
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. Sustain. , 10 March 2025
Sec. Circular Economy
Volume 6 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/frsus.2025.1536382
This article is part of the Research Topic Assessing Circular Economy Transitions: Quantitative Approaches and Policy Implications View all 4 articles
Single-use plastics (SUPs) are synonymous with the biopharmaceuticals sector, facilitating economies of scale, process efficiency, flexibility and sterility assurance, all with a seemingly negligible environmental footprint. Yet, in ever-tightening regulation, mandated by the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and by concern for large-scale industrial impacts, the sustainability of SUP consumption is increasingly being questioned. Whilst the sector contributes to human welfare, its transition risk is unlikely to remain immune to societal pressure for more sustainable production. This article aims to present a scoping review of the apparent contradiction between sectoral SUP adoption and the increasing importance of circularity. The approach to the review relies on three interwoven strands of evidence: [i] the intersectionality of sustainability policy and regulation with biopharmaceuticals, [ii] single-use technology in biopharmaceuticals and its impacts, and [iii] applications of circular economy principles to single-use technology. It is argued that, whilst life-cycle analysis (LCA) of SUPs in biopharmaceuticals articulates an environmental benefit vis-à-vis conventional technology, high energy intensity and embodied carbon in stainless steel renders the comparison redundant. Moreover, there is a dearth of evidence on circularity, post-use, and on end-of-life considerations. Likewise, there appears to be little sector-wide appetite for the adoption of embryonic solutions for enhancing circularity, such as biodegradables, carbon offsets, reusability, waste-to-energy, and ocean cleanup. Urgent mission-driven research is required on LCA, circular business model feasibility, materials innovation, regulatory frameworks, and sectoral-wide impact. A design-driven inquisition of their interactions, based on industrial symbiosis, could inform potential adoption pathways.
Sustainability has become a megatrend, influencing government policy, corporate strategy, consumer decision-making, education and lifestyle choice (Castellet-Viciano et al., 2022). Brundtland's (1987, p. 2) definition of sustainability as “development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs” enshrines a consciousness of human existence based on equality within planetary boundaries. In particular, SDG 12 advocates for responsible production and consumption, in which waste is eliminated through reduction, recycling and reuse. The biopharmaceuticals sector has increasingly adopted single-use systems in manufacturing, raising concerns about plastic waste streams. A recent Deloitte study, for instance, found that the sector generates an estimated 300 million tons of plastic waste annually (White, 2024). Despite evidence that SUT reduces water and energy requirements, concerns over the amount of plastic waste persist (Sinclair et al., 2024). A key implication is that post-handling of industrial materials matters, particularly in the biopharmaceuticals sector. To evaluate the growing impact of plastic waste generated by the sector, as it pivots to SUT, the magnitude of the biopharmaceuticals plastic waste streams must be determined or at least approximated, benchmarking it where possible to other sectors. The ideals of the circular economy reflect material flows that do not create waste, so that nature is regenerated. The notion of circularity, i.e., the extent to which circular economy ideals are implemented, is changing how material lifecycles are managed (MacArthur et al., 2016). Indeed, plastic waste has become a global concern. Due to their desirable properties and low costs, plastics have become pervasive, with circa. 20bn tons of waste generated annually (OECD, 2022), spurring multiple jurisdictions to mitigate their environmental and health risks through policy and regulation.
The biopharmaceuticals sector is not immune to the sustainability megatrend, with efforts focused on improving process efficiency (Whitford et al., 2019). It must balance health benefits (SDG 3) with negative socio-economic (e.g., SDG 1,2, 6, 8 and 12) and environmental impacts (e.g., SDGs 13, 14, and 15). Technological shifts from stainless steel to single-use equipment are emblematic of the challenge. Stakeholder concern is growing about the environmental burden of SUP (Barbaroux et al., 2020). Paradoxically, as the sector matures, trends toward flexibility and faster time-to-market are driving replacement of stainless-steel technology (SST) with single-use technology (SUT) (MacDonald, 2019). SUT improves process efficiency by reducing capital costs, improving flexibility, cutting start-up times, and eliminating non-value-added processes. In addition, it reduces liquid waste, labor costs and validation efforts. However, the negative impacts of SUT have become more evident since the rise in healthcare SUP consumption during the COVID-19 pandemic (Choudhury et al., 2022). Indeed, it is the growth of the biopharmaceuticals sector, estimated at 12.5% CAGR, coupled with its pivot toward SUT that brings urgency to enhancing sectoral SUP circularity. The latest SUT biopharmaceuticals plant manufactures products from a 60,000-liter scale compared with a smaller 6,000-liter scale when Lim et al. (2008) first explored the environmental impacts of SUPs. The sector continues to prioritize disposal to landfill and incineration (Whitford et al., 2021).
Notwithstanding, there is evidence of some sectoral actors adopting more responsible practices. For example, some component manufacturers are reducing packaging by combining multiple single-use bags in a single form. Biodegradable materials are also being explored as alternatives. Their compliance with registration, evaluation, authorization, and restriction of chemicals (REACH) regulation will likely limit their application to peripheral components. Progress in adopting circular initiatives appears slow (Royte, 2019). The sector makes overtones that it wants to lead by example, despite generating only 0.01% of all SUP waste (Barbaroux et al., 2020). The evidence for environmental impacts of SUT from life-cycle analysis (LCA) is clear, in that it has significantly lower impacts than traditional SST (Flanagan et al., 2014; Al-Jarshawi et al., 2022). However, Ottinger et al. (2022) captures the inherent paradox between SUT adoption and biopharmaceuticals sectoral sustainability, articulating ways in which both can be enhanced (Thiounn and Smith, 2020). Moreover, emerging commitments to a circular economy for plastics pose new opportunities (Barbaroux et al., 2022). The challenge lies in developing solutions that are consistent with circular principles for materials selection, component design, process optimisation, packaging, shipping, and post-use handling (Whitford et al., 2022).
This review examines SUT environmental and socio-economic impacts and their solutions, with trade-offs generated in ever-tightening sustainability policy objectives. It explores requisite business models, sustainability regulation and emergent technologies. Duly acknowledging the infancy of a circular economy for plastics, it reviews three interwoven strands of evidence to critically evaluate state-of-the-art thinking on the topic. First, sustainability policy and regulation intersectionality with the biopharmaceuticals sector is analyzed. Synergies and tensions across the SDGs and emerging priorities are identified, as the sector aligns with the socio-ecological imperatives of an increasingly influential sustainability policy agenda. Second, it examines the literature on SUT, addressing its impacts and practical solutions. Third, it explores the application of circular economy concepts (e.g., Simon, 2019) to SUPs. Finally, a synthesis of the literature in respect of how biopharmaceutical manufacturers can re-engineer their business models for SUP circularity is presented. A future mission-driven research agenda, focused on policy formulation, industry regulation and collaborative innovation across the value chain is outlined based on industrial symbiosis, whereby companies could exchange materials, energy or knowledge.
In seeking to resolve the dichotomy between the societal trend away from disposable products and processes and the sectoral pivot toward SUT, the primary aim of this review is to explore the implications of SUPs used in biopharmaceuticals from a sustainability perspective. We evaluate this sector's sustainability progress and challenges with respect to the SUT pivot, using the SDG framework as a guide, underpinned by the following research question.
RQ1: How best can the biopharmaceuticals sector optimize the sustainability return from single-use plastics?
Given the exploratory nature of the research, the evidence chosen spans the previous 20 years (circa. 2003–2023), focusing on three broad strands, encompassing scholarly articles, industry reports and research papers, with a focus on widely cited, seminal works. Searches in academic databases, such as Elsevier, JSTOR, ProQuest, Web of Science, PubMed, ScienceDirect, Scopus and Academic Search Complete were supplemented by verification on Google Scholar. Given the evolving nature of sustainability knowledge and sectoral responses, we undertook regular searches for new evidence to challenge and critique industry-insider perspectives. Table 1 summarizes selected search terms used as the essence of the inclusion criteria. Although the searches were neither linear nor systematic, they encompassed a range of sources, with abstracts or summaries checked for relevance. As insights were gleaned, a pearl-growing approach (Papaioannou et al., 2010) was applied to further searches for sub-topics, keeping in mind the advantages, impacts, and drawbacks of, and potential alternatives to SUPs. This type of approach is iterative and typically involves first identifying an authoritative article that meets the inclusion criteria, then builds on the information provided by identifying subsequent articles cited by the article. Once identified, articles were evaluated for relevance, quality, and reliability. Evidence was cataloged by creating a table, comprising: title; key authors; purpose; proposition/hypothesis (if relevant); research approach; findings. This led to the identification of 223 articles, categorized under one of the three broad strands. To prioritize currency and scholarly research, articles published prior to 2003 were excluded, as were those published in popular periodicals. A synthesis of the articles was undertaken in a recursive process by critically analyzing, comparing and contrasting their key features, such as purpose, research questions (or hypotheses), method, underlying assumptions, units of analysis, impact, strengths and limitations, enabling common themes and conflicting evidence to be elicited (Mateos and Solé, 2009).
First, sustainability policy and regulation and their intersectionality with the biopharmaceuticals sector are analyzed. In exploring this strand, the literature found is qualitative in orientation, setting a rhetorical tone for sustainability priorities. This strand of evidence serves as context setting for the remainder of this article. Given the primary author of this article is a professional from the biopharmaceuticals sector, there is an inherent emic leaning, in the second strand of literature, which carries its own biases. A thoughtful group of professionals promote best practices within the sector, documenting their implementation of SUT through the Bio-Process Systems Alliance (BPSA). They have published their work in BioProcess International, articulating three thematic complexities under [i] economic and environmental implications, [ii] life-cycle analysis, [iii] societal dimensions and stakeholder engagement. Other industry professionals offer insights, too, many of which share SUT practices from their organizations. In the third strand, we explore circular solutions that would enable the sector to enhance sustainability of SUPs. Some of the literature is, once again, emic in nature, as sectoral professionals proactively work to address SUP waste. Notwithstanding, literature external to the biopharmaceuticals sector also provides insight. Notably, at a theoretical and policy level, there is an accumulation of literature, post MacArthur et al.'s (2016) blueprint for a circular economy for plastics, outlining how their design and use must change to solve the plastic pollution crisis. Yet, there is little evidence of using this knowledge in professional practice, which provides a basis for the concluding section of this article. It summarizes key findings, including advantages and drawbacks of SUPs, their impacts, and potential alternatives. In this section, the findings are synthesized to provide a holistic perspective. The apparent paradoxical nature of plastics, as being economically beneficial and environmentally detrimental, is addressed, as an example of the type of system thinking challenges inherent in the pursuit of the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). More specifically, we propose a conceptual framework, based on industrial symbiosis, for how the biopharmaceuticals can pursue SUP circularity.
Sustainability has become a disruptive force in many industrial sectors. The biopharmaceuticals sector plays a role in global health, providing therapeutics and vaccines for diseases. To address corporate concern for ecological protection, prudent natural resource consumption and social responsibility, sustainability has become a priority for biopharmaceutical manufacturers, with many disclosing their environmental, social and governance (ESG) performance (e.g., Novartis, 2022), upon which investment is increasingly contingent (Bhattacharya and Bhattacharya, 2023). We begin with the sector's developmental milestones and future trajectory. We then identify how sustainability has become a strategic priority. The implications of the SDGs are highlighted, and key performance indicators of sustainability progress are discussed. Moreover, in line with SDG 12, the emerging circularity imperative for sector is highlighted.
Since regulatory approval for recombinant human insulin, biopharmaceuticals have grown into a global industrial sector, with a forecasted valuation of $800 bn by 2030 (BioSpace, 2022). Biopharmaceutical science has propelled healthcare advancements, and biomanufacturing has become integral to modern health, with treatments relying on increasingly complex biomolecules for debilitating disorders, such as cancers and infectious diseases. Table 2 lists the key types of biopharmaceutical products, which are commonly referred to as biologics.
The development of insulin ushered in an era of therapeutic agents derived from living organisms. Szkodny and Lee (2022) highlight how recombinant DNA revolutionized the sector in the 1970′s. In 2014, biologics reached double-digit approval rates. Since then, almost 100 biologics have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Jacquemart et al., 2016). Biologics now account for circa. 25% of all drugs approved by the FDA. Figure 1 provides a timeline for sectoral evolution, based on major milestones.
