- 1Department of Orthopedic, General Hospital of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, Ningxia, China
- 2First Clinical Medical College of Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan, Ningxia, China
Background: Human brucellosis is the most common bacterial zoonosis worldwide, with brucella spondylitis (BS) being one of its most severe forms, potentially leading to spinal deformity or paralysis. This study aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the current status and research trends in the BS field using bibliometric methods.
Methods: Publications on BS from January 1, 1980, to March 24, 2024, were retrieved from the Web of Science database. We used Biblioshiny, VOSviewer, Scimago Graphica, CiteSpace, and Microsoft Office Excel Professional Plus 2016 to analyze publication frequency, geographic distribution, institutional affiliations, international collaborations, authorship, journal sources, keyword usage, trends, and cited references.
Results: Between January 1, 1980, and March 24, 2024, 197 publications on BS were analyzed. Turkey emerged as the leading contributor, with 62 publications, accounting for 31.47%. Weibin Sheng was the most prolific author, contributing 7 papers (3.55%). Xinjiang Medical University was the leading institution with 13 documents (6.60%). Medicine and Rheumatology International each published 6 papers (3.05%). CiteSpace analysis highlighted “spinal brucellosis,” “spondylitis,” “complications,” “diagnosis,” and “involvement” as the core research areas in BS. Keyword clustering analysis identified 11 primary clusters representing the main research directions. Analysis of abstracts and keyword trends revealed that post-2020, emerging research frontiers include “instrumentation,” “management,” and “debridement.”
Conclusion: There has been significant progress in BS research, with a steady increase in publications. Current research focuses on diagnosis and complications, while future studies may explore management and instrumentation. Increased collaboration among countries and researchers is recommended.
1 Introduction
Human brucellosis (HB) is a widespread zoonotic infection caused by various species of the Brucella genus. Recent research indicates a significant global rise in HB incidence, with annual new cases estimated between 1.6 and 2.1 million (1, 2). Recognized as the most common bacterial zoonosis worldwide, HB remains a significant public health challenge (3), particularly in regions like the Mediterranean, India, Latin America, the Middle East, and numerous African countries north and south of the Sahara Desert (4). The disease is known for its chronic and recurrent nature, affecting multiple systems and organs, with brucella spondylitis (BS) being one of its most severe manifestations (5). The prevalence of spondylitis in brucellosis cases varies widely, ranging from 2% to 60% (6).
The clinical symptoms of BS are varied, including chronic progressive back pain, localized swelling, restricted movement, and fever. The wide range of symptoms and the absence of specific indicators often delay diagnosis, leading to severe complications such as spinal instability, spinal cord compression, epidural mass formation, or paralysis (7). Therefore, timely diagnosis is crucial for effective management and prognosis. Traditional microbiological and serological agglutination tests assist in diagnosing BS but have poor sensitivity (8). Early imaging is often indistinguishable from other forms of infectious spondylitis, such as spinal tuberculosis (STB), making early diagnosis challenging (9). Laboratory tests, including hemoglobin level, platelet count, white blood cell count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and C-reactive protein (CRP), are essential for assessing treatment efficacy and predicting prognosis. However, these tests do not offer diagnostic specificity for BS (10, 11). Recently, nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs) and molecular biology techniques have shown promise as early diagnostic tools, though extensive clinical studies are needed to confirm their accuracy and reliability (12, 13).
Conservative management is the most commonly reported treatment for BS (14). Early diagnosis, strict adherence to antibiotic regimens, and regular follow-ups contribute to successful management (15). However, relapse and sequelae remain significant concerns, and the optimal antibiotic regimen and course are still controversial (16). Surgery aims to restore spinal stability, relieve spinal cord or nerve compression, and remove diseased tissue. This includes filling defective areas, excising and draining abscesses, and performing biopsies for histopathological examination and culture to provide early diagnosis and treatment guidance (17). Unfortunately, there are no standardized indications for surgical intervention, which remains controversial (18, 19).
Bibliometrics is an invaluable scientific tool for analyzing research within a field. Using software such as Biblioshiny, VOSviewer, and CiteSpace, bibliometrics systematically processes publication data and precisely visualizes research content. This helps identify research focal points quickly and predict outcomes, guiding scholars toward specific research directions. By integrating and processing bibliometric information, comprehensive discussions within a field become more scientific and rigorous. Consequently, bibliometrics has gained increasing attention and application in recent years. This paper aims to provide a comprehensive analysis and summary of publications related to BS using bibliometric methods and to explore the research hotspots and frontiers of BS.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Sources of data
This study utilized the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) database, known for its comprehensive citation and publication data across various scientific disciplines.
2.2 Search strategies
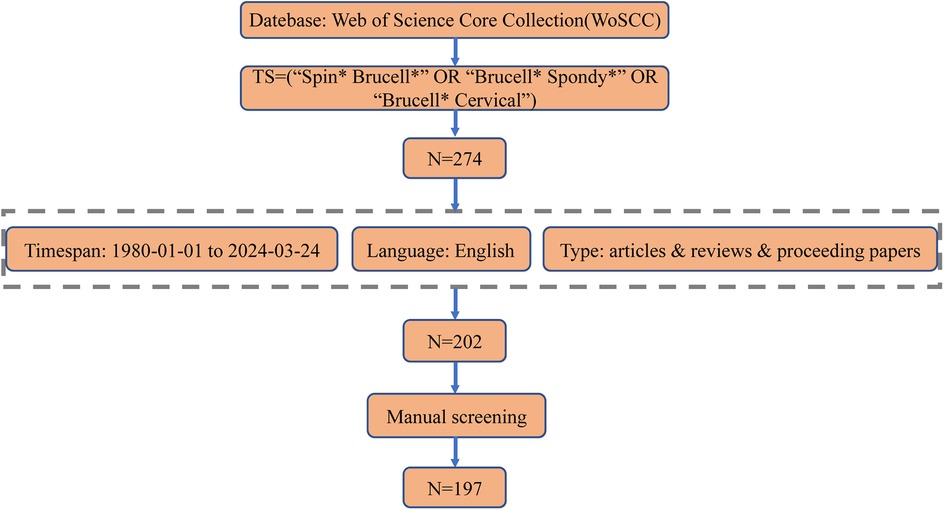
Two investigators searched WoSCC on March 24, 2024, to identify relevant studies published from January 1, 1980, to March 24, 2024. The search terms were as follows: TS = (“Spin* Brucell*” OR “Brucell* Spondy*” OR “Brucell* Cervical”) AND publishing year = (1980–2024) AND document types = (articles & reviews & proceedings papers) AND language = (English). This search yielded 274 articles. The following categories were excluded: editorial material, letters, book chapters, meeting abstracts, early access, retractions, retracted publications, and corrections. A manual review was conducted to ensure the selected publications were directly relevant to BS research. This review involved two authors (Zhangui Gu and Zongqiang Yang), with any discrepancies resolved by the experienced corresponding author (Jiandang Shi). The search results were exported as a plain text file, with the record content comprising the “Full Record and Cited References.” The final analysis included 197 publications. The retrieval strategy employed in the study is illustrated in Figure 1.
2.3 Bibliometric analysis
The bibliometric analysis was conducted systematically, beginning with an overview of publications and countries/regions using Microsoft Office Excel Professional Plus 2016. The data were then imported into Biblioshiny (R version 4.3.3), CiteSpace (6.3.R1), and VOSviewer (1.6.20) for further analysis, including institutions, authors, journals, document citations, reference co-citations, keywords, and trends. The country collaboration map was created using Scimago Graphica (1.0.41).
