- 1Department of Physical Education, Qufu Normal University, Qufu, China
- 2School of Physical Education, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
- 3School of Tourism, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Introduction: Smoking poses a significant threat to global human health, making smoking cessation a controllable means of preventing mortality. Exercise, as a means of promoting a healthy lifestyle, offers substantial benefits to individuals attempting to quit smoking. However, due to variations in experimental populations and conditions, the specific effects and benefits of exercise on smoking cessation remain unclear. In this meta-analysis, we comprehensively evaluated the withdrawal effects of different intensities of exercise on tobacco-dependent individuals.
Methods: Statistical analysis and graphing were performed using Stata 14 and Review Manager 5.4 software. A total of 47 literatures, encompassing 57 randomized controlled trials and involving 4,267 tobacco-dependent individuals, were included.
Results: The meta-analysis results showed that long-term exercise had no significant difference or impact on the degree of tobacco dependence between the exercise and control groups. However, acute exercise was associated with increased tobacco craving (desire and intensity) and more pronounced withdrawal symptoms.
Discussion: Acute aerobic exercise can significantly reduce craving and withdrawal symptoms among individuals attempting to quit smoking, demonstrating a certain role in smoking cessation. Acute aerobic exercise emerges as the most effective form of physical exercise for intervening in tobacco dependence.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, CRD42024550014.
1 Introduction
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) report, approximately 8 million people globally die from tobacco-related causes annually, with 7 million deaths attributed directly to smoking and around 1.2 million to exposure to secondhand smoke (1). Smoking, as a significant factor contributing to the high incidence of malignancies, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, respiratory diseases, diabetes, and other illnesses, poses a severe threat to human health (2). Furthermore, studies have shown that during the COVID-19 pandemic, smokers had a higher mortality rate due to viral pneumonia compared to non-smokers (3).
Therefore, addressing the difficulty of smoking cessation among smokers has become an issue worthy of in-depth exploration. There are various ways to assist in smoking cessation, such as psychological intervention, self-regulation, pharmacotherapy, and food substitution (4). Although these methods have certain effects on smoking cessation, they cannot meet the goal of long-term abstinence, and the results are not significant (5). For example, psychological intervention and pharmacotherapy may have certain dependency and side effects, making it difficult for smokers to quit smoking independently (6). Food substitution and other methods may lead to overeating and cause physical harm (7).
Through reviewing related literatures, it is known that exercise can effectively help smokers reduce smoking frequency, alleviate withdrawal symptoms, improve cardiopulmonary function, reduce anxiety about weight gain, and obtain social support and encouragement (8–10). This is because exercise releases chemicals such as dopamine by increasing neurotransmitter regulation, thereby alleviating withdrawal symptoms during the smoking cessation process (11). At the same time, exercise, as a positive alternative behavior, can replace smoking, which is a negative behavior (12). However, due to variations in exercise intensity and frequency, academic research on the effectiveness of exercise interventions for smoking cessation has yet to yield definitive conclusions.
The necessity of studying the impact of exercise interventions on tobacco dependence is further underscored by previous research, such as the reviews conducted by Zhou et al. (13), Santos et al. (14) and Klinsphone et al. (9), which examined the effect of exercise interventions on smoking cessation. However, despite these efforts, several gaps remain in our understanding of this complex relationship. First, some studies have analyzed single or scattered outcome indicators, limiting our comprehensive understanding of the effects of exercise. For instance, previous research focused on smoking cessation rates and mood, but relatively overlooked other potential indicators such as sleep quality. Second, subgroup analyses were not sufficiently detailed or comprehensive. Previous research primarily examined the effects on smoking cessation rates and smoking cravings (13), neglecting other important aspects that could further identify differential factors. For example, the differential effects of exercise on depression among smokers have not been thoroughly explored. A more nuanced approach to subgroup analysis is essential for gaining a deeper understanding of how exercise interventions can impact tobacco dependence. Furthermore, the quality of studies included in previous meta-analyses has been deemed suboptimal (9, 13), potentially affecting the credibility of the results. Improving the overall quality of research in this field is crucial, and one way to achieve this is by increasing the sample size. In light of these limitations, the present meta-analysis aims to further explore and analyze the topic of exercise interventions on tobacco dependence, building upon previous systematic reviews. By including more studies and focusing on a more comprehensive set of outcome indicators, this study seeks to address the gaps identified in previous research.
In summary, despite existing research on the effects of exercise interventions on tobacco dependence, there remains a need for a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of this relationship. The present study contributes to this understanding by conducting a meta-analysis that includes a larger number of studies, employs stricter screening and inclusion criteria, selects more comprehensive outcome indicators, and performs detailed subgroup analyses according to various indicators.
2 Methods and materials
This study was conducted according to the latest PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines for reporting systematic reviews (15). The study has been registered on the Prospero website (Registration Number: CRD42024550014).
2.1 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
2.1.1 Inclusion criteria
(1) Study Type: randomized controlled trials (RCTs), regardless of whether blinding was used. The language was limited to English.
(2) Population: Adult patients with a history of smoking (excluding pregnant women) who met the diagnostic criteria for tobacco dependence according to the “Chinese Clinical Guidelines for Smoking Cessation 2015.”
(3) Interventions: The experimental group received interventions with varying intensities of exercise for smoking cessation; the control group received adjuvant therapies such as health education lectures, reading, or sitting quietly. Other adjuvant means related to smoking cessation were consistent between the two groups.
(4) Outcome Indicators: Based on the tobacco withdrawal symptoms outlined in the “Chinese Clinical Guidelines for Smoking Cessation 2015,” the outcome indicators were divided into nine categories. Smoking cessation rates: 7-day smoking cessation rate and continuous smoking cessation rate; smoking craving: Desire to Smoke (Dts) and Strength of Desire to Smoke (SoD); withdrawal symptoms: sleep quality, depression, irritability; emotions: negative emotions and positive emotions.
2.1.2 Exclusion criteria
(1) Studies involving pregnant women, lactating women, or patients with other conditions that could affect smoking cessation.
(2) Studies where data could not be accurately extracted or where data were missing.
(3) Studies with inconsistent adoption of data indicators.
(4) Duplicate publications.
(5) Studies that were not focused on smoking dependence.
(6) Studies with non-randomized or semi-randomized control designs.
(7) Studies where the experimental group did not involve exercise interventions.
2.2 Literature search
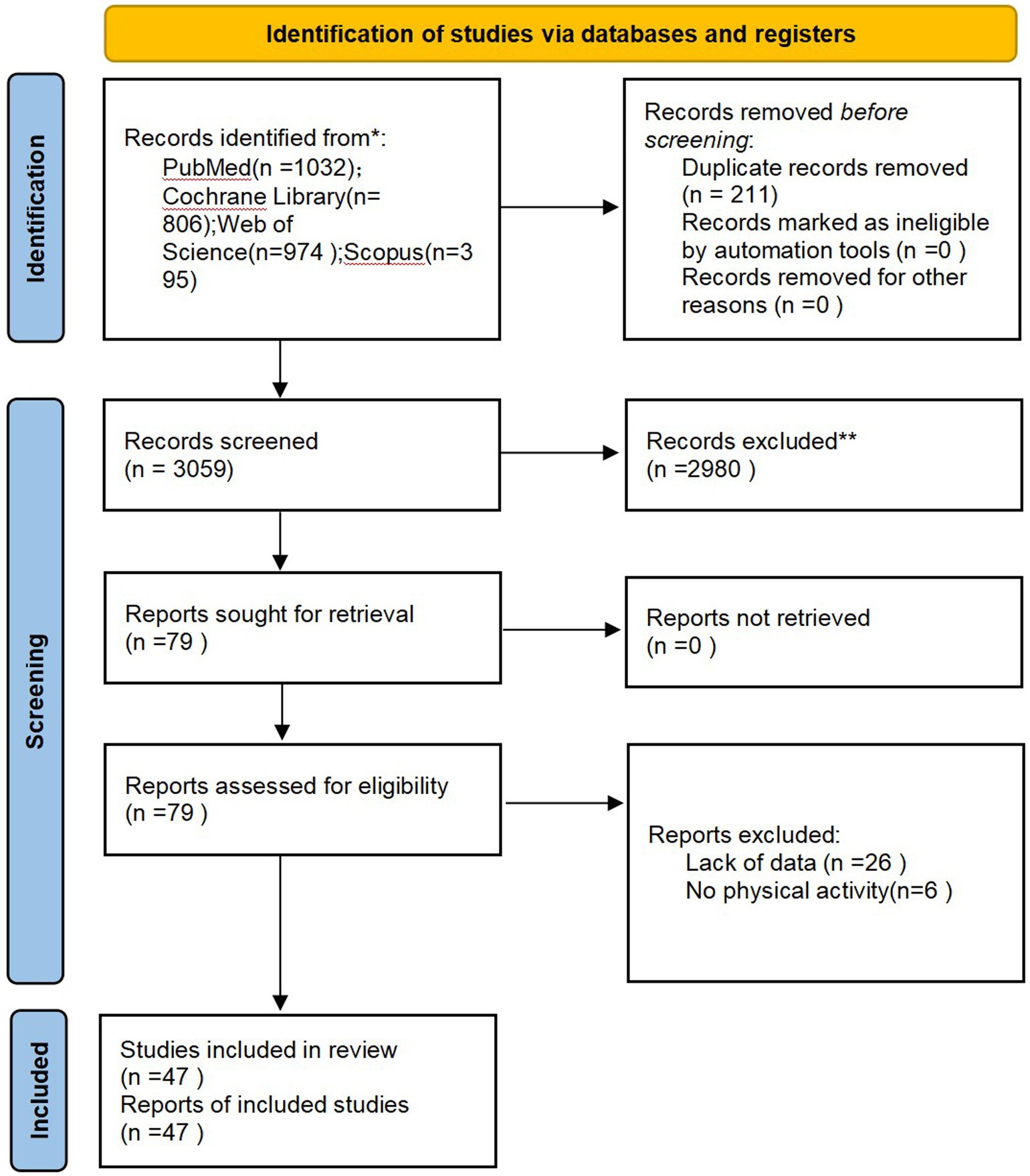
A computer-based search was conducted across the databases Web of Science, PubMed, The Cochrane Library, Embase, and Scopus to collect RCTs on exercise interventions for tobacco dependence. The search period covered from the inception of each database to May 2024. The search strategy combined the use of subject headings and free-text terms. Additionally, the references of the included studies were traced to supplement the acquisition of relevant literature. The search terms included: “Smoking,” “Exercises,” “Cessation,” “Acute Exercise,” and other relevant keywords (Figure 1).
