- 1Sleep Research Laboratory, John D. Dingell Veterans Affairs Medical Center, Detroit, MI, United States
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Wayne State University-School of Medicine, Detroit, MI, United States
- 3Department of Kinesiology and Health Science, York University, Toronto, ON, Canada
- 4Population Health Sciences, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States
- 5Department of Medical Education, Ascension Providence Hospital, Southfield, MI, United States
A corrigendum on
Role of automated detection of respiratory related heart rate changes in the diagnosis of sleep disordered breathing
by Maresh, S., Athikumar, A. K., Ahmed, N., Chandu, S., Prowting, J. L., Tumah, L., Najjar, A. A., Khan, H., Sankari, M., Lasisi, O., Ravelo, L. A., Peppard, P. E., Badr, M. S., and Sankari, A. (2023). Front. Sleep 2:1162652. doi: 10.3389/frsle.2023.1162652
In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Figure 4 as published. The corrected legend appears below.
Figure 4. Bland Altman Plots comparing (A) respiratory-related HRAI to AHI [ICC = 0.64 (0.61, 0.67)]; (B) respiratory-related RRDI to AHI [ICC = 0.38 (0.33, 0.42)]; (C) total HRAI to NPSG AHI [ICC = 0.22 (0.17, 0.27)]; and (D) total RRDI to NSPG AHI [ICC = 0.22 (0.16, 0.26)] in the discovery dataset. HRAI, heart rate acceleration index; RRDI, RR interval dips index; AHI, apnea–hypopnea index; NPSG, nocturnal polysomnography.
In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Figure 5 as published. The corrected legend appears below.
Figure 5. Bland Altman Plots comparing (A) respiratory-related HRAI to AHI [ICC =0.51 (0.45, 0.56)]; (B) respiratory-related RRDI to AHI [ICC = 0.18 (0.10, 0.25)]; (C) total HRAI to NPSG AHI [ICC = 0.19 (0.12, 0.26)]; and (D) total RRDI to NSPG AHI [ICC = 0.08 (0.003, 0.16)] in the validation dataset. HRAI, heart rate acceleration index; RRDI, RR interval dips index; AHI, apnea–hypopnea index; NPSG, nocturnal polysomnography.
