- 1Research Center for Safety, Metrology, and Nuclear Quality Technology, Research Organization for Nu-clear Energy (ORTN), National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN), South Tangerang, Indonesia
- 2Department of Radiation Science, Graduate School of Health Sciences, Hirosaki University, Hirosaki, Japan
- 3Directorate of Competency Development, The National Research and Innovation Agency of Indonesia (BRIN), Jakarta, Indonesia
- 4Polytechnic of Nuclear Technology, The National Research and Innovation Agency of Indonesia (BRIN), Sleman, Indonesia
- 5Polymer Chemical Engineering, Polytechnic STMI of Jakarta, Jakarta, Indonesia
- 6Research Center for Nuclear Fuel Cycle and Radioactive Waste Technology, Research Organization for Nuclear Energy (ORTN), National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN), South Tangerang, Indonesia
- 7Research Center for Nuclear Beam Analytics Technology, Research Organization for Nuclear Energy (ORTN), National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN), South Tangerang, Indonesia
- 8Institute of Radiation Emergency Medicine, Hirosaki University, Hirosaki, Japan
Introduction: Creating a safe living environment involves using healthy and sustainable building materials. Humans are exposed to natural radionuclides, such as 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K decay series, found in building materials that pose a radiological hazard. This study is aimed to investigate the radionuclides content of building materials used in Jakarta and its surrounding areas. The computer code RESRAD-BUILD was used to calculate the annual effective dose received by an adult living in a typical room constructed with the studied building materials.
Methods: Samples such as sand, cement, bricks, and Autoclaved Aerated Concrete (AAC) were collected. The 222Rn surface exhalation rate was determined using the closed chamber method using RAD7, while the activity concentration of natural radionuclide was measured using a gamma spectrometer.
Results and discussion: The 222Rn surface exhalation rate varies from 4 × 10−2 to 1.6 × 100 mBq m−2 s−1 with an average of 4 × 10−1 mBq m−2 s−1. The average 222Rn exhalation rate of the building materials studied was much lower than the global average value of 1.6 × 101 mBq m−2 s−1. The average activity concentration values of 232Th (21 Bq kg−1) and 40K (217 Bq kg−1) in all building materials studied are lower than the global average values of 45 and 412 Bq kg−1. In comparison, the average activity concentration of 226Ra (34 Bq kg−1) is similar to the global average value of 32 Bq kg−1. Furthermore, the assessed radiological hazard from the measured building material has an average activity index of 0.3, while the RESRAD-BUILD estimated total annual effective dose for a typical house constructed using a mixture of the building materials was 0.11 mSv, in which indoor 222Rn alone represents 92% of the total. From the assessment results, the building materials in Jakarta and its surrounding areas do not pose significant concerns regarding radiological hazards. However, the higher contribution of 222Rn suggests the need for a large-scale indoor 222Rn survey in the study area.
Highlights
• Transforming living spaces into safe environments that prioritize human health, environmental protection, and sustainable development is among the goals adopted by the United Nations under the framework of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
• The quality of building materials plays a vital role in the effort to create better cities. Building materials, such as bricks, sand, gravel, or Autoclaved Aerated Concrete (AAC) contain natural radioactive elements.
• This requires monitoring and assessing the risks of radiological exposure these materials would pose to the public within these infrastructures.
• This study monitored the concentration of natural radioactivity of the natural radionuclides, such as 226Ra, 232Th, 40K, and 222Rn, and the surface exhalation rate in building materials used in one of the largest urban concentration areas in the world—the megalopolis of Jakarta in Indonesia. A total of 81 building material samples were collected from 17 regional areas for this purpose.
1 Introduction
To transform the world into a better society, the United Nations adopted 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to be achieved by 2030. These SDGs foster the development of a more prosperous, healthy, safe, and peaceful living environment. Building materials contribute directly to achieving SDGs goals, especially SDGs goals 3, 7, 9, 11, 12, 13, and 15 (1). The use of non-hazardous building materials was one of the key aspects of green building to enhance human health (2).The use of non-hazardous building materials was one of the key aspects of green building to enhance human health. This poses a major challenge, particularly for megacities in developing countries. The safety of building materials counts among others, especially when it comes to their natural radioactivity content. Human exposure to radiation from natural radionuclides is the primary source of the total annual effective dose received from all sources—both natural and artificial (3). Among the natural sources, the level of exposure varies depending on the exposure pathway. On average, each individual receives an annual radiation effective dose of 2.4 mSv, consisting of 1.1 mSv from inhalation of 222Rn gas and 0.48 mSv from external gamma radiation, representing 48 and 20% of the total effective dose received annually, respectively. The remaining amounts are 0.29 mSv from ingestion (12%), and 0.39 mSv from cosmic radiation (16%) (4). 222Rn is the main contributor to the annual effective dose. 222Rn is a radioactive noble gas belonging to the 238U decay series found in soil and rocks (5). Epidemiological studies and dosimetric modeling provide evidence of a direct link between exposure to radon (222Rn) and the risk of lung cancer (6–10). 222Rn is recognized as a carcinogen element by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), and according to the World Health Organization (WHO), 222Rn is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking (11, 12). In addition, in certain countries, studies have been carried out to determine lung cancers attributable to exposure to 222Rn (13, 14). Furthermore, external gamma radiation is the second contributor to the annual effective dose after 222Rn (4). 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K are primordial radionuclides in soil and rocks. Their decay products are gamma emitters for 226Ra and 232Th and a direct gamma emitter for 40K, which participate in the external gamma exposure of humans (15). In some areas of the world, the building materials used to build houses/offices mostly come from rocks and soil, which contain natural radionuclides such as the 238U and 232Th decay series as well as 40K (16, 17). These building materials often constitute a significant source of indoor 222Rn and external gamma exposure.
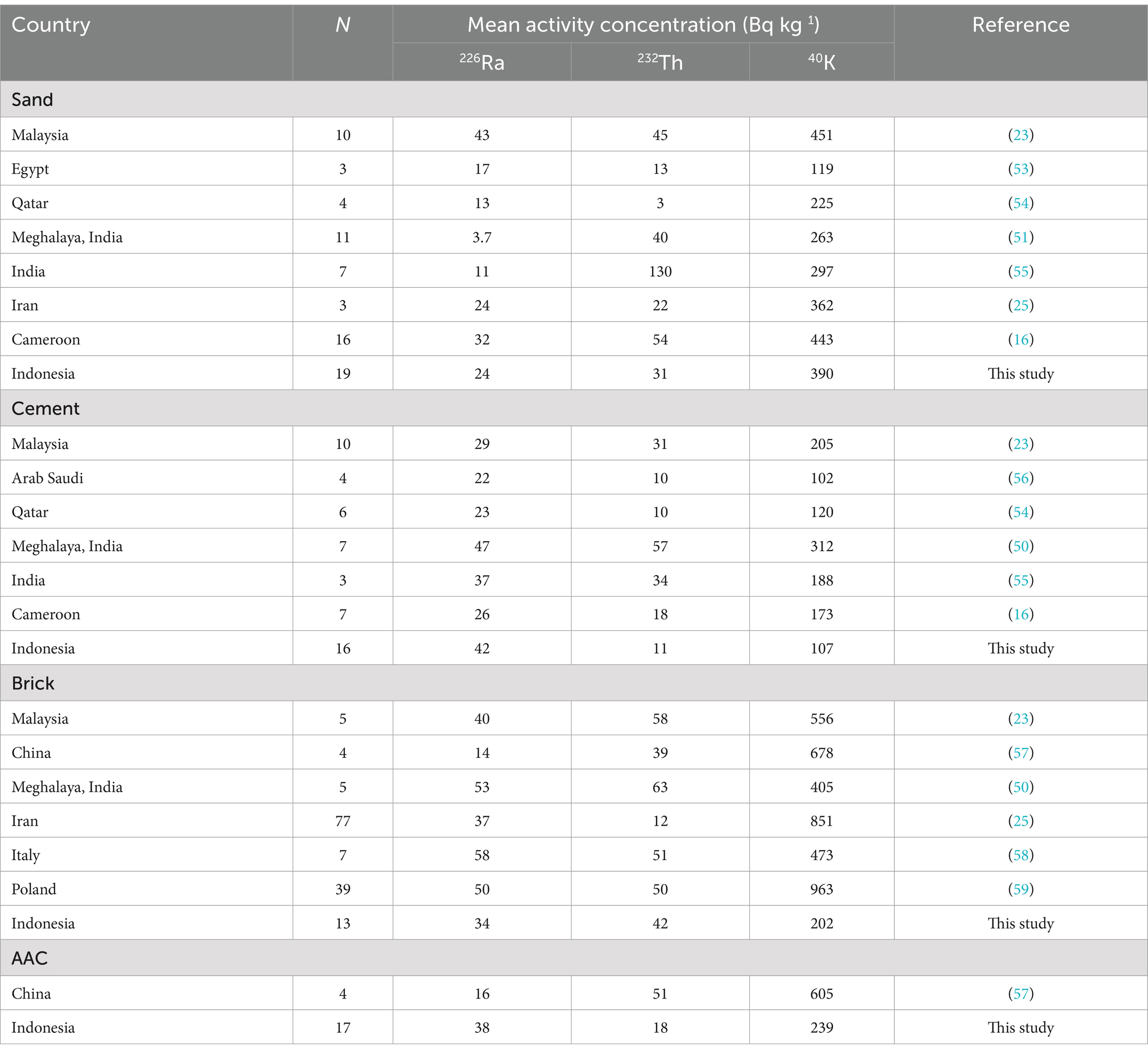
In urban areas, the majority of houses use walls as the primary building material, made of red brick or concrete blocks and usually coated with cement plaster (18). The main ingredient in cement and red brick is clay, which consists of silicate, aluminum oxide, and limestone, with calcium carbonate being the most significant compound. In big cities, such as Jakarta, autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC) is widely used for construction. AAC is made from quartz sand, cement, and developer. Also, sand material is widely used as a mixture for cement, concrete, or bricks (19). Natural radionuclides in building materials can pose external and internal radiation hazards to building occupants. The external radiation hazards are attributable to gamma radiation from the decay of radionuclides in the material (226Ra, 232Th, and 40K), and the internal radiation hazards are, in reality, due to the inhalation of radionuclide 222Rn and 220Rn decay products (20–22). Few researchers have conducted analyses of natural radionuclide content in building materials in the South East Asia region. In Malaysia, Abdullahi et al. analyzed tile materials, red bricks, cement bricks, sand, cement, gravel, white cement, fly ash, feldspar, lime, kaolin, pottery, clay soil, glaze, and talc with the results of the overall average activity concentration of all building materials ranging from 9.6 ± 0.7 to 222.8 ± 5.1 Bq kg−1; 8.6 ± 1 to 274.4 ± 8.1 Bq kg−1; and 46.3 ± 6.5 to 1589.2 ± 21.1 Bq kg−1 for 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K, respectively (23). Similar research has also been carried out on cement, gypsum, and sand materials, with the results of calculations obtaining the highest activity concentration values of 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K found in sand samples at 42.12, 27.79, and 316.2 Bq kg−1, respectively (24). Knowing radionuclide concentrations in building materials is vital in estimating potential radiological hazards for building occupants because most people spend 80% of their time indoors (25). This research will measure the activity concentrations of 226Ra, 232Th, 40K, and 222Rn, as well as the exhalation rate of 222Rn gas in building materials such as sand, cement, bricks, and AAC from Jakarta and its surrounding areas.
