
95% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
REVIEW article
Front. RNA Res. , 27 March 2025
Sec. RNA Processing and Regulation
Volume 3 - 2025 | https://doi.org/10.3389/frnar.2025.1556979
This article is part of the Research Topic RNA Methylation: Detection, Deposition, and Functions View all 6 articles
Most RNAs and many protein factors involved in mRNA maturation and translation are decorated by numerous and diverse chemical modifications, which contribute to the efficiency, fidelity and regulation of these complex and essential cellular processes. Among those modifications, methylation catalyzed mainly by S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) dependent methyltransferases (MTases) is the most common one. TRMT112 is a small protein acting as an allosteric regulator of several MTases. Initial studies focusing on TRMT112 and its associated MTases were performed in Saccharomyces cerevisiae whereas only few were expanded to human cells, leading to the identification and characterization of four TRMT112 partners in yeast (Trm11, Bud23, Mtq2 and Trm9) and five in human cells (TRMT11, BUD23, MTQ2/HemK2 and two Trm9 orthologues ALKBH8 and TRMT9B). Recent studies have identified several novel MTase partners of human TRMT112, namely METTL5, THUMPD2 and THUMPD3. Interestingly, all these TRMT112-MTase complexes modify factors (RNAs and proteins) involved in mRNA maturation and translation processes and growing evidence supports the importance of these MTases in cancer and correct brain development. In this review, we summarize the current knowledge on TRMT112 protein and its various MTase partners in eukaryotes and archaea.
Protein synthesis is a universal and sophisticated process responsible for the decoding of the genetic information embedded within messenger RNAs (mRNAs) into polypeptides. In addition to the mRNAs, it requires the ribosome, transfer RNAs (tRNAs), as well as several translational protein factors. The different RNA components involved in this process (mRNAs, tRNAs and ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs)) undergo a series of maturation steps such as for instance, splicing, endo- or exonucleolytic cleavages, co- or post-transcriptional modifications (or epitranscriptomic marks) to produce mature, diverse and functional molecules. In particular, the decoration of RNAs by various and sometimes complex chemical groups (epitranscriptomic marks) makes RNAs particularly interesting molecules and contributes a new layer of complexity to the regulation of gene expression (Saletore et al., 2012; Schwartz, 2016; Zaccara et al., 2019). The biological importance of these post-transcriptional modifications has emerged during the last decade since diseases such as cancers or neurological disorders have been linked to the dysfunction of RNA-modifying enzymes (or writers (Angelova et al., 2018; Barbieri and Kouzarides, 2020; Suzuki, 2021)).
The most frequent RNA epitranscriptomic marks are methylation either on the RNA bases or on the 2′-OH group of the ribose. Methyl groups are mainly deposited by S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAM) dependent RNA methyltransferases (MTases; (Schubert et al., 2003; Fenwick and Ealick, 2018; Strassler et al., 2022)), some of them being tightly regulated by associated proteins. Amongst them, TRMT112 (Trm112 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae) acts as a master regulator of several MTases modifying RNAs but also proteins involved in mRNA processing and translation. Initial studies focusing on Trm112 protein and its associated MTases were performed in S. cerevisiae while only a few were expanded to human TRMT112 protein (Bourgeois et al., 2017a). However, the human TRMT112 network recently emerged as much more complex than initially anticipated from studies performed in the yeast model system. In this review, we summarize our current knowledge on eukaryotic TRMT112 and its partners. We also discuss available information gained on archaeal Trm112 proteins, since these studies have fueled research on eukaryotic and in particular human proteins.
In this review, we will use mostly TRMT112, the metazoan name, when dealing with this protein family in general but also Trm112 when specifically dealing with fungal and prokaryotic proteins. TRMT112 are small proteins (6–15 kDa) found in eukaryotes but also in bacterial (named as YcaR in Escherichia coli) and archaeal genomes. In eukaryotes, this protein is composed of two domains (Figure 1A). The first domain is composed of a short α-helix (α1 at N-terminal) facing an antiparallel β-sheet composed of three or four β-strands (β1 to β3 or β4) in the crystal structures of S. cerevisiae Trm112 alone or bound to the Bud23 MTase, respectively (Heurgue-Hamard et al., 2006; Letoquart et al., 2015). This domain is found in all TRMT112 proteins (Figure 1A) and was initially named zinc knuckle domain, due to its structural similarity with this domain family and to the presence of four cysteine residues chelating one zinc atom in the crystal structure of S. cerevisiae Trm112 (Heurgue-Hamard et al., 2006). Although these four cysteine residues are strongly conserved in fungal (Heurgue-Hamard et al., 2006; Letoquart et al., 2014; Letoquart et al., 2015), parasitic (Liger et al., 2011), bacterial and some archaeal proteins (Wang et al., 2020), they diverge in metazoan proteins and in other archaeal proteins (Figure 1B). Yet, the overall structure of this domain in the different experimental TRMT112 structures determined to date, remains the same whether it binds zinc or not (Heurgue-Hamard et al., 2006; van Tran et al., 2018; Metzger et al., 2019; van Tran et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020). The second domain or helical domain, exclusively observed in eukaryotic TRMT112 proteins so far, is made of three α-helices and is inserted in the middle of the zinc knuckle domain between strands β1 and β2 (Heurgue-Hamard et al., 2006; Liger et al., 2011; Letoquart et al., 2014; Letoquart et al., 2015; Metzger et al., 2019; van Tran et al., 2019).
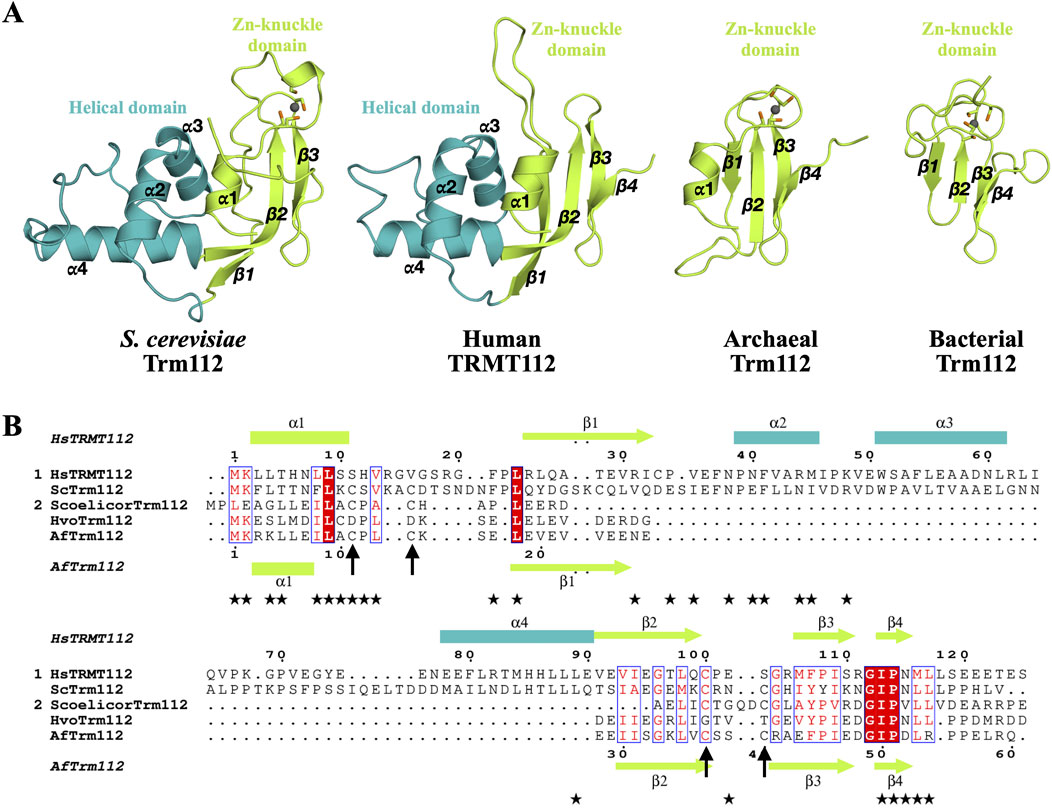
Figure 1. Organization of TRMT112 proteins. (A) Representation of the three dimensional structures of eukaryotic (S. cerevisiae; PDB code: 2J6A and human; PDB code: 6H2U), archaeal (A. fulgidus, PDB code: 6ZXW) and bacterial (Streptomyces coelicolor, PDB code: 2KPI) TRMT112 proteins. The zinc atom bound to the zinc knuckle domain is shown as a grey sphere. The side chains of the cysteine residues coordinating these zinc atoms are shown as sticks with the sulfur atom colored in orange. (B) Sequence alignment of some eukaryotic (group 1) and prokaryotic (group 2) TRMT112 proteins. Strictly conserved amino acids are colored white in a red background and relatively well conserved residues are colored red and boxed in blue. Amino acids from human TRMT112 that are involved in the interaction with METTL5 are highlighted with black stars below the sequence alignment. Secondary structure elements observed in the crystal structures of TRMT112 bound to either human METTL5 (PDB code: 6H2U) or A. fulgidus Trm11 (PDB code: 6ZXW) are indicated above and below the alignment, respectively, using the same color code as in (A) for the domains. Helices and strands are depicted as rectangles and arrows, respectively. The positions of the cysteine residues involved in zinc binding are indicated by black arrows.
Most studies focusing on TRMT112 proteins have been performed in eukaryotes and some in archaea. To our knowledge, the bacterial Trm112 orthologues have largely been neglected although several three-dimensional structures of bacterial Trm112-like proteins have been determined by structural genomics consortia (PDB codes: 2KPI; 2PK7; 2HF1; 2JS4; 2JNY and 2JR6, with no associated publications; Figure 1A). Initial studies performed in S. cerevisiae have shown that the deletion of the YNR046w gene encoding Trm112 severely affects growth and results in paromomycin hypersensitivity and cryo-sensitivity phenotypes (Figaro et al., 2012). The Trm112 protein is also important for ribosome synthesis and/or functions. Indeed, the S. cerevisiae trm112Δ strain exhibits a reduction in the 40S ribosomal subunit abundance, a concomitant accumulation of the 60S ribosomal subunit, and a decrease of polysome extent (Figaro et al., 2012). This is illustrated by an accumulation of 35S and reduction in the levels of 27S and 7S pre-rRNA precursors as well as a reduction of mature 18S and 25S rRNAs in the trm112Δ strain (Figaro et al., 2012; Sardana and Johnson, 2012). This phenomenon is due to the activation of the nucleolar surveillance pathway targeting pre-ribosomes for decay in the absence of Trm112. In yeast, Trm112 is also important for efficient pre-40S and pre-60S export from the nucleolus as well as for progression through mitosis (Figaro et al., 2012). Similarly, SMO2, the Arabidopsis thaliana TRMT112 orthologue, plays an essential role in regulating cell division progression during organ growth (Hu et al., 2010). Deletion of SMO2 gene in A. thaliana leads to a decreased growth rate of cells, delayed cell division, reduced leaf and root development rate as well as to an increase in the number of aborted seeds (Hu et al., 2010; Guo et al., 2023). A. thaliana plants lacking SMO2 suffer from nucleolar stress and accumulate some rRNA precursors (32S, 27SA/B and 18S-A3), indicative of rRNA processing defects (Guo et al., 2023), similarly to what has been described for yeast. Interestingly, despite the relatively low sequence identity (28%) between S. cerevisiae Trm112 and A. thaliana SMO2, the latter complements for the deletion of TRM112 gene in yeast, indicating that both proteins have an evolutionarily conserved function (Hu et al., 2010). In human cells (U2OS and HeLa), TRMT112 localizes both in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus but a clear exclusion from the nucleolus has been observed (Zorbas et al., 2015; Brumele et al., 2021). As observed in yeast and plants, the depletion in TRMT112 results in human rRNA processing defects with a clear accumulation of 18S-E and a small reduction in 30S rRNA precursors (Zorbas et al., 2015).
The striking property of eukaryotic TRMT112 proteins is their ability to interact with several SAM-dependent MTases and to act as allosteric regulators of these enzymes. All these enzymes belong to the class I MTase family, which is characterized by a central seven stranded β-sheet (with the following strand order 3↑2↑1↑4↑5↑7↓6↑) surrounded by three α-helices on one side and at least two on the other side. In S. cerevisiae, four MTases (Trm9, Trm11, Mtq2, and Bud23; Table 1), sharing less than 25% sequence identity, have been validated as direct Trm112 partners. Interestingly, all of them modify factors involved in mRNA translation (either tRNAs, rRNA or protein; (Bourgeois et al., 2017a)). Additional class I MTases (Nop1, Nop2 and Rcm1) as well as the saccharopine dehydrogenase Lys9, which exhibits structural similarities with class I MTases, have also been identified as potential interactors of yeast Trm112. However, none of these factors have been experimentally confirmed as direct partners ((Gavin et al., 2002; Figaro et al., 2012; Sardana and Johnson, 2012); MG unpublished results). Initially, human TRMT112 protein was proposed to interact with five proteins sharing significant sequence homology with the four above-mentioned yeast MTases (two human proteins, ALKBH8 and TRMT9B, are related to yeast Trm9; Table 1; (Bourgeois et al., 2017a; Gu et al., 2018)). However, recent studies performed in human cells have revealed that the TRMT112 interaction network is more complex than previously anticipated. Indeed, three additional human MTases with no orthologues in yeast, namely METTL5, THUMPD2 and THUMPD3, have been identified as direct partners of TRMT112 (Figure 2; Table 1; (Brumele et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2024)). Interestingly, these three novel TRMT112 MTase partners also modify RNAs involved in either pre-mRNA splicing or mRNA translation. Finally, in human cells, PYURF, a mitochondrial TRMT112-like protein, has also recently been shown to interact with some MTases or proteins with structural similarity with class I MTases (Rensvold et al., 2022).

Figure 2. The interaction network of human TRMT112 protein with methyltransferases. In human cells, TRMT112 interacts with at least eight class I SAM-dependent methyltransferases. The MTases are colored according to their known substrates. “?”: unknown substrate but strong similarity with tRNA MTases.
TRMT112 orthologues are detected by bioinformatics analyses in many but not all archaeal genomes (Bourgeois et al., 2017a). Interestingly, the binding preference of eukaryotic TRMT112 proteins for MTases is also observed in archaea as demonstrated for Haloferax volcanii Trm112 protein, which directly interacts with at least ten class I MTases. Some are orthologous to known TRMT112 eukaryotic MTases (Trm9, Trm11, Mtq2 and METTL5) while many others have neither established biochemical functions nor obvious similarities with eukaryotic proteins (van Tran et al., 2018; van Tran et al., 2019). Although the direct interaction between Trm11 and Trm112 proteins from H. volcanii could not be validated, the complex formed by these two proteins from another archaeon, Archaeoglobus fulgidus, has been purified and its crystal structure determined (Wang et al., 2020). As indicated above, much less is known about bacterial Trm112 interaction network. One large-scale study performed in the Desulfovibrio vulgaris Gram-negative bacterium has detected interaction between Trm112 (DVU_0656) protein and three class I MTases (Shatsky et al., 2016). However, to our knowledge, none of these interactions has been validated by other experimental means.
In the next sections, we will describe the current knowledge gained on the different MTase subunits known to interact with eukaryotic but also archaeal TRMT112 proteins as well as the relationships between these proteins and TRMT112 proteins. We will also focus on the link between these writers and diseases, especially cancers and neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs).
tRNAs are heavily modified RNA molecules. These modifications can be essential for the maintenance of translation efficiency and fidelity as well as for tRNA folding and stability (Phizicky and Hopper, 2023). In S. cerevisiae, Trm112 interacts with two tRNA MTases, Trm11 and Trm9, which catalyze the formation of N2-methylguanosine (m2G) at position 10 and 5-methoxycarbonylmethyl(2-thio)uridine (mcm5 (s2)U) at position 34, respectively (Purushothaman et al., 2005; Mazauric et al., 2010; Guy and Phizicky, 2014; Letoquart et al., 2015; Bourgeois et al., 2017b). Their functions are conserved in yeast, humans, and also archaea (Fu D. et al., 2010; Songe-Moller et al., 2010; van Tran et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2023). Furthermore, human TRMT112 interacts with THUMPD3, a protein with no yeast orthologue, to catalyze the formation of m2G at positions 6 and 7 on some cytoplasmic tRNAs (Yang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023).
Trm11 was the first MTase to be identified as a yeast Trm112 partner (Purushothaman et al., 2005), leading to the initial annotation of the YNR046w gene product as Trm11-2 (for the second subunit of the Trm11 tRNA methyltransferase complex, now annotated as Trm112). Archaeal and eukaryotic Trm11 proteins are composed of an N-terminal THUMP (for thiouridine synthases, RNA methyltransferases, and pseudouridine synthases) domain and a C-terminal class I MTase catalytic domain (Figure 3A; Armengaud et al., 2004; Hirata et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2020). The THUMP domain is found in several RNA-modifying enzymes (Aravind and Koonin, 2001; Hori, 2023). It is made of an NFLD subdomain (for N-terminal Ferredoxin-like domain) and a core THUMP subdomain consisting of three α-helices wrapping around the outer face of a curved seven-stranded β-sheet. One of its functions is to recognize the 3′-CCA end of tRNAs and most likely to position the nucleotide to be modified into the active site of the catalytic domain of the enzyme, thereby acting as a molecular ruler (Neumann et al., 2014). Moreover, Trm11 MTase domain belongs to the SAM-dependent class I MTase family and harbors a strongly conserved D [P/Y/A]PY motif, a signature found in the active site of MTases acting on planar NH2 groups present in DNA or RNA nucleotides but also in proteins (such as glutamine side chains; (Bujnicki, 2000; Heurgué-Hamard et al., 2002; Nakahigashi et al., 2002)).
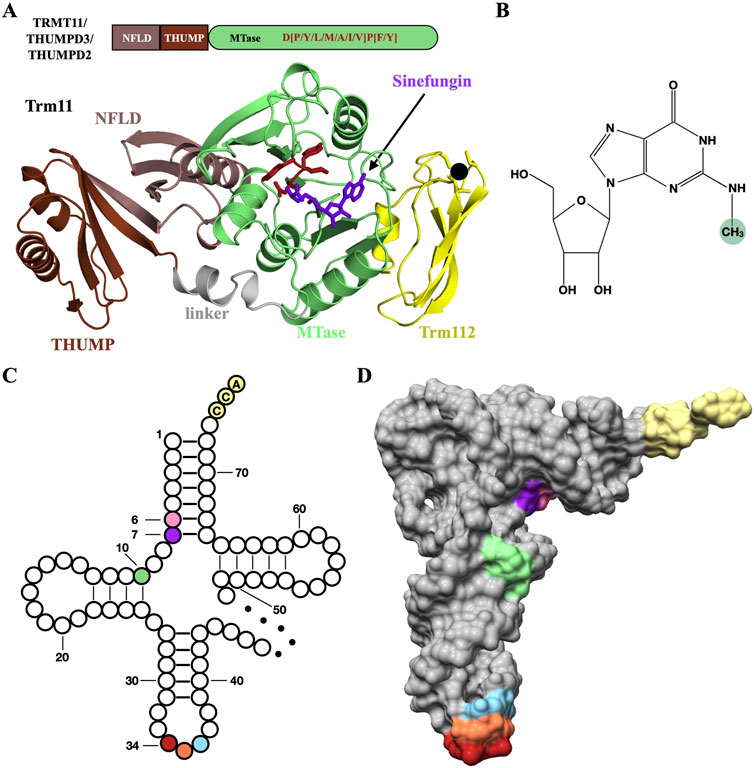
Figure 3. TRMT11 and THUMPD3 are tRNA m2G methyltransferases targeting positions 10 and 6/7, respectively. (A) Schematic depiction of the TRMT11/THUMPD3/THUMPD2 domain organization and ribbon representation of the crystal structure of the Trm11-Trm112 complex from Archaeoglobus fulgidus (PDB code : 6ZXW). The D[P/Y/L/M/A/I/V]P[F/Y] signature involved in the coordination of the N2 atom from the guanosine substrate in colored in firebrick. The linker region connecting the THUMP and MTase domains is colored in grey. The SAM-dependent MTase inhibitor sinefungin is shown as purple sticks. The zinc atom bound to Archaeoglobus fulgidus Trm112 (yellow) is shown as a black sphere. (B) Chemical structure of N2-methylguanosine (m2G) with the N2-methyl group highlighted by a green sphere. (C) Clover-leaf representation of cytosolic tRNAs highlighting the positions 6 (pink), 7 (purple) and 10 (light green) where THUMPD3-TRMT112 (positions 6 and 7) and TRMT11-TRMT112 (position 10) complexes install m2G modifications. The tRNA anticodon is colored firebrick, coral and light blue for positions 34, 35 and 36, respectively. The CCA tail at the 3’ end of tRNAs is colored in light yellow. The variable loop is depicted by a dotted line. (D) Surface representation of the crystal structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae tRNAPhe (PDB code: 1EHZ). Same color code as (C).
The S. cerevisiae Trm11 protein as well as its human (TRMT11) and archaeal orthologues catalyze the formation of m2G at position 10 of many tRNAs (Figures 3B–D; Armengaud et al., 2004; Purushothaman et al., 2005; Wang et al., 2023). In S. cerevisiae and human cells, Trm11/TRMT11 and Trm112/TRMT112 proteins interact tightly together (Purushothaman et al., 2005; Bourgeois et al., 2017b; Wang et al., 2023). Yeast Trm11 can be heterologously expressed and purified as an isolated and soluble protein. However, although this protein is well-folded, it is unstable, cannot interact with the SAM cofactor and consequently, is inactive (Bourgeois et al., 2017b). Its stability and ability to interact with SAM as well as its enzymatic activity are strongly enhanced by Trm112. Yet, Trm112 deletion in S. cerevisiae does not affect Trm11 stability in vivo (Sardana and Johnson, 2012), contrary to observations made for other MTases interacting with Trm112 (see other sections). Human TRMT11 cannot be expressed as a soluble protein in E. coli unless it is co-expressed with TRMT112, preventing further biochemical characterization of the isolated protein (Wang et al., 2023). The TRMT11 gene has also been characterized in the A. thaliana plant model, where a TRMT11 mutant is characterized by a strongly reduced level of m2G in tRNAs, an early flowering phenotype and a higher resistance to bacterial infection (Chen et al., 2010; Lv et al., 2025).
