- 1Key Laboratory of Health Technology Assessment of National Health Commission, School of Public Health, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 2School of Public Health, Hainan Medical University, Haikou, China
- 3Section of General Practice, Research Unit for General Practice, Department of Public Health, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark
- 4Research Unit for General Practice, Department of Public Health, University of Southern Denmark, Odense, Denmark
Purpose: The purpose of this study is to present the findings of a cross-sectional survey on health state utility (HSU) values, a crucial metric for economic evaluations, and to analyze the primary factors influencing the HSU values of individuals with normal cognition (NC) or mild cognitive impairment (MCI).
Methods: A community-based survey was conducted in Haikou City, China, employing cluster random sampling to select participants. The presence of NC and MCI was determined through the administration of the Chinese version of the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE). The assessment of HSU was conducted using the Chinese version of the Short Form Six Dimensions version 2 (SF-6Dv2), in conjunction with a questionnaire that collected data on socio-demographic characteristics, health-related behaviors, and health conditions. The HSU values were calculated using the SF-6Dv2 value set, which was developed for the Chinese population. A multiple linear regression model was constructed to identify the factors influencing HSU values.
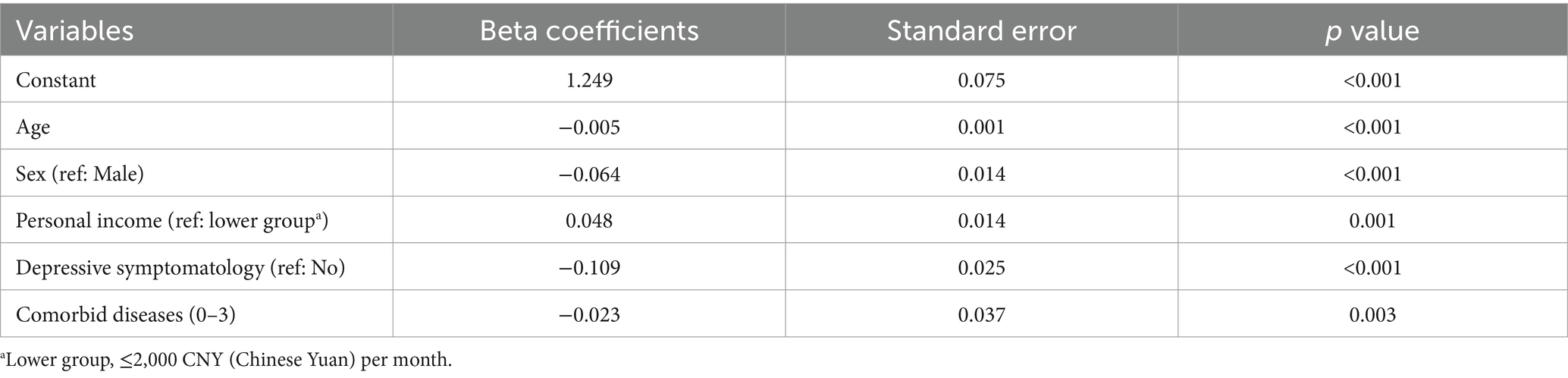
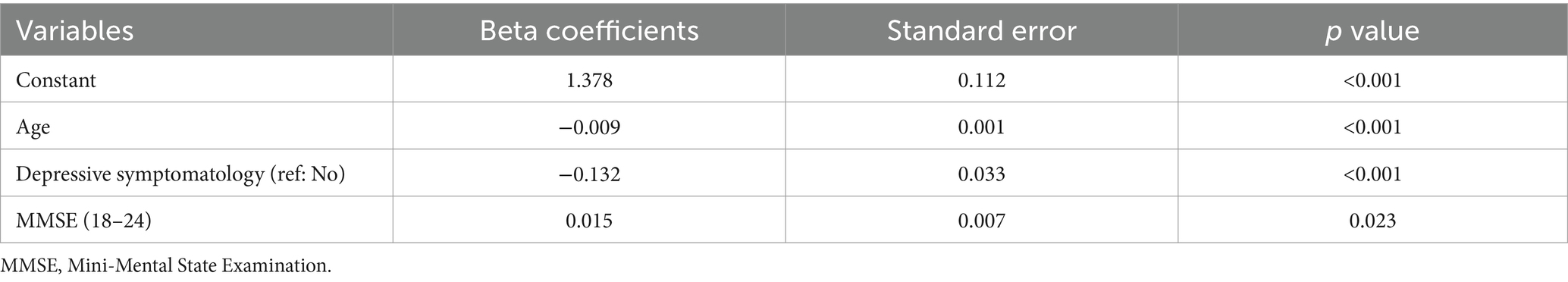
Results: The survey indicated that 536 older individuals were identified with NC (mean age 70.7, SD 7.1, 51.4% females), 245 were identified with MCI (mean age 73.0, SD 7.8, 67.4% females). The mean HSU values in NC group and MCI group were 0.792 (SD: 0.174) and 0.720 (SD: 0.199), respectively. The optimal multiple regression model for the MCI group demonstrated a linear relationship between age, depression symptomatology, and MMSE score with HSU, with coefficients of −0.009 (p < 0.001) for age and −0.132 (p < 0.001) for depression symptomatology. And for NC group, the optimal multiple linear regression model included five variables: age, sex, monthly personal income, depression symptomatology, and number of comorbidities.
Conclusion: This study presented findings on HSU and its influencing factors in both the NC and MCI groups. The older adult individuals with MCI demonstrated lower HSU compared to their cognitively normal counterparts. The results of the factor analysis indicated that intervention programs designed to enhance the health-related quality of life for older adult individuals with MCI should include strategies to address depression.
