
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Sustain. , 06 March 2025
Sec. Sustainable Organizations
Volume 6 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/frsus.2025.1545072
The social dimension of sustainability of urban MSMEs (micro, small, and medium enterprises) is understudied compared to the economic and environmental dimensions. This study assesses social sustainability of MSMEs in Makassar city, Indonesia and its relations with economic and environmental sustainability using primary data collected from 300 MSME owners and managers. The empirical analysis employs descriptive statistics and the regression method. Reasonably high levels of social sustainability of MSMEs were found in Makassar, and significant relation with economic and environmental sustainability was identified. In terms of social justice and equity (SJE), more than 80% of the respondents gave positive evaluations toward this dimension, while just under 10% gave negative perceptions. Likewise, the subdimensions of social capital (SCA) and social cohesion (SCO) received mostly positive responses (77 and 86%, respectively). The economic dimension was positively related with SJE and SCA and negatively related with SCO. In contrast, the environmental dimension had a negative relation with SJE and a positive relation with SCA. The findings suggest that devoting greater attention to social sustainability may lead to enhanced economic performance and improved environmental care. The study contributes to evidence of the application of the social principle to economic development and environmental care practices.
Since Our Common Future was reported by the World Commission on Environment and Development (Brundtland, 1987), sustainability, specifically sustainable development, has been a buzzword and debate in academic and practical fields for more than three decades. However, sustainability and sustainable development have different meanings: sustainability refers to a state of being, while sustainable development describes a process toward that state (Holmberg and Robert, 2000). Since the emergence of the term, academic and practical debates have been pushed into various aspects of life, such as economic, environmental, institutional, and social aspects. In the beginning, the discussion tends to revolve around the interconnection of economic and environmental issues. Therefore, it is more likely to ignore social sustainability (Shirazi and Keivani, 2018).
With urbanization, people relocate to urban areas to make a living. The increasing population in urban areas implies the importance of regarding people as a subject of academic studies. One of the most significant human activities in urban areas is micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs), which conducts economic activities, particularly in manufacturing and service sectors rather than agriculture, as is more salient in rural areas (Nurlinah et al., 2024). Furthermore, literature acknowledges that MSMEs play a role in sustainable development, especially in the economic dimension (Khurana et al., 2019; Weldeslassie et al., 2019; Ndubisi et al., 2021), even more so in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic (Shafi et al., 2020; Bai et al., 2021). However, the social sustainability of the MSMEs can be a challenge.
Rapid population growth in urban areas requires job creation and employment structure changes performed by MSMEs in both the formal and informal sectors. The formal sector tends to be considered as a class that comprises regulation, wages, taxes, and contracts between employers and workers, while the informal sector tends toward no regulation, no taxes, and no fixed contract.
This notion spreads to the city of Makassar, the largest city in Eastern Indonesia with a population of 1.4 million, 42% of which run MSMEs in both the formal and informal sectors (224,580 and 360,745, respectively) (BPS-Statistics of Makassar Municipality, 2021). However, this high level of economic activity also presents significant social and environmental challenges. For instance, daily waste production exceeds 1,200 metric tons, with a large portion generated from trade activities and household consumption (Maskun et al., 2020). This indicates that environmental issues, such as waste management and business sustainability, are crucial in the context of Makassar.
Additionally, local policies highlight the importance of a sustainability-driven approach to the city’s economic development. Makassar Mayor Regulation No. 36 of 2021 on Community-Based Waste Management emphasizes the involvement of MSMEs in recycling initiatives and waste reduction efforts. This policy is not only aimed at preserving the environment but also at creating new economic opportunities within the circular economy framework. Compared to other cities in Indonesia, Makassar has several significant differences. Its high urbanization rate, with over 80% of its population living in urban areas (BPS-Statistics of Makassar Municipality, 2021), puts greater pressure on infrastructure and the environment. The city also faces distinct geographical challenges, such as coastal erosion and rising sea levels, which are exacerbated by rapid industrial expansion and urbanization. Unlike cities such as Bandung or Yogyakarta, which are more oriented toward the creative industry and education, Makassar’s economy relies heavily on maritime trade, the fishing industry, and port services, making it a key economic hub in Eastern Indonesia.
There are mainly four social sustainability issues that need to be addressed. First, in urban areas, growth in the number of MSMEs shows a positive trend. Urban communities are increasingly motivated to establish businesses on the MSMEs scale to create jobs. This trend is also followed by the rising Gini coefficient, suggesting that inequality between two or more social classes is widening, despite the economic growth. Second, the three dimensions of sustainability are interrelated (Brundtland,1987). While social sustainability has become a crucial research topic worldwide (Ghahramanpouri et al., 2015), studies on the social sustainability of MSMEs in urban areas are relatively scarce and have largely focused on the measurement framework (McKenzie, 2004; Mani et al., 2016; Eizenberg and Jabareen, 2017; Shirazi and Keivani, 2017, 2018; Masocha, 2019; Larimian and Sadeghi, 2021). Third, social sustainability in urban areas is influenced by the government, politicians, developers, party networks, and business interests, especially for MSMEs (Colantonio and Dixon, 2011; Dixon, 2019). Therefore, social sustainability is applicable to the theoretical and practical fields, with direct relevance to local communities, MSMEs, and urban policymakers. Fourth, to what extent social sustainability of the MSMEs is exercised and influences the economic and environmental sustainability remains an unanswered question in literature. If social sustainability of MSMEs affects economic and environmental sustainability, attempts to ensure the social aspect of MSMEs should be incorporated into the strategic plan.
This study analyzes the relationship between social sustainability and economic and environmental dimensions of sustainability by investigating MSMEs as urban social classes. It starts by assessing the extent to which the MSME sector is socially sustainable in Makassar city and then reveal its association with economic and environmental sustainability.
Social sustainability of MSMEs refers to a condition of MSMEs with social relations to fulfill the concerned community’s needs without sacrificing other communities. Social activities of MSMEs enhance community participation, security, education, and community development (Turyakira et al., 2014; Margahana, 2020). Abed (2017) divides social sustainability into physical (e.g., public facilities) and non-physical components (e.g., accessibility, design, safety, sense of belonging, and community). Larimian and Sadeghi (2021) attempted to determine the social sustainability measurement scale, which resulted in several indicators, namely, social interaction, safety and security, social equity, social participation, neighborhood satisfaction, sense of place, and housing satisfaction.
Furthermore, a study in Ecuador (Sarango-Lalangui et al., 2018) shows that MSMEs in the process of operational improvement must pay immediate attention to social sustainability practices, which are measured through four components, namely, stakeholders, human resources, human rights, and image of firms. Notably, microenterprises showed the highest commitment to social sustainability through corporate vision, mission, and values.
Social issues typically facing MSMEs include job creation (Ayyagari et al., 2014), livelihoods provision, gender equity promotion (Tambunan, 2008), community empowerment (Kusumawardhani et al., 2015), human resources development, and social diversity consideration (Musa and Hasan, 2018). Social Justice and Equity ensures fair access to resources, opportunities, and policies that support MSME growth, particularly for marginalized entrepreneurs who often face systemic barriers in financing, market access, and business development (Qureshi, 2020). Addressing these disparities promotes a more inclusive economic landscape where small businesses can compete on a level playing field. Meanwhile, Social Capital plays a crucial role in the success of MSMEs by fostering trust, collaboration, and networking within business ecosystems (Oladele et al., 2024; Reniati et al., 2024). Given that MSMEs often lack the institutional support of larger corporations, their reliance on informal networks, business associations, and community trust becomes essential for knowledge-sharing, innovation, and financial resilience.
