
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW article
Front. Surg. , 27 February 2025
Sec. Surgical Oncology
Volume 12 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fsurg.2025.1535212
This article is part of the Research Topic New Approaches, Concepts and Treatments in Gastrointestinal and Surgical Oncology View all 5 articles
Background: Because of the high rate of recurrence, the prognosis of patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is still very poor despite underwent pancreatectomy and adjuvant chemotherapy. A few reports have suggested the feasibility and efficacy of surgical resection for pulmonary metastases of PDAC. However, the role of metastasectomy of recurrent PDAC remains controversial. The aim of this study is to evaluate the benefits of pulmonary metastasectomy in PDAC patients with lung metastases.
Methods: We searched the PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases and extracted the hazard ratio (HR) with 95% confidence interval (CI) from eligible studies. Pooled HR with 95% CI were used to reveal the association between pulmonary metastasectomy and survival.
Results: The meta-analysis encompassed data from nine studies, comprising 467 patients suffered PDAC with lung metastasis. The results (the pooled HR: 0.637, 95% CI: 0.531–0.764, I2 = 61.5%, p value = 0.008) indicated that patients with lung metastasis who underwent pulmonary metastasectomy seemed to have better survival when compared with patients who underwent only chemotherapy. The robustness of these pooled results was verified by our subgroup analysis and sensitivity analysis. Moreover, the varying sample sizes among studies contribute to the heterogeneity in the pooled hazard ratio (HR) for survival, as indicated by the meta-regression analysis (p value = 0.045).
Conclusion: Pulmonary metastasectomy could prolong the survival in patients with lung metastases from PDAC. However, the present study is based on a relatively small number of patients and may include a selection bias. More multi-institutional prospective study is needed to evaluated the clinical value of pulmonary metastasectomy.
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is recognized as one of the most aggressive malignant digestive system tumors with a 5-year survival rate less than 10% (1). Because of a high recurrence rate after surgery, the prognosis of pancreatic cancer is dismal even after curative pancreatic resection. The recurrence patterns of PDAC are diverse, with lung metastases being one of the most common sites of distant spread (2, 3). The incidence rates of pulmonary metastases ranging from 2.9% to 21.8% have been reported (4–6). Patients with lung metastases from PDAC tend to have a relatively better prognosis compared to those with other types of hematogenous disseminations, such as liver or peritoneal metastases (7). Median overall survival (OS) after the initial treatment can be varied from 51 to 121 months in metachronous lung metastasis (8).
Chemotherapy is seemed to be the only therapeutic strategy for metastatic pancreatic cancer and surgical resection is generally not recommended. Nonetheless, some studies have shown that resection of the pulmonary metastases in patients with colorectal cancer could prolong survival time (9). In addition, some case reports or case series, as well as few retrospective studies have shown that pulmonary resection of isolated lung metastases is associated with long-term survival in some patients (4, 10, 11). However, the effect of surgical resection on extending the survival is still unclear because the selection of patients with relatively indolent diseases might cause survival benefits after pulmonary resection. Furthermore, oncological outcomes and clinical benefits of pulmonary resection for patients with lung metastases have not been clarified. The aim of our meta-analysis is to evaluate the clinical values of surgical management for lung metastases from PDAC by performing a detailed investigation of postoperative oncological outcomes after pulmonary resection.
This systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement (12).
PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases were searched for eligible articles up to September 1st, 2024. The search was conducted using medical subject headings (MeSH) in combination with free text words. The following search headings were used: “pancreatic cancer”, “lung”, “metastasis”, “recurrence”, “resection”, and “surgery”, and we used “AND”, “OR”, “NOT” for combination of these headings to avoid missing and wrong articles. The search strategy is described in the Supplementary Materials.