Introduction
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) signifies an intermediary cognitive state that falls between the cognitive changes observed in the aging process and the criteria for diagnosing dementia (1). Around 15% of individuals with MCI progress to dementia within 2 years, with about 32% developing Alzheimer’s-related dementia within 5 years (2, 3). The study, based on Chinese data, estimated the prevalence of MCI among the older adult population in China is about 16%, with 38.8 million individuals affected by MCI in 2018 (4). As the Chinese population continues to age, it is estimated that there will be 29.5 million individuals aged 60 and above living with dementia by 2050. This is projected to have a significant impact on China’s population health and economy (5). It is therefore that interventions targeting individuals with MCI will become a critical public health strategy for early intervention.
Presently, early interventions for individuals with MCI primarily emphasize on non-pharmacological approaches, including cognitive training, physical exercise, dietary adjustment, and psychosocial interventions such as those targeting depressive symptoms (6, 7). Evidence from China indicates that cognitive training for individuals with normal cognition and those with MCI can help prevent or delay the decline in cognitive function (8). Compared to physical exercise and dietary intervention, cognitive training is still in a relatively developmental phase. Such programs typically require specific venues, specialized equipment, and professional support, resulting in a relatively higher average cost per participant. In urban areas with more advanced social welfare systems, such as Shanghai, cognitive training has been incorporated into public health service initiatives and is funded by the government (9). Nevertheless, despite its inclusion as a government procurement project, there is an absence of evidence regarding the economic value of cognitive interventions. This limitation precludes the possibility of conducting comparative analyses between cognitive training programs and other public health interventions, thereby impeding the ability of policymakers in other cities to make informed decisions regarding the incorporation of cognitive training into government-funded projects. Health state utility (HSU) is a crucial metric for economic evaluations. It provides a quantifiable measure of the value individuals place on different health states, enabling more accurate economic evaluations, cost-effectiveness analyses, and resource-allocation decisions in health-related research. However, a review of the existing literature reveals that HSU values for individuals with MCI in mainland China have not been reported (10).
This study aimed to measure HSU values using the Short Form Six Dimensions version 2 (SF-6Dv2) and to investigate associated factors in the older adult MCI population in Chinese communities. The reporting of HSU values will facilitate further research in other Chinese cities, providing a foundation for economic evaluations. Furthermore, the factors that influence HSU among older adult individuals with NC or MCI will be analyzed to inform the development of intervention programs designed to enhance the quality of life for this group.
Methods
Setting and sample
This study was conducted in Haikou City, the capital city of Hainan Province which located in the southmost part of China. Haikou City encompasses approximately 30% of the province’s older adult population (aged 60 and above) (11). This study employed a cluster random sampling method to select six communities out of 208 in Haikou City: Binlian, Jiahua, Binjiang, Yanfeng, Renmin, and Balun.
A community-based health status survey was conducted from April to July 2023. The survey team, in collaboration with the community health services centers (CHSC), recruited older adult individuals (aged 60 years and above) for the survey. When doctors at CHSC were conducting free physical examinations (funded by the government) for all older adult living in the target community, the survey team simultaneously carried out the recruitment work for this study. Exclusion criteria included those: (1) declining to provide informed consent; (2) with severe mental illness or other health issues preventing completion of the interview; and (3) not residing continuously in the designated communities for more than 6 months. Eligible participants provided informed consent and were interviewed face-to-face by trained investigators.
Instrument
All investigators received a standard training and completed a simulation test conducted by the project management team encompassing neurologists and epidemiologists. The graduate students with professional backgrounds in clinical medicine or preventive medicine from Hainan Medical University (HNMU) served as the investigators. The training included research design, cognitive assessment tools, questionnaires, interview techniques, and data recording. Two neurologists from the Neurology Department of the Second Affiliated Hospital of HNMU provided the training on the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE). To ensure questionnaire quality, researchers performed immediate quality checks after collection, requesting clarifications as needed.
MCI identification
MCI identification was based on the Chinese version of the MMSE, which has been widely used in medical or research institutions in China with solid reliability and validity performance among the Chinese population (12–14). The MMSE scores range from 0 to 30with lower scores indicating more severe cognitive impairment. The people with an MMSE score of less than 24 points and greater than 17 points are considered to have mild cognitive impairment (15).
Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) measurement
The HRQoL was measured using the Chinese version of SF-6Dv2 (16). The SF-6Dv2, an improvement on SF-6D, comprises six dimensions: physical functioning, role limitations, social functioning, pain, mental health, and vitality (17). With five or six choice levels in each dimension, there are a total of 18,750 possible health states. For example, a person’s health status of 132354 indicated that the person selected the first level in the physical functioning dimension, the third level in the role limitations dimension, and the remaining numbers correspond to the selection levels in the remaining dimensions. The SF-6Dv2 is commonly used to calculate health utility values for non-communicable diseases in China (18–21), and also been used in the field of MCI research in other countries (ref). In this study, the HSU value set for the SF-6Dv2 developed among Chinese adults in eight provinces was used (22). The HSU value was obtained by subtracting coefficients in the value set of SF-6Dv2 for each dimension level of the health state from 1. For example, for the health state 132354, the utility value would be 1 – (PF1 + RL3 + SF2 + PN3 + MH5 + VT4) = 1 − (0 + 0.059 + 0.047 + 0.083 + 0.134 + 0.108) = 0.569. The coefficients corresponding to the different choice levels for each dimension can be found in Supplementary material. For example, the coefficient corresponding to “RL3” is 0.059. The value range of all health states for the general population is between −0.277 (the worst health state: 555655) and 1.000 (the best health state: 111111) (22).
Associated factors
A questionnaire was developed to collect data on self-reported socio-demographic information (age, sex, education, and marital status), health-related behaviors such as drinking and smoking, living situation, Comorbid diseases such as hypertension, diabetes and stroke (Supplementary material), symptoms such as depressive symptomatology and hearing impairments, and living situations (4, 23, 24).
