- 1The Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, China
- 2School of Public Administration, Central South University, Changsha, China
- 3Key Laboratory of Medical Information Research (Central South University), College of Hunan Province, Changsha, China
- 4The Third Xiangya Hospital of Central South University, Changsha, China
- 5Clinical Research Center For Cardiovascular Intelligent Healthcare in Hunan Province, Changsha, China
Background: An evaluation system for comprehensively measuring medical insurance fund operational performance under China’s Diagnosis Related Groups (DRG) payment reform holds critical theoretical and practical significance, especially for enhancing the efficiency of medical insurance fund utilization and the quality of healthcare services. However, few studies undertake performance evaluations of medical insurance funds under DRG payments, especially those incorporating the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP)-Entropy Weight Method (EWM)- Fuzzy Comprehensive Evaluation (FCE) method model.
Methods: This study utilizes operational data from medical insurance funds across eight cities in S Province, China, from 2020 to 2022. It develops an innovative performance evaluation system for medical insurance funds utilizing the AHP-EWM-FCE evaluation method. Finally, it explores the key influencing factors by applying the Tobit regression model.
Results: As the reform of DRG payment methods has advanced, the operational performance scores related to the management, fundraising, utilization, and satisfaction of DRG medical insurance funds have consistently improved. Notably, the comprehensive indexes of QD and JN cities exhibit significant comparative advantages, resulting in higher performance evaluation scores for their medical insurance funds. Additionally, the performance scores assessed by the proposed evaluation system align closely with actual operational outcomes. Regression analysis further indicates that medical service capability is the key determinant influencing the operational performance of medical insurance funds.
Conclusion: This study develops a novel evaluation system for measuring medical insurance funds’ operational performance. The insights can help proactively foster the high-quality development of these funds, and modernization of the medical insurance governance system and governance capabilities; stimulate the fund’s productivity; and enhance the health and wellbeing of people.
Background
China has successfully established a universal basic medical insurance system. This system has achieved an impressive coverage rate of over 95% overall, which even approaches 100% in some cities (1). The urban employee medical insurance amount was raised to 5,737 yuan in 2022, while the urban–rural resident medical insurance increased to 1,029 yuan. The corresponding policy reimbursement rates stand at 84.2 and 68.3%, respectively (2). However, the current medical insurance funding system faces issues such as a large interest group in the field of medical services, information asymmetry, high technical barriers, and frequent policy risks. Consequently, a medical insurance service system that aligns with China’s unique characteristics is needed (3). Indeed, in terms of medical insurance payment model reform, China’s National Medical Security Administration has pioneered the implementation of the globally recognized scientific payment mode: DRG payment. Since 2019, this DRG payment model has been piloted in 30 cities across the country (4).
Capitalizing on the “law of large numbers” methodology, the DRG payment model offers a vital mechanism and management tool for macro-controls in modern medical insurance payment mode reforms. Here, an evaluation system for comprehensively measuring medical insurance fund operation performance, considering DRG payment, can be extremely useful in driving healthcare institutions to shift from “extensive” management to more “refined” approaches. For instance, such a performance evaluation system can promote the rational allocation of medical resources, reduce resource waste, and improve the quality and efficiency of medical insurance funds (5). In November 2021, the National Medical Security Administration released the Three-Year Action Plan for DRG/DIP Payment Mode Reform, which clearly stated that by 2025, DRG/Big Data Diagnosis-Intervention Packet (DIP) should be comprehensively implemented in four areas: overall planning, health care institutions, disease grouping, and medical insurance fund (6). This initiative aims to construct a robust health security network for the public, thereby serving as a powerful “stabilizer” for the steady progress of socialism with Chinese characteristics (7).
Still, a mature evaluation system for examining medical insurance fund operation performance is lacking both domestically and internationally. Currently, such an evaluation system considering the DRG payment mode reform has several shortcomings, including singularity, extensiveness, limitations in the dimensions and indicators considered, and the lack of comprehensive consideration for the medical insurance fund operations (8). Furthermore, due to the insufficient accumulation of historical data from the DRG payment model pilot cities in the early stages of implementation, it was unable to accurately analyze from the perspectives of institutional embedding, regulatory behavior, medical behavior, and social interaction (8). Consequently, constructing a rigorous and robust evaluation system of medical insurance fund operation performance under the DRG payment mode reform is a critical task.
The literature shows that the research focuses of foreign medical insurance funds are different. For example, Avedis Donabedian, the father of American medical management, divided medical insurance evaluation indicators into structure, process, and result evaluations, focusing on the efficiency and fairness of medical insurance fund allocation (9). British and Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) medical insurance emphasizes the fairness and accessibility of medical insurance but neglects efficiency evaluation (10–12). One study has used the content validity ratio to screen the identified factors to identify and rank critical factors affecting hospital performance using the best-worst method in Iran (13). In China, research on the performance evaluation system of medical insurance funds is still in the exploratory stage. An analysis of the medical insurance fund operation in Jiaxing City in 2019 used an evaluation system consisting of four dimensions and 10 indicators (14). Yu and Zhi empirically examined urban employee and rural resident basic insurance schemes in Yantai City, providing an initial overview of the status of the city’s medical insurance fund operations (15). Meanwhile, research has also evaluated the performance system of public hospitals based on single balanced scorecard theory and the AHP, thereby establishing a model for the performance system of public hospitals (16, 17). However, the above studies have certain limitations in terms of the selection of horizontal indicators, vertical time range, methodology, and empirical research. Thus, they have failed to perform a comprehensive and dynamic evaluation of the actual operation of the medical insurance fund. Therefore, a rigorous performance evaluation system that encompasses comprehensive indicators and can dynamically evaluate the medical insurance fund operation is lacking.