All studies included in the meta-analysis were selected according to the following inclusion criteria: (1) all patients were diagnosed with PDAC with synchronous or metachronous lung metastases; (2) patients underwent the pulmonary resection; (3) survival data can be collected in the literature; (4) Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale (NOS) score ≥ 6. The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) neuroendocrine tumor and other pathological types; (2) multiorgan metastases; (3) incomplete survival data; (4) abstracts, case reports, editorials, letters, systematic reviews, and comments; (5) overlapped or same population; and (6) duplicate studies.
Two investigators (Pengcheng Zhao and Qiaoqi Jiang) independently extracted the necessary data from the included studies, and any disagreements were resolved by discussion until a consensus was reached. The following data were extracted from each study: first author, publication year, country, study design, number of patients, tumor site, number of lung metastases, follow-up duration, median survival time, and overall survival.
The Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale (NOS) was used to evaluate the quality of the included studies. Studies with a score of six or higher were considered high-quality studies (13). This work was also performed independently by two investigators (Pengcheng Zhao and Qiaoqi Jiang). Details of NOS score were showed in Supplementary Table S1.
Stata 14.0 software was used for data analysis. The heterogeneity of the pooled effect was assessed using Cochran's Q test and the Higgins I2 statistic. Q test p value < 0.1 or I2 > 50% was considered significant heterogeneity, and a random-effect model was applied to estimate the pooled HR. While heterogeneity was not significant (Q test p value > 0.1 or I2 < 50%), a fixed-effect model was used. The graphical description of the statistical results was illustrated with forest plot. Sensitivity analysis was applied to reduce and explain heterogeneity among the studies. Furthermore, publication bias was visually checked through a funnel plot and then quantitatively analyzed using Begg's and Egger's tests. All statistical tests were two-sided, and a p value less than 0.05 were defined as statistically significant.
After the literature search, 2,361 articles were initially retrieved. After removing 186 duplicates, 2,175 articles remained. After screening the titles and abstracts, 2,112 articles were excluded for being irrelevant topics, reviews or meta-analysis, conference abstracts, letters, case reports, case series, or comments. Finally, 9 articles met our inclusion criteria, and 467 patients suffered PDAC with lung metastasis (10, 14–21). The detailed selection process was shown in Figure 1.
All the studies were retrospective studies, and were mainly published in the past five years. The sample size of enrolled studies varied from 13 to 117, and a total of 467 patients suffered PDAC with synchronous or metachronous pulmonary metastases were enrolled. Among the included 467 patients, 189 patients underwent resection of lung metastases. In all selected articles, the median survival time from the initial pancreatectomy was reported for both the pulmonary metastasectomy group and the adjuvant chemotherapy group. The main characteristics of the included studies were presented in Table 1.
Nine studies investigated the resection of lung metastases in metastatic PDAC patients (10, 14–21). Given the inherent variability in study designs, patient populations, and treatment protocols in retrospective studies, significant heterogeneity was anticipated. As illustrated in Figure 2, the results (the pooled HR: 0.637, 95% CI: 0.531–0.764, I2 = 61.5%, p value = 0.008) indicated that resection of lung metastases could prolong the survival of the PDAC patients with pulmonary metastases.