In archaea, several tRNAs harbor either m2G or m2,2G (N2,2-methylguanosine) at position 10 (Gupta, 1984; Gupta, 1986). Trm11 orthologues are present in archaea and some of these proteins have been shown to catalyze the formation of m2G and/or m2,2G at position 10 of tRNAs (Armengaud et al., 2004; Urbonavicius et al., 2006; Hirata et al., 2016; Hirata et al., 2019). Interestingly, Trm11 proteins from Pyrococcus abyssi or Thermococcus kodakarensis, two archaea with no Trm112 orthologues in their genome, are active on their own. However, Archaeoglobus fulgidus and Haloferax volcanii archaea encodes for a Trm112 orthologue, and consequently, Trm11 and Trm112 proteins from these organisms interact together similarly to the eukaryotic proteins (van Tran et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2020). Contrary to yeast Trm11 and human TRMT11, Trm11 protein from A. fulgidus (hereafter referred to as AfTrm11) does not need to interact with Trm112 (hereafter referred to as AfTrm112) for catalytic activity but its stability is reduced. According to the crystal structures of AfTrm11 alone or bound to AfTrm112, no significant conformational change in AfTrm11 is observed upon AfTrm112 binding (Wang et al., 2020). AfTrm112 strongly enhances AfTrm11 enzymatic activity but does not influence SAM binding (Wang et al., 2020). The thermostability of AfTrm11 is enhanced by AfTrm112 (melting temperature of 73°C for Trm11 alone vs. more than 92°C for the Trm11-Trm112 complex), which might be very important since the optimal growth temperature of A. fulgidus is between 75 and 90°C (Oliver et al., 2020). Kinetic and structural analyses have suggested that AfTrm112 might activate AfTrm11 by re-arranging the orientation of the tRNA substrate in the active site (Wang et al., 2020). The determination of the structures of AfTrm11 (either alone or bound to AfTrm112) bound to a tRNA molecule could bring more clues about the role of AfTrm112. Based on these observations, AfTrm11 could be the prototype of the « missing link » between Trm11 proteins from archaea lacking TRM112 genes and eukaryotic proteins that depend on TRMT112 to be active.
The THUMP domain appears as important for the recognition of the 3′-CCA tail and the aminoacyl acceptor arm of tRNA substrates according to the crystal structure of ThiI, a THUMP domain-containing protein involved in the formation of 4-thiouridine in the aminoacyl acceptor arm of tRNAs, bound to a truncated tRNA (Neumann et al., 2014). In agreement with this observation, the yeast Trm11-Trm112 complex is active only on mature tRNAs and requires the presence of the 3′-CCA tail (Bourgeois et al., 2017b; Nishida et al., 2022). Finally, the Trm112 subunit is also important for tRNA binding as mutations of several conserved residues from its zinc-binding domain affect the affinity of the corresponding Trm11-Trm112 complexes for a tRNA substrate (Bourgeois et al., 2017b). The role of Trm112 in tRNA accommodation is further supported by kinetics parameters obtained on AfTrm11 in the presence or absence of AfTrm112 (Wang et al., 2020). Indeed, AfTrm11 binds tRNA more strongly in the absence of AfTrm112, yet the AfTrm11-Trm112 complex exhibits a higher kcat value than AfTrm11 alone, for the m2G formation reaction using E. coli tRNAiMet as substrate. This strongly suggests that the function of AfTrm112 on AfTrm11 is to help either the binding of tRNA molecules to optimally position G10 substrate in the enzyme active site or the release of the modified tRNAs.
From a biological point-of-view, the role of the Trm11-dependent m2G10 tRNA modification remains unclear. Indeed, the S. cerevisiae trm11Δ strain does not exhibit any growth defect phenotype compared to the wild-type strain under standard laboratory conditions, indicating that Trm11 and potentially the m2G10 tRNA modification are not necessary for cell proliferation (Purushothaman et al., 2005). In the three-dimensional structure of yeast tRNAPhe (Shi and Moore, 2000), m2G10 is stacked onto m2,2G26 modification, which is catalyzed by the Trm1 MTase (Ellis et al., 1986). Interestingly, although the trm1Δ strain has no obvious phenotypes, the trm11Δ/trm1Δ double mutant strain grows much more slowly than the wild-type suggesting that the concomitant absence of both m2G10 and m2,2G26 in tRNAs may destabilize the functional L-shape structure of tRNA molecules and may impact tRNA maturation and processing (Purushothaman et al., 2005). A potential importance of m2G10 or m2,2G10 in stabilizing the tRNA structure is further supported by the growth defect phenotype observed for T. kodakarensis archaeon depleted for TRM11 gene at temperatures higher than 90°C (Hirata et al., 2019).
The function of human TRMT11 has been investigated in the HCT116 colon cancer cell line. Compared to the parental cell line, the HCT116 trmt11−/− cell line exhibited a slightly higher growth rate but a similar translation level (Wang et al., 2023). This indicates that the TRMT11 gene is not necessary for the proliferation of human HCT116 cell lines and this is reminiscent of the observations made for the S. cerevisiae trm11Δ strain. The depletion of TRMT11 resulted in a significant decrease (around 40%) of m2G levels in total tRNAs but did not affect tRNA aminoacylation, structure or stability (Wang et al., 2023). Genetic variants (namely single-nucleotide polymorphisms or SNPs) of the TRMT11 gene have been proposed to be associated with an increase in the time to treatment failure of patients with advanced prostate cancer treated with androgen deprivation therapy (ADT (Kohli et al., 2012)). However, such observations will need further confirmation. Similarly, TRMT11-GRIK2 fusion transcripts due to chromosomal rearrangement events have been identified in patients suffering from various types of cancer (Yu et al., 2014; Yu et al., 2019). These TRMT11-GRIK2 fusion transcripts correspond to the 24 N-terminal amino acids from human TRMT11 separated by a frameshift of the coding sequence for 22 amino acids from GRIK2 C-terminal extremity. Consequently, neither TRMT11 nor GRIK2 (Glutamate Ionotropic Receptor Kainate Type Subunit 2) are correctly expressed in these cells. Since GRIK2 has been identified as a potential tumor suppressor (Sinclair et al., 2004), the absence of TRMT11 may have no clear role in cancer development in these patients. So far, any implication of TRMT11 in cancer is currently speculative and further studies will be required to address this question.
In addition to the m2G10/m2,2G10 modifications discussed above, various tRNA molecules also exhibit m2G/m22G at positions 6, 7, 18, 26, 27 and 67 in different organisms (Matsuo et al., 1995; Juhling et al., 2009; Hirata et al., 2019; Petrosyan and Bohnsack, 2024). Besides Trm11, the archaeal proteins Trm14 and its bacterial orthologs TrmN, which share the same domain organization as Trm11 proteins, namely a THUMP domain followed by a class I MTase domain (Fislage et al., 2012), have been well-characterized as m2G tRNA MTases targeting position 6 (m2G6) on the acceptor stem of tRNA molecules (Menezes et al., 2011; Roovers et al., 2012). m2G6 is widely distributed among archaea, some bacteria, and metazoa but is absent in yeasts. Recently, human THUMPD3 protein, which shares 23% sequence similarity with Trm14 protein from Pyroccocus furiosus archaeon but with no orthologue in yeast, has been shown to be responsible for the formation of m2G6 on several human tRNAs but also of m2G7 on tRNATrp (Figure 3C (Yang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023)). Similarly to other m2G RNA MTases, THUMPD3 MTase domain harbors the conserved D [L/M]P [F/Y] signature (Figure 3A). While human THUMPD3 cannot be expressed alone as a soluble protein in E. coli (Wang et al., 2023), it can be purified upon expression in baculovirus-infected insect cell. However, this protein forms aggregates in solution, cannot interact with sinefungin, a well-known SAM analog inhibiting SAM-dependent MTases, and lacks enzymatic activity (Yang et al., 2021). Similarly to TRMT11, human THUMPD3 directly interacts with TRMT112 and the latter plays a critical role on THUMPD3 stability and activity (Brumele et al., 2021; Yang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023). Indeed, the human THUMPD3-TRMT112 complex, either expressed in E. coli or insect cells, forms heterodimers, interacts with sinefungin and catalyzes the formation of m2G6/7 in tRNAs in vitro (Yang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023). In agreement with the proposed role of THUMP domains in the recognition of the 3′-CCA tail of tRNA substrates, the human THUMPD3-TRMT112 complex cannot introduce m2G into a tRNA substrate lacking the 3′-CCA tail (Yang et al., 2021).
As indicated above, both human THUMPD3 and archaeal Trm14 catalyze the formation of m2G6 on tRNAs and share the same domain organization. This raises the question of whether archaeal Trm112 could also interact with Trm14. The only Trm14 protein, which enzymatic activity has been characterized in vitro is from Methanocaldococcus jannaschii archaeon (Menezes et al., 2011). However, since no detectable Trm112 orthologue could be identified in the genome of this archaeon, we cannot exclude that when they are present in an archaeal genome, Trm14 and Trm112 interact together similarly to human THUMPD3 and TRMT112. Efforts to try to co-express Trm112 and the putative Trm14 protein from A. fulgidus failed to demonstrate such interaction due to poor expression of the AfTrm14-like protein in E. coli (CW and MG, unpublished data). This should be further explored in the future.
The importance of THUMPD3 has been investigated by inactivating the expression of this protein by CRISPR-Cas9 in two different human cell lines: HEK293T and HCT116. The depletion of THUMPD3 led to an almost 20% decrease in m2G levels in total tRNAs but similarly to TRMT11, this affected neither tRNA structure, stability nor aminoacylation. Translation was marginally affected in both thumpd3−/− cell lines but an accumulation of 80S was evident (Yang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023). Finally, the cell proliferation of HEK293T thumpd3−/− cell lines was severely reduced (Yang et al., 2021) but this was not the case of HCT116 thumpd3−/− cells (Wang et al., 2023).
Many studies have described that the deletion of a single gene encoding for a bacterial or a eukaryotic tRNA modification enzyme does not result in a clear and detectable phenotype, whereas the concomitant deletion of genes encoding for two RNA modification enzymes can result in strong growth defects (Purushothaman et al., 2005; Alexandrov et al., 2006). This is indeed the case of a double KO HCT116 cell line depleted for TRMT11 and THUMPD3 proteins, which catalyze the formation of m2G in the tRNA acceptor stem. This cell line is characterized by the near complete absence of m2G in tRNAs but this did not significantly affect tRNA structure, stability and aminoacylation (Wang et al., 2023). However, significant reductions in cell proliferation, 80S, polysome levels and newly synthesized proteins were observed indicating that translation level is less efficient when both m2G6 and m2G10 are absent in tRNA molecules. This could be a direct consequence of the absence of both modifications in the tRNA acceptor arm, which could slow down the translation due, for instance, to improper accommodation of hypomodified tRNAs into the ribosomal A-site. However, due to the existence of tRNA modification circuits (Guy and Phizicky, 2015; Barraud et al., 2019), one cannot exclude that the absence of m2G6 and/or m2G10 modifications affects the deposition of another tRNA modification, which would then be important for translation. In the future, mapping the changes in other tRNA modifications when m2G6 and/or m2G10 modifications are absent could provide more details on how post-transcriptional modifications fine-tune tRNA functions.
The tRNA anticodon loop is often diversely modified and these modifications are among the most complex ones. They are particularly important for codon decoding and influence the structure of this loop as well as translation speed. In particular, modifications on the wobble uridine base (U34), which base pairs with the third nucleotide of the mRNA codon, have been found to influence tRNA preference towards certain sequences and to aid in the reading of non-cognate codons (Johansson et al., 2008; Zhou et al., 2021; Smith et al., 2024). A complex modification occurring at position U34 in the anticodon of eukaryotic but also some archaeal tRNAs is 5-methoxycarbonylmethyl-uridine (mcm5U) and its thio-derivative 5-methoxycarbonylmethyl-2-thiouridine (mcm5s2U; Figures 4A (van Tran et al., 2018)).

Figure 4. Trm9/ALKBH8 proteins catalyze late steps in the modification pathway of (S)-mchm5(s2)U at the wobble position of cytoplasmic tRNAs. (A) Chemical structure of (S)-5-methoxycarbonyl-hydroxymethyl-(2-thio)-uridine ((S)-mchm5(s2)U) with the hydroxyl and methyl groups added by ALKBH8 AlkB-like and MTase domains highlighted by kaki and firebrick spheres, respectively. (B) Schematic depiction of the fungal Trm9 and metazoan ALKBH8 and TRMT9B proteins. The intrinsically disordered region present in TRMT9B MTase domain is depicted by a black line. (C) Ribbon representation of the crystal structure of the Trm9-Trm112 complex from Yarrowia lipolytica yeast (PDB code: 5CM2). The zinc atom bound to Yarrowia lipolytica Trm112 (yellow) is shown as a black sphere. The SAM molecule (purple sticks with the methyl group to be transferred shown as a sphere) was modeled by superimposing the crystal structure of Rhodopseudomonas palustris RPA2492 protein bound to SAM onto Trm9 MTase domain. A calcium ion (dark green sphere) has been modeled by superimposing the crystal structure of CysG (PDB code: 9FCD) onto Trm9 MTase domain. (D) Zoom-in on Trm9/ALKBH8 MTase active site. Same color code as (C). The cm5U moiety (grey sticks) of a tRNA substrate has been modeled as described in Letoquart et al. (2015). Human ALKBH8 amino acids numbering is used in this panel. Potential hydrogen bonds between cm5U and active site residues are depicted as black dashed lines. (E) Ribbon representation of the crystal structure of the human RRM and AlkB-like domains of human ALKBH8 (PDB code: 3THP). A 2-oxoglutarate (2OG) molecule bound to AlkB-like domain is shown as purple sticks. The HxD…H catalytic triad of the AlkB-like domain is shown as sticks. A manganese ion bound to this triad is shown as a pink sphere. The zinc atom bound to the AlkB-like domain is shown as a black sphere and the amino acids coordinating it as sticks.
The biosynthetic pathway for this modification is complex and involves many proteins to generate several related modifications on U34. Firstly, Elongator, a six subunit complex formed by the Elp1-6 proteins, is required for uridine to be acetylated and form cm5U (Karlsborn et al., 2014; Selvadurai et al., 2014; Kolaj-Robin and Seraphin, 2017; Lin et al., 2019; Abbassi et al., 2020; Abbassi et al., 2024). The cm5U moiety can then be methylated by the fungal Trm9 and the metazoan ALKBH8 enzymes to give mcm5U (Kalhor and Clarke, 2003; Fu D. et al., 2010; Mazauric et al., 2010; Songe-Moller et al., 2010; Letoquart et al., 2015). According to the sub-cellular localization of ALKBH8, this modification should be added in the cytoplasm in human cells (Fu D. et al., 2010; Pastore et al., 2012; Brumele et al., 2021). While fungal Trm9 protein are made of a single MTase domain, ALKBH8 are multi-domain proteins (Figure 4B). Similarly to eukaryotic TRMT11 proteins, Trm9/ALKBH8 proteins interact with TRMT112 through their MTase domain and this interaction is important for the solubility of the MTase subunit (Figure 4C; Mazauric et al., 2010; Songe-Moller et al., 2010; Chen et al., 2011). The formation of the Trm112-Trm9 and TRMT112/ALKBH8 complexes is also critical for the formation of mcm5U (Mazauric et al., 2010; Songe-Moller et al., 2010; Chen et al., 2011; Liger et al., 2011). The mcm5U34 modification is not specific to eukaryotic tRNAs since it has been identified at least in H. volcanii tRNAs, where it is dependent on the presence of both Trm9 and Trm112 genes (van Tran et al., 2018). However, due to the presence of Elp3 and Trm9 orthologues in many archaea (Grosjean et al., 2008; Selvadurai et al., 2014; Bourgeois et al., 2017a), this modification should be widespread in archaea.
Based on the crystal structure of fungal Trm9-Trm112 complex (Letoquart et al., 2015), the active site of the Trm9 subunit has been mapped by site-directed mutagenesis unravelling amino acids important for tRNA modification. This led to the docking of a cm5U substrate into the active site (Figure 4D) and to propose similarity with the active sites of other O-MTases, namely TYW4 (synthesis of wybutosine in tRNA), glutamate MTase CheR and human LCMT-1 (methylation of the carboxyl terminal group of leucine from PP2A). Recently, the enzymatic activities of two additional O-MTases, BelI and CysG, which are involved in β-lactone synthesis, have been characterized, revealing the existence of a His-His … Asp active site motif involved in the coordination of a catalytically important calcium ion (Kuttenlochner et al., 2024). Both His (His122 and His123 from CysG) from this motif structurally match with His115 and His116 from S. cerevisiae Trm9 (His474 and His475 in human ALKBH8) and interestingly, as observed for Trm9 enzymatic activity (Letoquart et al., 2015), only the second His (His116 for yeast Trm9 and His123 for CysG) is critical for MTase activity. Tyr243 from Trm9 (Tyr627 in human ALKBH8), which is also important for catalytic activity, matches with Asp191 from CysG. In Trm9 proteins, it could also be involved in the coordination sphere of a calcium ion, as observed in some other calcium binding proteins (Kirberger et al., 2008). Altogether, this strongly suggests that similarly to CysG and BelI, Trm9 and ALKBH8 enzymatic activities could be optimal in the presence of a calcium ion.
In metazoa, mcm5U can be further hydroxylated to form (R)-mchm5U (5-methoxycarbonyl-hydroxymethyluridine) or (S)-mchm5U diastereoisomers. The first modification is formed by ALKBH4 (Kogaki et al., 2023) while (S)-mchm5U formation is catalyzed by the ALKBH8 protein (Fu Y. et al., 2010; Songe-Moller et al., 2010; van den Born et al., 2011). Indeed, in addition to the Trm9-like MTase domain, metazoan ALKBH8 proteins are made of two additional domains: a RNA recognition motif (or RRM) and a 2-oxoglutarate- and iron-dependent AlkB-like domain, the latter catalyzes the hydroxylation of mcm5U to form (S)-mchm5U ((Figures 4A, B, E; Fu et al., 2010b; van den Born et al., 2011; Pastore et al., 2012). Both the RRM and AlkB-like domains confer binding specificity for RNA vs. DNA to the ALKBH8 MTase domain (Fu D. et al., 2010). Metazoan ALKBH8 proteins are then unique in their ability to perform two sequential enzymatic reactions, namely methylation of cm5U to mcm5U followed by hydroxylation of mcm5U to (S)-mchm5U. Interestingly, in Arabidopsis thaliana but also more generally in plants, these two reactions are catalyzed by different proteins, similar to the MTase and the AlkB-like domains from ALKBH8 (Leihne et al., 2011).
Based on HITS-CLIP results, ALKBH8 seems to have a preference for mature, CCA modified tRNAs with a wobble uridine (underlined) such as tRNAArg (UCU), tRNAGln (UUG), tRNAGlu (UUC), tRNASec(UCA), tRNAGly (UCC), and tRNALys (UUU) (Cavallin et al., 2022). Interestingly, ALKBH8 is also able to bind to a wide range of RNA species including C/D box snoRNAs and vault RNAs, but enzymatic activity on RNAs other than tRNAs has not yet been reported in the literature. These interactions might not be specific since ALKBH8-TRMT112 complex has been shown to bind small RNAs (tRNAs and 17-mer oligonucleotides) in a sequence unspecific manner (Pastore et al., 2012).
The tRNA modifications catalyzed by Trm9/ALKBH8 proteins play important roles in decoding due to their location at the wobble position. The mcm5s2U modification favors decoding of both A- and G-ending codons (Johansson et al., 2008; Patil et al., 2012b; Vendeix et al., 2012). In yeast, it also enhances the translation of transcripts rich in these codons (AGA, CAA, GAA and AGG; (Begley et al., 2007; Deng et al., 2015)), including those coding for Rnr1 and Rnr3, two key proteins involved in the DNA damage response. Consequently, the deletion of the TRM9 gene in baker’s yeast results in a higher sensitivity to the DNA alkylating agent methyl methanesulfonate (MMS) and in a delayed G1 to S phase transition after MMS treatment. In addition, the absence of mcm5U tRNA modification upon Trm9 deletion results in translational infidelity and induces the activation of protein stress response pathways (Patil et al., 2012a). In human cells, the depletion of ALKBH8 increases the cellular sensitivity to DNA damaging reagents such as MMS and bleomycin while exposure to bleomycin increases ALKBH8 expression in wild-type cells (Fu D. et al., 2010). In a bladder cancer-derived cell line, siRNA mediated knockdown of ALKBH8 induced apoptosis and inhibited tumor growth in a corresponding mouse model (Shimada et al., 2009). The ALKBH8-dependent mcm5U34 and mcm5Um34 modifications present in tRNASec, which recognizes UGA codon, also play a key role in the synthesis of selenoproteins (Songe-Moller et al., 2010). Many selenoproteins are involved in stress response and since tRNASec is aberrantly modified in Albkh8−/− mice, a decreased recoding of the UGA stop codon to selenocysteine was observed, in particular for the glutathione peroxidase protein Gpx1 (Songe-Moller et al., 2010). The Albkh8−/− mice also exhibit enhanced sensitivity to stress such as exposure to naphtalene, an environmental toxic compound (Leonardi et al., 2020). Higher levels of mcm5U were detected in the brain of Albkh8−/− mice as compared to other tissues such as spleen and liver, suggesting that a partial compensatory pathway may exist specifically in this organ to maintain functional levels of mcm5U even in the absence of ALKBH8 (Honda et al., 2024). In fruit fly, ALKBH8 limits synaptic growth and oxidative stress and is important for learning and memory as well as for the synthesis of the selenophosphate synthetase 2 (SPS2) selenoprotein (Madhwani et al., 2024).