In the 1980s, biotechnology companies sought approval for innovative products, such as recombinant human growth hormone. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) emerged as a transformative class of biologics in subsequent decades, as an immunotherapy for life-threatening disease, such as cancer. The adaptation of Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, as a host for biological growth, enabled large-scale production. Pioneering work in mammalian cell culture processes guided the design of early bioreactors (Arathoon and Birch, 1986). Design methods included roller bottles and micro-carrier cultures, and suspension cell cultures. Advancements in formulations, such as serum-free media (Murakami, 1989), enabled high-density suspension cell cultures and greater productivity in producing recombinant proteins. Parallel to scientific advances, engineering innovations contributed to the sector. Single-use manufacturing began in the 1980s when plastic filter capsules replaced stainless-filter housings. Disposable bags were deployed, with advancements leading to larger-scale processing. From the 1990s, manufacturers began integrating tubing and filters into SUT, and by the 2000s, these had evolved to gamma-irradiated options. Innovations include disposable rocking-bag bioreactors, tank-liner bioreactors, and disposable sensors. More recent developments include sterile disconnectors and single-use filtration systems. Today, SUT encompasses an array of highly enabling disposable technologies, reducing production costs and investment requirements, and supporting wider access to treatment. Lower environmental impacts of SUT over SST are reported across the materials lifecycle (Pietrzykowski et al., 2013). Future developments will likely prioritize flexibility, speed, and personalized treatments as manufacturers shift to modular plants. Focus on novel therapeutic modalities, such as BioSpecifics, antibody-drug conjugates and viral vectors for cell and gene therapies (C, and GTs) is increasing. Nascent technologies, such as continuous manufacturing, offer agile solutions. Such trends are connected to sectoral assimilation of SUT, estimated to be worth $9 bn, the very antithesis to society pivoting from disposable products (Hederman, 2022). Given enormous growth of SUT in the sector, waste issues generated by SUPs vis-à-vis the transformative force of sustainability can no longer be ignored.
Megatrends, as transformative forces, reshape societies. With a focus on social responsibility, economic stability and environmental stewardship, sustainability has emerged as a compelling megatrend (Lubin and Esty, 2010). This is reflected in the SDGs, the current blueprint for sustainability. Interconnections between SDGs highlight the need for systems thinking (Pham-Truffert et al., 2020). Such decisions are driving pursuit of greener manufacturing (McDonagh et al., 2012). The biopharmaceuticals sector is expected to deliver greater access to health services and reduce negative environmental and socio-economic impacts. Sachs et al. (2019) identify two transformations, among others, [1] health and wellbeing and [2] industry, for SDG achievement. In industry, corporates and investors are increasingly required to comply with sustainable finance regulation. Sustainability reporting standards once fragmented, are consolidating into integrated frameworks (Stolowy and Paugam, 2023) as ESG becomes mainstream. Once voluntary, disclosure is becoming mandatory (de Gioia-Carabellese and Macrì, 2023). Taxonomies for sustainable investments require investors to be transparent about their sustainability intentions (Kirby et al., 2021, 2024). In response, sectoral collaborations, such as the Biopharma Sustainability Roundtable, identify financially material ESG topics, including pricing; risk management, ethics, human capital, supply chains; antimicrobial resistance; governance; product quality and patient safety. Moreover, ESG ratings agencies offer critiques of corporate sustainability performances (Paolone et al., 2022). To respond in kind to sustainability challenges associated with drug manufacturing, the biopharmaceuticals sector has formulated, and is pursuing bold strategies, covering responsible water consumption, carbon emissions reduction, sustainable supply chains, adoption of green chemistry principles, design for circularity, and appropriate waste management (Forrest, 2023). These strategies call for collaboration across the value chain along with continuous innovation to create processes that gain the trust of patients, the healthcare community and society.
Healing both people and planet brings SUT into the biopharmaceuticals sector's sustainability calculus. It is undergoing transformation under the influence of the SDGs, with SUT as one of its key sustainability value propositions (Whitford et al., 2019). Despite the resilience of global biologics, the sector is struggling to adapt to SDG challenges, such as climate change, poverty, and biodiversity. Table 3 outlines the most relevant SDGs to the biopharmaceuticals sector, as well as their financial and impact materiality. Responsible for more GHG emissions than the automotive sector, there is little research on decarbonising biomanufacturing (Belkhir and Elmeligi, 2019). Furthermore, the sector has manifested some high-profile negative environmental impacts (Patel et al., 2019), bringing it into disrepute. Whilst SUT contributes to the achievement of SDGs 6 and 13, it is accompanied by burdens of solid waste, which impact negatively on SDG 12. Hence, there is a growing sectoral imperative to pursue circular solutions, posing decision-making trade-offs. Although companies are working collaboratively to contribute to the SDGs, regulation is evolving rapidly, and they are struggling to keep pace. For example, the European Chemical Agency has proposed limiting polyfluoroalkyl (PFAS), which could result in banning 10,000+ substances by 2027. The transition risk is enormous, posing a threat to biologics manufacturing in Europe (Spyrakis and Dragani, 2023).
Scientific measures of sustainability offer ways to drive improvements. The application of LCA, based on ISO14040, to evaluate the environmental impacts of drug production is well established (Ottinger et al., 2022). Generally, LCA applies systems thinking concepts in evaluating data for sustainability decisions on processes, products, services, technologies, and policies. It is used to assess impacts from raw materials to end-of-life, including climate, ozone, ecotoxicity, water, land degradation, fossil fuels depletion, land changes, particulate matter formation and photochemical oxidants (Pietrzykowski et al., 2013). Whilst LCA is effective in calculating impacts, it is limited in its ability to highlight opportunities for circularity. Alternatives measures also exist. Budzinski et al.'s (2019) efforts to calculate the process mass index (PMI) of mAb production demonstrated that circa. 770 kg of input (90% water) is required to produce 1 kg of mAb. Likewise, the concept of circularity for plastics (Blank et al., 2020) offers a way for manufacturers to examine impacts of materials, component design, manufacturing, packaging, logistics and post-use (Barbaroux et al., 2021). Brändström and Saidani (2022) suggest that circularity metrics can align with LCA, and Samani (2023) demonstrates that LCA can serve as a proxy indicator of circularity. However, a myopic focus on circularity can yield unintended consequences if environmental impacts result outside of the materials domain. Hence, Barbaroux et al. (2022) elaborate on Valencia's (2017) more holistic measure, combining LCA, circularity and PMI, in a return on sustainability investment (ROSI) and advocating for sectoral collaboration on developing a sustainability index.
Biopharmaceuticals are integral to modern medicine, offering breakthrough treatments based on complex molecules. The sectoral trend is toward continuous processes for manufacturing complex therapies in lightweight facilities. A spotlight on sustainability has brought the sector under scrutiny. Multiple measurement techniques, such as LCA, circularity and PMI, each with idiosyncrasies, mitigate against pursuit of sector-wide sustainability enhancements. Societal dimensions must also be considered, in particular consumer activism and regulatory evolution. The societal shift from SUPs problematises the sector's pivot to SUT, particularly with respect to transition risk. Ottinger et al. (2022) cite legislative actions, bans, levies, and recycling mandates to curb SUP proliferation. However, Ottinger's paradox is not the sole sustainability challenge. The systematic nature of the SDGs requires new problem-solving competencies. Similar issues arise, for example, with respect to the emergence of green chemistry (Barbaroux et al., 2020). The literature suggests that sectoral-wide responses to SUT circularity, and other sustainability challenges, require collaboration across the value-chain. More engaged research on enhancing SUT sustainability in the biopharmaceuticals sector could facilitate orderly transition.
Samaras et al. (2022) illustrate how SUT benefits for manufacturers outweigh the associated waste issues that they then have to manage, thereby supporting its adoption, particularly in downstream processes for custom therapies. Given that the biopharmaceuticals sector is water and energy intensive, SUT adoption is predicated on reductions in their consumption, by eliminating cleaning and sterilization, yielding faster setup and changeover times (Morrow and Langer, 2020). Over two decades, single-use bioreactor capacity has grown from 1% to 13% volumetrically and the proportion of single-use bioreactors has risen from 30% to 46% of installed capacity (Oosterhuis and Junne, 2016). This section chronicles SUT adoption, its impacts, regulatory risk, and current thinking on its sustainability.
From its inception, the economic case for SUT adoption has been compelling. As the sector pivots to modular manufacturing, high value biologics and custom therapies, SUT's plug and play nature is congruent with innovating new medical treatments, such as gene therapy and vaccines. Whilst single-use components, such as tubing, have long been used, SUT gained momentum after the WAVE bioreactor's release in 1996 (Singh, 1999). In more recent years, the COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the demand for SUT in small-scale and mid-scale biomanufacturing of new vaccines and monoclonal antibody therapies (Langer, 2022). SUT spans multiple bioprocess equipment, including reactors, fermenters, perfusion systems and centrifuge systems and is transforming how bioprocesses are designed and operated. Moreover, it has become inherent to the agility and flexibility of continuous biomanufacturing processes, at a lower cost than alternative options (Jacquemart et al., 2016).
SUT addresses safety and cross-contamination concerns, allowing facilities to be controlled-not-classified environments. This simplifies facility design and offers flexibility for multiproduct manufacturing (Smith et al., 2018). Facility investment and process validation lead-time are much less, restricting SST facilities to high-volume manufacturing, and saving up 75% and 25% of CAPEX and OPEX respectively (Ravisé et al., 2010). This makes SUT popular with contract manufacturers (Roizman and Langer, 2019). In developing economies, the rapid ramp-up in vaccine production, in response to COVID-19, led to a surge in SUT demand (van Riel and de Wit, 2020), as they sought affordable localized solutions. The requirement to produce multiple different products in various quantities and at a faster rate is driving the demand for SUT. Facilities can eliminate process steps and, thus, increase rates at which drugs are manufactured. In the future, biologics manufacturers will rely on the flexibility that SUT affords in response to market trends at different scales, through the provision of hybrid facilities. In summary, SUT manufacturing is likely to be smaller and more modular, faster, and more flexible, greener, and safer, yielding better economic outcomes (Pollard and Pralong, 2018).
Notwithstanding, the limitations of SUP have hindered its adoption. These include risk of contamination due to materials compabability, with adverse impacts on patient safety and product quality, supply chain volatility, risk of product loss from connector leakage or bag rupture, and lack of equipment standardization (Samaras et al., 2022). The use of SUT reduces some of the risks that would otherwise come with required cleaning processes, such as cleaning residues and cross-contamination. A key concern is the possibility of unwarranted migration of contaminants from plastic (Kunert and Reinhart, 2016). The limited mechanical strength and stiffness of the plastics can result in poor scalability. Bylander et al. (2023) summarizes the challenges with SUT bioreactors, which are limited in volumetric capacity, oxygen supply, and adequate stirring. Finally, SUT requires a steady supply of disposable components, which brings storage facilities, logistics, supply chains and consumables costs into consideration (Frank, 2018). These disadvantages can be partially mitigated through risk management. For example, Takao et al. (2023) demonstrate the use of failure mode effect analysis in a case-study on reducing product loss.
Over 60% of bioreactors now deploy SUT. The number of mAbs production facilities applying SUT and their scale and volumes continue to rise. In 2000, SUT was primarily used for lab-based research. It was only in 2005 that the first 2000-liter bioreactors were deployed, operating two or three units in series. The newest facilities are adopting 10 units of 6,000-liters (for mammalian) and 1,000-liters (for microbial). In parallel, process intensification and improved product titers have reduced reliance on large process volumes. Table 4 summarizes common biopharmaceuticals SUT manufacturing processes.
Contrary to initial expectations that SUT might render SST facilities obsolete, evidence indicates that these facilities continue to be operational, incorporating bioreactors with capacities exceeding 10,000 liters. Despite this, the domain of single-use systems has gradually expanded in commercial scale manufacturing. In 2023, an inflection was reached with the establishment of single-use mAb facilities, such as a 6 × 4,000-liter facility, followed by a larger 10 × 6,000-liter facility (Nissinoff, 2023). Although most high-volume commercial biopharmaceutical production continues to rely on SST, single-use facilities are increasingly gaining precedence, not only in terms of sheer numbers but also in diversity of process lines and product range. This trend is progressively permeating mainstream manufacturing, as SUT facilities offer expedited pathways to market, aligning with increasing demand for speed in product development (Rader and Langer, 2019).