Biblioshiny evaluates several bibliometric indicators to assess the output of authors, institutions, and journals. The number of articles measures productivity, total citations indicate the impact on the scientific community, and local citations assess the impact in specific fields. These dimensions are used to evaluate research quality. The h-index, which combines productivity and effect, indicates that a researcher has published h papers, each cited at least h times. Additionally, Biblioshiny plotted a three-field plot and authors’ production over time. Data exported from VOSviewer were used in Scimago Graphica to generate a geographic distribution map of BS publications (20). In the VOSviewer map, nodes represent items such as countries, organizations, and authors, with node size indicating the number of these items. Lines between nodes reflect the degree of cooperation or citation among projects, indicated by the same color (21). CiteSpace, a Java application for bibliometric analysis developed by Chen, supports knowledge mining and data visualization (22). It generated bibliographic citations, reference co-citations, keyword co-occurrences, keyword clusters, and timeline plots and analyzed keyword bursts representing trending themes over time. Microsoft Office Excel Plus 2016 was used to create annual production and average citation graphs.
3 Results
3.1 Search results
The study included 197 publications, comprising 178 articles, 15 reviews, and 4 proceeding papers (Figure 1). The number of publications on BS has increased significantly, from 6 in 1999 to a peak of 18 in 2023 (Figure 2A). Figure 2B illustrates the trend in the number of BS-related publications and the average number of citations per year from 2009 to 2024.
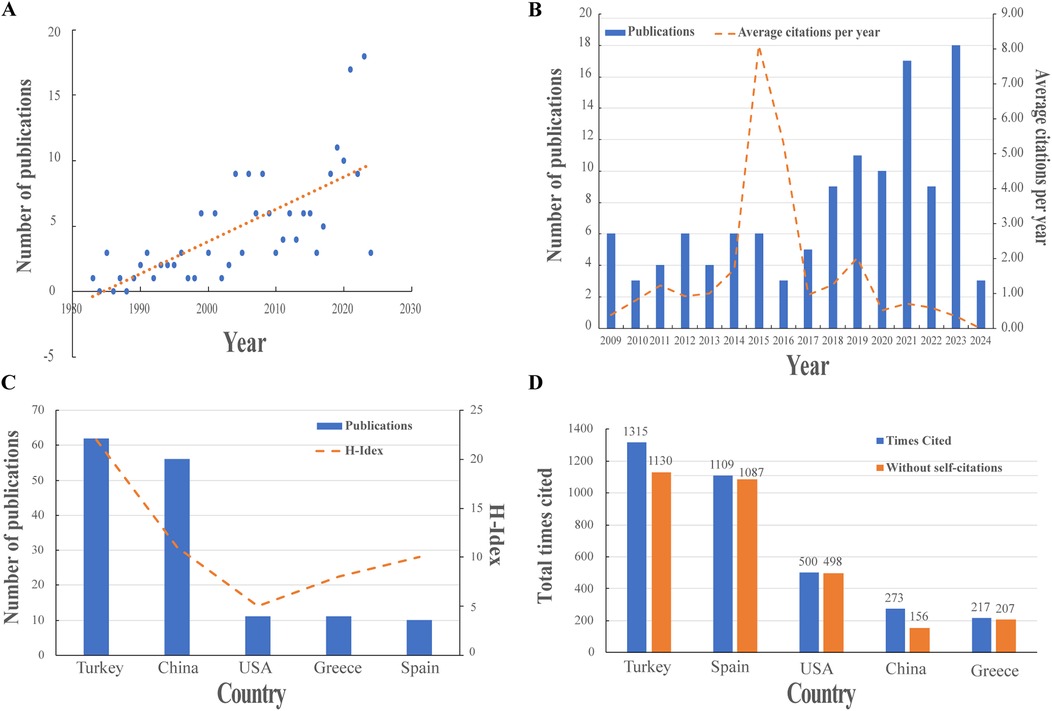
Figure 2. Visualization of publications. (A) The trend of BS publications. (B) The number of BS publications from 2009 to 2024. (C) Top five countries’ number of publications and H-index. (D) The top five countries in terms of citations.
3.2 Countries and institutions
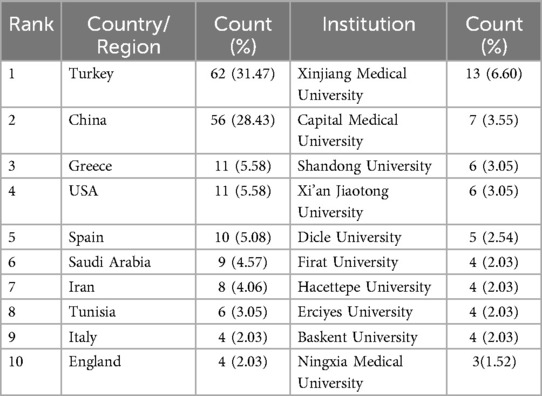
Researchers from 33 countries contributed to BS research, with Turkey leading in the number of publications (62, 31.47%), followed by China (56, 28.43%), the USA (11, 5.58%), Greece (11, 5.58%), and Spain (10, 5.08%) (Figure 2C). Table 1 lists the top 10 countries in terms of publications. Turkey also ranks first in citation count with 1315 citations, followed by Spain (1109) and the USA (500) (Figure 2D), highlighting Turkey's significant influence in this field. Figure 3A presents a map showing the number of publications and cooperation strength between countries, with the USA initiating and participating in the most collaborations, though generally with fewer partnerships involving other countries.
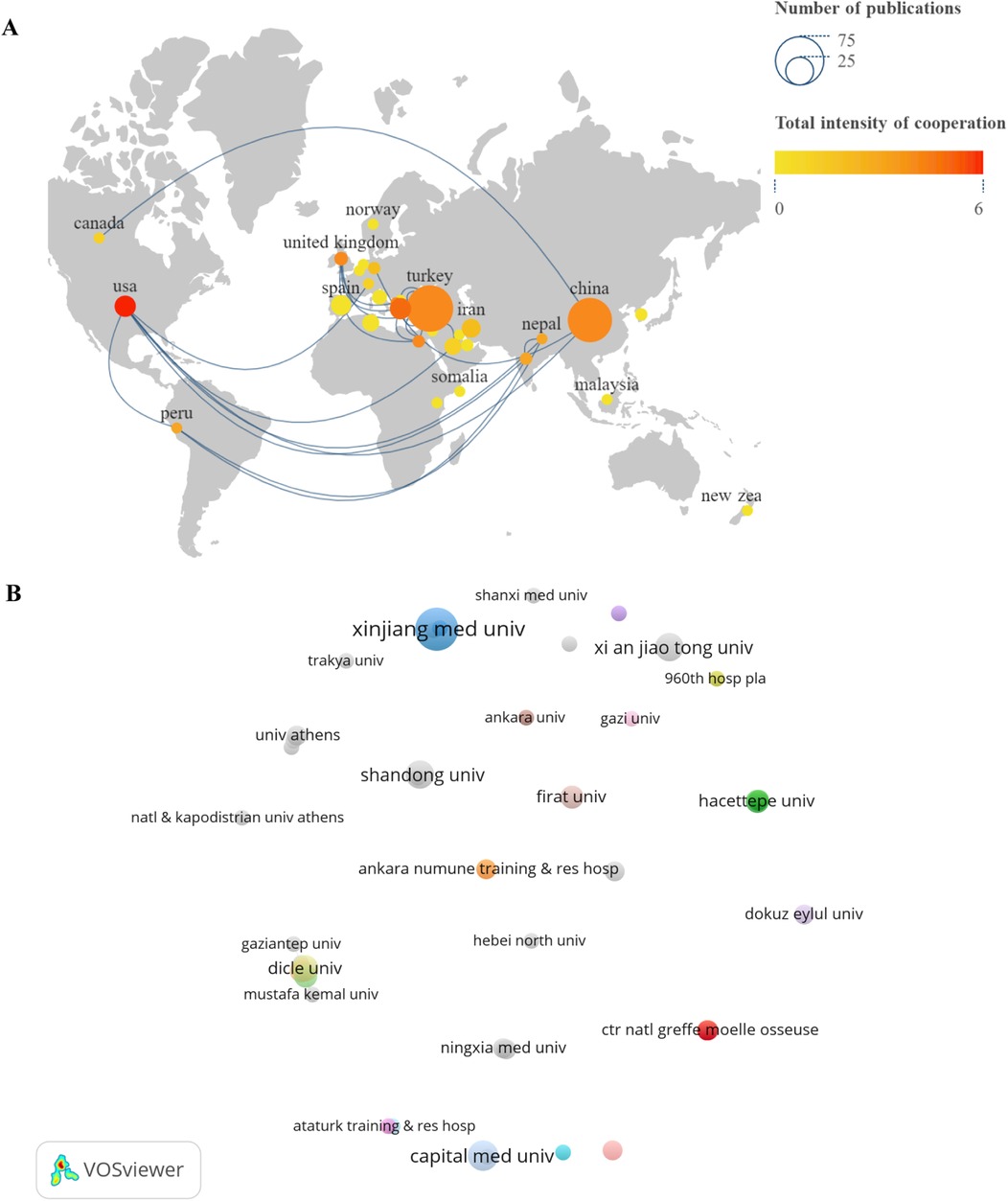
Figure 3. Visualize and analyze active countries and institutions. (A) Country cooperation map. (B) A collaborative network of institutions.
