
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Front. Soft Matter , 06 June 2022
Sec. Colloids and Emulsions
Volume 2 - 2022 | https://doi.org/10.3389/frsfm.2022.887610
 Stefan Wellert1
Stefan Wellert1 Ralf Stehle2,3
Ralf Stehle2,3 Samantha Micciulla4
Samantha Micciulla4 Margarethe Dahl1
Margarethe Dahl1 Roland Steitz2
Roland Steitz2 Thomas Hellweg3
Thomas Hellweg3 Olaf Holderer5*
Olaf Holderer5*The commercial availability of natural surfactants, e.g., alkyl-oligoglucosides and the solubilization of plant and food grade oils extends the field of applications for microemulsions. To study potential effects of the confinement on the structure and dynamics inside a microemulsion, neutron reflectometry and neutron spin echo spectroscopy under grazing incidence have been used. Measurements of the contact between a bicontinuous microemulsion and a hydrophilic and hydrophobic surface are compared and show a similar wetting behavior and near surface structuring.
Several applications, such as decontamination and cleaning of sensitive surfaces Mulligan et al. (2001); Giorgi et al. (2010); Vargas-Ruiz et al. (2016), benefit from the use of mild and environmentally compatible microemulsions made from sustainable resources. The contact between a microemulsion and a solid surface is characterized by the wetting properties and the interaction potential at the surface.
This presence of a confining surface results either in surface melting or ordering of the bulk structure of the fluid in the vicinity of the surface. This is a general phenomenon previously observed for a variety of systems like metals, molecular crystals, and also colloidal systems like thermotropic liquid crystals Lang et al. (2000), dispersions Klapp et al. (2008), micellar solutions, Gerstenberg et al. (1998), Gerstenberg et al. (2002); Gerstenberg and Pedersen (2001) and microemulsions Lang (2004). To investigate the inner structure of the adhering fluid, surface sensitive scattering (GISAXS, GISANS, neutron, and X-ray reflectometry), atomic or surface force measurements Fragneto-Cusani (2001); Majewski et al. (2000); Müller-Buschbaum (2013); Petrov et al. (1997) and spectroscopic techniques are frequently used.
In case of surfactant containing fluids previous work investigated the near surface structure of sponge phases Bowers et al. (2004); Hamilton et al. (2002) and bicontinous microemulsions on planar surfaces using scattering and numerical methods Zhou et al. (1992); Lee et al. (1995); Kerscher et al. (2011).
Recently, a combination of grazing incidence geometry with neutron spin echo spectroscopy (GINSES) was established. New experimental routes for the investigation of the dynamics near solid surfaces in the time range between a few ns up to 100 ns are opened. Experiments on shorter time and length scales compared to light scattering are possible and multiple scattering can be avoided. The GINSES technique was used to study the dynamics of CiEj surfactant based bicontinuous microemulsions near solid surfaces as a function of the neutron penetration depth Frielinghaus et al. (2012). Furthermore, the relaxation of thermal fluctuations near solid interfaces was also investigated for other soft matter systems. In addition to phospholipid membranes Jaksch et al. (2019), these also include adsorbed microgels, e.g., Witte et al. (2021).
In the present study, the influence of the chemical nature of the confining surface on the near surface structure and dynamics of a sugar surfactant based microemulsion is addressed. In this quaternary phase system cyclohexane is used as oil phase. Cyclohexane is frequently used as solvent in chemical and industrial applications. Moreover, the majority of experimental work on microemulsions uses nonpolar or polar linear hydrocarbons while studies using nonlinear or aromatic oils in such phase systems are rare Burauer et al. (2000). Previously, the phase behavior of this quaternary system and its bicontinuous bulk structure had been characterized Wellert et al. (2011).
To the best of our knowledge, most experiments addressing the interactions between solid surfaces and microemulsions were carried out either on non-ionic CiEj-type or ionic surfactants. Microemulsions coexisting with excess phases in the SDHS-toluene-saline water system were measured using contact angle measurements to study the solid-liquid-liquid wetting behavior Stammitti-Scarpone and Acosta (2019). Only few results from microemulsions made of bio-inspired surfactants were published. For several reasons, such experiments are crucial. Beside the differences in the composition of the amphiphilic interface and its tuning mechanism also the adsorption properties of these surfactants differ significantly Matsubara et al. (2009); Grosse and Estel (2000). For example, sugar surfactants as n-dodecyl-β-d maltoside adsorb well on hydrophilic surfaces as alumina, hematite, and titania but adsorb less on silica. Ethoxylated surfactants show the opposite behavior (Zhang et al. (2002); Lu et al. (2007). Here, we address the characterization of wetting behavior, inner structure and dynamics near a solid substrate of sugar-surfactant based microemulsions in the vicinity of hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. For this purpose, we combine contact angle measurements and the surface sensitivity of neutron reflectometry and GINSES.
As the amphiphilic components of the microemulsions under investigation Glucopon 220 and the medium chain alcohol pentanol (Sigma-Aldrich) were used. was used. of alkylpolyglucoside C8/10G1.3 (Cognis, Germany) Glucopon 220 is a technical grade aqueous stock solution (43%, aq.) of the alkylpolyglucoside C8/10G1.3 (Cognis, Germany). It was freeze dried to a residual water content less than 1%, determined by Karl-Fischer titration.