2.3 Literature screening and data extraction
The literature search records were documented using EndNotes software. The literature retrieved from the databases was imported into EndNotes for further merging and screening to identify duplicate articles. Two researchers independently conducted the article screening process by initially examining the titles, abstracts, and keywords. In cases of disagreement, the researchers resolved the issues through consultation or discussion with a third party. The extracted information primarily included the publication year, authors, number of subjects, and basic information of the control group (age, gender, sample size, tobacco dependence level). Additionally, the exercise plans during the intervention process for both the experimental and control groups were extracted (type of exercise, duration of exercise, frequency of exercise, exercise duration, and exercise intensity). The outcome indicators for both groups before and after the intervention (mean values, standard deviations) and literature quality assessment information were also recorded.
2.4 Risk of bias assessment
The Review Manager software version 5.4 was used to conduct a risk of bias assessment among included studies. The evaluation items included: ① bias arising from the randomization process; ② bias due to deviations from intended interventions (effectiveness of intervention allocation); ③ bias in outcome measurement; and ④ bias in selective reporting of results. The evaluation results were categorized as “low risk,” “some concerns,” and “high risk.” Two evaluators independently conducted the methodological quality evaluation, and in cases of disagreement, consensus was reached based on a third-party opinion.
Utilizing the Cochrane “Risk of Bias” tool, the quality of the included RCTs was assessed based on seven criteria: random sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of participants and personnel, blinding of outcome assessment, completeness of outcome data, selective reporting of results, and other potential sources of bias. The research quality was classified into three levels: high, moderate, and low. The assessment of bias risk was independently conducted by two review authors, and in cases of disagreement, consensus was reached based on a third-party opinion.
2.5 Statistical analysis
The Review Manager software version 5.4 and Stata 14 were used for meta-analysis and data synthesis. The study data included dichotomous variables and continuous variables. For dichotomous variables (smoking cessation rates), the relative risk (RR) with a 95% confidence interval was summarized. For continuous variables (craving for tobacco, withdrawal symptoms, and mood), if the outcome measures and units were consistent, the weighted mean difference (WMD) was used; if different measurement methods and units were used, the standardized mean difference (SMD) was reported (16), with a 95% CI. Heterogeneity among study results was tested using I2, where I2 values of 25, 50, and 75% were considered as thresholds for low, moderate, and high heterogeneity, respectively. A fixed-effects model was selected for analysis when I2 was low (<50%); otherwise, a random-effects model was used. Sensitivity analysis was conducted by excluding trials with a risk of bias to evaluate the stability of the meta-analysis results. Additionally, subgroup analysis was employed to identify sources of heterogeneity and assess whether various factors influenced the effect size estimates. When more than 10 studies were included for an outcome measure, funnel plots and Egger’s test were used to detect publication bias.
3 Results
3.1 Results of literature screening and data extraction
A total of 3,207 literatures related to this topic were retrieved from various databases. After removing duplicates, screening by reading titles and abstracts, and excluding articles that were not randomized controlled trials, not related to smoking cessation, or did not involve exercise interventions, 78 articles remained. Upon reading the full texts, six articles were excluded due to intervention methods in the experimental group not involving exercise and 26 articles due to lack of available data. Finally, 47 studies were included in the study (the inclusion process is illustrated in Figure 2).
3.2 Characteristics of included studies
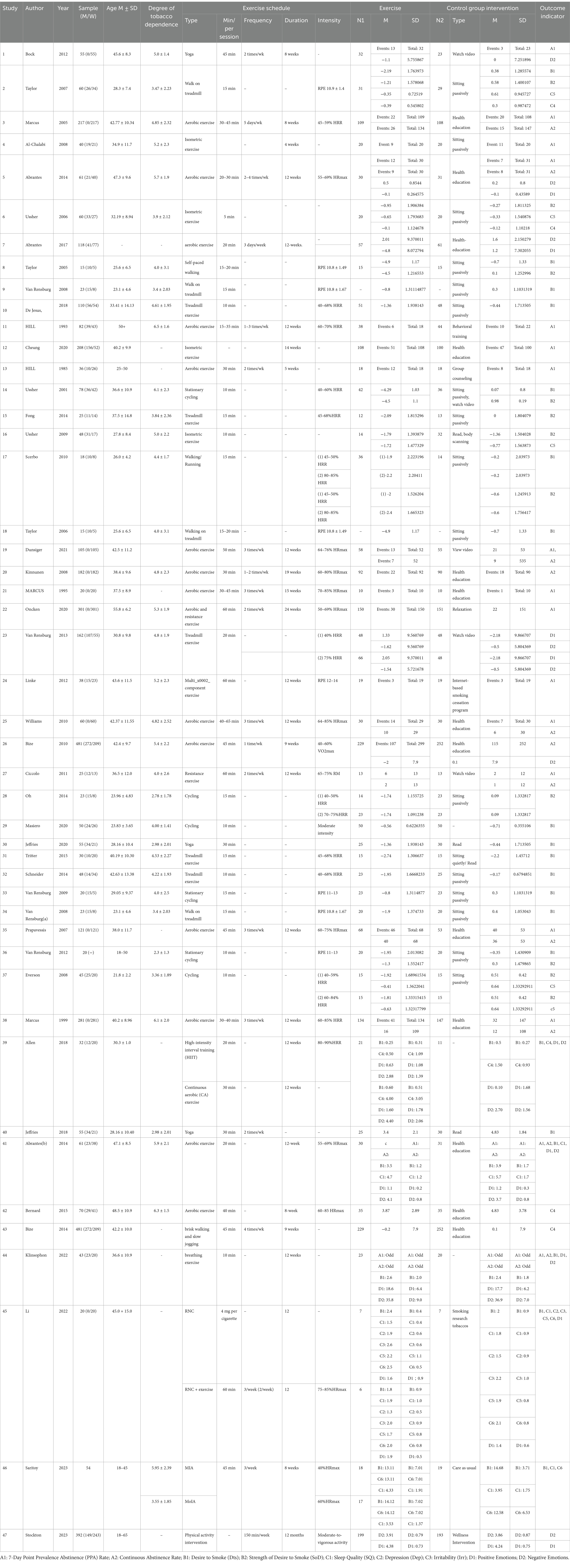
Table 1 provides an overview of the included studies. These 47 studies comprised a total of 57 RCTs, with five studies each including two RCTs. The meta-analysis included a total of 4,267 smokers. Among them, 10 studies focused solely on women, two studies did not specify the gender of participants, and 35 studies included both men and women. The age range of the participants in the experimental groups was between 18 and 65 years. The types of exercise included in these studies were aerobic exercises (such as cycling, walking, etc.), isometric exercises, yoga, walking, multi-component training, etc. Among them, 17 studies involved aerobic exercises ranging in duration from 0 to 45 min, which was the most common type of exercise.
3.3 Results of bias assessment
Figure 3 summarizes the risk of bias assessment for the included studies. All 47 included studies employed random assignment and did not selectively report their research findings. However, due to the objective nature of exercise interventions, it was not feasible to maintain double-blinding among participants. Consequently, most researchers chose to inform participants of the intervention or did not conceal it, and specific details regarding blinding were not described, leading to a high risk of bias. Some of the included data had missing information, with some providing corresponding explanations, but a few still posed a high risk (Figures 3A,B).