Depressive symptomatology was assessed using the 2-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-2) (23). This instrument is widely regarded as a suitable option for screening programs targeting older adults (24). Smoking was assessed as participants reported smoking status (yes/no), and if yes, information as being frequently exposed to passive smoking in the past week was obtained. Drinking was assessed as had any alcohol consumption in the past week (yes/no). Living situation was measured whether participants were living alone or not, determined as whether participants lived at home alone more than 5 days in the past week.
Data collection
Before the survey, the trained interviewers informed the participants about the survey’s purpose and obtained informed consent. The MMSE and SF-6Dv2 survey was conducted by one-on-one questioning. The quality-of-life survey was completed by the participants, with assistance provided for those who were illiterate or visually impaired. The investigator checked questionnaire completion asked participants to supplement any missing answers on-site.
Statistical analysis
Descriptive analysis for participants’ characteristics was performed. Counts and frequencies for MMSE scores were described. Differences in the HSU values across subgroups were assessed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) when the grouping variables were normally distributed or Mann–Whitney U rank-sum otherwise (25, 26). Omega squared (ω2) was used as an effect size in ANOVA analysis to correct for the bias in the estimation of the amount of variance explained (27). Multiple linear regression was employed to examine factors influencing utility values, using a stepwise approach to optimize the model for covariates adjustment (28, 29). In the multiple linear analysis, age and MMSE scores were treated as continuous variables within the model. Binary variables (e.g., sex, marital status) were coded as 0 and 1, while ordinal variables (e.g., years of education, number of comorbidities) were represented by integer values. The details of variable recoding were provided in Supplementary material. Statistically significance was set at less than 0.05 (p < 0.05).
All statistical analyses were performed using the statistical software SPSS version 27.0 (IBM, Chicago, IL, United States).
Ethics approval
This study was conducted in accordance with the World Medical Association’s Declaration of Helsinki. This study received ethical approval from the Ethics Committee of HNMU (HYLL-2022-301). Informed consent was obtained from all participants following detailed explanations of the study.
Results
Characteristics of participants
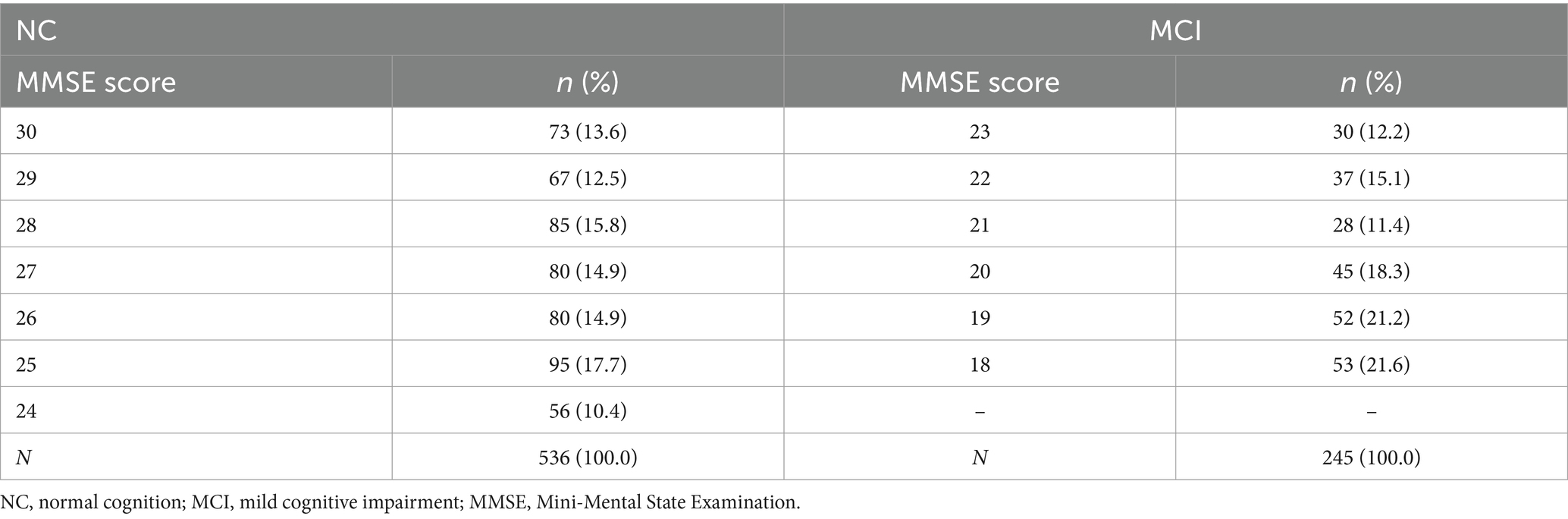
A total of 906 eligible older adults participated in the community survey. Screening with the MMSE identified 536 individuals with NC (normal cognition), 245 with MCI. The Cronbach’s alpha of the MMSE used in all older adult samples was 0.889. The Cronbach’s alphas of the MMSE in NC group and MCI were 0.785 and 0.921, respectively. In terms of MMSE scores, the people with a score of 25 was the largest in the NC group, accounting for 17.7% of the NC group (Table 1). In the MCI group, the people with a score of 18 was the largest, accounting for 21.6%, the people with a score of 21 was the smallest (11.4%).