The bulk phases of the microemulsions were formed by cyclohexane (Sigma-Aldrich) and D2O (purity ≥98%, isotopic purity ≥99.9%, Euriso-Top, France).
For cleaning the silicon substrates with RCA solution NH4OH at 30%, aq. and H2O2 (Sigma-Aldrich) were used. Water was puriefied with a Millipore Milli-Q system. For the surface scattering experiments, silicon blocks (5 × 8 × 1.5 cm) were purchased from Siliciumbearbeitung Andrea Holm, Tann, Germany. For the functionalization of the silicon substrates, dichlorodimethylsilane (HMDS), anhydrous chloroform, and methanol purchased from Sigma-Aldrich were used.
The bicontinuous microemulsions investigated in this work were prepared according to the composition given by the quaternary phase diagram shown in Supplementary Figure S1 in the supporting material. At a constant cyclohexane to water ratio of α = 0.5 the single phase domain is depicted as a function of the C8/10G1.3 (Glucopon 220) weight fraction γ and the total pentanol weight fraction δ. A more detailled discussion of the phase behavior can be found in the literature Wellert et al. (2011). At a surfactant concentration of γ = 0.124 the bicontinuous region appears. With increasing surfactant content above γ = 0.25 the one phase region passes into the lamellar phase. For the experiments a bicontinuous sample at γ = 0.21, safely far from the phase boundaries, was chosen.
The silicon blocks were cleaned with RCA solution (5:1:1 of water, NH4OH at 29%, H2O2 at 30%) at 72 ◦C for 10 min, then rinsed several times with water and dried in a nitrogen stream.
For functionalization the silicon blocks or wafers were transferred from water to chloroform by subsequent ultrasonication in mixtures of CHCl3/CH3OH = 1:1, 3:1 and pure CHCl3 for 10 min. Afterwards, the silicon substrates were put in an upright position in a desiccator with a residuum of approximately 6 μL) of HMDS in a vacuum desiccator at ambient temperature for 24 h. Then the substrates were transferred from chloroform to methanol by subsequent ultrasonication for 5 min in solvent mixtures of CHCl3: CH3OH from 1:0 → 0:1. The substrates were rinsed several times with water and dried in a nitrogen stream.
RCA 1 cleaned silicon blocks (static water contact angle ≤10 ◦), were used as hydrophilic surface, whereas HMDS-modified silicon blocks (static water contact angle (80 ± 10) ◦) were used as hydrophobic surface. The RCA cleaning protocol was applied just before sealing the substrate inside the solid/liquid cell dedicated to NR and GINSES measurements. In the remainder of this paper, hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces are termed h-Si respectively hp-Si.
The surface tension of the pure MilliQ-type water, cyclohexane, aqueous sugar surfactant solution (c (C8/10G1.3) in H2O of 20 mmol/ml) and the microemulsion were determined with a force tensiometer DCAT 11 (Dataphysics, Germany) applying the du Noüy ring method. Prior to each measurement, the platinum ring was flamed to remove any organic residuals. For each sample, 10 measurements were carried out and averaged at 25◦C.
Contact angles were measured with a drop contour analysis of sessile drops on the planar hydrophilic (h-Si) and hydrophobic (hp-Si) substrates using the OCA20 contact angle goniometer (Dataphysics, Germany). Prior to the measurements, the sample surfaces and the sessile droplets were placed in a quartz sample cell in a saturated vapor phase using the investigated liquids. Measurements of the surface energy components of h-Si and hp-Si substrates are shown in Supplementary Figure S2 and described in the supporting information.
Neutron reflectivity was measured at the neutron reflectometer V6 located at the NL4 neutron guide of the medium flux research reactor at the Helmholtz Zentrum Berlin (Germany). The neutron wavelength of 4.66 Å was selected by a graphite monochromator and filtered by a liquid nitrogen cooled Be filter. The beam profile was 1 × 40 mm which sets the instrument resolution to ΔQ = 2 × 10–3 Å−1. The sample cell consisted of a Teflon trough closed with the single crystal silicon block serving as the solid interface in a thermostated aluminium housing. This cell was placed horizontally in the collimated neutron beam. Both front ends of the cell were covered with cadmium shielding to prevent bulk phase scattering.
Reflectivity curves were measured in θ/2θ-geometry and recorded using a position sensitive detector. The scattering length densitites (SLDs) of the microemulsion components are 6.38 × 10–6 Å−2, 6.72 × 10–6 Å−2, 0.34 × 10–6 Å−2, and −0.32 × 10–6 Å−2 for D2O, deuterated cyclohexane (C6D12), C8/10G1.3 and pentanol (C5H11OH). Additionally, water with a SLD of −0.53 × 10−6Å−2 was used in a D2O/H2O mixture to adjust the bulk phase SLD. To obtain reliable fit results, the critical edge of total reflection of a reflectivity curve has to be within the probed Qz range. To achieve this, the contrast between oil phase and water phase was accordingly tuned, while still maintaining a SLD step towards higher SLD from Si (2.1 × 10–6 Å−2) to the average SLD of the microemulsion. Raw data were normalized and footprint corrected with the software provided by the HZB.