Social Cohesion strengthens the role of MSMEs in promoting stable and resilient communities (DiBella et al., 2023; Kussudyarsana et al., 2023). As small businesses create jobs, enhance local economic activity, and foster a sense of belonging, they contribute to social stability and collective wellbeing. A cohesive society supports MSMEs by providing a supportive consumer base, fostering trust between businesses and institutions, and encouraging inclusive economic participation. These three dimensions—justice, capital, and cohesion—are deeply interconnected, forming a comprehensive framework to assess how MSMEs not only survive but thrive in an equitable and socially sustainable economic environment.
How the social aspects of sustainability are linked to the economy can be found in some literature. Hasan et al. (2020) posit social capital as a component of social sustainability affecting economic attitudes in the peer-to-peer lending market in China. Du et al. (2020) suggest that inadequate access to jobs and lower property values can induce economic barriers in the labor and housing markets. A company’s social sustainability culture (SSC) positively affects the company’s economic performance in European countries (Schönborn et al., 2019). Within SSC, companies encourage social sustainability practices.
Masocha (2019) conducted case studies in South Africa and Sri Lanka. The former case revealed that MSMEs with social sustainability practices benefited their financial performance, according to the study with 238 MSMEs. The latter case showed that social sustainability positively affected economic sustainability of companies in the manufacturing sector, where social sustainability was measured through Internal Social Sustainability Practices (ISSP) and External Social Sustainability Practices (ESSP). Sudusinghe and Seuring (2020) argue that ISSP tends to have greater effects on economic sustainability than ESSP. A more specific and empirical case study through thematic analysis indicates that most companies consider the social dimension of sustainability to be related to the circular economy assessment for economic sustainability (Walker et al., 2021). Therefore, to evaluate circular economy practices, the social dimension can be a reference indicator.
Regarding social and environmental sustainability, social practices can reduce environmental risks. For example, the “cool biz, warm biz” workplace attire practice led to reducing environmental risks in Japan where lighter clothing was promoted in summer to reduce air conditioning use, while in winter, the use of heavier clothing was encouraged to minimize the use of indoor heating (Shove and Walker, 2014). Kusyk and Lozano (2007) analyze MSMEs as stakeholders that interact with the international political environment, national political environment, and industry competition. A more specific study found that enterprises with gender diversity in the work team tended to be more effective in the planning of environmental sustainability strategies (Glass et al., 2016).
The complexity of balancing economic, social, and environmental priorities in Makassar can be explained through trade-off theory. According to this framework, decision-makers often face conflicts when allocating limited resources to competing objectives (Haffar and Searcy, 2017). In Makassar, the need to promote economic growth and employment through MSMEs sometimes conflicts with environmental sustainability goals, particularly in waste management and pollution control. Many MSMEs operate on tight profit margins, making it difficult to adopt eco-friendly practices that require additional investment (Sommer, 2017). This tension reflects a broader challenge where short-term social and economic priorities can overshadow long-term environmental concerns.
Additionally, institutional theory helps explain how regulatory frameworks and social norms shape the behavior of economic actors (Bice, 2017; Brammer et al., 2012). In Makassar, policies such as waste management regulations attempt to institutionalize sustainable practices. However, the effectiveness of these policies depends on enforcement mechanisms and the willingness of businesses to comply. In developing economies, informal sector activities often escape formal regulations, leading to gaps between policy intent and actual practice (Webb et al., 2013). This suggests that successful sustainability initiatives in Makassar require not only top-down regulations but also bottom-up engagement with MSMEs to encourage voluntary compliance and innovation.
This study surveyed MSMEs in Makassar to collect primary data, while secondary data were obtained through journal articles, official documents, reports, and other research publications. The data were analyzed by descriptive and regression analyses.
Makassar is the center of Indonesia’s national activity (as per PEN Programme), and around 65% of the population depend on MSMEs for their living (Supari and Anton, 2022). The city has a vision of “acceleration of realizing Makassar as a global city that is sombere (sociable) and smart with strong immunity for all,” which characterizes urban social sustainability. Three subdistricts were purposively selected, Mariso, Rappocini, and Bontoala, as they represent the significant numbers of MSMEs and the highest population density in Makassar (Supplementary Figure S1 and Table 1).
The study was designed using social, economic, and environmental sustainability indicators (Table 2). Social sustainability can be measured by social justice and equity (SJE), social capital (SCA), and social cohesion (SCO) (Hemani et al., 2017; Shirazi and Keivani, 2019). The presence of SJE refers to meeting the community’s needs both intra-generationally and inter-generationally. It also refers to fair treatment of communities regardless of religion, ethnicity, race, gender, or other affiliations of society (Harvey, 2009), ensuring accessibility to economic and political opportunities (Magis and Shinn, 2009) and healthy and safe working conditions in MSMEs (Brady-Amoon, 2012).
SCA intangibly exists in interpersonal relations (McBain, 2015) and represents a state of mutual trust (obligations and expectations), mutual openness (information channels), and compliance with socially applicable rules in a social group (social norms) (Forrest and Kearns, 2001).
SCO exists in a social group that has a common goal, is in social order, is solidary, and has social interaction and a sense of belonging to its social environments (Forrest and Kearns, 2001). In addition, SCO measures refer to the intensity of interaction, community involvement, and the breadth of social networks as key aspects of SCO (Larimian and Sadeghi, 2021; Shirazi and Keivani, 2017).
Economic sustainability on a national scale can be assessed through sustainability of income per capita, the GDP per capita, or the GNP per capita (Gutierrez et al., 2009). Overall, the objective is similar: namely, to assess the average value of the standard of living in a given region. At the micro scale (e.g., households, individuals, or firms), the economy is measured through total income, according to Case et al. (2012), which is the total value of the sale of goods and services in a certain period (month, year, etc.).
In the context of MSMEs, usual economic measures are revenue, sales, profit, investment, and asset as well as their indicators. Profit can be calculated as the total value of the sale of goods and services minus cost, including tax, which is referred to as net income. However, this calculation is difficult to apply to the informal sector, which tends not to follow tax regulations and policies (Irwan et al., 2022). A revenue trend, net asset, and debt can be indicators of MSME’s economic sustainability (Case et al., 2012).
Global scale environmental sustainability covers such fields as climate change, deforestation, air pollution, and rising sea levels. MSMEs play a role in preventing these adverse impacts by strengthening policies and governance (UN DESA, 2019). Examples include improving access to capital and markets that promote environmental stewardship, as well as policies that encourage ease of green business operations. Environmental measures for MSMEs represent their eco-friendly operations; for instance, raw material efficiency, recyclability of raw materials and packaging, and energy and water consumption (Rao et al., 2006; Sundin et al., 2015; Dragomir, 2018).
The three indicators of social sustainability (SJE, SCA, and SCO) each consisted of eight sub-indicators, while ECO and ENV had three sub-indicators each. Thus, there were 30 sub-indicators in total. Accordingly, SJE, SCA, and SCO scores ranged from 8 to 40 while ECO and ENV scores ranged from 3 to 15. Higher scores represent higher sustainability. The mean score of sub-indicators was calculated to determine the aggregate indicator score.
The questionnaire collected 13 indicators representing social, economic, and environmental sustainability. All these variables were measured on a five-point Likert Scale from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree). The scores of the Likert items for each respondent were summed up to obtain a composite/total score for each dimension. The Department of Makassar Cooperative and MSMEs (2020) shows that the MSME population in Mariso, Rappocini, and Bontoala subdistricts were 517, 408, and 381, respectively, with a total of 1,306. The minimum sample size was calculated to be between 93 and 306 according to the margin of error between 5 and 10%, using the following formula:
where n is the minimum suggested sample size, N is the target population, e is the margin of error chosen to be 5% for Equation 1 and 10% for Equation 2. Accordingly, the total sample size was decided to be 300. The subsample size for the three subdistricts was calculated as follows:
where, Equation 3 is the sample size for MSMEs in the Mariso subdistrict, Equation 4 for Rappocini, and Equation 5 for Bontoala.
