
94% of researchers rate our articles as excellent or good
Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.
Find out more
BRIEF RESEARCH REPORT article
Front. RNA Res., 03 June 2024
Sec. RNA Processing and Regulation
Volume 2 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/frnar.2024.1415530
This article is part of the Research TopicRNA Methylation: Detection, Deposition, and FunctionsView all 6 articles
Methyltransferase ribozyme 1 (MTR1) is a catalytic RNA that has been isolated from a random RNA pool by in vitro selection. The ribozyme catalyzes site-specific formation of 1-methyl adenosine (m1A) using 6-methyl guanine (m6G) as a methyl group donor. The ribozyme has been extensively characterized by biochemical and structural analyses. Here, we describe high-throughput screening of single point mutants in the catalytic domain of MTR1 and determine their effect on ribozyme activity. Our mutational profiling method successfully assessed the activity of the 141 MTR1 variants tested in each experiment and revealed that the ribozyme is very sensitive to nucleotide substitutions in the catalytic core domain. Our technique can be applied to methyltransferase ribozymes that catalyze formation of different modifications such as 7-methylguanosine (m7G) or 3-methylcytidine (m3C).
RNA methylation is a fundamental chemical reaction observed in various cellular events and has been linked to diverse functions including RNA stabilization, RNA maturation, quality control of RNA, gene expression, RNA transport, and immune response (Hori, 2014). According to the Modomics database (https://iimcb.genesilico.pl/modomics/), 98 distinct methylated nucleosides have been found in the three domains of life until now (Boccaletto et al., 2022). In general, these RNA methylations are catalyzed by site-specific RNA methyltransferase (s) (Hori, 2014; Hori et al., 2018). Over the last two decades, high-throughput techniques for the detection of methylated nucleosides in RNA have been established to survey the status of RNA methylation (Li et al., 2017). These techniques use a common basic strategy wherein methylated RNAs are converted into cDNA by reverse transcription. Certain methylated nucleosides, such as 1-methyladenosine (m1A), 1-methylguanosine (m1G), 2,2-dimethylguanosine (m22G), 3-methylcytidine (m3C), and 3-methyluridine (m3U), prevent base pair formation during the reverse transcription reaction due to the methyl group(s) installed on the Watson-Crick face, thus inducing mis-incorporations in cDNA by the reverse transcriptase. These mutations in the cDNA can be detected by next-generation sequencing (Yamagami et al., 2022), providing positional and quantitative information on methylated nucleosides in RNA. Very recently, we developed a mutational profiling technique that was linked to high-throughput functional analysis of tRNA methyltransferase, called tRNA-MaP (Yamagami and Hori, 2023a; Yamagami and Hori, 2023b).
Methyltransferase ribozyme 1 (MTR1) is a newly discovered ribozyme that catalyzes site-specific formation of 1-methyladenosine (m1A) (Scheitl et al., 2020). This catalytic RNA uses 6-methyl guanine (m6G) as a methyl group donor (Figure 1A). The X-ray crystal structure of MTR1 revealed the m6G binding mechanism and detailed orientation of catalytic residues in the ribozyme (Deng et al., 2022; Scheitl et al., 2022). The m6G base is trapped by three nucleotides of MTR1: C47, U82, and the target A11 (Figures 1B, C). In addition, the triple base interactions of the m6G base are enclosed by three planar base interactions forming a top layer (A46-A83-A77), a second layer (C48-G78), and a layer at the bottom (G49-C77) (Figure 1C). Thus, m6G binding is regulated by a complex structural arrangement of multiple nucleotides in the catalytic core domain (Deng et al., 2022; Scheitl et al., 2022). Furthermore, the methyltransferase ribozyme can utilize m6G derivatives as an alkylation donor and label target RNAs with a fluorescent group (Scheitl et al., 2023).