Naturally, one may ask: How should we construct a comprehensive and dynamic performance evaluation system for medical insurance fund operation under the DRG payment method reform? One particular area can be using more rigorous and scientific research methods, which can enhance the focus ability and objectively evaluate the dynamic running differences of medical insurance funds. Among them, AHP can carry out step-by-step analysis and comprehensive evaluation of complex decision-making problems within a structured framework, thereby making more scientific and reasonable choices (18). AHP yields subjective weights, while the EWM yields objective weights. Then, the combination of EWM and AHP can be used to obtain and assign effective and true indicator weights (19). In addition, FCE can better handle the interaction between various complex factors, especially the performance evaluation of medical insurance funds, which has uncertainty, complexity, and dynamics (20–22). However, to the best of our knowledge, no studies have examined the comprehensive use of the AHP-EWM-FCE method for the performance evaluation of the medical insurance fund operation under the backdrop of DRG payments. Addressing this gap, this research uses operational data on medical insurance funds in eight cities in Province S of China over 3 years to construct a comprehensive and dynamic performance evaluation system for the medical insurance fund operation under the DRG payment method reform.
In summary, this study applies the AHP-EWM-FCE method to evaluate the operational performance of medical insurance funds within the context of the DRG payment system. Next, utilizing 3 years of operational data from medical insurance funds across eight cities in S Province, China, this study employs Tobit regression analysis to identify the key factors influencing the performance evaluation. The aim is to develop a comprehensive and dynamic performance evaluation system for medical insurance funds within the framework of the DRG payment reform.
Methods
Data sources and research methods
The literature and data for this study are sourced from both domestic and international databases, including the Web of Science, PubMed, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wanfang Data Knowledge Service Platform, and VIP Chinese Journal Service Database. The statistical data for the indicator system mainly come from the National Tertiary Public Hospital Performance Appraisal Operation Manual, National Healthcare Security Diagnostic Related Groups (CHS-DRG) Grouping Plan, National Medical insurance Diagnostic Related Groups (CHS-DRG) Grouping and Payment Technical Specifications, Statistical Yearbook of S Province, Health Statistics Yearbook of S Province, Statistical Yearbook of Population and Employment Statistics of S Province, Statistical Yearbook of Civil Affairs of S Province, Social Statistics Yearbook of S Province, performance assessment data from some hospitals in eight cities of S province, and information from official hospital websites. To ensure the richness and authenticity of the data, field visits and semi-structured interviews were carried out to gather first-hand interview materials.
Preliminary determination of medical insurance fund indicators using the Delphi method
Expert selection
This study employs the Delphi expert consultation method. First, expert inquiry forms are disseminated via Questionnaire Star to recruit experts. Then, consultations or interviews with selected theorists and field experts affiliated with the domain of medical insurance fund operation management (such as medical insurance bureaus, health commissions, hospital medical insurance offices, and clinical medical staff) are conducted. Aggregating diverse viewpoints and professional knowledge from this expert sample ensures the professionalism and practicality of constructing evaluation models, and elicits more scientifically valid evaluation indicators and suggestions.
Construction of the performance evaluation system
Establishment of subjective weights for performance evaluation indicators by AHP
This study utilizes AHP to delineate the subjective weights of the constructed performance evaluation indicators via four main steps: building a hierarchical model, constructing a judgment matrix, calculating indicator weights, and testing consistency. Meanwhile, the concentration of expert opinions is measured by the mean and full score rate, while the coordination of expert opinions is measured via the dispersion coefficient (23, 24). Finally, the resulting index system is subjected to reliability and validity tests.
Establishment of objective weights for performance evaluation indicators by EWM
