- National Pipeline Network Group Zhejiang Natural Gas Pipeline Network Co. Ltd., Hangzhou, China
Ferromagnetic materials are extensively utilized in industrial settings where the early detection and repair of defects is paramount for ensuring industrial safety. During the enhanced magnetic memory detection of micro-defects, many interference signals appear in the detection signal, which makes it difficult to accurately extract the characteristics of the micro-defect signals, significantly affecting detection effectiveness. When improved complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise (ICEEMDAN) is employed independently for signal denoising, the noise and feature signals of the transition components are retained or removed. When variational mode decomposition (VMD) is employed independently for signal denoising, the denoising effect is restricted because of the difficulty in determining the penalty factor
1 Introduction
Ferromagnetic materials are essential raw materials for modern industry and are widely used in various load-bearing structures, such as pipelines, pressure vessels, and bridges. Due to environmental and load factors, ferromagnetic components inevitably develop a variety of defects that can adversely affect their performance and safety, potentially leading to serious failures (Shi et al., 2020). Metal magnetic memory, as a nascent non-destructive testing method, fulfills the objective of identifying defects or stress concentrations in ferromagnetic materials by detecting changes in the magnetic field of the object under test due to defects or stress concentrations. Nevertheless, it possesses the disadvantage of weak changes in the magnetic field, which is readily drowned out by ambient noise. Enhancing magnetic memory detection by applying a magnetic field of a certain magnitude to the object to be tested so that the sample reaches unsaturation magnetization achieves the effect of enhancing the magnetic signal in the anomalous area and suppressing noise. Enhanced magnetic memory testing can not only detect micro-defects such as plastic deformation and stress concentration but also improve the detection rate of macro-defects such as cracks and corrosion, and thus has broad application prospects (Liu et al., 2022; Zhang and Liu, 2024; Liu et al., 2018). However, when there is strong interference in the detection environment, the enhanced magnetic memory signal and its gradient signal will still be severely affected, especially for the signals of micro-defects, which can easily lead to missed detection. Therefore, establishing an effective denoising method for the enhanced magnetic memory signals of micro-defects is of great significance.
The face of micro-defects when the magnetic field anomaly region is weak is easily covered in strong interference environments, and defects cannot be detected. Currently, the empirical mode decomposition (EMD) and related improved methods have been widely used in signal denoising for magnetic detection. Leng et al. (2010) and Chen et al. (2016) proposed an improved EMD method with different adaptive decomposition methods, and they achieved good application results in metal magnetic memory gradient signal denoising. However, they did not solve the problems of mode aliasing and endpoint effects that occur during EMD, and the loss of useful signals occurred due to the direct removal of high-order components. Luo et al. (2023) proposed an EMD-wavelet threshold denoising (WTD) method for metal magnetic memory signals and experimentally verified its feasibility. Song et al. (2019) and Bai (2019) applied an improved denoising method of ensemble empirical mode decomposition (EEMD) to metal magnetic memory detection. However, EEMD faces the problem that auxiliary white noise cannot be completely removed. Shi et al. (2019) and Liang (2020) proposed complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise (CEEMDAN) to solve the auxiliary white noise residual problem of the EEMD method. However, this can result in the emergence of spurious modes. Zhang et al. (2019) and Zhang et al. (2023) found that the improved complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise (ICEEMDAN) method can achieve a better signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and root mean square error than CEEMDAN, but there are still noise residuals and characteristic losses. Zhang et al. (2022) applied VMD to magnetic flux leakage detection and demonstrated that its noise reduction effect is better than that of EMD.
To effectively process the enhanced magnetic memory signals of micro-defects, we propose a denoising method for enhanced magnetic memory signals based on ICEEMDAN–VMD by comparing ICEEMDAN with VMD. SNR and fuzzy entropy (FE) were selected as evaluation indicators to compare the denoising effects of ICEEMDAN–VMD, ICEEMDAN, and VMD, and the result indicated that ICEEMDAN–VMD yielded a better denoising effect for the enhanced magnetic recording detection signal of micro-defects.
2 Test program and micro-defect signals using enhanced magnetic memory detection
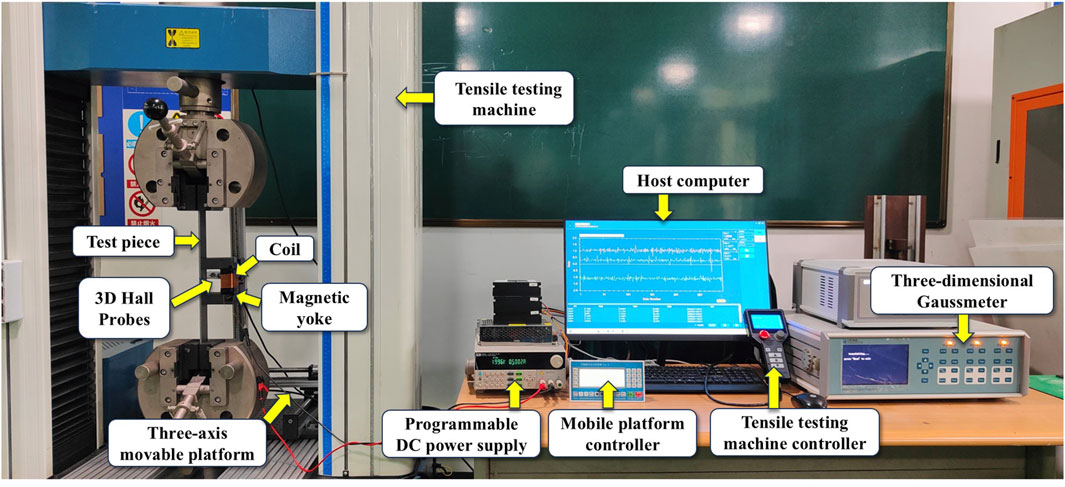
As shown in Figure 1, the enhanced magnetic memory detection system used in this study was composed of a loading device, magnetization device, and magnetic signal acquisition device. The loading device was a DF13.305T electronic universal testing machine, which was used to apply tensile loads to the specimens. The magnetization device was composed of an IT6862A programmable DC power supply and a U-shaped magnetic yoke. The tested area of the specimen was magnetized to a non-saturated state by applying excitation currents to a U-shaped magnetic yoke. The magnetic signal acquisition device consisted of a CH3600 three-dimensional Gaussian meter and a three-axis displacement control platform, enabling automatic scanning of magnetic signals of the tested area.