From the practical standpoint, convenience sampling was adopted, where MSMEs in the study area were visited one by one. Consent was sought for them to participate voluntarily in this research after being informed of the purpose of the study and the data collection process that would take place.
The questionnaire consisted of closed and open-ended questions. A pilot survey was conducted with 34 MSMEs to improve the survey instrument. Subsequently, the survey began and ended when 300 firms were interviewed. Finally, the raw data were entered into a spreadsheet and transferred into SPSS Statistic and R for quantitative analyses.
Prior to the analysis, it is crucial to calculate Cronbach’s alpha coefficients to assess the internal consistency of the indicators (Gliem and Gliem, 2003). The Cronbach score ranges from 0 to 1, expressing the lowest to the highest (Tavakol and Dennick, 2011). The generally accepted rule for the alpha level is the range of 0.6–0.95, implying that a score below 0.6 is not acceptable for representing the concept and that a score above 0.95 indicates redundancy on the items scale of the study (Ursachi et al., 2015). An acceptable alpha level indicates that the set of sub-indicators are usable for assessment and further regression analysis.
Descriptive statistics were used to assess social sustainability indicators. To examine their direct and linear relations with the economic and environmental indicators, regression analyses were performed by including the social indicators (SJE, SCA, SCO) as independent variables and the economic and environmental indicators as dependent variables. Other covariate variables were included as control variables, such as location, number of workers, and business scales, as well as the managing director’s personal profile, such as age, education, gender, and ethnicity (Makassar, Bugis, and others) (Table 3).
For the independent variables, sub-indicators in the ordinal scale were aggregated into interval scales through averaging over the several indicators. The categorical variables were converted into dummy variables, such as the location of MSMEs and gender. The same applied to the ordinal variable representing education. The regression model is described in Equations 6, 7:
where are economic and environmental indicators, respectively, are indicators of SJE, SCA, and SCO, respectively, and are the intercept terms, , are the slope coefficients for economic and environmental indicators, are the covariates, and ε is the random error term.
Summarizing the responses to the open-ended questions, the MSMEs in the sample came from 20 sectors, namely, retail, garment production, tailor, skull cap production, skull cap tailor, fashion, silversmith, welding workshop, repair shop, voucher stall, voucher stall and retail, printing service, printing and advertising, screen printing, computer service, culinary catering, drugstore, restaurant, syrup production, and coffee shop. These sectors were further categorized into six main sectors: services, retail, creative industry, culinary, fashion, and pharmacy. The largest proportion of MSMEs operated in the service sector (37%), followed by retail (23%), and the rest (40%) was from the four other industries. The mean venture capital was about 40 million rupiahs, with a standard deviation of 78 million rupiahs. Furthermore, venture capital was sourced from three fund providers: banks, government, and family or self-funding. Most Makassar MSMEs received funding from families, or self-funding accounted for 63%, as most are micro-enterprises that do not require large initial capital. MSMEs that receive bank assistance operate in the production sector and need significant initial money. In contrast, MSMEs that receive assistance from the government operate in the creative industry sector.
Table 4 shows the profile of representatives, the respondents in the study were owners and managers of MSMEs. The majority of the respondents (75%) were owners while the rest were managers. In addition, managers tended to be from medium-scale businesses, while owners tended to be from micro- and small-scale businesses. The proportions of female and male respondents were 56 and 44%, respectively. Secondary school completion was the most common education attainment among the MSMEs, while the other levels (primary or higher education) were varied, even on the medium scale there were merely secondary and tertiary levels. Owners of micro-enterprises tended to be workers themselves. Regarding ethnicity, Makassar was the majority accounting for more than a half of the respondents, followed by Bugis and Javanese ethnicity at 29 and 11%, respectively. The rest were Toraja, Mandar, Chinese, Minang, Sasak, Manado, and Sundanese. Based on the number of workers, most (70%) MSMEs were micro-scale businesses, while small- and medium-sized enterprises accounted for 20 and 2%, respectively. The mean number of workers and age were 4 people and 36 years, respectively.
The sets of sub-indicators met internal consistency. The SJE sub-indicators were in the confidence interval of 0.60–0.71, SCA 0.76–0.84, SCO 0.60–0.72, while ECO and ENV dimensions were in the confidence interval of 0.63–0.76 and 0.51–0.68, respectively (Table 5).
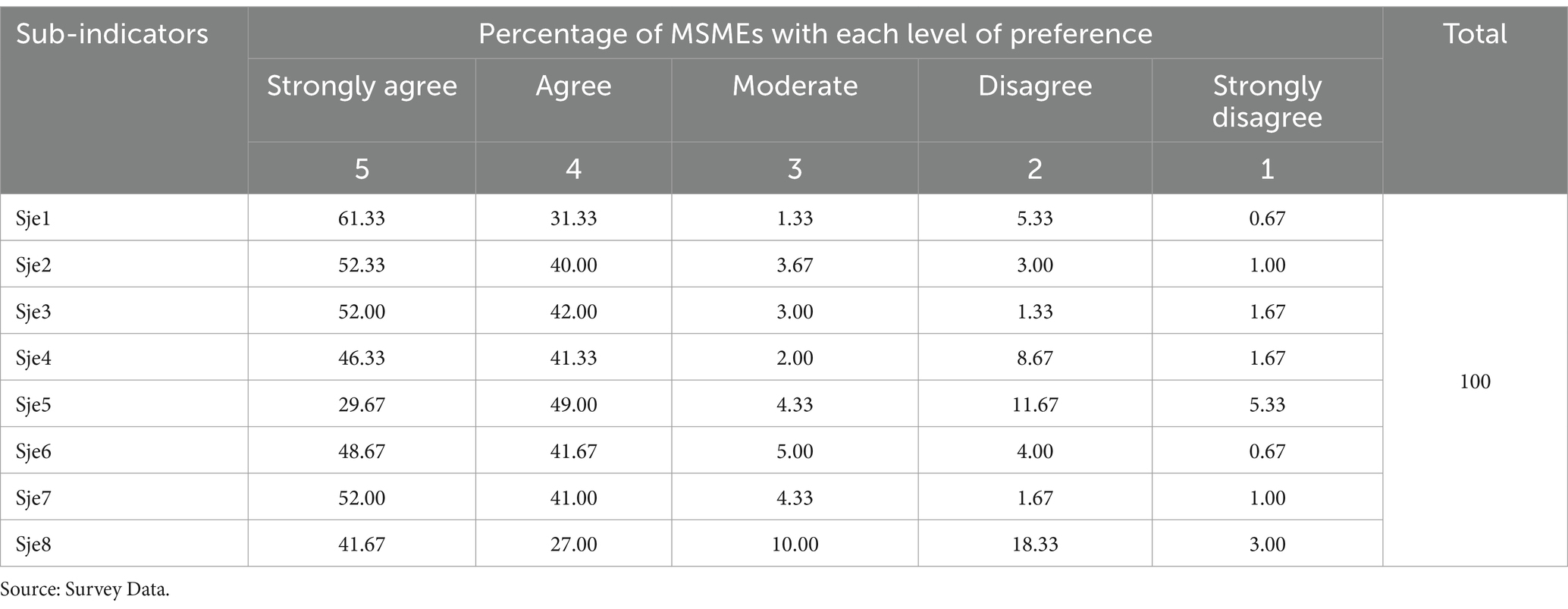
Table 5. Frequency distribution of social justice and equity sub-indicators of social sustainability (n = 300).
The overall mean of the SJE and SCA subdimensions was above the score of 4, with standard deviation of 0.50 and 0.63, respectively, which means that the ratings of both subdimensions were relatively high. Meanwhile, the SCO dimension had a mean score below 4 (SD 0.87) (Table 6).