Recently, the Indonesian government has been actively promoting the usage of environmentally friendly materials (eco-materials) in several areas, particularly in the construction sector, to achieve sustainable development goals, create a better environment, and provide affordable housing for low-income communities (26). An overall assessment of the safety of these materials is essential for a sustainable environment, including radiological hazards often associated with building materials (27, 28).
Until now, no investigation has been conducted on the local building materials to determine radionuclides concentrations and the 222Rn surface exhalation rate used in Jakarta and its surrounding areas. This study aims to undertake an extensive sampling of building materials in Jakarta and the surrounding areas, the major city of Indonesia, followed by laboratory analysis of 226Ra, 232Th, 40K, and 222Rn surface exhalation rate calculations from these samples that are also used as building materials. To determine the effective dose received by an adult from the exposition to the radionuclides contained in the building materials, the RESRAD-BUILD computer code was used to analyze the contributions of various exposure pathways.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study area
The study area in this study is Jakarta—a megacity of Indonesia and its surroundings located on Java Island (Figure 1). Jakarta city and the surrounding areas were chosen as the research locus because it has a reasonably high population with high levels of human activity indoors, both in the office and at home. Based on the Office of Statistical Agency (BPS) data for 2022, the population of Jakarta, West Java, and Banten provinces are 10,680,000, 49,405,000, and 12,252,000 people, respectively (18). Java Island is home to 154,000,000 people, 56% of the country’s total population of 275,000,000 people, making Java the most populated island in the world. Jakarta and its suburbs are home to almost a quarter of Java’s population (18). Jakarta is a tropical, humid city with annual temperatures between 24 and 34°C and a relative humidity of 75–85%. The average mean temperatures are 26°C in January and 28°C in October. The annual rainfall is more than 1,700 mm. Sea winds often modify temperatures. Jakarta, like any other large city, also has its share of air and noise pollution (29).
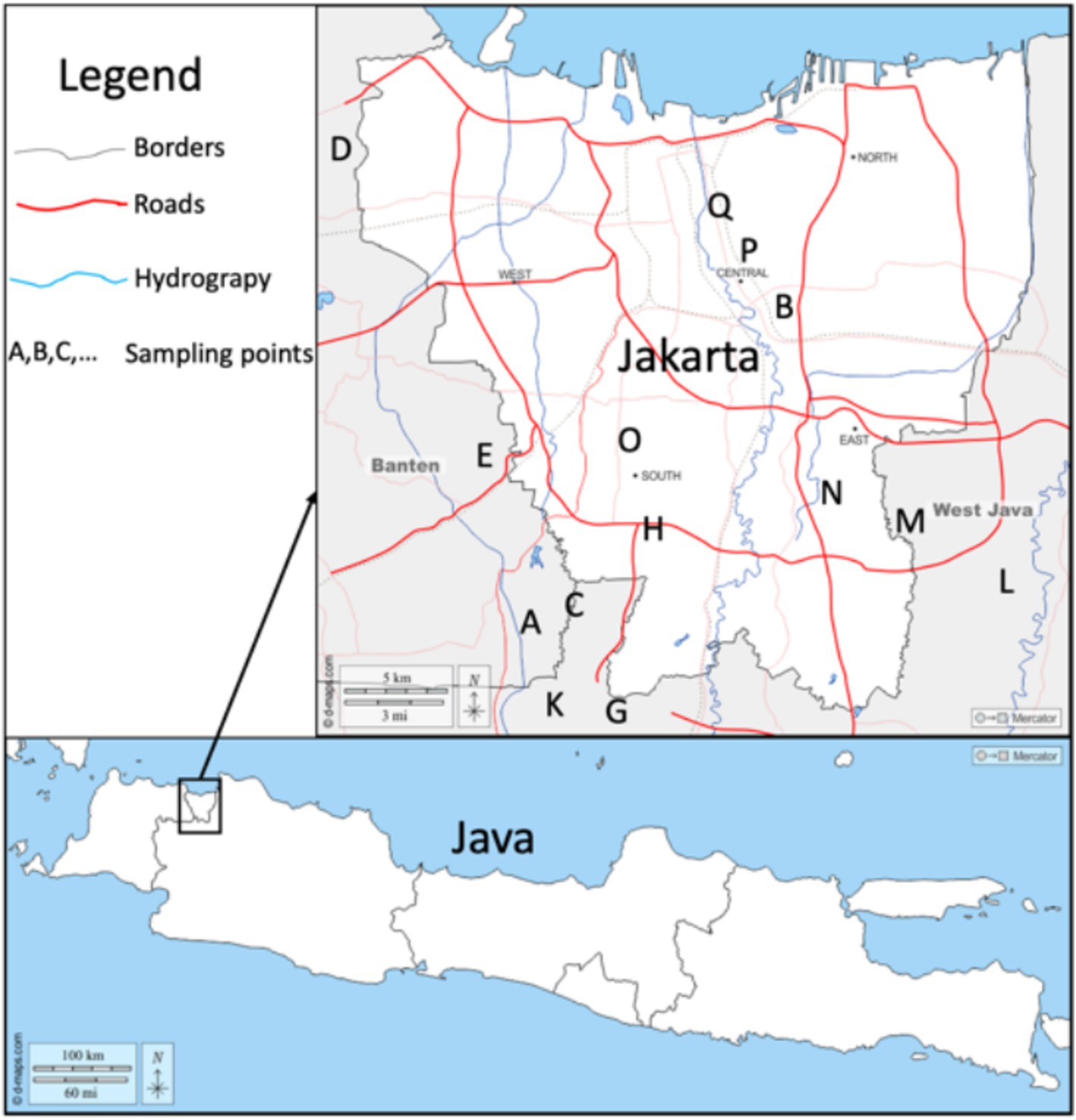
Figure 1. Map of the sampling points in the study area. Reprinted with permission © 2007–2025 https://d-maps.com; data from https://d-maps.com/carte.php?num_car=135659&lang=en and https://d-maps.com/carte.php?num_car=133900&lang=en were combined to create the figure.
2.2 Sampling and preparation of building materials
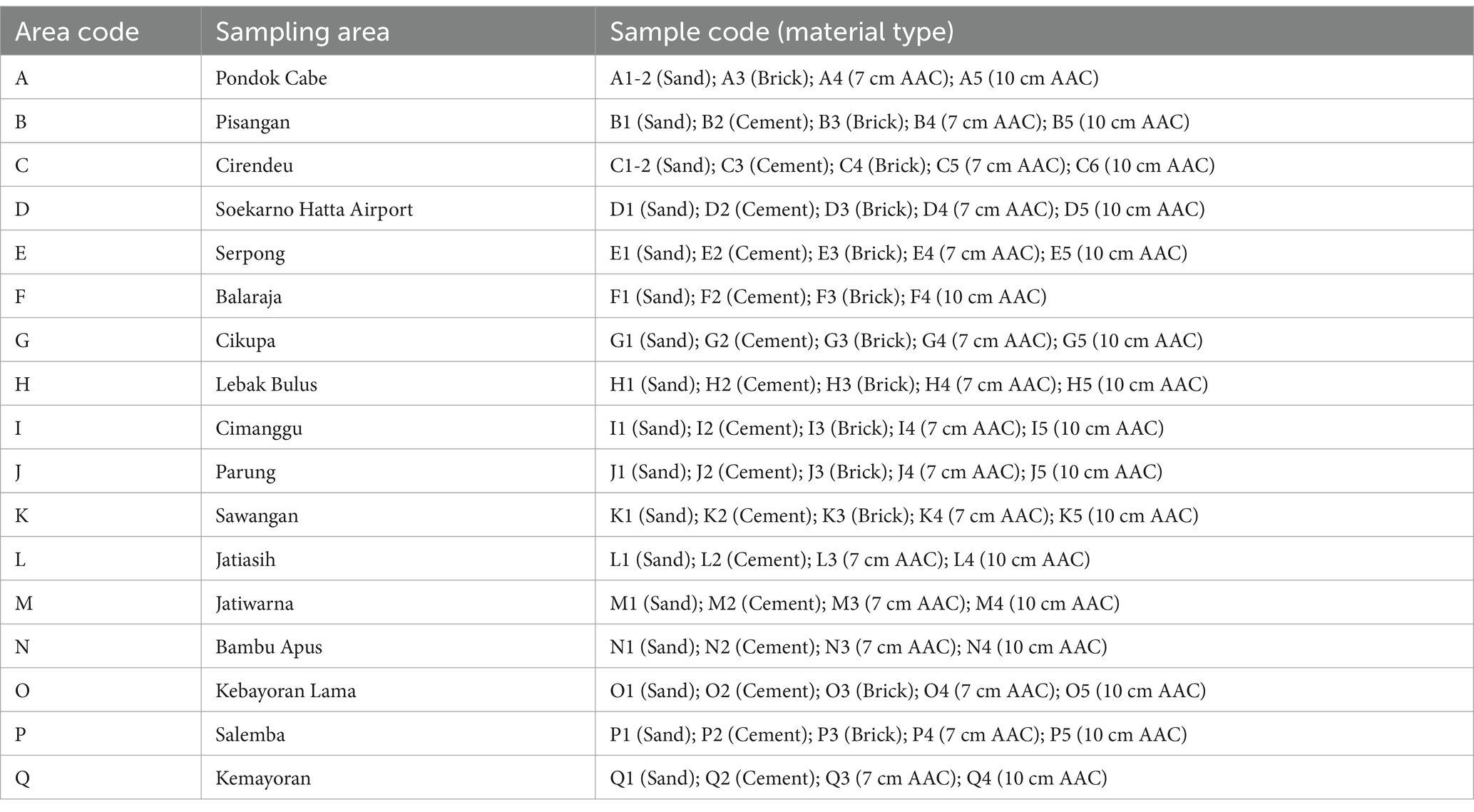
A total of 81 samples of building materials are used in the study area, among the types and brands, with details of 19 sand samples, 16 cement samples, 13 brick samples, 17 AAC samples of 10 cm thick, and 16 AAC samples of 7 cm thick. Sampling was carried out randomly at 17 regional areas, namely, Pondok Cabe (A), Pisangan (B), Cirendeu (C), Soekarno Hatta Airport (D), Serpong (E), Balaraja (F), Cikupa (G), Lebak Bulus (H), Cimanggu (I), Parung (J), Sawangan (K), Jatiasih (L), Jatiwarna (M), Bambu Apus (N), Kebayoran Lama (O), Salemba (P), and Kemayoran (Q). Details of building material samples are shown in Table 1. Samples were prepared in the laboratory using a similar protocol to Ndjana Nkoulou et al. study (16). First, they were dried using an oven set at 105°C for 24 h. After that, the samples were weighed, and their volumes were determined. Volume measurements were carried out directly on the material for brick and AAC samples. In contrast, volume measurements were carried out for sand and cement samples by measuring the volume of the sample holder.