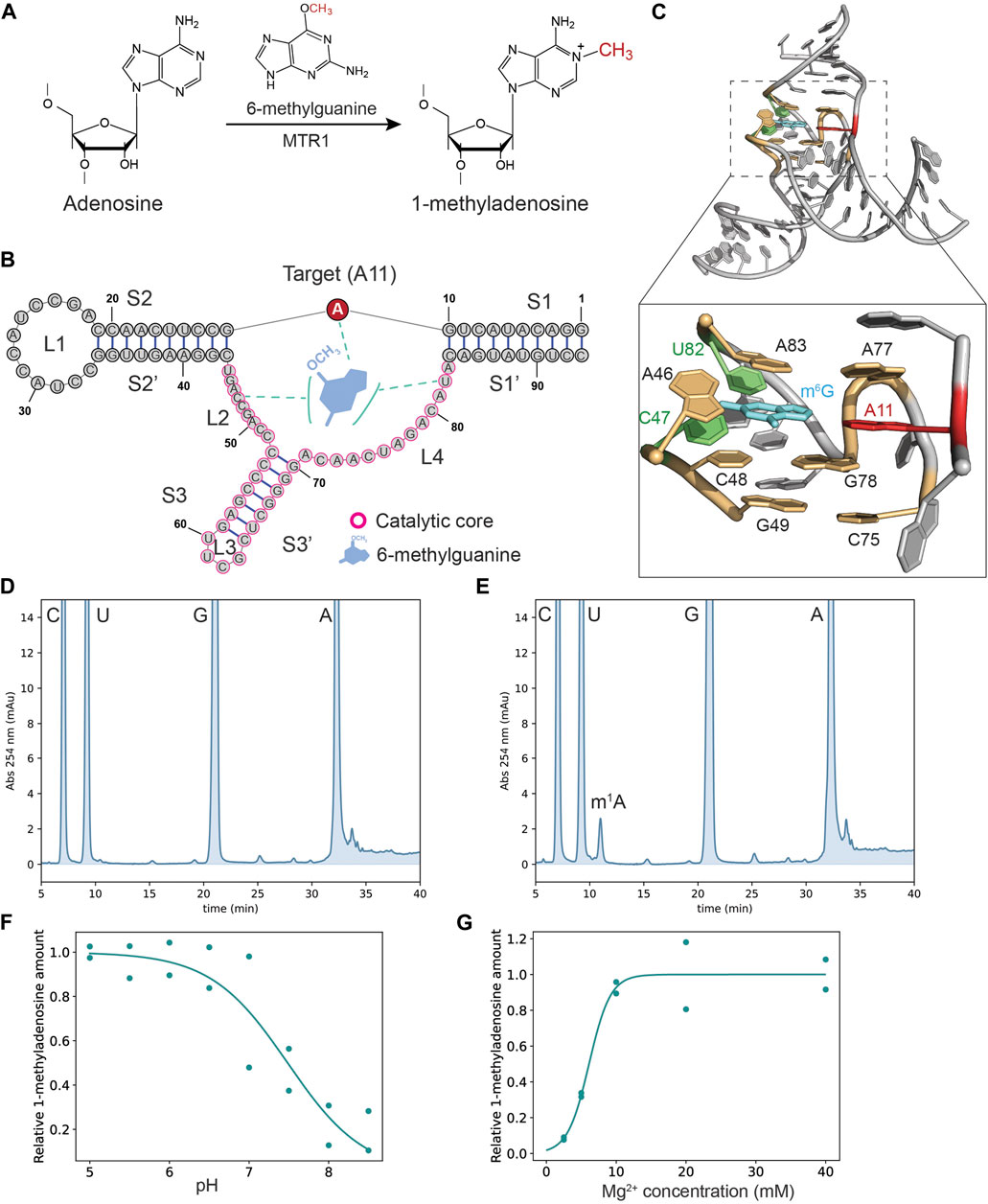
Figure 1. The MTR1 shows the catalytic activity under physiological conditions. (A) MTR1 catalyzes the formation of 1-methyladenosine from adenosine using 6-methylguanine as a methyl group donor. (B) Secondary structure of MTR1 with catalytic core domain highlighted (purple circles). (C) The crystal structure of MTR1 (PDB: 7Q7X) and a close-up view of the catalytic core region with target adenosine (red), m6G base (cyan), nucleotides trapping the m6G base (green) and nucleotides forming three planar layers (yellow). (D,E) Nucleotide analysis of MTR1 reaction products digested to nucleosides. Nucleosides in negative control reactions without m6G (D) and in MTR1 samples after incubation with m6G (E) were analyzed with HPLC. Unmodified As and m1A were eluted at ∼32 min and ∼12 min, respectively. (F,G) Profiling experiments to assess the impact of pH (F) and Mg2+ concentration (G) on 1-methyladenosine formation at position 11 in MTR1 were conducted for two biological replicates (n = 2). The plots were fitted to a sigmoid curve.
In previous studies, the MTR1 ribozyme has been characterized by gel- and chromatography-based methods which are time-consuming and low-throughput. Thus, while broad application of the methyltransferase ribozyme has been expected, a high-throughput method for screening mutants with altered ribozyme activity has not been established yet. In this research report, we describe a high-throughput assay to determine the effect of single nucleotide substitutions in MTR1 on methyltransferase activity.