3.4 Meta-analysis results
3.4.1 Forest plot
3.4.1.1 7-day point prevalence abstinence (PPA) rate (A1) and continuous abstinence rate (A2)
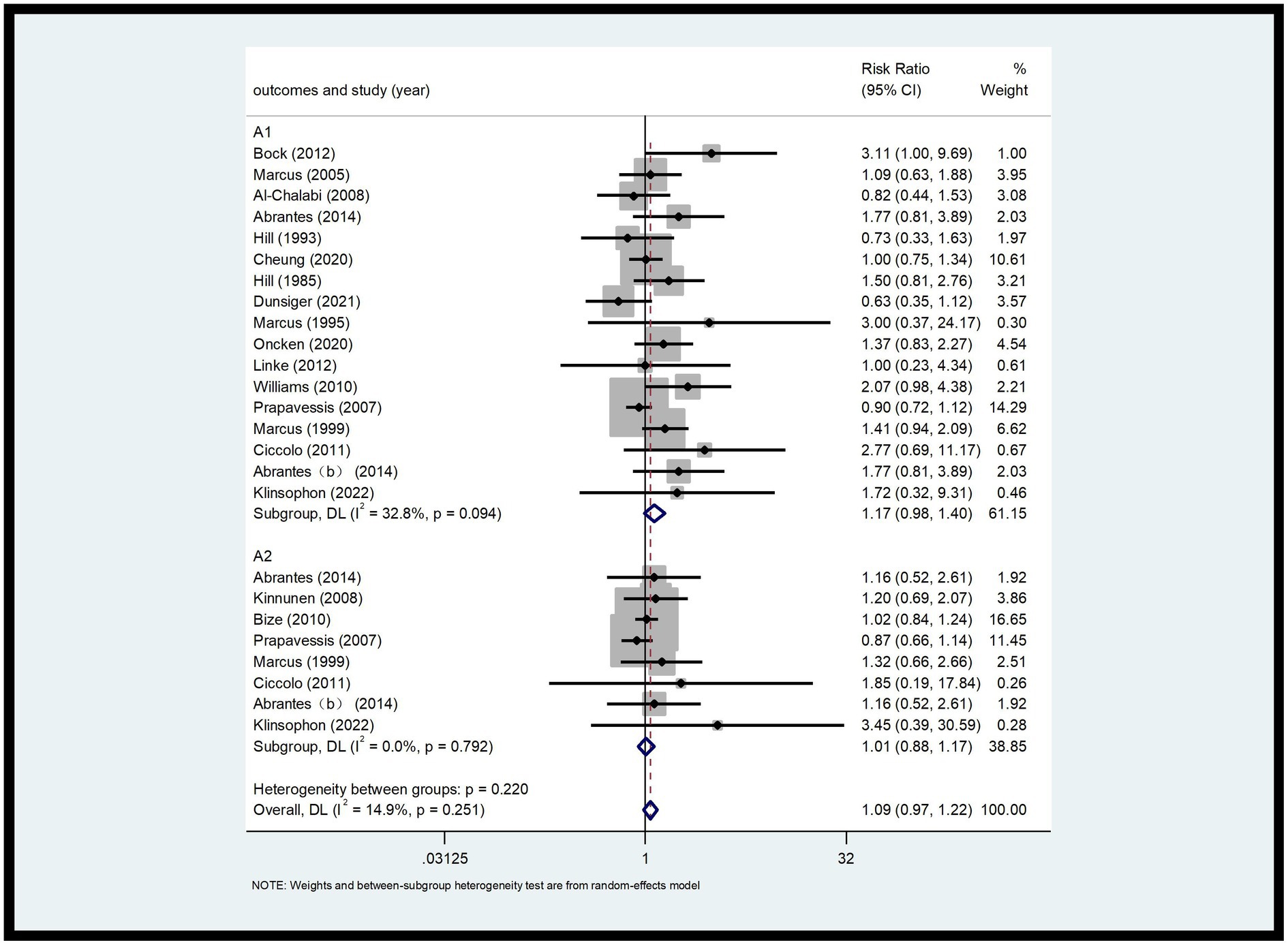
This analysis included 26 RCTs with a total of 2,902 participants (9, 17–29). The 7-day PPA rate (A1) and continuous abstinence rate (A2) were analyzed. As shown in Figure 4, the 7-day PPA rate (A1) had an I2 of 32.8%, indicating low heterogeneity. A fixed-effects model was used for analysis, with an RR of 1.17 and a 95% CI of 0.98, 1.40. For the continuous abstinence rate (A2), the I2 was 14.9%, also indicating low heterogeneity. Using a fixed-effects model, the RR was 1.01 with a 95% CI of 0.88, 1.17. Compared to the control group, the differences were not statistically significant (p > 0.05) (Figure 4).
3.4.1.2 Desire to smoke (B1) and strength of desire to smoke (B2)
Two Likert scales were used to assess smoking urge: Desire to Smoke (B1) and Strength of Desire (B2). Regarding B1, a total of 14 RCTs (involving 904 participants, with 468 in the exercise group and 436 in the control group) were included in the assessment. For B2, a total of 10 RCTs (involving 512 participants, with 257 in the exercise group and 255 in the control group) were included in the assessment (30–45).
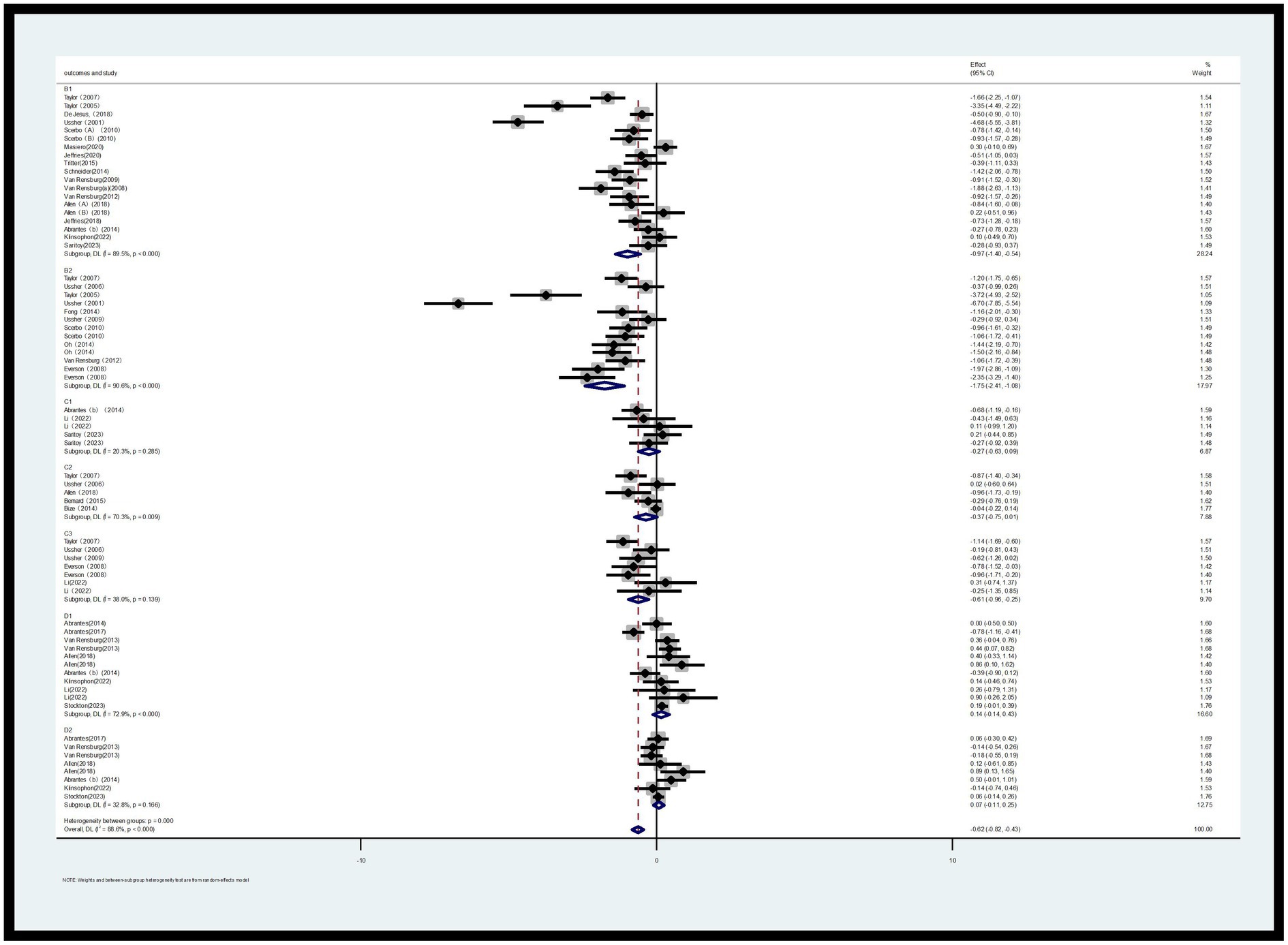
The meta-analysis revealed that, based on the random-effects model, the standardized mean difference (SMD) for B2 was-0.97 with a 95% confidence interval of −1.40 to −0.54, and p < 0.000, which was statistically significant. This indicates that acute exercise can significantly reduce the desire to smoke among smokers. Compared to the control group, the effect of acute exercise interventions on the strength of desire to smoke was also significant, with an SMD of −1.75 and a 95% CI of −2.41 to −1.08, p < 0.000 (Figure 5). Additionally, heterogeneity tests showed high levels of heterogeneity for both B1 (I2 = 89.5%, p < 0.000) and B2 (I2 = 90.6%, p < 0.000).