2.3 Determination of the 222Rn surface exhalation rates
222Rn surface exhalation rate is the flux of 222Rn per square meter per second or per hour from the source, such as rocks, soil, or building materials (30, 31). There are several methods for measuring 222Rn surface exhalation rate, namely the closed-chamber method (CCM) and the open-chamber method (OCM). The closed-chamber method (CCM) is commonly used to measure the exhalation rate in building materials by putting the sample inside an airtight container and measuring the 222Rn activity concentration in the air in the container (32, 33).
222Rn activity concentration was measured using a RAD7 222Rn monitor (DURRIDGE Company, Inc., USA) with an α solid-state detector. The diagram illustrating the measurement of the 222Rn exhalation rate by RAD7 is presented in Figure 2. When the container containing the sample is connected to the detector, 222Rn gas accumulated due to the exhalation of 222Rn in the sample will be pumped to flow into the drying column (Drierite, Drierite Company, Inc., USA) and then into the inlet filter of the RAD7 tool. In RAD7, the sample air will decay so that α particles emitted from the polonium isotope will be detected. RAD7 uses α spectrometry techniques to convert α particles into electrical signals. This detector can also separate electrical pulses produced from 218Po and 214Po with energies of 6 and 7.69 MeV, respectively (34, 35). The sampling cycle was set for 1 h with 6 cycles. The spectrum obtained was then analyzed using Capture software provided by DURRIDGE. 222Rn activity concentration measurements were conducted in dry conditions (relative humidity less than 10%). After each measurement, the 222Rn inside the RAD7 is purged by pumping clean air. The RAD7 was calibrated for 222Rn measurement in the 222Rn chamber of IREM (Institute of Radiation Emergency Medicine), Hirosaki University, Japan, which annually conducts intercomparison with the Federal Office for Radiation Protection (BfS), Germany. The 222Rn surface exhalation rate is determined using Equation 1 (35).
where ERn is 222Rn surface exhalation rate in Bq m−2 s−1, CRn is the average of the stabilized 222Rn activity concentration in Bq m−3 obtained by direct measurements using RAD7 device, V is the effective volume of the closed chamber as in the chamber volume of 1.42 × 10−2 m3 decreased by sample volume, λRn is 222Rn decay constant in 2.1 × 10−6 s−1, and As is the surface area of the sample in m2.
2.4 Determination of 232Th, 226Ra, and 40K activity concentrations in the building materials
After the measurements of 222Rn surface exhalation rates, the samples were crushed, sieved, and dried in an oven for the second time to remove moisture contained in the materials. After that, the samples were weighed and put into a U8-type vial container, a cylindrical polypropylene container sized 48 mm × 55 mm. The samples in the vials were then tightly sealed to prevent 222Rn gas from escaping from inside to allow secular equilibrium to be achieved after 30 days. The measurements are conducted using a calibrated gamma spectrometry system with a p-type High Purity Germanium detector (HPGe), GEM60-83-XLB-C-SMP (ORTEC, USA), with a relative efficiency of 60% and a resolution of 1.86 at 1.33 MeV of 60Co. The detector is mounted inside a 10-cm thick cylindrical lead shielding, lined with a layer of tin and copper to prevent ambient gamma interference on the measurements, and the X-rays of Compton scattering in the lead reach the detector. The pulse from the detector is analyzed by a multichannel analyzer that is directly connected to a PC with the associated reading software Gamma Vision (ORTEC, USA).
The calibration of the gamma spectroscopy system utilizes a soil matrix reference material from the intercomparison network of Analytical Laboratories for the Measurement of Environmental Radioactivity (ALMERA-IAEA), CRM IAEA soil 448, and CRM IAEA Soil 444. To maintain the reliability and validity of the spectrometry system, the laboratory keeps a routine internal calibration using a mixed radionuclide source. The laboratory also participates annually in the intercomparison network of ALMERA and the Indonesian metrology network for radionuclide measurement.
The 226Ra activity concentration is obtained by analyzing the photoelectric peaks of 295 keV; 351 keV of 214Pb; and the photoelectric peak of 609 keV of 214Bi. 232Th activity concentration is obtained by analyzing the photoelectric peaks of 238 keV of 212Pb and 911 keV of 228Ac. 40K activity concentration is determined by examining the single photoelectric peak of 1,460 keV (36). The measurement duration for each sample was 80,000 s. Equation 2 was used to determine the activity concentration A (Bq kg−1) of each radionuclide (15, 37, 38).
where Cs is the count rate of the sample (count s−1); Cbg is the count rate of the background (count s−1); 𝜀 is the detector efficiency; 𝛾 is the gamma emission probability; W is the sample weight (kg); fc is the correction factor; k is the coverage factor in k = 1.96 for a confidence interval of 95%; and U is the combined uncertainties of the measurements calculated obtained using Equation 3 (39).
Where u is the relative uncertainty from each sample count standard deviation, detector efficiency, measured sample weight, gamma emission probability, growth factor, attenuation factor, and summing factor. We also analyze the background radiation for each radionuclide to determine the detection limit (LD) using Equation 4 (40).
Where DT is the decision threshold based on the measured background, k is the coverage factor, and U is the uncertainty in measurement. The 40K, 226Ra, and 232Th detection limits were 0.21, 0.08, and 0.08 Bq kg−1, respectively.
2.5 Indoor 222Rn activity concentration emitted by the building materials
Indoor 222Rn concentration originates from sources such as inside/outside air exchange, water supply, cracks in the house’s basements, and building materials used, especially when the house is built from bricks, sand, and rocks. The contribution of building materials to the indoor 222Rn concentration is often significant. It is possible to assess that contribution by knowing that 226Ra contains the building materials since 222Rn is a 226Ra decay product. Equation 5 expresses the indoor 222Rn from the 226Ra in building materials in a steady state condition (16, 41, 42).
where is the 226Ra concentration in the building materials (Bq kg−1); ε the emanation fraction (0.2); λ the 222Rn decay constant (0.00756 h−1); τ the air exchange rate (0.5 h−1), and r is the density (100 kg m−3) and half-thickness layer (7 cm) of the structural elements (wall and floor) of the room, respectively; and A and V are the room surface area (m2) and inner volume (m−3), respectively. Activity index I was defined to estimate the radiological risk presented by building materials.
2.6 Activity index
The activity index I is calculated using 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K activity concentrations in the building materials. The Equation 6 expresses the different coefficients of calculation (43).
2.7 Annual effective doses from external, inhalation, and ingestion obtained using RESRAD-BUILD computer code
The assessment of the annual effective doses from external, inhalation, and ingestion received by an individual living in a typical house in the study area built using the studied building materials can be obtained using RESRAD-BUILD presented in Figure 3. This computer code is an open-access software developed by the Argonne National Laboratory (Argonne, USA) (41, 44). In detail, the dose resulting from exposure to external radiation emitted by walls and floor, dose received from inhalation of 222Rn decay products, and dose from ingestion of radionuclides deposited and resuspended in the house are obtained from RESRAD-BUILD computer software. The exposure scenario is for an average adult who is 1.60 m in height and 80 kg of weight. The flowing parameters were used along with radionuclide concentrations of building materials. The indoor occupancy factor is 0.8 (16, 44). A room model with the dimensions of 4 m × 3 m × 3 m is considered, the half layer walls’ thickness of 7 cm, 1 number of rooms per occupant, radionuclides deposition velocity of 0.01 m s−1, radionuclides resuspension rate of 5 × 10−7 s−1, adult individual breathing rate of 20 m3 day−1 were used (16, 45, 46).
Figure 3. RESRAD web page interface (44). Screenshot (left) from Argonne National Laboratory, RESRAD Family of Codes.
