- 1Department of Accounting and Finance, College of Business and Economics, Werabe University, Werabe, Ethiopia
- 2Department of Management, College of Business and Economics, Werabe University, Werabe, Ethiopia
- 3College of Finance, Management and Development, Ethiopian Civil Service University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
Introduction: Efficient resource management is essential for enhancing organizational performance; however, its implementation in micro and small enterprises (MSEs) has received limited academic attention. Taking into account these obvious reasons, this study aims to investigate the influence of resource management practices on the performance of micro and small enterprises in Werabe Town, Ethiopia.
Methods: We distributed a structured questionnaire to 265 randomly selected small business operators. Both descriptive and inferential statistical methods, including correlation and regression analysis were used to analyse the collected data.
Results: The findings indicate low overall MSE performance, driven by inadequate financial, human resource, material, and information management practices. Based on regression analysis, these four factors explain 64.3% of the variations in performance, showing that they have a positive and statistically significant effect.
Conclusion: Therefore, improving financial planning, cash flow, and working capital management is crucial for maintaining efficient financial operations. However, financial efficiency alone is not enough; a formal HR planning process, a well-defined job description, carrying out a recruiting and selection, and establishing a pay system are equally crucial. Additionally, streamlining material requirement planning, procurement processes, and inventory control systems ensures resource availability and operational efficiency. Furthermore, pre-made and streamlined information management software is appropriate to improve the flow of information for better decision-making across financial, human, and material resources.
1 Introduction
Micro and small enterprises (MSEs) have a profound influence on the social and economic structure of a nation (Manzoor et al., 2021). According to the World Trade Organization (2016), MSEs constitute over 90% of business, contribute to 60–70% of employment, and represent 55% of the gross domestic product (GDP) in developed countries (Malgas and Zondi, 2021). The existence of a strong MSEs is necessary for the boosting of the economy (Gebre-Egziabher and Meheret, 2010; Mengesha, 2019). By virtue of the size MSEs faced several challenges, mainly limited access to financial, human, and technological resources which require optimal resource management to deliver robust results. Resource management practices in MSEs can influence their performance in many ways.
Literally, resource is any asset that an organization utilizes to carry out an activity or to achieve its goals (Lee and Whitford, 2013), it encompasses all the assets, abilities, institutional processes, firm characteristics, knowledge, information, and other resources that are under the control of a firm and enable it to develop and execute strategies that enhance its effectiveness as well as efficiency (Varadarajan, 2020). Resources possessed by an organization are the main sources of competitive advantage, sustainability, growth, risk management and overall performance (Hitt et al., 2011). Due to this reason every organization required to establish better resource management strategies to deliver best out of resources at their disposal. Resource management in MSEs provides the necessary foundation for operational efficiency, risk management, competitiveness, growth, and innovation.
Resource management is an effective utilization and distribution of resources to the areas where they are required (Raja, 2015). It can be described as the utmost level of optimization and efficiency by enabling proactive allocation of resources to the firm. Studies indicated that managing resources effectively and efficiently is the key to continuous enhancement of the MSEs performance (Walter and Vincent, 2018), and on the other extreme poor resource management practice is highly attached with poor performance of MSEs (Aurangzeb Asif and Amin, 2021). Effective resource management is essential for enterprises, as they maintain resources that have the capacity to provide a competitive edge. However, such an opportunity will not be fulfilled if the organization lacks the necessary skills to exploit the resource (Newbert, 2008).
Albeit its relevance resource management in MSEs is challenging as they are operating in resource constraint environment and cannot implement formal management approach due to limited financial and managerial capabilities. These suggest the need for studies on existing state of resource management practices and developing innovative approaches for resource management in MSEs. Yet studies in Ethiopia are scantly available. This study is therefore conducted to examine the effect of resource management practices on the performance of MSEs in Ethiopia based on evidences from Werabe.
The preliminary survey of the researchers conducted on February 21, 2023 showed that MSEs in Werabe town administration are suffering problems related to effective management of their key resources like inefficiency in registering/recording financial transaction, poor human resource practice, not using information well. Hence, this focus on assessing how the management of human, financial, material, and information resources affected MSE performance in Ethiopia based on evidences from Werabe.
MSE performance refers to how well it is doing to reach its vision, mission, and goals (Contu, 2020). Executives, business owners, and decision-makers must know how well their enterprises are performing to figure out what strategic change is needed (Kaliappen and Abdullah, 2014). The most common performance indicators for every type of MSE, regardless of their operation, are organizational growth (development), quality of product (service), employee satisfaction, and customer satisfaction (Mahmudova and Kovács, 2018). Hence, the study used these indicators to measure the performance of MSEs for the purpose of the study and examined how resource management influenced the measure of MSE performance.
With this backdrop, the study attempted to measure resource management practices among MSEs in Werabe Town and explored how far resource management practices affected performances. The study will fill the literature gap on management practices and performance literature by showing the context of MSEs. The study adds to the literature on MSE management practices and firm performance as it reveals the need for enhancing resource management practices that have positive implications for their respective performance.
1.1 Objectives of the study
• To examine the effect of human resource practices on MSE performance.
• To examine the effect of financial management practices on MSE performance.
• To examine the effect of material management practices on MSE performance.
• To examine the effect of information management practices on MSE performance.