The measured reflectivity curves were analyzed with the fitting routine Parratt 32. This approach determines the neutron reflectivity from planar surfaces using a calculation based on Parratt’s recursion scheme for stratified media. An oscillating SLD profile of the form
was used in this approach. The SLD model assumes alternating layers of oil and water with a domain size Dz perpendicular to the confining substrate. The ordered structure vanishes according to a correlation length ξz. Based on Ginzburg–Landau theory this order parameter profile was obtained by including additional surface fields in the free energy functional Lee et al. (1995); Gompper and Schick (1990); Chernov and Mikheev (1988). Similar theoretical concepts are used for the description of planar amphiphilic membranes adhered to a planar solid substrate Charitat et al. (2008).
All NSE measurements were carried out on the J-NSE instrument at the FRM II neutron source in Garching, Germany Holderer et al. (2008). A neutron wavelength of 8 Å was used. All samples were measured at 25◦ C.
The preferred contrast for NSE is the “film contrast”, where only the interface layer contains hydrogenated materials and oil and water phase are deuterated with as little hydrogen as possible. Interface fluctuations can be best observed in this contrast. The measurements on the bulk sample were done in transmission geometry using standard quartz sample cells. The neutron path length in the Hellma quartz cells was 2 mm. The bulk sample was measured at Q = 0.08 Å−1 for reference.
Neutron spin echo spectroscopy under grazing incidence requires a well defined angle of incidence αi to provide a defined depth of neutron penetration Λ into the sample Frielinghaus et al. (2012); Holderer et al. (2014). Therefore the entrance aperture is reduced to 2 mm. Figure 1 illustrates the GINSES scattering geometry. The neutron beam enters the sample from the silicon block and is reflected at the interface. The critical angle of total reflection
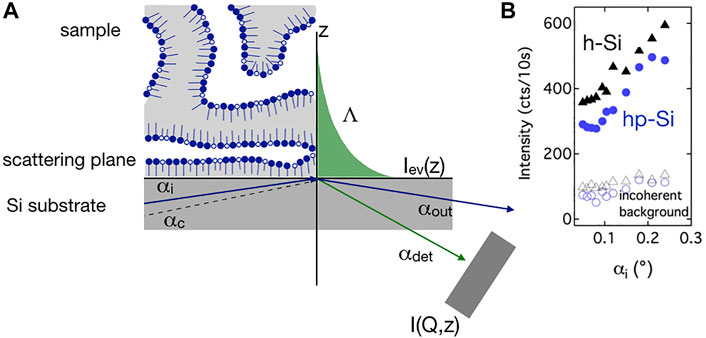
FIGURE 1. (A) Scheme of the grazing incidence neutron spin echo experiment. A neutron beam impings onto a silicon substrate covered with a sample layer under an angle of incidence αi. Below the critical angle of total reflection αc an evanescent wave is generated, penetrates the sample to a depth Λ and scattered from the sample layer. The scattered intensity I (Q,z) is detected at αdet. (B) Number of neutron counts per seconds, arriving at the detector plane, here a function of αi. Mainly, coherent intensity is detected. From this scan αi = 0.11◦ was chosen for the GINSES measurements.
Plot b) in Figure 1 shows the spin coherent and incoherent scattered intensities at Q = 0.08 Å−1 as a function of αi for both surfaces. In the spin-up configuration (all polarization flippers off) no spin manipulation occurs and mainly the coherent contribution is measured. Contrary, the spin-down configuration (180◦-polarization flip at the sample position) is dominated by incoherent scattering. At increasing angle of incidence αi the scattered intensities slightly increase until αc is reached. From the SLDs of deuterated cyclohexane and D2O, constituting the bulk phases of the bicontinuous microemulsion, a value of αc ≈ 0.15◦ was estimated. However, already below αc the coherent scattered intensities from the h-Si and hp-Si interfaces increase steeply. An angle of incidence αi = 0.11◦ close to the onset of this increase was chosen in the grazing incidence measurements. For this combination of αc and chosen αi, a neutron penetration Λ ≈ 70 nm was estimated using Eq. 2. This corresponds to a penetration into the sample over a distance of 4–5 domains. The scattered intensity was measured at Q = 0.08 Å−1.
To study the influence of the chemical composition of a confining substrate on the near surface dynamics of bicontinuous microemulsions, freshly cleaned silicon surfaces (h-Si) and HMDS-modified silicon surfaces (hp-Si) were used as hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces, respectively. For h-Si the measured surface energy was γSE=(69 ± 3) mN/m with
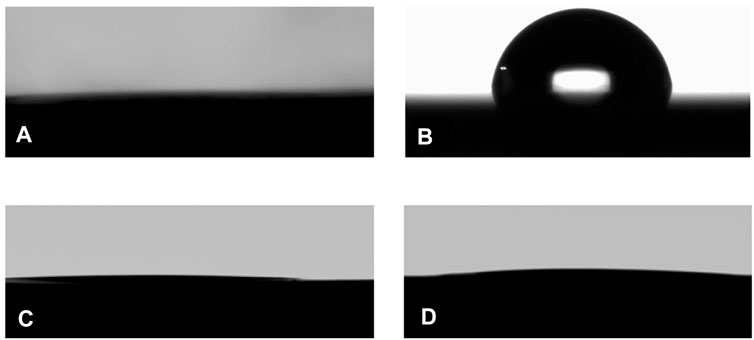
FIGURE 2. Side view images of static contact angles of water and a bicontinuous microemulsion sample at the cleaned bare silicon substrate (h-Si), (A) and (C), and the trimethylsilyl terminated silicon surface (hp-Si), (B) and (D). While water wets the bare silicon almost completely, it only partially wets the hydrophobically modified surface. In contrast to this behavior, the bicontinuous microemulsion wets both types of surface.