3 Results
3.1 222Rn activity concentration and surface exhalation rate of building materials
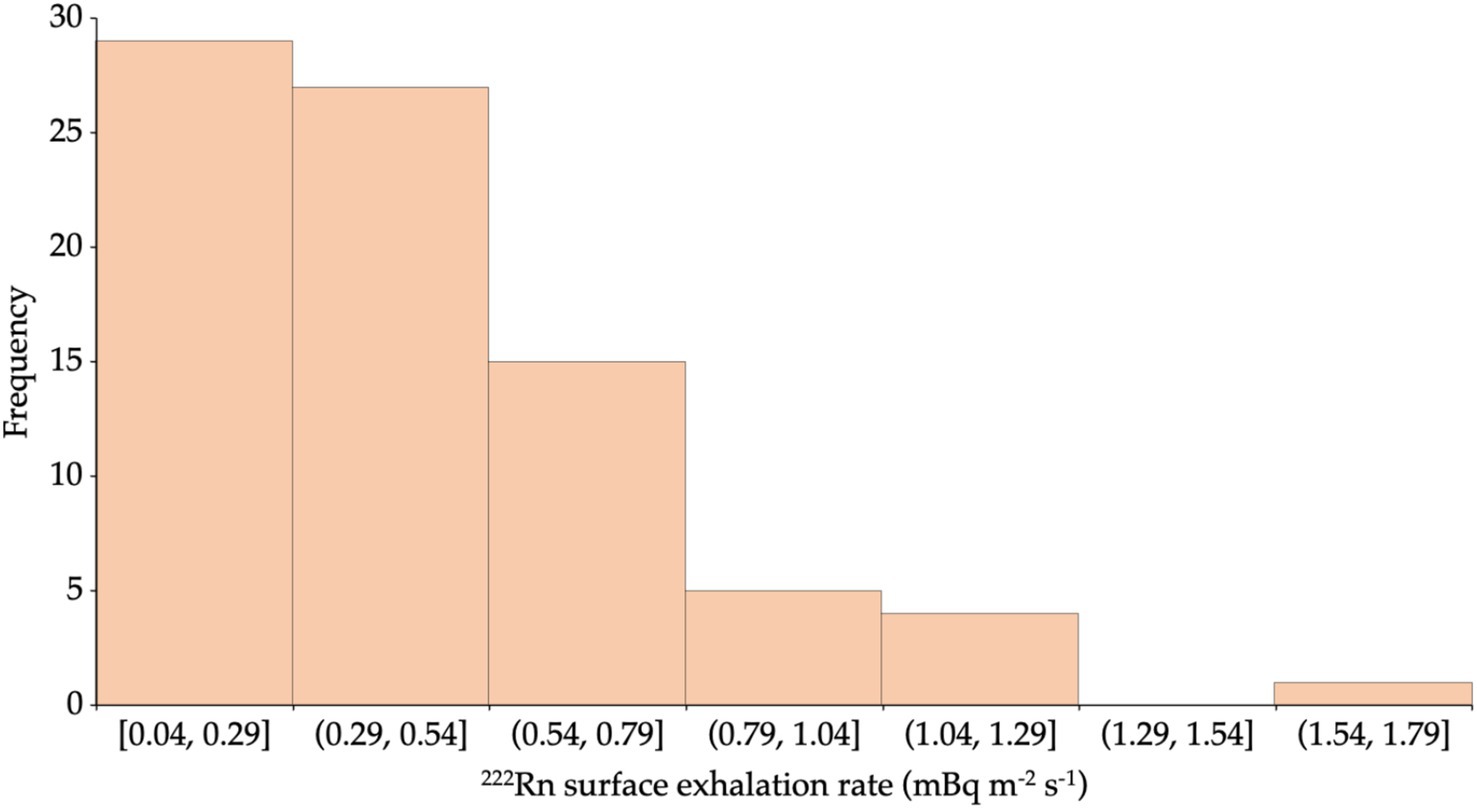
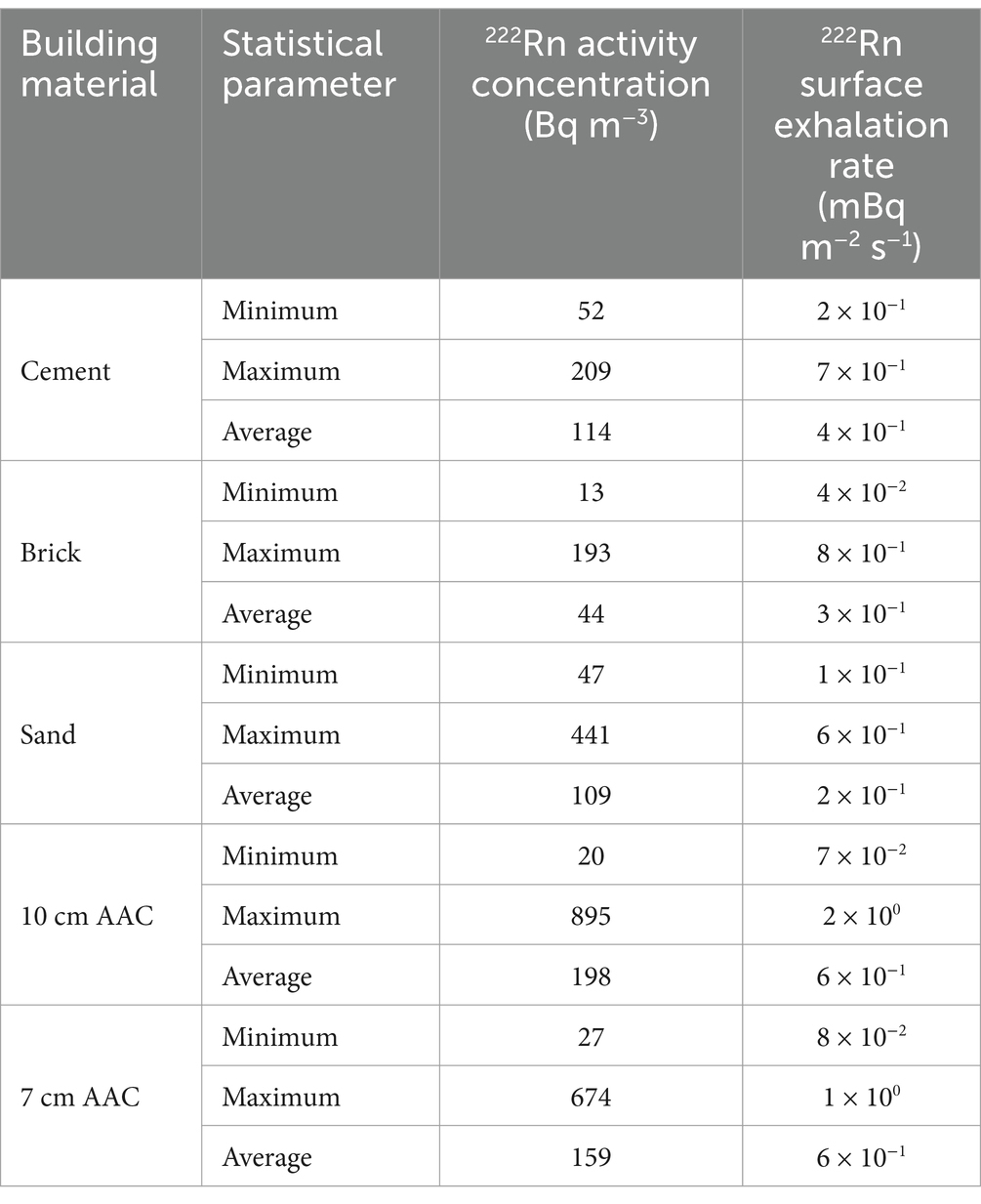
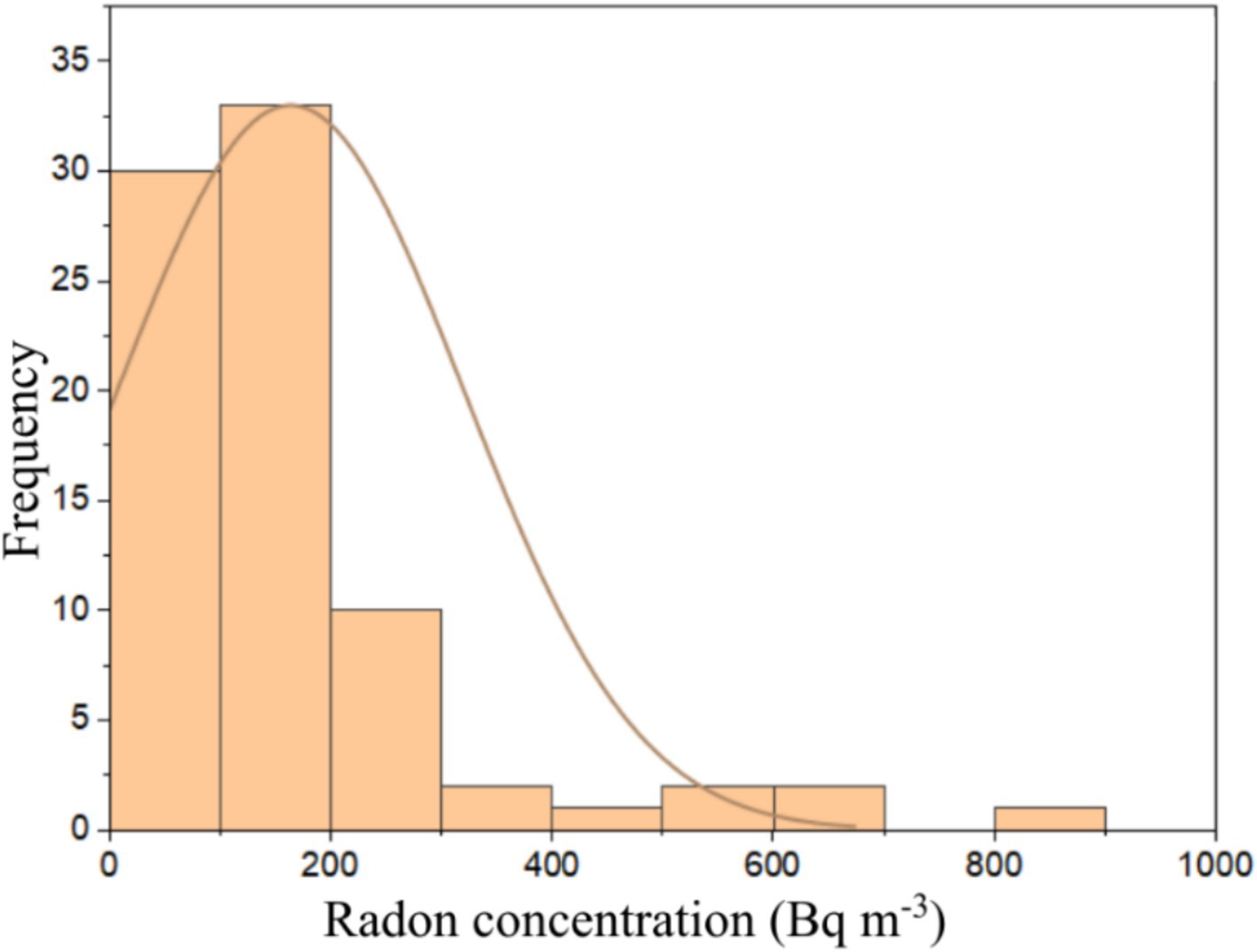
The 222Rn activity concentration values measured directly for the entire samples range from 13 ± 1 to 895 ± 9 Bq m−3 with an average value of 116 ± 7 Bq m−3. The lowest 222Rn activity concentration came from the brick sample (J3) from the Parung area. In contrast, the highest value came from the 10 cm thick AAC sample (I4) obtained from the Cimanggu area. The 222Rn activity concentration values obtained from the direct measurements were used to calculate the 222Rn surface exhalation rates by applying Equation 1. The distribution of the 222Rn surface exhalation rate for all the building materials studied is presented in Figure 4. The principal data obtained for each building material type, sand, cement, brick, 10 cm AAC, and 7 cm AAC was presented in Table 2. The 222Rn surface exhalation rate ranges from 4 × 10−2 to 1.6 × 10−0 mBq m−2 s−1 with an average of 4 × 10−1 mBq m−2 s−1.