2 Literature review and hypotheses development
Resource is any factor that is necessary to achieve the goal of the MSEs (Bryson et al., 2007) which often include employees, working space, equipment, or capital. According to Resource based theory, resources are anything that is possessed by an organization and they are the primary source of performance and competitive advantage (Walter and Vincent, 2018). Every activity in the MSE needs to have resources assigned to it (Kreifelts et al., 1993). According to Business Model Canvas approach, key resources are classified into four groups by their purposes, such as material resources, information resources, human resources, and financial resources. They are the components that every MSE needs to build out the value and without these resources they won't be able to bring in revenue or have a clear value proposition (Woo et al., 2016). Previous studies (Bhatti and Zaheer, 2014; Chioma and Etifit, 2018; Atnafu and Balda, 2018; Batista et al., 2022; Kontio, 2013; Gurski, 1955) conducted in different settings have highlighted the relevance of resource management practices to enhance MSE performance.
Resource management involves the allocation of resources to enable an MSE to efficiently accomplish its tasks (Raja, 2015). It also involves the process of planning, organizing, and distributing resources like personnel, finances, and technology for a certain project. Effective resource management ensures that resources are allocated appropriately and utilized at the optimal moment and for the intended purpose (Laslo, 2008). Resource management is an essential requirement for every organization that aims to maintain its competitiveness and surpass its competitors. The competitive advantage is not just determined by possessing resources but rather by how resources are merged, rearranged, and evolved together in response to emerging demands, resulting in improved performance (Kithusi, 2016). Yet studies reveled that management practices in MSEs is not sufficient enough to ensure optimal use of resource leading to profitable business operation in even in the developed countries (Forth and Bryson, 2018). The current study measured the performances of MSEs and resource management practices. The study tested the following four hypotheses on the effect of the later on the former variable in the study.
Human resource management is one of the indicators of resource management practice in this study which is hypothesized to have positive effect on MSE performance based on the review of related studies. According to Becker and Gerhart (1996) the success of any organization is heavily reliant on the talent and strength of its employees According to Armstrong (2008), HR is a key resource of any organization and its performance depends especially on the type of people involved in Mulolli et al. (2015). Hence, the aim of HRM is to enable the organization to achieve its goal through people, MSEs have to apply an effective HRM practice to improve their performances, develop competitive advantages (Mulolli et al., 2020). Various studies have showed that HRM practice plays a crucial role on MSEs performance (El Hazzam, 2016; Mathushan and Kengatharan, 2022; Mamun, 2022; Madhavkumar, 2023). Efficiently managed HR practices significantly contribute to organizational performance, and studies emphasize the importance of formal HRM practices on improving MSE productivity and performance (Anuradha and Ramesh, 2022). Formal HRM practices play a crucial role in enhancing the performance of MSEs. Moreover, empirical evidences suggest that elements like training and development, promotion, and job security have a significant influence on employee performance in MSEs, highlighting the positive impact of formal HRM practices on overall outcomes (Shaheen, 2020).
Research also indicates MSEs are trying to consider sector-specific HRM processes and the formalization of HRM practices to enhance productivity (Diana and Verónica, 2019), but encountered specific challenges in implementing effective human resource management practices, such as the high level of cyclicality (Singh et al., 2023) leading to unpredictability, the need for skilled manpower amidst a global shortage (Singh and Singh, 2023), and difficulties in Human Resource Information System (HRIS) implementation due to cost, technical knowledge, and staff training issues (Priyanka and Priti, 2023). To address these challenges, MSEs are also required to provide training on HRM skill of owners and managers, adopt innovative technologies for up skilling and reskilling the workforce, provide management support for HRIS implementation, and offer continuous training to enhance technical knowledge among employees. However, there was no specific study on HRM practices, literature on MSE performance indicated that lack the necessary expertise in HRM. Further lack of financial resources among MSEs is limiting investment on human resources training, recruitment, and employee development. As a result, they may struggle with tasks like performance evaluations, conflict resolution, and creating a positive work environment (Jin et al., 2024).
The current study attempted to understand the existing HRM practices and its implication on their overall performance in order to advance existing literature which scantly represents the effect of HRM as one of the resource management practices of MSEs in Ethiopia. Generally the literature implied, embracing formal HRM practices can lead to increased efficiency, HR performance, and ultimately, the success of MSEs albeit the difficulty of following the state of art in HRM in MSE. This study therefore has tested the following hypothesize which aimed at understanding how far the current HRM practices affected the performances of MSE in Ethiopia based on evidences from Werabe Town:
• Human resource management practices positively affected MSE performance in Werabe Town.
A material management practice is the second indicator of resource management which play a crucial role on enhancing the performances of MSEs (Kar and Jha, 2023). The use inventory management, procurement quality, and material planning systems, can lead to improved competitiveness, organizational performance, and supply chain performance (Dneil and Balda, 2018). Material management is a coordinating function responsible for planning and controlling materials flow (Arnold et al., 2001). Studies have shown that implementing material management practices such as system for procurement and storage, on-site material control, procurement quality, procurement costing, central procurement database, and material planning systems can improve material availability and reduce material waste, leading to better performance and sustainability (Kar and Jha, 2023). Similarl a positive effect was also documented in Adamu (2020). Additionally, Jagadish et al. (2022) found that effective materials management dimensions, such as interdepartmental collaboration among inventory, procurement, and storage departments, have been associated with increased organizational profitability in manufacturing companies in Ethiopia. Therefore, it can be hypothesized that:
• Materials management practices positively affected MSE performance in Werabe town.