Operating data on 28 medical insurance fund operation performance indicators across eight sampled cities are used to assess matrix entropy values, and the randomness and disorder of the indicators. Next, the entropy value is employed to determine the degree of dispersion among the indicators. The degree of variation in the indicators is ascertained based on their weights, thereby eliminating subjective interference. EWM is subsequently used to determine the objective weights of each evaluation factor. To avoid the impact of singularity on the results of FCE, the subjective and objective weights of AHP-EWM are reconstructed using the geometric mean method to obtain new combined weights (25).
FCE evaluation
Determining evaluation factors and membership evaluation criteria
The comprehensive evaluation results are divided into five levels, each corresponding to different judgment values. Simultaneously, to obtain more authoritative results, 10 experts are invited for scoring. The membership degree of evaluation factors to comment level is determined through expert scoring and percentage statistics. The fuzzy evaluation set is then calculated by combining the membership and matrix.
Fuzzy evaluation of medical insurance performance results
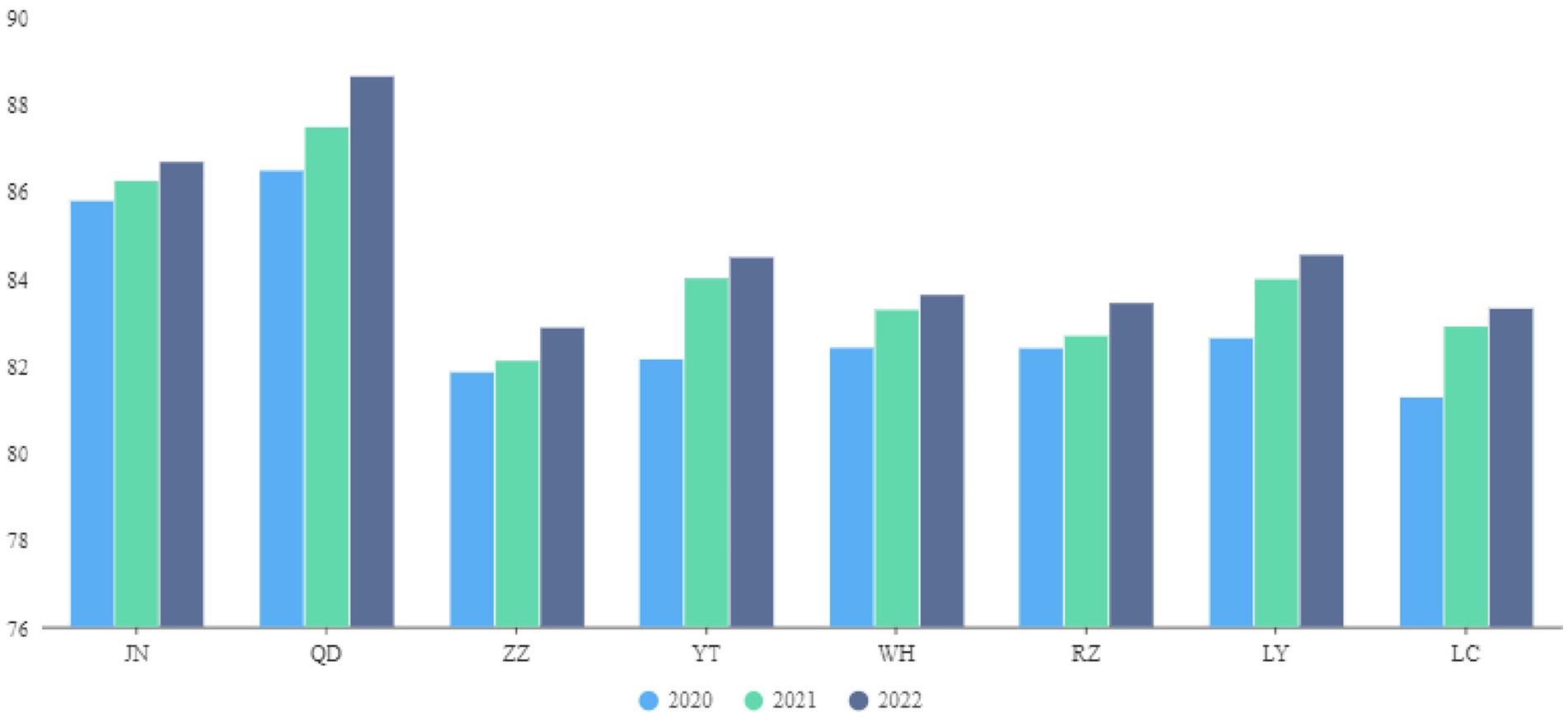
As noted above, the fuzzy evaluation result is the product of membership and matrix, C=B·VT, which produces the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of each criterion layer’s corresponding indicator (26). This outcome allows for horizontal and vertical comparisons of the performance of the medical insurance fund in eight cities in S Province from 2020 to 2022 (Figure 1). Horizontal comparison refers to assessing the performance of the medical insurance fund and vertical comparison involves examining the performance of the medical insurance fund during 2020–2022. Next, the following Tobit regression model is employed to analyze the key factors influencing the performance evaluation.
Here, the latent variable is expressed as Yi*.
The evaluation scores derived from the AHP-EWM-FCE method for the eight municipalities in S Province are used as the dependent variables, while eight secondary operational indicators serve as the independent variables. Stata 17.0 software has been used for the regression analysis.
Results
This study preliminarily constructs a comprehensive pool of 44 potential indicators through literature review and expert consultation. Then, through an in-depth analysis of correlations and importance of these indicators, those with low correlation and high redundancy are eliminated. Simultaneously, new indicators intuitively reflecting medical insurance fund performance evaluation are introduced. Ultimately, 33 core indicators have been carefully selected and integrated after expert inquiry. And the 33 core indicators were further verified through reliability and validity tests with their validity and operability. We subject this evaluation indicator system to the empirical case of the eight cities in S Province in China. Finally, the Tobit regression model is employed to analyze the key factors influencing the performance evaluation.
Determining performance evaluation indicators using the Delphi method
Basic information about experts
This study has engaged 28 experts from domestic universities, medical institutions, and medical insurance management departments. The experts are between 30 to 65 years old, with 90.00% holding a bachelor’s degree or above. In the two rounds of expert consultation, 28 and 22 questionnaires have been distributed, respectively, yielding effective recovery rates of 92.86 and 95.45%, respectively. The questionnaire recovery rate for both rounds is 94.00%, indicating that the experts have exhibited substantial enthusiasm in participating in the study.
Expert authority and opinion coordination degree
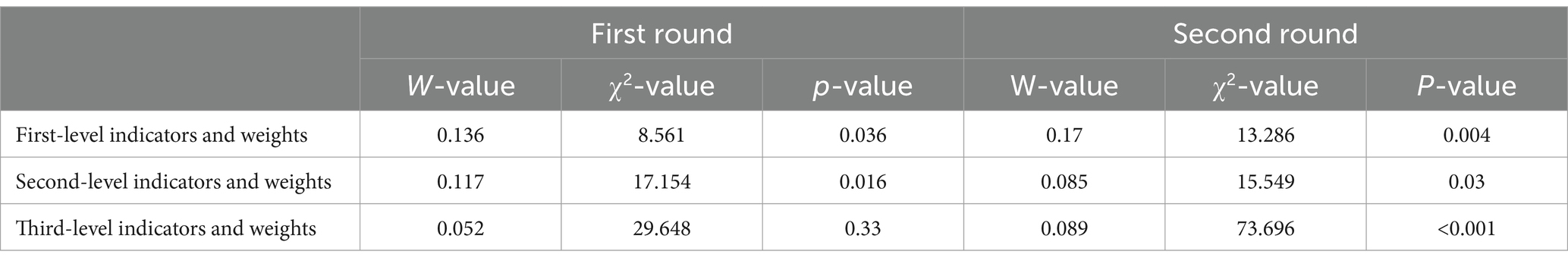
Table 1 shows that the authority coefficient of the experts is 0.865, indicating that this indicator aligns with the established standards. This supports the professionalism and authority of the evaluation process. The degree of expert coordination is depicted by Kendall’s W coordination coefficient. In the two rounds, the p-value (<0.001) for the third-level indicators showed reliable results.
After two rounds of expert consultation, the first-level indicators include medical insurance fund management, medical insurance fund raising, DRG operation and use of medical insurance fund, and satisfaction with medical institutions. Second-level indicators include medical insurance fund policy, platform construction, medical insurance fund raising, expenditure and balance, medical service capability, expense control, reimbursement, and satisfaction with medical institutions. Finally, 28 indicators exist in the third level, including the number of participants in basic medical insurance, financial subsidy for resident medical insurance, growth rate of medical insurance fund income, proportion of recovery of medical insurance funds, growth rate of total fund expenditure over the previous year, current balance rate of medical insurance fund, number of months supported by the medical insurance fund balance and so on. Further the DRG group number refers to a diseases classification system and the number of diseases based on clinical symptoms.