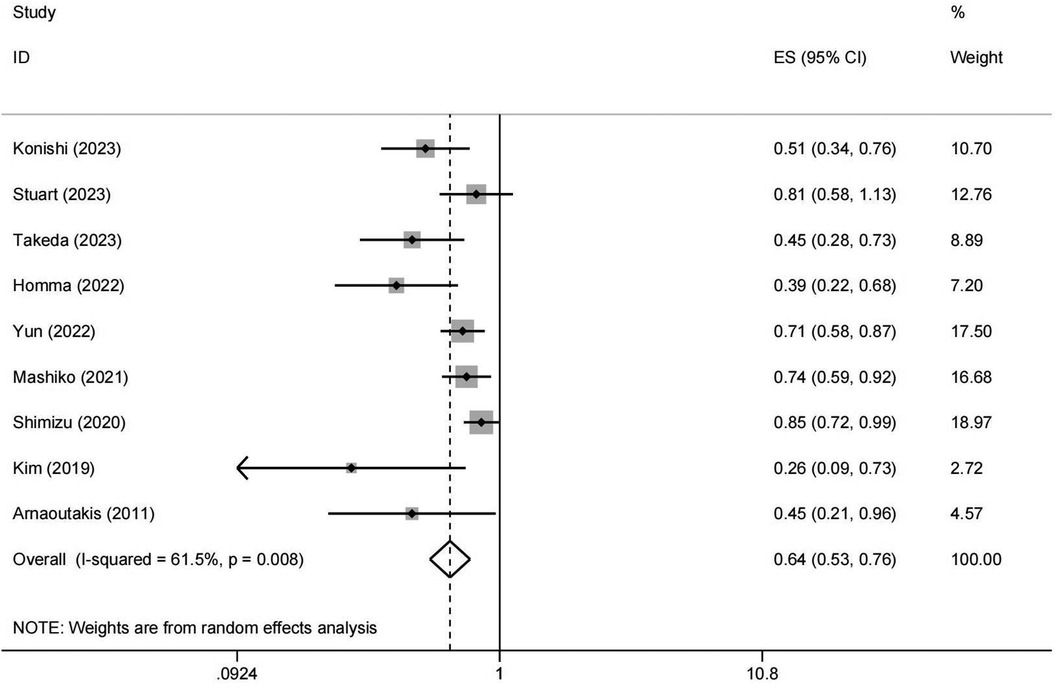
Figure 2. Forest plot of meta-analysis on OS between surgical and non-surgical groups. OS, overall survival; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval.
Sensitivity analysis was conducted to assess the effect of individual studies on the pooled HR, and the results suggested that omitting any individual study had no significant effect on the pooled HR (Figure 3). Furthermore, publication bias was investigated, Begg's test and Egger's test yielded p-values of 0.048 and 0.001, respectively. The funnel plot revealed that there was some extent of publication bias among included studies (Figure 4).
To explore and explain the heterogeneity, meta regression analysis was applied. The p value of PM subgroup was 0.045. The results of meta regression indicated that the relatively small sample size might be a source of heterogeneity. In addition, subgroup analyses were conducted based on the number of patients in the PM group. The cutoff value was defined as 15, the pool HR in the subgroup with patients number fewer than 15 was 0.719 (95% CI: 0.589–0.878, I2 = 52.0%, p value = 0.08), while the results of another subgroup was: pooled HR = 0.513, 95% CI: 0.354–0.744, I2 = 63.1%, p value = 0.043. The results of subgroup analysis were shown in Figure 5A. Moreover, the results of another subgroup analyses based on the timing of lung metastases and the recurrence-free interval (RFI) from primary lesion pancreatectomy to lung metastases were also presented in Figures 5B,C.