Financial management is also the most important are of resource management in MSEs that operate in an environment known for limited access to finance. Financial resources is “the funds or monetary assets that a business or an individual possesses or has access to for investment, spending, or saving” (Burton, 2003). Financial management basically deals with circulation and control of money for all kinds of business operations (Lasher, 2016) which is central activities for the success of small business (Dahmen and Rodríguez, 2014). MSEs financial profitability is the conceived result of financial management practices (Gregory et al., 1997). Various authors study on financial management and its effect on MSE performance as they implicated, good financial resource management affects every aspect of an MSE's operations, starting from its ability to invest in necessary equipment and technologies, to its ability to hire and retain competent employees, and even its capacity to market and advertise its products or services. Sufficient financial resources raised and used through effective financial management practices improve the performance of MSEs through investment on research and development, technology, human resource and new market developments. Poor financial management can severely limit MSE performance (Ghidey and Shete, 2023). Therefore, applying proper financial management in MSE appeared relevant for better performance and growth, as it increase access to and effective use of financial resources which are vital for survival and remaining competitive in the ever-changing business environment (Hunjra et al., 2010; Jindrichovska, 2013; Neequaye et al., 2017; Turyahebwa et al., 2013). This study hence hypothesized that:
• Financial resource management practices positively affected performance of MSEs in Werabe Town.
Information management as an indicator of resource management practice is a vital aspect of organizational performance in the current business environment, which cannot perform effectively without the proper use of Information and Communication Technology (ICT) and knowledge management (KM). These tools are crucial for the coordination and utilization of information from internal and external sources (Davenport and Prusak, 1998; Alavi and Leidner, 2001). According to Soudani (2012), information management is the economic, efficient, and effective handling of information, including its production, control, storage, retrieval, and dissemination. Effective information management practices, particularly through the use of information system enhance the performance of MSEs. Vatsal and Shah (2016) highlight the potential for MSEs to optimize their operations and outcomes through effective information management. Similarly, Mathew (2023) emphasizes the importance of integrating e-business technologies and information management systems to enhance the performance and competitive advantage of SMEs. Numerous studies have demonstrated the increasing adoption of digital technologies in MSEs, necessitating the development of information management strategies that embrace digital media to enhance competitiveness and adapt to changing market dynamics (Batista et al., 2022). Therefore, training and strategic planning are required to fully utilize information and communication technology in MSEs (Leni et al., 2023). The use of information systems enables MSEs to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and provide superior customer service (Kamau and Kyalo, 2022). Additionally, it facilitates the implementation of digital marketing strategies, which can positively impact performance through improved consumer relationship management (Qalati et al., 2022). Moreover, the transition to a digital content-based paradigm is essential for MSEs to effectively engage customers and build trust. The Covid-19 pandemic has further highlighted the urgency for MSEs to digitize their operations, with initiatives such as leveraging social media and online marketplaces becoming key strategies for digitalization (Anjar et al., 2020). By embracing digitalization, MSEs can gain a deeper understanding of suppliers and competitors, leading to more informed decision-making and a competitive edge in the market. Based on these considerations, the present study formulates the following hypothesis:
• Information management positively affected the performance of MSEs in Werabe Town.
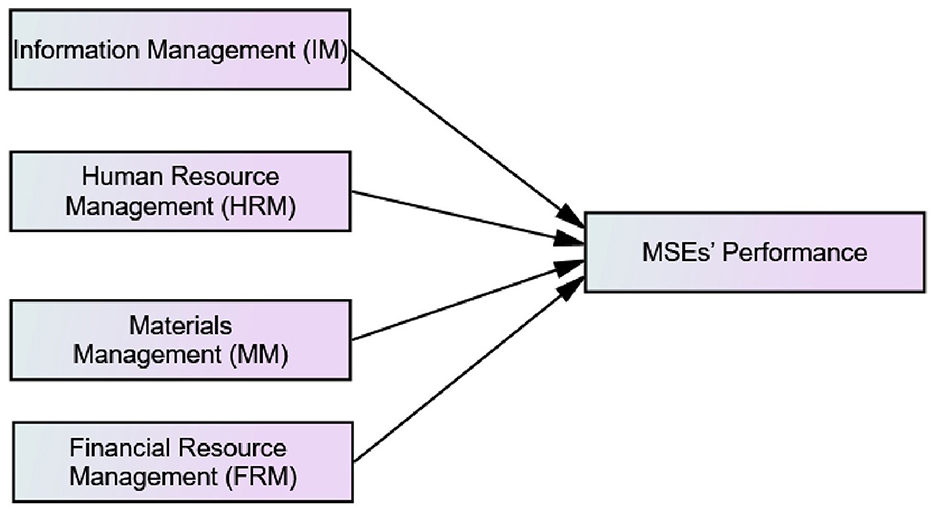
2.1 Conceptual framework
The conceptual framework, depicted in Figure 1, was developed by reviewing relevant literature on resource management practices and their impact on MSE performance. The framework is based on key insights from studies on human resource practices, financial resource management, materials management, and information management.
3 Methodology and research methods
This study aimed to investigate the impact of resource management practices (RMP) in Ethiopia, the case of Werabe Town. Both descriptive and explanatory research designs are used to assess the effect of resource management practices on MSE performance. We randomly selected 265 respondents from a total of 601 MSE's owners. Primary data was collected through a structured questionnaire developed based on a comprehensive review of relevant literature. Each variable was measured using a five-point Likert scale (1 = strongly disagree, 5 = strongly agree). The questionnaire comprised items as follows: 9 for human resource practices (HRM), 4 for financial resource management (FRM), 6 for materials management (MM), 5 for information management (IM), and 9 for MSE performance (MSE P). The data was analyzed using descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation, and multiple regression analysis.
Y = α + β1x1 + β2x2 + β3x3 + β4x4 + ε
Where: Y = dependent variable (MSE Performance).
α = is constant value indicating the value of Y where all independent variables are zeros.
β1 = the beta Financial Management Practices.
β2 = the beta value of the HRM Practices.
β3 = the beta value of Information Management Practices.
β4 = the beta value of Materials Management Practices.
ε = Error term.