Construction of performance evaluation system
Determination of AHP weight
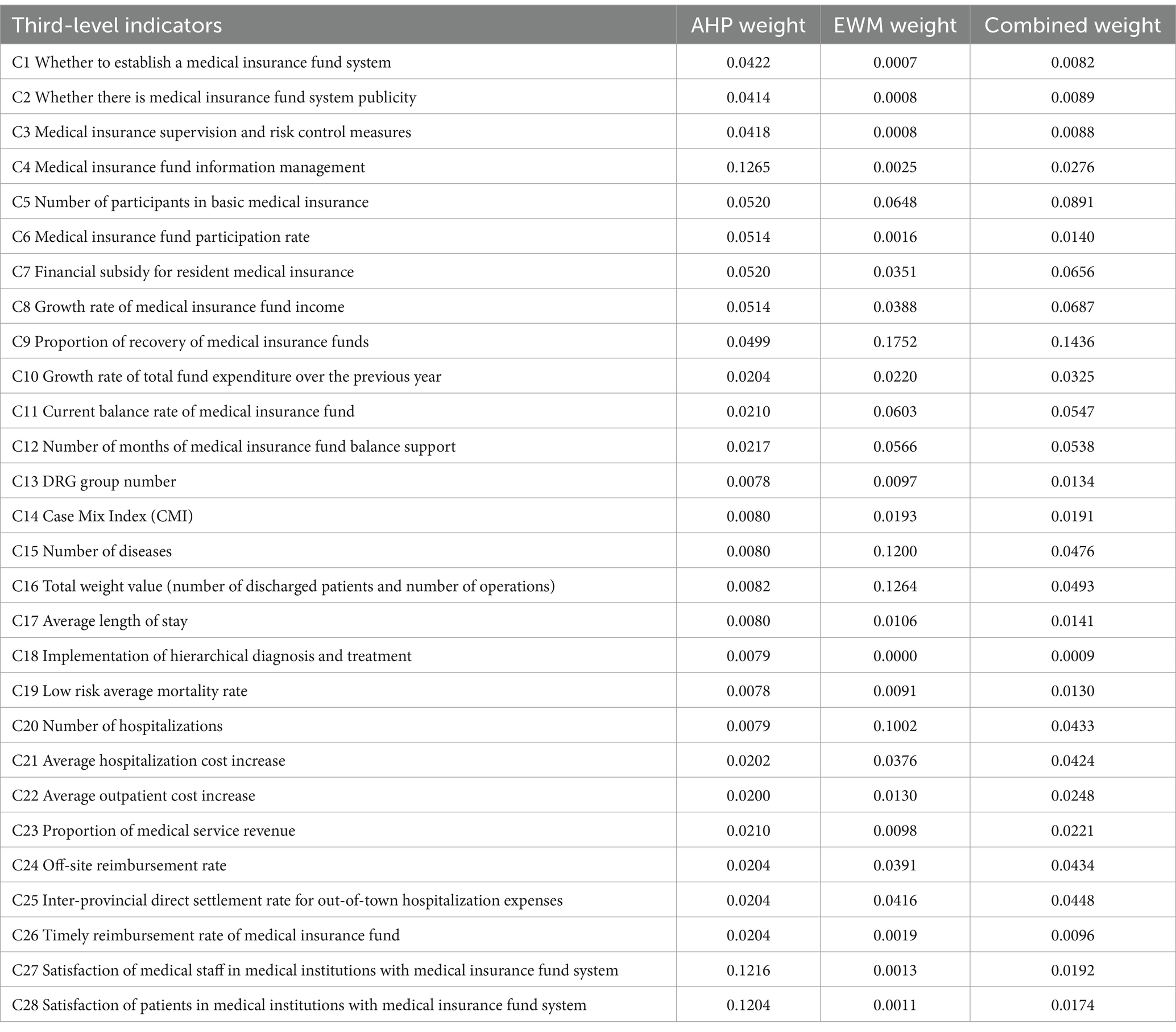
The composite weights are then calculated using AHP. The highest weight is for the medical insurance fund information management at 0.1265. Satisfaction of medical staff and patients in medical institutions with the medical insurance fund system have weights of 0.1216 and 0.1204, respectively. The weights for financial subsidy for resident medical insurance, number of participants in basic medical insurance, growth rate of medical insurance fund income, and medical insurance fund participation rate are 0.052, 0.052, 0.0514, and 0.0514, respectively. Next, the proportion of recovery of medical insurance funds, medical insurance supervision and risk control measures, and where there is any publicity and education work on the medical insurance fund system have weights of 0.0499, 0.0418, and 0.0414, respectively (Table 2).
Determination of EWM weight
Next, EWM is employed to construct the judgment matrix and calculate the information entropy of the comprehensive evaluation indicators to determine objective weights. The highest weight for the proportion of recovered medical insurance funds is 0.1752. The weights for total weight value (number of discharged patients and number of operations), number of diseases, and number of hospitalizations are 0.1264, 0.1200, and 0.1002, respectively. The weights for number of participants in basic medical insurance, current balance rate of medical insurance fund, number of months of medical insurance fund balance support, inter-provincial direct settlement rate for out-of-town hospitalization expenses, and off-site reimbursement rate are 0.0648, 0.0603, 0.0566, 0.0416, and 0.0391, respectively (Table 3).
Determination of AHP-EWM combined weights
The geometric average method is used to reconstruct the AHP subjective and EWM objective weights, highlighting the importance of weights and disparity after reconstruction to obtain the combined weights. The weight of proportion of recovery of medical insurance funds is the highest at 0.1436. Next, the weights for number of participants in basic medical insurance, growth rate of medical insurance fund income, financial subsidy for resident medical insurance, current balance rate of medical insurance fund, and number of months of medical insurance fund balance support are 0.0891, 0.0687, 0.0656, 0.0547, and 0.0538, respectively (Table 3).