TABLE 1. Surface tensions σ at 25◦C and contact angles of the bulk fluid components and the microemulsion at the hydrophilic (h-Si) and hydrophobic (hp-Si) silicon substrates.
The bicontinuous microemulsions show the same wetting behavior at the hp-Si and h-Si surfaces, as discussed in Section 4.1. This raises the question of whether there are differences in the microemulsion structure in the immediate proximity of the solid-liquid interfaces. Figure 3 shows the reflectivity curves of the investigated bicontinuous microemulsion in contact with the hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. The critical edge of total reflection was shifted into the Qz range accessible for the instrument mixing H2O/D2O to tune the SLD of the aqueous phase. The reflectivity curves show a broad but distinct Bragg peak which is slightly more pronounced and shifted to lower Qz in case of hp-Si. The Bragg peak originates from the structuring of the microemulsion at the solid/liquid interface. The reflectivity data can be described by using a oscillating variation of the SLD related to alternating oil and water rich regions of the bicontinuous structure given by Eq. 1.
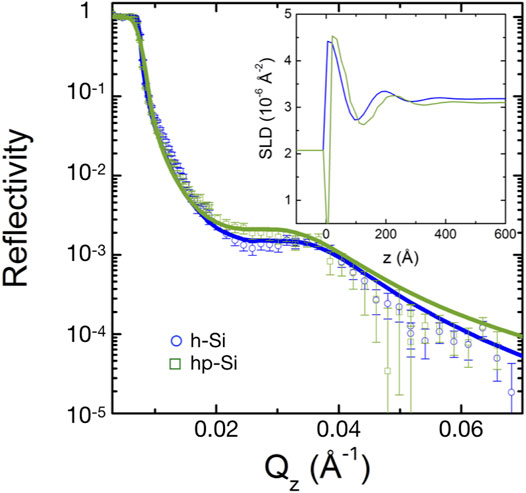
FIGURE 3. Reflectivity curves of a bicontinuous sample in contact with a hydrophilic and hydrophobized silicon surface. The lines are fits to the data calculated from the SLD profile given by 1 and shown in the inset.
The inset in Figure 3 shows the SLD profiles for the bicontinuous microemulsion on both, h-Si and hp-Si substrates. Starting from negative z, the profile corresponds to the silicon substrate, followed by the silicon oxide (thickness of 15 Å) and, in the case of the hp-Si, a negative SLD value for the trimethylsilyl surface layer. A similar oscillation behavior was observable for both measurements. The SLD oscillations decay over two oscillations to the bulk value at z → ∞.
From the interpretation of these results, one can say, that the bicontinous bulk structure remains unchanged up to the immediate vicinity of the h-Si and hp-Si substrate. For the layer in direct contact with the substrate, a very similar SLD profile was obtained, which suggests that the structure of the microemulsion in the vicinity of either a hydrophilic or a hydrophobic surface is governed by the same ordering of the bulk phases. This corresponds well to the results of the contact angle measurements.
However, since these measurements determine the reflectivity without additional information of the phase of the complex reflection coefficient, in the kinematical approxiamation the near surface structure could only be determined to a remaining ambiguity. Hence, no reliable conclusion can be drawn about the existence and composition of an adsorbed surfactant layer at the surface. The “phase problem” in neutron reflectometry, i.e., the loss of phase information due to the measurement of reflected intensities, could be addressed in principal by measuring the same sample in different contrasts by isotope substitution or by introducing a known reference layer at the interface and varying the interfacial contrast by polarization analysis.
However, the use of the oscillating SLD profile given by Eq. 1 enables the estimation of the domain size Dz and the correlation length ξz perpendicular to the confining substrate. These results and the corresponding values of the bulk microemulsion, dTS and ξTS, measured with SANS are compiled in Table 2. The sizes of the oil and water domains from the measurements at the h-Si and the hp-Si surfaces are similar. Compared to the bulk phase the correlation lengths are larger in case of the microemulsions in contact with the h-Si and the hp-Si surfaces. This difference suggests, that a small effect of the planar interface on the inner structure of the microemulsion exists. The SLD profiles of both measurements have a very similar course. This suggests a similar composition of the microemulsions in the near surface region of the two solid liquid interfaces.
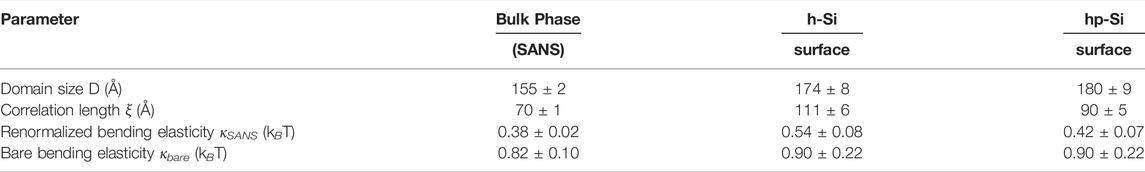
TABLE 2. Summary of domain sizes D, correlation lengths ξ determined from SANS in bulk and neutron reflectometry at the solid-liquid interface. The renormalized and bare bending elasticities κSANS and κbare obtained and calculated from the fit results of the reflectometry and previous SANS measurements. Data of the SANS measurements are taken from reference (Wellert et al. (2011)).