A total of 269 institutions produced the 197 publications. Among the top 10 institutions (Table 1), Xinjiang Medical University published the highest number of articles (13, 6.60%), followed by Capital Medical University (7, 3.55%), Shandong University (6, 3.05%), Xi'an Jiaotong University (6, 3.05%), and Dicle University (5, 2.54%). Figure 3B illustrates the collaboration between these institutions, with a network map highlighting the 50 institutions that published at least two articles. The size of the circles in the map represents the number of publications and the extent of collaboration within the same cluster.
3.3 Authors and journal distribution
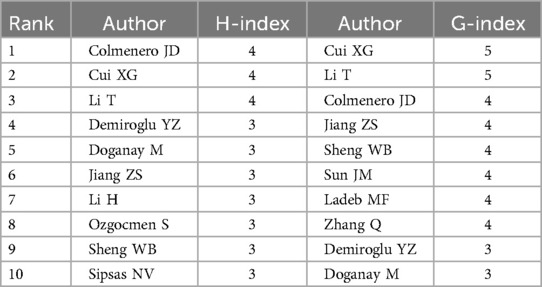
A total of 912 authors contributed to BS research. The top 10 authors, listed in Figure 4A, accounted for 46 publications (23.35%). Sheng WB was the most prolific, with 7 publications (3.55%), followed by Li T (5, 2.54%) and Cui XG (5, 2.54%). Figure 4B shows the publication years of the top 10 authors. Colmenero JD began his research on BS in 1992. Using the H-index and G-index for bibliometric assessment, Cui XG, Li T, and Colmenero JD emerged as the top three scholars in the field (Table 2). Figure 4C displays a network graph of authors with at least two publications, comprising 68 nodes and 13 clusters.
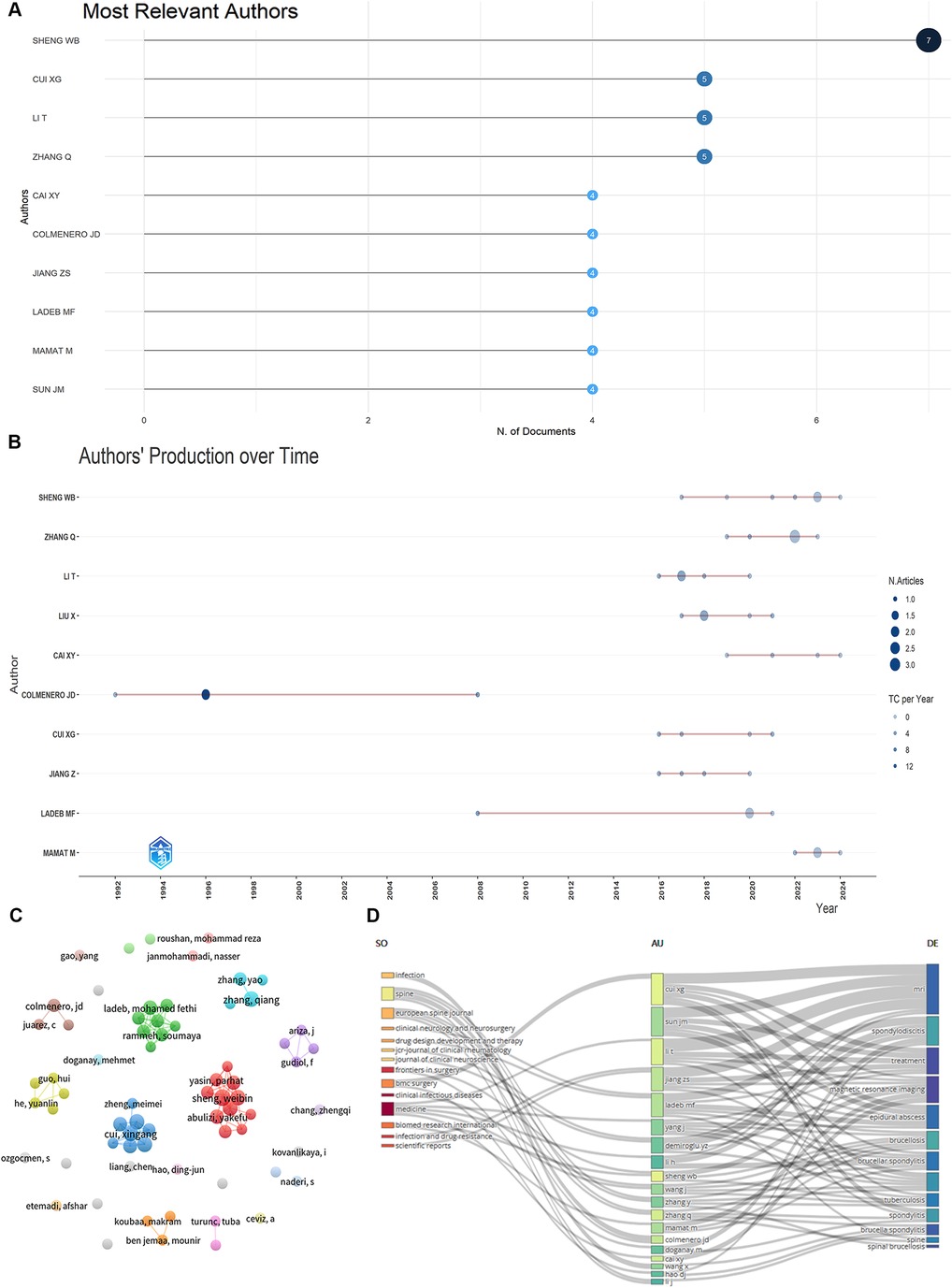
Figure 4. Visualize and analyze active authors. (A) Most relevant authors. (B) Authors’ production over time (The nodes’ size and darkness are proportional to the number of documents the connection produces). (C) The network map of authors. (D) Three-field plot (Middle field: Authors, left field: Sources, right field: Keywords).
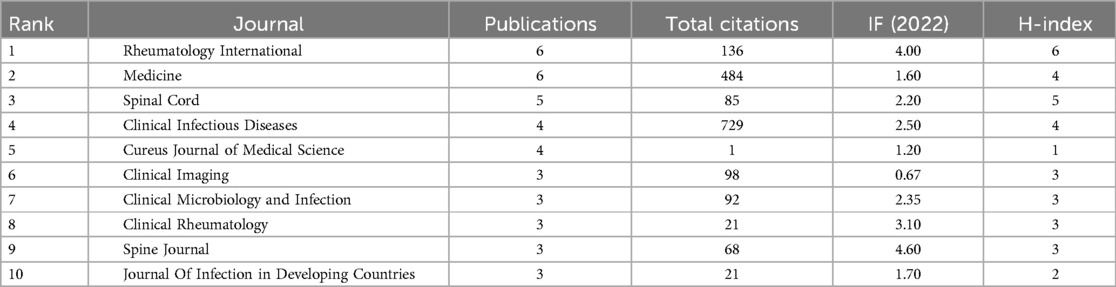
BS literature has been published in 130 academic journals, with the top 10 journals contributing 40 publications (20.30%) (Table 3). Rheumatology International and Medicine lead with 6 publications each (3.05%), followed by Spinal Cord (5, 2.54%) and Clinical Infectious Diseases (4, 2.03%). Figure 4D visualizes the distribution of authors across different topics and journals. The main research keywords among the top 20 authors include magnetic resonance imaging, spondylodiscitis, treatment, epidural abscess, brucellosis, and brucella spondylitis, with their work typically published in journals like Spine, European Spine Journal, and Medicine. A dual-map overlay of journals (Figure 5) shows BS article publications on the left and cited journals on the right, highlighting the topics covered by cited journals.