4 Result and discussion
4.1 Descriptive statistics for performance MSEs and resource management practices
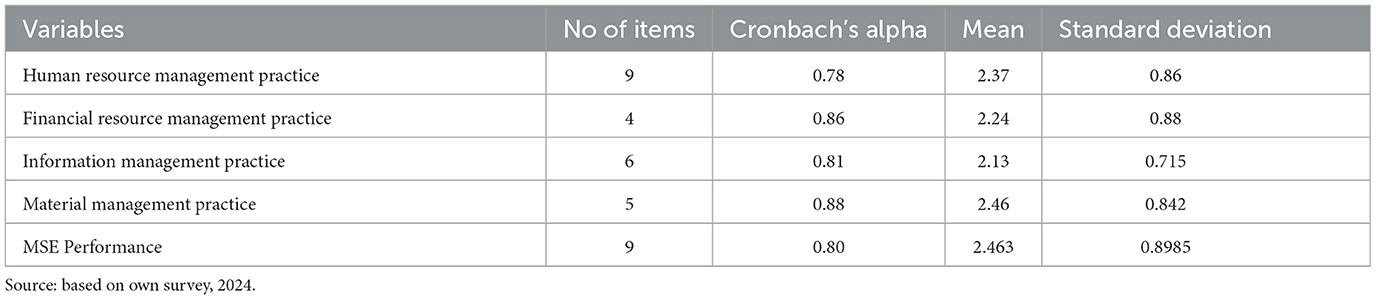
Table 1 presents the results of descriptive statistics computed for the study variables.
The result presented in Table 1 shows that the mean value of MSEs performance, as measured on a five-point Likert scale, was 2.46 (SD = 0.9). This suggests that the majority of MSEs have not been performing well. The MSE owners' perception analysis of their respective application resource management practices in finance, human resources, material, and information results shows mean values ranging from 2.13 (SD = 0.72) to 2.46 (SD = 0.84). These relatively low levels of resource management practices highlight the need for streamlining such practices to improve the apparent low performance of MSEs. To further understand the relationship between the variables under study, we employed a Pearson correlation and multiple regression analysis.
The correlation matrix in Table 2 indicates that all independent variables are moderately to strongly correlated (0.488 < r < 0.74) and are statistically significant at the 0.05 level of significance. Financial management practice exhibited the strongest correlation (r = 0.743, P < 0.001) with the performance of MSEs among the resource management indicators, whereas information management practice demonstrated the weakest correlation (r = 0.488, P < 0.001). These results indicated a direct linear relationship between the measures of resource management and the performance of MSEs. Furthermore, the results indicated a positive relationship exists; however, there is no strong correlation among the independent variables. The study also conducted a regression analysis to validate the hypotheses supporting the positive association between the resource management practice variables and MSE performance.
4.2 Regression analysis
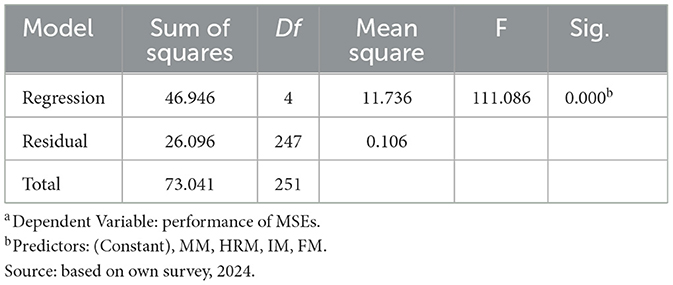
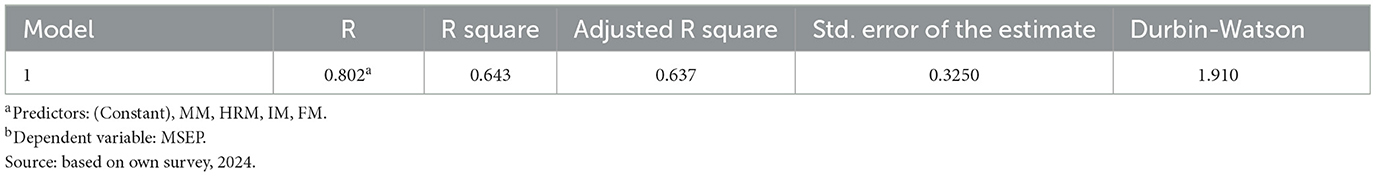
In line with its objectives, the study hypothesized that the measures of resources management practices, namely, financial management practices, HRM practices, Materials Management Practices, and Information Management Practices have statistically significant effects on the performances of MSEs. A multiple regression analysis was carried out to test these hypotheses and the results are presented in Tables 3–5.
ANOVA test result on Table 3 showed that the regression model is fit in explaining the dependent variable (F = 111.086, P = 0.000). This indicates that the selected four key resources management practice indicators (Financial management, human resource management, information management, and material management) all have positive and significant effect on MSE performance.
Table 4 showed that the four measures of resource management jointly explained about 64.3% of variation on the performances of SMEs in Werabe town. This suggests the need to improve resource management practices for optimally use scarce resources of MSEs to enhance their profitability and sustainable growth. The multiple regression coefficients for the effect of resource management on MSE performance presented in Table 5 are used to test how far resource management practices affected MSE performance as stated in the research hypothesis.