The sequence of MTR1 was retrieved from the literature (Scheitl et al., 2020). This MTR1 ribozyme is a cis-acting ribozyme that catalyzes the m1A formation within its ribozyme sequence. To prepare the ribozyme, the sequence of MTR1 was incorporated in a pipeline to prepare transcripts by one-pot in vitro transcription as described previously (Matsuda et al., 2024). In brief, DNA templates were synthesized from two DNA oligonucleotides (Thermo Fisher Scientific; Supplementary Table S1) by DNA polymerase extension in a 100 µL reaction containing 1x Dream-Taq buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 1 µM of each DNA oligonucleotide, 0.2 mM dNTPs (Toyobo), and 5 units Dream-Taq DNA polymerase (Thermo Fisher Scientific); the reaction conditions were: 94°C for 30 s; 25 cycles of 94°C for 30 s, 65°C for 30 s, 72°C for 30 s; 94°C for 5 min; 10°C hold. For in vitro transcription, the DNA polymerase reaction was mixed with 100 µL 2 X transcription solution containing 80 mM HEPES-KOH (pH 7.6), 10 mM DTT, 40 mM MgCl2, 2 mM Spermidine, 100 μg/mL Bovine Serum Albumin, 5 mM NTPs, and 2 µg T7 RNA polymerase (prepared in-house) and incubated at 37°C for 4 h. The MTR1 transcripts were separated by 10% denaturing PAGE (7 M urea) and purified by gel extraction.
For the MTR1 reaction, a TAM buffer system (100 mM Tris, 50 mM Acetate, and 50 mM MES) was used (Messina and Bevilacqua, 2018). For experiments shown in Figures 1D, E, the ribozyme reaction was performed in a 25 µL reaction mixture containing TAM buffer (pH 6.5), 40 mM MgCl2, 100 µM m6G base, 120 mM KCl, and 8 µM MTR1. The reaction mixture, without m6G and MgCl2, was heated at 90°C for 2 min to denature the RNA which was then allowed to refold by gradually cooling to room temperature for 10 min. The reaction was started by adding m6G and MgCl2 and after incubation at 37°C for 3 h stopped by adding 5 µL 500 mM EDTA. MTR1 RNA was recovered by ethanol precipitation and digested to nucleosides by Nuclease P1 and RNase A at 37°C for 2 h, followed by bacterial alkaline phosphatase (BAPC75) treatment at 37°C overnight. The nucleosides were analyzed by HPLC on an Elite LaChrom (Hitachi) system as described previously (Tomikawa et al., 2010; Takuma et al., 2015; Yamagami et al., 2016), using the included EZChrom Elite Version 3.1.8 aJ software to calculate peak areas of m1A and uridine. The m1A signal was normalized to the peak area of uridine.
For Figure 1F, reaction conditions were as above whereby the pH of the reactions was stepwise changed from pH 5 to pH 8.5, while for Figure 1G the final starting concentration of MgCl2 varied between the reactions from 2.5, 5, 10, and 20–40 mM. Negative control reactions were started by only adding MgCl2, omitting the reagent m6G.
For the high-throughput analysis of MTR1, we prepared an oPools (Integrated DNA Technologies) DNA oligonucleotide mixture of 141 distinct MTR1 variants that have a single point nucleotide substitution in the core domain (Supplementary Material S1) as described previously (Yamagami and Hori, 2023b). The MTR1 reaction was performed in a 50 µL mixture containing TAM buffer (pH 6.5), 5 mM MgCl2, 100 µM m6G, 120 mM KCl, and 8.5 µM MTR1 mixture at 37°C for 3 h. The RNA mixture was purified by phenol extraction and recovered by ethanol precipitation. As a negative control experiment, the reaction without m6G was performed. The RNA was dephosphorylated by treatment with rSAP (New England Biolabs) and libraries for next generation sequencing were prepared by reverse transcription with TGIRT (InGex) at 42°C for 16 h, circligation, and indexing PCR as described previously (Yamagami and Hori, 2023b). Single-end sequencing of the DNA library was done on a NextSeq 550 (Illumina) using 150 cycles, mid-output flow cells, and the standard Illumina sequencing primer.
Mutational profiling at A11 in each MTR1 variant was conducted as described previously (Yamagami and Hori, 2023a; Yamagami and Hori, 2023b). In brief, the 3′ adapter sequence was removed from sequence reads using Cutadapt (Martin, 2011) with the following command:
cutadapt -a CTGTAGGCACCATCAAT--nextseq-trim = 30 -j 0 -o output.fastq.gz input.fastq.gz.