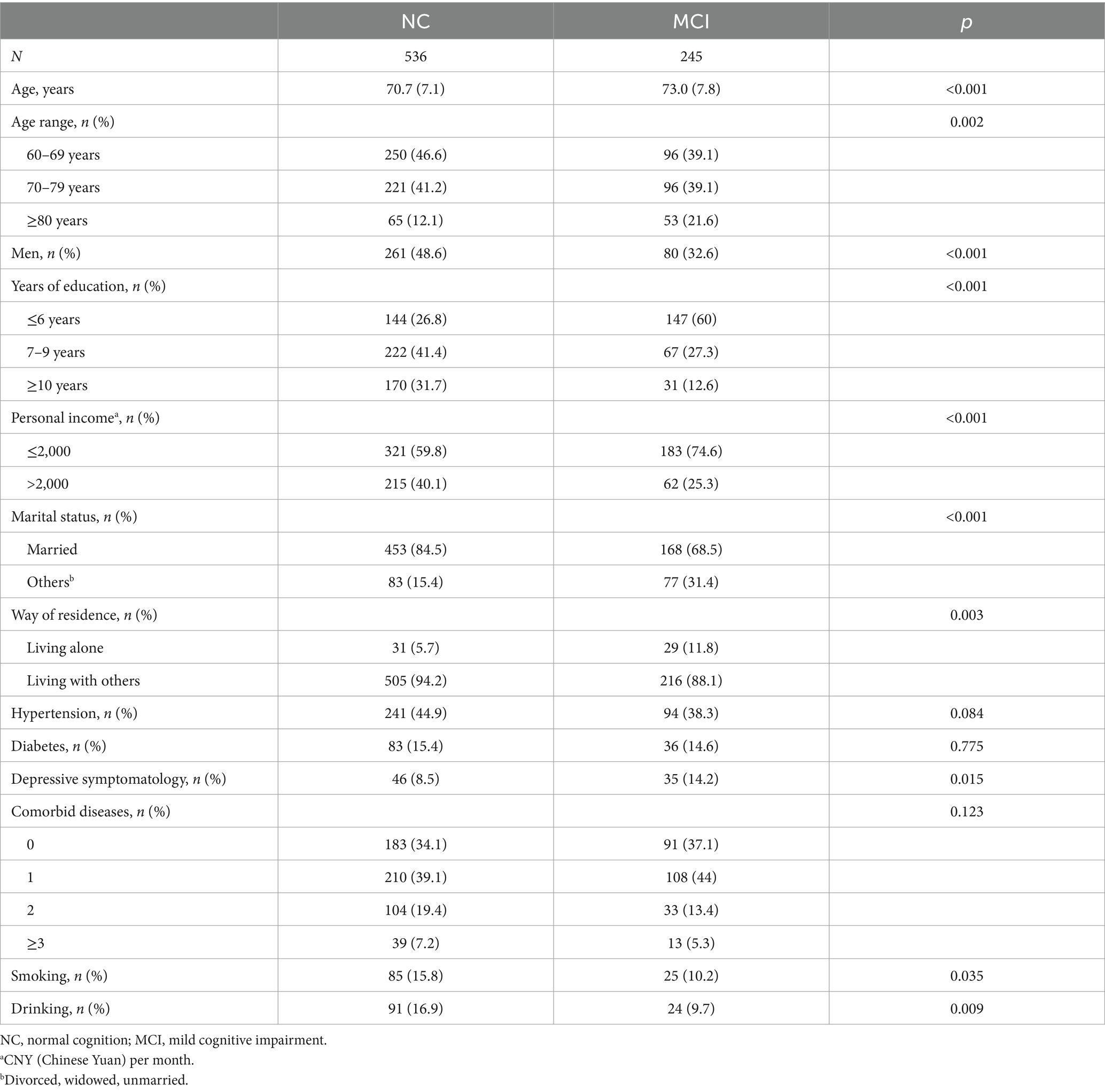
Table 2 presents the distribution of NC and MCI groups’ characteristics. The average ages of the NC and MCI group were 70.7 years (SD = 7.1) and 73.0 years (SD = 7.8), respectively. Among NC and MCI group, males accounted for 48.6 and 32.6%, 26.8 and 60.0% with a primary school education or less, 84.5 and 68.5% married, 59.8 and 74.6% had a monthly income below 2000 RMB, 5.7 and 11.8% lived alone, respectively. The above characteristics all showed significant differences between NC and MCI (p < 0.05).
Regarding diseases, among the NC and MCI groups, the prevalence rates of hypertension were 44.9 and 38.3%, the prevalence rates of diabetes were 15.4 and 14.6%, and the depression screening rates measured by PHQ-2 were 8.5 and 14.2%, respectively (Table 2). Only the difference in the depression screening rate between NC and MCI group was significant (p = 0.015). Moreover, at the time of the survey, 34.1 and 37.1% of the older adult in the NC and MCI groups, respectively, reported having no diseases. In terms of habits, the proportions of people who smoke or drink are both higher in the NC group than in the MCI group, which were 15.8% versus 10.2% (p = 0.035) and 16.9% versus 9.7% (p = 0.009), respectively.