3.4 Citation of documents and co-citation of references
Based on WoSCC citation data, the top 10 cited papers globally and locally are shown in Figures 6A,B. The top three globally cited articles had 436, 402, and 199 citations, authored by Colmenero JD, Berbari EF, and Solera J, respectively. The top locally cited paper, by Javier Solera, focuses on BS diagnosis and treatment.

Figure 6. Visualize and analyze documents analysis. (A) Most global cited documents. (B) Most local cited documents.
Co-cited references are depicted as nodes in Figure 7A, with the top three in terms of centrality intensity being “Brucellar spondylitis,” “Musculoskeletal involvement of brucellosis in different age groups: a study of 195 cases,” and “A case of brucella spondylodiscitis with extended, multiple-level involvement.” Figure 7B shows the top 20 references with the strongest citation bursts, highlighting their citation burst intensity and duration.
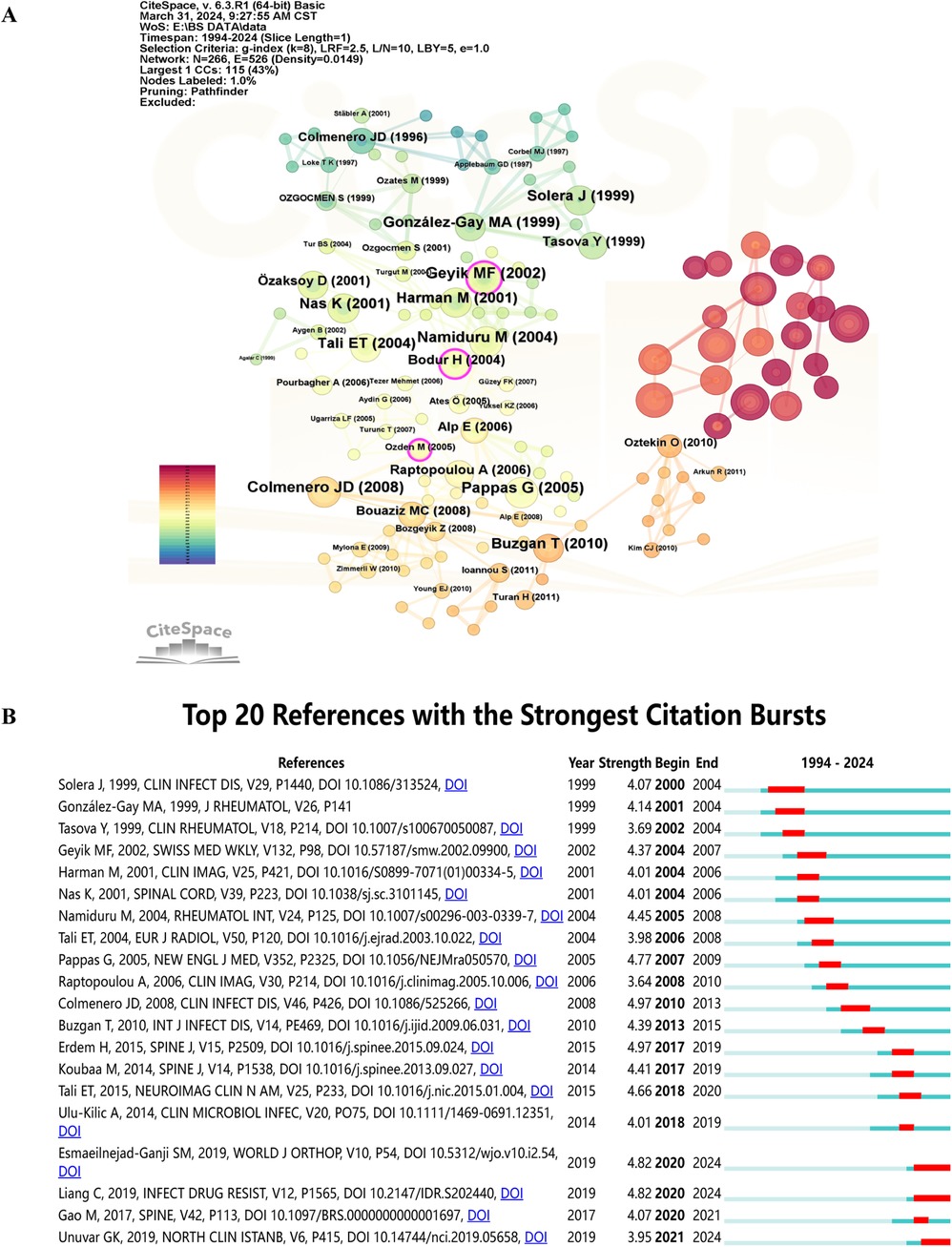
Figure 7. Visualize and analyze references analysis. (A) Cluster analysis of co-cited references. (B) Top 20 references with the strongest citation bursts.
3.5 Keywords and trends
Figure 8A presents a high-frequency network map of keywords generated by CiteSpace. The keywords “spinal brucellosis” and “spondylitis” were predominant, along with frequently used terms like “complications,” “diagnosis,” and “involvement.”
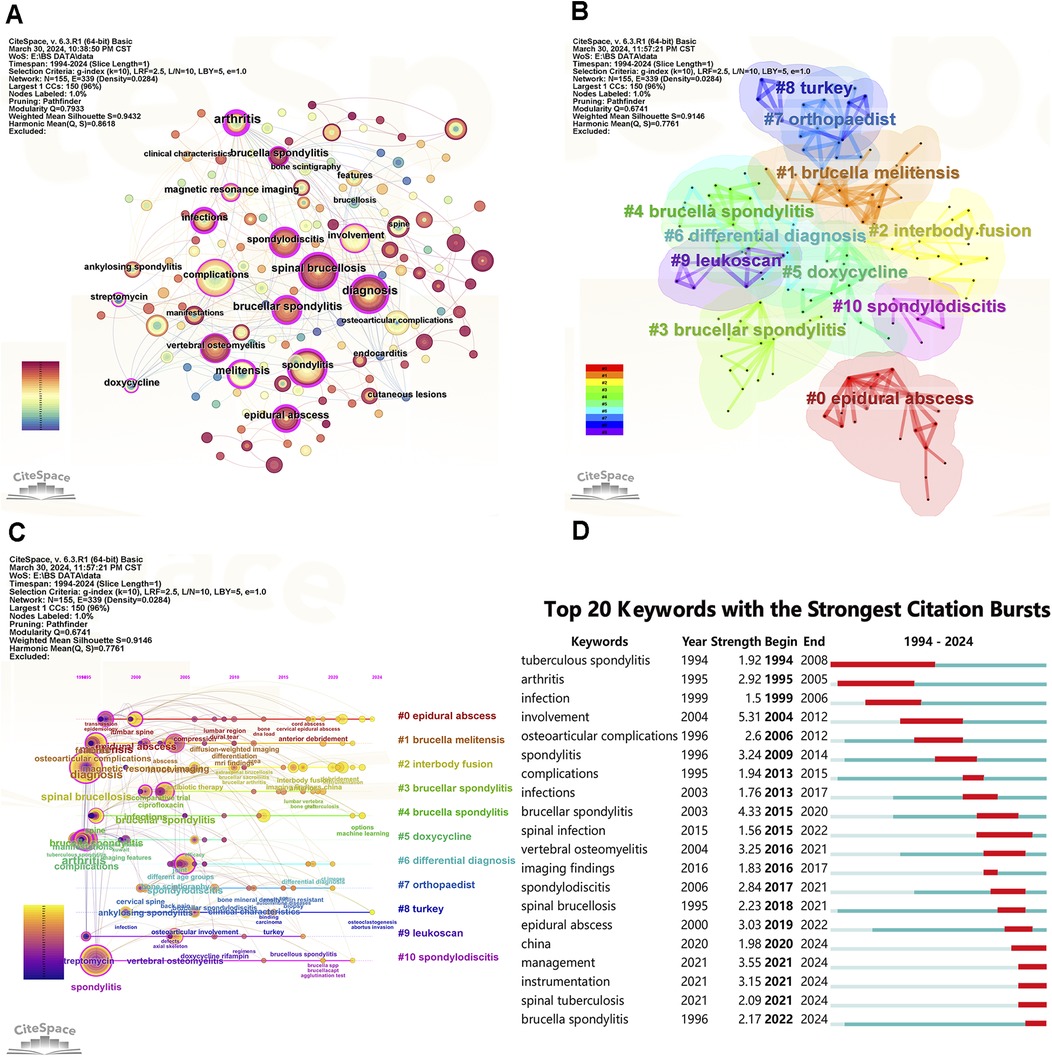
Figure 8. Visualize and analyze keywords analysis. (A) The network map of keywords. (B) Clusters of keywords. (C) Keyword timeline view in BS research. (D) Top 20 keywords with the strongest citation bursts.