3.4.1.3 Sleep quality (C1), depression (C2) and irritability (C3)
This study employed three indicators to evaluate withdrawal symptoms: sleep quality (C1), depression (C2), and irritability (C3). Regarding the outcome indicator for sleep quality (C1), a total of 4 RCTs involving 148 participants (72 in the exercise group and 76 in the control group) were included in the assessment. For depression (C2), a total of 5 RCTs with 683 participants (336 in the exercise group and 347 in the control group) were included. Regarding irritability (C3), a total of 7 RCTs with 233 participants (108 in the exercise group and 125 in the control group) were included in the assessment (30, 31, 46–51).
As shown in Figure 5, for sleep quality (C1), the I2 was 32.9%, indicating low heterogeneity. The SMD for the exercise group was −0.30 with a 95% CI of −0.72 to 0.11. Compared to the control group, the difference was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). For depression (C2), the I2 was 70.3%, indicating high heterogeneity, and the difference compared to the control group was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). For irritability (C3), the I2 was 38.0%, and the SMD was −0.61 with a 95% CI of −0.96 to −0.21. Compared to the control group, the difference was statistically significant (p < 0.05), indicating that acute aerobic exercise can alleviate withdrawal symptoms of irritability to some extent.
3.4.1.4 Positive emotions (D1) and negative emotions (D2)
This study investigated the emotions of smokers during the smoking cessation process, categorizing them into two broad domains: positive emotions and negative emotions. For negative emotions, a total of 11 RCTs involving 937 participants (487 in the exercise group and 450 in the control group) were included in the assessment. For positive emotions, a total of 8 RCTs involving 856 participants (444 in the exercise group and 412 in the control group) were included (9, 31, 47, 51–54).
As shown in Figure 5, the heterogeneity results indicate that for negative emotions, the I2 value is 72.9% (p < 0.000), suggesting a high level of heterogeneity. Therefore, a random-effects model was used for the analysis of positive emotions (note: this should likely be a clarification that the model choice was mentioned in the context of analysis overall, and not specifically for negative emotions as stated; however, following the instruction to ignore errors, we proceed with the translation as is). However, the presented results for negative emotions [standardized mean difference (SMD) = 0.14, 95% confidence interval (CI) (−0.14, 0.43), p < 0.000] indicate a statistical significance level that contradicts the statement that the difference is not statistically significant.
Meanwhile, for positive emotions, the I2 value is 32.8% (p = 0.166), indicating a lower level of heterogeneity. A fixed-effects model was used for analysis (if I2 < 50%, a fixed-effects model is adopted; otherwise, a random-effects model is used). The combined effect size shows an SMD of 0.06 with a 95% CI of −0.08 to 0.19 and p = 0.166. Compared to the control group, there is no significant difference in the impact on outcomes for the experimental group (Figure 5).
3.4.2 Subgroup analysis
3.4.2.1 Desire to smoke (B1) and strength of desire to smoke (B2)
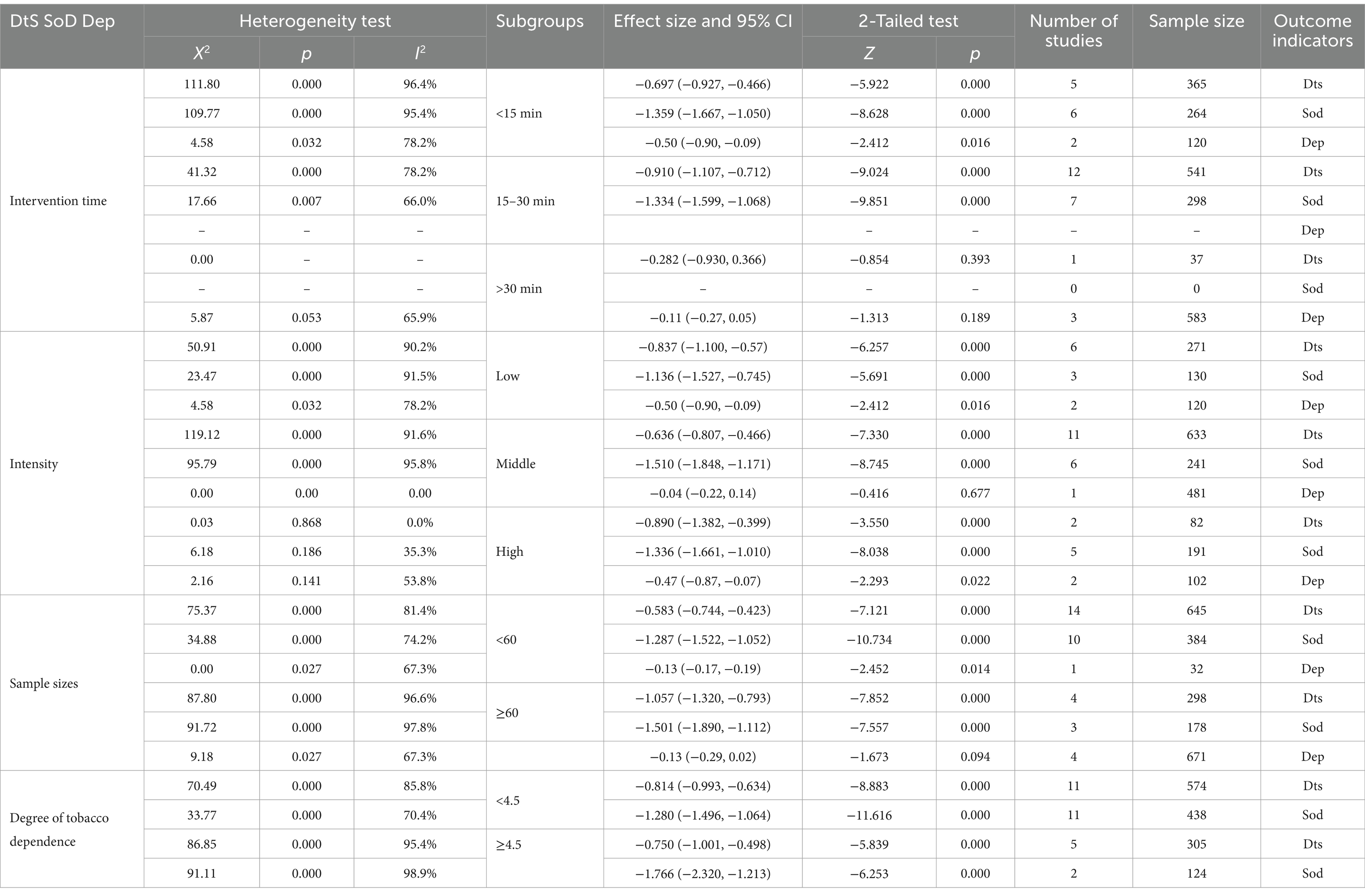
The exercise intervention programs were grouped based on various factors, including the duration of each exercise session (<15 min, 15–30 min, and >45 min), the intensity of the exercise, sample size (<60 and ≥60), and the degree of tobacco dependence (<4.5 and ≥4.5). Since all the included studies focused on aerobic exercises, aerobic exercise type was considered as a covariate premise, and a random-effects model was used for subgroup analysis. The results of the subgroup analysis for B1 and B2 are presented in Table 2. According to the subgroup analysis, there were statistical differences in the combined results among the various subgroups (p < 0.005). However, the grouping factors were not identified as sources of heterogeneity.
3.4.2.2 Depression (C2)
Based on the results of the subgroup analysis on depression (C2) according to the duration of each exercise session, the following findings were observed (Table 2). Comparison between the experimental group with 0–15 min of exercise and the control group showed an SMD of −0.44 with a 95% CI of −0.90 to −0.09 and I2 of 78.2%. The difference was statistically significant (p < 0.05). Comparison between the experimental group with >30 min of exercise and the control group showed an SMD of −0.30 with a 95% CI of −0.27 to 0.05 and I2 of 65.9%. The difference was also not statistically significant (p > 0.05). These results indicate that the duration of exercise is not a source of heterogeneity. Additionally, due to the limited number of studies assessing sleep quality and irritability as outcome indicators, insufficient data were available to conduct subgroup analyses for these factors (As shown in Table 2).