Evaluation index system construction and empirical research
Next, this article selects some designated medical institutions in the eight DRG payment pilot cities of S Province as case studies for the empirical research. According to the AHP-EWM-FCE evaluation results, the performance score of the medical insurance fund operation exhibits an upward trend across the sampled cities. The scores for JN and QD are relatively high between 2020 and 2022 at 85.76, 86.21, and 86.66, respectively, for JN, and 86.46, 87.46, and 88.62, respectively, for QD (Figure 1).
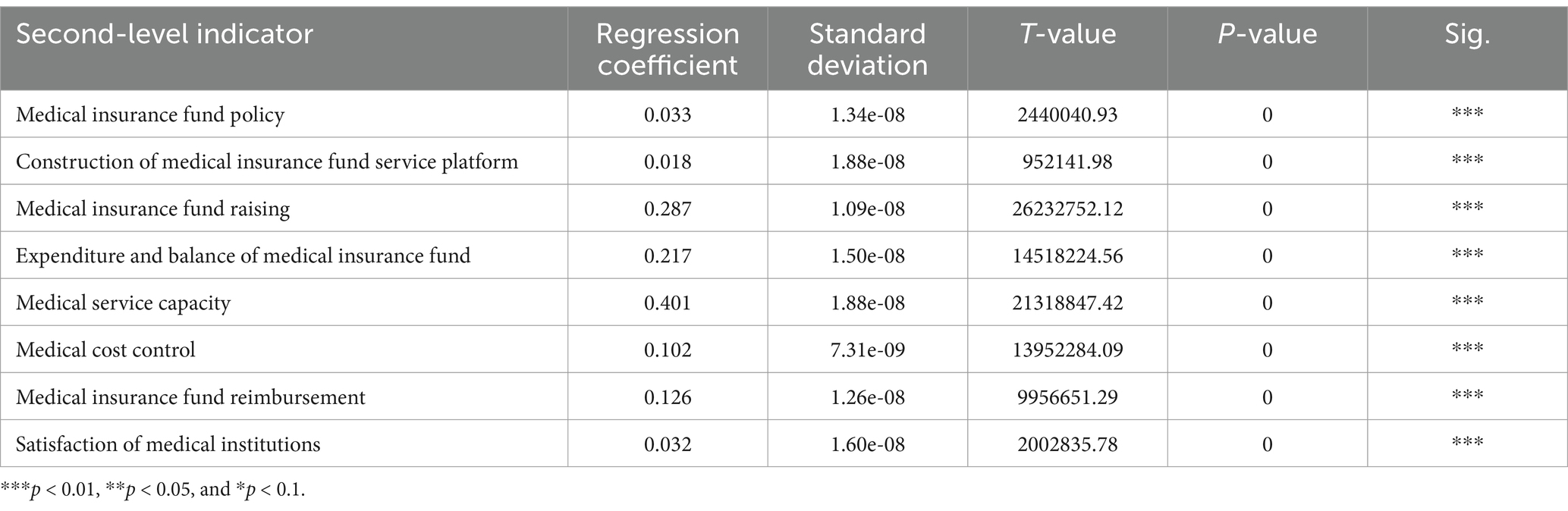
The Tobit regression analysis reveals that the two indices are significantly related to the medical insurance fund’s operational performance. Specifically, medical service capacity, medical insurance fund raising, and expenditure and balance of the medical insurance fund exhibit a significant positive coefficient with the operational performance of the medical insurance fund (Table 4).
Discussion
In May 2019, QD of S Province was selected as a pilot city among the initial batch of 30 cities by the National Healthcare Security Administration to implement DRG payment reforms. In September of the same year, the Provincial Healthcare Security Administration of S Province was among the first to initiate DRG payment method reforms in 10 pilot cities in stages. However, extant research on the performance evaluation of medical insurance fund operation in the backdrop of the DRG payment method reforms has certain limitations in terms of indicator selection, time period, and methodology. Addressing this gap, this study draws on the AHP-EWM-FCE method to construct a rigorous evaluation system for examining the medical insurance fund operation performance under the DRG payment method reform over the 2020–2022 in S Province. It also performs an empirical case study using data from mainly large-scale tertiary general hospitals, thereby appropriately reflecting the diverse situations from hospital operation, referral, to off-site reimbursement, among others. Thus, the relevant conclusions offer valuable practical guidance.
Evaluation system indicators
Extant research shows that establishing comprehensive performance evaluation indicators for the medical insurance fund operation can not only better reflect the operations, but also promote the efficient use of medical insurance funds and improvement of medical service levels (27). Accordingly, this study combines extant research and the actual operation of DRGs to establish 44 potential indicators of medical insurance fund operation. This number is reduced to 28 after two rounds of expert consultation and correction. Among them, the number of participants in basic medical insurance, financial subsidy for resident medical insurance, growth rate of medical insurance fund income, proportion of recovered medical insurance funds, growth rate of total fund expenditure over the previous year, current balance rate of the medical insurance fund, and number of months supported by the medical insurance fund balance are closely related to the efficiency and effectiveness of the use of medical insurance funds. The number of DRG groups, CMI, the number of diseases, and the total weight value (number of discharged patients and volume of surgeries) are closely related to the reform of the DRG payment method. Therefore, the selected evaluation indicators can comprehensively reflect the medical insurance fund operation under the DRG payment method.
Indicator weights
This study is the first to use the AHP-EWM-FCE method to establish the weights of performance evaluation indicators for the medical insurance fund operation in the background of the DRG payment method reform. Among the indicators, the AHP-EWM combined weight of DRG operation and use of medical insurance fund is 0.529, the highest among all weights. This indicates that DRG operation and the use of medical insurance funds are closely related to the performance evaluation of medical insurance fund operation. According, efforts can focus on further improving the efficiency of medical insurance fund use, and standardize hospital diagnosis and treatment behaviors based on the indicators of DRG operation and use of medical insurance funds (28).