Keyword clustering in Figure 8B reveals 11 significant research directions, including “epidural abscess,” “brucella melitensis,” “interbody fusion,” “brucellar spondylitis,” “brucella spondylitis,” “doxycycline,” “differential diagnosis,” “orthopaedist,” “turkey,” “leukoscan,” and “spondylodiscitis.”
The timeline view of keywords in Figure 8C shows that BS research primarily focuses on clinical studies, such as clinical features, diagnosis, imaging presentations, and complications. In recent years, areas like essential research and machine learning have emerged.
Keyword burst detection analysis reveals significant research trends and hotspots by identifying notable changes in keyword occurrence frequency (Figure 8D). Since 2020, the keywords with the strongest citation bursts are “management” (2021–2024), “instrumentation” (2021–2024), “spinal tuberculosis” (2021–2024), and “brucella spondylitis” (2022–2024). Trend Topics in Biblioshiny, shown in Figures 9A,B, further clarify abstract and keyword topic trends. These analyses indicate that “instrumentation,” “management,” and “debridement” have emerged as crucial research frontiers post-2020.
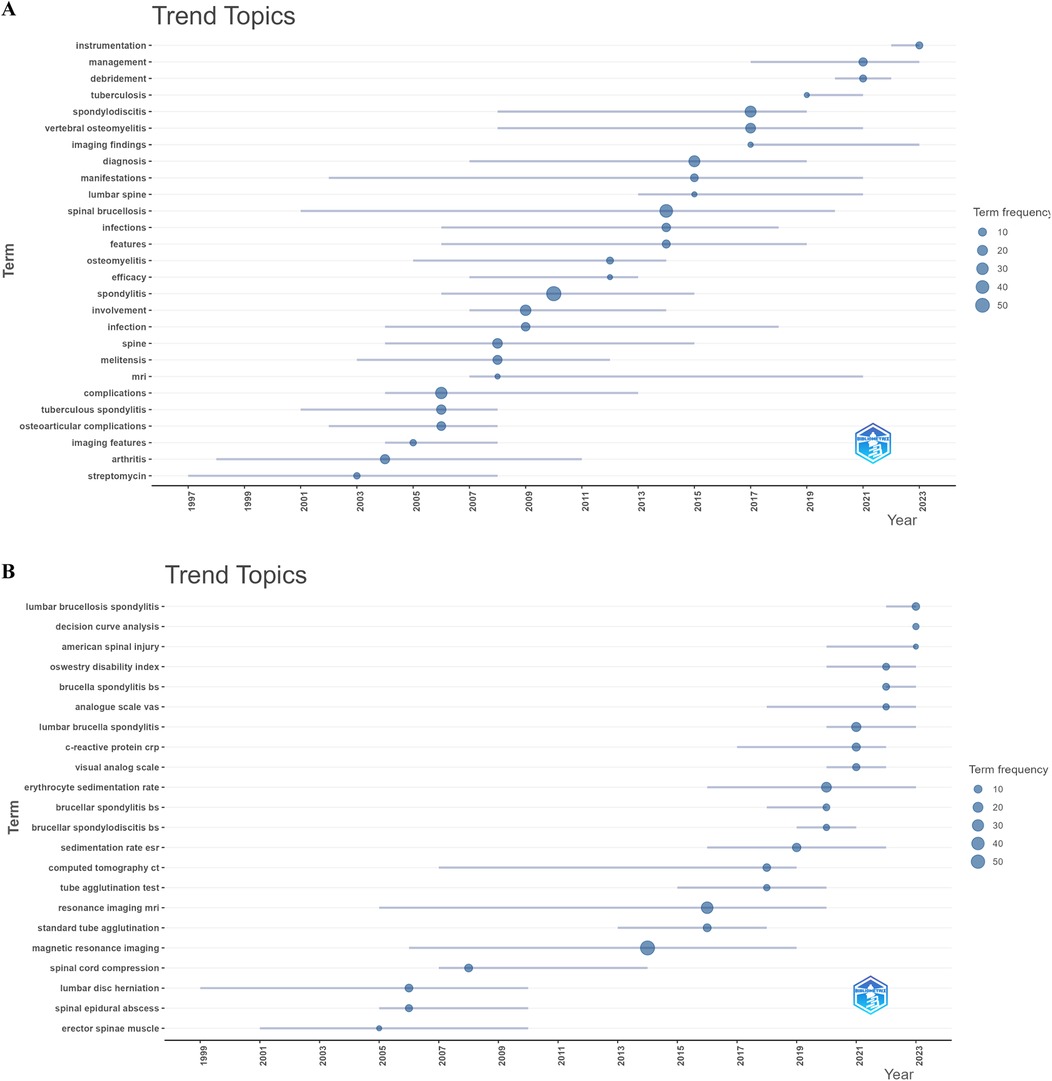
Figure 9. Visualize and analyze trend topics. (A) Abstracts (trigram). (B) Keywords plus (Circle size represents frequency).).
4 Discussion
4.1 Overview of Brucella spondylitis
BS is an acute or chronic spinal infection caused by Brucella species. Key clinical manifestations include fever, persistent back pain, neurological symptoms, and systemic signs. In the early stages of the disease, the clinical presentation of BS closely resembles that of spinal tuberculosis and pyogenic spondylitis, and differentiating these conditions based on laboratory tests, imaging, and pathology is challenging, further complicating the diagnosis (23). Misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis can result in severe complications such as spinal deformities, neurological impairment, or even permanent disability (24). Therefore, timely and accurate diagnosis and intervention are critical to prevent serious sequelae and to alleviate the economic burden on patients and society.
The treatment of BS is typically tailored according to the location and severity of the infection. Combination antibiotic therapy remains the cornerstone of treatment, with common regimens involving prolonged courses of antibiotics such as doxycycline and rifampicin (19). For patients experiencing neurological deficits or spinal instability, surgical intervention is often necessary. Common surgical procedures include debridement, interbody fusion, and mechanical stabilization using internal fixation devices (25). Minimally invasive surgical techniques have gained popularity due to their reduced trauma and faster recovery, making them particularly beneficial for patients with early-stage disease or mild neural compression. However, the choice of surgical approach should be based on the anatomical site of the lesion and the severity of the condition.