Several sectoral efforts have applied green chemistry principles to small-molecule drugs and biologics manufacturing (e.g., Anastas, 2003). There are tremendous advantages to applying green chemistry principles in the biopharmaceutical industry including but are not limited to environmental impact, meeting regulatory requirements, creating a positive public perception and corporate social responsibility, extracting cost savings and economic benefits, and pursuit of process efficiency. Table 5 lists a range of current common metrics used to guide process efficiency enhancements. PMI has become the main metric for efficiency improvements. Madabhushi et al. (2018) demonstrated its application to mAb production, aligning it with sustainability concepts by focusing on resource efficiency, thus establishing correlation with upstream life-cycle impacts. The WARIEN metric (Cataldo et al., 2020), extends PMI by linking energy and water consumption. Yet, Whitford et al. (2019) point to limitations in measuring impacts using single metrics, which fail to capture system interdependencies. Hence, the need, they argue, for an approach, such as LCA, which involves analyzing material and energy flows across life-cycle stages using multiple metrics for aggregate environmental impacts and trade-offs (Sevigné-Itoiz et al., 2021). Yet, LCA has challenges related to modeling complexity, boundary setting, time horizons, and scalability. These are very important in biopharmaceuticals, which rely on complex processes over geographically dispersed sites and globalized supply-chains (Sonnemann and Alvarado, 2018).
Lim et al.'s (2008) attempted assessment of impacts revealed SUT benefits in terms of material footprint. Likewise, Pora and Rawlings (2009) demonstrated that SUT could achieve lower energy impacts. Since then, circa. a dozen studies have been undertaken (Figure 2). Mauter (2009) compared SUT and SST bioreactors for mAb production. Results indicate that LCA can be useful in highlighting trade-offs in processes. Moreover, Mauter showed how operations are more impactful than waste streams. Pietrzykowski et al. (2013) documented the first cradle-to-grave LCA study (at GE Healthcare) of SUT v SST for mAb production at various volumetric scales. Their findings revealed that, whilst end-of-life impacts are marginally higher for SUT, overall impacts are lower across 18 environmental categories. A second GE study across multiple production facilities, geographical locations, product combinations and end-of-life treatments revealed lower impacts for SUT on climate, energy, water, health, and natural resource impacts (GE Healthcare, 2017). End-of-life impacts were found to be negligible relative to production impacts. From these studies, generalizations can be inferred. First, counterintuitively, SUT yields lower overall impacts than SST. Second, whilst SUT results in marginally higher end-of-life impacts, these account for only a small proportion of overall impacts. Third, water and energy demands are lower for SUT, due to elimination of clean-in-place (CIP) and steam-in-place (SIP) processes. Fourth, geography plays a role, due to logistics coordination and cleanliness of energy grids. Key limitations to the studies point to latent opportunities for enhancement. Given trends toward more modular manufacturing of personalized medicines, there is a dearth of evidence for their environmental impacts (Al-Jarshawi et al., 2022). Furthermore, there is limited assessment of energy impacts associated with facilities. There is notable diversity in the studies in terms of which impacts were evaluated, which metrics were used, and which life-cycle stage assessment was undertaken. All studies were restricted to single processes, or companies, with no scaled-up industry-level study yet undertaken. A significant limitation has been a failure to address SUP circularity. Moreover, the studies have been criticized for not sufficiently considering impacts at end-of-life (Herberz et al., 2020). Although measures of circularity are still in their infancy, the historical progression in the narrative of the studies (highlighted in Figure 2) is from one that initially highlights lower impacts of SUT to one that gradually recognizes a need to address circularity, particularly at end-of-life.
There is a growing body of evidence documenting the social and human health effects of litter and debris caused by mismanaged plastic waste leaking into the environment (Iñiguez et al., 2016). The accumulation of SUPs in marine environments and its health implications for circa. 40 million people who rely on maritime based income, such as income from fishing, marine tourism, aquaculture, and shipping, is well-documented (Aretoulaki et al., 2021). In particular, income for fishing and aquaculture is directly affected by marine plastic litter through the cost of maintenance of fishing fleets and facilities and loss of income due to impacts on fish stocks and to potential erosion in confidence in seafood quality from the presence of micro plastics. Collectively, the reduction in marine ecosystem service provision carries significant implications for human health, food production, recreation and heritage, particularly in coastal communities (Naeem et al., 2016). Notwithstanding, the socio-economic impacts of plastic through pollution are yet to be fully evaluated on a global scale (Paul et al., 2023). Given the relatively low cost of plastics, the socio-economic effects of marine plastic pollution appears to be more impactful in developing economies (e.g., Danquah et al., 2019; Nøklebye et al., 2023).
Regulation of SUT in biomanufacturing has historically focused on product quality and patient safety (Eibl and Eibl, 2019). Lopes (2015) explored the overlapping concerns of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA), including process validation, supply-chain security, contamination, risk management and documentation. Since the arrival of the SDGs, the FDA and EMA have become more sensitive to environmental concerns. Yet, regulatory challenges are more likely to come from outside the sector than from within. The world produces 300 m+ tons of plastics annually, two-thirds of which are short-lived consumables (Jambeck et al., 2015). With production set to triple by 2060, circularity considerations are more urgent. The ISPE (2023) sectoral survey found that 46% of leaders (n=18) in the biopharmaceuticals sector have initiatives focused on reducing SUP waste and 52% (n = 22) have initiatives on better end-of-life management. Sectoral responses advocate for improvements (Biophorum, 2023) with Barbaroux et al. (2022), in particular, stressing the imperative to foster circularity. Regulatory initiatives are still in their infancy. The FDA, for example, began approving mechanically recycled plastics for food-packaging applications almost two decades ago (Karmaus et al., 2018). Such materials are still unavailable with the quality required for biologics due to unacceptably high risk of contamination from leachables and extractables. Indeed, recycling has to contend with potential contamination across all stages of plastic product life cycles. Potentially harmful substances, such as additives, may not be fully filtered in the recycling process, posing a risk to human health. For example, brominated flame retardants, commonly used in polystyrene, were regulated out of food packaging given their association with cancer, endocrine disruption and reproductive toxicity (Shaw et al., 2014).
Given the criticality of medical access, environmental issues tend to be lower in priority within the sector. Nissinoff (2023) reported that, in 2013, 70% of sector professionals surveyed expressed a need for recycling, but with a mere 35% recycling rate. When surveyed again in 2020, the respective figures had changed to 89% and 25%. Alarmingly, 76% continued to rely on incineration or landfill disposal. In acknowledging the LCA advantage that SUT holds over SST, Whitford et al. (2021) underscore the urgency to address end-of-life considerations. Whilst some SUP suppliers have explored recycling, multilayered plastics components, such as bioreactors, inhibit opportunities. Barbaroux et al. (2021) advocate for pursuit of innovations to enhance circularity in line with MacArthur's (2013) “new plastics economy” principles. Whilst conceptually plausible, these proposed innovations do not offer real-world, case-study exemplars.
There is extensive case study evidence in the literature for the impact of SUPs (e.g., Diggle and Walker, 2022). Villarrubia-Gómez et al. (2024) suggests that plastics pollution exacerbates all planetary boundaries and, hence, requires international governance, due to their uncontrolled release to the environment and a failure to control chemicals added to them. As a novel entity comprising synthetic monomers and chemicals, their complex reality suggests that, once touted as being inert and safe, they pose threats, which are unpredictable and, therefore, necessitate a precautionary approach. Moreover, a myopic focus on pollution as merely a waste management issue may tilt companies, researchers and policymakers toward a narrow focus on end-of-life. In summary, this section highlights the overriding advantage that SUT carries over SST in terms of environmental impacts. However, there are significant, yet unquantified, impacts associated with SUPs, thereby providing a rationale for the pursuit of SUP circularity.
This section explores circularity exemplars, primarily from the plastics economy, in the context of how the biopharmaceuticals sector could develop industry-level solutions. It begins with an exploration of the plastic waste challenge and the new plastics economy. It then explores the theoretical concepts of the circular economy and how they apply to plastics. Finally, it examines the application of these concepts to biopharmaceuticals SUPs, providing empirical exemplars of reduce, re-engineer, reuse, recycle and energy recovery that could transform the sector. Since the production of Bakelite in 1907, plastics have emerged as materials of choice for many applications. Global production has increased exponentially, standing at circa. 390 million tons (MT) p.a. (Plastics Europe, 2022). Yet, despite their societal benefits, plastics pose environmental and health challenges, discussed below, as evidenced by waste quantities accumulating in marine environments and the leaching of additives with endocrine disrupting properties into the food chain (Freeland et al., 2022). The societal dilemma is aptly framed by MacArthur (2013), who poses the question: will society pursue a discontinuation of plastics, forging its benefits, or will it create a future for plastics based on circular economy principles?
Leakage to the environment due to improper waste disposal creates serious health implications (Bharti, 2024). Plastics are crucial to advancements in healthcare (Klemeš et al., 2021). Yet, they face a crisis of legitimacy due to overproduction and poor recyclability. Plastics can persist in natural environments for thousands of years (Andrady, 2015), degrading into micro plastics, small enough to be ingested by wildlife (Kannan and Vimalkumar, 2021). Whilst chemically inert, contrary to early beliefs that they would harmlessly pass through biological systems, their absorption, leading to health issues such as endocrine disruption, carcinogenic impacts, liver damage (Lehel and Murphy, 2021), reproductive issues and respiratory diseases (Çitar Daziroglu and Bilici, 2024), is largely unquantified. Various chemical additives can migrate and lead to human exposure (Hahladakis et al., 2018). Since the 1990s, plastic waste has more than tripled. Whilst a circular economy for plastics is emerging, it is not yet significant (Figure 3). Circa. 36% of all plastics materials are used for packaging, 85% of which ends up in landfill. GHG emissions associated with conventional plastics are estimated at 3.3% of annual global emissions (Ritchie, 2023). SUPs are particularly problematic as, by definition, there is little circularity built into their supply chains. With an estimated 75-199 MT of plastic in our oceans (McGlade et al., 2021), unless we change how we dispose of plastic, the amount of waste entering aquatic ecosystems could rise to a projected 23-37 MT p.a. by 2040. Van Sebille et al. (2015) estimates there are up to 51 trillion pieces of microplastic in the oceans, weighing 93 - 236 MT. Meijer et al. (2021) suggest that circa. only 1,000 rivers account for 80% of annual riverine plastic deposits into the oceans. Yet, plastic recycling rates are low compared to rates for other materials. Confronting this challenge requires efforts to reduce plastic production, improve waste management, and to innovate and alternative materials (Watkins et al., 2020).
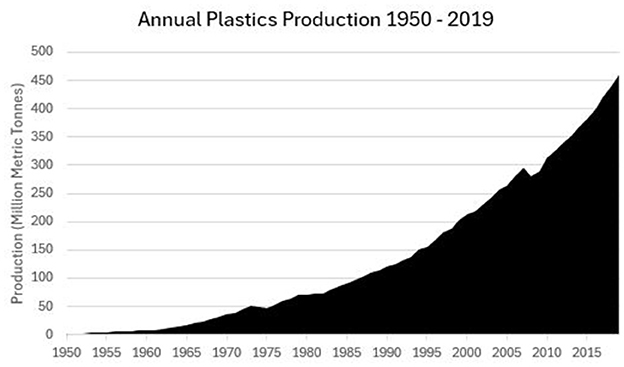
Figure 3. Historical plastic production since 1950. Source of Data: Hannah et al. (2023).
The CE stands for a change in thinking in resource usage. Whilst definitions vary (e.g., Murray et al., 2017; Sauvé et al., 2016,), unlike a linear economy (Figure 4A), which material follows a 'take-make-dispose' pattern, there is a self-replenishing pattern in which materials “loop”, minimizing waste, and new material (Figure 4B).
Bandh et al. (2024) emphasize three core principles: [1] designing out waste, [2] keeping products and materials in use, and [3] regenerating natural systems. These principles have been driven by policymakers (MacArthur et al., 2016), businesses (Brennan et al., 2015) and regulators (European Commission, 2015). Multiple studies have explored strategies for CE implementation (e.g., Kalmykova et al., 2018). Some critics point to a need to operationalise CE principles, (e.g., Pauliuk, 2018), to enhance coordinated action (e.g., Domenech and Bahn-Walkowiak, 2019), to improve regulation, and to establish a stronger relationship between CE and sustainable development (Kirchherr et al., 2018). Notwithstanding, SDG 12, in particular, provides legitimacy to these principles in addressing the plastics problem (Mrowiec, 2018; Schroeder et al., 2019). Researchers, policymakers, and businesses are beginning to collaborate on addressing the operationalization challenge by adopting a life-cycle approach. Policymakers, in particular, are addressing the challenge through green procurement (e.g., Singh et al., 2024), re-use and repair (e.g., European Commission, 2024), and, in the case of plastics, banning some SUP products (e.g., European Commission, 2019). Reinventing manufacturing processes and materials innovation present notable opportunities for businesses to implement CE principles. Business innovation, in this context, could mean the development of more efficient manufacturing techniques, discovering cost-effective materials, or the development of environmentally friendly processes. Nevertheless, plastic waste generation has not yet slowed, and waste management strategies, along with other actions across the value chain, must be improved (Gonçalves et al., 2024).