Next, the combined weight of the medical insurance fund raising indicator is 0.381, representing a relatively high weight. Research shows that an appropriate level and structure of financing for the medical insurance fund is key to promoting its accessibility, fairness, and sustainability (29). At present, China’s medical insurance fund largely depends on government subsidies, which is increasing annually (30). In recent years, Chinese scholars have explored the improvement of the medical insurance fund financing mechanism and sustainability of funds. They suggest modifications to the frequency, timing, and extent of medical insurance fund raising, alongside the establishment of actuarial models to achieve “basic, bottom-line, and sustainable” medical insurance funds (31). As such, the government and relevant medical insurance departments should establish institutionalized and standardized dynamic adjustment mechanisms for medical insurance fund raising.
Next, experts demonstrate a high degree of recognition of “medical insurance informatization.” This can assist in connecting medical information within designated medical insurance institutions and the real-time acquisition of patients’ medical insurance information. On the one hand, such efforts can facilitate the real-time monitoring of big data pertaining to medical insurance funds, and help promptly detect and correct phenomena such as the abuse of medical insurance funds, medical misconduct, and unreasonable medical expenses. On the other hand, it can aid in the promotion of hierarchical diagnosis and treatment (3). Further, the DRG payment mode reform requires accurate accounting of disease costs, which also necessitates the support of hospital information system. For instance, based on big data, Liu conducted an in-depth analysis of disease costs using the principles of Boston Matrix Analysis to identify the root cause of cost controls. Therefore, medical insurance informatization is conducive to the efficient use of medical insurance funds and refined implementation of the DRG payment reform (32).
Empirical analysis
The performance score of the medical insurance fund operation in the eight sampled cities shows a clear growth trend over the 2020–2022 period. Among them, QD has embedded the DRG payment system into the reconstruction of its incentive structure.
Medical insurance fund raising
Among the third-level indicators, the participants in basic medical insurance of QD and LY remain at a high level, and the medical insurance fund participation rates of JN, QD, ZZ, YT, LY, and LC all exceed 96%. Notably, the overall insurance coverage level in the eight cities exceeds the national average. This may be related to the success of the medical insurance policy promotion and universal medical insurance expansion. However, China currently adopts a voluntary participation approach for basic medical insurance. Some new employees are missing from the scheme, while coverage for workers in small and micro enterprises is not yet complete. Therefore, there is room for improvement in medical insurance coverage (33). Thus, future efforts focus on increasing publicity by the government and medical insurance companies to reduce missing coverage, increase the coverage rate of micro and small enterprises, and achieve universal medical insurance.
Analysis of DRG operation and medical insurance fund use
Expenditure and balance of medical insurance funds
Under the DRG payment reform, the long-term benefits provided by the medical insurance fund to insured patients determine the integration and coordination between the medical insurance system and high-quality hospital development (34–36). In this study, JN and QD score the highest in the use of medical insurance funds. However, there is a relatively prominent imbalance in the revenue and expenditure of medical insurance funds in the eight cities. At present, China’s medical insurance fund management adopts the principle of “vertical accumulation and actuarial balance.” The imbalance between fund expenditures and balances, whether too high or too low, is not conducive to the functioning of medical insurance funds. According to Jia, the number of months for the balance payment of the medical insurance fund is an important factor its sustainability, and 6–9 months being an appropriate number (37). Specifically, if the medical insurance fund balance is paid for more (less) than nine (six) months, the fund accumulation is excessive (too low).
Meanwhile, the balances of eight cities in S Province are too small, indicating that the ability of medical insurance funds to resist risks is weak. Still, there was no cumulative deficit. Yet, the number of balance payment months in most cities is 0–1 month, and only a few cities have a balance of more than 1 month. This may be related to the fact that in the face of public emergencies in recent years, the National Medical Insurance Administration has promptly adjusted payment policies, expanded the scope of medical insurance payment, and dynamically adjusted payment and budget (38). Hence, the regulation of medical insurance funds is crucial. It is recommended to conduct horizontal risk control, avoid rough expenditures, and reduce the accumulation or deficit of medical insurance funds, thus promoting the smooth and efficient development of fund operations (39). Currently, most countries adopt diversified financing methods to balance the fund expenditures and balances (40). Irregularities and misuse of funds can be prevented by establishing effective monitoring mechanisms and auditing processes,
Medical service capabilities
The service capabilities of medical institutions can somewhat reflect the management level of medical insurance funds, governments, and medical institutions in the region. The survey sample comprises tertiary-A general hospitals, wherein the number of DRG groups in JN, QD, ZZ, and YT cities is relatively complete. Meanwhile, the number of DRG groups in RZ, LY, and LC is slowly increasing, indicating that the latter’s DRG groups are becoming complete (41). The CMI values of QD and JN are higher than those of other cities, indicating that they have a relatively large number of highly weighted medical records. Compared with 2020, 70.5% of hospital departments significantly increased their CMI values in 2022. Thus, the tertiary-A general hospitals accurately position themselves in diagnosing and treating difficult cases. Moreover, the average length of stay in RZ and LY has dropped to 6.14 and 6.77, reflecting good control of hospital stays by medical institutions. However, shorter hospital stays do not necessarily mean better outcomes. For instance, blindly reducing hospital stays, and refusing difficult and complex patients will lead to a decrease in the CMI value (42).
Medical insurance fund reimbursement
Population mobility triggers off-site reimbursements from medical insurance funds. Owing to reasons such as education, employment, or relocation, young and transient populations might travel elsewhere. These groups are more likely to engage in activities like seeking medical treatment off-site (43). Indeed, the reimbursement indicators of medical insurance funds in the eight sampled cities in S Province have shown a significant increase. QD and RZ operate well in off-site reimbursements, with some areas achieving same-day reimbursement. Meanwhile, S Province continues to promote the national network of basic medical insurance and direct settlement of hospitalization expenses across provinces and places, which greatly facilitates the efficient use of medical insurance funds. Efforts should be made to increase the rate of same-day reimbursement off-site, which can not only meet the service needs of off-site medical treatment but also increase population mobility (44).