HSU values among subgroups
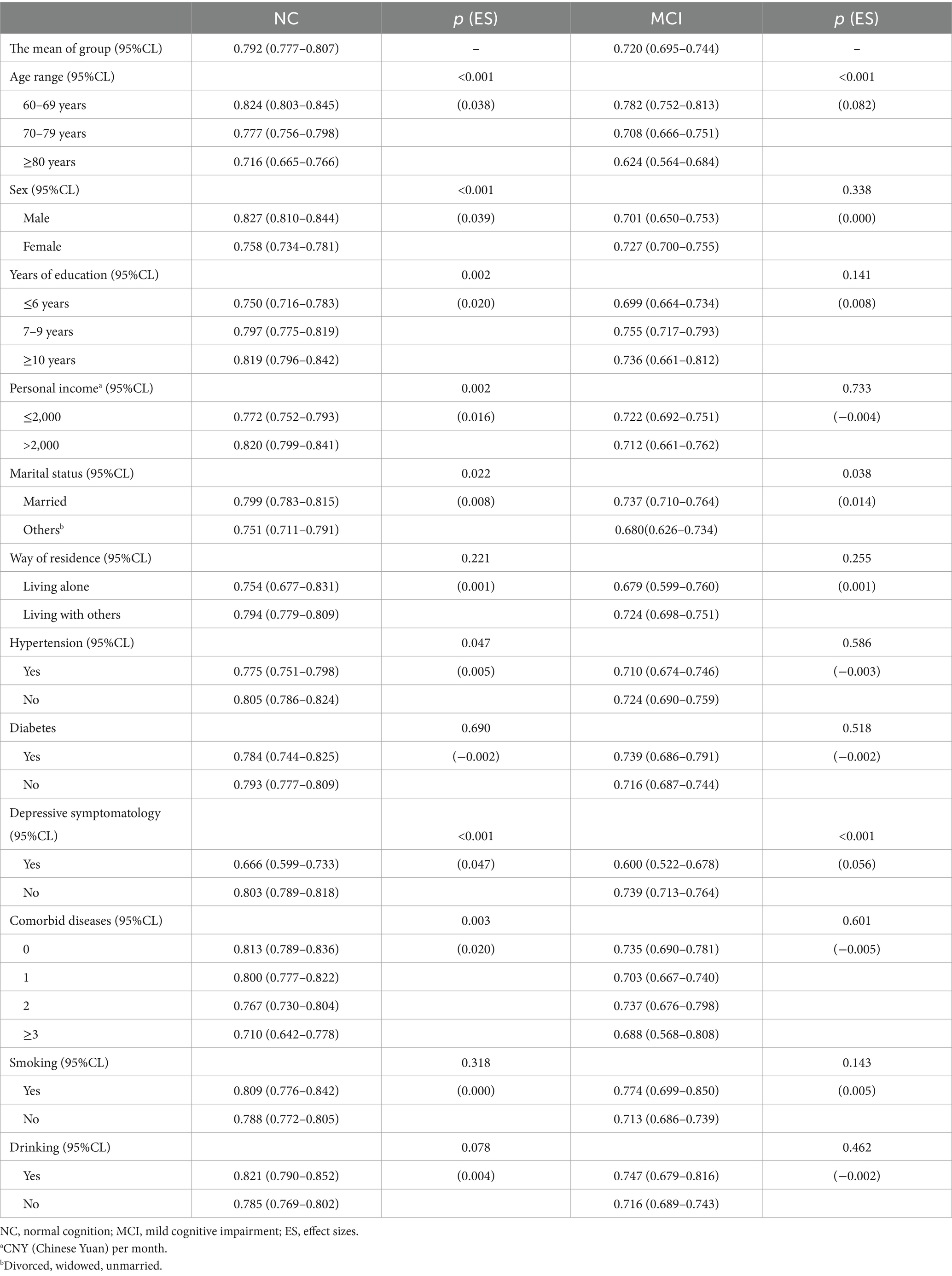
The mean HSU values for NC group and MCI group, respectively, were 0.792 (95%CL, 0.777–0.807) and 0.720 (95%CL, 0.695–0.744). Table 3 showed the differences in HSU values among subgroups in NC group and MCI group. Univariate analysis revealed that in the NC group, factors significantly associated with HSU were age (p < 0.001), sex (p < 0.001), years of education (p = 0.002), income (p = 0.002), marital status (p = 0.022), hypertension (p = 0.047), depression (p < 0.001), and number of comorbidities (p = 0.002). However, in the MCI group, only age (p < 0.001), marital status (p = 0.038), and depression (p < 0.001) were significantly associated with HSU. In both the NC and MCI groups, no significant differences in HSU were observed between smokers and non-smokers or between drinkers and non-drinkers.
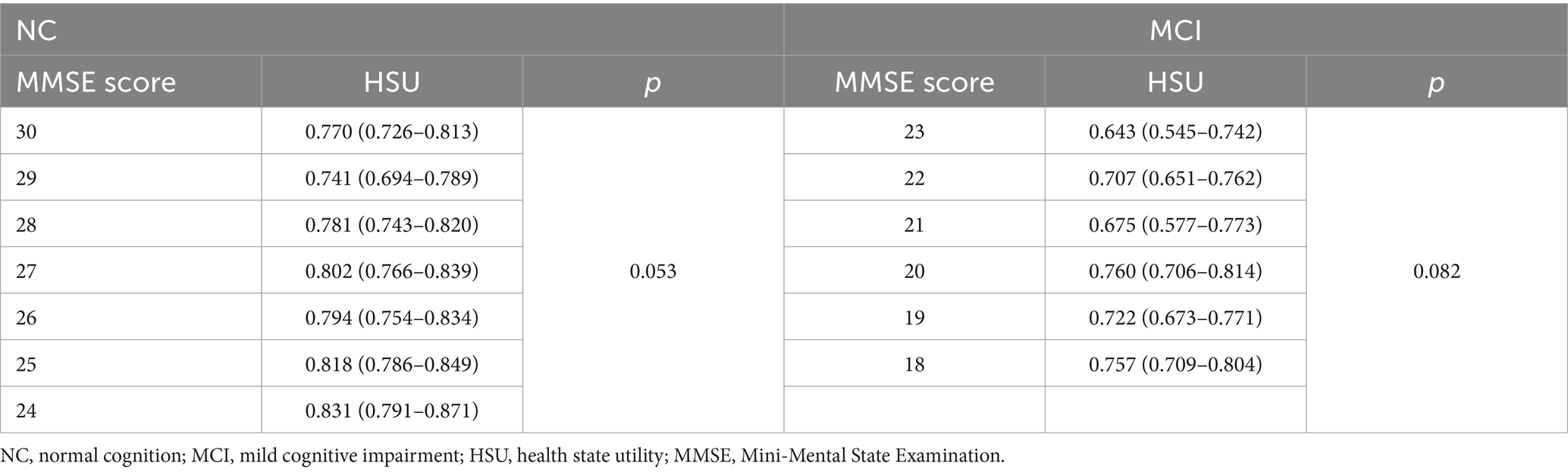
The variations in HSU across different MMSE score groups (Table 4) were not statistically significant in the NC group (p = 0.053) or the MCI group (p = 0.082).