For the profiling experiments of m1A at position 11, MTR1 samples that could be methylated and those that would not, by omission of m6G, were used. The mutation rate at A11 in each MTR1 variant was calculated as follows. Apart from wild-type reads, indicative for loss of modification at A11, mis-incorporation at A11 would generate A11T, A11G, and A11C in the DNA library, so that 141 × 4 = 564 different sequences were used as a reference. The number of reads matching each reference sequence was counted using SeqKit (Shen et al., 2016). The mutation rate at A11 (Mrate) was defined as
where ReadMutant is the number of reads for sequences with a mutation at position 11 in a MTR1 variant (sum of the read numbers for sequences with A11G, A11C, and A11U for that variant of MTR1) and ReadTotal is the total read number of that MTR1 variant (sum of all reads counted for that variant, covering A11, A11G, A11C, and A11U). Mrate (methylated sample) and Mrate (non-methylated sample) were calculated independently for each MTR1 variant. Then, the final Mrate was calculated by subtraction of Mrate (non-methylated sample) from Mrate (self-methylated sample). The mutational profiling data is provided in Supplementary Material S2.
To analyze the MTR1 activity, we first conducted self-methylation assays under various pH and MgCl2 conditions where we determined m1A formation in the ribozyme by classical nucleoside analysis using HPLC. By comparison to negative controls lacking the reagent (Figure 1D), the extent of m1A formation that depended on m6G inclusion (Figure 1E) could be established. The pH profiling experiment demonstrated that MTR1 catalysis is optimal under slightly acidic conditions (pH <7) (Figure 1F), consistent with the literature (Scheitl et al., 2022). At pH 6.5 ribozyme catalysis can be detected in the presence of 2.5 mM Mg2+ although this activity was about 10-fold less compared to conditions of >10 mM Mg2+ (Figure 1G). Since the concentration of free Mg2+ ions are roughly 0.5–3 mM in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells (Yamagami et al., 2018), the MTR1 ribozyme has the potential to methylate itself in living cells. Indeed, Scheitl and co-workers showed that the MTR1 ribozyme expressed in E. coli cells is catalytically active (Scheitl et al., 2020). Overall, MTR1 catalysis is robust under physiological conditions.
To characterize nucleotides important for ribozyme function we utilized mutational profiling (Figure 2A), a high-throughput technique to analyze the efficiency of modification on a particular RNA residue in response to a nucleotide change elsewhere in the molecule (Yamagami et al., 2022). This approach is based on the finding that m1A modification prevents formation of hydrogen bonds with deoxythymidine during reverse transcription, leading to termination and misincorporation of nucleotides other than dT in the cDNA (Siegfried et al., 2014; Busan and Weeks, 2018). The technique further relies on a pool of synthetic mutants. In this case, we generated MTR1 ribozyme variants in which a single point mutation was introduced in the catalytic domain. The catalytic domain in the MTR1 ribozyme is composed of 47 nucleotides comprising a stem (S3) and three loops (L2, L3, and L4) (Figure 1B), requiring 141 MTR1 variants as three different point mutations can be introduced at each nucleotide position. A mixture of these ribozyme variants was incubated with m6G at 37°C for 3 h (Figure 2A, Step 1) after which an adapter for initiating reverse transcription was attached to the 3′-end of the ribozyme molecules (Figure 2A, Step 2). After reverse transcription (Figure 2A, Step 3), a DNA library was prepared and subjected to next generation sequencing (NGS) (Figure 2A, Step 4). In the data analysis of mutations at the methylation site A11 (Figure 2A, Step 5), the high sequence similarity of MTR 1 variants made it possible to directly count the reads for a specified sequence with SeqKit (Shen et al., 2016), rather than using alignment software. About 70% of input reads were matched to the pool of reference sequences. Note that the remainder were excluded because the reads possess insertions/deletions which were not able to count by our method. For example, in the m1A profiling analysis of replicate 1, we used 14,366,644 total reads obtained from the reaction in the absence of m6G (negative reads), and 13,533,892 total reads obtained from the reaction in the presence of m6G (positive reads). Of these sequence reads, 9,279,856 negative reads (∼65%) and 9,068,605 positive reads (∼67%) were uniquely matched to the reference sequences (See Supplementary Material S2). As a result, we could detect mutation rates at A11 for all MTR variants tested (Figure 2B). We calculated relative mutation rates at A11 where the mutation frequency of the original MTR1 sequence (WT) was set at 1.0 (Figure 2B). In our previous study, we showed that mutation rates at the position of a m1A modification have a good correlation with m1A formation rates (Yamagami and Hori, 2023a). Thus, high mutation rates for MTR1 mutants indicate that these have a catalytic activity comparable to wild type, whereas low mutation rates for MTR1 variants correspond to low catalytic activity. For example, relative mutation rates at A11 were slightly higher than 1.0 in the case of loop L3 variants U60C and C62G, indicating that these substitutions do not affect catalytic activity (Figure 2B). In contrast, among the L2 and L4 variations, nearly all changes except for those at C51 and U76 caused loss of enzymatic function (Figure 2B). Also, point mutations in the terminal sequences of stem S3 significantly reduced the activity (Figure 2B). We saw that catalytic activity of the C66G variant is weak, although the altered nucleotide is located near the middle of stem S3 (Figure 2B). This mutation creates a sequence of five successive G residues which might fold into a stable structure specific for G-rich sequences such as a G-quadruplex structure (Lyons et al., 2017), or, alternatively, might induce an inactive organization of the catalytic domain by base pairing to the stretch of six C residues upstream. The results are summarized by mapping the nucleotides critical for catalytic activity on the secondary structure of MTR1 (Figure 3A) as well as the tertiary structure (Figure 3B). A single point variation in the nucleotides involved in m6G binding or in either of the three layers of planar base interactions diminished the catalytic activity, demonstrating that our m1A profiling data is consistent with the MTR1 structure (Figure 3B).