3.2 Activity concentration of 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K in building materials
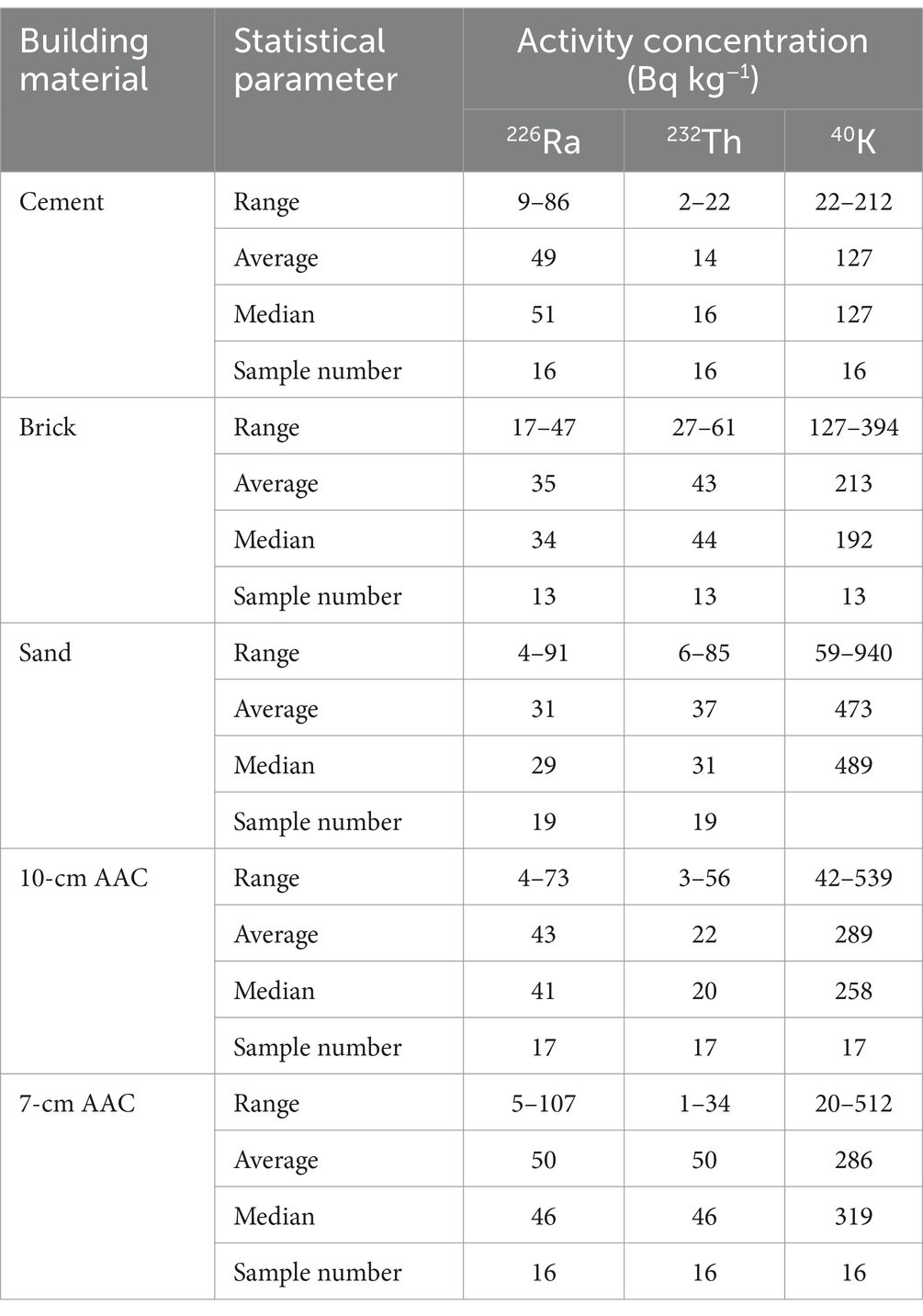
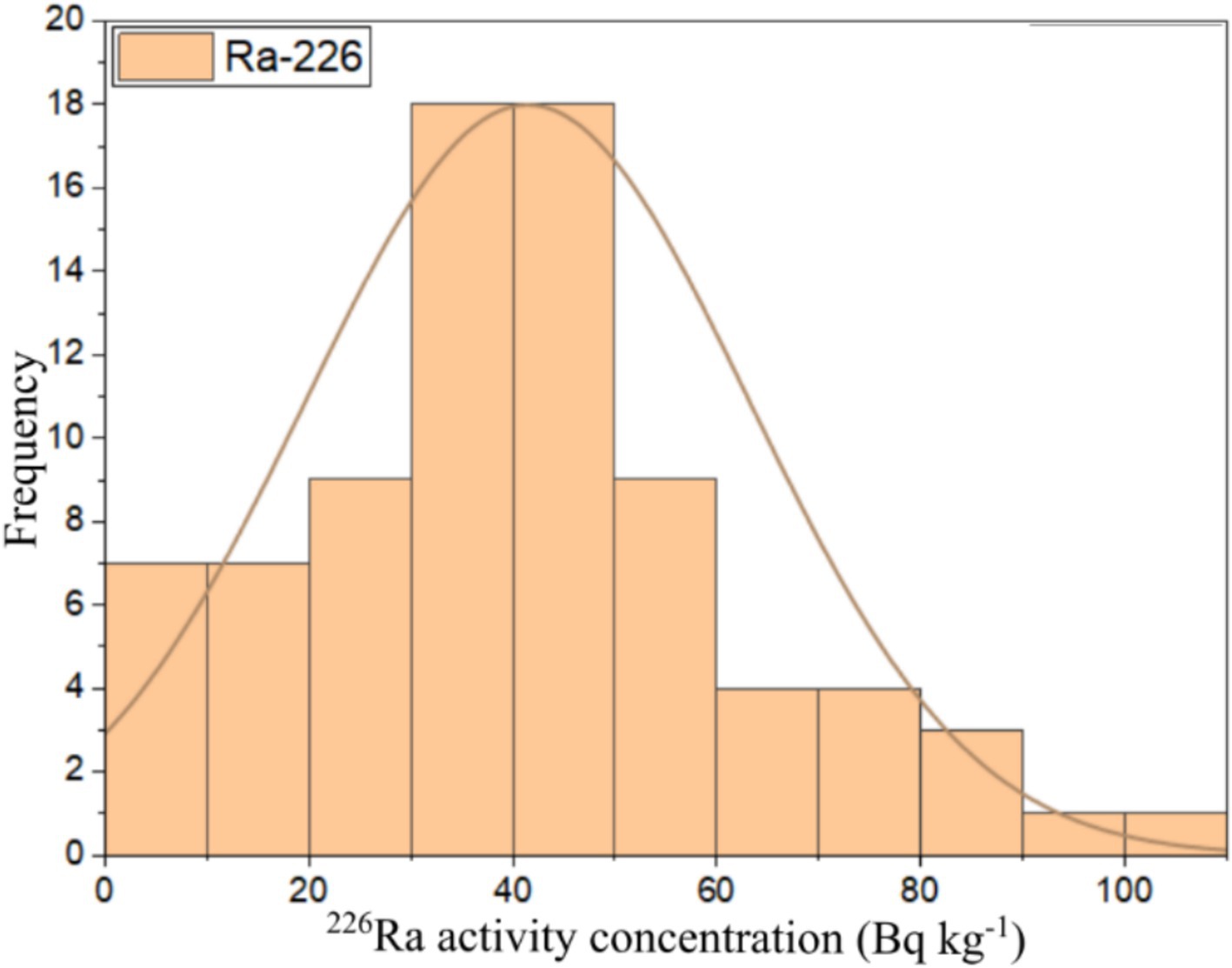
The results obtained from gamma spectrometry analysis of the building materials to determine 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K activity concentrations were presented in Table 3. The 226Ra activity concentration values ranged from 4 ± 0.2 to 107 ± 4 Bq kg−1; 232Th activity concentration ranged from 1 ± 0.1 to 85 ± 3 Bq kg−1; and 40K activity concentration ranged from 20 ± 1 to 940 ± 26 Bq kg−1. The lowest 226Ra activity concentration came from the 10-cm thick AAC sample (A4) obtained from the Pondok Cabe area. In comparison, the highest value came from the 7-cm thick AAC sample (I5) obtained from the Cimanggu area, and the lowest 232Th activity concentration came from the 7-cm thick AAC sample (A5) obtained from the Pondok Cabe area. In comparison, the highest 232Th activity concentration came from a sand sample (N1) obtained from the Bambu Apus area, and the lowest 40K activity concentration came from a 7-cm thick AAC sample (A5) obtained from the Pondok Cabe area. In contrast, the highest 40K activity concentration came from a sand sample (H1) obtained from the Lebak Bulus area.
3.3 Indoor 222Rn activity concentration originated from the building materials, activity index, and annual effective dose received by an adult individual from different exposure pathways
Using the typical room size in the study area and the average 226Ra content of the building materials, the contribution of the building materials to the indoor 222Rn activity concentration was calculated to be 28 Bq m−3. The activity index was calculated and ranged from 0.2 to 0.5, with an average of 0.3. The highest value of the activity index was obtained from 7-cm AAC, while the lowest value came from cement. Furthermore, the annual effective doses from different exposure pathways for various building materials calculated using the RESRAD-BUILD computer code are presented in Table 4. In a realistic situation, a typical house constructed with a mixture of building materials generated annual effective doses of 0.01 mSv by external directly from the source, 1.6 × 10−6 mSv by ingestion from deposition, and 0.1 mSv from 222Rn. The total annual effective derived from these exposures in the typical house is 0.11 mSv.
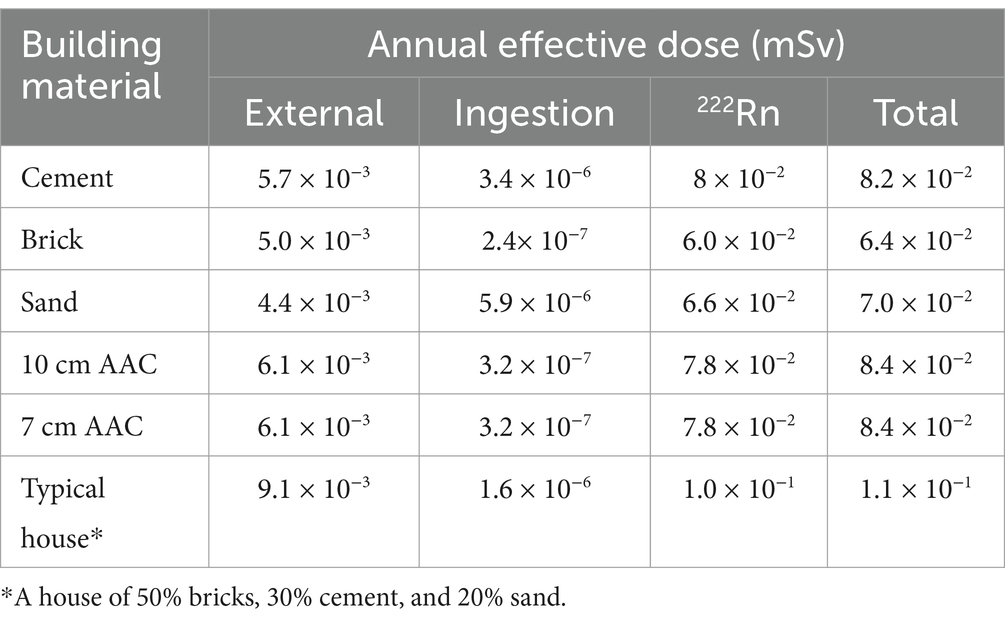
Table 4. The annual effective dose received by an individual living in the house from the building materials studied.