The ECO and ENV dimensions had significantly different overall mean scores, 3.62 (SD 0.87) and 2.93 (SD 1.14). Overall, the mean scores of all indicators ranged from moderate to positive attitudes (Mean = 2.93–4.25, SD = 0.50–1.14), and the number of respondents for each variable was 300.
In terms of SJE, most of the respondents answered either agree (39%) or strongly agree (48%), indicating that more than 80% of them gave positive evaluation toward this dimension, while just under 10% gave negative perception. Likewise, the subdimensions of SCA and SCO received mostly positive responses (77 and 86%, respectively). On the whole, 83% of the firms showed positive responses (agree and strongly agree) to the social dimension of sustainability, while 13% had negative responses (disagree and strongly disagree).
Most respondents gave positive attitude toward the SJE indicators. However, large proportions of the MSMEs showed negative attitudes in satisfaction with their business (Sje5) and satisfaction with the surrounding environment (Sje8) with a frequency of more than 20% each. At the same time, the relatively large proportions of moderate attitude were found for satisfaction with the surrounding environment (Sje8), satisfaction with income (Sje6), and satisfaction with their business (Sje5), with 10, 5, and 4%, respectively (Supplementary Table S1).
In terms of SCA, most respondents gave positive attitude in all sub-indicators. However, initiation of regular meetings with other MSMEs (Sca13) and providing input to the government (Sca15) showed significantly large proportions of negative attitudes (29 and 28%, respectively). This implies that few MSMEs initiated regular meetings and gave recommendations to the government. Many of the sub-indicators received negative responses from more than 10% of the MSMEs (Sca9, Sca10, Sca11, Sca12, Sca14, Sca16). Generally, MSMEs tended to know other MSMEs actors (Sca12), know consumers (Sca11), and often interact with the government (Sca14), consumers (Sca9), and fellow MSMEs (Sca10), which may encourage skill improvement and education (Sca16) (Supplementary Table S2).
In terms of SCO, positive attitude dominated the MSMEs. However, attitude related to pride in running a business in their environment (Sco18) and contributions to the progress of dwellers (Sco20) showed relatively large proportions of negative responses (17 and 21%, respectively) (Supplementary Table S3). The attitude to follow applicable rules and promotion of individual rights (civil and human rights) (Sco23 and Sco17) and good relationship with neighbors (Sco24) showed the large proportions of positive attitude, indicating that most MSMEs committed human rights and solidarity. Similarly, MSMEs tended to be responsible for social objectives and solidarity (Sco22), provide solutions (Sco21), and accept local people to work (Sco19). Nonetheless, MSMEs that are not proud of the environment around their business (Sco18) tended not to contribute to the development of urban dwellers (Sco20) (p = 0.001 in Spearman correlation).
Most (68%) MSMEs had positive attitude and the rest had moderate and negative attitude (5 and 27%, respectively) (Supplementary Table S4). In more detail, in the assessment of venture capital accessibility for MSMEs (Eco25) and their income (Eco26), the majority (44%) of MSMEs had positive attitude: 23% strongly agreeing to Eco25; 47% agreeing and 25% strongly agreeing to Eco26, suggesting that more than a half of MSMEs agreed to ease of obtaining capital, from both the government and the private sector. Meanwhile, the venture capital accessibility for MSMEs showed reasonably large proportions of negative attitude, with 2% disagreeing and 3% strongly disagreeing. When asked about their attitude toward the income-expenditure ratio, the majority (>50%) of MSMEs gave positive responses, while one third gave negative responses.
Regarding environmental dimensions, a half of the MSMEs had negative attitude in the overall indicator, while 23 and 21% agreed and strongly agreed, respectively. On the other hand, the proportion of positive attitude in Env29 was nearly 60%, suggesting that most MSMEs received training in developing their business.
Table 7 shows that most of the social sustainability indicators were significantly associated with the two other dimensions of sustainability of MSMEs. As for the economic dimension, a one-level increase in the SJE indicator increased ECO by 0.43 on average, holding the covariates constant. Likewise, a one-level increase in the SCA indicator raised ECO by 0.45 on average, holding other variables constant. On the other hand, the SCO indicator shows negative effects on ECO. For a one-level increase in SCO, ECO decreased by 0.36. Some location fixed effects were observed. Shifting the location from Mariso to Rappocini reduced ECO by 0.78 on average, holding other variables constant.
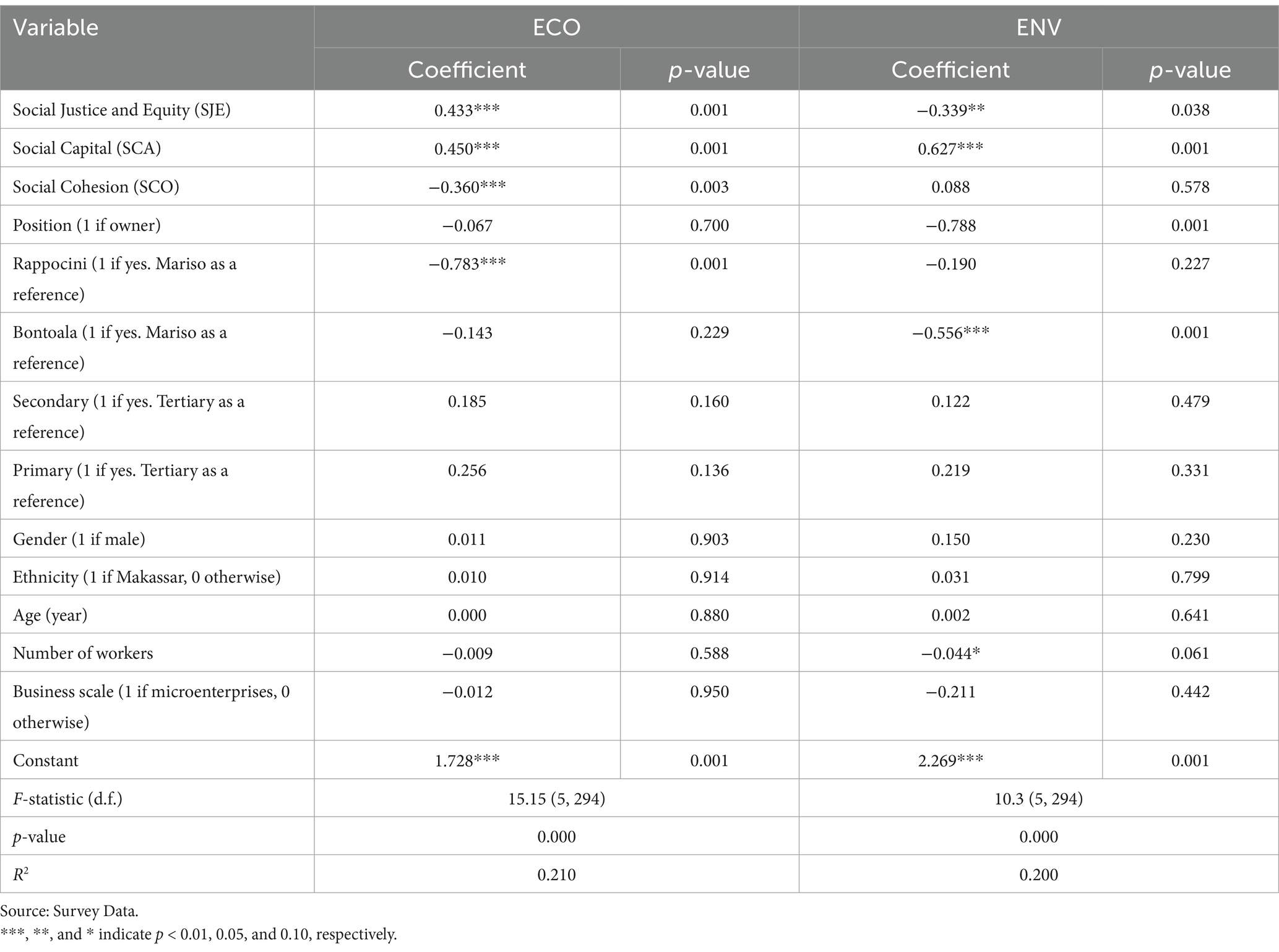
Table 7. The relationship between social sustainability and economic and environmental sustainability (n = 300): Ordinary Least Squares (OLS).