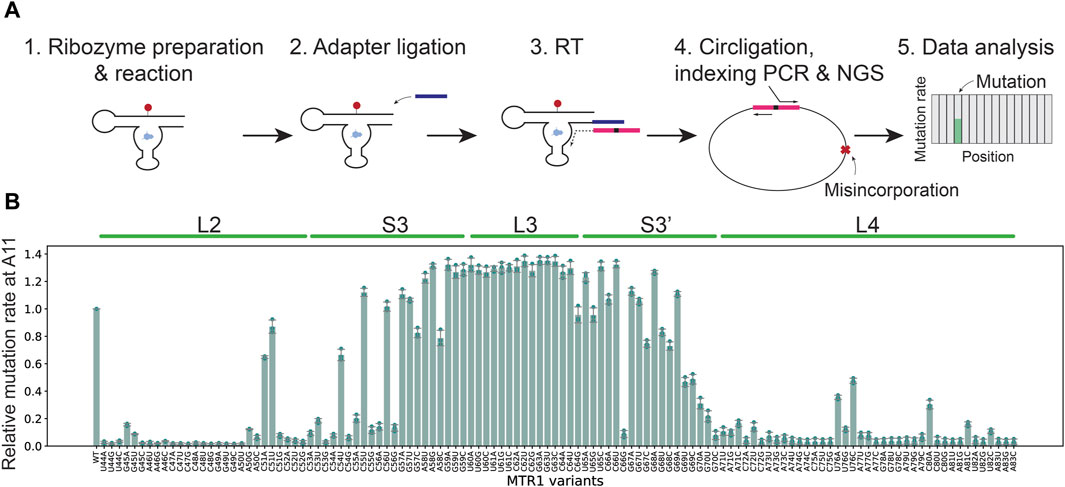
Figure 2. Mutational profiling detects ribozyme activity for 141 distinct MTR1 variants in a single experiment. (A) Schematic illustration of DNA library preparation and mutational profiling analysis (see text for details). The site representing A11 and misincorporated nucleotides is indicated by a red cross in step 4. (B) Relative mutation rates at A11 in all MTR1 sequences tested in this study for three biological replicates (n = 3). Error bars show standard deviations. Mutants supporting low relative mutation rates affect formation of m1A at A11.
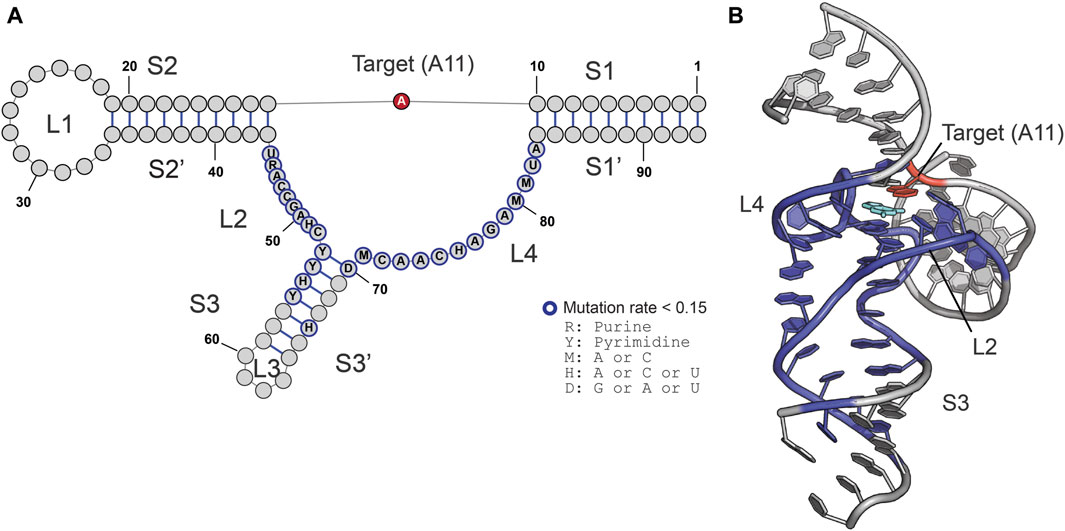
Figure 3. MTR1 is sensitive to nucleotide variations in the catalytic core domain. (A,B) The critical residues that scored low relative mutation rates at A11 (less than 0.15) are colored in blue in the secondary (A) and the tertiary (B) structures of MTR1. The target adenosine (methylation site, A11) and m6G are highlighted in red and cyan, respectively.