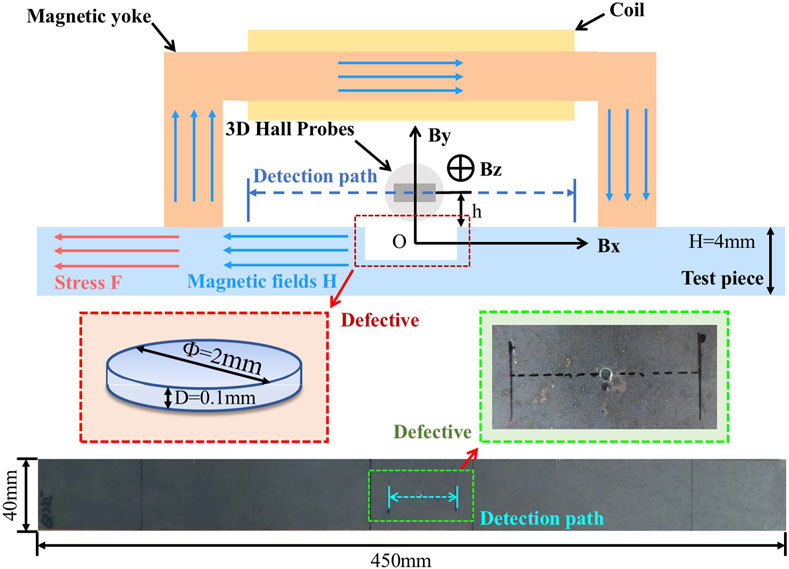
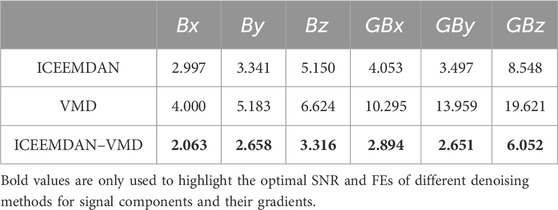
As shown in Figure 2, the specimens were made of Q235 steel with dimensions of 450 mm × 40 mm × 4 mm (length × width × thickness). A micro-defect 0.1 mm deep was simulated by a plastic indentation formed by pressing a Ø2 mm indenter at the center of the specimen. The excitation current was 0.5 A. The specimen was loaded to 400 MPa and was then kept loaded. The probe was lifted to a height of 1 mm. The horizontal component
The original detection signals of
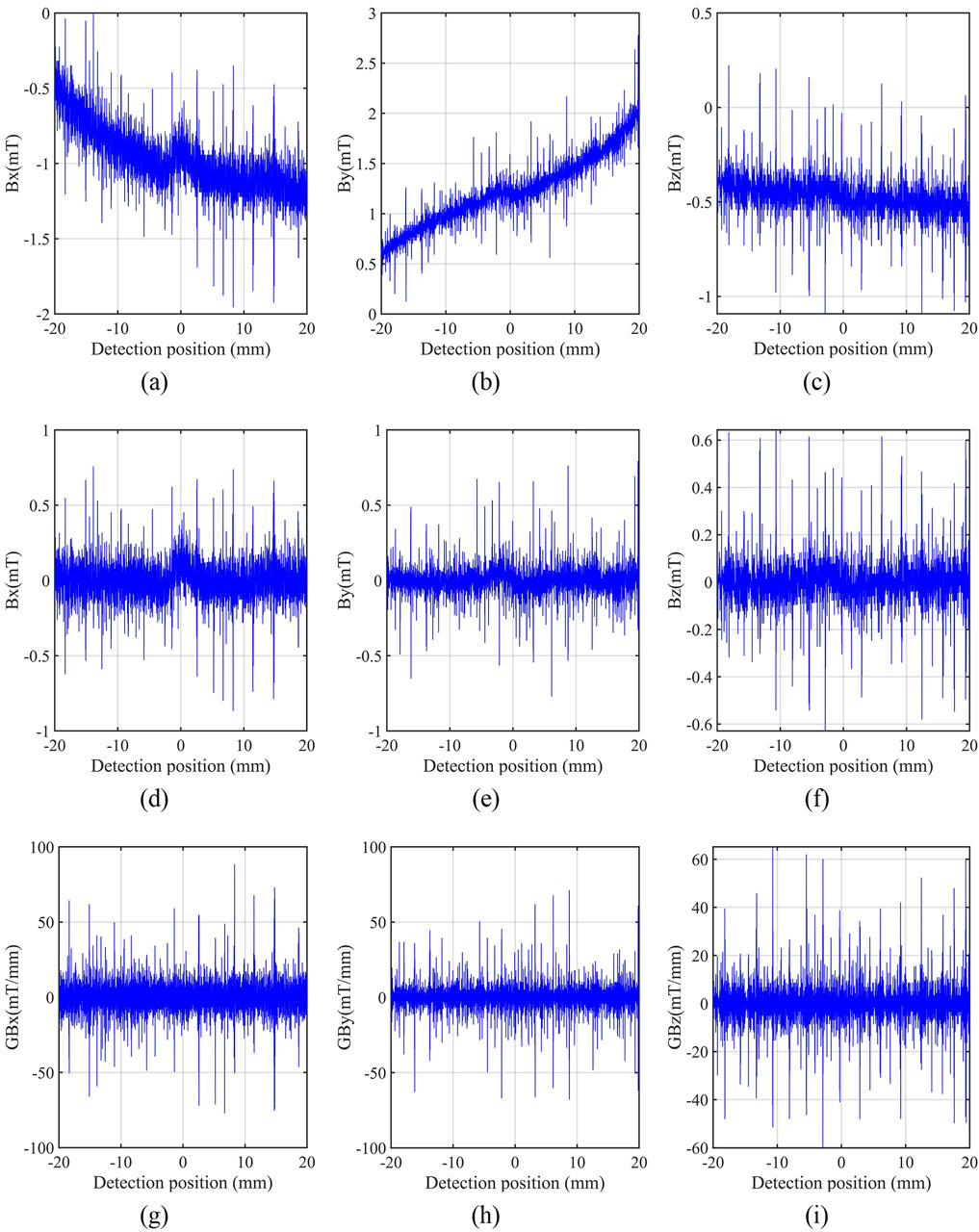
Figure 3. Detection signals and their gradient signals with trending components removed. (A) Original horizontal component
3 Analysis of ICEEMDAN and VMD denoising effects
3.1 Denoising processing steps and effect of ICEEMDAN