The differences between the results from the bulk measurements and those at the interface must be interpreted with caution. Due to the pronounced maximum in the scattering curve in bulk, the peak position can be found more accurately in the fit than in the analysis of the reflectivity data where the maximum is strongly broadened. It can be deduced from the results that the domain sizes are modified, if at all, only to a small extent by the presence of the interfaces.
In a SANS measurement, the renormalized and the bare bending elasticity constants κSANS and κbare of the surfactant membrane in the microemulsion Gompper et al. (2001); Gompper and Kroll (1998),
and
can be calculated from the structural parameters (domain size dTS and correlation length ξTS) obtained from the Teubner–Strey analysis of the SANS data. lc represents the thickness of the surfactant membrane. The same approach was applied to estimate the values of the renormalized and bare bending elasticity constants from the neutron reflectometry data. From the domain size Dz and correlation length ξz from reflectometry, the bendig rigidity has been calculated with Eq. 3. In particular the comparison between the hydrophilic and hydrophobic interface is possible with this approach, and it also gives a strong hint that the membrane elasticity is not significantly altered by the interface layer, as mentioned above.
The renormalized bending modulus κSANS and the bare bending modulus κbare characterize the elastic properties of the amphiphilic film at different length scales. On the length scale of the oil and water domains, κSANS is the effective bending modulus of the membrane. The bending motion of the membrane is superimposed with thermal fluctuations at smaller scales. Strong thermal fluctuations result in a larger deformation of the membrane Gompper et al. (2001); Pieruschka et al. (1995). The effective thickness of the surfactant membrane between the oil and water domains lc determines the bare bending elasticity κbare Gompper and Kroll (1998); Morse (1994). The values of κSANS are rather small, between 0.54 kBT and 0.42 kBT and support the conclusion of a highly flexible and very soft interface. These values are smaller compared to the results from previous experiments with bicontinuous microemulsions from the ternary phase system decane/H2O/C10E4 at hydrophilic surfaces. For these microemulsions, the formation of a lamellar ordering in the vicinity of the surface was found. The spatial expansion of this ordering away from the substrate extended up to a few domain sizes.
The membrane dynamics as measured with NSE spectroscopy can be described by calculating the intermediate scattering function S (Q,τNSE) of fluctuating membrane patches Zilman and Granek (1996); Mihailescu et al. (2001). Before applying often used approximations for large bending rigidities, the intermediate scattering function is:
This can be approximated by a stretched exponential function which shows typically a rate Γ ∝ Q3 and a stretching exponent β and yields by this information important hints if membrane dynamics is observed and what the direct effects of the interfacial confinement on the membrane dynamics are.
In Figure 4 three plots of normalized intermediate scattering functions (ISF) are shown. The ISF at the top was measured from the bulk sample in transmission geometry measured at a momentum transfer Q = 0.08 Å−1. Below this, two ISF’s were measured under grazing incidence at QGINSES ≈ Qz = 0.08 Å−1. The data from the bicontinuous microemulsion in contact with the hydrophilic (h-Si) sample are given in the middle graph. Plotted in the bottom graph is the ISF of the microemulsion adhered to the trimethylsilyl terminated surface (hp-Si). All three curves show a continuous, smooth decay within the Fourier time range τNSE.
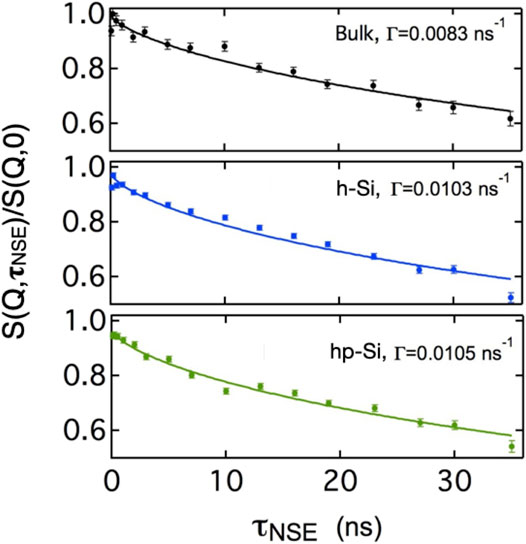
FIGURE 4. Normalized intermediate scattering functions of a bulk contrast microemulsion measured in top: bulk in transmission geometry, middle: in contact with a bare silicon substrate under grazing incidence and bottom: in contact with a hydrophobized silicon substrate under grazing incidence. The solid lines are fits to a stretched single exponential function with stretching exponent 2/3 as suggested by the Zilman-Granek approach for undulating membrane patches (The relative errors of the resulting relaxation rates are 9%, 5%, and 7%.)
As a first step in the analysis, a stretched exponential with a stretching exponent β = 2/3,
was fitted to the data. The decay rate Γ measures the relaxation of thermally excited fluctuations of the surfactant film. The resulting relaxation rates Γ are given in the plots. A comparison shows, that the relaxations close to the surface are slightly faster than in bulk but are the same for both types of surface within the precision of the fit.
A detailed analysis was achieved by applying the full integral evaluation, required for small bending rigidities of the order of 1 kBT, usually observed for bicontinuous microemulsions. In this model, the bending rigidity κ is the only fitting parameter.