To validate our high-throughput profiling results, we performed HPLC analysis using five MTR1 variants: C51U, C62U, C66G, C76C, and C80A (Figure 4). C51U is the only loop L2 variant that does not affect the methyltransferase activity according to our m1A profiling data (Figure 2B), while variants C62U, U76C, C80A, and C66G have high, modest, weak, and no MTR1 activity, respectively (Figure 2B). The amount of m1A obtained by nucleoside analysis for each variant was normalized to that of the wild type and plotted against the relative m1A amount determined by the MaP experiments (Figure 4). Linear regression analysis demonstrated a modest correlation between the relative m1A amounts of nucleoside analysis and MaP with an R-Squared value of 0.66 (Figure 4). Thus, our high-throughput technique has a detection sensitivity similar to that of HPLC.
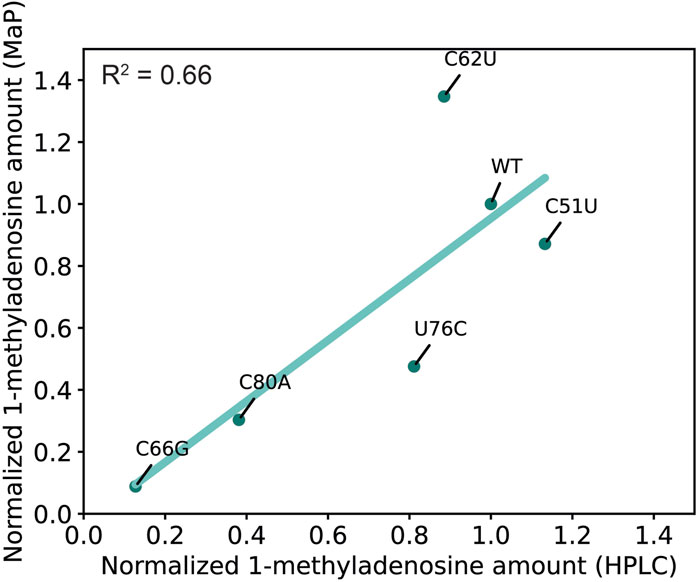
Figure 4. Similar detection sensitivities of mutational profiling and nucleoside analysis. The ribozyme activity detected with HPLC (X axis) and MaP (Y axis) was plotted. The average data (two biological replicates for HPLC and three biological replicates for mutational profiling) were fit to a line (green) by linear regression.
We have characterized the effect of single point mutations on the methylation activity of the MTR1 methyltransferase ribozyme. In classical methyltransferase (ribozyme) assays, radiolabeled methyl group donors such as 14C- and 3H-labeled SAM or internally labeled RNA, have been used (Jiang et al., 2021). Since the methyl group donor utilized by MTR1, the m6G nucleobase, is not commercially available in a radiolabeled form, the ribozyme activity has been monitored with LC-MS and by methods based on primer extension (Scheitl et al., 2020). These methods limit the number of samples that can be handled, which would be a major barrier for systematic analysis of modifying enzymes and technological applications. In this study, we investigated individual nucleotides for their role in sustaining the function of ribozyme MTR1 by mutational profiling. We generated 141 distinct MTR1 variants and determined the methyltransferase activity of each variant. Our high-throughput method provided insights for all variants (Figures 2B, 3) and demonstrated that most nucleotide residues in loops L2 and L4 were critical for catalytic activity; substitution of C51 or of U76 was tolerated as long as these positions were not occupied by a G-residue. As described in the Introduction, the m6G base is captured by C47, U82, and target A11 while enclosed by three planar layers consisting of ten nucleotides in total (Figure 1C). In addition to these nucleotides, our data showed that 12 other nucleotides in loops L2 and L4 are important for MTR1 activity (Figure 3). These observations indicate that the MTR1 catalytic core forms a complex nucleotide-interaction network that is very sensitive to variations in those loops.