Recently, ALKBH8 mutants have been identified as associated with a form of autosomal intellectual developmental disorder (ID). Indeed, fourteen patients with pathogenic variants of ALKBH8 have been reported in six distinct families (Monies et al., 2019; Saad et al., 2021; Maddirevula et al., 2022; Waqas et al., 2022; Yilmaz et al., 2024). The affected individuals exhibit global developmental delay, facial dysmorphic features, and in most cases, psychiatric problems. Of the six pathogenic ALKBH8 variants identified in these studies, one corresponds to a nonsense mutation (Arg554*); (Monies et al., 2019)) and two to a deletion of one nucleotide, thereby generating a frameshift that gives rise to the emergence of premature stop codons (Trp599Glyfs*19; (Monies et al., 2019); and Arg562Alafs*56; (Saad et al., 2021)). These three variants should generate truncated proteins, which are most probably unstable. In addition, three missense mutations (Trp504Ser (Waqas et al., 2022), Arg625His (Maddirevula et al., 2022) and Arg625Pro (Yilmaz et al., 2024)) affecting amino acids located in the MTase domain of the ALKBH8 protein, were identified in patients. These amino acids, namely Trp504 and Arg625, correspond to Trp145 and Arg241, respectively, in S. cerevisiae Trm9 protein. Interestingly, these two positions are located within Trm9 MTase active site (Figure 4D). Their substitution by alanine in yeast Trm9 strongly or completely abolishes the activity of the resulting Trm9-Trm112 complexes in vitro and in vivo (Letoquart et al., 2015). This is in agreement with mass spectrometry analyses, which have revealed the absence of mcm5U, mcm5s2U and (S)-mchm5U modifications in tRNAs extracted from some patient cells (Monies et al., 2019; Maddirevula et al., 2022). The importance of ALKBH8 function in animal central nervous system dysfunction is further supported by the observed reduced brain weight, pathological changes in the brain, lower interest in exploring novel objects, poorer motor coordination and balance of Albkh8−/− mice (Honda et al., 2024). Similarly, Albkh8−/− flies exhibit associative learning and memory impairments in a proboscis extension reflex feeding test (Madhwani et al., 2024). However, the importance of ALKBH8 protein is not restricted to brain development and function since Albkh8−/− mice also exhibit defects in erythroid differentiation, reduced body weight and survival rates (Madhwani et al., 2024; Nakai et al., 2024) while Albkh8−/− flies have cardiac development defect (Kim et al., 2004). In C. elegans worm, an internal deletion in the ALKBH8 ortholog C14B1.10 causes embryonic lethality or sterility in animals surviving to adulthood (Byrne et al., 2007). Altogether, these data support an important role of ALKBH8 proteins and hence modifications at the U34 wobble position of some tRNAs in organ development.
Translational regulation via tRNA modification by ALKBH8 has not yet been fully elucidated. The role of ALKBH8 in neurological pathologies and oxidative stress response could be due to a large number of direct and/or indirect effects. Future studies will be necessary to find direct links between ALKBH8-mediated translation regulation and specific oxidative stresses affecting behavior at different developmental stages. In parallel, further study of ID-associated ALKBH8 variants will be important to understand tRNA processing and function in the context of the nervous system and to draw links between disruption of tRNA modifications and neurological diseases. In the same vein, some preliminary data show the potential of antioxidants in improving learning performance in Albkh8−/− flies (Madhwani et al., 2024). Whether this could be explored as a form of therapeutics for individuals with ID-associated ALKBH8 variants remains to be investigated.
In metazoa, a second Trm9 orthologue is present, namely TRMT9B (also referred to as Trm9L, hTrm9L, KIAA1456, and C8ORF79 in the literature; see Table 1) (Fu D. et al., 2010). Contrary to ALKBH8, TRMT9B is made only of a MTase domain (Figure 4B), which shares 45.7% sequence identity with S. cerevisiae Trm9 (Towns and Begley, 2012). The TRMT9B protein also contains an intrinsically disordered region inserted within its MTase domain and absent in yeast and human Trm9/ALKBH8 proteins, which is subject to phosphorylation (Gu et al., 2018). Interestingly, human TRMT9B also interacts with TRMT112 (Gu et al., 2018) and is mostly found in the cytoplasm. To our knowledge, no enzymatic activity or substrate(s) have been identified for human TRMT9B. However, since all the amino acids that were shown to be critical for SAM binding and/or enzymatic activity for yeast Trm9 are strictly conserved in TRMT9B, it may also act as an RNA MTase catalyzing the formation of mcm5U in yet to be identified RNAs. The expression of TRMT9B in trm9Δ yeast, does not rescue the formation of mcm5s2U in tRNAs, while expression of human ALKBH8 does partially (Begley et al., 2013). However, we cannot exclude that human TRMT9B does not interact with yeast Trm112 in these complementation assays, explaining the absence of activity.
In a recent study performed in fruit fly (Hogan et al., 2023), TRMT9B protein was shown to be expressed mostly in neurons but also in glial and muscle cells and at synapses, contrary to ALKBH8, which is ubiquitously expressed at least in human cells (Uhlen et al., 2015). Interestingly, the expression of TRMT9B protein limits synaptic growth in Drosophila and this activity relies on the integrity of the putative MTase active site, strongly suggesting that the putative TRMT9B enzymatic activity is critical for this function (Hogan et al., 2023). Such importance of the TRMT9B putative enzymatic activity might not be related to a role in catalyzing the formation of mcm5s2U and related modifications in tRNAs since the levels of these modifications are unaffected upon deletion of TRMT9B gene in fruit fly contrary to the effect observed upon deletion of ALKBH8 (Hogan et al., 2023). However, we cannot exclude rescue effects by ALKBH8, explaining that levels of mcm5U and related modifications are not affected in the absence of TRMT9B. TRMT9B seems to have additional function(s), independent of its putative MTase activity. Indeed, the depletion of TRMT9B in flies results in a decrease in neurotransmitter release, which is rescued by ectopic expression of either the wild-type TRMT9B or its predicted enzymatically inactive mutants (Hogan et al., 2023).
Even though the exact function of human TRMT9B has not been clarified, there is much evidence that points towards a tumor suppressor function of TRMT9B in a number of cancers (Flanagan et al., 2004; Gu et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2018). Indeed, down-regulation of TRMT9B or loss of this gene appears to be associated with progression of cancer cells to a more aggressive state. Conversely, when TRMT9B is over-expressed, growth was suppressed in colorectal tumor cells, in which a functional SAM binding domain was required for the inhibition of tumorigenicity (Begley et al., 2013). In the case of lung cancer cells, TRMT9B over-expression led to changes in markers important in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition process, which overall favored a reduction in cancer cell invasion and metastasis (Wang et al., 2018).
TRMT9B might also be involved in cell response to external stresses. Indeed, in response to H2O2 exposure, TRMT9B is phosphorylated in its disordered loop and consequently, the phosphorylated TRMT9B protein interacts with several proteins from the 14-3-3 family (Gu et al., 2018). This indicates that TRMT9B may have a phospho-signaling role in response to oxidative stress.
Recently, TRMT9B has also been proposed to be involved in the codon-specific reprogramming of host translation machinery induced upon infection of mammalian cells by the Chikungunya virus (CHIKV; (Jungfleisch et al., 2022)). This mechanism promotes the translation of viral genomes over host mRNAs. CHIKV infection induced the over-expression of the TRMT9B protein, resulting in a significant increase in the levels of mcm5 modification. Interestingly, siRNA-mediated silencing of TRMT9B decreased mcm5U levels and inhibited CHIKV RNA and protein levels, suggesting that TRMT9B plays a role in CHIKV infection of mammalian cells.
To our knowledge, no conclusive evidence exists that TRMT9B is a bona fide tRNA methyltransferase catalyzing the formation of mcm5U in human tRNAs. Most studies focusing on TRMT9B have mainly investigated its role in the formation of tRNA mcm5U modification and have not accounted for the possibility that this protein could be methylating a non-tRNA substrate, or a small subset of tRNAs not detectable by bulk analysis. One cannot rule out the possibility that it is catalyzing an entirely unknown modification or a mcm5U-related modification in specific tissues or organs. This complicates drastically the identification of TRMT9B substrates, which is critical for further characterization of the protein and its cellular functions. This is particularly important in the context of cancer due to the observed role of TRMT9B as a tumor suppressor gene.
Many 2′OH ribose groups from rRNAs are methylated, mostly by a snoRNA-guided box C/D large ribonucleoparticle (Hofler and Carlomagno, 2020), except for one nucleotide (G2922) on the 25S rRNA, which is modified by the stand-alone enzyme Spb1 (Lapeyre and Purushothaman, 2004). In addition, some rRNA nucleotides are methylated on the base ring. These different rRNA modifications mostly cluster to functional sites of the ribosomes, namely the decoding center and the peptidyl transferase center (Sharma and Lafontaine, 2015; Natchiar et al., 2017; Pellegrino et al., 2023). Due to their localization in ribosome functional centers, one would expect that these modifications play critical roles during translation. However, studies carried out in S. cerevisiae or on human cells indicate that while several RNA modification enzymes are essential for normal growth under laboratory conditions, their enzymatic activity is not (White et al., 2008; Figaro et al., 2012; Bourgeois et al., 2015; Haag et al., 2015; Zorbas et al., 2015; Liao et al., 2022).
Eukaryotic TRMT112 proteins are known to interact with two MTases modifying nucleotide bases on the 18S rRNA, namely Bud23/WBSCR22 and METTL5.
The Bud23 protein from S. cerevisiae and its human orthologue WBSCR22 (hereafter named BUD23, see Table 1) catalyze the formation of N7-methylguanosine (m7G) at positions 1575 and 1639 in yeast and human 18S rRNA, respectively (Figure 5A White et al., 2008; Haag et al., 2015; Zorbas et al., 2015)). This position is located in the 40S head region, at the ridge between P- and E-site tRNAs in the mature 40S (Figure 5B). Eukaryotic BUD23 proteins interact with TRMT112 and this interaction is important for BUD23 stability in vivo and in cellulo as well as for the formation of m7G (Figaro et al., 2012; Sardana and Johnson, 2012; Letoquart et al., 2014; Sardana et al., 2014; Ounap et al., 2015; Zorbas et al., 2015; Guo et al., 2023; Song et al., 2024).
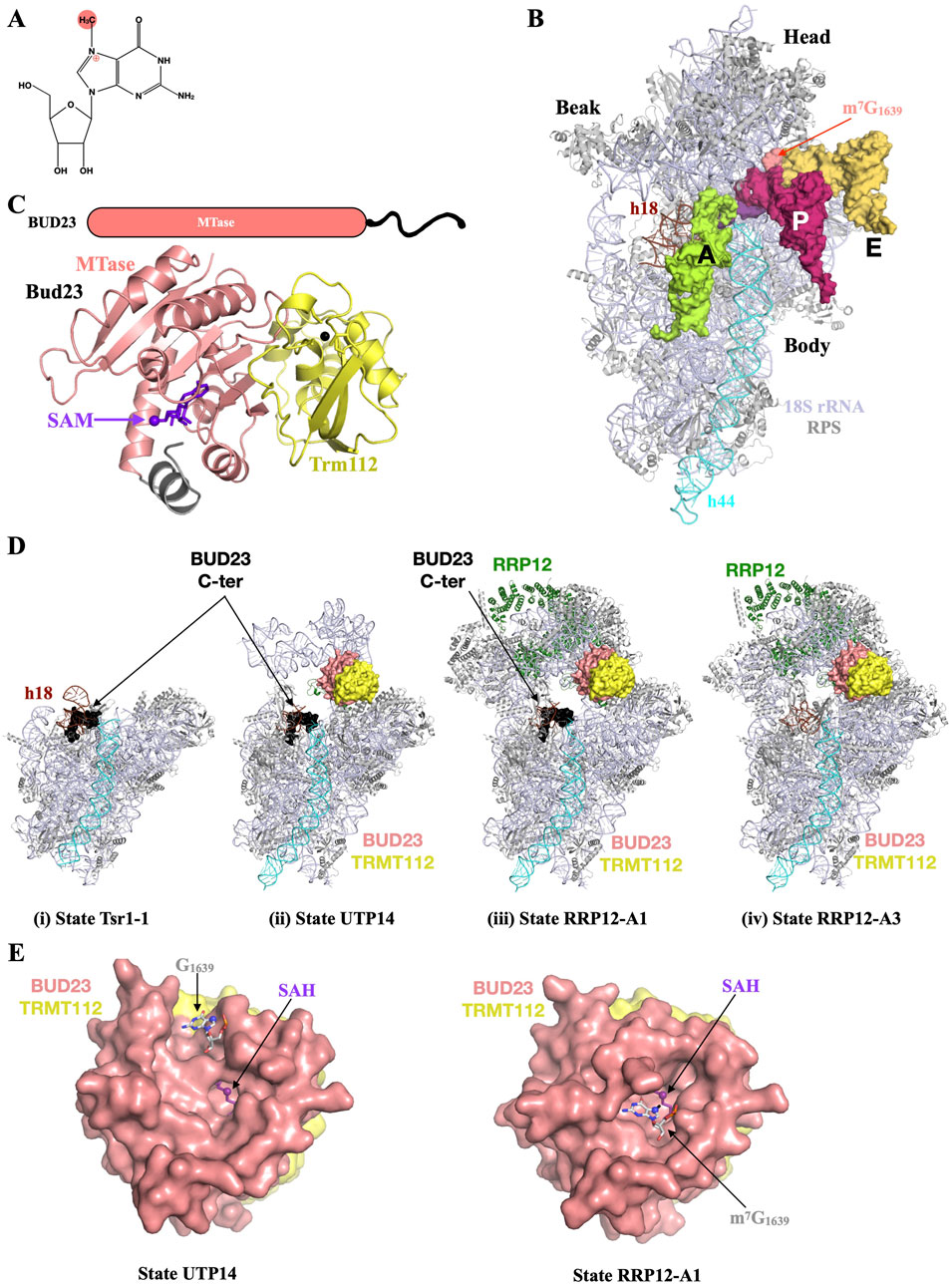
Figure 5. BUD32 plays a critical role for small ribosomal subunit biogenesis. (A) Chemical structure of N7-methylguanosine (m7G) with the methyl group added by BUD23 highlighted by a pink sphere. The positive charge introduced upon methylation on N7 is depicted by the ⊕ sign. (B) Overview of human 40S small ribosomal subunit (18S rRNA and small ribosomal subunit proteins colored light blue and grey, respectively) bound to a short mRNA (purple), tRNAs (light green, pink and light orange for A-, P- and E-site tRNAs, respectively) and highlighting the position of the m7G1639 modified nucleotide (pink) at the ridge near the anticodon loops from P- and E-site tRNAs. Helices h18 and h44 from 18S rRNA are colored in brown and cyan, respectively. The tRNAs and mRNA have been modeled by superposing the cryo-EM structure of rabbit 40S bound to tRNAs and eEF1A (PDB: 5LZS) onto the high resolution structure of human ribosome (PDB: 8QOI). For the sake of clarity, human 60S, rabbit 80S and eEF1A translation elongation factor have been omitted. (C) Schematic depiction of the BUD23 proteins and ribbon representation of the crystal structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Bud23-Trm112 complex bound to SAM (purple sticks; PDB code: 4QTU). The intrinsically disordered C-terminal end of BUD23 proteins, which is absent in the crystal structure, is shown as a black line on the schematic representation. The N-terminal region from yeast Bud23 MTase domain, which folds upon SAM binding, is colored in grey. (D) Snapshots highlighting the location of the BUD23-TRMT112 complex during the nucleocytoplasmic pre-40S maturation process. Same color code as (B). The BUD23 (pink for the MTase domain and black for the C-terminal region) and TRMT112 (yellow) proteins are shown as surface. Structures of the S. cerevisiae Tsr1-1 (i; PDB code: 7WTN) or human UTP14 (ii; PDB code : 7WTS), RRP12-A1 (iii; PDB code : 7WTT) and RRP12-A3 (iv; PDB code: 7WTW) states from Cheng et al (2022). (E) Zoom in on the active site of BUD23-TRMT112 complexes in the structures corresponding to states UTP14 (left) and RRP12-A3 (right) with the (m7)G1639 shown as grey sticks with the N7 atom shown as a sphere. Since the m7G1639 nucleotides occupy the same location in RRP12-A1 and RRP12-A3 states, only RRP12-A3 state is shown for the sake of clarity.
BUD23 proteins play an important role for the biogenesis of the 40S small ribosomal subunit. Indeed, the deletion of the BUD23 gene in S. cerevisiae results in a decreased amount of 40S subunits, an imbalance of rRNA precursors, i.e., accumulation of 20S rRNA and decrease in 27SA and 27S rRNAs and a nucleolar retention of pre-40S particles (White et al., 2008). Bud23 is also important for efficient A2 cleavage of the precursor rRNA, a step crucial for its proper maturation (Sardana et al., 2013). In human cells, the depletion of the BUD23 protein results in the accumulation of the 18S-E intermediate associated with a mild reduction of 30S and a decrease in mature 18S (Ounap et al., 2013; Haag et al., 2015; Zorbas et al., 2015). The central role of BUD23 proteins in 40S biogenesis rationalizes the strong growth defect phenotype of the bud23Δ yeast strain (White et al., 2008), the decreased proliferation of human HeLa cells upon BUD23 silencing (Ounap et al., 2013) and the observation that the homozygous BUD23 knock-down are embryonic lethal in mouse and worm (Piano et al., 2002; Baxter et al., 2020).
BUD23 proteins are made of a N-terminal class I SAM-dependent MTase domain, which directly interacts with TRMT112, followed by a long stretch of at least 50 amino acids (Figure 5C; White et al., 2008; Letoquart et al., 2014; Ameismeier et al., 2018; Cheng et al., 2022)). The crystal structure of the S. cerevisiae Bud23-Trm112 complex has revealed that upon SAM binding to the Bud23 subunit, a N-terminal region of the MTase domain folds back onto the SAM cofactor to adopt an α-helical conformation and then mould the substrate binding site (Letoquart et al., 2014). Bud23 C-terminal region is predicted to be unstructured and contains a nuclear localisation signal (White et al., 2008). In yeast, only the MTase domain is important for Bud23 activity in 40S synthesis (White et al., 2008). However, BUD23 MTase activity is not important for growth or rRNA processing in yeast or human cells, indicating that the m7G residue in the 40S has no critical functional roles (White et al., 2008; Lin et al., 2012; Letoquart et al., 2014; Haag et al., 2015; Zorbas et al., 2015). This is in line with the observation that the yeast G1575A 18S rRNA mutant has no growth phenotype (White et al., 2008). BUD23 proteins are recruited early to the pre-90S and remain associated with pre-40S middle and late stages (Figaro et al., 2012; Sardana et al., 2013). Several cryo-electron microscopy structures have brought useful information about the timing of the recruitment and the association of the BUD23-TRMT112 complex with pre-40S intermediates (Figure 5D; Ameismeier et al., 2018; Cheng et al., 2022). Indeed, in yeast, Bud23 is first anchored to early pre-40S through its C-terminal extremity, which binds to immature h18 of the 18S rRNA and stabilizes an immature conformation of the pre-40S. In this complex, Bud23 MTase domain and Trm112 as well as the 40S head region are not visible, probably due to high intrinsic flexibility (Figure 5D panel i). Next, the MTase domain from BUD23 (together with TRMT112) binds to the pre-40S head region but the nucleotide to be modified is not located in BUD23 active site (Figure 5D panel ii and Figure 5E left). Finally, the MTase domain binds to its nucleotide target (Figure 5D panel iii and Figure 5E right) and BUD23 C-terminal region is released from the pre-40S (Figure 5D panel iv). In this structure, several residues located in the BUD23 active site and that have been identified as being important for yeast Bud23 enzymatic activity are directly contacting G1639 as suggested in a previous docking model (Letoquart et al., 2014). During this process, the BUD23-TRMT112 complex physically interacts with several 40S biogenesis factors such as the yeast Dhr1 DEAH RNA helicase involved in the release of U3 snRNA from maturing 40S, as well as the 40S nuclear export factor Rrp12 (Letoquart et al., 2014; Sardana et al., 2014; Roychowdhury et al., 2019; Black et al., 2020; Black and Johnson, 2022). Altogether, these observations reveal a complex BUD23-TRMT112 choreography during pre-40S maturation and suggest that the role of BUD23 is to destabilize key interactions in the small subunit processome to promote progression to the pre-40S. This is compatible with the requirement of yeast Bud23 for A2 cleavage, an essential step for the separation of small and large subunit precursors. BUD23 proteins might also be important during 40S biogenesis by timing or chaperoning the correct folding of 18S rRNA during the many maturation steps it is undergoing. In this context, the BUD23-dependent formation of m7G, which occurs late during this maturation process (Figaro et al., 2012), could simply act as a signal that the subunit has successfully passed one or several quality-control checkpoints. Interestingly, the formation of m7G1575 in yeast does not depend on the presence of other modifications located in proximity, namely m6,6A1781 and m6,6A1782, and reciprocally (Letoquart et al., 2014). However, in C. elegans, the depletion in BUD23 results in a decrease in m7G but also of m6,6A associated with a concomitant increase in m6A at the positions which should be m6,6A (Liberman et al., 2023).