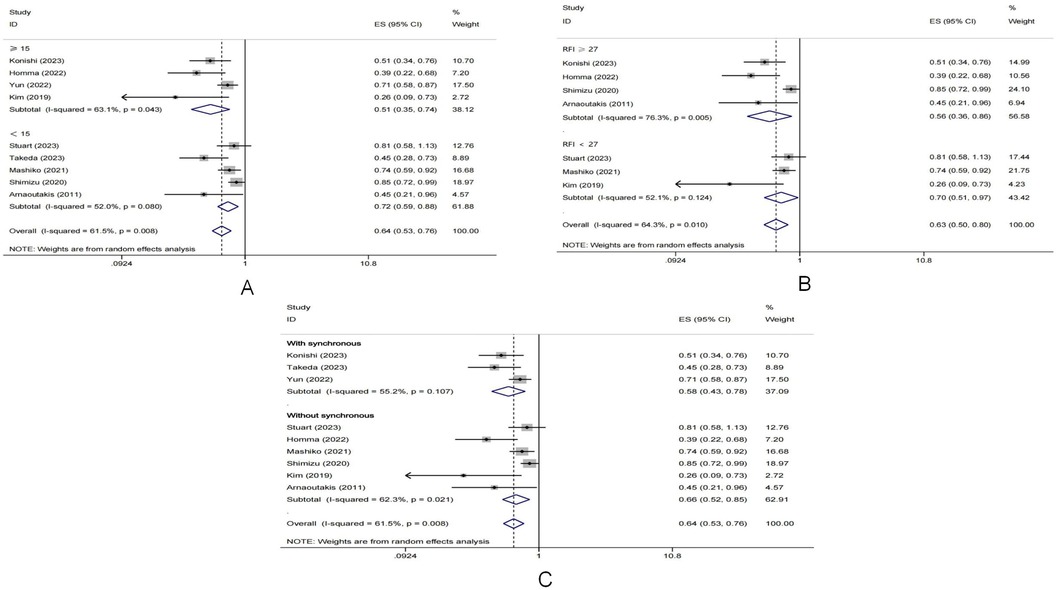
Figure 5. Forest plot of subgroup analyses based on (A) the number of patients underwent metastaectomy; (B) the length of RFI after primary pancreatectomy; (C) the timing of metastases.
Although surgical resection is the only treatment that offers long-term survival in selected patients with resectable pancreatic cancer, among patients who undergo pancreatectomy for PDAC, almost 80% patients develop locoregional and/or distant recurrence after primary pancreatectomy (22). The most common metastatic site is liver, followed by lung (2). Historically, palliative chemotherapy seemed to be the only option for PDAC patients with lung metastases. In recent years, pulmonary metastasectomy has been introduced as a novel treatment (23). We aimed to evaluate the benefits of pulmonary metastasectomy in PDAC patients with lung metastases.
In our meta-analysis, nine articles with 467 PDAC patients with synchronous or metachronous lung metastases were enrolled (10, 14–21). Our pooled analysis showed that pulmonary metastasectomy could significantly improve overall survival of PDAC patients with lung metastases compared to those patients who did not undergo resection of metastatic tumor (the pooled HR: 0.637, 95%CI: 0.531–0.764, I2 = 61.5%, p value = 0.008). Meta regression analysis was used to explore the heterogeneity. The p value was 0.045, less than 0.05, and the results indicated that the number of patients who underwent pulmonary metastasectomy might be the source of heterogeneity. Moreover, meta-regression analysis was also used based on the recurrence-free interval (RFI), and the p value was 0.627, suggesting that RFI may not be related to the heterogeneity. We believed that the the number of patients who underwent PM could have a significant impact on the survival, especially in the studies with a small number of patients. The smaller the sample size, the greater the heterogeneity of the results. The heterogeneity caused by publication bias could not be ignored either. In our study, Begg's test and Egger's test were used to evaluate the publication bias, and yielded p-values of 0.048 and 0.001, respectively. The results showed that there was a certain extent of publication bias in our study, which could impact the stability of the pooled results. To mitigate the impact of publication bias in future research, grey literature and unpublished studies should also be inculded. What's more, study design, patient population and treatment protocols might also be the potiential sources of heterogeneity. All included studies were retrospective, which inherently introduces variability in data collection methods and quality. Differences in study design, such as variations in patient selection criteria and the definition of lung metastases, may contribute to the observed heterogeneity. The characteristics of the patient populations varied across studies. Factors such as age, gender distribution, and tumor characteristics (e.g., synchronous vs. metachronous metastases) could influence survival outcomes. Variations in treatment protocols, including the type of pulmonary resection (e.g., wedge resection, segmentectomy, or lobectomy) and the use of adjuvant chemotherapy, could impact survival outcomes as well. The timing and duration of chemotherapy, both before and after pulmonary metastasectomy, may also differ across studies, contributing to the observed heterogeneity. To address this heterogeneity, we conducted subgroup analyses based on the number of patients undergoing pulmonary metastasectomy, the timing of lung metastases, and the RFI. These analyses provided insights into the potential sources of heterogeneity and helped identify subgroups where the benefits of pulmonary metastasectomy may be more pronounced.