In the published article, there was an error in the legend for Figure 6 as published. The corrected legend appears below.
Figure 6. Receiver operating characteristic curves for (A) respiratory-related HRAI to AHI; (B) respiratory-related RRDI to AHI; (C) total HRAI to NPSG AHI; and (D) total RRDI to NSPG AHI in the discovery dataset. HRAI, heart rate acceleration index; RRDI, RR interval dips index; AHI, apnea-hypopnea index; NPSG, nocturnal polysomnography”.
In Figure 7 the graphs were incorrectly ROC curves plotted. Below are the corrected ROC curves.
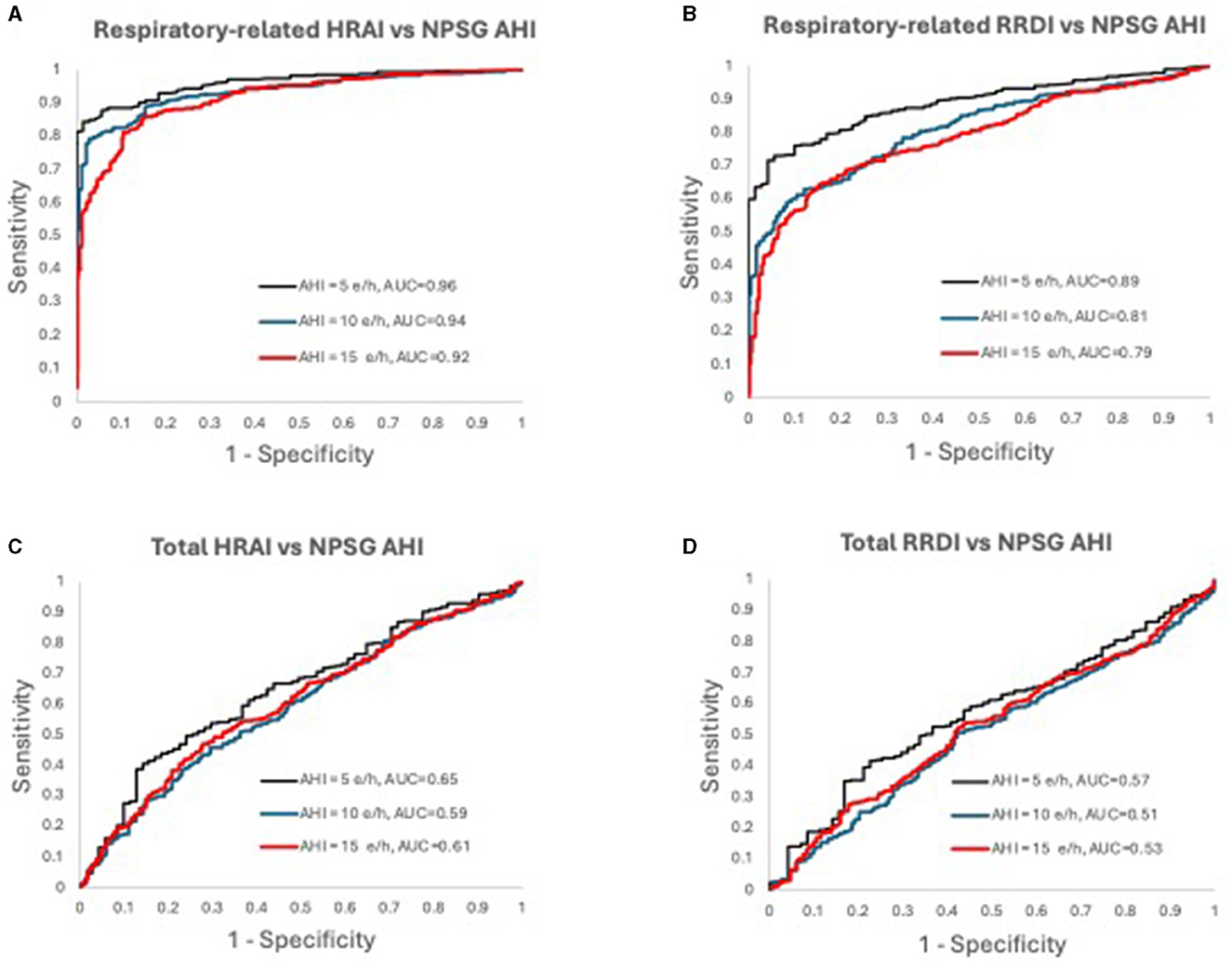
Figure 7. Receiver operating characteristic curves for (A) respiratory-related HRAI to AHI; (B) respiratory-related RRDI to AHI; (C) total HRAI to NPSG AHI; and (D) total RRDI to NSPG AHI in the validation dataset. HRAI, heart rate acceleration index; RRDI, RR interval dips index; AHI, apnea-hypopnea index; NPSG, nocturnal polysomnography.
The estimated sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and NPV were listed incorrectly. The corrected Table 3 and its caption appear below.
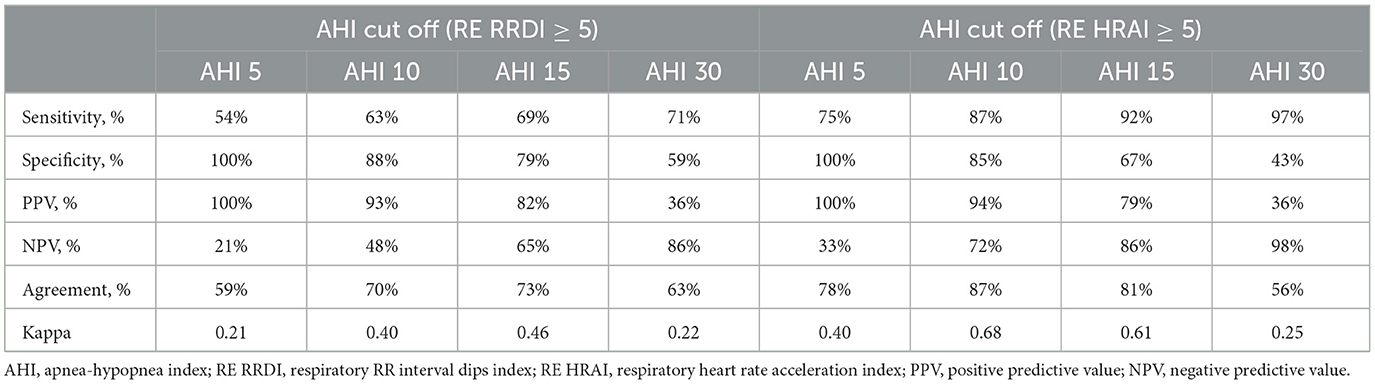
Table 3. Diagnostic testing for RE RRDI and HRAI as a metric of estimated AHI ≥ 5 for the validation dataset.
In the published article, there was an error in the Supplementary section for some sensitivity and specificity values. The Supplementary Tables S1, S2 has been updated in the original article.
In the published article, there was an error. Figure 4 and Table 2 are erroneously stated as correlating with AHI.