ICEEMDAN is an improved algorithm of CEEMDAN, which replaces the Gaussian white noise by the kth-order intrinsic mode function (IMF) component noise resulting from the original EMD during the CEEMDAN process. The process of ICEEMDAN is as follows (Marcelo et al., 2014).
Step 1: Adaptive Gaussian white noise is added to the original signal:
where
Step 2: EMD is conducted on the noise-added signal to obtain the first-order residual
where
Step 3: The residual signal
Step 4: The above steps are repeated until the residual cannot be decomposed, and the original signal is decomposed into a series of intrinsic mode functions and the residuals:
Step 5: In order to achieve more accurate judgment of the transition component, the comprehensive index
where
Step 6: The comprehensive index
According to the ICEEMDAN process, the
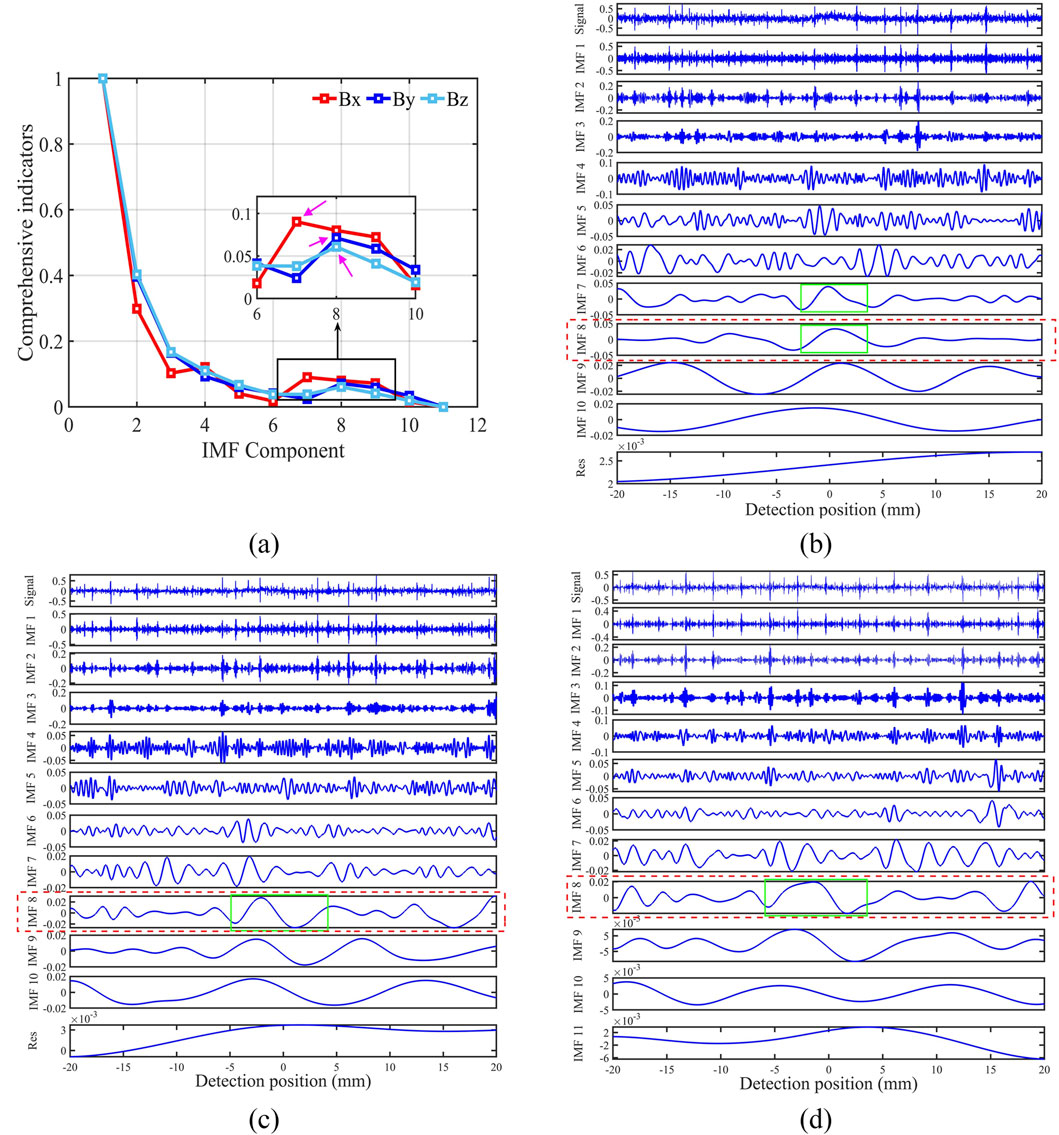
Figure 4. ICEEMDAN correlation coefficient selection and typical decomposition result charts. (A) Correlation coefficients of
Using
Figure 5. Denoising result of ICEEMDAN. (A) Horizontal component