4 Discussion
4.1 222Rn surface exhalation rates in building materials
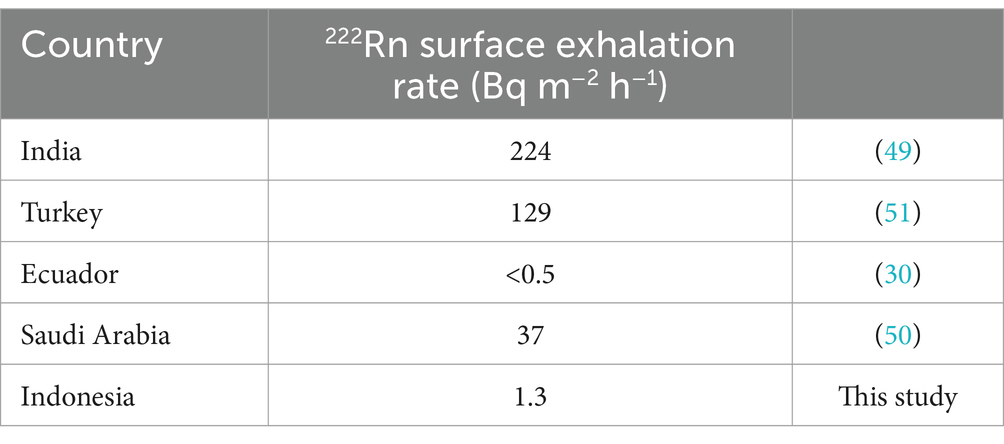
The average 222Rn surface exhalation rate values of the building materials studied were lower than the global average value estimated at 1.6 × 101 mBq m−2 s−1 (45). Surface exhalation rate measurements are essential to determine potential high-risk areas due to 222Rn inhalation (35). Among the all-studied building materials, the lowest 222Rn surface exhalation rate value comes from a brick sample (E3) from Serpong. In contrast, the highest value comes from a 10-cm thick AAC sample (I4) from Cimanggu. The 222Rn surface exhalation rate value varies from one sample to another. Factors that may influence the 222Rn exhalation rate are the level of 226Ra content in the material for 222Rn surface exhalation rate, grain size, porosity, humidity, 222Rn diffusion in the material’s pores, and changes in pressure and material texture (47). The 222Rn surface exhalation rate of building material with other countries was presented in Table 5. For comparison purposes, the 222Rn exhalation rate of bricks for selected countries was expressed in Bq m-2 h-1. It is noted that the results obtained in this remain lower than those of Turkey, Saudi Arabia, and India (48–50), but in the range of the results found in Ecuador (30). The 222Rn surface exhalation rate level does not pose a significant risk to the public regarding the 222Rn exhalation rate. Furthermore, the frequency distribution of 222Rn activity concentration was shown in Figure 5, and was tested for its normality by using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test can be used for more than 50 samples. The conditions that must be met when carrying out the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test are if the significance value is more than 0.05, then the data used in the research has a normal distribution. However, on the contrary, if the significance value is less than 0.05, then the data used does not have a normal distribution (51).
4.2 Activity concentration of natural radionuclides in the building materials
The average activity concentration values of 232Th (21 Bq kg−1) and 40K (217 Bq kg−1) in all building materials studied did not exceed the global average values of 45 Bq kg−1 and 412 Bq kg−1. In comparison, the average values of the activity concentration of 226Ra (34 Bq kg−1) are close to the global average value of 32 Bq kg−1 based on UNSCEAR reports (4). A comparison between the results of 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K activity concentrations in this study with the results of similar studies reported in various countries was shown in Table 6. In this study, the highest 226Ra activity concentration value was obtained at 42 Bq kg−1, lower than Italy and Malaysia; the highest 232Th activity was 42 Bq kg−1, lower than India, China, and Malaysia, while the highest 40K activity was 390 Bq kg−1 lower than Malaysia, China, Iran, Italy. The concentration values of natural radionuclides in building materials vary from one country to another. Variations in the activity concentration values of natural radionuclide activity may be caused by differences in mineral content in the soil and the geographical origin of the raw materials (17). The high activity concentration of 226Ra indicates the high uranium activity concentration in the soil and rocks in the raw material source area. The high activity concentration of 226Ra indicates the high uranium concentration in the soil and rocks in the raw material source area. A high activity concentration of 226Ra will have the potential for high 222Rn gas released by the material. High 232Th activity concentration activity will have the potential for high levels of thoron gas released by the material (24). On the results of research that has been carried out, the activity concentrations of 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K in sand samples (D1, G1, H1, and L1) and 10 cm thick AAC (N3) have values higher than the global average according to UNSCEAR (4). Sand samples with natural radionuclide concentrations exceeding the global average were obtained from different regions but came from the same mining area, namely Rangkasbitung. According to Lebak Regency Regional Regulation Number 2 of 2014, there are 25 sand mineral mining areas in Lebak Regency, one of which is the Rangkasbitung area (51). AAC samples with natural radionuclide concentrations higher than the global average come from the Tangerang, Gunung Sindur, and Serang areas. The high activity concentration values of 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K in these materials do not come from contamination but from natural radionuclides in the source materials.
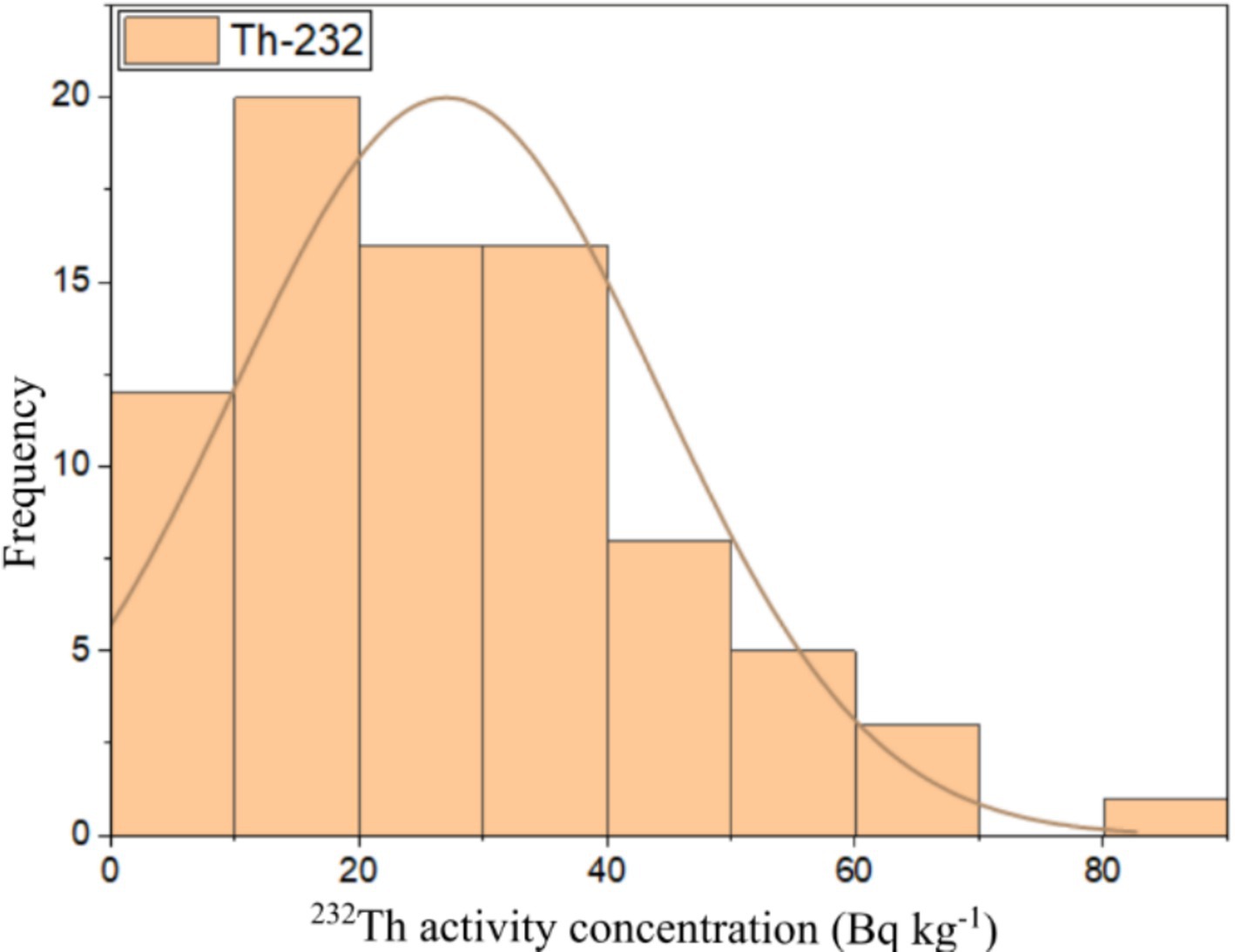
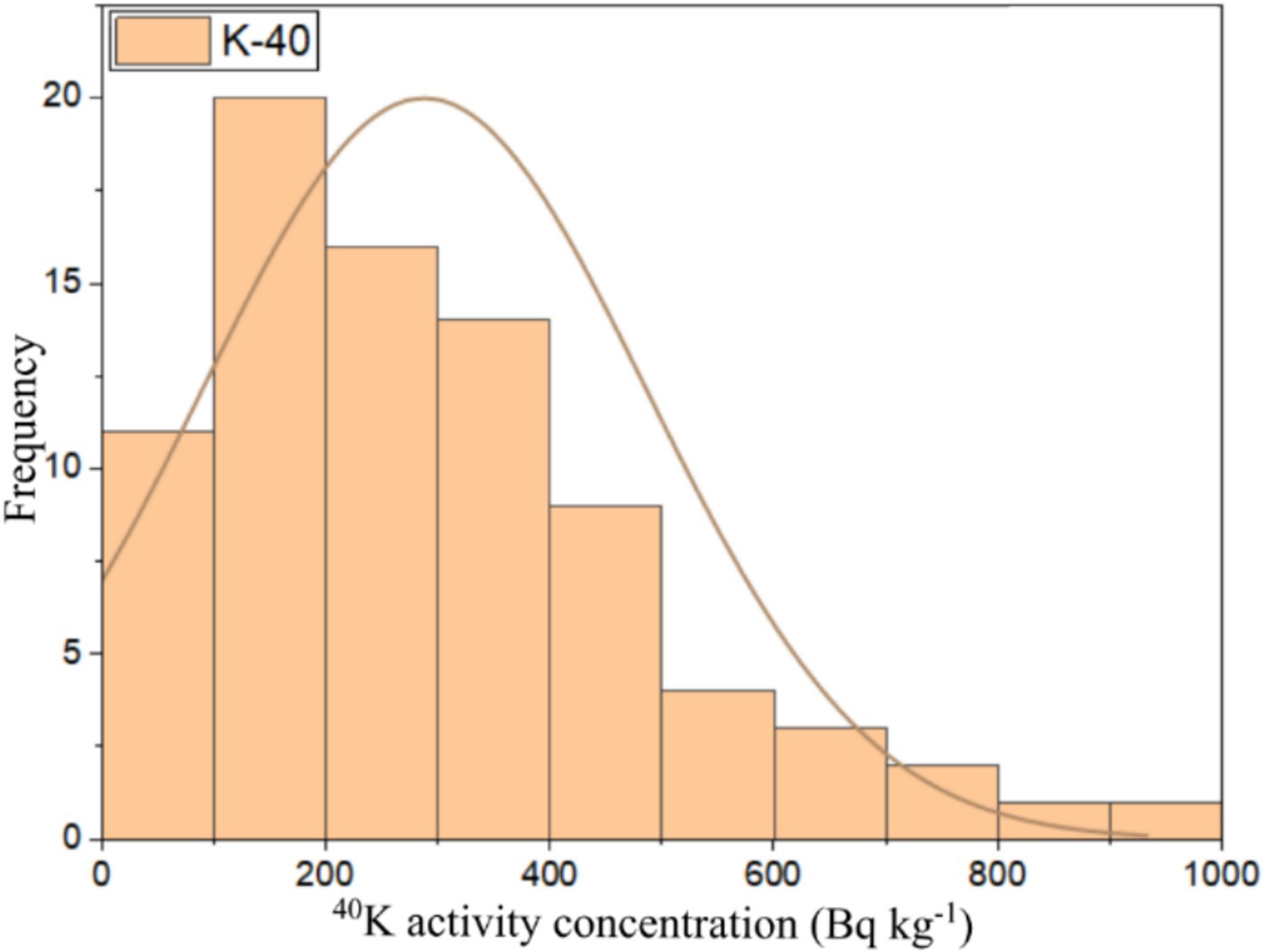
This study used numerical and graphical methods to investigate the normality distribution of 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K activity concentrations in building material samples. All statistical analyses were performed using ORIGIN PRO 2023 software (student version). The frequency distribution of radionuclides in building materials was assessed using the Kolmogorov–Smirnov normality test with significance values of 0.46, 0.67, and 0.06 for 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K, respectively. As all the significance values were more than 0.05, all the radionuclide distributions had a normal distribution. The graphical representation of the data distributions of 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K were presented in the form of histograms shown in Figures 6–8, respectively. It can be seen that 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K are distributed normally or lognormally.