In contrast, a one-level increase in SJE decreased ENV of MSMEs in Makassar city by 0.34 on average, holding the covariates constant. For SCA, an increase by one level resulted in improving ENV by 0.63 on average, holding the other variables constant. However, SCO was not significantly correlated with ENV for MSMEs. Shifting the location from Mariso to Bontoala reduced ENV by 0.56. The number of workers was related with ENV, where a one-person increase led to decreasing ENV by 0.04.
On the whole, social sustainability of MSMEs in the study area received positive evaluation. The finding is in line with MSMEs’ social sustainability evaluation conducted in Ecuador and New Zealand that showed high average scores (Lawrence et al., 2006; Sarango-Lalangui et al., 2018). SJE in the MSMEs focused on satisfaction, environmental security, and gender equity policies. The MSMEs in Makassar city were satisfied with their revenue and building (accommodation) and encouraged environmental safety, and they provided women with access to the decision-making process. Almost all sub-indicators of the SJE dimension received positive attitude from the representatives of the MSMEs. The MSMEs tend to follow applicable rules, respect individual rights, and have good relations with neighbors. However, several sub-indicators received a fairly large negative attitude, such as satisfaction with their business and surrounding environments. In terms of SCA, the MSMEs gave positive attitude on average in all sub-indicators (77%). The MSMEs tend to be responsible for social objectives and solidarity, providing solutions and accepting local people to work. The MSMEs in Makassar were networked with other MSMEs and customers and often interacted with the government as well. They tend to spend more in promoting social cohesion, such as making donations to maintain solidarity and promoting individual rights. Initiation of regular meetings with other MSMEs and providing input to the government received significant proportions of negative attitudes (29 and 28%, respectively). As for SCO, there was negative attitude from the MSMEs, especially in relation to pride in operating in their business environments and contributions to the progress of dwellers’ livelihoods.
MSMEs in Makassar operate in the services, retail, creative industry, culinary, fashion, and pharmacy sectors. Funding largely depends on their own financial sources or family assistance. Literature shows that MSMEs in various parts of the world are less likely to obtain bank loans, compared to large companies (Choudhury and Goswami, 2019; World Bank Group, 2019). This can be referred to as the financial gap, where the Asia Pacific and East regions are the largest (42%) and are followed by the Caribbean and Latin America (23%) and Central Asia and Europe (15%) (IFC, 2021).
This study found that social sustainability practices by urban MSMEs were somewhat positively linked to their economic and environmental sustainability, thereby reducing the vulnerability to economic crises and environmental risks. Boyer et al. (2016) indicate that social sustainability is a precondition for economic and environmental sustainability. Detailed discussions of each relational finding are provided in the subsequent sections.
Our findings show that economic sustainability depends positively on SJE. Literature shows that MSMEs implementing social justice and equity are more likely to improve their economic performance (Puri, 2017; Swalhi et al., 2017; Rahaman and Uddin, 2022). MSMEs that pay immediate attention to social sustainability practices are considered as better positioned to improve their business because the businesses run smoothly by ensuring equity and security for employees and customers and maintaining social relations across stakeholders (Ayyagari et al., 2014; Sarango-Lalangui et al., 2018; Masocha, 2019). In other countries, positive relationships were found between social sustainability and economic performance of enterprises (Masocha, 2019; Sudusinghe and Seuring, 2020; Walker et al., 2021). Social equity also translates into ease of doing business for all MSME actors and women’s access to top management positions (Kusyk and Lozano, 2007; Shove and Walker, 2014; Glass et al., 2016).
Unexpectedly, SJE had a negative relationship with environmental sustainability, suggesting that MSMEs in Makassar that encouraged social justice and equity tended to have negative perceptions of environmental sustainability of their businesses. Scholars are increasingly aware of the interdependence among elements in an ecosystem (Sabbagh and Schmitt, 2016; Syme, 2012). It is widely perceived that all activities of people have physical and non-physical impacts on environments, whereas there a strong claim that a just society will be environmentally sustainable (Stone, 2017). However, the mechanism behind the negative association between social justice and environmental sustainability can be understood through previous studies. For instance, Bogert et al. (2022), efforts to promote social justice often require the redistribution of economic resources, increased infrastructure development, and expanded access to social services. These activities, while essential for addressing inequalities, can lead to higher resource consumption and environmental degradation if not managed sustainably. The Environmental Kuznets Curve (EKC) hypothesis suggests that environmental degradation tends to increase during the early stages of economic and social development as countries focus on poverty reduction, social equity, and economic growth (Dinda, 2004; Rashid Gill et al., 2018).
This study found significant positive association between social capital and the economic sustainability of MSMEs. A one-level increase in the SCA indicator raised ECO by 0.45 on average, holding other variables constant. The role of social capital in the context of economic performance has been explored by many scholars. Mackie (1998) found in China that success of entrepreneurs in penetrating into the global network was due to two essential factors: maintaining trust (Xinyong) and developing personal relations (Guanxi). Literature agrees that social capital accumulation in MSMEs leads to increased sales, improved relationships with customers, and better access to debt or venture capital, especially in the informal sector (Meflinda et al., 2018; Habersetzer et al., 2019; Sinarwati et al., 2019; Hasan et al., 2020).
Likewise, this study found significant positive association between social capital and the environmental sustainability of MSMEs. This may be because the interactions with stakeholders in urban areas helped enhance MSMEs’ awareness of environments and strengthen policies toward natural resource conservation. This finding is in line with other studies (Pretty and Ward, 2001; Onyx et al., 2004) that confirmed linkage between social capital and positive perception of environments: such as having a compost at backyard, growing more trees, developing renewable energy, and recycling waste.
In this study, the relationship between social cohesion and economic sustainability was negative. In contrast, various assessments have demonstrated positive relationship between social cohesion and economic sustainability. Social cohesion could improve the performance of social institutions, which could induce economic growth (Sommer, 2019). In addition, social cohesion promotes equality in the distribution of resources and income (Hunko, 2017). Our finding would require further analysis of social cohesion in the context of MSMEs.
Although the role of social cohesion in environmental sustainability practices was significant in some literature (Uzzell et al., 2002; Cook and Swyngedouw, 2012), no such relationship was found in this study. This may be because the prior studies were in the context of large companies, while our study was on MSMEs. Admittedly, research linking social cohesion and environmental sustainability is still scarce. Further studies are needed to verify the influence of social cohesion on environmental practices by MSMEs.
The findings from this study not only reinforce existing theories but also contribute to expanding them by demonstrating how sustainability trade-offs in micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) in developing cities differ from those in more industrialized urban economies. While trade-off theory (Haffar and Searcy, 2017) traditionally assumes a zero-sum dynamic between economic and environmental goals, our findings suggest that in cities like Makassar, these trade-offs are more fluid and context-dependent, shaped by regulatory flexibility, informal economic structures, and community-driven initiatives. This implies that trade-offs in developing economies are not purely economic choices but are embedded within institutional and socio-cultural constraints.