Bulk microemulsions have a dispersion relation
This has been measured with GINSES for bicontinuous microemulsions Frielinghaus et al. (2012); Lipfert et al. (2014) and requires a fit with the full Zilman-Granek theory involving the numerical integration of all undulation waves of the membrane patches.
First, the bulk microemulsion has been fitted to determine the required parameters of the fitting function, especially the integration limit for long wavelength undulations, which is four times the correlation length determined from SANS. The bending rigidity has been fixed to κbare = 0.82 kBT to reduce the number of fitting parameters. This corresponds to the renormalized value of
In the next step, the fit of the microemulsion dynamics at both types of interfaces, the parameters were fixed by the bulk microemulsion except the characteristic distance
These results agree with the findings from the neutron reflectometry measurements and suggest minor differences in the coupling of the investigated bicontinuous microemulsion to both surfaces. Probably, the microemulsion bulk structure adheres to both solid interfaces without a distinct extended lamellar transition region. In a previous experiment with ternary bicontinuous microemulsions in the decane/H2O/C10E4 phase system in contact with a hydrophilic silicon substrate (h-Si) faster relaxation was found in the vicinity of the interface. On the other hand, for the contact between clay particle surfaces and bicontinuous microemulsion of the same phase system no difference between bulk and near surface relaxations in the microemulsions were found, which also was attributed to the absence of a lamellar transition region Frielinghaus et al. (2012).
The results of these GINSES experiments indicate a significant influence of the interaction between surfactant molecules and confining surface on the formation of an adjacent lamellar structure. Comparative studies on the adsorption of nonionic ethoxylated surfactants and of sugar surfactants on a variety of substrates revealed significant differences. The adsorption of a surfacatant is influenced by the chemical composition of the adsorbent. Moreover, although in both cases hydrogen bonding mediates the adhesion of the surfactant, at silicate surfaces ethoxylated surfactants were found to adsorb stronger than sugar surfactants Zhang et al. (2006); Zhang and Somasundaran (2006) which might support the formation of lamellar ordering in a CiEj based bicontinuous microemulsion.
\Wetting and neutron scattering measurements were combined to investigate the influence of the chemical composition of a solid surface on the interfacial structure and dynamics of a sugar surfactant-based bicontinuous microemulsion. Due to their environmental compatibility and temperature-independent phase behavior, sugar surfactant-based microemulsions are suitable for applications in temperature-variable environments, for example.
Bicontinuous microemulsions with cyclohexane as the nonpolar bulk phase were found to completely wet both, hydrophilic and hydrophobic surfaces. Investigation of the interfacial structure with neutron reflectometry showed nearly identical structuring at both interfaces in terms of similar sizes of the oil and water domains in the bulk and at the planar surfaces and a similar SLD profile indicating a similar composition of the layers in close proximity to the solid liquid interface. Slightly larger correlation lengths were found at the planar substrates.
Similar results were observed for the interfacial dynamics in these microemulsions. Here, deviations from the relaxation of thermal fluctuations in the bulk phase occur. An influence of the hydrophobicity of the surface or the chemical structure was not observed. In combination with the weak adsorption of the sugar surfactants, the formation of a extended lamellar structure close to the interface is suppressed or strongly hindered.
For technical applications where good wettability of hydrophobic and hydrophilic surfaces is required, such sugar surfactant-based microemulsions thus offer a promising medium, for example for extraction applications.
The raw data supporting the conclusion of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Conception and idea from SW, TH, and ROS. Sample preparation and contact angle measurements SM, MD, SW, SW, RAS, and ROS conducted and analyzed the neutron reflectometry experiments. SW, SM, and OH conducted and analyzed the neutron spin echo experiments. Further data evaluation and writing of the paper by SW and OH.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
We gratefully acknowledge funding by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) (Grants HE 2995/11-1 and WE). This work is based upon experiments performed at the J-NSE instrument operated by JCNS and at the V6 instrument at the Helmholtz-Center Berlin. The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support provided by the MLZ.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frsfm.2022.887610/full#supplementary-material
Bowers, J., Vergara-Gutierrez, M. C., and Webster, J. R. P. (2004). Surface Ordering of Amphiphilic Ionic Liquids. Langmuir 20, 309–312. doi:10.1021/la035495v
Burauer, S., Sottmann, T., and Strey, R. (2000). Nonionic Microemulsions with Cyclic Oils: Oil Penetration, Efficiency and Monomeric Solubility. Tenside Surf. Det. 37, 8–16.