In recent years, significant advancements have been made in understanding the pathogenesis and optimizing treatment strategies for BS. This study utilizes a bibliometric analysis of literature from the WoSCC database, spanning from 1980 to 2024, to elucidate the current research landscape, emerging trends, and key research topics in the field. The insights gained from this analysis offer clear directions for future research on BS, facilitating critical advancements in both basic research and clinical management of the disease.
4.2 General information
While the number of publications on BS remains lower than for other spinal infectious diseases like STB (26), there has been a significant increase in BS research from 1980 to 2024. Among the top five countries for BS publications, Turkey, Spain, and Greece, all in the Mediterranean region, contribute significantly, highlighting the higher prevalence of brucellosis in this area (4). Turkey leads with the highest number of papers (62, 31.47%) and total citations (1,315), likely due to a higher HB prevalence (27). China ranks second with 56 publications (28.43%) but has relatively low citations, indicating a need for improved research quality as HB has been re-emerging in China since the 1990s (28). Chinese research on BS began to surge in 2016, with Xinjiang Medical University and scholar Sheng WB making notable contributions. This aligns with earlier reports of high HB incidence in Chinese provinces like Ningxia, Xinjiang, and Inner Mongolia from 2016 to 2018 (29). In contrast, the incidence of HB in the United States dramatically declined during the 2000s (30), and BS cases are now rare (31). However, the U.S. has developed several influential clinical guidelines for diagnosing and treating BS (32). It plays a central role in international cooperation, particularly with Peru, Switzerland, India, Nepal, Iran, and China.
Among the top publishing institutions, five in China and four in Turkey have made significant contributions. However, the cooperation network diagram (Figure 3B) indicates that inter-institutional collaboration needs strengthening. Publications on BS are frequently found in Rheumatology International and Medicine, followed by Spinal Cord and Clinical Infectious Diseases. Influential studies by scholars like Bodur H, Ozden M, and Geyik MF form the foundational knowledge base of BS, providing critical insights into its clinical features and treatment. Citation analysis shows that works by Colmenero JD and Erdem H have a significant impact, with recent studies by Liang C and Esmaeilnejad-Ganji SM continuing to attract attention (33–39).
4.3 Hotspots and frontiers
The high-frequency co-occurrence of specific keywords highlights research hotspots in BS. The top five keywords are “Spinal brucellosis,” “Spondylitis,” “Complications,” “Diagnosis,” and “Involvement.” These terms dominate BS research, indicating key study areas (Figure 8A). “Involvement” and “complications” in BS research refer to osteoarticular involvement, a common brucellosis complication, and complications from BS progression, such as systemic symptoms, localized muscle spasms, radicular pain due to abscess compression, and spinal cord involvement leading to sensory or motor impairment or restricted spinal motion. medication-induced adverse drug reactions and surgical complications are also significant (40, 41). Due to the non-specific nature of early clinical signs, imaging manifestations, slow blood bacterial culture growth, and complex serodiagnosis, BS remains challenging to differentiate from atypical spinal metastases, STB, and other infectious diseases (42). The keyword “diagnostics” highlights the need for breakthroughs in recognizing these hard-to-distinguish diseases and serious complications. Many studies have explored clinical features, laboratory tests, microbiological tests, imaging, and machine learning for diagnostic advancements (8, 11, 19, 43–49).
The keyword “tuberculous spondylitis” had a burst from 1994 to 2008 and re-emerged as “spinal tuberculosis” from 2021 to 2024 (Figure 8D). This resurgence may reflect early diagnostic and therapeutic confusion between BS and STB, with recent advances in imaging and machine learning offering a deeper understanding of both diseases. Abstract analysis using the trigrams algorithm indicates a focus on clinical studies, with fewer basic studies (Figure 9A). Keyword co-occurrence, indicating a sudden increase in keyword citations, measures a keyword's influence and importance, reflecting research frontiers at specific times. Figures 8D, 9B show that “Instrumentation,” “Management,” and “Debridement” are research frontiers post-2020. Beyond bibliometric software predictions, machine learning could emerge as a research frontier after 2023.
Management of BS varies by the affected body part. Treatment options include prolonged antibiotic therapy and surgical intervention. Standard antibiotic regimens for patients without focal disease include doxycycline (100 mg BID) for six weeks combined with an aminoglycoside (gentamicin 5 mg/kg/day OD for 7–10 days or streptomycin 1 g OD for 2–3 weeks) or rifampicin (600–900 mg OD) plus doxycycline (100 mg BID) for six weeks (50, 51). The Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) recommends three months of antimicrobial therapy for most BS patients (32). The two most common regimens are streptomycin for 2–3 weeks with doxycycline for three months or doxycycline and rifampin, both for three months (52). The triple antibiotic regimen—rifampicin (600–900 mg OD for a minimum of 12 weeks), doxycycline (100 mg BID for a minimum of 12 weeks), and streptomycin (1 g OD for 2–3 weeks) or gentamicin (5 mg/kg/d OD for 5–7 days)—is effective and associated with lower recurrence rates (53).
Surgical management is indicated for patients with neurological symptoms due to spinal instability, spinal disruption, or epidural abscesses (54). The rise of “Instrumentation” and “Debridement” keywords indicates increased attention to surgical options. Evidence shows that spinal instrumentation is safe for patients with spinal infections (55). Traditional open surgery is recommended for patients with spinal instability, spinal cord or nerve compression, or progressive kyphosis deformity. Main surgical approaches include anterior debridement, posterior decompression (with or without instruments), and combined anterior and posterior approaches (56, 57).
Liu et al. conducted simple anterior lesion excision with internal fixation in six BS patients with cervical spine instability and cervical epidural abscess, recommending decompression and fusion for patients with combined cervical epidural abscesses (58). Yin et al. performed one-stage anterior internal fixation, debridement, and fusion in 16 lumbar brucella spondylitis (LBS) cases, concluding that this approach is safe and effective for LBS patients with spinal instability and abscess compression without posterior column involvement (59). Further studies indicate that posterior pedicle fixation, debridement, and interbody fusion are superior treatment options (18, 56, 57, 60–62). Wang et al. demonstrated that minimally invasive surgery for LBS involving portal endoscopic decompression, debridement, and interbody fusion with percutaneous screw fixation, is practical, safe, and feasible (63). The optimal surgical approach for BS remains debated and should be based on lesion location, degree of spondylolisthesis and nerve compression, and surgeon skill.
5 Strengths and limitations
To our knowledge, this study is the first systematic bibliometric analysis of BS. Using a comprehensive bibliometric approach, we identified significant trends, influential countries, and leading institutions. Our analysis reveals the current state of BS research, highlighting areas of active collaboration and potential gaps. These findings may provide a solid foundation for future research and policy decisions. We also realize that this study has some limitations. First, the analysis was based solely on data from the WoSCC database, potentially excluding relevant studies from other databases. Second, citation counts may be skewed by outdated studies and publication dates, affecting the perceived impact of specific research. Lastly, despite efforts to standardize the data, there may be inaccuracies in keyword extraction and incomplete content analysis due to the limitations of the analysis software. Nonetheless, these weaknesses are unlikely to affect the overall trends and conclusions of the study significantly.