Additionally, institutional theory often assumes that compliance with sustainability policies is driven primarily by formal regulations (Bice, 2017; Brammer et al., 2012). However, our study highlights the role of hybrid institutional mechanisms, where informal networks, traditional business practices, and local governance play a crucial role in shaping sustainability behavior. This is particularly relevant in the MSME sector, where businesses may not always operate within strict regulatory frameworks but instead respond to social pressures, consumer demand, and community norms. This expands the institutional theory lens by emphasizing non-state actors and informal institutions in shaping business sustainability.
One of the key barriers to sustainability adoption in MSMEs is the lack of knowledge and technical skills in waste management, energy efficiency, and sustainable sourcing. To address this, a structured sustainability training program should be developed, specifically targeting MSMEs in key sectors such as food and beverage, retail, and manufacturing. Many MSMEs in Makassar operate on thin profit margins, making it difficult to invest in sustainability measures. The local government should introduce financial and non-financial incentives to encourage businesses to transition toward environmentally friendly operations.
This study has certain limitations worth noting. First, although the role of social cohesion in environmental sustainability practices was significant in some literature (Uzzell et al., 2002; Cook and Swyngedouw, 2012), no such relationship was found in this study. This may be because the prior studies were in the context of large companies, while our study was on MSMEs. Admittedly, research linking social cohesion and environmental sustainability is still scarce. Further studies are needed to verify the influence of social cohesion on environmental practices by MSMEs. Second, the data were primarily based on perceptions of representatives of certain MSMEs and therefore did not take into account different positions in companies and general people in urban communities. Third, the sampling of companies incorporated an aspect of convenience sampling. The statistical results are therefore subject to estimation biases arising from the patters of inclusion into the sample. Further research should include other stakeholders, such as ordinary workers and urban dwellers, and apply a more probabilistic sampling method. In addition, in-depth policy analysis of local governments would enable prediction of the state of MSMEs sustainability in the future.
Previous studies revolve around the interconnection between economic and environmental issues, with a tendency to disregard the fundamental issues of social sustainability. This study gathered primary data from micro, small, and medium enterprises in Makassar city, evaluating their social sustainability through indicators such as social justice and equity, social capital, and social cohesion. The analysis revealed a relatively strong level of social sustainability, reflected in a high average score. In contrast, the scores for economic and environmental sustainability were moderate. The findings indicate that while a significant portion of MSMEs showed positive attitudes, a considerable number still expressed negative views regarding economic and environmental sustainability.
These results underscore the critical role of social sustainability in shaping the broader sustainability performance of MSMEs. The positive contributions of social justice and equity (SJE) and social capital (SCA) to economic and environmental sustainability suggest that strengthening these social dimensions could enhance MSMEs’ overall resilience. This study contributes to the discourse on MSME sustainability by emphasizing the interconnectedness of social, economic, and environmental factors. Policymakers and business stakeholders should integrate social sustainability considerations into MSME development strategies, fostering a more holistic approach to sustainability in urban economic landscapes.
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found at: https://doi.org/10.57760/sciencedb.07420.
The studies involving humans were approved by Prof. Dr. Veni Hadju, M.Sc, Ph.D – Faculty of Public Health, Hasanuddin University; Dr. Wahiduddin, SKM, M.Kes – Faculty of Public Health, Hasanuddin University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
MA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Project administration, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. TT: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing. SS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors would like to thank the editor of Frontiers in Political Science and four reviewers for their valuable comments on this paper. We also thank Febrianti Aulia Ansar and A. Hasyim Asyari for helping with the data collection, and Andika Anas prepared the figures.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frsus.2025.1545072/full#supplementary-material
Abed, A. R. (2017). Assessment of social sustainability: a comparative analysis. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers - Urban Design and Planning, 170, 72–82. doi: 10.1680/jurdp.16.00020
Ayyagari, M., Demirguc-Kunt, A., and Maksimovic, V. (2014). Who creates jobs in developing countries? Small Bus. Econ. 43, 75–99. doi: 10.1007/s11187-014-9549-5
Bai, C., Quayson, M., and Sarkis, J. (2021). COVID-19 pandemic digitization lessons for sustainable development of micro-and small- enterprises. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 27, 1989–2001. doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2021.04.035
Bice, S. (2017). Corporate social responsibility as institution: a social mechanisms framework. J. Bus. Ethics 143, 17–34. doi: 10.1007/s10551-015-2791-1
Bogert, J. M., Ellers, J., Lewandowsky, S., Balgopal, M. M., and Harvey, J. A. (2022). Reviewing the relationship between neoliberal societies and nature: implications of the industrialized dominant social paradigm for a sustainable future. Ecol. Soc. 27:art7. doi: 10.5751/ES-13134-270207
Boyer, R. H. W., Peterson, N. D., Arora, P., and Caldwell, K. (2016). Five approaches to social sustainability and an integratedway forward. Sustainability (Switzerland) 8:878. doi: 10.3390/su8090878
BPS-Statistics of Makassar Municipality. (2021). Makassar municipality in figures. Makassar: BPS-Statistics of Makassar Municipality.
Brady-Amoon, P. (2012) in Maslow, A. H. BT - encyclopedia of the history of psychological theories. ed. R. W. Rieber (New York, NY: Springer US), 663–664. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4419-0463-8_182
Brammer, S., Jackson, G., and Matten, D. (2012). Corporate social responsibility and institutional theory: new perspectives on private governance. Soc. Econ. Rev. 10, 3–28. doi: 10.1093/ser/mwr030
Brundtland, G. H. (1987). Our Common Future: Report of the World Commission on Environment and Development. Geneva: UN-Dokument A/42/427. Available at: http://www.un-documents.net/ocf-ov.htm
Case, K. E., Fair, R. C., and Oster, S. M. (2012). Principles of economics. 10th Edn. Harlow: Pearson Education.
Choudhury, M., and Goswami, C. (2019). MSME financing gaps – review of literature for the period 2005 to 2016. J. Small Bus. Entrepr. Dev. 7, 50–60. doi: 10.15640/jsbed.v7n2a5
Colantonio, A., and Dixon, T. (2011). “Social sustainability and sustainable communities: towards a conceptual framework” in Urban regeneration and social sustainability: best practice from European cities. eds. S. Brown, J. Henneberry, K. W. Chau, E. Worzala, A. Colantonio, and T. Dixon (Wiley-Blackwell), 18–36.
Cook, I. R., and Swyngedouw, E. (2012). Cities, social cohesion and the environment: towards a future research agenda. Urban Stud. 49, 1959–1979. doi: 10.1177/0042098012444887
Department of Makassar Cooperative and MSMEs. (2020). UMKM Kota Makassar. Makassar: Department of Makassar Cooperative and MSMEs.