Figure 5 depicts the lifecycle of plastics. Circa. 90% of plastics are petroleum-based (Zhao et al., 2020). Despite technological advancements, most are either incinerated or landfilled, with recycling rates at 14–18% (OECD, 2018). MacArthur et al. (2016) estimates post-use externalities associated with plastics at $40 billion p.a., demonstrating potential for a new plastics economy, with the primary aim of transforming how plastics are produced and consumed. Inter alia, objectives include waste reduction (Ten Brink et al., 2018), resource optimisation (Azapagic, 1999), economic resilience (Giannetti et al., 2023), behavioral change (Erickson et al., 2021), policy enhancement (De Kock et al., 2020) and impact reduction (Schwarz et al., 2021). Tracking material flows is challenging given that many products comprise multiple plastics, each with their own properties, or have plastics embedded in complex assemblies (Hahladakis et al., 2018). The European Commission (2015) dedicated strategy for plastics sets ambitious targets, including 10 MT of recycled plastics in new products by 2030.
Several voluntary initiatives have emerged, including: the UK Plastics Pact, and a UN commitment to forge a global plastics treaty (Bundela and Pandey, 2022). Yet, a better understanding of material loops is required to support policy formulation. Several material flow analyses (e.g., Hsu et al., 2021; Luan et al., 2021) have sought to address the data gap, affirming that most plastic waste still arrives at open dumps, landfills, or incinerators. There is also a dearth of evidence on environmental impact, with few studies on leakage (Alencar et al., 2022). Therefore, whilst LCA studies may be useful, there is uncertainty about the impacts on marine and terrestrial ecosystems, which will only emerge in time. Caution is called for in rushing to replace plastic with other materials given challenges in accounting for their impacts (Klemeš et al., 2021). Greater emphasis on recycling to displace virgin plastics seems like an obvious solution. Bernardo et al.'s (2016) meta-analyses of LCA studies of plastics conclude that recycling has a smaller carbon footprint than landfill or incineration. Mechanical recycling involves collecting, sorting, shredding, and cleaning waste plastic before pelletizing it back into a raw material. It is sensitive to contaminants, such as additives and food, so can be sub-divided into primary (closed-loop) recycling, which substitutes virgin materials in the same application, and secondary (open-loop) recycling, where used plastics, whose mechanical properties are degraded by the recycling process, are repurposed into less demanding applications. Material variability and post-use contamination hinders recycling. Whilst bioplastics offer possibilities for circularity through valorisation protocols (Ranjbari et al., 2021), sorting instructions for waste management of bioplastics are needed (Prieto, 2016). Payne et al. (2019) highlight the potential for chemical recycling, which involves converting polymers back to monomers through pyrolysis. New biological recycling technologies, in which genetically modified enzymes are used to breakdown common plastics (e.g., Yoshida et al., 2016), are also emerging. In Europe, energy recovery surpassed landfill as the primary mode of waste treatment in 2021, with recycled plastics accounting for 10% of production and bioplastics a further 2% (Plastics Europe, 2022). The challenge with energy recovery is that it relies on advanced air pollution control technologies to prevent of emissions of harmful materials, such as persistent organic pollutants and greenhouse gases (Van Caneghem et al., 2019).
In biopharmaceuticals contexts, post-use management of SUPs is receiving increased attention, with trade-offs between environmental sustainability, product recovery, bioprocess performance and patient safety being particularly acute. Despite arguments that the sector produces only a small fraction of global plastic waste (e.g., Pietrzykowski et al., 2013), that various LCA's studies demonstrate that SUT is less impactful than SST (e.g., Barbaroux et al., 2020), and that the societal benefits of its SUPs outweigh the environmental risks (e.g., Jacquemart et al., 2016), this article contends that the sector must urgently pursue greater circularity of its SUPs, given the uncertainty of their impacts vis-à-vis multiple planetary boundaries, and given the sector's continued growth and pivot to SUT. The next section discusses our findings and conjectures potential sectoral initiatives in pursuit of circularity, as a synthesis of state-of-the-art thinking.
An underlying motivation for this review is to unravel the dichotomy between the societal shift from disposable products and the biopharmaceutical sector's adoption of SUT. Using the SDGs as a guide, the underlying research objective is focused on optimizing sectoral sustainability returns from its SUPs. The review explores three strands of evidence: sustainability policy and regulation, SUT in biopharmaceuticals, and circular economy principles. In the first strand, we outlined the evolution of biopharmaceuticals, which has seen transformative developments with complex biomolecules playing an increasing role. SUT adoption has contributed to its expansion. We then explored the materiality of specific SDGs to biopharmaceuticals (Table 3), highlighting sectoral challenges in adapting to sustainability objectives, particularly regarding SUP waste. We delved into the complexities in measuring sustainability in biopharmaceuticals, discussing LCA studies and circularity concepts. The literature provides evidence of how the sector's pivot toward SUT, despite its reliance on plastic, offers environmental benefits, yet necessitates collaborative efforts and new problem-solving capabilities. In the second strand, a sectoral perspective on SUT adoption was provided. The economic case for its adoption is compelling in the transition to modular manufacturing of custom therapies. SUT offers advantages, such as addressing safety, embedding flexibility, and reducing validation lead-time. The literature reveals increasing integration of SUT in the sector. Despite initial expectations of rendering SST facilities obsolete, evidence suggests that both coexist with SUT being chosen for smaller and more flexible facilities. We also explored metrics for environmental sustainability. Whilst studies, based on LCA, demonstrate that SUT yields lower overall impacts than SST, there are limitations in measuring circularity and addressing end-of-life. Sectoral regulation has focused on product quality and patient safety, but recent initiatives indicate a growing sensitivity to environmental concerns. In the third strand, the evolution and challenges of plastics were discussed. Although plastics have become pervasive and essential for healthcare, their improper disposal poses, as of yet, unquantified environmental and health risks, as evidenced by accumulation of plastic waste in marine environments. The Circular Economy was introduced as a paradigm shift that promotes waste reduction, reuse of materials, and regenerating natural systems. The integration of circular principles into the plastics economy was explored, emphasizing transformative approaches to production, consumption, and post-use management. Some of the core themes emanating from the literature are discussed below. The three strands are inherently interrelated. The integration of policy frameworks, the adoption of SUT, and the application of circular economy principles are interconnected components that collectively drive sustainability within the biopharmaceuticals sector. Together, these strands can form the basis a cohesive strategy to reduce environmental impact whilst maintaining industry innovation and efficiency.
The biopharmaceuticals sector is increasingly focused on sustainability enhancements, particularly in the context of single-use plastics (SUPs), which are extensively used in biomanufacturing to yield lower energy usage, to reduce purified water usage and to greatly reduce risk of water contamination (Whitford et al., 2021). However, whilst the environmental impact of SUP waste is of growing concern, the state-of-the-art strategies and innovations for post-use SUP circularity are slow to develop. Latent opportunities exist through materials innovation, LCA, stakeholder collaboration, and regulation. Future research must understand stakeholder perspectives and how differing goals may aid or hinder sustainable practices. By assessing stakeholders' influence and identifying barriers to engagement, targeted actions and policies can be developed to address plastic waste in biopharmaceuticals. Addressing the need for sustainable single-use plastics (SUPs) through material innovations is key to reducing plastic pollution whilst maintaining efficiency in biopharmaceutical manufacturing processes.
Alternative materials with lower environmental impact, such as, bio-based polymers and biodegradable plastics show promise (Narancic et al., 2020). Materials such as Polylactic Acid (PLA) derived from sugarcane are being explored (Freeland et al., 2022). Research has been undertaken, analyzing the impact of bio-based materials to reduce energy consumption and GHG emissions (Weiss et al., 2012). Similar research on the use of bio-PET highlights issues with land-use competing with food production and water use for irrigation (Chen et al., 2016). Alternative sources, such as microalgae and yeast strains have also been investigated (Lu et al., 2012). Whilst this stream of materials research is promising, given compatibility with in vivo conditions, a lack of understanding of the causal factors influencing polymeric degradation, to date, held them back as viable alternatives in biologics manufacturing. Materials innovation can enhance lifecycle analysis work to reduce the environmental impact of SUPs in biopharmaceuticals.
LCA has been used to understand SUP impacts vis-à-vis SST (Budzinski et al., 2022; Flanagan et al., 2014; Gehring and Meyer, 2022; Pietrzykowski et al., 2013). LCA's comprehensive approach helps manufacturers make informed decisions about material selection, design, and end-of-life management. Although LCA studies have shown SUP disposal to have a negligible overall environmental impact, industry insiders consider it an area of growing concern, owing to the increasing amounts of waste being generated (Barbaroux et al., 2020; Erickson et al., 2021). By enhancing lifecycle analysis with stakeholder collaboration, the biopharmaceuticals sector can develop more sustainable solutions, which consider both environmental impacts and the needs of all involved.
There have been repeated calls and initiatives for sector-wide collaboration on sustainability (e.g., Budzinski et al., 2016; Gehring and Meyer, 2022). Stakeholders across supply-chains, including equipment and materials suppliers, customers, and regulatory bodies, are crucial for driving sustainability. Initiatives, such as shared responsibility models and industry-wide standards for sustainable plastics use are emerging but require further research. The literature points to only a few concerned groups, such as the Bioprocess Systems Alliance (BPSA), the American Chemical Society Green Chemistry Institute Pharmaceutical Roundtable (ACS GCIPR), and the Geselshaft für Chemishe Technik und Biotechnologie (DECHEMA). Stakeholder collaboration can help to ensure that sustainability efforts in the biopharmaceuticals sector meet regulatory requirements.
Regulatory frameworks are evolving to enhance the sustainability of plastics. Governments worldwide are implementing various policy and regulatory measures, ranging from outright bans on single-use plastics (SUPs) to detailed waste management regulations that focus on post-use plastic management. In the European Union, the Single-Use Plastics Directive (2019) aims to reduce plastic consumption by banning certain SUPs and mandating that by 2030, at least 30% of plastic bottles produced in the EU contain recycled content (Kumar et al., 2024). The EU's ban on single-use consumables is indicative of policy intended to address global plastic pollution. To manage SUP waste globally, international agreements are needed alongside regional and national legislation. Biopharmaceutical manufacturers are proactively aligning with similar regulations by adopting sustainable practices in advance of legal mandates. Meeting sustainability standards is becoming a competitive advantage. However, the proposed ban on PFAS use and the response of the biopharmaceuticals sector exposes just how far it remains removed from evolving societal expectations (Biophorum, 2023). A strong regulatory framework is crucial for improving plastic sustainability and post-use management of SUPs in the biopharmaceuticals sector.
Pursuit of SUP circularity in the biopharmaceuticals sector is a multifaceted endeavor involving innovation in materials, process optimisation, LCA, collaboration, regulatory alignment, and education. Some manufacturers are making efforts to advance these endeavors, recognizing their role in reducing SUP impacts, whilst maintaining product quality and safety. The sector is gradually turning its attention to the post-use management of SUPs and their ultimate destinations. Crippa et al. (2019), MacDonald (2019), Pora and Rawlings (2009), and Whitford et al. (2021) offer various solutions for SUP post-use management, synopsised in Table 6. Their feasibility in respect of SUP consumption is contingent on several factors, such as type of plastic, component separation requirements, waste volumes, transport and logistics, and regulatory conditions. Notwithstanding a comprehensive study is required to evaluate the impacts of current post-use methods within the sector based on the factors of those outlined above.