The BUD23-TRMT112 complex has recently been proposed to act as a tumor suppressor when over-expressed in pancreatic cancer (Khan et al., 2022). This is somehow surprising since an increased expression of human BUD23 was observed in many types of cancers and shown to promote migration, invasion and proliferation of cancer cells (Nakazawa et al., 2011; Tiedemann et al., 2012; Jangani et al., 2014; Stefanska et al., 2014; Yan et al., 2017; Chi et al., 2020). The latter implication in cancer is not surprising since highly proliferative cancer cells are very demanding in protein synthesis and hence ribosome production. BUD23 was also shown to bind a glucocorticoid receptor co-activator through its MTase domain and to play a role in histone 3 tri-methylation on Lys4. Consequently, this affects the recruitment of the glucocorticoid receptor to the chromatin and its function in transcription regulation (Jangani et al., 2014). The depletion of BUD23 in mouse reduces the translation efficiency of mitochondrially-encoded transcripts (Baxter et al., 2020). Since to our knowledge, no m7G modification has been identified in mitochondrial rRNAs, this most probably results from defects in cytoplasmic protein synthesis process. Indeed, BUD23 down-regulation decreases the abundance of protein components of the 40S and most likely the synthesis of mitochondrial ribosomal proteins, which are encoded by the nuclear genome. In BUD23-deficient cardiac muscles, this causes mitochondrial dysfunction in cardiomyocytes associated with a disorganization of mitochondria arrangement, resulting in cardiomyopathy. In C. elegans, the absence of BUD23 alters transition of genes involved in longevity and cell response (Liberman et al., 2023). Finally, two studies have linked BUD23 with viral infection. First, the BUD23-TRMT112 complex interacts with the L protein from Borna disease virus 1, a negative-strand RNA virus causing fatal neurological diseases in animals but rarely in mammals (Garcia et al., 2021). The BUD23-TRMT112 complex then plays a role in the recruitment of viral RNPs to chromosomes and its catalytic activity is mandatory for this process. This function has no role in viral mRNA expression. This complex also enriched on pre-40S together with the viral protein orf11 from Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus during lytic replication (Murphy et al., 2023). BUD23 appears as necessary for the expression of late viral transcripts and is essential for the production of new infectious virions.
Since there is no METTL5 orthologue in S. cerevisiae, the model organism initially used to characterize the eukaryotic TRMT112 interaction network, it was not anticipated that human METTL5, a class I SAM-dependent methyltransferase, could interact with TRMT112. However, a study performed in the H. volcanii archaeon, identified the Hvo_1475 putative MTase as a partner of HvoTrm112 (van Tran et al., 2018). Since Hvo_1475 shares 35% sequence identity with human METTL5, this suggested that the latter may interact with TRMT112. Indeed, the human METTL5 and TRMT112 proteins were shown to interact directly to form a stable complex (Figure 6A) and this is also the case for orthologous proteins from fruit fly and worm (van Tran et al., 2019; Ignatova et al., 2020; Leismann et al., 2020; Rong et al., 2020; Sepich-Poore et al., 2022). As observed for other MTases interacting with TRMT112, the latter is very important for human METTL5 cellular stability and for its over-expression as a soluble protein in E. coli (van Tran et al., 2019; Sepich-Poore et al., 2022).
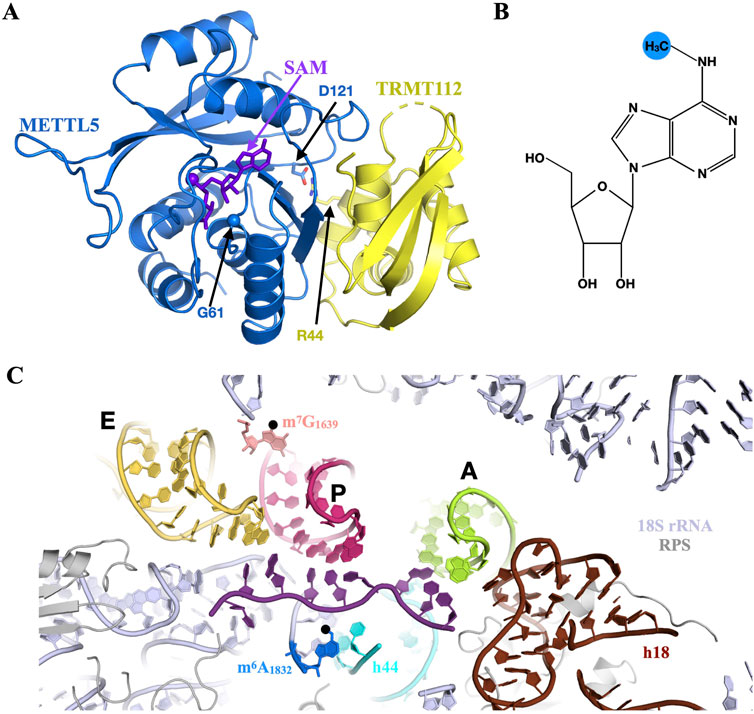
Figure 6. METTL5 catalyzes the formation of m6A in the decoding center of human ribosome. (A) Ribbon representation of the crystal structure of human METTL5-TRMT112 complex bound to SAM (purple sticks; PDB code: 6H2V). The C⍺ atom of Gly61 is shown as a sphere. The side chains of Asp121 from METTL5 and Arg44 from TRMT112, which form a salt bridge at the interface between both proteins, are shown as blue and yellow sticks, respectively. (B) Chemical structure of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) with the methyl group added by METTL5 highlighted by a blue sphere. (C) Overview of human 40S small ribosomal subunit decoding center (18S rRNA and small ribosomal subunit proteins colored light blue and grey, respectively) bound to a short mRNA (purple), tRNAs (light green, pink and light orange for A-, P- and E-site tRNAs, respectively) and highlighting the position of the m6A1832 (blue) and m7G1639 (pink) modified nucleotides. Helices h18 and h44 from 18S rRNA are colored in brown and cyan, respectively. The tRNAs and mRNA have been modeled as described in Figure 5B.
Metazoan and plant METTL5 proteins are the long-sought rRNA MTases responsible for the formation of N6-methyladenosine at position 1832 (m6A1832, the numbering of human ribosome is used; Figure 6B) on the 18S rRNA (Maden, 1986; van Tran et al., 2019; Ignatova et al., 2020; Leismann et al., 2020; Rong et al., 2020; Sendinc et al., 2020; Xing et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2021; Song et al., 2024). The 18S rRNA is the only known substrate of METTL5 but contrary to BUD23, METTL5 is not required for correct 18S rRNA biogenesis (van Tran et al., 2019; Leismann et al., 2020). The METTL5-dependent modification is located in close proximity to the P-site and is thought to influence mRNA binding to the decoding center of the ribosome (Figure 6C). Accordingly, METTL5 enzyme is important for global mRNA translation in some cell lines (Rong et al., 2020; Sepich-Poore et al., 2022; Chen et al., 2023). In nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells (NPC), METTL5 turns out to be important for 80S ribosome assembly and for the interaction of the 40S subunit with the large ribosomal proteins RPL24 and RPL41, which bridge 40S and 60S subunits (Chen et al., 2023). This is particularly interesting since in the cryo-EM structure of the human 80S (Holvec et al., 2024), the N-terminal extremity of RPL41 contacts m6A1832.
METTL5 appears to be important during brain development since several mutations in this gene have been identified in patients suffering from neurodevelopmental defects characterized by intellectual disorder, global developmental delay, facial abnormalities and microcephaly (Hu et al., 2019; Richard et al., 2019; Torun et al., 2022). Among the METTL5 mutations identified, two biallelic frameshift mutations (c.344_345delGA and c.571_572delAA) result in the expression of truncated and unstable METTL5 proteins (p.Arg115Asnfs∗19 and p. Lys191Valfs∗10 respectively; (Richard et al., 2019)). In parallel, two homozygous missense mutants (Gly61Asp, Asp121Gly) have been identified. Gly61 is located within the SAM binding site and its substitution by an aspartic acid affects METTL5 interaction with TRMT112 (Figure 6A; Hu et al., 2019). Asp121 is located at the interface between METTL5 and TRMT112, where it forms a salt bridge with Arg44 from TRMT112 (Torun et al., 2022). Its substitution by a glycine will eliminate this salt bridge and most likely affect the interaction between METTL5, thereby destabilizing the complex. Some of the phenotypes observed in patients have been recapitulated in model organisms. In zebrafish, Mettl5 knockdown recapitulates the microcephaly phenotype observed in human patients (Richard et al., 2019). Likewise, METTL5 deficient mice displayed visible craniofacial abnormalities, such as snout deviation and only a partial fusion of the frontal bone suture (Ignatova et al., 2020; Lei et al., 2023). Mettl5 KO mice also have impaired spatial learning and memory (Wang et al., 2022) whereas METTL5 KO flies exhibit severe disorientation and affected walking behavior (Leismann et al., 2020). The recapitulation of cranial and neurological defects observed in human patients with METTL5 mutants in knockout animals points towards the importance of conserved rRNA modifications and their involvement in human neurological disorders.
Many studies support that METTL5 is important for optimal cellular growth and/or differentiation (Rong et al., 2020; Xing et al., 2020; Chen et al., 2023). METTL5 is expressed at elevated levels in several cancers, including breast cancer, lung adenocarcinoma, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and this correlates with poor prognosis (Ignatova et al., 2020; Sun et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2023; Xia et al., 2023; Wang et al., 2024). In HCC, METTL5 was shown to promote the generation and release of the neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) network (Wang et al., 2024), and to regulate glycolysis and cell proliferation by the downstream stabilization of c-Myc (Xia et al., 2023). In NPC cells, METTL5 and its partner TRMT112 are over-expressed, with subsequently higher levels of m6A1832 on 18 rRNA (Chen et al., 2023). METTL5 promotes tumorigenesis as well as chemoresistance through its enzymatic activity (Chen et al., 2023). This oncogenic role of the METTL5-TRMT112 complex could rely on the regulation of the synthesis of the HSF4b transcription factor that mainly regulates the translation of heat shock proteins (HSPs) such as HSP90B1 (Chen et al., 2023). The latter directly interacts with the gain-of-function p53R280T mutant to inhibit its ubiquitination-dependent degradation, thereby enabling p53R280T to maintain its oncogenic functions.
METTL5 also turns out to be important for organism development. Indeed, Mettl5 KO mice have reduced viability, body size and weight compared to WT controls (Ignatova et al., 2020; Sepich-Poore et al., 2022; Wang et al., 2022). C. elegans animals lacking METTL5 have diminished fertility as well as decreased brood size. The latter phenotype is directly correlated with METTL5 enzymatic activity since a METTL5 catalytic mutant had similar effect on brood size as the depletion of METTL5, emphasizing on the importance of the 18S m6A1832 modification (Sendinc et al., 2020). In the plant model system A. thaliana, METTL5 protein is important for global translation and in particular for the translation of mRNAs involved in the response to blue light exposure (Song et al., 2024). Surprisingly, although two TRMT112 orthologues (TRMT112A and TRMT112B) are present in A. thaliana proteome, they do not interact with METTL5 and are not essential for the formation of m6A on 18S rRNA.
TRMT112 proteins also interact with the yeast Mtq2 or its metazoan orthologue HEMK2 (hereafter referred to as MTQ2; see Table 1 for the many other names used for this protein). Initially, the human MTQ2 gene was dubbed N6AMT1 due to significant sequence identity with bacterial DNA N6-methyltransferases according to in silico sequence analyses (Fedoreyeva and Vanyushin, 2002; Ratel et al., 2006). To date, only one study has documented the role of MTQ2 in the formation of N6-methyladenine in eukaryotic DNA (Xiao et al., 2018). However, several studies did not detect this modification in human DNA and the methods used to prove its presence in DNA are very criticized (Ratel et al., 2006; Liu et al., 2017; Schiffers et al., 2017; O'Brown et al., 2019; Kong et al., 2022). In addition, no biochemical MTase activity has been detected on DNA for MTQ2 proteins (Nie et al., 2009; Li et al., 2019; Woodcock et al., 2019). This is in agreement with the presence of a negatively charged substrate binding pocket surrounding MTQ2 active site (Liger et al., 2011; Li et al., 2019; Metzger et al., 2019), which is not favorable for nucleic acids binding. Hence, future studies might be important to definitely clarify this aspect.
The first clearly established MTQ2 substrate is the class I translation termination factor (eRF1 in eukaryotes and aRF1 in archaea (Heurgue-Hamard et al., 2006; van Tran et al., 2018)). Consequently, MTQ2 is unique since it is the only TRMT112 partner to modify proteins. MTQ2 proteins catalyze the methylation of the N5 amino group of the glutamine side chain from the universally conserved GGQ (for Gly-Gly-Gln) motif found in eRF1/aRF1 (Heurgue-Hamard et al., 2005; van Tran et al., 2018). Upon the recognition of a stop codon in the ribosomal A-site by eRF1/aRF1, the GGQ motif enters into the peptidyl transferase center of the ribosome to trigger the release of the newly synthesized proteins (Brown et al., 2015). Interestingly, bacterial class I translation termination factors RF1 and RF2 are structurally completely unrelated to eukaryotic eRF1 and archaeal aRF1 (Song et al., 2000; Vestergaard et al., 2001; Saito et al., 2010). Yet, the glutamine side chain of the GGQ motif is methylated in the three domains of life (Dincbas-Renqvist et al., 2000; Heurgue-Hamard et al., 2005; van Tran et al., 2018), and enzymes catalyzing this modification differ in their organization between archaea and eukaryotes on the one hand and bacteria on the other hand (Graille et al., 2005; Heurgue-Hamard et al., 2006). Altogether, this supports a critical role of this post-translational modification in the translation termination process since it has appeared independently during evolution in the three domains of life. The exact function of this methylation in eukaryotes remains unknown. However, studies in bacteria have shown that it is important for normal termination in vivo, enhances the rate of peptide release, favors stop codon recognition and stabilizes the GGQ loop in the peptidyl transferase center (Mora et al., 2007; Pierson et al., 2016; Pundir et al., 2021). One can then imagine that this post-translational modification will have very similar effects in eukaryotes and archaea.
MTQ2 proteins harbor a strictly conserved NPPY motif essential for the MTase activity since the substitution of the Asn from this motif by an Ala completely abolishes eRF1 methylation in vivo and in vitro (Liger et al., 2011; Li et al., 2019; Lacoux et al., 2020). Eukaryotic MTQ2 proteins as well as Mtq2 from H. volcanii archaeon interact with TRMT112 to form a stable complex and TRMT112 is mandatory for MTQ2 subunits to be enzymatically active in vivo and in vitro (Heurgue-Hamard et al., 2006; Figaro et al., 2008; Liger et al., 2011; van Tran et al., 2018; Lacoux et al., 2020). Several crystal structures of MTQ2-TRMT112 complexes (from human or Encephalitozoon cuniculi parasite) have been solved in the presence of SAM, S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine (SAH), one of the products of the enzymatic reaction, or of a methylated glutamine residue (Liger et al., 2011; Li et al., 2019; Gao et al., 2020). In particular, this highlighted the role of this NPPY signature in the coordination of the glutamine side chain from eRF1 into MTQ2 active site (Figure 7A).
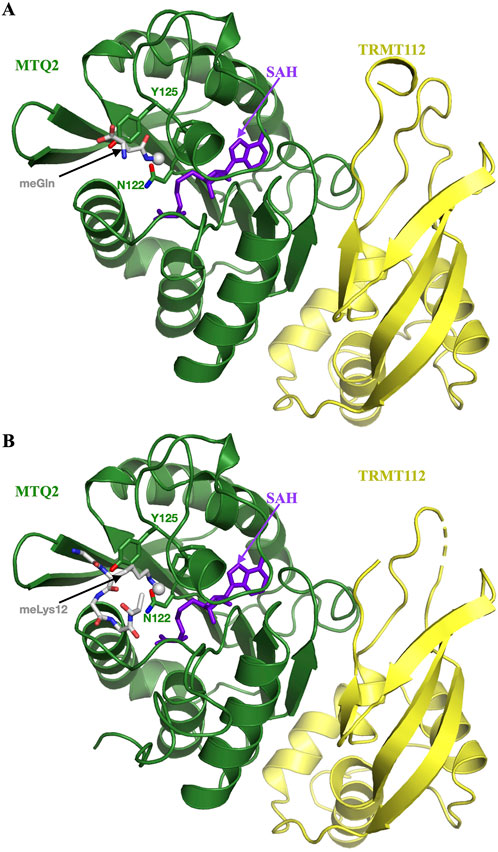
Figure 7. MTQ2, a multisubstrate protein methyltransferase. (A) Ribbon representation of the crystal structure of human MTQ2-TRMT112 complex bound to SAH and N5-methylglutamine (purple sticks and grey sticks, respectively; PDB code: 6KHS). The methyl group is shown as a grey sphere in both panels. The side chains of the NPPY signature from MTQ2 are shown as sticks. (B) Ribbon representation of the crystal structure of human MTQ2-TRMT112 complex bound to SAH and histone H4 peptide containing a monomethylated Lys (purple sticks and grey sticks, respectively; PDB code: 6H1E).
The role of TRMT112 on MTQ2 enzymatic activity can be explained by several observations. First, human TRMT112 stimulates SAM binding to the MTQ2 catalytic subunit (Liger et al., 2011). Second, it is enhancing the solubility and the stability of MTQ2 proteins expressed in E. coli as observed for other TRMT112 partners (Heurgue-Hamard et al., 2006; Figaro et al., 2008). Third, in yeast, Trm112 is important for Mtq2 stability (Sardana and Johnson, 2012), whereas human TRMT112 is not important for MTQ2 stability in cells (Leetsi et al., 2019). Finally, yeast Trm112 contributes to Mtq2 enzymatic activity most probably through a role in substrate binding, since several point mutations of conserved residues present at the surface of Trm112 and located in close proximity of Mtq2 active site in the crystal structure of eukaryotic Mtq2-Trm112 complex, are less efficient in eRF1 methylation (Liger et al., 2011). Interestingly, the eukaryotic MTQ2-TRMT112 complex from various organisms is active on the eRF1 protein in the presence of the GTP bound-form of the translational GTPase eRF3 but not on eRF1 alone or on the eRF1-eRF3-GDP complex (Heurgue-Hamard et al., 2005). The same is true for the Mtq2-Trm112 complex from H. volcanii archaeon, which is active only on the aRF1-aRF3-GTP complex (van Tran et al., 2018). However, it is noteworthy that contrary to what has been observed for eukaryotic MTQ2, Trm112 from H. volcanii is not required for the in vivo activity of HvoMtq2 on aRF1 (van Tran et al., 2018). This is reminiscent of our observations on A. fulgidus Trm11, which is active even in the absence of its Trm112 partner (Wang et al., 2020).
In S. cerevisiae yeast, the deletion of the MTQ2 gene results in a decreased growth rate in normal conditions, as well as in cryo-sensitivity, increased sensitivities to paromomycin, geneticin, high salt or calcium, caffeine and polymyxin-B (Polevoda et al., 2006). The mtq2Δ strain is also more resistant to thiabenzole and benomyl, two microtubule inhibiting drugs. Finally, in budding yeast, the Mtq2 protein and its enzymatic activity are important for the efficient production of the 5.8S and 25S rRNA and hence for the biosynthesis of the 60S large ribosomal subunit (Lacoux et al., 2020). Whether this role of Mtq2 on 60S biogenesis is linked to its function in eRF1 GGQ methylation is not clear and deserves further studies. Some studies performed in metazoan have started to clarify the function of MTQ2. Knocking down MTQ2 in fruit fly germline cells results in apoptosis of these cells, significantly reduces eRF1 methylation and induces ribosome stalling (Xu et al., 2024). The down-regulation of MTQ2 affects the expression of genes involved in female gametes production, oogenesis and germ cell development. In mice, the deficiency in MTQ2 is embryonic lethal (Liu et al., 2010), whereas its down-regulation reduces protein synthesis, affects the cell cycle distribution of murine cells by decreasing the percentage of cells in the G1 phase and increasing it in the S phase (Liu et al., 2009). In mice, this protein exists as two isoforms (Nie et al., 2009), both being also present in humans (Figaro et al., 2008; Leetsi et al., 2019). However, the shorter isoform is missing the NPPY active site signature, does not interact with TRMT112, and is rapidly degraded by the proteasome. The existence of this apparently inactive MTQ2 isoform in mammals is unclear but may suggest a regulatory role in the expression of active MTQ2. In human cells, the MTQ2 protein has both nuclear and cytoplasmic localization (Brumele et al., 2021). Both human MTQ2 protein and its enzymatic activity have recently been shown to be important for the cytoplasmic translation of two subunits of the mitochondrial RNase P enzyme (the TRMT10C tRNA methyltransferase and the PRORP nuclease), thereby affecting the processing of mitochondrial RNAs, mitochondrial translation and oxidative phosphorylation (Foged et al., 2024).