3.4.3 Sensitivity analysis
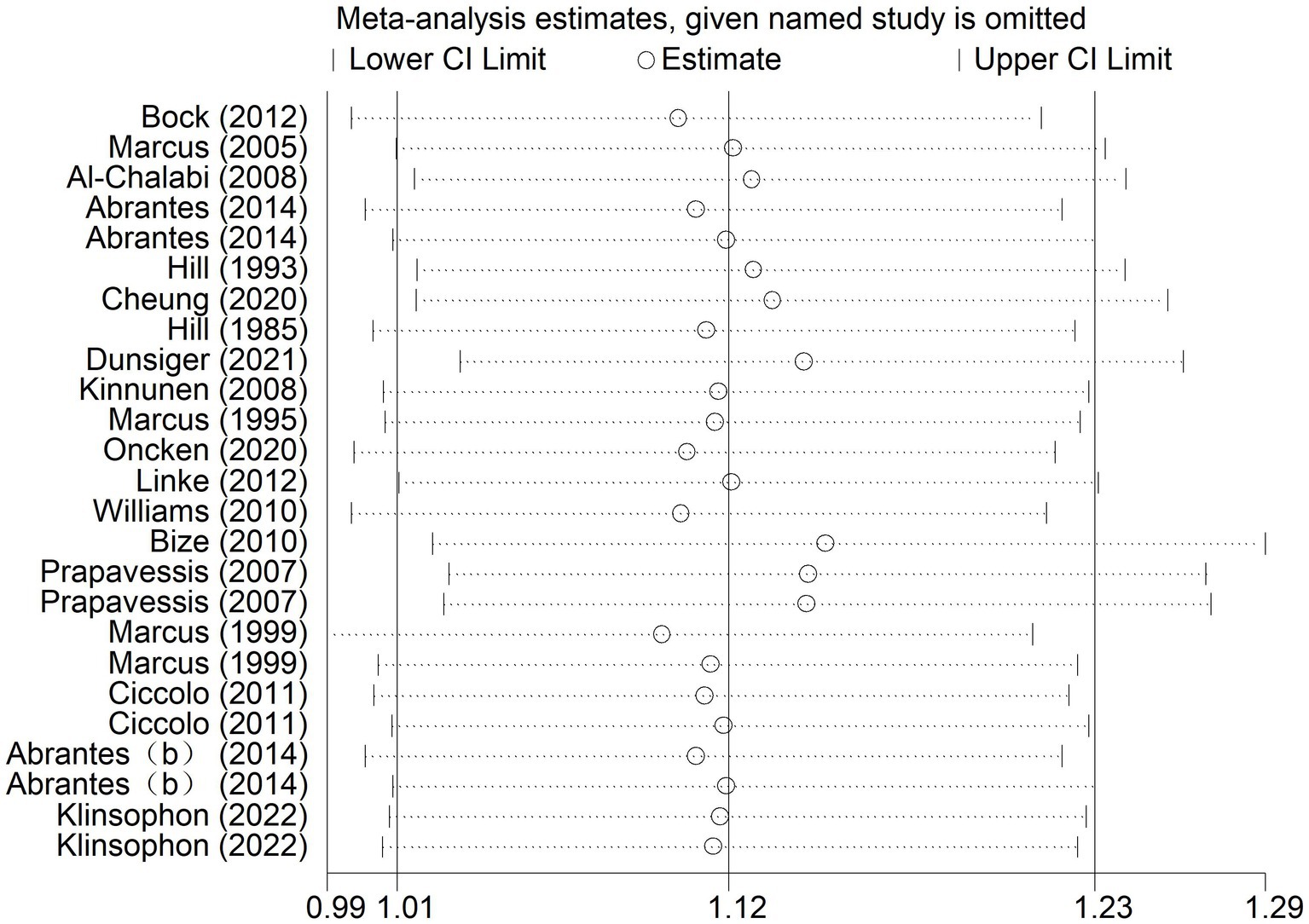
3.4.3.1 7-day point prevalence abstinence (A1) rate and continuous abstinence rate (A2)
According to the results of sensitivity analysis, it was found that some of the studies might have low sample stability. Sensitivity analysis was further conducted using Stata 14 software to determine the stability and reliability of the samples in the included studies. As shown in Figure 6, the overall data tended to be stable, and the combined results were not influenced by any individual study. The sensitivity was low, ensuring the stability and reliability of the combined results in the subsequent meta-analysis (Figure 6).
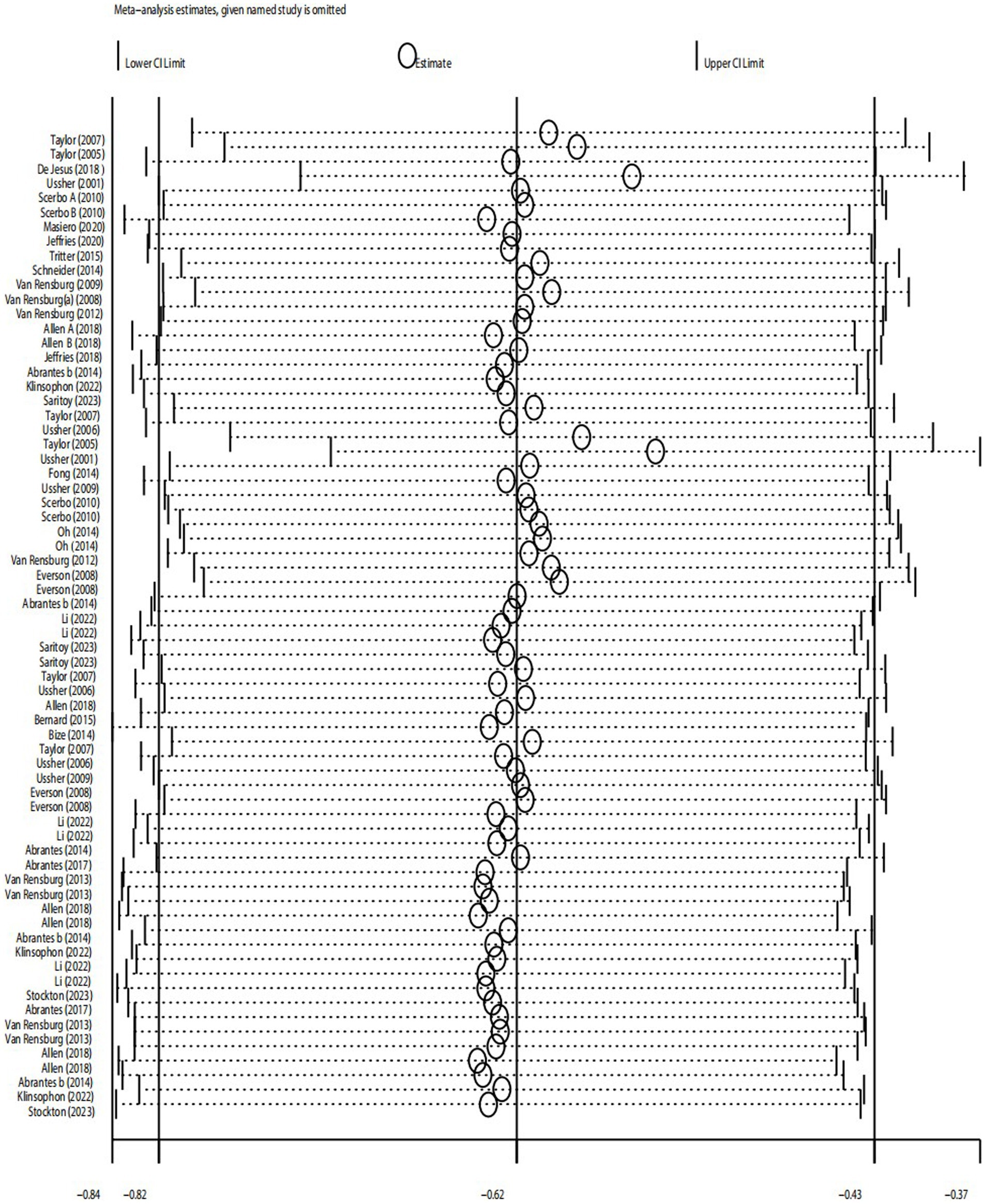
3.4.3.2 Desire to smoke (B1) and strength of desire to smoke (B2)
The results showed that for desire to smoke, the 95% confidence interval (CI) was (−1.40, −0.54), with an estimated median value of −0.97. For strength desire to smoke, the 95% CI was (−2.41, −1.08), with an estimated median value of −1.75. The overall data tended to be in a stable state, with the values in the graph fluctuating slightly around the median values of −0.97 (B1) or −1.75 (B2). Additionally, most of the confidence intervals tended to be negative, and the point estimates of the included studies were all within their respective confidence intervals. Therefore, the sensitivity analysis test showed that the results for desire to smoke (B1) and strength of desire to smoke (B2) were robust after excluding individual studies and conducting sensitivity analysis.
3.4.3.3 Sleep quality (C1), depression (C2) and irritability (C3)
The results of sensitivity analysis showed that for sleep quality, the 95% confidence interval was (−0.63, 0.09), with an estimated median value of −0.27. For depression, the 95% CI was (−0.75, 0.01), with an estimated median value of −0.37. For irritability, the 95% CI was (−0.96, −0.25), with an estimated median value of −0.61. The overall data tended to be in a stable state, with the values in the graph fluctuating slightly around the median values of −0.27 (sleep quality), −0.37 (depression), or −0.61 (irritability). Additionally, the point estimates of the included studies were all within their respective confidence intervals. Therefore, the sensitivity analysis test showed that after excluding individual studies and conducting sensitivity analysis, the results for depression were robust.
3.4.3.4 Positive emotions (D1) and negative emotions (D2)
The results showed that for negative emotions, the 95% confidence interval (CI) was (−0.14, 0.43), with an estimated median value of 0.14. For positive emotions, the 95% CI was (−0.11, 0.25), with an estimated median value of 0.07. Therefore, according to the sensitivity test, these two results were not robust. This suggests that the variability in the studies included in the analysis may have had a significant impact on the estimated effects of negative and positive emotions. Further investigation into the sources of heterogeneity and potential biases in the included studies is needed to improve the robustness of the results (Figure 7).