Conclusion
Based on operational data on medical insurance funds from eight cities in S province in China, this study comprehensively and dynamically evaluates the performance of the medical insurance fund under the DRG payment reform by constructing a rigorous performance evaluation system. This system can be used to improve the efficiency of using medical insurance funds and elevating the standard of medical services. This study is also the first to construct the evaluation system based on the AHP-EWM-FCE method. It identifies key indicators for the medical insurance fund operation, such as the DRG operation, use and management of medical insurance funds, fundraising, and satisfaction levels. Here, DRG operation and the use of medical insurance funds have the highest weights in the evaluation system. Furthermore, the performance of the proposed evaluation system is consistent with the actual operation and performance scores of the medical insurance fund across the eight cities. Overall, the proposed addresses the deficiencies in methodology, indicator system construction, and practical application with greater rigor, applicability, and promotability.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
ZW: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WC: Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Formal analysis, Software. AL: Conceptualization, Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Ethics Committee of the Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University which number is LYEC2024-K0201.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Tian, W, Wu, B, Yang, Y, Lai, Y, Miao, W, Zhang, X, et al. Degree of protection provided by poverty alleviation policies for the middle-aged and older in China: evaluation of effectiveness of medical insurance system tools and vulnerable target recognition. Health Res Policy Syst. (2022) 20:129. doi: 10.1186/s12961-022-00929-9
2. Qin, Z, Liu, S, Zhou, M, Chen, L, Huang, W, and Shen, L. Impacts of unifying urban and rural residents' medical insurance on the hospitalisation expenses of rural patients in eastern China: an interrupted time series analysis. BMJ Open. (2023) 13:e067198. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-067198
3. Wu, J, Qiao, J, Nicholas, S, Liu, Y, and Maitland, E. The challenge of healthcare big data to China's commercial health insurance industry: evaluation and recommendations. BMC Health Serv Res. (2022) 22:1189. doi: 10.1186/s12913-022-08574-2
4. Yu, L, and Lang, J. Diagnosis-related groups (DRG) pricing and payment policy in China: where are we? Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. (2020) 9:771–3. doi: 10.21037/hbsn-2020-8
5. Kwak, SH, Kim, JH, Kim, DH, Kim, JM, Byeon, HK, Kim, WS, et al. Impact of the Korean diagnosis-related groups payment system on the outcomes of adenotonsillectomy: a single center experience. Auris Nasus Larynx. (2018) 45:504–7. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2017.07.005
6. National Healthcare Security Administration. Notice of the National Healthcare Security Administration on issuing and issuing the three-year action plan on the reform of DRG/DIP payment method [EB/OL] no. 2021 48. Available at: http://www.nhsa.gov.cn/art/2021/11/26/art_37_7406.html.
7. Zhao, C, Wang, C, Shen, C, and Wang, Q. Diagnosis-related group (DRG)-based case-mix funding system, a promising alternative for fee for service payment in China. Biosci Trends. (2018) 12:109–15. doi: 10.5582/bst.2017.01289
8. Shi, Z, Zhang, Q, and Wang, X. Does the disclosure of medical insurance information affect patients' willingness to adopt the diagnosis related groups system. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1136178. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1136178
9. Donabedian, A. Evaluating the quality of medical care. Milbank Q. (2005) 83:691–729. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-0009.2005.00397.x
10. Hone, T, Macinko, J, and Millett, C. Revisiting Alma-Ata: what is the role of primary health care in achieving the sustainable development goals? Lancet. (2018) 392:1461–72. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31829-4
11. White, J. Can performance measurement make health care systemsmore sustainable or at least more efficient? OECD J Budg. (2019) 19:118–24. doi: 10.1787/2b3d3059-en
12. Borges, LC, Vaudelice, MM, Almeida, D, et al. Assessment of the quality of primary health care in Fortaleza, Brazil from the perspective of adult service users in 2019. Ciencia Saude Coletiva. (2021) 26:2083–96. doi: 10.1590/1413-81232021266.39722020
13. Shojaei, P, Pourmohammadi, K, Hatam, N, Bastani, P, and Hayati, R. Identification and prioritization of critical factors affecting the performance of Iranian public hospitals using the best-worst method: a prospective study. Iran J Med Sci. (2022) 47:549–57. doi: 10.30476/ijms.2021.91256.2237
14. Yu, H, and Shen, L. The practical exploration of the construction of the performance evaluation system of the medical insurance fund in Jiaxing City. Chin Med Insur. (2020) 7:54–8. doi: 10.19546/j.issn.1674-3830.2020.10.012
15. Yu, B, and Zhi, R. Performance evaluation model of medical insurance fund under uncertain information environment. Chin J Manag. (2018) 5:129–38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-884x.2018.12.014
16. Costa, E, Climent, E, Gawlitza, K, Wan, W, Weller, MG, and Rurack, K. Optimization of analytical assay performance of antibody-gated indicator-releasing mesoporous silica particles. J Mater Chem B. (2020) 8:4950–61.