Previous studies have revealed that the patients with pulmonary metastases often have a better prognosis than those with metastases at other sites, such as the liver. The prognosis of metastatic PDAC may be related to the duration of recurrence. It has been reported that late recurrence more commonly develops in the lung than in the liver or peritoneum (24). The definition of RFI was the interval between initial primary pancreatectomy and lung metastases. PDAC patients with a longer RFI could receive clinical benefits from pulmonary resection and have a better prognosis (10, 19). In Konishi's study (10), patients with an RFI of <28 months, as expected, had early tumor recurrence, resulting in continuous chemotherapy after lung metastases and poor prognosis, while patients with an RFI of ≥28 months did not have tumor recurrence within 12 months after pulmonary resection and had a longer chemotherapy-free interval. Univariate analyses also revealed that RFI from initial pancreatectomy to lung metastases of ≥28 months was associated with better disease-free survival (DFS) after pulmonary resection. Another study reported, in study of 15 cases, that patients who developed lung metastasis more than 17 months after initial pancreatectomy had a better prognosis compared to those who developed lung metastasis at an earlier time (25). Prolonged RFI from the initial pancreatectomy to the development of lung metastasis could be considered as a prognostic factor of PDAC patients with pulmonary metastases.
The number of lung metastases was also associated with the prognosis of patients. Patients with solitary metastases were more likely to undergo surgical resection and showed a longer median overall survival. In Homma's study, the results of multivariate analysis showed that solitary metastasis was identified as significant prognostic factor after lung resection (HR: 5.03; 95% CI: 1.195–21.144, p = 0.022) (16).
Oligometastases, defined as a state of limited number of metastases, were not equal to solitary metastases, and were considered as an intermediate state between solitary and multiple metastases. which may also benefit from surgical resection. Lung oligometastases were defined as having two to five lesions, based on previous reports on the local treatment of pulmonary metastatic lesions (26, 27). A study has reported that. patients with lung oligometastasis were more likely to undergo surgical resection (41% vs. 0%) and had a significantly better prognosis (41.3 vs. 17.6 months) than those with lung polymetastasis. Oligometastasis (HR, 0.43; 95% CI, 0.24–0.76) was identified as an independent factor predicting favourable OS in PDAC patients with distant metastasis confined to the lung (15). Moreover, the number and location of lung metastases would also determine the method of PM. The modalities for resection of lung metastases were wedge resection, segmentectomy and lobectomy. The type of pneumonectomy also had an effect on prognosis. In general, lobectomy was more thorough than wedge resection, but it also has a greater impact on lung function. Studies have shown that there is no significant difference in overall survival between lobectomy and wedge resection, but lobectomy may provide more complete tumor resection in some cases (28).
The role of chemotherapy was not ignored in the management of PDAC with pulmonary metastases equally. It was widely accepted that multidisciplinary treatment (MDT) was necessary for improving the prognosis of patients with advanced-stage pancreatic cancer (29, 30). In Yun's study, the results of multivariate analyses revealed that chemotherapy (HR = 0.434, p = 0.024), and chemotherapy cycles (HR = 0.300, p < 0.001) had significant effects on survival (17). One study also reported that 24 of 32 patients received adjuvant chemotherapy after pulmonary metastasectomy. The addition of postoperative chemotherapy after pulmonary resection significantly improved the time to recurrence to 41.5 months compared to the group without chemotherapy, and the median time from recurrence to death (RTD) was also longer in patients underwent postoperative chemotherapy (59.0 months vs. 7 months, p = 0.02). In the multivariate analysis, postoperative chemotherapy after metastasectomy (HR: 14.089; 95% CI: 1.729–114.77, p = 0.023) was identified as significant prognostic factors after lung resection (16). In summary, resection of lung metastases, especially lobectomy, combined with long RFI and adjuvant chemotherapy, could significantly improve overall survival of PDAC patients with pulmonary metastases.