4.3 Indoor 222Rn from building material, activity index, and effective dose from different pathways
The indoor 222Rn concentration derived from building materials calculated in this study is lower than the global average value of 40 Bq m−3, considerably less than the WHO reference value of 100 Bq m−3, and the Indonesian national reference level of 300 Bq m−3 (52). However, it exceeds the values obtained by Ndjana et al., where the authors reported values of 10 and 7 Bq m−3 from building materials (16). Therefore, a large indoor 222Rn survey should be undertaken in future studies. As presented in the results section, the effective dose from 222Rn represents 92% of the total effective inhalation dose. The activity index introduced by the IAEA to assess the radiological risk of natural radionuclides contained in building materials, as calculated in this study, was low. The activity index average value of 0.3 was below the reference value of 1 and does not require any restriction from their use (43). Also, the total annual effective doses from different exposure pathways calculated presented values ranging from 6.4 × 10−2 to 1.1 × 10−1 mSv depending on the building materials type. For the typical house built using a mixture of building materials, the total annual effective dose of 0.11 mSv was less than the global average value of 2.4 mSv, which resulted from all natural sources combined. This total annual effective dose is in the range of the results found in Ecuador by Tene et al. while studying the radiological exposure from building materials, and the range was from 0.019 up to 0.112 mSv (30).
5 Conclusion
In this study, a safety assessment of radiological hazards in building materials was conducted to ensure a sustainable environment. 81 building material samples were collected from 17 regional areas in Jakarta and its surrounding areas. The 222Rn surface exhalation rate from the collected building materials ranges from 4 × 10−2 to 1.6 × 100 mBq m−2 s−1 with an average of 4 × 10−1 mBq m−2 s−1. The average 222Rn surface exhalation rate of the building materials studied was much lower than the global average value of 16 mBq m−2 s−1 (45). The average activity concentration values of 232Th (21 Bq kg−1) and 40K (217 Bq kg−1) in all building materials studied are lower than the global average values of 45 Bq kg−1 and 412 Bq kg−1. In comparison, the average value of the activity concentration of 226Ra (34 Bq kg−1) is close to the global average value of 32 Bq kg−1 (4). Additionally, indoor 222Rn derived from building materials was calculated along with the activity index (I), and the computer code RESRAD-BUILD was used to estimate the total annual effective dose received from different exposure pathways for a typical house built using a mixture of building materials. It was found that the average activity index was below unity, and the total annual effective dose received was 0.11 mSv, in which 222Rn alone contributes to 92% of this value, which indicates the need for a large indoor 222Rn survey in the study area. In line with the SDGs defined by the United Nations, the building materials studied presented radionuclide concentrations and the activity index below the reference values of remediation action to be taken. From a radiological exposure perspective, these building materials are considered safe for building homes, offices, industries, and infrastructure.
Author’s note
What are the main findings? (1) The 222Rn exhalation rate ranges from 4 × 10−2 to 1.6 × 100 mBq m−2 s−1 with an average of 4 × 10−1 mBq m−2 s−1. The average activity concentration values of 226Ra, 232Th, and 40K were 34, 21, and 217 Bq kg−1, respectively, across all the building materials studied. (2) Furthermore, indoor 222Rn was derived from building materials, and the activity index was calculated. The computer code RESRAD-BUILD was used to calculate the annual effective dose received from different exposure pathways. The total annual effective dose received in a typical house constructed with a mixture of building materials was 0.11 mSv, and 222Rn alone contributed 92% of the total. What is the implication of the main finding? (1) From the measurement results, it was found that the building materials in Jakarta and its surrounding areas do not possess significant concerns regarding radioactivity. The building materials we studied showed radionuclide concentrations below the recommended reference values for remediation action, aligning perfectly with the SDGs. From a radiological exposure perspective, these building materials are considered safe for building homes, offices, industries, and infrastructure. (2) The high contribution of 222Rn to the total annual effective dose indicates the need for a large indoor 222Rn survey in the study area. Furthermore, this study can aid the regulatory body’s willingness to establish standards in the construction sector.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
EN: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. OBM: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. Wahyudi: Data curation, Software, Writing – original draft. RP: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. RM: Writing – review & editing. KM: Writing – review & editing. AT: Writing – review & editing. AR: Writing – review & editing. RK: Writing – review & editing. EF: Writing – review & editing. NH: Writing – review & editing. IW: Writing – review & editing. IR: Writing – review & editing. LR: Writing – review & editing. DP: Writing – review & editing. HP: Validation, Writing – review & editing. ST: Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Ministry of Research, Technology and Higher Education of Indonesia, the Indonesia Endowment Funds for Education (LPDP), and The National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN) through the research fund Riset Inovasi untuk Indonesia Maju (RIIM) Grant No.: RIIM-16 (EDN), the Management Talenta-BRIN through the Postdoctoral program 2023 (EDN and OBM), and the National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN) through HITN (Det-RoC-091).
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Institute of Geological and Mining Research of Cameroon (IRGM) for approving Oumar Bobbo Modibo to undertake a postdoctoral program at BRIN.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1539957/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Omer, MAB, and Noguchi, T. A conceptual framework for understanding the contribution of building materials in the achievement of sustainable development goals (SDGs). Sustain Cities Soc. (2020) 52:101869. doi: 10.1016/j.scs.2019.101869
2. Allen, JG, MacNaughton, P, Laurent, JGC, Flanigan, SS, Eitland, ES, and Spengler, JD. Green buildings and health. Curr Environ Health Rep. (2015) 2:250–8. doi: 10.1007/s40572-015-0063-y
3. Thurston, J. NCRP report no. 160: ionizing radiation exposure of the population of the United States. Phys Med Biol. (2010) 55:6327. doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/55/20/6327
4. UNSCEAR. Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation UNSCEAR. Report to the general assembly with scientific annexes, vol. I. New York: (2008). 2010 p.
5. BEIR VI. Health effects of exposure to radon: BEIR VI. National Research Council, editor. Washington, D.C.: National Academy Press (1999).
6. Clement, CH, Tirmarche, M, Harrison, JD, Laurier, D, Paquet, F, Blanchardon, E, et al. Lung Cancer risk from Radon and progeny and statement on Radon. Ann ICRP. (2010) 40:1–64. doi: 10.1016/j.icrp.2011.08.011
7. Al-Zoughool, M, and Krewski, D. Health effects of radon: a review of the literature. Int J Radiat Biol. (2009) 85:57–69. doi: 10.1080/09553000802635054
8. Amin, RM. A study of radon emitted from building materials using solid state nuclear track detectors. J Radiat Res Appl Sci. (2015) 8:516–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jrras.2015.06.001
9. Darby, S, Hill, D, Auvinen, A, Barros-Dios, JM, Baysson, H, Bochicchio, F, et al. Radon in homes and risk of lung cancer: collaborative analysis of individual data from 13 European case-control studies. Br Med J. (2005) 330:223–6. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38308.477650.63
10. Krewski, D, Lubin, JH, Zielinski, JM, Alavanja, M, Catalan, VS, William Field, R, et al. A combined analysis of north American case-control studies of residential Radon and lung Cancer. J Toxicol Environ Health A. (2006) 69:533–97. doi: 10.1080/15287390500260945
11. IARC. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. Ionizing radiation, part 2: some internally deposited radionuclides International Agency for Research on Cancer. Lyon, France: World Health Organization (2001). 595 p.
12. WHO In: H Zeeb and F Shannoun, editors. Handbook on indoor Radon a public health perspective. France: World Health Organization (2009)
13. Somsunun, K, Prapamontol, T, Pothirat, C, Liwsrisakun, C, Pongnikorn, D, Fongmoon, D, et al. Estimation of lung cancer deaths attributable to indoor radon exposure in upper northern Thailand. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:5169. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09122-y
14. US EPA. EPA assessment of risks from Radon in homes. (2003). Available at:https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-05/documents/402-r-03-003.pdf [Accessed August 21, 2024]
15. Guy Blanchard, D, Engola Louis, N, Nkoulou Joseph Emmanuel, NI, Siaka Yvette Flore, T, and Daniel, B. NORM measurements and radiological Hazard assessment in the gold mining areas of eastern Cameroon. Radiation Environ Med. (2017) 6:22–8. doi: 10.51083/radiatenvironmed.6.1_22
16. Ndjana Nkoulou, JE, Manga, A, Saïdou, GO, Sainz-Fernandez, C, and Kwato Njock, MG. Natural radioactivity in building materials, indoor radon measurements, and assessment of the associated risk indicators in some localities of the Centre region, Cameroon. Environ Sci Pollut Res. (2022) 29:54842–54. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-19781-z
17. Khatun, MA, Ferdous, J, and Haque, MM. Natural radioactivity measurement and assessment of radiological hazards in some building materials used in Bangladesh. J Environ Prot. (2018) 9:1034–48. doi: 10.4236/jep.2018.910064
18. BPS-Statistics Indonesia. Statistical yearbook of Indonesia 2023. Jakarta: Statistics Agency of Indonesia (2023).
19. Anggraeni, DF, Wijaya, GS, and Muharini, A. Analysis of external radiation exposure from building materials using resrad-build (case study: perumnas bumi guwosari). J Phys Conf Ser. (2020) 1436:012062. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1436/1/012062
20. Estokova, A, Singovszka, E, and Vertal, M. Investigation of building materials’ radioactivity in a historical building—a case study. Materials. (2022) 15. doi: 10.3390/ma15196876
21. Patale, Z, Guillaume Samuel, B, Kranrod, C, Modibo, OB, Didier, TSS, Abba, HY, et al. Contribution of Thoron and its progeny to the effective dose by inhalation in the uranium-thorium bearing regions of Mayo Kebbi and Guéra in Chad. Health Phys. (2024) 127:588–99. doi: 10.1097/hp.0000000000001849
22. Tokonami, S, Kranrod, C, Kazymbet, P, Omori, Y, Bakhtin, M, Poltabtim, W, et al. Residential radon exposure in Astana and Aqsu, Kazakhstan. J Radiol Prot. (2023) 43:023501. doi: 10.1088/1361-6498/acda41
23. Abdullahi, S, Ismail, AF, and Samat, S. Determination of indoor doses and excess lifetime cancer risks caused by building materials containing natural radionuclides in Malaysia. Nucl Eng Technol. (2019) 51:325–36. doi: 10.1016/j.net.2018.09.017
24. Safitri, RA, Setiawati, E, Gede, D, and Wijaya, S. Analisis aktivitas radionuklida alam dan dosis paparan radiasi pada material bangunan. Young Phys J. (2017) 6:1–8.