3.2 Denoising processing steps and the effect of VMD
VMD is an adaptive denoising method based on EMD. The decomposition process is based on the following formula (Zhang et al., 2022):
where
where
During the VMD, it is necessary to determine different optimal penalty factors
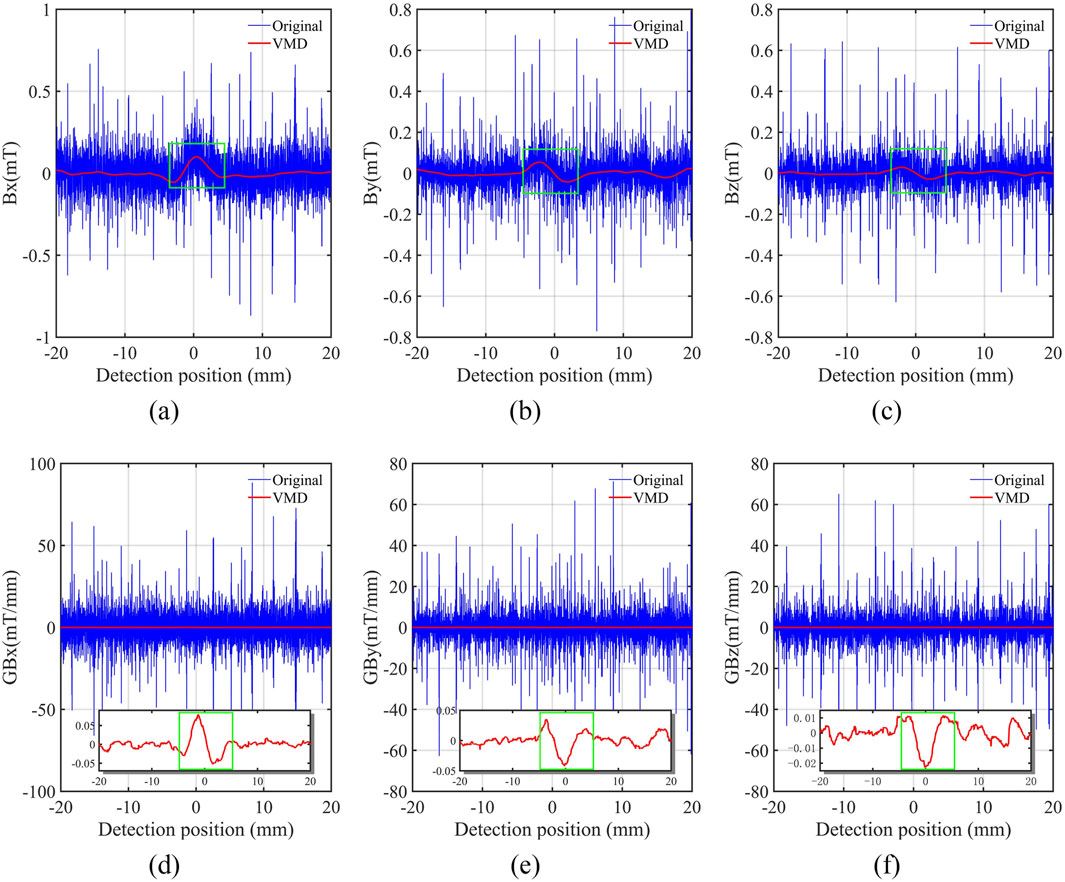
Figure 6. Denoising result of VMD. (A) Horizontal component
The results indicated that the signal anomalies of
4 Denoising processing steps and effect of ICEEMDAN–VMD
4.1 Denoising processing steps of ICEEMDAN–VMD
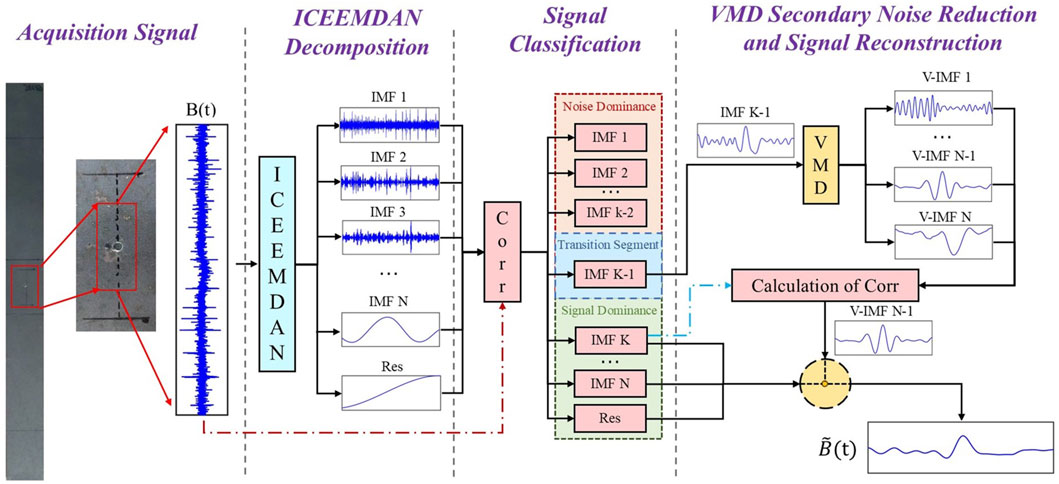
In response to the deficiencies of the ICEEMDAN and VMD methods, the ICEEMDAN–VMD joint signal denoising method is proposed, the process of which includes main four steps. The steps are shown in Figure 7 and described as follows:
Step 1: ICEEMDAN is performed on the original enhanced magnetic memory signals of the micro-defect to obtain m IMF components.