While our meta-analysis demonstrates potential survival benefits of pulmonary metastasectomy in PDAC patients with lung metastases, it is crucial to consider the broader clinical context, including perioperative risks and postoperative complications. Patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) often present with significant systemic disease burdens, which may affect their tolerance to surgery. The decision to proceed with pulmonary metastasectomy should be carefully weighed against the potential risks and benefits for each individual patient. Pulmonary metastasectomy is associated with inherent surgical risks, including anesthesia-related complications, bleeding, infection, and respiratory complications. Given the compromised overall health status of many PDAC patients, these risks may be further exacerbated. Postoperative complications, such as prolonged hospital stays, respiratory failure, and delayed recovery, can significantly impact patient outcomes and quality of life. Therefore, a thorough preoperative assessment is essential to identify patients who are likely to benefit from surgery without undue risk. In addition, stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) might be a promising alternative treatments for managing lung metastases in PDAC patients, offering high local control rates with minimal invasiveness. This approach may be particularly suitable for patients with significant comorbidities or those who are not surgical candidates due to poor performance status. Additionally, multidisciplinary collaboration in selecting patients for pulmonary metastasectomy was crucial for optimizing clinical outcomes.
This meta-analysis has several limitations. Firstly, all the included studies were retrospective. Retrospective studies are inherently prone to selection bias and recall bias, which may significantly influence the interpretation of our findings. Selection bias may arise from the non-randomized allocation of patients to surgical or non-surgical groups, potentially leading to an overestimation of the benefits of pulmonary metastasectomy. Additionally, the reliance on historical data may introduce recall bias, where the accuracy of data collection and reporting may vary between studies. These biases could affect the comparability between the surgical and non-surgical groups, and thus, the observed survival benefits attributed to pulmonary metastasectomy may not be entirely attributable to the intervention itself. Moreover, the retrospective design limits our ability to control for confounding variables that may influence survival outcomes, such as differences in patient demographics, tumor characteristics, and the quality of adjuvant therapies received. While we attempted to mitigate these biases through rigorous study selection criteria and quality assessment using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale, the inherent limitations of retrospective data cannot be fully overcome. Secondly, the results of Begg's test and Egger's revealed that there was some extent publication bias among included studies. Thirdly, the sample size was relatively small, and large, multicenter RCTs are urgently needed. Moreover, The survival benefit observed in our analysis may not be uniform across all molecular subtypes of PDAC. For instance, patients with specific genetic mutations or biomarker expressions may respond differently to pulmonary metastasectomy. Future research should explore the role of molecular profiling in identifying patients who are most likely to benefit from surgical intervention.
In summary, our meta-analysis revealed that PDAC patients with lung metastases who underwent pulmonary metastasectomy achieved longer survival compared with those who did not. Moreover, patients with long RFI and limited number of metastases are more likely to undergo metastasectomy and have a better survival. However, the retrospective nature of the included studies introduces significant limitations, including selection and recall biases, which may affect the validity of our findings. Therefore, caution should be exercised in interpreting these results. Prospective studies or randomized controlled trials are urgently needed to rigorously evaluate the clinical value of pulmonary metastasectomy in this patient population.