25. Imani, M, Adelikhah, M, Shahrokhi, A, Azimpour, G, Yadollahi, A, Kocsis, E, et al. Natural radioactivity and radiological risks of common building materials used in Semnan Province dwellings. Iran Environ Sci Pollut Res. (2021) 28:41492–503. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-13469-6/Published
26. Nurdiani, N, and Katarina, W. The study of building material quality of a low cost flats in Jakarta. IOP conference series: Earth and environmental science. Institute of Physics Publishing (2018)
27. Bulut, HA, and Radon, N. Concrete, buildings and human health—a review study. Buildings. (2024) 14. doi: 10.3390/buildings14020510
28. US EPA. Natural radioactivity in building materials. United States Environmental Protection Agency (2024) Available at:https://www.epa.gov/radtown/natural-radioactivity-building-materials [Accessed October 22, 2024]
29. Johan, Willem. Jakarta capital city, Indonesia. (2024) Available at:https://www.britannica.com/place/Indonesia/Soils [Accessed January 17, 2025]
30. Tene, T, Vacacela Gomez, C, Tubon Usca, G, Suquillo, B, and Bellucci, S. Measurement of radon exhalation rate from building materials: the case of Highland region of Ecuador. Constr Build Mater. (2021) 293:123282. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123282
31. Aremu, AA, Oni, OM, Oladapo, OO, Ayanlola, PS, and Lawal, MK. Determination of radon exhalation rate from different mixture of concrete. Mat Today Proc. (2023):47–50. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2023.02.224
32. Pacheco-Torgal, F, and Jalali, S. Toxicity of Building Materials a key issue in sustainable construction. Int J Sustain Eng (2012), 4:281–287. doi: 10.1080/19397038.2011.569583
33. Alhamdi, WA, and Abdullah, KM. Determination of radium and Radon exhalation rate as a function of soil depth of Duhok Province - Iraq. J Radiat Res Appl Sci. (2021) 14:486–94. doi: 10.1080/16878507.2021.1999719
34. Tamakuma, Y, Kranrod, C, Jin, Y, Kobayashi, H, Nugraha, ED, Sanpei, A, et al. Characterization of commercially available active-type radon–thoron monitors at different sampling flow rates. Atmosphere (Basel). (2021) 12. doi: 10.3390/atmos12080971
35. Hosoda, M, Nugraha, ED, Akata, N, Yamada, R, Tamakuma, Y, Sasaki, M, et al. A unique high natural background radiation area – dose assessment and perspectives. Sci Total Environ. (2021) 750:142346. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142346
36. Pradana, R, Nugraha, ED, Wahyudi, W, Untara, U, Wiyono, M, Devriany, A, et al. Car-borne survey and dose assessment from external radiation exposure in Bangka Island. Environ Sci Pollut Res. (2023) 30:89280–92. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-28640-4
37. Oumar Bobbo, M, Yang, G, Saïdou, TH, Akata, N, Kranrod, C, Hosoda, M, et al. Environmental radioactivity measurements in soil using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry and gamma-ray spectrometry in various areas in Cameroon. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. (2024) 333:2557–65. doi: 10.1007/s10967-023-09033-w
38. Rosianna, I, Nugraha, ED, Syaeful, H, Putra, S, Hosoda, M, Akata, N, et al. Natural radioactivity of laterite and volcanic rock sample for radioactive mineral exploration in mamuju, Indonesia. Geosciences (Switzerland). (2020) 10:1–13. doi: 10.3390/geosciences10090376
39. JCGM. Evaluation of measurement data-guide to the expression of uncertainty in measurement. JCGM 100:2008. Joint Committee for Guides in metrology. (2008). Available at:www.bipm.org
40. Nugraha, ED, Hosoda, M, Kusdiana, U, Mellawati, J, Nurokhim, TY, Ikram, A, et al. Comprehensive exposure assessments from the viewpoint of health in a unique high natural background radiation area, Mamuju, Indonesia. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:14578. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93983-2
41. NEA group of experts. Exposure to radiation from natural radioactivity in building materials. Paris. (1979). Available at:https://www.oecd-nea.org/upload/docs/application/pdf/2019-12/exposure-to-radiation-1979.pdf [Accessed November 17, 2024]
42. Yu, C., LePoire, D.J., Cheng, J.J., Gnanapragasam, E., Kamboj, S., Arnish, J., et al. User’s manual for RESRAD-BUILD version 3. (2003). Available at:http://www.doe.gov/bridge
43. IAEA. IAEA safety standards series no. SSG-32 protection of the public against exposure indoors due to radon and other natural sources of radiation. (2015). Available at:http://www-ns.iaea.org/standards/
44. Argonne National Laboratory. RESRAD family of codes. (2024) Available at:https://resrad.evs.anl.gov [Accessed October 25, 2024]
45. Dieu Souffit, G, Saïdou, S, Bobbo Modibo, O, Lepoire, D, and Tokonami, S. Risk assessment of exposure to natural radiation in soil using RESRAD-ONSITE and RESRAD-BIOTA in the cobalt-nickel bearing areas of Lomié in eastern Cameroon. Radiat Ther. (2022) 2:177–92. doi: 10.3390/radiation2020013
46. Abdullahi, S, Ismail, AF, and Yasir, MS. Radiological hazard analysis of Malaysia’s ceramic materials using generic and RESRAD-BUILD computer code approach. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. (2020) 324:301–15. doi: 10.1007/s10967-020-07070-3
47. UNSCEAR. Sources and effects of ionizing radiation: UNSCEAR 2000 report to the general assembly with scientific annexes, vol. 1. New York: UNSCEAR (2000).
48. Sharma, N, Singh, J, Esakki, SC, and Tripathi, RM. A study of the natural radioactivity and radon exhalation rate in some cements used in India and its radiological significance. J Radiat Res Appl Sci. (2016) 9:47–56. doi: 10.1016/j.jrras.2015.09.001
49. Soniya, SR, Jojo, PJ, and Khandaker, MU. Study of radium content and radon exhalation rates in raw building materials used in southern India. Physics Open. (2023) 17:100169. doi: 10.1016/j.physo.2023.100169
50. Lyngkhoi, B, and Nongkynrih, P. Radioactivity in building materials and assessment of risk of human exposure in the east Khasi Hills district, Meghalaya, India. Egypt J Basic App Sci. (2020) 7:194–209. doi: 10.1080/2314808X.2020.1781747
51. Çam Kaynar, S, Özbey, E, and Ereeş, FS. Determination of radon exhalation rate and natural radioactivity levels of building materials used in Istanbul-Turkey. J Radioanal Nucl Chem. (2015) 305:337–43. doi: 10.1007/s10967-015-3987-7
52. Indonesian Law. Peraturan Pemerintah No 45 tahun 2023 tentang Keselamatan Radiasi Pengion dan Keamanan Zat Radioaktif. (2023). Available at:https://jdih.bapeten.go.id/en/dokumen/peraturan/peraturan-pemerintah-no-45-tahun-2023-tentang-keselamatan-radiasi-pengion-dan-keamanan-zat-radioaktif [Accessed November 17, 2024]
53. Shoeib, MY, and Thabayneh, KM. Assessment of natural radiation exposure and radon exhalation rate in various samples of Egyptian building materials. J Radiat Res Appl Sci. (2014) 7:174–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jrras.2014.01.004
54. Al-Sulaiti, H, Alkhomashi, N, Al-Dahan, N, Al-Dosari, M, Bradley, DA, Bukhari, S, et al. Determination of the natural radioactivity in Qatarian building materials using high-resolution gamma-ray spectrometry. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res, Sect A. (2011) 652:915–9. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2011.01.020
55. Raghu, Y, Ravisankar, R, Chandrasekaran, A, Vijayagopal, P, and Venkatraman, B. Assessment of natural radioactivity and radiological hazards in building materials used in the Tiruvannamalai District, Tamilnadu, India, using a statistical approach. J Taibah Univ Sci. (2017) 11:523–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jtusci.2015.08.004
56. Al-Sewaidan, HA. Natural radioactivity measurements and dose rate assessment of selected ceramic and cement types used in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. J King Saud Univ Sci. (2019) 31:987–92. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2019.04.001
57. Tuo, F, Peng, X, Zhou, Q, and Zhang, J. Assessment of natural radioactivity levels and radiological hazards in building materials. Radiat Prot Dosim. (2020) 188:316–21. doi: 10.1093/rpd/ncz289
58. Righi, S, and Bruzzi, L. Natural radioactivity and radon exhalation in building materials used in Italian dwellings. J Environ Radioact. (2006) 88:158–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvrad.2006.01.009
Keywords: building material, natural radioactivity, radon, RESRAD-BUILD, effective dose, exhalation rate
Citation: Nugraha ED, Modibo OB, Wahyudi, Pradana R, Merdekawati RA, Megagasri K, Topandi A, Rachman AN, Kurniawan R, Fajrianshah EA, Hidayati N, Winarni ID, Rosianna I, Rixson L, Purnama DS, Prasetio H and Tokonami S (2025) Radon exhalation rate and natural radioactivity in the building materials used in metropolitan Jakarta and its surrounding areas, Indonesia. Front. Public Health. 13:1539957. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1539957
Edited by:
Christian Di Carlo, National Institute of Health (ISS), ItalyReviewed by:
Shams A. M. Issa, Al-Azhar University, EgyptTrilochana Shetty, Institut de Radioprotection et de Sûreté Nucléaire, France
Copyright © 2025 Nugraha, Modibo, Wahyudi, Pradana, Merdekawati, Megagasri, Topandi, Rachman, Kurniawan, Fajrianshah, Hidayati, Winarni, Rosianna, Rixson, Purnama, Prasetio and Tokonami. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Eka Djatnika Nugraha, ZWthZDAwMUBicmluLmdvLmlk
 Eka Djatnika Nugraha
Eka Djatnika Nugraha Oumar Bobbo Modibo
Oumar Bobbo Modibo Wahyudi
Wahyudi Radhia Pradana1,2
Radhia Pradana1,2 Rusbani Kurniawan
Rusbani Kurniawan Evans Azka Fajrianshah
Evans Azka Fajrianshah Ilma Dwi Winarni
Ilma Dwi Winarni Ilsa Rosianna
Ilsa Rosianna Leons Rixson
Leons Rixson Dikdik Sidik Purnama
Dikdik Sidik Purnama Shinji Tokonami
Shinji Tokonami