Multiple linear regression models for NC and MCI
For the NC group, the optimal multiple linear regression model included five variables: age, sex, monthly personal income (reference: lower-income group), depression symptomatology, and number of comorbidities (Table 5). Within this group, each additional year of age was associated with a 0.005 decrease in HSU (p < 0.001); HSU was 0.064 units lower in females compared to males (p < 0.001); HSU was 0.048 units higher in higher-income individuals than in those with lower incomes (p = 0.001); depression was associated with a 0.109-unit reduction in HSU compared to those without depression (p < 0.001); and each additional comorbidity was linked to a 0.023 decrease in HSU (p = 0.003).
For the MCI group, the optimal model comprised three variables: age, depression, and MMSE score (Table 6). Among individuals in this group, each additional year of age was associated with a 0.009 decrease in HSU (p < 0.001); depression was linked to a 0.132-unit reduction in HSU; and within the MMSE score range of 18 to 23 (inclusive), each additional point was associated with a 0.015 increase in HSU (p = 0.023).
Discussion
This study investigated the HSU among older adults with NC and with MCI in Chinese communities. Significant differences in HSU values based were observed based on age, marital status, living status, and depression. Although the mean HUS values for females and low-income MCI groups were lower than those for males and high-income groups, these differences were not statistically significant.
This study explored HSU and its influencing factors among older adult individuals with NC and those with MCI within Chinese communities. The HSU was found to be higher in the NC group compared to the MCI group (0.792 vs. 0.720, p < 0.001). Univariate analysis revealed significant differences in HSU related to age, sex, marital status, and depression symptomatology in both groups. While certain factors, such as sex, years of education, and income, showed significant differences in the NC group, these differences were not significant in the MCI group. Multiple linear regression analysis demonstrated a linear relationship between HSU and age, sex, income, depression symptomatology, and the number of comorbidities in the NC group. In the MCI group, the key factors were age, depression symptomatology, and MMSE score. The findings confirmed the disparity in HSU between the NC and MCI groups, highlighting both common and distinct influencing factors.
Currently, HSU values for MCI populations in developed countries have been reported in Canada (0.89), Germany (0.72), France (0.81), Netherlands (0.73), and United States (0.78) (30, 31). But there are no comparable data available for HSU values specifically for older adult Chinese individuals with MCI. Previous studies from China have indicated a significant link between cognitive impairment and decreased HRQoL, but they have not reported HUS values for the MCI group separately (32, 33). This may be due to the difficulty in collecting adequate samples of individuals with MCI compared to populations with moderate or severe cognitive impairments, the same challenge also noted in studies from Australia and Japan (34, 35). Although the reported HSU values were within a reasonable range compared to data from other countries, significant variability existed across different regions in China, and this study was limited to a provincial capital in southwestern China. Further research across diverse regions and various MCI populations were needed to better understand the causes of these differences.
Both univariate and multivariate analyses indicated that depression symptomatology is a significant influencing factor for HSU in both the NC and MCI groups. A study based on the French population had also demonstrated that depression is associated with poorer HRQoL in individuals with MCI (31). Consequently, interventions aimed at improving the quality of life for older adult individuals with MCI should consider incorporating psychological support for those experiencing depression (36).
Notably, while there was no significant correlation between HSU and MMSE scores in the NC group, a correlation was observed in the MCI group. This suggested that once cognitive function declines past a certain threshold, the deterioration in cognitive abilities becomes linearly related to reductions in HSU. Thus, cognitive interventions for the MCI population may enhance their HSU.
The results suggest that factors affecting MCI do not completely overlap with those influencing the HSU values in older MCI individuals. While smoking and alcohol consumption have been identified as risk factors for MCI according to previous studies (4, 37), this study did not find significant difference in HSU values between individuals with MCI who smoked or drank alcohol and those who did not. These results implied that traditional disease risk factors may no longer impact the quality of life for individuals who are already affected. Therefore, researchers should consider including additional factors beyond disease risks factors when assessing the quality of life for MCI patients.
This study had several limitations. First, due to its cross-sectional design, the associations between HSU and various factors cannot be interpreted as causal relationships. Second, community-based studies may overlook older adult individuals residing in hospitals and nursing homes, potentially leading to a healthier participant demographic compared to the broader older adult population. As such, future research should encompass studies of older adult populations in hospitals and nursing homes. In addition, in subsequent follow-up studies, data collection from more dimensions and sources needs to be considered. For example, measuring instrumental activities of daily living and collecting data from the perspective of caregivers (38, 39).
In conclusion, this study presented insights into HSU and its influencing factors in the NC and MCI groups in Chinese communities. Various factors were associated with participants’ quality of life, age and with depression significantly correlated with lower quality of life among older adults with NC and MCI.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Hainan Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
YD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. BZ: Data curation, Investigation, Project administration, Writing – review & editing. XW: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. TS: Investigation, Writing – review & editing. DL: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. JP: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JH: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This project received financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 82360673 for JP), Hainan Province Key Research and Development Project (No. ZDYF2024SHFZ064 for JP), and Hainan Medical University Talent Introduction Research Start-up Project (No. XRC2022005 for JP).