Charitat, T., Lecuyer, S., and Fragneto, G. (2008). Fluctuations and Destabilization of Single Phospholipid Bilayers. Biointerphases 3, FB3. FB3–FB15. doi:10.1116/1.2936938
Chernov, A. A., and Mikheev, L. V. (1988). Wetting of Solid Surfaces by a Structured Simple Liquid: Effect of Fluctuations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 60, 2488–2491. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.60.2488
Fragneto-Cusani, G. (2001). Neutron Reflectivity at the Solid/liquid Interface: Examples of Applications in Biophysics. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 13, 4973–4989. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/13/21/322
Frielinghaus, H., Kerscher, M., Holderer, O., Monkenbusch, M., and Richter, D. (2012). Acceleration of Membrane Dynamics Adjacent to a Wall. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 85, 041408. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.85.041408
Gerstenberg, M. C., Pedersen, J. S., Majewski, J., and Smith, G. S. (2002). Surface Induced Ordering of Triblock Copolymer Micelles at the Solid−Liquid Interface. 1. Experimental Results. Langmuir 18, 4933–4943. doi:10.1021/la0115637
Gerstenberg, M. C., Pedersen, J. S., and Smith, G. S. (1998). Surface Induced Ordering of Micelles at the Solid-Liquid Interface. Phys. Rev. E 58, 8028–8031. doi:10.1103/physreve.58.8028
Gerstenberg, M. C., and Pedersen, J. S. (2001). The Surface-Induced Ordering of Triblock Copolymer Micelles at the Solid−Liquid Interface. 2. Modeling. Langmuir 17, 7040–7046. doi:10.1021/la0106790
Giorgi, R., Baglioni, M., Berti, D., and Baglioni, P. (2010). New Methodologies for the Conservation of Cultural Heritage: Micellar Solutions, Microemulsions, and Hydroxide Nanoparticles. Acc. Chem. Res. 43, 695–704. doi:10.1021/ar900193h
Gompper, G., Endo, H., Mihailescu, M., Allgaier, J., Monkenbusch, M., Richter, D., et al. (2001). Measuring Bending Rigidity and Spatial Renormalization in Bicontinuous Microemulsions. Europhys. Lett. 56, 683–689. doi:10.1209/epl/i2001-00574-3
Gompper, G., and Kroll, D. M. (1998). Membranes with Fluctuating Topology: Monte Carlo Simulations. Phys. Rev. Lett. 81, 2284–2287. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.81.2284
Gompper, G., and Schick, M. (1990). Correlation between Structural and Interfacial Properties of Amphiphilic Systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 65, 1116–1119. doi:10.1103/physrevlett.65.1116
Grosse, I., and Estel, K. (2000). Thin Surfactant Layers at the Solid Interface. Colloid Polym. Sci. 278, 1000–1006. doi:10.1007/s003960000364
Hamilton, W. A., Porcar, L., Butler, P. D., and Warr, G. G. (2002). Local Membrane Ordering of Sponge Phases at a Solid-Solution Interface. J. Chem. Phys. 116, 8533–8546. doi:10.1063/1.1469602
Holderer, O., Monkenbusch, M., Schätzler, R., Kleines, H., Westerhausen, W., and Richter, D. (2008). The JCNS Neutron Spin-Echo Spectrometer J-NSE at the FRM II. Meas. Sci. Technol. doi:10.1088/0957-0233/19/3/034022
Holderer, O., Frielinghaus, H., Monkenbusch, M., Klostermann, M., Sottmann, T., and Richter, D. (2013). Experimental Determination of Bending Rigidity and Saddle Splay Modulus in Bicontinuous Microemulsions. Soft Matter 9, 2308–2313. doi:10.1039/c2sm27449c
Holderer, O., Frielinghaus, H., Wellert, S., Lipfert, F., Monkenbusch, M., von Klitzing, R., et al. (2014). Grazing Incidence Neutron Spin Echo Spectroscopy: Instrumentation Aspects and Scientific Opportunities. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 528, 012025. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/528/1/012025
Jaksch, S., Koutsioubas, A., Mattauch, S., Holderer, O., and Frielinghaus, H. (2019). Long-range Excitations in Phospholipid Membranes. Chem. Phys. Lipids 225, 104788. doi:10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2019.104788
Kerscher, M., Busch, P., Mattauch, S., Frielinghaus, H., Richter, D., Belushkin, M., et al. (2011). Near-surface Structure of a Bicontinuous Microemulsion with a Transition Region. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 83, 030401. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.83.030401
Klapp, S. H., Zeng, Y., Qu, D., and von Klitzing, R. (2008). Surviving Structure in Colloidal Suspensions Squeezed from 3d to 2d. Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 (14), 118303118303. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.118303
Kraus, M., and Seifert, U. (1994). Relaxation Modes of an Adhering Bilayer Membrane. J. Phys. II Fr. 4, 1117–1134. doi:10.1051/jp2:1994191
Lang, P., Steitz, R., and Braun, C. (2000). Surface Effects of Lyotropic Liquid Crystalline Phases of Nonionic Surfactants. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects 163, 91–101. doi:10.1016/s0927-7757(99)00434-3
Lang, P. (2004). Surface Induced Ordering Effects in Soft Condensed Matter Systems. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 16, R699–R720. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/16/23/r02
Lee, D. D., Chen, S. H., Majkrzak, C. F., and Satija, S. K. (1995). Bulk and Surface Correlations in a Microemulsion. Phys. Rev. E 52, R29–R32. doi:10.1103/physreve.52.r29