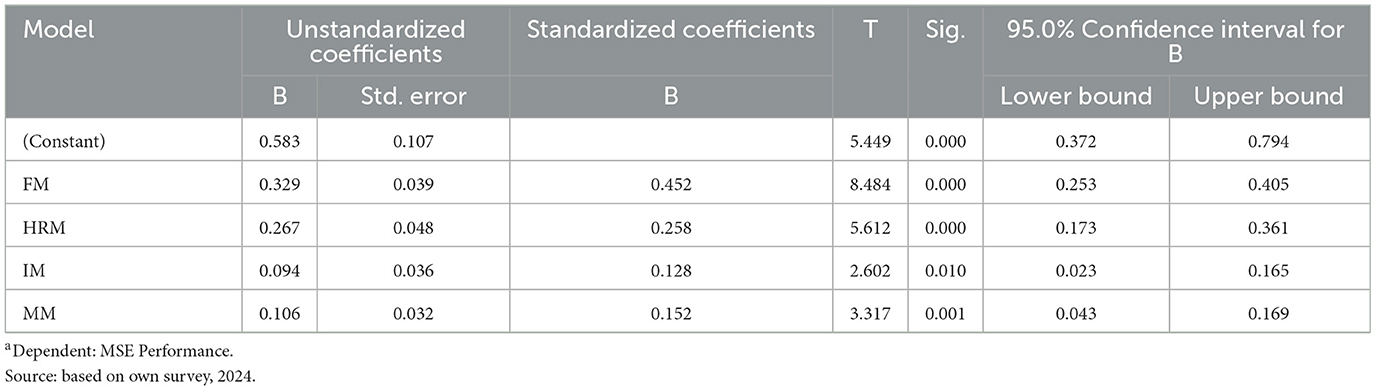
Table 5. Multiple regression coefficients for the effect of resource management practices on MSE performancea.
Results on Table 5 indicated a significant positive effect of financial management practices (β = 0.329, t = 8.484, P < 0.001) aligns with existing literature that highlighted the critical role of financial resource management in MSE success (El Hazzam, 2016; Mathushan and Kengatharan, 2022; Mamun, 2022; Madhavkumar, 2023). Effective financial management allows MSEs to secure necessary funds, invest in growth opportunities, and manage operational costs efficiently, which directly enhances their performance. Therefore, the hypothesis that financial resource management practices have a significant positive effect on the performance of MSEs in Werabe Town is supported in the current study.
These findings, which are consistent with theory and previous research, suggest that MSE owners' financial management capabilities should be strengthened in order to improve their sustainability (Ghidey and Shete, 2023). Better financial management in MSE not only improve the use of available resource but also enhance their ability of access to finance in the formal and semi-formal financial institutions. These in general suggested for targeted MSE financial literacy program to improve their financial record keeping, financial planning and controlling for optimal use of financial resource.
Similarly Table 5 indicated that the empirical results supported the hypothesis on the significant positive effect of human resource management practices on the performance of MSEs in Werabe Town (β = 0.267, t = 5.612, P < 0.001). This is consistent with the findings of Mulolli et al. (2015), and others who emphasize the importance of skilled and motivated employees for organizational success. The study confirms that investing in HR practices such as training, development, and effective recruitment significantly boosts MSE performance (El Hazzam, 2016; Mathushan and Kengatharan, 2022; Mamun, 2022; Madhavkumar, 2023) and enable them to develop competitive advantage (Mulolli et al., 2020). MSE owners and organization working on MSE development can enhance their productivity and performance through formal HRM practices (Shaheen, 2020).
Results from Table 5 also indicated that material management practices had a significant influence on MSE performance (β = 0.106, t = 3.317, P < 0.001). This finding corroborates studies by Kar and Jha (2023), Adamu (2020), and Jagadish et al. (2022), which document the positive impact of efficient material management on operational efficiency and the survival of MSEs. Consequently, the hypothesis that effective material management practices have a positive impact is supported by our results. This implies the need for MSEs to develop appropriate materials management systems to effectively manage inventory, procurement, and storage (Jagadish et al., 2022) to reduce inventory management costs without compromising the swift flow of production and service delivery, resulting in better performance.
Although information management practices showed the least effect among the four variables, It still had a statistically significant positive impact on MSE performance (β =.094, t = 2.602, P = 0.010). This suggests that while information management is crucial, it may not be as immediately impactful as financial or human resource management but still contributes to enhanced decision-making and operational efficiency (Soudani, 2012; Vatsal and Shah, 2016; Mathew, 2023). Therefore, the hypothesis that information management has a significant effect on the performance of MSEs is supported, consistent with increasing stock of literature that has been highlighting the benefits of effective management of information management system to improve the performances of MSEs (Vatsal and Shah, 2016; Mathew, 2023; Batista et al., 2022).
5 Conclusions
This research is carried out to examine the impact of resource management practices on the performance of micro and small enterprises (MSEs) in Ethiopia based on analysis of primary data collected through a questionnaire survey of randomly selected MSE owners from Werabe town of the Central Ethiopian Region. The study found that a poor performance of MSEs in Werabe had positive relationship with resource management practices. The four resource management practices variables in the regression model in the study explained about 64.3% of the change on MSE performance, suggesting the need for strengthening resource management practices to enhance efficacy of resource for MSE survival and sustainability. The research indicated that the management of finances, management of human resources, management of materials, and management of information are important areas of programs that targeted improving the business and managerial capability of MSEs.
Additionally, the research uncovered that financial management and human resource management techniques have more statistically and practically significant impacts on the performances of MSEs which suggests a strong focus on enhancing financial and human resource management techniques, although it is evident that improving overall resource management practices could boost the current performances of MSEs in Werabe Town. This study primarily highlights the necessity of enhancing the financial management process of MSEs by using simpler accounting and reporting methods. These methods will provide financial information that can be utilized for more effective financial management and decision-making. Improving MSE financial management techniques in areas such as financial planning, cash flow, and working capital management is crucial for maintaining efficient operations and making the most of the limited financial resources available to MSE owners. Furthermore, improving the techniques of managing human resources in MSEs might enhance their performance. Implementing formal human resource management (HRM), although difficult for most MSEs, is necessary to enhance overall performance in resource management, leading to increased productivity and long-term competitiveness. To enhance the technical and management capabilities to successfully configure other resources, it is necessary to adopt a formal HR planning process, build a well-defined job description, carry out recruiting and selection, and establish a pay system that is specifically designed for the context of MSEs.