Step 2: IMF component classification. The correlation coefficients between the IMF components obtained in step 1 and the original signal are calculated, and the decomposition components are classified into three types—the noise-dominated components from
Step 3: Secondary denoising by VMD. The penalty factors and the number of decompositions are selected based on experience, and a secondary decomposition on the transition component
Step 4: Signal reconstruction. The component
Compared with ICEEMDAN, ICEEMDAN–VMD can effectively remove noise signals in the transition components, reduce signal noise in non-defect areas, and make the gradient values more stable, as well as minimize the loss of useful signals to the greatest extent. Compared with VMD, ICEEMDAN–VMD can effectively solve the problem of the difficult selection of penalty factors and the number of decomposition layers and avoids the problem of small fluctuations in the signal gradient values caused by the extremely small noise signals after VMD denoising.
4.2 Analysis of the noise reduction effect of the ICEEMDAN–VMD signal processing method
The ICEEMDAN–VMD denoising method was used to process the detected signals of a micro-defect. The selection of penalty factor α and the number of decomposition layers m for the VMD method was made according to the predictions outlined in Xiaoya et al. (2022), with the stipulated values set to α = 3,600 and m = 4, with the results shown in Figure 8. The results indicate that the ICEEMDAN–VMD denoising method could effectively reduce the influence of noise signals on the defect characteristic signals
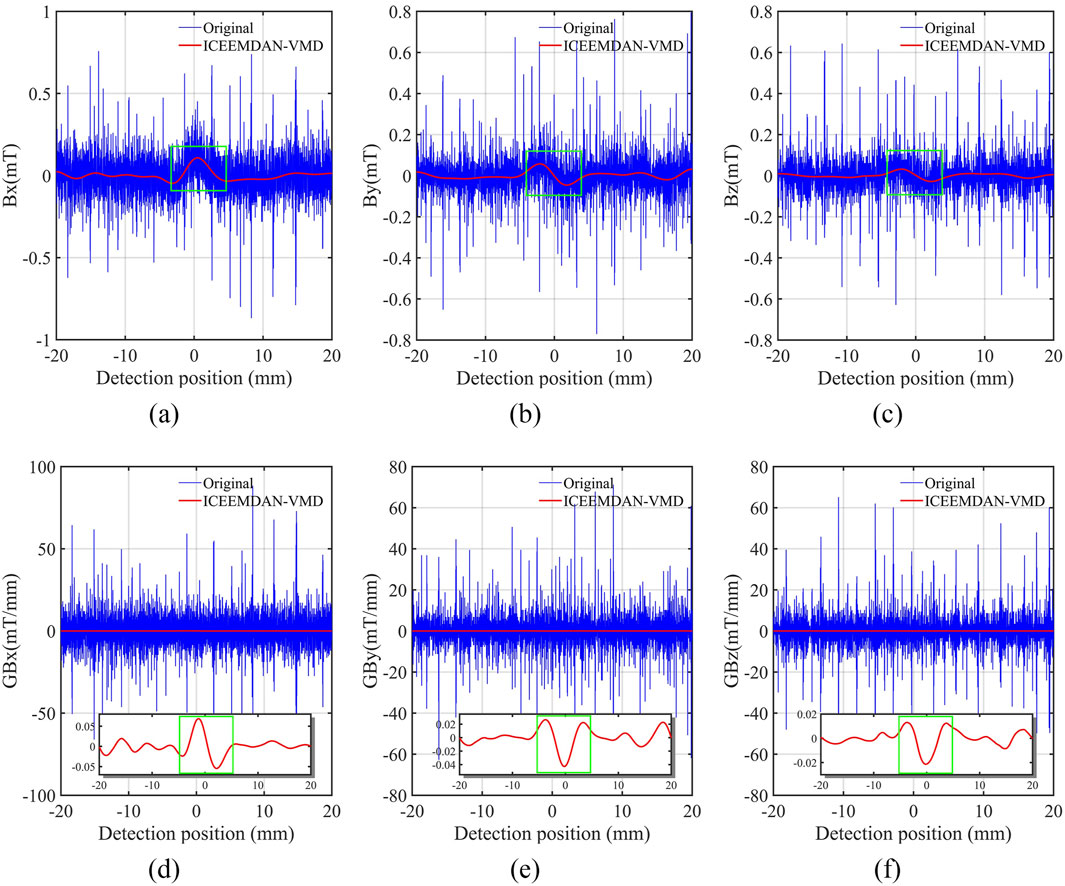
Figure 8. Denoising results of ICEEMDAN–VMD. (A) Horizontal component
Comparing the signals processed by ICEEMDAN, VMD, and ICEEMDAN-VMD, the signal components and their gradient curves processed by ICEEMDAN-VMD are smoothest, especially in non-defect areas where the signal fluctuation amplitude is smallest (Figure 9).