Additional substrates for human MTQ2 have been identified. First, using an in vitro peptide array approach, Kusevic and colleagues identified the GQX3R motif to be critical for methylation activity by the human MTQ2-TRMT112 complex and also observed a preference for Ser, Arg or Gly at position +1 (zero being the methylated glutamine) and for Arg at position +7, respectively (Kusevic et al., 2016). Based on these informations, several putative substrates have been identified in human. Many have been validated in vitro and two (CHD5 and NUT) in vivo (Kusevic et al., 2016; Weirich et al., 2024). MTQ2 has also been implicated in histone methylation. Indeed, it was reported that human MTQ2 could methylate histone 4 on its Lys12 (H4K12-met) in a glycine rich region, both in vitro and in vivo (Metzger et al., 2019). The crystal structure of the human MTQ2-TRMT112 complex bound to an H4 peptide centered around the methylated form of Lys12 was determined, highlighting again the importance of the NPPY active site signature in the coordination of the Lys12 side chain (Figure 7B; Metzger et al., 2019). In the same study, the knock-down of MTQ2 in PC3 prostate cancer cells results in a decrease in histone methylation and in cell proliferation. The authors also observed the co-localization of H4K12-met with MTQ2 and over 1,000 promoters, suggesting that human MTQ2 could regulate gene expression by alternatively methylating the promoter-bound histone, hence participating in transcription initiation, as these promoters also display decreased RNA polymerase occupancy in MTQ2 KO cell lines. The association between H4K12-met and MTQ2 was also described by the same team in additional human cell lines, such as respiratory tract cancer cells A549 (Baumert et al., 2020) or colorectal organoïd models (Berlin et al., 2022). However, the direct correlation between MTQ2 enzymatic activity and methylation of H4 on Lys12 needs to be clarified. Indeed, the MTQ2 enzymatic activity reported on H4K12 is comparable to that observed when eRF1 is used as sole substrate for the MTQ2-TRMT112 complex (Metzger et al., 2019). This activity is much lower that the activity of the same complex on eRF1 in the presence of eRF3 and GTP, two essential cofactors for eRF1 methylation by the MTQ2-TRMT112 complex (Heurgue-Hamard et al., 2006; Woodcock et al., 2019; Weirich et al., 2024). A recent study showed that SETD6 might be responsible for the formation of H4K12-met since it is more efficient than MTQ2-TRMT112 complex in methylating H4K12 (Weirich et al., 2024). Further studies are needed to clarify the role of MTQ2 in the formation of H4K12-met and its importance in the regulation of gene expression a well as its links with cancer.
MTQ2 proteins from yeast and human were also described to participate in the metabolism of organic arsenic, along with the arsenic MTase AS3MT, thereby contributing to the resistance to arsenic exposure (Ren et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2015; Lee and Levin, 2018). Yet, as for H4K12 methylation, MTQ2 is not the main factor responsible for organic arsenic methylation, as it could be AS3MT. Nevertheless, it may play a more important role in arsenic metabolism in tissues in which it is the most expressed, but also in cancer cells where its expression is disrupted.
In summary, the MTQ2-TRMT112 complex appears as a multifunctional enzyme that can methylate several substrates (eRF1, CHD5, NUT and potentially H4K12) either on Gln or Lys side chains and with implications in the control of gene expression at the translational but also at the transcriptional levels. Still, it might selectively recognize and methylate other substrates, which remain to be identified (Kusevic et al., 2016; Li et al., 2019; Metzger et al., 2019; Weirich et al., 2024).
The most recently characterized TRMT112 MTase partner is THUMP domain-containing protein 2 (THUMPD2), a nuclear protein only found in metazoa (Brumele et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2024). Similarly to TRMT11 and THUMPD3, THUMPD2 is made of a N-terminal THUMP domain followed by a C-terminal SAM-dependent MTase domain with a D [I/V]PFG signature characteristic of enzymes methylating planar amino groups on nucleic acid bases or Gln side chains (Figure 3A; Bujnicki, 2000). THUMPD2 is essential for the formation of m2G at position 72 of the U6 snRNA (Wang et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2024). The U6 snRNA plays a critical role in pre-mRNA splicing by dynamically interacting with other snRNAs and protein partners to form the catalytic center of the spliceosome. The U6 snRNA m2G72 modification is located two nucleotides upstream of U74, which is essential for the formation of the catalytic U6 snRNA triplex and the binding of the 2 Mg2+ ions directly involved in the splicing catalytic step (Figure 8; Fica et al., 2013; Wilkinson et al., 2020). In U6 snRNA, an internal stem loop (ISL) constitutes a major part of the spliceosome catalytic center by chelating the catalytic Mg2+ ions. The m2G72 modification is located within the ISL and G72 directly interacts with the catalytic Mg2+ ion (Bertram et al., 2020). Similarly to other TRMT112 partners, THUMPD2 alone shows no detectable activity but becomes active when it forms a complex with TRMT112 (Yang et al., 2024). In vitro assays have revealed that the THUMPD2-TRMT112 complex recognizes the 65GCGCA69 motif of the U6 ISL-apical loop and the U6-specific bulged structure around G72 for catalysis (Yang et al., 2024). THUMPD2 seems highly specific to U6 snRNA since no difference is observed in m2G levels in other types of RNAs when comparing parental and THUMPD2 KO cell lines (Wang et al., 2023).
Figure 8. THUMPD2 targets G72 from U6 snRNA and is important for optimal splicing. Representation of the cryo-EM structure of the RNA components found in the active site of the human spliceosome complex C (PDB code: 6ZYM). The G72 and U74 positions from U6 snRNA are colored grey and pink, respectively and the catalytic metal ion (Mg2+) coordinated (black dashed lines) by their phosphate groups is shown as a black sphere. The THUMPD2-TRMT112 complex methylates G72 on the N2 atom (shown as a sphere).
Due to its target and the nucleotide it is modifying, it is not surprising that the THUMPD2-TRMT112 complex and its enzymatic activity are important for alternative pre-mRNA splicing both in vitro and in vivo (Wang et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2024). Intron retention or skipped exons were the most affected types of alternative splicing events upon depletion of THUMPD2 in both HCT116 and HEK293T human cells (Wang et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2024). Introns retained in cells lacking THUMPD2 had lower splice site quality, shorter polypyrimidine tracts and were generally shorter than unaffected introns. This effect of THUMPD2 in optimal pre-mRNA splicing is reflected in the proliferation defects observed for human cell lines lacking THUMPD2 (Wang et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2024).
The lack of THUMPD2-mediated m2G methylation of the U6 snRNA affects the splicing of numerous endogenous pre-mRNA. While we did not observe significant enrichment in pre-mRNAs involved in specific cellular pathways in HCT116 cells (Wang et al., 2023), Yang and colleagues observed an upregulation of genes involved in nonsense mediated mRNA decay pathway upon depletion in THUMPD2 in HEK293T cell lines (Yang et al., 2024).
Studies aimed at understanding the importance of THUMPD2 in human diseases are in their infancy. The down-regulation of THUMPD2 was suggested to play a role in multidrug resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (Hayashi et al., 2019). Recently, the role of THUMPD2 in ovarian cancer was investigated, revealing that low expression of THUMPD2 in early stage enhanced tumor growth while high expression in the late stage favored metastasis (Hua et al., 2024). Finally, a THUMPD2 variant resulting in lower expression of this protein, has been identified in patients suffering from age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and a correlation between alternative splicing, THUMPD2 function and AMD was established (Yang et al., 2024). Exploring the THUMPD2 biological functions and the elements required for substrate recognition by the THUMPD2-TRMT112 complex will help to understand the molecular mechanisms of tumor occurrence and development.
In metazoa, PYURF (for PIGY upstream open reading frame) is a yet poorly characterized nuclear-encoded mitochondrial TRMT112-like protein. This protein is predicted to contain only the zinc knuckle domain similarly to bacterial proteins (Figure 9). The depletion of PYURF leads to K562 cell death in galactose media and reduces oxygen consumption, indicating its crucial role in the generation of ATP by the oxidative phosphorylation process (Arroyo et al., 2016). Further studies have shown that PYURF interacts with at least two class I SAM-dependent MTases, namely NDUFAF5 and COQ5 (Rensvold et al., 2022), which are respectively involved in the complex biosynthesis pathways of the NADH: ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I) and coenzyme Q (CoQ). Complex I is the first enzyme involved in the oxidative phosphorylation pathway (Sharma et al., 2009). It is composed of 44 proteins (including several anchored to the membrane) encoded by both nuclear and mitochondrial genomes. The assembly of human complex I proceeds via sub-complexes, which are built from specific subunits with assistance of assembly factors (Rhein et al., 2016). NDUFAF5 is one such assembly factor. Although it has a predicted classical class I SAM-dependent MTase structure, no MTase activity has been demonstrated for this protein to our knowledge but it has been shown to be essential for the hydroxylation of the complex I subunit NDUFS7 on Arg73 side chain (Rhein et al., 2016). PYURF is also involved in the biosynthesis of coenzyme Q (also known as ubiquinone (Acosta et al., 2016)), which plays a role in electron shuttling between complex I and other complexes from the respiratory chain. PYURF interacts with COQ5, a MTase modifying a carbon atom, which itself interacts with other CoQ proteins. Similarly to the role of TRMT112 on its MTase partners, PYURF is important for the cellular stability of both NDUFAF5 and COQ5 since the depletion of PYURF results in decreased abundance of both MTases (Rensvold et al., 2022). Further studies will be necessary to unravel the role of PYURF for the functions of these two partners but PYURF clearly emerges as an important protein for mitochondria functions. Indeed, PYURF mutations have been identified in patients suffering from a spectrum of symptoms such as muscle hypotonia, failure to thrive, developmental delay, optic atrophy, and elevated lactate levels in blood and cerebrospinal fluid (Rensvold et al., 2022).
Figure 9. Human PYURF, a mitochondrial TRMT112-like protein. Superposition of the human PYURF model (pink) generated by AlphaFold (version 3.0) onto the crystal structure of human TRMT112 (in complex with METTL5; PDB code: 6H2U, same color code as Figure 1A). For the sake of clarity, the PYURF MTS and METTL5 have been omitted.
Since the identification of TRMT112 proteins as intrinsic subunits of several MTase holoenzymes, numerous biochemical and structural studies have provided a wealth of information allowing a better understanding of the roles of TRMT112 proteins on these MTases.
In vitro studies on MTases known to interact with TRMT112 were initially hampered due to solubility problems encountered when these MTases are over-expressed alone in E. coli. With the exception of Trm11 (Purushothaman et al., 2005; Bourgeois et al., 2017b), no S. cerevisiae MTases (Trm9, Mtq2 or Bud23) could be over-expressed alone as soluble proteins using E. coli expression system (Heurgue-Hamard et al., 2006; Mazauric et al., 2010; Figaro et al., 2012). The same observations were made for human MTases known to interact with TRMT112 (Figaro et al., 2008; Songe-Moller et al., 2010; Zorbas et al., 2015; van Tran et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023), with the exception of MTQ2 or THUMPD3 for which some proteins could be purified following over-expression in E. coli or in baculovirus-infected insect cells, respectively (Yang et al., 2021). However, these three isolated proteins (yeast Trm11 and human MTQ2 or THUMPD3) proved to be very unstable or aggregated after purification and lacked any enzymatic activity (Purushothaman et al., 2005; Figaro et al., 2008; Liger et al., 2011; Bourgeois et al., 2017b). Interestingly, the co-expression of TRMT112 protein with any of its known eukaryotic or archaeal MTase partners led to drastic enhancement in the solubility of the MTase subunit and turned out to be critical for the purification of the corresponding complexes in large quantities (Purushothaman et al., 2005; Mazauric et al., 2010; Figaro et al., 2012; Zorbas et al., 2015; Bourgeois et al., 2017b; van Tran et al., 2018; van Tran et al., 2019; Yang et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023). This was pivotal for subsequent structural studies of many of these Trm112-MTase complexes using X-ray crystallography (Table 2). The crystal structures of the Trm112-Mtq2 complex from the intracellular parasite Encephalitozoon cuniculi (Liger et al., 2011), of the human TRMT112-MTQ2 or TRMT112-METTL5 complexes (Li et al., 2019; Metzger et al., 2019; van Tran et al., 2019), of the S. cerevisiae Trm112-Bud23 MTase domain (alone or bound to SAM; (Letoquart et al., 2014)), and of an N-terminally truncated Trm9 from Yarrowia lypolytica yeast bound to Trm112 (Letoquart et al., 2015) were determined. Several structures of yeast and human TRMT112-BUD23 complexes bound to pre-40S ribosomes undergoing the last maturation steps were also obtained by single particle cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM; (Ameismeier et al., 2018; Cheng et al., 2022)). To date, the experimental 3D structures of eukaryotic TRMT112-THUMPD2, TRMT112-THUMPD3, TRMT112-TRMT9B and TRMT112-TRMT11 complexes are still missing. However, the crystal structure of archaeal A. fulgidus Trm11 bound to Trm112 was also determined, offering important informations on the interaction mode between these two proteins (Wang et al., 2020). Finally, the structure of the complex formed by H. volcanii Trm112 with a yet uncharacterized putative archaeal MTase (Hvo_0019) has been determined (van Tran et al., 2018). Remarkably, all these structures reveal that the binding modes between TRMT112 proteins and these various MTases, which share less than 20% sequence identity but an overall similar fold (root mean square deviation values ranging from 2.2 Å to 3.2 Å) are highly similar. Indeed, these class I MTases all use the same region of their Rossmann fold to interact with the same region of TRMT112 proteins and consequently compete directly to interact with TRMT112 (Figure 10A). This is in agreement with different reports showing that increasing the expression level of a MTase interacting with TRMT112 reduced the amount of other MTases immunopurified with TRMT112 (Studte et al., 2008; Figaro et al., 2012).
Figure 10. All these methyltransferases compete to interact with TRMT112. (A) Cartoon representation of the superimposition of crystals structures of MTase-TRMT112 complexes (same PDB and color codes used as those used to generate Figures 3–7). The SAM or sinefungin inhibitor are shown as purple sticks. The zinc atoms bound to some Trm112 proteins are shown as grey spheres. To generate this figure, the TRMT112 proteins were superposed onto each others. The TRMT112 proteins from each complex are colored yellow. (B) Superposition of the crystal structures of S. cerevisiae Trm112 either in its apo form (grey; PDB code : 2J6A) or bound to Bud23 (PDB code: 4QTU; same color code as Figure 1A), showing the conformational change occurring at the C-terminal end of Trm112. For the sake of clarity, Bud23 has been omitted. (C) Cartoon representation of the human METTL5-TRMT112 crystal structure (PDB code: 6H2V) illustrating the role of the loop connecting strands β3 and β4 (colored in brown) from the MTase subunit and sandwiched between the SAM cofactor and TRMT112. The side chain of the amino acid residue interacting with the N6 atom of the adenosine moiety of SAM is shown as sticks.
One of the main features of the interfaces between TRMT112 proteins and these various MTases is the presence of a β-zipper formed by hydrogen bonds made between main chain atoms from TRMT112 strand β4 and strand β3 from the MTase domain. As a consequence, this forms a continuous β-sheet made of 11 β-strands (seven and four from the MTase and TRMT112 proteins, respectively). Since this interaction involves main chain atoms, it is much less affected by the variations of amino acid side chains located within strand β3 of the MTase domain but is strongly dependent on the maintenance of the correct structure of this region. This likely explains the ability of a specific MTase (from human or another yeast) to complement for the deletion of its budding yeast orthologue in vivo, meaning that hybrid Trm112-MTase complexes made between proteins from two different organisms can exist in vivo and be at least partially functional (Figaro et al., 2008; Begley et al., 2013; Ounap et al., 2013; Letoquart et al., 2015; Ounap et al., 2015; Lv et al., 2025).
Another important feature of the interaction mode between TRMT112 and these MTases is the location of the N-terminal extremity of TRMT112 proteins at the center of the interface with MTase subunits. This is critical since N-terminal tagging of TRMT112 affects the solubility of the complexes formed with MTases or disrupts the interaction with human BUD23 ((Ounap et al., 2015); MG, unpublished data). We would then like to take this opportunity to stress that the introduction of a single extra amino acid between the initial methionine and the second amino acid of TRMT112 proteins due to cloning bias or N-terminal tagging should severely affect their ability to form complexes with the MTases, and consequently the conclusions of functional experiments. It is then strongly advised to tag TRMT112 proteins at their C-terminal end in future functional studies.
The different structures of the complexes between MTases and TRMT112 proteins also revealed the presence of a large hydrophobic area at the interface. This explains the observed effect of TRMT112 proteins on the solubility and stability of many of these MTases (Mazauric et al., 2010; Figaro et al., 2012; Sardana and Johnson, 2012; Ounap et al., 2015; Zorbas et al., 2015; Bourgeois et al., 2017b; van Tran et al., 2019; Brumele et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023). It also rationalizes the effect of mutations disrupting the interface on the cellular abundance of the MTases interacting with TRMT112 proteins (Liger et al., 2011; Sardana and Johnson, 2012; Brumele et al., 2021). Indeed, in the absence of TRMT112 proteins, this hydrophobic region present at the surface of MTases would be exposed to the cellular aqueous solvant, which is not favorable for protein stability. Finally, three conserved electrostatic hot spots were identified from the comparison of the sequences of S. cerevisiae MTases interacting with Trm112 and the analyses of the initial crystal structures of Trm112-MTase complexes (Letoquart et al., 2015; Bourgeois et al., 2017a). First, Thr5 from Trm112 forms a conserved hydrogen bond with the side chain of a polar residue (Asp/Asn or Glu) present at the N-terminal end of strand β3 from the MTase domain. Second, Arg53 from Trm112 forms a salt bridge with a strictly conserved Asp from strand β4 of the MTase domain. Third, a conserved positively charged residue from the loop connecting strands β3 and β4 interacts with Asn7 side chain from Trm112. When analyzing the known 3D structures of human MTases bound to TRMT112 (Metzger et al., 2019; van Tran et al., 2019; Cheng et al., 2022), although the residues at these positions are relatively similar to those found in S. cerevisiae MTases, their side chains are not always involved in similar electrostatic interactions with the TRMT112 residues. This suggests that these hot spots might be less important in human complexes and hence could explain the higher number of MTases interacting with human TRMT112 compared to fungi. However, mutations of several of these residues on either TRMT112 or the MTase domain affect complex formation and consequently the stability of the MTase subunit (Sardana and Johnson, 2012; Letoquart et al., 2014; Letoquart et al., 2015; Brumele et al., 2021; Wang et al., 2023). Recently, an exhaustive site-directed mutagenesis study of human TRMT112 has shown that mutations of residues located at or near the interface with METTL5 do not affect to the same extent the interactions realized between TRMT112 and seven human MTases (namely MTQ2, BUD23, METTL5, TRMT11, ALKBH8, THUMPD2 and THUMPD3; (Brumele et al., 2021)), further supporting that some slight differences exist in these different human TRMT112-MTase interfaces.
Interestingly, the comparison of the crystal structures of S. cerevisiae Trm112 protein alone or bound to Bud23 MTase domain reveals that the C-terminal extremity of Trm112 (amino acids 128–135) undergoes a large conformational change upon Bud23 binding (Figure 10B; Heurgue-Hamard et al., 2006; Letoquart et al., 2014). In all complexes between MTases and TRMT112 proteins, this C-terminal TRMT112 region adopts the same conformation as in the complex with Bud23, supporting that this conformational changes in TRMT112 C-terminal end is necessary to avoid important steric clashes with the MTase domains.
Another function of eukaryotic TRMT112 proteins is in their ability to confer SAM binding property to several MTase subunits. Indeed, although isolated yeast Trm11 or human MTQ2 exhibited circular dichroism spectra typical of well folded class I MTases, none of these proteins could bind the essential SAM cofactor in the absence of their TRMT112 partner (Liger et al., 2011; Bourgeois et al., 2017b). Close inspection of the crystal structure of these MTase-Trm112 complexes bound to SAM reveals that no TRMT112 residue directly contacts SAM (Liger et al., 2011; Letoquart et al., 2014; Li et al., 2019; van Tran et al., 2019). However, a loop from the MTase domain contacting the SAM cofactor is also contacting TRMT112 and harbors a strictly conserved acidic residue, which forms a crucial hydrogen bond with the N6 atom from the adenosine moiety of the SAM cofactor (Figure 10C). Hence, it is very likely that in the absence of TRMT112 protein, this loop is too flexible to allow tight SAM binding to the MTase domain. Upon binding to TRMT112, this loop would be stabilized, allosterically allowing tighter binding of the SAM cofactor. Interestingly, SAM binding also impacts the interaction between the MTase subunit and TRMT112 since MTase mutants defective in SAM binding co-immunoprecipitate TRMT112 proteins less efficiently than WT and consequently are less stable in vivo (Liger et al., 2011; Lin et al., 2012; Letoquart et al., 2014; Lacoux et al., 2020). This supports a tripartite interaction mode between the MTase subunit, SAM cofactor and TRMT112. However, this property might be specific to eukaryotic proteins since archaeal AfTrm11 binds SAM with similar affinities whether it is in complex or not with AfTrm112 (Wang et al., 2020).
Finally, TRMT112 proteins may assist some MTase catalytic subunit for optimal substrate binding. Indeed, mutations of relatively well-conserved Trm112 residues located in the vicinity of the MTase subunit affect the enzymatic activity of S. cerevisiae Mtq2-Trm112 and Trm11-Trm112 complexes in vitro (Liger et al., 2011; Bourgeois et al., 2017b). Similarly, the archaeal AfTrm11-Trm112 complex has a lower Km for a tRNA substrate than the isolated AfTrm11 (Wang et al., 2020). This is most probably due to the presence of a negatively charged region on the AfTrm112 surface, which is located in the vicinity of the AfTrm11 active site. This region might repel the tRNA substrates and favor their release after methylation has occurred.
On the basis of these different observations, the TRMT112 protein should not be considered as a chaperone helping the correct folding of the MTase subunit, but as an integral component of different MTase-TRMT112 holoenzymes. Indeed, TRMT112 protein clearly acts as an allosteric activator subunit of the catalytic MTase subunit in these different holoenzymes.