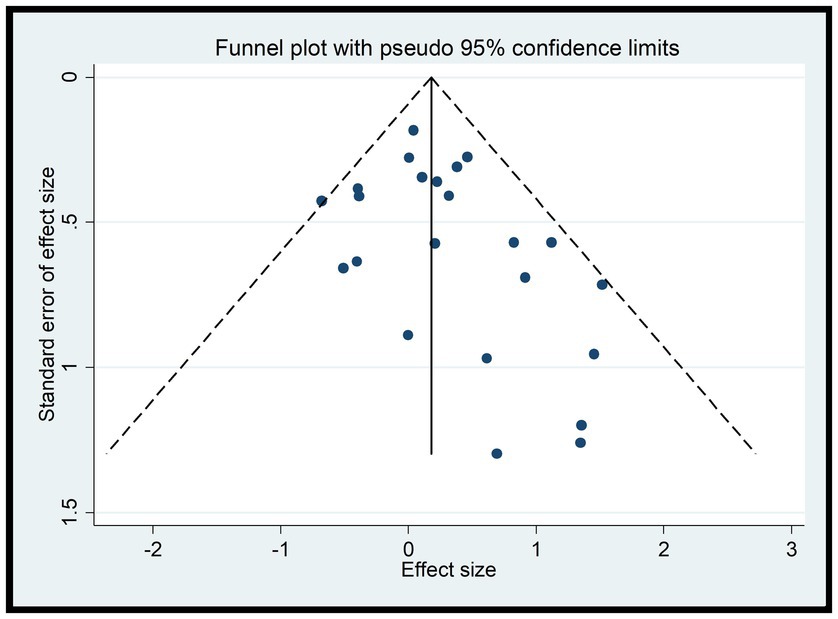
3.4.4 Results of funnel plot
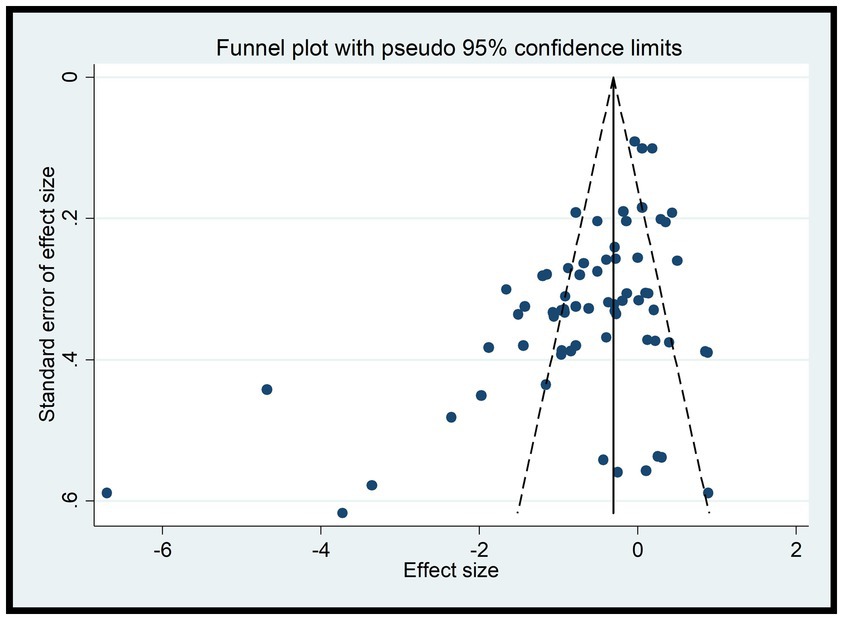
Since A1 and A2 were discussed as dichotomous variables separately from the others, they were not included in the funnel plot analysis for B1, B2, C1, C2, C3, D1, and D2. According to the funnel plots for these variables (Figure 8), a portion of the studies fall outside the 95% confidence interval, indicating the presence of high heterogeneity. Additionally, the funnel plots exhibit asymmetry with missing corners, suggesting the existence of publication bias. This may be due to the inclusion of low-quality studies with small sample sizes, which could lead to an overestimation of the combined effect, exaggerating the intervention effect, and causing bias.
To address these issues, further investigation into the sources of heterogeneity and potential biases in the included studies is necessary. This may involve conducting additional analyses, such as subgroup analyses or meta-regression, to explore the reasons for the heterogeneity and publication bias. Additionally, efforts should be made to identify and exclude low-quality studies or those with significant biases to improve the robustness and reliability of the results (Figure 8).
Consistent with the separate analysis for A1 and A2, the funnel plots for A1 and A2 reveal that most studies fall within the 95% confidence interval, indicating low heterogeneity (Figure 9). However, the funnel plots lack symmetry, suggesting the presence of publication bias. This could potentially be attributed to the inclusion of low-quality studies with small sample sizes, which may lead to an overestimation of the combined effect, exaggerating the intervention effect, and introducing bias (Figure 9).
3.4.5 Results of Egger test
In this study, the experimental variables are B1, B2, C1, C2, C3, while D1 and D2 are continuous variables. Therefore, the Egger test was used to assess publication bias. The Egger test results indicate a potential for publication bias in B1 (DtS) and B2 (SoD) with p-values less than 0.05, suggesting that the results for these variables may be influenced by the presence of unpublished or underreported studies. On the other hand, the results for C1, C2, C3, D1, and D2 show no significant publication bias with p-values greater than 0.05, indicating that the available studies for these variables may be more representative of the true effect.
It is important to note that the presence of publication bias can affect the reliability and validity of the research findings. Therefore, when interpreting the results of this study, readers should consider the potential impact of publication bias on the B1 and B2 variables. Additional efforts may be needed to identify and include all relevant studies, especially those that may have been overlooked or underreported, to obtain a more accurate and unbiased estimate of the true effect.
4 Discussion
In our study, we aimed to comprehensively analyze trial results using both dichotomous outcomes (including 7-Day Point Prevalence Abstinence Rate and Continuous Abstinence Rate) and continuous variables (encompassing Desire to Smoke, its Strength, sleep quality, depression, irritability, positive emotions, and negative emotions). Notably, the literature frequently employs the Risk Ratio (RR) to interpret outcomes related to these dichotomous variables (55) particularly the 7-day PPA and continuous abstinence rates, prompting us to discuss 7-Day Point Prevalence Abstinence Rate and Continuous Abstinence Rate separately.
Smoking desire (intensity) and withdrawal symptoms are crucial indicators for assessing tobacco dependence (56). Higher smoking desire leads to shorter intervals between cigarettes and more pronounced withdrawal symptoms, which are major relapse triggers. Previous research suggests that physical exercise increases the time until the first cigarette following exercise (57). Thus, using exercise to alleviate these symptoms is crucial (58). Our study confirmed that acute aerobic exercise reduces tobacco cravings and withdrawal symptoms among smokers trying to quit. Specifically, the desire to smoke decreases significantly immediately following exercise (10). However, long-term exercise does not significantly impact tobacco dependence. Additionally, exercise intervention positively influences smokers or those attempting to quit, generating certain positive emotions.
Subgroup analyses to explore heterogeneity sources were restricted by original study designs. After examining individual articles, we found that excluding Tritter (45) and Taylor (32) led to more consistent sample characteristics and reduced methodological differences, suggesting they were main sources of high heterogeneity. The former had specific subject and control group limitations, while the latter focused on temporary smoking cessation and had unclear intervention criteria.
Exercise intensity is a significant control condition (59). Our subgroup analysis found that low, medium, and high-intensity exercise can all reduce tobacco dependence and craving to some extent. Especially, moderate to high-intensity acute aerobic exercise is the most effective intervention, and smokers with high tobacco dependence may benefit from increased exercise intensity. High-intensity exercise can significantly reduce tobacco dependence in a short period, especially for smokers with high dependence (13, 60). However, low-intensity exercise is ineffective in reducing smoking desire and intensity.
Another key finding from subgroup analyses, which specifically focused on withdrawal symptoms, reveals that exercise has a significant positive impact on reducing irritability among smokers attempting to quit. This finding aligns with previous research suggesting that exercise can alleviate negative mood states often experienced during withdrawal (13). However, our results indicate that the combined effect size for the intervention effects of exercise on depression is not statistically significant in our study population. To further investigate the sources of heterogeneity, we conducted additional subgroup analyses for depression. Notably, we found that only short-duration exercise (less than 15 min) has a positive effect on depression. Besides, our results also indicate that the intervention effect of exercise on sleep quality is not statistically significant. Our findings have important implications for future research and practice. While exercise may be beneficial in reducing irritability and, under certain conditions (such as short durations), depression, it may not have a significant impact on these outcomes for all smokers or across all durations of exercise. Therefore, practitioners should assess smokers’ specific needs and tailor interventions accordingly. This personalized approach can enhance the effectiveness of quit-smoking programs and improve overall outcomes for smokers seeking to overcome their tobacco dependence.
Notably, acute aerobic exercise has been identified as significantly effective in reducing cravings and withdrawal symptoms among smokers. While previous research acknowledged the immediate benefits of acute exercise on cigarette cravings, withdrawal symptoms, and smoking behavior (61), it did not delve deeply into the long-term effects of exercise or provide a direct comparison between acute and long-term interventions. The present meta-analysis evaluates both acute and long-term aerobic exercise interventions in smoking cessation, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of the effects of exercise intensities and durations on tobacco dependence.