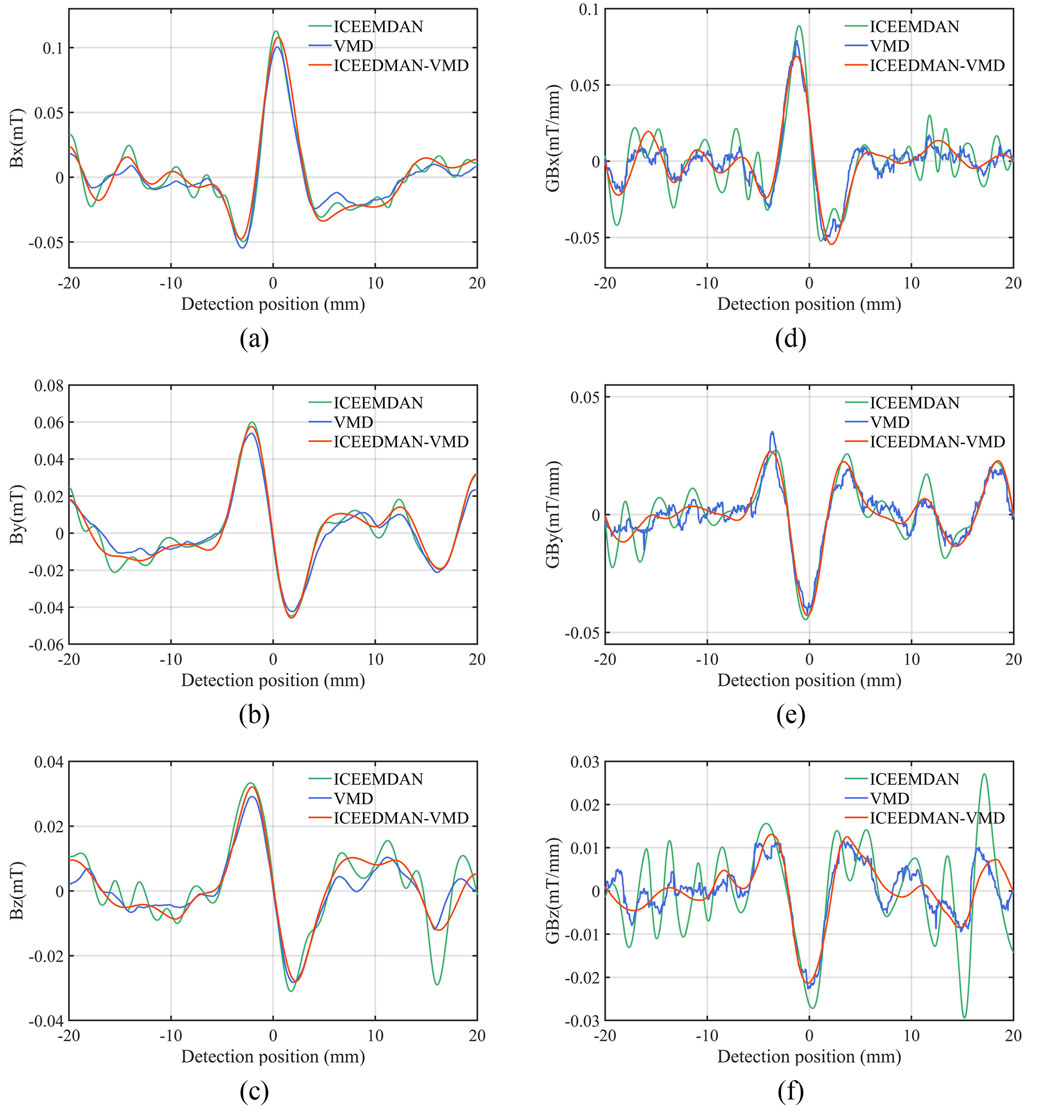
Figure 9. Comparison of ICEEMDAN, VMD, and ICEEMDAN–VMD results. (A) Horizontal component
Furthermore, to quantitatively compare the improved effect of the ICEEMDAN–VMD method, the SNR and FE were selected to evaluate its effect. The SNR is the ratio of useful signal energy to noise energy; the larger the SNR, the better the denoising effect. Since the original pure signal could not be obtained, the maximum amplitude of the useful signal was selected for comparison with the maximum amplitude of the noise signal for calculation. The SNR formula is shown as follows (Ren et al., 2021):
where
FE serves as a measurement of the probability that a time series will generate new patterns when the dimensionality varies. The higher the probability that the time series generates new patterns and the higher the complexity of the time series, the higher the FE of the time series. Therefore, the smaller the FE of the denoised signal, the better the denoising effect (Zhu et al., 2024) The FE calculation formula is:
Where
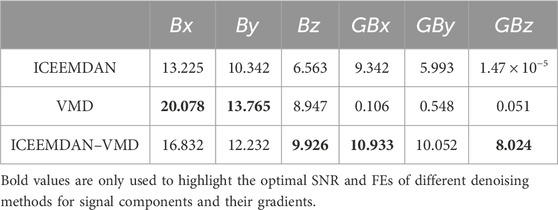
According to the results in Table 1, for
According to the results in Table 2, the FEs of
The VMD demonstrates the highest SNR at
To verify the applicability of ICEEMDAN-VMD to various paths, it was used to process detection signals from different paths within a 20 mm × 20 mm area near the defect, and the processed signals were used to create a pseudo-color map (Figure 10). Figures 10A–F display the unprocessed detection signals