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
PZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. KX: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Project administration, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. XL: Data curation, Project administration, Validation, Writing – review & editing. BT: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
The authors thank all medical staff who contributed to the maintenance of the medical record database.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsurg.2025.1535212/full#supplementary-material
1. Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. (2023) 73(1):17–48. doi: 10.3322/caac.21763
2. Groot VP, Rezaee N, Wu W, Cameron JL, Fishman EK, Hruban RH, et al. Patterns, timing, and predictors of recurrence following pancreatectomy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Ann Surg. (2018) 267(5):936–45. doi: 10.1097/sla.0000000000002234
3. Nakajima M, Ueno T, Suzuki N, Matsui H, Shindo Y, Sakamoto K, et al. Novel indications for surgical resection of metachronous lung metastases from pancreatic cancer after curative resection. J Clin Gastroenterol. (2017) 51(5):e34–e8. doi: 10.1097/mcg.0000000000000551
4. Yamashita K, Miyamoto A, Hama N, Asaoka T, Maeda S, Omiya H, et al. Survival impact of pulmonary metastasis as recurrence of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Dig Surg. (2015) 32(6):464–71. doi: 10.1159/000439545
5. Kamisawa T, Isawa T, Koike M, Tsuruta K, Okamoto A. Hematogenous metastases of pancreatic ductal carcinoma. Pancreas. (1995) 11(4):345–9. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199511000-00005
6. Wangjam T, Zhang Z, Zhou XC, Lyer L, Faisal F, Soares KC, et al. Resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas with recurrence limited in lung have a significantly better prognosis than those with other recurrence patterns. Oncotarget. (2015) 6(34):36903–10. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5054
7. Deeb A, Haque SU, Olowokure O. Pulmonary metastases in pancreatic cancer, is there a survival influence? J Gastrointest Oncol. (2015) 6(3):E48–51. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2078-6891.2014.114
8. Sakaguchi T, Valente R, Tanaka K, Satoi S, Del Chiaro M. Surgical treatment of metastatic pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a review of current literature. Pancreatology. (2019) 19(5):672–80. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2019.05.466
9. Beckers P, Berzenji L, Yogeswaran SK, Lauwers P, Bilotta G, Shkarpa N, et al. Pulmonary metastasectomy in colorectal carcinoma. J Thorac Dis. (2021) 13(4):2628–35. doi: 10.21037/jtd-2019-pm-14
10. Konishi T, Takano S, Takayashiki T, Kuboki S, Suzuki D, Sakai N, et al. Clinical benefits of pulmonary resection for lung metastases from pancreatic cancer. Langenbecks Arch Surg. (2023) 409(1):11. doi: 10.1007/s00423-023-03198-4
11. Lovecek M, Skalicky P, Chudacek J, Szkorupa M, Svebisova H, Lemstrova R, et al. Different clinical presentations of metachronous pulmonary metastases after resection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: retrospective study and review of the literature. World J Gastroenterol. (2017) 23(35):6420–8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i35.6420
12. Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The prisma 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Br Med J. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
13. Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC, Olkin I, Williamson GD, Rennie D, et al. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology: a proposal for reporting. Meta-analysis of observational studies in epidemiology (moose) group. JAMA. (2000) 283(15):2008–12. doi: 10.1001/jama.283.15.2008
14. Stuart CM, Kirsch MJ, Zhuang Y, Meguid CL, Sugawara T, Colborn KL, et al. Pulmonary metastasectomy is associated with survival after lung-only recurrence in pancreatic cancer. Surgery. (2023) 174(3):654–9. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2023.05.008
15. Takeda T, Sasaki T, Ichinose J, Inoue Y, Okamoto T, Mie T, et al. Outcomes of lung oligometastasis in pancreatic cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. (2023) 53(12):1144–52. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyad111