The literature points to several unresolved issues with respect to SUP post-use management in the biopharmaceuticals sector. First, current LCA sectoral studies are localized to individual processes, manufacturing sites or companies. Whilst context matters, it would be important for the biopharmaceuticals sector to understand how SUP impacts manifest at scale. Second, there appears to be little reconciliation between existing industry insider LCA studies and the impacts of plastic leakage to environment, echoed in the concerns of circular plastics economy literature. We may only know the true scale of plastics leakage in the fullness of time. In the interim, research is required to reconcile current LCA methods with circularity principles to develop a better understanding plastic materials footprint. Some research has been done in this respect (e.g., Joachimiak-Lechman et al., 2020; Venkatachalam et al., 2022). However, it needs to be contextualized to the SUPs consumed in the sector. Third, whilst the vast-majority of sectoral SUPs is still incinerated or landfilled, 30,000 tons according to Ottinger et al. (2022), there is no industry-wide data on the end-of-life destinations of biopharmaceuticals SUPs. Whilst the sector makes overtones about improving SUP circularity, there is a gap between rhetoric and reality. A benchmarking study is required to understand the status quo in this respect. Fourth, Ottinger et al. (2022) points out that enhancing SUP sustainability extends beyond technological and material-related issues. Regulation has a role to play. Yet, as has been seen with the proposed PFAS ban, regulating in the dark in pursuit of noble sustainability policy objectives without the supporting empirical evidence can be destabilizing. In fact, businesses may not choose to change, unless they are coerced to do so. A precautionary approach to regulation and understanding possible regulatory futures is, therefore, advisable. Fifth and, finally, in recognizing that pursuit of sustainable SUP post-use solutions requires establishing new business models, value chains, regulation and technological developments, sector actors need to collaborate on the most plausible adoption pathways to shift its strategic position in response to the SUP sustainability challenge. Hence, we propose a design-driven approach to addressing these unresolved issues (You et al., 2023). This approach would be based on industrial symbiosis (Castellet-Viciano et al., 2022), whereby sector actors would exchange materials, energy, or knowledge in a form of industrial metabolism (Lowe and Evans, 1995).
Theory and methodologies in industrial symbioses have been advancing for two decades, characterizing the exchange of materials and energy to enhance economic and ecological performance (Zhang et al., 2015). Among the most high-profile exemplars of an industrial symbiosis is manifested at Kalundborg eco-industrial park, Denmark, which has inspired several studies (e.g., Ehrenfeld and Chertow, 2002; Engberg, 1992). These studies are based on systematic methods derived from analyses of complex ecological or biological systems. The primary condition for industrial symbiosis is collaboration among companies (Chertow, 2000) to form a network for taking advantage of synergies between them to enhance their economic sustainability and environmental performance (Harper and Graedel, 2004) through the exchange of materials, energy waste and knowledge (Mirata and Emtairah, 2005). Analysis of enabling mechanisms for industrial symbioses tends to focus on three factors, namely: [1] economic driving forces, [2] regulation, [3] and technological innovations. Two methods of analysis are commonly used. First, industrial metabolism is used to analyse stocks and flows of energy and materials within an entire industrial process (e.g., Chen et al., 2010). By analyzing exchanges of materials and energy, resources identified as not being fully recycled can guide suggestions for sustainable development. Second, as the flows among companies form a network, the network analysis methods can provide useful insights (e.g., Fath and Patten, 1998). There is precedence for using industrial symbiosis methods in pursuit of plastics circularity (e.g., Maranesi and De Giovanni, 2020). So, theoretical travel to SUPs in the biopharmaceuticals sector is a plausible proposition.
The proposed approach would leverage a recalibrated LCA, developing a comprehensive impact assessment model, advocating for standardized and cross-regional actions, and employing a fitting research framework enriched with diverse theoretical insights. It has the potential to make a contribution to sustainable biologics manufacturing. It would not only address the pressing issue of SUP waste but also provide a pathway for the biopharmaceuticals sector to adopt more sustainable practices in alignment with global environmental goals, enshrined in the SDGs.
This review of the biopharmaceutical sector's use of single-use plastics (SUPs) reveals significant insights into the intersection of technological innovation, sustainability, and regulatory pressures. It sheds lights on several significant findings.
• Operational benefits: SUPs offer notable advantages in terms of economies of scale, process efficiencies, manufacturing flexibility, scalability, agility, and sterility assurance. These advantages are driving enormous growth in SUT adoption, enabling higher productivity, more streamlined and customized therapies.
• Environmental impact: Life-cycle analysis (LCA) of SUPs suggests a lower environmental footprint compared to traditional stainless-steel systems, primarily due to the high energy intensity and embodied carbon of the latter. There are notable reductions in in-process energy and water requirements associated with SUT.
• Waste management challenges: Despite the environmental benefits during use, the disposal of approximately 30,000 tons of SUPs annually through landfilling or incineration presents largely unquantified environmental and health challenges.
• Regulatory and societal pressure: Increasing regulatory demands aligned with the SDGs and societal pressure for sustainability are pushing the sector toward more sustainable practices. The proposed ban on PFAS, for example, could have an enormously disruptive impact on the biopharmaceuticals sector.
• Circular economy principles: Whilst the application of circular economy principles to SUPs is promising, the sector shows limited appetite for circularization due to conservatism and perceived risks. The current posturing within the sector has focused largely on seeking derogations from any circularity requirements.
Collectively, these findings advance our understanding of the dualistic nature of SUPs in the biopharmaceuticals sector. The studies reviewed show a clear operational advantage of SUPs but also highlight significant environmental and waste management issues. The literature reveals a gap in fully integrated lifecycle assessments that consider end-of-life stages, indicating a need for more comprehensive impact assessment models. Viewed from a life-cycle standpoint, plastics pollution is a complex “global, relational, integrated and intersectoral issue (Fuller et al., 2022, p. 536). The interplay between regulatory frameworks, societal expectations, and technological innovation underscores the complexity of transitioning toward sustainable practices. The implications of these findings are significant for both theory, practice and policy formulation. From a theoretical perspective, the review highlights the need for more nuanced lifecycle analyses that include end-of-life considerations. It also underscores the importance of integrating circular economy principles into biopharmaceuticals manufacturing. From a practical perspective, the insights emphasize the urgency of adopting more sustainable waste management practices and exploring alternative materials and technologies. Specific challenges that regulatory bodies face in the sector include: the balancing of sustainability objectives with safety considerations; the lack of standardized sustainability guidelines on SUPs; the lack of enforcement of end-of-life management practices; and pushback from biomanufacturers based on economic clout and the criticality of their medicinal products. By addressing these challenges, regulators can better support sustainability in the sector whilst maintaining safety and process efficiency. Suggestions for evolving regulations include the creation of clear waste protocols, mandating lifecycle analysis for all materials, the consolidation and harmonization of global regulations, the extension of producer responsibility, and phasing-in more stringent sustainability targets. We argue that regulatory bodies must use these suggestions to advance sectoral sustainability standards. Likewise, from a policy perspective, policymakers must leverage these insights to craft regulations, which promote sustainability without compromising the sector.
Whilst this review provides valuable insights, it also has limitations. The review is limited to existing literature and may not capture the latest technological advancements or emerging regulatory trends. The studies reviewed vary in their methodologies and contexts, which may affect the findings' generalisability. The focus has primarily been on developed regions, potentially overlooking challenges and opportunities in emerging markets. Urgent research is required to address unresolved questions and to explore new avenues, as summarized in Table 7. Addressing the sustainability challenges of SUPs in the biopharmaceuticals sector requires a meta solution, i.e., a multifaceted approach that synthesizes proven solutions, encompassing technological innovation, regulatory alignment, and the adoption of circular economy principles. Choudhury et al. (2024) offer a possible way forward, based on this approach, for biomedical waste. Industrial symbiosis would appear to offer an appropriate framework in which to scaffold solution design. Notwithstanding, we believe that this scoping review provides a foundation for future studies aimed at promoting more sustainable biomanufacturing practices in alignment with the UN SDGs. We call on researchers, biomanufacturers and policymakers to pursue urgent and responsible action, based on industrial symbiosis, to address the circularity of SUPs in the biopharmaceuticals sector and their impacts on the Earth system.
MG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AF: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CM: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. PO: Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by Technological University Dublin.
Although the primary (MG) author of this paper is a professional in the biopharmaceuticals sector, this review represents an independent piece of research.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Alencar, M. V., Gimenez, B. G., Sasahara, C., Elliff, C. I., Rodrigues, L. S., Conti, L. A., et al. (2022). How far are we from robust estimates of plastic litter leakage to the environment? J. Environ. Manage. 323:116195. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.116195
Al-Jarshawi, M., Lucassen, A., and Samuel, G. (2022). Environmental Impacts Associated With the Manufacturing of Personalised Medicines: a Scoping Review. London: UCL's Future Targeted Healthcare Manufacturing Hub.
Anastas, P. T. (2003). Zimmerman design through the twelve principles of green engineering. Environ. Sci. Technol. 37, 94A-101A. doi: 10.1021/es032373g
Andrady, A. L. (2015). “Persistence of plastic litter in the oceans,” in Marine Anthropogenic Litter, 57–72.
Andraos, J. (2005). Unification of reaction metrics for green chemistry: applications to reaction analysis. Org. Process Res. Dev. 9, 149–163. doi: 10.1021/op049803n
Arathoon, W. R., and Birch, J. R. (1986). Large-scale cell culture in biotechnology. Science 232, 1390–1395. doi: 10.1126/science.2424083
Aretoulaki, E., Ponis, S., Plakas, G., and Agalianos, K. (2021). Marine plastic littering: A review of socio economic impacts. J. Sustain. Sci. Manag. 16, 277–301.
Azapagic, A. (1999). Life cycle assessment and its application to process selection, design, and optimisation. Chem. Eng. J. 73, 1–21. doi: 10.1016/S1385-8947(99)00042-X
Bandh, S. A., Malla, F. A., Wani, S. A., and Hoang, A. T. (2024). “Waste management and circular economy,” in Waste Management in the Circular Economy (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 1–17.
Barbaroux, M., Horowski, B., Mokuolu, S., Petrich, M., Whitford, W., BPSA, S. S., et al. (2020). The green imperative: part one life cycle assessment and sustainability for single use technologies in the biopharmaceutical industry. Bioprocess Int. 18, 12–19. Available at: https://www.bioprocessintl.com/single-use/the-green-imperative-part-one-life-cycle-assessment-and-sustainability-for-single-use-technologies-in-the-biopharmaceutical-industry (accessed February 19, 2025).
Barbaroux, M., Horowski, B., Mokuolu, S., Petrich, M. A., Snyder, M., and Whitford, W. (2021). The green imperative: part two—engineering for sustainability in single-use technologies. Bioprocess Int. 19, 18–25.
Barbaroux, M., Pollard, D., Fisher, A., and Flanagan, B. (2022). Creating a Sustainability Index Framework to Support the Bioprocess Sustainability Goals of the Next Decade. Available at: https://www.sartorius.com/download/653430/white-paper-barbaroux-pollard-creating-a-susatainability-alt-data.pdf (accessed 4 September, 2023).
Belkhir, L., and Elmeligi, A. (2019). Carbon footprint of the global pharmaceutical industry and relative impact of its major players. J. Clean. Prod. 214, 185–194. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.11.204
Bernardo, C. A., Simões, C. L., and Pito, L. M. C. (2016). “Environmental and economic life cycle analysis of plastic waste management options. A review,” in AIP Conference Proceedings (Melville, NY: AIP Publishing).
Bharti, J. (2024). Effect of Improper Waste Disposal on Environmental, Physical, and Emotional Well-Being of Human Beings. In Waste Management and Treatment (pp. 26-38). CRC Press. doi: 10.1201/9781003258377-2
Bhattacharya, A., and Bhattacharya, S. (2023). Integrating ESG pillars for business model innovation in the biopharmaceutical industry. Austra. Account. Busin. Finan. J. 17, 127–150. doi: 10.14453/aabfj.v17i1.12
Biophorum (2023). Biophorum Response to the Annex XV Report on the Proposal for Universal PFAS Restrictions. Available at: https://www.biophorum.com/download/biophorum-response-to-the-annex-xv-report-on-the-proposal-for-universal-pfas-restrictions/ (accessed 6 September, 2023)
BioSpace (2022). Biopharmaceuticals Market Size to Hold USD 856.1 Bn By 2030. Available at: https://www.biospace.com/article/biopharmaceuticals-market-size-to-hold-usd-856-1-bn-by-2030/ (accessed 18 October 2023).
Blank, L. M., Narancic, T., Mampel, J., Tiso, T., and O'Connor, K. (2020). Biotechnological upcycling of plastic waste and other non-conventional feedstocks in a circular economy. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 62, 212–219. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2019.11.011
Brändström, J., and Saidani, M. (2022). Comparison between circularity metrics and LCA: a case study on circular economy strategies. J. Clean. Prod. 371:133537. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133537
Brennan, G., Tennant, M., and Blomsma, F. (2015). “Business and production solutions: closing loops and the circular economy,” in Sustainability (London: Routledge), 219–239.