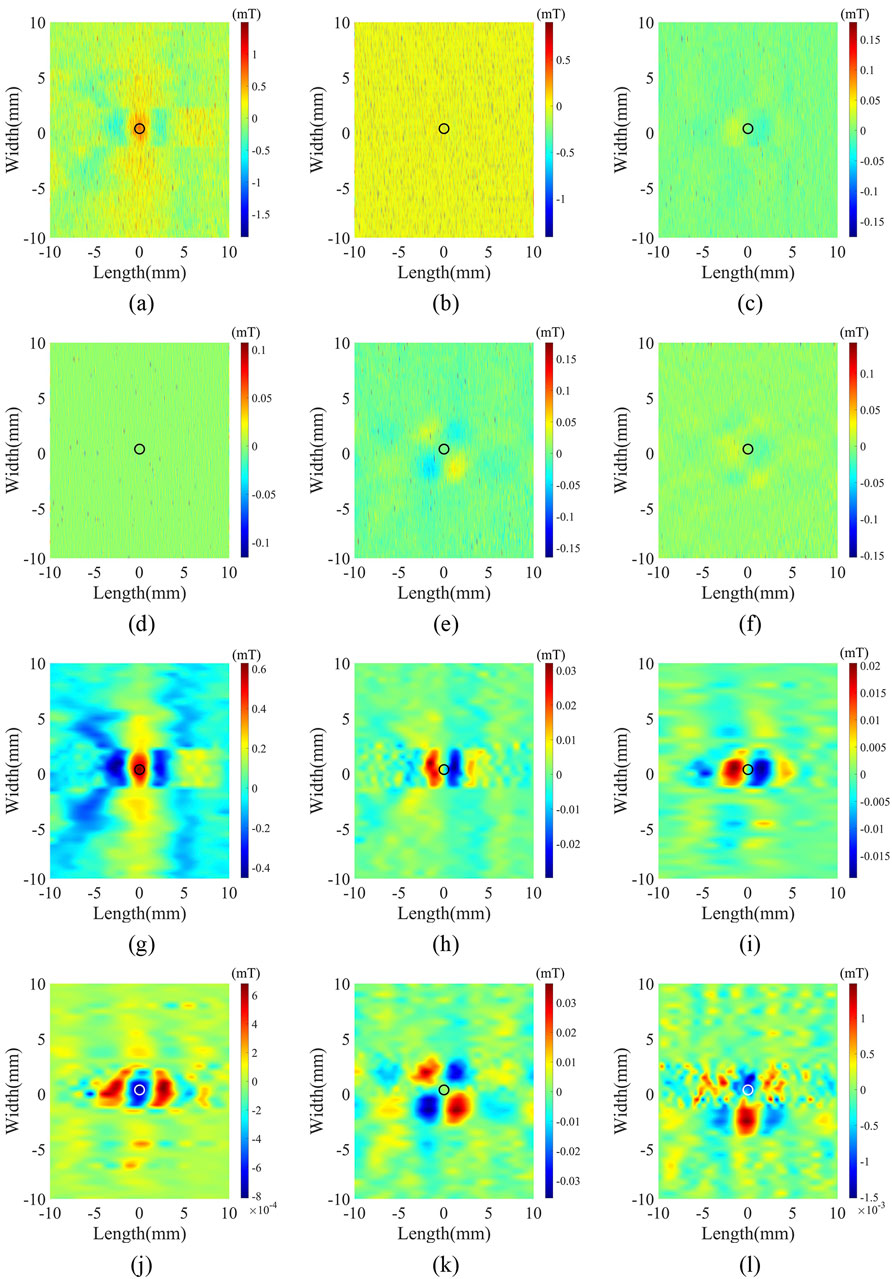
Figure 10. (A–F) specifically denote the unprocessed detection signals
5 Conclusion
To overcome the difficulty of identifying micro-defect feature signals caused by signal interference during enhanced magnetic memory detection, the ICEEMDAN–VMD denoising method is here proposed. The denoising effects of ICEEMDAN, VMD, and ICEEMDAN–VMD were analyzed in detail through experiments, and the improvement effect of ICEEMDAN–VMD was verified. The findings were as follows:
1. When ICEEMDAN is employed for the enhanced magnetic memory signal denoising, the transition component
2. The denoising method of ICEEMDAN–VMD could effectively overcome the shortcomings of ICEEMDAN and VMD, and it had a better denoising effect on enhanced magnetic memory signals. Compared with ICEEMDAN, ICEEMDAN–VMD could effectively reduce the noise signals of the transition components and non-defect areas, making
3. After the ICEEMDAN–VMD denoising process, the SNRs of
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
SJ: conceptualization, software, supervision, validation, writing–original draft, and writing–review and editing. JY: formal analysis, investigation, supervision, visualization, and writing–original draft. YL: data curation, formal analysis, funding acquisition, and writing–original draft. GH: conceptualization, formal analysis, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, resources, and writing–review and editing.