The findings addressing the beneficial impacts of materials management also indicated the necessity of investigating opportunities for enhancing MSE materials management methods, namely in the areas of material requirement planning, buying process, and inventory control systems. The study also identified a beneficial impact of information management strategies. Utilizing pre-made and streamlined information management software seems appropriate to improve the gathering, analysis, and utilization of information for more effective production and management decision-making. The utilization of information management systems is also improving the efficiency of companies in several aspects of resource management. It is advised to use pre-installed software on PCs and affordable off-the-shelf software to improve financial management, material management, and human resource management procedures. This would help streamline the entire impacts of MSE resource management practices, leading to improved performance.
6 Limitations and directions for further study
This study was conducted based on a cross-sectional survey. Future studies considering a longitudinal study could help to overcome the limitations of the study and advance resource management practices and MSE performance. Moreover, applying qualitative methods such as interviews and focus groups might yield more profound insights into the difficulties and possibilities encountered by MSEs in resource management implementations. This approach could provide a detailed comprehension of the factors affecting MSE growth and guide more focused solutions for sustainable growth.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Author contributions
MR: Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Validation. RH: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HL: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Software, Supervision. AS: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis, Validation, Visualization. EA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Adamu, G. (2020). Effect of material management on the performance of benue brewery industry, nigeria. Int. J. Res. 8, 228–234. doi: 10.29121/granthaalayah.v8.i2.2020.213
Alavi, M., and Leidner, D. (2001). Review: knowledge management and knowledge management systems: conceptual foundations and research issues. MIS Q. 1, 107–136. doi: 10.2307/3250961
Anjar, P., Abdul, M., and Vera Nur Aini Oktaviani, P. (2020). Identifying digital transformation paths in the business model of SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 6, 104. doi: 10.3390/joitmc6040104
Anuradha, T. S., and Ramesh, H. S. (2022). HRM practices in MSMEs-remained unprofessional. Int. J. Sci. Technol. Eng. 10, 1814–1820. doi: 10.22214/ijraset.2022.46708
Armstrong, M. (2008). Strategic Human Resource Management (4th Edn.). Replika Press Pvt Ltd. Available at: https://books.google.com.et/books/about/Strategic_Human_Resource_Management.html?id=NHSrhjGEua4C&redir_esc=y (accessed February 4, 2025).
Arnold, J. R. T., Chapman, S. N., and Clive, L. M. (2001). Introduction to Materials Management Casebook. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education, Inc.
Atnafu, D., and Balda, A. (2018). Inventory management practice in micro and small enterprise: the case of MSEs' manufacturing sub sector arsi zone, Ethiopia. Ind. Eng. Lett. 8, 13–20.
Aurangzeb Asif, M., and Amin, M. K. (2021). Resources management and Sme'S performance. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Rev. 9, 679–689. doi: 10.18510/hssr.2021.9367
Batista, A., Bessa, A. C. C., Junior, A. F. L. J., and Lobato, F. M. F. (2022). “Technology transfer in e-communication for small and medium enterprises as promoters of innovation and competitiveness,” in 2022 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Joint Conference on Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology (WI-IAT) (Niagara Falls, ON: IEEE), 527–533. doi: 10.1109/WI-IAT55865.2022.00083
Becker, B., and Gerhart, B. (1996). The impact of human resource management on organizational performance: progress and prospects. Acad. Manage. J. 39, 779–801. doi: 10.2307/256712
Bhatti, W. A., and Zaheer, A. (2014). The role of intellectual capital in creating and adding value to organizational performance: a conceptual analysis. Electron. J. Knowl. Manage. 12, 187–194. Available at: www.ejkm.com (accessed February 3, 2025).
Bryson, J. M., Ackermann, F., and Eden, C. (2007). Putting the resource-based view of strategy and distinctive competencies to work in public organizations. Public Adm. Rev. 67, 702–717. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-6210.2007.00754.x
Burton, N. (2003). “Financial resource management,” in Learning to Lead in the Secondary School: Becoming an Effective Head of Department, eds. M. Brundrett and I. Terrell (Routledge), 167–181. doi: 10.4324/9780203464557
Chioma, A., and Etifit, J. O. (2018). Material management and the effectiveness of selected manufacturing small and medium size firms in Enugu State. Asia Pac. J. Res. Bus. Manage. 9, 32–45. Available at: https://www.academia.edu/download/55868915/APJ4Jan18-4564.pdf (accessed February 4, 2025).
Contu, E. G. (2020). Organizational performance—theoretical and practical approaches; study on students' perceptions. Proc. Int. Conf. Bus. Excellence 14, 398–406. doi: 10.2478/picbe-2020-0038
Dahmen, P., and Rodríguez, E. (2014). Financial literacy and the success of small businesses: an observation from a small business development center. Numeracy 7, 1–12. doi: 10.5038/1936-4660.7.1.3
Davenport, T., and Prusak, L. (1998). Working Knowledge: How Organizations Manage What They Know. Boston, MA: Harvard Business Press.