The chosen platform for next generation sequencing yielded 13,533,892 reads in total (for the reaction in the presence of m6G, replicate 1) after adapter removal and quality trimming. This mid-scale experiment provided on average about 75 k reads for each variant (See Supplementary Material S2). Given that about 5,000 reads are required for m1A profiling, roughly 2,100 distinct MTR1 variants can in theory be simultaneously analyzed in a single mid-scale experiment, which is impossible to do by classical assay methods. In this experiment, we used TGIRT, a highly processive reverse transcriptase that tends to introduce misincorporations in cDNA rather than to terminate when encountering a modified nucleotide. We note, however, that other processive enzymes such as the Marathon reverse transcriptase (Guo et al., 2020) and the Induro reverse transcriptase (New England Biolabs) would be suitable for the experiment.
Besides the m1A modifying ribozyme MTR1, ribozymes catalyzing the formation of 3-methylcytidine (m3C), or 7-methylguanosine (m7G) have been reported, as well as a ribozyme utilizing a synthetic S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) analogue as the alkylating donor (Flemmich et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2021; Okuda et al., 2023). Reverse transcriptases are sensitive to nucleotides carrying such modifications provided that suitable reaction conditions are chosen, like using MnCl2 for the detection of m7G (Guo et al., 2020). Therefore, our profiling method is expected to be applicable to mutational analyses of these ribozymes without any protocol changes.
The NGS reads obtained in this research have been made available at the DNA Data Bank of Japan (DDBJ) Sequence Read Archive (SRA) under accession number DRR542363-DRR542368. All data obtained in this research are also available from the corresponding authors upon request.
RY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing–original draft, Writing–review and editing. HK: Investigation, Writing–review and editing. EK: Investigation, Writing–review and editing. HH: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing–review and editing.
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The research was supported by ACT-X from the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JPMJAX211I) and research grant No. 2124 from JGC- Scholarship Foundation.
We thank Dr. Naohito Tokunaga at the Advanced Research Support Center (ADRES at Ehime University) for assistance with the next-generation sequencing experiments.
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frnar.2024.1415530/full#supplementary-material
Boccaletto, P., Stefaniak, F., Ray, A., Cappannini, A., Mukherjee, S., Purta, E., et al. (2022). MODOMICS: a database of RNA modification pathways. 2021 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 50, D231–D235. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab1083
Busan, S., and Weeks, K. M. (2018). Accurate detection of chemical modifications in RNA by mutational profiling (MaP) with ShapeMapper 2. RNA 24, 143–148. doi:10.1261/rna.061945.117
Deng, J., Wilson, T. J., Wang, J., Peng, X., Li, M., Lin, X., et al. (2022). Structure and mechanism of a methyltransferase ribozyme. Nat. Chem. Biol. 18, 556–564. doi:10.1038/s41589-022-00982-z
Flemmich, L., Heel, S., Moreno, S., Breuker, K., and Micura, R. (2021). A natural riboswitch scaffold with self-methylation activity. Nat. Commun. 12, 3877. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-24193-7
Guo, L. T., Adams, R. L., Wan, H., Huston, N. C., Potapova, O., Olson, S., et al. (2020). Sequencing and structure probing of long RNAs using MarathonRT: a next-generation reverse transcriptase. J. Mol. Biol. 432, 3338–3352. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2020.03.022
Hori, H. (2014). Methylated nucleosides in tRNA and tRNA methyltransferases. Front. Genet. 5, 144. doi:10.3389/fgene.2014.00144
Hori, H., Kawamura, T., Awai, T., Ochi, A., Yamagami, R., Tomikawa, C., et al. (2018). Transfer RNA modification enzymes from thermophiles and their modified nucleosides in tRNA. Microorganisms 6, 110–152. doi:10.3390/microorganisms6040110
Jiang, H., Gao, Y., Zhang, L., Chen, D., Gan, J., and Murchie, A. I. H. (2021). The identification and characterization of a selected SAM-dependent methyltransferase ribozyme that is present in natural sequences. Nat. Catal. 4, 872–881. doi:10.1038/s41929-021-00685-z