Lipfert, F., Frielinghaus, H., Holderer, O., Mattauch, S., Monkenbusch, M., Arend, N., et al. (2014). Polymer Enrichment Decelerates Surfactant Membranes Near Interfaces. Phys. Rev. E Stat. Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 89, 042303. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.89.042303
Lu, S., Bian, Y., Zhang, L., and Somasundaran, P. (2007). pH Dependence of Adsorption of N-Dodecyl-β-D-Maltoside on Solids. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 316, 310–316. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2007.08.063
Majewski, J., Kuhl, T. L., Wong, J. Y., and Smith, G. S. (2000). X-ray and Neutron Surface Scattering for Studying Lipid/polymer Assemblies at the Air-Liquid and Solid-Liquid Interfaces. Rev. Mol. Biotechnol. 74, 207–231. doi:10.1016/s1389-0352(00)00011-8
Matsubara, H., Takumi, H., Takamatsu, T., Takiue, T., and Aratono, M. (2009). Surface Adsorption and Micelle Formation of Aqueous Solutions of Polyethyleneglycol and Sugar Surfactants. Colloid Polym. Sci. 287, 1077–1082. doi:10.1007/s00396-009-2066-4
Mihailescu, M., Monkenbusch, M., Endo, H., Allgaier, J., Gompper, G., Stellbrink, J., et al. (2001). Dynamics of Bicontinuous Microemulsion Phases with and without Amphiphilic Block-Copolymers. J. Chem. Phys. 115, 9563–9577. doi:10.1063/1.1413509
Morse, D. C. (1994). Topological Instabilities and Phase Behavior of Fluid Membranes. Phys. Rev. E 50, R2423–R2426. doi:10.1103/physreve.50.r2423
Müller-Buschbaum, P. (2013). Grazing Incidence Small-Angle Neutron Scattering: Challenges and Possibilities. Polym. J. 45, 34–42. doi:10.1038/pj.2012.190
Mulligan, C. N., Yong, R. N., and Gibbs, B. F. (2001). Surfactant-enhanced Remediation of Contaminated Soil: a Review. Eng. Geol. 60, 371–380. doi:10.1016/s0013-7952(00)00117-4
Petrov, P., Olsson, U., and Wennerström, H. (1997). Surface Forces in Bicontinuous Microemulsions: Water Capillary Condensation and Lamellae Formation. Langmuir 13, 3331–3337. doi:10.1021/la962085g
Pieruschka, P., Safran, S. A., and Marc̆elja, S. T. (1995). Comment on ''Fluctuating Interfaces in Microemulsion and Sponge Phases''. Phys. Rev. E 52, 1245–1247. doi:10.1103/physreve.52.1245
Seifert, U. (1994). Dynamics of a Bound Membrane. Phys. Rev. E 49, 3124–3127. doi:10.1103/physreve.49.3124
Stammitti-Scarpone, A., and Acosta, E. J. (2019). Solid-liquid-liquid Wettability of Surfactant-Oil-Water Systems and its Prediction Around the Phase Inversion Point. Langmuir 35, 4305–4318. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b03907
Vargas-Ruiz, S., Soltwedel, O., Micciulla, S., Sreij, R., Feoktystov, A., von Klitzing, R., et al. (2016). Sugar Surfactant Based Microemulsions at Solid Surfaces: Influence of the Oil Type and Surface Polarity. Langmuir 32, 11928–11938. doi:10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b03441
Wellert, S., Tiersch, B., Koetz, J., Richardt, A., Lapp, A., Holderer, O., et al. (2011). The Dfpase from loligo Vulgaris in Sugar Surfactant-Based Bicontinuous Microemulsions: Structure, Dynamics, and Enzyme Activity. Eur. Biophys. J. 40, 761–774. doi:10.1007/s00249-011-0689-0
Witte, J., Kyrey, T., Lutzki, J., Dahl, A. M., Kühnhammer, M., Klitzing, R. v., et al. (2021). Looking inside Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide) Microgels: Nanomechanics and Dynamics at Solid-Liquid Interfaces. ACS Appl. Polym. Mat. 3, 976–985. doi:10.1021/acsapm.0c01265
Zhang, L., Somasundaran, P., Mielczarski, J., and Mielczarski, E. (2002). Adsorption Mechanism of N-Dodecyl-β-D-Maltoside on Alumina. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 256, 16–22. doi:10.1006/jcis.2001.7858
Zhang, L., Zhang, R., and Somasundaran, P. (2006). Adsorption of Mixtures of Nonionic Sugar-Based Surfactants with Other Surfactants at Solid/liquid Interfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 302, 25–31. doi:10.1016/j.jcis.2006.06.068
Zhang, R., and Somasundaran, P. (2006). Advances in Adsorption of Surfactants and Their Mixtures at Solid/solution Interfaces. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 123-126, 213–229. doi:10.1016/j.cis.2006.07.004
Zhou, X.-L., Lee, L.-T., Chen, S.-H., and Strey, R. (1992). Observation of Surface-Induced Layering in Bicontinuous Microemulsions. Phys. Rev. A 46, 6479–6489. doi:10.1103/physreva.46.6479
Keywords: microemulsion, bending elasticity, neutron scattering, neutron spin echo, neutron reflectomery
Citation: Wellert S, Stehle R, Micciulla S, Dahl M, Steitz R, Hellweg T and Holderer O (2022) A Combined Wetting and Scattering Study of the Near Surface Ordering in Sugar Surfactant Based Bicontinuous Microemulsions at Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Surfaces. Front. Soft. Matter 2:887610. doi: 10.3389/frsfm.2022.887610
Received: 01 March 2022; Accepted: 22 April 2022;
Published: 06 June 2022.
Edited by:
Jordi Ignés-Mullol, University of Barcelona, SpainReviewed by:
Edgar Acosta, University of Toronto, CanadaCopyright © 2022 Wellert, Stehle, Micciulla, Dahl, Steitz, Hellweg and Holderer. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Olaf Holderer, by5ob2xkZXJlckBmei1qdWVsaWNoLmRl
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.