Diana, M., and Verónica, A. (2019). La relación entre la formalización de las prácticas de gestión humana y la productividad de las mipymes. Un artículo de revisión. Innovar-revista De Ciencias Administrativas Y Sociales. 29, 101–114. doi: 10.15446/innovar.v29n74.82091
Dneil, A., and Balda, A. (2018). The impact of inventory management practice on firms' competitiveness and organizational performance: Empirical evidence from micro and small enterprises in Ethiopia. Cogent. Bus. Manag. 5, 1–16. doi: 10.1080/23311975.2018.1503219
El Hazzam, M. (2016). The impact of human resource management practices on smes performance: study based in Southwest Algeria. مجلة البشائر الاقتصادية 5, 216. doi: 10.33704/1748-002-005-017
Forth, J., and Bryson, A. (2018). The Impact of Management Practices on SME Performance. IZA Discussion Paper No. 11399. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3153363
Gebre-Egziabher, T., and Meheret, A. (2010). Micro and small enterprises as vehicles for poverty reduction, employment creation, and business development : the Ethiopian experience. Available at: https://www.fssethiopia.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/01/FSS-Research-Report-No.6.pdf
Ghidey, N., and Shete, M. (2023). Determinants of final performing micro and small businesses in Jimma town, Oromia regional state. Available at: http://repository.smuc.edu.et/handle/123456789/7564
Gregory, G., Dess, G. T., and Lumpkin, J. G. C. (1997). Entrepreneurial strategy making and firm performance: tests of contingency and configurational models. Strategic Manage. J. 18, 677–695.doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0266(199710)18:9<677::AID-SMJ905>3.3.CO;2-H
Hitt, M. A., Ireland, R. D., Sirmon, D. G., and Trahms, C. A. (2011). Strategic entrepreneurship: creating value for individuals, organizations, and society. Acad. Manage. Perspect. 25, 57–75. doi: 10.5465/AMP.2011.61020802
Hunjra, A. I., Butt, B. Z., and Rehman, K. U. (2010). Financial management practices and their impact on organizational performance. World Appl. Sci. J. 9, 997–1002. doi: 10.2139/ssrn.1750391
Jagadish, G., Elifneh, Y. W., and Belew, A. Z. (2022). The impact of materials management on profitability of manufacturing companies in ethiopia: the case of Walia steel industry PLC. Int. J. Eng. Manage. Res. 12, 49–59. doi: 10.31033/ijemr.12.1.7
Jin, Y., Zhang, S., Yu, R., and Huang, T. (2024). Influencing factors of financing constraints of micro and small enterprises (mses) in china: a risk information conveyance perspective. Hum. Behav. Emer. Technol. doi: 10.1155/2024/3614328
Jindrichovska, I. (2013). Financial management in SMEs. Eur. Res. Stud. 16, 79–96. doi: 10.35808/ersj/405
Kaliappen, N., and Abdullah, H. H. (2014). Does service innovation act as a mediator in differentiation strategy and organizational performance nexus? An empirical study. Asian Soc. Sci. 10, 123–131. doi: 10.5539/ass.v10n11p123
Kamau, H. W., and Kyalo, J. K. (2022). Integration of management information systems and performance of small and medium enterprises in Embu County. East African Scholars Multidiscip. Bull. 5, 233–240. doi: 10.36349/easjmb.2022.v05i11.001
Kar, S., and Jha, K. (2023). Examining the effect of material management practices on material availability and waste reduction in construction projects. J. Constr. Eng. Manage. 149:04023035. doi: 10.1061/JCEMD4.COENG-13589
Kithusi, A. N. N. (2016). Firm Resources, External Environment, Entrepreneurial Stretegy and Performance of Micro, Small and Medium Furniture Sector Enterprises in Nairobi City County, Kenya. University of Nairobi, Nairobi. 1, 1–231.
Kontio, E. (2013). Information management for tactical decision-making in the cardiac care process. Available at: https://www.utupub.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/91405/Annales%20D%201083%20Kontio%20DISS.pdf?sequence=2
Kreifelts, T., Hinrichs, E., and Woetzel, G. (1993). “Sharing to-do lists with a distributed task manager,” in Proceedings of the Third European Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work (ECSCW'93) (Milan: Springer), 31–46. doi: 10.1007/978-94-011-2094-4_3
Laslo, A. I. G. (2008). Resource allocation under uncertainty in a multi-project matrix environment: is organizational conflict inevitable? Int. J. Project Manag. doi: 10.1016/j.ijproman.2007.10.003
Lee, S. Y., and Whitford, A. B. (2013). Assessing the effects of organizational resources on public agency performance: evidence from the US federal government. J. Pub. Adm. Res. Theory 23, 687–712. doi: 10.1093/jopart/mus050
Leni, C., Rahmat, H., and Marcelino, D. (2023). Strengthening digital capabilities and entrepreneurship for SMEs in the creative economy sector during a pandemic. J. Penyuluhan 19, 93–103. doi: 10.25015/19202342367
Madhavkumar, M. (2023). Human resource management practices as determinants of organizational performance. Productivity 63, 465–477. doi: 10.32381/PROD.2023.63.04.9
Mahmudova, L., and Kovács, J. K. (2018). Definitining the performance of small and medium enterprises. Netw. Intell. Stud. 6, 111–120. Available at: https://seaopenresearch.eu/Journals/articles/NIS_12_5.pdf (accessed February 3, 2025).