Li, X., Xiong, X., Zhang, M., Wang, K., Chen, Y., Zhou, J., et al. (2017). Base-resolution mapping reveals distinct m(1)A methylome in nuclear- and mitochondrial-encoded transcripts. Mol. Cell 68, 993–1005 e9. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2017.10.019
Lyons, S. M., Gudanis, D., Coyne, S. M., Gdaniec, Z., and Ivanov, P. (2017). Identification of functional tetramolecular RNA G-quadruplexes derived from transfer RNAs. Nat. Commun. 8, 1127. doi:10.1038/s41467-017-01278-w
Martin, M. (2011). Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 17, 10. doi:10.14806/ej.17.1.200
Matsuda, T., Hori, H., and Yamagami, R. (2024). Rational design of oligonucleotides for enhanced in vitro transcription of small RNA. RNA. doi:10.1261/rna.079923.123
Messina, K. J., and Bevilacqua, P. C. (2018). Cellular small molecules contribute to twister ribozyme catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 10578–10582. doi:10.1021/jacs.8b06065
Okuda, T., Lenz, A. K., Seitz, F., Vogel, J., and Hobartner, C. (2023). A SAM analogue-utilizing ribozyme for site-specific RNA alkylation in living cells. Nat. Chem. 15, 1523–1531. doi:10.1038/s41557-023-01320-z
Scheitl, C. P. M., Ghaem Maghami, M., Lenz, A.-K., and Höbartner, C. (2020). Site-specific RNA methylation by a methyltransferase ribozyme. Nature 587, 663–667. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2854-z
Scheitl, C. P. M., Mieczkowski, M., Schindelin, H., and Hobartner, C. (2022). Structure and mechanism of the methyltransferase ribozyme MTR1. Nat. Chem. Biol. 18, 547–555. doi:10.1038/s41589-022-00976-x
Scheitl, C. P. M., Okuda, T., Adelmann, J., and Hobartner, C. (2023). Ribozyme-catalyzed late-stage functionalization and fluorogenic labeling of RNA. Angew. Chem. 62, e202305463. doi:10.1002/anie.202305463
Shen, W., Le, S., Li, Y., and Hu, F. (2016). SeqKit: a cross-platform and ultrafast toolkit for FASTA/Q file manipulation. PLoS One 11, e0163962. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0163962
Siegfried, N. A., Busan, S., Rice, G. M., Nelson, J. A. E., and Weeks, K. M. (2014). RNA motif discovery by SHAPE and mutational profiling (SHAPE-MaP). Nat. Methods 11, 959–965. doi:10.1038/nmeth.3029
Takuma, H., Ushio, N., Minoji, M., Kazayama, A., Shigi, N., Hirata, A., et al. (2015). Substrate tRNA recognition mechanism of eubacterial tRNA (m1A58) methyltransferase (TrmI). J. Biol. Chem. 290, 5912–5925. doi:10.1074/jbc.m114.606038
Tomikawa, C., Yokogawa, T., Kanai, T., and Hori, H. (2010). N7-Methylguanine at position 46 (m7G46) in tRNA from Thermus thermophilus is required for cell viability at high temperatures through a tRNA modification network. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, 942–957. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp1059
Yamagami, R., Bingaman, J. L., Frankel, E. A., and Bevilacqua, P. C. (2018). Cellular conditions of weakly chelated magnesium ions strongly promote RNA stability and catalysis. Nat. Commun. 9, 2149. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-04415-1
Yamagami, R., and Hori, H. (2023a). Application of mutational profiling: new functional analyses reveal the tRNA recognition mechanism of tRNA m(1)A22 methyltransferase. J. Biol. Chem. 299, 102759. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102759
Yamagami, R., and Hori, H. (2023b). Functional analysis of tRNA modification enzymes using mutational profiling. Methods Enzym. 692, 69–101. doi:10.1016/bs.mie.2023.02.021
Yamagami, R., Sieg, J. P., Assmann, S. M., and Bevilacqua, P. C. (2022). Genome-wide analysis of the in vivo tRNA structurome reveals RNA structural and modification dynamics under heat stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 119, e2201237119. doi:10.1073/pnas.2201237119
Keywords: ribozyme, RNA methylation, mutational profiling, RNA, high-throughput analysis
Citation: Yamagami R, Kubota H, Kohno E and Hori H (2024) High-throughput mutational analysis of a methyltransferase ribozyme. Front. RNA Res. 2:1415530. doi: 10.3389/frnar.2024.1415530
Received: 10 April 2024; Accepted: 13 May 2024;
Published: 03 June 2024.
Edited by:
Marc Graille, École Polytechnique, FranceReviewed by:
Seán O’Leary, University of California, Riverside, United StatesCopyright © 2024 Yamagami, Kubota, Kohno and Hori. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ryota Yamagami, eWFtYWdhbWkucnlvdGEuYm5AZWhpbWUtdS5hYy5qcA==; Hiroyuki Hori, aG9yaS5oaXJveXVraS5teUBlaGltZS11LmFjLmpw
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Research integrity at Frontiers

Learn more about the work of our research integrity team to safeguard the quality of each article we publish.