Acknowledgments
Thank all the investigators from Hainan Medical University for their time and effort. All authors approved the final manuscript and have participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for appropriate portions of the content.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpubh.2025.1538665/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Petersen, RC. Mild cognitive impairment. N Engl J Med. (2011) 364:2227–34. doi: 10.1056/NEJMCP0910237
2. Petersen, RC, Lopez, O, Armstrong, MJ, Getchius, TSD, Ganguli, M, Gloss, D, et al. Practice guideline update summary: mild cognitive impairment. Neurology. (2018) 90:126–35. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004826
3. Ward, A, Tardiff, S, Dye, C, and Arrighi, HM. Rate of conversion from prodromal Alzheimer's disease to Alzheimer's dementia: a systematic review of the literature. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra. (2013) 3:320–32. doi: 10.1159/000354370
4. Jia, L, Du, Y, Chu, L, Zhang, Z, Li, F, Lyu, D, et al. Prevalence, risk factors, and management of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in adults aged 60 years or older in China: a cross-sectional study. Lancet Public Health. (2020) 5:e661–71. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(20)30185-7
5. Huang, YX, Li, XD, Liu, ZF, Huo, JH, Guo, JW, Chen, YY, et al. Projections of the economic burden of care for individuals with dementia in mainland China from 2010 to 2050. PLoS One. (2022) 17:e0263077. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263077
6. Giannouli, V, and Tsolaki, M. Unraveling Ariadne's thread into the labyrinth of aMCI: depression and financial capacity. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. (2021) 35:363–5. doi: 10.1097/WAD.0000000000000417
7. Giannouli, V, Stamovlasis, D, and Tsolaki, M. Longitudinal study of depression on amnestic mild cognitive impairment and financial capacity. Clin Gerontol. (2022) 45:708–14. doi: 10.1080/07317115.2021.2017377
8. Government S. Pilot project of elderly cognitive—impairment–friendly community in Xuhui district (2024).
9. Tian, R, Jiang, Y, Zhang, Y, Yan, X, Zhou, Y, and Chen, D. Cognitive training program improves cognitive ability and daily living ability in elderly patients with mild cognitive impairment. Aging Clin Exp Res. (2022) 34:997–1005. doi: 10.1007/s40520-021-02015-6
10. Du, Y, Sun, J, Di Liang, Huang J, and Petersen, JD. A comparison of the application of euroqol 5-dimension (eq-5d) and short form 6-dimension (sf-6d) in the elderly population with mild cognitive impairment (mci): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Prospero 2023 crd42023445068. (2023).
12. Karimi, L, Mahboub Ahari, A, Jahangiry, L, Sadeghi-Bazargani, H, and Farahbakhsh, M. A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies on screening for mild cognitive impairment in primary healthcare. BMC Psychiatry. (2022) 22:97. doi: 10.1186/s12888-022-03730-8
13. Zhang, S, Qiu, Q, Qian, S, Lin, X, Yan, F, Sun, L, et al. Determining appropriate screening tools and cutoffs for cognitive impairment in the Chinese elderly. Front Psych. (2021) 12:773281. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.773281
14. Jia, X, Wang, Z, Huang, F, Su, C, Du, W, Jiang, H, et al. A comparison of the mini-mental state examination (MMSE) with the Montreal cognitive assessment (MOCA) for mild cognitive impairment screening in Chinese middle-aged and older population: a cross-sectional study. BMC Psychiatry. (2021) 21:485. doi: 10.1186/s12888-021-03495-6
15. Tombaugh, TN, and McIntyre, NJ. The mini-mental state examination: a comprehensive review. J Am Geriatr Soc. (1992) 40:922–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1992.tb01992.x
16. Wu, J, Xie, S, He, X, Chen, G, and Brazier, JE. The simplified Chinese version of sf-6dv2: translation, cross-cultural adaptation and preliminary psychometric testing. Qual Life Res. (2020) 29:1385–91. doi: 10.1007/s11136-020-02419-3
17. Xie, S, Wang, D, Wu, J, Liu, C, and Jiang, W. Comparison of the measurement properties of sf-6dv2 and eq-5d-5l in a Chinese population health survey. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2022) 20:96. doi: 10.1186/s12955-022-02003-y
18. Zhang, W, Xie, S, Xue, F, Liu, W, Chen, L, Zhang, L, et al. Health-related quality of life among adults with haemophilia in China: a comparison with age-matched general population. Haemophilia. (2022) 28:776–83. doi: 10.1111/hae.14615
19. Xu, RH, Luo, N, and Dong, D. Measurement properties of the eq-5d-3l, eq-5d-5l, and sf-6dv2 in patients with late-onset pompe disease. Eur J Health Econ. (2024) 25:1505–15. doi: 10.1007/s10198-024-01682-2
20. Cong, J, Zhu, Y, Du, J, Lin, L, He, Y, Zhang, Q, et al. Mapping the Minnesota living with heart failure questionnaire (MLHFQ) to SF-6Dv2 in Chinese patients with heart failure. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2022) 20:98. doi: 10.1186/s12955-022-02004-x
21. Xie, S, Li, M, Wang, D, Hong, T, Guo, W, and Wu, J. Comparison of the measurement properties of the eq-5d-5l and sf-6dv2 among overweight and obesity populations in China. Health Qual Life Outcomes. (2023) 21:118. doi: 10.1186/s12955-023-02202-1