DiBella, J., Forrest, N., Burch, S., Rao-Williams, J., Ninomiya, S. M., Hermelingmeier, V., et al. (2023). Exploring the potential of SMEs to build individual, organizational, and community resilience through sustainability-oriented business practices. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 32, 721–735. doi: 10.1002/bse.3171
Dinda, S. (2004). Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis: a survey. Ecol. Econ. 49, 431–455. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2004.02.011
Dixon, T. (2019). Measuring the social sustainability of new housing development: a critical review of assessment methods. J. Sustain. Real Estate 11, 16–39. doi: 10.22300/1949-8276.11.1.16
Dragomir, V. D. (2018). How do we measure corporate environmental performance? A critical review. J. Clean. Prod. 196, 1124–1157. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.06.014
Du, M., Zhao, M., and Fu, Y. (2020). Revisiting urban sustainability from access to jobs: assessment of economic gain versus loss of social equity. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 85:106456. doi: 10.1016/j.eiar.2020.106456
Eizenberg, E., and Jabareen, Y. (2017). Social sustainability: a new conceptual framework. Sustainability (Switzerland) 9:68. doi: 10.3390/su9010068
Forrest, R., and Kearns, A. (2001). Social cohesion, social capital and the neighbourhood. Urban Stud. 38, 2125–2143. doi: 10.1080/00420980120087081
Ghahramanpouri, A., Abdullah, A. S., Sedaghatnia, S., and Lamit, H. (2015). Urban social sustainability contributing factors in Kuala Lumpur streets. Procedia. Soc. Behav. Sci. 201, 368–376. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.08.188
Glass, C., Cook, A., and Ingersoll, A. R. (2016). Do women leaders promote sustainability? Analyzing the effect of corporate governance composition on environmental performance. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 25, 495–511. doi: 10.1002/bse.1879
Gliem, J. A., and Gliem, R. R. (2003). Calculating, interpreting, and reporting Cronbach’s alpha reliability coefficient for Likert-type scales. Adult Contin. Commun. Educ. 3, 82–88. Available at: https://hdl.handle.net/1805/344
Gutierrez, C. M., Glassman, C. A., Steven, L. J., and Marcuss, R. D. (2009). “Measuring the economy: a primer on GDP and the national income and product accounts” in Measuring the economy: GDP and NIPAs, Bureau of Economic Analysis, US Department of Commerce. 1–32.
Habersetzer, A., Grèzes-Bürcher, S., Boschma, R., and Mayer, H. (2019). Enterprise-related social capital as a driver of firm growth in the periphery? J. Rural. Stud. 65, 143–151. doi: 10.1016/j.jrurstud.2018.10.009
Haffar, M., and Searcy, C. (2017). Classification of trade-offs encountered in the practice of corporate sustainability. J. Bus. Ethics 140, 495–522. doi: 10.1007/s10551-015-2678-1
Hasan, I., He, Q., and Lu, H. (2020). The impact of social capital on economic attitudes and outcomes. J. Int. Money Financ. 108, 102162–102116. doi: 10.1016/j.jimonfin.2020.102162
Hemani, S., Das, A. K., and Chowdhury, A. (2017). Influence of urban forms on social sustainability: a case of Guwahati, Assam. Urban Des. Int. 22, 168–194. doi: 10.1057/s41289-016-0012-x
Holmberg, J., and Robert, K. H. (2000). Backcasting from non-overlapping sustainability principles: a framework for strategic planning. Int J Sust Dev World 7, 291–308. doi: 10.1080/13504500009470049
Hunko, A. (2017). Fighting income inequality as a means of fostering social cohesion and economic development. Strasbourg: Committee on Social Affairs, Health and Sustainable Development.
Irwan, A. L., Haryanto, H., and Ansar, M. C. (2022). A study of prospective local own-source revenues in central Mamuju, Indonesia. Otoritas: Jurnal Ilmu Pemerintahan 12, 78–94. doi: 10.26618/ojip.v12i2.7271
Khurana, S., Haleem, A., and Mannan, B. (2019). Determinants for integration of sustainability with innovation for Indian manufacturing enterprises: empirical evidence in MSMEs. J. Clean. Prod. 229, 374–386. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.04.022
Kussudyarsana, K., Maulana, H. K., Maimun, M. H., Santoso, B., and Nugroho, M. T. (2023). The role of social capital, innovation, and capabilities on MSMEs’ resilience in economic hard times. Jurnal Manajemen Bisnis 14, 72–89. doi: 10.18196/mb.v14i1.15887
Kusumawardhani, D., Rahayu, A. Y., and Maksum, I. R. (2015). The role of government in MSMEs: the empowerment of MSMEs during the free trade era in Indonesia. Austral. Account. Bus. Finance J. 9, 23–42. doi: 10.14453/aabfj.v9i2.3
Kusyk, S. M., and Lozano, J. M. (2007). Corporate responsibility in small and medium-sized enterprises: SME social performance: a four-cell typology of key drivers and barriers on social issues and their implications for stakeholder theory. Corp. Gov. 7, 502–515. doi: 10.1108/14720700710820588
Larimian, T., and Sadeghi, A. (2021). Measuring urban social sustainability: scale development and validation. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 48, 621–637. doi: 10.1177/2399808319882950
Lawrence, S. R., Collins, E., Pavlovich, K., and Arunachalam, M. (2006). Sustainability practices of SMEs: the Case of NZ. Bus. Strateg. Environ. 15, 242–257. doi: 10.1002/bse.533
Mackie, J. (1998). “Chinese business organizations” in The encyclopedia of the Chinese overseas. ed. L. Pan (Singapore: Archipelago Press).
Magis, K., and Shinn, C. (2009). “Emergent principles of social sustainability” in Understanding the social dimension of sustainability (first). eds. J. Dillard, V. Dujon, and M. C. King (New York: Routledge Taylor and Francis Group).
Mani, V., Agarwal, R., Gunasekaran, A., Papadopoulos, T., Dubey, R., and Childe, S. J. (2016). Social sustainability in the supply chain: construct development and measurement validation. Ecol. Indic. 71, 270–279. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.07.007
Margahana, H. (2020). The effect of corporate social responsibility (CSR) on increasing the competitiveness of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in Oku Timur, Indonesia. Int. J. Econ. Bus. Account. Res. (IJEBAR) 4, 1–9. doi: 10.29040/ijebar.v4i03.1157
Maskun,, Amirullah, N. A., Rachman, W. A., Kurniasi, N. F., and Assidiq, H. (2020). A thousand of waste problems in Makassar: the fire in landfill case. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 575:012238. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/575/1/012238
Masocha, R. (2019). Social sustainability practices on small businesses in developing economies: a case of South Africa. Sustainability (Switzerland) 11:3257. doi: 10.3390/SU11123257
McBain, D. (2015). Is social Footprinting relevant to industrial ecology? J. Ind. Ecol. 19, 340–342. doi: 10.1111/jiec.12260
McKenzie, S. (2004). Social sustainability: towards some definitions, vol. 27. Adelaide: University of South Australia.
Meflinda, A., Mahyarni, M., Indrayani, H., and Wulandari, H. (2018). The effect of social capital and knowledge sharing to the small medium enterprise’s performance and sustainability strategies. Int. J. Law Manag. 60, 988–997. doi: 10.1108/IJLMA-03-2017-0073
Musa, C. I., and Hasan, M. (2018). The influence of social, economic, and demographic characteristic on working hours of micro, small, and medium enterprises (MSMEs) in Makassar city. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1028:012181. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1028/1/012181
Ndubisi, N. O., Zhai, X., and Lai, K. H. (2021). Small and medium manufacturing enterprises and Asia’s sustainable economic development. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 233:107971. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpe.2020.107971
Nurlinah,, Haryanto,, and Chaeroel Ansar, M. (2024). Comparative study of social welfare programme effectiveness perception in peri-urban and rural in Indonesia. Asia Pac. J. Soc. Work Dev. 34, 1–18. doi: 10.1080/29949769.2024.2342794
Oladele, S., Laosebikan, J., Oladele, F., Adigun, O., and Ogunlusi, C. (2024). How strong is your social capital? Interactions in a non-transparent entrepreneurial ecosystem. J. Entrepr. Emerg. Econ. 16, 602–625. doi: 10.1108/JEEE-05-2022-0151
Onyx, J., Osburn, L., and Bullen, P. (2004). Response to the environment: social capital and sustainability. Aust. J. Environ. Manag. 11, 212–219. doi: 10.1080/14486563.2004.10648615
Pretty, J., and Ward, H. (2001). Social capital and the environment. World Dev. 29, 209–227. doi: 10.1016/S0305-750X(00)00098-X
Qureshi, S. (2020). Why data matters for development? Exploring data justice, micro-entrepreneurship, mobile money and financial inclusion. Inf. Technol. Dev. 26, 201–213. doi: 10.1080/02681102.2020.1736820
Rahaman, A., and Uddin, S. (2022). The effect of promotion and job trainin on job satisfaction of employees: an empirical study of the SME sector in Bangladesh. J. Asian Finance 9, 255–260. doi: 10.13106/jafeb.2022.vol9.no2.0255
Rao, P., Castillo, O. l. O., Intal, P. S. Jr., and Sajid, A. (2006). Environmental indicators for small and medium enterprises in the Philippines: an empirical research. J. Clean. Prod. 16, 1699–1710. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2008.04.020
Rashid Gill, A., Viswanathan, K. K., and Hassan, S. (2018). The environmental Kuznets curve (EKC) and the environmental problem of the day. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 81, 1636–1642. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.05.247
Reniati, R., Susantyo, B., Irmayani, N. R., Sabri, F., and Widiastuti, W. (2024). The influence of leadership strategies and social capital on the business performance and resilience of Indonesian MSMEs. J. Knowl. Econ. doi: 10.1007/s13132-024-02254-8
Sabbagh, C., and Schmitt, M. (2016). “Justice and environmental sustainability” in Handbook of social justice theory and research. eds. C. Sabbagh and M. Schmitt (New York: Springer), 369–386.