Due to its involvement in four (in yeast) to eight (in human) eukaryotic holoenzymes methylating factors involved in pre-mRNA splicing and protein synthesis, TRMT112 proteins play critical roles at the cross-roads of mRNA maturation and translation processes (Figure 11). To our knowledge, TRMT112 proteins are somehow unique in their ability to interact via the same region with so many partners acting on various substrates. TRMT112 does not only bind to these MTase subunits but clearly contributes to their functions through its ability to stabilize most MTase subunits in cellulo, to enhance SAM binding and also to contribute to substrate binding in some cases. In this respect, TRMT112 cannot be considered as a chaperone since it remains associated with the MTase subunits. Although many studies have brought a wealth of information on the structure, mode of action and functions of these different holoenzymes, many aspects remain to be clarified. While, with the exception of TRMT9B, the biochemical functions of these MTases have been thoroughly characterized, their biological functions, i.e., the cellular processes directly impacted by these enzymes and the modifications they catalyze, remain to be elucidated in the future. It is already clear that the perturbation of the expression levels or of the function of several of the MTase subunits interacting with TRMT112 are associated with cancer or neurodevelopmental defects. Since mutations have been identified in some of these MTases and were associated with neurodevelopmental disorders, it will be also critical in the future to understand the role of the methyl group added by these TRMT112-MTase complexes on general cellular processes such as translation of specific proteins important for brain development for instance.
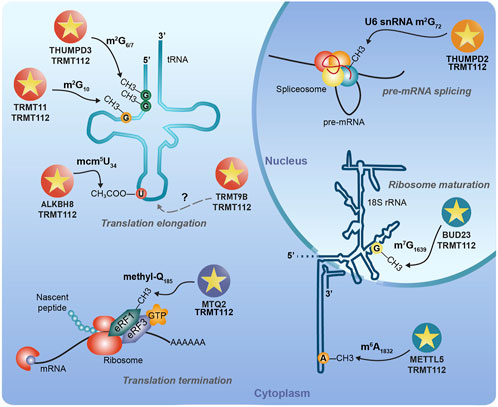
Figure 11. Summary of our current knowledge about human TRMT112-MTase complexes. The most characterized substrates of human TRMT112-MTase complexes are indicated. METTL5 and MTQ2 have been shown to be present both in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm. Here, we indicate their presence in the cytoplasm since we assume that TRMT112-METTL5 acts in the cytoplasm during the late steps of 40S particles maturation and that the TRMT112-MTQ2 dependent modification of eRF1 is cytoplasmic. We also postulate that the TRMT112-TRMT9B complex acts as a tRNA MTase but as far as we know this has never been demonstrated experimentally.
The competition observed between these MTases to interact with the same region of TRMT112 proteins raises several questions about the mechanisms underlying the interaction of TRMT112 protein with a specific MTase. Is the number of TRMT112 proteins in the cell equivalent to the sum of all the MTase proteins interacting with it? Could post-translational modifications such as phosphorylation of TRMT112 or of the MTases, specifically regulate the interaction of TRMT112 with some of these MTases? Is the level of a given MTase regulated at the transcriptional or post-transcriptional level in specific conditions? For instance, a recent study performed in S. cerevisiae yeast has revealed that upon decrease in SAM intracellular concentration due to the deletion of the SAM2 gene, the Trm9, Bud23 and Trm112 transcripts are down-regulated (Remines et al., 2024). Another important question is about the recruitment of TRMT112 to its MTase partners, which are unstable in cellulo, in the absence of TRMT112. Is a yet to be identified chaperone involved? One could also imagine that TRMT112 proteins are recruited to the ribosomes synthesizing these MTases for co-translational assembly of the complexes to assist in their folding during protein synthesis as has been shown to occur for some eukaryotic complexes (Shiber et al., 2018; Bertolini et al., 2021).
Although several 3D structures of TRMT112-MTase complexes have been determined, little structural information is available about these complexes bound to their respective substrate. The cryo-EM structure of human and yeast TRMT112-BUD23 complex bound to late 40S intermediates illustrate the roles of this complex during 40S maturation. Crystal structures of human TRMT112-MTQ2 bound to a short H4 peptide or to glutamine have also been determined, unravelling the importance of the conserved NPPY signature for the coordination of the amino acid to be methylated. Further efforts will be necessary to understand how most of these enzymes recognize their respective substrates, namely tRNAs, U6 snRNA, 40S and eRF1 translation termination factor.
Finally, this review mostly focuses on eukaryotic TRMT112-MTase complexes and also draws parallels with archaeal Trm112-MTase complexes due to the evolutionary conservation of many of these complexes between these two branches of the tree of life. Yet, the biochemical and biological functions of several Trm112-MTase complexes identified in the H. volcanii archaeon remain to be clarified (van Tran et al., 2018). To our knowledge, very little is known about bacterial Trm112 proteins. Future work should be focusing on the characterization of bacterial Trm112 functions and interaction networks. Some lines of evidences suggest that bacterial Trm112 proteins should also preferentially interact with MTases (Shatsky et al., 2016). This should foster our knowledge on this protein family and may reveal similarities with archaeal TRMT112 as well as PYURF interaction networks.
CW: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. LT: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. WH: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. MC: Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. MG: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Work on this topics in the Graille lab was supported by Ecole polytechnique, the CNRS (Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique), the Agence Nationale pour la Recherche (grants ANR-14-CE09-0016-02 and ANR-22-CE12-0010-01) and Fondation ARC pour la Recherche sur le Cancer. CW and WH were supported by PhD fellowships from the China Scholarship Council (CSC). LLET is the recipient of a PhD track fellowship from the Institut Polytechnique de Paris (IPP).
We apologize for the many studies that could not be cited due to space constraints. MG is very grateful to former lab members who have worked on this topics and to all the collaborators, who helped to unravel the functions of these different TRMT112-MTase complexes since almost 20 years.
MG is specialty co-chief editor of the « RNA processing and regulation» section of Frontiers in RNA research. He is also coeditor of this Research Topic: RNA Methylation: Detection, Deposition, and Functions. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commerical or finanical realtionships that could be construced as a potential conflict of interest
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbassi, N. E., Biela, A., Glatt, S., and Lin, T. Y. (2020). How elongator acetylates tRNA bases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (21), 8209. doi:10.3390/ijms21218209
Abbassi, N. E., Jaciuk, M., Scherf, D., Bohnert, P., Rau, A., Hammermeister, A., et al. (2024). Cryo-EM structures of the human Elongator complex at work. Nat. Commun. 15 (1), 4094. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-48251-y
Acosta, M. J., Vazquez Fonseca, L., Desbats, M. A., Cerqua, C., Zordan, R., Trevisson, E., et al. (2016). Coenzyme Q biosynthesis in health and disease. Biochimica Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics 1857 (8), 1079–1085. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2016.03.036
Alexandrov, A., Chernyakov, I., Gu, W., Hiley, S. L., Hughes, T. R., Grayhack, E. J., et al. (2006). Rapid tRNA decay can result from lack of nonessential modifications. Mol. Cell 21 (1), 87–96. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.10.036
Ameismeier, M., Cheng, J., Berninghausen, O., and Beckmann, R. (2018). Visualizing late states of human 40S ribosomal subunit maturation. Nature 558, 249–253. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0193-0
Angelova, M. T., Dimitrova, D. G., Dinges, N., Lence, T., Worpenberg, L., Carre, C., et al. (2018). The emerging field of epitranscriptomics in neurodevelopmental and neuronal disorders. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 6, 46. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2018.00046
Aravind, L., and Koonin, E. V. (2001). THUMP--a predicted RNA-binding domain shared by 4-thiouridine, pseudouridine synthases and RNA methylases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 26 (4), 215–217. doi:10.1016/s0968-0004(01)01826-6
Armengaud, J., Urbonavicius, J., Fernandez, B., Chaussinand, G., Bujnicki, J. M., and Grosjean, H. (2004). N2-methylation of guanosine at position 10 in tRNA is catalyzed by a THUMP domain-containing, S-adenosylmethionine-dependent methyltransferase, conserved in Archaea and Eukaryota. J. Biol. Chem. 279 (35), 37142–37152. doi:10.1074/jbc.M403845200
Arroyo, J. D., Jourdain, A. A., Calvo, S. E., Ballarano, C. A., Doench, J. G., Root, D. E., et al. (2016). A genome-wide CRISPR death screen identifies genes essential for oxidative phosphorylation. Cell Metab. 24 (6), 875–885. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2016.08.017
Barbieri, I., and Kouzarides, T. (2020). Role of RNA modifications in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 20 (6), 303–322. doi:10.1038/s41568-020-0253-2
Barraud, P., Gato, A., Heiss, M., Catala, M., Kellner, S., and Tisne, C. (2019). Time-resolved NMR monitoring of tRNA maturation. Nat. Commun. 10 (1), 3373. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-11356-w
Baumert, H. M., Metzger, E., Fahrner, M., George, J., Thomas, R. K., Schilling, O., et al. (2020). Depletion of histone methyltransferase KMT9 inhibits lung cancer cell proliferation by inducing non-apoptotic cell death. Cancer Cell Int. 20, 52. doi:10.1186/s12935-020-1141-2
Baxter, M., Voronkov, M., Poolman, T., Galli, G., Pinali, C., Goosey, L., et al. (2020). Cardiac mitochondrial function depends on BUD23 mediated ribosome programming. Elife 9. doi:10.7554/eLife.50705
Begley, U., Dyavaiah, M., Patil, A., Rooney, J. P., DiRenzo, D., Young, C. M., et al. (2007). Trm9-catalyzed tRNA modifications link translation to the DNA damage response. Mol. Cell 28 (5), 860–870. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.09.021
Begley, U., Sosa, M. S., Avivar-Valderas, A., Patil, A., Endres, L., Estrada, Y., et al. (2013). A human tRNA methyltransferase 9-like protein prevents tumour growth by regulating LIN9 and HIF1-α. EMBO Mol. Med. 5 (3), 366–383. doi:10.1002/emmm.201201161
Berlin, C., Cottard, F., Willmann, D., Urban, S., Tirier, S. M., Marx, L., et al. (2022). KMT9 controls stemness and growth of colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 82 (2), 210–220. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-1261
Bertolini, M., Fenzl, K., Kats, I., Wruck, F., Tippmann, F., Schmitt, J., et al. (2021). Interactions between nascent proteins translated by adjacent ribosomes drive homomer assembly. Science 371 (6524), 57–64. doi:10.1126/science.abc7151
Bertram, K., El Ayoubi, L., Dybkov, O., Agafonov, D. E., Will, C. L., Hartmuth, K., et al. (2020). Structural insights into the roles of metazoan-specific splicing factors in the human step 1 spliceosome. Mol. Cell 80 (1), 127–139.e6. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.09.012
Black, J. J., and Johnson, A. W. (2022). Release of the ribosome biogenesis factor Bud23 from small subunit precursors in yeast. RNA 28 (3), 371–389. doi:10.1261/rna.079025.121
Black, J. J., Sardana, R., Elmir, E. W., and Johnson, A. W. (2020). Bud23 promotes the final disassembly of the small subunit Processome in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS Genet. 16 (12), e1009215. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1009215
Bourgeois, G., Letoquart, J., van Tran, N., and Graille, M. (2017a). Trm112, a protein activator of methyltransferases modifying actors of the eukaryotic translational apparatus. Biomolecules 7 (1), 7. doi:10.3390/biom7010007
Bourgeois, G., Marcoux, J., Saliou, J. M., Cianferani, S., and Graille, M. (2017b). Activation mode of the eukaryotic m2G10 tRNA methyltransferase Trm11 by its partner protein Trm112. Nucleic Acids Res. 45 (4), 1971–1982. doi:10.1093/nar/gkw1271
Bourgeois, G., Ney, M., Gaspar, I., Aigueperse, C., Schaefer, M., Kellner, S., et al. (2015). Eukaryotic rRNA modification by yeast 5-methylcytosine-methyltransferases and human proliferation-associated antigen p120. PLoS One 10 (7), e0133321. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0133321
Brown, A., Shao, S., Murray, J., Hegde, R. S., and Ramakrishnan, V. (2015). Structural basis for stop codon recognition in eukaryotes. Nature 524 (7566), 493–496. doi:10.1038/nature14896
Brumele, B., Mutso, M., Telanne, L., Ounap, K., Spunde, K., Abroi, A., et al. (2021). Human trmt112-methyltransferase network consists of seven partners interacting with a common Co-factor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (24), 13593. doi:10.3390/ijms222413593
Bujnicki, J. M. (2000). Phylogenomic analysis of 16S rRNA:(guanine-N2) methyltransferases suggests new family members and reveals highly conserved motifs and a domain structure similar to other nucleic acid amino-methyltransferases. FASEB J. 14 (14), 2365–2368. doi:10.1096/fj.00-0076com
Byrne, A. B., Weirauch, M. T., Wong, V., Koeva, M., Dixon, S. J., Stuart, J. M., et al. (2007). A global analysis of genetic interactions in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Biol. 6 (3), 8. doi:10.1186/jbiol58
Cavallin, I., Bartosovic, M., Skalicky, T., Rengaraj, P., Demko, M., Schmidt-Dengler, M. C., et al. (2022). HITS-CLIP analysis of human ALKBH8 reveals interactions with fully processed substrate tRNAs and with specific noncoding RNAs. RNA 28 (12), 1568–1581. doi:10.1261/rna.079421.122
Chen, B., Huang, Y., He, S., Yu, P., Wu, L., and Peng, H. (2023). N(6)-methyladenosine modification in 18S rRNA promotes tumorigenesis and chemoresistance via HSF4b/HSP90B1/mutant p53 axis. Cell Chem. Biol. 30 (2), 144–158.e10. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2023.01.006
Chen, C., Huang, B., Anderson, J. T., and Bystrom, A. S. (2011). Unexpected accumulation of ncm(5)U and ncm(5)S(2) (U) in a trm9 mutant suggests an additional step in the synthesis of mcm(5)U and mcm(5)S(2)U. PLoS One 6 (6), e20783. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020783
Chen, P., Jager, G., and Zheng, B. (2010). Transfer RNA modifications and genes for modifying enzymes in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 10, 201. doi:10.1186/1471-2229-10-201
Cheng, J., Lau, B., Thoms, M., Ameismeier, M., Berninghausen, O., Hurt, E., et al. (2022). The nucleoplasmic phase of pre-40S formation prior to nuclear export. Nucleic Acids Res. 50 (20), 11924–11937. doi:10.1093/nar/gkac961
Chi, Y., Liang, Z., Guo, Y., Chen, D., Lu, L., Lin, J., et al. (2020). WBSCR22 confers cell survival and predicts poor prognosis in glioma. Brain Res. Bull. 161, 1–12. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.04.024
Deng, W., Babu, I. R., Su, D., Yin, S., Begley, T. J., and Dedon, P. C. (2015). Trm9-Catalyzed tRNA modifications regulate global protein expression by codon-biased translation. PLoS Genet. 11 (12), e1005706. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1005706
Dincbas-Renqvist, V., Engstrom, A., Mora, L., Heurgue-Hamard, V., Buckingham, R., and Ehrenberg, M. (2000). A post-translational modification in the GGQ motif of RF2 from Escherichia coli stimulates termination of translation. Embo J. 19 (24), 6900–6907. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.24.6900
Ellis, S. R., Morales, M. J., Li, J. M., Hopper, A. K., and Martin, N. C. (1986). Isolation and characterization of the TRM1 locus, a gene essential for the N2,N2-dimethylguanosine modification of both mitochondrial and cytoplasmic tRNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 261 (21), 9703–9709. doi:10.1016/s0021-9258(18)67571-4
Fedoreyeva, L. I., and Vanyushin, B. F. (2002). N(6)-Adenine DNA-methyltransferase in wheat seedlings. FEBS Lett. 514 (2-3), 305–308. doi:10.1016/s0014-5793(02)02384-0
Fenwick, M. K., and Ealick, S. E. (2018). Towards the structural characterization of the human methyltransferome. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 53, 12–21. doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2018.03.007
Fica, S. M., Tuttle, N., Novak, T., Li, N. S., Lu, J., Koodathingal, P., et al. (2013). RNA catalyses nuclear pre-mRNA splicing. Nature 503 (7475), 229–234. doi:10.1038/nature12734
Figaro, S., Scrima, N., Buckingham, R. H., and Heurgue-Hamard, V. (2008). HemK2 protein, encoded on human chromosome 21, methylates translation termination factor eRF1. FEBS Lett. 582 (16), 2352–2356. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2008.05.045
Figaro, S., Wacheul, L., Schillewaert, S., Graille, M., Huvelle, E., Mongeard, R., et al. (2012). Trm112 is required for Bud23-mediated methylation of the 18S rRNA at position G1575. Mol. Cell. Biol. 32 (12), 2254–2267. doi:10.1128/mcb.06623-11
Fislage, M., Roovers, M., Tuszynska, I., Bujnicki, J. M., Droogmans, L., and Versees, W. (2012). Crystal structures of the tRNA:m2G6 methyltransferase Trm14/TrmN from two domains of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 40 (11), 5149–5161. doi:10.1093/nar/gks163
Flanagan, J. M., Healey, S., Young, J., Whitehall, V., Trott, D. A., Newbold, R. F., et al. (2004). Mapping of a candidate colorectal cancer tumor-suppressor gene to a 900-kilobase region on the short arm of chromosome 8. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 40 (3), 247–260. doi:10.1002/gcc.20039
Foged, M. M., Recazens, E., Chollet, S., Lisci, M., Allen, G. E., Zinshteyn, B., et al. (2024). Cytosolic N6AMT1-dependent translation supports mitochondrial RNA processing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 121 (47), e2414187121. doi:10.1073/pnas.2414187121
Fu, D., Brophy, J. A., Chan, C. T., Atmore, K. A., Begley, U., Paules, R. S., et al. (2010a). Human AlkB homolog ABH8 Is a tRNA methyltransferase required for wobble uridine modification and DNA damage survival. Mol. Cell. Biol. 30 (10), 2449–2459. doi:10.1128/MCB.01604-09
Fu, Y., Dai, Q., Zhang, W., Ren, J., Pan, T., and He, C. (2010b). The AlkB domain of mammalian ABH8 catalyzes hydroxylation of 5-methoxycarbonylmethyluridine at the wobble position of tRNA. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 49 (47), 8885–8888. doi:10.1002/anie.201001242
Gao, J., Wang, B., Yu, H., Wu, G., Wan, C., Liu, W., et al. (2020). Structural insight into HEMK2-TRMT112-mediated glutamine methylation. Biochem. J. 477 (19), 3833–3838. doi:10.1042/BCJ20200594
Garcia, B. C. B., Horie, M., Kojima, S., Makino, A., and Tomonaga, K. (2021). BUD23-TRMT112 interacts with the L protein of Borna disease virus and mediates the chromosomal tethering of viral ribonucleoproteins. Microbiol. Immunol. 65 (11), 492–504. doi:10.1111/1348-0421.12934
Gavin, A. C., Bosche, M., Krause, R., Grandi, P., Marzioch, M., Bauer, A., et al. (2002). Functional organization of the yeast proteome by systematic analysis of protein complexes. Nature 415 (6868), 141–147. doi:10.1038/415141a
Graille, M., Heurgue-Hamard, V., Champ, S., Mora, L., Scrima, N., Ulryck, N., et al. (2005). Molecular basis for bacterial class I release factor methylation by PrmC. Mol. Cell 20 (6), 917–927. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2005.10.025
Grosjean, H., Gaspin, C., Marck, C., Decatur, W. A., and de Crecy-Lagard, V. (2008). RNomics and Modomics in the halophilic archaea Haloferax volcanii: identification of RNA modification genes. BMC Genomics 9, 470. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-9-470
Gu, C., Ramos, J., Begley, U., Dedon, P. C., Fu, D., and Begley, T. J. (2018). Phosphorylation of human TRM9L integrates multiple stress-signaling pathways for tumor growth suppression. Sci. Adv. 4 (7), eaas9184. doi:10.1126/sciadv.aas9184
Guo, Z., Wang, X., Li, Y., Xing, A., Wu, C., Li, D., et al. (2023). Arabidopsis SMO2 modulates ribosome biogenesis by maintaining the RID2 abundance during organ growth. Plant J. 114 (1), 96–109. doi:10.1111/tpj.16121
Gupta, R. (1984). Halobacterium volcanii tRNAs. Identification of 41 tRNAs covering all amino acids, and the sequences of 33 class I tRNAs. J. Biol. Chem. 259 (15), 9461–9471. doi:10.1016/s0021-9258(17)42723-2
Gupta, R. (1986). Transfer RNAs of Halobacterium volcanii: sequences of five leucine and three serine tRNAs. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 7, 102–105. doi:10.1016/s0723-2020(86)80131-x
Guy, M. P., and Phizicky, E. M. (2014). Two-subunit enzymes involved in eukaryotic post-transcriptional tRNA modification. RNA Biol. 11 (12), 1608–1618. doi:10.1080/15476286.2015.1008360