Funding
The authors declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
Authors SJ, JY, YL, and GH were employed by National Pipeline Network Group Zhejiang Natural Gas Pipeline Network Co. Ltd.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bai, B. (2019). Research on signal noise mechanism and noise reduction method of pipe pulse magnetic eddy current detection based on EEMD. M.s. thesis. Beijing, China: China University Petroleum.
Chen, H., Wang, C., and Zuo, X. (2016). Metal magnetic memory gradient tensor signal processing method. Syst. Eng. Electron., 488–493. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2017.03.05
Leng, J., Xu, M., and Zhang, J. (2010). Application of empirical mode decomposition in early diagnosis of magnetic memory signal. J. Central South Univ. Technol. 17 (03), 549–553. doi:10.1007/s11771-010-0521-5
Liang, X. (2020). Research on intelligent diagnosis and risk assessment methods of natural gas pipeline defects. Ph.D. dissertation. Beijing, China: China University Petroleum. doi:10.27643/d.cnki.gsybu.2020.000111
Liu, B., Zhang, J., and Zhang, Z. (2022). Modeling, simulation and experimental exploration of metal magnetic memory under weak magnetic excitation. Sn Appl. Sci. 4 (6), 167. doi:10.1007/s42452-022-05059-z
Liu, Z., Fei, Z., Huang, H., and Qian, Z. (2018). Study on strengthening mechanism of excitation magnetic field to stress-magnetization coupling effects. China Mech. Eng. 29 (09), 1108–1114. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2018.09.015
Luo, X., Wang, L., Cao, S., Xiao, Q., Yang, H., and Zhao, J. (2023). Signal processing methods of enhanced magnetic memory testing. Processes 11 (2), 302. doi:10.3390/pr11020302
Marcelo, A. C., Gastón, S., and María, E. T. (2014). Improved complete ensemble EMD: a suitable tool for biomedical signal processing. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 14, 19–29. doi:10.1016/j.bspc.2014.06.009
Ren, L., Liu, Z., and Zhou, J. (2021). Shaking noise elimination for detecting local flaw in steel wire ropes based on magnetic flux leakage detection. Ieee Trans. Instrum. Meas., 70: 1–9. doi:10.1109/tim.2021.3112792
Shi, M., Zhao, H., Huang, Z., and Liu, Q. (2019). Signal extraction using complementary ensemble empirical mode in pipeline magnetic flux leakage nondestructive evaluation. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 90 (7), 075101. doi:10.1063/1.5089475
Shi, P., Su, S., and Chen, Z. (2020). Overview of researches on the nondestructive testing method of metal magnetic memory: status and challenges. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 39 (2), 43. doi:10.1007/s10921-020-00688-z
Song, H., Dong, H., Yuan, Z., Zhu, J., Zhang, H., and Huang, Y. (2019). An EEMD-based electromagnetic induction method for nondestructive testing of buried metal conductors. Ieee Access 7, 142261–142271. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2944549
Xiaoya, W., Feng, G., Qi, T., Guo, J., Li, Z., Zhao, D., et al. (2022). Reduce the noise of transient electromagnetic signal based on the method of SMA-VMD-WTD. IEEE Sensors J., 22(15): 14959–14969. doi:10.1109/jsen.2022.3184697
Zhang, J., Chen, Q., and Ye, Q. (2023). Nondestructive testing of steel wire rope based on gagnetic signal and infrared information. Russ. J. Nondestruct. Test. 59 (9), 991–1004. doi:10.1134/S1061830923600399
Zhang, J., and Liu, P. (2024). Quantitative study on cross section damage of steel wire rope based on magnetic signal characteristics under weak magnetic excitation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 73, 1–7. doi:10.1109/tim.2024.3353842
Zhang, M., Wang, D., Guo, Y., Zhang, M., and Zhang, Z. (2022). Characteristics extraction and identification of pipeline magnetic flux leakage internal testing signals based on VMD-SVM. Oil Field Equip. 51 (06), 9–17. doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-3482.2022.06.002
Zhang, T., Wang, X., Chen, Y., Zia, U., Ju, H., and Zhao, Y. (2019). Non-contact geomagnetic detection using improved complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise and teager energy operator. Electronics 8 (3), 309. doi:10.3390/electronics8030309
Keywords: enhanced magnetic memory detection, micro-defects, signal denoising, ICEEMDAN, VMD
Citation: Ji S, Yan J, Liu Y and He G (2025) ICEEMDAN–VMD denoising method for enhanced magnetic memory detection signal of micro-defects. Front. Signal Process. 5:1518558. doi: 10.3389/frsip.2025.1518558
Received: 28 October 2024; Accepted: 07 January 2025;
Published: 12 February 2025.
Edited by:
Qiyu Sun, University of Central Florida, United StatesReviewed by:
Gang Li, Southwest Petroleum University, ChinaZhen Chen, Southwest Petroleum University, China
Copyright © 2025 Ji, Yan, Liu and He. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yang Liu, NDAyNTg1MTMzQHFxLmNvbQ==
 Shouhong Ji
Shouhong Ji Jie Yan
Jie Yan Yang Liu
Yang Liu