Briassoulis, D., Pikasi, A., and Hiskakis, M. (2021). Organic recycling of post-consumer/industrial bio-based plastics through industrial aerobic composting and anaerobic digestion-Techno-economic sustainability criteria and indicators. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 190:109642. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2021.109642
Brundtland, G. H. (1987). Our common future—Call for action. Environm. Conservat. 14, 291–294. doi: 10.1017/S0376892900016805
Budzinski, K., Blewis, M., Dahlin, P., D'Aquila, D., Esparza, J., Gavin, J., et al. (2019). Introduction of a process mass intensity metric for biologics. N. Biotechnol. 49, 37–42. doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2018.07.005
Budzinski, K. L., Constable, D., D'Aquila, D., Smith, P., Madabhushi, S. R., Whiting, A., et al. (2022). Streamlined life cycle assessment of single use technologies in biopharmaceutical manufacture. N. Biotechnol. 68, 28–36. doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2022.01.002
Budzinski, K. L., Koenig, S. G., O'Connor, D. A., and Wu, T. S. (2016). A call for industry to embrace green biopharma. Nat. Biotechnol. 34, 234–235. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3493
Bundela, A. K., and Pandey, K. K. (2022). The United Nations general assembly passes historic resolution to beat plastic pollution. Anthropoc. Sci. 1, 332–226. doi: 10.1007/s44177-022-00021-5
Bylander, K. C., Cehlin, E., Högberg, G., Lock, E., Meyer, E., and Söderberg, N. (2023). Bioproduction in Need of Change: An Investigation of the Needs and Bottlenecks of the Biomanufacturing Industry. Uppsala: Institution för biologisk grundutbildning, Uppsala universitet.
Castellet-Viciano, L., Hernández-Chover, V., Bellver-Domingo, Á., and Hernández-Sancho, F. (2022). Industrial symbiosis: a mechanism to guarantee the implementation of circular economy practices. Sustainability 14, 15872. doi: 10.3390/su142315872
Cataldo, A. L., Sissolak, B., Metzger, K., Budzinski, K., Shirokizawa, O., Luchner, M., et al. (2020). Water related impact of energy: cost and carbon footprint analysis of water for biopharmaceuticals from tap to waste. Chemical Eng. Sci. X 8:100083. doi: 10.1016/j.cesx.2020.100083
Chen, L., Pelton, R. E., and Smith, T. M. (2016). Comparative life cycle assessment of fossil and bio-based polyethylene terephthalate (PET) bottles. J. Clean. Prod. 137, 667–676. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.07.094
Chen, L., Wang, R., Yang, J., and Shi, Y. (2010). Structural complexity analysis for industrial ecosystems: a case study on LuBei industrial ecosystem in China. Ecol. Complex. 7, 179–187. doi: 10.1016/j.ecocom.2009.10.007
Chertow, M. R. (2000). Industrial symbiosis: literature and taxonomy. Ann. Rev. Energy Environm. 25, 313–337. doi: 10.1146/annurev.energy.25.1.313
Choudhury, M., Rajpal, A., Goswami, S., Chakravorty, A., and Raghavan, V. (2024). Analytical Case Studies on Municipal and Biomedical Waste Management: Perspectives on Sustainable Development Goals. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press.
Choudhury, M., Sahoo, S., Samanta, P., Tiwari, A., Tiwari, A., Chadha, U., et al. (2022). COVID-19: an accelerator for global plastic consumption and its implications. J. Environ. Public Health 2022:1066350. doi: 10.1155/2022/1066350
Çitar Daziroglu, M. E., and Bilici, S. (2024). The hidden threat to food safety and human health: microplastics. Environm. Dev. Sustainab. 26, 21913–21935. doi: 10.1007/s10668-023-03565-7
Coates, G. W., and Getzler, Y. D. (2020). Chemical recycling to monomer for an ideal, circular polymer economy. Nature Rev. Mater. 5, 501–516. doi: 10.1038/s41578-020-0190-4
Crippa, M., De Wilde, B., Koopmans, R., Leyssens, J., Linder, M., Muncke, J., et al. (2019). A Circular Economy for Plastics: Insights From Research and Innovation to Inform Policy and Funding Decisions. Brussels: European Commission EC.
Cudjoe, D., and Wang, H. (2022). Plasma gasification versus incineration of plastic waste: Energy, economic and environmental analysis. Fuel Proc. Technol. 237:107470. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2022.107470
Danquah, M., Amankwaa, E. F., and Amoyaw, N. (2019). Dealing with Single-Use Plastics: Examining the Economic Effect of a Ban in Ghana Project. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/365849407 (accessed November 13, 2024).
de Gioia-Carabellese, P., and Macrì, L. (2023). CSRD and CSDD: how the sustainability regulatory evolution impacts on sustainable and green investments. Eur. Comp. Law 20, 18–24 doi: 10.54648/EUCL2023010
De Kock, L., Sadan, Z., Arp, R., and Upadhyaya, P. (2020). A circular economy response to plastic pollution: Current policy landscape and consumer perception. S. Afr. J. Sci. 116, 1–2. doi: 10.17159/sajs.2020/8097
Dicks, A., Hent, A., Dicks, A. P., and Hent, A. (2015). “Atom economy and reaction mass efficiency,” in Green Chemistry Metrics: A Guide to Determining and Evaluating Process Greenness (London: Springer), 17–44.
Diggle, A., and Walker, T. R. (2022). Environmental and economic impacts of mismanaged plastics and measures for mitigation. Environments 9:15. doi: 10.3390/environments9020015
Domenech, T., and Bahn-Walkowiak, B. (2019). Transition towards a resource efficient circular economy in Europe: policy lessons from the EU and the member states. Ecol. Econ. 155, 7–19. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2017.11.001
Ehrenfeld, J. R., and Chertow, M. R. (2002). “Industrial symbiosis: the legacy of Kalundborg,” in A Handbook of Industrial Ecology (Cheltenham: Edward Elgar Publishing), 334.
Eibl, D., and Eibl, R. (2019). “Single-use equipment in biopharmaceutical manufacture: a brief introduction,” in Single-Use Technology in Biopharmaceutical Manufacture (Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons), 1–11.
Engberg, H. (1992). Industrial Symbiosis in Denmark. New York: New York University, Leonard N. Stern School of Business.
Erickson, J., Baker, J., Barrett, S., Brady, C., Brower, M., Carbonell, R., et al. (2021). End-to-end collaboration to transform biopharmaceutical development and manufacturing. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 118, 3302–3312. doi: 10.1002/bit.27688
European Commission (2015). “Closing the loop - an EU action plan for the circular economy,” in Communication from the Commission to the European Parliament, the Council, the European Economic and Social Committee and the Committee of the Regions, Brussels, Belgium (Brussels: European Commission).
European Commission (2019). Directive (EU) 2019/904 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 5 June 2019 on the Reduction of the Impact of Certain Plastic Products on the Environment. L155/1. Available at: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2019/904/oj/eng (Accessed 19 January, 2025).
European Commission (2024). Directive (EU) 2024/1799 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 13 June 2024 on Common Rules Promoting the Repair of Goods and Amending Regulation (EU) 2017/2394 and Directives (EU) 2019/771 and (EU) 2020/1828 (Text with EEA relevance). Available at: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2024/1799/oj (accessed 23 January, 2025).
Fath, B. D., and Patten, B. C. (1998). Network synergism: emergence of positive relations in ecological systems. Ecol. Modell. 107, 127–143. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3800(97)00213-5
Flanagan, W., Brown, A., Pietrzykowski, M., Pizzi, V., Monge, M., and Sinclair, A. (2014). An environmental lifecycle assessment of single-use and conventional process technology: comprehensive environmental impacts. BioPharm Int. 27:3. Availaboe at: https://www.biopharminternational.com/view/environmental-lifecycle-assessment-single-use-and-conventional-process-technology-comprehensive-envi (accessed February 20, 2025).
Forrest, F. (2023). Sustainability in biopharma: The challenges of ESG 2.0. Pharmaceutical Technology, 14th November 2023. Available at: https://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/sponsored/sustainability-in-biopharma-the-challenges-of-esg-2-0/ (accessed 20 January, 2024).
Frank, G. T. (2018). Transformation of biomanufacturing by single-use systems and technology. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 22, 62–70. doi: 10.1016/j.coche.2018.09.006
Freeland, B., McCarthy, E., Balakrishnan, R., Fahy, S., Boland, A., Rochfort, K. D., et al. (2022). A review of polylactic acid as a replacement material for single-use laboratory components. Materials 15:2989. doi: 10.3390/ma15092989
Frey, D., Claeboe, C., and Brammer Jr, L. (1999). Toward a ‘reagent-free' synthesis. Green Chem. 1, 57–59. doi: 10.1039/a901397k
Fuller, S., Ngata, T., Borrelle, S. B., and Farrelly, T. (2022). Plastics pollution as waste colonialism in Te Moananui. J. Polit. Ecol. 29, 534–560. doi: 10.2458/jpe.2401
GE Healthcare (2017). Single-Use Technology and Sustainability: Quantifying the Environmental Impact in Biologic Manufacturing. Sweden: GE Healthcare Bio-Sciences AB.
Gehring, M., and Meyer, H. P. (2022). Sustainability across the pharmaceutical value chain. Chimia 76, 800–804. doi: 10.2533/chimia.2022.800
Giannetti, B. F., Lopez, F. J. D., Liu, G., Agostinho, F., Sevegnani, F., and Almeida, C. M. (2023). A resilient and sustainable world: Contributions from cleaner production, circular economy, eco-innovation, responsible consumption, and cleaner waste systems. J. Clean. Prod. 384:135465. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.135465
Gonçalves, A., Cardeal, G., Henriques, E., and Ribeiro, I. (2024). Sustainable value roadmap for the plastics industry. Procedia CIRP 122, 419–424. doi: 10.1016/j.procir.2024.01.061
Hahladakis, J. N., Velis, C. A., Weber, R., Iacovidou, E., and Purnell, P. (2018). An overview of chemical additives present in plastics: Migration, release, fate and environmental impact during their use, disposal and recycling. J. Hazard. Mater. 344, 179–199. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.10.014
Han, W., Han, D., and Chen, H. (2023). Pyrolysis of waste tires: a review. Polymers 15:1604. doi: 10.3390/polym15071604
Hannah, R., Samborska, V., and Roser, M. (2023). Plastic Pollution. Available at: https://ourworldindata.org/plastic-pollution (accessed December 20, 2024).
Harper, E. M., and Graedel, T. E. (2004). Industrial ecology: a teenager's progress. Technol. Soc. 26, 433–445. doi: 10.1016/j.techsoc.2004.01.013
Hederman, J. (2022). A Brief History of Single-Use Manufacturing. Available at: https://www.medicaldesignbriefs.com/component/content/article/mdb/pub/features/articles/40742 (accessed 16 September, 2023).
Herberz, T., Barlow, C. Y., and Finkbeiner, M. (2020). Sustainability assessment of a single-use plastics ban. Sustainability 12:3746. doi: 10.3390/su12093746
Hsu, W. T., Domenech, T., and McDowall, W. (2021). How circular are plastics in the EU? MFA of plastics in the EU and pathways to circularity. Cleaner Environm. Syst. 2:100004. doi: 10.1016/j.cesys.2020.100004
Iñiguez, M. E., Conesa, J. A., and Fullana, A. (2016). Marine debris occurrence and treatment: a review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 64, 394–402. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.06.031
ISPE (2023). End-Of-Life Management for Single-Use Products in Bioproduction. Available at: https://ispe.org/pharmaceutical-engineering/ispeak/end-life-management-single-use-products-bioproduction (accessed 3 January, 2024).