17. Bao, HY. Performance evaluation and optimization research of public traditional Chinese medicine hospitals under the background of new medical reform. Southwestern Univ Fin Econ. (2023). doi: 10.27412/d.cnki.gxncu.2023.001496
18. Gehlot, MR, and Shrivastava, S. An AHP based sustainability assessment of cement mortar with synergistic utilization of granite cutting waste. J Build Eng. (2024) 86:108794. doi: 10.1016/j.jobe.2024.108794
19. Wang, SY, Yu, SX, Yang, X, Cui, DZ, Fu, XS, Wang, QZ, et al. Evaluation of quality attributes of different parts of Poria cocos during stress sweating process based on AHP-EWM and RSM. Ind Crop Prod. (2024) 210:118047–53. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2024.118047
20. Feng, Q. Electromagnetic properties and structure of superconducting materials based on AHP-FCE model. Appl Math Nonl Sci. (2024) 9:110–9. doi: 10.2478/amns.2023.2.00075
21. Li, Z, Wang, S, Cao, Y, and Ding, R. Dynamic risk evaluation method of collapse in the whole construction of shallow buried tunnels and engineering application. Math Biosci Eng. (2022) 19:4300–19. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2022199
22. Mousavi, SM, Yazdanirad, S, Althubiti, S, Majdabadi, MA, Najarian, F, and Sepehr, P. Determination and prioritization of factors affecting the occurrence of needle stick injuries among healthcare workers using techniques of Delphi and fuzzy analytical hierarchy process (FAHP). BMC Public Health. (2023) 23:2009. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-16969-x
23. Davies, S, Romano, PS, Schmidt, EM, Schultz, E, Geppert, JJ, and McDonald, KM. Assessment of a novel hybrid Delphi and nominal groups technique to evaluate quality indicators. Health Serv Res. (2011) 46:2005–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1475-6773.2011.01297.x
24. Pathan, AI, Girish, A, Said, S, et al. AHP and TOPSIS based flood risk assessment-a case study of the Navsari City, Gujarat, India. Environ Monit Assess. (2022) 194:509. doi: 10.1007/s10661-022-10111-x
25. Dolan, JG. Shared decision-making--transferring research into practice: the analytic hierarchy process (AHP). Patient Educ Couns. (2008) 73:418–25. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2008.07.032
26. Song, H, Lu, B, Ye, C, Li, J, Zhu, Z, and Zheng, L. Fraud vulnerability quantitative assessment of Wuchang rice industrial chain in China based on AHP-EWM and ANN methods. Food Res Int. (2021) 140:109805. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109805
27. Yan, YH, Kung, CM, and Chen, Y. The exploration of medical resources utilization among inguinal hernia repair in Taiwan diagnosis-related groups. BMC Health Serv Res. (2017) 17:708. doi: 10.1186/s12913-017-2665-6
28. Zhang, Q, and Li, X. Application of DRGs in hospital medical record management and its impact on service quality. Int J Qual Health Care. (2022) 34:090. doi: 10.1093/intqhc/mzac090
29. Qiu, X, Zhao, T, Kong, Y, and Chen, F. Influence of population aging on balance of medical insurance funds in China. Int J Health Plann Manag. (2020) 35:152–61. doi: 10.1002/hpm.2844
30. Manning, WG, and Marquis, MS. Health insurance: the tradeoff between risk pooling and moral hazard. J Health Econ. (1996) 15:609–39. doi: 10.1016/s0167-6296(96)00497-3
31. Zhu, K, Zhang, L, Yuan, S, Zhang, X, and Zhang, Z. Health financing and integration of urban and rural residents' basic medical insurance systems in China. Int J Equity Health. (2017) 16:194. doi: 10.1186/s12939-017-0690-z
32. Luo, AJ, Chang, WF, Xin, ZR, Ling, H, Li, JJ, Dai, PP, et al. Diagnosis related group grouping study of senile cataract patients based on E-CHAID algorithm. Int J Ophthalmol. (2018) 11:308–13. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2018.02.21
33. Li, Y, Li, L, and Liu, J. The impact of health insurance on self-protection of Chinese rural residents. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:874619. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.874619
34. Lyu, Y, Xu, Q, and Liu, J. Exploring the medical decision-making patterns and influencing factors among the general Chinese public: a binary logistic regression analysis. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:887. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18338-8
35. Fourie, C, Biller-Andorno, N, and Wild, V. Systematically evaluating the impact of diagnosisrelated groups (DRG) on health care delivery: a matrix of ethical implications. Health Policy. (2014) 115:157–64. doi: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2013.11.014
36. Wishnia, J, and Goudge, J. Impact of financial management centralisation in a health system under austerity: a qualitative study from South Africa. BMJ Glob Health. (2020) 5:e003524. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2020-003524
37. Jia, HB. Research on the appropriate contribution rate of basic medical Insurance in China. Liaon Univ. (2007). doi: 10.19851/j.cnki.cn11-1010/f.2009.03.026
38. Yu, ZQ, Chen, LP, Qu, JQ, Wu, WZ, and Zeng, Y. A study on the sustainability assessment of China's basic medical insurance fund under the background of population aging-evidence from Shanghai. Front Public Health. (2023) 11:1170782. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1170782
39. Bi, YN, and Liu, YA. The health insurance fund participates in controlling the epidemic: insights from german experience in dealing with the COVID-19 pandemic. Risk Manag Health Policy. (2023) 16:2391–404. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S427717
40. Sato, K, Ikeda, T, Watanabe, R, Kondo, N, Kawachi, I, and Kondo, K. Intensity of community-based programs by long-term care insurers and the likelihood of frailty: multilevel analysis of older Japanese adults. Soc Sci Med. (2020) 245:112701. doi: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2019.112701
41. Ockenga, J, Freudenreich, M, Zakonsky, R, Norman, K, Pirlich, M, and Lochs, H. Nutritional assessment and management in hospitalised patients: implication for DRG-based reimbursement and health care quality. Clin Nutr. (2005) 24:913–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2005.05.019
42. Li, X, Yuan, L, Gao, B, Chen, W, Wang, S, Xie, Y, et al. Comparison of diagnosis-related group based reimbursement and case-mix index within hospitalized patients before and after modified malnutrition diagnosis. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. (2023) 32:356–61. doi: 10.6133/apjcn.202309_32(3).0007
43. Xing, Y, Tarimo, CS, Ren, W, and Zhang, L. The impact of health insurance policy on the fertility intention of rural floating population in China: empirical evidence from cross-sectional data. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 20:175. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010175
Keywords: medical insurance funds, AHP-EWM-FCE methodology, performance evaluation, DRG payment reform, Tobit regression model
Citation: Wang Z, Chang W and Luo A (2025) A medical insurance fund operation performance evaluation system under the DRG payment mode reform. Front. Public Health. 13:1549575. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1549575
Edited by:
Fei Fan, Wuhan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Buyue Qian, Xi’an Jiaotong University, ChinaJiang Hua, Capital University of Economics and Business, China
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Chang and Luo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Aijing Luo, bHVvYWpAY3N1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Zijian Wang
Zijian Wang Weifu Chang
Weifu Chang Aijing Luo1,3,5*
Aijing Luo1,3,5*