6 Conclusion
Significant progress has been made in BS research, as evidenced by the increasing volume of publications. Current research predominantly focuses on diagnosis and complications, while management and instrumentation are emerging as potential future research frontiers. Enhancing international collaboration among researchers and institutions will be vital for driving further advancements in the field of BS.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. ZY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft. LF: Data curation, Writing – original draft. DW: Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft. LM: Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. QL: Software, Validation, Writing – original draft. JS: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Key research and development projects in Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region (2022BEG03090).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted without any commercial or financial relationships that could potentially create a conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Qureshi KA, Parvez A, Fahmy NA, Abdel Hady BH, Kumar S, Ganguly A, et al. Brucellosis: epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment-a comprehensive review. Ann Med. (2023) 55:2295398. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2295398
2. Laine CG, Johnson VE, Scott HM, Arenas-Gamboa AM. Global estimate of human brucellosis incidence. Emerg Infect Dis. (2023) 29(9):1789–97. doi: 10.3201/eid2909.230052
3. Pritam M, Kumar R. Pathophysiology, current therapeutic options, vaccine candidates, and drug targets for human brucellosis. Curr Mol Pharmacol. (2024) 17:e130723218680. doi: 10.2174/1874467217666230713093802
4. Franco MP, Mulder M, Gilman RH, Smits HL. Human brucellosis. Lancet Infect Dis. (2007) 7:775–86. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(07)70286-4
5. Zhu L, Zhang C, Liang C, Peng L, Yan H, Liang X, et al. Molecular epidemiological characteristics of osteoarthritis-associated Brucella melitensis in China: evidence from whole-genome sequencing-based analysis. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. (2024) 23:18. doi: 10.1186/s12941-024-00671-w
6. Turgut M, Turgut AT, Koşar U. Spinal brucellosis: Turkish experience based on 452 cases published during the last century. Acta Neurochir. (2006) 148:1033–44. doi: 10.1007/s00701-006-0877-3
7. Tali ET, Koc AM, Oner AY. Spinal brucellosis. Neuroimag Clin N Am. (2015) 25:233–45. doi: 10.1016/j.nic.2015.01.004
8. Yagupsky P, Morata P, Colmenero JD. Laboratory diagnosis of human brucellosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. (2019) 33:e00073–19. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00073-19
9. Jeyaraman N, Jeyaraman M, Nallakumarasamy A, Shanmugapriya K, Adhikari S, Rijal R, et al. A proposed management classification for spinal brucellosis from India. Travel Med Infect Dis. (2023) 54:102614. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2023.102614
10. Kalin Unuvar G. Current therapeutic strategy in osteoarticular brucellosis. North Clin Istanb. (2019) 6:415–20. doi: 10.14744/nci.2019.05658
11. Aktar F, Tekin R, Bektaş MS, Güneş A, Köşker M, Ertuğrul S, et al. Diagnostic role of inflammatory markers in pediatric Brucella arthritis. Ital J Pediatr. (2016) 42:3. doi: 10.1186/s13052-016-0211-5
12. Surucuoglu S, El S, Ural S, Gazi H, Kurutepe S, Taskiran P, et al. Evaluation of real-time PCR method for rapid diagnosis of brucellosis with different clinical manifestations. Pol J Microbiol. (2009) 58:15–9.19469281
13. Di Bonaventura G, Angeletti S, Ianni A, Petitti T, Gherardi G. Microbiological laboratory diagnosis of human brucellosis: an overview. Pathog (Basel Switz). (2021) 10:1623. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10121623
14. Ariza J, Bosilkovski M, Cascio A, Colmenero JD, Corbel MJ, Falagas ME, et al. Perspectives for the treatment of brucellosis in the 21st century: the ioannina recommendations. PLoS Med. (2007) 4:e317. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040317
15. Nas K, Gür A, Kemaloğlu M, Geyik M, Çevik R, Büke Y, et al. Management of spinal brucellosis and outcome of rehabilitation. Spinal Cord. (2001) 39:223–7. doi: 10.1038/sj.sc.3101145
16. Alp E, Doganay M. Current therapeutic strategy in spinal brucellosis. Int J Infect Dis. (2008) 12:573–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2008.03.014
17. Homagk L, Homagk N, Klauss JR, Roehl K, Hofmann GO, Marmelstein D. Spondylodiscitis severity code: scoring system for the classification and treatment of non-specific spondylodiscitis. Eur Spine J. (2016) 25:1012–20. doi: 10.1007/s00586-015-3936-8
18. Na P, Mingzhi Y, Yin X, Chen Y. Surgical management for lumbar Brucella spondylitis. Medicine. (2021) 100:e26076. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026076
19. Spernovasilis N, Karantanas A, Markaki I, Konsoula A, Ntontis Z, Koutserimpas C, et al. Brucella spondylitis: current knowledge and recent advances. J Clin Med. (2024) 13:595. doi: 10.3390/jcm13020595
20. Hassan-Montero Y, De-Moya-Anegón F, Guerrero-Bote VP. SCImago graphica: a new tool for exploring and visually communicating data. Prof inf. (2022) 31:e310502. doi: 10.3145/epi.2022.sep.02
21. Pan X, Yan E, Cui M, Hua W. Examining the usage, citation, and diffusion patterns of bibliometric mapping software: a comparative study of three tools. J Informetr. (2018) 12:481–93. doi: 10.1016/j.joi.2018.03.005
22. Chen C. Citespace II: detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J Am Soc Inf Sci Tec. (2006) 57:359–77. doi: 10.1002/asi.20317
23. Baran AI, Celik M, Arslan Y, Incecik S, Binici I, Toprak M, et al. A comparative perspective on brucellar, pyogenic, and tuberculous spondylodiscitis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2024) 28:2550–7. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202403_35761
24. Morovati S, Bozorgomid A, Mohammadi A, Ahmadi F, Arghand L, Khosravi Shadmani F, et al. Brucellar arthritis and sacroiliitis: an 8-year retrospective comparative analysis of demographic, clinical, and paraclinical features. Ther Adv Infect Dis. (2024) 11:20499361241246937. doi: 10.1177/20499361241246937
25. Liu C, Liu Q, Zheng J, Niu N, Shi J, Yang Z. Selection of treatment strategies for lumbar Brucella spondylitis: a retrospective clinical study. Front Surg. (2024) 11:1365498. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1365498
26. Zhang M, Hu X, Lei S, Jia J, Kang X. Trends and prospects in spinal tuberculosis research: a future-oriented approach. Eur Spine J. (2023) 32:4246–58. doi: 10.1007/s00586-023-07728-y
27. Yumuk Z, O’Callaghan D. Brucellosis in Turkey—an overview. Int J Infect Dis. (2012) 16:e228–235. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2011.12.011
28. Jiang H, O’Callaghan D, Ding J-B. Brucellosis in China: history, progress and challenge. Infect Dis Poverty. (2020) 9:55. doi: 10.1186/s40249-020-00673-8
29. Yang H, Zhang S, Wang T, Zhao C, Zhang X, Hu J, et al. Epidemiological characteristics and spatiotemporal trend analysis of human brucellosis in China, 1950–2018. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2020) 17:2382. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17072382
30. Pappas G, Papadimitriou P, Akritidis N, Christou L, Tsianos EV. The new global map of human brucellosis. Lancet Infect Dis. (2006) 6:91–9. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(06)70382-6
31. Dasari SP, Patel M, Saravanan V, Rybakowicz R, Jha P. A case of diffuse brucellar spondylodiscitis. Cureus. (2021) 13:e17874. doi: 10.7759/cureus.17874
32. Berbari EF, Kanj SS, Kowalski TJ, Darouiche RO, Widmer AF, Schmitt SK, et al. 2015 infectious diseases society of America (IDSA) clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of native vertebral osteomyelitis in adults. Clin Infect Dis. (2015) 61:e26–46. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ482