Malgas, M., and Zondi, W. B. (2021). Competitive factors between local and foreign national small business retailers in South Africa: the case of Cape Town's townships. J. Bus. Retail Manage. Res. 15, 48–61. doi: 10.24052/JBRMR/V15IS02/ART-06
Mamun, M. (2022). Human resource management practices and organisational performance: evidence from small and medium-sized enterprises in Australia. Corporate Ownership Control 19, 163–171. doi: 10.22495/cocv19i4art14
Manzoor, F., Wei, L., and Sahito, N. (2021). The role of SMEs in rural development: access of SMEs to finance as a mediator. PLoS ONE. 16:e0247598. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247598
Mathew, S. (2023). Development of the information-analytical base of accounting and analysis in SMEs under the conditions of digitalization. Smart Innovation Syst. Technol. 625, 101–108. doi: 10.1007/978-981-19-7411-3_11
Mathushan, P., and Kengatharan, N. (2022). Human resource management practices and corporate entrepreneurship: an empirical study in Sri Lankan SMEs. Manage. Anal. J. 11, 46–56. doi: 10.15294/maj.v11i1.54152
Mengesha, B. T. (2019). Determinants of micro and small business enterprises growth: the case of three selected Woreda, Gurage Zone, Ethiopia. Int. J. Sci. Res. 8, 868–880. doi: 10.21275/ART20196905
Mulolli, E., Boskovska, D., and Islami, X. (2020). The competitive role of human resource management strategies on SMES in a transitional economy. Int. J. Multidiscip. Curr. Res. 8, 521–529. doi: 10.14741/ijmcr/v.8.4.4
Mulolli, E., Islami, X., and Skenderi, N. (2015). Human resource management practices and SMEs performance: study based in Kosovo. Int. Rev. Manage. Bus. Res. 4, 2306–9007. Available at: https://ssrn.com/abstract=2813379 (accessed February 3, 2025).
Neequaye, E. N., Dechun, H., Sholihah, P. I., and Fynn, S. (2017). Financial management of micro, small, and medium enterprises (SMEs) kredit usaha rakyat (KUR) micro recipients. Int. J. Res. Bus. Technol. 10, 23–30. doi: 10.17722/ijrbt.v10i1
Newbert, S. L. (2008). Value, rareness, competitive advantage, and performance: a conceptual-level empirical investigation of the resource-based view of the firm. Strategic Manage. J. 29, 745–768. doi: 10.1002/smj.686
Priyanka, P., and Priti, S. (2023). Issues and challenges pertaining to skilled manpower: a study of MSME sector in India. Eur. Econ. Lett. 13, 12–17.
Qalati, S. A., Ostic, D., Sulaiman, M. A. B. A., Gopang, A. A., and Khan, A. (2022). Social media and SMEs' performance in developing countries: effects of technological-organizational-environmental factors on the adoption of social media. Sage Open 12, 1–15. doi: 10.1177/21582440221094594
Raja, V. A. J. (2015). A study on resource management, economic approach, and leadership quality in various organizations in the world. Int. J. Manage. 6, 39–46. Available at https://iaeme.com/Home/article_id/IJM_06_07_005
Shaheen, A. (2020). Human resource management practices as an antecedent of employee performance. Bus. Manage. Econ. Res. 6, 152–160. doi: 10.32861/bmer.610.152.160
Singh, A., and Singh, S. (2023). Relevance of human resource management strategies to meet challenges of recent business scenario: a review of indian msme. EPRA Int. J. Econ. Bus. Rev.. 11, 36–42. doi: 10.36713/epra12523
Singh, R. K., Bohra, N. S., Aswale, N. R., and Cacal Darwin, M. (2023). Effective HRM practices for MSME sector success: an empirical study. J. Inf. Educ. Res. 3, 1–10. doi: 10.52783/jier.v3i2.74
Soudani, S. N. (2012). The usefulness of an accounting information system for effective organizational performance. Int. J. Econ. Finance. 4, 136–145. doi: 10.5539/ijef.v4n5p136
Turyahebwa, A., Sunday, A., and Ssekajugo, D. (2013). Financial management practices and business performance of small and medium enterprises in western Uganda. Afr. J. Bus. Manage. 7, 3875–3885. doi: 10.5897/AJBM2013.6899
Varadarajan, R. (2020). Customer information resources advantage, marketing strategy and business performance: a market resources based view. Ind. Mark. Manage. J. Serv. Sci. Manag. 15, 89–97. doi: 10.1016/j.indmarman.2020.03.003
Vatsal, K., and Shah, K. (2016). “The effect of e-business and information management on supply chain operations for SMEs,” in Proceedings of the IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web Intelligence (WI) and Intelligent Agent Technology (IAT) (IEEE).
Walter, J. O., and Vincent, N. M. (2018). Organizational resources and performance of kenyan state corporations. Eur. Sci. J. 14, 91–106. doi: 10.19044/esj.2018.v14n34p91
Woo, C.-R., Cho, M. J., Choi, H. R., Lee, K., and Kim, D.-H. (2016). The business model for the sharing economy between SMEs based on business model canvas. J. Digital Convergence 14, 31–39. Available at: https://koreascience.kr/article/JAKO201633055670055.page (accessed February 3, 2025).
Keywords: financial management, human resource management, information management, materials management, MSE performance
Citation: Refera MK, Habib RS, Lemma HR, Seman AA and Antonios EA (2025) The impact of resource management practices on the performance of micro and small enterprises in Werabe Town, Ethiopia. Front. Sustain. 6:1503331. doi: 10.3389/frsus.2025.1503331
Received: 28 September 2024; Accepted: 27 January 2025;
Published: 17 February 2025.
Edited by:
Hamid Mattiello, Fachhochschule des Mittelstands, GermanyReviewed by:
Yustinus Budi Hermanto, Universitas Katolik Darma Cendika, IndonesiaDessy Isfianadewi, Islamic University of Indonesia, Indonesia
Copyright © 2025 Refera, Habib, Lemma, Seman and Antonios. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Matewos Kebede Refera, a3JtYXRld29zQGdtYWlsLmNvbQ==
 Matewos Kebede Refera
Matewos Kebede Refera Redela Seman Habib2
Redela Seman Habib2 Habtamu Regassa Lemma
Habtamu Regassa Lemma