16. Homma Y, Endo I, Matsuyama R, Sho M, Mizuno S, Seyama Y, et al. Outcomes of lung metastasis from pancreatic cancer: a nationwide multicenter analysis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. (2022) 29(5):552–61. doi: 10.1002/jhbp.1127
17. Yun WG, Kwon W, Han Y, Sohn HJ, Kim HS, Lee M, et al. Can surgical resection of metastatic lesions be beneficial to pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients with isolated lung metastasis? Cancers (Basel). (2022) 14(9):2067. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092067
18. Mashiko T, Nakano A, Masuoka Y, Yamamoto S, Ozawa S, Nakagohri T. Significance of pulmonary resection in patients with metachronous pulmonary metastasis from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Surg. (2021) 21(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12893-021-01236-w
19. Shimizu T, Taniguchi K, Asakuma M, Komeda K, Inoue Y, Lee SW, et al. Initial pulmonary metastasis after pancreatectomy for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Surg Today. (2020) 50(4):413–8. doi: 10.1007/s00595-019-01902-w
20. Kim YI, Song KB, Lee YJ, Park KM, Hwang DW, Lee JH, et al. Management of isolated recurrence after surgery for pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Br J Surg. (2019) 106(7):898–909. doi: 10.1002/bjs.11144
21. Arnaoutakis GJ, Rangachari D, Laheru DA, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Hruban RH, Herman JM, et al. Pulmonary resection for isolated pancreatic adenocarcinoma metastasis: an analysis of outcomes and survival. J Gastrointest Surg. (2011) 15(9):1611–7. doi: 10.1007/s11605-011-1605-8
22. Sperti C, Pasquali C, Piccoli A, Pedrazzoli S. Recurrence after resection for ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. World J Surg. (1997) 21(2):195–200. doi: 10.1007/s002689900215
23. Hajibandeh S, Hajibandeh S, Sutcliffe RP, Bartlett D. Meta-analysis of survival after pulmonary resection for isolated metachronous pancreatic cancer metastasis: a promising, albeit infrequent. Approach. HPB (Oxford). (2024) 26(9):1103–13. doi: 10.1016/j.hpb.2024.05.015
24. Van den Broeck A, Sergeant G, Ectors N, Van Steenbergen W, Aerts R, Topal B. Patterns of recurrence after curative resection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. (2009) 35(6):600–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2008.12.006
25. Ilmer M, Schiergens TS, Renz BW, Schneider C, Sargut M, Waligora R, et al. Oligometastatic pulmonary metastasis in pancreatic cancer patients: safety and outcome of resection. Surg Oncol. (2019) 31:16–21. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2019.08.010
26. Yamamoto T, Niibe Y, Aoki M, Shintani T, Yamada K, Kobayashi M, et al. Analyses of the local control of pulmonary oligometastases after stereotactic body radiotherapy and the impact of local control on survival. BMC Cancer. (2020) 20(1):997. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07514-9
27. Navarria P, Ascolese AM, Tomatis S, Cozzi L, De Rose F, Mancosu P, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy (sbrt) in lung oligometastatic patients: role of local treatments. Radiat Oncol. (2014) 9(1):91. doi: 10.1186/1748-717x-9-91
28. Miyashita Y, Ose N, Okami J, Takami K, Sakamaki Y, Ikeda N, et al. Outcomes of surgical resection for pulmonary metastasis from pancreatic cancer. Surg Today. (2023) 53(11):1236–46. doi: 10.1007/s00595-023-02701-0
29. Sakaguchi T, Satoi S, Yamamoto T, Yamaki S, Sekimoto M. The past, present, and future Status of multimodality treatment for resectable/borderline resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Surg Today. (2020) 50(4):335–43. doi: 10.1007/s00595-020-01963-2
Keywords: pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, lung metastases, pulmonary metastasectomy, chemotherapy, meta-analysis
Citation: Zhao P, Jiang Q, Xue K, Liu X and Tian B (2025) The role of pulmonary metastasectomy in patients suffering pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with lung metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Surg. 12:1535212. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1535212
Received: 27 November 2024; Accepted: 12 February 2025;
Published: 27 February 2025.
Edited by:
Agata Mikołajczyk-Martinez, Wroclaw University of Environmental and Life Sciences, PolandCopyright: © 2025 Zhao, Jiang, Xue, Liu and Tian. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bole Tian, aHh0YmwwMzM4QDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.