33. Bodur H, Erbay A, Colpan A, Akinci E. Brucellar spondylitis. Rheumatol Int. (2004) 24:221–6. doi: 10.1007/s00296-003-0350-z
34. Ozden M, Demirdag K, Kalkan A, Ozdemir H, Yuce P. A case of brucella spondylodiscitis with extended, multiple-level involvement. South Med J. (2005) 98:229–31. doi: 10.1097/01.SMJ.0000152755.07937.60
35. Geyik MF, Gür A, Nas K, Cevik R, Saraç J, Dikici B, et al. Musculoskeletal involvement of brucellosis in different age groups: a study of 195 cases. Swiss Med Wkly. (2002) 132:98–104. doi: 10.57187/smw.2002.09900
36. Colmenero JD, Ruiz-Mesa JD, Plata A, Bermúdez P, Martín-Rico P, Queipo-Ortuño MI, et al. Clinical findings, therapeutic approach, and outcome of brucellar vertebral osteomyelitis. Clin Infect Dis. (2008) 46:426–33. doi: 10.1086/525266
37. Erdem H, Elaldi N, Batirel A, Aliyu S, Sengoz G, Pehlivanoglu F, et al. Comparison of brucellar and tuberculous spondylodiscitis patients: results of the multicenter “Backbone-1 study”. Spine J. (2015) 15:2509–17. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2015.09.024
38. Liang C, Wei W, Liang X, De E, Zheng B. Spinal brucellosis in Hulunbuir, China, 2011–2016. Infect Drug Resist. (2019) 12:1565–71. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S202440
39. Esmaeilnejad-Ganji SM, Esmaeilnejad-Ganji SMR. Osteoarticular manifestations of human brucellosis: a review. World J Orthop. (2019) 10:54–62. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v10.i2.54
40. Alp E, Koc RK, Durak AC, Yildiz O, Aygen B, Sumerkan B, et al. Doxycycline plus streptomycin versus ciprofloxacin plus rifampicin in spinal brucellosis [ISRCTN31053647]. BMC Infect Dis. (2006) 6:72. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-6-72
41. Cingöz İD. Role of surgery in Brucella spondylodiscitis: an evaluation of 28 patients. Cureus. (2023) 15:e33542. doi: 10.7759/cureus.33542
42. Abulizi Y, Cai X, Xu T, Xun C, Sheng W, Gao L, et al. Diagnosis and surgical treatment of human brucellar spondylodiscitis. J Vis Exp. (2021) 171:10.3791/61840. doi: 10.3791/61840
43. Yasar K, Pehlivanoglu F, Cirek G, Sengroz G. The evaluation of the clinical, laboratory and the radiological findings of the fifty-five cases diagnosed with tuberculous, Brucellar and pyogenic spondylodiscitis. J Neurosci Rural Pract. (2012) 3:17–20. doi: 10.4103/0976-3147.91925
44. Tu L, Liu X, Gu W, Wang Z, Zhang E, Kahar A, et al. Imaging-assisted diagnosis and characteristics of suspected spinal brucellosis: a retrospective study of 72 cases. Med Sci Monit. (2018) 24:2647–54. doi: 10.12659/MSM.909288
45. Özaksoy D, Yücesoy K, Yücesoy M, Kovanlıkaya İ, Yüce A, Naderi S. Brucellar spondylitis: MRI findings. Eur Spine J. (2001) 10:529–33. doi: 10.1007/s005860100285
46. Yasin P, Yimit Y, Abliz D, Mardan M, Xu T, Yusufu A, et al. MRI-based interpretable radiomics nomogram for discrimination between brucella spondylitis and pyogenic spondylitis. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e23584. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23584
47. Yasin P, Mardan M, Xu T, Cai X, Abulizi Y, Wang T, et al. Development and validation of a diagnostic model for differentiating tuberculous spondylitis from Brucellar spondylitis using machine learning: a retrospective cohort study. Front Surg. (2023) 9:955761. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.955761
48. Yasin P, Mardan M, Abliz D, Xu T, Keyoumu N, Aimaiti A, et al. The potential of a CT-based machine learning radiomics analysis to differentiate brucella and pyogenic spondylitis. J Inflammation Res. (2023) 16:5585–600. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S429593
49. Wang W, Fan Z, Zhen J. MRI radiomics-based evaluation of tuberculous and Brucella spondylitis. J Int Med Res. (2023) 51:3000605231195156. doi: 10.1177/03000605231195156
50. Pappas G, Akritidis N, Bosilkovski M, Tsianos E. Brucellosis. N Engl J Med. (2005) 352:2325–36. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra050570
51. Yousefi-Nooraie R, Mortaz-Hejri S, Mehrani M, Sadeghipour P. Antibiotics for treating human brucellosis. Cochrane Db Syst Rev. (2019) 2019:CD007179. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007179.pub2
52. Saeed K, Esposito S, Ascione T, Bassetti M, Bonnet E, Carnelutti A, et al. Hot topics on vertebral osteomyelitis from the international society of antimicrobial chemotherapy. Int J Antimicrob Agents. (2019) 54:125–33. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2019.06.013
53. Bayindir Y, Sonmez E, Aladag A, Buyukberber N. Comparison of five antimicrobial regimens for the treatment of Brucellar spondylitis: a prospective, randomized study. J Chemother. (2003) 15:466–71. doi: 10.1179/joc.2003.15.5.466
54. Katonis P, Tzermiadianos M, Gikas A, Papagelopoulos P, Hadjipavlou A. Surgical treatment of spinal brucellosis. Clin Orthop Relat R. (2006) 444:66–72. doi: 10.1097/01.blo.0000203455.59393.9a
55. Lee MC, Wang MY, Fessler RG, Liauw J, Kim DH. Instrumentation in patients with spinal infection. Neurosurg Focus. (2004) 17:1. doi: 10.3171/foc.2004.17.6.7
56. Luan H, Liu K, Deng X, Sheng W, Mamat M, Guo H, et al. One-stage posterior surgery combined with anti-brucella therapy in the management of lumbosacral brucellosis spondylitis: a retrospective study. BMC Surg. (2022) 22:394. doi: 10.1186/s12893-022-01847-x
57. Jiang D, Ma L, Wang X, Xu Z, Sun G, Jia R, et al. Comparison of two surgical interventions for lumbar Brucella spondylitis in adults: a retrospective analysis. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:16684. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-43812-5
58. Li-Di L, Song Z, Yang L, Zhen-Shan L, Yuan-Zhe J, Shao-Kun Z. Surgical treatment of Brucellar cervical epidural abscess. World Neurosurg. (2024) 183:e838–45. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2024.01.040
59. Yin XH, Liu ZK, He BR, Hao DJ. One-stage surgical management for lumber brucella spondylitis with anterior debridement, autogenous graft, and instrumentation. Medicine (Baltimore). (2018) 97:e11704. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000011704
60. Li Y, Fei L, Shi J. Efficacy of posterior fixation and bone graft fusion for treatment of lumbar brucellosis spondylitis. Medicine (Baltimore). (2023) 102:e36577. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036577
61. Feng Z, Wang X, Yin X, Han J, Tang W. Analysis of the curative effect of posterior approach on lumbar brucellar spondylitis with abscess through magnetic resonance imaging under improved watershed algorithm. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. (2021) 2021:1. doi: 10.1155/2021/1933706
62. Zhang Y, Zhao C, Chen J, Zhang Q. Beneficial influence of single-stage posterior surgery for the treatment of lumbar Brucella spondylitis combined with spondylolisthesis. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:19459. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-24223-4
Keywords: brucella spondylitis, bibliometric analysis, management, research trends, spinal infections
Citation: Gu Z, Yang Z, Fei L, Wei D, Ma L, Liu Q and Shi J (2025) Quantifying research hotspots and trends in brucella spondylitis: a bibliometric analysis. Front. Surg. 11:1465319. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1465319
Received: 16 July 2024; Accepted: 24 December 2024;
Published: 7 January 2025.
Edited by:
Osvaldo Mazza, Bambino Gesù Children’s Hospital (IRCCS), ItalyReviewed by:
Claudio Bernucci, Humanitas University, ItalyAsma’a Al-Mnayyis, Yarmouk University, Jordan
Copyright: © 2025 Gu, Yang, Fei, Wei, Ma, Liu and Shi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiandang Shi, c2hpX2ppYW5kYW5nQG54bXUuZWR1LmNu
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Zhangui Gu
Zhangui Gu Zongqiang Yang
Zongqiang Yang Le Fei
Le Fei Daihao Wei1,2
Daihao Wei1,2 Long Ma
Long Ma Qiang Liu
Qiang Liu Jiandang Shi
Jiandang Shi