Our findings suggest that engaging in physical activity may positively influence smoking cessation attempts, potentially by providing a means to divert attention away from smoking cues and cravings. This aligns with previous research, such as the study by Hatzigeorgiadis et al. (62), which examined the acute effect of exercise on smoking delay among smokers. Notably, their results indicated that the use of self-regulation strategies, such as goal setting, could enhance the beneficial impact of exercise on reducing the urge to smoke immediately following physical activity (62–64). These strategies may facilitate the translation of the temporary relief from smoking cravings induced by exercise into more sustained smoking abstinence. Future research should explore the combined effects of exercise and self-regulation strategies on smoking cessation outcomes, potentially identifying optimal combinations and protocols that maximize the beneficial impact of these interventions.
Furthermore, compared to previous studies, the data in the present study is more comprehensive and up-to-date. It synthesizes data from 47 studies, including 57 randomized controlled trials, involving 4,267 participants. This larger sample size and more comprehensive dataset allow for a more robust analysis and more reliable conclusions.
This study has limitations. Firstly, blinding participants in exercise interventions is challenging, thereby presenting a significant risk of bias. Furthermore, incomplete outcome data further contributes to this bias. Additionally, some assumed and ignored calculations may have influenced our results. For instance, in the design of the experimental and control groups, it was challenging to ensure that the exercise intervention was the sole variable of difference. In some cases, participants were explicitly instructed not to smoke during the intervention period, which could potentially affect the test results by introducing an additional variable that was not fully accounted for in our analysis. Secondly, intervention specifics, such as intensity, were often incompletely reported, and exercise types lacked a consistent classification system. Lastly, future research should consider a wider range of outcome measures to comprehensively assess the effects of exercise on smoking behavior. For example, although emotion serves as a pivotal moderating variable, only a few studies explicitly outlined emotion classification criteria, which constrained the inclusion of emotion-related indicators in our analysis. To enhance the accuracy of future research, it is recommended to implement allocation concealment, ensure assessor blinding, augment the sample size, uphold data integrity, thoroughly consider and validate all relevant calculations, and carefully design experimental and control groups to minimize the impact of confounding variables.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
JX: Conceptualization, Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft. SZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Visualization, Writing – original draft. ZC: Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. ZW: Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. World health statistics 2023: monitoring health for the SDGs, sustainable development goals. 1st ed. Geneva: World Health Organization (2023). 1 p.
2. G, S, Choi, S, Krishnan, J, and K, R. Cigarette smoke and related risk factors in neurological disorders: an update. Biomed Pharmacother. (2017) 85:79–86. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.11.118
3. Zhu, J, and Yang, B. Study on the risk of coronary artery stenosis and smoking in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia infection. Chinese J CT MRI. (2024) 22:100–2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5131.2024.05.032
4. Evans, DE, To, C, and Ashare, RL. The role of cognitive control in the self-regulation and reinforcement of smoking behavior. Nicotine Tob Res. (2019) 21:747–54. doi: 10.1093/ntr/nty029
5. Glasgow, RE, and Lichtenstein, E. Long-term effects of behavioral smoking cessation interventions. Behav Ther. (1987) 18:297–324. doi: 10.1016/S0005-7894(87)80002-3
6. Hall, SM, Humfleet, GL, Reus, VI, Muñoz, RF, Hartz, DT, and Maude-Griffin, R. Psychological intervention and antidepressant treatment in smoking cessation. Arch Gen Psychiatry. (2002) 59:930. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.59.10.930
7. Prentice, AM. Overeating: the health risks. Obes Res. (2001) 9:234S–238S. doi: 10.1038/oby.2001.124
8. Linke, SE, Ciccolo, JT, Ussher, M, and Marcus, BH. Exercise-based smoking cessation interventions among women. Women’s Health (Lond Engl). (2013) 9:69–84. doi: 10.2217/WHE.12.63
9. Klinsophon, T, Thaveeratitham, P, Sitthipornvorakul, E, and Janwantanakul, P. Effect of exercise type on smoking cessation: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. BMC Res Notes. (2017) 10:442. doi: 10.1186/s13104-017-2762-y
10. Zourbanos, N, Hatzigeorgiadis, A, Tsiami, A, Tzatzaki, T, Georgakouli, K, Manthou, E, et al. An initial investigation of smokers’ urges to smoke and their exercise intensity preference: a mixed-methods approach. Cogent Med. (2016) 3:1149043. doi: 10.1080/2331205X.2016.1149043
11. Benowitz, NL. Neurobiology of nicotine addiction: implications for smoking cessation treatment. Am J Med. (2008) 121:S3–S10. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2008.01.015
12. American Diabetes Association. 4. Foundations of care: education, nutrition, physical activity, smoking cessation, psychosocial care, and immunization. Diabetes Care. (2015) 38:S20–30. doi: 10.2337/dc15-S007
13. Zhou, Y, Feng, W, Guo, Y, and Wu, J. Effect of exercise intervention on smoking cessation: a meta-analysis. Front Physiol. (2023) 14:1221898. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1221898
14. Santos, CP, Proença, M, Gouveia, TDS, Soares De Oliveira, CB, Tacao, GY, Trevisan, IB, et al. Effectiveness of aerobic exercise on smoking cessation in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Phys Act Health. (2021) 18:230–42. doi: 10.1123/jpah.2019-0339
15. Tetzlaff, J, Page, M, and Moher, D. PNS154 the PRISMA 2020 statement: development of and key changes in an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Value Health. (2020) 23:S312–3. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2020.04.1154
16. Higgins, JPT Cochrane Collaboration eds. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Second ed. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley-Blackwell (2019). 694 p.
17. Bock, BC, Fava, JL, Gaskins, R, Morrow, KM, Williams, DM, Jennings, E, et al. Yoga as a complementary treatment for smoking cessation in women. J Women’s Health. (2012) 21:240–8. doi: 10.1089/jwh.2011.2963
18. Marcus, B, Lewis, B, Hogan, J, King, T, Albrecht, A, Bock, B, et al. The efficacy of moderate-intensity exercise as an aid for smoking cessation in women: a randomized controlled trial. Nicotine Tob Res. (2005) 7:871–80. doi: 10.1080/14622200500266056
19. Al-Chalabi, L, Prasad, N, Steed, L, Stenner, S, Aveyard, P, Beach, J, et al. A pilot randomised controlled trial of the feasibility of using body scan and isometric exercises for reducing urge to smoke in a smoking cessation clinic. BMC Public Health. (2008) 8:349. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-8-349
20. Cheung, YT, Lam, TH, Chan, CHH, Ho, KS, Fok, WYP, Wang, MP, et al. Brief handgrip and isometric exercise intervention for smoking cessation: a pilot randomized trial. Addict Behav. (2020) 100:106119. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2019.106119
21. Hill, JS. Effect of a program of aerobic exercise on the smoking behaviour of a group of adult volunteers. Can J Public Health. (1982) 76:183–6.