Guy, M. P., and Phizicky, E. M. (2015). Conservation of an intricate circuit for crucial modifications of the tRNAPhe anticodon loop in eukaryotes. RNA 21 (1), 61–74. doi:10.1261/rna.047639.114
Haag, S., Kretschmer, J., and Bohnsack, M. T. (2015). WBSCR22/Merm1 is required for late nuclear pre-ribosomal RNA processing and mediates N7-methylation of G1639 in human 18S rRNA. RNA 21 (2), 180–187. doi:10.1261/rna.047910.114
Hayashi, M., Kawakubo, H., Fukuda, K., Mayanagi, S., Nakamura, R., Suda, K., et al. (2019). THUMP domain containing 2 protein possibly induces resistance to cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil in in vitro human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells as revealed by transposon activation mutagenesis. J. Gene Med. 21 (12), e3135. doi:10.1002/jgm.3135
Heurgué-Hamard, V., Champ, S., Engström, A., Ehrenberg, M., and Buckingham, R. H. (2002). ThehemKgene inEscherichia coliencodes the N(5)-glutamine methyltransferase that modifies peptide release factors. EMBO J. 21 (4), 769–778. doi:10.1093/emboj/21.4.769
Heurgue-Hamard, V., Champ, S., Mora, L., Merkoulova-Rainon, T., Kisselev, L. L., and Buckingham, R. H. (2005). The glutamine residue of the conserved GGQ motif in Saccharomyces cerevisiae release factor eRF1 is methylated by the product of the YDR140w gene. J. Biol. Chem. 280 (4), 2439–2445. doi:10.1074/jbc.M407252200
Heurgue-Hamard, V., Graille, M., Scrima, N., Ulryck, N., Champ, S., van Tilbeurgh, H., et al. (2006). The zinc finger protein Ynr046w is plurifunctional and a component of the eRF1 methyltransferase in yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 281 (47), 36140–36148. doi:10.1074/jbc.m608571200
Hirata, A., Nishiyama, S., Tamura, T., Yamauchi, A., and Hori, H. (2016). Structural and functional analyses of the archaeal tRNA m2G/m22G10 methyltransferase aTrm11 provide mechanistic insights into site specificity of a tRNA methyltransferase that contains common RNA-binding modules. Nucleic Acids Res. 44 (13), 6377–6390. doi:10.1093/nar/gkw561
Hirata, A., Suzuki, T., Nagano, T., Fujii, D., Okamoto, M., Sora, M., et al. (2019). Distinct modified nucleosides in tRNA(Trp) from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Thermococcus kodakarensis and requirement of tRNA m(2)G10/m(2) 2G10 methyltransferase (archaeal Trm11) for survival at high temperatures. J. Bacteriol. 201 (21). doi:10.1128/JB.00448-19
Hofler, S., and Carlomagno, T. (2020). Structural and functional roles of 2'-O-ribose methylations and their enzymatic machinery across multiple classes of RNAs. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 65, 42–50. doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2020.05.008
Hogan, C. A., Gratz, S. J., Dumouchel, J. L., Thakur, R. S., Delgado, A., Lentini, J. M., et al. (2023). Expanded tRNA methyltransferase family member TRMT9B regulates synaptic growth and function. EMBO Rep. 24 (10), e56808. doi:10.15252/embr.202356808
Holvec, S., Barchet, C., Lechner, A., Frechin, L., De Silva, S. N. T., Hazemann, I., et al. (2024). The structure of the human 80S ribosome at 1.9 A resolution reveals the molecular role of chemical modifications and ions in RNA. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 31, 1251–1264. doi:10.1038/s41594-024-01274-x
Honda, K., Hase, H., Tanikawa, S., Okawa, K., Chen, L., Yamaguchi, T., et al. (2024). ALKBH8 contributes to neurological function through oxidative stress regulation. PNAS Nexus 3 (3), pgae115. doi:10.1093/pnasnexus/pgae115
Hori, H. (2023). Transfer RNA modification enzymes with a thiouridine synthetase, methyltransferase and pseudouridine synthase (THUMP) domain and the nucleosides they produce in tRNA. Genes (Basel) 14 (2), 382. doi:10.3390/genes14020382
Hu, H., Kahrizi, K., Musante, L., Fattahi, Z., Herwig, R., Hosseini, M., et al. (2019). Genetics of intellectual disability in consanguineous families. Mol. Psychiatry 24 (7), 1027–1039. doi:10.1038/s41380-017-0012-2
Hu, Z., Qin, Z., Wang, M., Xu, C., Feng, G., Liu, J., et al. (2010). The Arabidopsis SMO2, a homologue of yeast TRM112, modulates progression of cell division during organ growth. Plant J. 61 (4), 600–610. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313x.2009.04085.x
Hua, M., Chen, Y., Jia, M., Lv, W., Xu, Y., and Zhang, Y. (2024). RNA-binding protein THUMPD2 inhibits proliferation and promotes metastasis in epithelial ovarian cancer. Heliyon 10 (13), e33201. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33201
Ignatova, V. V., Stolz, P., Kaiser, S., Gustafsson, T. H., Lastres, P. R., Sanz-Moreno, A., et al. (2020). The rRNA m(6)A methyltransferase METTL5 is involved in pluripotency and developmental programs. Genes Dev. 34 (9-10), 715–729. doi:10.1101/gad.333369.119
Jangani, M., Poolman, T. M., Matthews, L., Yang, N., Farrow, S. N., Berry, A., et al. (2014). The methyltransferase WBSCR22/Merm1 enhances glucocorticoid receptor function and is regulated in lung inflammation and cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 289 (13), 8931–8946. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.540906
Johansson, M. J., Esberg, A., Huang, B., Bjork, G. R., and Bystrom, A. S. (2008). Eukaryotic wobble uridine modifications promote a functionally redundant decoding system. Mol. Cell. Biol. 28 (10), 3301–3312. doi:10.1128/MCB.01542-07
Juhling, F., Morl, M., Hartmann, R. K., Sprinzl, M., Stadler, P. F., and Putz, J. (2009). tRNAdb 2009: compilation of tRNA sequences and tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 37 (Database issue), D159–D162. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn772
Jungfleisch, J., Bottcher, R., Tallo-Parra, M., Perez-Vilaro, G., Merits, A., Novoa, E. M., et al. (2022). CHIKV infection reprograms codon optimality to favor viral RNA translation by altering the tRNA epitranscriptome. Nat. Commun. 13 (1), 4725. doi:10.1038/s41467-022-31835-x
Kalhor, H. R., and Clarke, S. (2003). Novel methyltransferase for modified uridine residues at the wobble position of tRNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23 (24), 9283–9292. doi:10.1128/mcb.23.24.9283-9292.2003
Karlsborn, T., Tukenmez, H., Mahmud, A. K., Xu, F., Xu, H., and Bystrom, A. S. (2014). Elongator, a conserved complex required for wobble uridine modifications in eukaryotes. RNA Biol. 11 (12), 1519–1528. doi:10.4161/15476286.2014.992276
Khan, A. A., Huang, H., Zhao, Y., Li, H., Pan, R., Wang, S., et al. (2022). WBSCR22 and TRMT112 synergistically suppress cell proliferation, invasion and tumorigenesis in pancreatic cancer via transcriptional regulation of ISG15. Int. J. Oncol. 60 (3), 24. doi:10.3892/ijo.2022.5314
Kim, Y. O., Park, S. J., Balaban, R. S., Nirenberg, M., and Kim, Y. (2004). A functional genomic screen for cardiogenic genes using RNA interference in developing Drosophila embryos. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101 (1), 159–164. doi:10.1073/pnas.0307205101
Kirberger, M., Wang, X., Deng, H., Yang, W., Chen, G., and Yang, J. J. (2008). Statistical analysis of structural characteristics of protein Ca2+-binding sites. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 13 (7), 1169–1181. doi:10.1007/s00775-008-0402-7
Kogaki, T., Hase, H., Tanimoto, M., Tashiro, A., Kitae, K., Ueda, Y., et al. (2023). ALKBH4 is a novel enzyme that promotes translation through modified uridine regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 299 (9), 105093. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105093
Kohli, M., Riska, S. M., Mahoney, D. W., Chai, H. S., Hillman, D. W., Rider, D. N., et al. (2012). Germline predictors of androgen deprivation therapy response in advanced prostate cancer. Mayo Clin. Proc. 87 (3), 240–246. doi:10.1016/j.mayocp.2011.09.009
Kolaj-Robin, O., and Seraphin, B. (2017). Structures and activities of the elongator complex and its cofactors. Enzym. 41, 117–149. doi:10.1016/bs.enz.2017.03.001
Kong, Y., Cao, L., Deikus, G., Fan, Y., Mead, E. A., Lai, W., et al. (2022). Critical assessment of DNA adenine methylation in eukaryotes using quantitative deconvolution. Science 375 (6580), 515–522. doi:10.1126/science.abe7489
Kusevic, D., Kudithipudi, S., and Jeltsch, A. (2016). Substrate specificity of the HEMK2 protein glutamine methyltransferase and identification of novel substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 291 (12), 6124–6133. doi:10.1074/jbc.M115.711952
Kuttenlochner, W., Beller, P., Kaysser, L., and Groll, M. (2024). Deciphering the SAM- and metal-dependent mechanism of O-methyltransferases in cystargolide and belactosin biosynthesis: a structure-activity relationship study. J. Biol. Chem. 300, 107646. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107646
Lacoux, C., Wacheul, L., Saraf, K., Pythoud, N., Huvelle, E., Figaro, S., et al. (2020). The catalytic activity of the translation termination factor methyltransferase Mtq2-Trm112 complex is required for large ribosomal subunit biogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 48 (21), 12310–12325. doi:10.1093/nar/gkaa972
Lapeyre, B., and Purushothaman, S. K. (2004). Spb1p-directed formation of Gm2922 in the ribosome catalytic center occurs at a late processing stage. Mol. Cell 16 (4), 663–669. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2004.10.022
Lee, J., and Levin, D. E. (2018). Intracellular mechanism by which arsenite activates the yeast stress MAPK Hog1. Mol. Biol. Cell 29 (15), 1904–1915. doi:10.1091/mbc.E18-03-0185
Leetsi, L., Ounap, K., Abroi, A., and Kurg, R. (2019). The common partner of several methyltransferases TRMT112 regulates the expression of N6AMT1 isoforms in mammalian cells. Biomolecules 9 (9), 422. doi:10.3390/biom9090422
Lei, K., Xu, R., Wang, Q., Xiong, Q., Zhou, X., Li, Q., et al. (2023). METTL5 regulates cranial suture fusion via Wnt signaling. Fundam. Res. 3 (3), 369–376. doi:10.1016/j.fmre.2022.04.005
Leihne, V., Kirpekar, F., Vagbo, C. B., van den Born, E., Krokan, H. E., Grini, P. E., et al. (2011). Roles of Trm9-and ALKBH8-like proteins in the formation of modified wobble uridines in Arabidopsis tRNA. Nucleic Acids Res., gkr406. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr406
Leismann, J., Spagnuolo, M., Pradhan, M., Wacheul, L., Vu, M. A., Musheev, M., et al. (2020). The 18S ribosomal RNA m(6) A methyltransferase Mettl5 is required for normal walking behavior in Drosophila. EMBO Rep. 21 (7), e49443. doi:10.15252/embr.201949443
Leonardi, A., Kovalchuk, N., Yin, L., Endres, L., Evke, S., Nevins, S., et al. (2020). The epitranscriptomic writer ALKBH8 drives tolerance and protects mouse lungs from the environmental pollutant naphthalene. Epigenetics 15 (10), 1121–1138. doi:10.1080/15592294.2020.1750213
Letoquart, J., Huvelle, E., Wacheul, L., Bourgeois, G., Zorbas, C., Graille, M., et al. (2014). Structural and functional studies of Bud23-Trm112 reveal 18S rRNA N7-G1575 methylation occurs on late 40S precursor ribosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 111 (51), E5518–E5526. doi:10.1073/pnas.1413089111
Letoquart, J., van Tran, N., Caroline, V., Aleksandrov, A., Lazar, N., van Tilbeurgh, H., et al. (2015). Insights into molecular plasticity in protein complexes from Trm9-Trm112 tRNA modifying enzyme crystal structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 43 (22), 10989–11002. doi:10.1093/nar/gkv1009
Li, W., Shi, Y., Zhang, T., Ye, J., and Ding, J. (2019). Structural insight into human N6amt1-Trm112 complex functioning as a protein methyltransferase. Cell Discov. 5, 51. doi:10.1038/s41421-019-0121-y
Liao, H., Gaur, A., McConie, H., Shekar, A., Wang, K., Chang, J. T., et al. (2022). Human NOP2/NSUN1 regulates ribosome biogenesis through non-catalytic complex formation with box C/D snoRNPs. Nucleic Acids Res. 50 (18), 10695–10716. doi:10.1093/nar/gkac817
Liberman, N., Rothi, M. H., Gerashchenko, M. V., Zorbas, C., Boulias, K., MacWhinnie, F. G., et al. (2023). 18S rRNA methyltransferases DIMT1 and BUD23 drive intergenerational hormesis. Mol. Cell 83 (18), 3268–3282.e7. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2023.08.014
Liger, D., Mora, L., Lazar, N., Figaro, S., Henri, J., Scrima, N., et al. (2011). Mechanism of activation of methyltransferases involved in translation by the Trm112 'hub' protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 39 (14), 6249–6259. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr176
Lin, J. L., Yu, H. C., Chao, J. L., Wang, C., and Cheng, M. Y. (2012). New phenotypes generated by the G57R mutation of BUD23 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 29 (12), 537–546. doi:10.1002/yea.2934
Lin, T. Y., Abbassi, N. E. H., Zakrzewski, K., Chramiec-Glabik, A., Jemiola-Rzeminska, M., Rozycki, J., et al. (2019). The Elongator subunit Elp3 is a non-canonical tRNA acetyltransferase. Nat. Commun. 10 (1), 625. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-08579-2
Liu, B., Liu, X., Lai, W., and Wang, H. (2017). Metabolically generated stable isotope-labeled deoxynucleoside code for tracing DNA N(6)-methyladenine in human cells. Anal. Chem. 89 (11), 6202–6209. doi:10.1021/acs.analchem.7b01152
Liu, P., Nie, S., Li, B., Yang, Z. Q., Xu, Z. M., Fei, J., et al. (2010). Deficiency in a glutamine-specific methyltransferase for release factor causes mouse embryonic lethality. Mol. Cell. Biol. 30 (17), 4245–4253. doi:10.1128/MCB.00218-10
Liu, Y., Nie, D., Huang, Y., and Lu, G. (2009). RNAi-mediated knock-down of gene mN6A1 reduces cell proliferation and decreases protein translation. Mol. Biol. Rep. 36 (4), 767–774. doi:10.1007/s11033-008-9243-2
Lv, Z., Guan, L., Yao, R., Chen, H., Wang, H., Li, X., et al. (2025). AtTRM11 as a tRNA 2-methylguanosine methyltransferase modulates flowering and bacterial resistance via translational regulation. Plant Sci. 352, 112368. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2024.112368
Maddirevula, S., Alameer, S., Ewida, N., de Sousa, M. M. L., Bjoras, M., Vagbo, C. B., et al. (2022). Insight into ALKBH8-related intellectual developmental disability based on the first pathogenic missense variant. Hum. Genet. 141 (2), 209–215. doi:10.1007/s00439-021-02391-z
Maden, B. E. (1986). Identification of the locations of the methyl groups in 18 S ribosomal RNA from Xenopus laevis and man. J. Mol. Biol. 189 (4), 681–699. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(86)90498-5
Madhwani, K. R., Sayied, S., Ogata, C. H., Hogan, C. A., Lentini, J. M., Mallik, M., et al. (2024). tRNA modification enzyme-dependent redox homeostasis regulates synapse formation and memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 121 (46), e2317864121. doi:10.1073/pnas.2317864121
Matsuo, M., Yokogawa, T., Nishikawa, K., Watanabe, K., and Okada, N. (1995). Highly specific and efficient cleavage of squid tRNA(Lys) catalyzed by magnesium ions. J. Biol. Chem. 270 (17), 10097–10104. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.17.10097
Mazauric, M. H., Dirick, L., Purushothaman, S. K., Bjork, G. R., and Lapeyre, B. (2010). Trm112p is a 15-kDa zinc finger protein essential for the activity of two tRNA and one protein methyltransferases in yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 285 (24), 18505–18515. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.113100
Menezes, S., Gaston, K. W., Krivos, K. L., Apolinario, E. E., Reich, N. O., Sowers, K. R., et al. (2011). Formation of m2G6 in Methanocaldococcus jannaschii tRNA catalyzed by the novel methyltransferase Trm14. Nucleic Acids Res. 39 (17), 7641–7655. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr475
Metzger, E., Wang, S., Urban, S., Willmann, D., Schmidt, A., Offermann, A., et al. (2019). KMT9 monomethylates histone H4 lysine 12 and controls proliferation of prostate cancer cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 26 (5), 361–371. doi:10.1038/s41594-019-0219-9
Monies, D., Vagbo, C. B., Al-Owain, M., Alhomaidi, S., and Alkuraya, F. S. (2019). Recessive truncating mutations in ALKBH8 cause intellectual disability and severe impairment of wobble uridine modification. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 104 (6), 1202–1209. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.03.026
Mora, L., Heurgue-Hamard, V., de Zamaroczy, M., Kervestin, S., and Buckingham, R. H. (2007). Methylation of bacterial release factors RF1 and RF2 is required for normal translation termination in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 282 (49), 35638–35645. doi:10.1074/jbc.M706076200
Murphy, J. C., Harrington, E. M., Schumann, S., Vasconcelos, E. J. R., Mottram, T. J., Harper, K. L., et al. (2023). Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus induces specialised ribosomes to efficiently translate viral lytic mRNAs. Nat. Commun. 14 (1), 300. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-35914-5
Nakahigashi, K., Kubo, N., Narita, S., Shimaoka, T., Goto, S., Oshima, T., et al. (2002). HemK, a class of protein methyl transferase with similarity to DNA methyl transferases, methylates polypeptide chain release factors, and hemK knockout induces defects in translational termination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99 (3), 1473–1478. doi:10.1073/pnas.032488499
Nakai, M., Hase, H., Zhao, Y., Okawa, K., Honda, K., Ikuma, K., et al. (2024). RNA-modifying enzyme Alkbh8 is involved in mouse embryonic development. iScience 27 (9), 110777. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2024.110777
Nakazawa, Y., Arai, H., and Fujita, N. (2011). The novel metastasis promoter Merm1/Wbscr22 enhances tumor cell survival in the vasculature by suppressing Zac1/p53-dependent apoptosis. Cancer Res. 71 (3), 1146–1155. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2695
Natchiar, S. K., Myasnikov, A. G., Kratzat, H., Hazemann, I., and Klaholz, B. P. (2017). Visualization of chemical modifications in the human 80S ribosome structure. Nature 551 (7681), 472–477. doi:10.1038/nature24482
Neumann, P., Lakomek, K., Naumann, P. T., Erwin, W. M., Lauhon, C. T., and Ficner, R. (2014). Crystal structure of a 4-thiouridine synthetase-RNA complex reveals specificity of tRNA U8 modification. Nucleic Acids Res. 42 (10), 6673–6685. doi:10.1093/nar/gku249
Nie, D. S., Liu, Y. B., and Lu, G. X. (2009). Cloning and primarily function study of two novel putative N5-glutamine methyltransferase (Hemk) splice variants from mouse stem cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 36 (8), 2221–2228. doi:10.1007/s11033-008-9437-7
Nishida, Y., Ohmori, S., Kakizono, R., Kawai, K., Namba, M., Okada, K., et al. (2022). Required elements in tRNA for methylation by the eukaryotic tRNA (guanine-N(2)-) methyltransferase (Trm11-Trm112 complex). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (7), 4046. doi:10.3390/ijms23074046
O'Brown, Z. K., Boulias, K., Wang, J., Wang, S. Y., O'Brown, N. M., Hao, Z., et al. (2019). Sources of artifact in measurements of 6mA and 4mC abundance in eukaryotic genomic DNA. BMC Genomics 20 (1), 445. doi:10.1186/s12864-019-5754-6
Oliver, G. C., Cario, A., and Rogers, K. L. (2020). Rate and extent of growth of a model extremophile, Archaeoglobus fulgidus, under high hydrostatic pressures. Front. Microbiol. 11, 1023. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2020.01023
Ounap, K., Kasper, L., Kurg, A., and Kurg, R. (2013). The human WBSCR22 protein is involved in the biogenesis of the 40S ribosomal subunits in mammalian cells. PLoS One 8 (9), e75686. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0075686
Ounap, K., Leetsi, L., Matsoo, M., and Kurg, R. (2015). The stability of ribosome biogenesis factor WBSCR22 is regulated by interaction with TRMT112 via ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. PLoS One 10 (7), e0133841. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0133841
Pastore, C., Topalidou, I., Forouhar, F., Yan, A. C., Levy, M., and Hunt, J. F. (2012). Crystal structure and RNA binding properties of the RNA recognition motif (RRM) and AlkB domains in human AlkB homolog 8 (ABH8), an enzyme catalyzing tRNA hypermodification. J. Biol. Chem. 287 (3), 2130–2143. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.286187
Patil, A., Chan, C. T., Dyavaiah, M., Rooney, J. P., Dedon, P. C., and Begley, T. J. (2012a). Translational infidelity-induced protein stress results from a deficiency in Trm9-catalyzed tRNA modifications. RNA Biol. 9 (7), 990–1001. doi:10.4161/rna.20531
Patil, A., Dyavaiah, M., Joseph, F., Rooney, J. P., Chan, C. T., Dedon, P. C., et al. (2012b). Increased tRNA modification and gene-specific codon usage regulate cell cycle progression during the DNA damage response. Cell Cycle 11 (19), 3656–3665. doi:10.4161/cc.21919
Pellegrino, S., Dent, K. C., Spikes, T., and Warren, A. J. (2023). Cryo-EM reconstruction of the human 40S ribosomal subunit at 2.15 A resolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 51 (8), 4043–4054. doi:10.1093/nar/gkad194
Petrosyan, J., and Bohnsack, K. E. (2024). N2-methylguanosine and N2, N2-dimethylguanosine in cytosolic and mitochondrial tRNAs. Front. RNA Res. 2. doi:10.3389/frnar.2024.1460913