Jacquemart, R., Vandersluis, M., Zhao, M., Sukhija, K., Sidhu, N., and Stout, J. (2016). A single-use strategy to enable manufacturing of affordable biologics. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 14, 309–318. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2016.06.007
Jambeck, J. R., Geyer, R., Wilcox, C., Siegler, T. R., Perryman, M., Andrady, A., et al. (2015). Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 347, 768–771. doi: 10.1126/science.1260352
Jiménez-González, C., Poechlauer, P., Broxterman, Q. B., Yang, B. S., Am Ende, D., Baird, J., et al. (2011). Key green engineering research areas for sustainable manufacturing: a perspective from pharmaceutical and fine chemicals manufacturers. Org. Process Res. Dev. 15, 900–911. doi: 10.1021/op100327d
Joachimiak-Lechman, K., Garstecki, D., Konopczyński, M., and Lewandowska, A. (2020). Implementation of life cycle based tools in the circular economy context—Case study of plastic waste. Sustainability 12:9938. doi: 10.3390/su12239938
Kalmykova, Y., Sadagopan, M., and Rosado, L. (2018). Circular economy–From review of theories and practices to development of implementation tools. Resour. Conservat. Recycl. 135, 190–201. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.10.034
Kannan, K., and Vimalkumar, K. (2021). A review of human exposure to microplastics and insights into microplastics as obesogens. Front. Endocrinol. 12:724989. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.724989
Karmaus, A. L., Osborn, R., and Krishan, M. (2018). Scientific advances and challenges in safety evaluation of food packaging materials: Workshop proceedings. Regulat. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 98, 80–87. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2018.07.017
Kirby, D., MacMahon, C. H., and Thompson, S. (2024). The co-evolution of sustainable finance stakeholders under the EU taxonomy for sustainable activities: an exploratory study of Irish disclosure experiences. Sustainab. Account. Managem. Policy J. 15, 1257–1285. doi: 10.1108/SAMPJ-11-2023-0842
Kirby, D., Thompson, S., and MacMahon, C. H. (2021). Shifting the EU Taxonomy from Theory to Practice: A Review of the Literature highlighting Potential Academic Contributions to its Adoption, Implementation, and Impact (Dublin: Technological University Dublin). Available at: https://arrow.tudublin.ie/creaart/104/ (accessed October 31, 2024).
Kirchherr, J., Piscicelli, L., Bour, R., Kostense-Smit, E., Muller, J., Huibrechtse-Truijens, A., et al. (2018). Barriers to the circular economy: evidence from the European Union (EU). Ecol. Econom. 150, 264–272. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2018.04.028
Klemeš, J. J., Fan, Y. V., and Jiang, P. (2021). Plastics: friends or foes? The circularity and plastic waste footprint. Ener. Sourc. Part A. 43, 1549–1565. doi: 10.1080/15567036.2020.1801906
Kumar, S., Bajaj, R., and Singh, J. (2024). A comprehensive review on single-use plastics (SUP's): challenges and sustainable solutions. J. Appl. Sci. Innovat. Technol. 3, 60–70. Available at: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Dr-Jiwan-Singh/publication/387724021_A_comprehensive_review_on_Single-Use_Plastics_SUPs_Challenges_and_sustainable_solutions/links/677d231600aa3770e0df5ffd/A-comprehensive-review-on-Single-Use-Plastics-SUPs-Challenges-and-sustainable-solutions.pdf (accessed February 20, 2025).
Kunert, R., and Reinhart, D. (2016). Advances in recombinant antibody manufacturing. Appl. Microbial. Biotechnol. 100, 3451–3461. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7388-9
Langer, E. S. (2022). Single-use technology in biopharmaceutical manufacture and beyond. Chemie Ingenieur Technik 94, 1892–1901. doi: 10.1002/cite.202200095
Lehel, J., and Murphy, S. (2021). Microplastics in the food chain: food safety and environmental aspects. Rev. Environm. Contaminat. Toxicol. 259, 1–49. doi: 10.1007/398_2021_77
Lim, J., Cox, S., Leveen, L., Monge, M., and Sinclair, A. (2008). The environmental impact of disposable technologies. BioPharm International 2008:7.
Lopes, A. G. (2015). Single use in the biopharmaceutical industry: a review of current technology impact, challenges and limitations. Food Bioprod. Proc. 93, 98–114. doi: 10.1016/j.fbp.2013.12.002
Lopez, G., Artetxe, M., Amutio, M., Alvarez, J., Bilbao, J., and Olazar, M. (2018). Recent advances in the gasification of waste plastics. A critical overview. Renew. Sustain. Energy Reviews 82, 576–596. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2017.09.032
Lowe, E. A., and Evans, L. K. (1995). Industrial ecology and industrial ecosystems. J. Clean. Prod. 3, 47–53. doi: 10.1016/0959-6526(95)00045-G
Lu, W., Ness, J. E., Xie, W., Zhang, X., Liu, F., Cai, J., et al. (2012). “Biosynthesis of monomers for plastics from renewable oils,” in Biobased Monomers, Polymers, and Materials (Washington: American Chemical Society), 77–90.
Luan, X., Cui, X., Zhang, L., Chen, X., Li, X., Feng, X., et al. (2021). Dynamic material flow analysis of plastics in China from 1950 to 2050. J. Clean. Prod. 327:129492. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129492
Lubin, D. A., and Esty, D. C. (2010). The sustainability imperative. Harv. Bus. Rev. 88, 42–50. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3809958
MacArthur, D. E., Waughray, D., and Stuchtey, M. R. (2016). “The new plastics economy,” in Rethinking the Future of Plastics (Isle of Wight: Ellen McArthur Foundation).
MacArthur, E. (2013). Towards the circular economy. J. Indust. Ecol. 2, 23–44. Available at: https://www.werktrends.nl/app/uploads/2015/06/Rapport_McKinsey-Towards_A_Circular_Economy.pdf (accessed February 20, 2025).
MacDonald, G. J. (2019). Biopharma Keeps Shifting the Steel–Plastic Balance: Biopharma is stepping up its adoption of single-use technology—not just in preclinical and clinical development, but in commercial operations. Genetic Eng. Biotechnol. News 39, S4–S7. doi: 10.1089/gen.39.S3.02
Madabhushi, S. R., Gavin, J., Xu, S., Cutler, C., Chmielowski, R., Rayfield, W., et al. (2018). Quantitative assessment of environmental impact of biologics manufacturing using process mass intensity analysis. Biotechnol. Prog. 34, 1566–1573. doi: 10.1002/btpr.2702
Maranesi, C., and De Giovanni, P. (2020). Modern circular economy: Corporate strategy, supply chain, and industrial symbiosis. Sustainability 12:9383. doi: 10.3390/su12229383
Mateos, M., and Solé, I. (2009). Synthesising information from various texts: a study of procedures and products at different educational levels. Eur. J. Psychol. Educ. 24, 435–451. doi: 10.1007/BF03178760
Mauter, M. (2009). Environmental life-cycle assessment of disposable bioreactors. Bioprocess Int. 8, 18–28. Available at: https://www.bioprocessintl.com/supply-chain/environmental-life-cycle-assessment-of-disposable-bioreactors (accessed February 20, 2024).
McDonagh, P., Dobscha, S., and Prothero, A. (2012). “Sustainable consumption and production: Challenges for transformative consumer research,” in Transformative Consumer Research for Personal and Collective Well-Being (London: Routledge), 267–281.
McGlade, J., Samy Fahim, I., Green, D., Landrigan, P., Andrady, A., Costa, M., et al. (2021). From Pollution to Solution: A Global Assessment of Marine Litter and Plastic Pollution. Nairobi: UN Environmental Programme.
Meijer, L. J., Van Emmerik, T., Van Der Ent, R., Schmidt, C., and Lebreton, L. (2021). More than 1000 rivers account for 80% of global riverine plastic emissions into the ocean. Sci. Adv. 7:eaaz5803. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aaz5803
Mirata, M., and Emtairah, T. (2005). Industrial symbiosis networks and the contribution to environmental innovation: the case of the Landskrona industrial symbiosis programme. J. Clean. Prod. 13, 993–1002. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2004.12.010
Mondal, T., Choudhury, M., Kundu, D., Dutta, D., and Samanta, P. (2023). Landfill: An eclectic review on structure, reactions and remediation approach. Waste Managem. 164, 127–142. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2023.03.034
Morrow, J. K., and Langer, E. S. (2020). Rise of single-use bioprocessing technologies: dominating most R, and D and clinical manufacture. Am. Pharm. Rev. 23, 38–41. Available at: https://www.americanpharmaceuticalreview.com/Featured-Articles/561308-Rise-of-Single-Use-Bioprocessing-Technologies-Dominating-Most-R-D-and-Clinical-Manufacture/ (accessed February 20, 2025).
Mrowiec, B. (2018). Plastics in the circular economy (CE). Environm. Prot. Nat. Resour. 29, 16–19. doi: 10.2478/oszn-2018-0017
Murakami, H. (1989). Serum-free media used for cultivation of hybridomas. Adv. Biotechnol. Proc. 11, 107–141.
Murray, A., Skene, K., and Haynes, K. (2017). The circular economy: an interdisciplinary exploration of the concept and application in a global context. J. Busin. Ethics 140, 369–380. doi: 10.1007/s10551-015-2693-2
Naeem, S., Chazdon, R., Duffy, J. E., Prager, C., and Worm, B. (2016). Biodiversity and human well-being: an essential link for sustainable development. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 283, 20162091. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2016.2091
Narancic, T., Cerrone, F., Beagan, N., and O'Connor, K. E. (2020). Recent advances in bioplastics: application and biodegradation. Polymers 12:920. doi: 10.3390/polym12040920
Nissinoff, D. (2023). Survey Results Show What Could Finally Make Sustainability Stick. Bio Process Online, September 2023. Available at: https://www.bioprocessonline.com/doc/survey-results-show-what-could-finally-make-sustainability-stick-0001 (accessed 3 December, 2023).
Nøklebye, E., Adam, H. N., Roy-Basu, A., Bharat, G. K., and Steindal, E. H. (2023). Plastic bans in India–Addressing the socio-economic and environmental complexities. Environ. Sci. Policy 139, 219–227. doi: 10.1016/j.envsci.2022.11.005
Novartis (2022). Novartis in Society Integrated Report. Available at: https://www.novartis.com/sites/novartis_com/files/novartis-integrated-report-2022.pdf (accessed 3 April, 2023).
OECD (2018). Improving plastics management: trends, policy responses, and the role of international co-operation and trade. Environm. Policy Paper 12, 12–20.
OECD (2022). Global Plastics Outlook – Economic Drivers, Environmental Impacts and Policy Options. Paris: OECD Publishing.
Oosterhuis, N. M., and Junne, S. (2016). Design, applications, and development of single-use bioreactors. Bioreact. Design, Operat. Novel Appl. 2016, 261–294. doi: 10.1002/9783527683369.ch9
Ottinger, M., Wenk, I., Carvalho Pereira, J., John, G., and Junne, S. (2022). Single-use technology in the biopharmaceutical industry and sustainability: a contradiction? Chemie Ingenieur Technik 94, 1883–1891. doi: 10.1002/cite.202200105
Paolone, F., Cucari, N., Wu, J., and Tiscini, R. (2022). How do ESG pillars impact firms' marketing performance? A configurational analysis in the pharmaceutical sector. J. Busin. Indust. Market. 37, 1594–1606. doi: 10.1108/JBIM-07-2020-0356
Papaioannou, D., Sutton, A., Carroll, C., Booth, A., and Wong, R. (2010). Literature searching for social science systematic reviews: consideration of a range of search techniques. Health Info. Libr. J. 27, 114–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00863.x
Patel, M., Kumar, R., Kishor, K., Mlsna, T., Pittman Jr, C. U., and Mohan, D. (2019). Pharmaceuticals of emerging concern in aquatic systems: chemistry, occurrence, effects, and removal methods. Chem. Rev. 119, 3510–3673. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00299
Paul, S. S., Anirud, R., Bahl, B., Maheshwari, K., and Banerjee, A. (2023). “Impact of plastics in the socio-economic disaster of pollution and climate change: the roadblocks of sustainability in India,” in Visualization Techniques for Climate Change with Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence (London: Elsevier), 77–100.
Pauliuk, S. (2018). Critical appraisal of the circular economy standard BS 8001: 2017 and a dashboard of quantitative system indicators for its implementation in organizations. Resourc. Conservat. Recycl. 129, 81–92. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.10.019
Payne, J., McKeown, P., and Jones, M. D. (2019). A circular economy approach to plastic waste. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 165, 170–181. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2019.05.014
Pham-Truffert, M., Metz, F., Fischer, M., Rueff, H., and Messerli, P. (2020). Interactions among sustainable development goals: knowledge for identifying multipliers and virtuous cycles. Sustain. Dev. 28, 1236–1250. doi: 10.1002/sd.2073
Pietrzykowski, M., Flanagan, W., Pizzi, V., Brown, A., Sinclair, A., and Monge, M. (2013). An environmental life cycle assessment comparison of single-use and conventional process technology for the production of monoclonal antibodies. J. Clean. Prod. 41, 150–162. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2012.09.048
Plastics Europe (2022). Plastics – the Facts, 2022. Available at: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-facts-2022/ (accessed 24 November, 2023).