22. Wu, J, Xie, S, He, X, Chen, G, Bai, G, Feng, D, et al. Valuation of sf-6dv2 health states in China using time trade-off and discrete-choice experiment with a duration dimension. PharmacoEconomics. (2021) 39:521–35. doi: 10.1007/s40273-020-00997-1
23. Liu, Z, Yu, Y, Hu, M, Liu, H, Zhou, L, and Xiao, S. Phq-9 and phq-2 for screening depression in Chinese rural elderly. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e151042. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151042
24. Tsoi, KKF, Chan, JYC, Hirai, HW, and Wong, SYS. Comparison of diagnostic performance of two-question screen and 15 depression screening instruments for older adults: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry. (2017) 210:255–60. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.116.186932
25. Yu, Z, Guindani, M, Grieco, SF, Chen, L, Holmes, TC, and Xu, X. Beyond t test and ANVOA: applications of mixed-effects models for more rigorous statistical analysis in neuroscience research. Neuron (Cambridge, Mass). (2022) 110:21–35. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2021.10.030
26. Blanca, MJ, Alarcon, R, Arnau, J, Bono, R, and Bendayan, R. Non-normal data: is ANVOA still a valid option? Psicothema. (2017) 29:552–7. doi: 10.7334/psicothema2016.383
27. Lakens, D. Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: a practical primer for t-tests and ANVOAs. Front Psychol. (2013) 4:863. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00863
28. Nimon, KF, and Oswald, FL. Understanding the results of multiple linear regression. Organ Res Methods. (2013) 16:650–74. doi: 10.1177/1094428113493929
29. Knofczynski, GT, and Mundfrom, D. Sample sizes when using multiple linear regression for prediction. Educ Psychol Meas. (2008) 68:431–42. doi: 10.1177/0013164407310131
30. Landeiro, F, Mughal, S, Walsh, K, Nye, E, Morton, J, Williams, H, et al. Health-related quality of life in people with predementia Alzheimer’s disease, mild cognitive impairment or dementia measured with preference-based instruments: a systematic literature review. Alzheimers Res Ther. (2020) 12:154. doi: 10.1186/s13195-020-00723-1
31. Aye, S, Bouteloup, V, Tate, A, Wimo, A, Handels, R, Jean, D, et al. Health-related quality of life in subjective cognitive decline and mild cognitive impairment: a longitudinal cohort analysis. Alzheimers Res Ther. (2023) 15:200. doi: 10.1186/s13195-023-01344-0
32. Yuan, L, Zhang, X, Guo, N, Li, Z, Lv, D, Wang, H, et al. Prevalence of cognitive impairment in Chinese older inpatients and its relationship with 1-year adverse health outcomes: a multi-center cohort study. BMC Geriatr. (2021) 21:595. doi: 10.1186/s12877-021-02556-5
33. Pan, C, Wang, X, Ma, Q, Sun, H, Xu, Y, and Wang, P. Cognitive dysfunction and health-related quality of life among older Chinese. Sci Rep. (2015) 5:17301. doi: 10.1038/srep17301
34. Keramat, SA, Lee, V, Patel, R, Hashmi, R, and Comans, T. Cognitive impairment and health-related quality of life amongst older Australians: evidence from a longitudinal investigation. Qual Life Res. (2023) 32:2911–24. doi: 10.1007/s11136-023-03449-3
35. Kitamura, K, Nakamura, K, Ueno, K, and Nishiwaki, T. Cognitive function is maintained in noninstitutionalized elderly Japanese requiring care with high levels of health-related quality of life. Environ Health Prev Med. (2016) 21:585–90. doi: 10.1007/s12199-016-0572-9
36. Lang, C, Roessler, M, Schmitt, J, Bergmann, A, and Holthoff-Detto, V. Health-related quality of life in elderly, multimorbid individuals with and without depression and/or mild cognitive impairment using a telemonitoring application. Qual Life Res. (2021) 30:2829–41. doi: 10.1007/s11136-021-02848-8
37. Bai, W, Chen, P, Cai, H, Zhang, Q, Su, Z, Cheung, T, et al. Worldwide prevalence of mild cognitive impairment among community dwellers aged 50 years and older: a meta-analysis and systematic review of epidemiology studies. Age Ageing. (2022) 51:afac173. doi: 10.1093/ageing/afac173
38. Jekel, K, Damian, M, Wattmo, C, Hausner, L, Bullock, R, Connelly, PJ, et al. Mild cognitive impairment and deficits in instrumental activities of daily living: a systematic review. Alzheimers Res Ther. (2015) 7:17. doi: 10.1186/s13195-015-0099-0
Keywords: mild cognitive impairment, health utility, mini-mental state examination, SF-6Dv2, depression
Citation: Du Y, Zheng B, Wang X, Song T, Liang D, Petersen JD and Huang J (2025) Influencing factors of health utility values in older adult people with normal cognition or mild cognitive impairment: a cross-sectional survey. Front. Public Health. 13:1538665. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1538665
Edited by:
Simone Varrasi, University of Catania, ItalyReviewed by:
Vaitsa Giannouli, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, GreeceHafsah Arshad, Ibadat International University, Pakistan
Copyright © 2025 Du, Zheng, Wang, Song, Liang, Petersen and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jiayan Huang, amlheWFuaHVhbmdAZnVkYW4uZWR1LmNu; anlodWFuZ0BzaG11LmVkdS5jbg==; Jindong Ding Petersen, ZGluZ2ppbmRvbmdAaGFpbm1jLmVkdS5jbg==; amluZG9uZ0BoZWFsdGguc2R1LmRr
†ORCID: Yanqiu Du, orcid.org/0000-0003-2200-0477
Jindong Ding Petersen, orcid.org/0000-0001-6857-982X
 Yanqiu Du
Yanqiu Du Bingbing Zheng
Bingbing Zheng Xiuru Wang2
Xiuru Wang2 Di Liang
Di Liang Jindong Ding Petersen
Jindong Ding Petersen Jiayan Huang
Jiayan Huang