A correction has been made to Results, Agreement with AHI, paragraph one. This sentence previously stated:
“As shown in Table 2 and Figure 4, the estimated AHIs using respiratory-related HRAI and respiratory-related RRDI correlated significantly with AHI (p < 0.05).”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“As shown in Table 2, the estimated AHIs using respiratory-related HRAI and respiratory-related RRDI correlated significantly with AHI (p < 0.05) and as shown in Figure 4 there is significant agreement between RE HRAI, RE RRDI, and AHI.”
In the published article, there was an error. A citation for Figure 5 should be changed to Figure 4.
A correction has been made to Results, Agreement with AHI, paragraph two. This sentence previously stated:
“The Bland-Altman plots in Figure 5 compare the NPSG AHI of the participants with various heart rate-based AHI estimations (respiratory-related HRAI, respiratory-related RRDI, total HRAI, and total RRDI) in the discovery dataset.”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“The Bland-Altman plots in Figure 4 compare the NPSG AHI of the participants with various heart rate-based AHI estimations (respiratory-related HRAI, respiratory-related RRDI, total HRAI, and total RRDI) in the discovery dataset.”
In the published article, there was an error. A citation for Figure 6 should be changed to Figure 5.
A correction has been made to Results, Agreement with AHI, paragraph three. This sentence previously stated:
“The Bland-Altman plots in Figure 6 shows a similar relationship in the validation dataset for the respiratory-related measures and AHI (average RE HRAI–NPSG = −11; CI: −34–11 vs. average RE RRDI–NPSG = −14; CI: −44–15).”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“The Bland-Altman plots in Figure 5 shows a similar relationship in the validation dataset for the respiratory-related measures and AHI (average RE HRAI–NPSG = −11; CI: −34–11 vs. average RE RRDI–NPSG = −14; CI: −44–15).”
In the published article, there was an error in the levels of sensitivity and specificity.
A correction has been made to Results, Diagnostic performance, paragraph one. These sentences previously stated:
“In addition, a high level of sensitivity was found with respiratory-related HRAI (≥5 events/h) with traditional AHI cutoffs 5, 10, 15, and 30 events/h, respectively (100, 94, 79, and 36%, respectively). RE RRDI (≥5 events/h) showed less modest agreement (59, 70, 73, and 63%) for traditional AHI cutoffs 5, 10, 15, and 30 events/h, respectively, and lower specificity compared to HRAI, especially at a high AHI cutoff of 15 events/hour.”
The corrected sentences appear below:
“In addition, a high level of sensitivity was found with respiratory-related HRAI (≥5 events/h) with traditional AHI cutoffs, 5, 10, 15, and 30 events/h, respectively (75, 87, 92, 97%, respectively). RE RRDI (≥5 events/h) showed less modest agreement (59, 70, 73, 63%) for traditional AHI cutoffs 5, 10, 15, and 30 events/h, respectively, and higher specificity compared to HRAI.”
In the published article, there was an error. A citation for Figure 6 was excluded.
A correction has been made to Results, Diagnostic performance, third paragraph. This sentence previously stated:
“Figure 7 displays the receiver operating characteristic curves for respiratory-related HRAI/RRDI and total HRAI/RRDI with three AHI cutoffs for the diagnosis of SDB in validation datasets, respectively.”
The corrected sentence appears below:
“Figures 6, 7 display the receiver operating characteristic curves for respiratory-related HRAI/RRDI and total HRAI/RRDI with three AHI cutoffs for the diagnosis of SDB in the discovery and validation datasets, respectively.”
The authors apologize for these errors and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Keywords: sleep, heart rate, R-R interval (RRI), pulse oximeter, ECG, polysomnography, sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease
Citation: Maresh S, Athikumar AK, Ahmed N, Chandu S, Prowting JL, Tumah L, Najjar AA, Khan H, Sankari M, Lasisi O, Ravelo LA, Peppard PE, Badr MS and Sankari A (2024) Corrigendum: Role of automated detection of respiratory related heart rate changes in the diagnosis of sleep disordered breathing. Front. Sleep 3:1452220. doi: 10.3389/frsle.2024.1452220
Received: 20 June 2024; Accepted: 28 June 2024;
Published: 29 July 2024.
Edited and reviewed by: Anna Di Sessa, University of Campania Luigi Vanvitelli, Italy
Copyright © 2024 Maresh, Athikumar, Ahmed, Chandu, Prowting, Tumah, Najjar, Khan, Sankari, Lasisi, Ravelo, Peppard, Badr and Sankari. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Abdulghani Sankari, YXNhbmthcmlAd2F5bmUuZWR1
 Scott Maresh1,2
Scott Maresh1,2 Joel L. Prowting
Joel L. Prowting Muna Sankari
Muna Sankari M. Safwan Badr
M. Safwan Badr Abdulghani Sankari
Abdulghani Sankari