Sarango-Lalangui, P., Álvarez-García, J., and del Río-Rama, M.d.l. C. (2018). Sustainable practices in small and medium-sized enterprises in Ecuador. Sustainability (Switzerland) 10, 1–15. doi: 10.3390/su10062105
Schönborn, G., Berlin, C., Pinzone, M., Hanisch, C., Georgoulias, K., and Lanz, M. (2019). Why social sustainability counts: the impact of corporate social sustainability culture on financial success. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 17, 1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2018.08.008
Shafi, M., Liu, J., and Ren, W. (2020). Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on micro, small, and medium-sized enterprises operating in Pakistan. Res. Global. 2:100018. doi: 10.1016/j.resglo.2020.100018
Shirazi, M. R., and Keivani, R. (2017). Critical reflections on the theory and practice of social sustainability in the built environment–a meta-analysis. Local Environ. 22, 1526–1545. doi: 10.1080/13549839.2017.1379476
Shirazi, M. R., and Keivani, R. (2018). The triad of social sustainability: defining and measuring social sustainability of urban neighbourhoods. Urban Res. Pract. 12, 448–471. doi: 10.1080/17535069.2018.1469039
Shirazi, M. R., and Keivani, R. (2019). “Urban social sustainability: theory, policies and practices” in First. eds. M. R. Shirazi and R. Keivani (New York: Routledge Taylor and Francis Group).
Shove, E., and Walker, G. (2014). What is energy for? Social practice and energy demand. Theory Cult. Soc. 31, 41–58. doi: 10.1177/0263276414536746
Sinarwati, N. K., Budhi, M. K. S., Utama, M. S., and Marhaeni, A. A. I. N. (2019). The role of social capital for the performance of MSMEs. Russian J. Agric. Socio-Econ. Sci. 95, 147–153. doi: 10.18551/rjoas.2019-11.19
Sommer, C. (2017). Drivers and constraints for adopting sustainability standards in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) (21/2017). Discussion Paper. Bonn: German Development Institute.
Sommer, C. (2019). Social cohesion and economic development: unpacking the relationship (16/2019). Briefing Paper. Bonn: German Development Institute. doi: 10.23661/bp16.2019
Stone, M. (2017). Plato, environmental sustainability, and social justice. Athens J. Human. Arts 5, 105–118. doi: 10.30958/ajha.5.1.6
Sudusinghe, J. I., and Seuring, S. (2020). Social sustainability empowering the economic sustainability in the global apparel supply chain. Sustainability (Switzerland) 12, 1–18. doi: 10.3390/su12072595
Sundin, E., Nässlander, E., and Lelah, A. (2015). Sustainability indicators for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in the transition to provide product-service systems (PSS). Proc. CIRP 30, 149–154. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2015.02.155
Supari, S., and Anton, H. (2022). The impact of the national economic recovery program and digitalization on MSME resilience during the COVID-19 pandemic: a case study of Bank Rakyat Indonesia. Economies 10:160. doi: 10.3390/economies10070160
Swalhi, A., Zgoulli, S., and Hofaidhllaoui, M. (2017). The influence of organizational justice on job performance: the mediating effect of affective commitment. J. Manag. Dev. 36, 542–559. doi: 10.1108/JMD-11-2015-0162
Syme, G. (2012). “Justice and environmental decision-making” in Justice and conflicts. eds. E. Kals and J. Maes (Berlin Heidelberg: Springer), 283–295.
Tambunan, T. (2008). Development of SME in ASEAN with reference to Indonesia and Thailand. Chulalongkorn J. Econ. 20, 53–83. Available at: https://so05.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/saje/article/view/100234
Tavakol, M., and Dennick, R. (2011). Making sense of Cronbach’s alpha. Int. J. Med. Educ. 2, 53–55. doi: 10.5116/ijme.4dfb.8dfd
Turyakira, P., Venter, E., and Smith, E. (2014). The impact of corporate social responsibility factors on the competitiveness of small and medium-sized enterprises. SAJEM 17, 157–172. doi: 10.4102/sajems.v17i2.443
UN DESA. (2019). Micro-, small and medium-sized enterprises (MSMEs) and their role in achieving the sustainable development goals. New York, NY: United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs Division for Sustainable Development Goals.
Ursachi, G., Horodnic, I. A., and Zait, A. (2015). How reliable are measurement scales? External factors with indirect influence on reliability estimators. Proc. Econ. Finance 20, 679–686. doi: 10.1016/s2212-5671(15)00123-9
Uzzell, D., Pol, E., and Badenes, D. (2002). Place identification, social cohesion and environmental sustainability. Environ. Behav. 34, 26–53. doi: 10.1177/0013916502034001003
Walker, A. M., Opferkuch, K., Roos Lindgreen, E., Simboli, A., Vermeulen, W. J. V., and Raggi, A. (2021). Assessing the social sustainability of circular economy practices: industry perspectives from Italy and the Netherlands. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 27, 831–844. doi: 10.1016/j.spc.2021.01.030
Webb, J. W., Bruton, G. D., Tihanyi, L., and Ireland, R. D. (2013). Research on entrepreneurship in the informal economy: framing a research agenda. J. Bus. Ventur. 28, 598–614. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusvent.2012.05.003
Weldeslassie, H. A., Vermaack, C., Kristos, K., Minwuyelet, L., Tsegay, M., Tekola, N. H., et al. (2019). Contributions of Micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) to income generation, employment and GDP: case study Ethiopia. J. Sustain. Dev. 12:46. doi: 10.5539/jsd.v12n3p46
World Bank Group. (2019). Annual report financial year 2019: World Bank Group global knowledge and research hub in Malaysia. World Bank Group. Available at: https://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/874921628064158108
Keywords: social sustainability, urban social sustainability, MSME sustainability, sustainability, MSMEs, Indonesia
Citation: Ansar MC, Tsusaka TW and Syamsu S (2025) Social sustainability of micro, small, and medium enterprises: the case of Makassar city, Indonesia. Front. Sustain. 6:1545072. doi: 10.3389/frsus.2025.1545072
Received: 14 January 2025; Accepted: 19 February 2025;
Published: 06 March 2025.
Edited by:
Hamid Mattiello, Fachhochschule des Mittelstands, GermanyReviewed by:
Mochamad Kevin Romadhona, Airlangga University, IndonesiaCopyright © 2025 Ansar, Tsusaka and Syamsu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Muhammad Chaeroel Ansar, bWNoYWVyb2VsQHVuaGFzLmFjLmlk
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.