22. Dunsiger, S, Emerson, JA, Ussher, M, Marcus, BH, Miranda, R, Monti, PM, et al. Exercise as a smoking cessation treatment for women: a randomized controlled trial. J Behav Med. (2021) 44:794–802. doi: 10.1007/s10865-021-00236-8
23. Kinnunen, T, Leeman, R, Korhonen, T, Quiles, Z, Terwal, D, Garvey, A, et al. Exercise as an adjunct to nicotine gum in treating tobacco dependence among women. Nicotine Tobacco Res. (2008) 10:689–703. doi: 10.1080/14622200801979043
24. Oncken, C, Allen, S, Litt, M, Kenny, A, Lando, H, Allen, A, et al. Exercise for smoking cessation in postmenopausal women: a randomized, controlled trial. Nicotine Tobacco Res. (2020) 22:1587–95. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntz176
25. Linke, SE, Rutledge, T, and Myers, MG. Intermittent exercise in response to cigarette cravings in the context of an internet-based smoking cessation program. Ment Health Phys Act. (2012) 5:85–92. doi: 10.1016/j.mhpa.2012.02.001
26. Williams, DM, Whiteley, JA, Dunsiger, S, Jennings, EG, Albrecht, AE, Ussher, MH, et al. Moderate intensity exercise as an adjunct to standard smoking cessation treatment for women: a pilot study. Psychol Addict Behav. (2010) 24:349–54. doi: 10.1037/a0018332
27. Prapavessis, H, Cameron, L, Baldi, JC, Robinson, S, Borrie, K, Harper, T, et al. The effects of exercise and nicotine replacement therapy on smoking rates in women. Addict Behav. (2007) 32:1416–32. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2006.10.005
28. Marcus, BH, Albrecht, AE, King, TK, Parisi, AF, Pinto, BM, Roberts, M, et al. The efficacy of exercise as an aid for smoking cessation in women: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Intern Med. (1999) 159:1229. doi: 10.1001/archinte.159.11.1229
29. Ciccolo, JT, Dunsiger, SI, Williams, DM, Bartholomew, JB, Jennings, EG, Ussher, MH, et al. Resistance training as an aid to standard smoking cessation treatment: a pilot study. Nicotine Tob Res. (2011) 13:756–60. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntr068
30. Taylor, A, and Katomeri, M. Walking reduces cue-elicited cigarette cravings and withdrawal symptoms, and delays ad libitum smoking. Nicotine Tobacco Res. (2007) 9:1183–90. doi: 10.1080/14622200701648896
31. Abrantes, AM, Bloom, EL, Strong, DR, Riebe, D, Marcus, BH, Desaulniers, J, et al. A preliminary randomized controlled trial of a behavioral exercise intervention for smoking cessation. Nicotine Tob Res. (2014) 16:1094–103. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntu036
32. Taylor, AH, Katomeri, M, and Ussher, M. Acute effects of self-paced walking on urges to smoke during temporary smoking abstinence. Psychopharmacology. (2005) 181:1–7. doi: 10.1007/s00213-005-2216-4
33. De Jesus, S, and Prapavessis, H. Affect and cortisol mechanisms through which acute exercise attenuates cigarette cravings during a temporary quit attempt. Addict Behav. (2018) 80:82–8. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2018.01.007
34. Ussher, M, Nunziata, P, Cropley, M, and West, R. Effect of a short bout of exercise on tobacco withdrawal symptoms and desire to smoke. Psychopharmacology. (2001) 158:66–72. doi: 10.1007/s002130100846
35. Scerbo, F, Faulkner, G, Taylor, A, and Thomas, S. Effects of exercise on cravings to smoke: the role of exercise intensity and cortisol. J Sports Sci. (2010) 28:11–9. doi: 10.1080/02640410903390089
36. Jeffries, ER, Zvolensky, MJ, and Buckner, JD. The acute impact of hatha yoga on craving among smokers attempting to reduce or quit. Nicotine Tob Res. (2018) 22:446–51. doi: 10.1093/ntr/nty263
37. Fong, AJ, De Jesus, S, Bray, SR, and Prapavessis, H. Effect of exercise on cigarette cravings and ad libitum smoking following concurrent stressors. Addict Behav. (2014) 39:1516–21. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2014.05.027
38. Van Rensburg, K, Taylor, A, Benattayallah, A, and Hodgson, T. The effects of exercise on cigarette cravings and brain activation in response to smoking-related images. Psychopharmacology. (2012) 221:659–66. doi: 10.1007/s00213-011-2610-z
39. Masiero, M, Keyworth, H, Pravettoni, G, Cropley, M, and Bailey, A. Short bouts of physical activity are associated with reduced smoking withdrawal symptoms, but perceptions of intensity may be the key. Healthcare. (2020) 8:425. doi: 10.3390/healthcare8040425
40. Schneider, T, De Jesus, S, and Prapavessis, H. The effect of acute exercise on smoking topography: no evidence for cutting down one puff at a time. J Smok Cessat. (2015) 10:146–53. doi: 10.1017/jsc.2014.2
41. Van Rensburg, KJ, and Taylor, AH. The effects of acute exercise on cognitive functioning and cigarette cravings during temporary abstinence from smoking. Hum Psychopharmacol. (2008) 23:193–9. doi: 10.1002/hup.925
42. Janse Van Rensburg, K, Taylor, A, Hodgson, T, and Benattayallah, A. Acute exercise modulates cigarette cravings and brain activation in response to smoking-related images: an fMRI study. Psychopharmacology. (2009) 203:589–98. doi: 10.1007/s00213-008-1405-3
43. Van Rensburg, KJ, Taylor, A, and Hodgson, T. The effects of acute exercise on attentional bias towards smoking-related stimuli during temporary abstinence from smoking. Addiction. (2009) 104:1910–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2009.02692.x
44. Taylor, A, Katomeri, M, and Ussher, M. Effects of walking on cigarette cravings and affect in the context of Nesbitt’s paradox and the Circumplex model. J Sport Exerc Psychol. (2006) 28:18–31. doi: 10.1123/jsep.28.1.18
45. Tritter, A, Fitzgeorge, L, and Prapavessis, H. The effect of acute exercise on cigarette cravings while using a nicotine lozenge. Psychopharmacology. (2015) 232:2531–9. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-3887-0
46. Bize, R, Willi, C, Chiolero, A, Stoianov, R, Payot, S, Locatelli, I, et al. Participation in a population-based physical activity programme as an aid for smoking cessation: a randomised trial. Tob Control. (2010) 19:488–94. doi: 10.1136/tc.2009.030288
47. Allen, A, Carlson, SC, Bosch, TA, Eberly, LE, Okuyemi, K, Nair, U, et al. High-intensity interval training and continuous aerobic exercise interventions to promote self-initiated quit attempts in young adults who smoke: feasibility, acceptability, and lessons learned from a randomized pilot trial. J Addict Med. (2018) 12:373–80. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0000000000000414
48. Ussher, M, Cropley, M, Playle, S, Mohidin, R, and West, R. Effect of isometric exercise and body scanning on cigarette cravings and withdrawal symptoms. Addiction. (2009) 104:1251–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2009.02605.x
49. Everson, ES, Daley, AJ, and Ussher, M. The effects of moderate and vigorous exercise on desire to smoke, withdrawal symptoms and mood in abstaining young adult smokers. Ment Health Phys Act. (2008) 1:26–31. doi: 10.1016/j.mhpa.2008.06.001
50. Ussher, M, West, R, Doshi, R, and Sampuran, AK. Acute effect of isometric exercise on desire to smoke and tobacco withdrawal symptoms. Hum Psychopharmacol. (2006) 21:39–46. doi: 10.1002/hup.744
51. Abrantes, AM, Farris, SG, Minami, H, Strong, DR, Riebe, D, and Brown, RA. Acute effects of aerobic exercise on affect and smoking craving in the weeks before and after a cessation attempt. Nicotine Tob Res. (2018) 20:575–82. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntx104
52. Li, C, Yao, N, Miller, SL, Macpherson, C, Hassinger, T, Love, K, et al. Exercise and reduced nicotine content cigarettes in adult female smokers: a pilot trial. IJERPH. (2022) 19:6647. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19116647
53. Janse Van Rensburg, K, Elibero, A, Kilpatrick, M, and Drobes, DJ. Impact of aerobic exercise intensity on craving and reactivity to smoking cues. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol. (2013) 21:196–203. doi: 10.1037/a0032768
54. Stockton, MB, Ward, KD, McClanahan, BS, Vander, M, Coday, M, Wilson, N, et al. The efficacy of individualized, community-based physical activity to aid smoking cessation: a randomized controlled trial. J Smok Cessat. (2023) 2023:e4. doi: 10.1155/2023/5535832
55. Robbins, AS, Chao, SY, and Fonseca, VP. What’s the relative risk? A method to directly estimate risk ratios in cohort studies of common outcomes. Ann Epidemiol. (2002) 12:452–4. doi: 10.1016/S1047-2797(01)00278-2
56. Shiffman, S, West, R, and Gilbert, D. Recommendation for the assessment of tobacco craving and withdrawal in smoking cessation trials. Nicotine Tob Res. (2004) 6:599–614. doi: 10.1080/14622200410001734067
57. Georgakouli, K, Manthou, E, Georgoulias, P, Ziaka, A, Deli, CK, Draganidis, D, et al. HPA axis responses to acute exercise differ in smokers and non-smokers. Physiol Behav. (2020) 229:113258. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2020.113258
58. Hearing, CM, Chang, WC, Szuhany, KL, Deckersbach, T, Nierenberg, AA, and Sylvia, LG. Physical exercise for treatment of mood disorders: a critical review. Curr Behav Neurosci Rep. (2016) 3:350–9. doi: 10.1007/s40473-016-0089-y
59. Lansley, KE, DiMenna, FJ, Bailey, SJ, and Jones, AM. A ‘new’ method to normalise exercise intensity. Int J Sports Med. (2011) 32:535–41. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1273754
60. Roberts, V, Gant, N, Sollers, JJ, Bullen, C, Jiang, Y, and Maddison, R. Effects of exercise on the desire to smoke and physiological responses to temporary smoking abstinence: a crossover trial. Psychopharmacology. (2015) 232:1071–81. doi: 10.1007/s00213-014-3742-8
61. Taylor, AH, Ussher, MH, and Faulkner, G. The acute effects of exercise on cigarette cravings, withdrawal symptoms, affect and smoking behaviour: a systematic review. Addiction. (2007) 102:534–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2006.01739.x
62. Hatzigeorgiadis, A, Pappa, V, Tsiami, A, Tzatzaki, T, Georgakouli, K, Zourbanos, N, et al. Self-regulation strategies may enhance the acute effect of exercise on smoking delay. Addict Behav. (2016) 57:35–7. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2016.01.012
63. Angeli, M, Hatzigeorgiadis, A, Comoutos, N, Krommidas, C, Morres, ID, and Theodorakis, Y. The effects of self-regulation strategies following moderate intensity exercise on ad libitum smoking. Addict Behav. (2018) 87:109–14. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2018.06.029
Keywords: tobacco dependence, physical exercise, acute aerobic exercise, smoking cessation, meta-analysis
Citation: Xu J, Zhang S, Chen Z and Wu Z (2025) Effects of exercise intervention on tobacco dependence: a meta-analysis. Front. Public Health. 13:1538833. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1538833
Edited by:
Yannis Theodorakis, University of Thessaly, GreeceReviewed by:
Philip Hemphill, Tulane University, United StatesMaria Angeli, University of Thessaly, Greece
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Zhang, Chen and Wu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhusheng Wu, NzQxMDgyODU2QHFxLmNvbQ==
 Jinzhi Xu1
Jinzhi Xu1 Zichao Chen
Zichao Chen Zhusheng Wu
Zhusheng Wu