Pollard, D. J., and Pralong, A. (2018). “Single-use technology implementation for biologics and vaccines production,” in Biopharmaceutical Processing (London: Elsevier), 721–740.
Pora, H., and Rawlings, B. (2009). Managing solid waste from single-use systems in biopharmaceutical manufacturing. Bioprocess Int. 7, 18–25.
Prieto, A. (2016). To be, or not to be biodegradable… that is the question for the bio-based plastics. Microb. Biotechnol. 9, 652–657. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12393
Rader, R. A., and Langer, E. S. (2019). “Single-use technologies in biopharmaceutical manufacturing: A 10-year review of trends and the future,” in Single-Use Technology in Biopharmaceutical Manufacture (Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons), 193–200.
Ranjbari, M., Saidani, M., Esfandabadi, Z. S., Peng, W., Lam, S. S., Aghbashlo, M., et al. (2021). Two decades of research on waste management in the circular economy: Insights from bibliometric, text mining, and content analyses. J. Clean. Prod. 314:128009. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.128009
Ravisé, A., Cameau, E., De Abreu, G., and Pralong, A. (2010). Hybrid and disposable facilities for manufacturing of biopharmaceuticals: pros and cons. Disposable Bioreact. 2010, 185–219. doi: 10.1007/10_2008_24
Ritchie, H. (2023). “How much of global greenhouse gas emissions come from plastics?,” in OurWorldInData.org. Available at: https://ourworldindata.org/ghg-emissions-plastics (accessed 4 February, 2024).
Roizman, I., and Langer, E. S. (2019). CMOs leading the way on single-use systems adoption. Biopharm Int. 32, 10–14.
Royte, E. (2019). ‘Is Burning Plastic Waste a Good Idea?' National Geographic, 12th March 2019. Available at: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/environment/article/should-we-burn-plastic-waste (accessed 4 February, 2024).
Sachs, J. D., Schmidt-Traub, G., Mazzucato, M., Messner, D., Nakicenovic, N., and Rockström, J. (2019). Six transformations to achieve the sustainable development goals. Nature Sustainab. 2, 805–814. doi: 10.1038/s41893-019-0352-9
Samani, P. (2023). Synergies and gaps between circularity assessment and Life Cycle Assessment (LCA). Sci. Total Environm. 2023:166611. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.166611
Samaras, J. J., Micheletti, M., and Ding, W. (2022). Transformation of biopharmaceutical manufacturing through single-use technologies: current state, remaining challenges, and future development. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 13, 73–97. doi: 10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-092220-030223
Sauvé, S., Bernard, S., and Sloan, P. (2016). Environmental sciences, sustainable development and circular economy: alternative concepts for trans-disciplinary research. Environm. dev. 17, 48–56. doi: 10.1016/j.envdev.2015.09.002
Schroeder, P., Anggraeni, K., and Weber, U. (2019). The relevance of circular economy practices to the sustainable development goals. J. Indust. Ecol. 23, 77–95. doi: 10.1111/jiec.12732
Schwarz, A. E., Ligthart, T. N., Bizarro, D. G., De Wild, P., Vreugdenhil, B., and Van Harmelen, T. (2021). Plastic recycling in a circular economy; determining environmental performance through an LCA matrix model approach. Waste Managem. 121, 331–342. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2020.12.020
Schyns, Z. O., and Shaver, M. P. (2021). Mechanical recycling of packaging plastics: A review. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 42:2000415. doi: 10.1002/marc.202000415
Sevigné-Itoiz, E., Mwabonje, O., Panoutsou, C., and Woods, J. (2021). Life cycle assessment (LCA): informing the development of a sustainable circular bioeconomy? Philosoph. Trans. Royal Soc. A 379, 20200352. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2020.0352
Shaw, S. D., Harris, J. H., Berger, M. L., Subedi, B., and Kannan, K. (2014). “Brominated flame retardants and their replacements in food packaging and household products: uses, human exposure, and health effects,” in Toxicants in Food Packaging and Household Plastics: Exposure and Health Risks to Consumers, 61–93. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4471-6500-2_3
Sheldon, R. A. (2017). The E factor 25 years on: the rise of green chemistry and sustainability. Green Chem. 19, 18–43. doi: 10.1039/C6GC02157C
Shen, L., Worrell, E., and Patel, M. K. (2010). Open-loop recycling: A LCA case study of PET bottle-to-fibre recycling. Resourc. Conservat. Recycl. 55, 34–52. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2010.06.014
Sherwood, J. (2020). Closed-loop recycling of polymers using solvents: remaking plastics for a circular economy. Johnson Matthey Technol. Rev. 64, 4–15. doi: 10.1595/205651319X15574756736831
Simon, B. (2019). What are the most significant aspects of supporting the circular economy in the plastic industry? Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 141, 299–300. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2018.10.044
Sinclair, A., VanLoy, C., Goldstein, A., and Perrone, P. (2024). Plastic Process Waste in Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing. Pharmaceutical Engineering, December 2024. Available at: https://ispe.org/pharmaceutical-engineering/november-december-2024/plastic-process-waste-biopharmaceutical (accessed 19 January, 2025).
Singh, S., Singh, G., Singh, S., and Misra, S. C. (2024). Understanding green procurement dynamics: an assessment framework for public sector organizations. J. Environ. Manage. 351, 119756. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.119756
Singh, V. (1999). Disposable bioreactor for cell culture using wave-induced agitation. Cytotechnology 30,149–158. doi: 10.1023/A:1008025016272
Smith, M. T., Madsen, B., Hsiao, T. W., and Jones, N. (2018). Single-use bioreactors: performance and usability considerations part 1: performance for process control. Bioprocess Int. 16, 15–19.
Sonnemann, G., and Alvarado, C. (2018). “Improving the life cycle performance of chemical products and materials through data exchange along the value chain—synthesis of LCM2017 session presentations,” in Designing Sustainable Technologies, Products and Policies: From Science to Innovation, 95–100. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-66981-6_11
Spyrakis, F., and Dragani, T. A. (2023). The EU's per-and Polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) ban: A case of policy over science. Toxics 11:721. doi: 10.3390/toxics11090721
Stolowy, H., and Paugam, L. (2023). Sustainability reporting: Is convergence possible? Account. Eur. 20, 139–165. doi: 10.1080/17449480.2023.2189016
Szkodny, A. C., and Lee, K. H. (2022). Biopharmaceutical manufacturing: Historical perspectives and future directions. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 13, 141–165. doi: 10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-092220-125832
Takao, I. T. O., Wang, H., Hwang, S. H., Wang, B., Wang, L., and Somasundaram, G. (2023). Risk assessment for biopharmaceutical single-use manufacturing: a case study of upstream continuous processing. Biologicals 84:101713. doi: 10.1016/j.biologicals.2023.101713
Tan, A. F., Yu, S., Wang, C., Yeoh, G. H., Teoh, W. Y., and Yip, A. C. (2024). Reimagining plastics waste as energy solutions: challenges and opportunities. Mater. Sustainab. 2, 2. doi: 10.1038/s44296-024-00007-x
Ten Brink, P., Schweitzer, J. P., Watkins, E., Janssens, C., De Smet, M., Leslie, H., et al. (2018). “Circular economy measures to keep plastics and their value in the economy, avoid waste and reduce marine litter (No. 2018-3),” in Economics Discussion Papers (Kiel: Kiel Institute for the World Economy). Available at: econstor.eu/bitstream/10419/173128/1/1011145367.pdf (accessed February 19, 2025).
Thiounn, T., and Smith, R. C. (2020). Advances and approaches for chemical recycling of plastic waste. J. Polymer Sci. 58, 1347–1364. doi: 10.1002/pol.20190261
Uekert, T., Singh, A., DesVeaux, J. S., Ghosh, T., Bhatt, A., Yadav, G., et al. (2023). Technical, economic, and environmental comparison of closed-loop recycling technologies for common plastics. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 11, 965–978. doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.2c05497
Valencia, E. (2017). “Why circular economy business models need LCA,” in PRe Sustainability. Available at: https://www.pre-sustainability.com/news/why-circular-economy-business-models-need-lca (accessed May 14, 2023).
Van Caneghem, J., Van Acker, K., De Greef, J., Wauters, G., and Vandecasteele, C. (2019). Waste-to-energy is compatible and complementary with recycling in the circular economy. Clean Technol. Environm. Policy 21, 925–939. doi: 10.1007/s10098-019-01686-0
van Riel, D., and de Wit, E. (2020). Next-generation vaccine platforms for COVID-19. Nat. Mater. 19, 810–812. doi: 10.1038/s41563-020-0746-0
Van Sebille, E., Wilcox, C., Lebreton, L., Maximenko, N., Hardesty, B. D., Van Franeker, J. A., et al. (2015). A global inventory of small floating plastic debris. Environm. Res. Lett. 10:124006. doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/10/12/124006
Venkatachalam, V., Pohler, M., Spierling, S., Nickel, L., Barner, L., and Endres, H. J. (2022). Design for recycling strategies based on the life cycle assessment and end of life options of plastics in a circular economy. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 223:2200046. doi: 10.1002/macp.202200046
Villarrubia-Gómez, P., Almroth, B. C., Eriksen, M., Ryberg, M., and Cornell, S. E. (2024). Plastics pollution exacerbates the impacts of all planetary boundaries. One Earth 7, 2119–2138. doi: 10.1016/j.oneear.2024.10.017
Watkins, E., Romagnoli, V., Kirhensteine, I., Ruckley, F., Kreißig, J., Mitsios, A., et al. (2020). Support to the Circular Plastics Alliance in Establishing a Work Plan to Develop Guidelines and Standards on Design-for Recycling of Plastic Products. Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union.
Weiss, M., Haufe, J., Carus, M., Brandão, M., Bringezu, S., Hermann, B., et al. (2012). A review of the environmental impacts of biobased materials. J. Indust. Ecol. 16, S169–S181. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-9290.2012.00468.x
White, S. (2024). To Tackle the Plastic Waste Crisis in Pharma, Here's Where to Start. Pharmaceutical Executive, 30th October 2024. Available at: https://www.pharmexec.com/view/tackle-plastic-waste-crisis-pharma (accessed 19 January, 2025).
Whitford, B., Jones, D., and Kinnane, S. (2022). Biomanufacturing design: reducing the environmental burden. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 76:102717. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2022.102717
Whitford, W., Mokuolu, S., Barbaroux, M., Snyder, M., Petrich, M., Baillie, M., et al. (2021). The green imperative: part three - part 3 - postuse management of single-use bioprocessing materials, today and tomorrow. Bioprocess Int. 19, 12–19.
Whitford, W. G., Petrich, M. A., and Flanagan, W. P. (2019). “Environmental impacts of single-use systems,” Single-Use Technology in Biopharmaceutical Manufacture, 169–179.
Wojnowska-Baryła, I., Bernat, K., and Zaborowska, M. (2022). Plastic waste degradation in landfill conditions: the problem with microplastics, and their direct and indirect environmental effects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 19:13223. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192013223
Yoshida, S., Hiraga, K., Takehana, T., Taniguchi, I., Yamaji, H., Maeda, Y., et al. (2016). A bacterium that degrades and assimilates poly (ethylene terephthalate). Science :351, 1196–1199 doi: 10.1126/science.aad6359
You, L., Ji, T., Shao, B., Wu, X., and Shi, L. (2023). Design-driven regional industry transformation and upgrading under sustainable development. Sci. Rep. 13:17071. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44190-8
Zhang, Y., Zheng, H., Chen, B., Su, M., and Liu, G. (2015). A review of industrial symbiosis research: theory and methodology. Front. Earth Sci. 9, 91–104. doi: 10.1007/s11707-014-0445-8
Keywords: biopharmaceuticals, circularity, life-cycle analysis, single-use plastics, regulation, Sustainable Development Goals, symbiosis
Citation: Goggin M, Fleming A, MacMahon C and Owende P (2025) Exploring the sustainability of single use plastics in the biopharmaceuticals sector: a scoping review of challenges, opportunities, and impacts. Front. Sustain. 6:1536382. doi: 10.3389/frsus.2025.1536382
Received: 28 November 2024; Accepted: 11 February 2025;
Published: 10 March 2025.
Edited by:
Ioannis Kostakis, Harokopio University, GreeceReviewed by:
Moharana Choudhury, Voice of Environment (VoE), IndiaCopyright © 2025 Goggin, Fleming, MacMahon and Owende. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Malcolm Goggin, ZDE1MTI2Nzc4QG15dHVkdWJsaW4uaWU=
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.