain. Entropy 15, 3340–3360. doi: 10.3390/e15093340
Monastyrskaia, M. E. (2016). Urban challenges of globalization in the theoretical architectural and city planning discourse. Urban Construct. Archit. 6, 85–90. doi: 10.17673/Vestnik.2016.01.14
Mouratidis, K., and Hassan, R. (2020). Contemporary versus traditional styles in architecture and public space: a virtual reality study with 360-degree videos. Cities 97:102499. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2019.102499
Okabe, A., Satoh, T., and Sugihara, K. (2009). A kernel density estimation method for networks, its computational method and a GIS-based tool. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 23, 7–32. doi: 10.1080/13658810802475491
Oktaviana, U. N., and Azhar, Y. (2021). Garbage classification using ensemble DenseNet169. J. RESTI 5, 1207–1215. doi: 10.29207/resti.v5i6.3673
Olaode, A., and Naghdy, G. (2019). Review of the application of machine learning to the automatic semantic annotation of images. IET Image Process. 13, 1232–1245. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2018.6153
Qi, Y. (2024). Research on fast pedestrian detection algorithm based on deep learning. In C. Qin and H. Zhou (Eds.), International conference on image processing and artificial intelligence (ICIPAl 2024).
Ross, C. E., and Jang, S. J. (2000). Neighborhood disorder, fear, and mistrust: the buffering role of social ties with neighbors. Am. J. Community Psychol. 28, 401–420. doi: 10.1023/A:1005137713332
Saleh, K., Hossny, M., and Nahavandi, S. (2020). Spatio-temporal DenseNet for real-time intent prediction of pedestrians in urban traffic environments. Neurocomputing 386, 317–324. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.12.091
Sampson, R. J., and Raudenbush, S. W. (2004). Seeing disorder: neighborhood stigma and the social construction of “broken windows.”. Soc. Psychol. Q. 67, 319–342. doi: 10.1177/019027250406700401
Shach-Pinsly, D. (2021). Digital urban regeneration and its impact on urban renewal processes and development. Urban Plan. 6, 135–138. doi: 10.17645/up.v6i4.4905
Sharmin, S., and Kamruzzaman, M. (2018). Meta-analysis of the relationships between space syntax measures and pedestrian movement. Transp. Rev. 38, 524–550. doi: 10.1080/01441647.2017.1365101
Sheikh, W. T., and van Ameijde, J. (2022). Promoting livability through urban planning: a comprehensive framework based on the “theory of human needs.”. Cities 131:103972. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2022.103972
Wang, M., Zhang, F., and Wu, F. (2022). Governing urban redevelopment: a case study of Yongqingfang in Guangzhou, China. Cities 120:103420. doi: 10.1016/j.cities.2021.103420
Xia, Y., Yabuki, N., and Fukuda, T. (2021). Development of a system for assessing the quality of urban street-level greenery using street view images and deep learning. Urban For. Urban Green. 59:126995. doi: 10.1016/j.ufug.2021.126995
Xiao, Y., Sarkar, C., Webster, C., Chiaradia, A., and Lu, Y. (2017). Street network accessibility-based methodology for appraisal of land use master plans: an empirical case study of Wuhan, China. Land Use Policy 69, 193–203. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.09.013
Xu, X., Xu, X., Guan, P., Ren, Y., Wang, W., and Xu, N. (2018). The cause and evolution of urban street vitality under the time dimension: nine cases of streets in Nanjing City, China. Sustain. For. 10:2797. doi: 10.3390/su10082797
Ye, Y., Richards, D., Lu, Y., Song, X., Zhuang, Y., Zeng, W., et al. (2019a). Measuring daily accessed street greenery: a human-scale approach for informing better urban planning practices. Landsc. Urban Plan. 191:103434. doi: 10.1016/j.landurbplan.2018.08.028
Ye, Y., Xie, H., Fang, J., Jiang, H., and Wang, D. (2019b). Daily accessed street greenery and housing Price: measuring economic performance of human-scale streetscapes via new urban data. Sustain. For. 11:1741. doi: 10.3390/su11061741
Zhang, Z., Fort, J. M., and Giménez Mateu, L. (2023). Exploring the potential of artificial intelligence as a tool for architectural design: a perception study using Gaudí’sWorks. Buildings 13:1863. doi: 10.3390/buildings13071863
Zhang, K., Guo, Y., Wang, X., Yuan, J., and Ding, Q. (2019). Multiple feature reweight DenseNet for image classification. IEEE Access 7, 9872–9880. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2890127
Zhang, J., Hu, J., Zhang, X., Li, Y., and Huang, J. (2023). Towards a fairer green city: measuring unfairness in daily accessible greenery in Chengdu’s central city. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 23, 1776–1795. doi: 10.1080/13467581.2023.2270047
Zhang, J., Huang, Y., Li, Z., Li, Y., Yu, Z., and Li, M. (2024). Development of a method for commercial style transfer of historical architectural façades based on stable diffusion models. J. Imaging 10:165. doi: 10.3390/jimaging10070165
Zhao, J. (2020). Influencing factors of urban architectural style in China: a case study of Danzhou City, Hainan Province. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 510:062003. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/510/6/062003
Zhao, P., Miao, Q., Song, J., Qi, Y., Liu, R., and Ge, D. (2018). Architectural style classification based on feature extraction module. IEEE Access 6, 52598–52606. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2869976
Zheng, H. W., Shen, G. Q., and Wang, H. (2014). A review of recent studies on sustainable urban renewal. Habitat Int. 41, 272–279. doi: 10.1016/j.habitatint.2013.08.006
Zheng, W., Shen, G. Q., Wang, H., Hong, J., and Li, Z. (2017). Decision support for sustainable urban renewal: a multi-scale model. Land Use Policy 69, 361–371. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2017.09.019
Keywords: physical disorder in architectural façades, streetscape, accessibility, Space Syntax, deep learning, urban renewal
Citation: Xing H, Shi H and Sun Y (2024) Measuring physical disorder of architectural façades for informing better urban renewal using deep learning and space syntax. Front. Sustain. Cities. 6:1430071. doi: 10.3389/frsc.2024.1430071
Edited by:
Saeid Pourroostaei Ardakani, University of Lincoln, United KingdomReviewed by:
Hugo Wai Leung Mak, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong SAR, ChinaWenxiao Wang, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macao SAR, China
Dong Wei, Southwest Jiaotong University, China
Copyright © 2024 Xing, Shi and Sun. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Huiyue Xing, MjAyMDIxMTE0MDEwQG5qdGVjaC5lZHUuY24=
 Huiyue Xing
Huiyue Xing Haojun Shi
Haojun Shi