Phizicky, E. M., and Hopper, A. K. (2023). The life and times of a tRNA. RNA 29 (7), 898–957. doi:10.1261/rna.079620.123
Piano, F., Schetter, A. J., Morton, D. G., Gunsalus, K. C., Reinke, V., Kim, S. K., et al. (2002). Gene clustering based on RNAi phenotypes of ovary-enriched genes in C. elegans. Curr. Biol. 12 (22), 1959–1964. doi:10.1016/s0960-9822(02)01301-5
Pierson, W. E., Hoffer, E. D., Keedy, H. E., Simms, C. L., Dunham, C. M., and Zaher, H. S. (2016). Uniformity of peptide release is maintained by methylation of release factors. Cell Rep. 17 (1), 11–18. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2016.08.085
Polevoda, B., Span, L., and Sherman, F. (2006). The yeast translation release factors Mrf1p and Sup45p (eRF1) are methylated, respectively, by the methyltransferases Mtq1p and Mtq2p. J. Biol. Chem. 281 (5), 2562–2571. doi:10.1074/jbc.M507651200
Pundir, S., Ge, X., and Sanyal, S. (2021). GGQ methylation enhances both speed and accuracy of stop codon recognition by bacterial class-I release factors. J. Biol. Chem. 296, 100681. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100681
Purushothaman, S. K., Bujnicki, J. M., Grosjean, H., and Lapeyre, B. (2005). Trm11p and Trm112p are both required for the formation of 2-methylguanosine at position 10 in yeast tRNA. Mol. Cell Biol. 25 (11), 4359–4370. doi:10.1128/mcb.25.11.4359-4370.2005
Ratel, D., Ravanat, J. L., Charles, M. P., Platet, N., Breuillaud, L., Lunardi, J., et al. (2006). Undetectable levels of N6-methyl adenine in mouse DNA: cloning and analysis of PRED28, a gene coding for a putative mammalian DNA adenine methyltransferase. FEBS Lett. 580 (13), 3179–3184. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2006.04.074
Remines, M., Schoonover, M. G., Knox, Z., Kenwright, K., Hoffert, K. M., Coric, A., et al. (2024). Profiling the compendium of changes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae due to mutations that alter availability of the main methyl donor S-Adenosylmethionine. G3 Genes, Genomes, Genet. 14 (4). doi:10.1093/g3journal/jkae002
Ren, X., Aleshin, M., Jo, W. J., Dills, R., Kalman, D. A., Vulpe, C. D., et al. (2011). Involvement of N-6 adenine-specific DNA methyltransferase 1 (N6AMT1) in arsenic biomethylation and its role in arsenic-induced toxicity. Environ. Health Perspect. 119 (6), 771–777. doi:10.1289/ehp.1002733
Rensvold, J. W., Shishkova, E., Sverchkov, Y., Miller, I. J., Cetinkaya, A., Pyle, A., et al. (2022). Defining mitochondrial protein functions through deep multiomic profiling. Nature 606 (7913), 382–388. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04765-3
Rhein, V. F., Carroll, J., Ding, S., Fearnley, I. M., and Walker, J. E. (2016). NDUFAF5 hydroxylates NDUFS7 at an early stage in the assembly of human complex I. J. Biol. Chem. 291 (28), 14851–14860. doi:10.1074/jbc.M116.734970
Richard, E. M., Polla, D. L., Assir, M. Z., Contreras, M., Shahzad, M., Khan, A. A., et al. (2019). Bi-Allelic variants in METTL5 cause autosomal-recessive intellectual disability and microcephaly. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 105 (4), 869–878. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.09.007
Rong, B., Zhang, Q., Wan, J., Xing, S., Dai, R., Li, Y., et al. (2020). Ribosome 18S m(6)A methyltransferase METTL5 promotes translation initiation and breast cancer cell growth. Cell Rep. 33 (12), 108544. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108544
Roovers, M., Oudjama, Y., Fislage, M., Bujnicki, J. M., Versees, W., and Droogmans, L. (2012). The open reading frame TTC1157 of Thermus thermophilus HB27 encodes the methyltransferase forming N(2)-methylguanosine at position 6 in tRNA. RNA 18 (4), 815–824. doi:10.1261/rna.030411.111
Roychowdhury, A., Joret, C., Bourgeois, G., Heurgue-Hamard, V., Lafontaine, D. L. J., and Graille, M. (2019). The DEAH-box RNA helicase Dhr1 contains a remarkable carboxyl terminal domain essential for small ribosomal subunit biogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 47 (14), 7548–7563. doi:10.1093/nar/gkz529
Saad, A. K., Marafi, D., Mitani, T., Du, H., Rafat, K., Fatih, J. M., et al. (2021). Neurodevelopmental disorder in an Egyptian family with a biallelic ALKBH8 variant. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 185 (4), 1288–1293. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.62100
Saito, K., Kobayashi, K., Wada, M., Kikuno, I., Takusagawa, A., Mochizuki, M., et al. (2010). Omnipotent role of archaeal elongation factor 1 alpha (EF1α) in translational elongation and termination, and quality control of protein synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 107 (45), 19242–19247. doi:10.1073/pnas.1009599107
Saletore, Y., Meyer, K., Korlach, J., Vilfan, I. D., Jaffrey, S., and Mason, C. E. (2012). The birth of the Epitranscriptome: deciphering the function of RNA modifications. Genome Biol. 13 (10), 175. doi:10.1186/gb-2012-13-10-175
Sardana, R., and Johnson, A. W. (2012). The methyltransferase adaptor protein Trm112 is involved in biogenesis of both ribosomal subunits. Mol. Biol. Cell 23 (21), 4313–4322. doi:10.1091/mbc.E12-05-0370
Sardana, R., White, J. P., and Johnson, A. W. (2013). The rRNA methyltransferase Bud23 shows functional interaction with components of the SSU processome and RNase MRP. RNA 19 (6), 828–840. doi:10.1261/rna.037671.112
Sardana, R., Zhu, J., Gill, M., and Johnson, A. W. (2014). Physical and functional interaction between the methyltransferase Bud23 and the essential DEAH-box RNA helicase Ecm16. Mol. Cell. Biol. 34 (12), 2208–2220. doi:10.1128/MCB.01656-13
Schiffers, S., Ebert, C., Rahimoff, R., Kosmatchev, O., Steinbacher, J., Bohne, A. V., et al. (2017). Quantitative LC-MS provides No evidence for m(6) dA or m(4) dC in the genome of mouse embryonic stem cells and tissues. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56 (37), 11268–11271. doi:10.1002/anie.201700424
Schubert, H. L., Blumenthal, R. M., and Cheng, X. (2003). Many paths to methyltransfer: a chronicle of convergence. Trends Biochem. Sci. 28 (6), 329–335. doi:10.1016/S0968-0004(03)00090-2
Selvadurai, K., Wang, P., Seimetz, J., and Huang, R. H. (2014). Archaeal Elp3 catalyzes tRNA wobble uridine modification at C5 via a radical mechanism. Nat. Chem. Biol. 10 (10), 810–812. doi:10.1038/nchembio.1610
Sendinc, E., Valle-Garcia, D., Jiao, A., and Shi, Y. (2020). Analysis of m6A RNA methylation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell Discov. 6 (1), 47. doi:10.1038/s41421-020-00186-6
Sepich-Poore, C., Zheng, Z., Schmitt, E., Wen, K., Zhang, Z. S., Cui, X. L., et al. (2022). The METTL5-TRMT112 N(6)-methyladenosine methyltransferase complex regulates mRNA translation via 18S rRNA methylation. J. Biol. Chem. 298 (3), 101590. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101590
Sharma, L. K., Lu, J., and Bai, Y. (2009). Mitochondrial respiratory complex I: structure, function and implication in human diseases. Curr. Med. Chem. 16 (10), 1266–1277. doi:10.2174/092986709787846578
Sharma, S., and Lafontaine, D. L. J. (2015). 'View from A bridge': a new perspective on eukaryotic rRNA base modification. Trends Biochem. Sci. 40 (10), 560–575. doi:10.1016/j.tibs.2015.07.008
Shatsky, M., Allen, S., Gold, B. L., Liu, N. L., Juba, T. R., Reveco, S. A., et al. (2016). Bacterial interactomes: interacting protein partners share similar function and are validated in independent assays more frequently than previously reported. Mol. and Cell. Proteomics 15 (5), 1539–1555. doi:10.1074/mcp.M115.054692
Shi, H., and Moore, P. B. (2000). The crystal structure of yeast phenylalanine tRNA at 1.93 Å resolution: a classic structure revisited. RNA 6 (8), 1091–1105. doi:10.1017/s1355838200000364
Shiber, A., Doring, K., Friedrich, U., Klann, K., Merker, D., Zedan, M., et al. (2018). Cotranslational assembly of protein complexes in eukaryotes revealed by ribosome profiling. Nature 561 (7722), 268–272. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0462-y
Shimada, K., Nakamura, M., Anai, S., De Velasco, M., Tanaka, M., Tsujikawa, K., et al. (2009). A novel human AlkB homologue, ALKBH8, contributes to human bladder cancer progression. Cancer Res. 69 (7), 3157–3164. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-08-3530
Sinclair, P. B., Sorour, A., Martineau, M., Harrison, C. J., Mitchell, W. A., O'Neill, E., et al. (2004). A fluorescence in situ hybridization map of 6q deletions in acute lymphocytic leukemia: identification and analysis of a candidate tumor suppressor gene. Cancer Res. 64 (12), 4089–4098. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-1871
Smith, T. J., Giles, R. N., and Koutmou, K. S. (2024). Anticodon stem-loop tRNA modifications influence codon decoding and frame maintenance during translation. Seminars Cell and Dev. Biol. 154 (Pt B), 105–113. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2023.06.003
Song, H., Mugnier, P., Das, A. K., Webb, H. M., Evans, D. R., Tuite, M. F., et al. (2000). The crystal structure of human eukaryotic release factor eRF1--mechanism of stop codon recognition and peptidyl-tRNA hydrolysis. Cell 100 (3), 311–321. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80667-4
Song, P., Tian, E., Cai, Z., Chen, X., Chen, S., Yu, K., et al. (2024). Methyltransferase ATMETTL5 writes 6 on 18S ribosomal RNA to regulate translation in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 244, 571–587. doi:10.1111/nph.20034
Songe-Moller, L., van den Born, E., Leihne, V., Vagbo, C. B., Kristoffersen, T., Krokan, H. E., et al. (2010). Mammalian ALKBH8 possesses tRNA methyltransferase activity required for the biogenesis of multiple wobble uridine modifications implicated in translational decoding. Mol. Cell. Biol. 30 (7), 1814–1827. doi:10.1128/MCB.01602-09
Stefanska, B., Cheishvili, D., Suderman, M., Arakelian, A., Huang, J., Hallett, M., et al. (2014). Genome-wide study of hypomethylated and induced genes in patients with liver cancer unravels novel anticancer targets. Clin. Cancer Res. 20 (12), 3118–3132. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-0283
Strassler, S. E., Bowles, I. E., Dey, D., Jackman, J. E., and Conn, G. L. (2022). Tied up in knots: untangling substrate recognition by the SPOUT methyltransferases. J. Biol. Chem. 298 (10), 102393. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102393
Studte, P., Zink, S., Jablonowski, D., Bar, C., von der Haar, T., Tuite, M. F., et al. (2008). tRNA and protein methylase complexes mediate zymocin toxicity in yeast. Mol. Microbiol. 69 (5), 1266–1277. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06358.x
Sun, S., Fei, K., Zhang, G., Wang, J., Yang, Y., Guo, W., et al. (2021). Construction and comprehensive analyses of a METTL5-associated prognostic signature with immune implication in lung adenocarcinomas. Front. Genet. 11, 617174. doi:10.3389/fgene.2020.617174
Suzuki, T. (2021). The expanding world of tRNA modifications and their disease relevance. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 22 (6), 375–392. doi:10.1038/s41580-021-00342-0
Tiedemann, R. E., Zhu, Y. X., Schmidt, J., Shi, C. X., Sereduk, C., Yin, H., et al. (2012). Identification of molecular vulnerabilities in human multiple myeloma cells by RNA interference lethality screening of the druggable genome. Cancer Res. 72 (3), 757–768. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-2781
Torun, D., Arslan, M., Cavdarli, B., Akar, H., and Cram, D. S. (2022). Three Afghani siblings with a novel homozygous variant and further delineation of the clinical features of METTL5 related intellectual disability syndrome. Turk J. Pediatr. 64 (5), 956–963. doi:10.24953/turkjped.2020.3992
Towns, W. L., and Begley, T. J. (2012). Transfer RNA methytransferases and their corresponding modifications in budding yeast and humans: activities, predications, and potential roles in human health. DNA Cell Biol. 31 (4), 434–454. doi:10.1089/dna.2011.1437
Uhlen, M., Fagerberg, L., Hallstrom, B. M., Lindskog, C., Oksvold, P., Mardinoglu, A., et al. (2015). Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 347 (6220), 1260419. doi:10.1126/science.1260419
Urbonavicius, J., Armengaud, J., and Grosjean, H. (2006). Identity elements required for enzymatic formation of N2,N2-dimethylguanosine from N2-monomethylated derivative and its possible role in avoiding alternative conformations in archaeal tRNA. J. Mol. Biol. 357 (2), 387–399. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.12.087
van den Born, E., Vagbo, C. B., Songe-Moller, L., Leihne, V., Lien, G. F., Leszczynska, G., et al. (2011). ALKBH8-mediated formation of a novel diastereomeric pair of wobble nucleosides in mammalian tRNA. Nat. Commun. 2, 172. doi:10.1038/ncomms1173
van Tran, N., Ernst, F. G. M., Hawley, B. R., Zorbas, C., Ulryck, N., Hackert, P., et al. (2019). The human 18S rRNA m6A methyltransferase METTL5 is stabilized by TRMT112. Nucleic Acids Res. 47 (15), 7719–7733. doi:10.1093/nar/gkz619
van Tran, N., Muller, L., Ross, R. L., Lestini, R., Letoquart, J., Ulryck, N., et al. (2018). Evolutionary insights into Trm112-methyltransferase holoenzymes involved in translation between archaea and eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 46 (16), 8483–8499. doi:10.1093/nar/gky638
Vendeix, F. A., Murphy, F. V., Cantara, W. A., Leszczynska, G., Gustilo, E. M., Sproat, B., et al. (2012). Human tRNA(Lys3)(UUU) is pre-structured by natural modifications for cognate and wobble codon binding through keto-enol tautomerism. J. Mol. Biol. 416 (4), 467–485. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2011.12.048
Vestergaard, B., Van, L. B., Andersen, G. R., Nyborg, J., Buckingham, R. H., and Kjeldgaard, M. (2001). Bacterial polypeptide release factor RF2 is structurally distinct from eukaryotic eRF1. Mol. Cell 8 (6), 1375–1382. doi:10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00415-4
Wang, C., Ulryck, N., Herzel, L., Pythoud, N., Kleiber, N., Guerineau, V., et al. (2023). N 2-methylguanosine modifications on human tRNAs and snRNA U6 are important for cell proliferation, protein translation and pre-mRNA splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 51, 7496–7519. doi:10.1093/nar/gkad487
Wang, C., van Tran, N., Jactel, V., Guerineau, V., and Graille, M. (2020). Structural and functional insights into Archaeoglobus fulgidus m2G10 tRNA methyltransferase Trm11 and its Trm112 activator. Nucleic Acids Res. 48 (19), 11068–11082. doi:10.1093/nar/gkaa830
Wang, L., Liang, Y., Lin, R., Xiong, Q., Yu, P., Ma, J., et al. (2022). Mettl5 mediated 18S rRNA N6-methyladenosine (m(6)A) modification controls stem cell fate determination and neural function. Genes and Dis. 9 (1), 268–274. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2020.07.004
Wang, Q., Huang, Y., Zhu, Y., Zhang, W., Wang, B., Du, X., et al. (2024). The m6A methyltransferase METTL5 promotes neutrophil extracellular trap network release to regulate hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Cancer Med. 13 (7), e7165. doi:10.1002/cam4.7165
Wang, S., Liu, X., Huang, J., Zhang, Y., Sang, C., Li, T., et al. (2018). Expression of KIAA1456 in lung cancer tissue and its effects on proliferation, migration and invasion of lung cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 16 (3), 3791–3795. doi:10.3892/ol.2018.9119
Waqas, A., Nayab, A., Shaheen, S., Abbas, S., Latif, M., Rafeeq, M. M., et al. (2022). Case report: biallelic variant in the tRNA methyltransferase domain of the AlkB homolog 8 causes syndromic intellectual disability. Front. Genet. 13, 878274. doi:10.3389/fgene.2022.878274
Weirich, S., Ulu, G. T., Chandrasekaran, T. T., Kehl, J., Schmid, J., Dorscht, F., et al. (2024). Distinct specificities of the HEMK2 protein methyltransferase in methylation of glutamine and lysine residues. Protein Sci. 33 (2), e4897. doi:10.1002/pro.4897
White, J., Li, Z., Sardana, R., Bujnicki, J. M., Marcotte, E. M., and Johnson, A. W. (2008). Bud23 methylates G1575 of 18S rRNA and is required for efficient nuclear export of pre-40S subunits. Mol. Cell. Biol. 28 (10), 3151–3161. doi:10.1128/MCB.01674-07
Wilkinson, M. E., Charenton, C., and Nagai, K. (2020). RNA splicing by the spliceosome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 89, 359–388. doi:10.1146/annurev-biochem-091719-064225
Woodcock, C. B., Yu, D., Zhang, X., and Cheng, X. (2019). Human HemK2/KMT9/N6AMT1 is an active protein methyltransferase, but does not act on DNA in vitro, in the presence of Trm112. Cell Discov. 5, 50. doi:10.1038/s41421-019-0119-5
Xia, P., Zhang, H., Lu, H., Xu, K., Jiang, X., Jiang, Y., et al. (2023). METTL5 stabilizes c-Myc by facilitating USP5 translation to reprogram glucose metabolism and promote hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Cancer Commun. 43 (3), 338–364. doi:10.1002/cac2.12403
Xiao, C. L., Zhu, S., He, M., Chen, D., Zhang, Q., Chen, Y., et al. (2018). N(6)-Methyladenine DNA modification in the human genome. Mol. Cell 71 (2), 306–318.e7. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2018.06.015
Xing, M., Liu, Q., Mao, C., Zeng, H., Zhang, X., Zhao, S., et al. (2020). The 18S rRNA m(6) A methyltransferase METTL5 promotes mouse embryonic stem cell differentiation. EMBO Rep. 21 (10), e49863. doi:10.15252/embr.201949863
Xu, F., Suyama, R., Inada, T., Kawaguchi, S., and Kai, T. (2024). HemK2 functions for sufficient protein synthesis and RNA stability through eRF1 methylation during Drosophila oogenesis. bioRxiv, 2024.2001.2029.576963. doi:10.1101/2024.01.29.576963
Yan, D., Tu, L., Yuan, H., Fang, J., Cheng, L., Zheng, X., et al. (2017). WBSCR22 confers oxaliplatin resistance in human colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 15443. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-15749-z
Yang, W. Q., Ge, J. Y., Zhang, X., Zhu, W. Y., Lin, L., Shi, Y., et al. (2024). THUMPD2 catalyzes the N2-methylation of U6 snRNA of the spliceosome catalytic center and regulates pre-mRNA splicing and retinal degeneration. Nucleic Acids Res. 52, 3291–3309. doi:10.1093/nar/gkad1243
Yang, W. Q., Xiong, Q. P., Ge, J. Y., Li, H., Zhu, W. Y., Nie, Y., et al. (2021). THUMPD3-TRMT112 is a m2G methyltransferase working on a broad range of tRNA substrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 49 (20), 11900–11919. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab927
Yilmaz, M., Kamasak, T., Terali, K., Cebi, A. H., and Turkyilmaz, A. (2024). The first Turkish family with a novel biallelic missense variant of the ALKBH8 gene: a study on the clinical and variant spectrum of ALKBH8-related intellectual developmental disorders. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 194 (5), e63535. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.63535
Yu, D., Kaur, G., Blumenthal, R. M., Zhang, X., and Cheng, X. (2021). Enzymatic characterization of three human RNA adenosine methyltransferases reveals diverse substrate affinities and reaction optima. J. Biol. Chem. 296, 100270. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100270
Yu, Y. P., Ding, Y., Chen, Z., Liu, S., Michalopoulos, A., Chen, R., et al. (2014). Novel fusion transcripts associate with progressive prostate cancer. Am. J. Pathology 184 (10), 2840–2849. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2014.06.025
Yu, Y. P., Liu, P., Nelson, J., Hamilton, R. L., Bhargava, R., Michalopoulos, G., et al. (2019). Identification of recurrent fusion genes across multiple cancer types. Sci. Rep. 9 (1), 1074. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-38550-6
Zaccara, S., Ries, R. J., and Jaffrey, S. R. (2019). Reading, writing and erasing mRNA methylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 20 (10), 608–624. doi:10.1038/s41580-019-0168-5
Zhang, H., Ge, Y., He, P., Chen, X., Carina, A., Qiu, Y., et al. (2015). Interactive effects of N6AMT1 and As3MT in arsenic biomethylation. Toxicol. Sci. 146 (2), 354–362. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfv101
Zhou, J. B., Wang, E. D., and Zhou, X. L. (2021). Modifications of the human tRNA anticodon loop and their associations with genetic diseases. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 78 (23), 7087–7105. doi:10.1007/s00018-021-03948-x
Keywords: epitranscriptomics, heterodimeric methyltransferase, pre-mRNA splicing, mRNA translation, post-transcriptional/-translational modifications
Citation: Wang C, Tay LLE, Hu W, Corre M and Graille M (2025) TRMT112, a master activator of several methyltransferases modifying factors involved in RNA maturation and translation. Front. RNA Res. 3:1556979. doi: 10.3389/frnar.2025.1556979
Received: 07 January 2025; Accepted: 26 February 2025;
Published: 27 March 2025.
Edited by:
Nikolay Shirokikh, Australian National University, AustraliaReviewed by:
Urmila Sehrawat, Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Wang, Tay, Hu, Corre and Graille. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Marc Graille, bWFyYy5ncmFpbGxlQHBvbHl0ZWNobmlxdWUuZWR1
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.